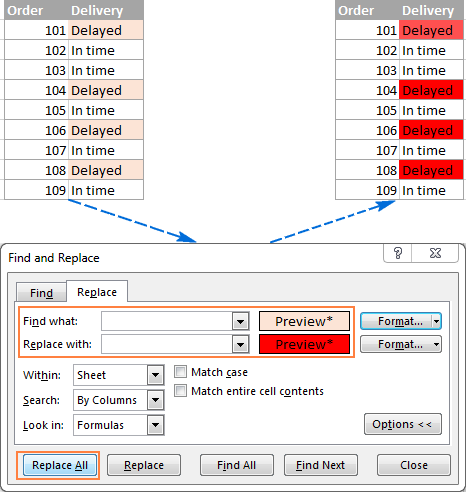
Use the Find and Replace features in Excel to search for something in your workbook, such as a particular number or text string. You can either locate the search item for reference, or you can replace it with something else. You can include wildcard characters such as question marks, tildes, and asterisks, or numbers in your search terms. You can search by rows and columns, search within comments or values, and search within worksheets or entire workbooks.
Find
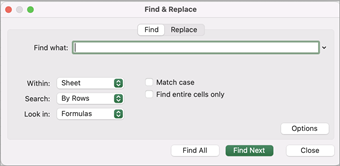
To find something, press Ctrl+F, or go to Home > Editing > Find & Select > Find.
Note: In the following example, we’ve clicked the Options >> button to show the entire Find dialog. By default, it will display with Options hidden.
-
In the Find what: box, type the text or numbers you want to find, or click the arrow in the Find what: box, and then select a recent search item from the list.
Tips: You can use wildcard characters — question mark (?), asterisk (*), tilde (~) — in your search criteria.
-
Use the question mark (?) to find any single character — for example, s?t finds «sat» and «set».
-
Use the asterisk (*) to find any number of characters — for example, s*d finds «sad» and «started».
-
Use the tilde (~) followed by ?, *, or ~ to find question marks, asterisks, or other tilde characters — for example, fy91~? finds «fy91?».
-
-
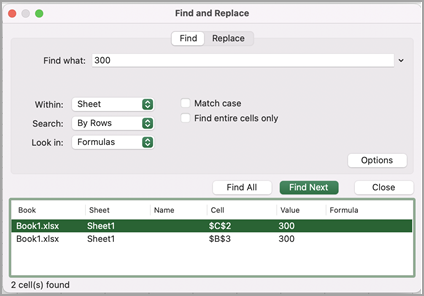
Click Find All or Find Next to run your search.
Tip: When you click Find All, every occurrence of the criteria that you are searching for will be listed, and clicking a specific occurrence in the list will select its cell. You can sort the results of a Find All search by clicking a column heading.
-
Click Options>> to further define your search if needed:
-
Within: To search for data in a worksheet or in an entire workbook, select Sheet or Workbook.
-
Search: You can choose to search either By Rows (default), or By Columns.
-
Look in: To search for data with specific details, in the box, click Formulas, Values, Notes, or Comments.
Note: Formulas, Values, Notes and Comments are only available on the Find tab; only Formulas are available on the Replace tab.
-
Match case — Check this if you want to search for case-sensitive data.
-
Match entire cell contents — Check this if you want to search for cells that contain just the characters that you typed in the Find what: box.
-
-
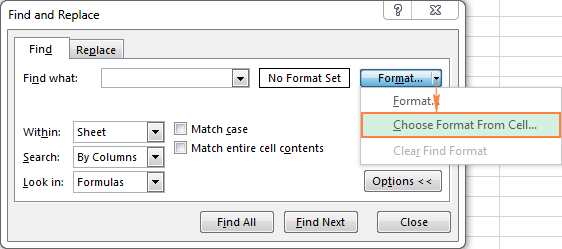
If you want to search for text or numbers with specific formatting, click Format, and then make your selections in the Find Format dialog box.
Tip: If you want to find cells that just match a specific format, you can delete any criteria in the Find what box, and then select a specific cell format as an example. Click the arrow next to Format, click Choose Format From Cell, and then click the cell that has the formatting that you want to search for.
Replace
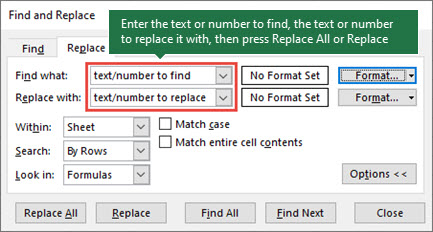
To replace text or numbers, press Ctrl+H, or go to Home > Editing > Find & Select > Replace.
Note: In the following example, we’ve clicked the Options >> button to show the entire Find dialog. By default, it will display with Options hidden.
-
In the Find what: box, type the text or numbers you want to find, or click the arrow in the Find what: box, and then select a recent search item from the list.
Tips: You can use wildcard characters — question mark (?), asterisk (*), tilde (~) — in your search criteria.
-
Use the question mark (?) to find any single character — for example, s?t finds «sat» and «set».
-
Use the asterisk (*) to find any number of characters — for example, s*d finds «sad» and «started».
-
Use the tilde (~) followed by ?, *, or ~ to find question marks, asterisks, or other tilde characters — for example, fy91~? finds «fy91?».
-
-
In the Replace with: box, enter the text or numbers you want to use to replace the search text.
-
Click Replace All or Replace.
Tip: When you click Replace All, every occurrence of the criteria that you are searching for will be replaced, while Replace will update one occurrence at a time.
-
Click Options>> to further define your search if needed:
-
Within: To search for data in a worksheet or in an entire workbook, select Sheet or Workbook.
-
Search: You can choose to search either By Rows (default), or By Columns.
-
Look in: To search for data with specific details, in the box, click Formulas, Values, Notes, or Comments.
Note: Formulas, Values, Notes and Comments are only available on the Find tab; only Formulas are available on the Replace tab.
-
Match case — Check this if you want to search for case-sensitive data.
-
Match entire cell contents — Check this if you want to search for cells that contain just the characters that you typed in the Find what: box.
-
-
If you want to search for text or numbers with specific formatting, click Format, and then make your selections in the Find Format dialog box.
Tip: If you want to find cells that just match a specific format, you can delete any criteria in the Find what box, and then select a specific cell format as an example. Click the arrow next to Format, click Choose Format From Cell, and then click the cell that has the formatting that you want to search for.
There are two distinct methods for finding or replacing text or numbers on the Mac. The first is to use the Find & Replace dialog. The second is to use the Search bar in the ribbon.
Find & Replace dialog
Search bar and options
-
Press Ctrl+F or go to Home > Find & Select > Find.
-
In Find what: type the text or numbers you want to find.
-
Select Find Next to run your search.
-
You can further define your search:
-
Within: To search for data in a worksheet or in an entire workbook, select Sheet or Workbook.
-
Search: You can choose to search either By Rows (default), or By Columns.
-
Look in: To search for data with specific details, in the box, click Formulas, Values, Notes, or Comments.
-
Match case — Check this if you want to search for case-sensitive data.
-
Match entire cell contents — Check this if you want to search for cells that contain just the characters that you typed in the Find what: box.
-
Tips: You can use wildcard characters — question mark (?), asterisk (*), tilde (~) — in your search criteria.
-
Use the question mark (?) to find any single character — for example, s?t finds «sat» and «set».
-
Use the asterisk (*) to find any number of characters — for example, s*d finds «sad» and «started».
-
Use the tilde (~) followed by ?, *, or ~ to find question marks, asterisks, or other tilde characters — for example, fy91~? finds «fy91?».
-
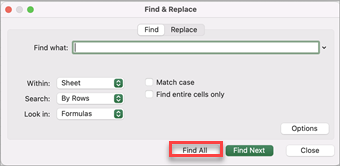
Press Ctrl+F or go to Home > Find & Select > Find.
-
In Find what: type the text or numbers you want to find.
-
Select Find All to run your search for all occurrences.
Note: The dialog box expands to show a list of all the cells that contain the search term, and the total number of cells in which it appears.
-
Select any item in the list to highlight the corresponding cell in your worksheet.
Note: You can edit the contents of the highlighted cell.
-
Press Ctrl+H or go to Home > Find & Select > Replace.
-
In Find what, type the text or numbers you want to find.
-
You can further define your search:
-
Within: To search for data in a worksheet or in an entire workbook, select Sheet or Workbook.
-
Search: You can choose to search either By Rows (default), or By Columns.
-
Match case — Check this if you want to search for case-sensitive data.
-
Match entire cell contents — Check this if you want to search for cells that contain just the characters that you typed in the Find what: box.
Tips: You can use wildcard characters — question mark (?), asterisk (*), tilde (~) — in your search criteria.
-
Use the question mark (?) to find any single character — for example, s?t finds «sat» and «set».
-
Use the asterisk (*) to find any number of characters — for example, s*d finds «sad» and «started».
-
Use the tilde (~) followed by ?, *, or ~ to find question marks, asterisks, or other tilde characters — for example, fy91~? finds «fy91?».
-
-
-
In the Replace with box, enter the text or numbers you want to use to replace the search text.
-
Select Replace or Replace All.
Tips:
-
When you select Replace All, every occurrence of the criteria that you are searching for is replaced.
-
When you select Replace, you can replace one instance at a time by selecting Next to highlight the next instance.
-
-
Select any cell to search the entire sheet or select a specific range of cells to search.
-
Press Command + F or select the magnifying glass to expand the Search bar and type the text or number you want to find in the search field.
Tips: You can use wildcard characters — question mark (?), asterisk (*), tilde (~) — in your search criteria.
-
Use the question mark (?) to find any single character — for example, s?t finds «sat» and «set».
-
Use the asterisk (*) to find any number of characters — for example, s*d finds «sad» and «started».
-
Use the tilde (~) followed by ?, *, or ~ to find question marks, asterisks, or other tilde characters — for example, fy91~? finds «fy91?».
-
-
Press return.
Notes:
-
To find the next instance of the item you are searching for, press return again or use the Find dialog box and select Find Next.
-
To specify additional search options, select the magnifying glass and select Search in Sheet or Search in Workbook. You can also select the Advanced option, which launches the Find dialog.
Tip: You can cancel a search in progress by pressing ESC.
-
Find
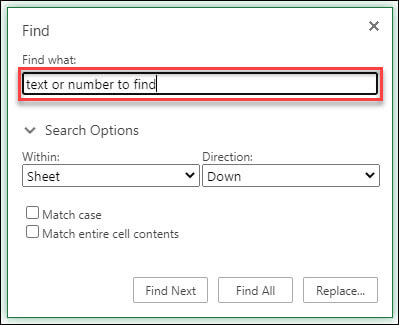
To find something, press Ctrl+F, or go to Home > Editing > Find & Select > Find.
Note: In the following example, we’ve clicked > Search Options to show the entire Find dialog. By default, it will display with Search Options hidden.
-
In the Find what: box, type the text or numbers you want to find.
Tips: You can use wildcard characters — question mark (?), asterisk (*), tilde (~) — in your search criteria.
-
Use the question mark (?) to find any single character — for example, s?t finds «sat» and «set».
-
Use the asterisk (*) to find any number of characters — for example, s*d finds «sad» and «started».
-
Use the tilde (~) followed by ?, *, or ~ to find question marks, asterisks, or other tilde characters — for example, fy91~? finds «fy91?».
-
-
Click Find Next or Find All to run your search.
Tip: When you click Find All, every occurrence of the criteria that you are searching for will be listed, and clicking a specific occurrence in the list will select its cell. You can sort the results of a Find All search by clicking a column heading.
-
Click > Search Options to further define your search if needed:
-
Within: To search for data within a certain selection, choose Selection. To search for data in a worksheet or in an entire workbook, select Sheet or Workbook.
-
Direction: You can choose to search either Down (default), or Up.
-
Match case — Check this if you want to search for case-sensitive data.
-
Match entire cell contents — Check this if you want to search for cells that contain just the characters that you typed in the Find what box.
-
Replace
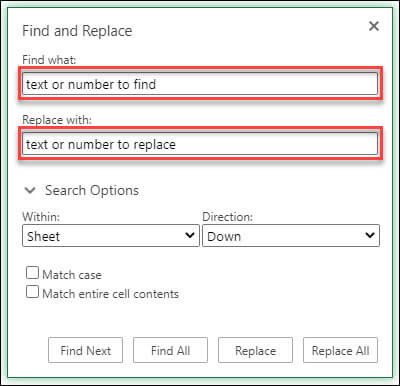
To replace text or numbers, press Ctrl+H, or go to Home > Editing > Find & Select > Replace.
Note: In the following example, we’ve clicked > Search Options to show the entire Find dialog. By default, it will display with Search Options hidden.
-
In the Find what: box, type the text or numbers you want to find.
Tips: You can use wildcard characters — question mark (?), asterisk (*), tilde (~) — in your search criteria.
-
Use the question mark (?) to find any single character — for example, s?t finds «sat» and «set».
-
Use the asterisk (*) to find any number of characters — for example, s*d finds «sad» and «started».
-
Use the tilde (~) followed by ?, *, or ~ to find question marks, asterisks, or other tilde characters — for example, fy91~? finds «fy91?».
-
-
In the Replace with: box, enter the text or numbers you want to use to replace the search text.
-
Click Replace or Replace All.
Tip: When you click Replace All, every occurrence of the criteria that you are searching for will be replaced, while Replace will update one occurrence at a time.
-
Click > Search Options to further define your search if needed:
-
Within: To search for data within a certain selection, choose Selection. To search for data in a worksheet or in an entire workbook, select Sheet or Workbook.
-
Direction: You can choose to search either Down (default), or Up.
-
Match case — Check this if you want to search for case-sensitive data.
-
Match entire cell contents — Check this if you want to search for cells that contain just the characters that you typed in the Find what box.
-
Need more help?
You can always ask an expert in the Excel Tech Community or get support in the Answers community.
Recommended articles
Merge and unmerge cells
REPLACE, REPLACEB functions
Apply data validation to cells
Содержание
- SUBSTITUTE function
- Description
- Syntax
- Example
- Examples of working with text function REPLACE in Excel
- How does the REPLACE function in Excel work?
- REPLACE function in Excel and examples of its use
- How to REPLACE a piece of text in Excel cell?
- REPLACE, REPLACEB functions
- Description
- Syntax
- Example
- SUBSTITUTE Function
- Related functions
- Summary
- Purpose
- Return value
- Arguments
- Syntax
- Usage notes
- Examples
- Related functions
- How to use Find and Replace in Excel most efficiently
- How to use Find in Excel
- Find value in a range, worksheet or workbook
- Excel Find — additional options
- Find cells with specific format in Excel
- Find cells with formulas in Excel
- How to select and highlight all found entries on a sheet
- How to use Replace in Excel
- Replace one value with another
- Replace text or number with nothing
- How to find or replace a line break in Excel
- How to change cell formatting on the sheet
- Excel Find and Replace with wildcards
- How to find and replace wildcard characters in Excel
- Shortcuts for find and replace in Excel
- Search and replace in all open workbooks
SUBSTITUTE function
This article describes the formula syntax and usage of the SUBSTITUTE function in Microsoft Excel.
Description
Substitutes new_text for old_text in a text string. Use SUBSTITUTE when you want to replace specific text in a text string; use REPLACE when you want to replace any text that occurs in a specific location in a text string.
Syntax
SUBSTITUTE(text, old_text, new_text, [instance_num])
The SUBSTITUTE function syntax has the following arguments:
Text Required. The text or the reference to a cell containing text for which you want to substitute characters.
Old_text Required. The text you want to replace.
New_text Required. The text you want to replace old_text with.
Instance_num Optional. Specifies which occurrence of old_text you want to replace with new_text. If you specify instance_num, only that instance of old_text is replaced. Otherwise, every occurrence of old_text in text is changed to new_text.
Example
Copy the example data in the following table, and paste it in cell A1 of a new Excel worksheet. For formulas to show results, select them, press F2, and then press Enter. If you need to, you can adjust the column widths to see all the data.
=SUBSTITUTE(A2, «Sales», «Cost»)
Substitutes Cost for Sales (Cost Data)
=SUBSTITUTE(A3, «1», «2», 1)
Substitutes first instance of «1» with «2» (Quarter 2, 2008)
=SUBSTITUTE(A4, «1», «2», 3)
Substitutes third instance of «1» with «2» (Quarter 1, 2012)
Источник
Examples of working with text function REPLACE in Excel
REPLACE function is included in the text functions of MS Excel and is intended to replace a specific area of the text string containing the source text on the specified text line (new text).
How does the REPLACE function in Excel work?
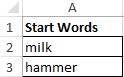
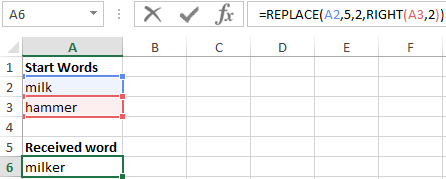
Example 1. In order to study in detail the operation of this function, we consider one of the simplest examples. Suppose we have several words in different columns, we need to get new words using the original ones. For this example, in addition to our main function REPLACE, we also use the RIGHT function — this function serves to return a certain number of characters from the end of a line of text. That is, for example, we have two words: milk and a skating rink, as a result we must get the word hammer.
REPLACE function in Excel and examples of its use
- Create a table with words on the sheet of the Excel spreadsheet workbook, as shown in the figure:
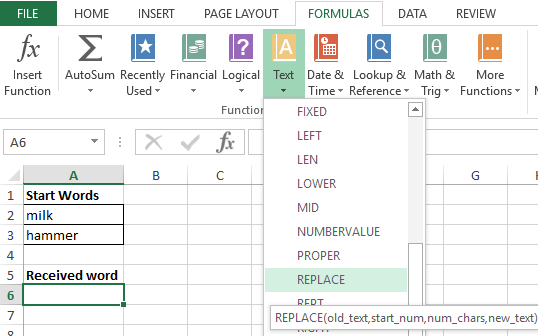
- Next, on the sheet of the workbook, we will prepare an area for placing our result — the resulting word “hammer”, as shown below. Place the cursor in cell A6 and call the function REPLACE:
- Fill the function with the arguments shown in the figure:
Let us explain the choice of these parameters as follows: cell A2 was chosen as the beginning of the text, the number 5 was set as beginning_, since it is from the fifth position of the word “Milk” we don’t take characters for our final word, the number_ of signs was set equal to 2, since this number It is not taken into account in the new word, as the new text, the set option RIGHT with the parameters of the cell A3 and taking the last two characters «ok».
Next, click on the «OK» button and get the result:
How to REPLACE a piece of text in Excel cell?
Example 2. Consider another small example. Suppose we have columns of words in the cells of the Excel spreadsheet. It is necessary to replace their letters in certain places so as to convert them.
- Let’s create a tablet with words on the sheet of an Excel workbook, as shown in the figure:
- Further, on the same sheet of the working book we will prepare an area for placing our result — modified words. Fill the cells with two types of formulas as shown in the picture:
Note! In the second formula, we use the operator “&” to add the character «s» to the male surname to convert it to the female. To solve this problem, one could use the function =CONCATENATE(B3,»s») instead of the formula =B3&»s» — the result is identical. But today it is strongly recommended to abandon this formula as it has its limitations and is more demanding on resources in comparison with a simple and convenient ampersand operator.
Источник
REPLACE, REPLACEB functions
This article describes the formula syntax and usage of the REPLACE and REPLACEB function in Microsoft Excel.
Description
REPLACE replaces part of a text string, based on the number of characters you specify, with a different text string.
REPLACEB replaces part of a text string, based on the number of bytes you specify, with a different text string.
These functions may not be available in all languages.
REPLACE is intended for use with languages that use the single-byte character set (SBCS), whereas REPLACEB is intended for use with languages that use the double-byte character set (DBCS). The default language setting on your computer affects the return value in the following way:
REPLACE always counts each character, whether single-byte or double-byte, as 1, no matter what the default language setting is.
REPLACEB counts each double-byte character as 2 when you have enabled the editing of a language that supports DBCS and then set it as the default language. Otherwise, REPLACEB counts each character as 1.
The languages that support DBCS include Japanese, Chinese (Simplified), Chinese (Traditional), and Korean.
Syntax
REPLACE(old_text, start_num, num_chars, new_text)
REPLACEB(old_text, start_num, num_bytes, new_text)
The REPLACE and REPLACEB function syntax has the following arguments:
Old_text Required. Text in which you want to replace some characters.
Start_num Required. The position of the character in old_text that you want to replace with new_text.
Num_chars Required. The number of characters in old_text that you want REPLACE to replace with new_text.
Num_bytes Required. The number of bytes in old_text that you want REPLACEB to replace with new_text.
New_text Required. The text that will replace characters in old_text.
Example
Copy the example data in the following table, and paste it in cell A1 of a new Excel worksheet. For formulas to show results, select them, press F2, and then press Enter. If you need to, you can adjust the column widths to see all the data.
Источник
SUBSTITUTE Function
Summary
The Excel SUBSTITUTE function replaces text in a given string by matching. For example =SUBSTITUTE(«952-455-7865″,»-«,»») returns «9524557865»; the dash is stripped. SUBSTITUTE is case-sensitive and does not support wildcards.
Purpose
Return value
Arguments
- text — The text to change.
- old_text — The text to replace.
- new_text — The text to replace with.
- instance — [optional] The instance to replace. If not supplied, all instances are replaced.
Syntax
Usage notes
The Excel SUBSTITUTE function can replace text by matching. Use the SUBSTITUTE function when you want to replace text based on matching, not position. Optionally, you can specify the instance of found text to replace (i.e. first instance, second instance, etc.).
SUBSTITUTE is case-sensitive. To replace one or more characters with nothing, enter an empty string («»).
Examples
Below are the formulas used in the example shown above:
The SUBSTITUTE function cannot replace more than one string at a time. However, SUBSTITUTE can be nested inside of itself to accomplish the same thing. For example, with the text «a (dog)» in cell A1, the formula below will strip parentheses () from text:
This same approach can be used in a more complex formula to normalize telephone numbers.
Use the REPLACE function to replace text at a known location in a text string. Use the SUBSTITUTE function to replace text by searching when the location is not known. Use FIND or SEARCH to determine the location of specific text.
Источник
How to use Find and Replace in Excel most efficiently

In this tutorial, you will learn how to use Find and Replace in Excel to search for specific data in a worksheet or workbook, and what you can do with those cells after finding them. We will also explore the advanced features of Excel search such as wildcards, finding cells with formulas or specific formatting, find and replace in all open workbooks and more.
When working with big spreadsheets in Excel, it’s crucial to be able to quickly find the information you want at any particular moment. Scanning through hundreds of rows and columns is certainly not the way to go, so let’s have a closer look at what the Excel Find and Replace functionality has to offer.
How to use Find in Excel
Below you will find an overview of the Excel Find capabilities as well as the detailed steps on how to use this feature in Microsoft Excel 365, 2021, 2019, 2016, 2013, 2010 and older versions.
Find value in a range, worksheet or workbook
The following guidelines tell you how to find specific characters, text, numbers or dates in a range of cells, worksheet or entire workbook.
- To begin with, select the range of cells to look in. To search across the entire worksheet, click any cell on the active sheet.
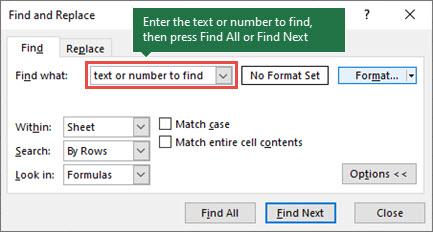
- Open the Excel Find and Replace dialog by pressing the Ctrl + F shortcut. Alternatively, go to the Home tab >Editing group and click Find & Select >Find…
- In the Find what box, type the characters (text or number) you are looking for and click either Find All or Find Next.
When you click Find Next, Excel selects the first occurrence of the search value on the sheet, the second click selects the second occurrence, and so on.
When you click Find All, Excel opens a list of all the occurrences, and you can click any item in the list to navigate to the corresponding cell.
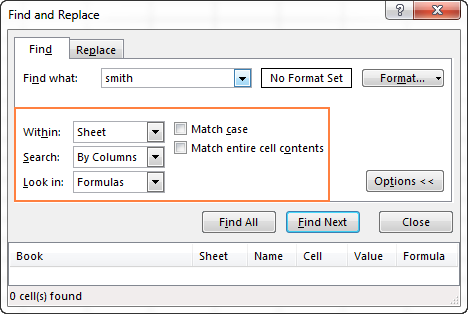
Excel Find — additional options
To fine-tune your search, click Options in the right-hand corner of the Excel Find & Replace dialog, and then do any of the following:
- To search for the specified value in the current worksheet or entire workbook, select Sheet or Workbook in the Within.
- To search from the active cell from left to right (row-by-row), select By Rows in the Search To search from top to bottom (column-by-column), select By Columns.
- To search among certain data type, select Formulas, Values, or Comments in the Look in.
- For a case-sensitive search, check the Match case check.
- To search for cells that contain only the characters you’ve entered in the Find what field, select the Match entire cell contents.
Tip. If you want to find a given value in a range, column or row, select that range, column(s) or row(s) before opening Find and Replace in Excel. For example, to limit your search to a specific column, select that column first, and then open the Find and Replace dialog.
Find cells with specific format in Excel
To find cells with certain formatting, press the Ctrl + F shortcut to open the Find and Replace dialog, click Options, then click the Format… button in the upper right corner, and define your selections in Excel Find Format dialog box.
If you want to find cells that match a format of some other cell on your worksheet, delete any criteria in the Find what box, click the arrow next to Format, select Choose Format From Cell, and click the cell with the desired formatting.
Note. Microsoft Excel saves the formatting options that you specify. If you search for some other data on a worksheet, and Excel fails to find the values that you know are there, clear the formatting options from the previous search. To do this, open the Find and Replace dialog, click the Options button on the Find tab, then click the arrow next to Format.. and select Clear Find Format.
Find cells with formulas in Excel
With Excel’s Find and Replace, you can only search in formulas for a given value, as explained in additional options of Excel Find. To find cells that contain formulas, use the Go to Special feature.
- Select the range of cells where you want to find formulas, or click any cell on the current sheet to search across the entire worksheet.
- Click the arrow next to Find & Select, and then click Go To Special. Alternatively, you can press F5 to open the Go To dialog and click the Special… button in the lower left corner.
- In the Go To Special dialog box, select Formulas, then check the boxes corresponding to the formula results you want to find, and click OK:
- Numbers — find formulas that return numeric values, including dates.
- Text — search for formulas that return text values.
- Logicals — find formulas that return Boolean values of TRUE and FALSE.
- Errors — find cells with formulas that result in errors such as #N/A, #NAME?, #REF!, #VALUE!, #DIV/0!, #NULL!, and #NUM!.

If Microsoft Excel finds any cells that meet your criteria, those cells are highlighted, otherwise a message will be displayed that no such cells have been found.
Tip. To quickly find all cells with formulas, regardless of the formula result, click Find & Select > Formulas.
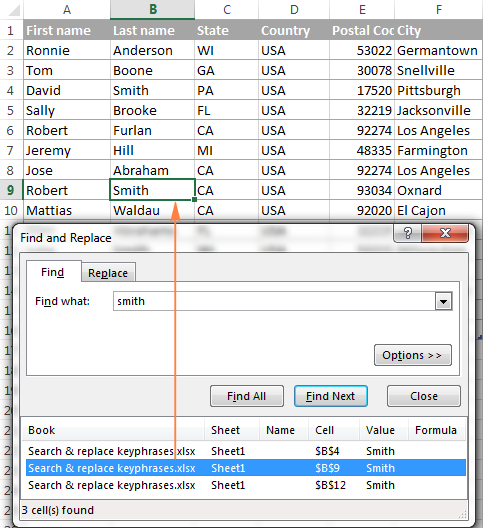
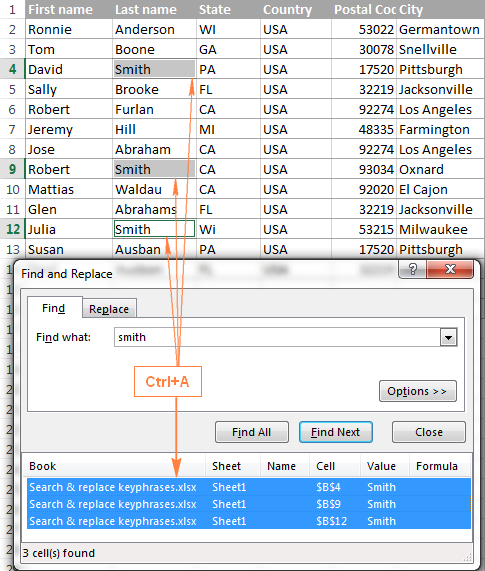
How to select and highlight all found entries on a sheet
To select all occurrences of a given value on a worksheet, open the Excel Find and Replace dialog, type the search term in the Find What box and click Find All.
Excel will display a list of found entities, and you click on any occurrence in the list (or just click anywhere within the results area to move the focus there), and press the Ctrl + A shortcut. This will select all found occurrences both on the Find and Replace dialog and on the sheet.
Once the cells are selected, you can highlight them by changing the fill color.
How to use Replace in Excel
Below you will find the step-by-step guidelines on how to use Excel Replace to change one value to another in a selected range of cells, entire worksheet or workbook.
Replace one value with another
To replace certain characters, text or numbers in an Excel sheet, make use of the Replace tab of the Excel Find & Replace dialog. The detailed steps follow below.
- Select the range of cells where you want to replace text or numbers. To replace character(s) across the entire worksheet, click any cell on the active sheet.
- Press the Ctrl + H shortcut to open the Replace tab of the Excel Find and Replace dialog.
Alternatively, go to the Home tab > Editing group and click Find & Select > Replace…
If you’ve just used the Excel Find feature, then simply switch to the Replace tab.

Tip. If something has gone wrong and you got the result different from what you’d expected, click the Undo button or press Ctrl + Z to restore the original values.
For additional Excel Replace features, click the Options button in the right-hand corner of the Replace tab. They are essentially the same as the Excel Find options we discussed a moment ago.
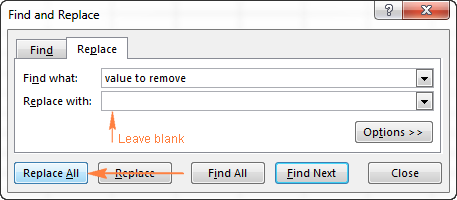
Replace text or number with nothing
To replace all occurrences of a specific value with nothing, type the characters to search for in the Find what box, leave the Replace with box blank, and click the Replace All button.
How to find or replace a line break in Excel
To replace a line break with a space or any other separator, enter the line break character in the Find what filed by pressing Ctrl + J . This shortcut is the ASCII control code for character 10 (line break, or line feed).
After pressing Ctrl + J , at first sight the Find what box will look empty, but upon a closer look you will notice a tiny flickering dot like in the screenshot below. Enter the replacement character in the Replace with box, e.g. a space character, and click Replace All.
To replace some character with a line break, do the opposite — enter the current character in the Find what box, and the line break ( Ctrl + J ) in Replace with.
How to change cell formatting on the sheet
In the first part of this tutorial, we discussed how you can find cells with specific formatting using the Excel Find dialog. Excel Replace allows you to take a step further and change the formatting of all cells on the sheet or in the entire workbook.
- Open the Replace tab of Excel’s Find and Replace dialog, and click the Options
- Next to the Find what box, click the arrow of the Format button, select Choose Format From Cell, and click on any cell with the format you want to change.
- Next to the Replace with box, either click the Format… button and set the new format using the Excel Replace Format dialog box; or click the arrow of the Format button, select Choose Format From Cell and click on any cell with the desired format.
- If you want to replace the formatting on the entire workbook, select Workbook in the Within box. If you want to replace formatting on the active sheet only, leave the default selection (Sheet).
- Finally, click the Replace All button and verify the result.
Note. This method changes the formats applied manually, it won’t work for conditionally formatted cells.
Excel Find and Replace with wildcards
The use of wildcard characters in your search criteria can automate many find and replace tasks in Excel:
- Use the asterisk (*) to find any string of characters. For example, sm* finds «smile» and «smell«.
- Use the question mark (?) to find any single character. For instance, gr?y finds «Gray» and «Grey«.
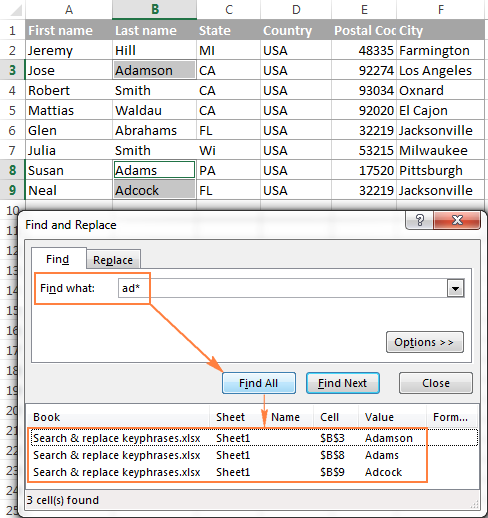
For example, to get a list of names that begin with «ad«, use «ad*» for the search criteria. Also, please keep in mind that with the default options, Excel will search for the criteria anywhere in a cell. In our case, it would return all the cells that have «ad» in any position. To prevent this from happening, click the Options button, and check the Match entire cell contents box. This will force Excel to return only the values beginning with «ad» as shown in the below screenshot.
How to find and replace wildcard characters in Excel
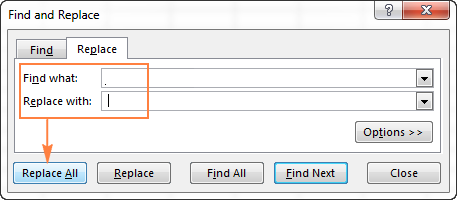
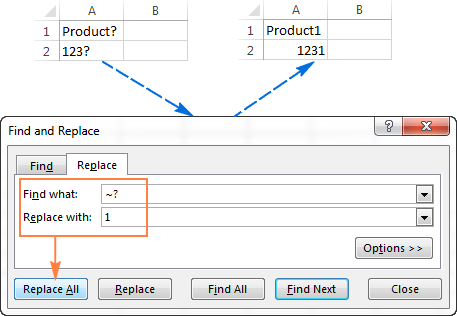
If you need to find actual asterisks or question marks in your Excel worksheet, type the tilde character (
) before them. For example, to find cells that contain asterisks, you would type
* in the Find what box. To find cells that contain question marks, use
? as your search criteria.
This is how you can replace all questions marks (?) on a worksheet with another value (number 1 in this example):
As you see, Excel successfully finds and replaces wildcards both in text and numeric values.
Tip. To find tilde characters on the sheet, type a double tilde (
) in the Find what box.
Shortcuts for find and replace in Excel
If you have been closely following the previous sections of this tutorial, you might have noticed that Excel provides 2 different ways to interact with Find and Replace commands — by clicking the ribbon buttons and by using the keyboard shortcuts.
Below there is a quick summary of what you’ve already learned and a couple more shortcuts that may save you a few more seconds.
- Ctrl+F — Excel Find shortcut that opens the Find tab of the Find & Replace
- Ctrl+H — Excel Replace shortcut that opens the Replace tab of the Find & Replace
- Ctrl+Shift+F4 — find the previous occurrence of the search value.
- Shift+F4 — find the next occurrence of the search value.
- Ctrl+J — find or replace a line break.
Search and replace in all open workbooks
As you have just see, Excel’s Find and Replace provides a lot of useful options. However, it can search only in one workbook at a time. To find and replace in all open workbooks, you can use the Advanced Find and Replace add-in by Ablebits.
The following Advanced Find and Replace features make search in Excel even more powerful:
- Find and Replace in all open workbooks or selected workbooks & worksheets.
- Simultaneous search in values, formulas, hyperlinks and comments.
- Exporting search results to a new workbook in a click.
To run the Advanced Find and Replace add-in, click on its icon on the Excel ribbon, which resides on the Ablebits Utilities tab > Search group. Alternatively, you can press Ctrl + Alt + F , or even configure it to open by the familiar Ctrl + F shortcut.
The Advanced Find and Replace pane will open, and you do the following:
- Type the characters (text or number) to search for in the Find what
- Select in which workbooks and worksheets you want to search. By default, all sheets in all open workbooks are selected.
- Choose what data type(s) to look in: values, formulas, comments, or hyperlinks. By default, all data types are selected.
Additionally, you have the following options:
- Select the Match case option to look for case-sensitive data.
- Select the Entire cell check box to search for exact and complete match, i.e. find cells that contain only the characters you’ve typed in the Find what
Click the Find All button, and you will see a list of found entries on the Search results tab. And now, you can replace all or selected occurrences with some other value, or export the found cells, rows or columns to a new workbook.
If you are willing to try the Advanced Find and Replace on your Excel sheets, you are welcome to download an evaluation version below.
I thank you for reading and hope to see you on our blog next week. In our text tutorial, we will dwell on Excel SEARCH and FIND as well as REPLACE and SUBSTITUTE functions, so please keep watching this space.
Источник
How to Replace Text in Excel with the REPLACE function (2023)
Need to replace text in multiple cells?
Excel’s REPLACE and SUBSTITUTE functions make the process much easier.
Let’s take a look at how the two functions work, how they differ, and how you put them to use in a real spreadsheet🔍
If you want to follow along with what I show you, download my workbook here.
Replacing characters in text with the REPLACE function
The REPLACE function substitutes a text string with another text string.
Let’s say your boss tells you that the product IDs for a product line must be changed.
But only a part of the product ID should be changed – not all of it.

Here, the “29FA” part of all the product IDs needs to be changed to “39LU”.
To do that with the REPLACE function, we’ll walk through the syntax of the REPLACE function, which goes like this:
=REPLACE(old_text, start_num, num_chars, new_text)
Don’t worry, it’s not as daunting as it looks. It’s actually pretty straightforward👍
Step 1: Old text
The old text argument is a reference to the cell where you want to replace some text. Write:
=REPLACE(A2

And put a comma to wrap up the first argument, and let’s move on to the next.
Step 2: Start num
The start_num argument determines where the REPLACE function should start replacing characters from.
In our case, the “29FA” part starts on the 3rd character in the text.

So, write:
=REPLACE(A2, 3,
Now, we’ve established where the REPLACE function should start to replace text.
Still with me? Then let’s dive into the next argument of the REPLACE syntax🤿
Step 3: Num chars
Also called the “number of characters” argument, this determines how many characters should be replaced with the new text.
Typically, this should be the length of the text you want to replace the old text with.
So, it ties together with the next argument.
If you want to replace “29FA” with “39LU”, then you’re replacing the next 4 characters.
Write:
=REPLACE(A2, 3, 4

And wrap it up with a comma🎁
There are situations where this num_chars argument should be a different length than the new_text argument. I’ll tell you more about that later.
Step 4: New text
The new_text argument is the replacement text for the old text.
So, simply write the new characters that should replace the old 4 characters:
=REPLACE(A2, 3, 4, “39LU”

Remember the double quotes when the replacement text is letters or a combination of numbers and letters.
Wrap up the formula with an end parenthesis and press Enter.
Now, the “29FA” part of the old product ID is replaced with “39LU”.

PRO TIP: Length of num_chars vs new_text
If you need the replacement text to be shorter or longer than the text it’s replacing, you can have a different length in the 3rd and 4th argument of REPLACE. Let me give you a few formula examples of that:
If you wanted to replace the “29FA” with “39L” instead, you’d write:
=REPLACE(A2, 3, 4, “39L”)
But the length of the 4th argument would be shorter than the 4 characters defined in the 3rd argument.
On the other hand, if you wanted to replace “FA” with “LLUU”, you’d write this:
=REPLACE(A2, 5, 2, “LLUU”)

Replacing text strings with the SUBSTITUTE function
If the string you want to replace doesn’t always appear in the same place, you’re better off using the SUBSTITUTE function.
The syntax of SUBSTITUTE goes like this:
=SUBSTITUTE(text, old_text, new_text, [instance_num])
This is a little different from the last syntax of the REPLACE function, so be careful not to get them mixed up⚠️
Step 1: Text
The text argument is just a cell reference to the cell where you want to replace text.
Write:
=SUBSTITUTE(A2

And of course, put a comma to go to the next argument.
Step 2: Old text
The SUBSTITUTE function doesn’t replace characters from a fixed position in a cell.
Instead, it cleverly searches for a text string and begins replacing characters from there🔍
So, if you want to replace the “FA” part of the product ID with “LU”, write:
=SUBSTITUTE(A2, “FU”

Step 3: New text
The new_text argument is what the old text should be replaced with.
For this example, that’s “LU”.
=SUBSTITUTE(A2, “FA”, “LU”

The new text doesn’t have to be the same length as the old text.
Step 4: Instance num
The optional instance num argument decides how many times the text should be replaced.
This is relevant if there is more than one instance of the old text.
The instance_num argument is optional. If you leave it blank, every instance of the old text is replaced by the new text😊
In the following formula example, the first 2 product IDs each have 2 instances of the “FA”. So, the instance num argument determines whether only the first instance of “FA” is replaced with “LU” or both instances of “FA” is replaced with “LU”.
As you can see from the picture below, write 1 if you want only the first instance of “FA” to be replaced.
=SUBSTITUTE(A2, “FA”, “LU”, 1)
Or don’t use the instance num argument if every instance of “FA” should be replaced:
=SUBSTITUTE(A2, “FA”, “LU”)

And that’s how to replace text dynamically based on the location of the text you want to replace.
The difference between REPLACE and SUBSTITUTE
There are a few subtle differences between these two “replace functions”.
Both of them replace one or more characters in a text string with another text string.
The difference lies in how the first string is identified.
REPLACE selects the first string based on the position. So you might replace four characters, starting with the sixth character in the string.
SUBSTITUTE selects based on whether the string matches a predefined search. You might tell Excel to replace any instance of “FA” with “LU” for example.
Other than that, the two functions are identical👬🏻
Replace text using Find and Replace
Another way to replace text is with the ‘Find and Replace’ feature of Excel.
It’s a way to substitute characters in the original cell instead of having to add additional columns with formulas.
1. Select all the cells that contain the text to replace.
2. From the ‘Home’ tab, click ‘ Find and Select’.

3. From the Find and Replace dialog box (in the replace tab) write the text you want to replace, in the ‘Find what:’ field.
4. Still within the ‘Find and Replace’ dialog box, write the new text to replace the old text with in the ‘Replace with:’ field.

5. When you click the ‘Replace all’ button, Excel replaces all instances of the old text with the new text, in the selected cells.
If you instead want to replace all instances of the text within the entire workbook, just select a single cell before opening the ‘Find and Replace’ dialog box.
(Instead of selecting multiple cells).
That’s it – Now what?
With the REPLACE and SUBSTITUTE functions, you can replace very specific strings with other strings. You can use letters, numbers, or other characters.
In short, you can replace text with extreme accuracy. And that saves you a great deal of time when you need to make a lot of edits.
Additionally, you can use the Find and Replace tool, which is the most underrated feature of Excel.
But no one got a job offer just based on their skills to replace characters in a text in Microsoft Excel.
Luckily, there are other areas of Excel that are magnets for job offers🧲
Click here to learn IF, SUMIF, VLOOKUP, and pivot tables (yup, that’s the magnets) for FREE in my 30-minute online Excel course.
Other resources
Replacing text is often used to clean up data so it’s ready for analysis, formulas, pivot tables, etc.
Other ways of cleaning up data are with other important Excel functions like LEFT, RIGHT, MID, and LEN.
Or with one of the two ways of deleting blank rows (one better than the other). Read all about it here.
Kasper Langmann2023-01-19T12:24:59+00:00
Page load link
REPLACE function is included in the text functions of MS Excel and is intended to replace a specific area of the text string containing the source text on the specified text line (new text).
How does the REPLACE function in Excel work?
Example 1. In order to study in detail the operation of this function, we consider one of the simplest examples. Suppose we have several words in different columns, we need to get new words using the original ones. For this example, in addition to our main function REPLACE, we also use the RIGHT function — this function serves to return a certain number of characters from the end of a line of text. That is, for example, we have two words: milk and a skating rink, as a result we must get the word hammer.
REPLACE function in Excel and examples of its use
- Create a table with words on the sheet of the Excel spreadsheet workbook, as shown in the figure:
- Next, on the sheet of the workbook, we will prepare an area for placing our result — the resulting word “hammer”, as shown below. Place the cursor in cell A6 and call the function REPLACE:
- Fill the function with the arguments shown in the figure:
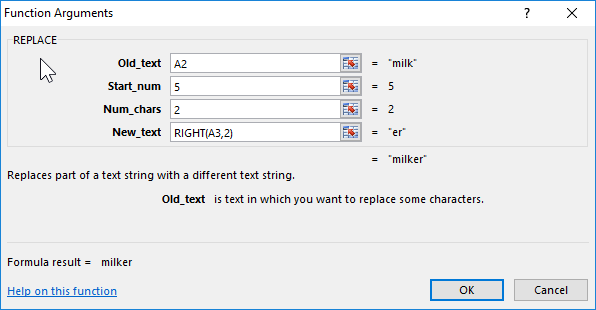
Let us explain the choice of these parameters as follows: cell A2 was chosen as the beginning of the text, the number 5 was set as beginning_, since it is from the fifth position of the word “Milk” we don’t take characters for our final word, the number_ of signs was set equal to 2, since this number It is not taken into account in the new word, as the new text, the set option RIGHT with the parameters of the cell A3 and taking the last two characters «ok».
Next, click on the «OK» button and get the result:
How to REPLACE a piece of text in Excel cell?
Example 2. Consider another small example. Suppose we have columns of words in the cells of the Excel spreadsheet. It is necessary to replace their letters in certain places so as to convert them.
- Let’s create a tablet with words on the sheet of an Excel workbook, as shown in the figure:
- Further, on the same sheet of the working book we will prepare an area for placing our result — modified words. Fill the cells with two types of formulas as shown in the picture:
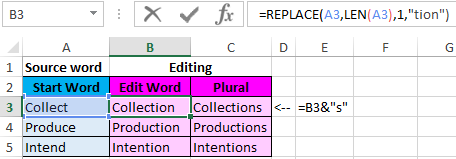
Download examples text function REPLACE in Excel
Note! In the second formula, we use the operator “&” to add the character «s» to the male surname to convert it to the female. To solve this problem, one could use the function =CONCATENATE(B3,»s») instead of the formula =B3&»s» — the result is identical. But today it is strongly recommended to abandon this formula as it has its limitations and is more demanding on resources in comparison with a simple and convenient ampersand operator.
Purpose
Replace text based on content
Usage notes
The Excel SUBSTITUTE function can replace text by matching. Use the SUBSTITUTE function when you want to replace text based on matching, not position. Optionally, you can specify the instance of found text to replace (i.e. first instance, second instance, etc.).
SUBSTITUTE is case-sensitive. To replace one or more characters with nothing, enter an empty string («»).
Examples
Below are the formulas used in the example shown above:
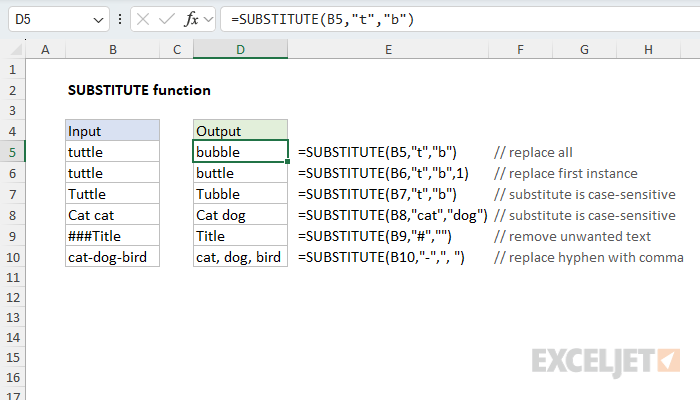
=SUBSTITUTE(B5,"t","b") // replace all t's with b's
=SUBSTITUTE(B6,"t","b",1) // replace first t with b
=SUBSTITUTE(B7,"cat","dog") // replace cat with dog
=SUBSTITUTE(B8,"&","") // replace # with nothing
=SUBSTITUTE(B9,"-",", ") // replace hyphen with comma
The SUBSTITUTE function cannot replace more than one string at a time. However, SUBSTITUTE can be nested inside of itself to accomplish the same thing. For example, with the text «a (dog)» in cell A1, the formula below will strip parentheses () from text:
=SUBSTITUTE(SUBSTITUTE(A1,"(",""),")","") // returns "a dog"
This same approach can be used in a more complex formula to normalize telephone numbers.
Related functions
Use the REPLACE function to replace text at a known location in a text string. Use the SUBSTITUTE function to replace text by searching when the location is not known. Use FIND or SEARCH to determine the location of specific text.
Notes
- SUBSTITUTE finds and replaces old_text with new_text in a text string.
- Instance limits SUBSTITUTE replacement a particular instance of old_text.
- When instance is omitted, all instances of old_text are replaced with new_text.
- SUBSTITUTE is case-sensitive and does not support wildcards.