Use the Find and Replace features in Excel to search for something in your workbook, such as a particular number or text string. You can either locate the search item for reference, or you can replace it with something else. You can include wildcard characters such as question marks, tildes, and asterisks, or numbers in your search terms. You can search by rows and columns, search within comments or values, and search within worksheets or entire workbooks.
Find
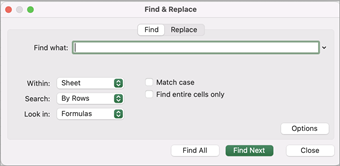
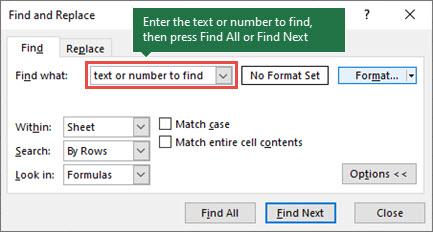
To find something, press Ctrl+F, or go to Home > Editing > Find & Select > Find.
Note: In the following example, we’ve clicked the Options >> button to show the entire Find dialog. By default, it will display with Options hidden.
-
In the Find what: box, type the text or numbers you want to find, or click the arrow in the Find what: box, and then select a recent search item from the list.
Tips: You can use wildcard characters — question mark (?), asterisk (*), tilde (~) — in your search criteria.
-
Use the question mark (?) to find any single character — for example, s?t finds «sat» and «set».
-
Use the asterisk (*) to find any number of characters — for example, s*d finds «sad» and «started».
-
Use the tilde (~) followed by ?, *, or ~ to find question marks, asterisks, or other tilde characters — for example, fy91~? finds «fy91?».
-
-
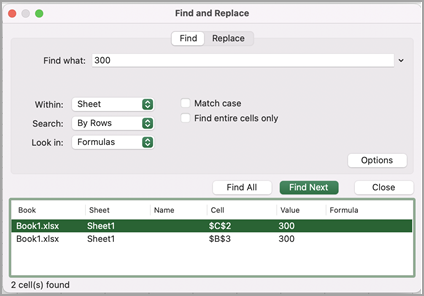
Click Find All or Find Next to run your search.
Tip: When you click Find All, every occurrence of the criteria that you are searching for will be listed, and clicking a specific occurrence in the list will select its cell. You can sort the results of a Find All search by clicking a column heading.
-
Click Options>> to further define your search if needed:
-
Within: To search for data in a worksheet or in an entire workbook, select Sheet or Workbook.
-
Search: You can choose to search either By Rows (default), or By Columns.
-
Look in: To search for data with specific details, in the box, click Formulas, Values, Notes, or Comments.
Note: Formulas, Values, Notes and Comments are only available on the Find tab; only Formulas are available on the Replace tab.
-
Match case — Check this if you want to search for case-sensitive data.
-
Match entire cell contents — Check this if you want to search for cells that contain just the characters that you typed in the Find what: box.
-
-
If you want to search for text or numbers with specific formatting, click Format, and then make your selections in the Find Format dialog box.
Tip: If you want to find cells that just match a specific format, you can delete any criteria in the Find what box, and then select a specific cell format as an example. Click the arrow next to Format, click Choose Format From Cell, and then click the cell that has the formatting that you want to search for.
Replace
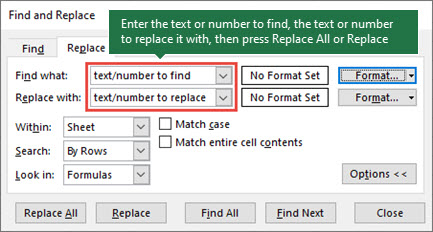
To replace text or numbers, press Ctrl+H, or go to Home > Editing > Find & Select > Replace.
Note: In the following example, we’ve clicked the Options >> button to show the entire Find dialog. By default, it will display with Options hidden.
-
In the Find what: box, type the text or numbers you want to find, or click the arrow in the Find what: box, and then select a recent search item from the list.
Tips: You can use wildcard characters — question mark (?), asterisk (*), tilde (~) — in your search criteria.
-
Use the question mark (?) to find any single character — for example, s?t finds «sat» and «set».
-
Use the asterisk (*) to find any number of characters — for example, s*d finds «sad» and «started».
-
Use the tilde (~) followed by ?, *, or ~ to find question marks, asterisks, or other tilde characters — for example, fy91~? finds «fy91?».
-
-
In the Replace with: box, enter the text or numbers you want to use to replace the search text.
-
Click Replace All or Replace.
Tip: When you click Replace All, every occurrence of the criteria that you are searching for will be replaced, while Replace will update one occurrence at a time.
-
Click Options>> to further define your search if needed:
-
Within: To search for data in a worksheet or in an entire workbook, select Sheet or Workbook.
-
Search: You can choose to search either By Rows (default), or By Columns.
-
Look in: To search for data with specific details, in the box, click Formulas, Values, Notes, or Comments.
Note: Formulas, Values, Notes and Comments are only available on the Find tab; only Formulas are available on the Replace tab.
-
Match case — Check this if you want to search for case-sensitive data.
-
Match entire cell contents — Check this if you want to search for cells that contain just the characters that you typed in the Find what: box.
-
-
If you want to search for text or numbers with specific formatting, click Format, and then make your selections in the Find Format dialog box.
Tip: If you want to find cells that just match a specific format, you can delete any criteria in the Find what box, and then select a specific cell format as an example. Click the arrow next to Format, click Choose Format From Cell, and then click the cell that has the formatting that you want to search for.
There are two distinct methods for finding or replacing text or numbers on the Mac. The first is to use the Find & Replace dialog. The second is to use the Search bar in the ribbon.
Find & Replace dialog
Search bar and options
-
Press Ctrl+F or go to Home > Find & Select > Find.
-
In Find what: type the text or numbers you want to find.
-
Select Find Next to run your search.
-
You can further define your search:
-
Within: To search for data in a worksheet or in an entire workbook, select Sheet or Workbook.
-
Search: You can choose to search either By Rows (default), or By Columns.
-
Look in: To search for data with specific details, in the box, click Formulas, Values, Notes, or Comments.
-
Match case — Check this if you want to search for case-sensitive data.
-
Match entire cell contents — Check this if you want to search for cells that contain just the characters that you typed in the Find what: box.
-
Tips: You can use wildcard characters — question mark (?), asterisk (*), tilde (~) — in your search criteria.
-
Use the question mark (?) to find any single character — for example, s?t finds «sat» and «set».
-
Use the asterisk (*) to find any number of characters — for example, s*d finds «sad» and «started».
-
Use the tilde (~) followed by ?, *, or ~ to find question marks, asterisks, or other tilde characters — for example, fy91~? finds «fy91?».
-
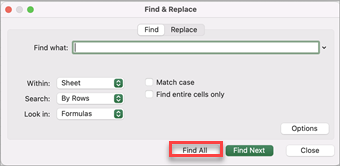
Press Ctrl+F or go to Home > Find & Select > Find.
-
In Find what: type the text or numbers you want to find.
-
Select Find All to run your search for all occurrences.
Note: The dialog box expands to show a list of all the cells that contain the search term, and the total number of cells in which it appears.
-
Select any item in the list to highlight the corresponding cell in your worksheet.
Note: You can edit the contents of the highlighted cell.
-
Press Ctrl+H or go to Home > Find & Select > Replace.
-
In Find what, type the text or numbers you want to find.
-
You can further define your search:
-
Within: To search for data in a worksheet or in an entire workbook, select Sheet or Workbook.
-
Search: You can choose to search either By Rows (default), or By Columns.
-
Match case — Check this if you want to search for case-sensitive data.
-
Match entire cell contents — Check this if you want to search for cells that contain just the characters that you typed in the Find what: box.
Tips: You can use wildcard characters — question mark (?), asterisk (*), tilde (~) — in your search criteria.
-
Use the question mark (?) to find any single character — for example, s?t finds «sat» and «set».
-
Use the asterisk (*) to find any number of characters — for example, s*d finds «sad» and «started».
-
Use the tilde (~) followed by ?, *, or ~ to find question marks, asterisks, or other tilde characters — for example, fy91~? finds «fy91?».
-
-
-
In the Replace with box, enter the text or numbers you want to use to replace the search text.
-
Select Replace or Replace All.
Tips:
-
When you select Replace All, every occurrence of the criteria that you are searching for is replaced.
-
When you select Replace, you can replace one instance at a time by selecting Next to highlight the next instance.
-
-
Select any cell to search the entire sheet or select a specific range of cells to search.
-
Press Command + F or select the magnifying glass to expand the Search bar and type the text or number you want to find in the search field.
Tips: You can use wildcard characters — question mark (?), asterisk (*), tilde (~) — in your search criteria.
-
Use the question mark (?) to find any single character — for example, s?t finds «sat» and «set».
-
Use the asterisk (*) to find any number of characters — for example, s*d finds «sad» and «started».
-
Use the tilde (~) followed by ?, *, or ~ to find question marks, asterisks, or other tilde characters — for example, fy91~? finds «fy91?».
-
-
Press return.
Notes:
-
To find the next instance of the item you are searching for, press return again or use the Find dialog box and select Find Next.
-
To specify additional search options, select the magnifying glass and select Search in Sheet or Search in Workbook. You can also select the Advanced option, which launches the Find dialog.
Tip: You can cancel a search in progress by pressing ESC.
-
Find
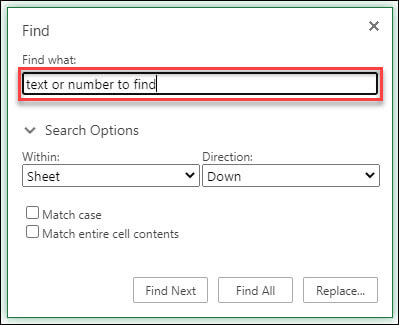
To find something, press Ctrl+F, or go to Home > Editing > Find & Select > Find.
Note: In the following example, we’ve clicked > Search Options to show the entire Find dialog. By default, it will display with Search Options hidden.
-
In the Find what: box, type the text or numbers you want to find.
Tips: You can use wildcard characters — question mark (?), asterisk (*), tilde (~) — in your search criteria.
-
Use the question mark (?) to find any single character — for example, s?t finds «sat» and «set».
-
Use the asterisk (*) to find any number of characters — for example, s*d finds «sad» and «started».
-
Use the tilde (~) followed by ?, *, or ~ to find question marks, asterisks, or other tilde characters — for example, fy91~? finds «fy91?».
-
-
Click Find Next or Find All to run your search.
Tip: When you click Find All, every occurrence of the criteria that you are searching for will be listed, and clicking a specific occurrence in the list will select its cell. You can sort the results of a Find All search by clicking a column heading.
-
Click > Search Options to further define your search if needed:
-
Within: To search for data within a certain selection, choose Selection. To search for data in a worksheet or in an entire workbook, select Sheet or Workbook.
-
Direction: You can choose to search either Down (default), or Up.
-
Match case — Check this if you want to search for case-sensitive data.
-
Match entire cell contents — Check this if you want to search for cells that contain just the characters that you typed in the Find what box.
-
Replace
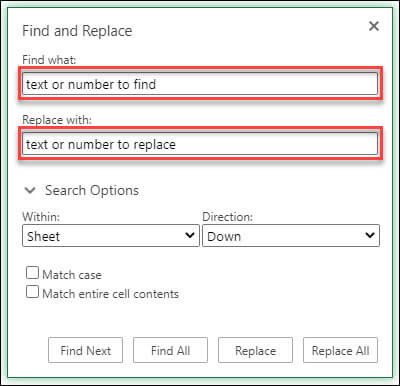
To replace text or numbers, press Ctrl+H, or go to Home > Editing > Find & Select > Replace.
Note: In the following example, we’ve clicked > Search Options to show the entire Find dialog. By default, it will display with Search Options hidden.
-
In the Find what: box, type the text or numbers you want to find.
Tips: You can use wildcard characters — question mark (?), asterisk (*), tilde (~) — in your search criteria.
-
Use the question mark (?) to find any single character — for example, s?t finds «sat» and «set».
-
Use the asterisk (*) to find any number of characters — for example, s*d finds «sad» and «started».
-
Use the tilde (~) followed by ?, *, or ~ to find question marks, asterisks, or other tilde characters — for example, fy91~? finds «fy91?».
-
-
In the Replace with: box, enter the text or numbers you want to use to replace the search text.
-
Click Replace or Replace All.
Tip: When you click Replace All, every occurrence of the criteria that you are searching for will be replaced, while Replace will update one occurrence at a time.
-
Click > Search Options to further define your search if needed:
-
Within: To search for data within a certain selection, choose Selection. To search for data in a worksheet or in an entire workbook, select Sheet or Workbook.
-
Direction: You can choose to search either Down (default), or Up.
-
Match case — Check this if you want to search for case-sensitive data.
-
Match entire cell contents — Check this if you want to search for cells that contain just the characters that you typed in the Find what box.
-
Need more help?
You can always ask an expert in the Excel Tech Community or get support in the Answers community.
Recommended articles
Merge and unmerge cells
REPLACE, REPLACEB functions
Apply data validation to cells
Содержание
- REPLACE, REPLACEB functions
- Description
- Syntax
- Example
- How to find and replace multiple values at once in Excel (bulk replace)
- Find and replace multiple values with nested SUBSTITUTE
- Search and replace multiple entries with XLOOKUP
- Multiple replace using recursive LAMBDA function
- Example 1. Search and replace multiple words / strings at once
- Example 2. Replace multiple characters in Excel
- Mass find and replace with UDF
- Bulk replace in Excel with VBA macro
- How to use the macro
- Multiple find and replace in Excel with Substring tool
REPLACE, REPLACEB functions
This article describes the formula syntax and usage of the REPLACE and REPLACEB function in Microsoft Excel.
Description
REPLACE replaces part of a text string, based on the number of characters you specify, with a different text string.
REPLACEB replaces part of a text string, based on the number of bytes you specify, with a different text string.
These functions may not be available in all languages.
REPLACE is intended for use with languages that use the single-byte character set (SBCS), whereas REPLACEB is intended for use with languages that use the double-byte character set (DBCS). The default language setting on your computer affects the return value in the following way:
REPLACE always counts each character, whether single-byte or double-byte, as 1, no matter what the default language setting is.
REPLACEB counts each double-byte character as 2 when you have enabled the editing of a language that supports DBCS and then set it as the default language. Otherwise, REPLACEB counts each character as 1.
The languages that support DBCS include Japanese, Chinese (Simplified), Chinese (Traditional), and Korean.
Syntax
REPLACE(old_text, start_num, num_chars, new_text)
REPLACEB(old_text, start_num, num_bytes, new_text)
The REPLACE and REPLACEB function syntax has the following arguments:
Old_text Required. Text in which you want to replace some characters.
Start_num Required. The position of the character in old_text that you want to replace with new_text.
Num_chars Required. The number of characters in old_text that you want REPLACE to replace with new_text.
Num_bytes Required. The number of bytes in old_text that you want REPLACEB to replace with new_text.
New_text Required. The text that will replace characters in old_text.
Example
Copy the example data in the following table, and paste it in cell A1 of a new Excel worksheet. For formulas to show results, select them, press F2, and then press Enter. If you need to, you can adjust the column widths to see all the data.
Источник
How to find and replace multiple values at once in Excel (bulk replace)

In this tutorial, we will look at several ways to find and replace multiple words, strings, or individual characters, so you can choose the one that best suits your needs.
How do people usually search in Excel? Mostly, by using the Find & Replace feature, which works fine for single values. But what if you have tens or even hundreds of items to replace? Surely, no one would want to make all those replacements manually one-by-one, and then do it all over again when the data changes. Luckily, there are a few more effective methods to do mass replace in Excel, and we are going to investigate each of them in detail.
Find and replace multiple values with nested SUBSTITUTE
The easiest way to find and replace multiple entries in Excel is by using the SUBSTITUTE function.
The formula’s logic is very simple: you write a few individual functions to replace an old value with a new one. And then, you nest those functions one into another, so that each subsequent SUBSTITUTE uses the output of the previous SUBSTITUTE to look for the next value.
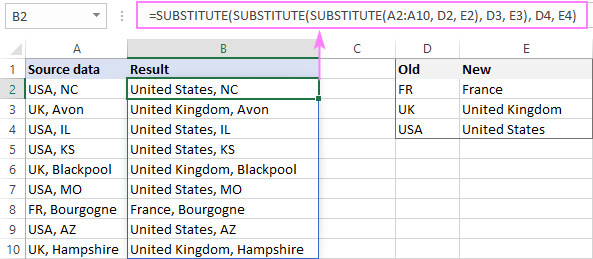
In the list of locations in A2:A10, suppose you want to replace the abbreviated country names (such as FR, UK and USA) with full names.
To have it done, enter the old values in D2:D4 and the new values in E2:E4 like shown in the screenshot below. And then, put the below formula in B2 and press Enter:
=SUBSTITUTE(SUBSTITUTE(SUBSTITUTE(A2:A10, D2, E2), D3, E3), D4, E4)
…and you will have all the replacements done at once:
Please note, the above approach only works in Excel 365 that supports dynamic arrays.
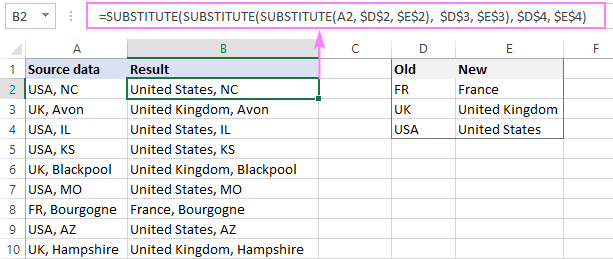
In pre-dynamic versions of Excel 2019, Excel 2016 and earlier, the formula needs to be written for the topmost cell (B2), and then copied to the below cells:
=SUBSTITUTE(SUBSTITUTE(SUBSTITUTE(A2, $D$2, $E$2), $D$3, $E$3), $D$4, $E$4)
Please pay attention that, in this case, we lock the replacement values with absolute cell references, so they won’t shift when copying the formula down.
Note. The SUBSTITUTE function is case-sensitive, meaning you should type the old values (old_text) in the same letter case as they appear in the original data.
As easy as it could possibly be, this method has a significant drawback — when you have dozens of items to replace, nested functions become quite difficult to manage.
Advantages: easy-to-implement; supported in all Excel versions
Drawbacks: best to be used for a limited number of find/replace values
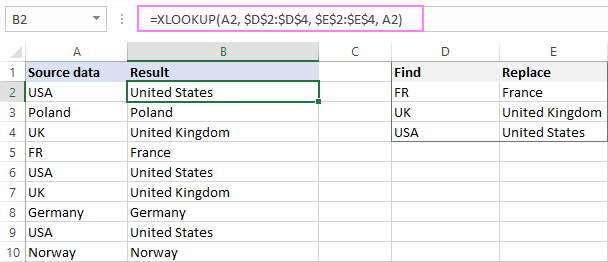
Search and replace multiple entries with XLOOKUP
In situation when you are looking to replace the entire cell content, not its part, the XLOOKUP function comes in handy.
Let’s say you have a list of countries in column A and aim to replace all the abbreviations with the corresponding full names. Like in the previous example, you start with inputting the «Find» and «Replace» items in separate columns (D and E respectively), and then enter this formula in B2:
=XLOOKUP(A2, $D$2:$D$4, $E$2:$E$4, A2)
Translated from the Excel language into the human language, here’s what the formula does:
Search for the A2 value (lookup_value) in D2:D4 (lookup_array) and return a match from E2:E4 (return_array). If not found, pull the original value from A2.
Double-click the fill handle to get the formula copied to the below cells, and the result won’t keep you waiting:
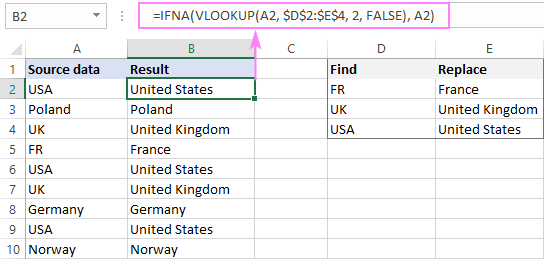
Since the XLOOKUP function is only available in Excel 365, the above formula won’t work in earlier versions. However, you can easily mimic this behavior with a combination of IFERROR or IFNA and VLOOKUP:
=IFNA(VLOOKUP(A2, $D$2:$E$4, 2, FALSE), A2)
Note. Unlike SUBSTITUTE, the XLOOKUP and VLOOKUP functions are not case-sensitive, meaning they search for the lookup values ignoring the letter case. For instance, our formula would replace both FR and fr with France.
Advantages: unusual use of usual functions; works in all Excel versions
Drawbacks: works on a cell level, cannot replace part of the cell contents
Multiple replace using recursive LAMBDA function
For Microsoft 365 subscribers, Excel provides a special function that allows creating custom functions using a traditional formula language. Yep, I’m talking about LAMBDA. The beauty of this method is that it can convert a very lengthy and complex formula into a very compact and simple one. Moreover, it lets you create your own functions that do not exist in Excel, something that was before possible only with VBA.
For the detailed information about creating and using custom LAMBDA functions, please check out this tutorial: How to write LAMBDA functions in Excel. Here, we will discuss a couple of practical examples.
Advantages: the result is an elegant and amazingly simple to use function, no matter the number of replacement pairs
Drawbacks: available only in Excel 365; workbook-specific and cannot be reused across different workbooks
Example 1. Search and replace multiple words / strings at once
To replace multiple words or text in one go, we’ve created a custom LAMBDA function, named MultiReplace, which can take one of these forms:
=LAMBDA(text, old, new, IF(old<>«», MultiReplace(SUBSTITUTE(text, old, new), OFFSET(old, 1, 0), OFFSET(new, 1, 0)), text))
=LAMBDA(text, old, new, IF(old=»», text, MultiReplace(SUBSTITUTE(text, old, new), OFFSET(old, 1, 0), OFFSET(new, 1, 0))))
Both are recursive functions that call themselves. The difference is only in how the exit point is established.
In the first formula, the IF function checks whether the old list is not blank (old<>«»). If TRUE, the MultiReplace function is called. If FALSE, the function returns text it its current form and exits.
The second formula uses the reverse logic: if old is blank (old=»»), then return text and exit; otherwise call MultiReplace.
The trickiest part is accomplished! What is left for you to do is to name the MultiReplace function in the Name Manager like shown in the screenshot below. For the detailed guidelines, please see How to name a LAMBDA function.
Once the function gets a name, you can use it just like any other inbuilt function.
Whichever of the two formula variations you choose, from the end-user perspective, the syntax is as simple as this:
- Text — the source data
- Old — the values to find
- New — the values to replace with
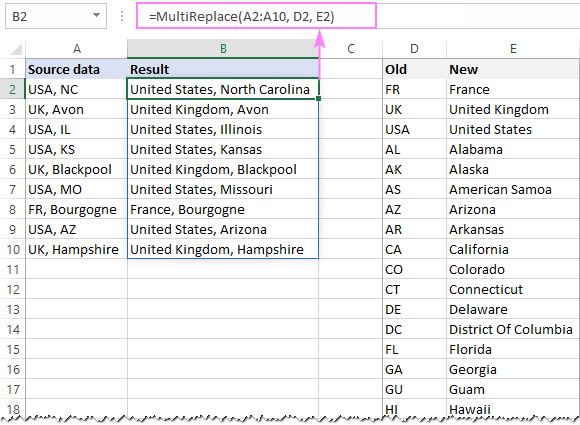
Taking the previous example a little further, let’s replace not only the country abbreviations but the state abbreviations as well. For this, type the abbreviations (old values) in column D beginning in D2 and the full names (new values) in column E beginning in E2.
In B2, enter the MultiReplace function:
=MultiReplace(A2:A10, D2, E2)
Hit Enter and enjoy the results 🙂
How this formula works
The clue to understanding the formula is understanding recursion. This may sound complicated, but the principle is quite simple. With each iteration, a recursive function solves one small instance of a bigger problem. In our case, the MultiReplace function loops through the old and new values and, with each loop, performs one replacement:
MultiReplace (SUBSTITUTE(text, old, new), OFFSET(old, 1, 0), OFFSET(new, 1, 0))
As with nested SUBSTITUTE functions, the result of the previous SUBSTITUTE becomes the text parameter for the next SUBSTITUTE. In other words, on each subsequent call of MultiReplace, the SUBSTITUTE function processes not the original text string, but the output of the previous call.
To handle all the items on the old list, we start with the topmost cell, and use the OFFSET function to move 1 row down with each interaction:
The same is done for the new list:
The crucial thing is to provide a point of exit to prevent recursive calls from proceeding forever. It is done with the help of the IF function — if the old cell is empty, the function returns text it its present form and exits:
=LAMBDA(text, old, new, IF(old=»», text, MultiReplace(…)))
=LAMBDA(text, old, new, IF(old<>«», MultiReplace(…), text))
Example 2. Replace multiple characters in Excel
In principle, the MultiReplace function discussed in the previous example can handle individual characters as well, provided that each old and new character is entered in a separate cell, exactly like the abbreviated and full names in the above screenshots.
If you’d rather input the old characters in one cell and the new characters in another cell, or type them directly in the formula, then you can create another custom function, named ReplaceChars, by using one of these formulas:
=LAMBDA(text, old_chars, new_chars, IF(old_chars<>«», ReplaceChars(SUBSTITUTE(text, LEFT(old_chars), LEFT(new_chars)), RIGHT(old_chars, LEN(old_chars)-1), RIGHT(new_chars, LEN(new_chars)-1)), text))
=LAMBDA(text, old_chars, new_chars, IF(old_chars=»», text, ReplaceChars(SUBSTITUTE(text, LEFT(old_chars), LEFT(new_chars)), RIGHT(old_chars, LEN(old_chars)-1), RIGHT(new_chars, LEN(new_chars)-1))))
Remember to name your new Lambda function in the Name Manager as usual:
And your new custom function is ready for use:
- Text — the original strings
- Old — the characters to search for
- New — the characters to replace with
To give it a field test, let’s do something that is often performed on imported data — replace smart quotes and smart apostrophes with straight quotes and straight apostrophes.
First, we input the smart quotes and smart apostrophe in D2, straight quotes and straight apostrophe in E2, separating the characters with spaces for better readability. (As we use the same delimiter in both cells, it won’t have any impact on the result — Excel will just replace a space with a space.)
After that, we enter this formula in B2:
=ReplaceChars(A2:A4, D2, E2)
And get exactly the results we were looking for:
It is also possible to type the characters directly in the formula. In our case, just remember to «duplicate» the straight quotes like this:
=ReplaceChars(A2:A4, «вЂњ ” ’», «»» «» ‘»)
How this formula works
The ReplaceChars function cycles through the old_chars and new_chars strings and makes one replacement at a time beginning from the first character on the left. This part is done by the SUBSTITUTE function:
SUBSTITUTE(text, LEFT(old_chars), LEFT(new_chars))
With each iteration, the RIGHT function strips off one character from the left of both the old_chars and new_chars strings, so that LEFT could fetch the next pair of characters for substitution:
ReplaceChars(SUBSTITUTE(text, LEFT(old_chars), LEFT(new_chars)), RIGHT(old_chars, LEN(old_chars)-1), RIGHT(new_chars, LEN(new_chars)-1))
Before each recursive call, the IF function evaluates the old_chars string. If it is not empty, the function calls itself. As soon as the last character has been replaced, the iteration process finishes, the formula returns text it its present form and exits.
Note. Because the SUBSTITUTE function used in our core formulas is case-sensitive, both Lambdas (MultiReplace and ReplaceChars) treat uppercase and lowercase letters as different characters.
Mass find and replace with UDF
In case the LAMBDA function is not available in your Excel, you can write a user-defined function for multi-replace in a traditional way using VBA.
To distinguish the UDF from the LAMBDA-defined MultiReplace function, we are going to name it differently, say MassReplace. The code of the function is as follows:
Like LAMBDA-defined functions, UDFs are workbook-wide. That means the MassReplace function will work only in the workbook in which you have inserted the code. If you are not sure how to do this correctly, please follow the steps described in How to insert VBA code in Excel.
Once the code is added to your workbook, the function will appear in the formula intellisense — only the function’s name, not the arguments! Though, I believe it’s no big deal to remember the syntax:
- Input_range — the source range where you want to replace values.
- Find_range — the characters, strings, or words to search for.
- Replace_range — the characters, strings, or words to replace with.
In Excel 365, due to support for dynamic arrays, this works as a normal formula, which only needs to be entered in the top cell (B2):
=MassReplace(A2:A10, D2:D4, E2:E4)
In pre-dynamic Excel, this works as an old-style CSE array formula: you select the entire source range (B2:B10), type the formula, and press the Ctrl + Shift + Enter keys simultaneously to complete it.
Advantages: a decent alternative to a custom LAMBDA function in Excel 2019, Excel 2016 and earlier versions
Drawbacks: the workbook must be saved as a macro-enabled .xlsm file
Bulk replace in Excel with VBA macro
If you love automating common tasks with macros, then you can use the following VBA code to find and replace multiple values in a range.
To make use of the macro right away, you can download our sample workbook containing the code. Or you can insert the code in your own workbook.
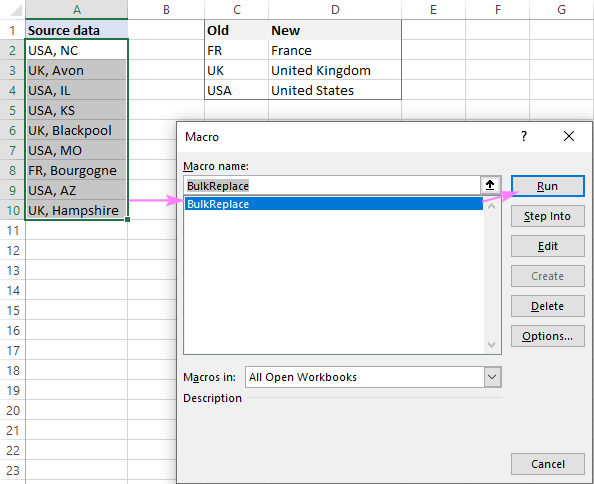
How to use the macro
Before running the macro, type the old and new values into two adjacent columns as shown in the image below (C2:D4).
And then, select your source data, press Alt + F8 , pick the BulkReplace macro, and click Run.
As the source rage is preselected, just verify the reference, and click OK:
After that, select the replace range, and click OK:
Done!
Advantages: setup once, re-use anytime
Drawbacks: the macro needs to be run with every data change
Multiple find and replace in Excel with Substring tool
In the very first example, I mentioned that nested SUBSTITUTE is the easiest way to replace multiple values in Excel. I admit that I was wrong. Our Ultimate Suite makes things even easier!
To do mass replace in your worksheet, head over to the Ablebits Data tab and click Substring Tools > Replace Substrings.
The Replace Substrings dialog box will appear asking you to define the Source range and Substrings range.
With the two ranges selected, click the Replace button and find the results in a new column inserted to the right of the original data. Yep, it’s that easy!
Tip. Before clicking Replace, there is one important thing for you to consider — the Case-sensitive box. Be sure to select it if you wish to handle the uppercase and lowercase letters as different characters. In this example, we tick this option because we only want to replace the capitalized strings and leave the substrings like «fr», «uk», or «ak» within other words intact.
If you are curious to know what other bulk operations can be performed on strings, check out other Substring Tools included with our Ultimate Suite. Or even better, download the evaluation version below and give it a try!
That’s how to find and replace multiple words and characters at once in Excel. I thank you for reading and hope to see you on our blog next week!
Источник
Download Article
Download Article
This wikiHow will show you how to find and replace cell values in Microsoft Excel. The Find and Replace tool is available in all versions of Excel, including the mobile Excel app.
-
1
Open your workbook in Excel. You can open your project by clicking the File menu and selecting Open. You can also open it by right-clicking the file and selecting Open With > Excel.
- This method should work for all versions of Microsoft Excel beginning with Excel 2007.
-
2
Click the Home tab. You’ll find this in the editing menu above your document.
Advertisement
-
3
Click Find & Select. You’ll find this in the «Editing» grouping of the Home tab with the icon of a magnifying glass.
-
4
Click Replace. This is usually the first listing in the drop-down menu.
-
5
Enter the original value in the «Find what» text box field. This is the text that will be replaced.
- You can use * to find a string of characters. For example, s*d will find «sad» as well as «started.»[1]
- You can use ? to replace a single character in a search. For example, s?t will find «sat» and «set.»[2]
- You can use * to find a string of characters. For example, s*d will find «sad» as well as «started.»[1]
-
6
Enter the new value in the «Replace with» text box field. This text will replace the original text.
- You can opt to match the case, so you can change every instance of «wikihow» to «wikiHow.»
- You can chose to contain your find and replace to the current worksheet or apply it to the entire workbook.
-
7
Click Replace All or Replace. If you want to decide to replace each original value individually, choose Replace, but if you want to replace all the original values at once, choose replace all.[3]
Advertisement
-
1
Open your project in Excel. This app icon looks like a green-and-white spreadsheet icon with an «X» next to it. You can find this app on the Home screen, in the app drawer, or by searching.
- If you don’t have the Excel app, you can get it for free from the App Store (iOS) and the Google Play Store (Android).
- Tap the Open tab in Excel to find all your recent documents.
-
2
Tap the search icon
that looks like a magnifying glass. You’ll see this in the top right corner of your screen.
- A search bar will appear at the top of your document.
-
3
Tap the gear icon
. You’ll see this next to the search bar that dropped down. Search options will appear.
-
4
Tap to select Find and Replace or Find and Replace All. As you tap an option, you’ll see the search bar at the top of the screen change to fit your selection.
- Tap Find and Replace if you want to replace each original value individually.
- Tap Find and Replace All if you want to replace all the original values instantly.
-
5
Tap Done (iOS) or X (Android). You’ll see this option at the top right of the search settings.
-
6
Type your original value into the «Find» bar. This is the current value located in your document.
-
7
Type the new value into the «Replace» bar. This value will replace the current value in the document.
-
8
Tap Replace or Replace All. You’ll see this with your «find and replace» terms.
Advertisement
Ask a Question
200 characters left
Include your email address to get a message when this question is answered.
Submit
Advertisement
Thanks for submitting a tip for review!
wikiHow Video: How to Replace Values in Excel
References
About This Article
Article SummaryX
To find and replace cell values on your computer, open your worksheet in Excel and click the Home tab. Click the Find & Select button on the toolbar, and then select Replace on the menu. On the «»Find and Replace»» window, enter the text you want to find into the «»Find what»» field. You can even use wildcards for a string of text. Wildcards are special characters that replace other characters in searches, like a question mark in place of a letter or an asterisk. In the «»Replace with»» field, type your replacement text exactly how it should appear. To replace all original values at once, click the Replace All button. If you’d rather approve each replacement, click Replace instead.
To replace cell values in the mobile Excel app, open Excel and select a file to edit. Tap the search icon at the top-right corner, and then tap the gear icon next to the search bar to view your options. If you want to replace multiple instances of the same text all at once, tap Find and Replace All. If you’d rather manually approve each replacement, select Replace instead. Then, Tap Done at the top-right corner. Now, type the text you want to replace into the «»Find»» bar, and the replacement text into the «»Replace»» bar. Finally, tap Replace or ‘Replace All to replace the cell values.
Did this summary help you?
Thanks to all authors for creating a page that has been read 18,609 times.
Is this article up to date?
Home > Microsoft Excel > How to Find and Replace in Excel? A Step-by-Step Guide
(Note: This guide on how to Find and Replace in Excel is suitable for all Excel versions including Office 365)
Have you ever faced a situation where you have to change a particular data in multiple places? Of course, you can choose to find and replace the data manually. However, finding and changing each data one after the other might be easy when the data are less. You will need an effective way to find and replace multiple data simultaneously.
In this article, I will tell you how to use find and replace in Excel along with its features.
You’ll Learn:
- What Is Find and Replace in Excel?
- How to Find and Replace in Excel?
- Additional Options to Find and Replace in Excel
Watch our video on how to use find and replace in Excel
Related Reads:
How to Calculate Factorial in Excel? Along with 2 Easy Examples
How to Graph a Function in Excel? 2 Easy Ways
Short Date Format in Excel – 3 Different Methods
What Is Find and Replace in Excel?
As its name suggests, the Find and Replace option in Excel is used to search for any particular data and replace it with the data of your choice. You can search for any number or string and replace them one after the other or replace all the data at the same time.
Additionally, Excel’s Find and Replace option allows you to use wildcards to find any missing data only by using a part of the data. And, you can also search between worksheets or whole workbooks.
How to Find and Replace in Excel?
Now, let us see how to use the Find and Replace option in Excel along with its functionalities.
In short, the Find option is mainly helpful when you want to find any particular data across multiple cells. The Replace option replaces the found data with any value of your choice. Using these options, you can find and replace the cells containing data across the spreadsheet or even the whole workbook.
Let us now see how the Find and Replace option works in Excel with an example.
Consider an Excel worksheet that consists of the consolidated mark list of 20 students for 20 subjects. There happened to be a small mishap in the validation process and the students who scored 100 marks should be changed to 99. So, you have to find the cells which house the value “100” and change them to “99”. This process can be a little tedious manually. In these cases, you can use the Find and Replace in Excel.
To find and replace the values, navigate to Home. From the Find & Select dropdown, click on Replace. Or, you can use the keyboard shortcut Ctrl+H.
This opens up the Find and Replace dialog box.
In the Find what: text box, enter the value you want to find. In the Replace with: dialog box, enter the value you want to replace the found value with. In this case, we want to search through the worksheet to find the value “100” and replace it with the value “99”.
Once you have entered the value, you can see two buttons to help you find the data and the other two buttons to help you replace the data. Let us see them one by one in detail.
Find Next
This option finds the particular value and highlights them to the user one after the other.
When you enter 100 and click on Find Next, Excel searches through the sheet and shows you the first occurrence of the particular data. When you click on the Find Next again, Excel searches for the next occurrence of the data in the worksheet.
When just finding the data, Excel goes in loops displaying the same occurrences even after highlighting all the entries.
Find All
This option finds all the entries of the particular data and shows them to the user in an instant.
When you click the Find All button, Excel shows you all the cells that contain the particular value. You can scroll down and click on the value to display it in the worksheet.
If you want to see all the cells with the particular value at the same time, press Ctrl+A. This shows you all the entries of the particular value in the worksheet.
Note: If you want to only find the occurrences of the values without any need to replace them, just click on the Find tab in the Find and Replace dialog.
Replace
This option is used to replace the values in cells one after the other. This is particularly helpful when you have to confirm the values before replacing them.
When you first click on the Replace button, Excel replaces the first instance of the value with the value in the Replace with: textbox and highlights the next occurrence of the value.
If you click on the Replace button again, the highlighted value will be replaced and the next occurrence of the value will be highlighted.
Clicking on the Replace button replaces the values one after the other. If you don’t want to replace the particular value, click on the Find Next button. This will skip replacing the value in the cell and move on to highlight the next occurrence of the particular value.
Once you have replaced all the entries of the particular value, Excel will throw a pop-up saying “Excel couldn’t find a match”. Click OK to close the pop-up.
Note: If you only want to find and replace the values in Excel, you can straight away click on the Replace or Replace All button instead of finding the values using the Find Next and Find All buttons.
Replace All
If you feel like replacing the values one after the other is a little less effective, click on the Replace All button to replace all the values in one go.
This replaces all the values in the Find what: textbox with the value from the Replace with: text box.
Once you click on Replace All, Excel replaces all the data and throws a pop-up showing the number of replacements done. Click OK to close the pop-up.
Note: Always be very cautious when using the Replace All button because it changes all the occurrences of the particular value in the worksheet. If you ever feel like there might be some instances that need not be replaced, you can just use the normal Replace button to check and replace the values one after the other.
| Replace All | Replaces all the cells with a particular value. |
| Replace | Replaces the cell with the particular value one after the other. |
| Find All | This option searches and finds the total occurrences of the particular value in a single go. |
| Find Next | Find Next option searches and displays the occurrence of the value one after the other. |
Also Read:
Excel String Compare – 5 Easy Methods
How to Add a Secondary Axis in Excel? 2 Easy Ways
How to Wrap Text in Excel? With 6 Simple Methods
Additional Options to Find and Replace in Excel
Excel has various functionalities to Find and Replace the data in any way possible. Clicking on the Options button in the Find and Replace dialog box shows you advanced options to find and replace any data in Excel. Let us see each option and its functionalities in detail.
Format Option
This option enables you to set the format of the cells where you can search or replace the values.
Only when the format of the cell is the same as the format specified in the Find what: textbox, Excel finds and displays the value. The same is true for the Replace with: text box. When you specify any format in the Replace with: textbox, Excel changes the format of the cell along with replacing the value.
There are two ways to set the format criteria.
- Click on the Format button. This opens the Format Cells dialog box. Select the formatting of the cell and click OK.
- Click on the dropdown near the Format button and select Choose Format from Cell. This navigates to the worksheet and you can select any cell to copy its formatting.
You can also clear the formatting criteria from the dropdowns in the Find and Replace text boxes.
Within Dropdown
Using this option, you can change the scope of the Find and Replace option. You can either limit the functionality of the search to the current worksheet or the entire workbook.
Search Dropdown
By default, Excel searches for the value in the Find textbox in a row-wise manner. Using this option, you can assign the order of search either row-wise or column-wise.
Look in Dropdown
This option helps you specify the type of place where the find option has to search. You can choose to look for the data in formulas, comments, or cells with values.
Match Case
When the match case option is checked, Excel searches and finds only the values that pertain to the case and format as specified in the text box. Check this option if you want the search to be case-sensitive.
Match Entire Cell Contents
When this checkbox is checked, Excel only takes into account the entire cell content. Partial data of any data type is ignored and only the complete entry in the textbox is searched.
Using Wildcards
Use the wildcards to search for any missing values. You can use the * wildcard to replace any character between the first and last characters, whereas using the ? wildcard between any two characters replaces exactly one character. Additionally, when you have to search for * or ? character, you can use the ~ tilde character along with * or ? to search for their occurrences in the worksheet.
Suggested Reads:
How to Merge Cells in Excel? 3 Easy Ways
How to Calculate Percentile in Excel? 3 Useful Formulas
How to Select Non Adjacent Cells in Excel? 5 Simple Ways
Frequently Asked Questions
How to minimize the extended dialog box without closing the Find and Replace dialog box?
To minimize the extended partition when you click on the Find All button, navigate to the corner of the dialog box and drag to the edges to hide them.
What are the advanced features of the Find and Replace option in Excel?
Clicking on the Option>>> button enables advanced options. From here, you can set the format criteria according to your needs.
How to access the find and replace option in Excel?
You can access the find and replace option by navigating to Home and under the Find & Select dropdown, click on Replace. You can also use the keyboard shortcut Ctrl+H.
Closing Thoughts
The Find and Replace function is really helpful and offers a variety of functionalities to help you search and replace data or values in Excel. You can search and replace any data in Excel irrespective of their data type or the cell formatting.
If you find this guide helpful and are looking for more guides, please visit our Excel resources center.
Want to skill up in Excel?
Simon Sez IT has been teaching Excel for ten years. For a low, monthly fee you can get access to 130+ IT training courses. Click here for advanced Excel courses with in-depth training modules.
Simon Calder
Chris “Simon” Calder was working as a Project Manager in IT for one of Los Angeles’ most prestigious cultural institutions, LACMA.He taught himself to use Microsoft Project from a giant textbook and hated every moment of it. Online learning was in its infancy then, but he spotted an opportunity and made an online MS Project course — the rest, as they say, is history!
Find and replace is an excel feature used to search for specific data in an excel worksheet or within a workbook and what you do with the data found. This article will explore different ways you can use find and replace together with using advanced find features.
Scanning through columns and rows in a large excel document to look for certain data may be difficult but using the «excel find and replace» feature, you can easily find any data you need within a big excel sheet in seconds.
Using the Excel Find in a range of cells
The find tool can help you look for certain information in your worksheet. To do this, select a range of cells to look in.
Go to the home tab > Editing group > click Find & Select > click Find. Alternatively, you can press the CTRL+F keyboard shortcut.
In the Find what box, type the characters you want to look for and click Find All or Find Next
Find All opens all the occurrences of the typed character and you can navigate to the corresponding cell by clicking any item in the list.
Find Next when you click this option, Excel selects the first occurrence of the search value on the sheet and when you click again it selects the second occurrence on the cell. This goes on until the last item is searched.
The find and replace changes the value of one cell to another within a range of cells in a worksheet. The replace tab can change characters, texts, and numbers in excel cells.
Steps
1. Select the range of cells where you want to replace the text or numbers.
2. Go to Home menu > editing ground > select Find & Select > Click Replace or press CTRL+H from the keyboard
3. On Find what box type the text or value you want to search for. In the Replace with box, type the text or value you want to replace with.
4. Click Replace button to replace a single text or click Replace All to replace the entire sheet with that value or text.
How to Find and Replace Multiple Values at once with VBA Code
Find and Replace can be used to find multiple values and replace them with values you desire using Excel VBA code.
Steps
1. Create the conditions that you need to use. This should be made of a list of old values and replace values.
2. Click on the Developer tab then select Visual basic under code group or hold down the ALT+F11 function key to open the Visual Basic window.
3. Click Insert > module, and paste the following code in the module window.
Sub MultiFindNReplace()
‘Update 20140722
Dim Rng As Range
Dim InputRng As Range, ReplaceRng As Range
xTitleId = «KutoolsforExcel»
Set InputRng = Application.Selection
Set InputRng = Application.InputBox(«Original Range «, xTitleId, InputRng.Address, Type:=8)
Set ReplaceRng = Application.InputBox(«Replace Range :», xTitleId, Type:=8)
Application.ScreenUpdating = False
For Each Rng In ReplaceRng.Columns(1).Cells
InputRng.Replace what:=Rng.Value, replacement:=Rng.Offset(0, 1).Value
Next
Application.ScreenUpdating = True
End Sub
4. Click Run or press the F5 Key to run this code. Specify the data range in the pop-up window.
5. Click OK and another prompt dialog box will appear for you to select the criteria you have created in step 1.
6. Then click ok. From the below screenshot, you can see all the values have been replaced with the new values.
Using Excel REPLACE Function
The REPLACE function in Excel allows you to find certain characters or a single character in a text string and change it with a different set of characters.
Syntax
REPLACE (old_text, start_num, num_chars, new_text)
Function arguments
Old_text – the original text (or a reference to a cell with the original text) in which you want to replace some characters.
Start_num – the position of the first character within old_text that you want to replace.
Num_chars – the number of characters you want to replace.
New_text – the replacement text.
Example: We want to replace the chef position in cell B22 to be a cook
Click ok.
Apply Nested Substitute Formula to Find and Replace
The SUBSTITUTE function replaces existing text with new text in the text string. We can nest the SUBSTITUTE function for multiple values to be replaced.
Example
1. Consider the data in the tables below. Column L has some random text data. The table on the right represents the value that has to be replaced with the new ones.
2. In the first output cell, Cell M5 the related formula will be:
=SUBSTITUTE(SUBSTITUTE(SUBSTITUTE(L5:L10,O5,P5),O6,P6),O7,P7)
3. Press Enter and you’ll get an array with the new text values at once. We have used the SUBSTITUTE formula thrice as we had to replace three different values under the table on the right
Using XLOOKUP Function to Search and Replace
The XLOOKUP function searches a range for a match and returns the corresponding item in the second range.
Example:
The old text column contains some text values. The second table on the right represents the data to be replaced simultaneously.
The required formula with XLOOKUP function in the first output cell, M5 should be:
=XLOOKUP($L10,$O$5:$O$10,$P$5:$P$10,$L10)
After pressing Enter and auto-filling the entire column will be displayed with the data the correct way.
To Find and Replace Formatting in Excel
This is an awesome feature when you want to replace existing formatting with some other formatting. For example, you may want to replace formats such as background colour, borders, font type/size/colour, and even merge cells, you can use the Find and Replace to do it.
Steps;
1. Select the cells or even an entire worksheet for which you want to replace the formatting
2. Go to Home-> Find and Select -> Replace (keyboard shortcut control + H)
3. Click on the Options button
4. Then click on the Find What format button and a drop-down with two options will show Format and Choose format from Cell.
5. You can either specify the format manually by clicking the Format button or you can select the format from a cell in the worksheet. To select a format from the cell, select the Choose Format from Cell option and then click on the cell from which you want to pick the format.
6. Once the format is selected manually from the dialogue box or from the cell, you will see the preview on the left of the Format button.
7. Then you need to specify the format that you want other than the one selected in step 6. Click on the Replace with Format button, a drop-down with two options will show; Format and Choose from Cell
8. You can either manually specify it or pick an existing format. Once a format is selected, you will see that as the Preview on the left of the format button
9. Click the Replace All button.
Combine IFNA And VLOOKUP Functions to Find and Substitute Multiple Values
The VLOOKUP (Vertical LOOKUP) function is an alternative to the XLOOKUP function
It determines the values at the leftmost column in a dataset and returns the value in the same row from a specific column. It will return a N/A error if the lookup value is not found. Therefore, to avoid such an error, you can include the IFNA function that corrects all the errors in the VLOOKUP Function.
Steps
1. Select the cell to type the formula, such as cell C5, and combine IFNA and VLOOKUP functions as seen below;
=IFNA(VLOOKUP($B5,$E$5:$F$10,2,FALSE),B5)
2. Press the Enter button and you will see the result displayed in cell C5.
3. You can now use the Fill Handle (+) icon to drag the formula down the column.
Using the LAMBDA Function to Multiple Replace
Those using Excel 365 can benefit from an already-enabled LAMBDA function (a traditional formula language) to find and replace multiple values. The method allows them to convert a very lengthy and complex formula to a simple and compact formula. It also creates new functions that do not exist in Excel, just like the VBA code. The only downside is that it is only available in Excel 365 and you cannot use it in different worksheets.
For example, if you want to find and replace multiple words, you can create a custom LAMBDA function and name it MultiReplace. The new name can take two formulas as shown below:
=LAMBDA(text, old, new, IF(old<>»», MultiReplace(SUBSTITUTE(text, old, new), OFFSET(old, 1, 0), OFFSET(new, 1, 0)), text))
Or
=LAMBDA(text, old, new, IF(old=»», text, MultiReplace(SUBSTITUTE(text, old, new), OFFSET(old, 1, 0), OFFSET(new, 1, 0))))
Although both formulas might look the same (recursive functions), you can note the difference using their exit points. For instance, the IF function in the first formula checks whether the old text is not blank (old<>””). If it is blank (TRUE), the MultiReplace function is called. If it is not blank (FALSE), the function gives a text in its current form and exits.
On the other hand, the IF function in the second formula uses reverse logic: if old is blank (old=»»), then it returns a text and exits. But if the old is not blank, call MultiReplace. Therefore, to use any of the formulas, you need to name the MultiReplace function in the Name Manager first. Then, once you get the name, you can now proceed to use it to find and replace multiple values as discussed below.
1. First, know the syntax of the MultiReplace function is:
MultiReplace(text, old, new), where;
text is the source data.
old is the value you need to find.
new are the values you need to replace with.
2. Type the formula in the cell (column) next to the data you want to find and replace. For example, if you want to replace values in column A, you can type the following formula in column B, say cell B2:
=MultiReplace(A2:A10, D2, E2)
3. Hit the Enter button and a new text will appear in cell B2.
4. Proceed to drag the formula down the column using an Autofill Handle.
Mass Find and Replace with UDF
You can also use a user-defined function (UDF) to mass-find and replace multiple values in Excel using traditional VBA code. The UDF is close to the LAMBDA-defined function, but you can differentiate them by naming the UDF technique as MassReplace. It is represented by the code:
Function MassReplace(InputRng As Range, FindRng As Range, ReplaceRng As Range) As Variant()
Dim arRes() As Variant ‘array to store the results
Dim arSearchReplace(), sTmp As String ‘array where to store the find/replace pairs, temporary string
Dim iFindCurRow, cntFindRows As Long ‘index of the current row of the SearchReplace array, count of rows
Dim iInputCurRow, iInputCurCol, cntInputRows, cntInputCols As Long ‘index of the current row in the source range, index of the current column in the source range, count of rows, count of columns
cntInputRows = InputRng.Rows.Count
cntInputCols = InputRng.Columns.Count
cntFindRows = FindRng.Rows.Count
ReDim arRes(1 To cntInputRows, 1 To cntInputCols)
ReDim arSearchReplace(1 To cntFindRows, 1 To 2) ‘preparing the array of find/replace pairs
For iFindCurRow = 1 To cntFindRows
arSearchReplace(iFindCurRow, 1) = FindRng.Cells(iFindCurRow, 1).Value
arSearchReplace(iFindCurRow, 2) = ReplaceRng.Cells(iFindCurRow, 1).Value
Next
‘Searching and replacing in the source range
For iInputCurRow = 1 To cntInputRows
For iInputCurCol = 1 To cntInputCols
sTmp = InputRng.Cells(iInputCurRow, iInputCurCol).Value
‘Replacing all find/replace pairs in each cell
For iFindCurRow = 1 To cntFindRows
sTmp = Replace(sTmp, arSearchReplace(iFindCurRow, 1), arSearchReplace(iFindCurRow, 2))
Next
arRes(iInputCurRow, iInputCurCol) = sTmp
Next
Next
MassReplace = arRes
End Function
The UDF or MassReplace function works in the workbooks you have inserted the code only. Hence, to apply it, you can use similar steps used to run a VBA code. Once you insert the code, the following formula will appear in the formula intellisense:
MassReplace(input_ range,find_range,replace_range), where;
Input_range is the source range you want to replace values.
Find_range is the entire string that includes the subject and words to check and look for.
Replace_range are new characters, strings, or texts to replace with.
Steps:
1. When using Excel 365 or versions that support dynamic arrays, you can enter the following formula in the cell next to the data you want to find and replace. For example, you can select cell B2 and write this formula:
=MassReplace(A2:A10,D2:D4,E2:E4)
2. Press the Enter button to display a new text or characters in cell B2.
3. You can now use the Autofill Handle to drag the formula down the column.
4. When using old Excel versions that do not support dynamic arrays, you can manually select the entire cell range, say B2:B10, and press Ctrl + Shift + Enter buttons simultaneously.
Multiple Find and Replace with Substring Tool
Using the substring tool is also among the easiest methods to find and replace multiple values in Excel. However, before replacing values, you should consider if you are dealing with a Case-sensitive box or not. For instance, you should decide if you want to treat uppercase and lowercase as different characters.
Steps:
1. Go to the Ablebits Data tab, click Substrings Tools and select Replace Substrings.
2. A new Replace Substrings dialog box will emerge asking you to specify the Source range and Substrings range.
3. After filling the two checkboxes hit the Replace button and you will see your results on a new column on the right side of the initial data.