Here’s what I need to do. I have these two columns in an excel sheet. With file names. First column has the current filename and the second column has the names I want the files to be renamed to. I need to use this as there’s no pattern in renaming. For example, the below may be a set of files …
Current Name > Rename To
---------------------------
Abc.jpg > Dinner.jpg
Xyz.jpg > Driving.jpg
123.jpg > Sunset.jpg
I know it should be easy to do this in VBA, but not exactly sure how. Any help would be much appreciated.
Jay
55.8k10 gold badges98 silver badges122 bronze badges
asked Sep 22, 2011 at 1:38
redGREENblueredGREENblue
3,0668 gold badges38 silver badges57 bronze badges
I think you could do something like this, using the Name function to rename the files, however, you will probably need to make sure the 2 columns have the complete file path, i.e. «C:TempABC.jpg»
Dim Source As Range
Dim OldFile As String
Dim NewFile As String
Set Source = Cells(1, 1).CurrentRegion
For Row = 1 To Source.Rows.Count
OldFile = ActiveSheet.Cells(Row, 1)
NewFile = ActiveSheet.Cells(Row, 2)
' rename files
Name OldFile As Newfile
Next
answered Sep 22, 2011 at 1:51
1
VBA in Excel does not restrict us to just a single application. VBA gives us access to the windows environment too. With this we can perform a lot of common file-based actions. One of the most common is to rename a file. In this post, we will look at 5 examples of renaming files with VBA.
To rename a file with VBA we use the Name command. Name appears in blue because it is a reserved word within VBA.
Example 1: Renaming a file
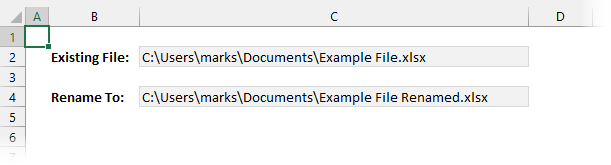
This example renames a file from Example File.xlsx to Example File Renamed.xlsx.
Sub VBARenameFile()
Name "C:UsersmarksDocumentsExample File.xlsx" As _
"C:UsersmarksDocumentsExample File Renamed.xlsx"
End SubExample 2: Rename a file based on cell values
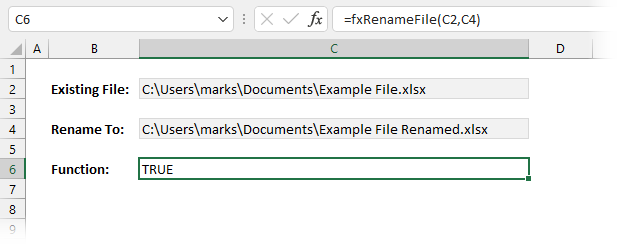
In this example, we rename a file based on cell values. The screenshot below shows the current file name in Cell C2 and the new file name in Cell C4.
We can run the following macro to rename a file using these cell values.
Sub VBARenameFileSheetNames()
Name ActiveSheet.Range("C2") As _
ActiveSheet.Range("C4")
End SubExample 3: Move a file with the Name command
Did you notice the Name command requires the file path and file name? Therefore, the Name command doesn’t just rename files but can also move files. For example, the code below moves the file from C:UsersmarksDocuments to C:Usersmarks, but the file name remains the same.
Sub VBAMoveFile()
Name "C:UsersmarksDocumentsExample File.xlsx" As _
"C:UsersmarksExample File.xlsx"
End SubExample 4: Avoiding errors when renaming files
Trying to move files that don’t exist, or are locked for editing can trigger errors. The errors are detailed in the section below.
If there is an error, we really want to avoid going through the Visual Basic error debugging process. Instead, a better option is to display a message box with an OK button.
Sub VBAAdvancedRenameFile()
'Create variables to hold file names
Dim filePath As String
Dim newFilePath As String
filePath = "C:UsersmarksDocumentsExample File.xlsx"
newFilePath = "C:UsersmarksDocumentsExample File Renamed.xlsx"
'Ignore errors
On Error Resume Next
'Rename file
Name filePath As newFilePath
'Display message if error occured
If Err.Number <> 0 Then
MsgBox Prompt:="Unable to rename file", Buttons:=vbOK, _
Title:="Rename file error"
End If
'Turn error checking back on
On Error GoTo 0
End SubExample 5: Reusable function
Finally, let’s create a reusable function for moving and renaming files.
The VBA function below accepts two string arguments; the existing file path and the new file path.
Function fxRenameFile(filePath As String, newFilePath As String)
'Ignore errors
On Error Resume Next
'Rename file
Name filePath As newFilePath
'Display message if error occured
If Err.Number <> 0 Then
fxRenameFile = False
Else
fxRenameFile = True
End If
'Turn error checking back on
On Error GoTo 0
End FunctionWe can use this function in two ways.
- Calling the function from another macro
- Calling the function from a worksheet
Let’s look at both of these in turn.
Calling the function from a macro
The macro below calls the function and displays a message box with the following values:
- True = File renamed
- False = Error occurred.
Sub CallFunction()
'Create variables to hold file names
Dim filePath As String
Dim newFilePath As String
filePath = "C:UsersmarksDocumentsExample File.xlsx"
newFilePath = "C:UsersmarksDocumentsExample File Renamed.xlsx"
'True = File Renamed
'False = Error Occured
MsgBox fxRenameFile(filePath, newFilePath)
End SubCalling the function from a worksheet
Alternatively, we can call the function just like a normal worksheet function.
Look at the screenshot above, our custom function is used in Cell C6:
=fxRenameFile(C2,C4)TRUE indicates that the file named in Cell C2 has been successfully renamed to the file named in Cell C4. If we run the function a second time, it will show FALSE, as the file has already been renamed.
Be aware the function executes each time cells C2 or C4 change, so be careful with the order in which you update the cells.
TOP TIP: If we use the fxRenameFile function inside an IF function, it will only executes when the condition is met. In the example below, the fxRenameFile function only executes if cell A6 equals Y.
=IF(A6="Y",fxRenameFile(C2,C4),"Do not rename")Using this method, we can control when and how the function executes. We just need to change cell A6 to another value when we don’t the function to execute.
Possible errors
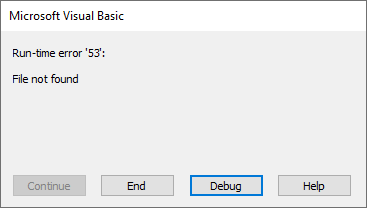
If we try to rename a file or folder path that does not exist, it triggers an error: Run-time error’53’: File not found.
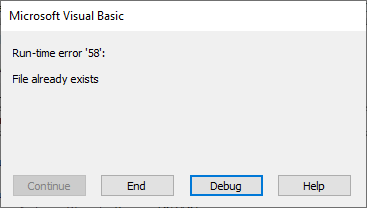
If the new file name is the same as an existing one, it triggers the following error: Run-time error ’58’: File already exists.
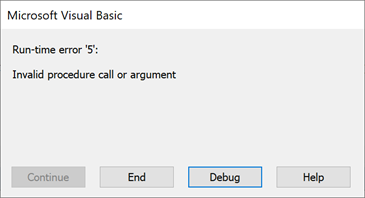
If either file name is not a valid format, it triggers the following error: Run-time error ‘5’: Invalid procedure call or argument
Notes on renaming files
We have used Excel workbooks in the examples, but we can use any file type. Also, we are not restricted to files; we can rename folders using the Name command too.
The Name command is core Visual Basic code. Therefore, it exists in other applications supporting VBA, such as Word and PowerPoint.
Related Posts:
- VBA code to copy, move, delete and manage files.
- VBA code library
- VBA Copy File – How to + 5 examples
About the author
Hey, I’m Mark, and I run Excel Off The Grid.
My parents tell me that at the age of 7 I declared I was going to become a qualified accountant. I was either psychic or had no imagination, as that is exactly what happened. However, it wasn’t until I was 35 that my journey really began.
In 2015, I started a new job, for which I was regularly working after 10pm. As a result, I rarely saw my children during the week. So, I started searching for the secrets to automating Excel. I discovered that by building a small number of simple tools, I could combine them together in different ways to automate nearly all my regular tasks. This meant I could work less hours (and I got pay raises!). Today, I teach these techniques to other professionals in our training program so they too can spend less time at work (and more time with their children and doing the things they love).
Do you need help adapting this post to your needs?
I’m guessing the examples in this post don’t exactly match your situation. We all use Excel differently, so it’s impossible to write a post that will meet everybody’s needs. By taking the time to understand the techniques and principles in this post (and elsewhere on this site), you should be able to adapt it to your needs.
But, if you’re still struggling you should:
- Read other blogs, or watch YouTube videos on the same topic. You will benefit much more by discovering your own solutions.
- Ask the ‘Excel Ninja’ in your office. It’s amazing what things other people know.
- Ask a question in a forum like Mr Excel, or the Microsoft Answers Community. Remember, the people on these forums are generally giving their time for free. So take care to craft your question, make sure it’s clear and concise. List all the things you’ve tried, and provide screenshots, code segments and example workbooks.
- Use Excel Rescue, who are my consultancy partner. They help by providing solutions to smaller Excel problems.
What next?
Don’t go yet, there is plenty more to learn on Excel Off The Grid. Check out the latest posts:
Хитрости »
15 Август 2012 129927 просмотров
В этой статье я хотел бы рассказать как средствами VBA переименовать, переместить или скопировать файл. В принципе методы переименования, перемещения и копирования, так сказать, встроены в VBA. Это значит что можно без вызова сторонних объектов переименовать, переместить или копировать любой файл. Все это делается при помощи всего двух команд: FileCopy и Name [Исходный файл] As [Новый файл]. Притом команда FileCopy выполняет только копирование, а Name [Исходный файл] As [Новый файл] — как переименование, так и перемещение. Разница лишь в том, что при переименовании мы указываем только новое имя файла, а при перемещении — другую директорию(папку), в которую следует переместить файл. Плюс рассмотрим пример удаления файла.
Так же разберем методы копирования, перемещения, переименования и удаления файлов и папок через библиотеку FileSystemObject (FSO).
Работа с файлами встроенными командами VBA
- Копирование файла
- Перемещение файла
- Переименование файла
- Удаление файла
Работа с файлами через объект FileSystemObject (FSO)
- Копирование файла
- Перемещение файла
- Переименование файла
- Удаление файла
Работа с папками через объект FileSystemObject (FSO)
- Копирование папки
- Перемещение папки
- Переименование папки
- Удаление папки
Во всех примерах работы с файлами встроенными функциями будет присутствовать проверка на наличие файла по указанному пути. Делать это будем при помощи встроенной функции Dir([PathName],[Attributes]).
PathName — указывается полный путь к файлу
Attributes — указывается признак свойств файла. Вообще их несколько(скрытый, архивный и т.п.), но нас для наших задач будет интересовать пока только один: 16(vbDirectory). Он отвечает за проверку папок и файлов без специальных свойств(т.е. не архивные, не скрытые и т.д.). Хотя по сути его можно вообще не указывать, и тогда будет по умолчанию применен атрибут 0(vbNormal) — проверка файлов без определенных свойств. Ни в том ни в другом случае ошибкой это не будет.
Sub Copy_File() Dim sFileName As String, sNewFileName As String sFileName = "C:WWW.xls" 'имя файла для копирования sNewFileName = "D:WWW.xls" 'имя копируемого файла. Директория(в данном случае диск D) должна существовать If Dir(sFileName, 16) = "" Then MsgBox "Нет такого файла", vbCritical, "www.excel-vba.ru" Exit Sub End If FileCopy sFileName, sNewFileName 'копируем файл MsgBox "Файл скопирован", vbInformation, "www.excel-vba.ru" End Sub
Sub Move_File() Dim sFileName As String, sNewFileName As String sFileName = "C:WWW.xls" 'имя исходного файла sNewFileName = "D:WWW.xls" 'имя файла для перемещения. Директория(в данном случае диск D) должна существовать If Dir(sFileName, 16) = "" Then MsgBox "Нет такого файла", vbCritical, "www.excel-vba.ru" Exit Sub End If Name sFileName As sNewFileName 'перемещаем файл MsgBox "Файл перемещен", vbInformation, "www.excel-vba.ru" End Sub
Sub Rename_File() Dim sFileName As String, sNewFileName As String sFileName = "C:WWW.xls" 'имя исходного файла sNewFileName = "C:WWW1.xls" 'имя файла для переименования If Dir(sFileName, 16) = "" Then MsgBox "Нет такого файла", vbCritical, "www.excel-vba.ru" Exit Sub End If Name sFileName As sNewFileName 'переименовываем файл MsgBox "Файл переименован", vbInformation, "www.excel-vba.ru" End Sub
Sub Delete_File() Dim sFileName As String sFileName = "C:WWW.xls" 'имя файла для удаления If Dir(sFileName, 16) = "" Then MsgBox "Нет такого файла", vbCritical, "www.excel-vba.ru" Exit Sub End If Kill sFileName 'удаляем файл MsgBox "Файл удален", vbInformation, "www.excel-vba.ru" End Sub
Как видно ничего сложного.
Так же можно проделать те же операции с файлами при помощи объекта FileSystemObject. Строк кода несколько больше и выполняться операции будут медленнее(хотя вряд ли это будет заметно на примере одного файла). Однако есть существенный плюс — при помощи FileSystemObject можно корректно производить операции с файлами и папками на сетевом диске. Хотя та же
Dir(sFileName, 16)
часто выдает ошибку при работе с сетевыми дисками.
Прежде всего следует, я думаю, пояснить что за зверь такой — FileSystemObject.
FileSystemObject (FSO)
— содержится в библиотеке типов Scripting, расположенной в файле библиотеки scrrun.dll. Объектная модель FSO дает возможность создавать, изменять, перемещать и удалять папки и файлы, собирать о них различную информацию: имена, атрибуты, даты создания или изменения и т.д. Чтобы работать с FSO необходимо создать переменную со ссылкой на объект библиотеки. Сделать это можно двумя способами: через ранее связывание и позднее. Я не буду сейчас вдаваться в подробности этих методов — тема довольно обширная и я опишу её в другой статье.
Ранее связывание:
для начала необходимо подключить библиотеку Microsoft Scripting Runtime. Делается это в редакторе VBA: References-находите там Microsoft Scripting Runtime и подключаете. Объявлять переменную FSO при раннем связывании следует так:
Dim objFSO As New FileSystemObject
Плюсы раннего связывания: с помощью Object Browser можно просмотреть список объектов, свойств, методов, событий и констант, включенных в FSO. Но есть значительный минус: если планируется использовать программу на нескольких компьютерах, то есть большая вероятность получить ошибку(читать подробнее).
Позднее связывание: ничего нигде не надо подключать, а просто используем метод CreateObject(именно этот способ используется мной в примерах ниже). Методы таким образом просмотреть не получится, но зато работать будет без проблем на любых компьютерах без дополнительных действий.
Sub Copy_File() Dim objFSO As Object, objFile As Object Dim sFileName As String, sNewFileName As String sFileName = "C:WWW.xls" 'имя исходного файла sNewFileName = "D:WWW.xls" 'имя файла для переименования 'создаем объект FileSystemObject Set objFSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject") 'проверяем наличие файла по указанному пути If objFSO.FileExists(sFileName) = False Then MsgBox "Нет такого файла", vbCritical, "www.excel-vba.ru" Exit Sub End If 'копируем файл Set objFile = objFSO.GetFile(sFileName) objFile.Copy sNewFileName MsgBox "Файл скопирован", vbInformation, "www.excel-vba.ru" End Sub
Sub Move_File() Dim objFSO As Object, objFile As Object Dim sFileName As String, sNewFileName As String sFileName = "C:WWW.xls" 'имя исходного файла sNewFileName = "D:WWW.xls" 'имя файла для переименования 'создаем объект FileSystemObject Set objFSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject") 'проверяем наличие файла по указанному пути If objFSO.FileExists(sFileName) = False Then MsgBox "Нет такого файла", vbCritical, "www.excel-vba.ru" Exit Sub End If 'перемещаем файл Set objFile = objFSO.GetFile(sFileName) objFile.Move sNewFileName MsgBox "Файл перемещен", vbInformation, "www.excel-vba.ru" End Sub
Sub Rename_File() Dim objFSO As Object, objFile As Object Dim sFileName As String, sNewFileName As String sFileName = "C:WWW.xls" 'имя исходного файла sNewFileName = "WWW1.xls" 'имя файла для переименования 'создаем объект FileSystemObject Set objFSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject") 'проверяем наличие файла по указанному пути If objFSO.FileExists(sFileName) = False Then MsgBox "Нет такого файла", vbCritical, "www.excel-vba.ru" Exit Sub End If 'переименовываем файл Set objFile = objFSO.GetFile(sFileName) objFile.Name = sNewFileName MsgBox "Файл переименован", vbInformation, "www.excel-vba.ru" End Sub
Хочу обратить внимание, что при переименовании файла через FileSystemObject необходимо указать только имя нового файла — путь указывать не надо. Иначе получите ошибку.
Удаление файла
Sub Delete_File() Dim objFSO As Object, objFile As Object Dim sFileName As String sFileName = "C:WWW.xls" 'имя файла для удаления 'создаем объект FileSystemObject Set objFSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject") 'проверяем наличие файла по указанному пути If objFSO.FileExists(sFileName) = False Then MsgBox "Нет такого файла", vbCritical, "www.excel-vba.ru" Exit Sub End If 'удаляем файл Set objFile = objFSO.GetFile(sFileName) objFile.Delete MsgBox "Файл удален", vbInformation, "www.excel-vba.ru" End Sub
Точно так же можно перемещать, копировать и удалять целые папки:
Копирование папки
Sub Copy_Folder() Dim objFSO As Object Dim sFolderName As String, sNewFolderName As String sFolderName = "C:test" 'имя исходной папки sNewFolderName = "D:tmp" 'имя папки, в которую копируем(нужен слеш на конце) 'создаем объект FileSystemObject Set objFSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject") 'проверяем наличие папки по указанному пути If objFSO.FolderExists(sFolderName) = False Then MsgBox "Нет такой папки", vbCritical, "www.excel-vba.ru" Exit Sub End If 'копируем папку objFSO.CopyFolder sFolderName, sNewFolderName MsgBox "Папка скопирована", vbInformation, "www.excel-vba.ru" End Sub
Sub Move_Folder() Dim objFSO As Object Dim sFolderName As String, sNewFolderName As String sFolderName = "C:test" 'имя исходной папки sNewFolderName = "C:tmptest" 'имя папки, в которую перемещаем(нужен слеш на конце) 'создаем объект FileSystemObject Set objFSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject") 'проверяем наличие папки по указанному пути If objFSO.FolderExists(sFolderName) = False Then MsgBox "Нет такой папки", vbCritical, "www.excel-vba.ru" Exit Sub End If 'перемещаем папку objFSO.MoveFolder sFolderName, sNewFolderName MsgBox "Папка перемещена", vbInformation, "www.excel-vba.ru" End Sub
Sub Rename_Folder() Dim objFSO As Object, objFolder As Object Dim sFolderName As String, sNewFolderName As String sFolderName = "C:test" 'имя исходной папки 'имя папки для переименования(только имя, без полного пути) sNewFolderName = "new folder name" 'создаем объект FileSystemObject Set objFSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject") 'проверяем наличие папки по указанному пути If objFSO.FolderExists(sFolderName) = False Then MsgBox "Нет такой папки", vbCritical, "www.excel-vba.ru" Exit Sub End If 'переименовываем папку 'получаем доступ к объекту Folder(папка) Set objFolder = objFSO.GetFolder(sFolderName) 'назначаем новое имя objFolder.Name = sNewFolderName MsgBox "Папка переименована", vbInformation, "www.excel-vba.ru" End Sub
Sub Delete_Folder() Dim objFSO As Object, objFolder As Object Dim sFolderName As String sFolderName = "C:test" 'имя папки для удаления 'создаем объект FileSystemObject Set objFSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject") 'проверяем наличие папки по указанному пути If objFSO.FolderExists(sFolderName) = False Then MsgBox "Нет такой папки", vbCritical, "www.excel-vba.ru" Exit Sub End If 'удаляем папку objFSO.DeleteFolder sFolderName MsgBox "Папка удалена", vbInformation, "www.excel-vba.ru" End Sub
FSO, конечно, способен на большее — но цель данной статьи была показать основные операции с папками и файлами как стандартными методами, так и более продвинутыми.
Статья помогла? Поделись ссылкой с друзьями!
Видеоуроки
Поиск по меткам
Access
apple watch
Multex
Power Query и Power BI
VBA управление кодами
Бесплатные надстройки
Дата и время
Записки
ИП
Надстройки
Печать
Политика Конфиденциальности
Почта
Программы
Работа с приложениями
Разработка приложений
Росстат
Тренинги и вебинары
Финансовые
Форматирование
Функции Excel
акции MulTEx
ссылки
статистика
Home / VBA / VBA Rename Workbook (Excel File)
To RENAME an Excel file that is stored on your computer, you need to use the “NAME” statement. In this statement, you need to define the old file name and the new name that you want to apply. But there’s one thing that you need to remember the file must be closed.
Here I have an Excel file that is stored in the “Data” folder on my desktop and there in this folder “SampleFile” that I want to rename to the “myFile” and code for this would be like the following.
Name "C:UsersDellDesktopmyFolderSampleFile.xlsx" As _
"C:UsersDellDesktopmyFoldermyNewFile.xlsx"Steps to use VBA to Rename Excel File
Now, let’s understand this line of code in detail.

- The name statement with which you need to start the code.
- Address of the file with the old name and file extension.
- “As” refers to the new name.
- Address of the file with the new name and file extension.
Helpful Links: Run a Macro – Macro Recorder – Visual Basic Editor – Personal Macro Workbook
To make the name states a little clearer you can use variables, just like the following code.

Sub vba_rename_workbook()
Dim oldName As String
Dim newName As String
oldName = "C:UsersDellDesktopmyFolderSampleFile.xlsx"
newName = "C:UsersDellDesktopmyFoldermyNewFile.xlsx"
Name oldName As newName
End SubMore on VBA Workbooks
VBA Save Workbook | VBA Close Workbook | VBA Delete Workbook | VBA ThisWorkbook | VBA Activate Workbook | VBA Combine Workbook | VBA Protect Workbook (Unprotect) | VBA Check IF a Workbook is Open | VBA Open Workbook | VBA Check IF an Excel Workbook Exists in a Folder| VBA Create New Workbook (Excel File)
- VBA Workbook
- Remove From My Forums
-
Question
-
Hi
I have an excel sheet that contains data. as per the data form one perticular cell. i need to rename a wave and a word file. Is this possible in VBA.
Thanks
Riya
Answers
-
Taken from the excel help files….
Name Statement Example
This example uses the Name statement to rename a file. For purposes of this example, assume that the directories or folders that are specified already exist. On the Macintosh, “HD:” is the default drive name and portions of the pathname are separated by colons instead of backslashes.
Dim OldName, NewName OldName = "OLDFILE": NewName = "NEWFILE" ' Define file names. Name OldName As NewName ' Rename file. OldName = "C:MYDIROLDFILE": NewName = "C:YOURDIRNEWFILE" Name OldName As NewName ' Move and rename file.