Syntagmatic Relation
between words in English. Lexical Valency & Collacability.
-
Syntagmatic relations of words. The importance of Syntagmatic
Analysis. -
Lexical & grammatical collacability.
-
Types of word-groups.
Syntagmatic relations of
words. The importance of Syntagmatic Analysis.
The relations existing between words as separate lexical units within
the vocabulary as a system are called paradigmatic or the relations
on the vertical axis. They define the meaning through its
interrelation with other members of the subgroup it belongs to within
the vocabulary system.
There are various types of semantic paradigmatic relations in
English:
-
Synonimic
-
Antonymic
-
Hyponimic & the others
In the flow of speech the word combines with other words forming a
kind of chain. These linear relations of words in connected speech
are called syntagmatic relations or the relations on the horizontal
level.
Syntactical relations define the meaning of a word
when it’s used in combination with other words in speech. Words put
together in speech make functional units called phrases or word-group
or word combinations or collacations.
Word-group – the largest, two-facet functional lexical units
(assuming that the word is the basic lexical unit), comprising more
than 1 word on the syntagmatic level of Analysis.
The immediate connections of the word lie within
the simple word-group consisting of 2 notional words. The relations
between these words depend on their semantic structure which in its
turn determines their combining power or collacability.
Thus, the word-group may represent that minimal stretch of speech of
the speech context that determines the individual, actual meaning of
the word in speech.
Syntagmatic Analysis – is the study of the semantic
characteristics of the word & its collacability, i.e. the ability
to combine with other words in speech on the basis of its typical
contexts or combinations with other words in speech.
It may be applied for different purposes:
-
to discover most frequently used collocations in English;
-
to study the possibilities of the realization of certain types of
mean, in certain collocations; -
to study the norms of valency & collacability of correlated
words in different languages which is very important in teaching
foreing languages, translation & lexicography.
Соседние файлы в папке Lecture9
- #
- #
- #
Before we discuss what syntagmatic relation is, let’s first have a look at semiotics, saussure, and syntagms.
Semiotics, saussure, and syntagms
The term ‘syntagmatic’ is closely related to the field of semiotics. Semiotics is the study of how meanings are produced by signs.
Road signs are a good example. You can understand the meaning of the signs even though there aren’t any words to explain what they mean. Look at the two road signs below. You know that the left one means ‘no u-turns’ and the right one means ‘slippery road’.


Ferdinand de Saussure (1857-1913) argued that:
- Words in a sentence are meaningfully related to each other. Saussure called this relationship syntagmatic, and the combinations of two or more words that create the chain of words he called syntagms.
When a single word or element of the chain is altered, the overall meaning is also changed. This chain concept is the basis of syntagmatic relations.
What is a syntagmatic relation?
Syntagmatic relation defines the relationship between words that co-occur in the same sentence. It focuses on two main parts: how the position and the word order affect the meaning of a sentence. Let’s look at an example:
↤ Syntagmatic relations ↦
Paul is roasting a chicken
The syntagmatic relation in this sentence explains:
- The word position and order: Paul + is roasting + a chicken
- The relationship between words gives a particular meaning to the sentence:
- It is a chicken that Paul is roasting, not something else.
- It is Paul who is roasting a chicken, not someone else.
Thus, the syntagmatic relation refers to a word’s ability to combine with other words, and the syntagmatic dimension (syntagm) always refers to the horizontal axis or linear aspect of a sentence.
The syntagmatic relation can also explain why specific words are often paired together (collocations), such as have + a party in ‘We had a party on Saturday’. If you hear someone say, ‘We made a party on Saturday’, you’ll probably cringe because make + a party doesn’t sound right.
The opposite of syntagmatic relation is paradigmatic relation. Paradigmatic relation refers to the relationship between words that can be substituted within the same word class (on the vertical axis).
Study tip: Syntagmatic relation is about word order and position. The meaning of syntagmatic is similar to syntax (the arrangement of words and phrases in a sentence).
Syntagmatic relations examples
Some examples of syntagmatic relations are shown in the table below:
| ↤ Syntagmatic relations ↦ | ||||
| Subject | verb | Object | ||
| Determiner | Adjective | Noun | Noun | |
| The | beautiful | woman | buys | some brioche |
| handsome | man | sold | some cake | |
| tall | boy | is eating |
a hotdog |
From these sentences, the syntagmatic relations are all the relationships between words within the same sentence. That means there is a syntagmatic relation in:
- The beautiful woman + buys + some brioche (sentence level).
- The + beautiful + woman (phrase level).
- The handsome man + sold + some cake; and the + handsome + man.
- The tall boy + is eating + a hotdog; and the + tall + boy.
Additionally, in all three sentences above, each grammatical function (ie, subject, verb, and object) is at the same level. But in some cases, if you change the order of the sentence structure, it can change the meaning completely. For example:
- The tall boy is eating a hotdog.
- A hotdog is eating the tall boy.
The two sentences use the same words (syntagms) but differ in order (syntagmatic relationship), which changes the meaning of the sentence.
Types of syntagmatic relations
Because syntagmatic relations have to do with the relationship between words, the syntagms can result in collocations and idioms.
Collocations
Collocations are word combinations that frequently occur together.
1. There are three interesting facts about collocations:
- There isn’t a specific rule for the way words go together (why A is commonly paired with B). It is based on what the speakers of a language commonly combine, and eventually, what sounds natural. That’s why when you read, ‘a handsome girl’ instead of ‘a pretty girl’ it feels odd.
2. Word substitution is possible
- Sticking with the example of handsome girl, technically, it isn’t wrong to say handsome girl because handsome means ‘good-looking’ (Oxford Learner’s Dictionary) which is gender-neutral. Therefore, you can say handsome girl, but it just doesn’t sound natural.
3. The collocation’s meaning can be traced back to the meaning of each component
- For instance, catch a cold means ‘getting a cold’ and office hours means ‘the hour someone dedicates to work’. The definition of each component forms the meaning of a collocation.
Here are some examples of collocations:
Verb + noun: do homework, take a risk, catch a cold.
Noun + noun: office hours, interest group, kitchen cabinet.
Adjective + adverb: good enough, close together, crystal clear.
Verb + preposition: protect from, angry at, take advantage of.
Adverb + verb: strongly suggest, deeply sorry, highly successful.
Adjective + noun: handsome man, quick shower, fast food.
1. The word combination is not interchangeable (fixed expressions).
- You can’t substitute the words in idioms, even with their synonyms. For instance, in ‘kill two birds with one stone’ the stone is substituted with rock and becomes ‘kill two birds with one rock’. This version of the idiom simply doesn’t exist, even though the overall meaning and construction of the sentence remains unchanged.
2. The meaning of each component is not equal to the meaning of the idiom
- It is difficult to find the meaning of an idiom based on the definition of the words alone. For example, red herring. If you define the idiom word by word, it means ‘red fish’, not ‘something that misleads’, which is the real meaning.
- Because of this, idioms can’t be translated to or from another language because the word definition isn’t equivalent to the idiom interpretation.
Here are some examples of popular idioms:
Break a leg.
Miss the boat.
Call it a day.
It’s raining cats and dogs.
Kill two birds with one stone.
Syntagmatic and paradigmatic relations examples in grammar
Paradigmatic relation describes the relationship between words that can be substituted for words with the same word class (eg replacing a noun with another noun). A paradigm in this sense refers to the vertical axis of word selection. This explains why paradigmatic relation is the opposite of syntagmatic relation.
Now that we have covered the paradigmatic and syntagmatic relations, we can say that:
- Paradigmatic relation describes a substitution relationship between words of the same word class. The substitution occurs on the vertical axis.
- Syntagmatic relation illustrates the linear relationship / position between the words in a sentence. The syntagmatic relation occurs on the horizontal axis.
|
↥ Paradigmatic relations ↧ |
↤ Syntagmatic relations ↦ | |||
| Subject | verb | Object | ||
| Determiner | Adjective | Noun | Noun | |
| The | beautiful | woman | buys | some brioche |
| The | unattractive | lady | buys | some bread |
| That | handsome | man | ate | some chicken |
Paradigmatic relation:
Let’s take ‘The beautiful woman buys some brioche‘.
- The beautiful woman can choose to buy: some bread or chicken instead of brioche.
- Brioche, bread, and chicken are parts of a paradigm of food that the beautiful woman can buy.
- All the items in the paradigm share some kind of function (in this example: the object of the sentence) and this paradigm represents the category they belong to (in this example: food).
- Some words from the sentence can also be substituted vertically: ‘An unattractive (antonym) lady (synonymy) buys some bread (hyponymy)’.
Syntagmatic relation:
Let’s take ‘That handsome man ate some chicken‘.
- The combination of ‘that handsome man + ate + some chicken’ forms a syntagmatic relationship.
- If the word position is changed, it also changes the meaning of the sentence, eg ‘Some chicken ate the handsome man’.
- Furthermore, the linear relationship also occurs at phrase-level: it is ‘handsome + man’, not ‘handsome + woman’ (collocation).
Syntagmatic Relations — Key takeaways
- Syntagmatic relation illustrates the relationship between words that co-occur in the same sentence. It occurs on the horizontal axis.
- Syntagmatic relation explains the concept of collocations and idioms.
- Collocations are words that frequently occur together. The word pairings in collocations are not fixed, but changing the word pairing will make the combination sound unnatural, eg handsome man vs. handsome girl.
- Idioms are fixed expressions that possess a meaning other than their literal one. The words in idioms can’t be substituted, eg miss the boat becomes miss the ship, which is not an idiom.
- Paradigmatic relation illustrates the relationship between words that can be substituted within the same grammatical position.
Подборка по базе: Документ Microsoft Word (3).docx, Документ Microsoft Word (3).docx, Документ Microsoft Word (2).docx, Документ Microsoft Word.docx, Документ Microsoft Word (2).docx, Документ Microsoft Word (3).docx, Документ Microsoft Word (2).docx, Microsoft Word Document.docx, Документ Microsoft Word.docx, Документ Microsoft Word.docx
Семинар 6 Combinability. Word Groups
KEY TERMS
Syntagmatics — linear (simultaneous) relationship of words in speech as distinct from associative (non-simultaneous) relationship of words in language (paradigmatics). Syntagmatic relations specify the combination of elements into complex forms and sentences.
Distribution — The set of elements with which an item can cooccur
Combinability — the ability of linguistic elements to combine in speech.
Valency — the potential ability of words to occur with other words
Context — the semantically complete passage of written speech sufficient to establish the meaning of a given word (phrase).
Clichе´ — an overused expression that is considered trite, boring
Word combination — a combination of two or more notional words serving to express one concept. It is produced, not reproduced in speech.
Collocation — such a combination of words which conditions the realization of a certain meaning
TOPICS FOR DISCUSSION AND EXERCISES
1. Syntagmatic relations and the concept of combinability of words. Define combinability.
Syntagmatic relation defines the relationship between words that co-occur in the same sentence. It focuses on two main parts: how the position and the word order affect the meaning of a sentence.
The syntagmatic relation explains:
• The word position and order.
• The relationship between words gives a particular meaning to the sentence.
The syntagmatic relation can also explain why specific words are often paired together (collocations)
Syntagmatic relations are linear relations between words
The adjective yellow:
1. color: a yellow dress;
2. envious, suspicious: a yellow look;
3. corrupt: the yellow press
TYPES OF SEMANTIC RELATIONS
Because syntagmatic relations have to do with the relationship between words, the syntagms can result in collocations and idioms.
Collocations
Collocations are word combinations that frequently occur together.
Some examples of collocations:
- Verb + noun: do homework, take a risk, catch a cold.
- Noun + noun: office hours, interest group, kitchen cabinet.
- Adjective + adverb: good enough, close together, crystal clear.
- Verb + preposition: protect from, angry at, advantage of.
- Adverb + verb: strongly suggest, deeply sorry, highly successful.
- Adjective + noun: handsome man, quick shower, fast food.
Idioms
Idioms are expressions that have a meaning other than their literal one.
Idioms are distinct from collocations:
- The word combination is not interchangeable (fixed expressions).
- The meaning of each component is not equal to the meaning of the idiom
It is difficult to find the meaning of an idiom based on the definition of the words alone. For example, red herring. If you define the idiom word by word, it means ‘red fish’, not ‘something that misleads’, which is the real meaning.
Because of this, idioms can’t be translated to or from another language because the word definition isn’t equivalent to the idiom interpretation.
Some examples of popular idioms:
- Break a leg.
- Miss the boat.
- Call it a day.
- It’s raining cats and dogs.
- Kill two birds with one stone.
Combinability (occurrence-range) — the ability of linguistic elements to combine in speech.
The combinability of words is as a rule determined by their meanings, not their forms. Therefore not every sequence of words may be regarded as a combination of words.
In the sentence Frankly, father, I have been a fool neither frankly, father nor father, I … are combinations of words since their meanings are detached and do not unite them, which is marked orally by intonation and often graphically by punctuation marks.
On the other hand, some words may be inserted between the components of a word-combination without breaking it.
Compare,
a) read books
b) read many books
c) read very many books.
In case (a) the combination read books is uninterrupted.In cases (b) and (c) it is interrupted, or discontinuous(read… books).
The combinability of words depends on their lexical, grammatical and lexico-grammatical meanings. It is owing to the lexical meanings of the corresponding lexemes that the word wise can be combined with the words man, act, saying and is hardly combinable with the words milk, area, outline.
The lexico-grammatical meanings of -er in singer (a noun) and -ly in beautifully (an adverb) do not go together and prevent these words from forming a combination, whereas beautiful singer and sing beautifully are regular word-combinations.
The combination * students sings is impossible owing to the grammatical meanings of the corresponding grammemes.
Thus one may speak of lexical, grammatical and lexico-grammatical combinability, or the combinability of lexemes, grammemes and parts of speech.
The mechanism of combinability is very complicated. One has to take into consideration not only the combinability of homogeneous units, e. g. the words of one lexeme with those of another lexeme. A lexeme is often not combinable with a whole class of lexemes or with certain grammemes.
For instance, the lexeme few, fewer, fewest is not combinable with a class of nouns called uncountables, such as milk, information, hatred, etc., or with members of ‘singular’ grammemes (i. e. grammemes containing the meaning of ‘singularity’, such as book, table, man, boy, etc.).
The ‘possessive case’ grammemes are rarely combined with verbs, barring the gerund. Some words are regularly combined with sentences, others are not.
It is convenient to distinguish right-hand and left-hand connections. In the combination my hand (when written down) the word my has a right-hand connection with the word hand and the latter has a left-hand connection with the word my.
With analytical forms inside and outside connections are also possible. In the combination has often written the verb has an inside connection with the adverb and the latter has an outside connection with the verb.
It will also be expedient to distinguish unilateral, bilateral and multilateral connections. By way of illustration we may say that the articles in English have unilateral right-hand connections with nouns: a book, the child. Such linking words as prepositions, conjunctions, link-verbs, and modal verbs are characterized by bilateral connections: love of life, John and Mary, this is John, he must come. Most verbs may have zero
(Come!), unilateral (birds fly), bilateral (I saw him) and multilateral (Yesterday I saw him there) connections. In other words, the combinability of verbs is variable.
One should also distinguish direct and indirect connections. In the combination Look at John the connection between look and at, between at and John are direct, whereas the connection between look and John is indirect, through the preposition at.
2. Lexical and grammatical valency. Valency and collocability. Relationships between valency and collocability. Distribution.
The appearance of words in a certain syntagmatic succession with particular logical, semantic, morphological and syntactic relations is called collocability or valency.
Valency is viewed as an aptness or potential of a word to have relations with other words in language. Valency can be grammatical and lexical.
Collocability is an actual use of words in particular word-groups in communication.
The range of the Lexical valency of words is linguistically restricted by the inner structure of the English word-stock. Though the verbs ‘lift’ and ‘raise’ are synonyms, only ‘to raise’ is collocated with the noun ‘question’.
The lexical valency of correlated words in different languages is different, cf. English ‘pot plants’ vs. Russian ‘комнатные цветы’.
The interrelation of lexical valency and polysemy:
• the restrictions of lexical valency of words may manifest themselves in the lexical meanings of the polysemantic members of word-groups, e.g. heavy, adj. in the meaning ‘rich and difficult to digest’ is combined with the words food, meals, supper, etc., but one cannot say *heavy cheese or *heavy sausage;
• different meanings of a word may be described through its lexical valency, e.g. the different meanings of heavy, adj. may be described through the word-groups heavy weight / book / table; heavy snow / storm / rain; heavy drinker / eater; heavy sleep / disappointment / sorrow; heavy industry / tanks, and so on.
From this point of view word-groups may be regarded as the characteristic minimal lexical sets that operate as distinguishing clues for each of the multiple meanings of the word.
Grammatical valency is the aptness of a word to appear in specific grammatical (or rather syntactic) structures. Its range is delimited by the part of speech the word belongs to. This is not to imply that grammatical valency of words belonging to the same part of speech is necessarily identical, e.g.:
• the verbs suggest and propose can be followed by a noun (to propose or suggest a plan / a resolution); however, it is only propose that can be followed by the infinitive of a verb (to propose to do smth.);
• the adjectives clever and intelligent are seen to possess different grammatical valency as clever can be used in word-groups having the pattern: Adj. + Prep. at +Noun(clever at mathematics), whereas intelligent can never be found in exactly the same word-group pattern.
• The individual meanings of a polysemantic word may be described through its grammatical valency, e.g. keen + Nas in keen sight ‘sharp’; keen + on + Nas in keen on sports ‘fond of’; keen + V(inf)as in keen to know ‘eager’.
Lexical context determines lexically bound meaning; collocations with the polysemantic words are of primary importance, e.g. a dramatic change / increase / fall / improvement; dramatic events / scenery; dramatic society; a dramatic gesture.
In grammatical context the grammatical (syntactic) structure of the context serves to determine the meanings of a polysemantic word, e.g. 1) She will make a good teacher. 2) She will make some tea. 3) She will make him obey.
Distribution is understood as the whole complex of contexts in which the given lexical unit(word) can be used. Есть даже словари, по которым можно найти валентные слова для нужного нам слова — так и называются дистрибьюшн дикшенери
3. What is a word combination? Types of word combinations. Classifications of word-groups.
Word combination — a combination of two or more notional words serving to express one concept. It is produced, not reproduced in speech.
Types of word combinations:
- Semantically:
- free word groups (collocations) — a year ago, a girl of beauty, take lessons;
- set expressions (at last, point of view, take part).
- Morphologically (L.S. Barkhudarov):
- noun word combinations, e.g.: nice apples (BBC London Course);
- verb word combinations, e.g.: saw him (E. Blyton);
- adjective word combinations, e.g.: perfectly delightful (O. Wilde);
- adverb word combinations, e.g.: perfectly well (O, Wilde);
- pronoun word combinations, e.g.: something nice (BBC London Course).
- According to the number of the components:
- simple — the head and an adjunct, e.g.: told me (A. Ayckbourn)
- Complex, e.g.: terribly cold weather (O. Jespersen), where the adjunct cold is expanded by means of terribly.
Classifications of word-groups:
- through the order and arrangement of the components:
• a verbal — nominal group (to sew a dress);
• a verbal — prepositional — nominal group (look at something);
- by the criterion of distribution, which is the sum of contexts of the language unit usage:
• endocentric, i.e. having one central member functionally equivalent to the whole word-group (blue sky);
• exocentric, i.e. having no central member (become older, side by side);
- according to the headword:
• nominal (beautiful garden);
• verbal (to fly high);
• adjectival (lucky from birth);
- according to the syntactic pattern:
• predicative (Russian linguists do not consider them to be word-groups);
• non-predicative — according to the type of syntactic relations between the components:
(a) subordinative (modern technology);
(b) coordinative (husband and wife).
4. What is “a free word combination”? To what extent is what we call a free word combination actually free? What are the restrictions imposed on it?
A free word combination is a combination in which any element can be substituted by another.
The general meaning of an ordinary free word combination is derived from the conjoined meanings of its elements
Ex. To come to one’s sense –to change one’s mind;
To fall into a rage – to get angry.
Free word-combinations are word-groups that have a greater semantic and structural independence and freely composed by the speaker in his speech according to his purpose.
A free word combination or a free phrase permits substitution of any of its elements without any semantic change in the other components.
5. Clichе´s (traditional word combinations).
A cliché is an expression that is trite, worn-out, and overused. As a result, clichés have lost their original vitality, freshness, and significance in expressing meaning. A cliché is a phrase or idea that has become a “universal” device to describe abstract concepts such as time (Better Late Than Never), anger (madder than a wet hen), love (love is blind), and even hope (Tomorrow is Another Day). However, such expressions are too commonplace and unoriginal to leave any significant impression.
Of course, any expression that has become a cliché was original and innovative at one time. However, overuse of such an expression results in a loss of novelty, significance, and even original meaning. For example, the proverbial phrase “when it rains it pours” indicates the idea that difficult or inconvenient circumstances closely follow each other or take place all at the same time. This phrase originally referred to a weather pattern in which a dry spell would be followed by heavy, prolonged rain. However, the original meaning is distanced from the overuse of the phrase, making it a cliché.
Some common examples of cliché in everyday speech:
- My dog is dumb as a doorknob. (тупой как пробка)
- The laundry came out as fresh as a daisy.
- If you hide the toy it will be out of sight, out of mind. (с глаз долой, из сердца вон)
Examples of Movie Lines that Have Become Cliché:
- Luke, I am your father. (Star Wars: The Empire Strikes Back)
- i am Groot. (Guardians of the Galaxy)
- I’ll be back. (The Terminator)
- Houston, we have a problem. (Apollo 13)
Some famous examples of cliché in creative writing:
- It was a dark and stormy night
- Once upon a time
- There I was
- All’s well that ends well
- They lived happily ever after
6. The sociolinguistic aspect of word combinations.
Lexical valency is the possibility of lexicosemantic connections of a word with other word
Some researchers suggested that the functioning of a word in speech is determined by the environment in which it occurs, by its grammatical peculiarities (part of speech it belongs to, categories, functions in the sentence, etc.), and by the type and character of meaning included into the semantic structure of a word.
Words are used in certain lexical contexts, i.e. in combinations with other words. The words that surround a particular word in a sentence or paragraph are called the verbal context of that word.
7. Norms of lexical valency and collocability in different languages.
The aptness of a word to appear in various combinations is described as its lexical valency or collocability. The lexical valency of correlated words in different languages is not identical. This is only natural since every language has its syntagmatic norms and patterns of lexical valency. Words, habitually collocated, tend to constitute a cliché, e.g. bad mistake, high hopes, heavy sea (rain, snow), etc. The translator is obliged to seek similar cliches, traditional collocations in the target-language: грубая ошибка, большие надежды, бурное море, сильный дождь /снег/.
The key word in such collocations is usually preserved but the collocated one is rendered by a word of a somewhat different referential meaning in accordance with the valency norms of the target-language:
- trains run — поезда ходят;
- a fly stands on the ceiling — на потолке сидит муха;
- It was the worst earthquake on the African continent (D.W.) — Это было самое сильное землетрясение в Африке.
- Labour Party pretest followed sharply on the Tory deal with Spain (M.S.1973) — За сообщением о сделке консервативного правительства с Испанией немедленно последовал протест лейбористской партии.
Different collocability often calls for lexical and grammatical transformations in translation though each component of the collocation may have its equivalent in Russian, e.g. the collocation «the most controversial Prime Minister» cannot be translated as «самый противоречивый премьер-министр».
«Britain will tomorrow be welcoming on an official visit one of the most controversial and youngest Prime Ministers in Europe» (The Times, 1970). «Завтра в Англию прибывает с официальным визитом один из самых молодых премьер-министров Европы, который вызывает самые противоречивые мнения».
«Sweden’s neutral faith ought not to be in doubt» (Ib.) «Верность Швеции нейтралитету не подлежит сомнению».
The collocation «documentary bombshell» is rather uncommon and individual, but evidently it does not violate English collocational patterns, while the corresponding Russian collocation — документальная бомба — impossible. Therefore its translation requires a number of transformations:
«A teacher who leaves a documentary bombshell lying around by negligence is as culpable as the top civil servant who leaves his classified secrets in a taxi» (The Daily Mirror, 1950) «Преподаватель, по небрежности оставивший на столе бумаги, которые могут вызвать большой скандал, не менее виновен, чем ответственный государственный служащий, забывший секретные документы в такси».
8. Using the data of various dictionaries compare the grammatical valency of the words worth and worthy; ensure, insure, assure; observance and observation; go and walk; influence and влияние; hold and держать.
| Worth & Worthy | |
| Worth is used to say that something has a value:
• Something that is worth a certain amount of money has that value; • Something that is worth doing or worth an effort, a visit, etc. is so attractive or rewarding that the effort etc. should be made. Valency:
|
Worthy:
• If someone or something is worthv of something, they deserve it because they have the qualities required; • If you say that a person is worthy of another person you are saying that you approve of them as a partner for that person. Valency:
|
| Ensure, insure, assure | ||
| Ensure means ‘make certain that something happens’.
Valency:
|
Insure — make sure
Valency:
|
Assure:
• to tell someone confidently that something is true, especially so that they do not worry; • to cause something to be certain. Valency:
|
| Observance & Observation | |
| Observance:
• the act of obeying a law or following a religious custom: religious observances such as fasting • a ceremony or action to celebrate a holiday or a religious or other important event: [ C ] Memorial Day observances [ U ] Financial markets will be closed Monday in observance of Labor Day. |
Observation:
• the act of observing something or someone; • the fact that you notice or see something; • a remark about something that you have noticed. Valency:
|
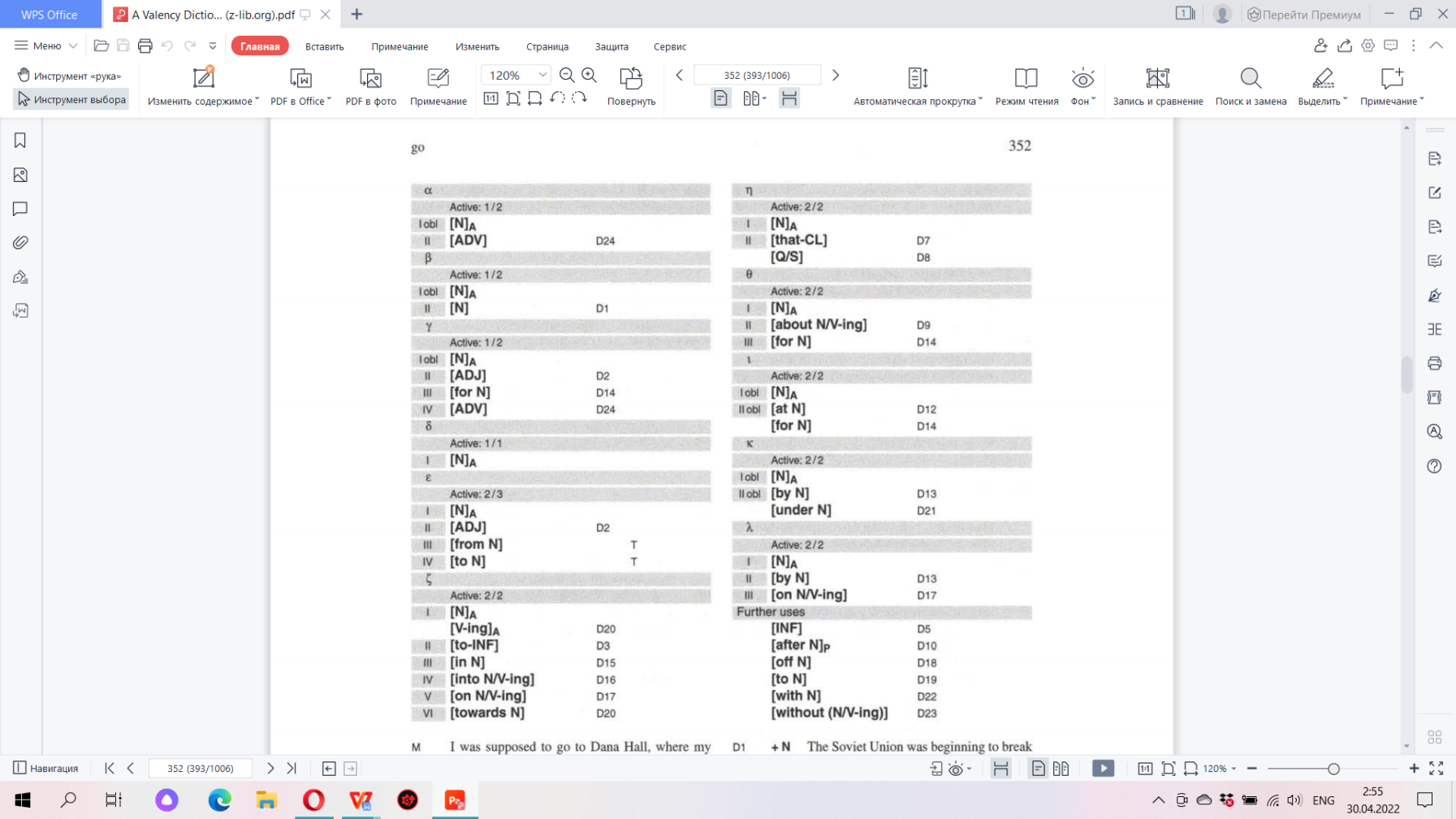
| Go & Walk | |
|
Walk can mean ‘move along on foot’:
• A person can walk an animal, i.e. exercise them by walking. • A person can walk another person somewhere , i.e. take them there, • A person can walk a particular distance or walk the streets. Valency:
|
| Influence & Влияние | |
| Influence:
• A person can have influence (a) over another person or a group, i.e. be able to directly guide the way they behave, (b) with a person, i.e. be able to influence them because they know them well. • Someone or something can have or be an influence on or upon something or someone, i.e. be able to affect their character or behaviour in some way Valency:
|
Влияние — Действие, оказываемое кем-, чем-либо на кого-, что-либо.
Сочетаемость:
|
| Hold & Держать | |
| Hold:
• to take and keep something in your hand or arms; • to support something; • to contain or be able to contain something; • to keep someone in a place so that they cannot leave. Valency:
|
Держать — взять в руки/рот/зубы и т.д. и не давать выпасть
Сочетаемость:
|
- Contrastive Analysis. Give words of the same root in Russian; compare their valency:
| Chance | Шанс |
|
|
| Situation | Ситуация |
|
|
| Partner | Партнёр |
|
|
| Surprise | Сюрприз |
|
|
| Risk | Риск |
|
|
| Instruction | Инструкция |
|
|
| Satisfaction | Сатисфакция |
|
|
| Business | Бизнес |
|
|
| Manager | Менеджер |
|
|
| Challenge | Челлендж |
|
|
10. From the lexemes in brackets choose the correct one to go with each of the synonyms given below:
- acute, keen, sharp (knife, mind, sight):
• acute mind;
• keen sight;
• sharp knife;
- abysmal, deep, profound (ignorance, river, sleep);
• abysmal ignorance;
• deep river;
• profound sleep;
- unconditional, unqualified (success, surrender):
• unconditional surrender;
• unqualified success;
- diminutive, miniature, petite, petty, small, tiny (camera, house, speck, spite, suffix, woman):
• diminutive suffix;
• miniature camera/house;
• petite woman;
• petty spite;
• small speck/camera/house;
• tiny house/camera/speck;
- brisk, nimble, quick, swift (mind, revenge, train, walk):
• brisk walk;
• nimble mind;
• quick train;
• swift revenge.
11. Collocate deletion: One word in each group does not make a strong word partnership with the word on Capitals. Which one is Odd One Out?
1) BRIGHT idea green
smell
child day room
2) CLEAR
attitude
need instruction alternative day conscience
3) LIGHT traffic
work
day entertainment suitcase rain green lunch
4) NEW experience job
food
potatoes baby situation year
5) HIGH season price opinion spirits
house
time priority
6) MAIN point reason effect entrance
speed
road meal course
7) STRONG possibility doubt smell influence
views
coffee language

advantage
situation relationship illness crime matter
- Write a short definition based on the clues you find in context for the italicized words in the sentence. Check your definitions with the dictionary.
| Sentence | Meaning |
| The method of reasoning from the particular to the general — the inductive method — has played an important role in science since the time of Francis Bacon. | The way of learning or investigating from the particular to the general that played an important role in the time of Francis Bacon |
| Most snakes are meat eaters, or carnivores. | Animals whose main diet is meat |
| A person on a reducing diet is expected to eschew most fatty or greasy foods. | deliberately avoid |
| After a hectic year in the city, he was glad to return to the peace and quiet of the country. | full of incessant or frantic activity. |
| Darius was speaking so quickly and waving his arms around so wildly, it was impossible to comprehend what he was trying to say. | grasp mentally; understand.to perceive |
| The babysitter tried rocking, feeding, chanting, and burping the crying baby, but nothing would appease him. | to calm down someone |
| It behooves young ladies and gentlemen not to use bad language unless they are very, very angry. | necessary |
| The Academy Award is an honor coveted by most Hollywood actors. | The dream about some achievements |
| In the George Orwell book 1984, the people’s lives are ruled by an omnipotent dictator named “Big Brother.” | The person who have a lot of power |
| After a good deal of coaxing, the father finally acceded to his children’s request. | to Agree with some request |
| He is devoid of human feelings. | Someone have the lack of something |
| This year, my garden yielded several baskets full of tomatoes. | produce or provide |
| It is important for a teacher to develop a rapport with his or her students. | good relationship |