Create a bibliography, citations, and references
-
Put your cursor at the end of the text you want to cite.
-
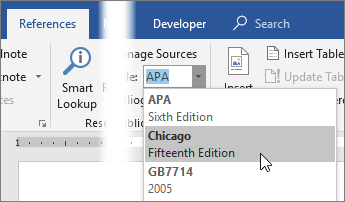
Go to References > Style, and choose a citation style.
-
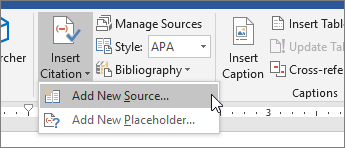
Select Insert Citation.
-
Choose Add New Source and fill out the information about your source.
Once you’ve added a source to your list, you can cite it again:
-
Put your cursor at the end of the text you want to cite.
-
Go to References > Insert Citation, and choose the source you are citing.
-
To add details, like page numbers if you’re citing a book, select Citation Options, and then Edit Citation.
Create a bibliography
With cited sources in your document, you’re ready to create a bibliography.
-
Put your cursor where you want the bibliography.
-
Go to References > Bibliography, and choose a format.
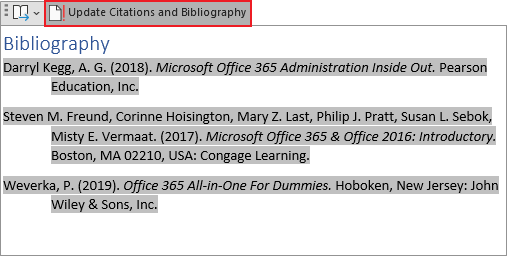
Tip: If you cite a new source, add it to the bibliography by clicking anywhere in the bibliography and selecting Update Citations and Bibliography.
Need more help?
Want more options?
Explore subscription benefits, browse training courses, learn how to secure your device, and more.
Communities help you ask and answer questions, give feedback, and hear from experts with rich knowledge.
If you use citations in your Word documents, you might need the bibliographic items for each source that you have referenced. Microsoft Word offers a useful tool to create a list of these bibliographic references, also named as Bibliography, References, or Works Cited, as a list of the citations added in the document.
A Bibliography is a list of all the sources in the document. In the MLA format (Modern Language Association), the list of sources is called Works Cited, that is a type of bibliography, which can include sources other than books. In the APA format (American Psychological Association), it is called a References list.
Before you create the Bibliography, References, or Works Cited, make sure you have replaced all placeholders with a proper citation (for more details, see how to create a citation, how to create a multi-source citation). If you inserted a placeholder for a citation, the source would not appear in the bibliography. However, if you later replace the placeholder with source information, the bibliography will be automatically updated, and the new source will be added to the bibliography.
Create a Bibliography, References, and Works Cited
To create a bibliography, follow the next steps:
1. Place the cursor where you want to insert the bibliography:
- Press Ctrl+End to get to the end of the document.
- Press Ctrl+Enter to insert a page break.
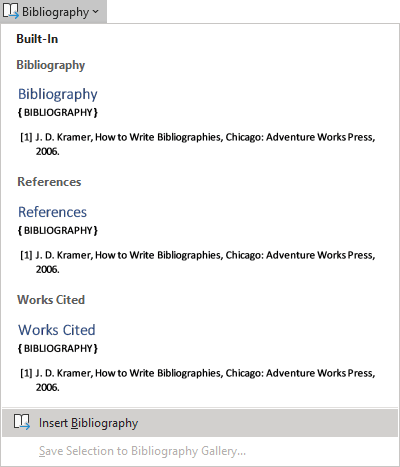
2. On the References tab, in the Citations & Bibliography group, click the Bibliography button and then do one of the following:
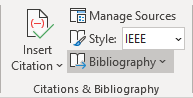
- Choose one of the built-in styles in the drop-down menu.
- Select Insert Bibliography at the bottom of the list:
Note: If you choose the Insert Bibliography option, you will need to add a heading such as Bibliography, References, or Works Cited.
Word creates the Bibliography, References, or the Works Cited based on the sources. For example, the Bibliography in the IEEE style (see more about styles below):
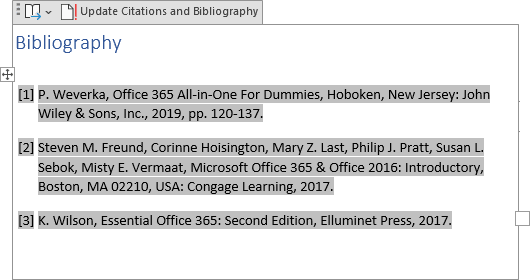
Note: The automatically created bibliography, it does not matter how you created it, contains all sources of the document, even if some were removed or added by mistake. See how to manage sources for the Bibliography, References, and Works Cited for more details.
Empty Bibliography, References, and Works Cited
After inserting a Bibliography, References, and Works Cited, Word can create a message “There are no sources in the current document.”:
The leading cause for this message is that Word could not find the citations created using the Citations & Bibliography functionality (see how to create a citation in a Word document). It is possible that there are placeholders in the document, but they are still empty.
To solve that problem, check the placeholders and citations. See how to manage sources for more details.
Don’t forget to update bibliography in a document!
Citation and bibliography formats
Depending on the selected style, the Bibliography, References, and Works Cited look quite different. For example, the Works Cited using the APA style:

To change the style, on the References tab, in the Citations & Bibliography group, open the Style drop-down list:
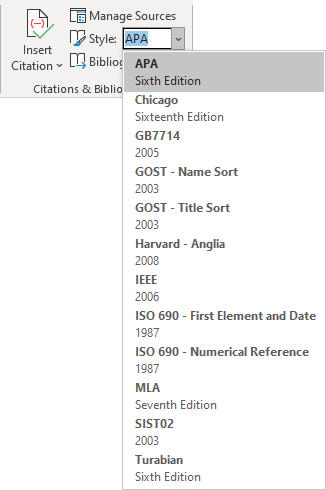
Choose the format you need:
- The American Psychological Association (APA) style is used for academic documents such as scholarly journal articles and books and in many social sciences.
- The Chicago style is used in history and economics and some social sciences.
- The Modern Language Association (MLA) style is most often used in the arts and the humanities, especially in English studies, modern languages and kinds of literature, comparative literature, literary criticism, media studies, cultural studies, and related disciplines.
- The American Sociological Association (ASA) style is used for writing university research papers in the field of sociology.
- The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) style is used for writing research papers, commonly used in technical fields, particularly in computer science.
- Oxford, Harvard, and others.
The specified format for citations and a bibliography can be the requirement for some types of the document.
Note: You do not need to create a bibliography to see how it will look for selected style. After choosing the bibliography style, you can preview the format in the Bibliography list:

Update a Bibliography, References, and Works Cited
Microsoft Word inserts a Bibliography, References, and Works Cited as a field:

or , if the Bibliography is inserted by clicking the Insert Bibliography command.
See how to turn on or turn off highlighting of fields in a Word document to display all fields in a document with a gray background.
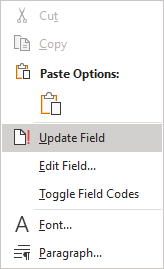
Word will not automatically update any type of Bibliography after adding, deleting, or modifying sources or placeholders. You need manually update it, to do so, click on the Bibliography and do one of the following:
- Right-click anywhere in the sources list and select Update Field from the popup menu:
- Click anywhere in the Bibliography to show the field options. At the top of the field borders, click the Update Citations and Bibliography… button:
See also how to lock and unlock updating for fields.
Modify a Bibliography, References, and Works Cited
Word offers very simple way to change Bibliography to Works Cited or to References, and vice versa. To do so, click on the Bibliography to show the field options. At the top of the field borders, click the Bibliographies button:
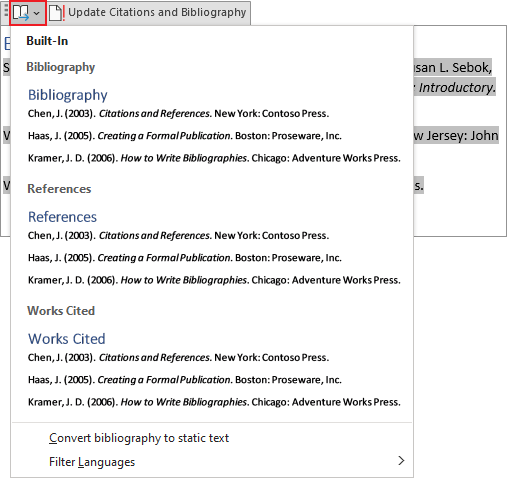
Choose the bibliography type you need: Bibliography, References, or Works Cited.
Word also proposed the commands:
- Convert bibliography to static text.
You can use this command for the final version of the document to avoid any changes for sources, updates, or style changes.
- Filter Languages to show the sources of different languages (see how to create citations for more details).
Note: If the source has the default language, it can be shown for any selected language.
Delete a Bibliography, References, and Works Cited
To delete a Bibliography, it isn’t enough to delete only visible information, it is necessary to delete all the field. To do so, do the following:
1. Select the total Bibliography lines, including the last, empty line right after the Bibliography entries.
Note: If possible, click inside to show the field options. At the top of the field borders, click the Field button to select all the bibliography lines:
2. Click the Delete key.
Note: All the citations and placeholders (source information) are still saved in the current document, as well as in Word’s Master list (see manage sources for more details).
See also this tip in French:
Comment créer une bibliographie.
Managing citations for research papers, theses, dissertations, and other nonfiction works can be overwhelming. However, you can ease the process by learning how to insert citations in Microsoft Word using the software’s citation and bibliography tools.
This tutorial covers six topics:
- How to select a citation style
- How to insert citations for new sources
- How to insert citations for existing sources
- How to edit sources
- How to use citation placeholders
- How to insert bibliographies, reference lists, or works cited lists
Important Note: At the time this tutorial was published, Microsoft Word did not offer the most up-to-date formatting for several of our primary style guides, including APA, Chicago, MLA, and Turabian. Therefore, I encourage you to review the available styles before using the citation and bibliography tools. We will cover the steps to customize citation and bibliography styles in a separate tutorial.
This tutorial is also available as a YouTube video showing all the steps in real time.
Watch more than 150 other writing-related software tutorials on my YouTube channel.
The images below are from Word in Microsoft 365. The steps are the same in Word 2021, Word 2019, and Word 2016. However, your interface may look slightly different in those older versions of the software.
How to Select a Citation Style in Microsoft Word
- Select the References tab in the ribbon.
- Select your citation style from the Style menu in the Citations & Bibliography group.
How to Insert Citations for New Sources in Microsoft Word
- Place your cursor where you want to insert the citation.
- Select the References tab in the ribbon (see figure 1).
- Select the Insert Citation button in the Citations & Bibliography group.
- Select Add New Source from the drop-down menu.
- Select the source type from the Type of Source menu in the Create Source dialog box.
- Enter the source information into the bibliography fields.
- (Optional Step) Select Show All Bibliography Fields if you need to add additional information.
- (Optional Step) Enter the source information into the additional fields.
- Select the OK button.
Your citation should appear in your text.
How to Insert Citations for Existing Sources in Microsoft Word
Once you enter a source, as shown in the section above, you can create additional citations for that source without reentering the information.
- Place your cursor where you want to insert the citation (see figure 3).
- Select the References tab in the ribbon (see figure 1).
- Select the Insert Citation button in the Citations & Bibliography group (see figure 4).
- Select the source from the drop-down menu.
Your citation should appear in your text (see figure 11).
How to Edit Sources in Microsoft Word
When you edit an existing source, you will also edit any existing citations for that source in your current document.
- Select the References tab in the ribbon (see figure 1).
- Select the Manage Sources button in the Citations & Bibliography group.
- Select the source you want to edit in the Master List or the Current List in the Source Manager dialog box.
Pro Tip: The Master List is stored in your computer and is accessible in all your documents. The Current List is part of your current file and is only accessible in that file. By default, Word stores new sources in the Master List and the Current List.
- Select the Edit button.
- Enter your edits in the Edit Source dialog box. (Select Show All Bibliography Fields, if necessary.)
- Select the OK button.
- Select Yes or No in the alert box stating that you will be updating the source in both the Master List and the Current List. (Strongly consider selecting Yes to update both lists if you plan to cite this source in future documents.)
- Select the Close button in the Source Manager dialog box.
How to Use Citation Placeholders in Microsoft Word
You can use placeholders if your source information is not available.
- Place your cursor where you want to insert the citation placeholder.
- Select the References tab in the ribbon (see figure 1).
- Select the Insert Citation button in the Citations & Bibliography group (see figure 4).
- Select Add New Placeholder from the drop-down menu.
- (Optional Step) Change the name of the placeholder in the Placeholder Name dialog box.
- Select the OK button.
Pro Tip: You can use the same placeholder in the future by selecting it from the Insert Citation drop-down menu (see figure 12).
- When you are ready to replace the placeholder with a source, complete the steps in How to Edit Sources above.
How to Insert Bibliographies, Reference Lists, or Works Cited Lists in Microsoft Word
These steps will only work if you inserted your sources using Word’s citation and bibliography tools.
- Place your cursor where you want to insert the bibliography, reference list, or works cited list.
- Select the References tab in the ribbon (see figure 1).
- Select the Bibliography button in the Citations & Bibliography group.
- Select Bibliography, References, or Works Cited from the drop-down menu.
Your bibliography, reference list, or works cited list should appear in your document.
Related Resources
How to Create Hanging Indents in Microsoft Word
How to Insert Footnotes and Endnotes in Microsoft Word
How to Convert Individual Footnotes to Endnotes in Microsoft Word (and Individual Endnotes to Footnotes)
How to Create a Cover Page in Microsoft Word (Built-In and Custom)
Updated August 22, 2022
Download Article
Download Article
Microsoft Word has many automatic features that can help you write a report or academic paper. Among these, you can keep a list of sources and citations to automatically generate a bibliography (also called a «Reference List» or «Works Cited») at the end of your paper. If you need footnotes or endnotes, Word has features that can help you format those as well.
-
1
Choose a citation style on the «References» tab. When you click on the «References» tab, you’ll see the word «Style» next to a drop-down menu. If you click on the drop-down menu, you can select the citation style you want to use for your references.
- Make sure the edition is the same as the one you need to use. Word typically offers the most recent edition of each style, but if you have an older version of Word you may need to upgrade. If you have a subscription version, simply download the latest update.[1]
- Make sure the edition is the same as the one you need to use. Word typically offers the most recent edition of each style, but if you have an older version of Word you may need to upgrade. If you have a subscription version, simply download the latest update.[1]
-
2
Click «Add New Source» to enter information about a source. On the «References» tab, click the «Insert Citation» button in the «Citations and Bibliography» group. Any sources you’ve already entered will appear in a drop-down. Select «Add New Source» if the source you want to cite isn’t already listed.
- A dialogue box will appear with the necessary fields for the citation, including spaces for the author, title, year of publication, city, and publisher. Enter all the information you have for your source, then click «OK.»
- If you have additional information about the source that doesn’t fit into any of these basic fields, check the box next to «Show All Bibliography Fields.»
Tip: If you don’t have all the information for the source, or if you don’t want to interrupt your train of thought to add a new source, you can click «Add New Placeholder» instead. This alerts you that you need to add a citation there.
Advertisement
-
3
Continue to insert citations as you write your paper. Set the cursor at the end of a sentence where you need a citation. Go back up to the «References» tab and click on «Insert Citation» to bring up the list of sources. Click on the source you want to cite, and Word will automatically generate an in-text citation in the style you’ve chosen.
- To edit an individual citation, such as if you wanted to add a page number for a direct quote, right-click the citation for citation options and click «Edit Citation.»[2]
- To edit an individual citation, such as if you wanted to add a page number for a direct quote, right-click the citation for citation options and click «Edit Citation.»[2]
-
4
Use the «Manage Sources» button to edit or delete sources. Particularly if you have a long paper with a lot of sources, you may find as you go that you have some duplicated sources or some that you no longer need to use. You can add, delete, or edit sources using the «Manage Sources» button in the «Citations & Bibliography» group under the «References» tab.
- Choose the source you want to edit from your master list. As you edit, you’ll see a preview of the final citation in the lower box.
- If you inserted placeholders while you were writing, you can also use this menu to add information for those sources.
Advertisement
-
1
Select the footnote or endnote option on the «References» tab. Set your cursor where you want the footnote or endnote number in your text. Typically this will be at the end of a sentence, but it may be after a signal phrase or author’s name. Go up to the «References» tab and click «Insert Footnote» or «Insert Endnote.»[3]
- Word will automatically create a superscripted number in your text and move the cursor to the footnote or endnote field.
Keyboard shortcuts:
Insert Footnote: Alt+Ctrl+F (PC); Command+Option+F (Mac)
Insert Endnote: Alt+Ctrl+D (PC); Command+Option+E (Mac) -
2
Use the «Expand» icon to adjust footnote or endnote settings. You can use sequential numbers, letters, or other symbols to mark your footnotes or endnotes. You can also specify what number or letter you want them to start from.[4]
- By default, footnotes or endnotes will continue sequential numbering throughout your document. If you want the numbers to restart at the beginning of each new section or chapter, you can specify this in the settings.
If you need to convert footnotes to endnotes, click on the «Insert» menu, then «Footnote,» then «Options.» Select «Convert» from the menu, then click on «Endnotes.»
-
3
Type your footnote or endnote into your document. You can enter your citation by hand, or you can use the «Insert Citation» tool to add a citation in your footnote or endnote. Choose your source from the drop-down or add a new source if you want to cite a source that you haven’t entered yet.[5]
- You can also use the «Placeholder» tool if you don’t yet have all the information for the source and need to add it in later.
- Check the formatting against your style guide to make sure it’s correct before you continue.
-
4
Double-click the footnote number to go back to the document. When you’re ready to go back up to where you left off and start writing again, double-click the number or other symbol at the beginning of the footnote. It will send the cursor back to the end of the text.[6]
- Similarly, you can double-click a superscripted footnote number in the text to check that footnote, edit, or add to it. While you can also simply scroll down the page, this is a quicker way to get there.
To delete a footnote or endnote, highlight the footnote or endnote number in your text and press the delete key. Word will automatically renumber your other footnotes or endnotes to accommodate for the deletion.
Advertisement
-
1
Choose the format for your bibliography. Word automatically builds your bibliography for you as you enter your sources. Select «Bibliography» fro the «References» tab, then choose the type of bibliography you want from the drop-down.[7]
- For example, if you’re writing your paper in MLA style, you would want a «Works Cited» bibliography. Assuming you chose MLA as the style for your source citations, the «Works Cited» format would be the first format option in the «Bibliography» drop-down menu.
-
2
Generate your bibliography with a click. When you find the format you want, simply select it from the drop-down menu and click. Word will automatically create your bibliography at the end of your document.[8]
- The bibliography is considered a separate object from the paper you’re writing, and will automatically start on a new page.
Tip: You don’t have to wait until you’ve finished writing your paper to create your bibliography. Word will auto-populate your bibliography with any new sources you add after the bibliography has been generated.
-
3
Proofread your bibliography carefully. Even though Word has done the hard work of formatting for you, you still need to double-check each entry. Make sure the source is correct and the entry is formatted correctly for the style you’ve chosen.[9]
- For example, if you made a typographical error when entering the information about the source, that error would carry over into your bibliography.
Advertisement
Ask a Question
200 characters left
Include your email address to get a message when this question is answered.
Submit
Advertisement
Thanks for submitting a tip for review!
-
The steps and information in this article are accurate for Word for Office 365, Word 2019, Word 2016, Word 2013, Word 2010, and Word 2007. If you have a different edition of Word, your menu options may differ slightly.[10]
Advertisement
About This Article
Thanks to all authors for creating a page that has been read 91,028 times.
Is this article up to date?

A bibliography is a list of sources referred to in a document. Many scholarly documents require one, and you probably had to create a few while in school. The list comprises citations, which include the title, author, publisher, date of publication, and so on for each source. You’ll use a bibliography to credit quotes and other facts to lend legitimacy to your document. The technical process in Microsoft Word is similar to footnote/endnotes or indexing and has three steps: Adding the sources as a citation, citing the citation, and then generating the bibliography. I’ll show you how simple it is to add sources and generate a bibliography.
I’m using Office 365, but you can use earlier versions of Word. When using the .doc format, you will lose some features. You can work with your own document or download the demonstration .docx and .doc files. Word’s browser edition will display existing bibliographies, but you can’t add or edit sources or generate a bibliography while in the browser.
LEARN MORE: Office 365 Consumer pricing and features
How to add a source in Microsoft Word
Sources can be any kind of published work, from books to articles on the web. The information you include for a source will depend on you or the publisher. Word supports several styles, but the three most common are Modern Language Association (MLA), American Psychological Association (APA) and Chicago. These styles determine the information needed and how that information is formatted. We won’t cover individual styles in this article–you will need to do a little research to determine what your publisher or recipient requires.
First, you need a source, so let’s run through a quick example.
- After entering the quote or fact that requires verification, click the Reference tab.
- In the Citations & Bibliography group, choose the appropriate style. APA is the default and, for our purposes, we’ll retain it.
- Click Insert Citation and choose Add New Source from the dropdown list.
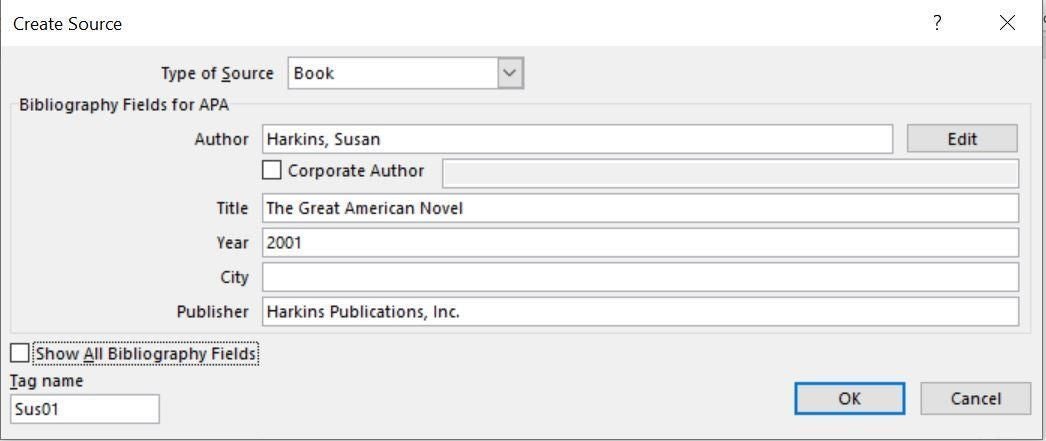
- In the resulting dialog, enter the fields required by your style (Figure A). You can enter the name using first name lastname or lastname, first name format. Separate multiple authors with a semi-colon ( ; ).
- Click OK. As you can see in Figure B, Word adds a text reference to the citation. (Don’t worry if your results don’t match mine.)
Figure A
Most of these fields (Figure A) are self-explanatory, though I want to call your attention to two options:
- Show All Bibliography Fields: When enabled, it shows a lot more fields. Most of us will never need those fields, but they’re available.
- Tag Name: This field is automated–it’s comprised of the author’s name and year. Word uses this tag internally to identify each citation.
Figure B
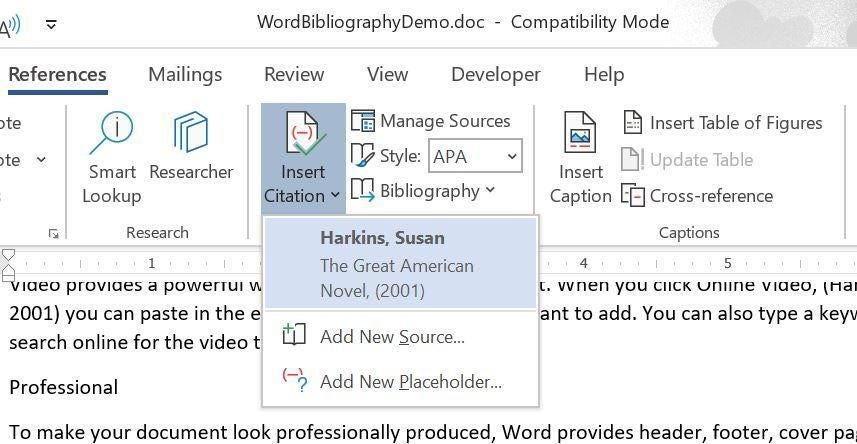
Once the citation exists, you don’t have to enter the information again. When referencing that source again, click Inert Citation in the Citations & Bibliography group and choose it from the resulting dropdown (Figure C).
Figure C
Note about the author name and tags: When entering author names, you should be consistent because of the tags. Word uses the first three characters of the first name you enter: Susan Harkins 2001 is Sus01 but Harkins, Susan 2001 is Har01.
Before we continue, enter a few more sources using the different types of sources (books, periodicals, etc.)–you’ll want more than one citation when you create the bibliography. Notice that the fields change with different source types. Although this tool is flexible, it can’t correct typos. Be careful with your case, spelling, and so on. Bibliographies are very difficult and tedious to proof after the fact.
How to add a bibliography in Microsoft Word
After you have added all your sources and cited (marked) all your text references, you’re ready to create the bibliography. It’s similar to adding an index or table of contents—Word does most of the work for you. To add the bibliography, follow these steps.
- Click where you want to insert the bibliography—usually at the end of the document.
- Click the Reference tab. Then, click Bibliography in the Citations & Bibliography group.
- From the resulting dropdown list, choose a bibliography. There are several, and I suggest you explore the options at another time.
That’s it! Everything you need is already in the document. Word will pull everything together for you. Figure D shows the results of choosing the first item in the dropdown list.
Figure D
If you had chosen a style other than APA, the list would be formatted a bit differently, but Word knows where to put all the commas, periods, what needs to be italicized or in quotes, and so on.
Understanding sources
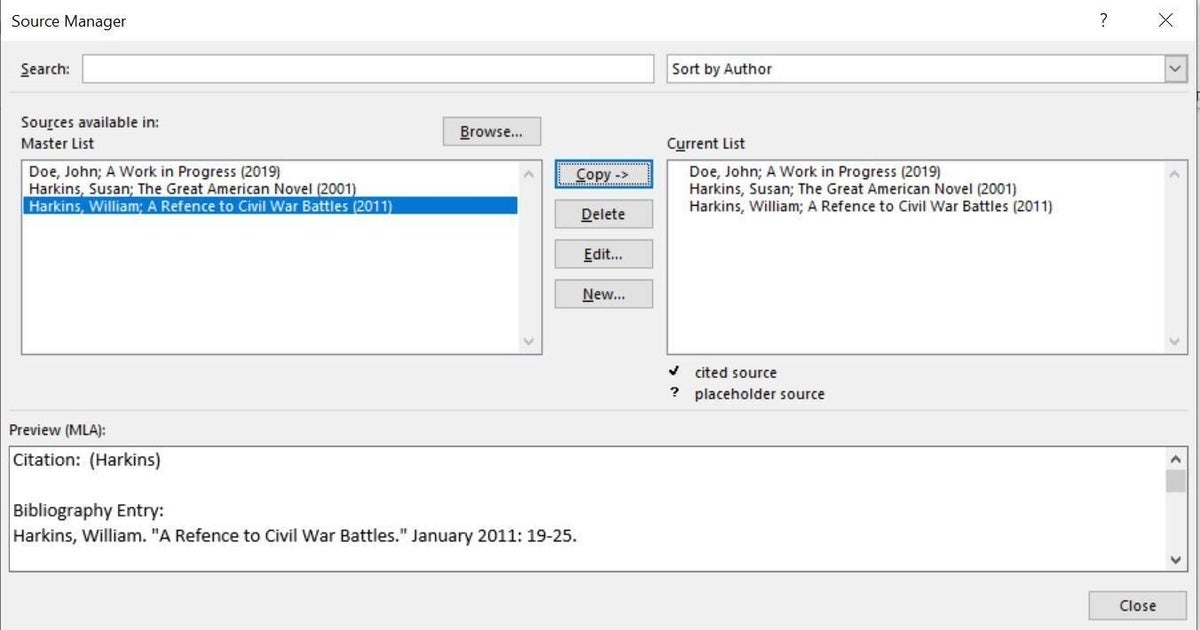
If you don’t get all the items you expected, you might need to take one more step. In the Citations & Bibliography group, click Manage Sources. If there are citations in the left list (which is the master list) that aren’t in the current list to the right but should be in the current document’s bibliography, copy them to the current list (Figure E). You can also see a preview of the APA style. Then, try again. This isn’t a bug–you control which citations go in the document and which don’t. Once you add a source, it’s available to other documents.
Figure E
The Source Manager gives you access to all sources. You can search for a title or sort by author. You can edit a source. Sources are stored separately from the document, so you can cite a source that you created for one document in another. The master and current lists represent all sources and sources for the current document, respectively.
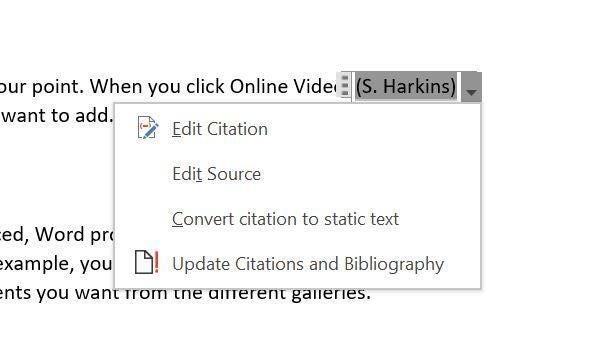
You can edit a source without using the Manage Sources dialog. You can do a lot from the citation at the document level because these “text” references are actually field codes. Simply click it and then click the dropdown arrow to display the available options shown in Figure F.
Figure F
How to fix a known bug with the APA style
There is a known bug with the APA style (sixth), and fortunately, it has an easy fix. If you end up with multiple citations from the same author, Word might fill in the title when it isn’t supposed to. If this happens, try this quick fix.
- Click the citation (code)—the one in the document that follows the in-text reference.
- Click the dropdown arrow and choose Edit Citation.
- Click Title checkbox and click OK.
Share your experiences of creating a bibliography in Word
Creating a bibliography in Word is easy. You can create a custom style if necessary, but doing so requires specialized knowledge in .xml development. If you’ve had trouble with a complex document and worked through it, share your experience in the comments section below.
Send me your Microsoft Office question
I answer readers’ questions when I can, but there’s no guarantee. Don’t send files unless requested; initial requests for help that arrive with attached files will be deleted unread. You can send screenshots of your data to help clarify your question. When contacting me, be as specific as possible. For example, “Please troubleshoot my workbook and fix what’s wrong” probably won’t get a response, but “Can you tell me why this formula isn’t returning the expected results?” might. Please mention the app and version that you’re using. I’m not reimbursed by TechRepublic for my time or expertise when helping readers, nor do I ask for a fee from readers I help. You can contact me at susansalesharkins@gmail.com.