Возможно, вы никогда не встречались с термином «референтные слова» (reference words), но наверняка вы встречали их при изучении английского языка. Референтные слова (или слова-ссылки) указывают на идеи и предметы, упомянутые ранее в тексте или разговоре, что позволяет не повторять одно и то же, и обеспечивает связность. Самый простой пример референтных слов – местоимения. Представите себе, как бы выглядела речь, если бы не было местоимений! Мы бы повторяли одно и то же множество раз и наши высказывания были бы похожи на набор слов. Референтные слова используются часто, потому что их основная функция – делать речь связной и избегать повторений.
Понимание того, к чему именно в тексте относятся референты – очень важный навык для всех, кто изучает английский язык. Чтобы понимать тексты, понимать речь на слух, просто необходимо соотносить референты с теми понятиями, на которые они указывают.
Рассмотрим простой пример:
My friends live in houses with big windows. They are quite new and spacious. – Мои друзья живут в домах с большими окнами. Они новые и просторные.
В данном примере референтное слово – they (они). Это слово указывает на что-то из первого предложения. Но на что именно? Кто они: друзья, дома или окна? По смыслу мы понимаем, что друзья и окна не могут быть новыми и просторными, соответственно they относится к слову houses.
А теперь представьте себе, что референтное слово связывает два абзаца в тексте. К примеру, в части Reading экзаменов FCE, CAE, CPE несколько заданий построено на умении распознавать референты. В части Reading TOEFL iBT также предлагаются вопросы на идентификацию референтов. А ведь предложения могут быть действительно запутанными, включать обороты, незнакомые слова, сложные грамматические конструкции. Что же делать? Давайте разбираться!
Самые простые референты – это личные местоимения. Кроме этого, референтами могут выступать указательные местоимения (this, these, that, those), слова who, which, that, one (ones), such и некоторые другие.
Мы рассмотрим, к чему может относиться тот или иной референт и приведем примеры.
It относится к ранее высказанной идее или ранее указанному предмету в единственном числе:
Learning English is a difficult process. It is undoubtedly useful for your career, though. – Изучение английского – сложный процесс. Однако это несомненно полезно для твоей карьеры.
They/ them относится к нескольким лицам, предметам, или нескольким идеям:
My friends took some excellent photographs of ancient temples. They were built more than 500 years ago! – Мои друзья сделали отличные снимки древних храмов. Они были построены более 500 лет назад! (They относится к слову temples.)
We got a number of questions from our clients, but I did not have time to answer them. – Мы получили ряд вопросов от наших клиентов, но у нас не было времени отвечать на них.
This относится к предмету или идее, которая находится близко к говорящему в пространстве и времени:
Our new invention is really revolutionary. This will change the world. – Наше новое изобретение революционное. Oно изменит мир.
These относится с нескольким предметам или идеям, которые находятся близко к говорящему в пространстве и времени:
I have bought some textbooks. These will help me to improve my grammar. – Я купил несколько учебников. Они помогут мне улучшить мою грамматику.
Thаt относится к предмету или идее, которая отдалена от говорящего в пространстве и времени:
Thank you for your help. That was so kind of you. – Спасибо за помощь. Это было так любезно с вашей стороны.
Those относится к нескольким предметам или идеям, которые отдалены от говорящего в пространстве и времени:
I did not even try to find the old letters. Those had been lost many years before. – Я даже не пытался найти старые письма. Они были потеряны много лет тому назад.
Who может относиться только к людям (в единственном и множественном числе):
There were children sitting at the desks who were writing something. – За партами были дети, которые что-то писали.
Which может относиться к идеям и предметам (в единственном и множественном числе):
Where are the shoes which I bought yesterday? – Где туфли, которые я купил вчера?
That относится к людям, предметам и идеям (в единственном и множественном числе):
Who will talk to the people that are waiting outside? – Кто поговорит с людьми, которые ждут на улице?
When he came, he saw the suitcase that has been already packed. – Когда он вошел, он увидел чемодан, который уже был упакован.
One используется, чтобы заменить существительное в единственном числе, которое было упомянуто ранее:
This dress is too small. Have you got a bigger one? – Это платье слишком маленькое. У вас есть побольше?
Ones используется, чтобы заменить существительное во множественном числе, которое было упомянуто ранее:
Hundreds of students applied for a grant, but only the best ones will get it. – Сотни студентов подали заявку на грант, но только самые лучшие его получат.
Such обозначает людей, предметы или идеи одного типа с ранее упомянутыми:
Your behaviour is outrageous. Such behaviour is inappropriate in the theatre. – Твое поведение возмутительно. Такое поведения неуместно в театре.
The former, the latter, respectively – используются в письменной речи, когда было упомянуто две идеи, два предмета, два лица. The former относится к первой упомянутой идее, the latter – ко второй, respectively относится к обоим идеям в порядке их упоминания (первый, затем второй):
Yesterday Mr Smith and Mr Reed called me. The former called me at 5 o’clock, the latter phoned at 6 o’clock. I arranged to meet them tomorrow at 9 and at 11 o’clock respectively. – Вчера мне позвонили мистер Смит и мистер Рид. Первый позвонил мне в 5 часов, второй – в 6 часов. Я договорился встретиться с ними в 9 и 11 соответственно.
Если вам помогла данная статья, оставляйте ваши комментарии и присоединяйтесь к нам Вконтакте, Instagram и Facebook! Успехов вам в изучении английского языка!
Увидели ошибку в тексте? Выделите её и нажмите на появившуюся стрелку или CTRL+Enter.
Futures – The forms we use
Share In this post we’re going to talk about the future. There are lots of different ways to talk about the future in English so
Proficiency Exam Corner
Share Proficiency Exam Corner Share Proficiency Exam Corner Share More Posts Read More Using… Read More Using Topic Sentences Share In the Cambridge Advanced
Would Rather & Would Prefer
Share Rather & Prefer In this post we will look at the different grammar of would rather and would prefer and the way we use each
Verb & Adverb Suffixes
Share Verb & Adverb Suffix Types We use a prefix at the beginning of the word to change the meaning and a suffix at the
Using Topic Sentences
Share In the Cambridge Advanced and Proficiency writing exams, the quality of answers depends on very good organisation of ideas and topics. In this
Use of English Part 2 – Finding the missing words
Share What is it? The Use of English Part 2 is where you need to put a single word into each gap. In this post we’ll look
Introduction
By John-Allen Payne, Ph.D.
Department of English
National Technical Institute for the Deaf
Rochester Institute of Technology
«Reference words» are one of the rhetorical devices that allow a writer to create cohesion throughout a text. They constitute a large group of mostly «pronouns» and «noun phrases,» less frequently other parts of speech. Reference words represent other elements in a text and allow the writer to manipulate these elements in different ways.
For examples of reference words, look at the highlighted words in the following paragraph about Germany:
Germany After World War 2
In 1939, Germany started World War 2; she was confident that she could conquer and control all of Europe. She spread death and destruction over much of the continent. But after several years of war, Germany herself began to suffer severe losses: Allied bombing raids destroyed German cities, farms, industries, and transportation systems. Food, water, and fuel began to disappear. And without these essentials, people could not care for themselves and their families. Berlin, the capital city, incurred even worse damage: Bombing raids destroyed seventy percent of its buildings. The city was left in ruins. People there lived in squalor. Vermin spread, bringing diseases: Rats and fleas infested people’s homes; roaches contaminated their food. Conditions worsened daily.
An examination of the highlighted words in the paragraph will reveal two notable features about them:
1. They cannot stand alone; rather, they need to connect with other words to complete their meanings.
2. They are used when new information is added about the things that they refer to, hence, the name «reference words.»
There is a small amount of research into the acquisition of reference words suggesting that hearing children begin to understand them after age 5, but that many deaf individuals as old as 17 and 18 continue to have problems with them. Moreover, experienced teachers in postsecondary programs for deaf students know that this failure to understand reference words correctly extends into the college years, as well.
In addition to this introduction, this module contains the following major sections:
A. A Grammatical/Process Summary that provides an overview of reference words with some examples of how they are used in English-Language discourse.
B. Research Findings and Implications that offers a small summary of some available studies on hearing and deaf children’s ability to use certain reference words.
C. Guided Practice exercises that offer practice in identifying reference words and their antecedents.
D. Action Steps that teachers may take in order to enhance students’ comprehension of reference words in their reading.
Major Considerations
1. Reference words are ubiquitous in all forms of written and spoken Modern English.
2. The ability to recognize reference words and understand them and use them correctly is a requisite for an adequate command of the English language.
3. Finding antecedents of reference words in a text poses a challenge for many young deaf students.
4. Course materials can be created in such a way as to improve students’ understanding of reference words in their reading.
attachment, apparatus, arrangement, assembly, device, element, facility, machine, gear, mean, project, rig, setup, station, structure, system, technology, unit, widget
* * *
устро́йство
с.
1. () apparatus, arrangement device, equipment, facility, means, gear
2. () arrangement, design
благодаря́ тако́му устро́йству … — by this arrangement, …
устро́йство авари́йной сигнализа́ции — alarm (device)
автоно́мное устро́йство — self-contained unit
автосцепно́е устро́йство — automatic coupler equipment
амортизи́рующее устро́йство — shock absorber
анало́говое устро́йство — analog device
анало́говое, вычисли́тельное устро́йство — analog computing device
анте́нное устро́йство () — scanner (assembly)
ба́зовое устро́йство () — mainframe
балансиро́вочное устро́йство — balancer
блоки́рующее устро́йство — interlock
бры́згальное устро́йство — spraying device
буквопеча́тающее устро́йство —
полигр.
character printing device;
вчт.
alphabetic printer
букси́рное устро́йство — towing arrangement, towing gear
бу́ферное устро́йство — buffer (unit)
валоповоро́тное устро́йство — barring [jacking, shaft-turning] gear
устро́йство вво́да —
вчт.
input device, input unit, input reader; () card reader
устро́йство вво́да-вы́вода
вчт.
— input-output [I/ O] device
взве́шивающее устро́йство — weigher
видеоконтро́льное устро́йство [ВКУ] — picture monitor
водозабо́рное устро́йство — water intake
водозабо́рное, высоконапо́рное устро́йство — high-pressure water intake
водозабо́рное, низконапо́рное устро́йство — low-pressure water intake
водоотво́дное устро́йство — drainage facility
воздухоспускно́е устро́йство — air bleeder
встря́хивающее устро́йство () — rapping gear
входно́е устро́йство — input device, input unit
устро́йство вы́вода —
вчт.
output device, output unit; () output writer; () output printer; () (output) card punch
выводно́е устро́йство
полигр.
— sheet delivery apparatus, delivery unit
выпрямля́ющее устро́йство — rectifier (unit)
вытяжно́е устро́йство — exhaust system
вычисли́тельное устро́йство — computer, computing device
вычисли́тельное, навигацио́нное устро́йство — navigation [flight] computer
газоочистно́е устро́йство — gas-cleaning system, gas scrubber
грузоподъё́мное устро́йство — hoisting apparatus, hoisting gear
дальноме́рное устро́йство — distance-measuring device; ranging unit
декоди́рующее устро́йство — decoder
декомпрессио́нное устро́йство — decompressor
демпфи́рующее устро́йство — damping device, damper;
изм.
dash-pot
устро́йство для маркиро́вки проводо́в — wire-marking machine
дози́рующее устро́йство — metering device; () measuring equipment
дрена́жное устро́йство — drain(age) system
забо́рное устро́йство — intake
загру́зочное устро́йство — charging device
задаю́щее устро́йство
автмт.
— reference-input element, reference-input unit, control-point setting device
устро́йство заде́ржки — delay device
зажи́мное устро́йство — clamping [holding] device
заземля́ющее устро́йство — earthing [grounding] connection
запомина́ющее устро́йство —
вчт.
storage, memory;
брит.
store
выводи́ть из запомина́ющего устро́йства — retrieve from storage [from memory]
засыла́ть в запомина́ющее устро́йство — transfer to [enter into] storage [memory]
обраща́ться к запомина́ющему устро́йству — access, storage [memory]
запомина́ющее, автоно́мное устро́йство — off-line storage, off-line memory
запомина́ющее, ана́логовое устро́йство — analog storage, analog memory
запомина́ющее, ассоциати́вное устро́йство — associative [content-addressable] memory
запомина́ющее устро́йство без разруше́ния информа́ции (при счи́тывании) — nondestructive (read-out) storage, NDRO storage, nondestructive memory
запомина́ющее, бу́ферное устро́йство — buffer storage, buffer memory
запомина́ющее, быстроде́йствующее устро́йство — quick-access [rapid-access] storage, quick-access [rapid-access] memory
запомина́ющее, вне́шнее устро́йство [ВЗУ] — external storage, external memory
запомина́ющее, вну́треннее устро́йство — internal storage, internal memory
запомина́ющее, вспомога́тельное устро́йство — auxiliary storage, auxiliary memory
запомина́ющее, динами́ческое устро́йство — dynamic storage, dynamic memory
запомина́ющее, долговре́менное устро́йство — permanent storage, permanent memory
запомина́ющее, магни́тное устро́йство — magnetic storage, magnetic memory
запомина́ющее, магнитострикцио́нное устро́йство — magnetostrictive (delay-line) storage, magnetostrictive (delay-line) memory
запомина́ющее, ма́тричное устро́йство — matrix storage, matrix memory
запомина́ющее устро́йство на бараба́нах — drum storage
запомина́ющее устро́йство на ди́сках — disk storage, disk memory
запомина́ющее устро́йство на ле́нтах — tape storage, tape memory
запомина́ющее устро́йство на магни́тных ка́ртах — magnetic card storage, magnetic card memory
запомина́ющее устро́йство на магни́тных плё́нках — magnetic-film storage, magnetic-film memory
запомина́ющее устро́йство на магни́тных серде́чниках — magnetic-core storage, magnetic-core memory
запомина́ющее устро́йство на перфоле́нтах — punch tape storage
запомина́ющее устро́йство на три́ггерах — flip-flop storage, flip-flop memory
запомина́ющее устро́йство на ферри́товых серде́чниках — (ferrite) core storage, (ferrite) core memory
запомина́ющее устро́йство на электроннолучевы́х тру́бках — cathode-ray tube memory, cathode-ray tube storage
запомина́ющее, односторо́ннее устро́йство — read-only memory, ROM
запомина́ющее, операти́вное устро́йство — on-line storage, on-line memory
запомина́ющее, опти́ческое устро́йство — optical storage, optical memory
запомина́ющее, оптоэлектро́нное устро́йство — optoelectronic (data) storage, optoelectronic (data) memory
запомина́ющее, после́довательное устро́йство — serial(-access) storage, serial(-access) memory
запомина́ющее, постоя́нное устро́йство — permanent [fixed] storage, permanent [fixed] memory
запомина́ющее, рабо́чее устро́йство — working storage, working memory
запомина́ющее устро́йство с бы́строй вы́боркой — quick-access [rapid-access] memory
запомина́ющее устро́йство с нестира́емой за́писью — nonerasable storage, nonerasable memory
запомина́ющее устро́йство со стира́емой за́писью — erasable storage, erasable memory
запомина́ющее устро́йство с поразря́дной вы́боркой — bit-organized memory
запомина́ющее устро́йство с произво́льной вы́боркой — random access storage, random access memory
запомина́ющее устро́йство с прямо́й вы́боркой () — word-organized [word-selection] storage, word-organized [word-selection] memory
запомина́ющее устро́йство с разруше́нием информа́ции — volatile storage, volatile memory
запомина́ющее устро́йство с совпаде́нием то́ков — coincident-current storage, coincident-current memory
запомина́ющее устро́йство стати́ческого ти́па — static storage
запомина́ющее устро́йство с центра́льным проце́ссором — on-line storage, on-line memory
запомина́ющее, три́ггерное устро́йство — flip-flop storage, flip-flop memory
запомина́ющее, цикли́ческое устро́йство — circulating [cyclic] storage, circulating [cyclic] memory
запомина́ющее, электроннолучево́е устро́йство — cathode-ray tube memory
заря́дное устро́йство — charging unit, charger
заря́дное, аккумуля́торное устро́йство — battery charger
защи́тное устро́йство — protection device; () safe-guard
звукозапи́сывающее устро́йство — sound recorder
золосмывно́е устро́йство — ash sluicing device
золотопромы́вочное устро́йство — gold washer
золоулови́тельное устро́йство — fly-ash collector
измери́тельное устро́йство — measuring device
индика́торное устро́йство
рлк.
— display unit, indicator (unit), (radar) scope
интегри́рующее устро́йство — integrator
ка́бельное устро́йство — cable (hauling) gear
кернова́тельное устро́йство
нефт.
— catcher, (split-ring) core lifter, spring lifter, core gripper
коди́рующее устро́йство — coding device, (en)coder
колошнико́вое устро́йство — (blast-furnace) top arrangement
колошнико́вое, загру́зочное устро́йство — top charging gear
контро́льное устро́йство — monitor (ing device)
концево́е, ка́бельное устро́йство — cable termination
копирова́льное устро́йство () — pantograph
корректи́рующее устро́йство
1.
автмт.
compensator, compensating device, compensating network, equalizer
предусма́тривать корректи́рующее устро́йство, напр. в цепи́ — use [place] a compensator around, e. g., a circuit
2.
полигр.
error correcting device
кра́новое устро́йство () — crown block
ле́ерное устро́йство
мор.
— life lines, life rails
лентопротя́жное устро́йство — tape transport, tape-moving device
логи́ческое устро́йство — logic unit
микрофо́нно-телефо́нное устро́йство — microphone-earphone device
мно́жительно-дели́тельное устро́йство — multiplication-division unit
мно́жительное устро́йство — multiplier unit
модели́рующее устро́йство — simulator
модели́рующее устро́йство в и́стинном масшта́бе вре́мени — real-time simulator
набо́рное устро́йство () — selector mechanism
нагру́зочное устро́йство — loading device
нажимно́е устро́йство () — screw-down mechanism
намо́точное устро́йство — coiler, winding machine
натяжно́е устро́йство — ()
прок.
bridle, bridling equipment; () tensioning device; () take-up
натяжно́е, винтово́е устро́йство — () screw take-up; () screw tensioner
натяжно́е устро́йство цепно́й переда́чи — chain tightener
устро́йство обега́ющего контро́ля — data logger
устро́йство обрабо́тки да́нных — data processor
устро́йство обрабо́тки информа́ции — data-processing unit
оконе́чное устро́йство — terminal
оповести́тельное устро́йство — annunciator
опу́дривающее устро́йство
пласт.
— duster, powdering device
ороси́тельное устро́йство — spraying device, spraying system
освети́тельное устро́йство — lighting unit
отклоня́ющее устро́йство — deflector; () deflection yoke
паропромы́вочное устро́йство — steam washer, steam scrubber
перегово́рное устро́йство — intercom, intercommunication(s) system, interphone system
перегово́рное, самолё́тное устро́йство — (aircraft) intercommunication [interphone] system
перезапи́сывающее устро́йство — transcriber
переключа́ющее устро́йство — switching device
переключа́ющее устро́йство регулиро́вки напряже́ния под нагру́зкой — on-load tap-changer
петлево́е устро́йство
прок.
— looper
печа́тающее устро́йство — printer
печа́тающее, автоно́мное устро́йство — off-line printer
печа́тающее устро́йство бараба́нного ти́па — drum-type printer
печа́тающее, бу́квенно-цифрово́е устро́йство — alpha(nu)merical printer
печа́тающее, выходно́е устро́йство — output printer
печа́тающее устро́йство колё́сного ти́па — wheel printer
печа́тающее, ма́тричное устро́йство — wire-matrix impact printer
печа́тающее, неавтоно́мное устро́йство — on-line printer
печа́тающее, операти́вное устро́йство () — on-line printer
печа́тающее, постро́чно устро́йство — line [line-at-a-time] printer
печа́тающее, ротацио́нное устро́йство — on-the-fly printer
печа́тающее, цепно́е устро́йство — chain printer
печа́тающее, цифрово́е устро́йство — numeric(al) printer
печа́тающее, шта́нговое устро́йство — bar printer
печа́тающее, электромехани́ческое устро́йство — electromechanical printer
печа́тающее, электро́нное устро́йство — electronic printer
печа́тающее, электростати́ческое устро́йство — electrostatic printer
пита́ющее устро́йство — feeding device, feeder
погру́зочно-разгру́зочные устро́йства — handling facilities
подъё́мное устро́йство — hoisting equipment, hoisting gear
предохрани́тельное устро́йство () — (safe) guard
приводно́е устро́йство — drive
противообледени́тельное устро́йство — () anti-icing device; () de-icer
противопомпа́жное устро́йство — antisurge device
противоуго́нное устро́йство — anti-theft device
пусково́е устро́йство — starting device, starter
путевы́е устро́йства — wayside apparatus, track arrangement
радиопередаю́щее устро́йство — radio transmitter
радиоприё́мное устро́йство — radio receiver
развё́ртывающее устро́йство — scanner, scanning system
развё́ртывающее устро́йство бараба́нного ти́па () — drum-type scanner
развё́ртывающее устро́йство плоскостно́го ти́па () — flat-bed scanner
развё́ртывающее устро́йство ти́па «бегу́щий луч» () — flying-spot scanner
разгру́зочное устро́йство — unloading installation, discharging device
раскатно́е устро́йство
устро́йство распознава́ния зна́ков — character recognition machine
устро́йство распознава́ния о́бразов — pattern recognition machine
распы́ливающее устро́йство — sprayer unit
расто́почное устро́йство — lighting-up equipment
устро́йство регистра́ции произво́дственных да́нных — process data logger
регули́рующее устро́йство — regulator [governor] device
резе́рвное устро́йство — stand-by facility, back-up device
рыбозащи́тное устро́йство — fish protection structure
рыбопропускно́е устро́йство — fish pass
устро́йство СДЦ с однокра́тным вычита́нием — single(-subtraction) canceller
сма́зочное устро́йство — lubricator
смеси́тельное устро́йство — mixing device, mixer
согласу́ющее устро́йство — matching device
спусково́е устро́йство
1.
мор.
launching arrangement
сра́внивающее устро́йство — comparator
ста́лкивающее устро́йство () — tripper
станцио́нные устро́йства — station accomodation, station facilities
стира́ющее устро́йство — eraser
сто́порное устро́йство () — stopper-rod device
сужа́ющее устро́йство
гидр.
— restriction, contraction
сумми́рующее устро́йство — () summer, summator; () adder
сцепно́е устро́йство — coupler
счё́тно-реша́ющее устро́йство — computing device, computer
счё́тно-реша́ющее, навигацио́нное устро́йство — navigation computer
счи́тывающее устро́йство
вчт.
— reader, reading machine
счи́тывающее, алфави́тно-цифрово́е устро́йство — alphanumeric reader
счи́тывающее, опти́ческое устро́йство — optical reader
счи́тывающее устро́йство, рабо́тающее с бума́жным носи́телем — paper reader
счи́тывающее, фотоэлектри́ческое устро́йство — photoelectric reader
счи́тывающее, электромехани́ческое устро́йство — electromechanical reader
телеизмери́тельное устро́йство — telemetering device
тормозно́е устро́йство () — arresting [checking] arrangement
транскоди́рующее устро́йство — transcoder
тягодутьево́е устро́йство — draft system
тя́нущее устро́йство () — draw-out equipment
устро́йство ультразвуково́й сва́рки — ultrasonic welding [bonding] machine
уплотни́тельное устро́йство — sealing device
устро́йство управле́ния — control unit
устро́йство устано́вки нуля́ () — origin-shift device
устано́вочное устро́йство — adjusting device, adjuster
фазосдвига́ющее устро́йство — phase shifter
фокуси́рующее устро́йство — focuser
фотопеча́тающее устро́йство — photoprinter
хрони́рующее устро́йство — timer, synchronizer
цепенатяжно́е устро́йство — chain tightener
цифрово́е устро́йство — digital device
чита́ющее устро́йство ()
вчт.
— reader, reading machine
шварто́вное устро́йство — mooring gear, mooring arrangement
шлю́почное устро́йство () — boat(-handling) gear
электро́нное устро́йство — electronic device
электропрои́грывающее устро́йство () — turntable
я́корное устро́йство — anchor(-handling) gear
я́корно-шварто́вное устро́йство — ground tackle
Referential words like above/below, preceding/following and overleaf describe location within a document and offer guidance for the reader. These words have no real meaning within the text, but indicate to the reader other parts of the text. Some words (above, following) are often used in informal and formal texts. Other words (aforementioned, hereinafter) are used mainly in very formal texts, for example legal documents.
Basic Textual Reference Terms
Here are some basic textual reference terms that we use in all kinds of documents. The left-hand column refers to things mentioned earlier in the text or further up on the same page. The right-hand column refers to things mentioned further down on the same page or later in the text.
| ↖ | ↘ |
|---|---|
| above | below |
| preceding | following |
| previous | next |
| overleaf | |
| continued cont’d PTO (BrE) |
Below are the dictionary definitions of the basic words above, with examples:
above: mentioned earlier or further up on the same page
- the two incidents described above
- at the above address
- as I was writing the above, I began to reconsider
below: mentioned further down on the same page, or further on in the text
- our house is pictured below right
- at the below address [American English]
preceding: what precedes or comes earlier
- in the preceding chapters we looked at human evolution
following: what follows or comes next; about to be mentioned
- the following are both grammatically correct sentences
- you are required to provide us with the following information
previous: what precedes or comes earlier
- as we learned in the previous section
next: what comes after the current words or passage
- in the next chapter we will discuss its history
overleaf: on the other side of the page or sheet
- the answers are printed overleaf
continued/cont’d: the text continues. We write continued at the foot of a page to show that the text carries on, usually though not necessarily on the next page or screen.
PTO: abbreviation for Please Turn Over [British English]. We write PTO at the foot of a page to show that the text continues on the other side.
Illustrated Examples of Textual References
The following diagrams illustrate the use of the above words, and are accompanied by examples in context.
It’s worth remembering that usage of these words developed in a world of print, when people read text on paper in books, magazines and newspapers. Today, in a digital age where we also read text on computer screens, tablets and mobiles, some words may be used misleadingly. There is no «overleaf» on a digital screen. An illustration that appears «opposite» on a computer may well appear «above» or «below» on a phone.
above / below
- The above prices are subject to change.
- The two cases described above happened last year.
- See above left for details.
- The apartments below are available now.
- The below apartments (AmE) are available.
- The hotel is pictured below left.
preceding / following
- The preceding section was hardly conclusive.
- The preceding cases have been settled but the following ones are still in court.
- Do you agree to the following rules?
- The examples that follow are based on historical evidence.
- In the following chapters we shall see how Henry VIII resolved his marital problems.
- We will explore dinosaurs in the pages that follow.
previous / next
- Please refer to the previous chapter for details.
- As we saw in previous pages…
- On the next page you can see…
- In the next example…
overleaf
- A price list is printed overleaf.
- Please see overleaf for more details.
- These apartments are available at the rates shown overleaf.
continued
The word continued, or the abbreviation cont’d, may be written at the end of a text to indicate that the text carries on, usually on the next page.
PTO
The abbreviation PTO or P.T.O. (for «Please Turn Over») may be written at the end of a page to show that the text continues on the other side. [British English]
opposite
Another word that describes location on a page is opposite, meaning «on the other side from the current location». Look at the illustration and example sentences. This word must be used with care in digital documents such as websites and ebooks. What is «opposite» on a large screen could well be «below» on a smaller screen.
- Please refer to the photo opposite.
- The table on the page opposite lists our hotels.
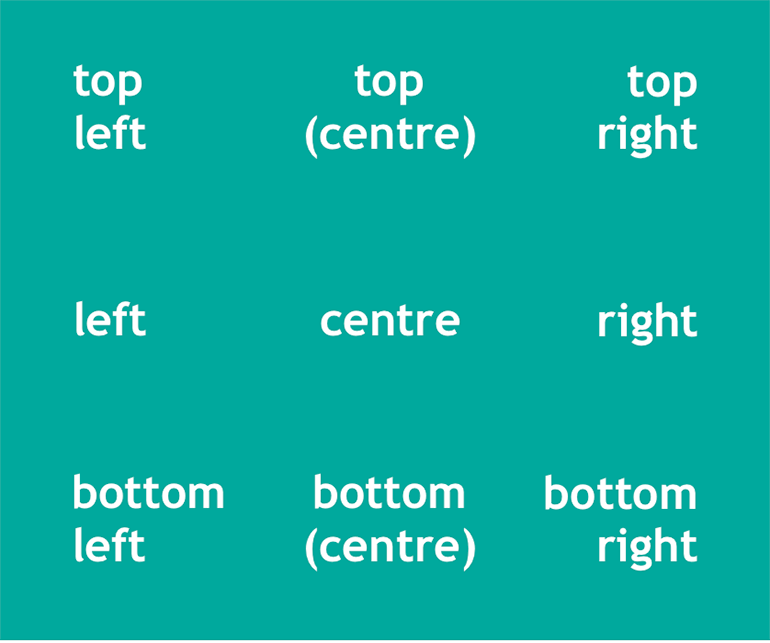
Page positions
In general, we can refer to the corners and sides of a paper page (and sometimes a digital page) with:
- top, bottom, centre
We can combine these words to make very specific locations, for example top left or bottom right. The illustration below shows nine common reference points on a page.