LESSON: 6:
Reading for Pleasure
School: Aidabol
secondary school
Date:
Teacher
name: Mukhamedzhanova G.B.
CLASS: 5
Number
present:
absent:
Learning
objectives(s) that this lesson is contributing to
5.R5 deduce meaning
from context in short texts on a limited range of familiar general and
curricular topics
5.S7 use appropriate
subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a limited range of
general topics
Lesson objectives
All
learners will be able to:
·
understand the events in the story from the book
·
recognize
unfamiliar words while reading the story
·
read, understand and reorder most of the events in the story
Most
learners will be able to:
·
use visual support to understand the events in the story and the
actions of the 3 bears and a Godlilocks
·
use their knowledge of the words during the role-play activity
·
read and reorder parts of a story without support
·
understand the moral of the story
Some
learners will be able to:
·
understand most of the language on the story
·
communicate using a widerange of vocabulary from the story
expressively during role-play
Language objectives
Use simple present tenses
Value links
Respect, Cooperation
Cross curricular links link
Literature
ICT skills
Projector or Smart board for presenting PPT and video image of
this story
Previous
learning
Learners read the
story working on unfamiliar words to the text. They got full information of
the story and ready to do some post-reading activities
Plan
Planned timings
Planned activities
Resources
0-5 minutes
6-10 minutes
11-15minutes
Lesson
hook.
Teacher shows a
picture of the story and asks what they see (for less motivated students).
They recall the title of the story “Godlilock and the three bears”. Then she
may ask where this episode took place in the story.
For more
motivated students she shows a video of the cartoon without sound for 30-50
seconds. Then she may ask what cartoon characters are talking about.
After the short
conversation, she introduces the lesson objectives and asks them to put them
down on their copy books:
§
To do vocabulary revision
on this story
§ Make up sentences using those words
§
Use those words in your
speech. (sequencing activity, role-play, ).
PPT. Slide 1-2
PPT slide-3
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YZ4gg8GLwA4
PPT slide-3
PPT slide-4
Middle
16-26minutes
27-35minutes
36-40minutes
41-61minutes
62-65minutes
66-78minutes
The first
post-reading activity.
Teacher asks learners
to find true or false statements. This task will be presented as a formative
assessment at the end they may check for their text comprehension using
assessment criteria. (if they collect 6 score out of 8 they could manage this
task and can be praised with a star). The answers will be checked with the
help of the teacher. In order to evaluate their work they may check each
other’s work.
1.
We read the story about 2
bears and a princess. F
2.
The girl’s mother asked
her daughter to go to the shop to buy some bread. F
3.
The girl likes to go for a
walk. T
4.
She meets 2 bears on the
road to the shop. F
5.
Bears were very friendly
to the girl. T
6.
When she comes to the
bears’ house, she eats baby bear’s porridge. T.
7.
She likes mother bear’
bed, because it is too soft. F.
8.
She gets home with three
bears. F.
The second
post-reading activity.
§ The quick vocabulary revision.Teacher shows a list of
words from the story and they together revise for meaning:
To pick up
flowers, to lose her way, to belong to, porridge, to smell, big bowl, feet
were sore, to climb up the stairs, to scream, to fall asleep, to wake someone
up, to apologize , to become friends
The third
post-reading activities.The teacher distributes the tasks
according to their levels. She explains their functions and shows assessment
criteria. Learners are given 20 minutes for preparation.
§ Less able studentsare given to make up sentences using the words above.
§ More able students should make up a story using those words.
§ High motivated students act out the story in three or four pupils. They
have to be reminded that this group of learners should have a narrator.
·
Formative assessment. Students are informed how they are going
to be assessed by the following criteria:
·
Creativity-10
·
Presentation
skills-10
·
Language
(Grammar and usage of new words)
·
Teacher nominates group of learners according to their
performance. Learners give peer feedback such as: Well done! Great job,
The best actors and actresses, The super English speakers and so on. Teacher
praises learners’ performance and suggests an improvement.
They start performing their tasks. Each group or peers listen to
their peers’ performance and assess each other according to the assessment
criteria.
appendix 1
Assessment sheet
PPT slide -5-6
PPT slide-7
appendix 2
PPT slide 8
End
78-80
Learners complete an evaluation of what they did during the
lesson by circling one word in each statement:
I can understand: all
/ most of / some of the story in the video.
I can understand: all
/ most of / some of the story when I read it.
I can say: all /
most of / some of the words in the role-play.
Evaluation worksheet
appendix 3
Additional
information
Differentiation
– how do you plan to give more support? How do you plan to challenge the more
able learners?
Assessment
– how are you planning to check learners’ learning?
Cross-curricular
links
Health and safety check
ICT links
Values links
·
More support can be given at the start and in middle of lesson
by providing less-able learners with story vocabulary in a word list so they
can read examples of words seen or heard.
·
Learners who are less confident at making up dialogue, can be
given copies of parts of the dialogue from the story to read aloud.
·
More-able learners can be encouraged to use the full range of
language from the video when they practise the role-play.
· Monitor how much vocabulary
learners can recall from images on the video without sound and then from
video with sound.
· Monitor learners as they
reorder events from the story. Can they read and understand each event and
can they sort them into chronological order? Notice any sentences which are
difficult for learners to understand and adapt for a future lesson.
·
Monitor groups of learners as they agree on and practise
dialogue for the role-play activity. Do they take turns to speak? Do they
contribute appropriate language for the role-play?
·
When
they perform true-false task they use ready-made answers in order to be able
to check for themselves or each other.
·
Post-reading
exercises with differentiated tasks are assessed by special assessment
criteria displayed on the screen.
·
Make sure they have shared their roles in the act out activity appropriately.
·
Learners should have sufficient space to feel comfortable while
they are acting.
·
Let them understand by holding a discussion that animals have
also intellect and instinct that are able to take care of themselves.
Reflection
Were the lesson objectives/learning objectives realistic?
What did the learners learn today?
What was the learning atmosphere like?
Did my planned differentiation work well?
Did I stick to timings? What changes did I make from my plan and
why?
Use the
space below to reflect on your lesson. Answer the most relevant questions
from the box on the left about your lesson.
Summary
evaluation
What two things went really well (consider both teaching and
learning)?
1:
2:
What two things would have improved the lesson (consider both
teaching and learning)?
1:
2:
What have
I learned from this lesson about the class or individuals that will inform my
next lesson?
LESSON PLAN
Unit: 6
School:
Date:
Teacher name: Nurgalymova A.M.
CLASS: 5
Number present:
Absent:
Lesson title:
Reading for pleasure
Learning objectives(s) that this lesson is contributing to (link to the Subject programme)
5.3.2.1 — ask simple questions to get information about a limited range of general topics
5.4.4.1- read with some support a limited range of short fiction and non-fiction texts
Lesson objectives
All learners will be able to:
pronounce some words and simple statements about types of literature with some support
Most learners will be able to:
say most of the words and simple statements about types of literature using basic adjectives and colors with little support
Some learners will be able to:
use all of the words and simple statements about types of literature with basic adjectives and colors to say what someone /something is or has without support
Assessment criteria
-
Say topic words
-
Describe things using adjectives
-
Make simple sentences using demonstrative pronouns
Language objective
Learners can: pronounce the words and simple statements about Fairy tales
Key words and phrases: Action and adventure is fiction. This fairy tales has good content.
Types of literature: action & adventure, fairy tale, science fiction, biography, fabies, horror, legends.
Colors: red, yellow, green, blue, orange, purple, pink, black, gray, white
Useful classroom language for dialogue/writing:
Do you read fairy tales ? How many books do you have ? Which type of literature is fiction? What colour has book?
I have He/she has…. This is…. These are… It’s….
Values links
Respect each other
Care about things
Cross-curricular links
History
Previous learning
Learners already know word about an events, colors and numbers 1 – 10
Plan
Planned timings
Planned activities
Resources
Start
0-10
Teacher greets learners.
Starter: teacher asks to students to make a circle and wish to each other wishes like : Have a good day! I wish to you good luck! Stay healthy ! Good marks ! Wish you a great day !
(W) Teacher asks learners to divide into 3 groups by the cards from the box
Then learners choose the cards with main definitions of literature and sit according to names (character, story, event) S-T
Box with the cards. By this cards divide into 3 g-s: character, story, event.
10-12
Lead in: (P) Learners revise some key words from previous learning (colours) showing the cards to each other. S-S
To guess the title of today`s lesson teacher shows a poster and cards with types of literature. On this poster we have 2 colons: Fiction and non-fiction. Students should stick the cards on the poster.
Teacher asks questions with support:
-
Do you read book ?
-
What types of books do you know ?
-
Do you read fairy tales ?
-
How many books do you have ?
-
Which type of literature is fiction ?
-
Which type of literature is non-fiction ?








|
Fairy tale |
Ертегілер |
|
Fables |
Ойдан шығарылған |
|
Horror |
Қорқынышты |
|
Legends |
Аңыз әңгіме |
|
Action & adventure |
Экшн және оқиғалы |
|
Biography |
Биография |
|
Science fiction |
Ғылыми ойдан шығалырған |
|
Articles in newspapers/magazines |
Газет пен журналдардағы мақала |
Possible answers:
1) Yes, I read (many) books!
2) Fairy tales, biography, history, horror
3) Yes, I read. / No, I don`t read.
4) I have (number of) books.
5) Fairy tale, science fiction, action & adventure, horror, mystery & suspense, fables, legends.
6)Biography, articles in newspapers/magazines
cards (colors and an events)
cards with types of literature, a poster
Middle
12-14
Modelling: Teacher puts several classroom objects on a table: points to an object asking Which type of literature is fiction? What color is the book? and asks learners to count them together showing the objects. Then using have … says I have three red books. Learners repeat. T-S
Types of literature: action & adventure, fairy tale, science fiction, biography, fables, horror, legends, articles in newspapers/magazines, mystery suspense.
14-17
Drilling: Learners repeat the sentences first with the teacher’s support in choral (all together, 3 times), with some support in a group (3 times) and then individually: I have six fiction books. And their`s colors are: 1 blue, 2 black, green, yellow, orange. I have four fiction books. etc. T-S
Fiction and non-fiction
17-20
20-25 minutes
25-33 minutes
Practice-Production: (G) Learners count the books picture with no support individually, and says I have two yellow books. Then learners practice saying He/she has … first with the teacher’s support and then individually S-S
One, two, three,…
Yellow, green, purple,..
-
Learners open the book p. 75 ex.2, look at the pictures, count books and write names of types of literature below the pictures.
In this a short story each group have to:
1st identify genre retelling
2nd mind map
3rd what they have understood – to draw an imagination

SB p. 75 ex.2
Appendix
He Stood Against My Window
by u/sabethook in shortscarystories
AfL PEER ASSESSMENT Criteria highlighting:
1st group
+using right order of sentence
+using 5-8 words from the text
+pronunciation
2nd group
+creativity
+using 4 adjectives from the text
+pronunciation
3rd group
+creativity, using colors
+showing the content of the text
(W) Learners do «Fishing game» activity. The rules of this game are: Teacher puts on the table aquarium. In this aquarium we have some facts about fiction and nonfiction.
-
Students should to fish and catch the fish with facts.
-
Then stick them on the poster rightly.
A poster with shape of aquarium, fish.
End
33-35 minutes
35-40 minutes
Plenary: (W), (f) Teacher has a set of cards of e.g. with characters behind this cards we have descriptions (a short story) to each character, from any stories, biography, action & adventure, fairy tale, horror, legends. Students should to read and stick on the poster, in right side.
1. 
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
Cards
Snow White, Prince, Shokan Ualikhanov, Abai Qunanbaev, giraffe, dragon, alien.
Teacher gives home-task. Says good-bye.
Additional information
Differentiation – how do you plan to give more support? How do you plan to challenge the more able learners?
Assessment – how are you planning to check learners’ learning?
Health and safety check
More support can be given by drilling less confident learners say a sentence with a partner. They can point to an object on the table by teacher’s command.
More able learner (a leader of the group) helps the group and
when doing the tasks.
During the lesson teacher gives model how to do the task.
Techer gives different tasks for different level.
For example:
1st retelling – only more able students
2nd mid able draw mind map
3rd drawing less able students
Walking around and listening learners as they practice saying sentences and asking questions.
Monitoring learners as they do the tasks using by adjectives and pronouns correctly
Noting which leaner says the sentence correctly: source of evidence may include recording.
Concept checking through formative assessment strategy: “Thumbs up, thumbs down”
Criteria highlighting
1st group
-using right order of sentences
-using 5-8 words from the text
-pronunciation
2nd group
-creativity
-using 4 adjectives from the text
-pronunciation
3rd group
-creativity, using colours
-showing the content of the text
Being aware of Health care techniques.
Doing Physical activities (make a circle ).
Organizing classroom space for movement.
Reflection
Were the lesson objectives/learning objectives realistic?
What did the learners learn today?
Use the space below to reflect on your lesson. Answer the most relevant questions from the box on the left about your lesson.
What two things went really well (consider both teaching and learning)?
1:
2:
What two things would have improved the lesson (consider both teaching and learning)?
1:
2:
What have I learned from this lesson about the class or achievements/difficulties of individuals that will inform my next lesson?
|
Unit 6 |
School: |
|||||||
|
Date:19.02.2019 |
Teacher name: |
|||||||
|
CLASS: |
Number present: 20 |
absent: |
||||||
|
Lesson title: |
Reading for pleasure STORIES |
|||||||
|
Learning objectives(s) that this lesson is contributing to (link to the Subject programme) |
5.L4 understand the main points of supported extended talk on a range of general and curricular topics 5.S8 recount basic stories and events on a range of general and curricular topics 5.W4 write with support a sequence of extended sentences in a paragraph to give basic personal information |
|||||||
|
Lesson objectives |
All learners will be able to understand with little support the main points in extended talk Most learners will be able to understand and speak with little support the main points in extended talk Some learners will be able to understand, speak with little support the main points in extended talk and use formal and informal registers in their talk |
|||||||
|
Assessment criteria |
uses the words with support. uses and explains the words without support . prepares and compares the lexical material with support. Prepares, compares and explains the lexical materials without support. |
|||||||
|
Values links |
Responsibility, Global Citizenship |
|||||||
|
Cross-curricular link |
Literature |
|||||||
|
Previous learning |
The learners already know the words and phrases of the theme. The existing knowledge should be activated in speaking and use the learned words in the sentences. |
|||||||
|
Plan |
||||||||
|
Planned timings |
Planned activities (replace the notes below with your planned activities) |
Resources |
||||||
|
5 min |
Org. moment Greeting. — Good afternoon, boys and girls. I am glad to see you at the lesson. At first let`s check your home task. Each pair prepared dialogue about “The role of books in our life”. If you are ready let`s start.
How do you think what is the theme of our lesson? I hide our theme, you should to find out the theme of today`s lesson. I suggest you to play a game with me. Look at the board. These are letter. “BOOK” What is the a letter? Call me a letter. Nowadays many people believe that reading is boring and that books are not necessary. So my first question is: 1. Why do we read? 2. What do you like to read? 3. Where and when do you read? 4. How much time do you spend on reading? 5. What is your favorite book? — You see, so many minds so many thoughts. But in all centuries there were the people who read books. |
|||||||
|
Middle 5 min 6 min 10 min 2 min 10 min |
Revision Brain storm. Learners look at the magic board. There are a lot of genres of books. What kind of them do you know? Adventure story, fairy, horror story, detective story, thriller, fiction, love story, funny story, comedy, fantastic story. Look and try to find what stories are they. Task 1 — I`ll give you these are Envelops. What is inside? How do you think? These are small pieces of paper with sentences. I cut it into parts and mixed. Your task is to match authors and genres with the books and definitions.
Prompts: 1b, 2d, 3i, 4a, 5c, 6k, 7e, 8g, 9f, 10h, 11j, 12L, 13f Descriptors: Match authors and genres with the books and definitions. Warm up with energizing song to involve and to practice physicallyhttps://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ljVl7poqcDg Task 2 -On this task you should move from your place and try to find prompts. It is gallery methods. You work on this task with your pair. How many questions you can answer? Try to find what film or book and who is author of this book. Card №1 It is fantasy novels written by British author J.K. Rowling. The novels chronicle the lives of a young wizard and his friends Hermione Granger and Ron Weasley. What book and film is this? Card №2 She was known for her 66 detective novels and 14 short story collections, particularly those revolving around her fictional detectives. And her nickname was Queen of Detective. Who was she? Card №3 This novel was famous all the world. It was tragedies of Romeo and Juliet. Their great love. Who wrote this novel? Card №4 He was great Kazakh writer. He was best known for introducing a Cyrillic alphabet for the Kazakh language and opened numerous Kazakh – Russian boarding school, technical schools and schools for girls. Who was this great writer? Card №5 In Kazakh literature there is an author whose children`s stories are read by several generations of adults and children. The book, which made the name of popular is called “My name is Kozha”. Who was author of this book? Descriptors: Find authors and films Analyzes and evaluates theirs work. |
Pictures sheet of paper CD with laptop cards |
||||||
|
2 min |
Feedback Writing his opinion on sheets of paper and sticks on the board. |
|||||||
|
Additional information |
||||||||
|
Differentiation – how do you plan to give more support? How do you plan to challenge the more able learners? |
Assessment – how are you planning to check learners’ learning? |
Health and safety check |
||||||
|
Leaners were asked to make up different questions to each other. While making sentenses about advantages and disadvantages of reading, learners think critically about the problem and argue, proving their point of view, using the learned lexical material. |
Criteria based assessment Leaners were given definite criteria. Pairs evaluate each other on the table of assessment given at the beginning of the lesson to know their level and to develop their reading and writing skills. |
Heath saving technologies. Using physical exercises and energizing activities with the help of a song with useful vocabulary. |
||||||
|
Reflection |
||||||||
|
Were the lesson objectives/ learning objectives realistic? |
||||||||
|
Were the lesson activities difficult for learners? |
||||||||
|
Did the learners do all the tasks? |
||||||||
|
Did my planned differentiation work well? |
School-lyceum №23
Grade:
Teacher:
SHYMKENT 2019
“A room without books is like
a body without a soul.”
Материалдар / Summative assessment for the unit “Reading for pleasure”
Аттестацияның пробный
сұрақтарын тапсырып
тестке дайындалыңыз!
Ұлттық тестілеу орталығының тақырыптары бойынша жасалған
Материал туралы қысқаша түсінік
Summative assessment for the unit “Reading for pleasure”
Excel for Kazakhstan, grade 7. Module 5, «Reading for pleasure» SAU. БЖБ 7 сынып, ағылшын тіліненб 5-ші модуль
Авторы:
Автор материалды ақылы түрде жариялады.
Сатылымнан түскен қаражат авторға автоматты түрде аударылады. Толығырақ
02 Ақпан 2022
2077
4 рет жүктелген
Бүгін алсаңыз
30% жеңілдік
беріледі
770 тг 539 тг
Тегін турнир Мұғалімдер мен Тәрбиешілерге
Дипломдар мен сертификаттарды алып үлгеріңіз!
Бұл бетте материалдың қысқаша нұсқасы ұсынылған. Материалдың толық нұсқасын жүктеп алып, көруге болады
Text Centered
«Ustaz tilegi» Республикалық ғылыми – әдістемелік журналы министірліктің №KZ09VPY00029937 куәлігімен ресми тіркелген.
Бұл сертификат «Ustaz tilegi» Республикалық ғылыми – әдістемелік журналының желілік басылымына өз авторлық жұмысын жарияланғанын растайды. Журнал Қазақстан Республикасы Ақпарат және Қоғамдық даму министрлігінің №KZ09VPY00029937 куәлігін алған. Сондықтан аттестацияға жарамды.
Сайтта заңсыз жарияланған материалды көрсеңіз бізге хабарласыңыз. Редакцияның көзқарасы автордың көзқарасымен сәйкес келмеуі мүмкін.
Материал іздеу
Сіз үшін 400 000 ұстаздардың еңбегі мен тәжірибесін біріктіріп, ең үлкен материалдар базасын жасадық. Төменде пәніңізді белгілеп, керек материалды алып сабағыңызға қолдана аласыз
Барлығы 663 959 материал жиналған
сабақ жоспары 5 сынып «Reading for Pleasure»
Материал жайлы қысқаша түсінік:
Материал 5 сыныпқа арналған ағылшын тілі пәнінен сабақ жоспары
Төмендегі Сабақ жоспары толық нұсқасы емес, тек сізге танысу үшін көрсетілген, сайтқа жарияланған документтен айырмашылығы болуы мүмкін. Жүктеу үшін осы беттің төменгі жағындағы жүктеу деген жазуды басу керек

сабақ жоспары 5 сынып «Reading for Pleasure»
Тұрсынқалиева Гүлмира Құрбанқызы
Маңғыстау облысы Ақтау қаласы «№6 Жалпы білім беретін орта мектебі» КММ ағылшын тілі пәні мұғалімі
26.03.2019
3878
11
Назар аударыңыз, сертификатты “менің материалдарым” деген бетте жүктеп алуға болады
Өз пікіріңізді қалдырыңыз
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 5Reading for pleasure.
Lesson plan
School:
Date:
Teacher’s name:
CLASS: 9
Number present:
absent:
Lesson title
Reading. Fiction.
Discussing a text about the benefits of reading.
Learning objectives(s)
9.S1 use formal and informal language registers in their talk on a range of general and curricular topics
9.S2 ask complex questions to get information about a wide range of general and curricular topics
9.S3 explain and justify their own and others’ point of view on a range of general and curricular topics
9.R3 understand the detail of an argument- both explicitly stated and implied in extended texts on a wide range of familiar general and curricular topics, and some unfamiliar topics
9.R4 read a wide range of extended fiction and non-fiction texts on familiar and unfamiliar general and curricular topics
9.L4 understand the main points of supported extended talk on a range of general and curricular topics
9.W1 plan, write, edit and proofread work at text level with support on a limited range of general and curricular topics
Lesson objectives
All learners will be able to:
-
Identify the theme, new words and use them as the basis for discussion.
-
Demonstrate knowledge for usage of the Past Simple speaking about the benefits of reading.Transfer information from the given information into a graphic organizer.
Most learners will be able to:
-
Select, compile, and synthesize information for an oral presentation
-
Provide a point of view in conversations and discussions; describe the plot of the story using active vocabulary.
Some learners will be able to:
-
Respond to and discuss the reading passage using interpretive, evaluative and creative thinking skills.
-
Make a presentation about the benefits of reading.
Level of thinking
Higher order thinking skills (according to the revised Bloom’s taxonomy).
Assessment criteria
-
Read the given text of description and identify the general information.
-
Demonstrate skills of organizing and expressing ideas accurately.
-
Illustrate a viewpoint in a discussion.
Target language
Benefits of, to pick up, to be a turning point, slowly but surely, a huge effect on, incidental information, snippets of information, , analytical skills.
Values links
Responsibility, Global Citizenship, Respect and Love to reading books, Care to modern technology, Love to nearest and dearest.
Cross-curricular link
Literature, Social Science, Psychology, Information Technology, Art.
Previous learning
Vocabulary relating to the benefits of reading
Plan
Planned timings
Planned activities
Resources
Start
3 min
Class organisation

The lesson greeting.
Warm up.
The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson.
Good afternoon, dear students and guests! Welcome to our English lesson! I give you these sheets of paper. Here you see three types of smiles; your task is to give yourselves marks putting ticks under the smiles. If you manage to do the work well put a tick opposite the happy smile. If not — opposite the sad one. If you are not sure put a tick under the neutral smile. On your desks you see folders with some files of different colours. You will need them during the lesson.
Pre-learning (W)
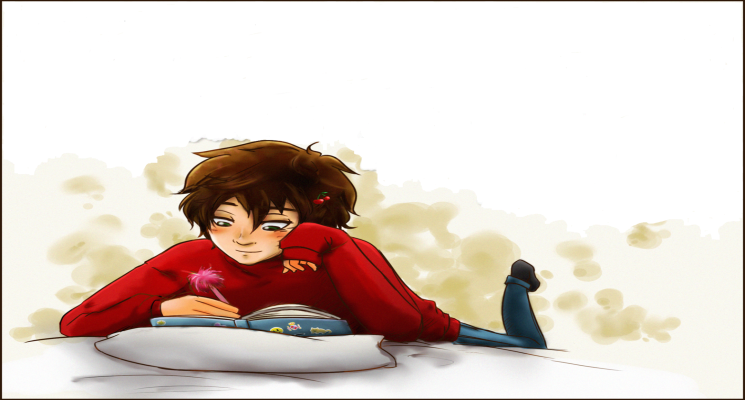

Look at the picture and say what is the boy doing and how is he doing it?
In front of you there is a poem. I’d like you to read it and in groups discuss the meaning of it?
What is a Book?
By Lora Daunt
A book is pages, pictures and words
A book is animals, people and birds
A book is stories of queens and kings
Poems and songs-so many things!
Curled in a corner where I can hide
With a book I can journey far and wide
Though it’s only paper from end to end
A book is a very special friend.
Each group prepares its presentation.
What does the boy prefer doing? Why?
Make a list of books you read while you have free time? (revision of genres of books).
Lead-in (W, I)
Pre-reading stage.

Slide (useful phrases)
Pictures
PPT
The picture of a boy reading a book
Whiteboard
Poem
A Table
Main part
15 min
Lead-in (W, I)
Pre-reading stage.
Listening and reading about the benefits of reading (W I)
-
Teacher suggests the list of new vocabulary with their synonyms or opposites for learners.
(P) Learners work with new vocabulary first. They get a list of words, read the words with the teacher. Learners create 3-4 sentences with new words to showthe meaning of the words.
Differentiation
Learners that are more able help the others to read the words correctly.
Now the Sts.are going to listen to the text and then read.
Ex.1 – 2 p.58
Each Sts. Tries to give a good title for the text.
Do you enjoy losing yourself in a good book?
(As for me…. As I think…. To my mind…).
Ex.4 p.58 Build Your vocabulary:
Find the active words from the text and explain by your own words.
Ex.5 p.58 (Group work).
Make a cinquain of a word” reading”.
What is the structure of a cinquain?
A cinquain consists of 5 unrhymed lines.
Each line has a set number of syllables see below:
Line 1 – 2 syllables
Line 2 – 4 Syllables
Line 3 – 6 Syllables
Line 4 – 8 syllables
Line 5 – 2 Syllables

Whiteboard
Writing
Worksheet
(new words)
CD 2.14
Student Book p.58
Teacher’s Book p.80.
Whiteboard
Writing
Worksheet
Whiteboard
End
3 min.
Home task.
Ex.5p.58 (w).
The story “The Fun they had”(I. Asimov)
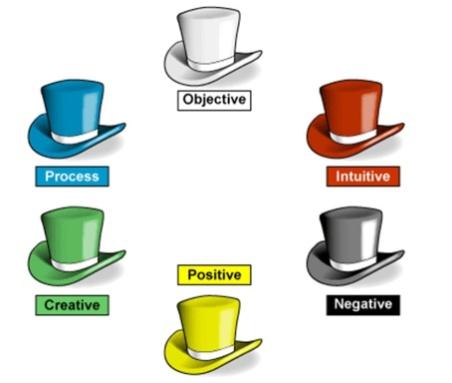
Students express their attitude to the lesson and give self-assessment using the method: “Six thinking hats”:
-
Green: How can you use today’s learning in different subjects?
-
Red: How do you feel about your work today?
-
White: What have you leant today?
-
Black: What were the weaknesses of your work?
-
Blue: How much progress have you made in this lesson? (Now I can, I still need to work on, I’ve improved in, Today I learnt…
-
Yellow: What did you like about today’s lesson?
Slide (Homework)
Slide «Six thinking hats»
Additional information
Differentiation – how do you plan to give more support? How do you plan to challenge the more able learners?
Assessment – how are you planning to check learners’ learning?
Health and safety check
Differentiation can be achieved through content (Based on the theory of Multiple Intelligences different tasks are used with the same text).
By support:
Less able learners will be supported through step-be-step instructions, glossaries, thinking time.
By task:
For more able learners additional leveled tasks are offered.
Assessment criteria:
-
Read the given passage and identify the general information.
-
Demonstrate skills of organizing and expressing ideas accurately.
-
Illustrate a viewpoint in a discussion.
Descriptors:
A learner
-
reads the text for global understanding;
-
selects meaningful information, constructs the answer;
-
presents information in the group discussion.
-
evaluates the peers’ answers.
Teacher’s observation using observation checklist (Appendix 2 — reference to the resource «Literature Circle Role Sheets» by Christine Boardman Moen. p.28) and monitoring.
Self-assessment.
Health saving technologies.
Make sure power cords are not a tripping hazard
Everyday classroom precautions
Long term plan module :
Unit 6: Reading for pleasure
Lesson: Learners read nonfiction books in
Kazakh, English, Russian languages
Date: 6.02.18
School: № 23
Teacher’s name: Barysheva A.S.
Number of present:
5 B
5 D
Absent:
5 B
5 D
Class: 5 B, 5 D
Learning objective(s) that this
lesson is contributing to:
Lesson objectives:
Assessment criteria
Value links
Crosscurricular links
Previous learning
5.L1understand a sequence of supported classroom instructions
5.R1 understand the main points in a limited range of short simple texts on
general and curricular topics
5.S4 respond with limited flexibility at sentence level to unexpected
comments on an increasing range of general and curricular topics
5.C4 evaluate and respond constructively to feedback from others
All learners will be able to: identify common classroom commands with
support; identify the main idea of the text; provide unprepared speech to
answer a variety of questions at sentence level with limited flexibility;
analyze given feedback and give constructive answers to it with support
Most of the students will be able to: identify common classroom
commands with support; identify the main idea of the text; provide
unprepared speech to answer a variety of questions at sentence level with
limited flexibility; analyze given feedback and give constructive answers to
it with some support
Some of the students will be able to: identify common classroom
commands with support; identify the main idea of the text; provide
unprepared speech to answer a variety of questions at sentence level with
limited flexibility; analyze given feedback and give constructive answers to
it without support
Identify common classroom commands with support
Identify the main idea of the text
Provide unprepared speech to answer a variety of questions at sentence
level with limited flexibility
Analyze given feedback and give constructive answers to it
Know and respect folk music and folk musical instruments
Literature
Lesson: Learners read nonfiction books in Kazakh, English, Russian
languages
Plan
Planned timing
Start (Beginning of
the lesson)
3 minutes
Planned activities
Organisation moment:
Good afternoon, boys and girls. I’m very glad to see you today at our lesson. How are
you, Ogylay? How are you, Nuray? And you, Ilya? Well, I’m fine, too. I see that you
are ready for the lesson: your bags are on the right places, your pens and pencils,
copybooks and books are on the desks , but are you ready to work hard and be active
today? ( Yes, we are ready ). Ok, let’s go. Stand up. Middle (of the
lesson)
5 minutes
3 minutes
Warm up: alphabet ( Brain training )
Teacher:
Today we are going to speak about one of the most wonderful things in the world.
Well, try to guess what it is. “It has no mouth but it speaks. It is not alive, but it can be
a good friend. It is not a tree, but it has leaves. What is it?” That’s right. It’s a book.
Task 1 «Mind map»
Students are given sheet of paper with the word « Books » , they write any ideas that
come to their mind. Teacher monitors. Sharing the ideas in whole class.
Books
2 minutes
2 minutes
Teacher:
Boys and girls, I have brought a book. Look at it: we can touch it, pages, see pictures,
words, smell paper scent, etc. Such a nice feeling!
Have you ever seen this book? Have you read it? ( The Wonderful Wizard of
Oz /Лаймен Фрэнк Баум / Волшебник Изумрудного города / Александр
Волков) Have you ever seen cartoon or movie? A lot of children around the world
like reading this book. And what about you? Do you like reading? What is your
favourite book? Does it have pictures? Is it big or small book? How many pages does
it have? Thank you for sharing!!!
There is one good phrase: «Books are our best friends». Books help us to be
better, to enrich our intellect and vocabulary, to improve your reading. What else?
Add your ideas. Thank you.
1.
And now, open your copybooks, write the date, day and theme: Books in our life.
Objectives: 1) Identify common classroom commands with support
2) Identify the main idea of the text
3) Apply new vocabulary in the speech
4) Analyze given feedback and give constructive answers to it
Rules:
be polite
respect each other
be active
help each other
Task 2
Teacher: Every book has its genre. It could be about magic, unnatural things, trips
and somebody’s life. Look at the board , please. There are some new words. These are
genres of books. Repeat after me.( Students pronounce the words with the teacher) .
Drilling
New vocabulary:
genre|
adventure story [ d vent
ˈʒɑː ə
nr |
ə ˈ
ri ]
ʃə
(r) st
ˈ ɔː 5 minutes
ɪˈ
ɪ
detective story [ d tek.t v ]
ˈ ə
ɪ
fairy tale[ fe .ri te l ]
ˈ ɒ ə
ˈ ɔː
horror story [ h r (r) st
ˈ
ɪə
ˈ ɪ
science fiction [ sa ns f k. n ]
ɪˈ ɒ ɪ
historical book [ h st r kl b k ]
ɪˈɒɡ ə
.r .fi ]
biography [ ba
ri ]
ʃə
ʊ
Task 3 » Sevenpetal flower «( group work )
Teacher: Some of the words are clear to understand, they sound similar to Russian.
Some of them you’ve heard earlier. But it’s very important also to memorize how to
pronounce and write them correctly. Let’s do the task more challenging. In a group of
four, find the definition to each genre.
Students are given petals with definitions and the image of a flower with names of
genres. The task is to find the meaning of the word and stick it .
6 minutes
genres
adventure story is a story of an unusual, exciting, and possibly dangerous activity,
such as a trip
detective story is a story about detectives and crimes.
fairy tale is a story in which animals or objects can speak
horror story is a story in which scary and unnatural things happen
science fiction is a book about actual or imagined scientific things or events.
historical book is a book with an old story about great events and people in ancient
times, which may not be true.
biography is a book about another person’s life.
FA: self assessment in a whole class
Warm up: song » Books are my best friends »
Task 4. Write complete sentences that are true for you.
Lessable learners are supported by sentence starters.
1. I like reading …. ( adventure, historical books… ) because they are ( exciting,
interesting, amazing ….)
2. I don’t like reading ….( adventure, historical books… ) because …( boring, not
interesting, difficult to read….)
3. I hate reading…. ( adventure, historical books… )
Moreable learners are supported by the table
Use verbs ending in ing after ( don’t )like, don’t mind, love, and hate
love
hate
don’t mind
like
don’t like
2 minutes
FA: sweets for each correct sentence
Task 5. «Gallery work » ( in pairs). Short stories are written on sheets of paper 5 minutes
and stuck on the walls. Students are given the answer sheet. They walk around
the class, read the paragraphs and write the answers ( matching )
1. Slowly he opened the door and looked inside the room. The portrait on
the wall had changed. It was now a mass of twisted branches and blood. He
let out a loud scream and ran out the stairs.
2. She waved her magic stick , and suddenly the frog turned into a
handsome prince.
3. They went away on their trip. The caves were not far away but it seemed
to be very long to travel by horseback.
4. The spaceship landed on the red planet with no animals, no people, plants
and oxygen but with a lot of underground cities.
5. Watson looked first at Holmes, and then at the gun on the table. » I know
who did it «, he said calmly.
6. Jack London was born John Griffith Chaney on January 12, 1876, in San
Francisco, California. After working in the Klondike, London returned
home and began publishing stories. London, who was also a journalist and
an outspoken socialist, died in 1916.
Answer sheet
Genres
A. biography
B. detective story
C. horror story
D. adventure story
E. science fiction
F. fairy tale
Numbers( 1,2,3,…..)
6
5
1
3
4
2
FA: mutual assessment. Answers on the board.
Homework : bring your favourite book and tell us about it.
5 minutes
1 minute End (of the lesson)
1 minute
Reflection:
Teacher’s
instructions and
questions
Writing ideas
Work with
definitions
Writing
sentences
Gallery work
Additional information:
Differentiation how do you
plan to give more support?
How do you plan to challenge
the more able learners?
Less able student: support by
positive feedback, mimics.
More able student: support by
positive feedback, box with
words
Assessment how are you
planning to check learners’
learning?
Cross – curricular links health and
safety check ICT links
Values links
Orally
Through the observation,
giving the cards
Peer feedback
Mutual assessment
Self assessment
5 B
5 D
Reflection
Were the lesson objectives /
learning objectives realistic?
What did the learners learn
today? What was the learning
atmosphere like?
Did my planned differentiation
work well?
Did I stick to timings? What
changes did I make from my
plan and why?
Summary evaluation
What two things went really well (consider both teaching and learning)?
1.
2.
What two things would have improved the lessons (consider both teachings and learning)?
1.
2.
What have learned from his lesson about this lesson about the class or individuals that will inform
my next lesson?
Summative assessment for the unit “Reading for pleasure”
Материал жайлы қысқаша түсінік:
Summative assessment for the unit “Reading for pleasure”
Excel for Kazakhstan, grade 7. Module 5, «Reading for pleasure» SAU. БЖБ 7 сынып, ағылшын тіліненб 5-ші модуль
Жұмағалиұлы Әлішер
3 Ақпан 2022
#Шет тілі
#Сабақ жоспары
#7 сынып
2078
4
docx
ғылыми-әдістемелік
орталығы
Материалдың толық нұсқасын
жүктеп алып көруге болады





















