Today in this article we will see the simple approach of Read/Write Excel files in .NET Core using EPPlus.
In our last post, we saw the usage of OpenXML SDK (open source SDK from Microsoft) to work with Office Word, Excel, and PowerPoint using the C# language.
Today, in this article we shall cover the below using EPPLus,
- You don’t need Microsoft Office
- Getting Started
- Read the content of the Excel file using EPPlus
- JSON to Generic Type Conversion Dynamically
- Read Excel as JSON output
- Client-side Code
- Export/Write the data to an Excel file using EPPlus API
- Summary
Please see below for your reference,
- Read/Write excel file .NET Core using OpemXML SDK
EPPLus provides API for working with Office Excel documents.
EPPlus is a .NET library that helps read and write Excel files using the Office OpenXML format.
This library can be installed from NuGet as a package.
You don’t need Microsoft Office
Please note that Reading and Creating Excel in C# is possible without installing Microsoft Office.
Today we will see a few possible and easy-to-implement approaches.
Getting Started
Let’s create a .NET Core project, you can choose any project template.
EPPlus API works perfectly fine for any .NET Core Project template.
Here to keep it simple I am using a Console .NET Core application.
The NuGet Package name is EPPlus.
PM> Install-Package EPPlus 4.5.3.1
[Note: Please use the latest available version]
Let’s look at a simple example, I have a simple Excel file with below columns and rows details. We shall first read this file programmatically.
Please make sure to add below using statements as needed,
using OfficeOpenXml;
Read the content of the Excel file using EPPlus
Please use the below ‘Ready to Use’ Method in your application.
This method returns the result as a type so that you can read the excel result in the type of your choice.
private static T ReadFromExcel<T>(string path, bool hasHeader = true)
{
using (var excelPack = new ExcelPackage())
{
//Load excel stream
using (var stream = File.OpenRead(path))
{
excelPack.Load(stream);
}
//Lets Deal with first worksheet.(You may iterate here if dealing with multiple sheets)
var ws = excelPack.Workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Get all details as DataTable -because Datatable make life easy :)
DataTable excelasTable = new DataTable();
foreach (var firstRowCell in ws.Cells[1, 1, 1, ws.Dimension.End.Column])
{
//Get colummn details
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(firstRowCell.Text))
{
string firstColumn = string.Format("Column {0}", firstRowCell.Start.Column);
excelasTable.Columns.Add(hasHeader ? firstRowCell.Text : firstColumn);
}
}
var startRow = hasHeader ? 2 : 1;
//Get row details
for (int rowNum = startRow; rowNum <= ws.Dimension.End.Row; rowNum++)
{
var wsRow = ws.Cells[rowNum, 1, rowNum, excelasTable.Columns.Count];
DataRow row = excelasTable.Rows.Add();
foreach (var cell in wsRow)
{
row[cell.Start.Column - 1] = cell.Text;
}
}
//Get everything as generics and let end user decides on casting to required type
var generatedType = JsonConvert.DeserializeObject<T>(JsonConvert.SerializeObject(excelasTable));
return (T)Convert.ChangeType(generatedType, typeof(T));
}
}
JSON to Generic Type Conversion Dynamically
Please refer to this article – logic will generate type dynamically which can be cast to the appropriate type as needed.
Read Excel as JSON output
Excel as JSON will be generated using the below one-liner code.
string strJSON = JsonConvert.SerializeObject(excelasTable)
After executing the above API, The results will be printed on the console as below.
Here I have used the simple accessor class UserDetails.
This class will help in serializing and deserializing the Excel data.
public class UserDetails
{
public string ID { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public string City { get; set; }
public string Country { get; set; }
}
Client-side Code
Below is an example of client-side code,
List<UserDetails> userDetails = ReadFromExcel<List<UserDetails>>(@"C:UsersTestDataRead.xlsx");
Export/Write the data to an Excel file using EPPlus API
Let’s try now exporting data to a new Excel file.
Here is the sample data/object which we want to save as an Excel file.
List<UserDetails> persons = new List<UserDetails>()
{
new UserDetails() {ID="9999", Name="ABCD", City ="City1", Country="USA"},
new UserDetails() {ID="8888", Name="PQRS", City ="City2", Country="INDIA"},
new UserDetails() {ID="7777", Name="XYZZ", City ="City3", Country="CHINA"},
new UserDetails() {ID="6666", Name="LMNO", City ="City4", Country="UK"},
};
Here we need to use ExcelPackage class to create a new excel file with the required details.
Writing data to file and creating new excel is just a 2-3 liner code.
Please make a note of below one line doing the magic of loading DataTable into the Excel sheet
I am creating a new excel file in the same project folder to keep everything simple (the Excel file will get created in the ‘bin’ folder of the project)
private static void WriteToExcel(string path)
{
//Let use below test data for writing it to excel
List<UserDetails> persons = new List<UserDetails>()
{
new UserDetails() {ID="9999", Name="ABCD", City ="City1", Country="USA"},
new UserDetails() {ID="8888", Name="PQRS", City ="City2", Country="INDIA"},
new UserDetails() {ID="7777", Name="XYZZ", City ="City3", Country="CHINA"},
new UserDetails() {ID="6666", Name="LMNO", City ="City4", Country="UK"},
};
// let's convert our object data to Datatable for a simplified logic.
// Datatable is the easiest way to deal with complex datatypes for easy reading and formatting.
DataTable table = (DataTable)JsonConvert.DeserializeObject(JsonConvert.SerializeObject(persons), (typeof(DataTable)));
FileInfo filePath = new FileInfo(path);
using (var excelPack = new ExcelPackage(filePath))
{
var ws = excelPack.Workbook.Worksheets.Add("WriteTest");
ws.Cells.LoadFromDataTable(table, true, OfficeOpenXml.Table.TableStyles.Light8);
excelPack.Save();
}
}
After executing the above API, new Excel file will be created with the above custom object transformation into respective Excel columns and rows details as below,
That’s all, we just learned how to import and export data to/from Excel in the .NET Core framework.
Above ready to use API can be used in .NET Core console, or test project or ASP.Net Core application or logic can be modified as per your requirements. Please visit the GitHub link for the complete code.
I have validated the above approaches in .NET Core .NET 3.1 and found it to be working fine in all versions.
Other References:
- OpenXML SDK (open source SDK from Microsoft) to work with Office Word, Excel, and PowerPoint.
- Read/Write excel file .NET Core using OpemXML SDK
- NPOI library for reading and writing excel file in .NET Core,
- Read/Write Excel files in .NET Core using NPOI
Summary
Today we learned, how to import and export data to/from excel in the .NET Core framework using the EPPlus library.
The legacy so-called applications like Excel are no more legacy and can be used on any platform. EPPlus makes it easy to deal with Excel files allowing us to perform reading or create spreadsheets easily.
Please bookmark this page and share it with your friends. Please Subscribe to the blog to receive notifications on freshly published best practices and guidelines for software design and development.
Introduction
In this tutorial, i will show you how to read an excel file in C# by using the EPPlus library.
EPPLUS Download and Installation
EPPlus is a .NET library that allows you to read from and write to excel files. To download this library:
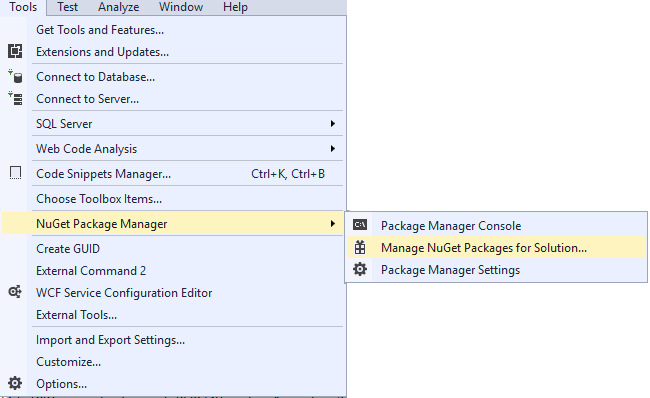
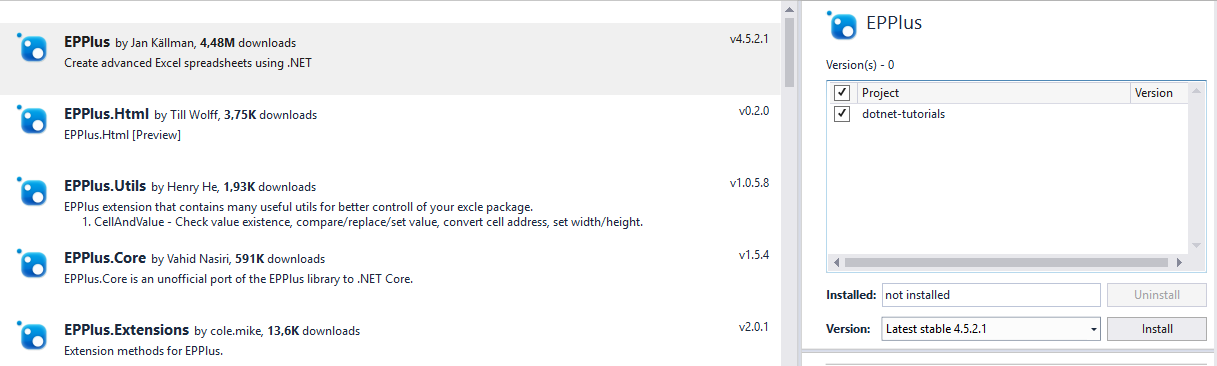
1- Go to Tools > NuGet Package Manager > Manage NuGet Packages for Solution…
2- Search for EPPlus.
3- Choose the first search result, check your project and click the install button.
4- Click the ok button.
EPPLUS Usage
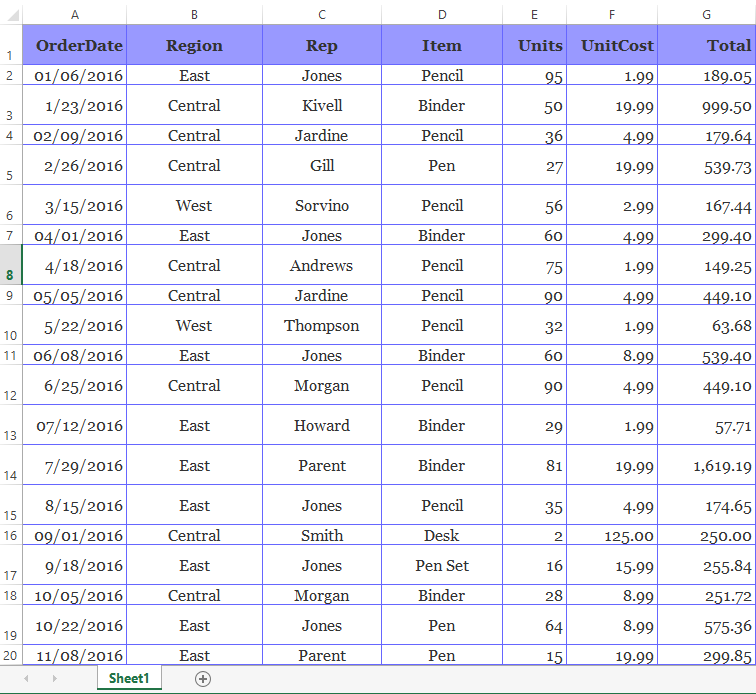
For the purpose of this tutorial, we will use the below excel sample data.
The following code illustrates how to read the above excel file.
// path to your excel file
string path = "C:/****/sample_data.xlsx";
FileInfo fileInfo = new FileInfo(path);
ExcelPackage package = new ExcelPackage(fileInfo);
ExcelWorksheet worksheet = package.Workbook.Worksheets.FirstOrDefault();
// get number of rows and columns in the sheet
int rows = worksheet.Dimension.Rows; // 20
int columns = worksheet.Dimension.Columns; // 7
// loop through the worksheet rows and columns
for (int i = 1; i <= rows; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= columns; j++) {
string content = worksheet.Cells[i, j].Value.ToString();
/* Do something ...*/
}
}
In preceding code, we create a new instance of the ExcelPackage by passing the FileInfo object as a parameter of its constructor
, wich enables us to access our excel file. package.Workbook.Worksheets provides access to multiple worksheets. Since our excel file
contains only one worksheet, we use the FirstOrDefault method to access it. After that we loop through our worksheet and we get the value
of each column of each row.
Note: by using the Dimension object, you need to be sure that the excel file you’re working with is not empty.
Otherwise, it will return null.
Namespace
To use EPPlus in your code, you have to include this namespace:
using OfficeOpenXml;See also
- Edit an excel file in c#
Содержание
- Read excel with epplus
- EPPLUS Download and Installation
- EPPLUS Usage
- Namespace
- Read excel file in C# (.XLSX or .XLS using OLEDB / EPPlus or Interop)
- Disadvantage of using OLEDB for Excel
- Reading Excel file using EPPlus
- Read Excel using MS Office Interop
- Старт работы с Excel на C#
- Историческая справка
- Задача
- Первый запуск
- Вывод данных
- Стилизация
- Размер ячеек
- Формат данных
- Выравнивание
- Стиль текста
- Границы
- График
- Заключение
Read excel with epplus
In this tutorial, i will show you how to read an excel file in C# by using the EPPlus library.
EPPLUS Download and Installation
EPPlus is a .NET library that allows you to read from and write to excel files. To download this library:
1- Go to Tools > NuGet Package Manager > Manage NuGet Packages for Solution.
2- Search for EPPlus.
3- Choose the first search result, check your project and click the install button.
4- Click the ok button.
EPPLUS Usage
For the purpose of this tutorial, we will use the below excel sample data.
The following code illustrates how to read the above excel file.
In preceding code, we create a new instance of the ExcelPackage by passing the FileInfo object as a parameter of its constructor , wich enables us to access our excel file. package.Workbook.Worksheets provides access to multiple worksheets. Since our excel file contains only one worksheet, we use the FirstOrDefault method to access it. After that we loop through our worksheet and we get the value of each column of each row.
Note: by using the Dimension object, you need to be sure that the excel file you’re working with is not empty. Otherwise, it will return null .
Namespace
To use EPPlus in your code, you have to include this namespace:
Источник
Read excel file in C# (.XLSX or .XLS using OLEDB / EPPlus or Interop)
Whether you are working on Windows or on Web or on Console application, at one stage we need to process data and excel file is widely used for it, so in previous article, we have explained about creating excel in C# without interop but in this article, I am going to provide you code to open and read excel file (.xls or .xlsx) in C# line by line in Console application using OLEDB or EPPlus or Interop (all 3 methods), you can use the same code C# code to fill ASP.NET GridView or MVC application table.
So, let’s get started with it.
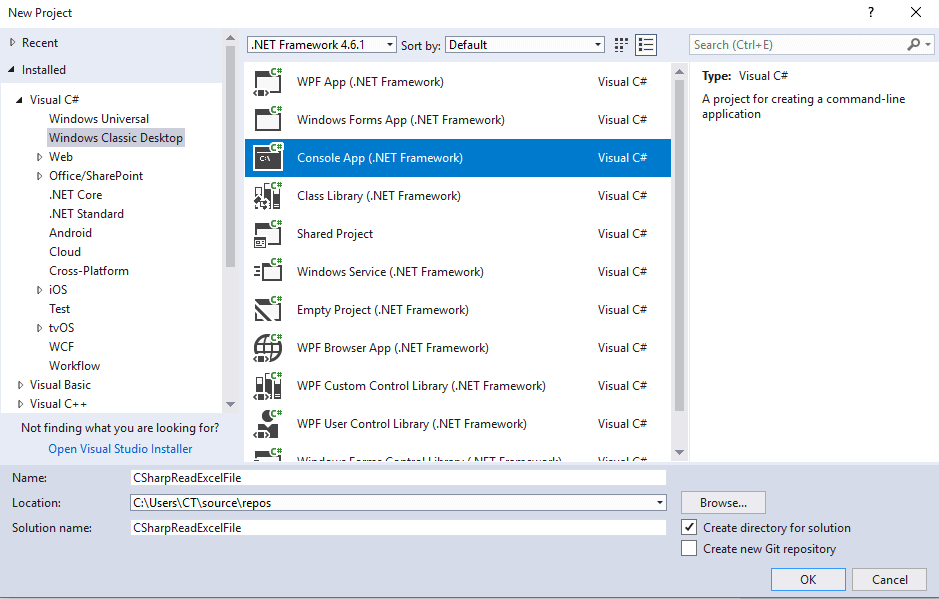
Step 1: Create a new Console applicaiton in your Visual Studio, by navigating to File->New->Project-> Select «Windows Classic dekstop» from left-pane & «Console-App» from right-pane -> Provide a name to your application «CSharpReadExcelFile» -> Click «OK»
Step 2: Now we have our Console application and we need to add C# code using OLEDB to read excel file, for that we would need connection string with the source URL of excel file.
In the given example as I am using .XLS excel file, here is my connection string
For Excel 97-2003 Format we can use “Microsoft Jet OLEDB Driver 4.0”, while for the Connection String for Excel 2007 Format (.XLSX), we can use “Microsoft Ace OLEDB Driver 12.0” and it’s connection string would be as below
In the above Connection string’s you may see extended properties HDR=Yes & HDR =No
Use HDR=YES if first excel row contains headers, alternatively,use HDR=NO when your excel’s first row is not headers and it’s data.
Now, we have connection string , we need to create connection using OLEDB and open it
Read the excel file using OLEDB connection and fill it in dataset
in the above code Sample-spreadsheet-file is the name of Sheet.
Note: With the help of sheet name, you can refer to Excel data, you need to use ‘$’ with sheet name, e.g. Select * from [Sheet1$]
Now loop through each row of excel sheet and print it in Console app
If you are using ASP.NET, you can bind it with Grid View using below code instead of printing it
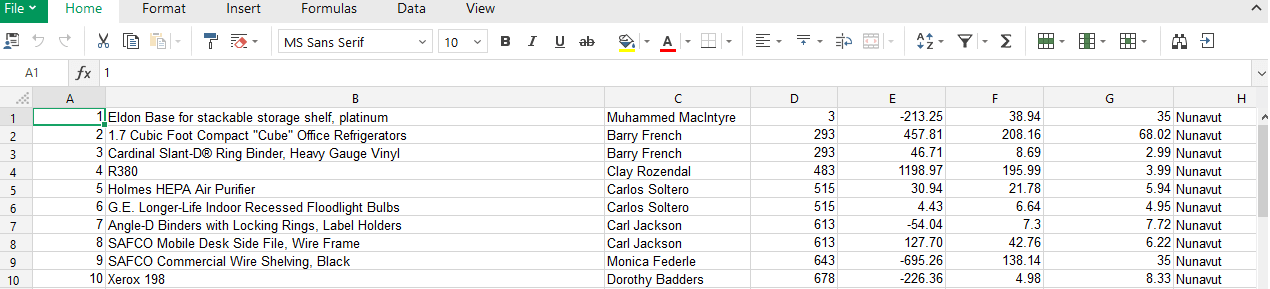
Now, we have discussed each step, suppose this is out Excel file
and ese the code below in your Console application, build and execute it.
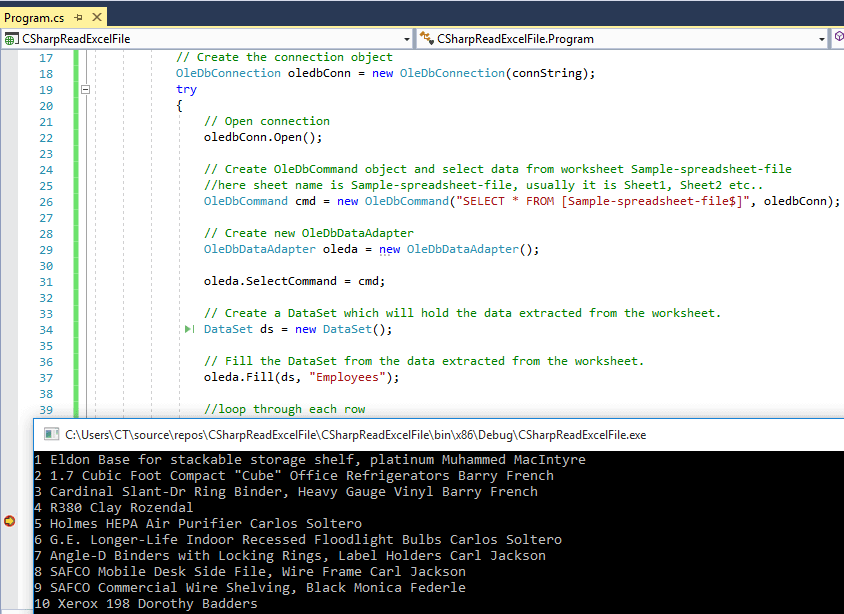
Output of the above code will be as below
Now, if you are working on 64 bit operating system, you may get this error «The ‘Microsoft.Jet.OLEDB.4.0’ provider is not registered on the local machine.«.
Resolving this error: If your application is Desktop based, compile your EXE with x86 CPU (Menu Tools, Options, select Projects And Solutions, check the show advanced build configurations. Now in the Build Menu you will be able to go to the Config Manager and set output to x86.)
If your application is web based, then Enable ’32-Bit Applications’ in application pool.
On IIS, change the «Enable 32-bit Applications» setting to True, in the Advanced Settings for the Application Pool.
Disadvantage of using OLEDB for Excel
With OLEDB, you cannot format data that you inserted/updated in EXCEL sheet but Interop can do it efficiently. You cannot perform any mathematical operation or working on graphs using OLEDB, but it is really a good way to insert/update data in EXCEL where no Excel application is installed.
Reading Excel file using EPPlus
If you don’t want to use OleDb, you can try using EPPlus Nuget package based solution.
For this, you would have to install EPPlus, so navigate to «Tools»-> «Nuget package manager»-> «Manage Nuget for this solution» -> Select «Browse» tab and search for «EPPlus», then install the nuget package.
Once you have installed the package, in your Console application «Program.cs», you can use the code below
Here is the image, which shows console application output with sample excel file (.xlsx), we are using .xlsx file here for reading in C# using EPPlus
You can use above EPPlus example to work in .NET Core C# also, to read excel file in .NET Core.
Read Excel using MS Office Interop
You can also read Excel file in C# using MS Office Interop easily.
First you will have to add reference for » Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel «, so in your Console, Windows or Web-Application, right-click on «Reference» and then in «Assemblies» search for «Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel»
So, here is the C# Code for it, considering we have sample XLSX file as above
As you can see we have used Interop to open and read excel rows/columns, one of the drawbacks of using MS office Interop is that you need it installed on Server also.
That’s it, feel free to provide your feedback in the below comment’s section.
Источник
Старт работы с Excel на C#
В современном мире разработки приложений нередко встает необходимость работы с Excel документами. Чаще всего это разного рода отчеты, но иногда xls/x файлы используются в качестве хранилища данных. Например, если пользователь должен иметь возможность загрузить данные в приложение или выгрузить, в человеко-читаемом виде, Excel де-факто является стандартом. Относительно дружелюбный интерфейс, прозрачная структура, в купе с его распространенностью. трудно навскидку назвать решение лучше.
Однако, у многих Excel до сих пор ассоциируется с чем-то тяжелым, неповоротливым и сложным. Давайте посмотрим, как мы — обычные C# разработчики, можем легко сформировать простой Excel документ, на примере табличного отчета.
Историческая справка
Времена, когда доминировал проприетарный формат .xls(Excel Binary File Format) давно прошли и сейчас мы имеем только .xlsx(Excel Workbook), в рамках Office Open XML. Последний представляет собой обычный .zip архив с XML файлами. Не будем углубляться в его структуру, я искренне надеюсь что вам это никогда не понадобится.
На github, и не только, можно найти ряд библиотек, бесплатных и не только. Пожалуй самой популярной является EPPlus. До определенной степени, она довольно хорошо отражает концепцию Excel, именно по этому я всегда использую EPPlus. Версия 4 полностью бесплатна, начиная с 5‐й версии вам потребуется приобрести лицензию для коммерческого использования.
Задача
Итак, предположим, продукт-мэнеджеру ударила в голову идея того, что возможность выгружать некий отчет в формате Excel увеличит кол-во пользователей на 100500%. Проджет-менеджер решает выкатить эту киллер-фичу как хотфикс прямо сегодня — ведь работы всего на пару часов.
Сам по себе, отчет содержит краткое описание компании и историю изменения некоторых экономических показателей. Для простоты все свойства компании — строки. Экономические показатели — большие целые числа и числа с плавающей точкой, а также даты. Предположим, что где-то в недрах микросервисного backend-да есть сервис-генератор подобных отчетов, например по id компании. Однако, поскольку id нет смысла выводить пользователю, идентификатор отсутствует в самой модели отчета.
Аналитик, в свою очередь, выдает задачу с феноменально точным описанием — «Сгенерировать excel отчет на базе данных MarketReport». Что ж, для нашего примера, создадим заглушку — генератор фейковых данных:
Первый запуск
Подключим EPPlus версии 4.5.3.3 и создадим базовую обвязку для будущего генератора.
Сердцем генератора будет метод Generate. ExcelPackage это модель документа, через которую мы и будем осуществлять все взаимодействия с ним. Также имеется конструктор для передачи пути к файлу или потока.
В методе main создается генератор отчетов, а также генератор Excel файлов. Далее полученный файл просто записывается на диск.
При попытке запустить приложение, получаем exception: InvalidOperationException: The workbook must contain at least one worksheet
Все правильно, Excel документ не может существовать без страниц, должна быть хотя бы одна. Добавляем ее, все интуитивно понятно:
Запускаем снова и. вот оно! Теперь наше приложение генерирует документ и, хотя там еще ничего нет, он уже весит 2,5KB — значит мы работаем с Excel правильно и все идет как надо.
Вывод данных
Давайте выведем основную информацию по компании в шапку. Для доступа к конкретной ячейки объект Cells на странице пакета снабжен удобным индексатором. При этом, до конкретной ячейки можно достучаться как через номер строки и столбца, так и по привычному всем буквенно-числовому коду:
Полный код вывода шапки.
Для вывода исторических данных понадобится как минимум шапка таблицы и цикл по массиву History:
Предлагаю обратить внимание на метод LoadFromArrays, который заполняет диапазон ячеек рваным(зубчатым) массивом. Здесь мы можем видеть, что типизация теряется и передавая массив object мы ожидаем что EPPlus в конечном итоге использует ToString, чтобы записать переданное в ячейки.
Стилизация
Если вы прямо сейчас откроете документ, то вы возможно увидите не то, что хотелось бы отдать в продакшн в пятницу вечером.
Как это выглядит
Во-первых, шапка никак не выделяется, во-вторых таблица не имеет границ. выравнивание пляшет, даты отображаются магическими числами, а капитализация «уходит в какую-то математику» — как это прокомментировал аналитик.
Да, на все эти красивости у нас уйдет больше года кода, чем на сам вывод данных, и, в конечном тоге, получившаяся каша из логики вывода данных и разметки заставит некоторых усомниться в их компетентности. но, мы же backend разработчики, так давайте сверстаем Excel Sheet!
Размер ячеек
Из коробки у нас есть возможность сделать автофит а так же вручную выставить ширину в соответствии с нашей ситуацией. А ситуация у нас не самая хорошая — по задумке аналитика в шапке у ячеек должен быть автофит, а у ячеек таблицы — тоже автофит. Так в чем же подвох?
Если вы когда-нибудь до этого открывали Excel, то возможно знаете, что ширина ячеек не может отличаться в рамках столбца и автофит будет по самому широкому контенту ячейки. Однако, простые вещи бывает нетак то просто объяснить. Но если вы справитесь, то вот как это будет выглядеть в коде:
Формат данных
Как и большая часть стиля ячейки, он задается через одноименное свойство Style. Обратите внимание на вычисление 3-го аргумента индексатора. Это звоночек некачественного кода, но к этому мы вернемся в позже.
Выравнивание
Его можно задать как на ячейке, так и на диапазоне. На самом деле, для EPPlus, это одна и та же сущность — некий ExcelRange, описывающий диапазон ячеек, в том числе и со всего 1 ячейкой.
Стиль текста
Также легко задается, используя Style.Font, кстати, здесь, на 2-й строчке, мы впервые указываем диапазон так, как привыкли его видеть пользователи Excel:
Границы
Задаем стиль линии, а также ее толщину. К этому моменту от кол-ва магических чисел-параметров индексатора уже рябит в глазах, но мы уже на финишной прямой. не так ли?
График
«Ну что за отчет без графиков, верно, Карл?» — ловко подметит специалист по тестированию, и не важно, что этого не было в ТЗ а на часах уже половина 9-го.
Хотя график как сущность сам по себе сложнее таблиц и с графиками мы не работаем каждый день, EPPlus предоставляет довольно понятный API. Давайте добавим простейший график, отражающий рост капитализации:
Еще, может понадобиться защитить страницу от редактирования:
На этом все, репозиторий с рабочим приложением находится здесь.
Заключение
Во-первых, прежде всего, о том, что мы успешно справились с задачей, а именно, сгенерировали свой первый Excel отчет, поработали со стилями и даже решили пару попутных проблем.
Во-вторых, возможно имеет смысл искать новою работу, но, забегая вперед, я бы с этим не спешил. Если данная публикация наберет 1+ просмотров, то во второй части мы поговорим о том, как можно отделить стилизацию от логики заполнения данными, упростить манипуляции над ячейками и в целом сделаем код боле поддерживаемым.
Источник
You can read and write data from and to your spreadsheet in a few different ways. The most obvious is to use the Cells property of the ExcelWorksheet class, shown on the Getting Started page. There are also a few other ways to import/export/read data from/into spreadsheets with EPPlus.
Load data into a spreadsheet
From the Cells property (ExcelRange) you can access these methods to load data from various sources:
-
LoadFromTextandLoadFromTextAsync— Read a csv text file and load the data into a range on a worksheet. -
LoadFromDataReaderandLoadFromDataReaderAsync— Loads data into a range from a DataReader -
LoadFromDataTable— Loads data into a range from a DataTable. Can be used for importing data from a range of sources, like XML (example provided) and databases. -
LoadFromCollection— Loads data into a range from an IEnumerable using reflection. -
LoadFromCollection using attributes— Loads data into a range/table from an IEnumerable using reflection. Uses attributes that specifies styling, number formats, formulas, etc. -
LoadFromDictionaries— Loads data into a range from an IEnumerable of ExpandoObject/dynamic objects (via their IDictionary<string, object> interface. Useful for importing json data, example provided. -
LoadFromArrays— Loads data into a range from an IEnumerable of object[] where each object array becomes a row in the worksheet.
You can optionally specify a parameter to create an ExcelTable when you use these methods. For more detailed examples, have a look at sample 4 & 5 the sample project Sample-.NET Framework or Sample-.NET Framework.
Export data from a spreadsheet
From the Cells property (ExcelRange) you can access these methods to write:
-
ToTextandToTextAsync— Writes a range to a csv string. -
SaveToTextandSaveToTextAsync— Writes a range to a csv file. -
ToDataTable— Exports data from a range to a System.Data.DataTable -
ToCollection— Exports data from a range to anIEnumerable<T>where T is a class. -
ToJson— Exports data from a range to Json. -
CreateHtmlExporter— Exports data from a range to html/css. -
GetValue<T>— Gets a value, with the option to specify a datatype -
Value— Gets or sets the value of the range.
You can also use the GetValue and SetValue methods directly on the worksheet object.
(This will give a little bit better performance than reading/writing via the range):
-
GetValue<T>— Gets a value of a single cell, with the option to specify a datatype -
SetValue— Sets a value of a single cell
Since the Cells property implements the IEnumerable interface, you can use Linq to query data from a worksheet.
var query1= (from cell in sheet.Cells["d:d"] where cell.Value is double && (double)cell.Value >= 9990 && (double)cell.Value <= 10000 select cell);
Most of these methods are demonstrated in the sample project.
Время на прочтение
7 мин
Количество просмотров 69K
В современном мире разработки приложений нередко встает необходимость работы с Excel документами. Чаще всего это разного рода отчеты, но иногда xls/x файлы используются в качестве хранилища данных. Например, если пользователь должен иметь возможность загрузить данные в приложение или выгрузить, в человеко-читаемом виде, Excel де-факто является стандартом. Относительно дружелюбный интерфейс, прозрачная структура, в купе с его распространенностью… трудно навскидку назвать решение лучше.
Однако, у многих Excel до сих пор ассоциируется с чем-то тяжелым, неповоротливым и сложным. Давайте посмотрим, как мы — обычные C# разработчики, можем легко сформировать простой Excel документ, на примере табличного отчета.
Историческая справка
Времена, когда доминировал проприетарный формат .xls(Excel Binary File Format) давно прошли и сейчас мы имеем только .xlsx(Excel Workbook), в рамках Office Open XML. Последний представляет собой обычный .zip архив с XML файлами. Не будем углубляться в его структуру, я искренне надеюсь что вам это никогда не понадобится.
На github, и не только, можно найти ряд библиотек, бесплатных и не только. Пожалуй самой популярной является EPPlus. До определенной степени, она довольно хорошо отражает концепцию Excel, именно по этому я всегда использую EPPlus. Версия 4 полностью бесплатна, начиная с 5‐й версии вам потребуется приобрести лицензию для коммерческого использования.
Задача
Итак, предположим, продукт-мэнеджеру ударила в голову идея того, что возможность выгружать некий отчет в формате Excel увеличит кол-во пользователей на 100500%. Проджет-менеджер решает выкатить эту киллер-фичу как хотфикс прямо сегодня — ведь работы всего на пару часов.
Сам по себе, отчет содержит краткое описание компании и историю изменения некоторых экономических показателей. Для простоты все свойства компании — строки. Экономические показатели — большие целые числа и числа с плавающей точкой, а также даты. Предположим, что где-то в недрах микросервисного backend-да есть сервис-генератор подобных отчетов, например по id компании. Однако, поскольку id нет смысла выводить пользователю, идентификатор отсутствует в самой модели отчета.
Аналитик, в свою очередь, выдает задачу с феноменально точным описанием — «Сгенерировать excel отчет на базе данных MarketReport». Что ж, для нашего примера, создадим заглушку — генератор фейковых данных:
Первый запуск
Подключим EPPlus версии 4.5.3.3 и создадим базовую обвязку для будущего генератора.
Сердцем генератора будет метод Generate. ExcelPackage это модель документа, через которую мы и будем осуществлять все взаимодействия с ним. Также имеется конструктор для передачи пути к файлу или потока.
В методе main создается генератор отчетов, а также генератор Excel файлов. Далее полученный файл просто записывается на диск.
При попытке запустить приложение, получаем exception:InvalidOperationException: The workbook must contain at least one worksheet
Все правильно, Excel документ не может существовать без страниц, должна быть хотя бы одна. Добавляем ее, все интуитивно понятно:
var sheet = package.Workbook.Worksheets
.Add("Market Report");Запускаем снова и… вот оно! Теперь наше приложение генерирует документ и, хотя там еще ничего нет, он уже весит 2,5KB — значит мы работаем с Excel правильно и все идет как надо.
Вывод данных
Давайте выведем основную информацию по компании в шапку. Для доступа к конкретной ячейки объект Cells на странице пакета снабжен удобным индексатором. При этом, до конкретной ячейки можно достучаться как через номер строки и столбца, так и по привычному всем буквенно-числовому коду:
sheet.Cells["B2"].Value = "Company:";
sheet.Cells[2, 3].Value = report.Company.Name;Полный код вывода шапки.
sheet.Cells["B2"].Value = "Company:";
sheet.Cells[2, 3].Value = report.Company.Name;
sheet.Cells["B3"].Value = "Location:";
sheet.Cells["C3"].Value = $"{report.Company.Address}, " +
$"{report.Company.City}, " +
$"{report.Company.Country}";
sheet.Cells["B4"].Value = "Sector:";
sheet.Cells["C4"].Value = report.Company.Sector;
sheet.Cells["B5"].Value = report.Company.Description;Для вывода исторических данных понадобится как минимум шапка таблицы и цикл по массиву History:
sheet.Cells[8, 2, 8, 4].LoadFromArrays(new object[][]{ new []{"Capitalization", "SharePrice", "Date"} });
var row = 9;
var column = 2;
foreach (var item in report.History)
{
sheet.Cells[row, column].Value = item.Capitalization;
sheet.Cells[row, column + 1].Value = item.SharePrice;
sheet.Cells[row, column + 2].Value = item.Date;
row++;
}Предлагаю обратить внимание на метод LoadFromArrays, который заполняет диапазон ячеек рваным(зубчатым) массивом. Здесь мы можем видеть, что типизация теряется и передавая массив object мы ожидаем что EPPlus в конечном итоге использует ToString, чтобы записать переданное в ячейки.
Стилизация
Если вы прямо сейчас откроете документ, то вы возможно увидите не то, что хотелось бы отдать в продакшн в пятницу вечером.
Как это выглядит

Во-первых, шапка никак не выделяется, во-вторых таблица не имеет границ… выравнивание пляшет, даты отображаются магическими числами, а капитализация «уходит в какую-то математику» — как это прокомментировал аналитик.
Да, на все эти красивости у нас уйдет больше года кода, чем на сам вывод данных, и, в конечном тоге, получившаяся каша из логики вывода данных и разметки заставит некоторых усомниться в их компетентности… но, мы же backend разработчики, так давайте сверстаем Excel Sheet!
Размер ячеек
Из коробки у нас есть возможность сделать автофит а так же вручную выставить ширину в соответствии с нашей ситуацией. А ситуация у нас не самая хорошая — по задумке аналитика в шапке у ячеек должен быть автофит, а у ячеек таблицы — тоже автофит. Так в чем же подвох?
Если вы когда-нибудь до этого открывали Excel, то возможно знаете, что ширина ячеек не может отличаться в рамках столбца и автофит будет по самому широкому контенту ячейки. Однако, простые вещи бывает нетак то просто объяснить… Но если вы справитесь, то вот как это будет выглядеть в коде:
sheet.Cells[1, 1, row, column + 2].AutoFitColumns();
sheet.Column(2).Width = 14;
sheet.Column(3).Width = 12;Формат данных
Как и большая часть стиля ячейки, он задается через одноименное свойство Style. Обратите внимание на вычисление 3-го аргумента индексатора. Это звоночек некачественного кода, но к этому мы вернемся в позже…
sheet.Cells[9, 4, 9 + report.History.Length, 4].Style.Numberformat.Format = "yyyy";
sheet.Cells[9, 2, 9 + report.History.Length, 2].Style.Numberformat.Format = "### ### ### ##0";Выравнивание
Его можно задать как на ячейке, так и на диапазоне. На самом деле, для EPPlus, это одна и та же сущность — некий ExcelRange, описывающий диапазон ячеек, в том числе и со всего 1 ячейкой.
sheet.Column(2).Style.HorizontalAlignment = ExcelHorizontalAlignment.Left;
sheet.Cells[8, 3, 8 + report.History.Length, 3].Style.HorizontalAlignment = ExcelHorizontalAlignment.Center;Стиль текста
Также легко задается, используя Style.Font, кстати, здесь, на 2-й строчке, мы впервые указываем диапазон так, как привыкли его видеть пользователи Excel:
sheet.Cells[8, 2, 8, 4].Style.Font.Bold = true;
sheet.Cells["B2:C4"].Style.Font.Bold = true;Границы
Задаем стиль линии, а также ее толщину. К этому моменту от кол-ва магических чисел-параметров индексатора уже рябит в глазах, но мы уже на финишной прямой… не так ли?
sheet.Cells[8, 2, 8 + report.History.Length, 4].Style.Border.BorderAround(ExcelBorderStyle.Double);
sheet.Cells[8, 2, 8, 4].Style.Border.Bottom.Style = ExcelBorderStyle.Thin;График
«Ну что за отчет без графиков, верно, Карл?» — ловко подметит специалист по тестированию, и не важно, что этого не было в ТЗ а на часах уже половина 9-го…
Хотя график как сущность сам по себе сложнее таблиц и с графиками мы не работаем каждый день, EPPlus предоставляет довольно понятный API. Давайте добавим простейший график, отражающий рост капитализации:
var capitalizationChart = sheet.Drawings.AddChart("FindingsChart", OfficeOpenXml.Drawing.Chart.eChartType.Line);
capitalizationChart.Title.Text = "Capitalization";
capitalizationChart.SetPosition(7, 0, 5, 0);
capitalizationChart.SetSize(800, 400);
var capitalizationData = (ExcelChartSerie)(capitalizationChart.Series.Add(sheet.Cells["B9:B28"], sheet.Cells["D9:D28"]));
capitalizationData.Header = report.Company.Currency;Еще, может понадобиться защитить страницу от редактирования:
sheet.Protection.IsProtected = true;На этом все, репозиторий с рабочим приложением находится здесь.
Заключение
О чем говорит финальная версия метода Generate?
public byte[] Generate(MarketReport report)
{
var package = new ExcelPackage();
var sheet = package.Workbook.Worksheets
.Add("Market Report");
sheet.Cells["B2"].Value = "Company:";
sheet.Cells[2, 3].Value = report.Company.Name;
sheet.Cells["B3"].Value = "Location:";
sheet.Cells["C3"].Value = $"{report.Company.Address}, " +
$"{report.Company.City}, " +
$"{report.Company.Country}";
sheet.Cells["B4"].Value = "Sector:";
sheet.Cells["C4"].Value = report.Company.Sector;
sheet.Cells["B5"].Value = report.Company.Description;
sheet.Cells[8, 2, 8, 4].LoadFromArrays(new object[][]{ new []{"Capitalization", "SharePrice", "Date"} });
var row = 9;
var column = 2;
foreach (var item in report.History)
{
sheet.Cells[row, column].Value = item.Capitalization;
sheet.Cells[row, column + 1].Value = item.SharePrice;
sheet.Cells[row, column + 2].Value = item.Date;
row++;
}
sheet.Cells[1, 1, row, column + 2].AutoFitColumns();
sheet.Column(2).Width = 14;
sheet.Column(3).Width = 12;
sheet.Cells[9, 4, 9+ report.History.Length, 4].Style.Numberformat.Format = "yyyy";
sheet.Cells[9, 2, 9+ report.History.Length, 2].Style.Numberformat.Format = "### ### ### ##0";
sheet.Column(2).Style.HorizontalAlignment = ExcelHorizontalAlignment.Left;
sheet.Cells[8, 3, 8 + report.History.Length, 3].Style.HorizontalAlignment = ExcelHorizontalAlignment.Center;
sheet.Column(4).Style.HorizontalAlignment = ExcelHorizontalAlignment.Right;
sheet.Cells[8, 2, 8, 4].Style.Font.Bold = true;
sheet.Cells["B2:C4"].Style.Font.Bold = true;
sheet.Cells[8, 2, 8 + report.History.Length, 4].Style.Border.BorderAround(ExcelBorderStyle.Double);
sheet.Cells[8, 2, 8, 4].Style.Border.Bottom.Style = ExcelBorderStyle.Thin;
var capitalizationChart = sheet.Drawings.AddChart("FindingsChart", OfficeOpenXml.Drawing.Chart.eChartType.Line);
capitalizationChart.Title.Text = "Capitalization";
capitalizationChart.SetPosition(7, 0, 5, 0);
capitalizationChart.SetSize(800, 400);
var capitalizationData = (ExcelChartSerie)(capitalizationChart.Series.Add(sheet.Cells["B9:B28"], sheet.Cells["D9:D28"]));
capitalizationData.Header = report.Company.Currency;
sheet.Protection.IsProtected = true;
return package.GetAsByteArray();
}Во-первых, прежде всего, о том, что мы успешно справились с задачей, а именно, сгенерировали свой первый Excel отчет, поработали со стилями и даже решили пару попутных проблем.
Во-вторых, возможно имеет смысл искать новою работу, но, забегая вперед, я бы с этим не спешил… Если данная публикация наберет 1+ просмотров, то во второй части мы поговорим о том, как можно отделить стилизацию от логики заполнения данными, упростить манипуляции над ячейками и в целом сделаем код боле поддерживаемым.
Example
//create a list to hold all the values
List<string> excelData = new List<string>();
//read the Excel file as byte array
byte[] bin = File.ReadAllBytes("C:\ExcelDemo.xlsx");
//or if you use asp.net, get the relative path
byte[] bin = File.ReadAllBytes(Server.MapPath("ExcelDemo.xlsx"));
//create a new Excel package in a memorystream
using (MemoryStream stream = new MemoryStream(bin))
using (ExcelPackage excelPackage = new ExcelPackage(stream))
{
//loop all worksheets
foreach (ExcelWorksheet worksheet in excelPackage.Workbook.Worksheets)
{
//loop all rows
for (int i = worksheet.Dimension.Start.Row; i <= worksheet.Dimension.End.Row; i++)
{
//loop all columns in a row
for (int j = worksheet.Dimension.Start.Column; j <= worksheet.Dimension.End.Column; j++)
{
//add the cell data to the List
if (worksheet.Cells[i, j].Value != null)
{
excelData.Add(worksheet.Cells[i, j].Value.ToString());
}
}
}
}
}
Introduction
There are some popular libraries that can help us deal with Excel files, such as DotNetCore.NPOI, npoi and EPPlus .etc.
In this article, we will use EPPlus to import and export Excel files in ASP.NET Core. EPPlus is a .NET library that reads and writes Excel files using the Office Open XML format (.xlsx). EPPlus has no dependencies other than .NET.
Let’s take a look at how to do that.
Preparations
Create a new ASP.NET Core Web API Application and install EPPlus via nuGet.
- Install-Package EPPlus -Version 4.5.2.1
Create two classes we need for this demo, one is UserInfo class that contains two properties.
- public class UserInfo
- {
- public string UserName { get; set; }
- public int Age { get; set; }
- }
The other one is DemoResponse which unifies the response structure.
- public class DemoResponse<T>
- {
- public int Code { get; set; }
- public string Msg { get; set; }
- public T Data { get; set; }
- public static DemoResponse<T> GetResult(int code, string msg, T data = default(T))
- {
- return new DemoResponse<T>
- {
- Code = code,
- Msg = msg,
- Data = data
- };
- }
- }
Adding a new Web API controller named EPPlusController, we will add import and export methods here.
Import
In the real world, import functionality is complex and it involves validation, applying business rules and finally saving it in the database. But to show you, will define an import handler method to read and return the data of the Excel file.
- [HttpPost(«import»)]
- public async Task<DemoResponse<List<UserInfo>>> Import(IFormFile formFile, CancellationToken cancellationToken)
- {
- if (formFile == null || formFile.Length <= 0)
- {
- return DemoResponse<List<UserInfo>>.GetResult(-1, «formfile is empty»);
- }
- if (!Path.GetExtension(formFile.FileName).Equals(«.xlsx», StringComparison.OrdinalIgnoreCase))
- {
- return DemoResponse<List<UserInfo>>.GetResult(-1, «Not Support file extension»);
- }
- var list = new List<UserInfo>();
- using (var stream = new MemoryStream())
- {
- await formFile.CopyToAsync(stream, cancellationToken);
- using (var package = new ExcelPackage(stream))
- {
- ExcelWorksheet worksheet = package.Workbook.Worksheets[0];
- var rowCount = worksheet.Dimension.Rows;
- for (int row = 2; row <= rowCount; row++)
- {
- list.Add(new UserInfo
- {
- UserName = worksheet.Cells[row, 1].Value.ToString().Trim(),
- Age = int.Parse(worksheet.Cells[row, 2].Value.ToString().Trim()),
- });
- }
- }
- }
- return DemoResponse<List<UserInfo>>.GetResult(0, «OK», list);
- }
We have an Excel file named aa.xlsx, and the following screenshot shows the contents of it.
We will import this file, and may get the following result.
Export
There are two ways to export an Excel file.
- Create a file and return the download link
- Return the file directly
For the first way,
- private readonly IHostingEnvironment _hostingEnvironment;
- public EPPlusController(IHostingEnvironment hostingEnvironment)
- {
- this._hostingEnvironment = hostingEnvironment;
- }
- [HttpGet(«export»)]
- public async Task<DemoResponse<string>> Export(CancellationToken cancellationToken)
- {
- string folder = _hostingEnvironment.WebRootPath;
- string excelName = $«UserList-{DateTime.Now.ToString(«yyyyMMddHHmmssfff«)}.xlsx»;
- string downloadUrl = string.Format(«{0}://{1}/{2}», Request.Scheme, Request.Host, excelName);
- FileInfo file = new FileInfo(Path.Combine(folder, excelName));
- if (file.Exists)
- {
- file.Delete();
- file = new FileInfo(Path.Combine(folder, excelName));
- }
- await Task.Yield();
- var list = new List<UserInfo>()
- {
- new UserInfo { UserName = «catcher», Age = 18 },
- new UserInfo { UserName = «james», Age = 20 },
- };
- using (var package = new ExcelPackage(file))
- {
- var workSheet = package.Workbook.Worksheets.Add(«Sheet1»);
- workSheet.Cells.LoadFromCollection(list, true);
- package.Save();
- }
- return DemoResponse<string>.GetResult(0, «OK», downloadUrl);
- }
After executing this method, we will get the link, and it will create a file in the wwwroot folder,

Opening this file, you may get the following content.
- [HttpGet(«exportv2»)]
- public async Task<IActionResult> ExportV2(CancellationToken cancellationToken)
- {
- await Task.Yield();
- var list = new List<UserInfo>()
- {
- new UserInfo { UserName = «catcher», Age = 18 },
- new UserInfo { UserName = «james», Age = 20 },
- };
- var stream = new MemoryStream();
- using (var package = new ExcelPackage(stream))
- {
- var workSheet = package.Workbook.Worksheets.Add(«Sheet1»);
- workSheet.Cells.LoadFromCollection(list, true);
- package.Save();
- }
- stream.Position = 0;
- string excelName = $«UserList-{DateTime.Now.ToString(«yyyyMMddHHmmssfff«)}.xlsx»;
- return File(stream, «application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.spreadsheetml.sheet», excelName);
- }
After executing this method, we will get the file directly.

Summary
This short article shows how to use EPPlus library to import and export the Excel 2007+ file in ASP.NET Core simply. There are many other usages you can do with EPPlus, such as Cell styling, Charts. etc. We can visit its Github page for more information.