10000+ результатов для ‘question words future simple’
Let’s discuss!
Случайное колесо
Daily Routines
Future simple
past simple
present simple
question
Future Simple
Привести в порядок
Начальная школа / начальная
Future Simple
EF beginner 7A (b)
Привести в порядок
Beginner
5-й класс
6 класс
7-й класс
Начальная школа / начальная
Средняя школа
Среднее образование
English
EF
English File
Present Simple
Question words
Answers-Questions
Сопоставить
Дошкольник
1-й класс
English
present simple
question
Spotlight 1
Will or not?
Случайные карты
7-й класс
Средняя школа
Среднее образование
Activity
English
Future simple
Will
Simple Passives
Пропущенное слово
Средняя школа
English
Future Simple passive
Past Simple Passive
Present Simple Passive
Tenses Quiz
Викторина
future
past simple
present continuous
present simple
EF beginner 7A (a)
Викторина
Beginner
5-й класс
6 класс
7-й класс
8 класс
Начальная школа / начальная
Средняя школа
Среднее образование
English
A1
EF
English File
Question words
Question words
Пропущенное слово
A2
4-й класс
question words
Верещагина 4 класс
GUESS WHO mystery cards
Случайные карты
adjectives
Chinese
English
汉语
appearance
Question words
Вопросительные слова
Will / Won’t
Случайное колесо
7-13
Fly High 3
Future Simple
Spotlight 4
How many days ….?
Привести в порядок
make up questions
question words
SM1
Super minds starter
-
Главная
- /
-
База знаний
- /
-
Времена в английском
Как строить вопросы в будущем простом времени
15756 21.01.2022 (обновлена 01.04.2022)
Вопросительные предложения Future Simple образуются с использованием вспомогательного глагола will и V1
Поговорим о каждом типе вопроса в отдельности ⬇️
Общие вопросы в Future Simple
Запомните схему образования:
Will + подлежащее + V1?
| Will it rain all day? | Дождь будет идти весь день? | |
| Will she stay at home? | Она останется дома? |
Специальные вопросы в Future Simple
Wh–questions начинаются с вопросительных слов, после которых ставится вспомогательный глагол. Формула образования:
Вопросительное слово + will + подлежащее + V1?
| When will it rain all day? | Когда пойдет дождь? | |
| What will she do? | Что она будет делать? |
Вопрос к подлежащему в Future Simple
Этот тип вопроса строится как утвердительное предложение, но в роли подлежащего выступают слова Who / What. Запомните схему:
Who / What + will + V1?
| Who will win? | Кто победит? | |
| What will happen? | Что случится? |
Теперь вы умеете строить вопросительные предложения во времени Future Simple 🎉🎉🎉 Читать дальше:
Слова-маркеры Future Simple — простого будущего времени в английском
Распознать Future Simple помогут слова, которые относят действие к будущему и обычно стоят в конце предложения: tomorrow, next week / month / year, soon, later, in the future, etc.
Прогресс урока
Вопросительные предложения Future Simple
Прогресс страницы 0%, попробуйте завершить ее, прежде чем идти дальше!
Wh-вопросы (Wh-Qusestions) в Future Simple
Как правило, Future Simple вопросы строятся вместе с такими вопросительными наречиями, как What, When, Why, и другими – ниже даются примеры с самыми часто используемыми. Изучите схему построения:
Wh— + will + подлежащее (he/I/you…) + базовый глагол (eat/work/play…)
Wh- слова – синий цвет;
Глагол Will – красный цвет;
Подлежащее – зелёный цвет;
Базовый глагол – коричневый цвет.
Примеры вопросов |
Возможные ответы |
| What will they eat today? | They will eat pasta all day long. |
| Что они будут сегодня есть? | Они будут весь день есть макароны. |
| Who/whom will we drive to the airport? | We will drive my father’s sister. |
| Кого мы повезём в аэропорт? | Мы повезём сестру моего отца. |
| Where will we meet? | We will meet in the park. |
| Где мы встретимся? | Мы встретимся в парке. |
| When will she be back? | She will be back tomorrow morning. |
| Когда она вернётся? | Она возвратится завтра утром. |
| Why will they be angry with me? | Because they will clean your room for you. |
| Почему они будут злиться на меня? | Потому что они будут убирать за тебя твою комнату. |
| How will you get (your) driver’s license? | I will pass driver’s license tests. |
| Как ты получишь водительские права? | Я сдам тесты(экзамены) на водительские права. |
Видеоурок на тему специальных (Wh-) вопросов
Ваше имя:
*
Ваш Email:
*
Подробности (URL не обязательно):
*
Содержание: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
Future Simple
Вопросы
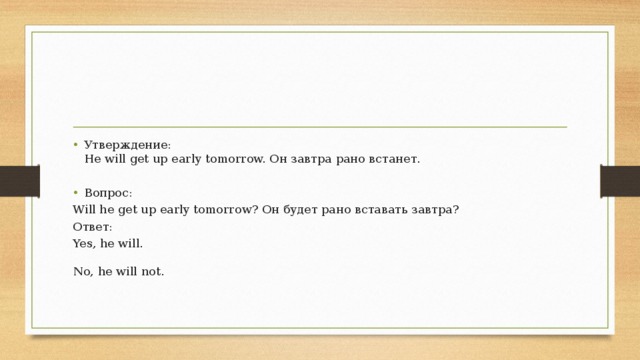
Вопросительные предложения в Future Simple
Will + действующее лицо + действие (глагол в начальной форме)?
- Утверждение: He will get up early tomorrow. Он завтра рано встанет.
- Вопрос:
Will he get up early tomorrow? Он будет рано вставать завтра?
Ответ:
Yes, he will. No, he will not.
Составь вопросительные предложения:
- They will sail this yacht next summer.
- He will show you our city.
- Nora will plant flowers tomorrow.
- They will organize the meeting next Friday.
- You’ll spend next month in the language camp.
- Monica and Sam will clean the flat tomorrow.
- She will put on her warm sweater.
- He will buy some fruit.
- People will travel to other planets in future.
- It will rain tomorrow.
Специальные вопросы в Future Simple
Специальные вопросы задаются при помощи следующих вопросительных слов:
- What — что
- Where — где
- Which — какой
- Why — почему
- When — когда
- Who — кто
- How — как
- Вопросительное слово + will + действующее лицо + действие (глагол в начальной форме)?
- What will they do tomorrow? Что они будут делать завтра?
- When will she buy a new phone? Когда она купит новый телефон?
- How long will you do your homework? Как долго ты будешь делать свою домашнюю работу?
- Where will he live next year? Где он будет жить в следующем году?
Составьте вопрос к выделенным словосочетаниям.
- The postman will deliver fresh newspapers in the morning .
- We will have a picnic in the park .
- Her brother will translate this article next week.
- Alex will return home at seven o’clock .
- You will read my report very attentively .
- My friend will soon send me an e-mail letter.
- Her cousin will give you some discs in two days .
- Jane will learn this poem .
- My mother will feed the fish in the evening.
- They will drive to the country next Sunday.
- В чем разница между will и to be going to? В английском языке есть конструкция to be going to, которая переводится как «собираться что-либо сделать». Конструкцию to be going to мы используем, когда решение взвешенно и обдумано заранее. То есть у вас есть предварительный план сделать что-то.
Составь 5 вопросов о будущем для своего одноклассника.
The Future Simple is probably the simplest tense of all tenses in the English language.
If you are learning the Future Simple after the Present Simple and the Past Simple, it will be easy for you to understand the Future Simple.
What is Future Simple tense?
The Future Simple is a very important tense. We use the Future Simple to say what will or may happen in the future.
It doesn’t matter what kind of future we’re talking about. We can use the Future Simple when we are talking about something that will happen in a second or 1000 years from the moment of speaking.
We use the Future Simple to express:
- Something that will or will not happen.
- Something that we will or will not do.
- Promises.
- Events in the future will happen because we cannot influence them.
- Warnings and threats.
Take a look at these examples:
The game will be over soon.
Dad will be at work tomorrow.
John will buy a new car in a year.
I will call you back in five minutes.
They will not go to the theater.

How to form sentences
I said that The Future Simple is one of the simplest tenses for a reason. Because the Future Simple is very simple to form.
To form the Future Simple, you do not need to add or change any endings of the main verb.
All sentences in the Future Simple are built in the most usual way. Except for the fact that we need to add the auxiliary verb to the sentence, which indicates that you are talking about the future. This is the verb will.
We use will the same way regardless of who is the subject. Regardless of what type of sentence we form: affirmative (positive), interrogative (question), or negative. We always use will in all types of sentences.
How to form Affirmative (Positive) Sentences in Future Simple
To form an affirmative (positive) sentence, we put the auxiliary verb will after the subject. Then we add the main verb in the base form without the to.
Subject (I, you, John, Dog, Friends) + will + Main verb (love, watch, jump) + the rest of the sentence.
I will take your car!
John will visit Sarah.
We will go Home.
How to form Negative Sentences in Future Simple
To form a negative sentence, we add the negative not after the auxiliary verb will.
Will not.
We use will not after the subject and before the main verb.
Subject (I, You, John, Dog, Friends) + will not + main verb (love, watch, jump) + the rest of the sentence.
John will not visit Jennifer.
Daddy will not buy a new car.
We will not go to school tomorrow.
The dog will not catch up with this cat.
How to form Interrogative (Question) Sentences in Future Simple
We form an interrogative (question) sentence in the same way as the affirmative (positive). Only we put the auxiliary verb will before the subject at the beginning of the sentence.
will + Subject (I, You, John, Dog, Friends) + main verb (love, watch, jump) + the rest of the sentence.
Will you come to visit me?
Will we win this game?
Will we like our new teacher?
Will Jessica marry John?
Wh-Question in Future Simple
Special or Wh-Questions are questions that we use to find out more information.
We can ask:
Will John visit Max?
By asking this question, we can find out whether John will visit Max or not. This is a question that can be answered with simple YES or NO.
But what if we want to know when exactly John will visit Max? Or why will John visit Max? To find out this additional information, we need question words or even whole phrases.
When will John visit Max?
Who will John visit Max with?
Question words help us get more information. Here are the most popular Question words:
- how
- why
- when
- who
- what
- where
- which
Wh-Questions in the Future Simple are formed in the same way as General or Yes/No Questions. Only at the beginning of the question, we put an additional, question word or phrase. After that we put the auxiliary verb will, then the subject, then the main verb in the base form without the particle to. Then we can add the rest of the sentence.
Question word or phrase (who, what, where) + will + Subject (I, You, John, Dog, Friends) + main verb (love, watch, jump) + the rest of the sentence.
When will you see your friend?
Where will you go first?
Where will it be available?
How to Answer Questions
There are two main ways you can answer questions in English:
- Short positive/negative answer
- Full positive/negative answer
We form a Short Positive Answer using this pattern:
Yes + Subject + Will.
Will you find a new job?
Yes, I will.Will you meet Jessica at the train station?
Yes, I will.
Will in the answer means the same verb that was the main verb in the question.
Will you meet Jessica at the train station?
Yes, I will. (Yes I will meet)
We form a short negative answer in the same way, only at the beginning of the sentence we put No and we add the negative not to the auxiliary verb will. Will + not + Will not:
No + Subject + Will not.
Will you meet Jessica at the train station?
No, I will not (No, I will not meet).
Now let’s talk about full answers.
To form a full affirmative (positive) answer, we turn the question into a Positive sentence. We also put Yes at the beginning of the sentence.
Yes + Subject + Will + Main verb + Rest of the sentence
Will you help me?
Yes, I will help you.
To form a full negative answer, we use the word No instead of Yes. We add the negative not after will.
No + Subject + Will not + Main verb + Rest of the sentence.
Will you help me?
No, I will not help you.
What is the abbreviation (short form) for will and will not?
In the Future Simple we often contract the auxiliary will.
| Full | Short |
|---|---|
| I will | I’ll |
| He will | He’ll |
| She will | She’ll |
| It will | It’ll |
| We will | We’ll |
| They will | They’ll |
| You will | You’ll |
In the affirmative (positive), the will is contracted to two letters -ll which are added to the subject:
- I’ll – I will
- He’ll – He will
- She’ll – She will
- It’ll – It will
- We’ll – We will
- They’ll – They will
- You’ll – You will
I’ll help you tomorrow = I will help you tomorrow
The contraction for the negative form will.
| Full | Short |
|---|---|
| I will not | I won’t |
| He will not | He won’t |
| She will not | She won’t |
| It will not | It won’t |
| We will not | We won’t |
| They will not | They won’t |
| You will not | You won’t |
We contract the negative will in a slightly unusual way. The letter “o” appears in this abbreviation. Will not turns into Won’t. It looks like this:
- I won’t – I will not
- He won’t – He will not
- She won’t – She will not
- It won’t – It will not
- We won’t – We will not
- They won’t – They will not
- You won’t – You will not
I won’t do this = I will not do this.
When We Use the Future Simple
- We use the Future Simple when we talk about a single event that will or will not happen in the future. Or when we indicate the exact time when something will happen.
I will visit him soon.
She will talk to John tomorrow.
We will go to Grandma’s next weekend.
I will call you at lunchtime.
- We use the Future Simple when we talk about some kind of spontaneous decision.
You know what… I will take your car!
I will not sleep, I want to play more!
- When we talk about some action that will occur and will be repeated in the future.
Next month Jessica and I will go to the theater three times.
John will visit his grandmother two times next year.
- The Future Simple is good for making a promise to someone to do something. Or when we threaten someone.
I swear I will study well this year.
Nothing will stop me! I will catch you and send you to jail!
We also use the Future Simple when we offer to do something or help someone. In this case, we change will to shall. Such sentences look like a question.
KEEP IN MIND: We use shall only with the pronouns I or We.
Shall we clean the room?

- We use the Future Simple when we predict some events or actions and this prediction is based on the personal opinion of the speaker.
I think we will win this game.
He thinks a new teacher will be better than Mr. Gordon.
I’m afraid you will fail.
I am afraid this building will collapse soon.

You can also read the full article When we use Future Simple: 15 use cases.
To be in Future Simple
The verb to be is easy to use in the Future Simple.
Why?
For example, in the Present Simple or the Past Simple, the verb to be has different forms. In the Future Simple, the verb to be has only one form: WILL BE. To be in Future Simple forms questions, negations, or affirmations with the help of the auxiliary verb will.
Isn’t it easy to remember?
How to form Affirmative (Positive) Sentences with to be
The verb to be in Present Simple looks like will be. We use will be regardless of who is the subject.
Look at the affirmative (positive) sentence in the Future Simple with the verb love.
I will love you.
Look at the word order we used in the sentence.
We use exactly the same word order with the verb to be. Only instead of the main verb we use be.
Subject + will + be + rest of the sentence.
I will be there at six o’clock in the evening.
See how easy it is?
How to form Interrogative (question) sentences with to be
To ask a question, we use the same formula that we use with any other verbs in the Future Simple. Only instead of the main verb we use be.
will + subject + be + rest of the sentence.
Will you be at work tomorrow morning?
How to form Negative Sentences in with to be
A negative sentence is formed in the same way as a regular negative sentence with any other verb in Future Simple.
Subject + will not + bе + rest of the sentence
I will not be home for dinner.
Do we use Shall in Future Simple?
Shall is another auxiliary (and modal) verb in English. Sometimes we use shall instead of will but only with the pronouns I and We.
Shall cannot be used with You, He, It …
- I shall (Can be used instead of I will)
- He will (We cannot say
He shall) - She Will (We cannot say
She shall) - It will (We cannot say
It shall) - We shall (Can be used instead of We will)
- They will (We cannot say
They shall) - You will (We cannot say
You shall)
Remember, we rarely use shall in modern English. Most often it can be found in interrogative (question) sentences when someone offers to help someone.
Of course, you need to know how to properly use shall in the Future Simple. Because you may find this verb in books, business correspondence, etc.
So remember, shall can be used in positive, question, and negative sentences in the Future Simple just like will. But only with pronouns I and We.
Affirmative (positive) sentences with shall:
I shall open this box.
We shall help you, my friend!
Similarly, in a Positive sentence, we can put the verb will instead of shall:
I will open this box.
We will help you, my friend!
You shall not pass!

Question sentences with shall.
Shall I open this box?
Shall we help you, my friend?
We can put will instead of shall, but it can change the meaning of the sentence from what we were trying to say.
Will I open this box?
Will we help you, my friend?
In those examples, the sentences with will do not sound anymore as an offer to help. With will instead of shall it sounds more like questions.
Negative sentences with shall.
I shall not open this box.
We shall not help you, my friend!
Similarly, in Negative sentences, you can put the verb will instead of shall:
I will not open this box.
We will not help you, my friend!
How to use To be going to
What is to be going to?
To be going to is a very interesting and useful phrase in English. You will come across this phrase very often.
To be going to is another way of saying that something will happen in the future.
To be going to is used to talk about:
- Your or someone else’s plans for the future.
- Events likely to occur in the future.
I am going to tell you the whole truth about the English language.
We are going to paint the house green.
How to form sentences with To be going to in Present Simple
If you look closely at To be going to, you will see that the first part is the verb to be.
To form this phrase, we just need to change the first part in accordance with our subject. Let’s remember how the verb to be changes in the Present Simple:
- I am
- He is
- She is
- It is
- We are
- They are
- You are
Together with going to, the complete construction looks like this:
- I am going to
- He is going to
- She is going to
- It is going to
- We are going to
- They are going to
- You are going to
Questions are also formed according to the rules of the verb to be in the Present Simple:
Am I going to?
Is she going to?
Are they going to?
Are you going to?
Negative sentences are also formed according to the rules of the verb to be in the Present Simple:
I am not going to…
She is not going to…
They are not going to…
You are not going to…
The short form is also formed according to the same rules as we contract the verb to be in the Present Simple:
- They‘re going to or They aren’t going to
- He‘s going to or He isn’t going to
- I‘m not going to
- You‘re not going to or You aren’t going to
What is the difference between Will vs To be going to
Let’s take a look at the difference between will and to be going to.
Take a look at two examples:
John is going to become a doctor.
John will be a doctor.

In one sentence we used will in the other to be going to.
These two methods are very similar and can often replace each other. In these cases, we can use both sentences to say about John’s future.
But will and be going to do not always mean the same thing.
We use to be going to to say about a thought-out decision. Not just a spontaneous decision, but a deliberate one.
Imagine John needs a new car. John made enough money. John has chosen the model of the car he wants to buy. John plans to buy a car next week. This is not a spontaneous decision. This is a deliberate decision. Therefore, John can say this using to be going to:
I‘m going to buy a new car.
Everyone who hears John understands that this decision is deliberate. And John seriously decided to buy a new car.
We often use the Future Simple to talk about plans that are not accurate. That is, in our example with John, John had not thought about buying a car before. John didn’t choose the model of the car. But suddenly he got such an idea. John can say this using the Future Simple:
I will buy a new car.
The Future Simple is well suited for those decisions that were made spontaneously right at the time of the conversation. For example:
John is hanging out with his friends. The friends tell John that John has an old car, maybe he needs a new car? John makes a spontaneous decision:
I will buy a new car.
If he says about this decision using to be going to, it would no longer sound like a spontaneous decision, but like his plans for which he has been ready for some time.
We use To be going to when a decision is planned.
We use Will when the decision is spontaneous.
How to use will not as a refusal
Now let’s talk about one nuance of will, or rather its negative form will not.
Will not (won’t) often does NOT mean that someone will not do something in the future. Will not often means that someone refuses to do something in the future.
John won’t help mom.
This example may mean that John does not want to, he refuses to help his mother.
If you doubt that someone can misunderstand you, then it is better to use to be going to.
John is not going to help mom.
One more difference between will and to be going to is that:
We often use to be going to when we talk about plans for the near future.
We often use Will when we talk about plans for the distant future.
Markers of Future Simple
In the Future Simple, we often use special words that indicate this tense. We call such words markers. The Future Simple markers indicate some time in the future. This time can be specified exactly, such as “tomorrow at 6 hours” or approximately as “soon”.
- tonight
- next hour
- next day
- next week
- next month
- next year
- soon
- later
- in ten days
- in 2035
- in a month
- in two months
- in two years
- as soon as
- tomorrow

Examples of Future Simple
Take a look at the sentences in which we use the Future Simple. Think about the rules used in these sentences.
Dad will go to work tomorrow.
I’ll buy a car.
I’m going to get married next month!
We will study well.
John and Jessica will go to the theater three times next month.
Will John go to Grandma’s next week?
How many times will you call him?
They will write you a letter shortly.
The house will soon fall apart.
Max will visit his friend.