Improve Article
Save Article
Like Article
Improve Article
Save Article
Like Article
Prerequisites: docx
Word documents contain formatted text wrapped within three object levels. Lowest level- run objects, middle level- paragraph objects and highest level- document object. So, we cannot work with these documents using normal text editors. But, we can manipulate these word documents in python using the python-docx module.
Python docx module allows user to manipulate docs by either manipulating the existing one or creating a new empty document and manipulating it. It is a powerful tool as it helps you to manipulate the document to a very large extend. You can also add and manipulate tables using this module.
To add a table we will use add_table() method as it will add a table in the word document.
Syntax:
doc.add_table(rows = None, cols = None)
Parameters:
- rows: Add n number of rows in the table.
- cols: Add n number of cols in the table.
First, we will save all the data in a list then we will create a table object with values of rows = 1 and cols = 2. Then we will add the headings in the table. After that, we will use .add_row() method to add a row then we will add the data in it.
Table can only take a string as an input in its cells, so we have to convert the data into string if it is not.
Installation
Pip command to install this module is:
pip install python-docx
Approach
- Import module
- Declare docx object
- Add table data as a list
- Create table using above function
- Save to document
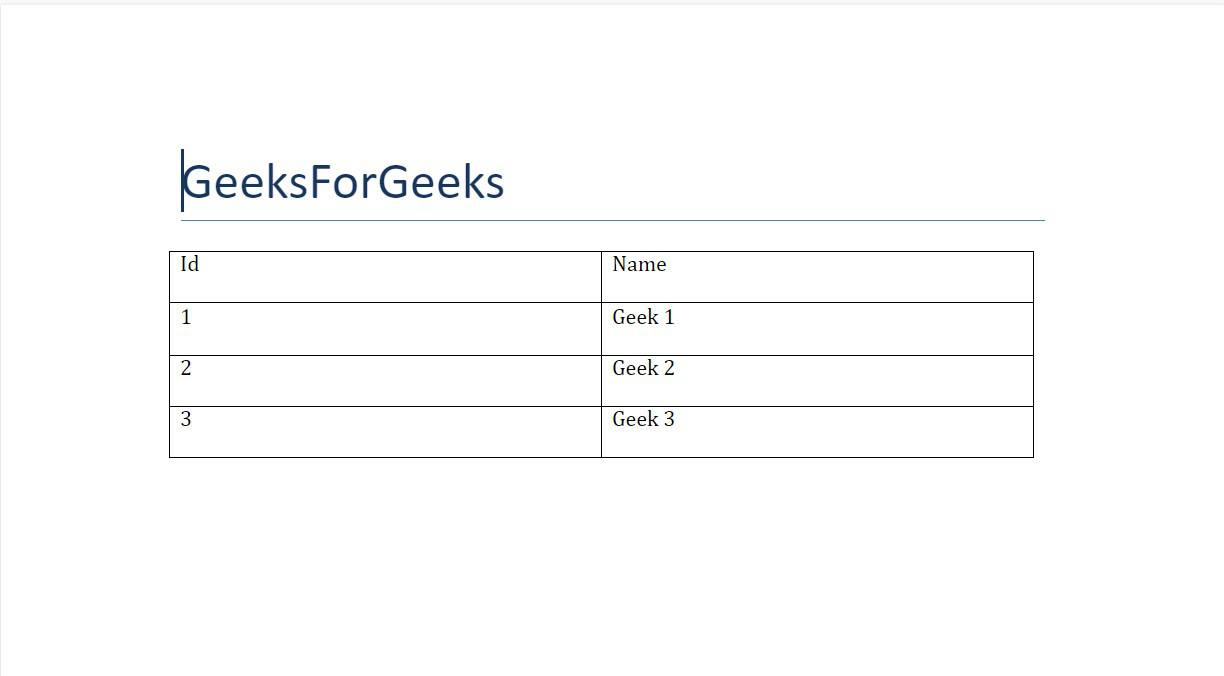
Example 1: Adding a table in a Word document.
Python3
import docx
doc = docx.Document()
doc.add_heading('GeeksForGeeks', 0)
data = (
(1, 'Geek 1'),
(2, 'Geek 2'),
(3, 'Geek 3')
)
table = doc.add_table(rows=1, cols=2)
row = table.rows[0].cells
row[0].text = 'Id'
row[1].text = 'Name'
for id, name in data:
row = table.add_row().cells
row[0].text = str(id)
row[1].text = name
doc.save('gfg.docx')
Output:
The table so obtained is a simple table, but docx supports mechanism to style it. To style a table we use style method to select a style.
Syntax:
table.style = String style_name
Parameter:
- String style_name: It is the name of the style from the list mentioned below.
Approach
- Import module
- Create data to be inserted as list
- Create table
- Style it as required
- Save to document
Example 2: Adding a table with style in a word document.
Python3
import docx
doc = docx.Document()
doc.add_heading('GeeksForGeeks', 0)
data = (
(1, 'Geek 1'),
(2, 'Geek 2'),
(3, 'Geek 3')
)
table = doc.add_table(rows=1, cols=2)
row = table.rows[0].cells
row[0].text = 'Id'
row[1].text = 'Name'
for id, name in data:
row = table.add_row().cells
row[0].text = str(id)
row[1].text = name
table.style = 'Colorful List'
doc.save('gfg.docx')
Output:
Like Article
Save Article
Python-docx provides a lot of features for creating and modifying word documents. In this tutorial, we will implement table feature and use table rows and columns to add data to tables. For API documentation of tables in python-docx, check documentation on this url.
https://python-docx.readthedocs.io/en/latest/api/table.html
Tables are constructed using add_table() method in python-docx document. We can provide following options while creating a table.
- rows: Number of rows for table
- cols: Number of columns for table
- style: (default
None) Specify a style, style may be a paragraph style object or paragraph style name.
For complete list of table styles, view on python-docx.
Create Table
Lets Create a table with 2 rows and 2 colums using add_table method. Table style can be defined using style argument which in this case is Table Grid.
from docx import Document
# create document
doc = Document()
# add grid table
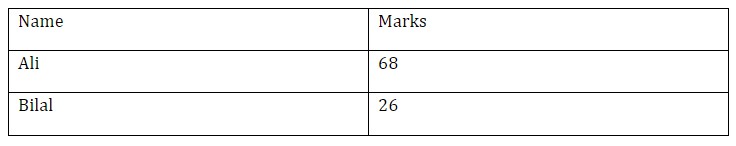
table = doc.add_table(rows=2, cols=2, style="Table Grid")Now table rows and columns can be accessed using table.rows or table.columns attribute respectively and then we can access each cell in that row using row.cells. Lets add headings to 1st row.
# access first row's cells
heading_row = table.rows[0].cells
# add headings
heading_row[0].text = "Name"
heading_row[1].text = "Marks"Same way we can add other info to rows
# access second row's cells
data_row = table.rows[1].cells
# add headings
data_row[0].text = "Ali"
data_row[1].text = "68"Add rows
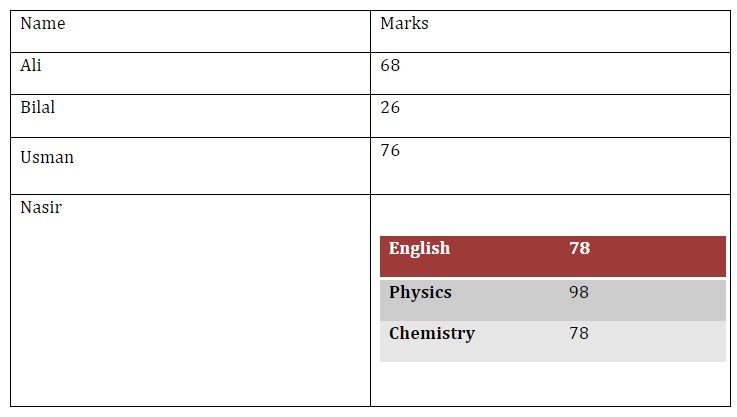
We can also add rows after table creation using add_row method which adds a row in table and we can add data to that row.
# add new row to table
data_row = table.add_row().cells
# add headings
data_row[0].text = "Bilal"
data_row[1].text = "26"It creates a table with 3 rows and 2 columns with information.
Cell Margin
We can use OpenXML to modify and set any style using python-docx. Here we can specify margin to any cell where we can add or completely remove a cell margin.
from docx.oxml.shared import OxmlElement
from docx.oxml.ns import qn
def set_cell_margins(cell, **kwargs):
"""
cell: actual cell instance you want to modify
usage:
set_cell_margins(cell, top=50, start=50, bottom=50, end=50)
provided values are in twentieths of a point (1/1440 of an inch).
read more here: http://officeopenxml.com/WPtableCellMargins.php
"""
tc = cell._tc
tcPr = tc.get_or_add_tcPr()
tcMar = OxmlElement('w:tcMar')
for m in ["top", "start", "bottom", "end"]:
if m in kwargs:
node = OxmlElement("w:{}".format(m))
node.set(qn('w:w'), str(kwargs.get(m)))
node.set(qn('w:type'), 'dxa')
tcMar.append(node)
tcPr.append(tcMar)From Stackoverflow: https://stackoverflow.com/a/55177526/6663675
Now we can add margin in any cell to increase space.
# access second row's cells
data_row = table.add_row().cells
set_cell_margins(data_row[0], top=100, start=100, bottom=100, end=50)
# add headings
data_row[0].text = "Usman"
data_row[1].text = "76"Nested Table
We can also created nested tables where we can add a table to a cell. For example, if for 1 person, we want to add marks for multiple subjects. We can add a table to parent table cells.
marks = {"English" : 78, "Physics" : 98, "Chemistry" : 78}
# add new row
data_row = table.add_row().cells
# name of person
data_row[0].text = "Nasir"
# We add a table to 2nd cell with rows equal to our entries (3)
marks_table = data_row[1].add_table(rows=len(marks), cols=2)Now we can iterate over values and add to table.
for i, row in enumerate(marks.items()): # iterate over 3 values
marks_table.rows[i].cells[0].text = row[0] # sub table first cell
marks_table.rows[i].cells[1].text = str(row[1]) # second cellWe can also show images inside tables.
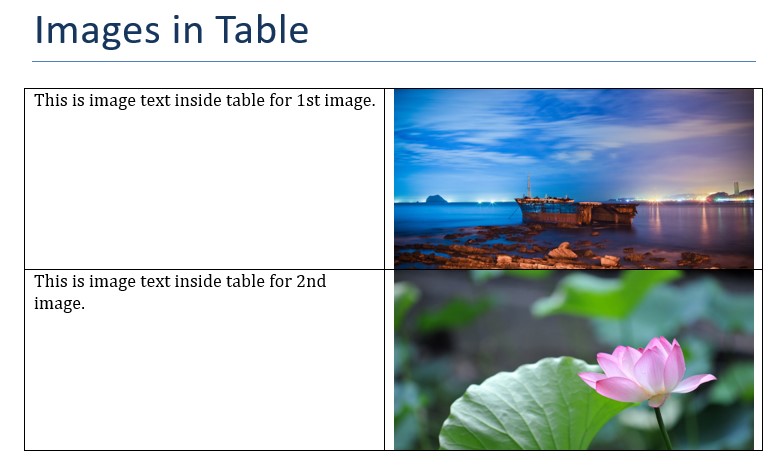
Table Images
In table paragraphs, we can add images to table. Here is a simple example to add two images to table. Here we get paragraph for a cell where we want to display image and then use add_picture method to add an image from path. and we also specify height and width in Inches.
from docx.shared import Inches, Cm
doc = Document() # create doc
doc.add_heading('Images in Table', 0) # add heading
# create table with two rows and columns
table = doc.add_table(rows=2, cols=2, style="Table Grid")
# add first image with text
table.rows[0].cells[0].text = 'This is image text inside table for 1st image.'
# add image to table
paragraph = table.rows[0].cells[1].paragraphs[0]
run = paragraph.add_run()
run.add_picture('image-1.jpg', width=Inches(3), height=Inches(1.5))
table.rows[1].cells[0].text = 'This is image text inside table for 2nd image.'
# add image to table
paragraph = table.rows[1].cells[1].paragraphs[0]
run = paragraph.add_run()
run.add_picture('image-2.jpg', width=Inches(3), height=Inches(1.5))
# save to file
doc.save("images-table.docx")So it creates a table with text in 1st column and images in 2nd column for each row.
View can add data from csv file, text file or any other file to tables in docx. So for more info view python docx documentation.
https://python-docx.readthedocs.io/en/latest/api/table.html
С помощью модуля python-docx можно создавать и изменять документы MS Word с расширением .docx. Чтобы установить этот модуль, выполняем команду
> pip install python-docx
При установке модуля надо вводить python-docx, а не docx (это другой модуль). В то же время при импортировании модуля python-docx следует использовать import docx, а не import python-docx.
Чтение документов MS Word
Файлы с расширением .docx обладают развитой внутренней структурой. В модуле python-docx эта структура представлена тремя различными типами данных. На самом верхнем уровне объект Document представляет собой весь документ. Объект Document содержит список объектов Paragraph, которые представляют собой абзацы документа. Каждый из абзацев содержит список, состоящий из одного или нескольких объектов Run, представляющих собой фрагменты текста с различными стилями форматирования.
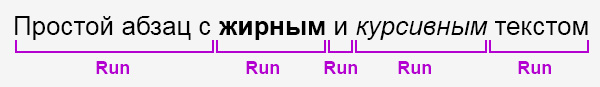
import docx doc = docx.Document('example.docx') # количество абзацев в документе print(len(doc.paragraphs)) # текст первого абзаца в документе print(doc.paragraphs[0].text) # текст второго абзаца в документе print(doc.paragraphs[1].text) # текст первого Run второго абзаца print(doc.paragraphs[1].runs[0].text)
6 Название документа Простой абзац с жирным и курсивным текстом Простой абзац с
Получаем весь текст из документа:
text = [] for paragraph in doc.paragraphs: text.append(paragraph.text) print('n'.join(text))
Название документа Простой абзац с жирным и курсивным текстом Заголовок, уровень 1 Выделенная цитата Первый элемент маркированного списка Первый элемент нумерованного списка
Стилевое оформление
В документах MS Word применяются два типа стилей: стили абзацев, которые могут применяться к объектам Paragraph, стили символов, которые могут применяться к объектам Run. Как объектам Paragraph, так и объектам Run можно назначать стили, присваивая их атрибутам style значение в виде строки. Этой строкой должно быть имя стиля. Если для стиля задано значение None, то у объекта Paragraph или Run не будет связанного с ним стиля.
Стили абзацев
NormalBody TextBody Text 2Body Text 3CaptionHeading 1Heading 2Heading 3Heading 4Heading 5Heading 6Heading 7Heading 8Heading 9Intense QuoteListList 2List 3List BulletList Bullet 2List Bullet 3List ContinueList Continue 2List Continue 3List NumberList Number 2List Number 3List ParagraphMacro TextNo SpacingQuoteSubtitleTOCHeadingTitle
Стили символов
EmphasisStrongBook TitleDefault Paragraph FontIntense EmphasisSubtle EmphasisIntense ReferenceSubtle Reference
paragraph.style = 'Quote' run.style = 'Book Title'
Атрибуты объекта Run
Отдельные фрагменты текста, представленные объектами Run, могут подвергаться дополнительному форматированию с помощью атрибутов. Для каждого из этих атрибутов может быть задано одно из трех значений: True (атрибут активизирован), False (атрибут отключен) и None (применяется стиль, установленный для данного объекта Run).
bold— Полужирное начертаниеunderline— Подчеркнутый текстitalic— Курсивное начертаниеstrike— Зачеркнутый текст
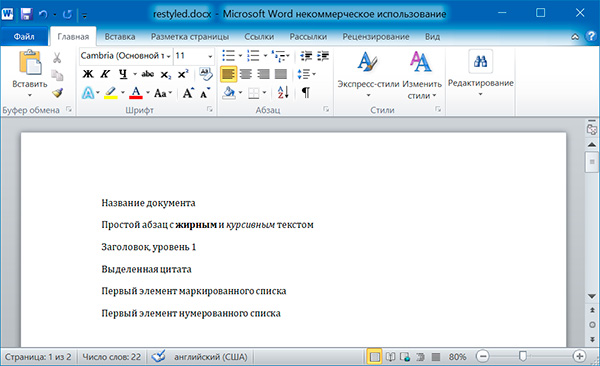
Изменим стили для всех параграфов нашего документа:
import docx doc = docx.Document('example.docx') # изменяем стили для всех параграфов for paragraph in doc.paragraphs: paragraph.style = 'Normal' doc.save('restyled.docx')
А теперь восстановим все как было:
import docx os.chdir('C:\example') doc1 = docx.Document('example.docx') doc2 = docx.Document('restyled.docx') # получаем из первого документа стили всех абзацев styles = [] for paragraph in doc1.paragraphs: styles.append(paragraph.style) # применяем стили ко всем абзацам второго документа for i in range(len(doc2.paragraphs)): doc2.paragraphs[i].style = styles[i] doc2.save('restored.docx')
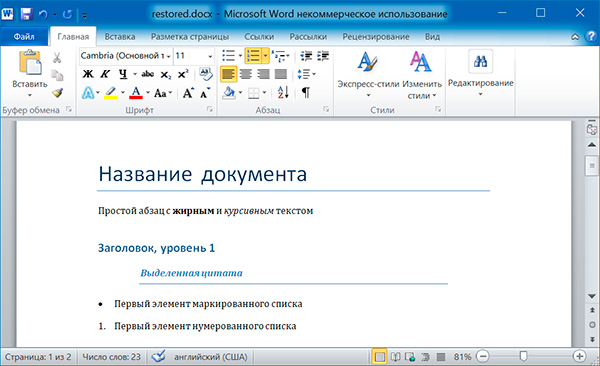
Изменим форматирвание объектов Run второго абзаца:
import docx doc = docx.Document('example.docx') # добавляем стиль символов для runs[0] doc.paragraphs[1].runs[0].style = 'Intense Emphasis' # добавляем подчеркивание для runs[4] doc.paragraphs[1].runs[4].underline = True doc.save('restyled2.docx')
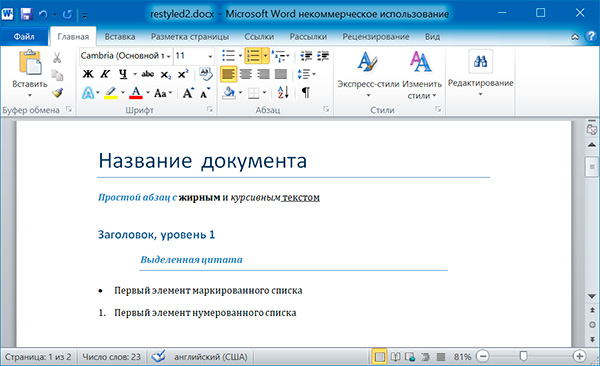
Запись докуменов MS Word
Добавление абзацев осуществляется вызовом метода add_paragraph() объекта Document. Для добавления текста в конец существующего абзаца, надо вызвать метод add_run() объекта Paragraph:
import docx doc = docx.Document() # добавляем первый параграф doc.add_paragraph('Здравствуй, мир!') # добавляем еще два параграфа par1 = doc.add_paragraph('Это второй абзац.') par2 = doc.add_paragraph('Это третий абзац.') # добавляем текст во второй параграф par1.add_run(' Этот текст был добавлен во второй абзац.') # добавляем текст в третий параграф par2.add_run(' Добавляем текст в третий абзац.').bold = True doc.save('helloworld.docx')
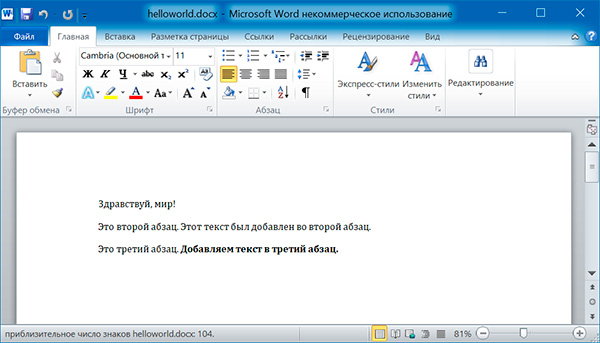
Оба метода, add_paragraph() и add_run() принимают необязательный второй аргумент, содержащий строку стиля, например:
doc.add_paragraph('Здравствуй, мир!', 'Title')
Добавление заголовков
Вызов метода add_heading() приводит к добавлению абзаца, отформатированного в соответствии с одним из возможных стилей заголовков:
doc.add_heading('Заголовок 0', 0) doc.add_heading('Заголовок 1', 1) doc.add_heading('Заголовок 2', 2) doc.add_heading('Заголовок 3', 3) doc.add_heading('Заголовок 4', 4)
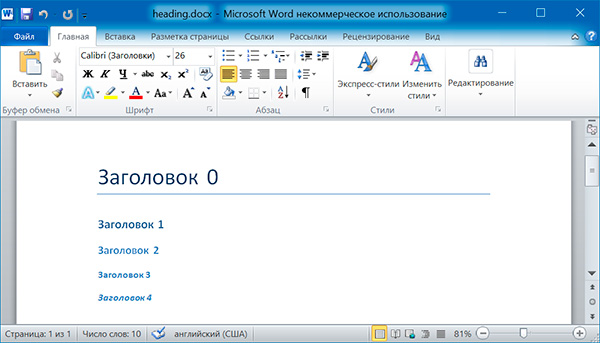
Аргументами метода add_heading() являются строка текста и целое число от 0 до 4. Значению 0 соответствует стиль заголовка Title.
Добавление разрывов строк и страниц
Чтобы добавить разрыв строки (а не добавлять новый абзац), нужно вызвать метод add_break() объекта Run. Если же требуется добавить разрыв страницы, то методу add_break() надо передать значение docx.enum.text.WD_BREAK.PAGE в качестве единственного аргумента:
import docx doc = docx.Document() doc.add_paragraph('Это первая страница') doc.paragraphs[0].runs[0].add_break(docx.enum.text.WD_BREAK.PAGE) doc.add_paragraph('Это вторая страница') doc.save('pages.docx')
Добавление изображений
Метод add_picture() объекта Document позволяет добавлять изображения в конце документа. Например, добавим в конец документа изображение kitten.jpg шириной 10 сантиметров:
import docx doc = docx.Document() doc.add_paragraph('Это первый абзац') doc.add_picture('kitten.jpg', width = docx.shared.Cm(10)) doc.save('picture.docx')
Именованные аргументы width и height задают ширину и высоту изображения. Если их опустить, то значения этих аргументов будут определяться размерами самого изображения.
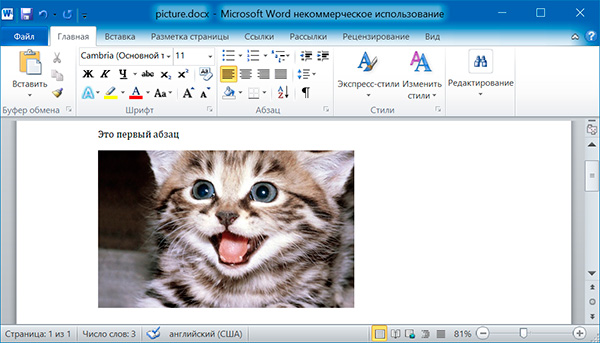
Добавление таблицы
import docx doc = docx.Document() # добавляем таблицу 3x3 table = doc.add_table(rows = 3, cols = 3) # применяем стиль для таблицы table.style = 'Table Grid' # заполняем таблицу данными for row in range(3): for col in range(3): # получаем ячейку таблицы cell = table.cell(row, col) # записываем в ячейку данные cell.text = str(row + 1) + str(col + 1) doc.save('table.docx')
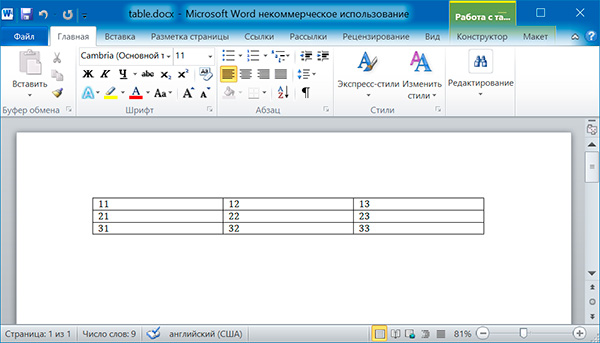
import docx doc = docx.Document('table.docx') # получаем первую таблицу в документе table = doc.tables[0] # читаем данные из таблицы for row in table.rows: string = '' for cell in row.cells: string = string + cell.text + ' ' print(string)
11 12 13 21 22 23 31 32 33
Дополнительно
- Документация python-docx
Поиск:
MS • Python • Web-разработка • Word • Модуль
Каталог оборудования
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit, sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua.
Производители
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit, sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua.
Функциональные группы
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit, sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua.
Creating Word documents using the Python Docx package is very powerful and allows us to present our data and findings in an automated way.
Many times, we are working with data and want to output this data into a table.
Outputting data to a table in a Word Document in Python is not difficult, but making this process efficient and fast is the key to making our work as good as it can be.
Creating a Table in a Word Document using Python Docx Efficiently
Creating a table and filling the table with data in a Word document using Python Docx is easy.
To create a table, all we need to do is:
import docx
doc = docx.Document()
table = doc.add_table(rows=ROWS, cols=COLS)
doc.save("output_file_path.docx")When writing small tables to word, we can loop through the table and there will not be any performance problems.
Let’s say we are reading some data from an XLSX file and we want to output it in a table in a Word document.
If the data is small, we can easily output the table without problems.
import docx
import pandas as pd
data = pd.read_excel("some_data.xlsx")
doc = docx.Document()
table = doc.add_table(rows=data.shape[0], cols=data.shape[1])
for i in range(df.shape[0]):
for j in range(df.shape[1]):
table.cell(i,j).text = str(df.values[i,j])
doc.save("output_file_path.docx")But, the problem is that when you use “table.cell(i,j).text”, this updates the table in the Word document and is very slow.
The more efficient way is to do the following:
import docx
import pandas as pd
data = pd.read_excel("some_bigger_data.xlsx")
doc = docx.Document()
table = doc.add_table(rows=data.shape[0], cols=data.shape[1])
table_cells = table._cells
for i in range(data.shape[0]):
for j in range(data.shape[1]):
table_cells[j + i * data.shape[1]].text = str(data.values[i][j])
doc.save("output_file_path.docx")The key is to use table._cells to “pop” out the cells from the table. With this line, we limit the amount of calls to the table in the Word document. By updating the Word document only after you have filled the table, you will improve the efficiency and speed of your program.
Hopefully this has been helpful in helping you write a table from a dataframe to Word document faster, and with this code, you can make your processes more efficient and take less time.
Let me know if you have any questions, and thank you for reading.
About The Programming Expert
The Programming Expert is a compilation of a programmer’s findings in the world of software development, website creation, and automation of processes.
Programming allows us to create amazing applications which make our work more efficient, repeatable and accurate.
At the end of the day, we want to be able to just push a button and let the code do it’s magic.
You can read more about us on our about page.