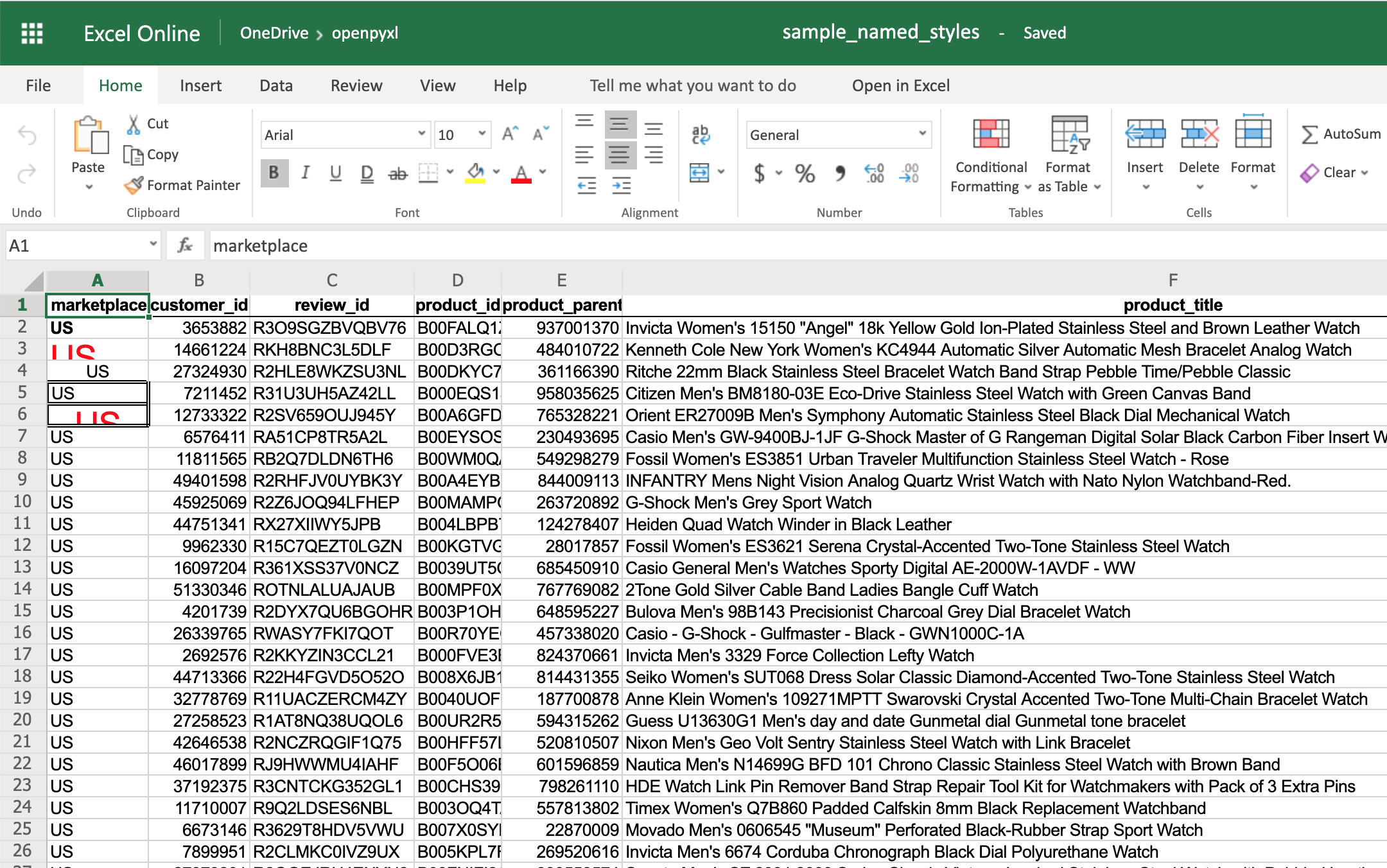
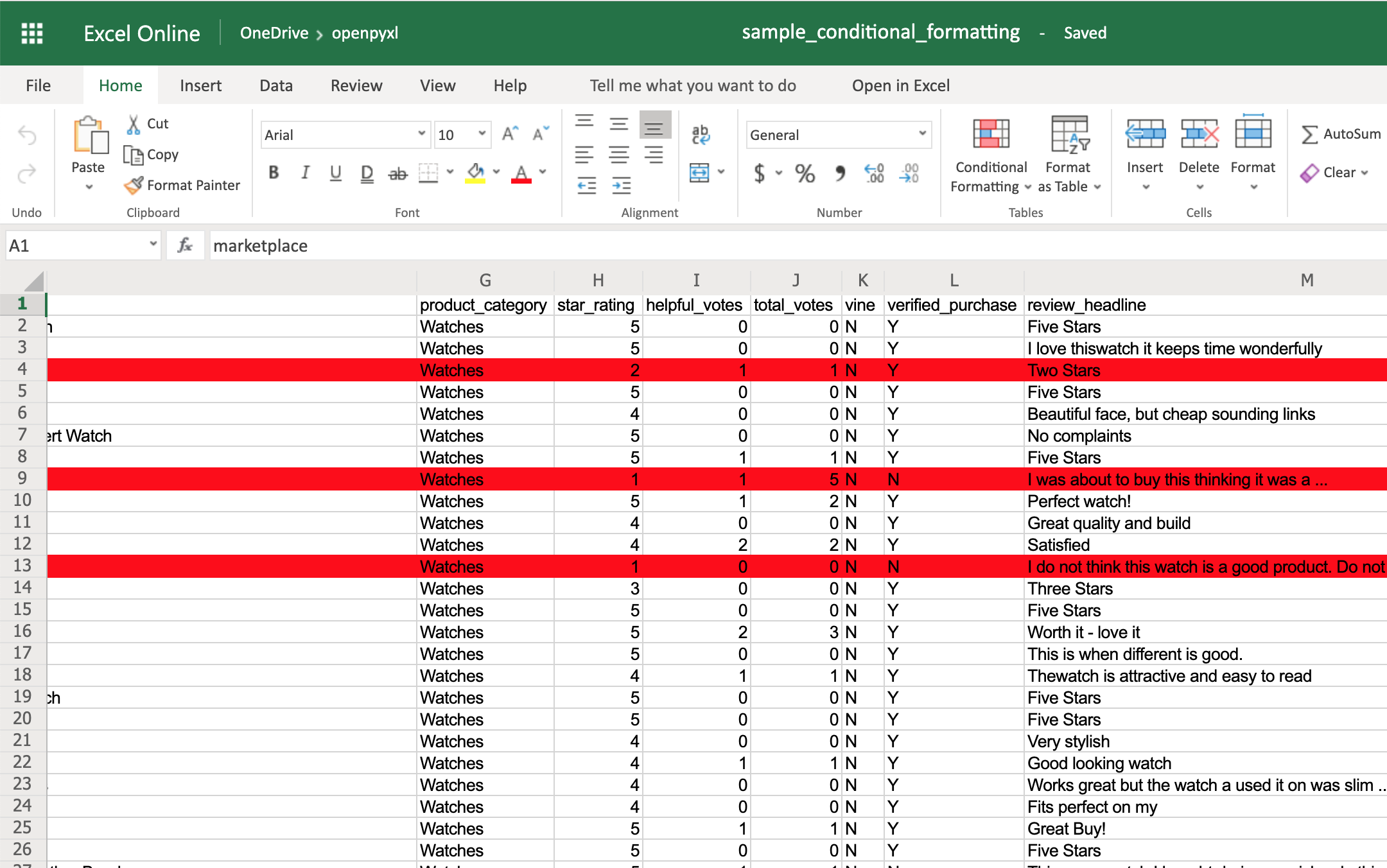
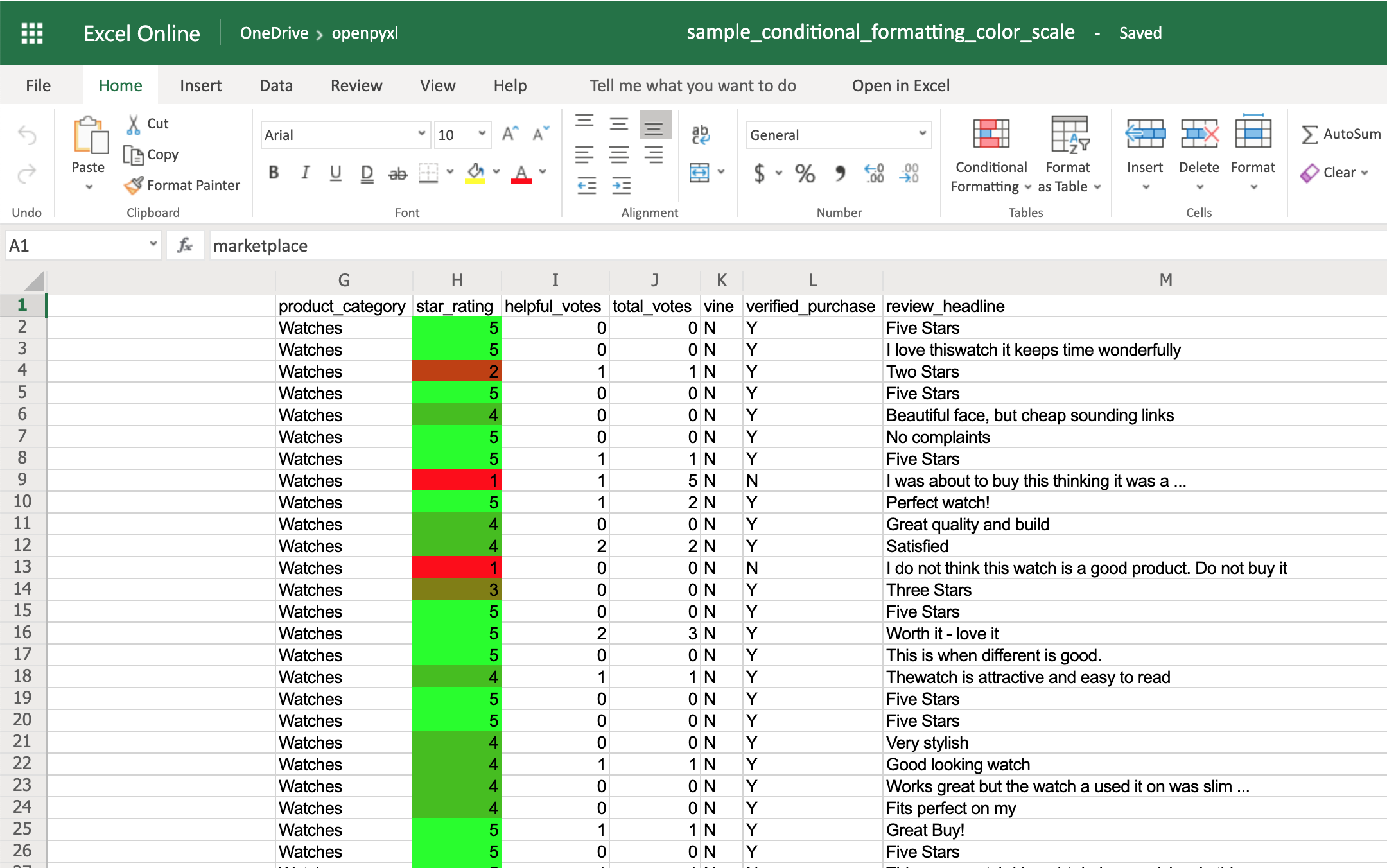
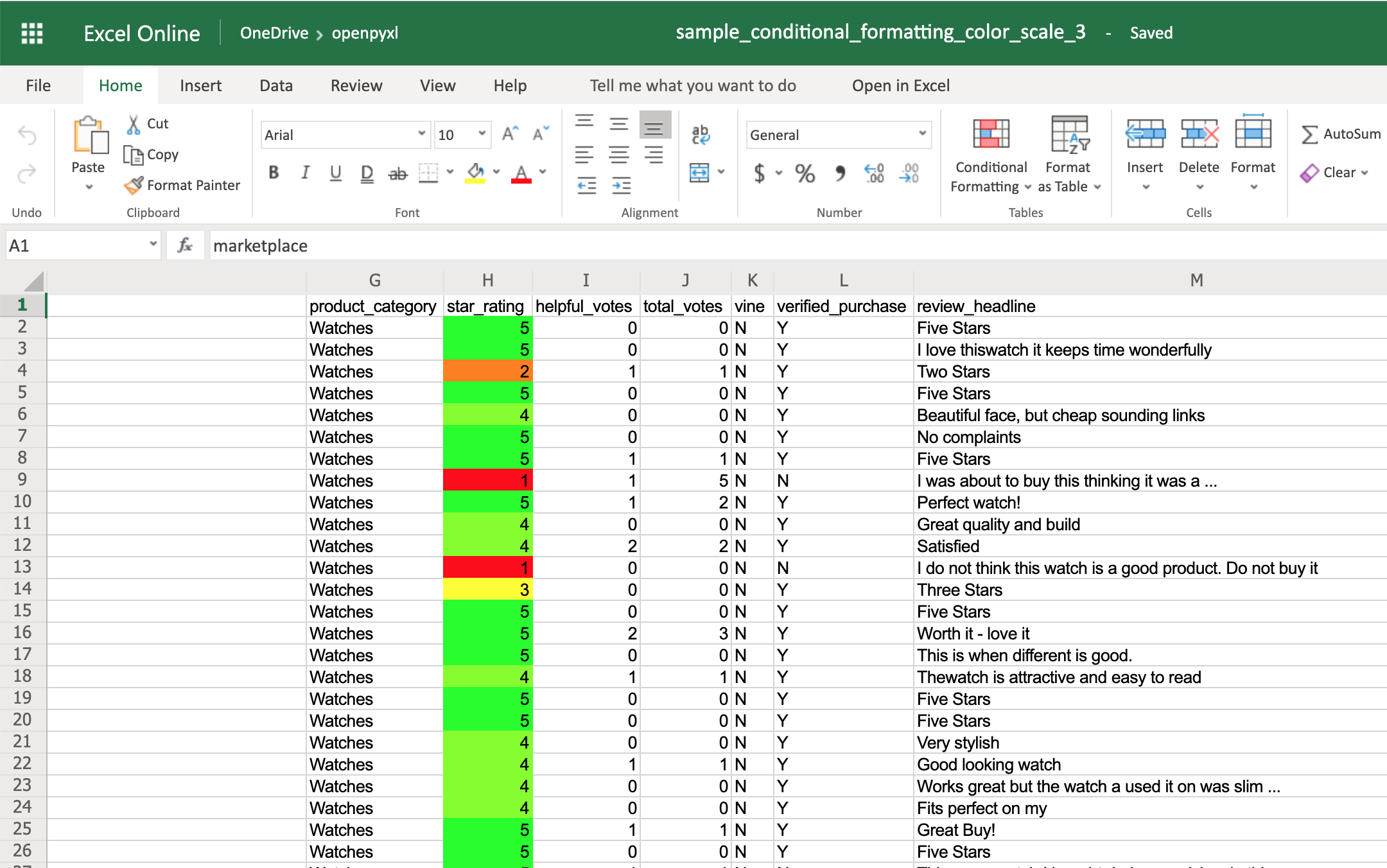
Excel supports three different types of conditional formatting: builtins, standard and custom. Builtins combine specific rules with predefined styles. Standard conditional formats combine specific rules with custom formatting. In additional it is possible to define custom formulae for applying custom formats using differential styles.
Note
The syntax for the different rules varies so much that it is not
possible for openpyxl to know whether a rule makes sense or not.
The basic syntax for creating a formatting rule is:
>>> from openpyxl.formatting import Rule >>> from openpyxl.styles import Font, PatternFill, Border >>> from openpyxl.styles.differential import DifferentialStyle >>> dxf = DifferentialStyle(font=Font(bold=True), fill=PatternFill(start_color='EE1111', end_color='EE1111')) >>> rule = Rule(type='cellIs', dxf=dxf, formula=["10"])
Because the signatures for some rules can be quite verbose there are also some convenience factories for creating them.
Builtin formats¶
The builtins conditional formats are:
- ColorScale
- IconSet
- DataBar
Builtin formats contain a sequence of formatting settings which combine a type with an integer for comparison. Possible types are: ‘num’, ‘percent’, ‘max’, ‘min’, ‘formula’, ‘percentile’.
ColorScale¶
You can have color scales with 2 or 3 colors. 2 color scales produce a gradient from one color to another; 3 color scales use an additional color for 2 gradients.
The full syntax for creating a ColorScale rule is:
>>> from openpyxl.formatting.rule import ColorScale, FormatObject >>> from openpyxl.styles import Color >>> first = FormatObject(type='min') >>> last = FormatObject(type='max') >>> # colors match the format objects: >>> colors = [Color('AA0000'), Color('00AA00')] >>> cs2 = ColorScale(cfvo=[first, last], color=colors) >>> # a three color scale would extend the sequences >>> mid = FormatObject(type='num', val=40) >>> colors.insert(1, Color('00AA00')) >>> cs3 = ColorScale(cfvo=[first, mid, last], color=colors) >>> # create a rule with the color scale >>> from openpyxl.formatting.rule import Rule >>> rule = Rule(type='colorScale', colorScale=cs3)
There is a convenience function for creating ColorScale rules
>>> from openpyxl.formatting.rule import ColorScaleRule >>> rule = ColorScaleRule(start_type='percentile', start_value=10, start_color='FFAA0000', ... mid_type='percentile', mid_value=50, mid_color='FF0000AA', ... end_type='percentile', end_value=90, end_color='FF00AA00')
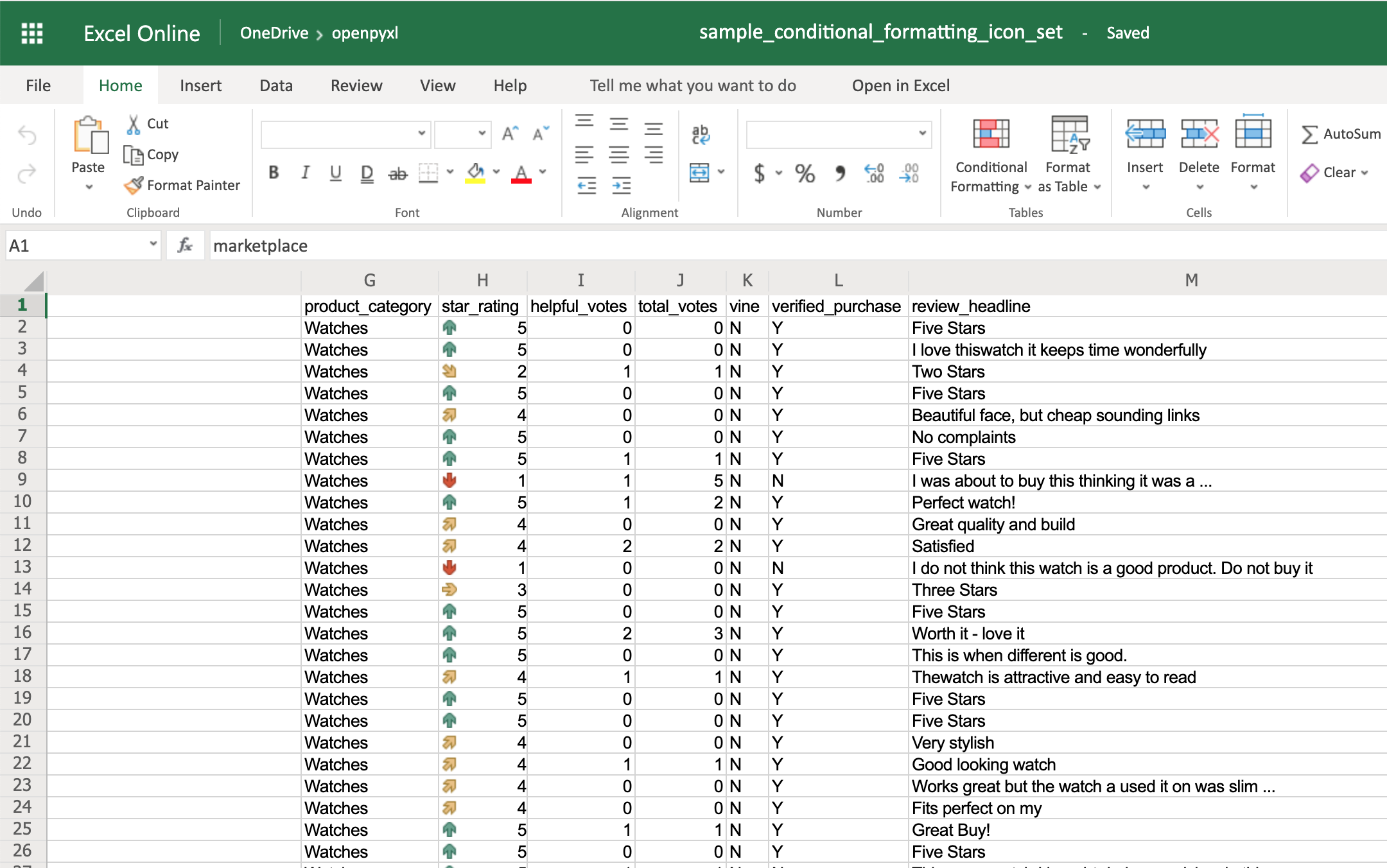
IconSet¶
Choose from the following set of icons: ‘3Arrows’, ‘3ArrowsGray’, ‘3Flags’, ‘3TrafficLights1’, ‘3TrafficLights2’, ‘3Signs’, ‘3Symbols’, ‘3Symbols2’, ‘4Arrows’, ‘4ArrowsGray’, ‘4RedToBlack’, ‘4Rating’, ‘4TrafficLights’, ‘5Arrows’, ‘5ArrowsGray’, ‘5Rating’, ‘5Quarters’
The full syntax for creating an IconSet rule is:
>>> from openpyxl.formatting.rule import IconSet, FormatObject >>> first = FormatObject(type='percent', val=0) >>> second = FormatObject(type='percent', val=33) >>> third = FormatObject(type='percent', val=67) >>> iconset = IconSet(iconSet='3TrafficLights1', cfvo=[first, second, third], showValue=None, percent=None, reverse=None) >>> # assign the icon set to a rule >>> from openpyxl.formatting.rule import Rule >>> rule = Rule(type='iconSet', iconSet=iconset)
There is a convenience function for creating IconSet rules:
>>> from openpyxl.formatting.rule import IconSetRule >>> rule = IconSetRule('5Arrows', 'percent', [10, 20, 30, 40, 50], showValue=None, percent=None, reverse=None)
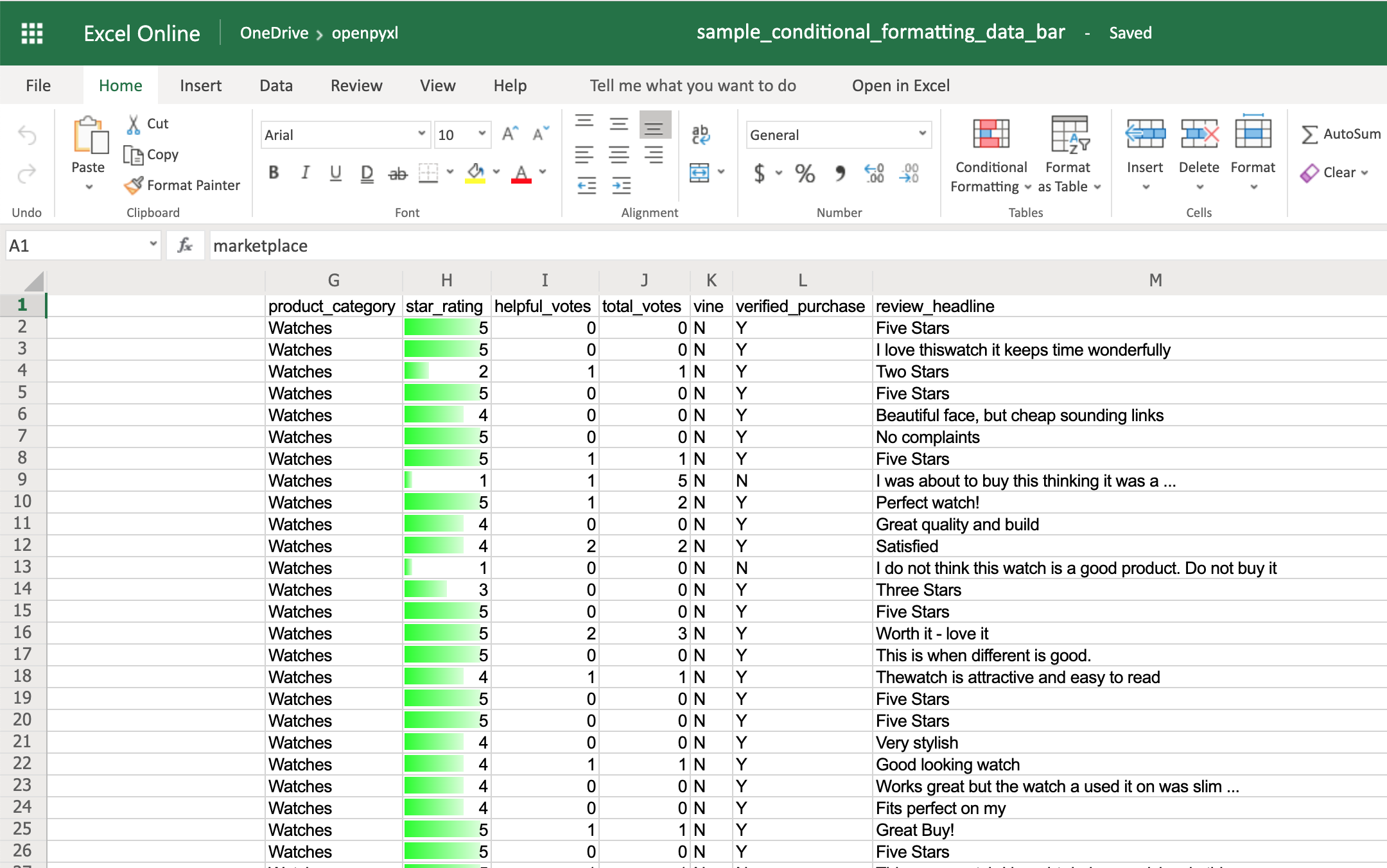
DataBar¶
Currently, openpyxl supports the DataBars as defined in the original specification. Borders and directions were added in a later extension.
The full syntax for creating a DataBar rule is:
>>> from openpyxl.formatting.rule import DataBar, FormatObject >>> first = FormatObject(type='min') >>> second = FormatObject(type='max') >>> data_bar = DataBar(cfvo=[first, second], color="638EC6", showValue=None, minLength=None, maxLength=None) >>> # assign the data bar to a rule >>> from openpyxl.formatting.rule import Rule >>> rule = Rule(type='dataBar', dataBar=data_bar)
There is a convenience function for creating DataBar rules:
>>> from openpyxl.formatting.rule import DataBarRule >>> rule = DataBarRule(start_type='percentile', start_value=10, end_type='percentile', end_value='90', ... color="FF638EC6", showValue="None", minLength=None, maxLength=None)
Standard conditional formats¶
The standard conditional formats are:
- Average
- Percent
- Unique or duplicate
- Value
- Rank
>>> from openpyxl import Workbook >>> from openpyxl.styles import Color, PatternFill, Font, Border >>> from openpyxl.styles.differential import DifferentialStyle >>> from openpyxl.formatting.rule import ColorScaleRule, CellIsRule, FormulaRule >>> >>> wb = Workbook() >>> ws = wb.active >>> >>> # Create fill >>> redFill = PatternFill(start_color='EE1111', ... end_color='EE1111', ... fill_type='solid') >>> >>> # Add a two-color scale >>> # Takes colors in excel 'RRGGBB' style. >>> ws.conditional_formatting.add('A1:A10', ... ColorScaleRule(start_type='min', start_color='AA0000', ... end_type='max', end_color='00AA00') ... ) >>> >>> # Add a three-color scale >>> ws.conditional_formatting.add('B1:B10', ... ColorScaleRule(start_type='percentile', start_value=10, start_color='AA0000', ... mid_type='percentile', mid_value=50, mid_color='0000AA', ... end_type='percentile', end_value=90, end_color='00AA00') ... ) >>> >>> # Add a conditional formatting based on a cell comparison >>> # addCellIs(range_string, operator, formula, stopIfTrue, wb, font, border, fill) >>> # Format if cell is less than 'formula' >>> ws.conditional_formatting.add('C2:C10', ... CellIsRule(operator='lessThan', formula=['C$1'], stopIfTrue=True, fill=redFill)) >>> >>> # Format if cell is between 'formula' >>> ws.conditional_formatting.add('D2:D10', ... CellIsRule(operator='between', formula=['1','5'], stopIfTrue=True, fill=redFill)) >>> >>> # Format using a formula >>> ws.conditional_formatting.add('E1:E10', ... FormulaRule(formula=['ISBLANK(E1)'], stopIfTrue=True, fill=redFill)) >>> >>> # Aside from the 2-color and 3-color scales, format rules take fonts, borders and fills for styling: >>> myFont = Font() >>> myBorder = Border() >>> ws.conditional_formatting.add('E1:E10', ... FormulaRule(formula=['E1=0'], font=myFont, border=myBorder, fill=redFill)) >>> >>> # Highlight cells that contain particular text by using a special formula >>> red_text = Font(color="9C0006") >>> red_fill = PatternFill(bgColor="FFC7CE") >>> dxf = DifferentialStyle(font=red_text, fill=red_fill) >>> rule = Rule(type="containsText", operator="containsText", text="highlight", dxf=dxf) >>> rule.formula = ['NOT(ISERROR(SEARCH("highlight",A1)))'] >>> ws.conditional_formatting.add('A1:F40', rule) >>> wb.save("test.xlsx")
Formatting Entire Rows¶
Sometimes you want to apply a conditional format to more than one cell, say a row of cells which contain a particular value.
>>> ws.append(['Software', 'Developer', 'Version']) >>> ws.append(['Excel', 'Microsoft', '2016']) >>> ws.append(['openpyxl', 'Open source', '2.6']) >>> ws.append(['OpenOffice', 'Apache', '4.1.4']) >>> ws.append(['Word', 'Microsoft', '2010'])
We want to highlight the rows where the developer is Microsoft. We do this by creating an expression rule and using a formula to identify which rows contain software developed by Microsoft.
>>> red_fill = PatternFill(bgColor="FFC7CE") >>> dxf = DifferentialStyle(fill=red_fill) >>> r = Rule(type="expression", dxf=dxf, stopIfTrue=True) >>> r.formula = ['$A2="Microsoft"'] >>> ws.conditional_formatting.add("A1:C10", r)
Note
The formula uses an absolute reference to the column referred to, B in this case; but a relative row number, in this case 1 to the range over which the format is applied. It can be tricky to get this right but the rule can be adjusted even after it has been added to the worksheet’s conditional format collection.
How do I format cells in Excel with python?
In particular I need to change the font of several subsequent rows
to be regular instead of bold.
jonrsharpe
114k25 gold badges228 silver badges425 bronze badges
asked Jun 22, 2009 at 21:30
1
Using xlwt:
from xlwt import *
font0 = Font()
font0.bold = False
style0 = XFStyle()
style0.font = font0
wb = Workbook()
ws0 = wb.add_sheet('0')
ws0.write(0, 0, 'myNormalText', style0)
font1 = Font()
font1.bold = True
style1 = XFStyle()
style1.font = font1
ws0.write(0, 1, 'myBoldText', style1)
wb.save('format.xls')
answered Jun 22, 2009 at 21:49
mechanical_meatmechanical_meat
162k24 gold badges225 silver badges222 bronze badges
1
For using Python for Excel operations in general, I highly recommend checking out this site. There are three python modules that allow you to do pretty much anything you need: xlrd (reading), xlwt (writing), and xlutils (copy/modify/filter). On the site I mentioned, there is quite a bit of associated information including documentation and examples. In particular, you may be interested in this example. Good luck!
answered Jun 22, 2009 at 22:03
Brendan WoodBrendan Wood
6,1803 gold badges29 silver badges28 bronze badges
For generic examples of Excel scripting from Python, this snippet is very handy. It doesn’t specifically do the «change font to regular», but that’s just range.Font.Bold = False in a function otherwise very similar to the set_border one in that snippet.
answered Jun 22, 2009 at 21:41
Alex MartelliAlex Martelli
844k167 gold badges1213 silver badges1391 bronze badges
Here is a brief introduction to using xlwt and the complementary xlrd (for reading .xls files). However, the Reddit thread where I discovered that article has a huge number of useful bits of advice, including some cautionary notes and how to use the win32com module to write Excel files better (see this comment, for example) — frankly, I think the code is easier to read/maintain. You can probably learn a lot more over at the pretty active python-excel group.
answered Jun 22, 2009 at 22:59
spiffymanspiffyman
5644 silver badges9 bronze badges
OpenPyXL gives you the ability to style your cells in many different ways. Styling cells will give your spreadsheets pizazz! Your spreadsheets can have some pop and zing to them that will help differentiate them from others. However, don’t go overboard! If every cell had a different font and color, your spreadsheet would look like a mess.
You should use the skills that you learn in this article sparingly. You’ll still have beautiful spreadsheets that you can share with your colleagues. If you would like to learn more about what styles OpenPyXL supports, you should check out their documentation.
In this article, you will learn about the following:
- Working with fonts
- Setting the alignment
- Adding a border
- Changing the cell background-color
- Inserting images into cells
- Styling merged cells
- Using a built-in style
- Creating a custom named style
Now that you know what you’re going to learn, it’s time to get started by discovering how to work with fonts using OpenPyXL!
Working with Fonts
You use fonts to style your text on a computer. A font controls the size, weight, color, and style of the text you see on-screen or in print. There are thousands of fonts that your computer can use. Microsoft includes many fonts with its Office products.
When you want to set a font with OpenPyXL, you will need to import the Font class from openpyxl.styles. Here is how you would do the import:
from openpyxl.styles import Font
The Font class takes many parameters. Here is the Font class’s full list of parameters according to OpenPyXL’s documentation:
class openpyxl.styles.fonts.Font(name=None, sz=None, b=None, i=None, charset=None, u=None,
strike=None, color=None, scheme=None, family=None, size=None, bold=None, italic=None,
strikethrough=None, underline=None, vertAlign=None, outline=None, shadow=None,
condense=None, extend=None)
The following list shows the parameters you are most likely to use and their defaults:
- name=’Calibri’
- size=11
- bold=False
- italic=False
- vertAlign=None
- underline=’none’
- strike=False
- color=’FF000000′
These settings allow you to set most of the things you’ll need to make your text look nice. Note that the color names in OpenPyXL use hexadecimal values to represent RGB (red, green, blue) color values. You can set whether or not the text should be bold, italic, underlined, or struck-through.
To see how you can use fonts in OpenPyXL, create a new file named font_sizes.py and add the following code to it:
# font_sizes.py
import openpyxl
from openpyxl.styles import Font
def font_demo(path):
workbook = openpyxl.Workbook()
sheet = workbook.active
cell = sheet["A1"]
cell.font = Font(size=12)
cell.value = "Hello"
cell2 = sheet["A2"]
cell2.font = Font(name="Arial", size=14, color="00FF0000")
sheet["A2"] = "from"
cell2 = sheet["A3"]
cell2.font = Font(name="Tahoma", size=16, color="00339966")
sheet["A3"] = "OpenPyXL"
workbook.save(path)
if __name__ == "__main__":
font_demo("font_demo.xlsx")
This code uses three different fonts in three different cells. In A1, you use the default, which is Calibri. Then in A2, you set the font size to Arial and increase the size to 14 points. Finally, in A3, you change the font to Tahoma and the font size to 16 points.
For the second and third fonts, you also change the text color. In A2, you set the color to red, and in A3, you set the color to green.
When you run this code, your output will look like this:
Try changing the code to use other fonts or colors. If you want to get adventurous, you should try to make your text bold or italicized.
Now you’re ready to learn about text alignment.
Setting the Alignment
You can set alignment in OpenPyXL by using openpyxl.styles.Alignment. You use this class to rotate the text, set text wrapping, and for indentation.
Here are the defaults that the Alignment class uses:
- horizontal=’general’
- vertical=’bottom’
- text_rotation=0
- wrap_text=False
- shrink_to_fit=False
- indent=0
It’s time for you to get some practice in. Open up your Python editor and create a new file named alignment.py. Then add this code to it:
# alignment.py
from openpyxl import Workbook
from openpyxl.styles import Alignment
def center_text(path, horizontal="center", vertical="center"):
workbook = Workbook()
sheet = workbook.active
sheet["A1"] = "Hello"
sheet["A1"].alignment = Alignment(horizontal=horizontal,
vertical=vertical)
sheet["A2"] = "from"
sheet["A3"] = "OpenPyXL"
sheet["A3"].alignment = Alignment(text_rotation=90)
workbook.save(path)
if __name__ == "__main__":
center_text("alignment.xlsx")
You will center the string both horizontally and vertically in A1 when you run this code. Then you use the defaults for A2. Finally, for A3, you rotate the text 90 degrees.
Try running this code, and you will see something like the following:
That looks nice! It would be best if you took the time to try out different text_rotation values. Then try changing the horizontal and vertical parameters with different values. Pretty soon, you will be able to align your text like a pro!
Now you’re ready to learn about adding borders to your cells!
Adding a Border
OpenPyXL gives you the ability to style the borders on your cell. You can specify a different border style for each of the four sides of a cell.
You can use any of the following border styles:
- ‘dashDot’
- ‘dashDotDot’
- ‘dashed’
- ‘dotted’
- ‘double’
- ‘hair’
- ‘medium’
- ‘mediumDashDot’
- ‘mediumDashDotDot’,
- ‘mediumDashed’
- ‘slantDashDot’
- ‘thick’
- ‘thin’
Open your Python editor and create a new file named border.py. Then enter the following code in your file:
# border.py
from openpyxl import Workbook
from openpyxl.styles import Border, Side
def border(path):
pink = "00FF00FF"
green = "00008000"
thin = Side(border_style="thin", color=pink)
double = Side(border_style="double", color=green)
workbook = Workbook()
sheet = workbook.active
sheet["A1"] = "Hello"
sheet["A1"].border = Border(top=double, left=thin, right=thin, bottom=double)
sheet["A2"] = "from"
sheet["A3"] = "OpenPyXL"
sheet["A3"].border = Border(top=thin, left=double, right=double, bottom=thin)
workbook.save(path)
if __name__ == "__main__":
border("border.xlsx")
This code will add a border to cell A1 and A3. The top and bottom of A1 use a “double” border style and are green, while the cell sides are using a “thin” border style and are colored pink.
Cell A3 uses the same borders but swaps them so that the sides are now green and the top and bottom are pink.
You get this effect by creating Side objects in the border_style and the color to be used. Then you pass those Side objects to a Border class, which allows you to set each of the four sides of a cell individually. To apply the Border to a cell, you must set the cell’s border attribute.
When you run this code, you will see the following result:
This image is zoomed in a lot so that you can easily see the borders of the cells. It would be best if you tried modifying this code with some of the other border styles mentioned at the beginning of this section so that you can see what else you can do.
Changing the Cell Background Color
You can highlight a cell or a range of cells by changing its background color. Highlighting a cell is more eye-catching than changing the text’s font or color in most cases. OpenPyXL gives you a class called PatternFill that you can use to change a cell’s background color.
The PatternFill class takes in the following arguments (defaults included below):
- patternType=None
- fgColor=Color()
- bgColor=Color()
- fill_type=None
- start_color=None
- end_color=None
There are several different fill types you can use. Here is a list of currently supported fill types:
- ‘none’
- ‘solid’
- ‘darkDown’
- ‘darkGray’
- ‘darkGrid’
- ‘darkHorizontal’
- ‘darkTrellis’
- ‘darkUp’
- ‘darkVertical’
- ‘gray0625’
- ‘gray125’
- ‘lightDown’
- ‘lightGray’
- ‘lightGrid’
- ‘lightHorizontal’
- ‘lightTrellis’
- ‘lightUp’
- ‘lightVertical’
- ‘mediumGray’
Now you have enough information to try setting the background color of a cell using OpenPyXL. Open up a new file in your Python editor and name it background_colors.py. Then add this code to your new file:
# background_colors.py
from openpyxl import Workbook
from openpyxl.styles import PatternFill
def background_colors(path):
workbook = Workbook()
sheet = workbook.active
yellow = "00FFFF00"
for rows in sheet.iter_rows(min_row=1, max_row=10, min_col=1, max_col=12):
for cell in rows:
if cell.row % 2:
cell.fill = PatternFill(start_color=yellow, end_color=yellow,
fill_type = "solid")
workbook.save(path)
if __name__ == "__main__":
background_colors("bg.xlsx")
This example will iterate over nine rows and 12 columns. It will set every cell’s background color to yellow if that cell is in an odd-numbered row. The cells with their background color changes will be from column A through column L.
When you want to set the cell’s background color, you set the cell’s fill attribute to an instance of PatternFill. In this example, you specify a start_color and an end_color. You also set the fill_type to “solid”. OpenPyXL also supports using a GradientFill for the background.
Try running this code. After it runs, you will have a new Excel document that looks like this:
Here are some ideas that you can try out with this code:
- Change the number of rows or columns that are affected
- Change the color that you are changing to
- Update the code to color the even rows with a different color
- Try out other fill types
Once you are done experimenting with background colors, you can learn about inserting images in your cells!
Inserting Images into Cells
OpenPyXL makes inserting an image into your Excel spreadsheets nice and straightforward. To make this magic happen, you use the Worksheet object’s add_image() method. This method takes in two arguments:
img– The path to the image file that you are insertinganchor– Provide a cell as a top-left anchor of the image (optional)
For this example, you will be using the Mouse vs. Python logo:
The GitHub repository for this book has the image for you to use.
Once you have the image downloaded, create a new Python file and name it insert_image.py. Then add the following:
# insert_image.py
from openpyxl import Workbook
from openpyxl.drawing.image import Image
def insert_image(path, image_path):
workbook = Workbook()
sheet = workbook.active
img = Image("logo.png")
sheet.add_image(img, "B1")
workbook.save(path)
if __name__ == "__main__":
insert_image("logo.xlsx", "logo.png")
Here you pass in the path to the image that you wish to insert. To insert the image, you call add_image(). In this example, you are hard-coding to use cell B1 as the anchor cell. Then you save your Excel spreadsheet.
If you open up your spreadsheet, you will see that it looks like this:
You probably won’t need to insert an image into an Excel spreadsheet all that often, but it’s an excellent skill to have.
Styling Merged Cells
Merged cells are cells where you have two or more adjacent cells merged into one. If you want to set the value of a merged cell with OpenPyXL, you must use the top left-most cell of the merged cells.
You also must use this particular cell to set the style for the merged cell as a whole. You can use all the styles and font settings you used on an individual cell with the merged cell. However, you must apply the style to the top-left cell for it to apply to the entire merged cell.
You will understand how this works if you see some code. Go ahead and create a new file named style_merged_cell.py. Now enter this code in your file:
# style_merged_cell.py
from openpyxl import Workbook
from openpyxl.styles import Font, Border, Side, GradientFill, Alignment
def merge_style(path):
workbook = Workbook()
sheet = workbook.active
sheet.merge_cells("A2:G4")
top_left_cell = sheet["A2"]
light_purple = "00CC99FF"
green = "00008000"
thin = Side(border_style="thin", color=light_purple)
double = Side(border_style="double", color=green)
top_left_cell.value = "Hello from PyOpenXL"
top_left_cell.border = Border(top=double, left=thin, right=thin,
bottom=double)
top_left_cell.fill = GradientFill(stop=("000000", "FFFFFF"))
top_left_cell.font = Font(b=True, color="FF0000", size=16)
top_left_cell.alignment = Alignment(horizontal="center",
vertical="center")
workbook.save(path)
if __name__ == "__main__":
merge_style("merged_style.xlsx")
Here you create a merged cell that starts at A2 (the top-left cell) through G4. Then you set the cell’s value, border, fill, font and alignment.
When you run this code, your new spreadsheet will look like this:
Doesn’t that look nice? You should take some time and try out some different styles on your merged cell. Maybe come up with a better gradient than the gray one used here, for example.
Now you’re ready to learn about OpenPyXL’s built-in styles!
Using a Built-in Style
OpenPyXL comes with multiple built-in styles that you can use as well. Rather than reproducing the entire list of built-in styles in this book, you should go to the official documentation as it will be the most up-to-date source for the style names.
However, it is worth noting some of the styles. For example, here are the number format styles you can use:
- ‘Comma’
- ‘Comma [0]’
- ‘Currency’
- ‘Currency [0]’
- ‘Percent’
You can also apply text styles. Here is a listing of those styles:
- ‘Title’
- ‘Headline 1’
- ‘Headline 2’
- ‘Headline 3’
- ‘Headline 4’
- ‘Hyperlink’
- ‘Followed Hyperlink’
- ‘Linked Cell’
OpenPyXL has several other built-in style groups. You should check out the documentation to learn about all the different styles that are supported.
Now that you know about some of the built-in styles you can use, it’s time to write some code! Create a new file and name it builtin_styls.py. Then enter the following code:
# builtin_styles.py
from openpyxl import Workbook
def builtin_styles(path):
workbook = Workbook()
sheet = workbook.active
sheet["A1"].value = "Hello"
sheet["A1"].style = "Title"
sheet["A2"].value = "from"
sheet["A2"].style = "Headline 1"
sheet["A3"].value = "OpenPyXL"
sheet["A3"].style = "Headline 2"
workbook.save(path)
if __name__ == "__main__":
builtin_styles("builtin_styles.xlsx")
Here you apply three different styles to three different cells. You use “Title”, “Headline 1” and “Headline 2”, specifically.
When you run this code, you will end up having a spreadsheet that looks like this:
As always, you should try out some of the other built-in styles. Trying them out is the only way to determine what they do and if they will work for you.
But wait! What if you wanted to create your style? That’s what you will cover in the next section!
Creating a Custom Named Style
You can create custom styles of your design using OpenPyXL as well. To create your style, you must use the NamedStyle class.
The NamedStyle class takes the following arguments (defaults are included too):
- name=”Normal”
- font=Font()
- fill=PatternFill()
- border=Border()
- alignment=Alignment()
- number_format=None
- protection=Protection()
- builtinId=None
- hidden=False
- xfId=None
You should always provide your own name to your NamedStyle to keep it unique. Go ahead and create a new file and call it named_style.py. Then add this code to it:
# named_style.py
from openpyxl import Workbook
from openpyxl.styles import Font, Border, Side, NamedStyle
def named_style(path):
workbook = Workbook()
sheet = workbook.active
red = "00FF0000"
font = Font(bold=True, size=22)
thick = Side(style="thick", color=red)
border = Border(left=thick, right=thick, top=thick, bottom=thick)
named_style = NamedStyle(name="highlight", font=font, border=border)
sheet["A1"].value = "Hello"
sheet["A1"].style = named_style
sheet["A2"].value = "from"
sheet["A3"].value = "OpenPyXL"
workbook.save(path)
if __name__ == "__main__":
named_style("named_style.xlsx")
Here you create a Font(), Side(), and Border() instance to pass to your NamedStyle(). Once you have your custom style created, you can apply it to a cell by setting the cell’s style attribute. Applying a custom style is done in the same way as you applied built-in styles!
You applied the custom style to the cell, A1.
When you run this code, you will get a spreadsheet that looks like this:
Now it’s your turn! Edit the code to use a Side style, which will change your border. Or create multiple Side instances so you can make each side of the cell unique. Play around with different fonts or add a custom background color!
Wrapping Up
You can do a lot of different things with cells using OpenPyXL. The information in this article gives you the ability to format your data in beautiful ways.
In this article, you learned about the following topics:
- Working with fonts
- Setting the alignment
- Adding a border
- Changing the cell background-color
- Inserting images into cells
- Styling merged cells
- Using a built-in style
- Creating a custom named style
You can take the information that you learned in this article to make beautiful spreadsheets. You can highlight exciting data by changing the cell’s background color or font. You can also change the cell’s format by using a built-in style. Go ahead and give it a try.
Experiment with the code in this article and see how powerful and valuable OpenPyXL is when working with cells.
Related Reading
- Reading Spreadsheets with OpenPyXL and Python
- Creating Spreadsheets with OpenPyXL and Python
- Automating Excel with Python (book)
In this article, we will use Python scripts for data formatting in Microsoft Excel sheet with various examples.
Introduction
Python is an object-oriented, high-level programming language popular among the data scientists. SQL Server also supports executing Python code from Azure data studio and SQL Server Management Studio. We have many useful publications on SQLShack for the Python, along with its use-cases, especially for DBAs and developers.
Before you go further, I would recommend you to go through the following articles for the basic understanding of it:
- Python in SQL Server: The Basics
- The importance of Python in SQL Server Administration
- Why would a SQL Server DBA be interested in Python?
- Using Python SQL scripts for Importing Data from Compressed files
Usually, DBAs share export required data in an Excel sheet, do the formatting, and share it with the concerned authorities. It is a regular practice. Python integrates with Microsoft Excel very well.
This article covers the following topics:
- Create a sample excel file using the Python
- Import data from an excel file using Python
- Format data in excel sheet using Python
- Prepare excel charts using Python
Pre-requisites
- In this article, we use SQL Notebooks of Azure Data Studio. Refer to SQL Notebooks introduction and overview for detailed information on it
-
Download the Python latest version 3.8.2 for Windows from this URL
- Configure SQL Notebook for Python kernel. Refer to the article Use Python SQL scripts in SQL Notebooks of Azure Data Studio for it
-
Install XlsxWriter and xlrd Python module using pip utility
-
XlsxWriter: We use the XlsxWriter Python module to write the Microsoft Excel files in XLSX format. It provides various formatting options, charts, textboxes, Rich multi-format strings, Macros for excel files
For the installation of XlsxWrite, use the following command in Python3 kernel of the SQL Notebook:
It downloads the package and installs it as shown in the following screenshot:
-
Xlrd: It is also a Python library and useful to read data from the excel files. It supports both XLS and XLSX extension for reading data and formatting information from Excel files. It gives many formatting features as well for excel files
Use the following command for installing the xlrd Python module:
Work with excel files using Python scripts and libraries
In the previous step, we installed the Python libraries XlsxWriter and xlrd using SQL Notebooks of Azure Data Studio.
Create a basic excel file
Let’s create a sample excel file without any formatting. Run the following code in Python:
import xlsxwriter
workbook = xlsxwriter.Workbook(‘c:\temp\Welocme.xlsx’)
worksheet = workbook.add_worksheet()
worksheet.write(‘A1’, ‘Welcome to Python’)
workbook.close()
- Import Xlsxwrite module
- Creates a workbook Welcome.xlsx in the C:temp folder
- Add a new worksheet in this workbook
- Writes the text ‘Welcome to Python’ in the A1 column
- Closes the workbook
You can browse the directory and open the Welcome.xlsx excel workbook. It shows the data entered by the Python code:
Split the words into multiple columns
Let’s modify the above code and split the words into different columns A1, B1, and C1:
import xlsxwriter
workbook = xlsxwriter.Workbook(‘c:\temp\Welocme.xlsx’)
worksheet = workbook.add_worksheet()
worksheet.write(‘A1’, ‘Welcome’)
worksheet.write(‘B1’, ‘To’)
worksheet.write(‘C1’, ‘Python’)
workbook.close()
Once we execute the above code, it overwrites the existing Welcome.xlsx file. Open it, and you see words in different columns A1, B1, and C1:
Data in multiple rows and columns along with column headers
Suppose we want to create an excel sheet with the following data using Python scripts. It includes multiple columns and rows:
We use the following Python scripts for preparing this kind of excel sheet:
-
We defined column names using worksheet.write()
worksheet.write(‘A1’, ‘Name’)
worksheet.write(‘B1’, ‘Department’)
- We start index for rows and columns. For the first row and first column, it uses a zero indexing counter. We specified column names in the previous step, so my counter starts from row=1 and col=0
-
We write the required data in an array format in the data variable. It contains the data that we wish to display in the excel:
data = (
[‘Rajendra’, ‘IT’],
[‘Kashish’,‘Physiotherapist’],
[‘Arun’, ‘Student’],
[‘Rohan’,‘Bank Manager’],
)
-
The code contains a FOR interaction loop to go through each row and column. It writes in the respective row and column for the worksheet:
for name, score in (data):
worksheet.write(row, col, name)
worksheet.write(row, col + 1, score)
row += 1
The complete Python scripts for preparing this excel is as follows:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
import xlsxwriter
workbook = xlsxwriter.Workbook(‘c:\temp\Welocme.xlsx’)
worksheet = workbook.add_worksheet()
worksheet.write(‘A1’, ‘Name’)
worksheet.write(‘B1’, ‘Department’)
row = 1
col = 0
data = (
[‘Rajendra’, ‘IT’],
[‘Kashish’,‘Physiotherapist’],
[‘Arun’, ‘Student’],
[‘Rohan’,‘Bank Manager’],
)
for name, score in (data):
worksheet.write(row, col, name)
worksheet.write(row, col + 1, score)
row += 1
workbook.close()
Bold characters using Python Scripts
In many cases, we make column names in bold characters so that users can differentiate column with the actual data. In Python, we enable the bold property, as shown below:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
bold = workbook.add_format({‘bold’: True})</p>
<p>
Later, we use this variable in the worksheet.write() function. It changes the respective column font in the bold color.
</p>
<p>
Execute the following code to create an excel sheet similar to the previous one except columns are in bold font:
</p>
<pre lang=«python»>import xlsxwriter
workbook = xlsxwriter.Workbook(‘c:\temp\Welocme1.xlsx’)
worksheet = workbook.add_worksheet()
bold = workbook.add_format({‘bold’: True})
worksheet.write(‘A1’, ‘Name’, bold)
worksheet.write(‘B1’, ‘Department’, bold)
row = 1
col = 0
data = (
[‘Rajendra’, ‘IT’],
[‘Kashish’,‘Physiotherapist’],
[‘Arun’, ‘Student’],
[‘Rohan’,‘Bank Manager’],
)
for name, score in (data):
worksheet.write(row, col, name)
worksheet.write(row, col + 1, score)
row += 1
workbook.close()
In the excel, you can view columns Name and Department in bold letters:
Modify a column width of Microsoft Excel columns
Look at the following excel sheet. In this, text written in column B is span across multiple columns. Usually, in excel, we change the column width to display it appropriately. It does not conflict with text written in other columns:
We can define the row and column width for excel cells in Python as well. For this we use worksheet.set_column function along with column width. We specify column in format of [column:column].
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
worksheet.set_column(‘B:B’, 60)</p>
<p>
In the code above, we added the column width 60 so that it does not conflict with text in column C:
</p>
<pre lang=«python»>import xlsxwriter
workbook = xlsxwriter.Workbook(‘c:\temp\Welocme1.xlsx’)
worksheet = workbook.add_worksheet()
bold = workbook.add_format({‘bold’: True})
worksheet.write(‘A1’, ‘Name’, bold)
worksheet.write(‘B1’, ‘Department’, bold)
row = 1
col = 0
data = (
[‘Rajendra’, ‘Hi, You are on SQLShack.com, refer to all SQL Server related contents.’],
[‘Kashish’,‘How do you get to see a physiotherapist?’],
[‘Arun’, ‘I am a student of class 1 in Bookburn primary school.’],
[‘Rohan’,‘Are you a Bank Manager?’],
)
worksheet.set_column(‘B:B’, 60)
for name, score in (data):
worksheet.write(row, col, name)
worksheet.write(row, col + 1, score)
row += 1
workbook.close()
Look at the difference in the output. It changed the column width to the appropriate size.
Change font color and size
Now, let’s look at changing font color and size for the column headers.
We define font color using font_color and font size using set_font_size variables in Python scripts. For this demonstration, let’s add red color for the column header with font size 16:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
import xlsxwriter
workbook = xlsxwriter.Workbook(‘c:\temp\Welocme1.xlsx’)
worksheet = workbook.add_worksheet()
cell_format = workbook.add_format({‘bold’: True, ‘font_color’: ‘red’})
cell_format.set_font_size(16)
worksheet.write(‘A1’, ‘Name’, cell_format)
worksheet.write(‘B1’, ‘Department’, cell_format)
row = 1
col = 0
data = (
[‘Rajendra’, ‘Hi, You are on SQLShack.com, refer to all SQL Server related contents.’],
[‘Kashish’,‘How do you get to see a physiotherapist?’],
[‘Arun’, ‘I am a student of class 1 in Bookburn primary school.’],
[‘Rohan’,‘Are you a Bank Manager?’],
)
worksheet.set_column(‘B:B’, 60)
worksheet.set_column(‘B:B’, 60)
for name, score in (data):
worksheet.write(row, col, name)
worksheet.write(row, col + 1, score)
row += 1
workbook.close()
Executing the code gives the following output:
Add an underline for the column header
We can add a column header using the cell format function set_underline(). Add the following line in the code, and it generates column headers with an underline:
cell_format.set_underline()
Let’s execute the following code for the column header underline:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
import xlsxwriter
workbook = xlsxwriter.Workbook(‘c:\temp\Welocme1.xlsx’)
worksheet = workbook.add_worksheet()
cell_format = workbook.add_format({‘bold’: True, ‘font_color’: ‘red’})
cell_format.set_font_size(16)
cell_format.set_underline()
worksheet.write(‘A1’, ‘Name’, cell_format)
worksheet.write(‘B1’, ‘Department’, cell_format)
row = 1
col = 0
data = (
[‘Rajendra’, ‘Hi, You are on SQLShack.com, refer to all SQL Server related contents.’],
[‘Kashish’,‘How do you get to see a physiotherapist?’],
[‘Arun’, ‘I am a student of class 1 in Bookburn primary school.’],
[‘Rohan’,‘Are you a Bank Manager?’],
)
worksheet.set_column(‘B:B’, 60)
worksheet.set_column(‘B:B’, 60)
for name, score in (data):
worksheet.write(row, col, name)
worksheet.write(row, col + 1, score)
row += 1
workbook.close()
It gives the following output:
We have few underline options available as below:
- 1 = Default format
- 2 = Double underline
- 33 = Single accounting underline
- 34 = Double accounting underline
We can format data for double accounting underline using the below code:
cell_format.set_underline(34)
If we change the format to double underline, you get the following output:
cell_format.set_underline(2)
Text Alignments
In a Microsoft Excel worksheet, we can arrange a text in the left, right, center in respective columns. In the following screenshot, we applied formatting options:
- The header should be center-aligned
- Other rows of data color should be in blue and center-aligned
In this case, we have two formats – one for the column header and another for the rest of the columns. In the following Python scripts, we defined cell_format and cell_format1:
In the Cell_format, we add another line for font alignment.
cell_format.set_align(‘center’)
In another format, we defined font color using property font_color and set the alignment to center.
cell_format1 = workbook.add_format({‘font_color’: ‘blue’})
cell_format1.set_align(‘center’)
We have two kinds of text format now. We need to apply them to appropriate columns only. For example, column headers look the same as in the previous example with a difference that it is aligned center. We use cell_format for the column headers:
cell_format = workbook.add_format({‘bold’: True, ‘font_color’: ‘red’})
cell_format.set_font_size(16)
cell_format.set_underline(2)
cell_format.set_align(‘center’)
For the rest of the data, we require center alignment and font in blue color. We define another cell format for this:
cell_format1 = workbook.add_format({‘font_color’: ‘blue’})
cell_format1.set_align(‘center’)
Later, we apply this new cell format for data from B2 to B5 and A1 to A5 using the worksheet.set_column function:
worksheet.set_column(‘B2:B5’,60,cell_format1)
worksheet.set_column(‘A1:A5’, 20,cell_format1)
We can view the complete code below and execute it to get the required results:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
import xlsxwriter
workbook = xlsxwriter.Workbook(‘c:\temp\Welocme1.xlsx’)
worksheet = workbook.add_worksheet()
cell_format = workbook.add_format({‘bold’: True, ‘font_color’: ‘red’})
cell_format.set_font_size(16)
cell_format.set_underline(2)
cell_format.set_align(‘center’)
cell_format1 = workbook.add_format({‘font_color’: ‘blue’})
cell_format1.set_align(‘center’)
worksheet.write(‘A1’, ‘Name’, cell_format)
worksheet.write(‘B1’, ‘Department’, cell_format)
row = 1
col = 0
data = (
[‘Rajendra’, ‘Hi, You are on SQLShack.com, refer to all SQL Server related contents.’],
[‘Kashish’,‘How do you get to see a physiotherapist?’],
[‘Arun’, ‘I am a student of class 1 in Bookburn primary school.’],
[‘Rohan’,‘Are you a Bank Manager?’],
)
worksheet.set_column(‘B1:B1’, 60)
worksheet.set_column(‘B2:B5’,60,cell_format1)
worksheet.set_column(‘A1:A5’, 20,cell_format1)
for name, score in (data):
worksheet.write(row, col, name)
worksheet.write(row, col + 1, score)
row += 1
workbook.close()
Conclusion
In this article, we explored Python scripts for data formatting in Microsoft Excel. Python is a powerful language, and we can do much work with a few lines of code. SQL Server 2017 onwards, we can execute Python code inside SQL Server. This article will help you in working with data in Python itself without doing formatting in Excel.
- Author
- Recent Posts
Hi! I am Rajendra Gupta, Database Specialist and Architect, helping organizations implement Microsoft SQL Server, Azure, Couchbase, AWS solutions fast and efficiently, fix related issues, and Performance Tuning with over 14 years of experience.
I am the author of the book «DP-300 Administering Relational Database on Microsoft Azure». I published more than 650 technical articles on MSSQLTips, SQLShack, Quest, CodingSight, and SeveralNines.
I am the creator of one of the biggest free online collections of articles on a single topic, with his 50-part series on SQL Server Always On Availability Groups.
Based on my contribution to the SQL Server community, I have been recognized as the prestigious Best Author of the Year continuously in 2019, 2020, and 2021 (2nd Rank) at SQLShack and the MSSQLTIPS champions award in 2020.
Personal Blog: https://www.dbblogger.com
I am always interested in new challenges so if you need consulting help, reach me at rajendra.gupta16@gmail.comView all posts by Rajendra Gupta
-
Watch Now This tutorial has a related video course created by the Real Python team. Watch it together with the written tutorial to deepen your understanding: Editing Excel Spreadsheets in Python With openpyxl
Excel spreadsheets are one of those things you might have to deal with at some point. Either it’s because your boss loves them or because marketing needs them, you might have to learn how to work with spreadsheets, and that’s when knowing openpyxl comes in handy!
Spreadsheets are a very intuitive and user-friendly way to manipulate large datasets without any prior technical background. That’s why they’re still so commonly used today.
In this article, you’ll learn how to use openpyxl to:
- Manipulate Excel spreadsheets with confidence
- Extract information from spreadsheets
- Create simple or more complex spreadsheets, including adding styles, charts, and so on
This article is written for intermediate developers who have a pretty good knowledge of Python data structures, such as dicts and lists, but also feel comfortable around OOP and more intermediate level topics.
Before You Begin
If you ever get asked to extract some data from a database or log file into an Excel spreadsheet, or if you often have to convert an Excel spreadsheet into some more usable programmatic form, then this tutorial is perfect for you. Let’s jump into the openpyxl caravan!
Practical Use Cases
First things first, when would you need to use a package like openpyxl in a real-world scenario? You’ll see a few examples below, but really, there are hundreds of possible scenarios where this knowledge could come in handy.
Importing New Products Into a Database
You are responsible for tech in an online store company, and your boss doesn’t want to pay for a cool and expensive CMS system.
Every time they want to add new products to the online store, they come to you with an Excel spreadsheet with a few hundred rows and, for each of them, you have the product name, description, price, and so forth.
Now, to import the data, you’ll have to iterate over each spreadsheet row and add each product to the online store.
Exporting Database Data Into a Spreadsheet
Say you have a Database table where you record all your users’ information, including name, phone number, email address, and so forth.
Now, the Marketing team wants to contact all users to give them some discounted offer or promotion. However, they don’t have access to the Database, or they don’t know how to use SQL to extract that information easily.
What can you do to help? Well, you can make a quick script using openpyxl that iterates over every single User record and puts all the essential information into an Excel spreadsheet.
That’s gonna earn you an extra slice of cake at your company’s next birthday party!
Appending Information to an Existing Spreadsheet
You may also have to open a spreadsheet, read the information in it and, according to some business logic, append more data to it.
For example, using the online store scenario again, say you get an Excel spreadsheet with a list of users and you need to append to each row the total amount they’ve spent in your store.
This data is in the Database and, in order to do this, you have to read the spreadsheet, iterate through each row, fetch the total amount spent from the Database and then write back to the spreadsheet.
Not a problem for openpyxl!
Learning Some Basic Excel Terminology
Here’s a quick list of basic terms you’ll see when you’re working with Excel spreadsheets:
| Term | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Spreadsheet or Workbook | A Spreadsheet is the main file you are creating or working with. |
| Worksheet or Sheet | A Sheet is used to split different kinds of content within the same spreadsheet. A Spreadsheet can have one or more Sheets. |
| Column | A Column is a vertical line, and it’s represented by an uppercase letter: A. |
| Row | A Row is a horizontal line, and it’s represented by a number: 1. |
| Cell | A Cell is a combination of Column and Row, represented by both an uppercase letter and a number: A1. |
Getting Started With openpyxl
Now that you’re aware of the benefits of a tool like openpyxl, let’s get down to it and start by installing the package. For this tutorial, you should use Python 3.7 and openpyxl 2.6.2. To install the package, you can do the following:
After you install the package, you should be able to create a super simple spreadsheet with the following code:
from openpyxl import Workbook
workbook = Workbook()
sheet = workbook.active
sheet["A1"] = "hello"
sheet["B1"] = "world!"
workbook.save(filename="hello_world.xlsx")
The code above should create a file called hello_world.xlsx in the folder you are using to run the code. If you open that file with Excel you should see something like this:
Woohoo, your first spreadsheet created!
Reading Excel Spreadsheets With openpyxl
Let’s start with the most essential thing one can do with a spreadsheet: read it.
You’ll go from a straightforward approach to reading a spreadsheet to more complex examples where you read the data and convert it into more useful Python structures.
Dataset for This Tutorial
Before you dive deep into some code examples, you should download this sample dataset and store it somewhere as sample.xlsx:
This is one of the datasets you’ll be using throughout this tutorial, and it’s a spreadsheet with a sample of real data from Amazon’s online product reviews. This dataset is only a tiny fraction of what Amazon provides, but for testing purposes, it’s more than enough.
A Simple Approach to Reading an Excel Spreadsheet
Finally, let’s start reading some spreadsheets! To begin with, open our sample spreadsheet:
>>>
>>> from openpyxl import load_workbook
>>> workbook = load_workbook(filename="sample.xlsx")
>>> workbook.sheetnames
['Sheet 1']
>>> sheet = workbook.active
>>> sheet
<Worksheet "Sheet 1">
>>> sheet.title
'Sheet 1'
In the code above, you first open the spreadsheet sample.xlsx using load_workbook(), and then you can use workbook.sheetnames to see all the sheets you have available to work with. After that, workbook.active selects the first available sheet and, in this case, you can see that it selects Sheet 1 automatically. Using these methods is the default way of opening a spreadsheet, and you’ll see it many times during this tutorial.
Now, after opening a spreadsheet, you can easily retrieve data from it like this:
>>>
>>> sheet["A1"]
<Cell 'Sheet 1'.A1>
>>> sheet["A1"].value
'marketplace'
>>> sheet["F10"].value
"G-Shock Men's Grey Sport Watch"
To return the actual value of a cell, you need to do .value. Otherwise, you’ll get the main Cell object. You can also use the method .cell() to retrieve a cell using index notation. Remember to add .value to get the actual value and not a Cell object:
>>>
>>> sheet.cell(row=10, column=6)
<Cell 'Sheet 1'.F10>
>>> sheet.cell(row=10, column=6).value
"G-Shock Men's Grey Sport Watch"
You can see that the results returned are the same, no matter which way you decide to go with. However, in this tutorial, you’ll be mostly using the first approach: ["A1"].
The above shows you the quickest way to open a spreadsheet. However, you can pass additional parameters to change the way a spreadsheet is loaded.
Additional Reading Options
There are a few arguments you can pass to load_workbook() that change the way a spreadsheet is loaded. The most important ones are the following two Booleans:
- read_only loads a spreadsheet in read-only mode allowing you to open very large Excel files.
- data_only ignores loading formulas and instead loads only the resulting values.
Importing Data From a Spreadsheet
Now that you’ve learned the basics about loading a spreadsheet, it’s about time you get to the fun part: the iteration and actual usage of the values within the spreadsheet.
This section is where you’ll learn all the different ways you can iterate through the data, but also how to convert that data into something usable and, more importantly, how to do it in a Pythonic way.
Iterating Through the Data
There are a few different ways you can iterate through the data depending on your needs.
You can slice the data with a combination of columns and rows:
>>>
>>> sheet["A1:C2"]
((<Cell 'Sheet 1'.A1>, <Cell 'Sheet 1'.B1>, <Cell 'Sheet 1'.C1>),
(<Cell 'Sheet 1'.A2>, <Cell 'Sheet 1'.B2>, <Cell 'Sheet 1'.C2>))
You can get ranges of rows or columns:
>>>
>>> # Get all cells from column A
>>> sheet["A"]
(<Cell 'Sheet 1'.A1>,
<Cell 'Sheet 1'.A2>,
...
<Cell 'Sheet 1'.A99>,
<Cell 'Sheet 1'.A100>)
>>> # Get all cells for a range of columns
>>> sheet["A:B"]
((<Cell 'Sheet 1'.A1>,
<Cell 'Sheet 1'.A2>,
...
<Cell 'Sheet 1'.A99>,
<Cell 'Sheet 1'.A100>),
(<Cell 'Sheet 1'.B1>,
<Cell 'Sheet 1'.B2>,
...
<Cell 'Sheet 1'.B99>,
<Cell 'Sheet 1'.B100>))
>>> # Get all cells from row 5
>>> sheet[5]
(<Cell 'Sheet 1'.A5>,
<Cell 'Sheet 1'.B5>,
...
<Cell 'Sheet 1'.N5>,
<Cell 'Sheet 1'.O5>)
>>> # Get all cells for a range of rows
>>> sheet[5:6]
((<Cell 'Sheet 1'.A5>,
<Cell 'Sheet 1'.B5>,
...
<Cell 'Sheet 1'.N5>,
<Cell 'Sheet 1'.O5>),
(<Cell 'Sheet 1'.A6>,
<Cell 'Sheet 1'.B6>,
...
<Cell 'Sheet 1'.N6>,
<Cell 'Sheet 1'.O6>))
You’ll notice that all of the above examples return a tuple. If you want to refresh your memory on how to handle tuples in Python, check out the article on Lists and Tuples in Python.
There are also multiple ways of using normal Python generators to go through the data. The main methods you can use to achieve this are:
.iter_rows().iter_cols()
Both methods can receive the following arguments:
min_rowmax_rowmin_colmax_col
These arguments are used to set boundaries for the iteration:
>>>
>>> for row in sheet.iter_rows(min_row=1,
... max_row=2,
... min_col=1,
... max_col=3):
... print(row)
(<Cell 'Sheet 1'.A1>, <Cell 'Sheet 1'.B1>, <Cell 'Sheet 1'.C1>)
(<Cell 'Sheet 1'.A2>, <Cell 'Sheet 1'.B2>, <Cell 'Sheet 1'.C2>)
>>> for column in sheet.iter_cols(min_row=1,
... max_row=2,
... min_col=1,
... max_col=3):
... print(column)
(<Cell 'Sheet 1'.A1>, <Cell 'Sheet 1'.A2>)
(<Cell 'Sheet 1'.B1>, <Cell 'Sheet 1'.B2>)
(<Cell 'Sheet 1'.C1>, <Cell 'Sheet 1'.C2>)
You’ll notice that in the first example, when iterating through the rows using .iter_rows(), you get one tuple element per row selected. While when using .iter_cols() and iterating through columns, you’ll get one tuple per column instead.
One additional argument you can pass to both methods is the Boolean values_only. When it’s set to True, the values of the cell are returned, instead of the Cell object:
>>>
>>> for value in sheet.iter_rows(min_row=1,
... max_row=2,
... min_col=1,
... max_col=3,
... values_only=True):
... print(value)
('marketplace', 'customer_id', 'review_id')
('US', 3653882, 'R3O9SGZBVQBV76')
If you want to iterate through the whole dataset, then you can also use the attributes .rows or .columns directly, which are shortcuts to using .iter_rows() and .iter_cols() without any arguments:
>>>
>>> for row in sheet.rows:
... print(row)
(<Cell 'Sheet 1'.A1>, <Cell 'Sheet 1'.B1>, <Cell 'Sheet 1'.C1>
...
<Cell 'Sheet 1'.M100>, <Cell 'Sheet 1'.N100>, <Cell 'Sheet 1'.O100>)
These shortcuts are very useful when you’re iterating through the whole dataset.
Manipulate Data Using Python’s Default Data Structures
Now that you know the basics of iterating through the data in a workbook, let’s look at smart ways of converting that data into Python structures.
As you saw earlier, the result from all iterations comes in the form of tuples. However, since a tuple is nothing more than an immutable list, you can easily access its data and transform it into other structures.
For example, say you want to extract product information from the sample.xlsx spreadsheet and into a dictionary where each key is a product ID.
A straightforward way to do this is to iterate over all the rows, pick the columns you know are related to product information, and then store that in a dictionary. Let’s code this out!
First of all, have a look at the headers and see what information you care most about:
>>>
>>> for value in sheet.iter_rows(min_row=1,
... max_row=1,
... values_only=True):
... print(value)
('marketplace', 'customer_id', 'review_id', 'product_id', ...)
This code returns a list of all the column names you have in the spreadsheet. To start, grab the columns with names:
product_idproduct_parentproduct_titleproduct_category
Lucky for you, the columns you need are all next to each other so you can use the min_column and max_column to easily get the data you want:
>>>
>>> for value in sheet.iter_rows(min_row=2,
... min_col=4,
... max_col=7,
... values_only=True):
... print(value)
('B00FALQ1ZC', 937001370, 'Invicta Women's 15150 "Angel" 18k Yellow...)
('B00D3RGO20', 484010722, "Kenneth Cole New York Women's KC4944...)
...
Nice! Now that you know how to get all the important product information you need, let’s put that data into a dictionary:
import json
from openpyxl import load_workbook
workbook = load_workbook(filename="sample.xlsx")
sheet = workbook.active
products = {}
# Using the values_only because you want to return the cells' values
for row in sheet.iter_rows(min_row=2,
min_col=4,
max_col=7,
values_only=True):
product_id = row[0]
product = {
"parent": row[1],
"title": row[2],
"category": row[3]
}
products[product_id] = product
# Using json here to be able to format the output for displaying later
print(json.dumps(products))
The code above returns a JSON similar to this:
{
"B00FALQ1ZC": {
"parent": 937001370,
"title": "Invicta Women's 15150 ...",
"category": "Watches"
},
"B00D3RGO20": {
"parent": 484010722,
"title": "Kenneth Cole New York ...",
"category": "Watches"
}
}
Here you can see that the output is trimmed to 2 products only, but if you run the script as it is, then you should get 98 products.
Convert Data Into Python Classes
To finalize the reading section of this tutorial, let’s dive into Python classes and see how you could improve on the example above and better structure the data.
For this, you’ll be using the new Python Data Classes that are available from Python 3.7. If you’re using an older version of Python, then you can use the default Classes instead.
So, first things first, let’s look at the data you have and decide what you want to store and how you want to store it.
As you saw right at the start, this data comes from Amazon, and it’s a list of product reviews. You can check the list of all the columns and their meaning on Amazon.
There are two significant elements you can extract from the data available:
- Products
- Reviews
A Product has:
- ID
- Title
- Parent
- Category
The Review has a few more fields:
- ID
- Customer ID
- Stars
- Headline
- Body
- Date
You can ignore a few of the review fields to make things a bit simpler.
So, a straightforward implementation of these two classes could be written in a separate file classes.py:
import datetime
from dataclasses import dataclass
@dataclass
class Product:
id: str
parent: str
title: str
category: str
@dataclass
class Review:
id: str
customer_id: str
stars: int
headline: str
body: str
date: datetime.datetime
After defining your data classes, you need to convert the data from the spreadsheet into these new structures.
Before doing the conversion, it’s worth looking at our header again and creating a mapping between columns and the fields you need:
>>>
>>> for value in sheet.iter_rows(min_row=1,
... max_row=1,
... values_only=True):
... print(value)
('marketplace', 'customer_id', 'review_id', 'product_id', ...)
>>> # Or an alternative
>>> for cell in sheet[1]:
... print(cell.value)
marketplace
customer_id
review_id
product_id
product_parent
...
Let’s create a file mapping.py where you have a list of all the field names and their column location (zero-indexed) on the spreadsheet:
# Product fields
PRODUCT_ID = 3
PRODUCT_PARENT = 4
PRODUCT_TITLE = 5
PRODUCT_CATEGORY = 6
# Review fields
REVIEW_ID = 2
REVIEW_CUSTOMER = 1
REVIEW_STARS = 7
REVIEW_HEADLINE = 12
REVIEW_BODY = 13
REVIEW_DATE = 14
You don’t necessarily have to do the mapping above. It’s more for readability when parsing the row data, so you don’t end up with a lot of magic numbers lying around.
Finally, let’s look at the code needed to parse the spreadsheet data into a list of product and review objects:
from datetime import datetime
from openpyxl import load_workbook
from classes import Product, Review
from mapping import PRODUCT_ID, PRODUCT_PARENT, PRODUCT_TITLE,
PRODUCT_CATEGORY, REVIEW_DATE, REVIEW_ID, REVIEW_CUSTOMER,
REVIEW_STARS, REVIEW_HEADLINE, REVIEW_BODY
# Using the read_only method since you're not gonna be editing the spreadsheet
workbook = load_workbook(filename="sample.xlsx", read_only=True)
sheet = workbook.active
products = []
reviews = []
# Using the values_only because you just want to return the cell value
for row in sheet.iter_rows(min_row=2, values_only=True):
product = Product(id=row[PRODUCT_ID],
parent=row[PRODUCT_PARENT],
title=row[PRODUCT_TITLE],
category=row[PRODUCT_CATEGORY])
products.append(product)
# You need to parse the date from the spreadsheet into a datetime format
spread_date = row[REVIEW_DATE]
parsed_date = datetime.strptime(spread_date, "%Y-%m-%d")
review = Review(id=row[REVIEW_ID],
customer_id=row[REVIEW_CUSTOMER],
stars=row[REVIEW_STARS],
headline=row[REVIEW_HEADLINE],
body=row[REVIEW_BODY],
date=parsed_date)
reviews.append(review)
print(products[0])
print(reviews[0])
After you run the code above, you should get some output like this:
Product(id='B00FALQ1ZC', parent=937001370, ...)
Review(id='R3O9SGZBVQBV76', customer_id=3653882, ...)
That’s it! Now you should have the data in a very simple and digestible class format, and you can start thinking of storing this in a Database or any other type of data storage you like.
Using this kind of OOP strategy to parse spreadsheets makes handling the data much simpler later on.
Appending New Data
Before you start creating very complex spreadsheets, have a quick look at an example of how to append data to an existing spreadsheet.
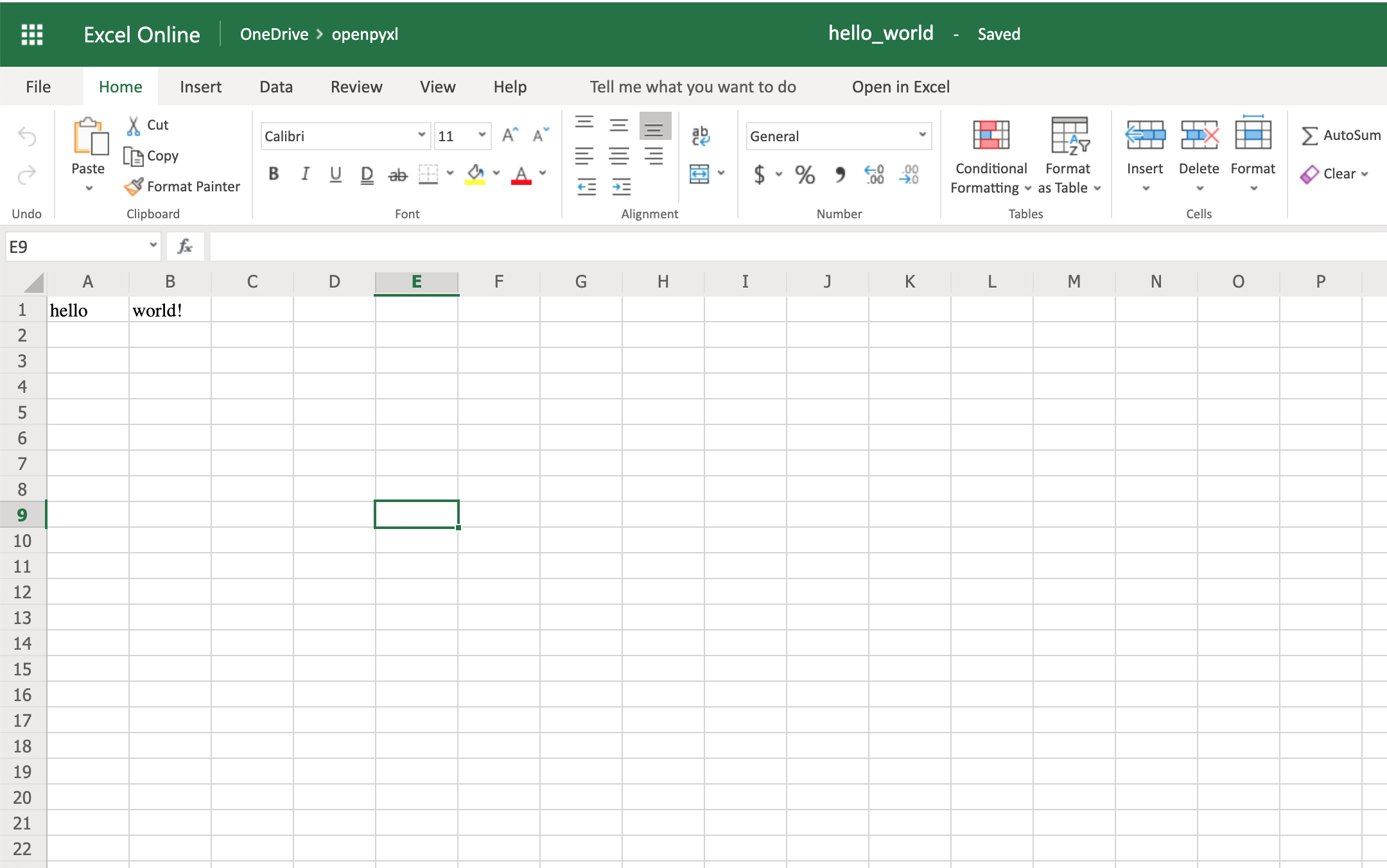
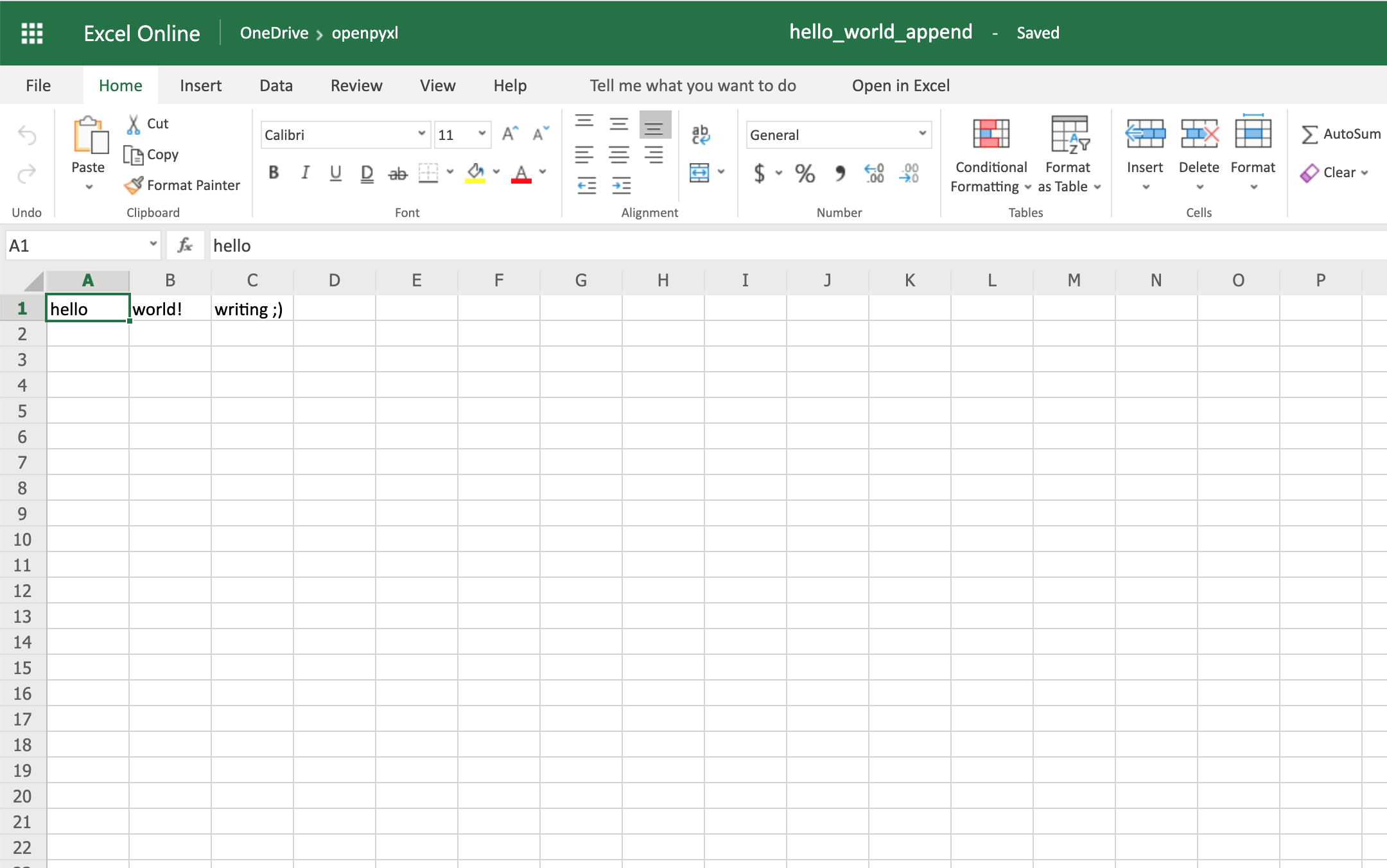
Go back to the first example spreadsheet you created (hello_world.xlsx) and try opening it and appending some data to it, like this:
from openpyxl import load_workbook
# Start by opening the spreadsheet and selecting the main sheet
workbook = load_workbook(filename="hello_world.xlsx")
sheet = workbook.active
# Write what you want into a specific cell
sheet["C1"] = "writing ;)"
# Save the spreadsheet
workbook.save(filename="hello_world_append.xlsx")
Et voilà, if you open the new hello_world_append.xlsx spreadsheet, you’ll see the following change:
Notice the additional writing 
C1.
Writing Excel Spreadsheets With openpyxl
There are a lot of different things you can write to a spreadsheet, from simple text or number values to complex formulas, charts, or even images.
Let’s start creating some spreadsheets!
Creating a Simple Spreadsheet
Previously, you saw a very quick example of how to write “Hello world!” into a spreadsheet, so you can start with that:
1from openpyxl import Workbook
2
3filename = "hello_world.xlsx"
4
5workbook = Workbook()
6sheet = workbook.active
7
8sheet["A1"] = "hello"
9sheet["B1"] = "world!"
10
11workbook.save(filename=filename)
The highlighted lines in the code above are the most important ones for writing. In the code, you can see that:
- Line 5 shows you how to create a new empty workbook.
- Lines 8 and 9 show you how to add data to specific cells.
- Line 11 shows you how to save the spreadsheet when you’re done.
Even though these lines above can be straightforward, it’s still good to know them well for when things get a bit more complicated.
One thing you can do to help with coming code examples is add the following method to your Python file or console:
>>>
>>> def print_rows():
... for row in sheet.iter_rows(values_only=True):
... print(row)
It makes it easier to print all of your spreadsheet values by just calling print_rows().
Basic Spreadsheet Operations
Before you get into the more advanced topics, it’s good for you to know how to manage the most simple elements of a spreadsheet.
Adding and Updating Cell Values
You already learned how to add values to a spreadsheet like this:
>>>
>>> sheet["A1"] = "value"
There’s another way you can do this, by first selecting a cell and then changing its value:
>>>
>>> cell = sheet["A1"]
>>> cell
<Cell 'Sheet'.A1>
>>> cell.value
'hello'
>>> cell.value = "hey"
>>> cell.value
'hey'
The new value is only stored into the spreadsheet once you call workbook.save().
The openpyxl creates a cell when adding a value, if that cell didn’t exist before:
>>>
>>> # Before, our spreadsheet has only 1 row
>>> print_rows()
('hello', 'world!')
>>> # Try adding a value to row 10
>>> sheet["B10"] = "test"
>>> print_rows()
('hello', 'world!')
(None, None)
(None, None)
(None, None)
(None, None)
(None, None)
(None, None)
(None, None)
(None, None)
(None, 'test')
As you can see, when trying to add a value to cell B10, you end up with a tuple with 10 rows, just so you can have that test value.
Managing Rows and Columns
One of the most common things you have to do when manipulating spreadsheets is adding or removing rows and columns. The openpyxl package allows you to do that in a very straightforward way by using the methods:
.insert_rows().delete_rows().insert_cols().delete_cols()
Every single one of those methods can receive two arguments:
idxamount
Using our basic hello_world.xlsx example again, let’s see how these methods work:
>>>
>>> print_rows()
('hello', 'world!')
>>> # Insert a column before the existing column 1 ("A")
>>> sheet.insert_cols(idx=1)
>>> print_rows()
(None, 'hello', 'world!')
>>> # Insert 5 columns between column 2 ("B") and 3 ("C")
>>> sheet.insert_cols(idx=3, amount=5)
>>> print_rows()
(None, 'hello', None, None, None, None, None, 'world!')
>>> # Delete the created columns
>>> sheet.delete_cols(idx=3, amount=5)
>>> sheet.delete_cols(idx=1)
>>> print_rows()
('hello', 'world!')
>>> # Insert a new row in the beginning
>>> sheet.insert_rows(idx=1)
>>> print_rows()
(None, None)
('hello', 'world!')
>>> # Insert 3 new rows in the beginning
>>> sheet.insert_rows(idx=1, amount=3)
>>> print_rows()
(None, None)
(None, None)
(None, None)
(None, None)
('hello', 'world!')
>>> # Delete the first 4 rows
>>> sheet.delete_rows(idx=1, amount=4)
>>> print_rows()
('hello', 'world!')
The only thing you need to remember is that when inserting new data (rows or columns), the insertion happens before the idx parameter.
So, if you do insert_rows(1), it inserts a new row before the existing first row.
It’s the same for columns: when you call insert_cols(2), it inserts a new column right before the already existing second column (B).
However, when deleting rows or columns, .delete_... deletes data starting from the index passed as an argument.
For example, when doing delete_rows(2) it deletes row 2, and when doing delete_cols(3) it deletes the third column (C).
Managing Sheets
Sheet management is also one of those things you might need to know, even though it might be something that you don’t use that often.
If you look back at the code examples from this tutorial, you’ll notice the following recurring piece of code:
This is the way to select the default sheet from a spreadsheet. However, if you’re opening a spreadsheet with multiple sheets, then you can always select a specific one like this:
>>>
>>> # Let's say you have two sheets: "Products" and "Company Sales"
>>> workbook.sheetnames
['Products', 'Company Sales']
>>> # You can select a sheet using its title
>>> products_sheet = workbook["Products"]
>>> sales_sheet = workbook["Company Sales"]
You can also change a sheet title very easily:
>>>
>>> workbook.sheetnames
['Products', 'Company Sales']
>>> products_sheet = workbook["Products"]
>>> products_sheet.title = "New Products"
>>> workbook.sheetnames
['New Products', 'Company Sales']
If you want to create or delete sheets, then you can also do that with .create_sheet() and .remove():
>>>
>>> workbook.sheetnames
['Products', 'Company Sales']
>>> operations_sheet = workbook.create_sheet("Operations")
>>> workbook.sheetnames
['Products', 'Company Sales', 'Operations']
>>> # You can also define the position to create the sheet at
>>> hr_sheet = workbook.create_sheet("HR", 0)
>>> workbook.sheetnames
['HR', 'Products', 'Company Sales', 'Operations']
>>> # To remove them, just pass the sheet as an argument to the .remove()
>>> workbook.remove(operations_sheet)
>>> workbook.sheetnames
['HR', 'Products', 'Company Sales']
>>> workbook.remove(hr_sheet)
>>> workbook.sheetnames
['Products', 'Company Sales']
One other thing you can do is make duplicates of a sheet using copy_worksheet():
>>>
>>> workbook.sheetnames
['Products', 'Company Sales']
>>> products_sheet = workbook["Products"]
>>> workbook.copy_worksheet(products_sheet)
<Worksheet "Products Copy">
>>> workbook.sheetnames
['Products', 'Company Sales', 'Products Copy']
If you open your spreadsheet after saving the above code, you’ll notice that the sheet Products Copy is a duplicate of the sheet Products.
Freezing Rows and Columns
Something that you might want to do when working with big spreadsheets is to freeze a few rows or columns, so they remain visible when you scroll right or down.
Freezing data allows you to keep an eye on important rows or columns, regardless of where you scroll in the spreadsheet.
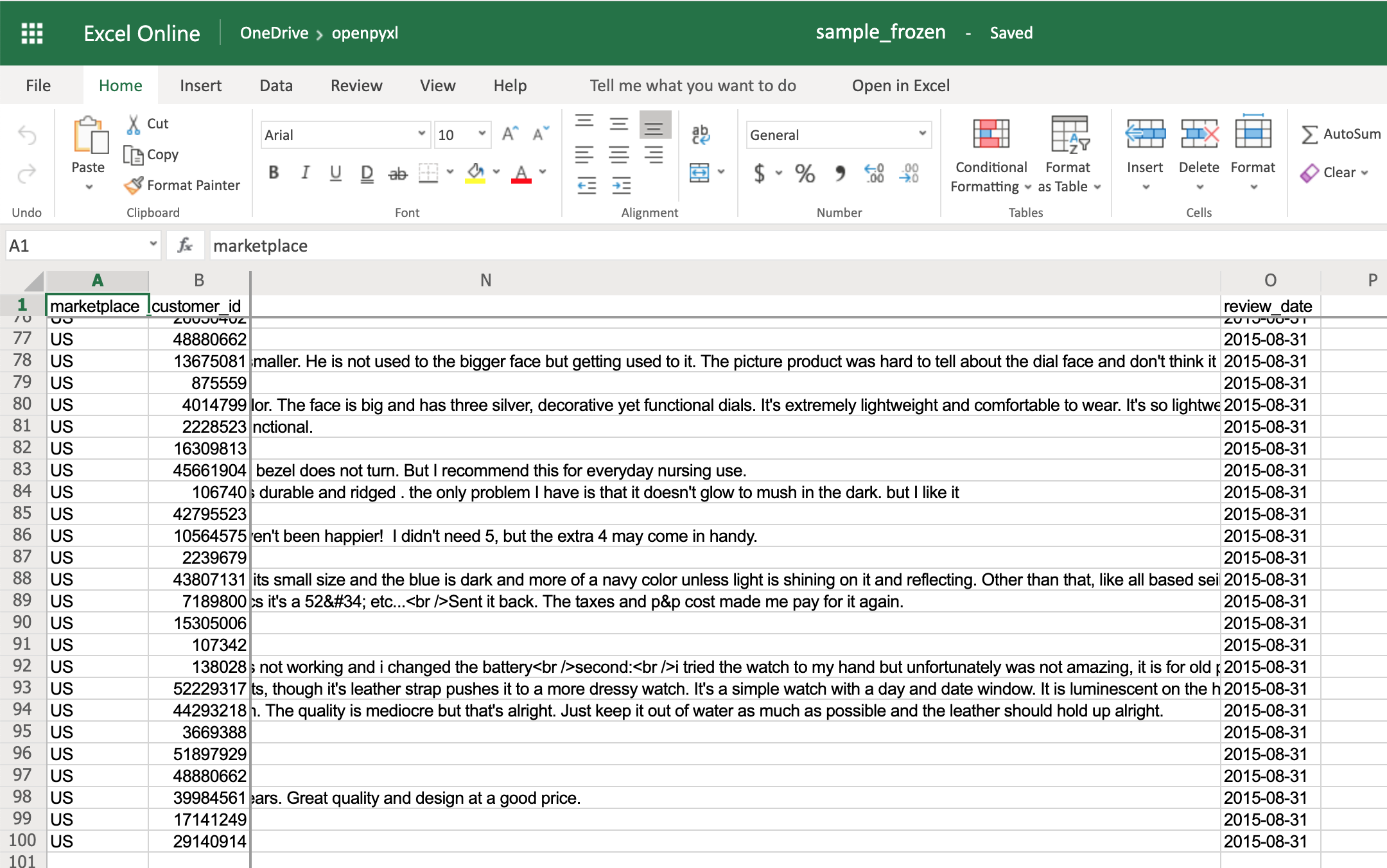
Again, openpyxl also has a way to accomplish this by using the worksheet freeze_panes attribute. For this example, go back to our sample.xlsx spreadsheet and try doing the following:
>>>
>>> workbook = load_workbook(filename="sample.xlsx")
>>> sheet = workbook.active
>>> sheet.freeze_panes = "C2"
>>> workbook.save("sample_frozen.xlsx")
If you open the sample_frozen.xlsx spreadsheet in your favorite spreadsheet editor, you’ll notice that row 1 and columns A and B are frozen and are always visible no matter where you navigate within the spreadsheet.
This feature is handy, for example, to keep headers within sight, so you always know what each column represents.
Here’s how it looks in the editor:
Notice how you’re at the end of the spreadsheet, and yet, you can see both row 1 and columns A and B.
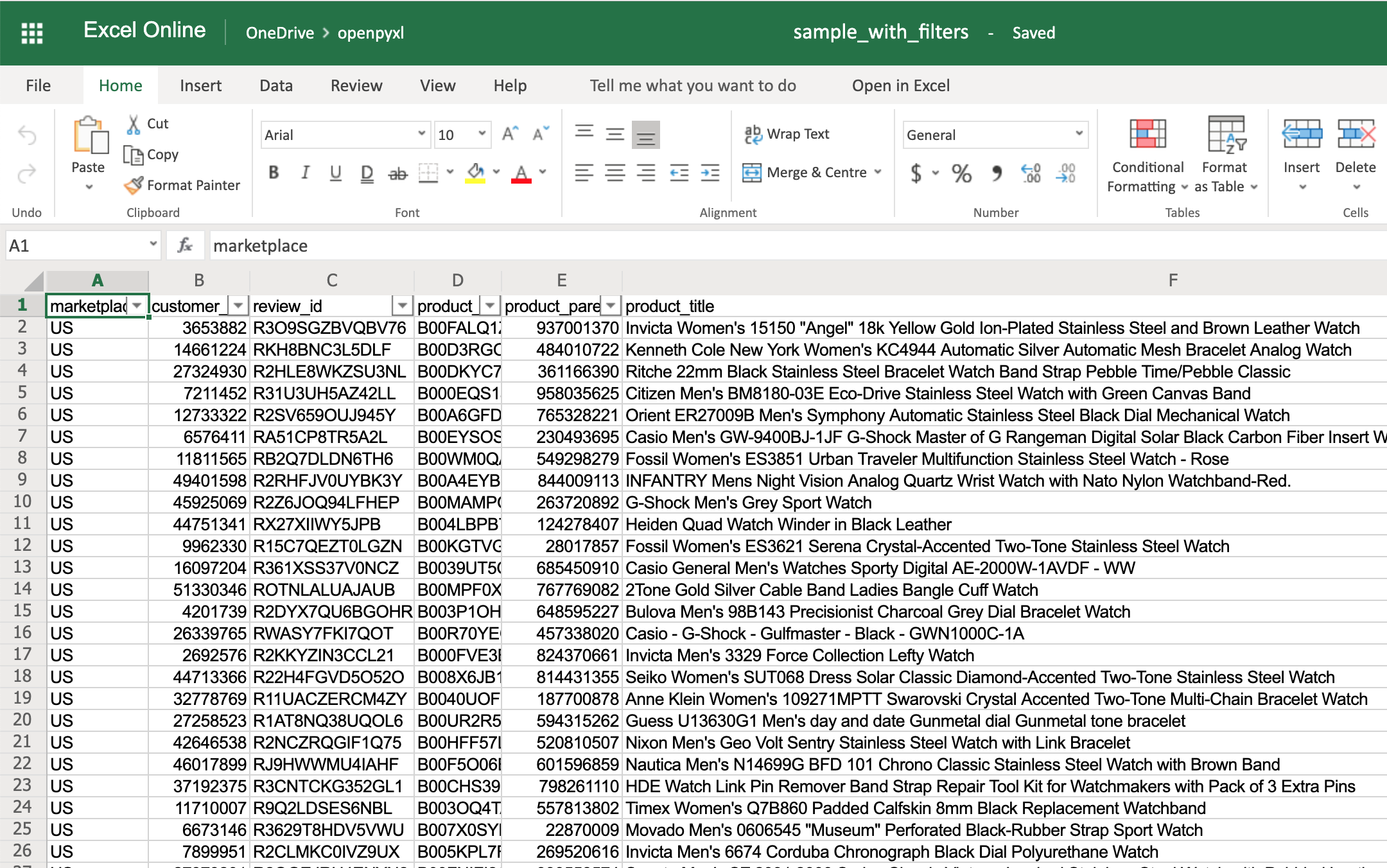
Adding Filters
You can use openpyxl to add filters and sorts to your spreadsheet. However, when you open the spreadsheet, the data won’t be rearranged according to these sorts and filters.
At first, this might seem like a pretty useless feature, but when you’re programmatically creating a spreadsheet that is going to be sent and used by somebody else, it’s still nice to at least create the filters and allow people to use it afterward.
The code below is an example of how you would add some filters to our existing sample.xlsx spreadsheet:
>>>
>>> # Check the used spreadsheet space using the attribute "dimensions"
>>> sheet.dimensions
'A1:O100'
>>> sheet.auto_filter.ref = "A1:O100"
>>> workbook.save(filename="sample_with_filters.xlsx")
You should now see the filters created when opening the spreadsheet in your editor:
You don’t have to use sheet.dimensions if you know precisely which part of the spreadsheet you want to apply filters to.
Adding Formulas
Formulas (or formulae) are one of the most powerful features of spreadsheets.
They gives you the power to apply specific mathematical equations to a range of cells. Using formulas with openpyxl is as simple as editing the value of a cell.
You can see the list of formulas supported by openpyxl:
>>>
>>> from openpyxl.utils import FORMULAE
>>> FORMULAE
frozenset({'ABS',
'ACCRINT',
'ACCRINTM',
'ACOS',
'ACOSH',
'AMORDEGRC',
'AMORLINC',
'AND',
...
'YEARFRAC',
'YIELD',
'YIELDDISC',
'YIELDMAT',
'ZTEST'})
Let’s add some formulas to our sample.xlsx spreadsheet.
Starting with something easy, let’s check the average star rating for the 99 reviews within the spreadsheet:
>>>
>>> # Star rating is column "H"
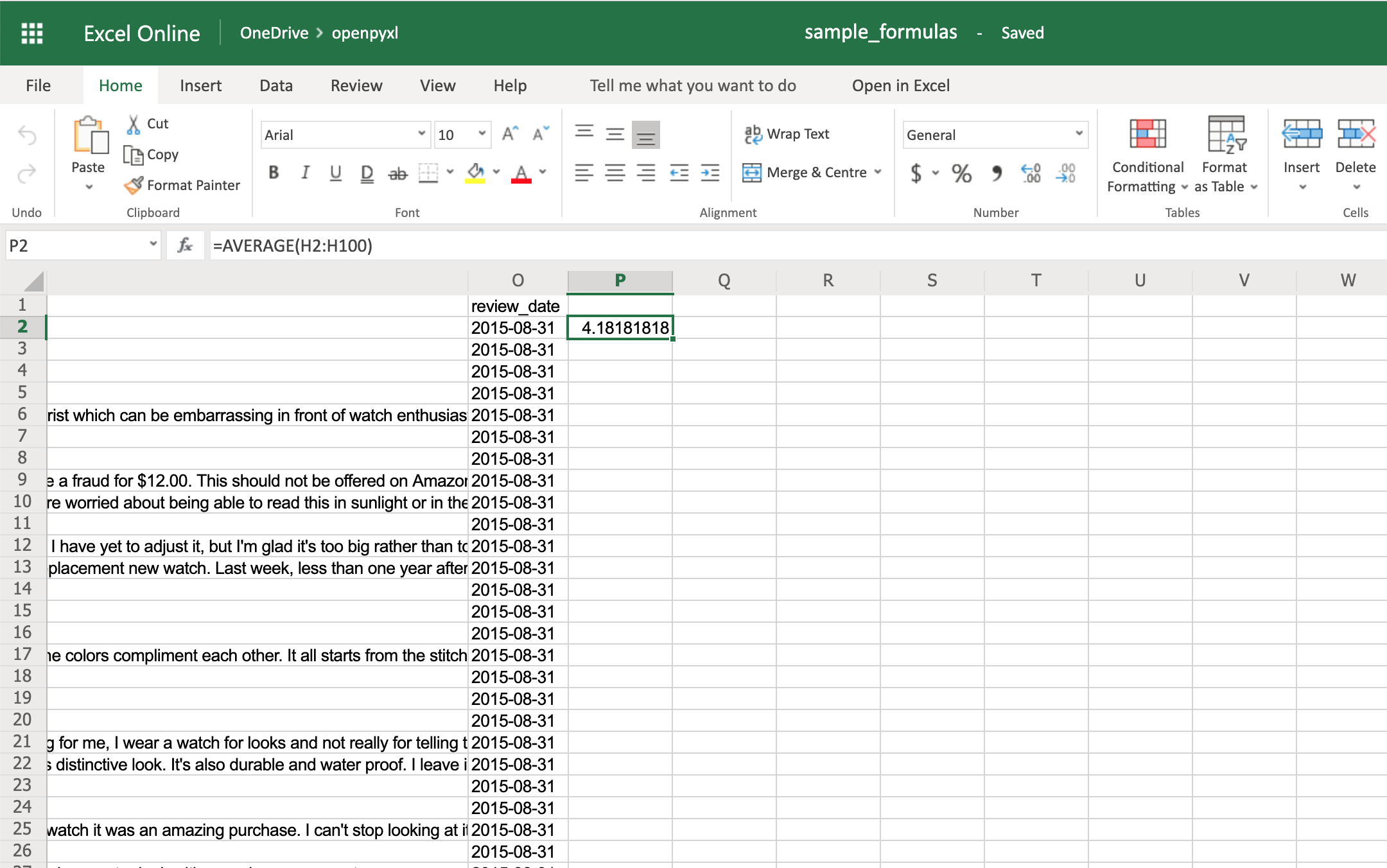
>>> sheet["P2"] = "=AVERAGE(H2:H100)"
>>> workbook.save(filename="sample_formulas.xlsx")
If you open the spreadsheet now and go to cell P2, you should see that its value is: 4.18181818181818. Have a look in the editor:
You can use the same methodology to add any formulas to your spreadsheet. For example, let’s count the number of reviews that had helpful votes:
>>>
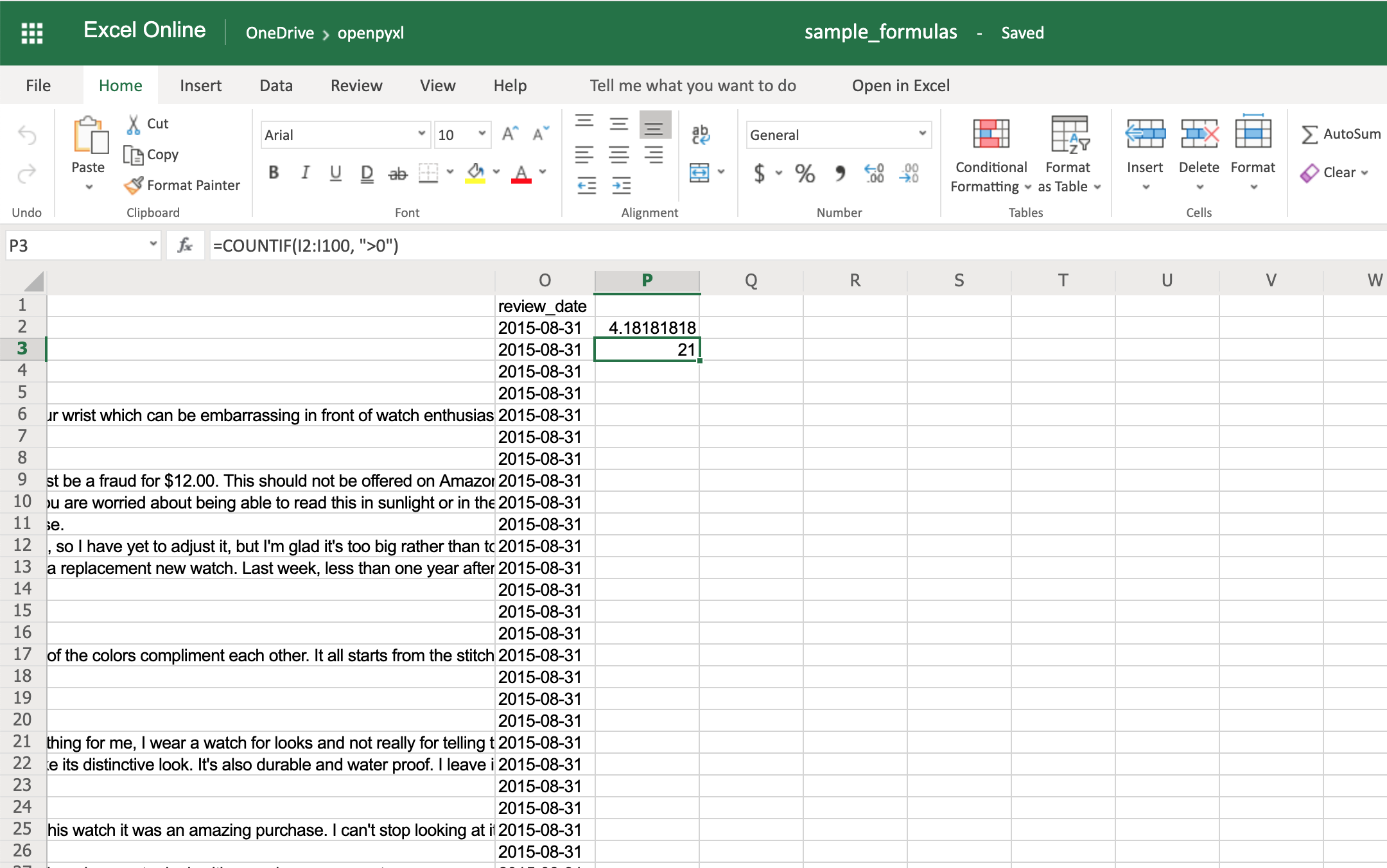
>>> # The helpful votes are counted on column "I"
>>> sheet["P3"] = '=COUNTIF(I2:I100, ">0")'
>>> workbook.save(filename="sample_formulas.xlsx")
You should get the number 21 on your P3 spreadsheet cell like so:
You’ll have to make sure that the strings within a formula are always in double quotes, so you either have to use single quotes around the formula like in the example above or you’ll have to escape the double quotes inside the formula: "=COUNTIF(I2:I100, ">0")".
There are a ton of other formulas you can add to your spreadsheet using the same procedure you tried above. Give it a go yourself!
Adding Styles
Even though styling a spreadsheet might not be something you would do every day, it’s still good to know how to do it.
Using openpyxl, you can apply multiple styling options to your spreadsheet, including fonts, borders, colors, and so on. Have a look at the openpyxl documentation to learn more.
You can also choose to either apply a style directly to a cell or create a template and reuse it to apply styles to multiple cells.
Let’s start by having a look at simple cell styling, using our sample.xlsx again as the base spreadsheet:
>>>
>>> # Import necessary style classes
>>> from openpyxl.styles import Font, Color, Alignment, Border, Side
>>> # Create a few styles
>>> bold_font = Font(bold=True)
>>> big_red_text = Font(color="00FF0000", size=20)
>>> center_aligned_text = Alignment(horizontal="center")
>>> double_border_side = Side(border_style="double")
>>> square_border = Border(top=double_border_side,
... right=double_border_side,
... bottom=double_border_side,
... left=double_border_side)
>>> # Style some cells!
>>> sheet["A2"].font = bold_font
>>> sheet["A3"].font = big_red_text
>>> sheet["A4"].alignment = center_aligned_text
>>> sheet["A5"].border = square_border
>>> workbook.save(filename="sample_styles.xlsx")
If you open your spreadsheet now, you should see quite a few different styles on the first 5 cells of column A:
There you go. You got:
- A2 with the text in bold
- A3 with the text in red and bigger font size
- A4 with the text centered
- A5 with a square border around the text
You can also combine styles by simply adding them to the cell at the same time:
>>>
>>> # Reusing the same styles from the example above
>>> sheet["A6"].alignment = center_aligned_text
>>> sheet["A6"].font = big_red_text
>>> sheet["A6"].border = square_border
>>> workbook.save(filename="sample_styles.xlsx")
Have a look at cell A6 here:
When you want to apply multiple styles to one or several cells, you can use a NamedStyle class instead, which is like a style template that you can use over and over again. Have a look at the example below:
>>>
>>> from openpyxl.styles import NamedStyle
>>> # Let's create a style template for the header row
>>> header = NamedStyle(name="header")
>>> header.font = Font(bold=True)
>>> header.border = Border(bottom=Side(border_style="thin"))
>>> header.alignment = Alignment(horizontal="center", vertical="center")
>>> # Now let's apply this to all first row (header) cells
>>> header_row = sheet[1]
>>> for cell in header_row:
... cell.style = header
>>> workbook.save(filename="sample_styles.xlsx")
If you open the spreadsheet now, you should see that its first row is bold, the text is aligned to the center, and there’s a small bottom border! Have a look below:
As you saw above, there are many options when it comes to styling, and it depends on the use case, so feel free to check openpyxl documentation and see what other things you can do.
Conditional Formatting
This feature is one of my personal favorites when it comes to adding styles to a spreadsheet.
It’s a much more powerful approach to styling because it dynamically applies styles according to how the data in the spreadsheet changes.
In a nutshell, conditional formatting allows you to specify a list of styles to apply to a cell (or cell range) according to specific conditions.
For example, a widespread use case is to have a balance sheet where all the negative totals are in red, and the positive ones are in green. This formatting makes it much more efficient to spot good vs bad periods.
Without further ado, let’s pick our favorite spreadsheet—sample.xlsx—and add some conditional formatting.
You can start by adding a simple one that adds a red background to all reviews with less than 3 stars:
>>>
>>> from openpyxl.styles import PatternFill
>>> from openpyxl.styles.differential import DifferentialStyle
>>> from openpyxl.formatting.rule import Rule
>>> red_background = PatternFill(fgColor="00FF0000")
>>> diff_style = DifferentialStyle(fill=red_background)
>>> rule = Rule(type="expression", dxf=diff_style)
>>> rule.formula = ["$H1<3"]
>>> sheet.conditional_formatting.add("A1:O100", rule)
>>> workbook.save("sample_conditional_formatting.xlsx")
Now you’ll see all the reviews with a star rating below 3 marked with a red background:
Code-wise, the only things that are new here are the objects DifferentialStyle and Rule:
DifferentialStyleis quite similar toNamedStyle, which you already saw above, and it’s used to aggregate multiple styles such as fonts, borders, alignment, and so forth.Ruleis responsible for selecting the cells and applying the styles if the cells match the rule’s logic.
Using a Rule object, you can create numerous conditional formatting scenarios.
However, for simplicity sake, the openpyxl package offers 3 built-in formats that make it easier to create a few common conditional formatting patterns. These built-ins are:
ColorScaleIconSetDataBar
The ColorScale gives you the ability to create color gradients:
>>>
>>> from openpyxl.formatting.rule import ColorScaleRule
>>> color_scale_rule = ColorScaleRule(start_type="min",
... start_color="00FF0000", # Red
... end_type="max",
... end_color="0000FF00") # Green
>>> # Again, let's add this gradient to the star ratings, column "H"
>>> sheet.conditional_formatting.add("H2:H100", color_scale_rule)
>>> workbook.save(filename="sample_conditional_formatting_color_scale.xlsx")
Now you should see a color gradient on column H, from red to green, according to the star rating:
You can also add a third color and make two gradients instead:
>>>
>>> from openpyxl.formatting.rule import ColorScaleRule
>>> color_scale_rule = ColorScaleRule(start_type="num",
... start_value=1,
... start_color="00FF0000", # Red
... mid_type="num",
... mid_value=3,
... mid_color="00FFFF00", # Yellow
... end_type="num",
... end_value=5,
... end_color="0000FF00") # Green
>>> # Again, let's add this gradient to the star ratings, column "H"
>>> sheet.conditional_formatting.add("H2:H100", color_scale_rule)
>>> workbook.save(filename="sample_conditional_formatting_color_scale_3.xlsx")
This time, you’ll notice that star ratings between 1 and 3 have a gradient from red to yellow, and star ratings between 3 and 5 have a gradient from yellow to green:
The IconSet allows you to add an icon to the cell according to its value:
>>>
>>> from openpyxl.formatting.rule import IconSetRule
>>> icon_set_rule = IconSetRule("5Arrows", "num", [1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
>>> sheet.conditional_formatting.add("H2:H100", icon_set_rule)
>>> workbook.save("sample_conditional_formatting_icon_set.xlsx")
You’ll see a colored arrow next to the star rating. This arrow is red and points down when the value of the cell is 1 and, as the rating gets better, the arrow starts pointing up and becomes green:
The openpyxl package has a full list of other icons you can use, besides the arrow.
Finally, the DataBar allows you to create progress bars:
>>>
>>> from openpyxl.formatting.rule import DataBarRule
>>> data_bar_rule = DataBarRule(start_type="num",
... start_value=1,
... end_type="num",
... end_value="5",
... color="0000FF00") # Green
>>> sheet.conditional_formatting.add("H2:H100", data_bar_rule)
>>> workbook.save("sample_conditional_formatting_data_bar.xlsx")
You’ll now see a green progress bar that gets fuller the closer the star rating is to the number 5:
As you can see, there are a lot of cool things you can do with conditional formatting.
Here, you saw only a few examples of what you can achieve with it, but check the openpyxl documentation to see a bunch of other options.
Adding Images
Even though images are not something that you’ll often see in a spreadsheet, it’s quite cool to be able to add them. Maybe you can use it for branding purposes or to make spreadsheets more personal.
To be able to load images to a spreadsheet using openpyxl, you’ll have to install Pillow:
Apart from that, you’ll also need an image. For this example, you can grab the Real Python logo below and convert it from .webp to .png using an online converter such as cloudconvert.com, save the final file as logo.png, and copy it to the root folder where you’re running your examples:
Afterward, this is the code you need to import that image into the hello_word.xlsx spreadsheet:
from openpyxl import load_workbook
from openpyxl.drawing.image import Image
# Let's use the hello_world spreadsheet since it has less data
workbook = load_workbook(filename="hello_world.xlsx")
sheet = workbook.active
logo = Image("logo.png")
# A bit of resizing to not fill the whole spreadsheet with the logo
logo.height = 150
logo.width = 150
sheet.add_image(logo, "A3")
workbook.save(filename="hello_world_logo.xlsx")
You have an image on your spreadsheet! Here it is:
The image’s left top corner is on the cell you chose, in this case, A3.
Adding Pretty Charts
Another powerful thing you can do with spreadsheets is create an incredible variety of charts.
Charts are a great way to visualize and understand loads of data quickly. There are a lot of different chart types: bar chart, pie chart, line chart, and so on. openpyxl has support for a lot of them.
Here, you’ll see only a couple of examples of charts because the theory behind it is the same for every single chart type:
For any chart you want to build, you’ll need to define the chart type: BarChart, LineChart, and so forth, plus the data to be used for the chart, which is called Reference.
Before you can build your chart, you need to define what data you want to see represented in it. Sometimes, you can use the dataset as is, but other times you need to massage the data a bit to get additional information.
Let’s start by building a new workbook with some sample data:
1from openpyxl import Workbook
2from openpyxl.chart import BarChart, Reference
3
4workbook = Workbook()
5sheet = workbook.active
6
7# Let's create some sample sales data
8rows = [
9 ["Product", "Online", "Store"],
10 [1, 30, 45],
11 [2, 40, 30],
12 [3, 40, 25],
13 [4, 50, 30],
14 [5, 30, 25],
15 [6, 25, 35],
16 [7, 20, 40],
17]
18
19for row in rows:
20 sheet.append(row)
Now you’re going to start by creating a bar chart that displays the total number of sales per product:
22chart = BarChart()
23data = Reference(worksheet=sheet,
24 min_row=1,
25 max_row=8,
26 min_col=2,
27 max_col=3)
28
29chart.add_data(data, titles_from_data=True)
30sheet.add_chart(chart, "E2")
31
32workbook.save("chart.xlsx")
There you have it. Below, you can see a very straightforward bar chart showing the difference between online product sales online and in-store product sales:
Like with images, the top left corner of the chart is on the cell you added the chart to. In your case, it was on cell E2.
Try creating a line chart instead, changing the data a bit:
1import random
2from openpyxl import Workbook
3from openpyxl.chart import LineChart, Reference
4
5workbook = Workbook()
6sheet = workbook.active
7
8# Let's create some sample sales data
9rows = [
10 ["", "January", "February", "March", "April",
11 "May", "June", "July", "August", "September",
12 "October", "November", "December"],
13 [1, ],
14 [2, ],
15 [3, ],
16]
17
18for row in rows:
19 sheet.append(row)
20
21for row in sheet.iter_rows(min_row=2,
22 max_row=4,
23 min_col=2,
24 max_col=13):
25 for cell in row:
26 cell.value = random.randrange(5, 100)
With the above code, you’ll be able to generate some random data regarding the sales of 3 different products across a whole year.
Once that’s done, you can very easily create a line chart with the following code:
28chart = LineChart()
29data = Reference(worksheet=sheet,
30 min_row=2,
31 max_row=4,
32 min_col=1,
33 max_col=13)
34
35chart.add_data(data, from_rows=True, titles_from_data=True)
36sheet.add_chart(chart, "C6")
37
38workbook.save("line_chart.xlsx")
Here’s the outcome of the above piece of code:
One thing to keep in mind here is the fact that you’re using from_rows=True when adding the data. This argument makes the chart plot row by row instead of column by column.
In your sample data, you see that each product has a row with 12 values (1 column per month). That’s why you use from_rows. If you don’t pass that argument, by default, the chart tries to plot by column, and you’ll get a month-by-month comparison of sales.
Another difference that has to do with the above argument change is the fact that our Reference now starts from the first column, min_col=1, instead of the second one. This change is needed because the chart now expects the first column to have the titles.
There are a couple of other things you can also change regarding the style of the chart. For example, you can add specific categories to the chart:
cats = Reference(worksheet=sheet,
min_row=1,
max_row=1,
min_col=2,
max_col=13)
chart.set_categories(cats)
Add this piece of code before saving the workbook, and you should see the month names appearing instead of numbers:
Code-wise, this is a minimal change. But in terms of the readability of the spreadsheet, this makes it much easier for someone to open the spreadsheet and understand the chart straight away.
Another thing you can do to improve the chart readability is to add an axis. You can do it using the attributes x_axis and y_axis:
chart.x_axis.title = "Months"
chart.y_axis.title = "Sales (per unit)"
This will generate a spreadsheet like the below one:
As you can see, small changes like the above make reading your chart a much easier and quicker task.
There is also a way to style your chart by using Excel’s default ChartStyle property. In this case, you have to choose a number between 1 and 48. Depending on your choice, the colors of your chart change as well:
# You can play with this by choosing any number between 1 and 48
chart.style = 24
With the style selected above, all lines have some shade of orange:
There is no clear documentation on what each style number looks like, but this spreadsheet has a few examples of the styles available.
Here’s the full code used to generate the line chart with categories, axis titles, and style:
import random
from openpyxl import Workbook
from openpyxl.chart import LineChart, Reference
workbook = Workbook()
sheet = workbook.active
# Let's create some sample sales data
rows = [
["", "January", "February", "March", "April",
"May", "June", "July", "August", "September",
"October", "November", "December"],
[1, ],
[2, ],
[3, ],
]
for row in rows:
sheet.append(row)
for row in sheet.iter_rows(min_row=2,
max_row=4,
min_col=2,
max_col=13):
for cell in row:
cell.value = random.randrange(5, 100)
# Create a LineChart and add the main data
chart = LineChart()
data = Reference(worksheet=sheet,
min_row=2,
max_row=4,
min_col=1,
max_col=13)
chart.add_data(data, titles_from_data=True, from_rows=True)
# Add categories to the chart
cats = Reference(worksheet=sheet,
min_row=1,
max_row=1,
min_col=2,
max_col=13)
chart.set_categories(cats)
# Rename the X and Y Axis
chart.x_axis.title = "Months"
chart.y_axis.title = "Sales (per unit)"
# Apply a specific Style
chart.style = 24
# Save!
sheet.add_chart(chart, "C6")
workbook.save("line_chart.xlsx")
There are a lot more chart types and customization you can apply, so be sure to check out the package documentation on this if you need some specific formatting.
Convert Python Classes to Excel Spreadsheet
You already saw how to convert an Excel spreadsheet’s data into Python classes, but now let’s do the opposite.
Let’s imagine you have a database and are using some Object-Relational Mapping (ORM) to map DB objects into Python classes. Now, you want to export those same objects into a spreadsheet.
Let’s assume the following data classes to represent the data coming from your database regarding product sales:
from dataclasses import dataclass
from typing import List
@dataclass
class Sale:
quantity: int
@dataclass
class Product:
id: str
name: str
sales: List[Sale]
Now, let’s generate some random data, assuming the above classes are stored in a db_classes.py file:
1import random
2
3# Ignore these for now. You'll use them in a sec ;)
4from openpyxl import Workbook
5from openpyxl.chart import LineChart, Reference
6
7from db_classes import Product, Sale
8
9products = []
10
11# Let's create 5 products
12for idx in range(1, 6):
13 sales = []
14
15 # Create 5 months of sales
16 for _ in range(5):
17 sale = Sale(quantity=random.randrange(5, 100))
18 sales.append(sale)
19
20 product = Product(id=str(idx),
21 name="Product %s" % idx,
22 sales=sales)
23 products.append(product)
By running this piece of code, you should get 5 products with 5 months of sales with a random quantity of sales for each month.
Now, to convert this into a spreadsheet, you need to iterate over the data and append it to the spreadsheet:
25workbook = Workbook()
26sheet = workbook.active
27
28# Append column names first
29sheet.append(["Product ID", "Product Name", "Month 1",
30 "Month 2", "Month 3", "Month 4", "Month 5"])
31
32# Append the data
33for product in products:
34 data = [product.id, product.name]
35 for sale in product.sales:
36 data.append(sale.quantity)
37 sheet.append(data)
That’s it. That should allow you to create a spreadsheet with some data coming from your database.
However, why not use some of that cool knowledge you gained recently to add a chart as well to display that data more visually?
All right, then you could probably do something like this:
38chart = LineChart()
39data = Reference(worksheet=sheet,
40 min_row=2,
41 max_row=6,
42 min_col=2,
43 max_col=7)
44
45chart.add_data(data, titles_from_data=True, from_rows=True)
46sheet.add_chart(chart, "B8")
47
48cats = Reference(worksheet=sheet,
49 min_row=1,
50 max_row=1,
51 min_col=3,
52 max_col=7)
53chart.set_categories(cats)
54
55chart.x_axis.title = "Months"
56chart.y_axis.title = "Sales (per unit)"
57
58workbook.save(filename="oop_sample.xlsx")
Now we’re talking! Here’s a spreadsheet generated from database objects and with a chart and everything:
That’s a great way for you to wrap up your new knowledge of charts!
Bonus: Working With Pandas
Even though you can use Pandas to handle Excel files, there are few things that you either can’t accomplish with Pandas or that you’d be better off just using openpyxl directly.
For example, some of the advantages of using openpyxl are the ability to easily customize your spreadsheet with styles, conditional formatting, and such.
But guess what, you don’t have to worry about picking. In fact, openpyxl has support for both converting data from a Pandas DataFrame into a workbook or the opposite, converting an openpyxl workbook into a Pandas DataFrame.
First things first, remember to install the pandas package:
Then, let’s create a sample DataFrame:
1import pandas as pd
2
3data = {
4 "Product Name": ["Product 1", "Product 2"],
5 "Sales Month 1": [10, 20],
6 "Sales Month 2": [5, 35],
7}
8df = pd.DataFrame(data)
Now that you have some data, you can use .dataframe_to_rows() to convert it from a DataFrame into a worksheet:
10from openpyxl import Workbook
11from openpyxl.utils.dataframe import dataframe_to_rows
12
13workbook = Workbook()
14sheet = workbook.active
15
16for row in dataframe_to_rows(df, index=False, header=True):
17 sheet.append(row)
18
19workbook.save("pandas.xlsx")
You should see a spreadsheet that looks like this:
If you want to add the DataFrame’s index, you can change index=True, and it adds each row’s index into your spreadsheet.
On the other hand, if you want to convert a spreadsheet into a DataFrame, you can also do it in a very straightforward way like so:
import pandas as pd
from openpyxl import load_workbook
workbook = load_workbook(filename="sample.xlsx")
sheet = workbook.active
values = sheet.values
df = pd.DataFrame(values)
Alternatively, if you want to add the correct headers and use the review ID as the index, for example, then you can also do it like this instead:
import pandas as pd
from openpyxl import load_workbook
from mapping import REVIEW_ID
workbook = load_workbook(filename="sample.xlsx")
sheet = workbook.active
data = sheet.values
# Set the first row as the columns for the DataFrame
cols = next(data)
data = list(data)
# Set the field "review_id" as the indexes for each row
idx = [row[REVIEW_ID] for row in data]
df = pd.DataFrame(data, index=idx, columns=cols)
Using indexes and columns allows you to access data from your DataFrame easily:
>>>
>>> df.columns
Index(['marketplace', 'customer_id', 'review_id', 'product_id',
'product_parent', 'product_title', 'product_category', 'star_rating',
'helpful_votes', 'total_votes', 'vine', 'verified_purchase',
'review_headline', 'review_body', 'review_date'],
dtype='object')
>>> # Get first 10 reviews' star rating
>>> df["star_rating"][:10]
R3O9SGZBVQBV76 5
RKH8BNC3L5DLF 5
R2HLE8WKZSU3NL 2
R31U3UH5AZ42LL 5
R2SV659OUJ945Y 4
RA51CP8TR5A2L 5
RB2Q7DLDN6TH6 5
R2RHFJV0UYBK3Y 1
R2Z6JOQ94LFHEP 5
RX27XIIWY5JPB 4
Name: star_rating, dtype: int64
>>> # Grab review with id "R2EQL1V1L6E0C9", using the index
>>> df.loc["R2EQL1V1L6E0C9"]
marketplace US
customer_id 15305006
review_id R2EQL1V1L6E0C9
product_id B004LURNO6
product_parent 892860326
review_headline Five Stars
review_body Love it
review_date 2015-08-31
Name: R2EQL1V1L6E0C9, dtype: object
There you go, whether you want to use openpyxl to prettify your Pandas dataset or use Pandas to do some hardcore algebra, you now know how to switch between both packages.
Conclusion
Phew, after that long read, you now know how to work with spreadsheets in Python! You can rely on openpyxl, your trustworthy companion, to:
- Extract valuable information from spreadsheets in a Pythonic manner
- Create your own spreadsheets, no matter the complexity level
- Add cool features such as conditional formatting or charts to your spreadsheets
There are a few other things you can do with openpyxl that might not have been covered in this tutorial, but you can always check the package’s official documentation website to learn more about it. You can even venture into checking its source code and improving the package further.
Feel free to leave any comments below if you have any questions, or if there’s any section you’d love to hear more about.
Watch Now This tutorial has a related video course created by the Real Python team. Watch it together with the written tutorial to deepen your understanding: Editing Excel Spreadsheets in Python With openpyxl