Word for Microsoft 365 Outlook for Microsoft 365 Word 2021 Outlook 2021 Word 2019 Outlook 2019 Word 2016 Outlook 2016 Word 2013 Outlook 2013 Word 2010 Outlook 2010 Word 2007 Outlook 2007 More…Less
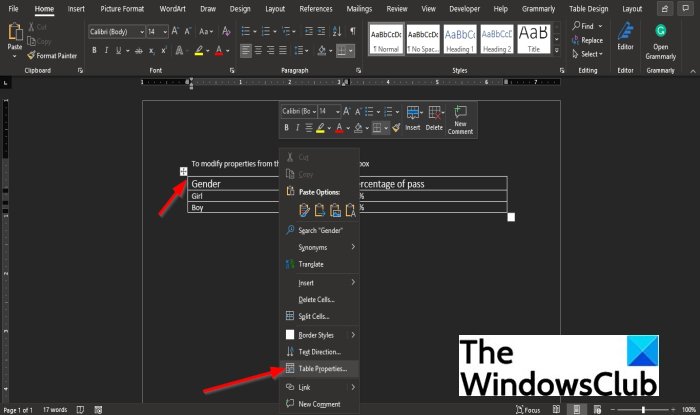
To set or change table options in Word or Outlook, right-click a table and choose Table Properties.
Note: If you want to set properties for a particular row, column, or cell, click in that row, column, or cell before making changes in the Table Properties dialog box.
In this article
-
Table properties
-
Row properties
-
Column properties
-
Cell properties
-
Alt text
Table properties

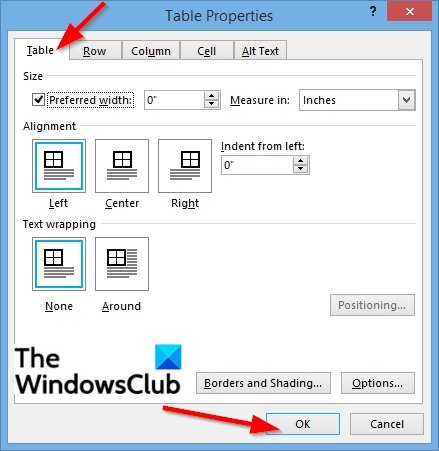
Click the Table tab to apply settings to your entire table:
-
Under Size, set the table’s overall width by selecting Preferred width and choosing a size. In the Measure in box, choose whether you want to measure the width in inches or a percentage of the page.
-
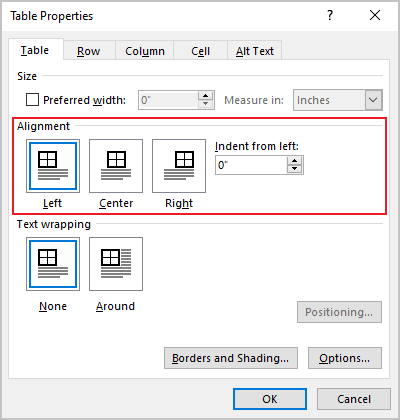
Under Alignment, choose whether you want to align your table to the left, center, or right of page. If you select Left, you can select an indentation distance in the Indent from Left box.
-
Under Text wrapping, select Around if you want nearby text on your page to wrap around your table; you can make text wrapping more precise by clicking Positioning, and then choosing options in the Table Positioning dialog box. If you don’t want text wrapping, select None.
-
Click Borders and Shading to change the border style, line color, and line width of your table.
-
Click Options to set more table properties, including top and bottom cell margins, cell spacing, and automatic resizing of cell contents.
Top of Page
Row properties
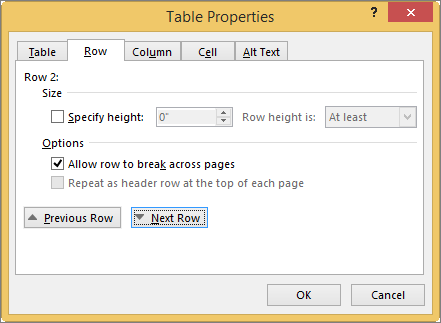
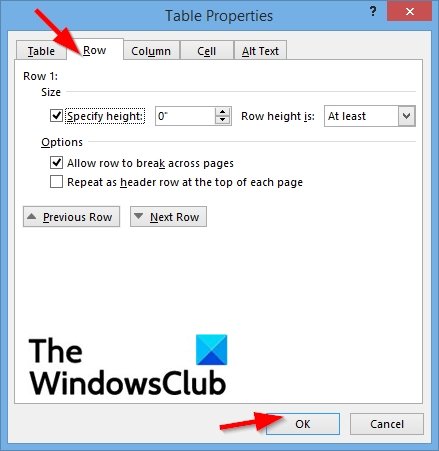
First, click in the row or select the rows you want to change, right-click, choose Table Properties, and then click the Row tab.
-
Under Size, set the row’s height by selecting Preferred height and choosing a size; you can further refine the height by selecting an option in the Row height is box.
-
Under Options, select options for breaking rows across pages or creating header rows.
-
To display the currently selected row at the top of the tab and navigate between rows without leaving the Table Properties dialog box, click Previous Row or Next Row.
Top of Page
Column properties
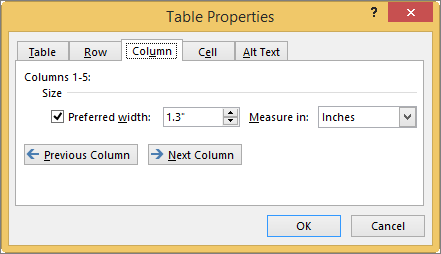
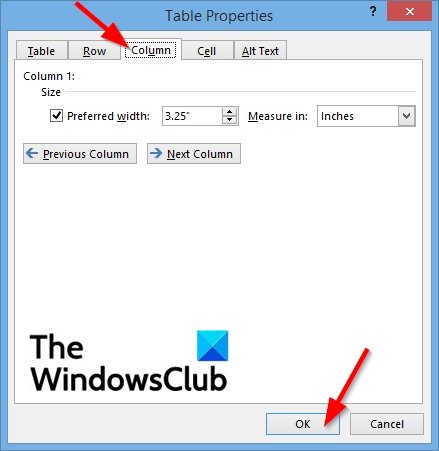
First, click in the column or select the columns you want to change, right-click, choose Table Properties, and then click the Column tab.
-
Under Size, set the column’s width by selecting Preferred width and choosing a size. In the Measure in box, choose whether you want to measure the width in inches or a percentage.
-
To display the currently selected column or columns at the top of the tab and navigate between columns without leaving the Table Properties dialog box, click Previous Column or Next Column.
Top of Page
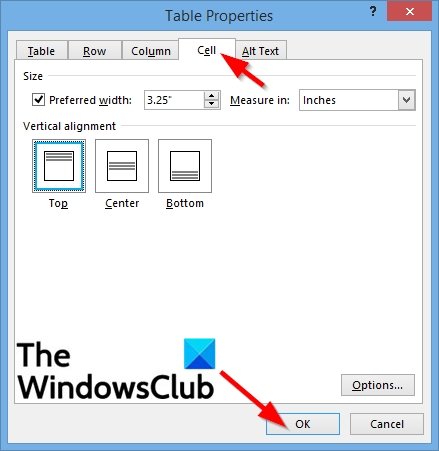
Cell properties
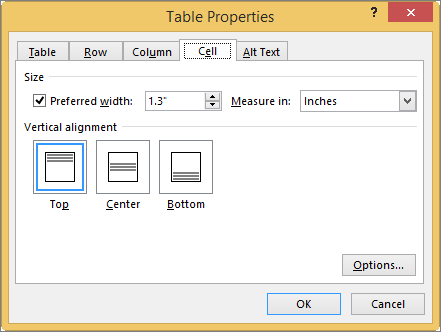
First, click in the cell that you want to change, right-click, choose Table Properties, and then click the Cell tab.
-
Under Size, set the cell’s width by selecting Preferred width and choosing a size. In the Measure in box, choose whether you want to measure the width in inches or a percentage.
-
Under Vertical alignment, choose an alignment option for the cell contents—Top (the default alignment), Center, or Bottom.
-
Click Options to set more cell properties, including top and bottom cell margins and text wrapping and fit options.
Top of Page
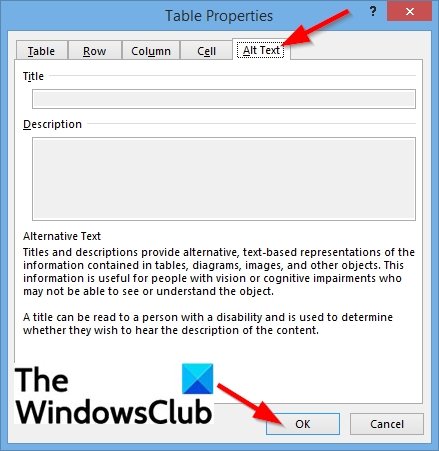
Alt text
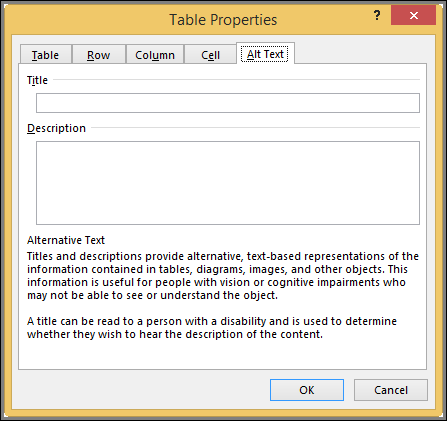
You can create alternative text (alt text) for your table to help people with screen readers understand the content of the table.
-
In the Description box, enter an explanation of the table.
-
In the Title box, enter a brief summary of the table.
Note: Unless you have a complex table, you will usually want to enter text in just the Description box. When you have complex content to describe, filling in the Title field is useful so that reading the full description is not necessary unless desired.
Top of Page
Need more help?
Want more options?
Explore subscription benefits, browse training courses, learn how to secure your device, and more.
Communities help you ask and answer questions, give feedback, and hear from experts with rich knowledge.
Table Properties are used to change or set table options in Microsoft Word or Outlook. The Table Properties are used to control different table options. In the Table Properties, dialog box users can change Table, Column, Row, and Cell settings.
How do I open the Table Properties dialog box in Word?
To open the Properties dialog box is easy to open. This tutorial will discuss opening the Table Properties dialog box to modify the table to your desired look.
What Type of settings is in the Table Properties dialog box?
In the Table Properties dialog box, there are several settings, such as:
- Table: This is used to apply settings to your entire table.
- Row: changes the settings for the rows of the table.
- Column: changes the settings of the columns of the table.
- Cell: change settings for the cells of the table.
- Alt-Text: creates alternative text, especially for people with poor visions or cognitive impairments who cannot see or understand the object.
To display and modify table properties in Microsoft Word, follow the steps below.
- Launch Word
- Create Table Properties
- Create Row Properties
- Create Column Properties
- Create Cell Properties
- Create Alt-Text.
1] Table Properties
Launch Microsoft Word.
Create a table or use an existing table
Right-click the table in the document and select Table Properties from the context menu.
A Table Properties dialog box will appear.
You can change the Table, Row, Column, Cell, and Alt-text settings in the Table Properties dialog box by clicking their tabs.
We will discuss the Table tab.
You can set the overall table width on the table settings by clicking the checkbox for Preferred width and choosing a size from the box by clicking the arrows within the box.
In the Measuring in box, you can measure the table’s width in Inches or a Percentage of the page.
Under the Alignment section, you can align the table Left, Right, and Center of the page.
If you choose to select Left, you can select an indentation distance in the Indent from left box.
Under the Text Wrapping, if you want the nearby text to wrap around your table, you can select Around.
If you want the Text Wrapping to be more detailed, click the Positioning button and then choose the options you want from the Table Positioning dialog box.
If you do not want a Text Wrapping, click None.
You can change the table’s Border style, Line color, and Line width by clicking the Border and Shading button.
To set more table properties, including Top and Bottom Cell margins, Cell spacing, and Automatic resizing of cell contents, click the Options button.
Click OK.
2] Row Properties
Click the row or highlight rows you want to change and then right-click and select Table Properties.
A Table Properties dialog box will pop up.
Click the Row tab to change the settings of the rows.
Under the Size section, check the checkbox for Specify height to set the height of the row.
Choose the height from the Specify height box.
You can choose an option from the Row height box, which includes At least and Exactly.
Under Options, you choose to check the checkboxes for Allow row to break across pages or Repeat as header row at the top of each page.
To navigate between rows in your table without leaving the Table Properties dialog box, you can click the Previous row and Next row buttons.
Then click OK.
3] Column Properties
Click the column or highlight columns you want to change and then right-click and select Table Properties.
A Table Properties dialog box will appear.
Click the Column tab to change the settings of the columns.
Under Size, check the checkbox for Preferred width and choosing a size from the box.
Within the Measuring in the box, you can choose an option such as Inches or Percent.
To navigate between columns in your table without leaving the Table Properties dialog box, you can click the Previous column and Next column buttons.
Click OK.
4] Cell Properties
Click the cell you want to change, then right-click and select Table Properties from the context menu.
A Table Properties dialog box will appear.
Then click the Cell tab
Under Size, check the checkbox for Preferred width and choose a size from the box.
Within the Measuring box, you can choose an option such as Inches or Percent.
Under Vertical alignment, you can choose an alignment option for the cell contents, such as Top (default), Center, and Bottom.
To set more cell properties, including Top and Bottom cell margins and options such as Text Wrapping and Fit, click the Options button on the bottom right.
Then click OK.
5] Alt-Text
To create alternative text, especially for people with poor visions or cognitive impairments who cannot see or understand the object.
Click the Alt Text tab.
In the Title box, enter a summary of the table.
In the Description box, enter an explanation of the table.
Then click OK.
We hope this tutorial helps you understand how to display and modify table properties in Word; if you have questions about the tutorial, let us know in the comments.
If the document contains tables, it must be formatted according to the requirements accepted by your college, university, company, established on the project, etc. Most requirements, including accessibility, tell that tables should contain titles, column headers, alternate text, etc. In addition, tables must be correctly positioned on the page, using the pre-defined alignment, padding, and text-wrapping guidelines.
Usually, the table contains the following basic components:
- The table number (e.g., Table 1) and the title appear above the table body (see how to create a caption for tables).
- The table includes column headings, including a stub heading (heading for the leftmost, or stub, column). Some tables also include column spanners, decked heads, and table spanners. See how to format tables in a Word document.
- The table body contains all the rows and columns of a table (including the headings row). A cell is the point of intersection between a row and a column. See how to select and format table elements.
- All types of notes (general, specific, and probability) appear below the table if there are notes. Notes describe contents of the table that cannot be understood from the table title or body alone (e.g., definitions of abbreviations, copyright attribution, etc.).
See also how to create cross-references to a table.
Align the table on the page
By default, Word aligns the table to the Left. If you want to change an alignment of the table on the page, select it and do one of the following:
- On the Home tab, in the Paragraph group, select the alignment you prefer:
- Open the Table Properties dialog box by doing one of the following:
- On the Table Layout tab, in the Table group, click the Properties button:
- Right-click the table and select Table Properties… in the popup menu:
In the Table Properties dialog box, on the Table tab, in the Alignment section, select the option you prefer:
- On the Table Layout tab, in the Table group, click the Properties button:
- Press the keyboard shortcuts:
- Ctrl+L to align a table to the Left (by default),
- Ctrl+E to Center the table,
- Ctrl+R to align a table to the Right.
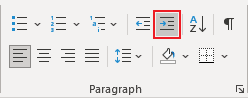
Add indent from left
The Indent from left controls the distance of the table from the left margin. To add the Indent from left, do one of the following:
- On the Home tab, in the Paragraph group, click the Increase Indent button:
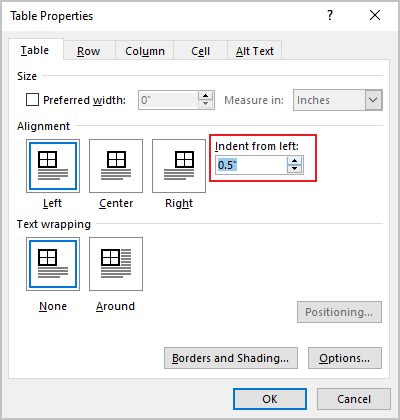
- Open the Properties dialog box. In the Table Properties dialog box, on the Table tab, in the Alignment section, type or choose the value you need in the Indent from left field:
Note: The Indent from left field is active only for the Left alignment.
For example, the table with a left indent 0.5 inches:

Text Wrapping for a table
Word offers to customize the text wrapping style for a table, as well as for figures. To customize a text wrapping style, do the following:
1. Select a table.
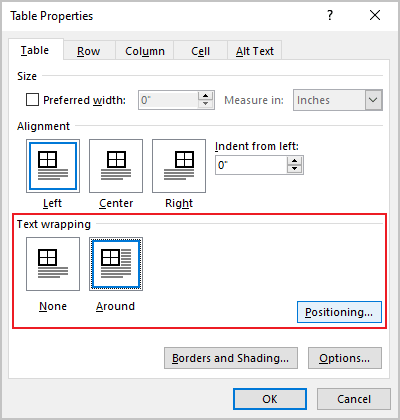
2. Open the Table Properties dialog box. In the Table Properties dialog box, on the Table tab, in the Text wrapping section:
- Select None to disable text wrapping for the table
- Select the Around option to have text wrapping around the table. Then click the Positioning… button for more customization:
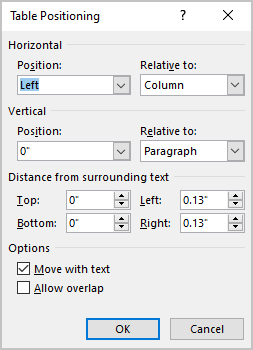
In the Table Positioning dialog box:
Position a table
- In the Horizontal sections, specify:
- Position to the Left, Right, Center, Inside, or Outside,
- Relative to the Margin, Page, or Column.
For example, with Position to the Right relative to Margin:
- In the Vertical section, specify:
- Position to the Top, Bottom, Center, Inside, or Outside,
- Relative to the Margin, Page, or Column.
For example, with Position to the Top relative to Page:
Increase the space between text and table
- In the Distance from surrounding text section, enter custom values for the distance between the text and the table independently for:
- Top (0 by default),
- Bottom (0 by default),
- Left (1.13 inches by default),
- Right (1.13 inches by default).
For example, with the 0.3-inch distance on all sides:
Note: See also how to change a distance within a table.
Text wrapping options
- In the Options section:
- The Move with text option moves the table along with the text in which it is located.
Select the Move with Text option if the text is directly related to the table data. The table is vertically aligned to the related paragraph around it. If the table data applies to the whole document, keep the Move with Text option unselected.
- Allow overlap allows to layer table on top of each other.
- The Move with text option moves the table along with the text in which it is located.
Position a large table
Control where a table is split
When working with a long table, or when a table needs to be placed at the bottom of the page, splitting up a table into two separate tables is necessary. By default, if a page break occurs within a large row, Microsoft Word allows a page break to split the line between two pages (see How to prevent a table break between pages).
To insert a table break at a specific location, position the cursor on the cell on the row, or select the row that should appear on the next page, then do one of the following:
- Press Ctrl+Enter.
- On the Table Layout tab, in the Merge group, click the Split Table button:
Be careful! Word applies the chosen style to the new table. If you Undo the table splitting, the formatting may not be Undone correctly.
Add an Alternative text (Alt Text)
Most requirements recommend adding alternative text for visual objects, including tables (see how to turn off automatically creating the Alternative text).
To add an alternative text for a table, do the following:
1. Select a table.
2. Do one of the following:
- On the Table Layout tab, in the Table group, click the Properties button.
- Right-click the table and select Table Properties… in the popup menu.
3. In the Table Properties dialog box, on the Alt Text tab:
- In the Title field, type a title, if necessary.
- In the Description field, fill the description for the table.
- Click the OK button.
Are you struggling to get your message across? When your Microsoft Word project contains information, try presenting it in the form of a Word table. Learn how to make tables in Word quickly with a template.
A table is a kind of chart that organizes and presents data in rows and columns. It makes information easier to grasp, understand, and analyze at a glance, compared to explaining the same data through plain text.
Microsoft Word gives you various ways to insert or create a table. And you’ve got granular control over the formatting, layout, and appearance of Microsoft Word tables. Table charts are useful in different types of Word projects, whether for personal, educational, or business use.
This article will show you how to make a table in Word using a template. Then edit and format it to change its appearance.
(Note: The screenshots and instructions that follow are made using Microsoft Word for Mac version 16.4. If you’re using a different version of Word, then the interface and steps may be different.)
How to Make & Edit MS Word Tables (Video)
In this video, you’ll learn how to quickly make tables in Mircosoft Word. Find out how to start with a premium template. Quickly customize it to make an attractive, professional MS Word table you can use and reuse.
To learn even more about MS Word tables and about templates than can be used for tables, study the step-by-step tutorial below:
How to Make Basic Tables in Word
Let’s start by learning how to make a basic table in Microsoft Word:
1. Insert a Table
You can create a basic Microsoft Word table in one of two ways:
Method 1. The Insert Tab
Click on the Insert tab, then click the Table button on the ribbon.
The Insert Table panel appears. Drag the cursor over the squares to specify the number of columns and rows you want to create. Click to apply.
Method 2. The Insert Menu
Go to Insert > Table….
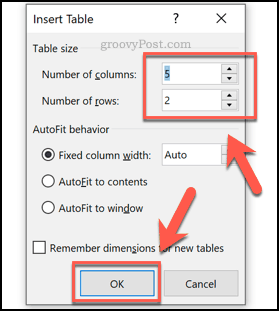
The Insert Table panel opens. Specify the number of columns and rows you need. (You can always add or remove columns and rows later.)
Also select the Autofit Behavior you want the table to have. You’ve got several options:
- Initial column width. The default setting is Auto, which divides the entire width of your page window across the number of columns in the table. Or, you can specify a different column width.
- AutoFit to contents. Resizes the column width based on the width of the content inside the column.
- AutoFit to window. Distributes the columns equally across the entire width of the page window.
- Set as default for new tables. Check this option if you want the settings to be applied globally to all new tables you create.
When you’re happy with the options you’ve selected, click OK.
2. Draw a Table
Or, you can draw a table in MS Word. This is a useful feature if you want to create an irregular or more complicated table with columns and/or rows of varying widths.
To draw a table, click Insert > Table > Draw Table.
With your mouse or trackpad, click and drag the cursor to start drawing your table. You can begin by drawing the outermost boundary of the table first.
Then, click and drag the cursor to create columns and rows inside the table. When you’re done, click anywhere outside the table.
Here’s an example of an “irregular” table you can draw using this feature.
If you make a mistake, click Layout > Eraser to erase a line from the table.
Click and drag the eraser along the line you wish to erase. The line that’ll be erased appears as a thick, red line. Release the mouse or trackpad to erase.
Click outside the table when you’re done.
3. Convert Text to Tables and Vice Versa
Another way to create a table is by converting text into a table. This means you can take non-tabular data from a CSV or plain TXT file and convert them into a table.
First, copy and paste the non-tabular data into your Word document.
With the text selected, go to Insert > Table > Convert Text to Table….
The Convert Text to Table panel opens. Specify the settings you wish to use. Click OK.
The text is then converted into a table.
You can also do the opposite, which is to convert a table into text.
Select the cells or entire table you want to convert. Next, click on the Layout tab then click the Convert Table to Text icon.
The Convert Table to Text panel opens. This is where you’ll decide how you want to separate text that’s currently in different columns. When you’ve made a selection, click OK.
For this example, I chose to separate text with commas. This is what the converted table looks like.
4. Advanced: How to Insert a Table from Excel
If you’ve already created a table in Excel, you can embed it into your Word document.
Open the Excel file. Click and drag the mouse to select the table.
Go back to your Word document. Go to Edit > Paste Special ….
In the Paste Special panel, select Microsoft Excel Binary Worksheet Object, then click OK.
This embeds the Excel table into Word. It’s still an Excel table, which means you can’t edit or format the table in MS Word. You’ve got to do so in Excel.
Double-click anywhere in the table to launch the source file in Excel. When you make any changes to the table in Excel, the table embedded in your Word project automatically updates to reflect those changes.
Now you know how to make a table in MS Word using various options.
How to Edit Tables
At any time after creating your table, you can edit and customize it to look the way you want it to. Here are some steps for editing tables in Microsoft Word:
1. Add a Column or Row
To add a row or column, click inside a table cell. Right-click on the mouse, then click Insert.
Select one of the following:
- Columns to the Left. Adds a column to the left of the current column
- Columns to the Right. Adds a column to the right of the current column
- Rows Above. Adds a row above the current row
- Rows Below. Adds a row below the current row
- Cells … Inserts a cell and shifts the rest of the cells either to the right or down from where the cursor is
- Table … Inserts a table inside the current cell
Or, with the cursor in one of the cells, you can click on the Layout tab.
Then choose of the following buttons on the ribbon:
- Insert Above. Inserts a row above the current cell
- Insert Below. Inserts a row below the current cell
- Insert Columns to the Left. Inserts a column to the left of the current cell
- Insert Columns to the Right. Inserts a column to the right of the current cell
Finally, you can add a new row when you’ve reached the last cell in the last row of your table. Simply press tab and a new row appears.
2. Delete a Column or Row
To delete a cell, column, row, or table, click on the Layout tab > Delete.
Select one of the options that appear:
- Delete Cells …
- Delete Columns
- Delete Rows
- Delete Table
You can use the same steps to edit a table you’ve drawn. Or, you can use the Layout tab to add or delete rows and columns.
Merge Cells
Sometimes you may want to merge cells to present information more clearly. To merge cells, click and drag the cursor to select the cells you wish to merge.
On the Layout tab, click on the Merge Cells button.
Or, after selecting the cells to be merged, right-click on your mouse, then click Merge Cells.
Now the cells have been merged into one.
Split Cells
After merging cells, you can always split them again into separate cells.
Place the cursor in the merged cell, then click Layout > Split Cells.
Or, right-click on your mouse, then click Split Cells….
Either way, the Split Cells panel pops up. Specify the number of columns and rows you want to split the cell into. Click OK.
Split Table
You may decide that it makes more sense to split up a table into two separate tables. Microsoft Word lets you do that easily, too.
In this example, I want to split the table right above the Accessories cell. And so, I’ll place the cursor in that cell. Next, click on the Layout tab, then click the Split Table button.
Now, we’ve got two separate tables.
Table Formatting
When you first create a table, it looks plain and boring. But Microsoft Word has many features so you can format tables to look exactly the way you want them. Here are some common ways to format tables:
1. Table Styles
The easiest way to format a table is by using one of the pre-formatted table styles. Put the cursor in any cell in the table. Click on the Table Design tab. Next, click on the arrow to expand the Table Styles group.
Click on a style you want to use and it’s applied immediately.
You can change any style you’ve selected. Again, click on Table Design, expand the Table Style group, then click Modify Style.
The Modify Style panel opens. Make the selections you want, then click OK.
2. Use Your Own Formatting
The Table Design tab gives you control over the appearance of every aspect of your table. Click on the Table Design tab and any of the appropriate buttons on the ribbon.
Resize a Table
You can also resize your table. Click on any cell to select the table, then click and drag one of the corners to resize it.
Or, you can use the Layout tab to resize individual cells, specific rows or columns, or the entire table. Select the columns or rows you wish to resize. Specify the height and/or width you wish to apply.
You can also adjust column width by hand by using the Table Ruler. Click inside a column you want to change. Then, drag the sliders in the Table Ruler to set to desired width.
Text Wrapping
If you want text to flow around the table, you can do so by changing its text wrapping.
Click in any cell to select the table. Click Table > Table Properties….
In the Table Properties panel and under Text Wrapping, click Around > OK.
Now the text flows around the table.
Take note that the Table Properties panel allows you to format other qualities of the table, including:
- Size
- Alignment
- Positioning
- Borders and Shading
On the other tabs, you can change:
- Column, Row, and Cell Size
- Allow row to break across pages
- Repeat as header row at the top of each page
- Cell Vertical Alignment
- Alt Text (Title and Description) — more information about the table, to help people with vision or cognitive impairment who may not see the table
Find Great Styles for Microsoft Word
You don’t have to start from scratch to create an impressive and effective Word document — even if you don’t have design skills. You can find great styles by using a template for Word.
One great source for great Microsoft Word templates and professional graphics is Envato Elements. For one low monthly subscription, you get unlimited downloads of templates, graphics, fonts, and other creative tools you need for your project. It’s a terrific option if you create plenty of materials.
For single projects, GraphicRiver is an outstanding source for templates for Word. This marketplace gives you access to thousands of creative elements on a pay-per-use basis.
Learn More
Microsoft Word has many robust features to help you realize the vision you’ve got for your document. But with power comes complexity. That’s why it’s a good idea to learn how to use Microsoft Word.
These articles will help you get started:
Visualize Your Data with Microsoft Word Tables
Make your information clearer and easier to understand by learning how to make a table in Microsoft Word. Tables organize data into rows and columns, which makes them easier to grasp at a glance. Follow the steps in this article to create, format, and customize tables in Word.
You can also use a premium Word template to get a premium design created by designers. Get Word templates from Envato Elements, if you want unlimited downloads of templates, graphics, and other creative tools you need — all for one flat monthly fee.
Or, get premium templates for Word from GraphicRiver if you prefer to pay for each use of an item. Both sources give you access to thousands of design elements created by professionals, so you can save time, energy, and effort while creating an outstanding Word document.
Did you find this post useful?
Marketing & Communications Professional and Lifelong Learner/Canada
Lexi Rodrigo is a marketing and communications professional, copywriter, and course creator who helps remarkable brands and people get seen, heard, and known. Writing for the web since 2008, she has over 100+ blog posts published on Envato Tuts, Acadium, Mirasee, Vero, Copyblogger, FreelanceFolder, Business2Community, and others.
Lexi has supported multimillion-dollar companies and nonprofits in various marketing and communication roles. She has driven results like tripling the organic search traffic of a blog in three months and generating over $65 million in revenues, donations, and sponsorships.
She has a Bachelor of Arts degree in communications. She is also the co-author of «Blog Post Ideas: 21 Proven Ways to Create Compelling Content and Kiss Writer’s Block Goodbye.» When she’s not reading or writing, Lexi bakes bread, grows food, and takes long walks.
You can organize data in a Word document by using tables. Here’s how to add and customize tables in Word.
You can use a few methods to organize the content in a Word document, but one of the best is to use a table. This allows you to separate your content into columns and rows, allowing for better presentation.
There are a few methods you can use to create tables in Microsoft Word. You can insert, draw, or copy in a table from elsewhere, should you want to. Here’s how to create and customize tables in Microsoft Word following these methods.
How to Insert a Table in Microsoft Word
You can insert a table in Microsoft Word in several ways, but three ways are worth mentioning in particular. You can add a table by inserting it automatically with a set size, or you can draw a table manually using your mouse or trackpad.
Alternatively, you can also copy and paste a grouping of cells from Microsoft Excel. Once pasted, Word will convert these cells into the format of a table. The instructions below should work for all recent versions of Word. There may be slight differences in older versions of Office, however.
To add a table in Word, you’ll need first to open a blank or existing Word document and press the Insert tab on the ribbon bar. From here, click the Table button.
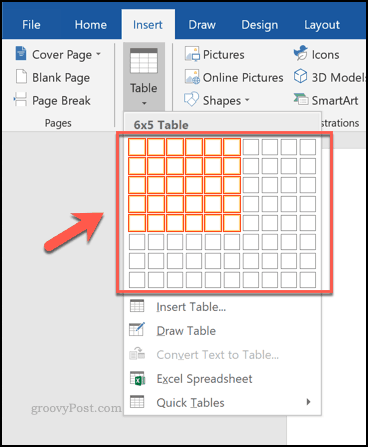
This will display a drop-down menu with various options. To insert a table automatically, select the size you want from the grid.
Once pressed, the table will be inserted onto the page using the number of rows and columns you select.
Alternatively, press the Insert Table option, selecting the number of rows and columns you need from the Insert Table pop-up box that appears afterward.
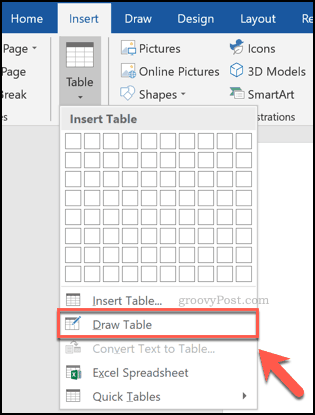
You can also draw a table instead. From the Table drop-down menu, click the Draw Table option.
Using your mouse or trackpad, draw a table to the size you want on your chosen page.
Once you’ve created the outer border for your table, you’ll need to draw downwards inside the table to add a column or horizontally to add a row.
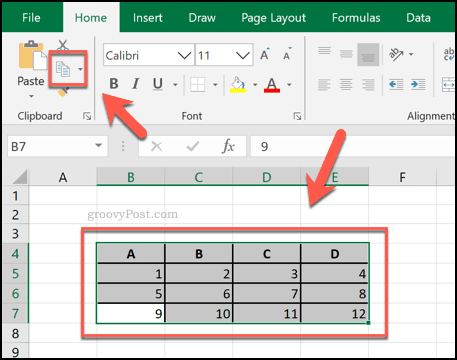
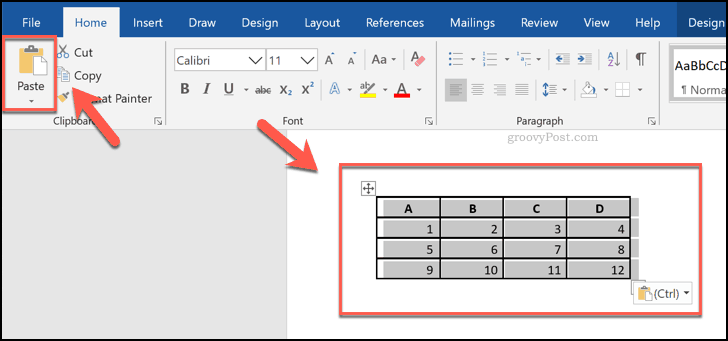
As we’ve mentioned, you can also paste in a table using cells from a Microsoft Excel spreadsheet.
To do this, open an Excel spreadsheet, select a grouping of cells and press Ctrl + C on your keyboard (or press Home > Copy).
Return to your Word document, then press Ctrl + V on your keyboard to paste the cells into your document (or press Home > Paste).
Formatting a Microsoft Word Table
Once your table is created in Word, you can then begin to format it. You can resize the table once it’s been created, as well as alter the bordering, font style, and more.
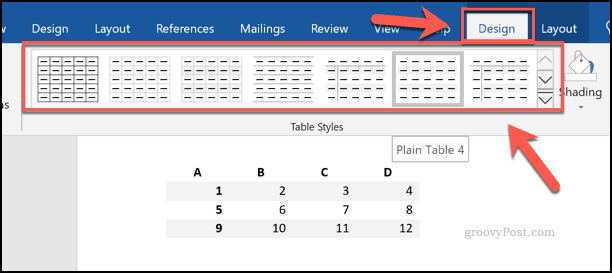
One easy way to format your table is by using a table style. These apply preset formatting choices to your table. To add these, select your table, then press the Design tab under the Table Tools section on the ribbon bar.
Click one of the options from the Table Styles section to apply that style to your table.
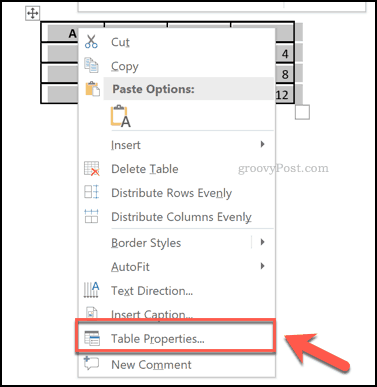
To add your own formatting, select and right-click your table, then press Table Properties.
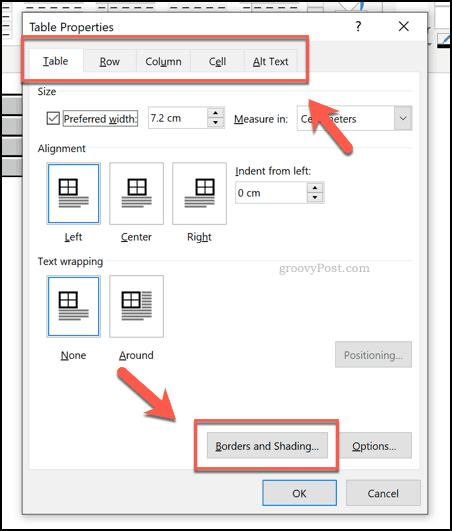
You can set the size of your table using the options shown in the various tabbed menus in the Table Properties box. These include options to alter the length, width, and alignment of your table columns and rows.
To change the border and shadings of your table, press the Borders and Shadings button at the bottom of the Table tab.
You can easily change other table formatting options, including the font, color, and other text styles, using the standard formatting options in Word.
To do this, select the text in your table, then use the formatting options from the Font and Paragraph sections in the Home tab on the ribbon bar to make changes.
Bringing Microsoft Office Skills Together
Creating tables in a Word document is, as we’ve mentioned, a good way to organize and present your data. There are other ways you can do this, however. You could add and edit images in Microsoft Word to get your points across visually, for instance.
If you want to stick with tables, don’t forget that it’s easy to copy data from Microsoft Excel and paste it into your Word document later. If you’re new to Excel, you might find these Excel beginner tips helpful.