A project manager’s job does only revolve around overseeing various projects because there is more to it than what meets the eye. As a project manager, your usual task is to present information to people and let them understand the progress and development of a certain undertaking, whether constructing a new building or running a marketing campaign. On top of that, you should also put a finger in planning, procurement, and other relevant phases of a project. But how do you write a compelling narrative report? Start by learning what a project report is. After that, use your resources such as report forms to come up with the desired outcome. When all this is covered, structuring a report is a lot easier. Continue reading below.
73+ Project Reports
What Is a Project Report?
A project report plays a vital role in every project’s success. It is also a common document used in various fields like education, business, law, or construction, among other things, and suggests recommendations for specific actions. One of the reasons why a report is written is to present facts in an organized manner and define issues at hand as well as analyze them. Most importantly, the main smart goal of a project report is to echo observation to a specific group of people clearly and concisely.
People who make reports for a living found a way to create this important document easily. They use project report forms to tailor the readers’ needs and expectations. By using a project report form, even if you are not a professional, you can outline a comprehensive report. With report forms, you can fill them with relevant details related to a project you are managing.
Only a few people know report forms became an essential part of fighting against the Covid-19 pandemic. In 2019, the contagious coronavirus spread and since then a lot of people have become vulnerable. Based on a survey conducted by Statista, the accumulated number of cases of coronavirus infection worldwide is 120,695,785. As of March 2021, this number is still rising. The only way to curb the infection is to know the number of infected people. Hence, authorities use report forms to document cases daily. Doing this helps them understand the tendencies of the health crisis and come up with an action plan.
What Are the Different Types of Report Forms?
There are different types of report forms depending on the purpose it serves. Choosing the right report form to use relies on this. That is why it is important to fully understand the reason to write one. When this is covered, the right report form is just right at the corner. Let us take a look at the most common project report forms that you might need now or in the coming days.
Incident Report: By definition, an incident refers to an unexpected event that can affect an operation. Based on an article published by Safeopedia, an incident is any unintentional occurrence that delays conventional processes, specifically at the workplace in line with occupational health and safety. Such an episode covers from a near miss to a deadly accident. Therefore, an incident report is a written or digitally produced document that contains a structured narrative of what happened during an incident. Usually, an incident report forms is required by Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) to avoid occupational risks and hazards.Assessment Report: Whether be it in academic, business-oriented, medicine, law and so much more, an assessment report is an important tool. To produce a solid assessment report, the assessor should present the collected data from an assessment and structure this using a comprehensive format. If an assessment report is used right, people who need to know about the interpretation of data will potentially gain awareness of what is expected from these results. As one of the top-notched industries, the business industry takes advantage of assessment reports. How? For example, a company that focuses on services is not doing very well with business returns will conduct an assessment to find out the factors affecting low sales.Book Report: Book reports are commonly seen in schools. This written material is usually one of the requirements to pass a term. If one of your teachers asked you to read a book and write an essay about it afterward, then you might have had written a book report before. Headings and subheadings are needed in writing this type of report. Basically, a book report is an essay that tackles book content. The main ideas should be simplified into smaller ideas. Provide supporting details to elaborate the thought more. Expense Report: Whether it be a small business or a corporation, managers use expense reports in reaching specific goals. Usually, this report is made using a spreadsheet to note how organizations and the people who work for them spend on something that is business-related. Aside from documenting how much money was spent on a certain undertaking, an expense report is also useful in managing finance, taxes, and accounting purposes.Narrative Report: A narrative report is a piece of writing in which content is chronologically arranged. Anyone who has done storytelling can tell its similarity with a narrative report. Both involve narration of what happened in a story or a series of events from the beginning until the ending. On the other hand, what makes a narrative report different from storytelling is it contains information based on facts or statistics from reliable sources. In business, a narrative report is crucial too. With this type of report, you can outline the entire business plan, marketing strategy, you name it. Make sure to put the details in order so that you can convey your message well.
How Do You Write a Project Report?
Indeed, you can write a project report using a lot of ways. Because a project report is considered one of the most important business documents, many invest in making such a report. Some might have held training to help people write project reports, especially big companies. But do not sweat it out when you are just started with a report-making task. If you do not know where to start, you can kick off research. You do not need a high-end information gathering system to learn the basics of report-writing. The internet offers a lot of resources about formal writing. Just make sure to go to the right places and look for reliable sources. We created a list of tips to help you draft a comprehensive project report. Let us get started.
Tip 1: Begin with a Plan and Take Some Time to Prepare
Every successful project starts with a quality plan. The same thing goes with writing a report for that project. Setting your goals and the things you want to achieve when your project report is done is very important. This will help you establish actions, steps in achieving these goals at hand. If you do not take some time to create a plan, there is nothing to guide you from start to finish. Also, you might miss a step along the way without a concrete plan because nothing will walk you through the process of writing your report.
If there are some things left on the gray side of your mind, this calls for extending your research. Go in-depth about the things you want to know. Additionally, ask yourself the following questions: (1) who are the readers?; (2) what is the purpose of the report?; (3) why is the report needed?; and (4) what information should be included in the incident report?
Tip 2: Before Writing the Report, Identify Your Audience First
Once your plan is made, the next step you should take is to identify your audience, which in this case is the readers. Readers are s group of people who will use the project report for specific purposes. Knowing who will read your report help you choose what language to use upon writing. It is also important to keep in mind that people read the project report, not for entertainment purposes, but to obtain relevant details that are useful to them. Thus, use simple words to make the report easy to understand and convey your message well. As the writer of the technical report, you should put your readers’ concerns first before anything else.
Tip 3: Collect Support Information to Elaborate the Report More
After identifying your readers, start collecting supporting information for your project report. In terms of project reports, most organizations appoint a project manager to write the project report. Say, for example, the head of the marketing team of a corporation has been managing campaigns for a long time. Because of that, this person has all the relevant information of all marketing undertaking. It makes sense if he or she has to write a project report by using details from actual events.
Tip 4: Use a Report Form Template
To some, writing a project report is a challenging task. But we will make it more convenient at your end. You do not have to start from the bottom in making this report because with a template, making a report is never been this easy. The best thing about using a template is it promotes consistency not just in your incident report but also in various documents like statements, receipts, Project Proposals, among other things.
For more ready-made templates, check the collection above or visit our website today. You can sign up for any of our subscription plans and enjoy exclusive perks. With a template, editing your incident report will be so much easier. Each template comes in with suggested content that you can modify or leave as it is. By using a compatible editing tool, completing any report is at your fingertip.
FAQs
What are the things I should include in my project report?
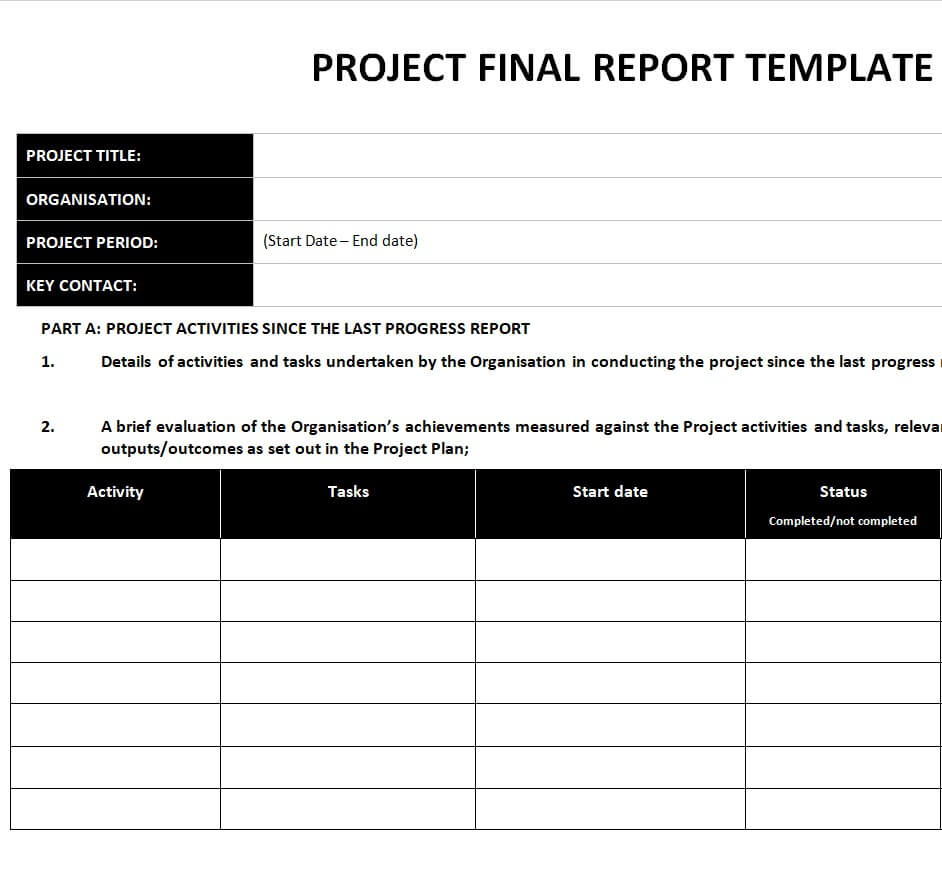
Your project report should contain facts related to a project including the following:
- Summary/Overall Health of the Project
- Facts on the Project Progress
- Target vs. Actual Accomplishments
- Analysis
- Actions Taken
- Risks and Issues
- Resources
- Budget
- Schedule
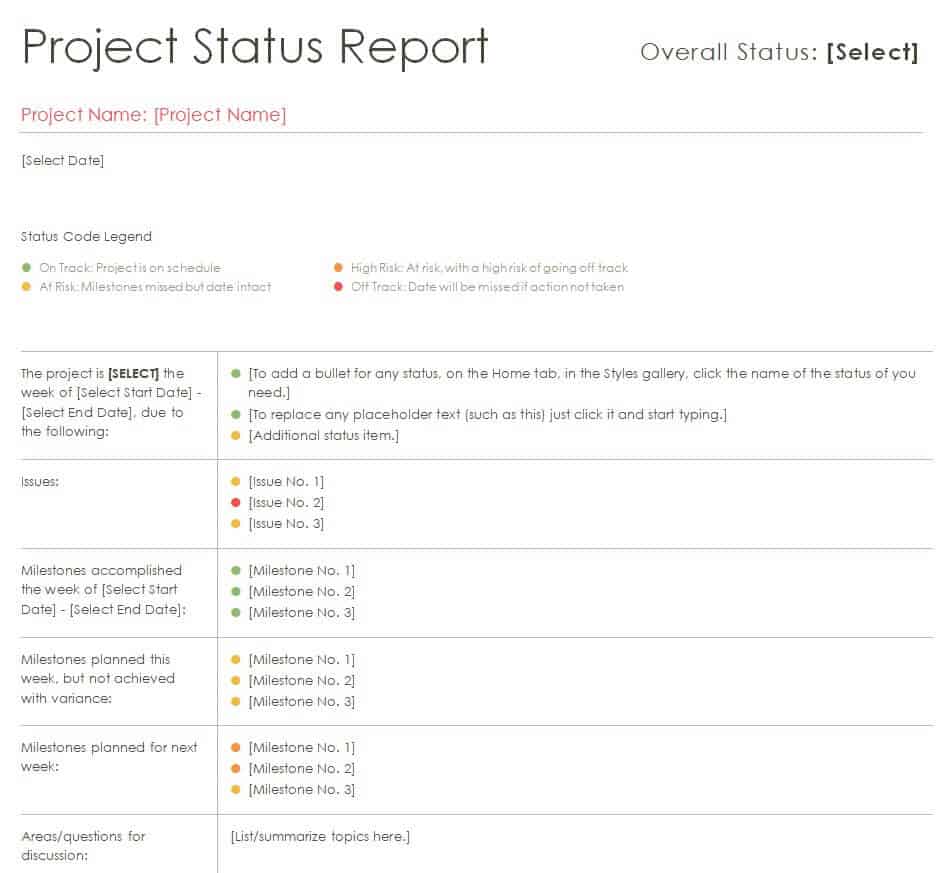
How to keep a project status report effective?
- Submit the report on time.
- Give complete and accurate information.
- Do not cover up bad news or adverse reports.
- Be proud of the team working on the project and their accomplishments.
- Anticipate questions from other people.
- Be familiar with the culture of the organization and respect the information hierarchy they follow.
- Craft the report without overloading it with too much information.
Why is a report form relevant?
In order to properly record the number of people who are infected by the coronavirus, authorities use report forms. When this is done properly, authorities will know how to fight back and curb Covid-19 cases globally. According to a report by Statista, there are 120,695,785 cases of coronavirus worldwide as of March 16, 2021. This number is increasing as of the moment of writing. This is only one of the many importance of report forms.
Letting the people know the progress and development plan of a project they are involved in help in achieving the desired outcome for that project. A project report is also crucial for the job of a project manager. With this, they will know what step to take next. Also, it helps in making big decisions.
You may also like these articles
-
28+ SAMPLE Behavior Incident Reports in PDF | MS Word
Does the person usually approach you immediately preceding the behavior? Is the behavior often connected with the termination of certain activities? Consider these questions while determining the function of…
continue reading
share this :
Rating :
-
34+ SAMPLE Customer Service Report in PDF | MS Word | Google Docs | Apple Pages
Most businesses produce items or perform services for their consumer market. Feedback from consumers is a critical component for organizations to provide quality items and services to customers. It ensures a company…
continue reading
share this :
Rating :
Make your own report
- Click Report > New Report.
- Pick one of the four options, and then click Select.
- Give your report a name and start adding information to it. Blank Creates a blank canvas. Use the Report Tools Design tab to add charts, tables, text, and images.
What is the format for a project report?
The project reports should be like conference papers: concise and focussing on what you did. Format: Use 1 inch margins (left and right), 1 inch margins (top and bottom), 11 point times font for the main text, and use 10 point courier font for computer code.
How do you start writing a project report?
How to Write an Effective Project Report in 7 Steps
- Decide the Objective. Take some time to think about the purpose of the report.
- Understand Your Audience. Writing a formal annual report for your stakeholders is very different from a financial review.
- Report Format and Type.
- Gather the Facts and Data.
- Structure the Report.
- Readability.
- Edit.
What is project template?
A project template is a project that includes work packages and actions that you know you will frequently apply to various projects. You may also want to use a project template if you want to standardize the tasks you are using for projects, such as obtaining building permits, or creating architectural drawings.
How do you start a project?
6 Simple Steps to Start any Project
- Define Your Goals. First things first: decide what you want to achieve.
- Identify Your Team Members. The second step on the ladder to beginning any project is the identification of the various team members to be involved.
- Define Your Work.
- Develop Your Plan.
- Delegate (smartly)
- Execute and Monitor.
How long is a formal proposal?
25 to 50 pages
What is a formal business proposal?
Simply put, a formal business proposal is strategic sales-based business document that you use to present your company and the solution you want to offer to a potential client to persuade them to buy from your company instead of buying from one of your competitors.
What are the elements of a business proposal?
At a high level your business proposal should include the following parts:
- Title.
- Table of Contents.
- Executive Summary.
- The Problem Statement.
- The Proposed Solution.
- Qualifications.
- The Timeline.
- Pricing, Billing and Legal.
What is included in a formal proposal?
A formal business proposal is a document used to present the specifics of the offer, be it a project, a solution or goods and services. The proposal should be thorough and present both the company and the work being proposed in a good light.
How do you write a project proposal?
Sample Project Proposal Outline
- Section 1: Project Information.
- Section 2: Project Summary.
- Section 3: Project Methodology.
- Section 4: Project Risk Management.
- Section 5: Project Costs.
- Section 6: Conclusion.
- Section 7: Appendix.
What is Project Outline?
A project outline is a company’s internal document used for project management. Its purpose is to guide a project by clearly stating what needs to be done for it to succeed. In doing that, determine what’s required to complete the project successfully.
What are the four parts of technical proposal?
This can include things like technical approach, technical specifications, past performance, resumes, management plan, staffing plan, general business information. Your financial proposal is going to contain anything that has financial information about your product or service.
What does a proposal outline look like?
A synopsis of the proposed project, including the rationale for the proposed research, a statement of specific aims and objectives, the experimental approaches to be used, and the potential significance of the research.
What is proposal in writing a project?
The Project Proposal is the initial document used to define an internal or external project. The proposal includes sections such as title, start and end dates, objectives and goals, requirements, and a descriptor of the proposed solution.
Project Online Desktop Client Project Professional 2021 Project Standard 2021 Project Professional 2019 Project Standard 2019 Project Professional 2016 Project Standard 2016 Project Professional 2013 Project Standard 2013 Project 2010 Project Standard 2010 More…Less
With Project, you can create and customize striking graphical reports of whatever project data you want, without having to rely on any other software. As you work on the project, the reports change to reflect the latest info — no manual updates required! See a list of all reports and how you can use them.
-
Click the Report tab.
-
In the View Reports group, click the type of report you want and then pick a specific report.
For example, to open the Project Overview report, click Report > Dashboards > Project Overview.
The Project Overview report combines graphs and tables to show where each phase of the project stands, upcoming milestones, and tasks that are past their due dates.

Project provides dozens of reports you can use right away, but you don’t have to let that limit your choices. You can customize the content and the look of any of the reports, or build a new one from scratch.
Work with your report
-
Change the data in a report
-
Example
-
-
Change how a report looks
-
Example
-
-
Make your own report
-
Share a report
-
Make a new report available for future projects
-
More ways to report project info
Change the data in a report
You can choose the data that Project shows in any part of a report.
-
Click the table or chart you want to change.
-
Use the Field list pane on the right of the screen to pick fields to show and filter information.
Tip: When you click a chart, three buttons also pop up directly to the right of the chart. Use the Chart Elements 

Example
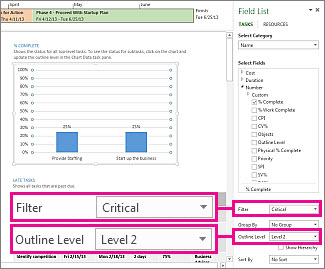
In the Project Overview report, you could change the % Complete chart to show critical subtasks instead of top-level summary tasks:
-
Click anywhere in the % Complete chart.
-
In the Field List pane, go to the Filter box and pick Critical.
-
In the Outline Level box, pick Level 2. For this example, this is the first level of the outline that has subtasks instead of summary tasks.
The chart changes as you make your selections.
Change how a report looks
With Project, you control the look of your reports, from no-nonsense black and white to explosions of colors and effects.
Tip: You can make a report part of a split view so you can see the report change in real time as you work on project data. To learn more, see Split a view.
Click anywhere in the report and then click Report Tools Design to see the options for changing the look of the whole report. From this tab, you can change the font, color, or theme of the whole report. You can also add new images (including photos), shapes, charts, or tables here.
When you click individual elements (charts, tables, and so on) of a report, new tabs appear at the top of the screen with options for formatting that part.

-
Drawing Tools Format tab. Format shapes and text boxes.
-
Picture Tools Format tab. Add effects to pictures.
-
Table Tools Design and Table Tools Layout tabs. Configure and tweak tables, like you would in other Office programs.
-
Chart Tools Design and Chart Tools Format tabs. Configure and tweak charts.
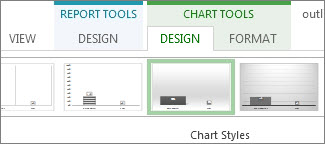
Tip: When you click a chart, three buttons also pop up directly to the right of the chart. Click the Chart Styles button 
Example
Say you decide that the % Complete chart in the Project Overview report needs a facelift.

-
Click anywhere in the % Complete chart, and then click Chart Tools Design.
-
Pick a new style from the Chart Styles group. This style removes the lines and adds shadows to the columns.
-
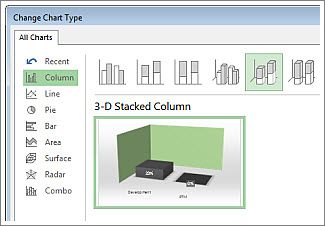
Give the chart some depth. Click Chart Tools Design > Change Chart Type.
-
Click Column > 3-D Stacked Column.
-
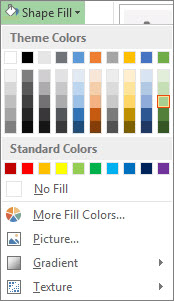
Add a background color. Click Chart Tools Format > Shape Fill, and pick a new color.
-
Change the bar colors. Click the bars to select them, then click Chart Tools Format > Shape Fill, and pick a new color.
-
Move the numbers off the bars. Click the numbers to select them, and then drag them upward.
Just a few clicks make a big difference. And we only scratched the surface of the formatting options.

Make your own report
-
Click Report > New Report.
-
Pick one of the four options, and then click Select.
-
Give your report a name and start adding information to it.
Blank Creates a blank canvas. Use the Report Tools Design tab to add charts, tables, text, and images.
Chart Project creates a chart comparing Actual Work, Remaining Work, and Work by default. Use the Field List pane to pick different fields to compare, and use the controls to change the color and format of the chart.
Table Use the Field List pane to choose what fields to display in the table (Name, Start, Finish, and % Complete appear by default). The Outline level box lets you select how many levels in the project outline the table should show. You can change the look of the table on the Table Tools Design and Table Tools Layout tabs.
Comparison Sets two charts side-by-side. The charts have the same data at first. Click one chart and pick the data you want in the Field List pane to begin differentiating them.
Any of the charts you create from scratch are fully customizable. You can add and delete elements and change the data to meet your needs.
Share a report
-
Click anywhere in the report.
-
Click Report Tools Design > Copy Report.
-
Paste the report into any program that displays graphics.
Tip: You might need to resize and line up the report when you paste it into its new home.
You can also print the report to share it the old-fashioned way.
Make a new report available for future projects
Use the Organizer to copy a new report into the global template for use in future projects.
More ways to report project info
-
See a list of all reports and how you can use them.
-
Compare actual work against your estimates with burndown reports.
-
Create a timeline of key tasks and milestones.
-
Set the status date for project reporting.
Visual reports allow you to view Project information graphically using enhanced PivotTables in Excel 2010. Once Project information has been exported to Excel, you can customize the reports further with Excel 2010 enhanced PivotTable features, such as filter slicers, searching within PivotTables, sparklines within PivotTables to show trends instantly, and OLAP write-back improvements.
The report templates in Project 2010 are divided into six categories in the Visual Reports — Create Report dialog box, which you can access by clicking Visual Reports in the Reports group of the Project tab. The following sections provide descriptions of the visual reports in each category.
You can also create your own custom reports. Custom reports will appear in the category for the type of data used.
Task Usage category
The following table describes the visual reports in the Task Usage category. These reports are based on timephased task data.
Note: Timephased assignment data is available in reports in the Assignment Usage category.
|
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Cash Flow Report |
Excel |
Use this report to view a bar graph with cost and cumulative cost amounts illustrated over time. |
|
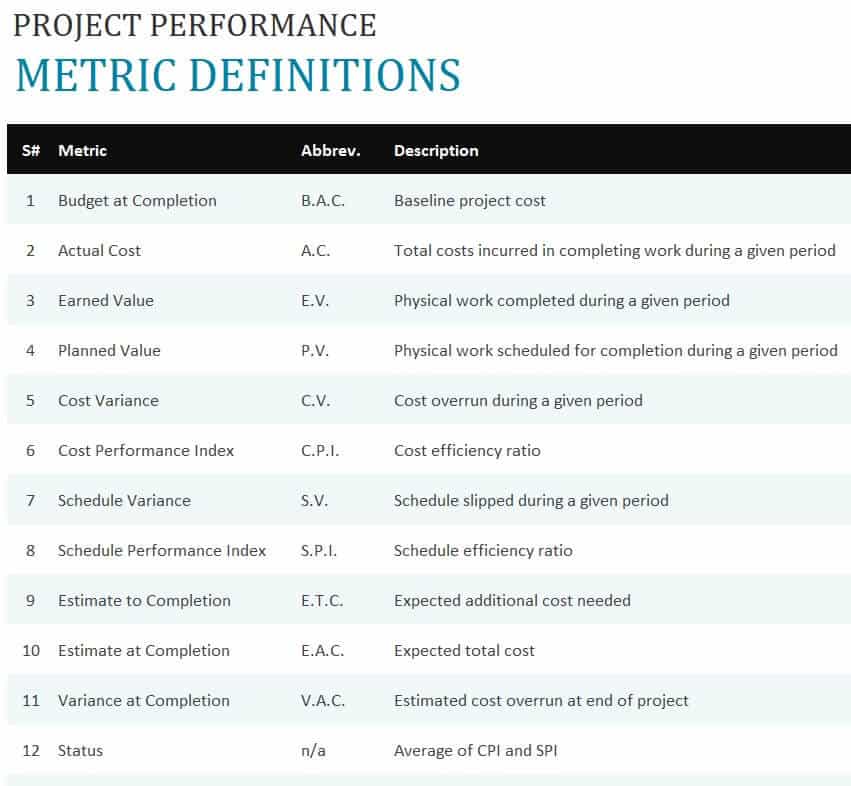
Earned Value Over Time Report |
Excel |
Use this report to view a chart that plots AC (actual cost of work performed), planned value (budgeted cost of work scheduled), and earned value (budgeted cost of work performed) over time. |
Resource Usage category
The following table describes the visual reports in the Resource Usage category. These reports are based on the timephased resource data.
Note: Timephased assignment data is available in reports in the Assignment Usage category.
|
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Cash Flow Report |
Visio |
Use this report to view a diagram that shows planned and actual costs for your project over time. Costs are broken down by resource type (work, material, and cost). An indicator shows if planned costs exceed baseline costs. |
|
Resource Availability Report |
Visio |
Use this report to view a diagram that shows the work and remaining availability for your project’s resources, broken down by resource type (work, material, and cost). A red flag is displayed next to each resource that is overallocated. |
|
Resource Cost Summary Report |
Excel |
Use this report to view a pie chart that illustrates the division of resource cost between the three resource types: cost, material, and work. |
|
Resource Work Availability Report |
Excel |
Use this report to view a bar graph with total capacity, work, and remaining availability for work resources illustrated over time. |
|
Resource Work Summary Report |
Excel |
Use this report to view a bar graph with total resource capacity, work, remaining availability, and actual work illustrated in work units. |
Assignment Usage category
The following table describes the visual reports in the Assignment Usage category. These reports are based on the timephased data, similar to the data found in the Task Usage and Resource Usage views.
|
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Baseline Cost Report |
Excel |
Use this report to view a bar graph with baseline cost, planned cost, and actual cost for your project illustrated across tasks. |
|
Baseline Report |
Visio |
Use this report to view a diagram of your project broken down by quarter, then by task. This report compares planned work and cost to baseline work and cost. Indicators are used to show when planned work exceeds baseline work, and when planned cost exceeds baseline cost. |
|
Baseline Work Report |
Excel |
Use this report to view a bar graph with baseline work, planned work, and actual work for your project illustrated across tasks. |
|
Budget Cost Report |
Excel |
Use this report to view a bar graph with budget cost, baseline cost, planned cost, and actual cost illustrated over time. |
|
Budget Work Report |
Excel |
Use this report to view a bar graph with budget work, baseline work, planned work, and actual work illustrated over time. |
|
Earned Value Over Time Report |
Excel |
Use this report to view a chart that plots AC (actual cost of work performed), planned value (budgeted cost of work scheduled), and earned value (budgeted cost of work performed) over time. |
Task, Resource, and Assignment Summary categories
The following table describes the visual reports in the Task Summary, Resource Summary, and Assignment Summary categories. Summary reports do not include timephased data.
|
Category |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Task Summary |
Critical Tasks Status Report |
Visio |
Use this report to view a diagram showing the work and remaining work for both critical and non-critical tasks. The data bar indicates the percent of work complete. |
|
Task Summary |
Task Status Report |
Visio |
Use this report to view a diagram of the work and percent of work complete for tasks in your project, with symbols indicating when baseline work exceeds work, when baseline work equals work, and when work exceeds baseline work. The data bar indicates the percent of work complete. |
|
Resource Summary |
Resource Remaining Work Report |
Excel |
Use this report to view a bar graph with remaining work and actual work for each work resource, illustrated in work units. |
|
Assignment Summary |
Resource Status Report |
Visio |
Use this report to view a diagram of the work and cost values for each of your project’s resources. The percent of work complete is indicated by the shading in each of the boxes on the diagram. The shading gets darker as the resource nears completion of the assigned work. |
Create a visual report by using a template
-
On the Project tab, in the Reports group, click Visual Reports.
-
In the Visual Reports dialog box, on the All tab, click the report that you want to create.
If the report that you want to create is not listed, select the Include report templates from check box, and then click Modify to browse to the location that contains your report.
Tip: If you know which category contains the report, you can click that category’s tab to view a shorter list of reports. If you only want to list reports that open in either Excel or Visio, select or clear the Microsoft Excel or Microsoft Visio check box.
-
To change the level of usage data included in the report, select Years, Quarters, Months, Weeks, or Days from the Select level of usage data to include in the report list.
Note: By default, Project sets the level of usage data to what it recommends for your project’s size. For most projects, this will be weeks. If you choose to include data at a more detailed level, report performance may be decreased. For best performance, if you are viewing multiple reports for the same project at one time, refrain from changing the data level. If you change the data level, the temporary reporting database stored locally must be recreated. If you don’t need to include usage data in your reports, set the data level to Years for best performance.
-
Click View to generate the report and open it in Excel or Visio.
Edit an existing visual report template
-
On the Project tab, in the Reports group, click Visual Reports.
-
In the Visual Reports dialog box, on the All tab, click the report that you want to edit.
Tip: If you know which category contains the report, you can click that category’s tab to view a shorter list of reports. If you only want to list reports that open in either Excel or Visio, select or clear the Microsoft Excel or Microsoft Visio check boxes.
-
Click Edit Template.
-
On the Visual Reports — Field Picker dialog box, click the fields that you want to add or remove from the report, and then click Add, Remove, or Remove All to move fields between the Available Fields and Selected Fields boxes, or between the Available Custom Fields and Selected Custom Fields boxes.
Fields in the Selected Fields and Selected Custom Fields boxes are included in the report.
-
Click Edit Template to create the report with the modified list of fields.
-
On the Visual Reports — Field Picker dialog box, some fields are identified as dimensions. It is important to select fewer than six dimensions for your report. If you select more than six dimensions, report performance is significantly decreased.
-
Not all fields are available in all reports. Some fields are only available in Visio reports, but not in Excel reports.
-
If you are unable to locate the field you want to include on the Visual Reports — Field Picker dialog box, it may be stored in a different category of data. For example, many fields that you might think of as Task Summary fields are actually Assignment Summary fields.
Create a new visual report template
-
On the Project tab, in the Reports group, click Visual Reports.
-
In the Visual Reports dialog box, click New Template.
-
In the Select Application section, click Excel to create an Excel template, or click Visio (Metric) to create a Visio template.
-
In the Select Data Type section, select the type of data that you want to use in the report.
To include timephased data, select Task Usage, Resource Usage, or Assignment Usage from the list in the Select Data Type section.
-
Click Field Picker.
-
On the Visual Reports — Field Picker dialog box, hold CTRL and click the default Project fields that you want to add to the report in the Available Fields box.
-
Click Add to move them to the Selected Fields box.
-
Hold CTRL and click the custom fields that you want to add to the report in the Available Custom Fields box.
-
Click Add to move them to the Selected Custom Fields box.
-
If you have the English version of Office Project 2007 installed, you have the option to create a Visio template that uses U.S. units.
-
To remove a field from the report, on the Visual Reports — Field Picker dialog box, click the field in the Selected Fields or Selected Custom Fields box, and then click Remove. To remove all default or custom fields from the report, click Remove All in the Select Fields or Select Custom Fields section.
-
Not all fields are available in all reports. Some fields are only available in Visio reports, and not in Excel reports.
-
If you are unable to locate the field you want to include on the Visual Reports — Field Picker dialog box, it may be stored in a different category of data. For example, many fields that you might think of as Task Summary fields are actually Assignment Summary fields.
-
On the Visual Reports — Field Picker dialog box, some fields are identified as dimensions. It is important to select fewer than six dimensions for your report. If you select more than six dimensions, report performance is significantly decreased.
-
When you have finished creating your visual report, you can choose to save it to the default template location (c:Program FilesMicrosoft OfficeTemplates) or to another location on your computer or your network. Templates saved in the default template location automatically appear on the Visual Reports — Create Report dialog box.
-
If you begin using a different language pack after saving a custom visual report template, the template remains available but is not populated. The original field names are not recognized in the new language and are not included in the report.
Export report data
You can select specific data to export within a category (OLAP cube), or you can export all project data as a reporting database.
Export data as an OLAP cube
-
On the Project tab, in the Reports group, click Visual Reports.
-
In the Visual Reports dialog box, click Save Data.
-
In the Save Reporting Cube section, select the category that contains the type of data that you want to save.
-
Click Field Picker to modify the fields included in the list of data to export.
-
On the Visual Reports — Field Picker dialog box, click the fields that you want to add or remove from the list of data to export, and then click Add, Remove, or Remove All to move fields between the Available Fields and Selected Fields boxes, or between the Available Custom Fields and Selected Custom Fields boxes.
Fields in the Selected Fields and Selected Custom Fields boxes are included in the exported data.
-
Click OK on the Visual Reports — Field Picker dialog box, and then click Save Cube.
-
Browse to the location where you want to save the cube data, and then click Save.
-
Cube data is saved as a .cub file.
-
When accessing cube data with Visio, the .cub file cannot be stored on a network share.
Export data as a reporting database
-
On the Project tab, in the Reports group, click Visual Reports.
-
In the Visual Reports dialog box, click Save Data.
-
Click Save Database.
-
Browse to the location where you want to save the database, and then click Save.
The data is saved as a Microsoft Office Access database (.mdb) file.
Project for the web offers two main options for reporting: Excel and Power BI Desktop. Excel reporting comes with Microsoft 365, while Power BI Desktop is licensed separately.
Excel
When managing a project in Project for the web, export your project to Excel allows you to:
-
Create reports and visuals
-
Send a file containing project details to external stakeholders
-
Archive copies of your project data for audit and compliance
-
Print copies of your project
Here’s how to export your project:
-
Go to project.microsoft.com and open the project you want to export to Excel.
-
In the top right corner, select the three dots (…), then select Export to Excel.
-
When you see the message «All done! We’ve exported [your project name].» at the bottom of the screen, you can look for your new Excel file where you store your downloads.
When you open the Excel file containing your project, you’ll see a worksheet named «Project tasks» that contains a summary of project-wide information at the top, including its name, project manager, and the start and finish dates, duration, and percent complete for the whole project. You’ll also see what date it was exported. Under that, you’ll see a table of all the information for your project.
More about Excel Report options
-
Import and analyze data
-
Create a PivotTable to analyze worksheet data
-
Ideas in Excel
Power BI Desktop
To get started, connect to Project for the web data through Power BI Desktop, then open the Project Power BI template and explore the reports it includes.
Important: You’ll need a Power BI subscription (and a Project subscription in many cases) to use this reporting tool. See the following section for details.
Licensing
To use Power BI reports on Project for the web data, you need to be a licensed user of Power BI Desktop or Power BI Pro. See Power BI Pricing for more information.
To build or customize Power BI reports on Project for the web data, you’ll also need Project Plan 3 (formerly Project Online Professional) or Project Plan 5 (formerly Project Online Premium).
Need more help?
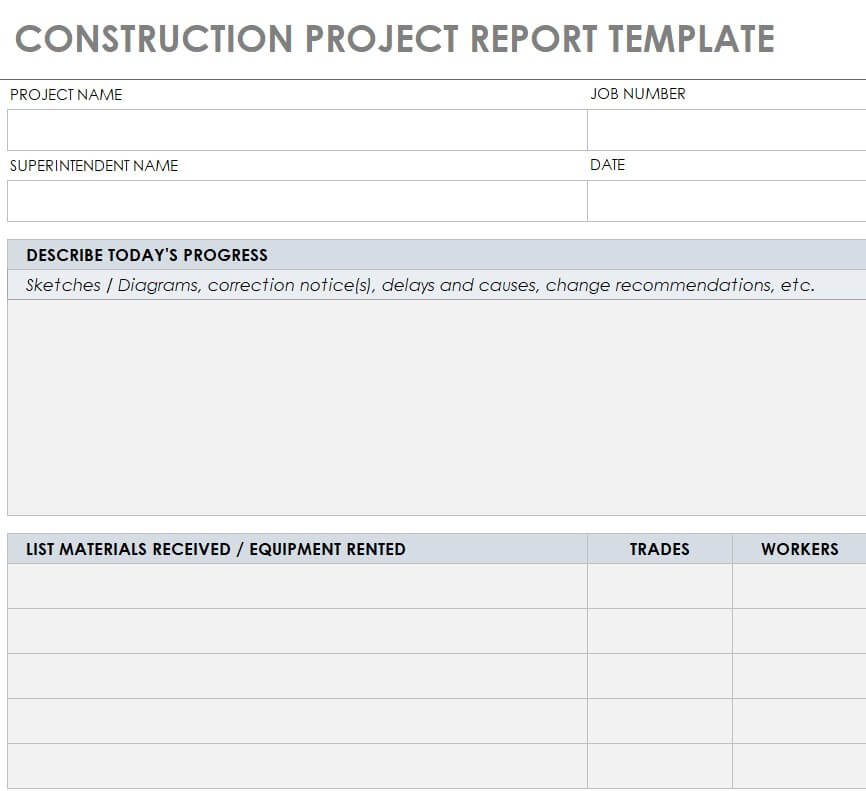
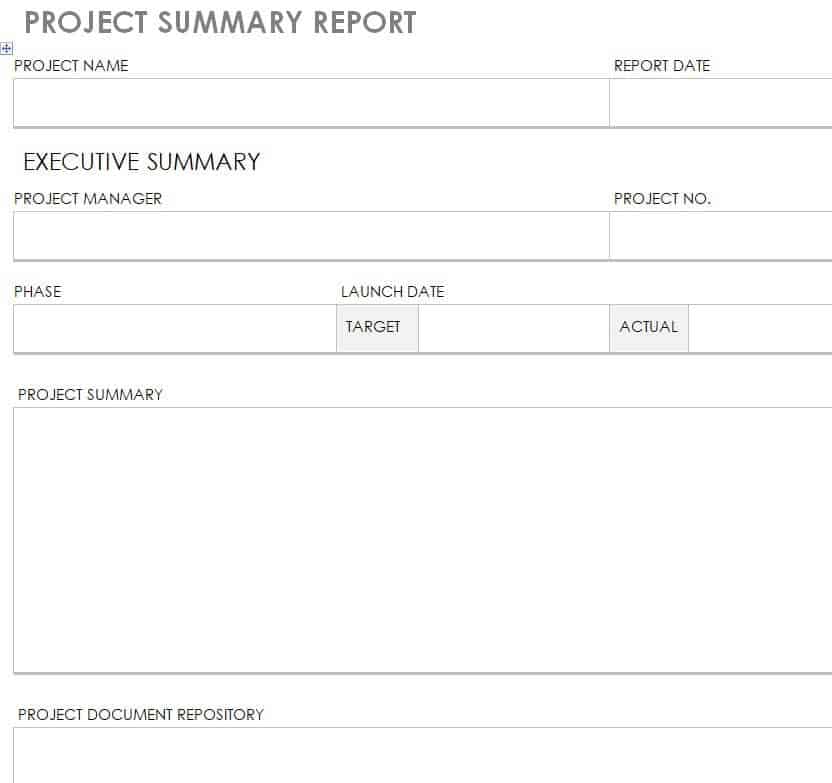
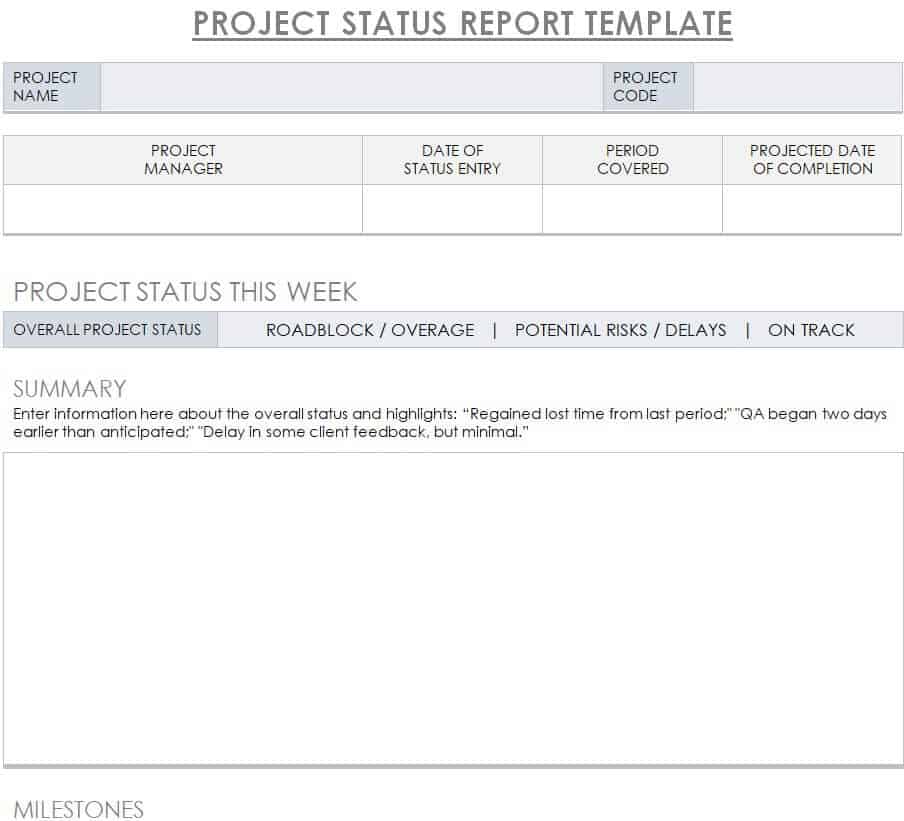
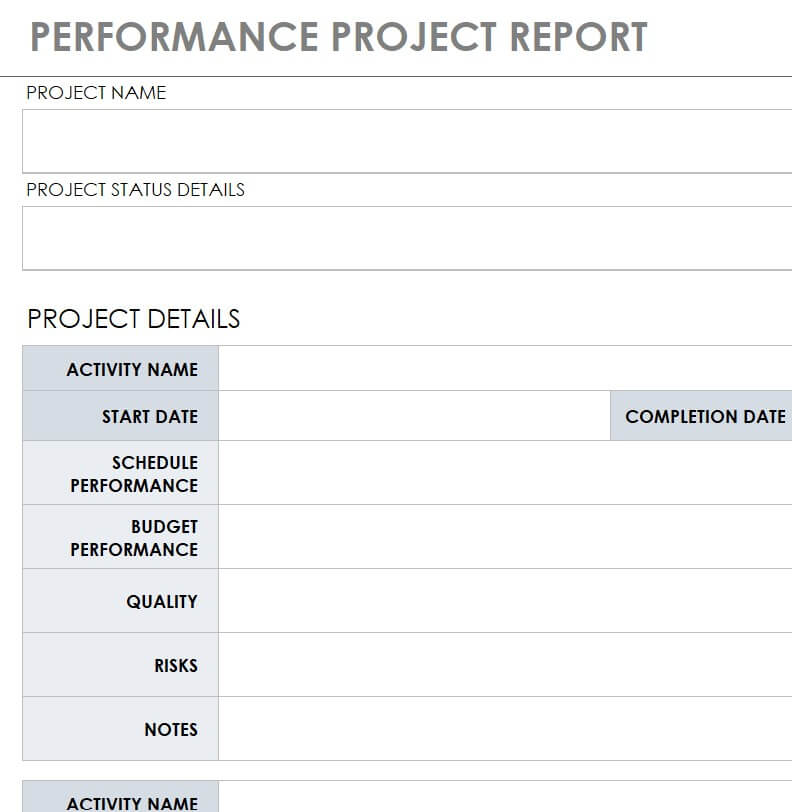
Our below-listed editable project report templates combine elegant formatting with a professional and easy-to-use layout. The use of these templates is a quick and perfect way to rapidly turn your all details and information about the project into a comprehensive project report in a few minutes. A project report is a document describing an account of information from the project proposal to the proposed plan and set of activities to get the project accomplished in a timely manner.
The project report contains answers to all questions related to the progress and status of the project in a detailed manner. Writing a project report is one of the basic responsibilities of project manager and he or she should prepared it carefully with concise words to make it easily understandable by all. Project reports are generally written about the accomplishment or progress of project milestones and other details but may be requested by the client or a supervisor at any time.
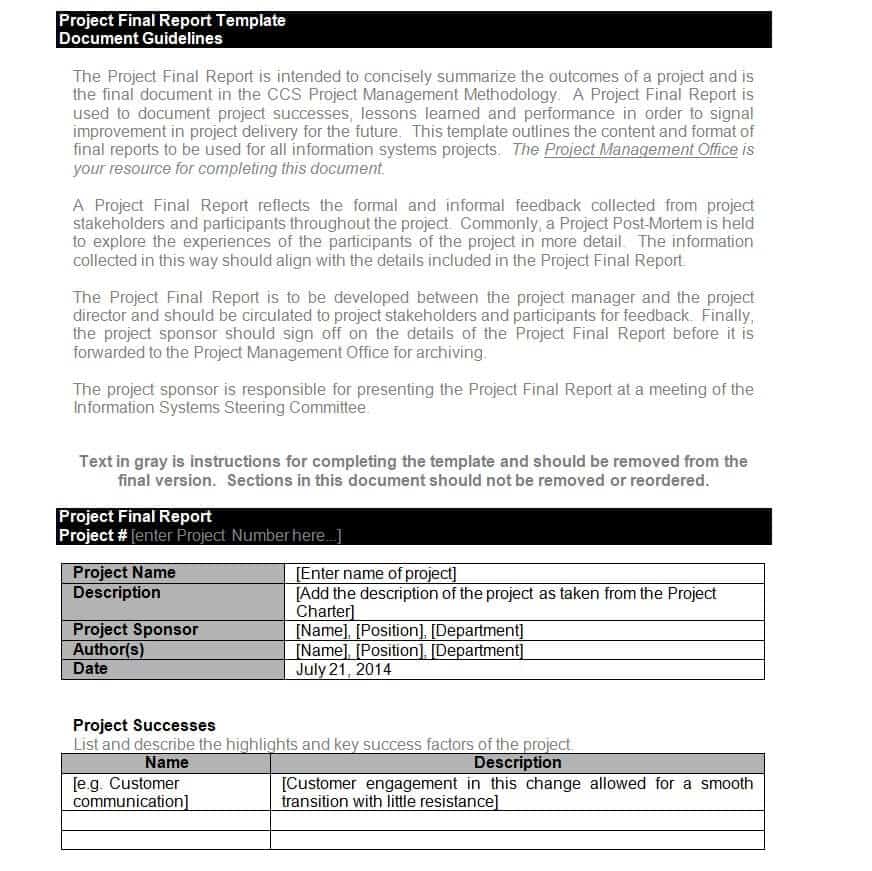
Free Project Report Template:
The major purpose of the project report is to provide readers with information related to the project just as the project’s goals, action plan, budget, results, etc. A project report is a vital document in project management in which you can write anything which is significant and you want to highlight it for management to get issues resolved. Project report writing can be a big job for you to carry out for the very first time.
However, using a few basic report writing techniques and instructions you can produce an effective project report to show your seniors that you are fully organized and able to deliver basic and important information about the project. Here you can get a free and easily editable project report template and we are sure you will find it as a good starting point when writing a project report. All contents and elements of the template are editable so you can easily change the text to make it perfect as per your needs.