В этом уроке я покажу Вам самые популярные макросы в VBA Excel, которые вы сможете использовать для оптимизации своей работы. VBA — это язык программирования, который может использоваться для расширения возможностей MS Excel и других приложений MS Office. Это чрезвычайно полезно для пользователей MS Excel, поскольку VBA может использоваться для автоматизации вашей работы и значительно увеличить Вашу эффективность. В этой статье Вы познакомитесь с VBA и я вам покажу некоторые из наиболее полезных, готовых к использованию примеров VBA. Вы сможете использовать эти примеры для создания собственных скриптов, соответствующих Вашим потребностям.
Вам не нужен опыт программирования, чтобы воспользоваться информаций из этой статьи, но вы должны иметь базовые знания Excel. Если вы еще учитесь работать с Excel, я бы рекомендовал Вам прочитать статью 20 формул Excel, которые вам нeобходимо выучить сейчас, чтобы узнать больше о функциональных возможностях Excel.
Я подготовил для вас несколько самых полезных примеров VBA Excel с большой функциональностью, которую вы сможете использовать для оптимизации своей работы. Чтобы их использовать, вам необходимо записать их в файл. Следующий параграф посвящен установке макроса Excel. Пропустите эту часть, если вы уже знакомы с этим.
Table of Contents
Как включить макросы в Excel
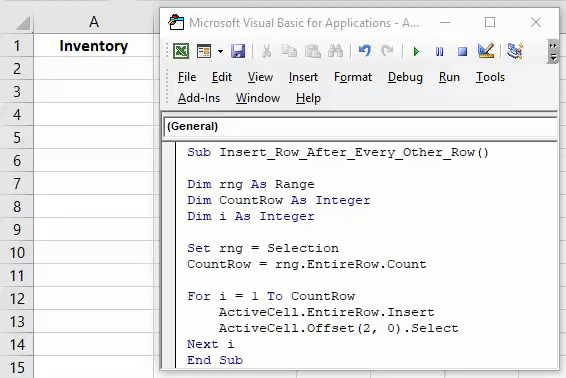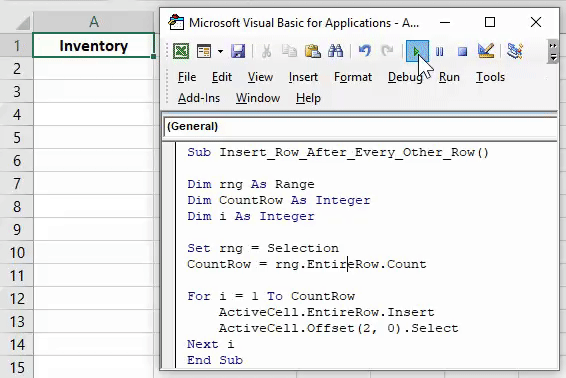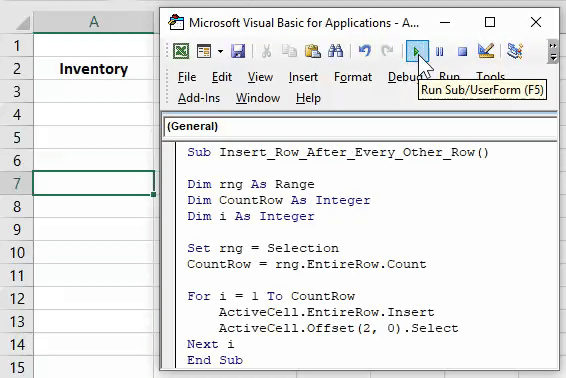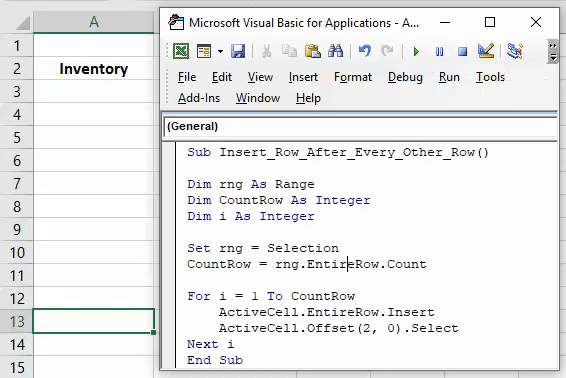
В Excel нажмите комбинацию клавиш alt + F11. Это приведет вас к редактору VBA в MS Excel. Затем щелкните правой кнопкой мыши папку Microsoft Excel Objects слева и выберите Insert => Module. Это место, где сохраняются макросы. Чтобы использовать макрос, вам нужно сохранить документ Excel как макрос. Из табуляции File => Save as, выберите Save as macro-enabled Workbok (расширение .xlsm) Теперь пришло время написать свой первый макрос!
1. Копирование данных из одного файла в другой.
Очень полезный макрос, поскольку он показывает, как скопировать ряд данных изнутри vba и как создать и назвать новую книгу. Вы можете изменить этот макрос в соответствии с вашими собственными требованиями:
Sub CopyFiletoAnotherWorkbook() Sheets("Example 1").Range("B4:C15").Copy Workbooks.Add ActiveSheet.Paste Application.DisplayAlerts = False ActiveWorkbook.SaveAs Filename:="C:TempMyNewBook.xlsx" Application.DisplayAlerts = True End Sub
2. Отображение скрытых строк
Иногда большие файлы Excel можно содержать скрытые строки для большей ясности И для лучшего удобства пользователей. Вот один макрос, который отобразит все строки из активной рабочей таблицы:
Sub ShowHiddenRows() Columns.EntireColumn.Hidden = False Rows.EntireRow.Hidden = False End Sub
3. Удаление пустых строк и столбов
Пустые строки в Excel — может быть проблемой для обработки данных. Вот как избавиться от них:
Sub DeleteEmptyRowsAndColumns() Dim MyRange As Range Dim iCounter As Long Set MyRange = ActiveSheet.UsedRange For iCounter = MyRange.Rows.Count To 1 Step -1 If Application.CountA(Rows(iCounter).EntireRow) = 0 Then Rows(iCounter).Delete End If Next iCounter For iCounter = MyRange.Columns.Count To 1 Step -1 If Application.CountA(Columns(iCounter).EntireColumn) = 0 Then Columns(iCounter).Delete End If Next iCounter End Sub
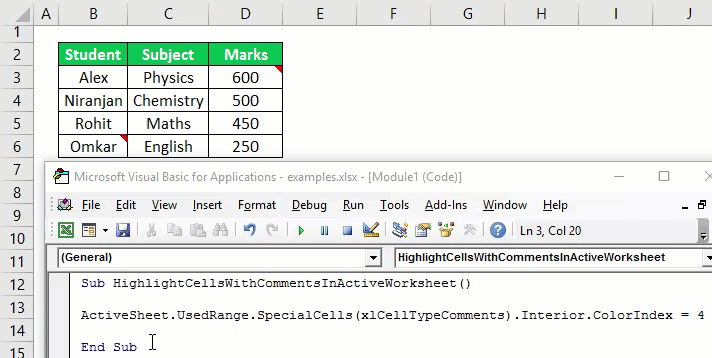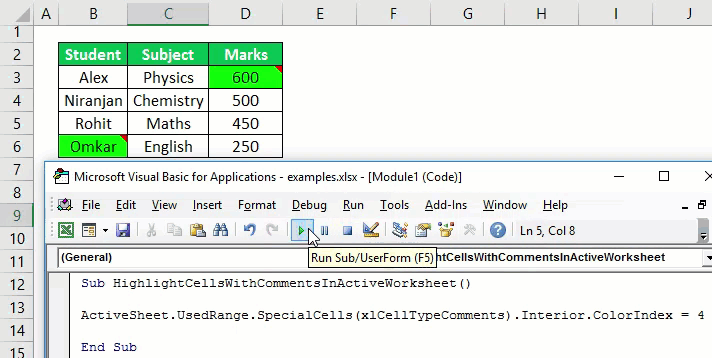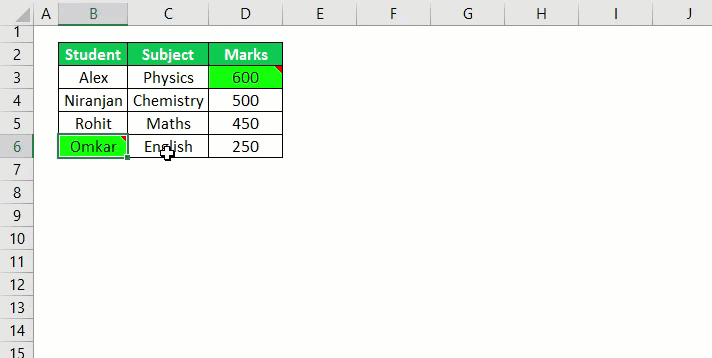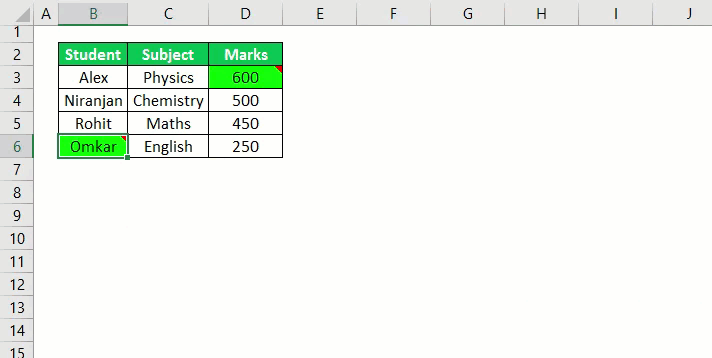
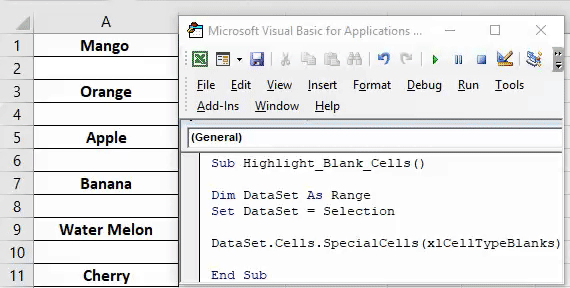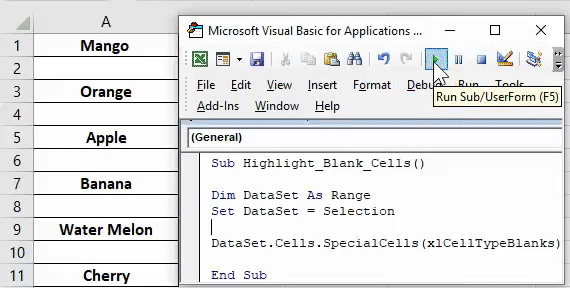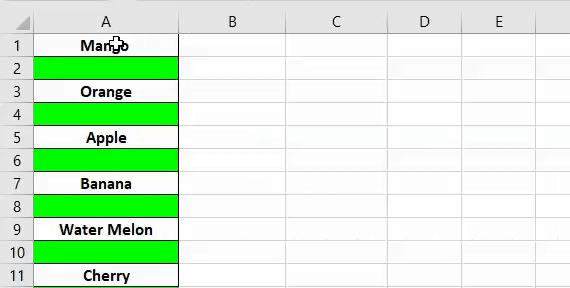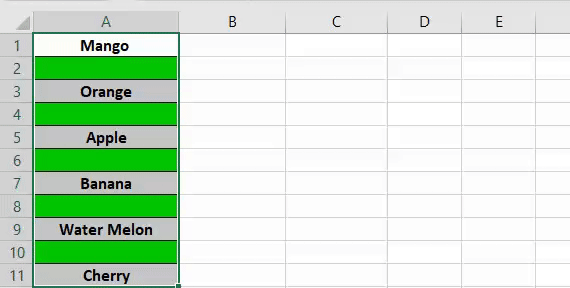
4. Нахождение пустых ячеек
Sub FindEmptyCell() ActiveCell.Offset(1, 0).Select Do While Not IsEmpty(ActiveCell) ActiveCell.Offset(1, 0).Select Loop End Sub
#### 5. Заполнение пустых ячеек
Как упоминалось ранее, пустые ячейки препятствуют обработке данных и созданию сводных таблиц. Вот один примерный код, который заменяет все пустые ячейки на 0. Этот макрос имеет очень большое приложение, потому что Вы можете использовать его для поиска и замены результатов N/A, а также других символов, таких как точки, запятые или повторяющиеся значения:
Sub FindAndReplace() Dim MyRange As Range Dim MyCell As Range Select Case MsgBox("Can't Undo this action. " & _ "Save Workbook First?", vbYesNoCancel) Case Is = vbYes ThisWorkbook.Save Case Is = vbCancel Exit Sub End Select Set MyRange = Selection For Each MyCell In MyRange If Len(MyCell.Value) = 0 Then MyCell = 0 End If Next MyCell End Sub
#### 6. Сортировка данных
Следующий макрос сортирует по возрастанию все числа из столбца активной ячейки. Просто дважды нажмите любую ячейку из столбца, который вы хотите отсортировать.
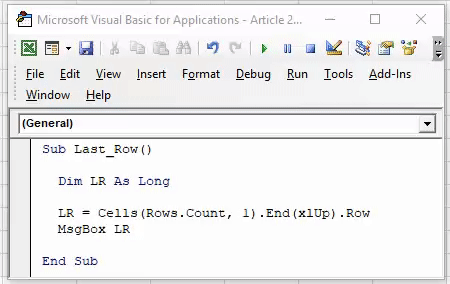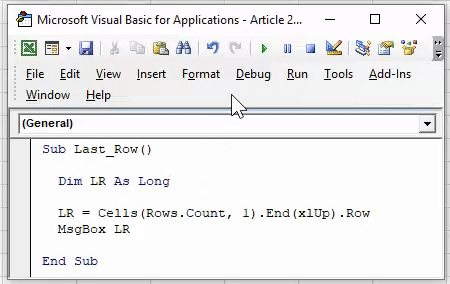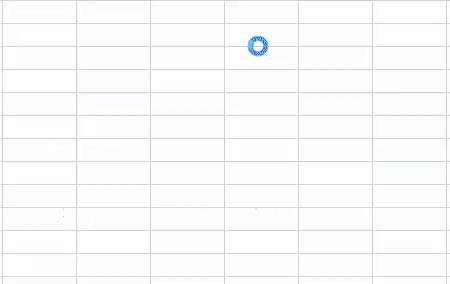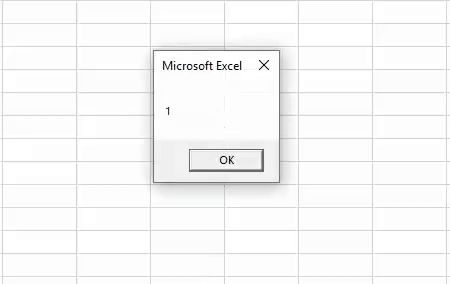
NB: Здесь нам нужно поставить этот код в Sheet1 (папка Microsoft Excel Objects), а не в Module1 (папка Modules):
Private Sub Worksheet_BeforeDoubleClick (ByVal Target as Range, Cancel As Boolean) Dim LastRow As Long LastRow = Cells (Rows.Count, 1) .End (xlUp) .Row Rows ("6:" & LastRow) .Sort _ Key1: = Cells (6, ActiveCell.Column), _ Order1: = xlAscending End Sub
#### 7. Удаление пустых пространств
Иногда данные в книге содержат дополнительные пробелы (whitespace charachters), которые могут мешать анализу данных и коррумпировать формулы. Вот один макрос, который удалит все пробелы из предварительно выбранного диапазона ячеек:
Sub TrimTheSpaces() Dim MyRange As Range Dim MyCell As Range Select Case MsgBox("Can't Undo this action. " & _ "Save Workbook First?", vbYesNoCancel) Case Is = vbYes ThisWorkbook.Save Case Is = vbCancel Exit Sub End Select Set MyRange = Selection For Each MyCell In MyRange If Not IsEmpty(MyCell) Then MyCell = Trim(MyCell) End If Next MyCell End Sub
#### 8. Выделение дубликатов цветом
Иногда в нескольких столбцах, которые мы хотели бы осветить, есть повторяющиеся значения. Этот макрос делает именно это:
Sub HighlightDuplicates() Dim MyRange As Range Dim MyCell As Range Set MyRange = Selection For Each MyCell In MyRange If WorksheetFunction.CountIf(MyRange, MyCell.Value) > 1 Then MyCell.Interior.ColorIndex = 36 End If Next MyCell End Sub
#### 9. Выделение десяти самых высоких чисел
Этот код будет отображать десять самых высоких чисел из набора ячеек:
Sub TopTen() Selection.FormatConditions.AddTop10 Selection.FormatConditions(Selection.FormatConditions.Count).SetFirstPriority With Selection.FormatConditions(1) .TopBottom = xlTop10Top .Rank = 10 .Percent = False End With With Selection.FormatConditions(1).Font .Color = -16752384 .TintAndShade = 0 End With With Selection.FormatConditions(1).Interior .PatternColorIndex = xlAutomatic .Color = 13561798 .TintAndShade = 0 End With Selection.FormatConditions(1).StopIfTrue = False End Sub
Вы можете легко настроить код, чтобы выделить различное количество чисел.
#### 10. Выделение данных больших чем данные число
Когда вы запустите этот код, появится окно. Вам надо написать число, которое вы хотите сравнить с выбранными ячейками.
Sub HighlightGreaterThanValues() Dim i As Integer i = InputBox("Enter Greater Than Value", "Enter Value") Selection.FormatConditions.Delete Selection.FormatConditions.Add Type:=xlCellValue, Operator:=xlGreater, Formula1:=i Selection.FormatConditions(Selection.FormatConditions.Count).SetFirstPriority With Selection.FormatConditions(1) .Font.Color = RGB(0, 0, 0) .Interior.Color = RGB(31, 218, 154) End With End Sub
Вы тоже можете настроить этот код, чтобы выделить более низкие чисел.
#### 11. Выделение ячеек комментариями
Простой макрос, который выделяет все ячейки, содержащие комментарии:
Sub HighlightCommentCells() Selection.SpecialCells(xlCellTypeComments).Select Selection.Style= "Note" End Sub
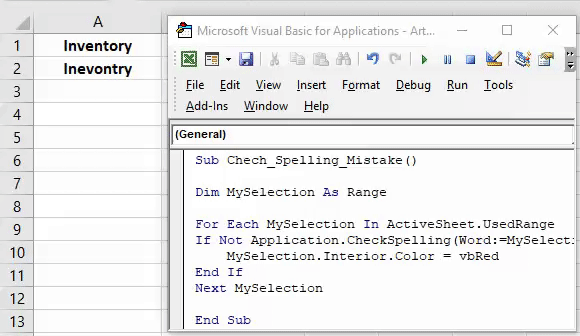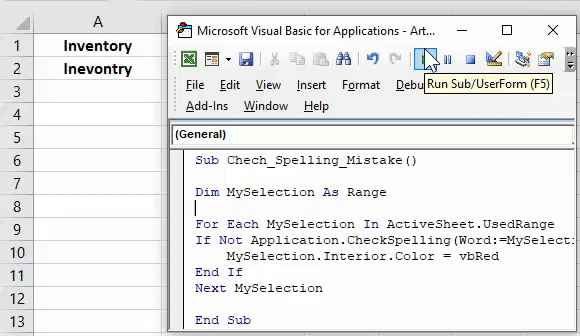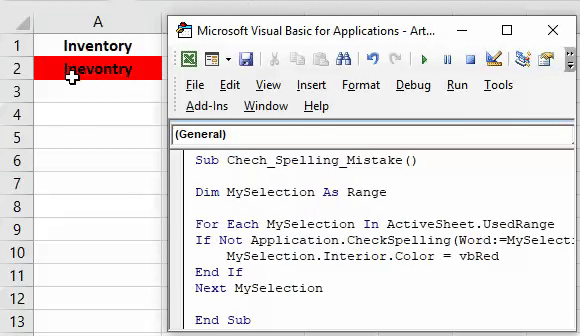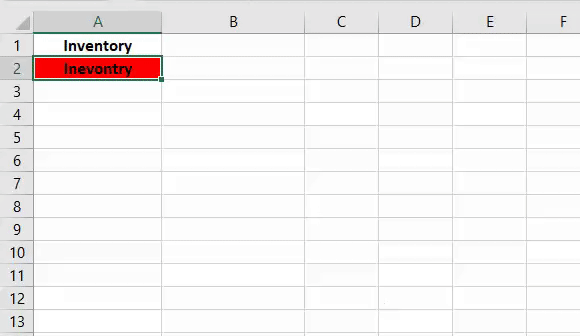
#### 12. Выделение ячеек со словами с ошибками
Это очень полезно, когда вы работаете с функциями, которые принимают строки, однако кто-то ввел строку с ошибкой, и ваши формулы не работают. Вот как решить эту проблему:
Sub ColorMispelledCells() For Each cl In ActiveSheet.UsedRange If Not Application.CheckSpelling(Word:=cl.Text) Then _ cl.Interior.ColorIndex = 28 Next cl End Sub
13. Создание сводной таблицы
Вот как создать сводную таблицу в MS Excel (версия 2007). Особенно полезно, когда вы делаете индивидуальный отчет каждый день. Вы можете оптимизировать создание сводной таблицы следующим образом:
Sub PivotTableForExcel2007() Dim SourceRange As Range Set SourceRange = Sheets("Sheet1").Range("A3:N86") ActiveWorkbook.PivotCaches.Create( _ SourceType:=xlDatabase, _ SourceData:=SourceRange, _ Version:=xlPivotTableVersion12).CreatePivotTable _ TableDestination:="", _ TableName:="", _ DefaultVersion:=xlPivotTableVersion12 End Sub
14. Отправка активного файла по электронной почте
Мой любимый код VBA. Он позволяет вам прикреплять и отправлять файл, с которым вы работаете, с предопределенным адресом электронной почты, заголовком сообщения и телом сообщения! Сначала Вам нужно сделать референцию в Excel на Microsoft Outlook (в редакторе Excel VBA, нажмите tools => references и выберите Microsoft Outlook).
Sub SendFIleAsAttachment() Dim OLApp As Outlook.Application Dim OLMail As Object Set OLApp = New Outlook.Application Set OLMail = OLApp.CreateItem(0) OLApp.Session.Logon With OLMail .To = "admin@datapigtechnologies.com; mike@datapigtechnologies.com" .CC = "" .BCC = "" .Subject = "This is the Subject line" .Body = "Hi there" .Attachments.Add ActiveWorkbook.FullName .Display End With Set OLMail = Nothing Set OLApp = Nothing End Sub
15. Вставка всех графиков Excel в презентацию PowerPoint
Очень удобный макрос, который позволяет вам добавлять все ваши графики Excel в презентацию Powerpoint одним щелчком мыши:
Sub SendExcelFiguresToPowerPoint() Dim PP As PowerPoint.Application Dim PPPres As PowerPoint.Presentation Dim PPSlide As PowerPoint.Slide Dim i As Integer Sheets("Slide Data").Select If ActiveSheet.ChartObjects.Count < 1 Then MsgBox "No charts existing the active sheet" Exit Sub End If Set PP = New PowerPoint.Application Set PPPres = PP.Presentations.Add PP.Visible = True For i = 1 To ActiveSheet.ChartObjects.Count ActiveSheet.ChartObjects(i).Chart.CopyPicture _ Size:=xlScreen, Format:=xlPicture Application.Wait (Now + TimeValue("0:00:1")) ppSlideCount = PPPres.Slides.Count Set PPSlide = PPPres.Slides.Add(SlideCount + 1, ppLayoutBlank) PPSlide.Select PPSlide.Shapes.Paste.Select PP.ActiveWindow.Selection.ShapeRange.Align msoAlignCenters, True PP.ActiveWindow.Selection.ShapeRange.Align msoAlignMiddles, True Next i Set PPSlide = Nothing Set PPPres = Nothing Set PP = Nothing End Sub
16. Вставка таблицы Excel в MS Word
Таблицы Excel обычно помещаются внутри текстовых документов. Вот один автоматический способ экспорта таблицы Excel в MS Word:
Sub ExcelTableInWord() Dim MyRange As Excel.Range Dim wd As Word.Application Dim wdDoc As Word.Document Dim WdRange As Word.Range Sheets("Revenue Table").Range("B4:F10").Cop Set wd = New Word.Application Set wdDoc = wd.Documents.Open _ (ThisWorkbook.Path & "" & "PasteTable.docx") wd.Visible = True Set WdRange = wdDoc.Bookmarks("DataTableHere").Rangе On Error Resume Next WdRange.Tables(1).Delete WdRange.Paste WdRange.Tables(1).Columns.SetWidth _ (MyRange.Width / MyRange.Columns.Count), wdAdjustSameWidth wdDoc.Bookmarks.Add "DataTableHere", WdRange Set wd = Nothing Set wdDoc = Nothing Set WdRange = Nothing End Sub
17. Извлечение слов из текста
Мы можем использовать формулы, если хотим извлечь определенное количество символов. Но что, если мы хотим извлечь только одно слово из предложения или диапазон слов в ячейке? Для этого мы можем сами создать функцию Excel с помощью VBA. Это одна из самых удобных функций VBA, поскольку она позволяет создавать собственные формулы, которые отсутствуют в MS Excel. Давайте продолжим и создадим две функции: findword() и findwordrev():
Function FindWord(Source As String, Position As Integer) As String On Error Resume Next FindWord = Split(WorksheetFunction.Trim(Source), " ")(Position - 1) On Error GoTo 0 End Function Function FindWordRev(Source As String, Position As Integer) As String Dim Arr() As String Arr = VBA.Split(WorksheetFunction.Trim(Source), " ") On Error Resume Next FindWordRev = Arr(UBound(Arr) - Position + 1) On Error GoTo 0 End Function
Отлично, мы уже создали две новые функции в Excel! Теперь попробуйте использовать их в Excel. Функция = FindWordRev (A1,1) берет последнее слово из ячейки A1. Функция = FindWord (A1,3) берет третье слово из ячейки A1 и т. Д.
18. Защита данных в MS Excel
Иногда мы хотим защитить данных нашего файла, чтобы только мы могли его изменять. Вот как это сделать с VBA:
Sub ProtectSheets() Dim ws As Worksheet For Each ws In ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets ws.Protect Password:="1234" Next ws End Sub
Поздравления! Поскольку вы все еще читаете это, вы действительно заинтересованы в изучении VBA. Как вы уже сами видели, язык программирования VBA чрезвычайно полезен и может сэкономить нам много времени. Надеюсь, вы нашли эту информацию полезной и использовали ее, чтобы стать мастером MS Excel, VBA и компьютерных наук в целом.
© 2018 Атанас Йонков
Литература:
1. ExcelChamps.com: Top 100 Useful Excel Macro [VBA] Codes Examples.
2. Michael Alexander, John Walkenbach (2012). 101 Ready-To-Use Excel Macros.
3. BG Excel.info: 14 ready-to-use Macros for Excel.
Время на прочтение
7 мин
Количество просмотров 312K
Приветствую всех.
В этом посте я расскажу, что такое VBA и как с ним работать в Microsoft Excel 2007/2010 (для более старых версий изменяется лишь интерфейс — код, скорее всего, будет таким же) для автоматизации различной рутины.

VBA (Visual Basic for Applications) — это упрощенная версия Visual Basic, встроенная в множество продуктов линейки Microsoft Office. Она позволяет писать программы прямо в файле конкретного документа. Вам не требуется устанавливать различные IDE — всё, включая отладчик, уже есть в Excel.
Еще при помощи Visual Studio Tools for Office можно писать макросы на C# и также встраивать их. Спасибо, FireStorm.
Сразу скажу — писать на других языках (C++/Delphi/PHP) также возможно, но требуется научится читать, изменять и писать файлы офиса — встраивать в документы не получится. А интерфейсы Microsoft работают через COM. Чтобы вы поняли весь ужас, вот Hello World с использованием COM.
Поэтому, увы, будем учить Visual Basic.
Чуть-чуть подготовки и постановка задачи
Итак, поехали. Открываем Excel.
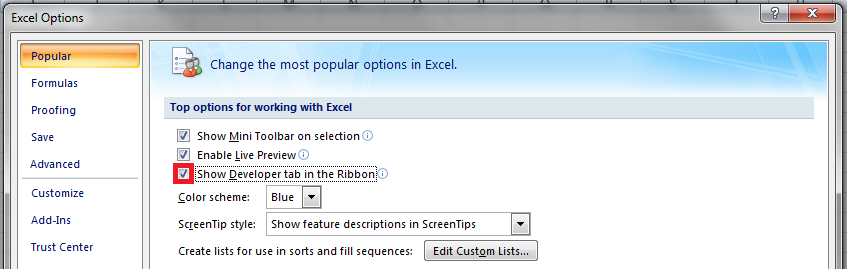
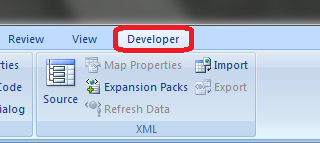
Для начала давайте добавим в Ribbon панель «Разработчик». В ней находятся кнопки, текстовые поля и пр. элементы для конструирования форм.
Появилась вкладка.
Теперь давайте подумаем, на каком примере мы будем изучать VBA. Недавно мне потребовалось красиво оформить прайс-лист, выглядевший, как таблица. Идём в гугл, набираем «прайс-лист» и качаем любой, который оформлен примерно так (не сочтите за рекламу, пожалуйста):
То есть требуется, чтобы было как минимум две группы, по которым можно объединить товары (в нашем случае это будут Тип и Производитель — в таком порядке). Для того, чтобы предложенный мною алгоритм работал корректно, отсортируйте товары так, чтобы товары из одной группы стояли подряд (сначала по Типу, потом по Производителю).
Результат, которого хотим добиться, выглядит примерно так:
Разумеется, если смотреть прайс только на компьютере, то можно добавить фильтры и будет гораздо удобнее искать нужный товар. Однако мы хотим научится кодить и задача вполне подходящая, не так ли?
Кодим
Для начала требуется создать кнопку, при нажатии на которую будет вызываться наша програма. Кнопки находятся в панели «Разработчик» и появляются по кнопке «Вставить». Вам нужен компонент формы «Кнопка». Нажали, поставили на любое место в листе. Далее, если не появилось окно назначения макроса, надо нажать правой кнопкой и выбрать пункт «Назначить макрос». Назовём его FormatPrice. Важно, чтобы перед именем макроса ничего не было — иначе он создастся в отдельном модуле, а не в пространстве имен книги. В этому случае вам будет недоступно быстрое обращение к выделенному листу. Нажимаем кнопку «Новый».
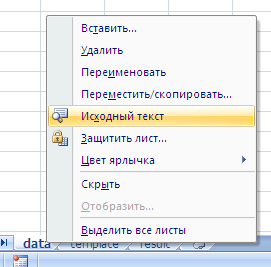
И вот мы в среде разработки VB. Также её можно вызвать из контекстного меню командой «Исходный текст»/«View code».
Перед вами окно с заглушкой процедуры. Можете его развернуть. Код должен выглядеть примерно так:
Sub FormatPrice()End Sub
Напишем Hello World:
Sub FormatPrice()
MsgBox "Hello World!"
End Sub
И запустим либо щелкнув по кнопке (предварительно сняв с неё выделение), либо клавишей F5 прямо из редактора.
Тут, пожалуй, следует отвлечься на небольшой ликбез по поводу синтаксиса VB. Кто его знает — может смело пропустить этот раздел до конца. Основное отличие Visual Basic от Pascal/C/Java в том, что команды разделяются не ;, а переносом строки или двоеточием (:), если очень хочется написать несколько команд в одну строку. Чтобы понять основные правила синтаксиса, приведу абстрактный код.
Примеры синтаксиса
' Процедура. Ничего не возвращает
' Перегрузка в VBA отсутствует
Sub foo(a As String, b As String)
' Exit Sub ' Это значит "выйти из процедуры"
MsgBox a + ";" + b
End Sub' Функция. Вовращает Integer
Function LengthSqr(x As Integer, y As Integer) As Integer
' Exit Function
LengthSqr = x * x + y * y
End FunctionSub FormatPrice()
Dim s1 As String, s2 As String
s1 = "str1"
s2 = "str2"
If s1 <> s2 Then
foo "123", "456" ' Скобки при вызове процедур запрещены
End IfDim res As sTRING ' Регистр в VB не важен. Впрочем, редактор Вас поправит
Dim i As Integer
' Цикл всегда состоит из нескольких строк
For i = 1 To 10
res = res + CStr(i) ' Конвертация чего угодно в String
If i = 5 Then Exit For
Next iDim x As Double
x = Val("1.234") ' Парсинг чисел
x = x + 10
MsgBox xOn Error Resume Next ' Обработка ошибок - игнорировать все ошибки
x = 5 / 0
MsgBox xOn Error GoTo Err ' При ошибке перейти к метке Err
x = 5 / 0
MsgBox "OK!"
GoTo ne
Err:
MsgBox
"Err!"
ne:
On Error GoTo 0 ' Отключаем обработку ошибок
' Циклы бывает, какие захотите
Do While True
Exit DoLoop 'While True
Do 'Until False
Exit Do
Loop Until False
' А вот при вызове функций, от которых хотим получить значение, скобки нужны.
' Val также умеет возвращать Integer
Select Case LengthSqr(Len("abc"), Val("4"))
Case 24
MsgBox "0"
Case 25
MsgBox "1"
Case 26
MsgBox "2"
End Select' Двухмерный массив.
' Можно также менять размеры командой ReDim (Preserve) - см. google
Dim arr(1 to 10, 5 to 6) As Integer
arr(1, 6) = 8Dim coll As New Collection
Dim coll2 As Collection
coll.Add "item", "key"
Set coll2 = coll ' Все присваивания объектов должны производится командой Set
MsgBox coll2("key")
Set coll2 = New Collection
MsgBox coll2.Count
End Sub
Грабли-1. При копировании кода из IDE (в английском Excel) есь текст конвертируется в 1252 Latin-1. Поэтому, если хотите сохранить русские комментарии — надо сохранить крокозябры как Latin-1, а потом открыть в 1251.
Грабли-2. Т.к. VB позволяет использовать необъявленные переменные, я всегда в начале кода (перед всеми процедурами) ставлю строчку Option Explicit. Эта директива запрещает интерпретатору заводить переменные самостоятельно.
Грабли-3. Глобальные переменные можно объявлять только до первой функции/процедуры. Локальные — в любом месте процедуры/функции.
Еще немного дополнительных функций, которые могут пригодится: InPos, Mid, Trim, LBound, UBound. Также ответы на все вопросы по поводу работы функций/их параметров можно получить в MSDN.
Надеюсь, что этого Вам хватит, чтобы не пугаться кода и самостоятельно написать какое-нибудь домашнее задание по информатике. По ходу поста я буду ненавязчиво знакомить Вас с новыми конструкциями.
Кодим много и под Excel
В этой части мы уже начнём кодить нечто, что умеет работать с нашими листами в Excel. Для начала создадим отдельный лист с именем result (лист с данными назовём data). Теперь, наверное, нужно этот лист очистить от того, что на нём есть. Также мы «выделим» лист с данными, чтобы каждый раз не писать длинное обращение к массиву с листами.
Sub FormatPrice()
Sheets("result").Cells.Clear
Sheets("data").Activate
End Sub
Работа с диапазонами ячеек
Вся работа в Excel VBA производится с диапазонами ячеек. Они создаются функцией Range и возвращают объект типа Range. У него есть всё необходимое для работы с данными и/или оформлением. Кстати сказать, свойство Cells листа — это тоже Range.
Примеры работы с Range
Sheets("result").Activate
Dim r As Range
Set r = Range("A1")
r.Value = "123"
Set r = Range("A3,A5")
r.Font.Color = vbRed
r.Value = "456"
Set r = Range("A6:A7")
r.Value = "=A1+A3"
Теперь давайте поймем алгоритм работы нашего кода. Итак, у каждой строчки листа data, начиная со второй, есть некоторые данные, которые нас не интересуют (ID, название и цена) и есть две вложенные группы, к которым она принадлежит (тип и производитель). Более того, эти строки отсортированы. Пока мы забудем про пропуски перед началом новой группы — так будет проще. Я предлагаю такой алгоритм:
- Считали группы из очередной строки.
- Пробегаемся по всем группам в порядке приоритета (вначале более крупные)
- Если текущая группа не совпадает, вызываем процедуру AddGroup(i, name), где i — номер группы (от номера текущей до максимума), name — её имя. Несколько вызовов необходимы, чтобы создать не только наш заголовок, но и всё более мелкие.
- После отрисовки всех необходимых заголовков делаем еще одну строку и заполняем её данными.
Для упрощения работы рекомендую определить следующие функции-сокращения:
Function GetCol(Col As Integer) As String
GetCol = Chr(Asc("A") + Col)
End FunctionFunction GetCellS(Sheet As String, Col As Integer, Row As Integer) As Range
Set GetCellS = Sheets(Sheet).Range(GetCol(Col) + CStr(Row))
End FunctionFunction GetCell(Col As Integer, Row As Integer) As Range
Set GetCell = Range(GetCol(Col) + CStr(Row))
End Function
Далее определим глобальную переменную «текущая строчка»: Dim CurRow As Integer. В начале процедуры её следует сделать равной единице. Еще нам потребуется переменная-«текущая строка в data», массив с именами групп текущей предыдущей строк. Потом можно написать цикл «пока первая ячейка в строке непуста».
Глобальные переменные
Option Explicit ' про эту строчку я уже рассказывал
Dim CurRow As Integer
Const GroupsCount As Integer = 2
Const DataCount As Integer = 3
FormatPrice
Sub FormatPrice()
Dim I As Integer ' строка в data
CurRow = 1
Dim Groups(1 To GroupsCount) As String
Dim PrGroups(1 To GroupsCount) As String
Sheets(
"data").Activate
I = 2
Do While True
If GetCell(0, I).Value = "" Then Exit Do
' ...
I = I + 1
Loop
End Sub
Теперь надо заполнить массив Groups:
На месте многоточия
Dim I2 As Integer
For I2 = 1 To GroupsCount
Groups(I2) = GetCell(I2, I)
Next I2
' ...
For I2 = 1 To GroupsCount ' VB не умеет копировать массивы
PrGroups(I2) = Groups(I2)
Next I2
I = I + 1
И создать заголовки:
На месте многоточия в предыдущем куске
For I2 = 1 To GroupsCount
If Groups(I2) <> PrGroups(I2) Then
Dim I3 As Integer
For I3 = I2 To GroupsCount
AddHeader I3, Groups(I3)
Next I3
Exit For
End If
Next I2
Не забудем про процедуру AddHeader:
Перед FormatPrice
Sub AddHeader(Ty As Integer, Name As String)
GetCellS("result", 1, CurRow).Value = Name
CurRow = CurRow + 1
End Sub
Теперь надо перенести всякую информацию в result
For I2 = 0 To DataCount - 1
GetCellS("result", I2, CurRow).Value = GetCell(I2, I)
Next I2
Подогнать столбцы по ширине и выбрать лист result для показа результата
После цикла в конце FormatPrice
Sheets("Result").Activate
Columns.AutoFit
Всё. Можно любоваться первой версией.
Некрасиво, но похоже. Давайте разбираться с форматированием. Сначала изменим процедуру AddHeader:
Sub AddHeader(Ty As Integer, Name As String)
Sheets("result").Range("A" + CStr(CurRow) + ":C" + CStr(CurRow)).Merge
' Чтобы не заводить переменную и не писать каждый раз длинный вызов
' можно воспользоваться блоком With
With GetCellS("result", 0, CurRow)
.Value = Name
.Font.Italic = True
.Font.Name = "Cambria"
Select Case Ty
Case 1 ' Тип
.Font.Bold = True
.Font.Size = 16
Case 2 ' Производитель
.Font.Size = 12
End Select
.HorizontalAlignment = xlCenter
End With
CurRow = CurRow + 1
End Sub
Уже лучше:
Осталось только сделать границы. Тут уже нам требуется работать со всеми объединёнными ячейками, иначе бордюр будет только у одной:
Поэтому чуть-чуть меняем код с добавлением стиля границ:
Sub AddHeader(Ty As Integer, Name As String)
With Sheets("result").Range("A" + CStr(CurRow) + ":C" + CStr(CurRow))
.Merge
.Value = Name
.Font.Italic = True
.Font.Name = "Cambria"
.HorizontalAlignment = xlCenterSelect Case Ty
Case 1 ' Тип
.Font.Bold = True
.Font.Size = 16
.Borders(xlTop).Weight = xlThick
Case 2 ' Производитель
.Font.Size = 12
.Borders(xlTop).Weight = xlMedium
End Select
.Borders(xlBottom).Weight = xlMedium ' По убыванию: xlThick, xlMedium, xlThin, xlHairline
End With
CurRow = CurRow + 1
End Sub
Осталось лишь добится пропусков перед началом новой группы. Это легко:
В начале FormatPrice
Dim I As Integer ' строка в data
CurRow = 0 ' чтобы не было пропуска в самом начале
Dim Groups(1 To GroupsCount) As String
В цикле расстановки заголовков
If Groups(I2) <> PrGroups(I2) Then
CurRow = CurRow + 1
Dim I3 As Integer
В точности то, что и хотели.
Надеюсь, что эта статья помогла вам немного освоится с программированием для Excel на VBA. Домашнее задание — добавить заголовки «ID, Название, Цена» в результат. Подсказка: CurRow = 0 CurRow = 1.
Файл можно скачать тут (min.us) или тут (Dropbox). Не забудьте разрешить исполнение макросов. Если кто-нибудь подскажет человеческих файлохостинг, залью туда.
Спасибо за внимание.
Буду рад конструктивной критике в комментариях.
UPD: Перезалил пример на Dropbox и min.us.
UPD2: На самом деле, при вызове процедуры с одним параметром скобки можно поставить. Либо использовать конструкцию Call Foo(«bar», 1, 2, 3) — тут скобки нужны постоянно.
Macro codes can save you a ton of time.
You can automate small as well as heavy tasks with VBA codes.
And do you know?
With the help of macros…
…you can break all the limitations of Excel which you think Excel has.
And today, I have listed some of the useful codes examples to help you become more productive in your day to day work.
You can use these codes even if you haven’t used VBA before that.
But here’s the first thing to know:
What is a Macro Code?
In Excel, macro code is a programming code which is written in VBA (Visual Basic for Applications) language.
The idea behind using a macro code is to automate an action which you perform manually in Excel, otherwise.
For example, you can use a code to print only a particular range of cells just with a single click instead of selecting the range -> File Tab -> Print -> Print Select -> OK Button.
How to use a Macro Code in Excel
Before you use these codes, make sure you have your developer tab on your Excel ribbon to access VB editor. Once you activate developer tab you can use below steps to paste a VBA code into VB editor.
List of Top 100 macro Examples (CODES) for VBA beginners
I have added all the codes into specific categories so that you can find your favorite codes quickly. Just read the title and click on it to get the code.
- This is my Ultimate VBA Library which I update on monthly basis with new codes and Don’t forget to check the VBA Examples Sectionꜜ at the end of this list.
- VBA is one of the Advanced Excel Skills.
- To manage all of these codes make sure to read about Personal Macro Workbook to use these codes in all the workbooks.
- I have tested all of these codes in different versions of Excel (2007, 2010, 2013, 2016, and 2019). If you found any error in any of these codes, make sure to share with me.
Basic Codes
These VBA codes will help you to perform some basic tasks in a flash which you frequently do in your spreadsheets.
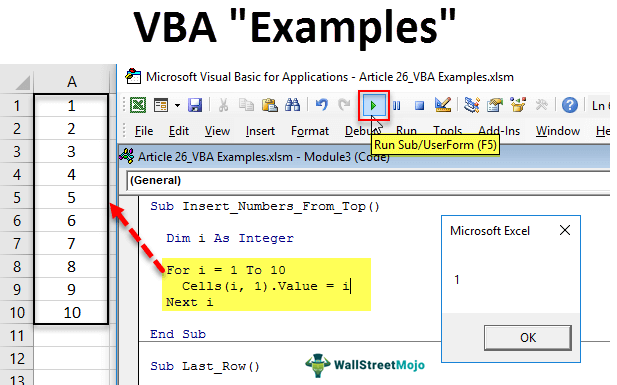
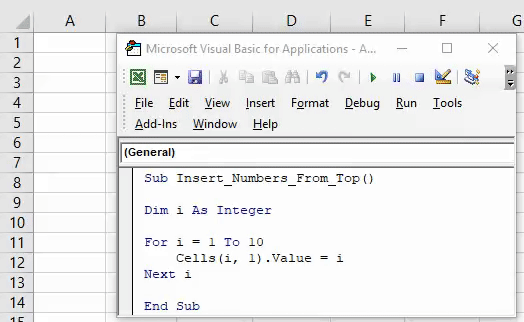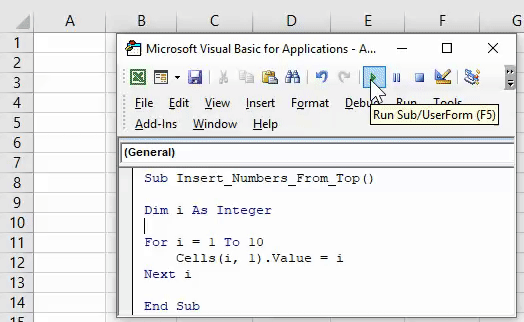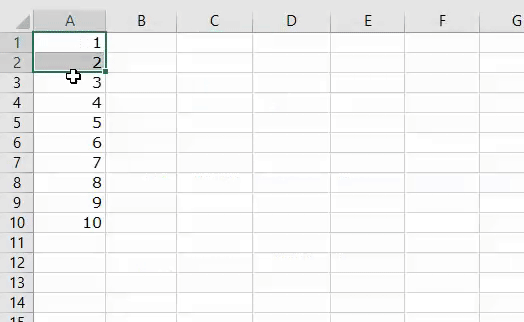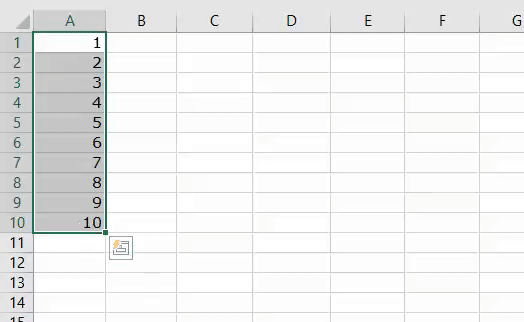
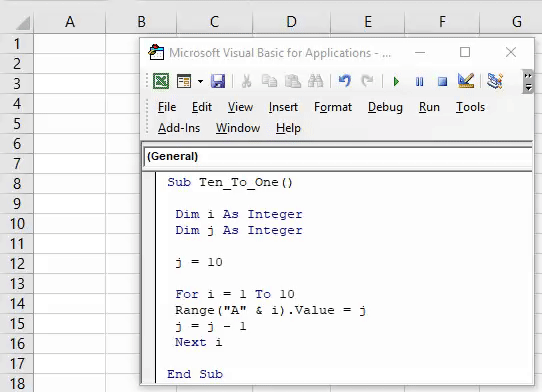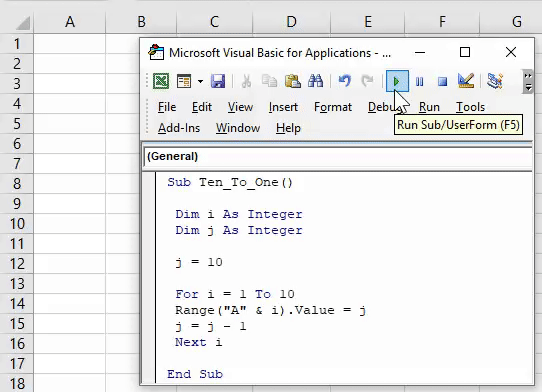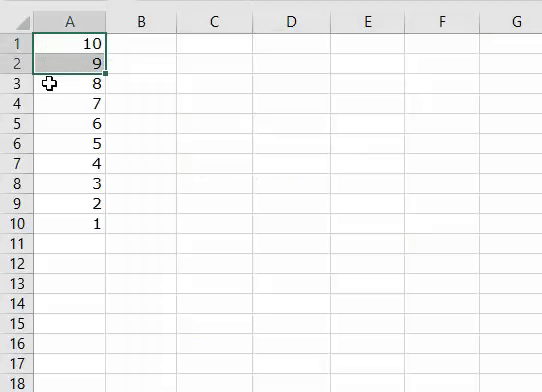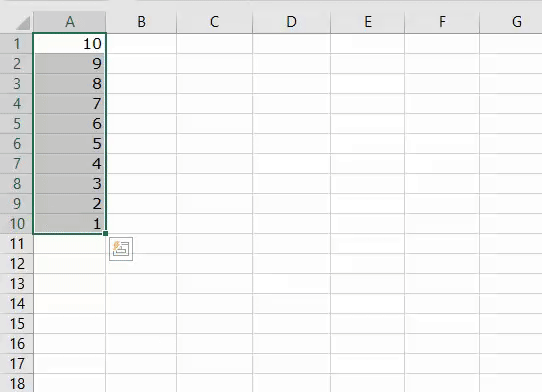
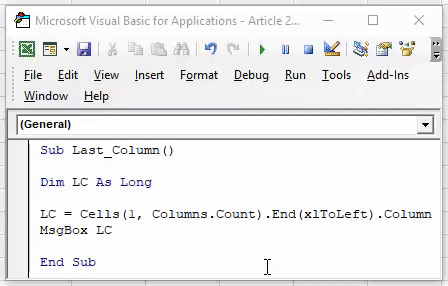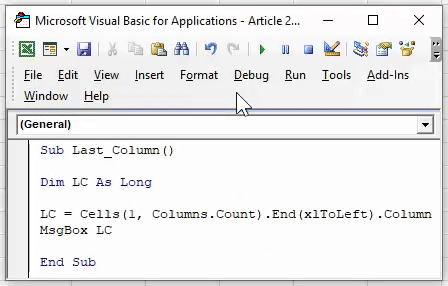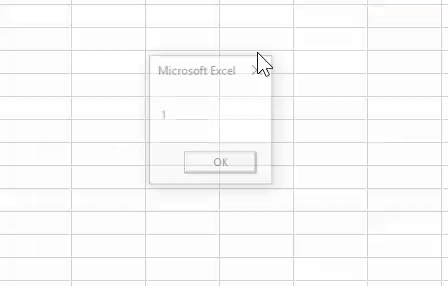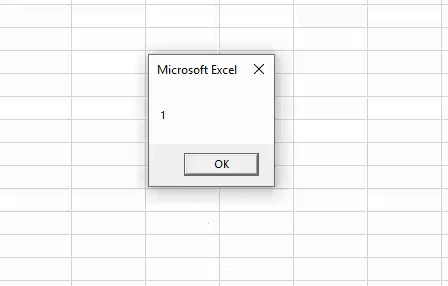
1. Add Serial Numbers
Sub AddSerialNumbers()
Dim i As Integer
On Error GoTo Last
i = InputBox("Enter Value", "Enter Serial Numbers")
For i = 1 To i
ActiveCell.Value = i
ActiveCell.Offset(1, 0).Activate
Next i
Last:Exit Sub
End Sub
This macro code will help you to automatically add serial numbers in your Excel sheet which can be helpful for you if you work with large data.
To use this code you need to select the cell from where you want to start the serial numbers and when you run this it shows you a message box where you need to enter the highest number for the serial numbers and click OK. And once you click OK, it simply runs a loop and add a list of serial numbers to the cells downward.
2. Insert Multiple Columns
Sub InsertMultipleColumns()
Dim i As Integer
Dim j As Integer
ActiveCell.EntireColumn.Select
On Error GoTo Last
i = InputBox("Enter number of columns to insert", "Insert Columns")
For j = 1 To i
Selection.Insert Shift:=xlToRight, CopyOrigin:=xlFormatFromRightorAbove
Next j
Last: Exit Sub
End Sub
This code helps you to enter multiple columns in a single click. When you run this code it asks you the number columns you want to add and when you click OK, it adds entered number of columns after the selected cell. If you want to add columns before the selected cell, replace the xlToRight to xlToLeft in the code.
3. Insert Multiple Rows
Sub InsertMultipleRows()
Dim i As Integer
Dim j As Integer
ActiveCell.EntireRow.Select
On Error GoTo Last
i = InputBox("Enter number of columns to insert", "Insert Columns")
For j = 1 To i
Selection.Insert Shift:=xlToDown, CopyOrigin:=xlFormatFromRightorAbove
Next j
Last: Exit Sub
End Sub
With this code, you can enter multiple rows in the worksheet. When you run this code, you can enter the number of rows to insert and make sure to select the cell from where you want to insert the new rows. If you want to add rows before the selected cell, replace the xlToDown to xlToUp in the code.
4. Auto Fit Columns
Sub AutoFitColumns() Cells.Select Cells.EntireColumn.AutoFit End Sub
This code quickly auto fits all the columns in your worksheet. So when you run this code, it will select all the cells in your worksheet and instantly auto-fit all the columns.
5. Auto Fit Rows
Sub AutoFitRows() Cells.Select Cells.EntireRow.AutoFit End Sub
You can use this code to auto-fit all the rows in a worksheet. When you run this code it will select all the cells in your worksheet and instantly auto-fit all the row.
6. Remove Text Wrap
Sub RemoveTextWrap()
Range("A1").WrapText = False
End Sub
This code will help you to remove text wrap from the entire worksheet with a single click. It will first select all the columns and then remove text wrap and auto fit all the rows and columns. There’s also a shortcut that you can use (Alt + H +W) for but if you add this code to Quick Access Toolbar it’s convenient than a keyboard shortcut.
7. Unmerge Cells
Sub UnmergeCells() Selection.UnMerge End Sub
This code simply uses the unmerge options which you have on the HOME tab. The benefit of using this code is you can add it to the QAT and unmerge all the cell in the selection. And if you want to un-merge a specific range you can define that range in the code by replacing the word selection.
8. Open Calculator
Sub OpenCalculator() Application.ActivateMicrosoftApp Index:=0 End Sub
In Windows, there is a specific calculator and by using this macro code you can open that calculator directly from Excel. As I mentioned that it’s for windows and if you run this code in the MAC version of VBA you’ll get an error.
9. Add Header/Footer Date
Sub DateInHeader() With ActiveSheet.PageSetup .LeftHeader = "" .CenterHeader = "&D" .RightHeader = "" .LeftFooter = "" .CenterFooter = "" .RightFooter = "" End With End Sub
This macro adds a date to the header when you run it. It simply uses the tag «&D» for adding the date. You can also change it to the footer or change the side by replacing the «» with the date tag. And if you want to add a specific date instead of the current date you can replace the «&D» tag with that date from the code.
10. Custom Header/Footer
Sub CustomHeader()
Dim myText As String
myText = InputBox("Enter your text here", "Enter Text")
With ActiveSheet.PageSetup
.LeftHeader = ""
.CenterHeader = myText
.RightHeader = ""
.LeftFooter = ""
.CenterFooter = ""
.RightFooter = ""
End With
End Sub
When you run this code, it shows an input box that asks you to enter the text which you want to add as a header, and once you enter it click OK.
If you see this closely you have six different lines of code to choose the place for the header or footer. Let’s say if you want to add left-footer instead of center header simply replace the “myText” to that line of the code by replacing the «» from there.
Formatting Codes
These VBA codes will help you to format cells and ranges using some specific criteria and conditions.
11. Highlight Duplicates from Selection
Sub HighlightDuplicateValues() Dim myRange As Range Dim myCell As Range Set myRange = Selection For Each myCell In myRange If WorksheetFunction.CountIf(myRange, myCell.Value) > 1 Then myCell.Interior.ColorIndex = 36 End If Next myCell End Sub
This macro will check each cell of your selection and highlight the duplicate values. You can also change the color from the code.
12. Highlight the Active Row and Column
Private Sub Worksheet_BeforeDoubleClick(ByVal Target As Range, Cancel As Boolean) Dim strRange As String strRange = Target.Cells.Address & "," & _ Target.Cells.EntireColumn.Address & "," & _ Target.Cells.EntireRow.Address Range(strRange).Select End Sub
I really love to use this macro code whenever I have to analyze a data table. Here are the quick steps to apply this code.
- Open VBE (ALT + F11).
- Go to Project Explorer (Ctrl + R, If hidden).
- Select your workbook & double click on the name of a particular worksheet in which you want to activate the macro.
- Paste the code into it and select the “BeforeDoubleClick” from event drop down menu.
- Close VBE and you are done.
Remember that, by applying this macro you will not able to edit the cell by double click.
13. Highlight Top 10 Values
Sub TopTen() Selection.FormatConditions.AddTop10 Selection.FormatConditions(Selection.FormatConditions.Count).S tFirstPriority With Selection.FormatConditions(1) .TopBottom = xlTop10Top .Rank = 10 .Percent = False End With With Selection.FormatConditions(1).Font .Color = -16752384 .TintAndShade = 0 End With With Selection.FormatConditions(1).Interior .PatternColorIndex = xlAutomatic .Color = 13561798 .TintAndShade = 0 End With Selection.FormatConditions(1).StopIfTrue = False End Sub
Just select a range and run this macro and it will highlight top 10 values with the green color.
14. Highlight Named Ranges
Sub HighlightRanges() Dim RangeName As Name Dim HighlightRange As Range On Error Resume Next For Each RangeName In ActiveWorkbook.Names Set HighlightRange = RangeName.RefersToRange HighlightRange.Interior.ColorIndex = 36 Next RangeName End Sub
If you are not sure about how many named ranges you have in your worksheet then you can use this code to highlight all of them.
15. Highlight Greater than Values
Sub HighlightGreaterThanValues()
Dim i As Integer
i = InputBox("Enter Greater Than Value", "Enter Value")
Selection.FormatConditions.Delete
Selection.FormatConditions.Add Type:=xlCellValue, _
Operator:=xlGreater, Formula1:=i
Selection.FormatConditions(Selection.FormatConditions.Count).S
tFirstPriority
With Selection.FormatConditions(1)
.Font.Color = RGB(0, 0, 0)
.Interior.Color = RGB(31, 218, 154)
End With
End Sub
Once you run this code it will ask you for the value from which you want to highlight all greater values.
16. Highlight Lower Than Values
Sub HighlightLowerThanValues()
Dim i As Integer
i = InputBox("Enter Lower Than Value", "Enter Value")
Selection.FormatConditions.Delete
Selection.FormatConditions.Add _
Type:=xlCellValue, _
Operator:=xlLower, _
Formula1:=i
Selection.FormatConditions(Selection.FormatConditions.Count).S
tFirstPriority
With Selection.FormatConditions(1)
.Font.Color = RGB(0, 0, 0)
.Interior.Color = RGB(217, 83, 79)
End With
End Sub
Once you run this code it will ask you for the value from which you want to highlight all lower values.
17. Highlight Negative Numbers
Sub highlightNegativeNumbers() Dim Rng As Range For Each Rng In Selection If WorksheetFunction.IsNumber(Rng) Then If Rng.Value < 0 Then Rng.Font.Color= -16776961 End If End If Next End Sub
Select a range of cells and run this code. It will check each cell from the range and highlight all cells the where you have a negative number.
18. Highlight Specific Text
Sub highlightValue()
Dim myStr As String
Dim myRg As range
Dim myTxt As String
Dim myCell As range
Dim myChar As String
Dim I As Long
Dim J As Long
On Error Resume Next
If ActiveWindow.RangeSelection.Count > 1 Then
myTxt = ActiveWindow.RangeSelection.AddressLocal
Else
myTxt = ActiveSheet.UsedRange.AddressLocal
End If
LInput: Set myRg = _
Application.InputBox _
("please select the data range:", "Selection Required", myTxt, , , , , 8)
If myRg Is Nothing Then
Exit Sub
If myRg.Areas.Count > 1 Then
MsgBox "not support multiple columns"
GoTo LInput
End If
If myRg.Columns.Count <> 2 Then
MsgBox "the selected range can only contain two columns "
GoTo LInput
End If
For I = 0 To myRg.Rows.Count - 1
myStr = myRg.range("B1").Offset(I, 0).Value
With myRg.range("A1").Offset(I, 0)
.Font.ColorIndex = 1
For J = 1 To Len(.Text)
Mid(.Text, J, Len(myStr)) = myStrThen
.Characters(J, Len(myStr)).Font.ColorIndex = 3
Next
End With
Next I
End Sub
Suppose you have a large data set and you want to check for a particular value. For this, you can use this code. When you run it, you will get an input box to enter the value to search for.
19. Highlight Cells with Comments
Sub highlightCommentCells() Selection.SpecialCells(xlCellTypeComments).Select Selection.Style= "Note" End Sub
To highlight all the cells with comments use this macro.
20. Highlight Alternate Rows in the Selection
Sub highlightAlternateRows() Dim rng As Range For Each rng In Selection.Rows If rng.Row Mod 2 = 1 Then rng.Style = "20% -Accent1" rng.Value = rng ^ (1 / 3) Else End If Next rng End Sub
By highlighting alternate rows you can make your data easily readable, and for this, you can use below VBA code. It will simply highlight every alternate row in selected range.
21. Highlight Cells with Misspelled Words
Sub HighlightMisspelledCells() Dim rng As Range For Each rng In ActiveSheet.UsedRange If Not Application.CheckSpelling(word:=rng.Text) Then rng.Style = "Bad" End If Next rng End Sub
If you find hard to check all the cells for spelling error then this code is for you. It will check each cell from the selection and highlight the cell where is a misspelled word.
22. Highlight Cells With Error in the Entire Worksheet
Sub highlightErrors() Dim rng As Range Dim i As Integer For Each rng In ActiveSheet.UsedRange If WorksheetFunction.IsError(rng) Then i = i + 1 rng.Style = "bad" End If Next rng MsgBox _ "There are total " & i _ & " error(s) in this worksheet." End Sub
To highlight and count all the cells in which you have an error, this code will help you. Just run this code and it will return a message with the number error cells and highlight all the cells.
23. Highlight Cells with a Specific Text in Worksheet
Sub highlightSpecificValues()
Dim rng As range
Dim i As Integer
Dim c As Variant
c = InputBox("Enter Value To Highlight")
For Each rng In ActiveSheet.UsedRange
If rng = c Then
rng.Style = "Note"
i = i + 1
End If
Next rng
MsgBox "There are total " & i & " " & c & " in this worksheet."
End Sub
This code will help you to count the cells which have a specific value which you will mention and after that highlight all those cells.
24. Highlight all the Blank Cells Invisible Space
Sub blankWithSpace() Dim rng As Range For Each rng In ActiveSheet.UsedRange If rng.Value = " " Then rng.Style = "Note" End If Next rng End Sub
Sometimes there are some cells which are blank but they have a single space and due to this, it’s really hard to identify them. This code will check all the cell in the worksheet and highlight all the cells which have a single space.
25. Highlight Max Value In The Range
Sub highlightMaxValue() Dim rng As Range For Each rng In Selection If rng = WorksheetFunction.Max(Selection) Then rng.Style = "Good" End If Next rng End Sub
It will check all the selected cells and highlight the cell with the maximum value.
26. Highlight Min Value In The Range
Sub Highlight_Min_Value() Dim rng As Range For Each rng In Selection If rng = WorksheetFunction.Min(Selection) Then rng.Style = "Good" End If Next rng End Sub
It will check all the selected cells and highlight the cell with the Minimum value.
27. Highlight Unique Values
Sub highlightUniqueValues() Dim rng As Range Set rng = Selection rng.FormatConditions.Delete Dim uv As UniqueValues Set uv = rng.FormatConditions.AddUniqueValues uv.DupeUnique = xlUnique uv.Interior.Color = vbGreen End Sub
This codes will highlight all the cells from the selection which has a unique value.
28. Highlight Difference in Columns
Sub columnDifference()
Range("H7:H8,I7:I8").Select
Selection.ColumnDifferences(ActiveCell).Select
Selection.Style= "Bad"
End Sub
Using this code you can highlight the difference between two columns (corresponding cells).
29. Highlight Difference in Rows
Sub rowDifference()
Range("H7:H8,I7:I8").Select
Selection.RowDifferences(ActiveCell).Select
Selection.Style= "Bad"
End Sub
And by using this code you can highlight difference between two row (corresponding cells).
Printing Codes
These macro codes will help you to automate some printing tasks which can further save you a ton of time.
30. Print Comments
Sub printComments() With ActiveSheet.PageSetup .printComments = xlPrintSheetEnd End With End Sub
Use this macro to activate settings to print cell comments in the end of the page. Let’s say you have 10 pages to print, after using this code you will get all the comments on 11th last page.
31. Print Narrow Margin
Sub printNarrowMargin() With ActiveSheet.PageSetup .LeftMargin = Application .InchesToPoints (0.25) .RightMargin = Application.InchesToPoints(0.25) .TopMargin = Application.InchesToPoints(0.75) .BottomMargin = Application.InchesToPoints(0.75) .HeaderMargin = Application.InchesToPoints(0.3) .FooterMargin = Application.InchesToPoints(0.3) End With ActiveWindow.SelectedSheets.PrintOut _ Copies:=1, _ Collate:=True, _ IgnorePrintAreas:=False End Sub
Use this VBA code to take a print with a narrow margin. When you run this macro it will automatically change margins to narrow.
32. Print Selection
Sub printSelection() Selection.PrintOut Copies:=1, Collate:=True End Sub
This code will help you print selected range. You don’t need to go to printing options and set printing range. Just select a range and run this code.
33. Print Custom Pages
Sub printCustomSelection()
Dim startpage As Integer
Dim endpage As Integer
startpage = _
InputBox("Please Enter Start Page number.", "Enter Value")
If Not WorksheetFunction.IsNumber(startpage) Then
MsgBox _
"Invalid Start Page number. Please try again.", "Error"
Exit Sub
End If
endpage = _
InputBox("Please Enter End Page number.", "Enter Value")
If Not WorksheetFunction.IsNumber(endpage) Then
MsgBox _
"Invalid End Page number. Please try again.", "Error"
Exit Sub
End If
Selection.PrintOut From:=startpage, _
To:=endpage, Copies:=1, Collate:=True
End Sub
Instead of using the setting from print options you can use this code to print custom page range. Let’s say you want to print pages from 5 to 10. You just need to run this VBA code and enter start page and end page.
Worksheet Codes
These macro codes will help you to control and manage worksheets in an easy way and save your a lot of time.
34. Hide all but the Active Worksheet
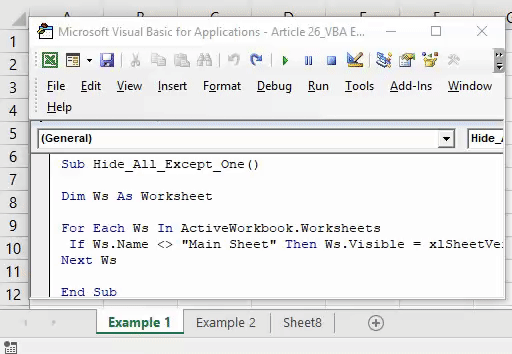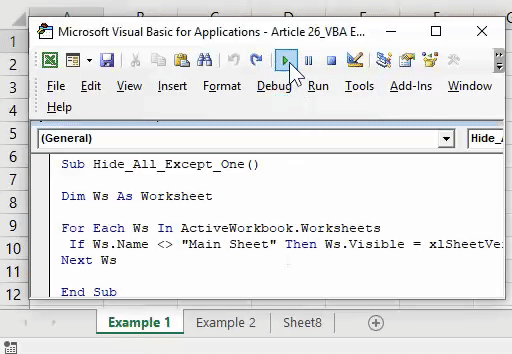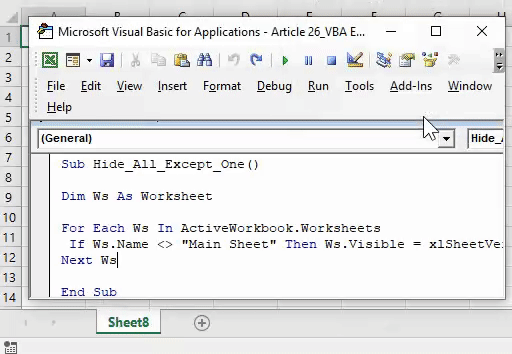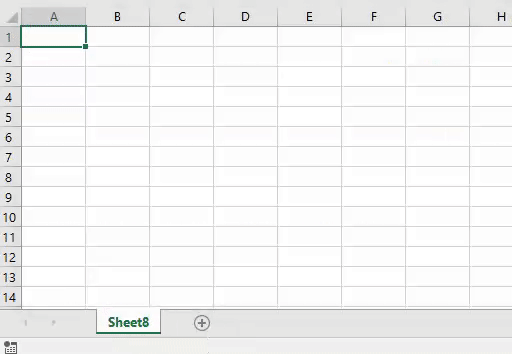
Sub HideWorksheet() Dim ws As Worksheet For Each ws In ThisWorkbook.Worksheets If ws.Name <> ThisWorkbook.ActiveSheet.Name Then ws.Visible = xlSheetHidden End If Next ws End Sub
Now, let’s say if you want to hide all the worksheets in your workbook other than the active worksheet. This macro code will do this for you.
35. Unhide all Hidden Worksheets
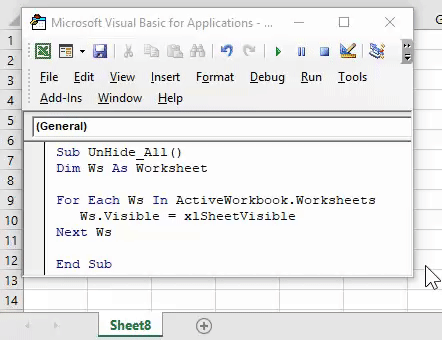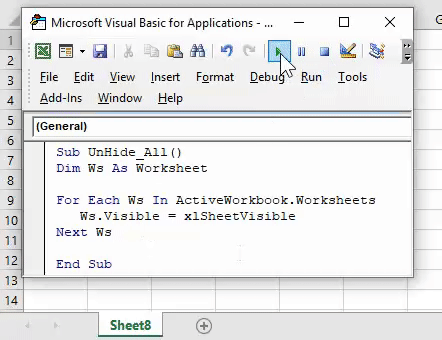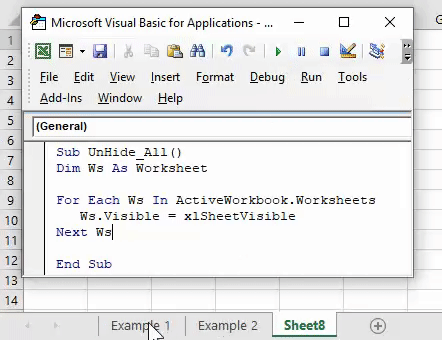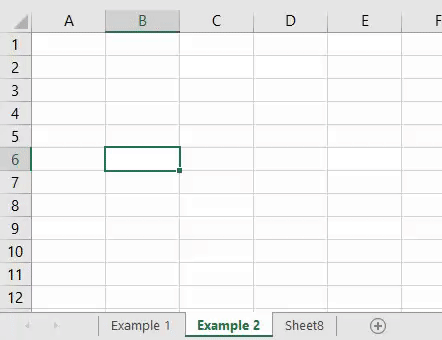
Sub UnhideAllWorksheet() Dim ws As Worksheet For Each ws In ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets ws.Visible = xlSheetVisible Next ws End Sub
And if you want to un-hide all the worksheets which you have hide with previous code, here is the code for that.
36. Delete all but the Active Worksheet
Sub DeleteWorksheets() Dim ws As Worksheet For Each ws In ThisWorkbook.Worksheets If ws.name <> ThisWorkbook.ActiveSheet.name Then Application.DisplayAlerts = False ws.Delete Application.DisplayAlerts = True End If Next ws End Sub
If you want to delete all the worksheets other than the active sheet, this macro is useful for you. When you run this macro it will compare the name of the active worksheet with other worksheets and then delete them.
37. Protect all Worksheets Instantly
Sub ProtectAllWorskeets()
Dim ws As Worksheet
Dim ps As String
ps = InputBox("Enter a Password.", vbOKCancel)
For Each ws In ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets
ws.Protect Password:=ps
Next ws
End Sub
If you want to protect your all worksheets in one go here is a code for you. When you run this macro, you will get an input box to enter a password. Once you enter your password, click OK. And make sure to take care about CAPS.
38. Resize All Charts in a Worksheet
Sub Resize_Charts() Dim i As Integer For i = 1 To ActiveSheet.ChartObjects.Count With ActiveSheet.ChartObjects(i) .Width = 300 .Height = 200 End With Next i End Sub
Make all chart same in size. This macro code will help you to make all the charts of the same size. You can change the height and width of charts by changing it in macro code.
39. Insert Multiple Worksheets
Sub InsertMultipleSheets()
Dim i As Integer
i = _
InputBox("Enter number of sheets to insert.", _
"Enter Multiple Sheets")
Sheets.Add After:=ActiveSheet, Count:=i
End Sub
You can use this code if you want to add multiple worksheets in your workbook in a single shot. When you run this macro code you will get an input box to enter the total number of sheets you want to enter.
40. Protect Worksheet
Sub ProtectWS() ActiveSheet.Protect "mypassword", True, True End Sub
If you want to protect your worksheet you can use this macro code. All you have to do just mention your password in the code.
41. Un-Protect Worksheet
Sub UnprotectWS() ActiveSheet.Unprotect "mypassword" End Sub
If you want to unprotect your worksheet you can use this macro code. All you have to do just mention your password which you have used while protecting your worksheet.
42. Sort Worksheets
Sub SortWorksheets()
Dim i As Integer
Dim j As Integer
Dim iAnswer As VbMsgBoxResult
iAnswer = MsgBox("Sort Sheets in Ascending Order?" & Chr(10) _
& "Clicking No will sort in Descending Order", _
vbYesNoCancel + vbQuestion + vbDefaultButton1, "Sort Worksheets")
For i = 1 To Sheets.Count
For j = 1 To Sheets.Count - 1
If iAnswer = vbYes Then
If UCase$(Sheets(j).Name) > UCase$(Sheets(j + 1).Name) Then
Sheets(j).Move After:=Sheets(j + 1)
End If
ElseIf iAnswer = vbNo Then
If UCase$(Sheets(j).Name) < UCase$(Sheets(j + 1).Name) Then Sheets(j).Move After:=Sheets(j + 1)
End If
End If
Next j
Next i
End Sub
This code will help you to sort worksheets in your workbook according to their name.
43. Protect all the Cells With Formulas
Sub lockCellsWithFormulas() With ActiveSheet .Unprotect .Cells.Locked = False .Cells.SpecialCells(xlCellTypeFormulas).Locked = True .Protect AllowDeletingRows:=True End With End Sub
To protect cell with formula with a single click you can use this code.
44. Delete all Blank Worksheets
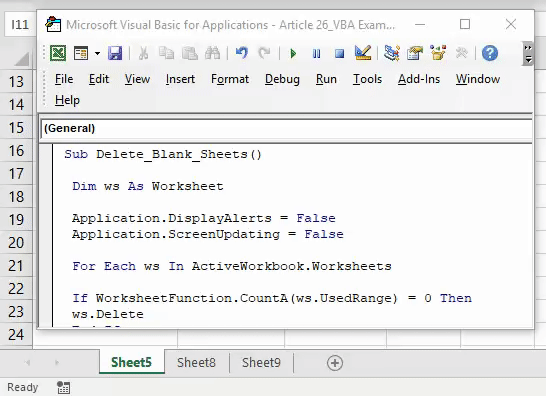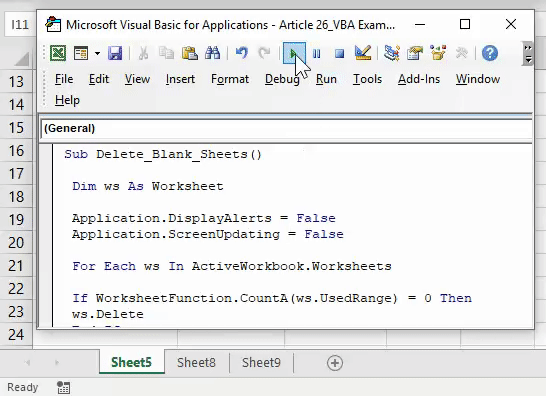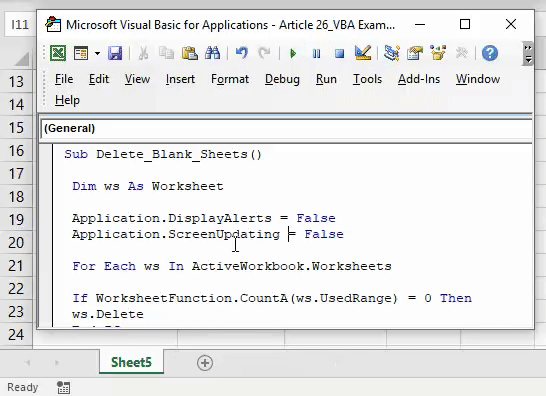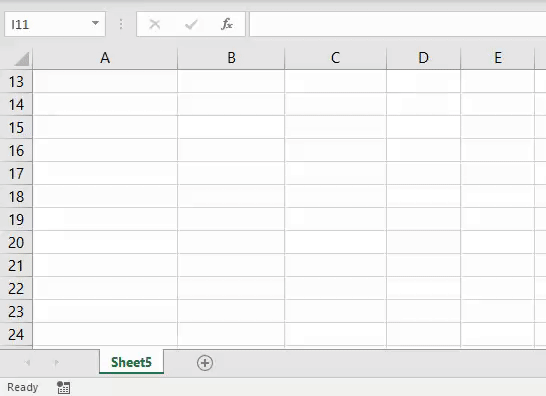
Sub deleteBlankWorksheets() Dim Ws As Worksheet On Error Resume Next Application.ScreenUpdating= False Application.DisplayAlerts= False For Each Ws In Application.Worksheets If Application.WorksheetFunction.CountA(Ws.UsedRange) = 0 Then Ws.Delete End If Next Application.ScreenUpdating= True Application.DisplayAlerts= True End Sub
Run this code and it will check all the worksheets in the active workbook and delete if a worksheet is blank.
45. Unhide all Rows and Columns
Sub UnhideRowsColumns() Columns.EntireColumn.Hidden = False Rows.EntireRow.Hidden = False End Sub
Instead of unhiding rows and columns on by one manually you can use this code to do this in a single go.
46. Save Each Worksheet as a Single PDF
Sub SaveWorkshetAsPDF() Dimws As Worksheet For Each ws In Worksheets ws.ExportAsFixedFormat _ xlTypePDF, _ "ENTER-FOLDER-NAME-HERE" & _ ws.Name & ".pdf" Next ws End Sub
This code will simply save all the worksheets in a separate PDF file. You just need to change the folder name from the code.
47. Disable Page Breaks
Sub DisablePageBreaks() Dim wb As Workbook Dim wks As Worksheet Application.ScreenUpdating = False For Each wb In Application.Workbooks For Each Sht In wb.Worksheets Sht.DisplayPageBreaks = False Next Sht Next wb Application.ScreenUpdating = True End Sub
To disable page breaks use this code. It will simply disable page breaks from all the open workbooks.
Workbook Codes
These codes will help you to perform workbook level tasks in an easy way and with minimum efforts.
48. Create a Backup of a Current Workbook
Sub FileBackUp() ThisWorkbook.SaveCopyAs Filename:=ThisWorkbook.Path & _ "" & Format(Date, "mm-dd-yy") & " " & _ ThisWorkbook.name End Sub
This is one of the most useful macros which can help you to save a backup file of your current workbook.
It will save a backup file in the same directory where your current file is saved and it will also add the current date with the name of the file.
49. Close all Workbooks at Once
Sub CloseAllWorkbooks() Dim wbs As Workbook For Each wbs In Workbooks wbs.Close SaveChanges:=True Next wb End Sub
Use this macro code to close all open workbooks. This macro code will first check all the workbooks one by one and close them. If any of the worksheets is not saved, you’ll get a message to save it.
50. Copy Active Worksheet into a New Workbook
Sub CopyWorksheetToNewWorkbook() ThisWorkbook.ActiveSheet.Copy _ Before:=Workbooks.Add.Worksheets(1) End Sub
Let’s say if you want to copy your active worksheet in a new workbook, just run this macro code and it will do the same for you. It’s a super time saver.
51. Active Workbook in an Email
Sub Send_Mail()
Dim OutApp As Object
Dim OutMail As Object
Set OutApp = CreateObject("Outlook.Application")
Set OutMail = OutApp.CreateItem(0)
With OutMail
.to = "Sales@FrontLinePaper.com"
.Subject = "Growth Report"
.Body = "Hello Team, Please find attached Growth Report."
.Attachments.Add ActiveWorkbook.FullName
.display
End With
Set OutMail = Nothing
Set OutApp = Nothing
End Sub
Use this macro code to quickly send your active workbook in an e-mail. You can change the subject, email, and body text in code and if you want to send this mail directly, use «.Send» instead of «.Display».
52. Add Workbook to a Mail Attachment
Sub OpenWorkbookAsAttachment() Application.Dialogs(xlDialogSendMail).Show End Sub
Once you run this macro it will open your default mail client and attached active workbook with it as an attachment.
53. Welcome Message
Sub auto_open() MsgBox _ "Welcome To ExcelChamps & Thanks for downloading this file." End Sub
You can use auto_open to perform a task on opening a file and all you have to do just name your macro «auto_open».
54. Closing Message
Sub auto_close() MsgBox "Bye Bye! Don't forget to check other cool stuff on excelchamps.com" End Sub
You can use close_open to perform a task on opening a file and all you have to do just name your macro «close_open».
55. Count Open Unsaved Workbooks
Sub VisibleWorkbooks() Dim book As Workbook Dim i As Integer For Each book In Workbooks If book.Saved = False Then i = i + 1 End If Next book MsgBox i End Sub
Let’s you have 5-10 open workbooks, you can use this code to get the number of workbooks which are not saved yet.
Pivot Table Codes
These codes will help you to manage and make some changes in pivot tables in a flash.
56. Hide Pivot Table Subtotals
Sub HideSubtotals() Dim pt As PivotTable Dim pf As PivotField On Error Resume Next Set pt = ActiveSheet.PivotTables(ActiveCell.PivotTable.Name) If pt Is Nothing Then MsgBox "You must place your cursor inside of a PivotTable." Exit Sub End If For Each pf In pt.PivotFields pf.Subtotals(1) = True pf.Subtotals(1) = False Next pf End Sub
If you want to hide all the subtotals, just run this code. First of all, make sure to select a cell from your pivot table and then run this macro.
57. Refresh All Pivot Tables
Sub vba_referesh_all_pivots() Dim pt As PivotTable For Each pt In ActiveWorkbook.PivotTables pt.RefreshTable Next pt End Sub
A super quick method to refresh all pivot tables. Just run this code and all of your pivot tables in your workbook will be refresh in a single shot.
58. Create a Pivot Table
Follow this step by step guide to create a pivot table using VBA.
59. Auto Update Pivot Table Range
Sub UpdatePivotTableRange()
Dim Data_Sheet As Worksheet
Dim Pivot_Sheet As Worksheet
Dim StartPoint As Range
Dim DataRange As Range
Dim PivotName As String
Dim NewRange As String
Dim LastCol As Long
Dim lastRow As Long
'Set Pivot Table & Source Worksheet
Set Data_Sheet = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("PivotTableData3")
Set Pivot_Sheet = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Pivot3")
'Enter in Pivot Table Name
PivotName = "PivotTable2"
'Defining Staring Point & Dynamic Range
Data_Sheet.Activate
Set StartPoint = Data_Sheet.Range("A1")
LastCol = StartPoint.End(xlToRight).Column
DownCell = StartPoint.End(xlDown).Row
Set DataRange = Data_Sheet.Range(StartPoint, Cells(DownCell, LastCol))
NewRange = Data_Sheet.Name & "!" & DataRange.Address(ReferenceStyle:=xlR1C1)
'Change Pivot Table Data Source Range Address
Pivot_Sheet.PivotTables(PivotName). _
ChangePivotCache ActiveWorkbook. _
PivotCaches.Create(SourceType:=xlDatabase, SourceData:=NewRange)
'Ensure Pivot Table is Refreshed
Pivot_Sheet.PivotTables(PivotName).RefreshTable
'Complete Message
Pivot_Sheet.Activate
MsgBox "Your Pivot Table is now updated."
End Sub
If you are not using Excel tables then you can use this code to update pivot table range.
60. Disable/Enable Get Pivot Data
Sub activateGetPivotData() Application.GenerateGetPivotData = True End Sub Sub deactivateGetPivotData() Application.GenerateGetPivotData = False End Sub
To disable/enable GetPivotData function you need to use Excel option. But with this code you can do it in a single click.
Charts Codes
Use these VBA codes to manage charts in Excel and save your lot of time.
61. Change Chart Type
Sub ChangeChartType() ActiveChart.ChartType = xlColumnClustered End Sub
This code will help you to convert chart type without using chart options from the tab. All you have to do just specify to which type you want to convert.
Below code will convert selected chart to a clustered column chart. There are different codes for different types, you can find all those types from here.
62. Paste Chart as an Image
Sub ConvertChartToPicture()
ActiveChart.ChartArea.Copy
ActiveSheet.Range("A1").Select
ActiveSheet.Pictures.Paste.Select
End Sub
This code will help you to convert your chart into an image. You just need to select your chart and run this code.
63. Add Chart Title
Sub AddChartTitle()
Dim i As Variant
i = InputBox("Please enter your chart title", "Chart Title")
On Error GoTo Last
ActiveChart.SetElement (msoElementChartTitleAboveChart)
ActiveChart.ChartTitle.Text = i
Last:
Exit Sub
End Sub
First of all, you need to select your chart and the run this code. You will get an input box to enter chart title.
Advanced Codes
Some of the codes which you can use to preform advanced task in your spreadsheets.
64. Save Selected Range as a PDF
Sub HideSubtotals() Dim pt As PivotTable Dim pf As PivotField On Error Resume Next Set pt = ActiveSheet.PivotTables(ActiveCell.PivotTable.name) If pt Is Nothing Then MsgBox "You must place your cursor inside of a PivotTable." Exit Sub End If For Each pf In pt.PivotFields pf.Subtotals(1) = True pf.Subtotals(1) = False Next pf End Sub
If you want to hide all the subtotals, just run this code. First of all, make sure to select a cell from your pivot table and then run this macro.
65. Create a Table of Content
Sub TableofContent()
Dim i As Long
On Error Resume Next
Application.DisplayAlerts = False
Worksheets("Table of Content").Delete
Application.DisplayAlerts = True
On Error GoTo 0
ThisWorkbook.Sheets.Add Before:=ThisWorkbook.Worksheets(1)
ActiveSheet.Name = "Table of Content"
For i = 1 To Sheets.Count
With ActiveSheet
.Hyperlinks.Add _
Anchor:=ActiveSheet.Cells(i, 1), _
Address:="", _
SubAddress:="'" & Sheets(i).Name & "'!A1", _
ScreenTip:=Sheets(i).Name, _
TextToDisplay:=Sheets(i).Name
End With
Next i
End Sub
Let’s say you have more than 100 worksheets in your workbook and it’s hard to navigate now.
Don’t worry this macro code will rescue everything. When you run this code it will create a new worksheet and create a index of worksheets with a hyperlink to them.
66. Convert Range into an Image
Sub PasteAsPicture() Application.CutCopyMode = False Selection.Copy ActiveSheet.Pictures.Paste.Select End Sub
Paste selected range as an image. You just have to select the range and once you run this code it will automatically insert a picture for that range.
67. Insert a Linked Picture
Sub LinkedPicture() Selection.Copy ActiveSheet.Pictures.Paste(Link:=True).Select End Sub
This VBA code will convert your selected range into a linked picture and you can use that image anywhere you want.
68. Use Text to Speech
Sub Speak() Selection.Speak End Sub
Just select a range and run this code. Excel will speak all the text what you have in that range, cell by cell.
69. Activate Data Entry Form
Sub DataForm() ActiveSheet.ShowDataForm End Sub
There is a default data entry form which you can use for data entry.
70. Use Goal Seek
Sub GoalSeekVBA()
Dim Target As Long
On Error GoTo Errorhandler
Target = InputBox("Enter the required value", "Enter Value")
Worksheets("Goal_Seek").Activate
With ActiveSheet.Range("C7")
.GoalSeek_ Goal:=Target, _
ChangingCell:=Range("C2")
End With
Exit Sub
Errorhandler: MsgBox ("Sorry, value is not valid.")
End Sub
Goal Seek can be super helpful for you to solve complex problems. Learn more about goal seek from here before you use this code.
71. VBA Code to Search on Google
Sub SearchWindow32()
Dim chromePath As String
Dim search_string As String
Dim query As String
query = InputBox("Enter here your search here", "Google Search")
search_string = query
search_string = Replace(search_string, " ", "+")
'Uncomment the following line for Windows 64 versions and comment out Windows 32 versions'
'chromePath = "C:Program FilesGoogleChromeApplicationchrome.exe"
'Uncomment the following line for Windows 32 versions and comment out Windows 64 versions
'chromePath = "C:Program Files (x86)GoogleChromeApplicationchrome.exe"
Shell (chromePath & " -url http://google.com/#q=" & search_string)
End Sub
Formula Codes
These codes will help you to calculate or get results which often you do with worksheet functions and formulas.
72. Convert all Formulas into Values
Sub convertToValues()
Dim MyRange As Range
Dim MyCell As Range
Select Case _
MsgBox("You Can't Undo This Action. " _
& "Save Workbook First?", vbYesNoCancel, _
"Alert")
Case Is = vbYes
ThisWorkbook.Save
Case Is = vbCancel
Exit Sub
End Select
Set MyRange = Selection
For Each MyCell In MyRange
If MyCell.HasFormula Then
MyCell.Formula = MyCell.Value
End If
Next MyCell
End Sub
Simply convert formulas into values. When you run this macro it will quickly change the formulas into absolute values.
73. Remove Spaces from Selected Cells
Sub RemoveSpaces()
Dim myRange As Range
Dim myCell As Range
Select Case MsgBox("You Can't Undo This Action. " _
& "Save Workbook First?", _
vbYesNoCancel, "Alert")
Case Is = vbYesThisWorkbook.Save
Case Is = vbCancel
Exit Sub
End Select
Set myRange = Selection
For Each myCell In myRange
If Not IsEmpty(myCell) Then
myCell = Trim(myCell)
End If
Next myCell
End Sub
One of the most useful macros from this list. It will check your selection and then remove all the extra spaces from that.
74. Remove Characters from a String
Public Function removeFirstC(rng As String, cnt As Long) removeFirstC = Right(rng, Len(rng) - cnt) End Function
Simply remove characters from the starting of a text string. All you need is to refer to a cell or insert a text into the function and number of characters to remove from the text string.
It has two arguments «rng» for the text string and «cnt» for the count of characters to remove. For Example: If you want to remove first characters from a cell, you need to enter 1 in cnt.
75. Add Insert Degree Symbol in Excel
Sub degreeSymbol( ) Dim rng As Range For Each rng In Selection rng.Select If ActiveCell <> "" Then If IsNumeric(ActiveCell.Value) Then ActiveCell.Value = ActiveCell.Value & "°" End If End If Next End Sub
Let’s say you have a list of numbers in a column and you want to add degree symbol with all of them.
76. Reverse Text
Public Function rvrse(ByVal cell As Range) As String rvrse = VBA.strReverse(cell.Value) End Function
All you have to do just enter «rvrse» function in a cell and refer to the cell in which you have text which you want to reverse.
77. Activate R1C1 Reference Style
Sub ActivateR1C1() If Application.ReferenceStyle = xlA1 Then Application.ReferenceStyle = xlR1C1 Else Application.ReferenceStyle = xlR1C1 End If End Sub
This macro code will help you to activate R1C1 reference style without using Excel options.
78. Activate A1 Reference Style
Sub ActivateA1() If Application.ReferenceStyle = xlR1C1 Then Application.ReferenceStyle = xlA1 Else Application.ReferenceStyle = xlA1 End If End Sub
This macro code will help you to activate A1 reference style without using Excel options.
79. Insert Time Range
Sub TimeStamp() Dim i As Integer For i = 1 To 24 ActiveCell.FormulaR1C1 = i & ":00" ActiveCell.NumberFormat = "[$-409]h:mm AM/PM;@" ActiveCell.Offset(RowOffset:=1, ColumnOffset:=0).Select Next i End Sub
With this code, you can insert a time range in sequence from 00:00 to 23:00.
80. Convert Date into Day
Sub date2day() Dim tempCell As Range Selection.Value = Selection.Value For Each tempCell In Selection If IsDate(tempCell) = True Then With tempCell .Value = Day(tempCell) .NumberFormat = "0" End With End If Next tempCell End Sub
If you have dates in your worksheet and you want to convert all those dates into days then this code is for you. Simply select the range of cells and run this macro.
81. Convert Date into Year
Sub date2year() Dim tempCell As Range Selection.Value = Selection.Value For Each tempCell In Selection If IsDate(tempCell) = True Then With tempCell .Value = Year(tempCell) .NumberFormat = "0" End With End If Next tempCell End Sub
This code will convert dates into years.
82. Remove Time from Date
Sub removeTime() Dim Rng As Range For Each Rng In Selection If IsDate(Rng) = True Then Rng.Value = VBA.Int(Rng.Value) End If Next Selection.NumberFormat = "dd-mmm-yy" End Sub
If you have time with the date and you want to remove it then you can use this code.
83. Remove Date from Date and Time
Sub removeDate() Dim Rng As Range For Each Rng In Selection If IsDate(Rng) = True Then Rng.Value = Rng.Value - VBA.Fix(Rng.Value) End If NextSelection.NumberFormat = "hh:mm:ss am/pm" End Sub
It will return only time from a date and time value.
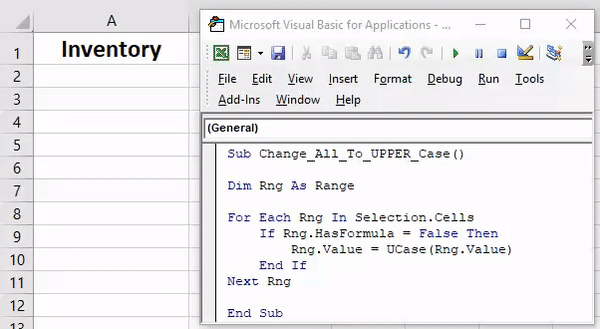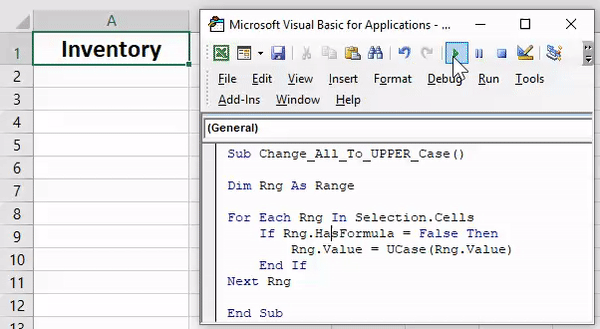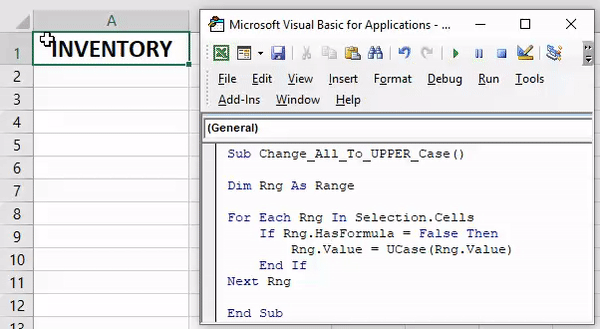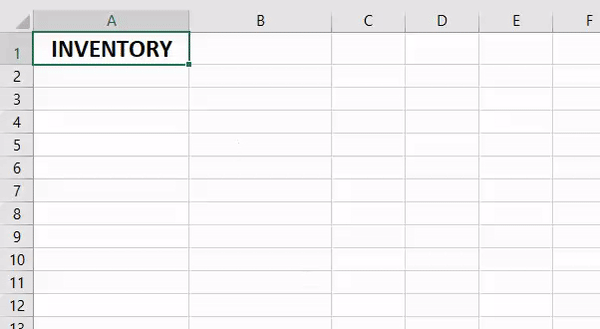
84. Convert to Upper Case
Sub convertUpperCase() Dim Rng As Range For Each Rng In Selection If Application.WorksheetFunction.IsText(Rng) Then Rng.Value = UCase(Rng) End If Next End Sub
Select the cells and run this code. It will check each and every cell of selected range and then convert it into upper case text.
85. Convert to Lower Case
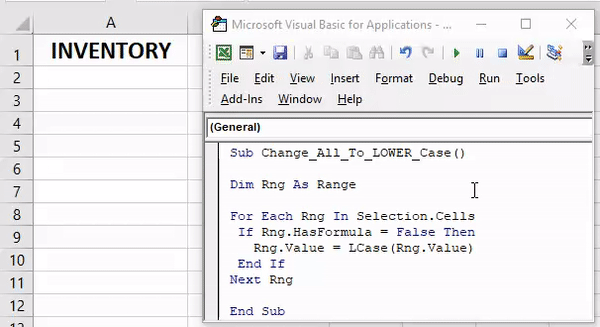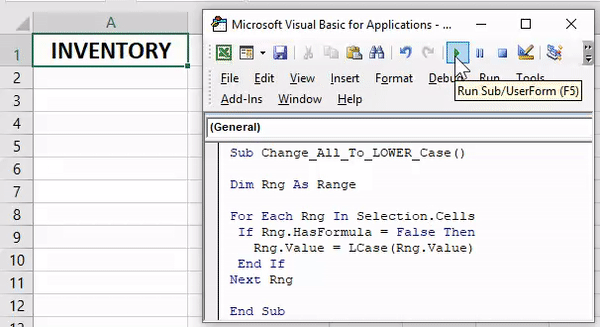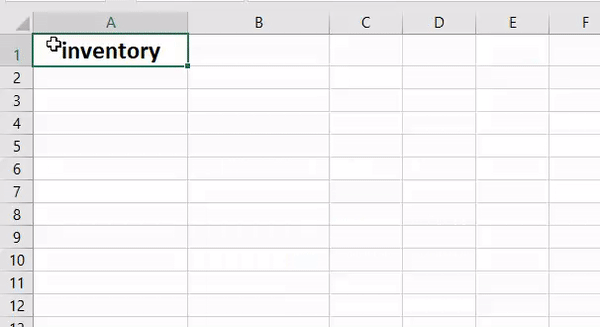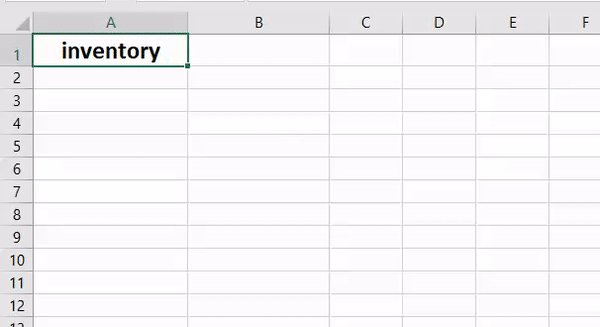
Sub convertLowerCase() Dim Rng As Range For Each Rng In Selection If Application.WorksheetFunction.IsText(Rng) Then Rng.Value= LCase(Rng) End If Next End Sub
This code will help you to convert selected text into lower case text. Just select a range of cells where you have text and run this code. If a cell has a number or any value other than text that value will remain same.
86. Convert to Proper Case
Sub convertProperCase() Dim Rng As Range For Each Rng In Selection If WorksheetFunction.IsText(Rng) Then Rng.Value = WorksheetFunction.Proper(Rng.Value) End If Next End Sub
And this code will convert selected text into the proper case where you have the first letter in capital and rest in small.
87. Convert to Sentence Case
Sub convertTextCase() Dim Rng As Range For Each Rng In Selection If WorksheetFunction.IsText(Rng) Then Rng.Value = UCase(Left(Rng, 1)) & LCase(Right(Rng, Len(Rng) - 1)) End If Next Rng End Sub
In text case, you have the first letter of the first word in capital and rest all in words in small for a single sentence and this code will help you convert normal text into sentence case.
88. Remove a Character from Selection
Sub removeChar()
Dim Rng As Range
Dim rc As String
rc = InputBox("Character(s) to Replace", "Enter Value")
For Each Rng In Selection
Selection.Replace What:=rc, Replacement:=""
Next
End Sub
To remove a particular character from a selected cell you can use this code. It will show you an input box to enter the character you want to remove.
89. Word Count from Entire Worksheet
Sub Word_Count_Worksheet() Dim WordCnt As Long Dim rng As Range Dim S As String Dim N As Long For Each rng In ActiveSheet.UsedRange.Cells S = Application.WorksheetFunction.Trim(rng.Text) N = 0 If S <> vbNullString Then N = Len(S) - Len(Replace(S, " ", "")) + 1 End If WordCnt = WordCnt + N Next rng MsgBox "There are total " _ & Format(WordCnt, "#,##0") & _ " words in the active worksheet" End Sub
It can help you to count all the words from a worksheet.
90. Remove the Apostrophe from a Number
Sub removeApostrophes() Selection.Value = Selection.Value End Sub
If you have numeric data where you have an apostrophe before each number, you run this code to remove it.
91. Remove Decimals from Numbers
Sub removeDecimals() Dim lnumber As Double Dim lResult As Long Dim rng As Range For Each rng In Selection rng.Value = Int(rng) rng.NumberFormat = "0" Next rng End Sub
This code will simply help you to remove all the decimals from the numbers from the selected range.
92. Multiply all the Values by a Number
Sub addNumber()
Dim rng As Range
Dim i As Integer
i = InputBox("Enter number to multiple", "Input Required")
For Each rng In Selection
If WorksheetFunction.IsNumber(rng) Then
rng.Value = rng + i
Else
End If
Next rng
End Sub
Let’s you have a list of numbers and you want to multiply all the number with a particular. To use this code: Select that range of cells and run this code. It will first ask you for the number with whom you want to multiple and then instantly multiply all the numbers with it.
93. Add a Number in all the Numbers
Sub addNumber()
Dim rng As Range
Dim i As Integer
i = InputBox("Enter number to multiple", "Input Required")
For Each rng In Selection
If WorksheetFunction.IsNumber(rng) Then
rng.Value = rng + i
Else
End If
Next rng
End Sub
Just like multiplying you can also add a number into a set of numbers.
94. Calculate the Square Root
Sub getSquareRoot() Dim rng As Range Dim i As Integer For Each rng In Selection If WorksheetFunction.IsNumber(rng) Then rng.Value = Sqr(rng) Else End If Next rng End Sub
To calculate square root without applying a formula you can use this code. It will simply check all the selected cells and convert numbers to their square root.
95. Calculate the Cube Root
Sub getCubeRoot() Dim rng As Range Dimi As Integer For Each rng In Selection If WorksheetFunction.IsNumber(rng) Then rng.Value = rng ^ (1 / 3) Else End If Nextrng End Sub
To calculate cube root without applying a formula you can use this code. It will simply check all the selected cells and convert numbers to their cube root.
96. Add A-Z Alphabets in a Range
Sub addsAlphabets1() Dim i As Integer For i = 65 To 90 ActiveCell.Value = Chr(i) ActiveCell.Offset(1, 0).Select Next i End Sub
Sub addsAlphabets2() Dim i As Integer For i = 97 To 122 ActiveCell.Value = Chr(i) ActiveCell.Offset(1, 0).Select Next i End Sub
Just like serial numbers you can also insert alphabets in your worksheet. Beloware the code which you can use.
97. Convert Roman Numbers into Arabic Numbers
Sub convertToNumbers() Dim rng As Range Selection.Value = Selection.Value For Each rng In Selection If Not WorksheetFunction.IsNonText(rng) Then rng.Value = WorksheetFunction.Arabic(rng) End If Next rng End Sub
Sometimes it’s really hard to understand Roman numbers as serial numbers. This code will help you to convert roman numbers into Arabic numbers.
98. Remove Negative Signs
Sub removeNegativeSign() Dim rng As Range Selection.Value = Selection.Value For Each rng In Selection If WorksheetFunction.IsNumber(rng) Then rng.Value = Abs(rng) End If Next rng
This code will simply check all the cell in the selection and convert all the negative numbers into positive. Just select a range and run this code.
99. Replace Blank Cells with Zeros
Sub replaceBlankWithZero() Dim rng As Range Selection.Value = Selection.Value For Each rng In Selection If rng = "" Or rng = " " Then rng.Value = "0" Else End If Next rng End Sub
For data where you have blank cells, you can use the below code to add zeros in all those cells. It makes easier to use those cells in further calculations.
More Codes
100. More VBA Examples and Tutorials
- User Defined Function [UDF] in Excel using VBA
- VBA Interview Questions
- Add a Comment in a VBA Code (Macro)
- Add a Line Break in a VBA Code (Single Line into Several Lines)
- Add a New Line (Carriage Return) in a String in VBA
- Personal Macro Workbook (personal.xlsb)
- Record a Macro in Excel
- VBA Exit Sub Statement
- VBA Immediate Window (Debug.Print)
- VBA Module
- VBA MSGBOX
- VBA Objects
- VBA With Statement
- Count Rows using VBA
- Excel VBA Font (Color, Size, Type, and Bold)
- Excel VBA Hide and Unhide a Column or a Row
- Excel VBA Range – Working with Range and Cells in VBA
- Apply Borders on a Cell using VBA in Excel
- Find Last Row, Column, and Cell using VBA in Excel
- Insert a Row using VBA in Excel
- Merge Cells in Excel using a VBA Code
- Select a Range/Cell using VBA in Excel
- How to SELECT ALL the Cells in a Worksheet using a VBA Code
- use ActiveCell in VBA in Excel
- How to use Special Cells Method in VBA in Excel
- How to use UsedRange Property in VBA in Excel
- VBA AutoFit (Rows, Column, or the Entire Worksheet)
- VBA ClearContents (from a Cell, Range, or Entire Worksheet)
- VBA Copy Range to Another Sheet + Workbook
- VBA Enter Value in a Cell (Set, Get and Change)
- VBA Insert Column (Single and Multiple)
- VBA Named Range
- VBA Range Offset
- VBA Sort Range | (Descending, Multiple Columns, Sort Orientation
- VBA Wrap Text (Cell, Range, and Entire Worksheet)
- How to CLEAR an Entire Sheet using VBA in Excel
- How to Copy and Move a Sheet in Excel using VBA
- How to COUNT Sheets using VBA in Excel
- How to DELETE a SHEET using VBA in Excel
- How to Hide & Unhide a Sheet using VBA in Excel
- How to PROTECT and UNPROTECT a Sheet using VBA in Excel
- RENAME a Sheet using VBA
- Write a VBA Code to Create a New Sheet
- VBA Worksheet Object
- Activate a Sheet using VBA
- Copy an Excel File (Workbook)
- VBA Activate Workbook (Excel File)
- VBA Close Workbook (Excel File)
- VBA Combine Workbooks (Excel Files)
- VBA Create New Workbook (Excel File)
- VBA Delete Workbook (Excel File)
- VBA Open Workbook (Excel File)
- VBA Protect/Unprotect Workbook (Excel File)
- VBA Rename Workbook (Excel File)
- VBA Save Workbook (Excel File)
- VBA ThisWorkbook (Current Excel File)
- VBA Workbook
- Declare Global Variable (Public) in VBA
- Range or a Cell as a Variable in VBA
- Option Explicit Statement in VBA
- Variable in a Message Box
- VBA Constants
- VBA Dim Statement
- VBA Variables (Declare, Data Types, and Scope)
- VBA Add New Value to the Array
- VBA Array
- VBA Array Length (Size)
- VBA Array with Strings
- VBA Clear Array (Erase)
- VBA Dynamic Array
- VBA Loop Through an Array
- VBA Multi-Dimensional Array
- VBA Range to an Array
- VBA Search for a Value in an Array
- VBA Sort Array
- How to Average Values in Excel using VBA
- Get Today’s Date and Current Time using VBA
- Sum Values in Excel using VBA
- Match Function in VBA
- MOD in VBA
- Random Number
- VBA Calculate (Cell, Range, Row, & Workbook)
- VBA Concatenate
- VBA Worksheet Function (Use Excel Functions in a Macro)
- How to Check IF a Sheet Exists using VBA in Excel
- VBA Check IF a Cell is Empty + Multiple Cells
- VBA Check IF a Workbook Exists in a Folder (Excel File)
- VBA Check IF a Workbook is Open (Excel File)
- VBA Exit IF
- VBA IF – IF Then Else Statement
- VBA IF And (Test Multiple Conditions)
- VBA IF Not
- VBA IF OR (Test Multiple Conditions)
- VBA Nested IF
- VBA SELECT CASE Statement (Test Multiple Conditions)
- VBA Automation Error (Error 440)
- VBA Error 400
- VBA ERROR Handling
- VBA Invalid Procedure Call Or Argument Error (Error 5)
- VBA Object Doesn’t Support this Property or Method Error (Error 438)
- VBA Object Required Error (Error 424)
- VBA Out of Memory Error (Error 7)
- VBA Overflow Error (Error 6)
- VBA Runtime Error (Error 1004)
- VBA Subscript Out of Range Runtime Error (Error 9)
- VBA Type Mismatch Error (Error 13)
- Excel VBA Do While Loop and (Do Loop While)
- How to Loop Through All the Sheets using VBA
- Loop Through a Range using VBA
- VBA FOR LOOP
- VBA GoTo Statement
- Input Box in VBA
- VBA Create and Write to a Text File
- VBA ScreenUpdating
- VBA Status Bar
- VBA Wait and Sleep
About the Author
Puneet is using Excel since his college days. He helped thousands of people to understand the power of the spreadsheets and learn Microsoft Excel. You can find him online, tweeting about Excel, on a running track, or sometimes hiking up a mountain.
Представляю Вашему вниманию огромный сборник макросов и функций, все макросы сгруппированы по главам, для удобства добавил оглавление с гиперссылками.
P.S.: Где скачал не помню.
Запуск макроса с поиском ячейки
Запуск макроса при открытии книги
Запуск макроса при вводе в ячейку «2»
Запуск макроса при нажатии «Ентер»
Добавить в панель свою вкладку «Надстройки» (Формат ячейки)
Проверка наличия файла по указанному пути_1
Проверка наличия файла по указанному пути_2
Проверка наличия файла по указанному пути_3
Поиск нужного файла_1
Поиск нужного файла_2
Поиск нужного файла_3
Поиск нужного файла_4
Автоматизация удаления файлов
Произвольный текст в строке состояния
Восстановление строки состояния
Бегущая строка в строке состояния
Быстрое изменение заголовка окна
Быстрое изменение заголовка окна_2
Изменение заголовка окна (со скрытием названия файла)
Возврат к первоначальному заголовку
Что открыто в данный момент
Работа с текстовыми файлами
Запись и чтение текстового файла
Обработка нескольких текстовых файлов
Определение конца строки текстового файла
Копирование из текстового файла в эксель
Копирование содержимого в текстовый файл_1
Копирование содержимого в текстовый файл_2
Экспорт данных в HТМL
Создание резервных копий ценных файлов
Подсчет количества открытий файла
Вывод пути к файлу в активную ячейку
Копирование содержимого файла RTF в эксель
Копирование данных из закрытой книги
Извлечение данных из закрытого файла
Поиск слова в файлах
Создание текстового файла и ввод текста в файл
Создание текстового файла и ввод текста (определение конца файла)
Создание документов Word на основе таблицы Excel
Команды создания и удаления каталогов
Получение текущего каталога
Посмотреть все файлы в каталоге_1
Посмотреть все файлы в каталоге_2
Посмотреть все файлы в каталоге_3
Количество имен рабочей книги
Защита рабочей книги
Запрет печати книги
Открытие книги (или текстовых файлов)
Открытие книги и добавление в ячейку А1 текста
Сколько книг открыто
Закрытие всех книг
Закрытие рабочей книги только при выполнении условия
Сохранение рабочей книги с именем, представляющим собой текущую дату
Сохранена ли рабочая книга
Создать книгу с одним листом
Удаление ненужных имен
Быстрое размножение рабочей книги
Сортировка листов
Поиск максимального значения на всех листах книги
Проверка наличия защиты рабочего листа
Список отсортированных листов
Создать новый лист_1
Копирование листа в книге
Копирование листа в новую книгу (создается)
Перемещение листа в книге
Перемещение нескольких листов в новую книгу
Заменить существующий файл
Вставка колонтитула с именем книги, листа и текущей датой
Существует ли лист
Существует ли лист_2
Вывод количества листов в активной книге
Вывод количества листов в активной книге в виде гиперссылок
Вывод имен активных листов по очереди
Вывод имени и номеров листов текущей книги
Сделать лист невидимым
Сколько страниц на всех листах?
Копирование строк на другой лист
Копирование столбцов на другой лист
Подсчет количества ячеек, содержащих указанные значения_1
Подсчет количества ячеек в диапазоне, содержащих указанные значения_2
Подсчет количества видимых ячеек в диапазоне
Определение количества ячеек в диапазоне и суммы их значений
Подсчет количества ячеек
Автоматический пересчет данных таблицы при изменении ее значений
Ввод данных в ячейки
Ввод данных с использованием формул
Ввод текстоввых данных в ячейки
Вывод в ячейки названия книги, листа и количества листов
Удаление пустых строк_1
Удаление пустых строк_2
Удаление пустых строк_3
Удаление строки по условию
Удаление используемых скрытых строк или строк с нулевой высотой
Удаление дубликатов по маске
Выделение диапазона над текущей ячейкой
Выделение диапазона над текущей ячейкой_2
Выделение отрицательных значений
Выделение диапазона и использование абсолютных адресов
Выделение ячеек через интервал_2
Движение по ячейкам
Поиск ближайшей пустой ячейки столбца
Поиск максимального значения
Поиск и замена по шаблону
Поиск значения с отображением результата в отдельном окне
Поиск с выделением найденных данных_1
Поиск с выделением найденных данных_2
Поиск по условию в диапазоне
Поиск последней непустой ячейки диапазона
Поиск последней непустой ячейки столбца
Поиск последней непустой ячейки строки
Поиск ячейки синего цвета в диапазоне
Поиск наличия значения в столбце
Поиск совпадений в диапазоне
Поиск ячейки в диапазоне_1
Поиск ячейки в диапазоне_2
Поиск приближенного значения в диапазоне
Поиск начала и окончания диапазона, содержащего данные
Автоматическая замена значений
Быстрое заполнение диапазона (массив)
Заполнение через интервал(массив)
Заполнение указанного диапазона(массив)
Заполнение диапазона(массив)
Расчет суммы первых значений диапазона
Размещение в ячейке электронных часов
«Будильник»
Адрес активной ячейки
Координаты активной ячейки
Формула активной ячейки
Получение из ячейки формулы
Тип данных ячейки
Вывод адреса конца диапазона
Получение информации о выделенном диапазоне
Создание изменяемого списка (таблица)
Умножение выделенного диапазона на 2
Одновременное умножение всех данных диапазона
Деление диапазона на 100
Суммирование данных только видимых ячеек
Сумма ячеек с числовыми значениями
При суммировании — курсор внутри диапазона
Начисление процентов в зависимости от суммы_1
Начисление процентов в зависимости от суммы_2
Начисление процентов в зависимости от суммы_3
Сводный пример расчета комиссионного вознаграждения
Движение по диапазону
Сдвиг от выделенной ячейки
Создание заливки диапазона
Подбор параметра ячейки
Разбиение диапазона
Объединение данных диапазона
Объединение данных диапазона_2
Узнать максимальную колонку или строку.
Ограничение возможных значений диапазона
Тестирование скорости чтения и записи диапазонов
Открыть MsgBox при выборе ячейки
Скрытие строки
Скрытие нескольких строк
Скрытие столбца
Скрытие нескольких столбцов
Скрытие строки по имени ячейки
Скрытие нескольких строк по адресам ячеек
Скрытие столбца по имени ячейки
Скрытие нескольких столбцов по адресам ячеек
Мигание ячейки
Вывод на экран всех примечаний рабочего листа
Функция извлечения комментария
Список примечаний защищенных листов
Перечень примечаний в отдельном списке_1
Перечень примечаний в отдельном списке_2
Перечень примечаний в отдельном списке_3
Подсчет количества примечаний_1
Подсчет примечаний_3
Выделение ячеек с примечаниями
Отображение всех примечаний
Изменение цвета примечаний
Добавление примечаний
Добавление примечаний в диапазон по условию
Перенос комментария в ячейку и обратно
Перенос значений из ячейки в комментарий_1
Перенос значений из ячейки в комментарий_2
Дополнение панели инструментов
Добавление кнопки на панель инструментов
Панель с одной кнопкой
Панель с двумя кнопками
Создание панели справа
Вызов предварительного просмотра
Создание пользовательского меню (вариант 1)
Создание пользовательского меню (вариант 2)
Создание пользовательского меню (вариант 3)
Создание пользовательского меню (вариант 4)
Создание пользовательского меню (вариант 5)
Создание списка пунктов главного меню Excel
Создание списка пунктов контекстных меню
Отображение панели инструментов при определенном условии
Скрытие и отображение панелей инструментов
Создать подсказку к моим кнопкам
Создание меню на основе данных рабочего листа
Создание контекстного меню
Блокировка контекстного меню
Добавление команды в меню Сервис
Добавление команды в меню Вид
Создание панели со списком
Мультфильм с помощником в главной роли
Дополнение помощника текстом, заголовком, кнопкой и значком
Новые параметры помощника
Использование помощника для выбора цвета заливки
Функция INPUTBOX (через ввод значения)
Настройка ввода данных в диалоговом окне
Открытие диалогового окна (“Открыть файл”)_1
Вызов броузера из Экселя
Диалоговое окно ввода данных
Значения по умолчанию
Вывод списка доступных шрифтов
Выбор из текста всех чисел
Прописная буква только в начале текста
Подсчет количества повторов искомого текста
Выделение из текста произвольного элемента
Отображение текста «задом наперед»
Запуск таблицы символов из Excel
Получить имя пользователя
Вывод разрешения монитора
Получение информации об используемом принтере
Просмотр информации о дисках компьютера
Построение диаграммы с помощью макроса
Сохранение диаграммы в отдельном файле
Построение и удаление диаграммы нажатием одной кнопки
Применение случайной цветовой палитры
Эффект прозрачности диаграммы
Построение диаграммы на основе данных нескольких рабочих листов
Создание подписей к данным диаграммы
Программа для составления кроссвордов
Игра «Минное поле»
Игра «Угадай животное»
Расчет на основании ячеек определенного цвета
Вызов функциональных клавиш
Расчет среднего арифметического значения
Перевод чисел в «деньги»
Поиск ближайшего понедельника
Подсчет количества полных лет
Расчет средневзвешенного значения
Преобразование номера месяца в его название
Использование относительных ссылок
Преобразование таблицы Excel в HТМL-формат
Генератор случайных чисел
Случайные числа — на основании диапазона
Применение функции без ввода ее в ячейку
Подсчет именованных объектов
Включение автофильтра с помощью макроса
Создание бегущей строки
Создание бегущей картинки
Вращающиеся автофигуры
Вызов таблицы цветов
Создание калькулятора
Склонение фамилии, имени и отчества
Вывод даты и времени_1
Вывод даты и времени_2
Получение системной даты
Извлечение даты и часов
Функция ДатаПолная
К сообщению приложен файл: macros.rar (83Kb)
ГЛАВА 1. МАКРОСЫ
Запуск макроса с поиском ячейки
Запуск макроса при открытии книги
Запуск макроса при вводе в ячейку «2»
Запуск макроса при нажатии «Ентер»
Добавить в панель свою вкладку «Надстройки» (Формат ячейки)
ГЛАВА 2. РАБОТА С ФАЙЛАМИ (Т.Е.ОБМЕН ДАННЫМИ С ТХТ, RTF, XLS И Т.Д.)
Проверка наличия файла по указанному пути_1
Проверка наличия файла по указанному пути_2
Проверка наличия файла по указанному пути_3
Поиск нужного файла_1
Поиск нужного файла_2
Поиск нужного файла_3
Поиск нужного файла_4
Автоматизация удаления файлов
Произвольный текст в строке состояния
Восстановление строки состояния
Бегущая строка в строке состояния
Быстрое изменение заголовка окна
Быстрое изменение заголовка окна_2
Изменение заголовка окна (со скрытием названия файла)
Возврат к первоначальному заголовку
Что открыто в данный момент
Работа с текстовыми файлами
Запись и чтение текстового файла
Обработка нескольких текстовых файлов
Определение конца строки текстового файла
Копирование из текстового файла в эксель
Копирование содержимого в текстовый файл_1
Копирование содержимого в текстовый файл_2
Экспорт данных в HТМL
Создание резервных копий ценных файлов
Подсчет количества открытий файла
Вывод пути к файлу в активную ячейку
Копирование содержимого файла RTF в эксель
Копирование данных из закрытой книги
Извлечение данных из закрытого файла
Поиск слова в файлах
Создание текстового файла и ввод текста в файл
Создание текстового файла и ввод текста (определение конца файла)
Создание документов Word на основе таблицы Excel
Команды создания и удаления каталогов
Получение текущего каталога
Посмотреть все файлы в каталоге_1
Посмотреть все файлы в каталоге_2
Посмотреть все файлы в каталоге_3
ГЛАВА 3. РАБОЧАЯ ОБЛАСТЬ MICROSOFT EXCEL
Количество имен рабочей книги
Защита рабочей книги
Запрет печати книги
Открытие книги (или текстовых файлов)
Открытие книги и добавление в ячейку А1 текста
Сколько книг открыто
Закрытие всех книг
Закрытие рабочей книги только при выполнении условия
Сохранение рабочей книги с именем, представляющим собой текущую дату
Сохранена ли рабочая книга
Создать книгу с одним листом
Удаление ненужных имен
Быстрое размножение рабочей книги
Сортировка листов
Поиск максимального значения на всех листах книги
Проверка наличия защиты рабочего листа
Список отсортированных листов
Создать новый лист_1
Копирование листа в книге
Копирование листа в новую книгу (создается)
Перемещение листа в книге
Перемещение нескольких листов в новую книгу
Заменить существующий файл
Вставка колонтитула с именем книги, листа и текущей датой
Существует ли лист
Существует ли лист_2
Вывод количества листов в активной книге
Вывод количества листов в активной книге в виде гиперссылок
Вывод имен активных листов по очереди
Вывод имени и номеров листов текущей книги
Сделать лист невидимым
Сколько страниц на всех листах?
Копирование строк на другой лист
Копирование столбцов на другой лист
Подсчет количества ячеек, содержащих указанные значения_1
Подсчет количества ячеек в диапазоне, содержащих указанные значения_2
Подсчет количества видимых ячеек в диапазоне
Определение количества ячеек в диапазоне и суммы их значений
Подсчет количества ячеек
Автоматический пересчет данных таблицы при изменении ее значений
Ввод данных в ячейки
Ввод данных с использованием формул
Ввод текстоввых данных в ячейки
Вывод в ячейки названия книги, листа и количества листов
Удаление пустых строк_1
Удаление пустых строк_2
Удаление пустых строк_3
Удаление строки по условию
Удаление используемых скрытых строк или строк с нулевой высотой
Удаление дубликатов по маске
Выделение диапазона над текущей ячейкой
Выделение диапазона над текущей ячейкой_2
Выделение отрицательных значений
Выделение диапазона и использование абсолютных адресов
Выделение ячеек через интервал_2
Движение по ячейкам
Поиск ближайшей пустой ячейки столбца
Поиск максимального значения
Поиск и замена по шаблону
Поиск значения с отображением результата в отдельном окне
Поиск с выделением найденных данных_1
Поиск с выделением найденных данных_2
Поиск по условию в диапазоне
Поиск последней непустой ячейки диапазона
Поиск последней непустой ячейки столбца
Поиск последней непустой ячейки строки
Поиск ячейки синего цвета в диапазоне
Поиск наличия значения в столбце
Поиск совпадений в диапазоне
Поиск ячейки в диапазоне_1
Поиск ячейки в диапазоне_2
Поиск приближенного значения в диапазоне
Поиск начала и окончания диапазона, содержащего данные
Автоматическая замена значений
Быстрое заполнение диапазона (массив)
Заполнение через интервал(массив)
Заполнение указанного диапазона(массив)
Заполнение диапазона(массив)
Расчет суммы первых значений диапазона
Размещение в ячейке электронных часов
«Будильник»
Адрес активной ячейки
Координаты активной ячейки
Формула активной ячейки
Получение из ячейки формулы
Тип данных ячейки
Вывод адреса конца диапазона
Получение информации о выделенном диапазоне
Создание изменяемого списка (таблица)
Умножение выделенного диапазона на 2
Одновременное умножение всех данных диапазона
Деление диапазона на 100
Суммирование данных только видимых ячеек
Сумма ячеек с числовыми значениями
При суммировании — курсор внутри диапазона
Начисление процентов в зависимости от суммы_1
Начисление процентов в зависимости от суммы_2
Начисление процентов в зависимости от суммы_3
Сводный пример расчета комиссионного вознаграждения
Движение по диапазону
Сдвиг от выделенной ячейки
Создание заливки диапазона
Подбор параметра ячейки
Разбиение диапазона
Объединение данных диапазона
Объединение данных диапазона_2
Узнать максимальную колонку или строку.
Ограничение возможных значений диапазона
Тестирование скорости чтения и записи диапазонов
Открыть MsgBox при выборе ячейки
Скрытие строки
Скрытие нескольких строк
Скрытие столбца
Скрытие нескольких столбцов
Скрытие строки по имени ячейки
Скрытие нескольких строк по адресам ячеек
Скрытие столбца по имени ячейки
Скрытие нескольких столбцов по адресам ячеек
Мигание ячейки
ГЛАВА 4. РАБОТА С ПРИМЕЧАНИЯМИ
Вывод на экран всех примечаний рабочего листа
Функция извлечения комментария
Список примечаний защищенных листов
Перечень примечаний в отдельном списке_1
Перечень примечаний в отдельном списке_2
Перечень примечаний в отдельном списке_3
Подсчет количества примечаний_1
Подсчет примечаний_3
Выделение ячеек с примечаниями
Отображение всех примечаний
Изменение цвета примечаний
Добавление примечаний
Добавление примечаний в диапазон по условию
Перенос комментария в ячейку и обратно
Перенос значений из ячейки в комментарий_1
Перенос значений из ячейки в комментарий_2
ГЛАВА 5 . ПОЛЬЗОВАТЕЛЬСКИЕ ВКЛАДКИ НА ЛЕНТЕ
Дополнение панели инструментов
Добавление кнопки на панель инструментов
Панель с одной кнопкой
Панель с двумя кнопками
Создание панели справа
Вызов предварительного просмотра
Создание пользовательского меню (вариант 1)
Создание пользовательского меню (вариант 2)
Создание пользовательского меню (вариант 3)
Создание пользовательского меню (вариант 4)
Создание пользовательского меню (вариант 5)
Создание списка пунктов главного меню Excel
Создание списка пунктов контекстных меню
Отображение панели инструментов при определенном условии
Скрытие и отображение панелей инструментов
Создать подсказку к моим кнопкам
Создание меню на основе данных рабочего листа
Создание контекстного меню
Блокировка контекстного меню
Добавление команды в меню Сервис
Добавление команды в меню Вид
Создание панели со списком
Мультфильм с помощником в главной роли
Дополнение помощника текстом, заголовком, кнопкой и значком
Новые параметры помощника
Использование помощника для выбора цвета заливки
ГЛАВА 6. ДИАЛОГОВЫЕ ОКНА
Функция INPUTBOX (через ввод значения)
Настройка ввода данных в диалоговом окне
Открытие диалогового окна (“Открыть файл”)_1
Вызов броузера из Экселя
Диалоговое окно ввода данных
Значения по умолчанию
ГЛАВА 7.ФОРМАТИРОВАНИЕ ТЕКСТА. ТАБЛИЦЫ. ГРАНИЦЫ И ЗАЛИВКА.
Вывод списка доступных шрифтов
Выбор из текста всех чисел
Прописная буква только в начале текста
Подсчет количества повторов искомого текста
Выделение из текста произвольного элемента
Отображение текста «задом наперед»
Запуск таблицы символов из Excel
ГЛАВА 8 ИНФОРМАЦИЯ О ПОЛЬЗОВАТЕЛЕ, КОМПЬЮТЕРЕ, ПРИНТЕРЕ И Т.Д.
Получить имя пользователя
Вывод разрешения монитора
Получение информации об используемом принтере
Просмотр информации о дисках компьютера
ГЛАВА 9. ДИАГРАММЫ
Построение диаграммы с помощью макроса
Сохранение диаграммы в отдельном файле
Построение и удаление диаграммы нажатием одной кнопки
Применение случайной цветовой палитры
Эффект прозрачности диаграммы
Построение диаграммы на основе данных нескольких рабочих листов
Создание подписей к данным диаграммы
ГЛАВА 10. РАЗНЫЕ ПРОГРАММЫ.
Программа для составления кроссвордов
Игра «Минное поле»
Игра «Угадай животное»
Расчет на основании ячеек определенного цвета
ГЛАВА 11. ДРУГИЕ ФУНКЦИИ И МАКРОСЫ
Вызов функциональных клавиш
Расчет среднего арифметического значения
Перевод чисел в «деньги»
Поиск ближайшего понедельника
Подсчет количества полных лет
Расчет средневзвешенного значения
Преобразование номера месяца в его название
Использование относительных ссылок
Преобразование таблицы Excel в HТМL-формат
Генератор случайных чисел
Случайные числа — на основании диапазона
Применение функции без ввода ее в ячейку
Подсчет именованных объектов
Включение автофильтра с помощью макроса
Создание бегущей строки
Создание бегущей картинки
Вращающиеся автофигуры
Вызов таблицы цветов
Создание калькулятора
Склонение фамилии, имени и отчества
ГЛАВА 12. ДАТА И ВРЕМЯ
Вывод даты и времени_1
Вывод даты и времени_2
Получение системной даты
Извлечение даты и часов
Функция ДатаПолная
ГЛАВА 1. МАКРОСЫ
Запуск макроса с поиском ячейки
‘ Sub GotoFixedCell:
‘ Делает активной ячейку, содержащую значение vVariant на
‘ рабочем листе sSheetName в активной рабочей книге.
‘
‘ Note: Содержимое ячеек интерпретируется как ‘значение’!
‘
Public Sub GotoFixedCell(vValue As Variant, sSheetName As String)
Dim c As Range, cStart As Range, cForFind As Range
Dim i As Integer
On Error GoTo errhandle:
Set cForFind = Worksheets(sSheetName).Cells ‘ Диапазон поиска
With cForFind
Set c = .Find(What:=vValue, After:=ActiveCell, LookIn:=xlValues, _
LookAt:= xlРart, SearchOrder:=xlByRows,_
SearchDirection:=xlNext, MatchCase:=False)
Set cStart = c
While Not c Is Nothing
Set c = .FindNext(c)
If c.Address = cStart.Address Then
c.Select
Exit Sub
End If
Wend
End With
Exit Sub
errНandle:
MsgBox Err.Descriрtion, vbExclamation, «Error #» & Err.Number
End Sub
Запуск макроса при открытии книги
Sub Auto_Oрen()
Запуск макроса при вводе в ячейку «2»
Private Sub Worksheet_Change(ByVal Target As Range)
Dim w As Object
‘On Error Resume Next
If Range(«A1»).Value = 2 Then
MsgBox «Ох! Значение ячейки стало равным 2-м!»
MsgBox «Я попробую сейчас открыть модуль с процедурой, которая все это делает!»
Application.VBE.MainWindow.SetFocus
Application.VBE.Windows(1).SetFocus
SendKeys «{F7}», True
End If
End Sub
Запуск макроса при нажатии «Ентер»
в модуле листа
Private Sub Worksheet_Selectiоnchange(ByVal Target As Range)
Application.OnKey «{~}», «StartEnter»
End Sub
в модуле книги
Sub StartEnter()
MsgBox («sadfsdfsf»)
End Sub
Добавить в панель свою вкладку «Надстройки» (Формат ячейки)
Код в модуле рабочего листа
Sub Worksheet_Change(ByVal Target As Excel.Range)
Call updаtеToolbar
End Sub
Sub Worksheet_Selectiоnchange(ByVal Target As Excel.Range)
Call updаtеToolbar
End Sub
Листинг 2.43. Код в стандартном модуле
Sub FastChangeNumberFormat()
Dim bar As CommandBar
Dim button As CommandBarButton
‘ Удаление существующей панели инструментов (если она есть)
On Error Resume Next
CommandBars(«Числовой формат»).Delete
On Error GoTo 0
‘ Формирование новой панели
Set bar = CommandBars.Add
With bar
.Name = «Числовой формат»
.Visible = True
End With
‘ Создание кнопки
Set button = CommandBars(«Числовой формат»).Controls.Add _
(Type:=msoControlButton)
With button
.Caption = «»
.OnAction = «ChangeNumFormat»
.TooltipText = «Щелкните для изменения числового формата»
.Style = msoButtonCaption
End With
‘ Обновление созданной панели инструментов
Call updаtеToolbar
End Sub
Sub updаtеToolbar()
‘ Обновление панели инструментов (если она создана)
On Error Resume Next
‘ Изменение заголовка кнопки (на название формата выделенной ячейки)
CommandBars(«Числовой формат»).Controls(1).Caption = _
ActiveCell.NumberFormat
End Sub
Sub ChangeNumFormat()
‘ Отображение диалогового окна изменения формата ячейки
Application.Dialogs(xlDialogFormatNumber).Show
Call updаtеToolbar
End Sub
ГЛАВА 2. РАБОТА С ФАЙЛАМИ (Т.Е.ОБМЕН ДАННЫМИ С ТХТ, RTF, XLS И Т.Д.)
Проверка наличия файла по указанному пути_1
Sub VerifyFileLocation()
Dim strFileName As String
Dim strFileTitle As String
‘ Имя и путь искомого файла
strFileTitle = «primer.xls»
strFileName = «C:Документыprimer.xls»
‘ Проверка наличия файла (функция Dir возвращает пустую _
строку, если по указанному пути файл обнаружить не удалось)
If Dir(strFileName) <> «» Then
MsgBox «Файл » & strFileTitle & » найден»
Else
MsgBox «Файл » & strFileTitle & » не найден»
End If
End Sub
Проверка наличия файла по указанному пути_2
Sub VerifyFileLocation1()
Dim strFileName As String
‘ Имя искомого файла
strFileName = «C:Документыprimer.xls»
‘ Проверка наличия файла (функция Dir возвращает пустую _
строку, если по указанному пути файл обнаружить не удалось)
If Dir(strFileName) <> «» Then
MsgBox «Файл » & strFileName & » найден»
Else
MsgBox «Файл » & strFileName & » не найден»
End If
End Sub
Проверка наличия файла по указанному пути_3
Sub Check_Disk()
On Error Resume Next
If Dir(«\192.168.1.200c», vbSystem) <> «» Then
If Err = 52 Then
Err.Clear
MsgBox «Диска нет!», 48, «Ошибка»
Exit Sub
End If
If Err <> 0 Then
MsgBox «Произошло ошибка!», 48, «Ошибка»
Exit Sub
Else
On Error GoTo 0
MsgBox «Диск есть!», 64, «»
End If
End If
End Sub
Поиск нужного файла_1
Sub FileSearch()
Dim strFileName As String
Dim strFolder As String
Dim strFullPath As String
‘ Задание имени папки для поиска
strFolder = InputBox(«Определите папку:»)
If strFolder = «» Then Exit Sub
‘ Задание имени файла для поиска
strFileName = Application.InputBox(«Введите имя файла:»)
If strFileName = «» Then Exit Sub
‘ При необходимости дополняем имя папки «»
If Right(strFolder, 1) <> «» Then strFolder = strFolder & «»
‘ Полный путь файла
strFullPath = strFolder & strFileName
‘ Вывод окна с отчетом о поиске средствами VBA
MsgBox «Использование команды VBA…» & vbCrLf & vbCrLf & _
dhSearchVBA(strFullPath), vbInformation, strFullPath
‘ Вывод окна с отчетом о поиске средствами объекта FileSearch
MsgBox «Использование объекта FileSearch…» & vbCrLf & _
vbCrLf & dhSearchFileSearch(strFolder, strFileName), vbInformation, _
strFullPath
‘ Вывод окна с отчетом о поиске средствами объекта _
FileSystemObject
MsgBox «Использование объекта FileSystemObject…» & vbCrLf & _
vbCrLf & dhSearchFileSystemObject(strFullPath), vbInformation, _
strFullPath
End Sub
Поиск нужного файла_2
Function dhSearchVBA(varFullPath As Variant) As Boolean
‘ Использование команды VBA
dhSearchVBA = Dir(varFullPath) <> «»
End Function
Поиск нужного файла_3
Function dhSearchFileSearch(varFolder As Variant, varFileName _
As Variant) As Boolean
‘ Использование объекта FileSearch
With Application.FileSearch
‘ Создание нового поиска
.NewSearch
‘ Имя для поиска
.FileName = varFileName
‘ Папка поиска
.LookIn = varFolder
‘ Собственно поиск
.Execute
dhSearchFileSearch = .FoundFiles.Count <> 0
End With
End Function
Поиск нужного файла_4
Function dhSearchFileSystemObject(varFullPath As Variant) As Boolean
Dim objFSObject As Object
‘ Использование объекта FileSystemObject
Set objFSObject = CreateObject(«sсriрting.FileSystemObject»)
dhSearchFileSystemObject = objFSObject.FileExists(varFullPath)
End Function
Автоматизация удаления файлов
Листинг 3.51. Удаление файла
Sub DeleteFile()
Kill «C:Документыprimer.xls»
End Sub
Листинг 3.52. Удаление группы файлов
Sub DeleteFiles()
‘ Удаление всех файлов с расширением XLS из заданной папки
Kill «C:Документы» & «*.xls»
End Sub
Произвольный текст в строке состояния
Sub ChangeStatusBarText()
Application.StatusBar = «Как надоело работать!!!»
End Sub
Восстановление строки состояния
Sub ReturnStatusBarText()
Application.StatusBar = False
End Sub
Бегущая строка в строке состояния
Sub MovingTextInStatusBar()
Dim intSpaces As Integer
‘ Изменение количества пробелов в начале строки (от 20 до 0) — _
строка бежит (скорее, ползет) влево
For intSpaces = 20 To 0 Step -1
‘ Запись текста в строку состояния
Application.StatusBar = Space(intSpaces) & «Как надоело работать!!!»
‘ Выдерживаем паузу
Application.Wait Now + TimeValue(«00:00:01»)
‘ Дадим Excel обработать пользовательский ввод
DoEvents
Next
Application.StatusBar = False
End Sub
Быстрое изменение заголовка окна
Sub NewTitle()
Application.Caption = «Какая хорошая погода»
End Sub
Быстрое изменение заголовка окна_2
Sub NewTitle()
Application.Caption = «Какая хорошая погода»
ActiveWindow.Caption = «А завтра будет дождь»
End Sub
Изменение заголовка окна (со скрытием названия файла)
Sub NewTitle()
Application.Caption = «Какая хорошая погода»
ActiveWindow.Caption = «»
End Sub
Возврат к первоначальному заголовку
Sub ReturnTitle()
‘ Возвращение заголовка приложения (то есть Excel)
Application.Caption = Empty
‘ Указание правильного названия открытого файла (книги)
ActiveWindow.Caption = ThisWorkbook.Name
End Sub
Что открыто в данный момент
Sub WorkBooksList()
Dim book As Object
‘ Вывод имени каждой рабочей книги
For Each book In Workbooks
MsgBox (book.Name)
Next
End Sub
Работа с текстовыми файлами
Открываются файлы командой Open, а закрываются — командой Close.
Sub Test()
Open «file.txt» For Input As #1
Close #1
End Sub
Запись и чтение текстового файла
Sub Test()
Open «file.txt» For Output As #1
Print #1, «Этот текст будет записан в файл»
Close #1
Open «file.txt» For Input As #1
Dim s As String
Input #1, s
MsgBox s
Close #1
End Sub
Для записи используется оператор Print, а для чтения — Input. У этих операторов есть свои особенности.
Print #1, «Hello , File»
Оператор Input #1 прочитает только Hello и все. Запятая воспринимается как разделитеть. Чтобы прочитать строку целиком, используется оператор Line Input.
Sub Test()
Open «file.txt» For Output As #1
Print #1, «Hello , File»
Close #1
Open «file.txt» For Input As #1
Dim s As String
Line Input #1, s
MsgBox s
Close #1
End Sub
Обработка нескольких текстовых файлов
Sub ImportTextFiles()
Dim fsSearch As FileSearch
Dim strFileName As String
Dim strPath As String
Dim i As Integer
‘ Задание пути и возможного имени файла
strFileName = ThisWorkbook.path & «»
strPath = «text??.txt»
‘ Создание объекта FileSearch
Set fsSearch = Application.FileSearch
‘ Настройка объекта для поиска
With fsSearch
‘ Маска для поиска
.LookIn = strFileName
‘ Путь для поиска
.FileName = strPath
‘ Поиск всех файлов, удовлетворяющих маске
.Execute
‘ Выход, если файлы не существуют
If .FoundFiles.Count = 0 Then
MsgBox «Файлы не обнаружены»
Exit Sub
End If
End With
‘ Обработка найденных файлов
For i = 1 To fsSearch.FoundFiles.Count
Call ImportTextFile(fsSearch.FoundFiles(i))
Next i
End Sub
Sub ImportTextFile(FileName As String)
‘ Импорт файла
Workbooks.OpenText FileName:=FileName, _
Origin:=xlWindows, _
StartRow:=1, _
DataType:=xlFixedWidth, _
FieldInfo:= _
Array(Array(0, 1), Array(3, 1), Array(12, 1))
‘ Ввод формул суммирования
Range(«D1»).Value = «A»
Range(«D2»).Value = «B»
Range(«D3»).Value = «C»
Range(«E1:E3»).Formula = «=COUNTIF(B:B,D1)»
Range(«F1:F3»).Formula = «=SUMIF(B:B,D1,C:C)»
End Sub
Определение конца строки текстового файла
Sub Test()
Open «file.txt» For Output As #1
Print #1, «Hello , File»
Close #1
Open «file.txt» For Input As #1
Dim s As String
While Not EOF(1)
Input #1, s
MsgBox s
Wend
Close #1
End Sub
Копирование из текстового файла в эксель
Dim TextLine
i = 1
Open «C:MyFile.txt» For Input As #1
Do While Not EOF(1)
Line Input #1, TextLine
ThisWorkbook.Worksheets(«Лист1»).Cells(i, 1).Value = TextLine
i = i + 1
Loop
Close #1
Копирование содержимого в текстовый файл_1
Sub Range2TXT()
MyFile = «C:File.txt» ‘путь к файлу
Open MyFile For Output As #1 ‘открыли для записи
For Each i In Selection ‘листаем ячейки выделенного диапазона
Print #1, i ‘пишем (с начала)
Next
Close #1 ‘закрываем
End Sub
Копирование содержимого в текстовый файл_2
Sub SaveAsText()
Dim cell As Range
‘ Открытие файла для сохранения (имя файла соответствует имени _
рабочей книги, но отличается расширением — TXT)
Open ThisWorkbook.Path & «» & ThisWorkbook.Name & «.txt» _
For Output As #1
‘ Запись содержимого заполненных ячеек таблицы в файл
For Each cell In ActiveSheet.UsedRange
If Not IsEmpty(cell) Then
Print #1, cell.Address, cell.Formula
End If
Next
‘ Не забываем закрывать файл
Close #1
End Sub
Экспорт данных в txt
Sub ExportAsText()
Dim lngRow As ****
Dim intCol As Integer
‘ Открытие файла для сохранения
Open «C:primer.txt» For Output As #1
‘ Запись выделенной части таблицы в файл (построчно)
For lngRow = 1 To Selection.Rows.Count
‘ Запись содержимого всех столбцов строки lngRow
For intCol = 1 To Selection.Columns.Count
Write #1, Selection.Cells(lngRow, intCol).Value;
Next intCol
‘ Начнем новую строку в файле
Print #1, «»
Next lngRow
‘ Не забываем закрыть файл
Close #1
End Sub
Sub ImportText()
Dim strLine As String ‘ Одна строка файла
Dim strCurChar As String * 1 ‘ Анализируемый символ строки файла
Dim strValue As String ‘ Значение для записи в ячейку
Dim lngRow As **** ‘ Номер текущей строки
Dim intCol As Integer ‘ Номер текущего столбца
Dim i As Integer
‘ Открытие импортируемого файла
Open «C:primer.txt» For Input As #1
‘ Считываем все строки файла и записываем данные, разделенные _
запятой, в ячейки таблицы (начиная с текущей ячейки)
Do Until EOF(1)
‘ Считываем строку из файла
Line Input #1, strLine
‘ Разбираем считанную строку
For i = 1 To Len(strLine)
strCurChar = Mid(strLine, i, 1)
If strCurChar = «,» Then
‘ Найден разделитель столбцов — запятая. Запишем _
сформированное значение в ячейку
ActiveCell.Offset(lngRow, intCol) = strValue
intCol = intCol + 1
strValue = «»
ElseIf i = Len(strLine) Then
‘ Конец строки — запишем в таблицу последнее _
значение в строке (перед этим дополним его последним _
символом строки, кроме кавычки)
If strCurChar <> Chr(34) Then
strValue = strValue & strCurChar
End If
‘ Запись в таблицу
ActiveCell.Offset(lngRow, intCol) = strValue
strValue = «»
ElseIf strCurChar <> Chr(34) Then
‘ Добавление символа в формируемое значение ячейки _
(кавычки игнорируются)
strValue = strValue & strCurChar
End If
Next i
‘ Переход к новой строке таблицы
intCol = 0
lngRow = lngRow + 1
Loop
‘ Закрываем файл
Close #1
End Sub
Экспорт данных в HТМL
Sub ExportAsHТМLFile()
Dim strStyle As String ‘ Параметры стиля отображения ячейки
Dim strAlign As String ‘ Параметры выравнивания ячейки
Dim strOut As String ‘ Выходная строка с HТМL-кодом
Dim cell As Object ‘ Обрабатываемая ячейка
Dim strCellText As String ‘ Текст обрабатываемой ячейки
Dim lngRow As **** ‘ Номер строки обрабатываемой ячейки
Dim lngLastRow As **** ‘ Номер строки предыдущей ячейки
Dim strTemp As String
Dim strFileName As String ‘ Имя файла для сохранения HТМL-кода
Dim i As ****
‘ Запрос у пользователя имени файла для сохранения
strFileName = Application.GetSaveAsFilename( _
InitialFileName:=»Primer.htm», _
fileFilter:=»HТМL Files(*.htm), *.htm»)
‘ Проверка, задал ли пользователь имя файла (если нет, _
то можно выходить)
If strFileName = «» Then Exit Sub
lngLastRow = Selection.Row
‘ Просмотр всех выделенных ячеек
For Each cell In Selection
‘ Значение строки для рассматриваемой ячейки
lngRow = cell.Row
‘ Если перешли на другую строку, то вставляем <tr>
If lngRow <> lngLastRow Then
strOut = strOut & vbTab & «</tr>» & vbCrLf & vbTab & _
«<tr>» & vbCrLf
‘ Переход на следующую сроку
lngLastRow = lngRow
End If
‘ Задание шрифта ячейки
If Not IsNull(cell.Font.Size) Then
strStyle = » style=» & «font-size: » & Int(100 * _
cell.Font.Size / 19) & «%;»
End If
‘ Для полужирного шрифта вставляем <b>
If cell.Font.Bold Then
strCellText = «<b>» & strCellText & «</b>»
End If
‘ Задание выравнивания
If cell.HorizontalAlignment = xlRight Then
‘ По правому краю
strAlign = » align=» & «right»
ElseIf cell.HorizontalAlignment = xlCenter Then
‘ По центру
strAlign = » align=» & «center»
Else
‘ По левому краю (по умолчанию)
strAlign = «»
End If
‘ Чтение текста в ячейке
strCellText = cell.Text
‘ Если нужно, то вертикальный вывод текста (в строку strTemp _
с последующим перенесением обратно в strCellText)
If cell.Orientation <> xlHorizontal Then
strTemp = «»
‘ Печать после каждого символа специального _
разделителя — <br>
For i = 1 To Len(strCellText)
strTemp = strTemp & Mid$(strCellText, i, 1) & «<br>»
Next i
strCellText = strTemp
strStyle = «»
End If
strOut = strOut & vbTab & vbTab & «<td» & strStyle & _
strAlign & «>» & strCellText & «</td>» & vbCrLf
Next
‘ Вставка <tr> для первой строки и </tr> — для последней
strOut = vbTab & «<tr>» & vbCrLf & strOut & vbTab & «</tr>» & vbCrLf
‘ Вставка дескриптора <table>
strOut = «<table border=1 cellpadding=3 cellspacing=1>» _
& vbCrLf & strOut & vbCrLf & «</table>»
‘ Сохранение HТМL-кода в файл
Open strFileName For Output As 1
Print #1, strOut
Close 1
‘ Вывод окна с информационным сообщением о результатах работы
MsgBox Selection.Count & » ячеек экспортировано в файл » & _
strFileName
End Sub
Импорт данных, для которых нужно более 256 столбцов
Sub ImportWideSheet()
Dim rgRange As Range ‘ Хранит заполняемую ячейку
Dim lngRow As **** ‘ Хранит номер текущей строки
Dim intCol As Integer ‘ Хранит номер текущего столбца
Dim i As Integer
Dim strLine As String ‘ Обрабатываемая строка (из файла)
Dim strCurChar As String * 1
Dim strCellValue As String ‘ В этой строке формируется значение _
заполняемой ячейки таблицы
Dim wshtCurrentSheet As Worksheet ‘ Лист, на котором находится _
заполняемая ячейка
‘ Отключение обновления изображения
Application.ScreenUpdating = False
‘ Создание книги с одним листом
Workbooks.Add xlWorksheet
Set rgRange = ActiveWorkbook.Sheets(1).Range(«A1»)
‘ Чтение первой строки из файла (по этой строке определяется _
ширина таблицы)
Open ThisWorkbook.Path & «Primer.txt» For Input As #1
Line Input #1, strLine
‘ Обработка первой строки с добавлением новых листов по мере _
необходимости
For i = 1 To Len(strLine)
strCurChar = Mid(strLine, i, 1)
‘ Проверка — закончились столбцы или нет
If intCol <> 0 And intCol Mod 256 = 0 Then
‘ Столбцы текущего листа закончились — добавим новый лист _
и перейдем к его первому столбцу
Set wshtCurrentSheet = ActiveWorkbook.Sheets.Add(, _
ActiveWorkbook.Sheets(ActiveWorkbook.Sheets.Count))
Set rgRange = wshtCurrentSheet.Range(«A1»)
intCol = 0
End If
‘ Проверка — закончилось поле или нет
If strCurChar = «,» Then
‘ Запишем данные в таблицу
rgRange.Offset(lngRow, intCol) = strCellValue
intCol = intCol + 1
strCellValue = «»
Else
‘ Добавляем очередной символ в строку со значением текущей _
ячейки
strCellValue = strCellValue & Mid(strLine, i, 1)
‘ Проверка — конец строки или нет
If i = Len(strLine) Then
‘ Дошли до конца строки — запишем значение последней ячейки
rgRange.Offset(lngRow, intCol) = strCellValue
intCol = 0
strCellValue = «»
End If
End If
Next i
‘ Чтение остальных строк файла
Do Until EOF(1)
Set rgRange = ActiveWorkbook.Sheets(1).Range(«A1»)
lngRow = lngRow + 1
intCol = 0
Line Input #1, strLine
‘ Обработка считанной строки
For i = 1 To Len(strLine)
strCurChar = Mid(strLine, i, 1)
‘ Проверка — закончились столбцы или нет
If intCol <> 0 And intCol Mod 256 = 0 Then
‘ Столбцы текущего листа закончились — добавим новый лист _
и перейдем к его первому столбцу
Set wshtCurrentSheet = ActiveWorkbook.Sheets.Add(, _
ActiveWorkbook.Sheets(ActiveWorkbook.Sheets.Count))
Set rgRange = wshtCurrentSheet.Range(«A1»)
intCol = 0
End If
‘ Проверка — закончилось поле или нет
If strCurChar = «,» Then
‘ Запишем данные в таблицу
rgRange.Offset(lngRow, intCol) = strCellValue
intCol = intCol + 1
strCellValue = «»
Else
‘ Добавляем очередной символ в строку со значением текущей _
ячейки
strCellValue = strCellValue & Mid(strLine, i, 1)
‘ Проверка — конец строки или нет
If i = Len(strLine) Then
‘ Дошли до конца строки — запишем значение последней _
ячейки
rgRange.Offset(lngRow, intCol) = strCellValue
strCellValue = «»
End If
End If
Next i
Loop
‘ Не забываем закрыть входной файл
Close #1
‘ и разрешить обновление изображения
Application.ScreenUpdating = True
End Sub
Создание резервных копий ценных файлов
Этот макрос сохраняет текущую книгу в папку C:TEMP, добавляя к имени книги текущее время и дату.
Sub Backup_Active_Workbook()
Dim x As String
strPath = «c:TEMP»
On Error Resume Next
x = GetAttr(strPath) And 0
If Err = 0 Then ‘ если путь существует — сохраняем копию книги
strDate = Format(Now, «dd/mm/yy hh-mm»)
FileNameXls = strPath & «» & Left(ActiveWorkbook.Name, _
Len(ActiveWorkbook.Name) — 4) & » » & strDate & «.xls»
ActiveWorkbook.SaveCopyAs Filename:=FileNameXls
Else ‘если путь не существует — выводим сообщение
MsgBox «Папка » & strPath & » недоступна или не существует!», vbCritical
End If
End Sub
При желании можно заменить первую строку на:
Private Sub Workbook_BeforeClose(Cancel As Boolean)
и поместить этот макрос не в Module1 как обычно, а в модуль ЭтаКнига (ThisWorkbook) — тогда автоматическое сохранение резервной копии будет происходить каждый раз перед закрытием файла.
Подсчет количества открытий файла
Количество открытий файла (вариант 1)
Sub Auto_Open()
Worksheets(1).Cells(1) = Worksheets(1).Cells(1) + 1
End Sub
Количество открытий файла (вариант 2)
Sub Auto_Open()
Worksheets(1).Cells(1, 1) = Worksheets(1).Cells(1, 1) + 1
End Sub
Количество открытий файла (вариант 3)
Sub Auto_Open()
Worksheets(1).Range(«A1») = Worksheets(1).Range(«A1») + 1
End Sub
Вывод пути к файлу в активную ячейку
Sub ExcelSearch()
Dim fname As String
Dim result As Integer
With Application.FileDialog(1) ‘ ?????? : With Application.FileDialog(msoFileDialogOpen) ‘
.Title = «Select Excel file»
.InitialFileName = «C:» ‘default path’
.AllowMultiSelect = False
.Filters.Clear
.Filters.Add «Pack files», «*.xls», 1
result = .Show
If result = 0 Then Exit Sub
fname = Trim(.SelectedItems.Item(1))
End With
‘On Error Resume Next
ActiveCell = fname
End Sub
Копирование содержимого файла RTF в эксель
Sub OpenRtfAndPasteToSheets()
Dim wd As Object
Dim ns As Worksheet
On Error Resume Next
‘запустим Ворд
Set wd = GetObject(«», «Word.Application»)
If Err.Number <> 0 Then
Err.Clear
Set wd = CreateObject(«Word.Application»)
If Err.Number <> 0 Then Exit Sub
End If
On Error GoTo BAD
Do
‘получим имя очередного файла
f = Application.GetOpenFilename(«Файлы RTF, *.rtf,Все файлы, *.*»)
If TypeName(f) = «Boolean» Then Exit Do ‘если Отмена — выход
‘откроем выбранный очередной файл
Set wdd = wd.Documents.Open(f)
‘ wd.Visible = True
‘скопируем содержимое документа
t = wdd.Content.Copy
‘создадим лист для этого документа
Set ns = ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets.Add
‘вставим скопированное в новый лист
ns.Paste Destination:=ns.Cells(1, 1)
‘немного выравним вид
ns.Cells.WrapText = False
ns.Columns.AutoFit
ns.Rows.AutoFit
wdd.Close
Loop
wd.Quit
Set wd = Nothing
Exit Sub
BAD:
MsgBox Err.Desсriрtion
On Error Resume Next
wd.Quit
Set wd = Nothing
End
End Sub
Копирование данных из закрытой книги
ActiveCell.FormulaR1C1 = «=’D:contactszakaz[zakaz.xls]Лист1′!R1C1»
Извлечение данных из закрытого файла
Sub GetDataFromFile()
Range(«A1»).Formula = «=’C:[Example.xls]Лист1′!A1»
End Sub
Поиск слова в файлах
Option Explicit
Sub Поиск_во_всех_файлах()
Dim iShtName$, iPath$, iFileName$, firstAddress$
Dim iSheet As Worksheet, iFoundSht As Worksheet
Dim iTempWB As Workbook, iBazaWB As Workbook
Dim TextToFind As Variant, iFoundRng As Range
Dim FD As FileDialog, iLastRow&
Dim FoundAny As Boolean
TextToFind = Application.InputBox(«Введите текст для поиска:», «Поиск»)
If TextToFind = «» Or TextToFind = False Then Exit Sub
TextToFind = Trim(TextToFind)
Set FD = Application.FileDialog(msoFileDialogFilePicker)
With FD
.AllowMultiSelect = False
.Title = «Укажите любой файл в папке»
.ButtonName = «Выбрать папку»
If .Show = False Then Exit Sub Else iPath = Mid(.SelectedItems(1), 1, InStrRev(.SelectedItems(1), «»))
End With
Set FD = Nothing
Workbooks.Add
Sheets.Add.Name = «Поиск»
Set iFoundSht = ActiveSheet
iFoundSht.Cells(1, 1) = «Ищем: » & TextToFind
iFoundSht.Cells(1, 1).Font.Bold = True
With Application
.ScreenUpdating = False
.Calculation = xlManual
.StatusBar = «Идёт поиск…»
.ShowWindowsInTaskbar = False
iFileName = Dir(iPath & «*.xls»)
Do While iFileName$ <> «»
Set iTempWB = Workbooks.Open(Filename:=iPath & iFileName, updаtеLinks:=False, ReadOnly:=True)
For Each iSheet In iTempWB.Sheets
If iSheet.FilterMode = True Then iSheet.ShowAllData
Set iFoundRng = iSheet.Cells.Find(What:=TextToFind, LookIn:=xlFormulas, LookAt:=xlPart)
If Not iFoundRng Is Nothing Then
FoundAny = True
firstAddress = iFoundRng.Address
Do
With iFoundSht
iLastRow = .Cells(.Rows.Count, 1).End(xlUp).Row
If iLastRow = 1 Then iLastRow = 2
If iShtName <> iSheet.Name Then ‘если новый файл
With .Cells(iLastRow + 2, 1)
.Value = «Файл: » & iTempWB.Name & «, Лист: » & iSheet.Name
.Font.Bold = True
End With
End If
iFoundRng.EntireRow.Copy Destination:=.Cells(.Cells(.Rows.Count, 1).End(xlUp).Row + 1, 1) ‘копируем всю строку
iShtName = iSheet.Name
End With
Set iFoundRng = iSheet.Cells.FindNext(iFoundRng)
Loop While iFoundRng.Address <> firstAddress
Else
End If
Next
iTempWB.Close SaveChanges:=False
iFileName = Dir
Loop
.StatusBar = False
.ShowWindowsInTaskbar = True
.EnableEvents = True
.Calculation = xlCalculationAutomatic
.ScreenUpdating = True
End With
If FoundAny = False Then
MsgBox «Текст ‘» & TextToFind & «‘ ни в одном из файлов в папке:» & Chr(10) & iPath & Chr(10) & » не был найден!», 48, «Отчёт»
iFoundSht.Parent.Close SaveChanges:=False
Exit Sub
End If
MsgBox «Поиск » & TextToFind & » завершён!», 64, «Поиск»
End Sub
Создание текстового файла и ввод текста в файл
Sub Test()
Open «c:2.txt» For Output As #1
Print #1, «Hello File»
Close #1
Open «c:1.txt» For Input As #1
Dim s As String
Input #1, s
MsgBox s
Close #1
End Sub
Создание текстового файла и ввод текста (определение конца файла)
Sub Test()
Open «c:1.txt» For Output As #1
Print #1, «Hello , File»
Close #1
Open «c:1.txt» For Input As #1
Dim s As String
While Not EOF(1)
Input #1, s
MsgBox s
Wend
Close #1
End Sub
Создание документов Word на основе таблицы Excel
Sub ReportToWord()
Dim intReportCount As Integer ‘ Количество сообщений
Dim strForWho As String ‘ Получатель сообщения
Dim strSum As String ‘ Сумма за товар
Dim strProduct As String ‘ Название товара
Dim strOutFileName As String ‘ Имя файла для сохранения сообщения
Dim strMessage As String ‘ Текст дополнительного сообщения
Dim rgData As Range ‘ Обрабатываемые ячейки
Dim objWord As Object
Dim i As Integer
‘ Создание объекта Word
Set objWord = CreateObject(«Word.Application»)
‘ Информация с рабочего листа
Set rgData = Range(«A1»)
strMessage = Range(«E6»)
‘ Просмотр записей на листе Лист1
intReportCount = Application.CountA(Range(«A:A»))
For i = 1 To intReportCount
‘ Динамические сообщения в строке состояния
Application.StatusBar = «Создание сообщения » & i
‘ Назначение данных переменным
strForWho = rgData.Cells(i, 1).Value
strProduct = rgData.Cells(i, 2).Value
strSum = Format(rgData.Cells(i, 3).Value, «#,000»)
‘ Имя файла для сохранения отчета
strOutFileName = ThisWorkbook.path & «» & strForWho & «.doc»
‘ Передача команд в Word
With objWord
.Documents.Add
With .Selection
‘ Заголовок сообщения
.Font.Size = 14
.Font.Bold = True
.ParagraphFormat.Alignment = 1
.TypeText Text:=»О Т Ч Е Т»
‘ Дата
.TypeParagraph
.TypeParagraph
.Font.Size = 12
.ParagraphFormat.Alignment = 0
.Font.Bold = False
.TypeText Text:=»Дата:» & vbTab & _
Format(Date, «mmmm d, yyyy»)
‘ Получатель сообщения
.TypeParagraph
.TypeText Text:=»Кому: менеджеру » & vbTab & strForWho
‘ Отправитель
.TypeParagraph
.TypeText Text:=»От:» & vbTab & Application.UserName
‘ Сообщение
.TypeParagraph
.TypeParagraph
.TypeText strMessage
.TypeParagraph
.TypeParagraph
‘ Название товара
.TypeText Text:=»Продано товара:» & vbTab & strProduct
.TypeParagraph
‘ Сумма за товар
.TypeText Text:=»На сумму:» & vbTab & _
Format(strSum, «$#,##0»)
End With
‘ Сохранение документа
.ActiveDocument.SaveAs FileName:=strOutFileName
End With
Next i
‘ Удаление объекта Word
objWord.Quit
Set objWord = Nothing
‘ Обновление строки состояния
Application.StatusBar = False
‘ Вывод на экран информационного сообщения
MsgBox intReportCount & » заметки создано и сохранено в папке » _
& ThisWorkbook.path
End Sub
Команды создания и удаления каталогов
Sub Test()
MkDir («c:test»)
End Sub
И удаляем.
Sub Test()
RmDir («c:test»)
End Sub
Получение текущего каталога
Sub Test()
MsgBox (CurDir)
End Sub
Смена каталога
Sub Test()
ChDir («c:windows»)
MsgBox (CurDir)
End Sub
Посмотреть все файлы в каталоге_1
Sub Test()
Dim s As String
s = Dir(«c:windowsinf*.*»)
Debug.Print s
Do While s <> «»
s = Dir
Debug.Print s
Loop
End Sub
Посмотреть все файлы в каталоге_2
‘ Объявление API-функции для отображения стандартного окна _
просмотра папок
Declare Function SHBrowseForFolder Lib «shell32.dll» _
Alias «SHBrowseForFolderA» (lpBrowseInfo As BROWSEINFO) As ****
‘ Объявление API-функции для преобразования данных, возвращаемых _
функцией SHBrowseForFolder, в строку
Declare Function SHGetPathFromIDList Lib «shell32.dll» _
Alias «SHGetPathFromIDListA» (ByVal pidl As ****, ByVal _
pszPath As String) As ****
‘ Структура используется функцией SHBrowseForFolder
Type BROWSEINFO
hwndOwner As **** ‘ Родительское окно (для диалога)
pidlRoot As **** ‘ Корневая папка для просмотра
strDisplayName As String
strTitle As String ‘ Заголовок окна
ulFlags As **** ‘ Флаги для окна
‘ Следующие три параметра в VBA не используются
lpfn As ****
lParam As ****
iImage As ****
End Type
Sub BrowseFolder()
Dim strPath As String ‘ Папка, список файлов которой выводится
Dim strFile As String
Dim intRow As **** ‘ Текущая строка таблицы
‘ Выбор папки
strPath = dhBrowseForFolder()
If strPath = «» Then Exit Sub
If Right(strPath, 1) <> «» Then strPath = strPath & «»
‘ Оформление заголовка отчета
ActiveSheet.Cells.ClearContents
ActiveSheet.Cells(1, 1) = «Имя файла»
ActiveSheet.Cells(1, 2) = «Размер»
ActiveSheet.Cells(1, 3) = «Дата/время»
ActiveSheet.Range(«A1:C1»).Font.Bold = True
‘ Просмотр объектов в папке…
‘ Первый объект папки
strFile = Dir(strPath, 7)
intRow = 2
Do While strFile <> «»
‘ Запись в столбец «A» имени файла
ActiveSheet.Cells(intRow, 1) = strFile
‘ Запись в столбец «B» размера файла
ActiveSheet.Cells(intRow, 2) = FileLen(strPath & strFile)
‘ Запись в столбец «C» времени изменения файла
ActiveSheet.Cells(intRow, 3) = FileDateTime(strPath & strFile)
‘ Следующий объект папки
strFile = Dir
intRow = intRow + 1
Loop
End Sub
Function dhBrowseForFolder() As String
Dim biBrowse As BROWSEINFO
Dim strPath As String
Dim lngResult As ****
Dim intLen As Integer
‘ Заполнение полей структуры BROWSEINFO
‘ Корневая папка — Рабочий стол
biBrowse.pidlRoot = 0&
‘ Заголовок окна
biBrowse.strTitle = «Выбор папки»
‘ Тип возвращаемой папки
biBrowse.ulFlags = &H1
‘ Вывод стандартного окна просмотра папок
lngResult = SHBrowseForFolder(biBrowse)
‘ Обработка результата работы окна
If lngResult Then
‘ Получение пути (по возвращенным данным)
strPath = Space$(512)
If SHGetPathFromIDList(ByVal lngResult, ByVal strPath) Then
‘ Строка пути заканчивается символом Chr(0)
intLen = InStr(strPath, Chr$(0))
‘ Выделение и возврат пути
dhBrowseForFolder = Left(strPath, intLen — 1)
Else
‘ Не удалось получить путь
dhBrowseForFolder = «»
End If
Else
‘ Пользователь нажал кнопку «Отмена»
dhBrowseForFolder = «»
End If
End Function
Посмотреть все файлы в каталоге_3
‘ Объявление API-функции для отображения стандартного окна _
просмотра папок
Declare Function SHBrowseForFolder Lib «shell32.dll» _
Alias «SHBrowseForFolderA» (lpBrowseInfo As BROWSEINFO) As ****
‘ Объявление API-функции для преобразования данных, возвращаемых _
функцией SHBrowseForFolder, в строку
Declare Function SHGetPathFromIDList Lib «shell32.dll» _
Alias «SHGetPathFromIDListA» (ByVal pidl As ****, ByVal _
pszPath As String) As ****
‘ Структура используется функцией SHBrowseForFolder
Type BROWSEINFO
hwndOwner As **** ‘ Родительское окно (для диалога)
pidlRoot As **** ‘ Корневая папка для просмотра
strDisplayName As String
strTitle As String ‘ Заголовок окна
ulFlags As **** ‘ Флаги для окна
‘ Следующие три параметра в VBA не используются
lpfn As ****
lParam As ****
iImage As ****
End Type
Sub BrowseFolder1()
Dim strPath As String ‘ Папка, список файлов которой выводится
Dim strFile As String
Dim intRow As **** ‘ Текущая строка таблицы
‘ Выбор папки
strPath = dhBrowseForFolder()
If strPath = «» Then Exit Sub
If Right(strPath, 1) <> «» Then strPath = strPath & «»
‘ Оформление заголовка отчета
ActiveSheet.Cells.ClearContents
ActiveSheet.Cells(1, 1) = «Имя файла»
ActiveSheet.Cells(1, 2) = «Размер»
ActiveSheet.Cells(1, 3) = «Дата/время»
ActiveSheet.Range(«A1:C1»).Font.Bold = True
‘ Просмотр объектов в папке…
‘ Первый объект папки
strFile = Dir(strPath, 7)
intRow = 2
Do While strFile <> «»
‘ Запись в столбец «A» имени файла
ActiveSheet.Cells(intRow, 1) = strPath & strFile
‘ Запись в столбец «B» размера файла
ActiveSheet.Cells(intRow, 2) = FileLen(strPath & strFile)
‘ Запись в столбец «C» времени изменения файла
ActiveSheet.Cells(intRow, 3) = FileDateTime(strPath & strFile)
‘ Следующий объект папки
strFile = Dir
intRow = intRow + 1
Loop
End Sub
Function dhBrowseForFolder() As String
Dim biBrowse As BROWSEINFO
Dim strPath As String
Dim lngResult As ****
Dim intLen As Integer
‘ Заполнение полей структуры BROWSEINFO
‘ Корневая папка — Рабочий стол
biBrowse.pidlRoot = 0&
‘ Заголовок окна
biBrowse.strTitle = «Выбор папки»
‘ Тип возвращаемой папки
biBrowse.ulFlags = &H1
‘ Выводим стандартное окно просмотра папок
lngResult = SHBrowseForFolder(biBrowse)
‘ Обработка результата работы окна
If lngResult Then
‘ Получение пути (по возвращенным данным)
strPath = Space$(512)
If SHGetPathFromIDList(ByVal lngResult, ByVal strPath) Then
‘ Строка пути заканчивается символом Chr(0)
intLen = InStr(strPath, Chr$(0))
‘ Выделение и возврат пути
dhBrowseForFolder = Left(strPath, intLen — 1)
Else
‘ Не удалось получить путь
dhBrowseForFolder = «»
End If
Else
‘ Пользователь нажал кнопку «Отмена» в окне
dhBrowseForFolder = «»
End If
End Function
ГЛАВА 3. РАБОЧАЯ ОБЛАСТЬ MICROSOFT EXCEL
Рабочая книга
Количество имен рабочей книги
Sub CountNames()
Dim intNamesCount As Integer
‘ Получаем и отображаем количество имен на активном _
листе рабочей книги
intNamesCount = Names.Count
If intNamesCount = 0 Then
MsgBox «Имен нет»
Else
MsgBox «Имен: » & intNamesCount & » шт.»
End If
End Sub
Защита рабочей книги
Sub Worksheet_BeforeRightClick(ByVal Target As Range, _
Cancel As Boolean)
If Target.Address = «$D$2» Then
‘ Установка защиты рабочей книги (с паролем «123», _
включенной защитой структуры книги и защитой расположения _
окон)
ThisWorkbook.Protect «123», True, True
‘ Указание не обрабатывать нажатие кнопки мыши _
в этой ячейке
Cancel = True
ElseIf Target.Address = «$E$5» Then
‘ Снятие защиты с книги (необходимо указать ранее установленный _
пароль)
ThisWorkbook.Unprotect «123»
Cancel = True
End If
End Sub
Запрет печати книги
Sub Workbook_BeforePrint(Cancel As Boolean)
‘ Установка флага в True заставляет Exсel игнорировать команду _
отправки книги на печать
Cancel = True
End Sub
Открытие книги (или текстовых файлов)
Sub Test()
Application.Workbooks.Open («c:file_03.txt»)
End Sub
Открытие книги и добавление в ячейку А1 текста
Dim Ex As New Excel.Application
Ex.Workbooks.Open «Путь к Файлу»
Ex.Visible = False
‘В ячейку «A2» добавляем «Visual Basic»
Ex.ActiveWorkbook.Sheets.Application.Range(«A2») = «Visual Basic»
Ex.ActiveWorkbook.Save
Ex.ActiveWorkbook.Close
Сколько книг открыто
Sub Test()
MsgBox (Str(Application.Workbooks.Count))
End Sub
Закрытие всех книг
Sub Test()
Application.Workbooks.Item(1).Close ‘(еxprеssion.Close(SaveChanges, FileName, RouteWorkbook)
End Sub
Закрытие рабочей книги только при выполнении условия
Sub Workbook_BeforeClose(Cancel As Boolean)
If Range(«A1»).Value <> «Можно закрывать» Then
‘ Условие закрытия не выполнено. Укажем Exсel игнорировать _
команду
Cancel = True
End If
End Sub
Сохранение рабочей книги с именем, представляющим собой текущую дату
Sub SaveAsDate()
Dim strDate As String
‘ Получение текущей даты и представление ее в формате «ддммгг»
strDate = Format(Now(), «ddmmyy»)
‘ Сохранение книги в текущую папку под новым именем
ActiveWorkbook.SaveAs ActiveWorkbook.Path & «» & strDate
End Sub
Сохранена ли рабочая книга
Function dhBookIsSaved() As Boolean
‘ Если путь файла рабочей книги не задан, то она _
не сохранена (ThisWorkbook.path равняется «»)
dhBookIsSaved = ThisWorkbook.path <> «»
End Function
Создать книгу с одним листом
Sub NewOneSheetBook()
Workbooks.Add xlWBATWorksheet
End Sub
Создать книгу
Sub Test()
Application.Workbooks.Add («Êíèãà»)
End Sub
Удаление ненужных имен
Sub EraseNames()
Dim nmName As Name
Dim strMessage As String
‘ Проверка наличия в книге определенных имен
If ThisWorkbook.Names.Count = 0 Then
‘ В книге нет определенных имен
MsgBox «Имена не определены»
Exit Sub
End If
‘ Просмотр всей коллекции определенных имен и удаление тех, _
которые пользователю не нужны
For Each nmName In ThisWorkbook.Names
With nmName
‘ Спрашиваем пользователя о необходимости удалить _
найденное имя
strMessage = «Удалить имя » & .Name & » ? » & vbCr & _
«относящееся к » & .RefersTo
If MsgBox(strMessage, vbYesNo + vbQuestion) = vbYes Then
‘ Имя можно удалить
.Delete
End If
End With
Next
End Sub
Быстрое размножение рабочей книги
Sub DuplicateBook()
Dim avarFileNames As Variant
‘ Формирование массива из путей для копий книги
avarFileNames = Array(«C:» & _
ActiveWorkbook.Name, «D:» & ActiveWorkbook.Name)
‘ Сохранение книги
ActiveWorkbook.SaveAs avarFileNames
End Sub
Сортировка листов
Sub SortSheets()
Dim astrSheetNames() As String ‘ Массив для хранения имен листов
Dim intSheetCount As Integer
Dim i As Integer
Dim objActiveSheet As Object
‘ Если нет активной рабочей книги — закрыть процедуру
If ActiveWorkbook Is Nothing Then Exit Sub
‘ Проверка защищенности структуры рабочей книги
If ActiveWorkbook.ProtectStructure Then
‘ Сортировка листов защищенной рабочей книги невозможна
MsgBox «Структура книги » & ActiveWorkbook.Name & _
» защищена. Сортировка листов невозможна.», _
vbCritical
Exit Sub
End If
‘ Сохраняем ссылку на активный лист книги
Set objActiveSheet = ActiveSheet
‘ Отключение сочетания клавиш Ctrl+Pause Break
Application.EnableCancelKey = xlDisabled
‘ Отключение обновления экрана
Application.ScreenUpdating = False
intSheetCount = ActiveWorkbook.Sheets.Count
‘ Заполнение массива astrSheetNames именами листов книги
ReDim astrSheetNames(1 To intSheetCount)
For i = 1 To intSheetCount
astrSheetNames(i) = ActiveWorkbook.Sheets(i).Name
Next i
‘ Сортировка массива имен в порядке возрастания
Call Sort(astrSheetNames)
‘ Перемещение листов книги
For i = 1 To intSheetCount
ActiveWorkbook.Sheets(astrSheetNames(i)).Move _
ActiveWorkbook.Sheets(i)
Next i
‘ Переход на исходный рабочий лист
objActiveSheet.Activate
‘ Включение обновления экрана
Application.ScreenUpdating = True
‘ Включение сочетания клавиш Ctrl+Pause Break
Application.EnableCancelKey = xlInterrupt
End Sub
Sub Sort(astrNames() As String)
‘ Сортировка массива строк по алфавиту (в порядке возрастания)
Dim i As Integer, j As Integer
Dim strBuffer As String
Dim fBuffer As Boolean
For i = LBound(astrNames) To UBound(astrNames) — 1
For j = i + 1 To UBound(astrNames)
If astrNames(i) > astrNames(j) Then
‘ Меняем i-й и j-й элементы массива местами
strBuffer = astrNames(i)
astrNames(i) = astrNames(j)
astrNames(j) = strBuffer
End If
Next j
Next i
End Sub
Поиск максимального значения на всех листах книги
Function dhMaxInBook(cell As Range) As Double
Dim sheet As Worksheet
Dim dblMax As Double
Dim dblResult As Double
Dim fFirst As Boolean
fFirst = True
‘ Расчет максимальных значений на всех листах рабочей книги _
и выбор наибольшего из них
For Each sheet In cell.Parent.Parent.Worksheets
‘ Расчет максимального значения на листе
dblResult = Application.WorksheetFunction.Max(sheet.UsedRange)
If fFirst Then
‘ Найдено первое значение — его не с чем сравнивать
dblMax = dblResult
fFirst = False
End If
‘ Выбираем большее из dblMax и dbmResult
If dblResult > dblMax Then
dblMax = dblResult
End If
Next sheet
‘ Возврат результата
dhMaxInBook = dblMax
End Function
РАБОЧИЙ ЛИСТ
Проверка наличия защиты рабочего листа
Sub IsSheetProtected()
‘ Проверка, установлена ли защита на содержимое листа
If Worksheets(1).ProtectContents Then
MsgBox «Защита листа включена»
Else
MsgBox «Защита листа не включена»
End If
End Sub
Список отсортированных листов
Sub SortSheets2()
Dim astrSheetNames() As String ‘ Массив для хранения имен листов
Dim intSheetCount As Integer
Dim i As Integer
Dim objActiveSheet As Object
‘ Если нет активной рабочей книги — закрыть процедуру
If ActiveWorkbook Is Nothing Then Exit Sub
‘ Проверка защищенности структуры рабочей книги
If ActiveWorkbook.ProtectStructure Then
‘ Сортировка листов защищенной рабочей книги невозможна
MsgBox «Структура книги » & ActiveWorkbook.Name & _
» защищена. Сортировка листов невозможна.», _
vbCritical
Exit Sub
End If
‘ Сохраняем ссылку на активный лист книги
Set objActiveSheet = ActiveSheet
‘ Отключение сочетания клавиш Ctrl+Pause Break
Application.EnableCancelKey = xlDisabled
‘ Функция обновления экрана отключается
Application.ScreenUpdating = False
With ActiveWorkbook
‘ Cоздаем новый лист «Сортировка» (если он еще не создан)
On Error Resume Next
If .Sheets(«Сортировка») Is Nothing Then
.Sheets.Add.Name = «Сортировка»
End If
On Error GoTo 0
‘ Размещение данных на листе «Сортировка» (в столбец «A»)
intSheetCount = .Sheets.Count
For i = 1 To intSheetCount
.Sheets(«Сортировка»).Cells(i, 1) = .Sheets(i).Name
Next i
‘ Сортировка данных в ячейках листа «Сортировка» по содержимому _
столбца A
.Sheets(«Сортировка»).Range(«A1»).Sort _
Key1:=.Sheets(«Сортировка»).Range(«A1»), _
Order1:=xlAscending
‘ Заполнение массива имен отсортированными строками
ReDim astrSheetNames(1 To intSheetCount)
For i = 1 To intSheetCount
astrSheetNames(i) = .Sheets(«Сортировка»).Cells(i, 1)
Next i
‘ Перемещение листов
For i = 1 To intSheetCount
.Sheets(astrSheetNames(i)).Move .Sheets(i)
Next i
End With
‘ Переход на исходный рабочий лист
objActiveSheet.Activate
‘ Включаем обновление экрана
Application.ScreenUpdating = True
‘ Включение сочетания клавиш Ctrl+Pause Break
Application.EnableCancelKey = xlInterrupt
End Sub
Создать новый лист_1
Sub NewSheet()
Worksheets.Add
End Sub
‘Sub Tes2t()
‘With Application.Workbooks.Item(ActiveWorkbook.Name)
‘Sheets.Add
‘End With
‘End Sub
‘Dim ExNew As Worksheet
‘Set ExNew = ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets.Add
‘ExNew.Name = «Имя Листа»
Создать новый лист_2
Worksheets.Add.Name = «List12345.xls»
Удаление листов в зависимости от даты
‘ Function DelSheetByDate
‘ Удаляет рабочий лист sSheetName в активной рабочей книге,
‘ если дата dDelDate уже наступила
‘ В случае успеха возвращает True, иначе — False
Public Function DelSheetByDate(sSheetName As String, _
dDelDate As Date) As Boolean
On Error GoTo errHandle
DelSheetByDate = False
‘ Проверка даты
If dDelDate <= Date Then
‘ Не выводить подтверждение на удаление
Application.DisplayAlerts = False
ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets(sSheetName).Delete
DelSheetByDate = True
Application.DisplayAlerts = True
End If
Exit Function
errHandle:
MsgBox Err.Desсriрtion, vbCritical, «Ошибка №» & Err.Number
End Function
Копирование листа в книге
Sub Test()
With Application.Workbooks.Item(«Test.xls»)
Sheets(«Test»).Copy , after:=Sheets(«Лист3»)
End With
End Sub
Копирование листа в новую книгу (создается)
Sub Test()
With Application.Workbooks.Item(«Test.xls»)
Sheets(«Test»).Copy
End With
End Sub
Перемещение листа в книге
Sub Test()
With Application.Workbooks.Item(«Test.xls»)
Sheets(«Test»).Move , after:=Sheets(«Лист3»)
End With
End Sub
Перемещение нескольких листов в новую книгу
Sheets(Array(«Лист1», «Лист2», «Лист3»)).Select
Sheets(«Лист3»).Activate
Sheets(Array(«Лист1», «Лист2», «Лист3»)).Copy
Заменить существующий файл
Sub copy_sheet()
ShName = ActiveSheet.Name
Sheets(ShName).Copy
ActiveWorkbook.SaveAs «c:» & ShName & «.xls»
End Sub
Чтобы не вылезало диалоговое окно надо добавить
Application.DisplayAlerts = False ‘ вылючаем все предупреждения
ActiveWorkbook.SaveAs «c:» & ShName & «.xls»
Application.DisplayAlerts = True ‘обратно включаем предупреждения.
«Перелистывание» книги
Sub SheetsOfBook()
Dim sheet As Object
‘ Отображение имен всех листов активной рабочей книги
For Each sheet In ActiveWorkbook.Sheets
MsgBox (sheet.Name)
Next
End Sub
Вставка колонтитула с именем книги, листа и текущей датой
Sub AddPageHeader()
Dim i As Integer
With ThisWorkbook
‘ Вставка колонтитулов на все листы рабочей книги
For i = 1 To .Worksheets.Count — 1
.Worksheets(i).PageSetup.LeftHeader = .FullName
.Worksheets(i).PageSetup.CenterHeader = Worksheets(i).Name
.Worksheets(i).PageSetup.RightHeader = Now()
Next
End With
End Sub
Существует ли лист
Function dhSheetExist(strSheetName As String) As Boolean
Dim objSheet As Object
On Error GoTo HandleError ‘ При ошибке перейти на HandleError
‘ Пытаемся получить ссылку на заданный лист
objSheet = ActiveWorkbook.Sheets(strSheetName)
‘ Ошибки не возникло — лист существует
dhSheetExist = True
Exit Function
HandleError:
‘ При попытке получить доступ к листу с заданным именем _
возникла ошибка, значит, такого листа не существует
dhSheetExist = False
End Function
Существует ли лист_2
L = 0
For Each Sheet In Worksheets
If Sheet.Name = «List12» Then
L = 1
MsgBox «List12 совпадает с расчетным листом. Переименуйте свой List12 на какое нибудь другое имя!»
End If
Next
If L = 0 Then
Worksheets.Add.Name = «List12»
Worksheets(1).Visible = True
Worksheets(«List12»).Visible = True
Worksheets(«List12»).Activate
End If
Вывод количества листов в активной книге
Sub Test()
MsgBox (Str(Application.Workbooks.Item(ActiveWorkbook.Name).Sheets.Count))
End Sub
Вывод количества листов в активной книге в виде гиперссылок
Sub SheetNamesAsHyperLinks()
Dim sheet As Worksheet
Dim cell As Range
With ActiveWorkbook
‘ Просмотр всех листов книги и создание гиперссылок на них _
на первом листе
For Each sheet In ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets
Set cell = Worksheets(1).Cells(sheet.Index, 1)
.Worksheets(1).Hyperlinks.Add Anchor:=cell, Address:=»», _
SubAddress:=»‘» & sheet.Name & «‘» & «!A1»
cell.Formula = sheet.Name
Next
End With
End Sub
Вывод имен активных листов по очереди
Sub Test()
With Application.Workbooks.Item(ActiveWorkbook.Name)
For x = 1 To .Sheets.Count
MsgBox (Sheets.Item(x).Name)
Next x
End With
End Sub
Вывод имени и номеров листов текущей книги
Sub ShowInfo()
Dim i As Integer
‘ Выводим имя файла рабочей книги
Range(«A1») = ActiveWorkbook.Name
‘ Выводим имя текущего листа
Range(«B1») = ActiveSheet.Name
‘ Выводим номера листов
For i = 1 To ActiveWorkbook.Sheets.Count
ActiveSheet.Cells(i, 3) = i
Next i
End Sub
Сделать лист невидимым
Sub Test()
With Application.Workbooks.Item(«Test.xls»)
.Sheets.Item(«Лист5»).Visible = False
End With
End Sub
Сколько страниц на всех листах?
Sub GetPrintPagesCount()
Dim wshtSheet As Worksheet
Dim intPagesCount As Integer
‘ Суммирование количества страниц, необходимых для печати всех _
листов книги
For Each wshtSheet In Worksheets
intPagesCount = intPagesCount + (wshtSheet.HPageBreaks.Count + 1) * _
(wshtSheet.VPageBreaks.Count + 1)
Next
MsgBox «Всего страниц: » & intPagesCount
End Sub
Ячейка и диапазон (столбцы и строки)
Копирование строк на другой лист
Sub CopyRows2()
Dim iCells As Range
For Each iCells In Range(«A2:A5»)
Range(iCells, iCells.Offset(, 7)).Copy
Workbooks.Add
ActiveSheet.Paste
ActiveWorkbook.SaveAs Filename:=»C:Temp» & iCells & «.xls»
Next iCells
End Sub
Копирование столбцов на другой лист
On Error Resume Next
s = Names(«sourcefilename»).Value
On Error GoTo 0
If s = «» Then
sfile = «progcall234_56g»
Call get_file
s = sfile
Else
s = Mid(s, 3, Len(s) — 3)
End If
If s = «» Then Exit Sub
Workbooks.Open (s)
Dim snm As String
snm = ActiveWorkbook.Name
ncol = WorksheetFunction.CountA(Range(«1:1»)) ‘ Range(«a1»).SpecialCells(xlLastCell).Column
nrow = WorksheetFunction.CountA(Range(«a:a»)) ‘Range(«a1»).SpecialCells(xlLastCell).Row
Range(Cells(1, 1), Cells(nrow, ncol)).Copy
Workbooks(s1).Activate
Range(«a1»).Activate
ActiveSheet.Paste
Application.DisplayAlerts = False
Workbooks(snm).Close
Подсчет количества ячеек, содержащих указанные значения_1
Function dhCount(rgn As Range, LowBound As Double, _
UpperBound As Double) As ****
Dim cell As Range
Dim lngCount As ****
‘ Проходим по всем ячейкам диапазона rgn и подсчитываем значения, _
попадающие в интервал от LowBound до UpperBound
For Each cell In rgn
If cell.Value >= LowBound And cell.Value <= UpperBound Then
‘ Значение попадает в заданный интервал
lngCount = lngCount + 1
End If
Next
dhCount = lngCount
End Function
Подсчет количества ячеек в диапазоне, содержащих указанные значения_2
Function dhCountSomeCells(rgRange As Range, dblMin As Double, _
dblMax As Double) As ****
‘ Расчет количества ячеек со значениями от dblMin до dblMax _
с использованием стандартной функции CountIf
With Application.WorksheetFunction
dhCountSomeCells = .CountIf(rgRange, «>=» & dblMin) — _
.CountIf(rgRange, «>» & dblMax)
End With
End Function
Подсчет количества видимых ячеек в диапазоне
Function dhCountVisibleCells(rgRange As Range)
Dim lngCount As ****
Dim cell As Range
‘ Проходим по всему диапазону и подсчитываем непустые _
видимые ячейки
For Each cell In rgRange
‘ Проверка, есть ли данные в ячейке
If Not IsEmpty(cell) Then
‘ Проверка, видима ли ячейка
If Not cell.EntireRow.Hidden And Not _
cell.EntireColumn.Hidden Then
‘ Еще одна видимая ячейка
lngCount = lngCount + 1
End If
End If
Next cell
dhCountVisibleCells = lngCount
End Function
Определение количества ячеек в диапазоне и суммы их значений
Sub CalculateSum()
Dim i As Integer
Dim intSum As Integer
‘ Расчет суммы ячеек столбца «A» (с первой по пятую)
For i = 1 To 5
intSum = intSum + Cells(i, 1)
Next
MsgBox «Сумма ячеек: » & intSum
End Sub
Подсчет количества ячеек
Sub CountOfCells()
MsgBox (Range(«A1:A20, D1:D20»).Count)
End Sub
Автоматический пересчет данных таблицы при изменении ее значений
Sub Worksheet_Change(ByVal Target As Range)
Dim rgData As Range
Dim cell As Range
Dim dblMax As Double, dblMin As Double, dblAverage As Double
‘ Получение контролируемого диапазона ячеек
Set rgData = Range(«B2:B11»)
‘ Проверка, не входит ли измененная ячейка в контролируемый _
диапазон
If Not (Application.Intersect(Target, rgData) Is Nothing) Then
If Application.WorksheetFunction.CountA(rgData) > 0 Then
‘ Изменена ячейка из контролируемого диапазона
‘ Заново рассчитываем минимальное, максимальное и среднее _
значения в контролируемом диапазоне ячеек
dblMin = Application.WorksheetFunction.Min(rgData)
dblMax = Application.WorksheetFunction.Max(rgData)
dblAverage = Application.WorksheetFunction.Average(rgData)
‘ Проверяем каждую ячейку из контролируемого диапазона _
и изменяем цвет шрифта ячеек с минимальным и максимальным _
значениями, а также помечаем желтым цветом ячейки _
со значениями больше среднего
For Each cell In rgData
If cell.Value = dblMax Then
‘ Ячейку с максимальным значением выделим красным цветом
cell.Font.Bold = True
cell.Font.Color = RGB(255, 0, 0)
ElseIf cell.Value = dblMin Then
‘ Ячейку с минимальным значением выделим синим цветом
cell.Font.Bold = False
cell.Font.Color = RGB(0, 0, 255)
Else
cell.Font.Bold = False
cell.Font.Color = RGB(0, 0, 0)
End If
If cell.Value > dblAverage Then
‘ Значение в ячейке больше среднего — выделим ее _
желтым цветом
cell.Interior.Color = RGB(255, 255, 0)
Else
cell.Interior.ColorIndex = xlNone
End If
Next
Else
rgData.Interior.ColorIndex = xlNone
End If
End If
End Sub
Ввод данных в ячейки
Sub SetCellData()
‘ Заполнение значениями ячеек А3 и В4
Range(«A3») = «Данные для ячейки A3»
Range(«B4») = «Данные для ячейки B4»
End Sub
Ввод данных с использованием формул
Sub SetCellFormula()
‘ Запись в ячейку А6 формулы «=A5+B5»
Range(«A6») = «=A5+B5»
End Sub
Последовательный ввод данных
Sub StreamInput()
Dim strDate As String
Dim strSum As String
Dim lngRow As ****
‘ Ввод данных в цикле (повторяется до тех пор, пока пользователь _
не введет пустую строку или не нажмет «Отмена» в окне ввода)
Do
lngRow = Range(«A65536»).End(xlUp).Row + 1
‘ Ввод даты
strDate = InputBox(«Вводим дату»)
If strDate = «» Then Exit Sub
‘ Ввод выручки
strSum = InputBox(«Вводим выручку»)
If strSum = «» Then Exit Sub
‘ Запись данных в ячейки
Cells(lngRow, 1) = strDate
Cells(lngRow, 2) = strSum
Loop
End Sub
Ввод текстоввых данных в ячейки
Sub insеrtCustomText()
‘ Заполнение текущей ячейки
ActiveCell = «Генеральный директор»
Selection.Font.Bold = True
‘ Фамилия на три столбца правее должности
Cells(ActiveCell.Row, ActiveCell.Column + 3).Select
ActiveCell.FormulaR1C1 = «А. Б. Рублев»
Selection.Font.Bold = True
‘ Ячейка с «Главный бухгалтер» на три столбца левее _
и на три строки ниже ячейки с фамилией директора
Cells(ActiveCell.Row + 3, ActiveCell.Column — 3).Select
ActiveCell = «Главный бухгалтер»
Selection.Font.Bold = True
‘ Фамилия на три столбца правее должности
Cells(ActiveCell.Row, ActiveCell.Column + 3).Select
ActiveCell = «Т. С. Копейкин»
Selection.Font.Bold = True
End Sub
Вывод в ячейки названия книги, листа и количества листов
Sub Test()
Dim book As String
Dim sheet As String
Dim addr As String
addr = «C»
book = Application.ActiveWorkbook.Name
sheet = Application.ActiveSheet.Name
Workbooks(book).Activate
Worksheets(sheet).Activate
Range(«A1») = book
Range(«B1») = sheet
Dim xList As Integer
xList = Application.Sheets.Count
For x = 1 To xList
Dim s As String
s = addr + LTrim(Str(x))
Range(s) = x
Next x
End Sub
Удаление пустых строк_1
Selection.SpecialCells(xlCellTypeBlanks).Select
Selection.Delete Shift:=xlUp
Удаление пустых строк_2
Sub DeleteEmptyStrings()
Dim intLastRow As Integer ‘ Номер последней используемой строки
Dim intRow As Integer ‘ Номер проверяемой строки
‘ Получение номера последней используемой строки
intLastRow = Worksheets(ActiveSheet.Index).UsedRange.Row + _
Worksheets(ActiveSheet.Index).UsedRange.Rows.Count — 1
‘ Счетчик устанавливается на используемую первую строку
intRow = Worksheets(ActiveSheet.Index).UsedRange.Row
‘ Удаление пустых строк
Do While intRow <= intLastRow
If ActiveSheet.Rows(intRow).Text = «» Then
‘ Удаление строки
ActiveSheet.Rows(intRow).Delete
‘ Данные сдвинулись вверх, поэтому номер последней _
строки уменьшился, а текущей — не изменился
intLastRow = intLastRow — 1
Else
‘ Текущая строка заполнена — переходим к следующей
intRow = intRow + 1
End If
Loop
End Sub
Удаление пустых строк_3
Sub DeleteEmptyStrings1()
Dim intRow As Integer
Dim intLastRow As Integer
‘ Получение номера последней используемой строки
intLastRow = ActiveSheet.UsedRange.Row + _
ActiveSheet.UsedRange.Rows.Count — 1
‘ Удаление пустых строк
For intRow = intLastRow To 1 Step -1
If ActiveSheet.Rows(intRow).Text = «» Then
ActiveSheet.Rows(intRow).Delete
End If
Next intRow
End Sub
Удаление строки по условию
Sub Макрос1()
Dim iRange As Range
Dim TextToFindArray As Variant
Dim i As ****
TextToFindArray = Array(«Toyota», «ВАЗ»)
With Application
.ScreenUpdating = False
.Calculation = xlCalculationManual
For i = 0 To 1
With ActiveSheet.Cells
Set iRange = .Find(What:=TextToFindArray(i), LookIn:=xlFormulas, LookAt:=xlPart)
If Not iRange Is Nothing Then
Do
iRange.EntireRow.Delete
Set iRange = .Find(What:=TextToFindArray(i), LookIn:=xlFormulas, LookAt:=xlPart)
Loop While Not iRange Is Nothing
End If
End With
Next i
.Calculation = xlCalculationAutomatic
.ScreenUpdating = True
End With
MsgBox «Строки с текстом » & TextToFindArray(0) & » и » & TextToFindArray(1) & » удалены!», 64, «Конец»
End Sub
Удаление скрытых строк
Sub KillHiddenRows()
For Each x In ActiveSheet.Rows
If x.Hidden Then x.Delete
Next
End Sub
Удаление используемых скрытых строк или строк с нулевой высотой
Sub KillUsedHiddenThinRows()
Dim x
For Each x In ActiveSheet.UsedRange.Rows
If x.Hidden Or x.Height = 0 Then x.EntireRow.Delete
Next
End Sub
Удаление дубликатов по маске
Function Two2One(Text As String) As String
Dim Polki, i As Byte, tmp As String
Application.Volatile
Polki = Split(Text, «@»)
For i = 1 To UBound(Polki)
If InStr(1, Polki(i), «:») > 0 Then
If Polki(i) <> Polki(i — 1) Then tmp = tmp & «@» & Polki(i)
Else: tmp = tmp & «@» & Polki(i)
End If
Next
Two2One = Polki(0) & tmp
End Function
Выделение диапазона над текущей ячейкой
Sub SelectCellRange()
Dim strSelTop As String, strSelBottom As String
‘ Получение адресов нижней и верхней ячеек диапазона для выделения
strSelBottom = ActiveCell.Address
strSelTop = Cells(1, ActiveCell.Column).Address
‘ Выделяем все ячейки выше текущей (вместе с текущей ячейкой)
Range(strSelTop & «:» & strSelBottom).Select
End Sub
Выделение диапазона над текущей ячейкой_2
Sub SelectColumnData()
‘ что делать при ошибке
On Error GoTo errors
‘ нижний адрес
Dim a1 As String
‘ верхний адрес
Dim a2 As String
‘ диапазое
Dim ran As Range
‘ если не верхнея ячейка
If (ActiveCell.Row <> 1) Then
‘ пойти вверх
ActiveCell.Offset(-1, 0).Select
‘ взять адрес ячейки
a1 = ActiveCell.Address
‘ будем подниматься
For x = 1 To (ActiveCell.Row — 1)
‘ на одну вверх
ActiveCell.Offset(-1, 0).Select
‘ если не число выход
If IsNumeric(ActiveCell.Value) <> True Then
‘ на одну вниз
ActiveCell.Offset(1, 0).Select
‘ выход
GoTo nexts
End If
‘ если пустая
If IsEmpty(ActiveCell.Value) = True Then
‘ на одну вниз
ActiveCell.Offset(1, 0).Select
‘ выход
GoTo nexts
End If
Next x
nexts:
‘ получаем адрес вырехней
a2 = ActiveCell.Address
‘ строим диапазон
Set ran = Range(a1 + «:» + a2)
‘ выбеляем
ran.Select
End If
‘ выходим из процедуры
Exit Sub
‘ ошибка зовем на помощь
errors:
MsgBox «Ошибка сообщите разработчику»
End Sub
Выделить ячейку и поместить туда число
Sub Test()
With Application.Workbooks.Item(«Test.xls»)
Worksheets(«Лист2»).Activate
Range(«A2») = 2
Range(«A3») = 3
End With
End Sub
Выделение отрицательных значений
Sub NegSelect()
Dim cell As Range
‘ Просмотр всех ячеек выделенного диапазона и пометка тех, _
которые содержат отрицательные значения
For Each cell In Selection
If cell.Value < 0 Then
cell.Interior.Color = RGB(255, 0, 0)
Else
cell.Interior.ColorIndex = xlNone
End If
Next cell
End Sub
Выделение диапазона и использование абсолютных адресов
Sub Test()
With Application.Workbooks.Item(«Test.xls»)
Worksheets(«Лист2»).Activate
Dim HelloRange As Range
Set HelloRange = Range(«D3:D10») ‘можно через запятую выделять несколько интервалов или яче
HelloRange.Range(«A1») = 3
End With
End Sub
Выделение ячеек через интервал_1
Sub IntervalCellSelect()
Dim intFirstRow As Integer ‘ Первая строка для выделения
Dim intLastRow As Integer ‘ Последняя строка для выделения
Dim rgCells As Range ‘ Объединение выделяемых ячеек
Dim intRow As Integer
intFirstRow = 3
intLastRow = 300
‘ Формирование объединения ячеек в столбце «B» от строки _
intFirstRow до строки intLastRow с шагом 3
For intRow = intFirstRow To intLastRow Step 3
If rgCells Is Nothing Then
‘ Первая ячейка в объединении
Set rgCells = Cells(intRow, 1)
Else
‘ Добавление очередной ячейки в объединение
Set rgCells = Union(rgCells, Cells(intRow, 1))
End If
Next
‘ Выделение всех ячеек в объединении
rgCells.Select
End Sub
Выделение ячеек через интервал_2
Sub IntervalCellSelect()
Dim intFirstRow As Integer ‘ Первая строка для выделения
Dim intLastRow As Integer ‘ Последняя строка для выделения
Dim rgCells As Range ‘ Объединение выделяемых ячеек
Dim cell As Range ‘ Текущая ячейка
Dim intRow As Integer
intFirstRow = 3
intLastRow = 300
‘ Формирование объединения ячеек в столбце «B» от строки _
intFirstRow до строки intLastRow с шагом 3
For intRow = intFirstRow To intLastRow Step 3
Set cell = Cells(intRow, 1)
Set rgCells = Union(cell, _
IIf(intRow = intFirstRow, cell, rgCells))
Next
‘ Выделение всех ячеек в объединении
rgCells.Select
End Sub
Выделение нескольких диапазонов
Sub SelectRange()
Range(«D3:D10, A3:A10 , F3»).Select
End Sub
Движение по ячейкам
переменная.Offset(RowOffset, ColumnOffset)
В качестве переменных может выступать как ячейка так и диапазон (Range) удобно пользоваться этой функцией для смещения относительно текущей ячейки.
Например, смещение ввниз на одну ячейку и выделение ее:
ActiveCell.Offset(1, 0).Select
Если нужно двигаться вверх, то нужно использовать отрицательное число:
ActiveCell.Offset(-1, 0).Select
Функция ниже использует эту возможность для того, чтобы пробежаться вниз до первой пустой ячейки.
Sub beg()
Dim a As Boolean
Dim d As Double
Dim c As Range
a = True
Set c = Range(ActiveCell.address)
c.Select
d = c.Value
c.Value = d
While (a = True)
ActiveCell.Offset(1, 0).Select
If (IsEmpty(ActiveCell.Value) = False) Then
Set c = Range(ActiveCell.address)
c.Select
d = c.Value
c.Value = d
Else
a = False
End If
Wend
End Sub
Поиск ближайшей пустой ячейки столбца
Sub FindEmptyCell()
‘ Поиск ближайшей пустой ячейки в текущем столбце
Do While Not IsEmpty(ActiveCell.Value)
ActiveCell.Offset(1, 0).Select
Loop
End Sub
Поиск максимального значения
Sub FindMaxValue()
On Error Goto NoCell
If Selection.Count > 1 Then
‘ Поиск максимального значения в выделенных ячейках
Selection.Find(Application.Max(Selection)).Select
Else
‘ Поиск максимального значения во всех ячейках листа
ActiveSheet.Cells.Find(Application.Max(ActiveSheet.Cells)).Select
End If
Exit Sub
NoCell:
MsgBox «Максимальное значение не найдено»
End Sub
Поиск и замена по шаблону
Sub ReplaceCellsData()
Dim cell As Range
‘ Просмотр всех ячеек диапазона G1:K20 и замена искомого текста
For Each cell In [G1:K20]
If cell.Value Like «*Доход*» Then
cell.Value = «Выручка»
cell.Interior.Color = RGB(255, 255, 0)
Else
cell.Interior.Color = RGB(255, 255, 255)
End If
Next
End Sub
Поиск значения с отображением результата в отдельном окне
Sub Search()
Dim rgResult As Range
‘ Поиск заданного значения в диапазоне B1:B20 и вывод результата
Set rgResult = Range(«B1:B20»).Find(9999, , xlValues)
If rgResult Is Nothing Then
MsgBox «Поиск не дал результатов»
Else
MsgBox rgResult.Address
End If
End Sub
Поиск с выделением найденных данных_1
Sub FindAndSelect()
Dim strStartAddr As String ‘ Хранит координаты первого найденного _
значения
Dim rgResult As Range
‘ Поиск первого входжения искомого слова
Set rgResult = Range(«B1:B10»).Find(«Прибыль», , xlValues)
If Not rgResult Is Nothing Then
‘ Сохраним адрес найденной ячейки (чтобы контролировать _
зацикливание поиска)
strStartAddr = rgResult.Address
End If
Do While Not rgResult Is Nothing
‘ Обработка результата поиска
rgResult.Interior.Color = RGB(255, 255, 0)
‘ Новый поиск
Set rgResult = Range(«B1:B10»).FindNext(rgResult)
If rgResult.Address = strStartAddr Then
‘ Поиск завершен
Exit Do
End If
Loop
End Sub
Поиск с выделением найденных данных_2
Sub CustomSearch()
Dim strFindData As String
Dim rgFound As Range
Dim i As Integer
‘ Ввод строки для поиска
strFindData = InputBox(«Введите данные для поиска»)
‘ Просмотр всех рабочих листов книги
For i = 1 To Worksheets.Count
With Worksheets(i).Cells
‘ Поиск на i-м листе
Set rgFound = .Find(strFindData, LookIn:=xlValues)
If Not rgFound Is Nothing Then
‘ Ячейка с заданным значением найдена — выделим ее
Sheets(i).Select
rgFound.Select
Exit Sub
End If
End With
Next
‘ Поиск завершен. Ячейка не найдена
MsgBox («Поиск не дал результатов»)
End Sub
Поиск по условию в диапазоне
Option Explicit
Sub Поиск()
Dim iFoundRng As Range
Dim AutoNum As String
Dim firstAddress As String
Dim LastFoundRng As String
AutoNum = Range(«E5»)
If AutoNum = «» Then
MsgBox «Вы не указали номер авто в ячейке Е5!», 48, «Ошибка»
Exit Sub
End If
On Error Resume Next
LastFoundRng = ActiveWorkbook.Names(«LastFoundRngName»).RefersToRange.Address
If LastFoundRng = «» Then LastFoundRng = «$C$1»
With Columns(«C»)
Set iFoundRng = .Find(What:=AutoNum, After:=Range(LastFoundRng), LookIn:=xlFormulas, LookAt:=xlWhole)
If iFoundRng Is Nothing Then
MsgBox «Авто с номером » & AutoNum & » не найдено в столбце С!», «48», «Ошибка»
Exit Sub
End If
ActiveWorkbook.Names.Add Name:=»LastFoundRngName», RefersTo:=»=» & ActiveSheet.Name & «!» & iFoundRng.Address, Visible:=False
End With
[E7] = iFoundRng.Offset(0, 1)
[F7] = iFoundRng.Offset(0, 2)
End Sub
Поиск последней непустой ячейки диапазона
Function dhLastUsedCell(rgRange As Range) As ****
Dim lngCell As ****
‘ Пойдем по диапазону с конца (тогда первая попавшаяся _
заполненная ячейка и будет искомой)
For lngCell = rgRange.Count To 1 Step -1
If Not IsEmpty(rgRange(lngCell)) Then
‘ Нашли непустую ячейку
dhLastUsedCell = lngCell
Exit Function
End If
Next lngCell
‘ Непустую ячейку не нашли
dhLastUsedCell = 0
End Function
Поиск последней непустой ячейки столбца
Function dhLastColUsedCell(rgColumn As Range) As Variant
‘ Вывод значения последней непустой ячейки столбца
dhLastColUsedCell = rgColumn.Parent.Cells(Rows.Count, _
rgColumn.Column).End(xlUp).Value
End Function
Поиск последней непустой ячейки строки
Function dhLastRowUsedCell(rgRow As Range) As Variant
‘ Вывод значения последней непустой ячейки строки
dhLastRowUsedCell = rgRow.Parent.Cells(rgRow.Row, 256). _
End(xlToLeft).Address
End Function
Поиск ячейки синего цвета в диапазоне
Sub Макрос1()
Dim myRange As Range ‘диапазон для поиска
Dim FoundRng As Range ‘найденная ячейка
Dim iRow As ****
Dim iColumn As ****
Set myRange = Range(«B1:B100»)
Application.FindFormat.Interior.ColorIndex = 5 ‘будем искать синий цвет
Set FoundRng = myRange.Find(What:=»», SearchFormat:=True)
If Not FoundRng Is Nothing Then
iRow = FoundRng.Row
iColumn = FoundRng.Column
MsgBox «Ячейка найдена по адресу: » & Chr(13) & «Ряд: » & iRow & Chr(13) & «Столбец: » & iColumn, vbInformation, «»
Else
MsgBox «Ячейка не найдена!», vbExclamation, «»
End If
End Sub
Поиск наличия значения в столбце
Sub Макрос1()
Dim iCell As Range
Set iCell = Columns(1).Find(What:=»*», LookIn:=xlFormulas, SearchDirection:=xlPrevious)
If Not iCell Is Nothing Then
MsgBox «Номер последней заполненной строки в столбце A: » & iCell.Row, , «»
Else
MsgBox «Столбец «»A»» не содержит данных», vbExclamation, «»
End If
End Sub
Поиск совпадений в диапазоне
Option Explicit
Sub compare_areas()
Dim r As Range, ar As Range, nm As String, col As Range
Set r = Selection
If r.Count < 2 Then Exit Sub
‘Dim r_prog As Integer
‘r_prog = prog
‘prog = 1
Application.ScreenUpdating = False
nm = ActiveSheet.Name
Sheets.Add
For Each ar In r.Areas
For Each col In ar.Columns
col.Copy
ActiveSheet.Paste
ActiveCell.SpecialCells(xlLastCell).Offset(1, 0).Select
Next
Next
Range(Cells(1, 1), Cells(r.Cells.Count, 2)).Select
Selection.Sort Key1:=Range(«A1»), Order1:=xlAscending, Header:=xlGuess, _
OrderCustom:=1, MatchCase:=False, Orientation:=xlTopToBottom, _
DataOption1:=xlSortTextAsNumbers
Rows(«1:1»).Select
Selection.insеrt Shift:=xlDown
Cells(2, 2).FormulaR1C1 = «=IF((RC[-1]=R[-1]C[-1])+(RC[-1]=R[1]C[-1]),1,0)»
Range(«b2»).Select
Selection.AutoFill Destination:=Range(Cells(2, 2), Cells(r.Cells.Count + 1, 2)), Type:=xlFillDefault
Range(Cells(2, 2), Cells(r.Cells.Count + 1, 2)).Copy
Cells(2, 2).PasteSpecial Paste:=xlPasteValues, Operation:=xlNone, SkipBlanks _
:=False, Transpose:=False
Application.CutCopyMode = False
For Each ar In r.Cells
If ar.Value <> Empty Then
If WorksheetFunction.VLookup(ar.Value, Range(Cells(2, 1), Cells(r.Count + 1, 2)), 2, 0) Then
ar.Interior.ColorIndex = 3
End If
End If
Next
Application.DisplayAlerts = False
ActiveSheet.Delete
Sheets(nm).Select
ActiveCell.Select
Application.DisplayAlerts = True
Application.ScreenUpdating = True
‘prog = r_prog
End Sub
Sub uncolor()
Selection.Interior.ColorIndex = xlNone
End Sub
Поиск ячейки в диапазоне_1
Dim r As Range
Dim foundCell As Range
Set r = ActiveSheet.Range(«A1:A6»)
Set foundCell = r.Find(«Ichiro», LookIn:=xlValues)
If Not foundCell Is Nothing Then
foundCell.Select
Else
MsgBox «String not found.»
End If
Поиск ячейки в диапазоне_2
Sub findtekst()
Dim c As Range
Set c = Range(«c3:c98»).Find(«*ГКИ*», , , xlWhole)
If Not c Is Nothing Then c.Select
MsgBox (c)
End Sub
Также для финда по xlWhole вариации:
«*a» — заканчивается на a
«?a*» — 2-я буква a
«??a*» — 3-я буква а
«a?» — начинается на a и содержит ещё 1 любую букву
«a?*» — 2+ буквы минимум и начинается на a (например a1, a10, a12, a55, a55dd56 всё посчитается)
«*слово*» — находит слова содержащие «слово» в любой части строки (включая начало и конец)
«слово*» — находит ячейки начинающиеся со «слово» или просто ячейку «слово» без дополнительных букв
Поиск приближенного значения в диапазоне
Sub wwe()
Dim foundCell As Range
ActiveWorkbook.Names.Add Name:=»ev», RefersToR1C1:= _
«=INDEX(Лист1!R11C2:R34C2,MATCH(MIN(ABS(Лист1!R36C2:R234C2-Лист1!R28C1)),ABS(Лист1!R36C2:R234C2-Лист1!R28C1),0))»
Set foundCell = [ev]
Names(«ev»).Delete
If Not foundCell Is Nothing Then
foundCell.Select
Else
MsgBox «String not found.»
End If
End Sub
Поиск начала и окончания диапазона, содержащего данные
Sub FindSheetData()
‘ Выводим диапазон используемых ячеек листа
MsgBox ActiveSheet.UsedRange.Address
End Sub
Поиск начала данных
Sub FindStartOfData()
With ActiveSheet
‘ Заносим текст в ячейку, являющуюся левой верхней _
ячейкой используемого диапазона
.Cells(.UsedRange.Row, .UsedRange.Column).Value = _
«Начало данных»
End With
End Sub
Автоматическая замена значений
Sub ReplaceValues()
Dim cell As Range
‘ Проверка каждой ячейки диапазона на возможность замены _
значения в ней (отрицательные значения заменяются на -1, _
положительные — на 1)
For Each cell In Range(«C1:C3»).Cells
If cell.Value < 0 Then
cell.Value = -1
ElseIf cell.Value > 0 Then
cell.Value = 1
End If
Next
End Sub
Быстрое заполнение диапазона (массив)
Sub FillCells()
Dim intStartVal As Integer ‘ Начальное значение
Dim intStep As Integer ‘ Шаг при изменении значения
Dim intEndVal As Integer ‘ Конечное значение
Dim intVal As Integer ‘ Текущее значение
Dim intCellOffset As Integer ‘ Смещение от начальной ячейки
‘ Установка параметров заполнения
intStartVal = 1
intStep = 1
intEndVal = 100
‘ Заполнение ячеек текущего столбца значениями от 1 до 100
For intVal = intStartVal To intEndVal Step intStep
ActiveCell.Offset(intCellOffset, 0).Value = intVal
intCellOffset = intCellOffset + 1
Next intVal
End Sub
Заполнение через интервал(массив)
Sub FillCells()
Dim intStartVal As Integer ‘ Начальное значение
Dim intStep As Integer ‘ Шаг при изменении значения
Dim intEndVal As Integer ‘ Конечное значение
Dim intVal As Integer ‘ Текущее значение
Dim intCellOffset As Integer ‘ Смещение от начальной ячейки
Dim intCellStep As Integer ‘ Шаг при перемещении между _
заполняемыми ячейками
‘ Установка параметров заполнения
intStartVal = 3
intStep = 3
intEndVal = 30
intCellStep = 3
‘ Заполнение ячеек текущего столбца значениями от 3 до 30
For intVal = intStartVal To intEndVal Step intStep
ActiveCell.Offset(intCellOffset, 0).Value = intVal
intCellOffset = intCellOffset + intCellStep
Next intVal
End Sub
Заполнение указанного диапазона(массив)
Sub FillCellRect()
Dim lngRows As ****, intCols As Integer ‘ Количество ячеек по _
горизонтали и вертикали
Dim lngRow As ****, intCol As Integer ‘ Координаты текущей ячейки
Dim lngStep As ****, lngVal As ****
‘ Установка начального значения и шага заполнения
lngVal = 1
lngStep = 1
‘ Ввод количества ячеек по горизонтали и вертикали, которое _
необходимо заполнить
lngRows = Val(InputBox(«Количество ячеек в высоту»))
intCols = Val(InputBox(«Количество ячеек в ширину»))
‘ Отключение обновления экрана
Application.ScreenUpdating = False
‘ Заполнение ячеек значениями
For lngRow = 1 To lngRows
For intCol = 1 To intCols
ActiveCell.Offset(lngRow, intCol).Value = lngVal
lngVal = lngVal + lngStep
Next intCol
Next lngRow
‘ Включение обновления экрана
Application.ScreenUpdating = True
End Sub
Заполнение диапазона(массив)
Sub FillCellRect1()
Dim lngRows As ****, intCols As Integer
Dim lngRow As ****, intCol As Integer
Dim lngStep As ****, lngVal As ****
Dim alngValues() As ****
Dim rgRange As Range
‘ Установка начального значения и шага заполнения
lngVal = 1
lngStep = 1
‘ Ввод количества ячеек по горизонтали и вертикали, которое _
необходимо заполнить
lngRows = Val(InputBox(«Количество ячеек в высоту»))
intCols = Val(InputBox(«Количество ячеек в ширину»))
ReDim alngValues(1 To lngRows, 1 To intCols)
Set rgRange = ActiveCell.Range(Cells(1, 1), _
Cells(lngRows, intCols))
‘ Заполнение массива alngValues значениями
For lngRow = 1 To lngRows
For intCol = 1 To intCols
alngValues(lngRow, intCol) = lngVal
lngVal = lngVal + lngStep
Next intCol
Next lngRow
‘ Перенос значений из массива в таблицу
rgRange.Value = alngValues
End Sub
Расчет суммы первых значений диапазона
Листинг 2.65. Функция dhNSum
Function dhNSum(ByVal intCount As Integer, _
rgValues As Range) As Double
Dim i As Integer
Dim dblSum As Double
If intCount > rgValues.Count Then
‘ Задано количество элементов большее, чем есть _
в переданном диапазоне
intCount = rgValues.Count
End If
‘ Расчет суммы первых intCount элементов
For i = 1 To intCount
dblSum = dblSum + rgValues(i)
Next i
‘ Возврат результата
dhNSum = dblSum
End Function
Размещение в ячейке электронных часов
Sub updаtеTime()
Dim varNextCall As Variant
‘ Записываем в ячейку текущее время
Cells(1, 1).Value = Now
‘ Записываем в varNextCall время, когда вызвать этот макрос _
в следующий раз (через 1 секунду)
varNextCall = TimeSerial(Hour(Now), Minute(Now), Second(Now) + 1)
‘ Уведомляем Excel в необходимости вызова макроса
Application.OnTime varNextCall, «updаtеTime»
End Sub
«Будильник»
Sub Clock()
‘ Уведомляем Excel, что процедуру Alarm нужно вызвать в 20:55
Application.OnTime TimeValue(«20:55:00»), «Alarm»
End Sub
Sub Alarm()
MsgBox «Пора ужинать!!!»
End Sub
Оформление верхней и нижней границ диапазона
Sub RangeBorder()
Dim rgRange As Range
Set rgRange = Range(«B2:D5»)
‘ Оформление верхней границы диапазона
With rgRange.Borders(xlEdgeTop)
.Weight = xlThick
.LineStyle = xlContinuous
.Color = RGB(0, 0, 255)
End With
‘ Оформление нижней границы диапазона
With rgRange.Borders(xlEdgeBottom)
.Weight = xlMedium
.LineStyle = xlDash
.Color = RGB(255, 0, 255)
End With
End Sub
Адрес активной ячейки
Sub Worksheet_Selectiоnchange(ByVal Target As Range)
‘ Вывод адреса ячейки в различных форматах
MsgBox Target.Address() & vbCr & _
Target.Address(RowAbsolute:=False) & vbCr & _
Target.Address(ReferenceStyle:=xlR1C1) & vbCr & _
Target.Address(ReferenceStyle:=xlR1C1, _
RowAbsolute:=False, ColumnAbsolute:=False, _
RelativeTo:=Worksheets(1).Cells(2, 2))
End Sub
Координаты активной ячейки
ActiveCell.Row и ActiveCell.Column — покажут координаты активной ячейки.
Формула активной ячейки
s = Range(«A3»).Formula
Получение из ячейки формулы
Sub Test()
With Application.Workbooks.Item(«Test.xls»)
Worksheets(«Лист2»).Activate
Range(«A2») = 2
Range(«A3») = «=A2+2»
MsgBox Range(«A3″).Formula + » — » + Str(Range(«A3»).Value)
End With
End Sub
Тип данных ячейки
Function dhCellType(rgRange As Range) As String
‘ Переходим к левой верхней ячейке, если rgRange — диапазон, _
а не одна ячейка
Set rgRange = rgRange.Range(«A1»)
‘ Определение типа значения в ячейке
Select Case True
Case IsEmpty(rgRange)
‘ Ячейка пуста
dhCellType = «Пусто»
Case Application.IsText(rgRange)
‘ В ячейке текст
dhCellType = «Текст»
Case Application.IsLogical(rgRange)
‘ В ячейке логическое значение (True или False)
dhCellType = «Булево выражение»
Case Application.IsErr(rgRange)
‘ При вычислении значения в ячейке произошла ошибка
dhCellType = «Ошибка»
Case IsDate(rgRange)
‘ В ячейке дата
dhCellType = «Дата»
Case InStr(1, rgRange.Text, «:») <> 0
‘ В ячейке время
dhCellType = «Время»
Case IsNumeric(rgRange)
‘ В ячейке числовое значение
dhCellType = «Число»
End Select
End Function
Вывод адреса конца диапазона
Sub TestRange()
Dim r As Range
Set r = Range(«rrrrr»)
MsgBox (r.Columns.End(xlUp).Address)
MsgBox (r.Columns.End(xlDown).Address)
End Sub
Получение информации о выделенном диапазоне
Sub TypeOfSelection()
Dim rgSelUnion As Range ‘ Объединение выделенных областей
Dim strTitle As String ‘ Заголовок сообщения
Dim strMessage As String ‘ Текст сообщения
Dim strSelType As String ‘ Тип выделения (простой или _
множественный)
Dim intBlockCount As Integer ‘ Количество блоков в выделении
Dim intCellCount As **** ‘ Общее количество выделенных ячеек
Dim intColCount As Integer ‘ Количество выделенных столбцов
Dim intRowCount As **** ‘ Количество выделенных строк
Dim intAreasCount As Integer ‘ Количество выделенных областей
Dim strCurSelType As String
Dim rgArea As Range
‘ Подсчет количества выделенных областей и определение типа выделения: _
простое (одна область) или сложное(несколько областей)
intAreasCount = Selection.Areas.Count
If intAreasCount = 1 Then
strTitle = «Простое выделение»
Else
strTitle = «Множественное выделение»
End If
‘ Определение типа выделения первой области
strSelType = dhGetAreaType(Selection.Areas(1))
‘ Создание объединения во избежание повторного учета _
пересекающихся участков выделенных диапазонов
Set rgSelUnion = Selection.Areas(1)
For Each rgArea In Selection.Areas
strCurSelType = dhGetAreaType(rgArea)
‘ Изменение надписи о типе всего выделения, если _
есть выделения различного типа
If strCurSelType <> strSelType Then
strSelType = «Множественный»
End If
‘ Определение количества блоков перед их добавлением в объединение
If strCurSelType = «Block» Then
intBlockCount = intBlockCount + 1
End If
‘ Добавление в объединение
Set rgSelUnion = Union(rgSelUnion, rgArea)
Next rgArea
‘ Просматриваются элементы созданного объединения
For Each rgArea In rgSelUnion.Areas
Select Case dhGetAreaType(rgArea)
Case «Строка»
intRowCount = intRowCount + rgArea.Rows.Count
Case «Столбец»
intColCount = intColCount + rgArea.Columns.Count
Case «Лист»
intColCount = intColCount + rgArea.Columns.Count
intRowCount = intRowCount + rgArea.Rows.Count
End Select
Next rgArea
‘ Определение количества неперекрывающихся ячеек
intCellCount = rgSelUnion.Count
‘ Формирование и вывод итогового сообщения
strMessage = «Тип выделения:» & vbTab & strSelType & vbCrLf & _
«Количество областей: » & vbTab & intAreasCount & vbCrLf & _
«Полных столбцов: » & vbTab & intColCount & vbCrLf & _
«Полных строк: » & vbTab & intRowCount & vbCrLf & _
«Блоков ячеек: » & vbTab & intBlockCount & vbCrLf & _
«Всего ячеек: » & vbTab & Format(intCellCount, «#,###»)
MsgBox strMessage, vbInformation, strTitle
End Sub
Function dhGetAreaType(rgRangeArea As Range) As String
‘ Определение типа диапазона
If rgRangeArea.Count = Cells.Count Then
‘ Все ячейки рабочего листа
dhGetAreaType = «Лист»
ElseIf rgRangeArea.Cells.Count = 1 Then
‘ Одна ячейка
dhGetAreaType = «Ячейка»
ElseIf rgRangeArea.Rows.Count = Cells.Rows.Count Then
‘ Весь столбец
dhGetAreaType = «Столбец»
ElseIf rgRangeArea.Columns.Count = Cells.Columns.Count Then
‘ Вся строка
dhGetAreaType = «Строка»
Else
‘ Блок ячеек
dhGetAreaType = «Блок»
End If
End Function
Взять слово с 13 символа в ячейке
‘берём значение ячейка А4 из Отчёта
iMonth = «за период с Июль 2 008 по Июль 2 008 »
‘берём слово начиная с 13-го символа
iMonth = Evaluate(«MID(TRIM(» & «»»» & iMonth & «»»» & «),13,(SEARCH(«» «»,TRIM(» & «»»» & iMonth & «»»» & «),13)-13))»)
‘вставляем это слово в книгу Ведомость
AddressSht.Range(«A1») = iMonth
Создание изменяемого списка (таблица)
Sub Макрос2()
With ActiveSheet
.ListObjects.Add(xlSrcRange, .Range(«$A$8:$AR$» & .Cells(Rows.Count, 1).End(xlUp).Row), , xlYes).Name = _
«Список1»
End With
End Sub
Проверка на пустое значение
IsNull(выражение) — проверка на пустое значение
Пересечение ячеек
Sub Test()
With ActiveWorkbook
Worksheets(«Лист1»).Activate
Dim Range1 As Range
Set Range1 = Range(«A1:A8 A8:D8»)
Range1.Value = «test»
End With
End Sub
Умножение выделенного диапазона на 2
Sub Test()
Dim cur_range As Range
With ActiveSheet
Set cur_range = Selection
cur_range.Activate
For x = 1 To cur_range.Rows.Count
For y = 1 To cur_range.Columns.Count
‘ значению ячейки присвоить значение умноженно на 2
cur_range(x, y) = cur_range(x, y).Value * 2
Next y
Next x
End With
End Sub
Одновременное умножение всех данных диапазона
Sub MultAllCells()
Dim dblMult As Double
Dim cell As Range
‘ Ввод коэффициента для умножения
dblMult = InputBox(«Введите коэффициент, на который следует умножать»)
‘ Умножение содержимого на введенный коэффициент
For Each cell In Selection
If IsNumeric(cell.Value) And cell.Value <> «» Then
‘ Умножаются только ячейки, содержащие числовые данные
cell.Value = cell.Value * dblMult
Else
MsgBox «В ячейке » & cell.Address & » нечисловое значение»
End If
Next
End Sub
Деление диапазона на 100
Sub Test23()
Dim iRange As Range
Dim kRange As Range
i = 1
j = 1
m = 5
n = 2
Set iRange = Range(Cells(i, j), Cells(m, n))
For Each kRange In iRange
kRange.Value = kRange.Value / 100
Next
End Sub
Возведение каждой ячейки диапазона в квадрат
Суммирование данных только видимых ячеек
Function СуммаВид(Диапазон) As Double
‘ Просмотр всех ячеек заданного диапазона
For Each Ячейка In Диапазон
‘ Анализ только видимых ячеек
If Not Ячейка.EntireRow.Hidden And Not _
Ячейка.EntireColumn.Hidden Then
‘ При расчете учитываются только ячейки _
с численными значениями
If IsNumeric(Ячейка) = True Then
СуммаВид = СуммаВид + Ячейка
End If
End If
Next
End Function
Сумма ячеек с числовыми значениями
Sub CalculateSum()
Dim i As Integer
Dim intSum As Integer
‘ Расчет суммы ячеек столбца «A» (с первой по пятую)
For i = 1 To 5
If IsNumeric(Cells(i, 1)) Then
intSum = intSum + Cells(i, 1)
End If
Next
MsgBox «Сумма ячеек: » & intSum
End Sub
При суммировании — курсор внутри диапазона
Function Сумма(Диапазон, АдресЯчейки) As Double
‘ Просмотр всех ячеек диапазона
For Each Ячейка In Диапазон
‘ Проверка, чтобы в суммировании не участвовала _
ячейка с формулой
If АдресЯчейки.Address <> Ячейка.Address Then
‘ В суммировании участвуют только ячейки _
с численными значениями
If IsNumeric(Ячейка) = True Then
Сумма = Сумма + Ячейка
End If
End If
Next
End Function
Начисление процентов в зависимости от суммы_1
Function dhCalculatePercent(lngSum As ****) As Double
‘ Процентные ставки (декларация констант)
Const dblRate1 As Double = 0.09
Const dblRate2 As Double = 0.11
Const dblRate3 As Double = 0.15
‘ Граничные суммы вкладов (декларация констант)
Const intSum1 As **** = 5000
Const intSum2 As **** = 10000
‘ Возвращаем сумму, умноженную на соответствующую ставку
If lngSum < intSum1 Then
dhCalculatePercent = lngSum * dblRate1
ElseIf lngSum < intSum2 Then
dhCalculatePercent = lngSum * dblRate2
Else
dhCalculatePercent = lngSum * dblRate3
End If
End Function
Начисление процентов в зависимости от суммы_2
Function dhCalculatePercent(lngSum As ****) As Double
‘ Процентные ставки (декларация констант)
Const dblRate1 As Double = 0.09
Const dblRate2 As Double = 0.11
Const dblRate3 As Double = 0.15
‘ Граничные суммы вкладов (декларация констант)
Const intSum1 As **** = 5000
Const intSum2 As **** = 10000
‘ Возвращаем сумму, умноженную на соответствующую ставку
Select Case lngSum
Case Is < intSum1
dhCalculatePercent = lngSum * dblRate1
Case Is < intSum2
dhCalculatePercent = lngSum * dblRate2
Case Else
dhCalculatePercent = lngSum * dblRate3
End Select
End Function
Начисление процентов в зависимости от суммы_3
Function dhCalculatePercent(Sales As ****, IsTemporal As Boolean) As Double
‘ Процентные ставки (декларация констант)
Const dblRate1 As Double = 0.09
Const dblRate2 As Double = 0.11
Const dblRate3 As Double = 0.15
Const dblAdd As Double = 1.1
‘ Граничные суммы
Const lngSum1 As **** = 5000
Const lngSum2 As **** = 10000
‘ Расчет суммы для выплаты (как обычно)
If Sales < lngSum1 Then
dhCalculatePercent = Sales * dblRate1
ElseIf Sales < lngSum2 Then
dhCalculatePercent = Sales * dblRate2
Else
dhCalculatePercent = Sales * dblRate3
End If
If IsTemporal Then
‘ Для сторонних вкладчиков — надбавка
dhCalculatePercent = dblAdd * dhCalculatePercent
End If
End Function
Сводный пример расчета комиссионного вознаграждения
Function dhCalculateCom(dblSales As Double) As Double
Const dblRate1 = 0.09
Const dblRate2 = 0.11
Const dblRate3 = 0.15
‘ Расчет комиссионных с продаж (без выслуги) в зависимости _
от суммы
Select Case dblSales
Case 0 To 4999.99: dhCalculateCom = dblSales * dblRate1
Case 5000 To 9999.99: dhCalculateCom = dblSales * dblRate2
Case Is >= 10000: dhCalculateCom = dblSales * dblRate3
End Select
End Function
Function dhCalculateCom2(dblSales As Double, intYears As Double) _
As Double
Const dblRate1 = 0.09
Const dblRate2 = 0.11
Const dblRate3 = 0.15
‘ Расчет комиссионных с продаж (без учета выслуги лет) _
в зависимости от суммы
Select Case dblSales
Case 0 To 4999.99: dhCalculateCom2 = dblSales * dblRate1
Case 5000 To 9999.99: dhCalculateCom2 = dblSales * dblRate2
Case Is >= 10000: dhCalculateCom2 = dblSales * dblRate3
End Select
‘ Надбавка за выслугу лет
dhCalculateCom2 = dhCalculateCom2 + _
(dhCalculateCom2 * intYears / 100)
End Function
Sub ComCalculator()
Dim strMessage As String
Dim dblSales As Double
Dim ан As Integer
Calc:
‘ Отображение окна для ввода данных
dblSales = Val(InputBox(«Сумма реализации:», _
«Расчет комиссионного вознаграждения»))
‘ Формирование сообщения (с одновременным расчетом _
вознаграждения)
strMessage = «Объем продаж:» & vbTab & Format(dblSales, «$#,##0») & _
vbCrLf & «Сумма вознаграждения:» & vbTab & _
Format(dhCalculateCom(dblSales), «$#,##0») & _
vbCrLf & vbCrLf & «Считаем дальше?»
‘ Вывод окна с сообщением (о рассчитанной сумме и вопросом _
о продолжении расчетов)
If MsgBox(strMessage, vbYesNo, _
«Расчет комиссионного вознаграждения») = vbYes Then
‘ Продолжение расчетов
GoTo Calc
End If
End Sub
Движение по диапазону
Sub FullShach()
For Each c In Range(addressdiap)
If c.Value > yr1 Then
c.Select
With Selection.Interior
.ColorIndex = 6
.Pattern = xlSolid
End With
Selection.Font.ColorIndex = yrcolor1
If c.Value > yr2 Then
c.Select
Selection.Font.ColorIndex = yrcolor2
If c.Value > yr3 Then
c.Select
Selection.Font.ColorIndex = yrcolor3
End If
End If
End If
Next c
End Sub
Сдвиг от выделенной ячейки
Sub Test()
Dim cur_range As Range
Set cur_range = Range(«A1»)
Set cur_range = cur_range.Offset(1, 0)
Debug.Print cur_range.Address
End Sub
Перебор ячеек вниз по колонне
Sub beg()
Dim a As Boolean
Dim d As Double
Dim c As Range
a = False
Set c = Range(ActiveCell.Address)
c.Select
d = c.Value
c.Value = d
While (a = False)
ActiveCell.Offset(1, 0).Select
If (IsEmpty(ActiveCell.Value) = False) Then
Set c = Range(ActiveCell.Address)
c.Select
d = c.Value
c.Value = d
Else
a = False
End If
Wend
End Sub
Создание заливки диапазона
Sub FillRange()
‘ Заливка диапазона
With Range(«B1:E10»)
‘ Задаем узор — сетчатый
.Interior.Pattern = xlPatternChecker
‘ Цвет узора — синий
.Interior.PatternColor = RGB(0, 0, 255)
‘ Цвет ячейки — красный
.Interior.Color = RGB(255, 0, 0)
End With
End Sub
Подбор параметра ячейки
Sub Макрос1()
‘ Сочетание клавиш: Ctrl+ф
Range(«G5»).GoalSeek Goal:=4, ChangingCell:=Range(«G4»)
End Sub
Разбиение диапазона
Function ExtractElement(Txt, n, Separator) As String
‘ Функция выдает n-ый элемент текстовой строки Txt, где
‘ символ Separator используется как разделитель
Dim Txt1 As String, TempElement As String
Dim ElementCount As Integer, i As Integer
Txt1 = Txt
‘ Если в качестве разделителя используется пробел, то убираем лишние
‘ и двойные пробелы
If Separator = Chr(32) Then Txt1 = Application.Trim(Txt1)
‘ Добавляем разделитель в конец строки (если необходимо)
If Right(Txt1, 1) <> Separator Then Txt1 = Txt1 & Separator
‘ Начальные значения
ElementCount = 0
TempElement = «»
‘ Извлекаем элемент
For i = 1 To Len(Txt1)
If Mid(Txt1, i, 1) = Separator Then
ElementCount = ElementCount + 1
If ElementCount = n Then
‘ Found it, so exit
ExtractElement = TempElement
Exit Function
Else
TempElement = «»
End If
Else
TempElement = TempElement & Mid(Txt1, i, 1)
End If
Next i
ExtractElement = «»
End Function
Закройте редактор и вернитесь в Excel командой File — Close and return to Microsoft Excel.
Теперь в любой ячейке листа Вы можете использовать эту функцию через меню Вставка — Функция — категория Определенные пользователем, где в аргументах:
• Txt — ячейка с текстом, который надо разделить,
• n — порядковый номер извлекаемого элемента,
• Separator — символ-разделитель.
Объединение данных диапазона
Function Couple(Diapazon)
‘ Объединение данных, содержащихся в ячейках диапазона _
Diapazon (разделитель между значениями — пробел)
‘ iCell — текущая ячейка
For Each iCell In Diapazon
‘ Сцепляются данные только заполненных ячеек
If IsEmpty(iCell) <> True Then
‘ Добавление значения ячейки в выходную строку
If Couple = «» Then
Couple = iCell
Else
Couple = Couple & » » & iCell
End If
End If
Next
End Function
Объединение данных диапазона_2
Function CoupleFormat(Diapazon)
‘ Объединение текстовых данных, содержащихся в ячейках _
диапазона Diapazon (разделитель между значениями — пробел)
‘ iCell — текущая ячейка
For Each iCell In Diapazon
‘ Сцепляются данные только заполненных ячеек
If IsEmpty(iCell) <> True Then
‘ Добавление текста ячейки в выходную строку
If CoupleFormat = «» Then
CoupleFormat = iCell.Text
Else
CoupleFormat = CoupleFormat & » » & iCell.Text
End If
End If
Next
End Function
Узнать максимальную колонку или строку.
Sub Test()
With ActiveSheet
Dim cur_range As Range
Set cur_range = .UsedRange
Debug.Print cur_range.Address
End With
End Sub
Ограничение возможных значений диапазона
Sub Worksheet_Change(ByVal Target As Excel.Range)
Dim rgInputRange As Range
Dim cell As Range
Dim strMessage As String
Dim varResult As Variant
‘ Диапазон, в котором контролируется ввод
Set rgInputRange = Range(«A1:E10»)
‘ Просмотр всех измененных ячеек и контроль ввода в тех, которые _
принадлежат заданному диапазону
For Each cell In Target
‘ Проверка принадлежности диапазону
If Union(cell, rgInputRange).Address = rgInputRange.Address Then
‘ Контроль правильности ввода
varResult = IsCellDataValid(cell)
If varResult = True Then
‘ Введено корректное значение
Exit Sub
Else
‘ Формирование и вывод сообщения об ошибке
strMessage = «Ячейка » & cell.Address(False, False) & «:» _
& vbCrLf & vbCrLf & varResult
MsgBox strMessage, vbCritical, «Неправильное значение»
‘ Очистка ввода
Application.EnableEvents = False
cell.ClearContents
cell.Activate
Application.EnableEvents = True
End If
End If
Next cell
End Sub
Function IsCellDataValid(cell As Range) As Variant
‘ Возвращает True, если в ячейку вводится целое число _
в диапазоне от 1 до 12. В противном случае выдается _
соответствующее сообщение
‘ Проверка, является ли содержимое ячейки числом
If Not WorksheetFunction.IsNumber(cell.Value) Then
IsCellDataValid = «Нечисловое значение»
Exit Function
End If
‘ Проверка, является ли введенное число целым
If Int(cell.Value) <> cell.Value Then
IsCellDataValid = «Введите целое число»
Exit Function
End If
‘ Проверка соответствия числа диапазону
If cell.Value < 1 Or cell.Value > 12 Then
IsCellDataValid = «Значение должно быть от 1 до 12»
Exit Function
End If
‘ В ячейку введено допустимое значение
IsCellDataValid = True
End Function
Тестирование скорости чтения и записи диапазонов
Sub TableSpeedTest()
Dim alngData() As **** ‘ Массив с числами
Dim lngCount As **** ‘ Количество элементов в массиве
Dim dtStart As Date ‘ Хранит время (и даже дату) начала _
тестирования
Dim strArrayToTable As String ‘ Время записи в таблицу
Dim strTableToArray As String ‘ Время чтения из таблицы
Dim strMessage As String
Dim i As ****
‘ Подготовка диапазона ячеек
Range(«A:A»).ClearContents
‘ Ввод размера массива, формирование массива заданного размера
lngCount = InputBox(«Введите количество элементов»)
ReDim alngData(1 To lngCount)
‘ Заполнение массива данными
For i = 1 To lngCount
alngData(i) = i
Next i
‘ Перенос массива в таблицу
Application.ScreenUpdating = False
dtStart = Timer
For i = 1 To lngCount
Cells(i, 1) = i
Next i
strArrayToTable = Format(Timer — dtStart, «00:00»)
‘ Чтение данных из таблицы обратно в массив
dtStart = Timer
For i = 1 To lngCount
alngData(i) = Cells(i, 1)
Next i
strTableToArray = Format(Timer — dtStart, «00:00»)
Application.ScreenUpdating = True
‘ Вывод на экран результатов тестирования
strMessage = «Запись: » & strArrayToTable & vbCrLf & _
«Чтение: » & strTableToArray
MsgBox strMessage, , lngCount & » элементов»
End Sub
Открыть MsgBox при выборе ячейки
Private Sub Worksheet_Selectiоnchange(ByVal Target As Range)
If Target.Address = «$A$1» Then MsgBox «Hello world»
End Sub
Скрытие строки
Sub HideString()
Rows(2).Hidden = True
End Sub
Скрытие нескольких строк
Sub HideStrings()
Rows(«3:5»).Hidden = True
End Sub
Скрытие столбца
Sub HideCollumn()
Columns(2).Hidden = True
End Sub
Скрытие нескольких столбцов
Sub HideCollumns()
Columns(«E:F»).Hidden = True
End Sub
Скрытие строки по имени ячейки
Sub HideCell()
Range(«Секрет»).EntireRow.Hidden = True
End Sub
Скрытие нескольких строк по адресам ячеек
Sub HideCell()
Range(«B3:D4»).EntireRow.Hidden = True
End Sub
Скрытие столбца по имени ячейки
Sub HideCell()
Range(«Секрет»).EntireColumn.Hidden = True
End Sub
Скрытие нескольких столбцов по адресам ячеек
Sub HideCell()
Range(«C2:D5»).EntireColumn.Hidden = True
End Sub
Мигание ячейки
Sub BlinkingCell()
Static intCalls As Integer ‘ Счетчик количества миганий
‘ Если ячейка мигала менее 10 раз, то изменим _
в очередной раз ее цвет
If intCalls < 10 Then
intCalls = intCalls + 1
‘ Определение, какой цвет необходимо установить
If Range(«A1»).Interior.Color <> RGB(255, 0, 0) Then
‘ Цвет ячейки не красный, так что теперь назначим _
именно красный цвет
Range(«A1»).Interior.Color = RGB(255, 0, 0)
Else
‘ Назначим ячейке зеленый цвет
Range(«A1»).Interior.Color = RGB(0, 255, 0)
End If
‘ Эту процедуру необходимо вызвать через 5 секунд
Application.OnTime Now + TimeValue(«00:00:05»), «BlinkingCell»
Else
‘ Хватит мигать
Range(«A1»).Interior.ColorIndex = xlNone
intCalls = 0
End If
End Sub
ГЛАВА 4. РАБОТА С ПРИМЕЧАНИЯМИ
Вывод на экран всех примечаний рабочего листа
Sub ShowComments()
Dim cell As Range
Dim rgCells As Range
‘ Получение всех ячеек с примечаниями
Set rgCells = Selection.SpecialCells(xlComments)
If rgCells Is Nothing Then
‘ Примечаний нет
Exit Sub
End If
‘ Проходим по всем ячейкам диапазона
For Each cell In rgCells
‘ Вывод примечаний в соседнюю ячейку
cell.Next.Value = cell.Comment.Text
Next
End Sub
Функция извлечения комментария
Function GetCommentText(rCommentCell As Range)
Dim strGotIt As String
On Error Resume Next
strGotIt = WorksheetFunction.Clean _
(rCommentCell.Comment.Text)
GetCommentText = strGotIt
On Error GoTo 0
End Function
вставить в модуль эксель
Список примечаний защищенных листов
Sub ShowComments1()
Dim cell As Range
Dim strFirstAddress As String
Dim strComments As String
‘ Получаем все ячейки выделения, в которых есть комментарий
Set cell = Selection.Find(«*», LookIn:=xlComments)
If Not cell Is Nothing Then
‘ Сохранение адреса первой найденной ячейки _
(для предотвращения зацикливания поиска)
strFirstAddress = cell.Address
Do
‘ Добавление текста примечания в выходную строку
strComments = strComments & «Комментарий: » & _
cell.Comment.Text & Chr(13)
‘ Продолжение поиска
Set cell = Selection.FindNext(cell)
Loop While Not cell Is Nothing And _
cell.Address <> strFirstAddress
End If
If strComments <> «» Then
‘ Отображение окна с текстом примечаний
MsgBox strComments
Else
MsgBox «В выделенной ячейке/ячейках комментариев нет»
End If
End Sub
Перечень примечаний в отдельном списке_1
Sub ListOfComments()
Dim cell As Range
Dim rgCells As Range
Dim intRow As Integer
‘ Получение всех ячеек с примечаниями
On Error Resume Next
Set rgCells = Selection.SpecialCells(xlComments)
If rgCells Is Nothing Then
‘ Примечаний нет
Exit Sub
End If
‘ Проходим по всем ячейкам диапазона
For Each cell In rgCells
‘ Вывод примечаний в ячейку столбца «C»
intRow = intRow + 1
Cells(intRow, 3) = cell.Comment.Text
Next
End Sub
Перечень примечаний в отдельном списке_2
Sub ListOfComments1()
Dim cell As Range
Dim strFirstAddress As String
Dim intRow As Integer
‘ Получение всех ячеек выделения, в которых есть примечания
Set cell = Cells.Find(«*», LookIn:=xlComments)
If Not cell Is Nothing Then
‘ Сохранение адреса первой найденной ячейки _
(для предотвращения зацикливания поиска)
strFirstAddress = cell.Address
Do
‘ Вывод текста в столбец «C»
intRow = intRow + 1
Cells(intRow, 3) = cell.Comment.Text
‘ Продолжение поиска
Set cell = Cells.FindNext(cell)
Loop While Not cell Is Nothing And _
cell.Address <> strFirstAddress
End If
End Sub
Перечень примечаний в отдельном списке_3
Sub ListOfCommentsToFile()
Dim rgCells As Range ‘ Ячейки с примечаниями
Dim intDefListCount As Integer ‘ Используется для временного _
хранения количества листов в книге по умолчанию
Dim strSheet As String ‘ Имя анализируемого листа
Dim strWorkBook As String ‘ Имя книги с анализируемым листом
Dim intRow As Integer
Dim cell As Range
‘ Получение ячеек с примечаниями
On Error Resume Next
Set rgCells = ActiveSheet.Cells.SpecialCells(xlComments)
On Error GoTo 0
‘ Если примечаний нет, то можно не продолжать
If rgCells Is Nothing Then
MsgBox «Текущая рабочая книга не содержит примечаний.», _
vbInformation
Exit Sub
End If
‘ Сохранение имен анализируемого листа и книги
strSheet = ActiveSheet.Name
strWorkBook = ActiveWorkbook.Name
‘ Создание отдельной книги с одним листом _
для отображения результатов
intDefListCount = Application.SheetsInNewWorkbook
Application.SheetsInNewWorkbook = 1
Workbooks.Add
Application.SheetsInNewWorkbook = intDefListCount
ActiveWorkbook.Windows(1).Caption = «Comments for » & strSheet & _
» in » & strWorkBook
‘ Создание списка примечаний
Cells(1, 1) = «Адрес»
Cells(1, 2) = «Содержимое»
Cells(1, 3) = «Комментарий»
Range(Cells(1, 1), Cells(1, 3)).Font.Bold = True
intRow = 2 ‘ Данные начинаются со второй строки
For Each cell In rgCells
Cells(intRow, 1) = cell.Address(rowabsolute:=False, _
columnabsolute:=False)
Cells(intRow, 2) = » » & cell.Formula
Cells(intRow, 3) = cell.comment.Text
intRow = intRow + 1
Next
End Sub
Подсчет количества примечаний_1
Sub CountOfComments()
Dim intCommentCount As Integer
‘ Получение и отображение количества примечаний
intCommentCount = ActiveSheet.Comments.Count
If intCommentCount = 0 Then
MsgBox «Текущая рабочая книга не содержит примечаний.», _
vbInformation
Else
MsgBox «В текущей рабочей книге содержится » & intCommentCount _
& » комментариев.», vbInformation
End If
End Sub
Подсчет количества примечаний_2
‘ Function IsCommentsPresent
‘ Возвращает TRUE, если на активном рабочем листе имеется хотя бы
‘ одна ячейка с комментарием, иначе возвращает FALSE
‘
Public Function IsCommentsPresent() As Boolean
IsCommentsPresent = ( ActiveSheet.Comments.Count <> 0 )
End Function
Подсчет примечаний_3
Sub CountOfComment()
Dim intCommentCount As Integer
‘ Получение и отображение количества примечаний _
на текущем листе
intCommentCount = ActiveSheet.Comments.Count
If intCommentCount = 0 Then
MsgBox «Примечаний нет»
Else
MsgBox «Примечаний: » & intCommentCount & » шт.»
End If
End Sub
Выделение ячеек с примечаниями
Sub SelectComments()
‘ Выделение всех ячеек с примечаниями
Cells.SpecialCells(xlCellTypeComments).Select
End Sub
Отображение всех примечаний
Sub ShowComments()
‘ Отображение всех примечаний
If Application.DisplayCommentIndicator = xlCommentAndIndicator Then
Application.DisplayCommentIndicator = xlCommentIndicatorOnly
Else
Application.DisplayCommentIndicator = xlCommentAndIndicator
End If
End Sub
Изменение цвета примечаний
Sub ChangeCommentColor()
‘ Автоматическое изменение цвета комментариев
Dim comment As comment
For Each comment In ActiveSheet.Comments
‘ Задаем случайные цвета заливки и шрифта комментариев
comment.Shape.Fill.ForeColor.SchemeColor = Int((80) * Rnd + 1)
comment.Shape.TextFrame.Characters.Font.ColorIndex = Int((56 _
) * Rnd + 1)
Next
End Sub
Добавление примечаний
Dim r As Range
Dim rwIndex As Integer
For rwIndex = 1 To 3
Set r = Worksheets(«WombatBattingAverages»).Cells(rwIndex, 2)
With r
If .Value >= 0.3 Then
.AddComment «All Star!»
End If
End With
Next rwIndex
Добавление примечаний в диапазон по условию
Sub CreateComments()
Dim cell As Range
‘ Производим поиск по всем ячейкам диапазона и добавляем примечания _
ко всем ячейкам, содержащим слово «Выручка»
For Each cell In Range(«B1:B100»)
If cell.Value Like «*Выручка*» Then
cell.ClearComments
cell.AddComment «Неучтенная наличка»
End If
Next
End Sub
Перенос комментария в ячейку и обратно
Sub Комментарий_в_ячейку_в_диапазоне()
‘переносит комментарий в ячейку
Dim i As ****
Dim c As Range, cc As Range
Dim iCommment As Comments
Application.DisplayCommentIndicator = xlCommentIndicatorOnly
Application.ScreenUpdating = False
Application.Calculation = xlCalculationManual
Set cc = Selection
‘если выделили 1 ячейку, то выход
If cc.Rows.Count = 1 And cc.Columns.Count = 1 Then
MsgBox «Выделено слишком мало ячеек!», , «Ошибка»
End
End If
Set cc = Selection.SpecialCells(xlCellTypeVisible)
For Each c In cc
If Not c.Comment Is Nothing Then
c.Value = c.Comment.Text
‘c.ClearComments ‘если надо удалить комментарий
i = i + 1
End If
End If
Next
Application.Calculation = xlCalculationAutomatic
Application.ScreenUpdating = True
MsgBox «Перенесено » & i & » комментариев!»
Exit Sub
End Sub
Перенос значений из ячейки в комментарий_1
Sub Добавить_комментарий_в_диапазоне()
‘копирует значение ячейки в комментарий в видемом диапазоне
Dim c As Range, cc As Range
Dim i As ****
On Error GoTo ErrorHandler
Application.DisplayCommentIndicator = xlCommentIndicatorOnly
Set cc = Selection
‘если выделили 1 ячейку, то выход
If cc.Rows.Count = 1 And cc.Columns.Count = 1 Then
MsgBox «Выделено слишком мало ячеек!», , «Ошибка»
End
End If
Set cc = Selection.SpecialCells(xlCellTypeVisible)
For Each c In cc
If c.Value <> Empty Then
c.AddComment CStr(c.Value)
i = i + 1
End If
Next
MsgBox «Добавлено » & i & » комментарий!»
Exit Sub
End Sub
Перенос значений из ячейки в комментарий_2
Sub Comment_in_Cell()
Dim c As Range
Dim r As Range
If ActiveSheet.Comments.Count = 0 Then MsgBox «Без комментариев!»: Exit Sub
Set sh = ActiveSheet
Set shnew = Sheets.Add
sh.Select
Set r = Range(Cells(1, 1), Cells(Cells.Find(«*», [A1], xlComments, , xlByRows, _
xlPrevious).Row, Cells.Find(«*», [A1], xlComments, , xlColumns, _
xlPrevious).Column))
For Each c In r
If Not c.Comment Is Nothing Then
shnew.Range(c.Address) = c.Comment.Text
End If
Next
End Sub
ГЛАВА 5 . ПОЛЬЗОВАТЕЛЬСКИЕ ВКЛАДКИ НА ЛЕНТЕ
Дополнение панели инструментов
Sub AddCustomCommandBar()
‘ Добавление кнопки на панель инструментов
With Application.CommandBars(3).Controls.Add(Type:=msoControlButton)
.FaceId = 42 ‘ Значок Word
.Caption = «Кнопка»
.OnAction = «Макрос»
End With
End Sub
Добавление кнопки на панель инструментов
Sub AddCustomButton()
‘ Добавление кнопки на панель инструментов
With Application.Toolbars(1).ToolbarButtons.Add(button:=222)
.Name = «Кнопка»
.OnAction = «Макрос»
End With
End Sub
Панель с одной кнопкой
Sub CreateCustomControlBar()
‘ Создание панели инструментов
With Application.CommandBars.Add(Name:=»Панель», Temporary:=True)
‘ Создание и настройка кнопки
With .Controls.Add(Type:=msoControlButton)
.Style = msoButtonIconAndCaption
.FaceId = 66
.Caption = «Просто кнопка»
End With
‘ Покажем панель
.Visible = True
End With
End Sub
Панель с двумя кнопками
Sub CreateCustomControlBar()
‘ Создание панели инструментов
With Application.CommandBars.Add(Name:=»Панель», Temporary:=True, _
Position:=msoBarLeft)
‘ Создание и настройка первой кнопки
With .Controls.Add(Type:=msoControlButton)
.Style = msoButtonWrapCaption
.Caption = «Просто кнопка»
End With
‘ Создание и настройка второй кнопки
With .Controls.Add(Type:=msoControlButton)
.Style = msoButtonIconAndWrapCaption
.Caption = «Кнопка»
.FaceId = 225
End With
‘ Покажем панель
.Visible = True
End With
End Sub
Создание панели справа
Sub CreateCustomControlBar()
‘ Создание панели инструментов
With Application.CommandBars.Add(Name:=»Правая панель», _
Temporary:=True)
‘ Создание и настройка кнопки
With .Controls.Add(Type:=msoControlButton)
.Style = msoButtonWrapCaption
.Caption = «Кнопка»
End With
‘ Задание позиции — справа
.Position = msoBarRight
‘ Покажем панель
.Visible = True
End With
End Sub
Вызов предварительного просмотра
Sub Test()
With Application.Workbooks.Item(«Test.xls»)
Sheets(«Test»).PrintPreview
End With
End Sub
Создание пользовательского меню (вариант 1)
Sub AddCustomMenu()
‘ Добавление меню
With Application.CommandBars(1).Controls.Add(Type:=msoControlPopup, _
Temporary:=True)
.Caption = «Архив»
With .Controls
‘ Добавление и настройка первого пункта
With .Add(Type:=msoControlButton)
.FaceId = 280
.Caption = «Просмотр»
.OnAction = «Макрос1»
End With
‘ Добавление вложенного меню
With .Add(Type:=msoControlPopup)
.Caption = «База данных»
With .Controls
‘ Добавление и настройка первого пункта _
вложенного меню
With .Add(Type:=msoControlButton)
.FaceId = 1643
.Caption = «Поставщики»
.OnAction = «Макрос2»
End With
‘ Добавление и настройка второго пункта _
вложенного меню
With .Add(Type:=msoControlButton)
.FaceId = 1000
.Caption = «Покупатели»
.OnAction = «Макрос3»
End With
End With
End With
End With
End With
End Sub
Создание пользовательского меню (вариант 2)
Sub AddCustomMenu1()
‘ Добавление меню с названием «Архив» в часть меню, _
относящуюся к рабочей книге
With MenuBars(«Worksheet»).Menus.Add(Caption:=»Архив»)
‘ Добавление кнопки
.MenuItems.Add Caption:=»Просмотр», OnAction:=»Макрос1″
‘ Добавление подменю
With .MenuItems.AddMenu(Caption:=»База данных»)
‘ Добавление пунктов подменю
.MenuItems.Add Caption:=»Поставщики», OnAction:=»Макрос2″
.MenuItems.Add Caption:=»Покупатели», OnAction:=»Макрос3″
End With
End With
End Sub
Создание пользовательского меню (вариант 3)
Sub AddCustomMenu2()
‘ Добавление меню с названием «Архив» в часть меню, _
относящуюся к рабочей книге
With MenuBars(«Worksheet»).Menus.Add(Caption:=»Архив»)
‘ Добавление кнопки
.MenuItems.Add Caption:=»Просмотр», OnAction:=»Макрос1″
‘ Добавление подменю
With .MenuItems.AddMenu(Caption:=»База данных»)
‘ Добавление первого пункта подменю
With .MenuItems.Add(Caption:=»Поставщики»)
‘ Настройка кнопки
.OnAction = «Макрос2»
End With
‘ Добавление второго пункта подменю
With .MenuItems.Add(Caption:=»Покупатели»)
‘ Настройка кнопки
.OnAction = «Макрос3»
End With
End With
End With
End Sub
Создание пользовательского меню (вариант 4)
Sub Workbook_Open()
‘ Задание имени меню
strMenuName = «MyCommandBarName»
‘ Создание меню
CreateCustomMenu
End Sub
Создание пользовательского меню (вариант 5)
Sub Workbook_BeforeClose(Cancel As Boolean)
‘ Удаление меню перед закрытием книги
DeleteCustomMenu
End Sub
Public strMenuName As String ‘ Имя строки меню
Private cbrcBar As CommandBarControl
Sub CreateCustomMenu()
Dim cbrMenu As CommandBar
Dim cbrcMenu As CommandBarControl ‘ Выпадающее меню «Меню»
Dim cbrcSubMenu As CommandBarControl ‘ Выпадающее меню «Дополнительно»
‘ Если уже есть пользовательское меню, то оно удаляется
DeleteCustomMenu
‘ Создание меню вместо стандартного
Set cbrMenu = Application.CommandBars.Add(strMenuName, msoBarTop, _
True, True)
‘ Создание выпадающего меню с названием «Меню»
Set cbrcMenu = cbrMenu.Controls.Add(msoControlPopup, , , , True)
With cbrcMenu
.Caption = «&Меню»
End With
‘ Создание пункта меню
With cbrcMenu.Controls.Add(Type:=msoControlButton, _
Temporary:=True)
.Caption = «&Меню1»
.OnAction = «CallMenu1»
End With
‘ Создание пункта меню
With cbrcMenu.Controls.Add(Type:=msoControlButton, _
Temporary:=True)
.Caption = «Меню2»
.OnAction = «CallMenu2»
End With
‘ Создание подменю первого уровня
Set cbrcSubMenu = cbrcMenu.Controls.Add(Type:=msoControlPopup, _
Temporary:=True)
With cbrcSubMenu
.Caption = «Подменю1»
.BeginGroup = True
End With
‘ Создание пункта меню
With cbrcMenu.Controls.Add(Type:=msoControlButton, _
Temporary:=True)
.Caption = «Вкл/Выкл»
.OnAction = «MenuOnOff»
.Style = msoButtonIconAndCaption
.FaceId = 463
End With
‘ Создание пункта меню в подменю первого уровня
With cbrcSubMenu.Controls.Add(Type:=msoControlButton, _
Temporary:=True)
.Caption = «Подменю1»
.OnAction = «CallSubMenu1»
.Style = msoButtonIconAndCaption
.FaceId = 2950
.State = msoButtonDown
End With
‘ Cоздание пункта меню в подменю первого уровня (его состояние _
изменяется посредством пункта «Вкл/Выкл»), для чего сохраним ссылку _
на созданный пункт меню
Set cbrcBar = cbrcSubMenu.Controls.Add(Type:=msoControlButton, _
Temporary:=True)
With cbrcBar
.Caption = «Подменю2»
.OnAction = «CallSubMenu2»
‘ Сначала меню деактивировано
.Enabled = False
End With
‘ Создание подменю второго уровня
Set cbrcSubMenu = cbrcSubMenu.Controls.Add(Type:=msoControlPopup, _
Temporary:=True)
With cbrcSubMenu
.Caption = «ПодчПодменю1»
.BeginGroup = True
End With
‘ Cоздание пункта меню в подменю второго уровня
With cbrcSubMenu.Controls.Add(Type:=msoControlButton, _
Temporary:=True)
.Caption = «ПослМеню1»
.OnAction = «CallLastMenu1»
.Style = msoButtonIconAndCaption
.FaceId = 71
.State = msoButtonDown
End With
‘ Cоздание пункта меню в подменю второго уровня
With cbrcSubMenu.Controls.Add(Type:=msoControlButton, _
Temporary:=True)
.Caption = «ПослМеню2»
.OnAction = «CallLastMenu2»
.Style = msoButtonIconAndCaption
.FaceId = 72
.Enabled = True
End With
‘ Отображение меню
cbrMenu.Visible = True
Set cbrcSubMenu = Nothing
Set cbrcMenu = Nothing
Set cbrMenu = Nothing
End Sub
Sub DeleteCustomMenu()
‘ Удаление строки меню
On Error Resume Next
Application.CommandBars(strMenuName).Delete
On Error GoTo 0
End Sub
Sub CallMenu1()
‘ Обработка вызова Меню1
MsgBox «Приветствует меню 1!», vbInformation, ThisWorkbook.Name
End Sub
Sub CallMenu2()
‘ Обработка вызова Меню2
MsgBox «Приветствует меню 2!», vbInformation, ThisWorkbook.Name
End Sub
Sub CallSubMenu1()
‘ Обработка вызова Подменю1
MsgBox «Приветствует подменю 1!», vbInformation, ThisWorkbook.Name
End Sub
Sub CallSubMenu2()
‘ Обработка вызова Подменю2
MsgBox «Приветствует подменю 2!», vbInformation, ThisWorkbook.Name
End Sub
Sub CallLastMenu1()
‘ Обработка вызова Последнего меню1
MsgBox «Приветствует последнее меню 1!», vbInformation, ThisWorkbook.Name
End Sub
Sub CallLastMenu2()
‘ Обработка вызова Последнего меню2
MsgBox «Приветствует последнее меню 2!», vbInformation, ThisWorkbook.Name
End Sub
Sub MenuOnOff()
‘ Активация или деактивация пункта «Меню-Подменю1-Подменю2»
cbrcBar.Enabled = Not cbrcBar.Enabled
End Sub
Создание пользовательского меню (вариант 6)
Sub CreateMenu()
Dim cbrMenu As CommandBar
Dim cbrcNewMenu As CommandBarControl
‘ Удаление меню, если оно уже есть
Call DeleteMenu
‘ Добавление строки пользовательского меню
Set cbrMenu = CommandBars.Add(MenuBar:=True)
With cbrMenu
.Name = «Моя строка меню»
.Visible = True
End With
‘ Копирование стандартного меню «Файл»
CommandBars(«Worksheet Menu Bar»).FindControl(ID:=30002).Copy _
CommandBars(«Моя строка меню»)
‘ Добавление нового меню — «Дополнительно»
Set cbrcNewMenu = cbrMenu.Controls.Add(msoControlPopup)
cbrcNewMenu.Caption = «&Дополнительно»
‘ Добавление команды в новое меню
With cbrcNewMenu.Controls.Add(msoControlButton)
.Caption = «&Восстановить обычную строку меню»
.OnAction = «DeleteMenu»
End With
‘ Добавление команды в новое меню
With cbrcNewMenu.Controls.Add(Type:=msoControlButton)
.Caption = «&Справка»
End With
End Sub
Sub DeleteMenu()
‘ Пытаемся удалить меню (успешно, если оно ранее создано)
On Error Resume Next
CommandBars(«Моя строка меню»).Delete
On Error GoTo 0
End Sub
Список панелей инструментов и контекстных меню
Sub ListOfMenues()
Dim intRow As Integer ‘ Хранит текущую строку
Dim cbrBar As CommandBar
‘ Очистка всех ячеек текущего листа
Cells.Clear
intRow = 1 ‘ Начинаем запись с первой строки
‘ Просматриваем список панелей инструментов и меню _
и записываем информацию о каждом элементе в таблицу
For Each cbrBar In CommandBars
‘ Порядковый номер
Cells(intRow, 1) = cbrBar.Index
‘ Название
Cells(intRow, 2) = cbrBar.Name
‘ Тип
Select Case cbrBar.Type
Case msoBarTypeNormal
Cells(intRow, 3) = «Панель инструментов»
Case msoBarTypeMenuBar
Cells(intRow, 3) = «Строка меню»
Case msoBarTypePopup
Cells(intRow, 3) = «Контекстное меню»
End Select
‘ Встроенный элемент или созданный пользователем
Cells(intRow, 4) = cbrBar.BuiltIn
‘ Переходим на следующую строку
intRow = intRow + 1
Next
End Sub
Создание списка пунктов главного меню Excel
Листинг 3.90. Список содержимого главного меню
Sub ListOfMenues()
Dim intRow As Integer ‘ Текущая строка, куда идет запись
Dim cbrcMenu As CommandBarControl ‘ Главное меню
Dim cbrcSubMenu As CommandBarControl ‘ Подменю
Dim cbrcSubSubMenu As CommandBarControl ‘ Подменю в подменю
‘ Очищаем ячейки текущего листа
Cells.Clear
‘ Начинаем запись с первой строки
intRow = 1
‘ Просматриваем все элементы строки меню
On Error Resume Next ‘ Игнорируем ошибки
For Each cbrcMenu In CommandBars(1).Controls
‘ Просматриваем элементы выпадающего меню cbrcMenu
For Each cbrcSubMenu In cbrcMenu.Controls
‘ Просматриваем элементы подменю cbrcSubMenu
For Each cbrcSubSubMenu In cbrcSubMenu.Controls
‘ Выводим название главного меню
Cells(intRow, 1) = cbrcMenu.Caption
‘ Выводим название подменю
Cells(intRow, 2) = cbrcSubMenu.Caption
‘ Выводим название вложенного подменю
Cells(intRow, 3) = cbrcSubSubMenu.Caption
‘ Переходим на следующую строку
intRow = intRow + 1
Next cbrcSubSubMenu
Next cbrcSubMenu
Next cbrcMenu
End Sub
Создание списка пунктов контекстных меню
Листинг 3.91. Список содержимого контекстных меню
Sub ListOfContextMenues()
Dim intRow As ****
Dim intControl As Integer
Dim cbrBar As CommandBar
‘ Очистка ячеек активного листа
Cells.Clear
‘ Начинаем вывод с первой строки
intRow = 1
‘ Просмотр списка контекстных меню и вывод информации о них
For Each cbrBar In CommandBars
If cbrBar.Type = msoBarTypePopup Then
‘ Порядковый номер
Cells(intRow, 1) = cbrBar.Index
‘ Название
Cells(intRow, 2) = cbrBar.Name
‘ Просмотр всех элементов контекстного меню и вывод _
названий этих элементов в ячейки текущей строки
For intControl = 1 To cbrBar.Controls.Count
Cells(intRow, intControl + 2) = _
cbrBar.Controls(intControl).Caption
Next intControl
‘ Переход на следующую строку таблицы
intRow = intRow + 1
End If
Next cbrBar
‘ Делаем ширину ячеек таблицы оптимальной для просмотра
Cells.EntireColumn.AutoFit
End Sub
Отображение панели инструментов при определенном условии
Листинг 3.92. Код в модуле рабочего листа
Sub Worksheet_Selectiоnchange(ByVal Target As Excel.Range)
‘ Проверка условия отображения
If Union(Target, Range(«A1:D5»)).Address = _
Range(«A1:D5»).Address Then
‘ Условие выполнено — можно показывать панель
CommandBars(«AutoSense»).Visible = True
Else
‘ Условие не выполнено — панель нужно скрыть
CommandBars(«AutoSense»).Visible = False
End If
End Sub
Листинг 3.93. Код в стандартном модуле
Sub CreatePanel()
Dim cbrBar As CommandBar
Dim button As CommandBarButton
Dim i As Integer
‘ Удаление одноименной панели (при ее наличии)
On Error Resume Next
CommandBars(«AutoSense»).Delete
On Error GoTo 0
‘ Создание панели инструментов
Set cbrBar = CommandBars.Add
‘ Создание кнопок и их настройка
For i = 1 To 4
Set button = cbrBar.Controls.Add(msoControlButton)
With button
.OnAction = «Buttоnclick» & i
.FaceId = i + 37
End With
Next i
cbrBar.Name = «AutoSense»
End Sub
Sub Buttоnclick3()
‘ Перемещение вниз
On Error Resume Next
ActiveCell.Offset(1, 0).Activate
End Sub
Sub Buttоnclick1()
‘ Перемещение вверх
On Error Resume Next
ActiveCell.Offset(-1, 0).Activate
End Sub
Sub Buttоnclick2()
‘ Перемещение вправо
On Error Resume Next
ActiveCell.Offset(0, 1).Activate
End Sub
Sub Buttоnclick4()
‘ Перемещение влево
On Error Resume Next
ActiveCell.Offset(0, -1).Activate
End Sub
Скрытие и отображение панелей инструментов
Листинг 3.94. Управление отображением панелей инструментов
Sub HidePanels()
Dim cbrBar As CommandBar
Dim intRow As Integer ‘ Номер текущей строки листа
‘ Отключение обновления экрана
Application.ScreenUpdating = False
‘ Подготовка к сохранению
Cells.Clear
‘ Скрытие видимых панелей и сохранение их названий
intRow = 1 ‘ Запись имен с первой строки
For Each cbrBar In CommandBars
If cbrBar.Type = msoBarTypeNormal Then
If cbrBar.Visible Then
cbrBar.Visible = False
Cells(intRow, 1) = cbrBar.Name
intRow = intRow + 1
End If
End If
Next
‘ Включение обновления экрана
Application.ScreenUpdating = True
End Sub
Sub ShowPanels()
Dim cell As Range ‘ Текущая ячейка листа
‘ Отключение обновления экрана
Application.ScreenUpdating = False
‘ Отображение скрытых панелей
On Error Resume Next
For Each cell In Range(«A:A»).SpecialCells( _
xlCellTypeConstants)
CommandBars(cell.Value).Visible = True
Next cell
‘ Включение обновления экрана
Application.ScreenUpdating = True
End Sub
Создать подсказку к моим кнопкам
‘ Cоздаем тулбар
Рublic Sub InitToolBar()
Dim cmdbarSM As CommandBar
Dim ctlNewBtn As CommandBarButton
Set cmdbarSM = CommandBars.Add(Name:=»MyToolBar»,
Position:=msoBarFloating, _
temporary:=True)
With cmdbarSM
‘ 1) Добавляем кнопку
Set ctlNewBtn = .Controls.Add(Type:=msoControlButton)
With ctlNewBtn
. FaceId = 26
.OnAction = «OnButton1_Click»
.TooltipText = «My tooltip message!»
End With
‘ 2) Добавляем ещё кнопку
Set ctlNewBtn = .Controls.Add(Type:=msoControlButton)
With ctlNewBtn
.FaceId = 44
.OnAction = «OnButton2_Click»
.TooltipText = «Another tooltip message!»
End With
.Visible = True
End With
End Sub
Создание меню на основе данных рабочего листа
Листинг 3.95. Код в модуле ЭтаКнига
Sub Workbook_Open()
‘ Создание меню
Call CreateCustomMenu
End Sub
Sub Workbook_BeforeClose(Cancel As Boolean)
‘ Удаление меню перед закрытием книги
Call DeleteCustomMenu
End Sub
Листинг 3.96. Код в стандартном модуле
Sub CreateMenu()
Dim sheet As Worksheet ‘ Лист с описанием меню
Dim intRow As Integer ‘ Считываемая строка
Dim cbrpBar As CommandBarPopup ‘ Выпадающее меню
Dim objNewItem As Object ‘ Элемент меню cbrpBar
Dim objNewSubItem As Object ‘ Элемент подменю objNewItem
Dim intMenuLevel As Integer ‘ Уровень вложенности пункта меню
Dim strCaption As String ‘ Название пункта меню
Dim strAction As String ‘ Макрос пункта меню
Dim fIsDevider As Boolean ‘ Нужен разделитель
Dim intNextLevel As Integer ‘ Уровень вложенности следующего _
пункта меню
Dim strFaceID As String ‘ Номер значка пункта меню
‘ Расположение данных для меню
Set sheet = ThisWorkbook.Sheets(«ЛистМеню»)
‘ Удаление одноименного меню (при его наличии)
Call DeleteMenu
‘ Данные считываем со второй строки
intRow = 2
‘ Добавление меню
Do Until IsEmpty(sheet.Cells(intRow, 1))
‘ Считываем информацию о пункте меню
With sheet
‘ Уровень вложенности
intMenuLevel = .Cells(intRow, 1)
‘ Название
strCaption = .Cells(intRow, 2)
‘ Название макроса для меню
strAction = .Cells(intRow, 3)
‘ Нужен ли разделитель перед меню?
fIsDevider = .Cells(intRow, 4)
‘ Номер стандартного значка (если значок нужен)
strFaceID = .Cells(intRow, 5)
‘ Уровень вложенности следующего меню
intNextLevel = .Cells(intRow + 1, 1)
End With
‘ Создаем меню в зависимости от уровня его вложенности
Select Case intMenuLevel
Case 1
‘ Создаем меню
Set cbrpBar = Application.CommandBars(1). _
Controls.Add(Type:=msoControlPopup, _
Before:=strAction, _
Temporary:=True)
cbrpBar.Caption = strCaption
Case 2
‘ Создаем элемент меню
If intNextLevel = 3 Then
‘ Следующий элемент вложен в создаваемый, то есть _
создаем раскрывающееся подменю
Set objNewItem = _
cbrpBar.Controls.Add(Type:=msoControlPopup)
Else
‘ Создаем команду меню
Set objNewItem = _
cbrpBar.Controls.Add(Type:=msoControlButton)
objNewItem.OnAction = strAction
End If
‘ Установка названия нового пункта меню
objNewItem.Caption = strCaption
‘ Установка значка нового пункта меню (если нужно)
If strFaceID <> «» Then
objNewItem.FaceId = strFaceID
End If
‘ Если нужно, то добавим разделитель
If fIsDevider Then
objNewItem.BeginGroup = True
End If
Case 3
‘ Создание элемента подменю
Set objNewSubItem = _
objNewItem.Controls.Add(Type:=msoControlButton)
‘ Установка его названия
objNewSubItem.Caption = strCaption
‘ Назначение макроса (или команды)
objNewSubItem.OnAction = strAction
‘ Установка значка (если нужно)
If strFaceID <> «» Then
objNewSubItem.FaceId = strFaceID
End If
‘ Если нужно, то добавим разделитель
If fIsDevider Then
objNewSubItem.BeginGroup = True
End If
End Select
‘ Переход на следующую строку таблицы
intRow = intRow + 1
Loop
End Sub
Sub DeleteMenu()
Dim sheet As Worksheet ‘ Лист с описанием меню
Dim intRow As Integer ‘ Считываемая строка
Dim strCaption As String ‘ Название меню
Set sheet = ThisWorkbook.Sheets(«ЛистМеню»)
‘ Данные начинаются со второй строки
intRow = 2
‘ Считываем данные, пока есть значения в столбце «A», _
и удаляем созданные ранее меню (с уровнем вложенности 1)
On Error Resume Next
Do Until IsEmpty(sheet.Cells(intRow, 1))
If sheet.Cells(intRow, 1) = 1 Then
strCaption = sheet.Cells(intRow, 2)
Application.CommandBars(1).Controls(strCaption).Delete
End If
intRow = intRow + 1
Loop
On Error GoTo 0
End Sub
Создание контекстного меню
Листинг 3.97. Код в модуле рабочего листа
Sub Worksheet_BeforeRightClick(ByVal Target As Excel.Range, _
Cancel As Boolean)
‘ Проверка, попадает ли выделенная ячейка в диапазон
If Union(Target.Range(«A1»), Range(«A2:D5»)).Address = _
Range(«A2:D5»).Address Then
‘ Показываем свое контекстное меню
CommandBars(«MyContextMenu»).ShowPopup
Cancel = True
End If
End Sub
Листинг 3.98. Код в модуле ЭтаКнига
Sub Workbook_Open()
‘ Создание контекстного меню при открытии книги
Call CreateCustomContextMenu
End Sub
Sub Workbook_BeforeClose(Cancel As Boolean)
‘ Удаление меню при закрытии книги
Call DeleteCustomContextMenu
End Sub
Код в стандартном модуле
Sub CreateCustomContextMenu()
‘ Удаление одноименного меню
Call DeleteCustomContextMenu
‘ Создание меню
With CommandBars.Add(«MyContextMenu», msoBarPopup, , True).Controls
‘ Создание и настройка кнопок меню
‘ Кнопка «Числовой формат»
With .Add(msoControlButton)
.Caption = «&Числовой формат…»
.OnAction = «ShowFormatNumber»
.FaceId = 1554
End With
‘ Кнопка «Выравнивание»
With .Add(msoControlButton)
.Caption = «&Выравнивание…»
.OnAction = «ShowFormatAlignment»
.FaceId = 217
End With
‘ Кнопка «Шрифт»
With .Add(msoControlButton)
.Caption = «&Шрифт…»
.OnAction = «ShowFormatFont»
.FaceId = 291
End With
‘ Кнопка «Границы»
With .Add(msoControlButton)
.Caption = «&Границы…»
.OnAction = «ShowFormatBorder»
.FaceId = 149
.BeginGroup = True
End With
‘ Кнопка «Узор»
With .Add(msoControlButton)
.Caption = «&Узор…»
.OnAction = «ShowFormatPatterns»
.FaceId = 1550
End With
‘ Кнопка «Защита»
With .Add(msoControlButton)
.Caption = «&Защита…»
.OnAction = «ShowFormatProtection»
.FaceId = 2654
End With
End With
End Sub
Блокировка контекстного меню
Sub Worksheet_BeforeRightClick(ByVal Target As Range, Cancel As Boolean)
Static intCount As Integer ‘ Счетчик нажатий кнопки мыши
Dim x As Integer, y As Integer
‘ Блокировать обработку щелчка правой кнопкой мыши
Cancel = True
‘ Отображение текстового поля с количеством щелчков правой _
кнопкой мыши
x = Target.Left
y = Target.Top
intCount = intCount + 1
ActiveSheet.Shapes.AddTextbox(msoTextOrientationHorizontal, _
x, y, 35, 20).TextFrame.Characters.Text = intCount
End Sub
Добавление команды в меню Сервис
Sub AddMenuItem()
Dim cbrpMenu As CommandBarPopup
‘ Удаление аналогичной команды (при ее наличии)
Call DeleteMenuItem
‘ Получение доступа к меню «Сервис»
Set cbrpMenu = CommandBars(1).FindControl(ID:=30007)
If cbrpMenu Is Nothing Then
‘ Не удалось получить доступ
MsgBox «Невозможно добавить элемент.»
Exit Sub
Else
‘ Добавление новой команды в меню
With cbrpMenu.Controls.Add(Type:=msoControlButton)
‘ Название команды
.Caption = «Очистить в&се, кроме формул»
‘ Значок
.FaceId = 348
‘ Сочетание клавиш (только надпись на кнопке)
.ShortcutText = «Ctrl+Shift+C»
‘ Сопоставленный макрос
.OnAction = «ExecuteCommand»
‘ Добавление разделителя перед командой
.BeginGroup = True
End With
End If
‘ Сопоставление с макросом сочетания клавиш Ctrl+Shift+C
Application.MacroOptions _
Macro:=»ExecuteCommand», _
HasShortcutKey:=True, _
ShortcutKey:=»C»
End Sub
Sub ExecuteCommand()
‘ Очистка содержимого всех ячеек (кроме формул)
On Error Resume Next
Cells.SpecialCells(xlCellTypeConstants, 23).ClearContents
End Sub
Sub DeleteMenuItem()
‘ Удаление команды из меню
On Error Resume Next
CommandBars(1).FindControl(ID:=30007). _
Controls(«Очистить в&се, кроме формул»).Delete
End Sub
Добавление команды в меню Вид
Листинг 3.110. Код в стандартном модуле
Dim AppObject As New Class1
Sub AddCommand()
Dim cbrpBar As CommandBarPopup
‘ Удаление аналогичной команды (при ее наличии)
Call DeleteCommand
‘ Получение доступа к меню «Вид»
Set cbrpBar = CommandBars(1).FindControl(ID:=30004)
If cbrpBar Is Nothing Then
‘ Не удалось получить доступ к меню
MsgBox «Невозможно добавить элемент меню.»
Exit Sub
Else
‘ Добавление команды
With cbrpBar.Controls.Add(Type:=msoControlButton)
.Caption = «&Линии сетки»
.OnAction = «GhangeGridlinesState»
End With
End If
‘ Даем объекту AppObject обрабатывать события
Set AppObject.AppEvents = Application
End Sub
Sub DeleteCommand()
‘ Удаление каманды из меню (если она там есть)
On Error Resume Next
CommandBars(1).FindControl(ID:=30004). _
Controls(«&Линии сетки»).Delete
End Sub
Sub GhangeGridlinesState()
‘ Изменение состояния отображения линий сетки _
на противоположное (если нет — покажем, если есть — скроем)
If TypeName(ActiveSheet) = «Worksheet» Then
ActiveWindow.DisplayGridlines = _
Not ActiveWindow.DisplayGridlines
‘ Установка или снятие флажка в меню
Call CheckGridlines
End If
End Sub
Sub CheckGridlines()
Dim button As CommandBarButton
On Error Resume Next
‘ Поиск команды «Линии сетки» в меню «Вид»
Set button = CommandBars(1).FindControl(ID:=30004). _
Controls(«&Линии сетки»)
‘ Изменение состояния флажка на противоположное
If ActiveWindow.DisplayGridlines Then
‘ Установка
button.State = msoButtonDown
Else
‘ Снятие
button.State = msoButtonUp
End If
End Sub
Создание панели со списком
Sub DeleteCustomContextMenu()
‘ Удаление меню
On Error Resume Next
CommandBars(«MyContextMenu»).Delete
End Sub
Sub ShowFormatNumber()
‘ Число
Application.Dialogs(xlDialogFormatNumber).Show
End Sub
Sub ShowFormatAlignment()
‘ Выравнивание
Application.Dialogs(xlDialogAlignment).Show
End Sub
Sub ShowFormatFont()
‘ Шрифт
Application.Dialogs(xlDialogFormatFont).Show
End Sub
Sub ShowFormatBorder()
‘ Граница
Application.Dialogs(xlDialogBorder).Show
End Sub
Sub ShowFormatPatterns()
‘ Вид (Узор)
Application.Dialogs(xlDialogPatterns).Show
End Sub
Sub ShowFormatProtection()
‘ Защита
Application.Dialogs(xlDialogCellProtection).Show
End Sub
Sub CreatePanel()
Dim i As Integer
On Error Resume Next
‘ Удаление одноименной панели (если есть)
CommandBars(«Список месяцев»).Delete
On Error GoTo 0
‘ Создание панели «Список месяцев»
With CommandBars.Add
.Name = «Список месяцев»
‘ Создание списка месяцев
With .Controls.Add(Type:=msoControlDropdown)
‘ Настройка (имя, макрос, стиль)
.Caption = «DateDD»
.OnAction = «SetMonth»
.Style = msoButtonAutomatic
‘ Добавление в список названий месяцев
For i = 1 To 12
.AddItem Format(DateSerial(1, i, 1), «mmmm»)
Next i
‘ Выделение первого месяца
.ListIndex = 1
End With
‘ Показываем созданную панель
.Visible = True
End With
End Sub
Sub SetMonth()
‘ Перенос названия выделенного месяца в ячейку
On Error Resume Next
With CommandBars(«Список месяцев»).Controls(«DateDD»)
ActiveCell.Value = .List(.ListIndex)
End With
End Sub
Мультфильм с помощником в главной роли
Листинг 4.1. «Танцующий» помощник
Sub RunAssistantDance()
Static intAction As Integer
‘ Заставляем помощника выполнять действие (всего 16)
DoAssistantAction intAction
intAction = intAction + 1
If intAction < 16 Then
‘ Следующее действие через 3 секунды
Application.OnTime Time + TimeValue(«00:00:3»), _
«RunAssistantDance»
End If
End Sub
Sub DoAssistantAction(intAction As Integer)
Dim astAssistant As Assistant
Set astAssistant = Application.Assistant
‘ Помещаем помощника в центр активного окна
astAssistant.Top = Application.ActiveWindow.Top _
+ Application.ActiveWindow.Height / 2
astAssistant.Left = Application.ActiveWindow.Left _
+ Application.ActiveWindow.Width / 2
‘ Показываем помощника
astAssistant.On = True
astAssistant.Visible = True
‘ Показываем заданное параметром intAction действие
Select Case intAction
Case 0
astAssistant.Animation = msoAnimationAppear
Case 1
astAssistant.Animation = msoAnimationCheckingSomething
Case 2
astAssistant.Animation = msoAnimationBeginSpeaking
Case 3
astAssistant.Animation = msoAnimationCharacterSuccessMajor
Case 4
astAssistant.Animation = msoAnimationEmptyTrash
Case 5
astAssistant.Animation = msoAnimationGestureDown
Case 5
astAssistant.Animation = msoAnimationGestureLeft
Case 6
astAssistant.Animation = msoAnimationGestureRight
Case 7
astAssistant.Animation = msoAnimationGestureUp
Case 8
astAssistant.Animation = msoAnimationGetArtsy
Case 9
astAssistant.Animation = msoAnimationGetAttentionMajor
Case 10
astAssistant.Animation = msoAnimationGetAttentionMinor
Case 11
astAssistant.Animation = msoAnimationGetTechy
Case 12
astAssistant.Animation = msoAnimationGetWizardy
Case 13
astAssistant.Animation = msoAnimationGoodbye
Case 14
astAssistant.Animation = msoAnimationGreeting
Case 15
astAssistant.Animation = msoAnimationDisappear
End Select
End Sub
Дополнение помощника текстом, заголовком, кнопкой и значком
Листинг 4.2. Настройка помощника
Sub AssistantMessage()
Dim strTitle As String ‘ Заголовок сообщения
Dim strMessage As String ‘ Текст сообщения
‘ Содержимое заголовка и текста в окне помощника
strTitle = «Спрашивайте — ответим»
strMessage = «{cf 249}{ul 1} Руки мыли{ul 0}?» _
& vbCr & «{cf 6} Не забыть обновить антивирус!»
‘ Настраиваем помощника
With Application.Assistant
‘ Включаем и показываем помощника
.On = True
.Visible = True
‘ Создаем окно сообщения
With .NewBalloon
.BalloonType = msoBalloonTypeButtons
‘ Кнопка «ОК» в окне помощника
.button = msoButtonSetOK
‘ Значок в окне помощника
.Icon = msoIconAlert
‘ Заголовок в окне помощника
.Heading = strTitle
‘ Текст в окне помощника
.Text = strMessage
‘ Отображение окна
.Show
End With
End With
End Sub
Новые параметры помощника
Листинг 4.3. Новые параметры помощника
Sub AssistantCheckboxes()
Dim i As Integer
Dim strMessage As String
With Assistant
‘ Включение и отображение помощника
.On = True
.Visible = True
‘ Создание окна сообщения
With .NewBalloon
‘ Настройка окна…
‘ Тип окна
.BalloonType = msoBalloonTypeButtons
‘ Заголовок
.Heading = «Выберите страну»
‘ Добавление флажков
.CheckBoxes(1).Text = «Россия»
.CheckBoxes(2).Text = «США»
.CheckBoxes(3).Text = «Южная Африка»
.button = msoButtonSetOkCancel
‘ Отображение окна
If .Show = msoBalloonButtonOK Then
‘ Вывод информационного окна в зависимости _
от установленных флажков
For i = 1 To 3
If .CheckBoxes(i).Checked Then
strMessage = strMessage & _
.CheckBoxes(i).Text & vbCr
End If
Next
‘ Отображение окна сообщения (имеется в виду _
стандартное окно)
If Len(strMessage) = 0 Then
MsgBox «No choice.»
Else
MsgBox strMessage
End If
End If
End With
End With
End Sub
Использование помощника для выбора цвета заливки
Листинг 4.4. Выбор цвета заливки рабочего листа
Sub AssistantChooseColor()
Dim intChoise As Integer
With Assistant
‘ Включение и отображение помощника
.On = True
.Visible = True
With .NewBalloon
‘ Настройка окна…
‘ Тип
.BalloonType = msoBalloonTypeButtons
‘ Заголовок
.Heading = «Какой нужен цвет?»
‘ Первый цвет
.Labels(1).Text = «Красный»
‘ Второй цвет
.Labels(2).Text = «Желтый»
‘ Третий цвет
.Labels(3).Text = «Зеленый»
‘ Тип кнопок
.button = msoButtonSetNone
‘ Оображение окна
intChoise = .Show
‘ Информационное сообщение о выбранном цвете
MsgBox «Выбран: » & .Labels(intChoise).Text
End With
End With
‘ Настройка цветов ячеек (присвоение выбранного цвета)
Select Case intChoise
Case 1
‘ Красный цвет
ActiveSheet.Cells.Interior.Color = RGB(255, 0, 0)
Case 2
‘ Желтый цвет
ActiveSheet.Cells.Interior.Color = RGB(255, 255, 0)
Case 3
‘ Зеленый цвет
ActiveSheet.Cells.Interior.Color = RGB(0, 255, 0)
End Select
End Sub
ГЛАВА 6. ДИАЛОГОВЫЕ ОКНА
Функция INPUTBOX (через ввод значения)
Public Sub ИнпутБокс()
Dim текст As Variant
MsgBox «Если в InputBox нажать Отмена, в ячейке будут удалены все данные»
текст = InputBox(«Введите текст», «Окно ввода текста», «222»)
MsgBox текст
If текст <> «» Then
Range(«H7») = текст
MsgBox «Как сделать так, чтобы при выборе пользователем в InputBox — Отмена он закрывался и прекращалось выполнение процедуры?»
Else
Exit Sub
End If
End Sub
Вызов предварительного просмотра
Sub Test()
With Application.Workbooks.Item(«Test.xls»)
Sheets(«Test»).PrintPreview
End With
End Sub
Настройка ввода данных в диалоговом окне
Sub DialogInputData()
Dim intMin As Integer, intMax As Integer ‘ Диапазон значений
Dim strInput As String ‘ Введенная пользователем строка
Dim strMessage As String
Dim intValue As Integer
intMin = 1 ‘ Минимальное значение
intMax = 50 ‘ Максимальное значение
strMessage = «Введите значение от » & intMin & » до » & intMax
‘ Ввод значения (цикл завершается, когда пользователь вводит _
значение из заданного диапазона или отменяет ввод)
Do
strInput = InputBox(strMessage)
If strInput = «» Then Exit Sub ‘ Отмена ввода
‘ Проверка, содержит ли введенная пользователем строка число
If IsNumeric(strInput) Then
intValue = CInt(strInput)
‘ Проверка, удовлетворяет ли значение диапазону
If intValue >= intMin And intValue <= intMax Then
‘ Все условия выполнены
Exit Do
End If
End If
‘ Формирование сообщения с текстом ошибки
strMessage = «Вы ввели некорректное значение.» & vbNewLine & _
«Введите число от » & intMin & » до » & intMax
Loop
‘ Внесение данных в ячейку
ActiveSheet.Range(«A1»).Value = strInput
End Sub
Открытие диалогового окна (“Открыть файл”)_1
Sub Test()
Application.Dialogs(xlDialogOpen).Show «*.dbf»
End Sub
Открытие диалогового окна (“Открыть файл”)_2
fileToOpen = Application.GetOpenFilename(«Text Files (*.txt), *.txt»)
If fileToOpen <> False Then
MsgBox «Open » & fileToOpen
End If
Открытие диалогового окна (“Печать”)
Application.Dialogs(xlDialogPrint).Show
Другие диалоговые окна
xlDialogClear — очистка ячейки или диапазона
xlDialogDisplay — параметры отображения ячеек
xlDialogFileDelete — удаление файла
xlDialogSaveWorkbook — сохранить книгу
xlDialogSearch — поиск в документе
xlDialogWorkbookName — переименование листа
Вызов броузера из Экселя
Надо создать кнопку которой добавить код:
Sub Button1_Click()
Call ShellExecute(GetDesktopWindow, «Open», «www.armentel.com/avb», «», «c:», SW_SHOWNORMAL)
End Sub
И функция:
Private Declare Function ShellExecute& Lib «shell32.dll» Alias «ShellExecuteA» (ByVal hwnd As ****, ByVal _
lpOperation As String, ByVal lpFile As String, ByVal lpParameters As String, ByVal lpDirectory As String, _
ByVal nShowCmd As ****)
Private Declare Function GetDesktopWindow Lib «user32» () As ****
Const SW_SHOWNORMAL = 1
Диалоговое окно ввода данных
Sub InputDialog()
Dim strInput As String
‘ Вызов стандартного диалогового окна ввода данных
strInput = InputBox(«Введите данные», «Ввод данных»)
End Sub
Диалоговое окно настройки шрифта
Sub ShowFontDialog()
‘ Вызов стандартного окна настройки шрифта текущей ячейки
Application.Dialogs(xlDialogActiveCellFont).Show
End Sub
Значения по умолчанию
Sub NewInputDialog()
Dim strInput As String
‘ Вызов стандартного диалогового окна ввода со значением _
по умолчанию
strInput = InputBox(«Введите данные», «Ввод данных», _
«Значение по умолчанию», 200, 200)
End Sub
ГЛАВА 7.ФОРМАТИРОВАНИЕ ТЕКСТА. ТАБЛИЦЫ. ГРАНИЦЫ И ЗАЛИВКА.
Вывод списка доступных шрифтов
Листинг 3.104. Список шрифтов
Sub ListOfFonts()
Dim cbrcFonts As CommandBarControl
Dim cbrBar As CommandBar
Dim i As Integer
‘ Получение доступа к списку шрифтов (элемент управления в виде _
раскрывающегося списка на панели инструментов «Форматирование»)
Set cbrcFonts = Application.CommandBars(«Formatting»). _
FindControl(ID:=1728)
If cbrcFonts Is Nothing Then
‘ Панель «Форматирование» не открыта — откроем ее
Set cbrBar = Application.CommandBars.Add
Set cbrcFonts = cbrBar.Controls.Add(ID:=1728)
End If
‘ Подготовка к выводу шрифтов (очистка ячеек)
Range(«A:A»).ClearContents
‘ Вывод списка шрифтов в столбец «A» текущего листа
For i = 0 To cbrcFonts.ListCount — 1
Cells(i + 1, 1) = cbrcFonts.List(i + 1)
Next i
‘ Закрытие панели инструментов «Форматирование», если мы были _
вынуждены ее открывать
On Error Resume Next
cbrBar.Delete
End Sub
Выбор из текста всех чисел
Листинг 2.48. Функция ExtractNumeric
Function ExtractNumeric(iCell)
‘ Анализируется каждый символ входной строки iCell
For iCount = 1 To Len(iCell)
‘ Проверка, является ли анализируемый символ числом
If IsNumeric(Mid(iCell, iCount, 1)) = True Then
‘ Число добавляется в выходную строку
ExtractNumeric = ExtractNumeric & Mid(iCell, iCount, 1)
End If
Next
End Function
Прописная буква только в начале текста
Листинг 2.49. Функция ПрописнНач
Function ПрописнНач(Текст)
‘ Пустой текст функция не обрабатывает
If Текст = «» Then ПрописнНач = «<>»: Exit Function
‘ Выделение первого символа и перевод его в верхний регистр
ПервыйСимвол = UCase(Left(Текст, 1))
‘ Выделение остальной части строки и перевод _
ее в нижний регистр
Обрубок = LCase(Mid(Текст, 2))
‘ Соединение частей строки и возврат значения
ПрописнНач = ПервыйСимвол & Обрубок
End Function
Подсчет количества повторов искомого текста
Листинг 2.51. Функция CoincideCount
Function CoincideCount(Text, Search)
‘ Проверка правильности входных данных _
(аргумента Search)
If IsArray(Search) = True Then Exit Function
If IsError(Search) = True Then Exit Function
If IsEmpty(Search) = True Then Exit Function
‘ Просмотр заданного в параметре Text диапазона
For Each iCell In Text
‘ Анализируются только ячейки, содержащие _
корректные значения
If Not IsError(iCell) Then
‘ iText — строка для просмотра (в нижнем регистре)
iText = LCase(iCell)
‘ iSearch — искомое значение (в нижнем регистре)
iSearch = LCase(Search)
‘ Длина искомой строки
iLen = Len(Search)
‘ Первый поиск строки iSearch в строке iText _
(этот и последующий поиски производятся без _
учета регистра символов)
iNumber = InStr(iText, iSearch)
While iNumber > 0
‘ Поиск следующего вхождения строки
iNumber = InStr(iNumber + iLen, iText, iSearch)
‘ Подсчет количества вхождений
CoincideCount = CoincideCount + vbNull
Wend
End If
Next
End Function
Выделение из текста произвольного элемента
Листинг 2.76. Выделение элемента текста
Function dhGetTextItem(ByVal strTextIn As String, intItem As _
Integer, strSeparator As String) As String
Dim intStart As Integer ‘ Позиция начала текущего элемента
Dim intEnd As Integer ‘ Позиция конца текущего элемента
Dim i As Integer ‘ Номер текущего элемента
‘ Проверка корректности номера элемента
If intItem < 1 Then Exit Function
‘ Убираются лишние пробелы, если разделитель — пробел
If strSeparator = » » Then strTextIn = Application.Trim(strTextIn)
‘ Разделитель добавляется в конец строки
If Right(strTextIn, Len(strTextIn)) <> strSeparator Then _
strTextIn = strTextIn & strSeparator
‘ Поиск всех элементов в строке до нужного
For i = 1 To intItem
‘ Начало элемента (перемещение вперед по строке)
intStart = intEnd + 1
‘ Конец элемента
intEnd = InStr(intStart, strTextIn, strSeparator)
If (intEnd = 0) Then
‘ Дошли до конца строки, но элемент не нашли
Exit Function
End If
Next i
‘ Выделение текста из входной строки
dhGetTextItem = Mid(strTextIn, intStart, intEnd — intStart)
End Function
Отображение текста «задом наперед»
Листинг 2.71. Преобразование текста в обратном порядке
Function dhReverseText(strText As String) As String
Dim i As Integer
‘ Переписываем символы из входной строки в выходную _
в обратном порядке
For i = Len(strText) To 1 Step -1
dhReverseText = dhReverseText & Mid(strText, i, 1)
Next i
End Function
Sub ReverseText()
Dim strText As String
‘ Ввод строки посредством стандартного окна ввода
strText = InputBox(«Введите текст:»)
‘ Реверсия строки и вывод результата
MsgBox dhReverseText(strText), , strText
End Sub
Англоязычный текст — заглавными буквами
Листинг 2.70. Английский текст — в верхнем регистре
Function dhFormatEnglish(strText As String) As String
Dim i As Integer
Dim strCurChar As String * 1
‘ Анализируется каждый символ строки strText. Каждый символ _
латинского алфавита преобразуется в верхний регистр
For i = 1 To Len(strText)
strCurChar = Mid(strText, i, 1)
‘ Код латинских строчных символов лежит в пределах _
от 97 до 122
If Asc(strCurChar) >= 97 And Asc(strCurChar) <= 122 Then
‘ Переводим символ в верхний регистр
dhFormatEnglish = dhFormatEnglish & UCase(strCurChar)
Else
‘ Просто добавляем символ в выходную строку
dhFormatEnglish = dhFormatEnglish & strCurChar
End If
Next i
End Function
Запуск таблицы символов из Excel
Листинг 3.106. Вызов таблицы символов
Sub ShowSymbolTable()
On Error Resume Next
‘ Запуск Charmap.exe — таблицы символов
Shell «Charmap.exe», vbNormalFocus
If Err <> 0 Then
MsgBox «Невозможно запустить таблицу символов.», vbCritical
End If
End Sub
Листинг 3.107. Таблица символов
‘ Декларация API-функций:
‘ для открытия процесса
Declare Function OpenProcess Lib «kernel32» _
(ByVal dwDesiredAccess As ****, ByVal bInheritHandle As ****, _
ByVal dwProcessId As ****) As ****
‘ для получения кода завершения процесса
Declare Function GetExitCodeProcess Lib «kernel32» _
(ByVal hProcess As ****, lpExitCode As ****) As ****
‘ для закрытия процесса
Declare Function CloseHandle Lib «kernel32» _
(hProcess) As ****
Sub ShowSymbolTable1()
Dim lProcessID As ****
Dim hProcess As ****
Dim lExitCode As ****
On Error Resume Next
‘ Запуск таблицы символов (Charman.exe). Функция возвращает _
идентификатор созданного процесса
lProcessID = Shell(«Charmap.exe», 1)
If Err <> 0 Then
MsgBox «Нельзя запустить Charman.exe», vbCritical, «Ошибка»
Exit Sub
End If
‘ Открытие процесса по идентификатору (lProcessID). Функция _
возвращает дескриптор процесса (handle)
hProcess = OpenProcess(&H400, False, lProcessID)
‘ Ждем, пока процесс завершится, для этого периодически _
получаем код завершения процесса (пока Charman.exe исполняется, _
функция GetExitCodeProcess возвращает &H103)
Do
GetExitCodeProcess hProcess, lExitCode
DoEvents
Loop While lExitCode = &H103
‘ Закрытие процесса
CloseHandle (hProcess)
‘ Вывод на экран информационного сообщения
MsgBox «Charmap.exe завершает свою работу»
End Sub
Листинг 3.64. Формат «два знака после запятой»
Sub ChangeNumberFormat()
Selection.NumberFormat = «0.00»
End Sub
Листинг 3.65. Использование разделителя по разрядам
Sub ThreeNullSepatator()
Selection.NumberFormat = «#,##»
End Sub
Листинг 3.66. Изменение формата
Sub ChangeNumerFormatEx()
Selection.NumberFormat = «#,##0.00»
End Sub
Листинг 3.67. Помещение последнего символа над строкой
Sub LastCharUp()
‘ Изменение расположения последнего символа ячейки
With ActiveCell.Characters(Start:=Len(Selection), Length:=1).Font
.Supersсriрt = True
End With
End Sub
Листинг 3.68. Нестандартная рамка
Sub ChangeSelGrid()
‘ Оформление границ выделения
‘ Левая граница
With Selection.Borders(xlEdgeLeft)
.LineStyle = xlContinuous
.Weight = xlThin
.ColorIndex = xlAutomatic
End With
‘ Правая граница
With Selection.Borders(xlEdgeRight)
.LineStyle = xlContinuous
.Weight = xlThin
.ColorIndex = xlAutomatic
End With
‘ Верхняя граница
With Selection.Borders(xlEdgeTop)
.LineStyle = xlContinuous
.Weight = xlThin
.ColorIndex = xlAutomatic
End With
‘ Нижняя граница
With Selection.Borders(xlEdgeBottom)
.LineStyle = xlContinuous
.Weight = xlThin
.ColorIndex = xlAutomatic
End With
‘ Изменение сетки внутри выделения
‘ Вертикальные линии сетки
With Selection.Borders(xlInsideVertical)
.LineStyle = xlContinuous
.Weight = xlHairline
.ColorIndex = xlAutomatic
End With
‘ Горизонтальные линии сетки
With Selection.Borders(xlInsideHorizontal)
.LineStyle = xlContinuous
.Weight = xlHairline
.ColorIndex = xlAutomatic
End With
End Sub
ГЛАВА 8 ИНФОРМАЦИЯ О ПОЛЬЗОВАТЕЛЕ, КОМПЬЮТЕРЕ, ПРИНТЕРЕ И Т.Д.
Получить имя пользователя
Логин юзера получить просто:
Dim UserName As String
UserName = CreateObject(«Wsсriрt.Network»).UserName
А как отслеживать — вариатнов много.
Я, например, просто не выполняю макрос, если логин не тот:
If ThisWorkbook.Sheets(«Rules»).Range(«Admin»).Find(CreateObject(«Wsсriрt.Network»).UserName, _
LookAt:=xlWhole, LookIn:=xlValues) Is Nothing Then Exit Sub
MsgBox «Имя пользователя : » & CreateObject(«Wsсriрt.Network»).UserNam
CreateObject(«Wsсriрt.Network»).UserName вместо Application.UserName
Вывод разрешения монитора
Листинг 3.73. Разрешение монитора
‘Объявление API-функции
Declare Function GetSystemMetrics Lib «user32» _
(ByVal nIndex As ****) As ****
‘ Константы, которые передаются в функцию для определения _
горизонтального и вертикального размеров изображения
Const SM_CXSCREEN = 0
Const SM_CYSCREEN = 1
Sub GetMonitorResolution()
Dim lngHorzRes As ****
Dim lngVertRes As ****
‘ Получение ширины и высоты изображения на мониторе
lngHorzRes = GetSystemMetrics(SM_CXSCREEN)
lngVertRes = GetSystemMetrics(SM_CYSCREEN)
‘ Отображение сообщения
MsgBox «Текущее разрешение: » & lngHorzRes & «x» & lngVertRes
End Sub
Получение информации об используемом принтере
Информация о принтере
‘ Объявление API-функции
Declare Function GetProfileStringA Lib «kernel32» _
(ByVal lpAppName As String, ByVal lpKeyName As String, _
ByVal lpDefault As String, ByVal lpReturnedString As _
String, ByVal nSize As ****) As ****
Sub Принтер()
Dim strFullInfo As String * 255 ‘ Буфер для API-функции
Dim strInfo As String ‘ Строка с полной информацией
Dim strPrinter As String ‘ Название принтера
Dim strDriver As String ‘ Драйвер принтера
Dim strPort As String ‘ Порт принтера
Dim strMessage As String
Dim intPrinterEndPos As Integer
Dim intDriverEndPos As Integer
‘ Заполнение буфера пробелами
strFullInfo = Space(255)
‘ Получение полной информации о принтере
Call GetProfileStringA(«Windows», «Device», «», strFullInfo, 254)
‘ Удаление лишних символов из конца возвращенной строки
‘ Строка strInfo имеет формат <имя_принтера>,<драйвер>,<порт>:
strInfo = Trim(strFullInfo)
‘ Поиск запятых в строке (окончаний названий принтера и драйвера)
intPrinterEndPos = Application.Find(«,», strInfo, 1)
intDriverEndPos = Application.Find(«,», strInfo, intPrinterEndPos + 1)
‘ Определение названия принтера
strPrinter = Left(strInfo, intPrinterEndPos — 1)
‘ Определение драйвера
strDriver = Mid(strInfo, intPrinterEndPos + 1, intDriverEndPos _
— intPrinterEndPos — 1)
‘ Определение порта (его название заканчивается символом «:»)
strPort = Mid(strInfo, intDriverEndPos + 1, InStr(1, strInfo, «:») _
— intDriverEndPos — 1)
‘ Формирование информационного сообщения
strMessage = «Принтер:» & Chr(9) & strPrinter & Chr(13)
strMessage = strMessage & «Драйвер:» & strDriver & Chr(13)
strMessage = strMessage & «strPort:» & Chr(9) & strPort
‘ Вывод информационного сообщения
MsgBox strMessage, vbInformation, «Сведения о принтере по умолчанию»
End Sub
Просмотр информации о дисках компьютера
Sub DrivesInfo()
Dim objFileSysObject As Object ‘ Объект для работы _
с файловой системой
Dim objDrive As Object ‘ Анализируемый диск
Dim intRow As Integer ‘ Заполняемая строка листа
‘ Создание объекта для работы с файловой системой
Set objFileSysObject = CreateObject(«sсriрting.FileSystemObject»)
‘ Очистка листа
Cells.Clear
‘ Запись с первой строки
intRow = 1
‘ Запись на лист информации о дисках компьютера
On Error Resume Next
For Each objDrive In objFileSysObject.Drives
‘ Буква диска
Cells(intRow, 1) = objDrive.DriveLetter
‘ Готовность
Cells(intRow, 2) = objDrive.IsReady
‘ Тип диска
Select Case objDrive.DriveType
Case 0
Cells(intRow, 3) = «Неизвестно»
Case 1
Cells(intRow, 3) = «Съемный»
Case 2
Cells(intRow, 3) = «Жесткий»
Case 3
Cells(intRow, 3) = «Сетевой»
Case 4
Cells(intRow, 3) = «CD-ROM»
Case 5
Cells(intRow, 3) = «RAM»
End Select
‘ Метка диска
Cells(intRow, 4) = objDrive.VolumeName
‘ Общий размер
Cells(intRow, 5) = objDrive.TotalSize
‘ Свободное место
Cells(intRow, 6) = objDrive.AvailableSpace
intRow = intRow + 1
Next
End Sub
ГЛАВА 9. ДИАГРАММЫ
Построение диаграммы с помощью макроса
Листинг 5.1. Макрос построения диаграммы
Sub CreateChart()
‘ Создание и настройка диаграммы
With Charts.Add
‘ Данные из первого листа
.SetSourceData Source:=Worksheets(1).Range(«A1:E4»)
‘ Заголовок
.HasTitle = True
.ChartTitle.Text = «Выручка по магазинам»
‘ Активизируем диаграмму
.Activate
End With
End Sub
Листинг 5.2. Построение внедренной диаграммы
Sub CreateеmbеddedChart()
‘ Создание и настройка внедренной диаграммы
With Worksheets(1).ChartObjects.Add(100, 60, 250, 200)
‘ Объемная диаграмма
.Chart.ChartType = xl3DArea
‘ Источник данных
.Chart.SetSourceData Source:=Worksheets(1).Range(«A1:E4»)
End With
End Sub
Листинг 5.3. Создание диаграммы на основе выделенных данных
Sub CreateCharOnSelection()
‘ Создание диаграммы (с заданием положения на листе)
With ActiveSheet.ChartObjects.Add( _
Selection.Left + Selection.Width, _
Selection.Top + Selection.Height, 300, 200).Chart
‘ Тип диаграммы
.ChartType = xlColumnClustered
‘ Источник данных — выделение
.SetSourceData Source:=Selection, PlotBy:=xlColumns
‘ Без легенды
.HasLegend = False
‘ Без заголовка
.HasTitle = True
.ChartTitle.Characters.Text = «Выручка за период»
‘ Выделение диаграммы
.Parent.Select
End With
End Sub
Сохранение диаграммы в отдельном файле
Листинг 5.4. Сохранение диаграммы
Sub SaveChart()
‘ Сохранение выделенной диаграммы в файл
If ActiveChart Is Nothing Then
‘ Нет выделенных диаграмм
MsgBox «Выделите диаграмму»
Else
‘ Сохранение…
ActiveChart.Export ActiveWorkbook.path & «Диаграмма.gif», «GIF»
End If
End Sub
Листинг 5.5. Сохранение диаграммы под указанным именем
Sub InteractiveSaveChart()
Dim strFileName As String ‘ Имя файла для сохранения
‘ Проверка, выделена ли диаграмма
If ActiveChart Is Nothing Then
‘ Нет выделенных диаграмм
MsgBox «Выделите диаграмму»
Else
‘ Выбор файла для сохранения
strFileName = Application.GetSaveAsFilename( _
ActiveChart.Name & «.gif», «Файлы GIF (*.gif), *.gif», 1, _
«Сохранить диаграмму в формате GIF»)
‘ Проверка, выбран ли файл
If strFileName <> «» Then
‘ Сохранение выделенной диаграммы в файл
ActiveChart.Export strFileName, «GIF»
End If
End If
End Sub
Построение и удаление диаграммы нажатием одной кнопки
Листинг 5.6. Быстрое построение и удаление диаграммы
Sub CreateChart()
‘ Создание диаграммы
Charts.Add
‘ Параметры диаграммы
‘ Тип диаграммы
ActiveChart.ChartType = xlLineMarkers
‘ Заголовок
ActiveChart.SetSourceData Range(«B1:E2»), xlRows
ActiveChart.Location xlLocationAsObject, Name
‘ Остальные параметры
With ActiveChart
‘ Заголовок
.HasTitle = True
.ChartTitle.Characters.Text = Name
‘ Заголовок оси категорий
.Axes(xlCategory, xlPrimary).HasTitle = True
.Axes(xlCategory, xlPrimary).AxisTitle.Characters.Text _
= Sheets(Name).Range(«A1»).Value
‘ Заголовок оси значений
.Axes(xlValue, xlPrimary).HasTitle = True
.Axes(xlValue, xlPrimary).AxisTitle.Characters.Text _
= Sheets(Name).Range(«A2»).Value
‘ Отображение легенды
.HasLegend = False
.HasDataTable = True
.DataTable.ShowLegendKey = True
‘ Настройка отображения сетки
With .Axes(xlCategory)
.HasMajorGridlines = True
.HasMinorGridlines = False
End With
With .Axes(xlValue)
.HasMajorGridlines = True
.HasMinorGridlines = False
End With
End With
End Sub
Sub DeleteChart()
‘ Удаление диаграммы
ActiveSheet.ChartObjects.Delete
End Sub
Вывод списка диаграмм в отдельном окне
Листинг 5.7. Внедренные диаграммы
Sub ShowSheetCharts()
Dim strMessage As String
Dim i As Integer
‘ Формирование списка диаграмм
For i = 1 To ActiveSheet.ChartObjects.Count
strMessage = strMessage & ActiveSheet.ChartObjects(i).Name _
& vbNewLine
Next i
‘ Отображение списка
MsgBox strMessage
End Sub
Листинг 5.8. Перечень рабочих листов, содержащих обычные диаграммы
Sub ShowBookCharts()
Dim crt As chart
Dim strMessage As String
‘ Формирование списка диаграмм
For Each crt In ActiveWorkbook.Charts
strMessage = strMessage & crt.Name & vbNewLine
Next
‘ Отображение списка
MsgBox strMessage
End Sub
Применение случайной цветовой палитры
Листинг 5.9. Случайная цветовая палитра
Sub RandomChartColors()
Dim intGradientStyle As Integer, intGradientVariant As Integer
Dim i As Integer
‘ Проверка, выделена ли диаграмма
If ActiveChart Is Nothing Then Exit Sub
‘ Изменение оформления всех категорий
For i = 1 To ActiveChart.SeriesCollection.Count
With ActiveChart.SeriesCollection(i)
‘ Вид градиентной заливки (случайный)
intGradientStyle = Int(Rnd * 7) + 1
If intGradientStyle = 6 Then intGradientStyle = 1
If intGradientStyle = 7 Then
intGradientVariant = Int(Rnd * 2) + 1
Else
intGradientVariant = Int(Rnd * 4) + 1
End If
‘ Применение градиента
.Fill.TwoColorGradient Style:=intGradientStyle, _
Variant:=intGradientVariant
‘ Установка случайных цветов фона и обводки (используются _
для градиента)
.Fill.ForeColor.SchemeColor = Int(Rnd * 57) + 1
.Fill.BackColor.SchemeColor = Int(Rnd * 57) + 1
End With
Next i
End Sub
Эффект прозрачности диаграммы
Листинг 5.10. Эффект прозрачности диаграммы
Sub TransparentChart()
Dim shpShape As Shape
Dim dblColor As Double
Dim srSerie As Series
Dim intBorderLineStyle As Integer
Dim intBorderColorIndex As Integer
Dim intBorderWeight As Integer
‘ Проверка, есть ли выделенная диаграмма
If ActiveChart Is Nothing Then Exit Sub
‘ Изменение отображения каждой категории
For Each srSerie In ActiveChart.SeriesCollection
If (srSerie.ChartType = xlColumnClustered Or _
srSerie.ChartType = xlColumnStacked Or _
srSerie.ChartType = xlColumnStacked100 Or _
srSerie.ChartType = xlBarClustered Or _
srSerie.ChartType = xlBarStacked Or _
srSerie.ChartType = xlBarStacked100) Then
‘ Сохранение прежнего цвета категории
dblColor = srSerie.Interior.Color
‘ Сохранение стиля линий
intBorderLineStyle = srSerie.Border.LineStyle
‘ Цвет границы
intBorderColorIndex = srSerie.Border.ColorIndex
‘ Толщина линий границы
intBorderWeight = srSerie.Border.Weight
‘ Создание автофигуры
Set shpShape = ActiveSheet.shapes.AddShape _
(msoShapeRectangle, 1, 1, 100, 100)
With shpShape
‘ Закрашиваем нужным цветом
.Fill.ForeColor.RGB = dblColor
‘ Делаем прозрачной
.Fill.Transparency = 0.4
‘ Убираем линии
.Line.Visible = msoFalse
End With
‘ Копируем автофигуру в буфер обмена
shpShape.CopyPicture Appearance:=xlScreen, _
Format:=xlPicture
‘ Вставляем автофигуру в изображения столбцов _
категории и настраиваем
With srSerie
‘ Собственно вставка
.Paste
‘ Возвращаем на место толщину линий
.Border.Weight = intBorderWeight
‘ Стиль линий
.Border.LineStyle = intBorderLineStyle
‘ Цвет границы
.Border.ColorIndex = intBorderColorIndex
End With
‘ Автофигура больше не нужна
shpShape.Delete
End If
Next srSerie
End Sub
Построение диаграммы на основе данных нескольких рабочих листов
Листинг 5.11. Одновременное создание нескольких диаграмм
Sub ManyCharts()
Dim intTop As ****, intLeft As ****
Dim intHeight As ****, intWidth As ****
Dim sheet As Worksheet
Dim lngFirstRow As **** ‘ Первая строка с данными
Dim intSerie As Integer ‘ Текущая категория диаграммы
Dim strErrorSheets As String ‘ Список листов, для которых _
не удалось построить диаграммы
intTop = 1 ‘ Верхняя точка первой диаграммы
intLeft = 1 ‘ Левая точка каждой диаграммы
intHeight = 180 ‘ Высота каждой диаграммы
intWidth = 300 ‘ Ширина каждой диаграммы
‘ Постоение диаграммы для каждого листа, кроме текущего
For Each sheet In ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets
If sheet.Name <> ActiveSheet.Name Then
‘ Первый заполненный ряд
lngFirstRow = 3
‘ Первая категория
intSerie = 1
On Error GoTo DiagrammError
‘ Добавление и настройка диаграммы
With ActiveSheet.ChartObjects.Add _
(intLeft, intTop, intWidth, intHeight).Chart
Do Until IsEmpty(sheet.Cells(lngFirstRow + intSerie, 1))
‘ Создание ряда
.SeriesCollection.NewSeries
‘ Значения для ряда
.SeriesCollection(intSerie).Values = _
sheet.Range(sheet.Cells(lngFirstRow + intSerie, 2), _
sheet.Cells(lngFirstRow + intSerie, 4))
‘ Диапазон данных для подписей
.SeriesCollection(intSerie).XValues = _
sheet.Range(«B3:D3»)
‘ Название ряда (берется из столбца «A» таблицы с данными)
.SeriesCollection(intSerie).Name = sheet.Cells( _
lngFirstRow + intSerie, 1)
intSerie = intSerie + 1
Loop
‘ Настройка внешнего вида диаграммы
.ChartType = xl3DColumnClustered
.ChartGroups(1).GapWidth = 20
.PlotArea.Interior.ColorIndex = xlNone
.ChartArea.Font.Size = 9
‘ Диаграмма с легендой
.HasLegend = True
‘ Заголовок
.HasTitle = True
.ChartTitle.Characters.Text = sheet.Range(«A1»)
‘ Задание диапазона значений на осях
.Axes(xlValue).MinimumScale = 0
.Axes(xlValue).MaximumScale = 120000
‘ Стиль линий сетки (прерывистый)
.Axes(xlValue).MajorGridlines.Border. _
LineStyle = xlDot
End With
On Error GoTo 0
‘ Сдвиг верхней точки следующей диаграммы на высоту _
текущей диаграммы
intTop = intTop + intHeight
AfterError:
End If
Next sheet
If strErrorSheets <> «» Then
‘ Отобразим список листов, для которых не построили диаграммы
MsgBox «Не удалось построить диаграммы для листов:» & Chr(13) _
& strErrorSheets, vbExclamation
End If
Exit Sub
DiagrammError:
‘ Добавление в список имени листа, для которого не смогли _
построить диаграмму (ошибка в данных для диаграммы)
strErrorSheets = strErrorSheets & sheet.Name & Chr(13)
‘ Удаление пустой диаграммы на текущем листе
ActiveSheet.ChartObjects(ActiveSheet.ChartObjects.Count).Delete
‘ Продолжаем работу с другими листами
Resume AfterError
End Sub
Создание подписей к данным диаграммы
Листинг 5.12. Подписи к данным диаграммы
Sub ShowLabels()
Dim rgLabels As Range ‘ Диапазон с подписями
Dim chrChart As Chart ‘ Диаграмма
Dim intPoint As Integer ‘ Точка, для которой добавляется подпись
‘ Определение диаграммы
Set chrChart = ActiveSheet.ChartObjects(1).Chart
‘ Запрос на ввод диапазона с исходными данными
On Error Resume Next
Set rgLabels = Application.InputBox _
(prompt:=»Укажите диапазон с подписями», Type:=8)
If rgLabels Is Nothing Then Exit Sub
On Error GoTo 0
‘ Добавление подписей
chrChart.SeriesCollection(1).ApplyDataLabels _
Type:=xlDataLabelsShowValue, _
AutoText:=True, _
LegendKey:=False
‘ Просмотр диапазона и назначение подписей
For intPoint = 1 To chrChart.SeriesCollection(1).Points.Count
chrChart.SeriesCollection(1). _
Points(intPoint).DataLabel.Text = rgLabels(intPoint)
Next intPoint
End Sub
Sub DeleteLabels()
‘ Удаление подписей диаграммы
ActiveSheet.ChartObjects(1).Chart.SeriesCollection(1). _
HasDataLabels = False
End Sub
ГЛАВА 10. РАЗНЫЕ ПРОГРАММЫ.
Программа для составления кроссвордов
Листинг 6.1. Программа для составления кроссворда
Const dhcMinCol = 1 ‘ Номер первого столбца кроссворда
Const dhcMaxCol = 35 ‘ Номер последнего столбца кроссворда
Const dhcMinRow = 1 ‘ Номер первой строки кроссворда
Const dhcMaxRow = 35 ‘ Номер последней строки кроссворда
Sub Clear()
‘ Выделение и очистка всех используемых для кроссворда ячеек
Range(Cells(dhcMinRow, dhcMinCol), _
Cells(dhcMaxRow, dhcMaxCol)).Select
Selection.Clear
‘ Удаление сетки всего кроссворда
ClearGrid
Range(«A1»).Select
End Sub
Sub ClearGrid()
‘ Удаление сетки кроссворда (в выделенных ячейках)…
‘ Возврат прежнего цвета ячеек
Selection.Interior.ColorIndex = xlNone
‘ Задание начертания границ ячеек по умолчанию
Selection.Borders(xlDiagonalDown).LineStyle = xlNone
Selection.Borders(xlDiagonalUp).LineStyle = xlNone
Selection.Borders(xlEdgeLeft).LineStyle = xlNone
Selection.Borders(xlEdgeTop).LineStyle = xlNone
Selection.Borders(xlEdgeBottom).LineStyle = xlNone
Selection.Borders(xlEdgeRight).LineStyle = xlNone
Selection.Borders(xlInsideVertical).LineStyle = xlNone
Selection.Borders(xlInsideHorizontal).LineStyle = xlNone
End Sub
Sub DrowCrosswordGrid()
‘ Процедура начертания сетки кроссворда
‘ Задание цвета всех ячеек кроссворда
Selection.Interior.ColorIndex = 35
‘ Линии по диагонали не нужны
Selection.Borders(xlDiagonalDown).LineStyle = xlNone
Selection.Borders(xlDiagonalUp).LineStyle = xlNone
‘ Задание начертания границ всех диапазонов, входящих _
в выделение, а также границ между соседними ячейками _
всех диапазонов
On Error Resume Next
‘ Левые границы
With Selection.Borders(xlEdgeLeft)
.LineStyle = xlContinuous
.Weight = xlThin
.ColorIndex = xlAutomatic
End With
‘ Правые границы
With Selection.Borders(xlEdgeRight)
.LineStyle = xlContinuous
.Weight = xlThin
.ColorIndex = xlAutomatic
End With
‘ Верхние границы
With Selection.Borders(xlEdgeTop)
.LineStyle = xlContinuous
.Weight = xlThin
.ColorIndex = xlAutomatic
End With
‘ Нижние границы
With Selection.Borders(xlEdgeBottom)
.LineStyle = xlContinuous
.Weight = xlThin
.ColorIndex = xlAutomatic
End With
‘ Вертикальные границы между ячейками
With Selection.Borders(xlInsideVertical)
.LineStyle = xlContinuous
.Weight = xlThin
.ColorIndex = xlAutomatic
End With
‘ Горизонтальные границы между ячейками
With Selection.Borders(xlInsideHorizontal)
.LineStyle = xlContinuous
.Weight = xlThin
.ColorIndex = xlAutomatic
End With
End Sub
Sub DisplayGrid()
‘ Включение сетки на листе
ActiveWindow.DisplayGridlines = True
End Sub
Sub HideGrid()
‘ Выключение сетки на листе
ActiveWindow.DisplayGridlines = False
End Sub
Sub AutoNumber()
‘ Нумерация клеток, являющихся началом слов
Dim intRow As Integer ‘ Текущая строка
Dim intCol As Integer ‘ Текущий ряд
Dim cell As Range ‘ Текущая ячейка (с координатами _
(intRow, intCol))
Dim fTop As Boolean ‘ = True, если cell имеет соседей сверху
Dim fBottom As Boolean ‘ = True, если cell имеет соседей снизу
Dim fLeft As Boolean ‘ = True, если cell имеет соседей слева
Dim fRight As Boolean ‘ = True, если cell имеет соседей справа
Dim intDigit As Integer ‘ Текущий номер слова в кроссворде
intDigit = 1 ‘ Нумерация слов с 1
‘ Проходим по всем клеткам диапазона, используемого _
для кроссворда, сверху вниз слева направо и анализируем _
каждую угловую и крайнюю (левую и верхнюю) ячейки
For intRow = dhcMinRow To dhcMaxRow
For intCol = dhcMinCol To dhcMaxCol
‘ Текущая ячейка
Set cell = Cells(intRow, intCol)
‘ Проверка, входит ли ячейка в кроссворд (по ее цвету)
If cell.Interior.ColorIndex = 35 Then
fLeft = False
fRight = False
fTop = False
fBottom = False
On Error Resume Next
‘ Определение наличия соседей у ячейки…
‘ сверху
fTop = cell.Offset(-1, 0).Interior.ColorIndex = 35
‘ снизу
fBottom = cell.Offset(1, 0).Interior.ColorIndex = 35
‘ слева
fLeft = cell.Offset(0, -1).Interior.ColorIndex = 35
‘ справа
fRight = cell.Offset(0, 1).Interior.ColorIndex = 35
On Error GoTo 0
‘ Анализ положения ячейки
If (Not fTop And Not fLeft) Or _
(Not fBottom And Not fLeft And fRight) Or _
(Not fLeft And fRight) Or _
(Not fTop And fBottom) Then
‘ Ячейка подходит для начала слова
SetDigit intDigit, cell
intDigit = intDigit + 1
End If
End If
Next intCol
Next intRow
End Sub
Sub SetDigit(intDigit As Integer, cell As Range)
‘ Вставка цифры intDigit в ячейку, заданную параметром cell
cell.Value = intDigit
‘ Изменение настроек шрифта так, чтобы было похоже _
на настоящий кроссворд
‘ Маленький размер шрифта
cell.Font.Size = 6
‘ Выравнивание текста по левому верхнему углу ячейки
cell.HorizontalAlignment = xlLeft
cell.VerticalAlignment = xlTop
End Sub
Sub ToPrint()
‘ Удаление цветовой подсветки кроссворда
Cells.Interior.ColorIndex = xlNone
End Sub
Sub ToNumber()
‘ Закрытие первой формы и переход ко второй
UserForm1.Hide
UserForm2.Show
End Sub
Создать обложку DVD
Sub Обложка_DVD()
On Error Resume Next
Sheets(«Обложка»).Select
If Err > 0 Then GoTo 10 Else MsgBox («Такой лист уже присутствует в книге…»): Exit Sub
10:
Sheets.Add.Name = «Обложка» ‘ создаем новый лист в текущей книге с именем «Обложка»
Sheets(«Обложка»).Range(«A1»).Select ‘ становимся в ячейку А1
Application.Dialogs(xlDialoginsеrtPicture).Show ‘вызываем диологовое окно «Вставка рисунка из файла»
Selection.ShapeRange.LockAspectRatio = msoFalse ‘
‘ Selection.ShapeRange.Height = 530.25 ‘ подгоняем размеры под размеры коробки
‘ Selection.ShapeRange.Width = 726# ‘
Selection.ShapeRange.Height = 530.2 ‘ подгоняем размеры под размеры коробки
Selection.ShapeRange.Width = 724# ‘
Selection.ShapeRange.Rotation = 0# ‘
Selection.Locked = False ‘
With ActiveSheet.PageSetup ‘ разносим поля листа на максимальные расстояния
.LeftMargin = Application.InchesToPoints(0.17)
.RightMargin = Application.InchesToPoints(0.17)
.TopMargin = Application.InchesToPoints(0.27)
.BottomMargin = Application.InchesToPoints(0.27)
.HeaderMargin = Application.InchesToPoints(0.17)
.FooterMargin = Application.InchesToPoints(0.17)
.Zoom = 100
.FitToPagesWide = 1
.FitToPagesTall = 1
.Orientation = xlLandscape ‘ придаем листу горизантальное положение (АЛЬБОМНЫЙ)
End With
If MsgBox(«Печать текущего изображения», vbYesNo, «Вывод на печать») = vbYes Then Sheets(«Обложка»).PrintOut Copies:=1, Collate:=True
Application.DisplayAlerts = False ‘ Выключили системные сообщения…
If MsgBox(«Удалить лист ОБЛОЖКА», vbYesNo, «Удаление листа…») = vbYes Then Sheets(«Обложка»).Delete Else Application.CommandBars(«Picture»).Visible = True
Application.DisplayAlerts = True ‘Включили системные сообщения…
End Sub
Игра «Минное поле»
Листинг 6.2. Код в модуле рабочего листа
Sub Worksheet_Selectiоnchange(ByVal Target As Range)
Dim intCol As Integer, intRow As Integer
Dim intMinesAround As Integer
Dim fInGameField As Boolean
‘ Определим, попадает ли в игровое поле выделенная ячейка
fInGameField = (Target.Row >= 2) And (Target.Row <= 7) _
And (Target.Column >= 2) And (Target.Column <= 7)
‘ Обрабатываем выделение ячейки
If Target.Value = «*» And fInGameField Then
‘ Пользователь выделил ячейку с миной — покажем мину
Target.Font.Color = RGB(0, 0, 0)
Target.Interior.Color = RGB(255, 0, 0)
‘ Пользователь проиграл!
EndGame
ElseIf fInGameField Then
‘ Пользователь выделил пустую ячейку. Оформим эту ячейку
Target.Interior.Color = RGB(0, 0, 255)
Target.Font.Color = RGB(0, 255, 0)
Target.Font.Size = 16
‘ Подсчитаем количество мин рядом с ячейкой (вокруг ячейки)
For intCol = Target.Column — 1 To Target.Column + 1
For intRow = Target.Row — 1 To Target.Row + 1
If Target.Worksheet.Cells(intRow, intCol).Value = «*» _
Then
‘ Нашли очередную мину
intMinesAround = intMinesAround + 1
End If
Next
Next
‘ Отображение количества мин
Target.Value = intMinesAround
End If
End Sub
Листинг 6.3. Код в стандартном модуле
Sub NewGame()
‘ Начало новой игры
‘ Подготовим поле для игры
InitGame
Dim intRow As Integer, intCol As Integer
Dim intMinesCount As Integer ‘ Количество мин
‘ Расставляем мины (то есть в случайные ячейки помещаем _
значения «*» и делаем цвет шрифта таким же, как цвет _
фона этих ячеек)
For intMinesCount = 1 To 10
‘ Строка для мины (от 2 до 7)
intRow = Int((6 * Rnd) + 1) + 1
‘ Столбец для мины (от 2 до 7)
intCol = Int((6 * Rnd) + 1) + 1
‘ Ставим мину, если ячейка пустая
If Cells(intRow, intCol) <> «*» Then
Cells(intRow, intCol).Font.Color = _
Cells(intRow, intCol).Interior.Color
Cells(intRow, intCol).Value = «*»
Else
‘ В данной ячейке мина есть — продолжим поиск ячеек
intMinesCount = intMinesCount — 1
End If
Next
‘ Вывод информации о количестве мин в строку состояния
Application.StatusBar = «Количество мин » & intMinesCount
End Sub
Sub InitGame()
‘ Раскраска (оформление) листа перед началом игры
Dim intRow As Integer, intCol As Integer
‘ Цвет фона всех ячеек
Cells.Interior.Color = RGB(0, 200, 75)
‘ Цвет шрифта всех ячеек
Cells.Font.Color = RGB(0, 0, 0)
‘ Размер шрифта
Cells.Font.Size = 18
‘ Все надписи — по центру
Cells.HorizontalAlignment = xlCenter
‘ Всем ячейкам игрового поля назначим особый цвет
For intRow = 2 To 7
For intCol = 2 To 7
Cells(intRow, intCol).Interior.Color = RGB(200, 200, 200)
Cells(intRow, intCol).Value = «»
Next
Next
End Sub
Sub EndGame()
‘ Завершение игры (поражение)
Dim intRow As Integer, intCol As Integer
‘ Покажем все мины. Для этого сделаем цвет шрифта всех ячеек _
черным (ведь во всех ячейках с минами «*» цвет шрифта и цвет _
заливки одинаковы)
For intRow = 2 To 7
For intCol = 2 To 7
If Cells(intRow, intCol).Value = «*» Then
Cells(intRow, intCol).Font.Color = RGB(0, 0, 0)
End If
Next
Next
MsgBox «Проигрыш»
End Sub
Игра «Угадай животное»
Листинг 6.4. Игра «Угадай животное»
Sub StartGame()
Dim intLastRow As Integer ‘ Номер строки для вставки записей
Dim intRow As Integer ‘ Номер текущей строки
Dim intYesRow As Integer ‘ Номер строки, из которой брать _
данные при утвердительном ответе
Dim intNoRow As Integer ‘ Номер строки, из которой брать _
данные при отрицательном ответе
Dim strText As String ‘ Строка с вопросом или названием _
животного
Dim strNewName As String ‘ Строка с названием нового животного
Dim strNewQuestion As String ‘ Строка с новым вопросом
Dim intRes As Integer
‘ Начало игры
MsgBox «Начнем игру. Задумайте животное.», vbOKOnly, _
«Задумайте животное»
‘ Определение номера ряда для вставки записей. _
intLastRow-1 — номер последнего ряда, содержащего данные
intLastRow = Worksheets(«Data»).Range(«D1»).Value + 1
‘ Данные в таблице идут с первого ряда
intRow = 1
Do While intRow < intLastRow
‘ Текст вопроса или название животного из столбца «A»
strText = Worksheets(«Data»).Cells(intRow, 1).Value
‘ Номер ряда, из которого брать данные при утвердительном _
ответе, берем из столбца «B»
intYesRow = Worksheets(«Data»).Cells(intRow, 2).Value
‘ Номер ряда, из которого брать данные при отрицательном _
ответе, берем из столбца «C»
intNoRow = Worksheets(«Data»).Cells(intRow, 3).Value
If intYesRow > 0 Then
‘ В строке strText содержится вопрос. Зададим его
intRes = MsgBox(strText, vbYesNo, «Вопрос»)
If intRes = vbYes Then
‘ Переходим по утвердительному ответу
intRow = intYesRow
Else
‘ Переходим по отрицательному ответу
intRow = intNoRow
End If
Else
‘ Альтернативы закончились. В строке strText — название _
животного. Спросим, его ли загадали
intRes = MsgBox(«Это » & strText & «?», vbYesNo, «Вопрос»)
If intRes = vbYes Then
‘ Животное угадано
MsgBox «Угадано! Спасибо за игру!», vbOKOnly, _
«Игра завершена»
Exit Do
Else
‘ Животное не угадали, но данные уже занкончились. _
Нужно пополнить наши данные, чтобы отличать животное _
с названием strText от загаданного
‘ Ввод названия нового животного
strNewName = InputBox(«Сдаюсь. Кто это?», _
«Напечатайте название животного»)
If strNewName <> «» Then
‘ Ввод вопроса, по которому отличать животных
strNewQuestion = InputBox(«Задайте вопрос, по » & _
«которому можно отличить ‘» & strNewName & _
«‘ от ‘» & strText & «‘», «Напечатайте вопрос»)
If strNewQuestion <> «» Then
‘ Определение, какое из животных соответствует _
утвердительному ответу на вопрос
intRes = MsgBox(«Правильный ответ на ваш » & _
«вопрос — » & strNewName & «‘», vbYesNo, _
«Какой ответ на вопрос?»)
‘ Добавление в таблицу названия нового животного
Worksheets(«Data»).Cells(intLastRow, 1). _
Value = strNewName
‘ Перемещения названия животного, которое было _
ранее, в конец таблицы
Worksheets(«Data»).Cells(intLastRow + 1, 1). _
Value = strText
‘ Замена названия этого животного вопросом
Worksheets(«Data»).Cells(intRow, 1). _
Value = strNewQuestion
‘ Корректировка номеров строк для перехода _
в зависимости от того, какое животное является _
правильным ответом на введенный пользователем вопрос
If intRes = vbYes Then
‘ Новое животное — правильный ответ
Worksheets(«Data»).Cells(intRow, 2). _
Value = intLastRow
Worksheets(«Data»).Cells(intRow, 3). _
Value = intLastRow + 1
Else
‘ Бывшее ранее животное — правильный ответ
Worksheets(«Data»).Cells(intRow, 2). _
Value = intLastRow + 1
Worksheets(«Data»).Cells(intRow, 3). _
Value = intLastRow
End If
‘ Сохраним номер строки для добавления записей
Worksheets(«Data»).Range(«D1»).Value = _
intLastRow + 2
End If
End If
‘ Игра завершена. Таблица дополнена
MsgBox «Спасибо за игру!», vbOKOnly, «Игра завершена»
Exit Do
End If
End If
Loop
End Sub
Расчет на основании ячеек определенного цвета
Листинг 6.5. Код в стандартном модуле
Const dhcSum As Integer = 0
Const dhcAvg As Integer = 1
Const dhcMax As Integer = 2
Const dhcMin As Integer = 3
Const dhcCount As Integer = 4
Const dhcSumPlus As Integer = 5
Const dhcSumMinus As Integer = 6
Const dhcCountFull As Integer = 7
Const dhcCountNotNull As Integer = 8
Const dhcCountPlus As Integer = 9
Const dhcCountMinus As Integer = 10
Sub CalcColors()
‘ Отображение формы
Load frmColorCalc
frmColorCalc.Show
End Sub
Public Function ColorCalc(strRange As String, _
lngColor As ****, fBackBolor As Boolean, _
intMode As Integer, Optional fAbsence As Boolean) As Double
‘ Операции над ячейками с установленным цветом шрифта _
или заливки
Dim rgData As Range ‘ Диапазон ячеек для расчетов
Dim i As Integer
Dim Values() As Variant ‘ Массив со значениями для расчета
Dim intCount As Integer ‘ Количество значений в массиве
Dim cell As Range
Dim varOut As Variant ‘ В этой переменной хранятся _
результаты промежуточных подсчетов _
и окончательный результат
Set rgData = Range(strRange)
ReDim Values(1 To rgData.Count)
‘ Просматриваются все ячейки входного диапазона. Значения тех из них, _
цвет которых удовлетворяет условию, записываются в массив Values
For Each cell In rgData.Cells
‘ Если нужно суммировать по заливке:
If fBackBolor = True Then
‘ Включение ячейки в сумму в зависимости от цвета _
заливки и фильтра
If fAbsence Then
‘ Если ячейка имеет заданный цвет, то она не включается _
в вычисления
If cell.Interior.Color <> lngColor Then
intCount = intCount + 1
Values(intCount) = cell.Value
End If
Else
‘ Если ячейка имеет заданный цвет, то она включается _
в вычисления
If cell.Interior.Color = lngColor Then
intCount = intCount + 1
Values(intCount) = cell.Value
End If
End If
‘ В противном случае — суммируется по шрифту
Else
‘ Включение ячейки в сумму в зависимости _
от ее цвета и фильтра
If fAbsence Then
‘ Если ячейка имеет заданный цвет, то она не включается _
в вычисления
If cell.Font.Color <> lngColor Then
intCount = intCount + 1
Values(intCount) = cell.Value
End If
Else
‘ Если ячейка имеет заданный цвет, то она включается _
в вычисления
If cell.Font.Color = lngColor Then
intCount = intCount + 1
Values(intCount) = cell.Value
End If
End If
End If
Next cell
‘ Выполнение над собранными значениями операции, заданной в intMode
For i = 1 To intCount
Select Case intMode
Case dhcSum, dhcAvg
‘ Подсчет суммы значений
varOut = varOut + Values(i)
Case dhcSumPlus
‘ Подсчет суммы положительных значений
If Values(i) > 0 Then varOut = varOut + Values(i)
Case dhcSumMinus
‘ Посчет суммы отрицательных значений
If Values(i) < 0 Then varOut = varOut + Values(i)
Case dhcMax
‘ Нахождение максимального значения
If Values(i) > varOut Then varOut = Values(i)
Case dhcMin
‘ Нахождение минимального значения
If i = LBound(Values) Then varOut = Values(i)
If Values(i) < varOut Then varOut = Values(i)
Case dhcCount
‘ Подсчет количества значений
varOut = varOut + 1
Case dhcCountFull
‘ Подсчет количества заполненных ячеек
If Not IsEmpty(Values(i)) Then varOut = varOut + 1
Case dhcCountNotNull
‘ Подсчет количества пустых ячеек
If Not IsEmpty(Values(i)) And Values(i) <> 0 Then _
varOut = varOut + 1
Case dhcCountPlus
‘ Подсчет количества положительных значений
If Values(i) > 0 Then varOut = varOut + 1
Case dhcCountMinus
‘ Подсчет количества отрицательных значений
If Values(i) < 0 Then varOut = varOut + 1
End Select
Next i
‘ Окончательные операции для некоторых видов расчета
If intMode = dhcAvg Then
‘ Вычисление среднего значения
ColorCalc = varOut / intCount
Else
ColorCalc = varOut
End If
End Function
Листинг 6.6. Код в модуле формы
Dim lngCurColor As **** ‘ Выбранный цвет, по которому _
идентифицировать (отбирать) ячейки
Dim intMode As Integer ‘ Номер типа вычисления в списке
Sub cmbApplyColor_Click()
If cboOtherColor.Value >= 0 Then
‘ Вычисление с использованием выбранного в списке цвета
lngCurColor = cboOtherColor.Value
SetColorSum
End If
End Sub
Sub cmbColor1_Click()
‘ Вычисление с использованием цвета нажатой кнопки
lngCurColor = cmbColor1.BackColor
SetColorSum
End Sub
Sub cmbColor2_Click()
‘ Вычисление с использованием цвета нажатой кнопки
lngCurColor = cmbColor2.BackColor
SetColorSum
End Sub
Sub cmbColor3_Click()
‘ Вычисление с использованием цвета нажатой кнопки
lngCurColor = cmbColor3.BackColor
SetColorSum
End Sub
Sub cmbColor4_Click()
‘ Вычисление с использованием цвета нажатой кнопки
lngCurColor = cmbColor4.BackColor
SetColorSum
End Sub
Sub cmbColor5_Click()
‘ Вычисление с использованием цвета нажатой кнопки
lngCurColor = cmbColor5.BackColor
SetColorSum
End Sub
Sub cmbColor6_Click()
‘ Вычисление с использованием цвета нажатой кнопки
lngCurColor = cmbColor6.BackColor
SetColorSum
End Sub
Sub cmbColor7_Click()
‘ Вычисление с использованием цвета нажатой кнопки
lngCurColor = cmbColor7.BackColor
SetColorSum
End Sub
Sub cmbColor8_Click()
‘ Вычисление с использованием цвета нажатой кнопки
lngCurColor = cmbColor8.BackColor
SetColorSum
End Sub
Sub cmbColor9_Click()
‘ Вычисление с использованием цвета нажатой кнопки
lngCurColor = cmbColor9.BackColor
SetColorSum
End Sub
Sub cmbColor10_Click()
‘ Вычисление с использованием цвета нажатой кнопки
lngCurColor = cmbColor10.BackColor
SetColorSum
End Sub
Sub cmbColor11_Click()
‘ Вычисление с использованием цвета нажатой кнопки
lngCurColor = cmbColor11.BackColor
SetColorSum
End Sub
Sub cmbColor12_Click()
‘ Вычисление с использованием цвета нажатой кнопки
lngCurColor = cmbColor12.BackColor
SetColorSum
End Sub
Sub SetColorSum()
‘ Вычисление с использованием заданного цвета
Dim strFormula As String
‘ Проверка правильности введенных диапазонов и номеров ячеек
If txtResCell.Value = «» Then
MsgBox «Введите адрес ячейки вставки функции», _
vbCritical, «Внимание!»
txtResCell.SetFocus
Exit Sub
ElseIf txtRange.Value = «» Then
MsgBox «Введите адрес диапазона суммирования», _
vbCritical, «Внимание!»
txtRange.SetFocus
Exit Sub
End If
‘ Формирование формулы
strFormula = «=ColorCalc(» & «»»» & txtRange.Value & «»»» _
& «,» & lngCurColor & «,» & CInt(tglType.Value) & «,» _
& intMode & «,» & CInt(chkVarify.Value) & «)»
‘ Запись формулы в ячейку
Range(txtResCell.Value).Formula = strFormula
End Sub
Sub cmbExit_Click()
‘ Закрытие формы
Unload Me
End Sub
Sub cboCalcTypes_Afterupdаtе()
‘ Изменение режима вычисления — сохраним в переменной _
номер вычисления
intMode = cboCalcTypes.ListIndex
End Sub
Sub cboOtherColor_Change()
‘ Изменение выделенного цвета в списке «Другой»
If cboOtherColor.Text <> «» Then
‘ Сохранение выбранного цвета в переменной
lngCurColor = Val(cboOtherColor.Value)
End If
End Sub
Sub tglType_Click()
‘ Изменение типа идентификации ячеек
If tglType.Value = -1 Then
‘ Идентификация по цвету заливки
tglType.Caption = «Заливка»
Else
‘ Идентификация по цвету шрифта
tglType.Caption = «Шрифт»
End If
GetColors
End Sub
Sub txtRange_Afterupdаtе()
‘ Изменение диапазона с исходными данными — покажем _
кнопки с цветами, представленными в новом диапазоне
GetColors
End Sub
Sub txtRange_Beforeupdаtе(ByVal Cancel As MSForms.ReturnBoolean)
‘ Проверка корректности данных, введенных в поле _
диапазона исходных данных
Dim rgData As Range
Dim cell As Range
‘ Проверка, введен ли диапазон данных
If txtRange.Text = «» Then
MsgBox «Введите адрес диапазона суммирования!», _
vbCritical, «Ошибка выполнения»
Cancel = True
End If
If txtResCell.Text = «» Then Exit Sub
On Error GoTo Err1
‘ Проверка отсутствия циклических ссылок (чтобы одна _
из входных ячеек не была одновременно и выходной)
Set rgData = Range(txtRange.Text)
For Each cell In rgData.Cells
If cell.Address(False, False) = _
Range(txtResCell.Text).Address(False, False) Then
‘ Нашли циклическую ссылку
MsgBox «Введите другой адрес во избежание » & _
«появления циклических ссылок», vbCritical, _
«Внимание!»
Cancel = True
Exit Sub
End If
Next cell
Exit Sub
Err1:
‘ Обработка ошибок при работе с ячейками
If Err.Number = 1004 Then
MsgBox «Введите корректный адрес ячейки», vbCritical, _
«Ошибка ввода»
Cancel = True
Exit Sub
Else
MsgBox Err.Desсriрtion, vbCritical, «Ошибка ввода»
Cancel = True
Exit Sub
End If
End Sub
Sub txtResCell_Beforeupdаtе(ByVal Cancel As MSForms.ReturnBoolean)
‘ Проверка корректности данных, введенных в поле _
адреса выходной ячейки
Dim rgData As Range
Dim cell As Range
‘ Проверка, введен ли диапазон данных
If txtRange.Text = «» Then
MsgBox «Введите адрес диапазона суммирования!», _
vbCritical, «Ошибка выполнения»
Cancel = True
End If
If txtResCell.Text = «» Then Exit Sub
On Error GoTo Err1
‘ Проверка отсутствия циклических ссылок (чтобы одна _
из входных ячеек не была одновременно и выходной)
Set rgData = Range(txtRange.Text)
For Each cell In rgData.Cells
If cell.Address(False, False) = _
Range(txtResCell.Text).Address(False, False) Then
‘ Нашли циклическую ссылку
MsgBox «Введите другой адрес во избежание » & _
«появления циклических ссылок», vbCritical, _
«Внимание!»
Cancel = True
Exit Sub
End If
Next cell
Exit Sub
Err1:
‘ Обработка ошибок при работе с ячейками
If Err.Number = 1004 Then
MsgBox «Введите корректный адрес ячейки», vbCritical, _
«Ошибка ввода»
Cancel = True
Exit Sub
Else
MsgBox Err.Desсriрtion, vbCritical, «Ошибка ввода»
Cancel = True
Exit Sub
End If
End Sub
Sub UserForm_Activate()
‘ Инициализация формы при активации
Dim intFunc As Integer
Dim strFunc As String
‘ Заполение списка доступных операций
cboCalcTypes.AddItem «0»
cboCalcTypes.List(0, 1) = «Сумма»
cboCalcTypes.AddItem «1»
cboCalcTypes.List(1, 1) = «Среднее»
cboCalcTypes.AddItem «2»
cboCalcTypes.List(2, 1) = «Максимум»
cboCalcTypes.AddItem «3»
cboCalcTypes.List(3, 1) = «Минимум»
cboCalcTypes.AddItem «4»
cboCalcTypes.List(4, 1) = «Количество ячеек»
cboCalcTypes.AddItem «5»
cboCalcTypes.List(5, 1) = «Сумма положительных»
cboCalcTypes.AddItem «6»
cboCalcTypes.List(6, 1) = «Сумма отрицательных»
cboCalcTypes.AddItem «7»
cboCalcTypes.List(7, 1) = «Количество непустых»
cboCalcTypes.AddItem «8»
cboCalcTypes.List(8, 1) = «Количество непустых ненулевых»
cboCalcTypes.AddItem «9»
cboCalcTypes.List(9, 1) = «Количество положительных»
cboCalcTypes.AddItem «10»
cboCalcTypes.List(10, 1) = «Количество отрицательных»
‘ Заполнение списка дополнительных цветов
cboOtherColor.AddItem «255»
cboOtherColor.List(0, 1) = «Красный»
cboOtherColor.AddItem «52479»
cboOtherColor.List(1, 1) = «Оранжевый»
cboOtherColor.AddItem «65535»
cboOtherColor.List(2, 1) = «Желтый»
cboOtherColor.AddItem «32768»
cboOtherColor.List(3, 1) = «Зеленый»
cboOtherColor.AddItem «16776960»
cboOtherColor.List(4, 1) = «Голубой»
cboOtherColor.AddItem «16711680»
cboOtherColor.List(5, 1) = «Синий»
cboOtherColor.AddItem «16711935»
cboOtherColor.List(6, 1) = «Фиолетовый»
cboOtherColor.AddItem «16777215»
cboOtherColor.List(7, 1) = «Белый»
cboOtherColor.AddItem «0»
cboOtherColor.List(8, 1) = «Черный»
If Selection.Cells.Count = 1 Then
‘ На листе есть выделенная ячейка. Определим, есть ли в этой _
ячейке формула с функцией ColorCalc
intFunc = InStr(Selection.Formula, «ColorCalc(«)
If intFunc > 0 Then
‘ Формула есть, заполним поля формы для вычислений
‘ Адрес ячейки с результатом
txtResCell.Text = Selection.Address(False, False)
‘ Выделяем аргументы функции…
‘ Номера ячеек с исходными данными
strFunc = Mid(Selection.Formula, intFunc + 11)
intFunc = InStr(strFunc, «»»»)
txtRange.Text = Left(strFunc, intFunc — 1)
‘ Тип идентификации ячеек (по шрифту или цвету)
strFunc = Mid(strFunc, intFunc + 2)
intFunc = InStr(strFunc, «,»)
strFunc = Mid(strFunc, intFunc + 1)
intFunc = InStr(strFunc, «,»)
tglType.Value = Left(strFunc, intFunc — 1)
‘ Режим вычислений
strFunc = Mid(strFunc, intFunc + 1)
strFunc = Left(strFunc, Len(strFunc) — 1)
intFunc = InStr(strFunc, «,»)
cboCalcTypes.Text = cboCalcTypes.List(Val(Left$( _
strFunc, intFunc — 1)), 1)
strFunc = Mid(strFunc, intFunc + 1)
chkVarify.SetFocus
chkVarify.Value = CBool(strFunc)
lblChoose.Visible = True
GetColors
Else
‘ Будем применять формулу для выделенной ячейки
txtRange.Value = Selection.Address(False, False)
‘ В выделенной ячейке конкретная функция не задана. _
Выберем первую функцию в списке
cboCalcTypes.Text = «Сумма»
End If
Else
‘ Будем применять формулу для выделенной ячейки
txtRange.Value = Selection.Address(False, False)
‘ В выделенной ячейке конкретная функция не задана. _
Выберем первую функцию в списке
cboCalcTypes.Text = «Сумма»
End If
End Sub
Sub GetColors()
‘ Отображение кнопок выбора цвета окрашенными в цвета, _
встречающиеся среди ячеек заданного диапазона
Dim rgCells As Range
Dim i As Integer
Dim intColorNumber As Integer ‘ Номер следующей кнопки _
выбора цвета
Dim lngCurColor As **** ‘ Анализируемый цвет
Dim fColorPresented As Boolean ‘ Кнопка с цветом _
lngCurColor уже существует
Dim ctrl As Control
Dim strCtrl As String
Dim fBackColor As Boolean ‘ = True, если ячейки _
идентифицируются по цвету фона, _
= False — по цвету шрифта
fBackColor = tglType.Value
On Error Resume Next
‘ Скрытие всех кнопок выбора цвета
For Each ctrl In Me.Controls
If Left(ctrl.Name, 
ctrl.Visible = False
End If
Next ctrl
On Error GoTo ErrRange
Set rgCells = Range(txtRange.Text)
On Error GoTo 0
‘ Получение цвета первой ячейки
If fBackColor = False Then
lngCurColor = rgCells.Cells(i).Font.Color
Else
lngCurColor = rgCells.Cells(i).Interior.Color
End If
‘ Назначения цвета первой ячейки первой кнопке
cmbColor1.BackColor = lngCurColor
cmbColor1.Visible = True
‘ Просмотр остальных ячеек и при нахождении новых цветов _
отображение кнопок, окрашенных в эти цвета
intColorNumber = 2
For i = 2 To rgCells.Cells.Count
fColorPresented = False
‘ Получение цвета i-й ячейки
If fBackColor = False Then
lngCurColor = rgCells.Cells(i).Font.Color
Else
lngCurColor = rgCells.Cells(i).Interior.Color
End If
‘ Проверка, отображается ли уже кнопка с таким цветом
For Each ctrl In Me.Controls
If Left(ctrl.Name, 
ctrl.Visible = True Then
If lngCurColor = ctrl.BackColor Then
‘ Кнопка с цветом i-й ячейки уже отображается
fColorPresented = True
Exit For
End If
End If
Next ctrl
If Not fColorPresented Then
‘ Кнопки с цветом lngCurColor еще нет — покажем ее
intColorNumber = intColorNumber + 1
strCtrl = «cmbColor» & intColorNumber
Me.Controls(strCtrl).BackColor = lngCurColor
Me.Controls(strCtrl).Visible = True
End If
Next i
Exit Sub
ErrRange:
‘ Обработка ошибок при работе с диапазоном
If txtRange.Text = «» Then
MsgBox «Введите адрес диапазона суммирования», _
vbCritical, «Внимание!»
Else
MsgBox «Введен некорректный адрес диапазона суммирования», _
vbCritical, «Ошибка!»
End If
‘ Установка курсора в поле ввода диапазона
txtRange.SetFocus
End Sub
ГЛАВА 11. ДРУГИЕ ФУНКЦИИ И МАКРОСЫ
Вызов функциональных клавиш
Sub Test()
SendKeys («{F1}»)
End Sub
Расчет среднего арифметического значения
Sub CalculateAverage()
Dim strFistCell As String
Dim strLastCell As String
Dim strFormula As String
‘ Условия закрытия процедуры
If ActiveCell.Row = 1 Then Exit Sub
‘ Определение положения первой и последней ячеек для расчета
strFistCell = ActiveCell.Offset(-1, 0).End(xlUp).Address
strLastCell = ActiveCell.Offset(-1, 0).Address
‘ Формула для расчета среднего значения
strFormula = «=AVERAGE(» & strFistCell & «:» & strLastCell & «)»
‘ Ввод формулы в текущую ячейку
ActiveCell.Formula = strFormula
End Sub
Перевод чисел в «деньги»
Листинг 2.50. Функция RubKop
Function RubKop(Число)
‘ Пустые ячейки и ячейки, содержащие текст, функция _
не обрабатывает
If IsNumeric(Число) = False Or Число = «» Then RubKop = _
«<>»: Exit Function
‘ Из числа целой части — рубли
ДлинаЧисла = Len(Число)
ЦелаяЧасть = Fix(Число)
ДлинаЦелой = Len(ЦелаяЧасть)
‘ Вычисление длины дробной части
ДлинаДроби = ДлинаЧисла — ДлинаЦелой
If ДлинаДроби <> 0 Then
ДлинаДроби = ДлинаЧисла — ДлинаЦелой — 1
End If
‘ Формирование количества копеек в зависимости от длины _
дробной части
If ДлинаДроби = 0 Then
‘ Ноль копеек
Копейки = «00»
ElseIf ДлинаДроби = 1 Then
‘ Дробная часть состоит из одного числа — это _
десятки копеек
Копейки = Right(Число, ДлинаДроби) & «0»
ElseIf ДлинаДроби = 2 Then
‘ Дробная часть полностью соответствует количеству копеек
Копейки = Right(Число, ДлинаДроби)
Else
‘ Длина дробной части больше двух — округлим _
дробную часть
Копейки = Right(Число, ДлинаДроби)
If Mid(Копейки, 3, 1) > 4 Then
Копейки = Left(Копейки, 2) + 1
Else
Копейки = Left(Копейки, 2)
End If
End If
‘ Составление полной надписи из количества рублей и копеек
Рубли = ЦелаяЧасть
RubKop = Рубли & » » & «руб.» & » » & Копейки & » » & «коп.»
End Function
Поиск ближайшего понедельника
Листинг 2.60. Ближайший день недели по отношению к дате
Function dhGetNextMonday(datDate As Date) As Date
‘ Определение даты следующего понедельника (функция Weekday _
возвращает номер дня недели, считая от понедельника, если _
в качестве второго аргумента задавать vbMonday)
If Weekday(datDate, vbMonday) = 1 Then
‘ Заданная дата и есть понедельник
dhGetNextMonday = datDate
Else
‘ Расчет даты следующего понедельника
dhGetNextMonday = datDate + 8 — Weekday(datDate, vbMonday)
End If
End Function
Подсчет количества полных лет
Листинг 2.61. Функция dhCalculateAge
Function dhCalculateAge(datDate As Date) As ****
Dim lngAge As ****
‘ Находим разность между текущей датой и указанной (лет)
lngAge = DateDiff(«yyyy», datDate, Date)
If DateSerial(Year(datDate) + lngAge, Month(datDate), _
Day(datDate)) > Date Then
‘ В этом году день рождения еще не наступил
lngAge = lngAge — 1
End If
dhCalculateAge = lngAge
End Function
Расчет средневзвешенного значения
Листинг 2.63. Расчет средневзвешенного значения
Function dhAverageWithWeight(rgWeights As Range, rgValues As Range) _
As Double
If (rgWeights.Count <> rgValues.Count) Then
‘ Количество весов не соответствует количеству аргументов
dhAverageWithWeight = 0
Exit Function
End If
Dim i As Integer
Dim dblSum As Double ‘ Сумма значений
Dim dblSumWeight As Double ‘ Взвешенная сумма значений
‘ Вычисление…
For i = 1 To rgWeights.Count
‘ Взвешенной суммы значений
dblSumWeight = dblSumWeight + rgWeights(i) * rgValues(i)
‘ Суммы значений
dblSum = dblSum + rgWeights(i)
Next
‘ Возвращение средневзвешенного значения
dhAverageWithWeight = dblSumWeight / dblSum
End Function
Преобразование номера месяца в его название
Листинг 2.64. Название месяца
Function dhMonthName(intMonth As Integer) As String
‘ Возвращение имени месяца по его номеру (intMonth _
является номером элемента в массиве с названиями месяцев)
dhMonthName = Choose(intMonth, «Январь», «Февраль», «Март», _
«Апрель», «Май», «Июнь», «Июль», «Август», «Сентябрь», _
«Октябрь», «Ноябрь», «Декабрь»)
End Function
Использование относительных ссылок
Листинг 2.73. Функция dhSheetOffset
Function dhSheetOffset(offset As Integer, cell As Range) As Variant
‘ Возврат корректного значения ячейки cell листа, смещение _
которого относительно текущего задано переменной offset
dhSheetOffset = Sheets(Application.Caller.Parent.Index _
+ offset).Range(cell.Address)
End Function
Листинг 2.74. Функция dhSheetOffset2
Function dhSheetOffset2(offset As Integer, cell As Range) As Variant
‘ Корректировка смещения (чтобы ссылка была на рабочий лист)
Do While TypeName(Sheets(cell.Parent.Index + offset)) _
<> «Worksheet»
If offset > 0 Then
‘ Пропускаем лист и проходим вперед по книге
offset = offset + 1
Else
‘ Пропускаем лист и проходим назад по книге
offset = offset — 1
End If
Loop
‘ Возврат корректного значения ячейки cell листа, смещение _
которого относительно текущего задано переменной offset _
с пропуском листов с диаграммами
dhSheetOffset2 = Sheets(cell.Parent.Index _
+ offset).Range(cell.Address)
End Function
Преобразование таблицы Excel в HТМL-формат
Листинг 3.60. Преобразование таблицы в HТМL-формат
Sub ExportAsHТМL()
Dim strStyle As String ‘ Параметры стиля отображения ячейки
Dim strAlign As String ‘ Параметры выравнивания ячейки
Dim strOut As String ‘ Выходная строка с HТМL-кодом
Dim cell As Object ‘ Обрабатываемая ячейка
Dim strCellText As String ‘ Текст обрабатываемой ячейки
Dim lngRow As **** ‘ Номер строки обрабатываемой ячейки
Dim lngLastRow As **** ‘ Номер строки предыдущей ячейки
Dim strTemp As String
Dim objWordApp As Object
Dim i As ****
lngLastRow = Selection.Row
‘ Просмотр всех выделенных ячеек
For Each cell In Selection
‘ Значение строки для рассматриваемой ячейки
lngRow = cell.Row
‘ Если перешли на другую строку, то вставляем <tr>
If lngRow <> lngLastRow Then
strOut = strOut & vbTab & «</tr>» & vbCrLf & vbTab & _
«<tr>» & vbCrLf
‘ Переход на следующую строку
lngLastRow = lngRow
End If
‘ Задание шрифта ячейки
If Not IsNull(cell.Font.Size) Then
strStyle = » style=» & «font-size: » & Int(100 * _
cell.Font.Size / 19) & «%;»
End If
‘ Для полужирного шрифта вставляем <b>
If cell.Font.Bold Then
strCellText = «<b>» & strCellText & «</b>»
End If
‘ Задание выравнивания
If cell.HorizontalAlignment = xlRight Then
‘ По правому краю
strAlign = » align=» & «right»
ElseIf cell.HorizontalAlignment = xlCenter Then
‘ По центру
strAlign = » align=» & «center»
Else
‘ По левому краю (по умолчанию)
strAlign = «»
End If
‘ Чтение текста в ячейке
strCellText = cell.Text
‘ Если нужно, то вертикальный вывод текста (в строку strTemp _
с последующим перенесением обратно в strCellText)
If cell.Orientation <> xlHorizontal Then
strTemp = «»
‘ Печать после каждого символа специального _
разделителя — <br>
For i = 1 To Len(strCellText)
strTemp = strTemp & Mid$(strCellText, i, 1) & «<br>»
Next i
strCellText = strTemp
strStyle = «»
End If
strOut = strOut & vbTab & vbTab & «<td» & strStyle & strAlign _
& «>» & strCellText & «</td>» & vbCrLf
Next
‘ Вставка <tr> для первой строки и </tr> — для последней
strOut = vbTab & «<tr>» & vbCrLf & strOut & vbTab & «</tr>» & vbCrLf
‘ Вставка дескриптора <table>
strOut = «<table border=1 cellpadding=3 cellspacing=1>» & vbCrLf & _
strOut & vbCrLf & «</table>»
‘ Запускаем Word и показываем в нем сформированный HТМL-код
Set objWordApp = CreateObject(«Word.Application»)
objWordApp.documents.Add
objWordApp.Selection = strOut
objWordApp.Selection.Copy
objWordApp.Visible = True
Set objWordApp = Nothing
End Sub
Генератор случайных чисел
Листинг 2.77. Функция dhGetRandomValues
Function dhGetRandomValues() As Variant
Dim intRow As Integer ‘ Номер текущей строки
Dim intCol As Integer ‘ Номер текущего столбца
Dim aintOut() As Integer ‘ Выходной массив (двумерный)
Dim aintValues() As Integer ‘ Массив с возможными значениями
Dim intMax As Integer ‘ Последний доступный элемент массива _
aintValues
Dim i As Integer
ReDim aintOut(1 To Application.Caller.Rows.Count, 1 To _
Application.Caller.Columns.Count)
‘ Всего нужно чисел…
intMax = Application.Caller.Rows.Count * _
Application.Caller.Columns.Count
ReDim aintValues(1 To intMax)
‘ Заполнение массива aintValues значениями от 1 до intMax
For i = 1 To intMax
aintValues(i) = i
Next i
‘ Занесение значений в выходной массив aintOut, в произвольном _
порядке выбирая их из aintValues
Randomize
For intRow = 1 To Application.Caller.Rows.Count
For intCol = 1 To Application.Caller.Columns.Count
‘ Определение номера элемента из aintValues
i = Rnd * intMax
If i = 0 Then i = 1
‘ Занесение этого элемента в выходной массив
aintOut(intRow, intCol) = aintValues(i)
‘ Уменьшение массива aintValues (то есть еще один его _
элемент выбран) — замена выбранного элемента последним _
в массиве
aintValues(i) = aintValues(intMax)
intMax = intMax — 1
Next intCol
Next intRow
‘ Возвращение массива значений
dhGetRandomValues = aintOut
End Function
Случайные числа — на основании диапазона
Листинг 2.78. Функция dhGetRandomValues1
Function dhGetRandomValues1(rgSource As Range) As Variant
Dim intRow As Integer ‘ Номер текущей строки
Dim intCol As Integer ‘ Номер текущего столбца
Dim avarOut() As Variant ‘ Выходной массив (двумерный)
Dim avarValues() As Variant ‘ Массив с возможными значениями
Dim intValCount As Integer ‘ Количество возможных значений
Dim cell As Range
Dim i As Integer
ReDim avarOut(1 To Application.Caller.Rows.Count, 1 To _
Application.Caller.Columns.Count)
‘ Всего нужно чисел…
intValCount = rgSource.Rows.Count * rgSource.Columns.Count
ReDim avarValues(1 To intValCount)
‘ Заполнение массива avarValues значениями из указанного _
диапазона
For Each cell In rgSource
i = i + 1
avarValues(i) = cell.Value
Next cell
‘ Занесение значений в выходной массив avarOut, в произвольном _
порядке выбирая их из avarValues
Randomize
For intRow = 1 To Application.Caller.Rows.Count
For intCol = 1 To Application.Caller.Columns.Count
‘ Определение номера элемента из avarValues
i = Rnd * intValCount
If i = 0 Then i = 1
‘ Занесение этого элемента в выходной массив
avarOut(intRow, intCol) = avarValues(i)
Next intCol
Next intRow
‘ Возвращение массива значений
dhGetRandomValues1 = avarOut
End Function
Применение функции без ввода ее в ячейку
Листинг 3.14. Применение функции без ввода в ячейку
Sub Func()
[A1] = Application.Sum([B5:B10])
End Sub
Подсчет именованных объектов
Листинг 3.29. Количество именованных объектов
Sub CountNames()
Dim intNamesCount As Integer
‘ Получаем и отображаем количество имен в активной _
рабочей книге
intNamesCount = ActiveWorkbook.Names.Count
If intNamesCount = 0 Then
MsgBox «Имен нет»
Else
MsgBox «Имен: » & intNamesCount & » шт.»
End If
End Sub
Включение автофильтра с помощью макроса
Листинг 3.63. Включение автофильтра
Sub EnableAutoFilter()
On Error Resume Next
Selection.AutoFilter
End Sub
Создание бегущей строки
Листинг 3.76. Создание бегущей строки
Dim intSpacesLeft As Integer ‘ Количество пробелов в начале строки
Sub Start()
‘ Установка начального количества пробелов
intSpacesLeft = 10
‘ Первый вызов функции бегущей строки
MovingString
End Sub
Sub MovingString()
If intSpacesLeft >= 0 Then
‘ Отображение строки
Range(«A1»).Value = Space(intSpacesLeft) & «Привет!»
intSpacesLeft = intSpacesLeft — 1
‘ Указывем Excel, что данную процедуру нужно вызвать через _
1 секунду
Application.OnTime Now + TimeValue(«00:00:01»), «MovingString»
End If
End Sub
Создание бегущей картинки
Листинг 3.77. Бегущая картинка
Sub MovingImage()
Dim i As Integer
Dim image As Object
‘ Создание изображения (в ячейке «A1»)
With Range(«A1»)
‘ Формирование значения в ячейке:
‘ текст
.Value = «Привет!»
‘ полужирный шрифт
.Font.Bold = True
‘ цвет
.Font.Color = RGB(233, 133, 229)
‘ размер шрифта
.Font.Size = 16
‘ угол наклона
.Orientation = 30
‘ Отображение текста полностью
.EntireColumn.AutoFit
‘ Копирование в буфер обмена
.Copy
‘ Создание самостоятельного изображения (на основе _
скопированных в буфер обмена данных)
Set image = ActiveSheet.Pictures.Paste(Link:=False)
‘ Содержимое ячейки больше не нужно
.Clear
End With
‘ Задание начального положения изображения (левый верхний _
угол листа)
With image
.Top = 0
.Left = 0
End With
MsgBox «ПУСК!»
With image
‘ Перемещение изображения по диагонали
For i = 0 To 100
.Top = i
.Left = i
Next
‘ Удаление изображения
.Delete
End With
‘ Удаление ссылки на изображение
Set image = Nothing
End Sub
Вращающиеся автофигуры
Листинг 3.79. Вращение автофигур
Sub RotatingAutoShapes()
Static fRunning As Boolean
‘ Проверка, выполняется ли уже этот макрос
If fRunning Then
‘ При повторном запуске останавливаем все запущенные макросы
fRunning = False
End
End If
‘ Укажем, что макрос запущен
fRunning = True
Dim cell As Range ‘ Рабочая ячейка
Dim intLeftBorder As **** ‘ Левая граница ячейки
Dim intRightBorder As **** ‘ Правая граница ячейки
Dim intTopBorder As **** ‘ Верхняя граница ячейки
Dim intBottomBorder As **** ‘ Нижняя граница ячейки
Dim alngVertSpeed(1 To 2) As **** ‘ Массивы со значениями
Dim alngHorzSpeed(1 To 2) As **** ‘ горизонтальной и вертикальной
‘ составляющих скоростей фигур
Dim ashShapes(1 To 2) As Shape ‘ Массив перемещаемых автофигур
Dim i As Integer
‘ Заполнение массива автофигур
Set ashShapes(1) = ActiveSheet.shapes(1)
Set ashShapes(2) = ActiveSheet.shapes(2)
‘ Заполнение массива скоростей:
‘ для первой фигуры
alngVertSpeed(1) = 3
alngHorzSpeed(1) = 3
‘ для второй фигуры
alngVertSpeed(2) = 4
alngHorzSpeed(2) = 4
‘ Получение границ рабочей ячейки
Set cell = Range(«B2»)
intLeftBorder = cell.Left
intRightBorder = cell.Left + cell.Width
intTopBorder = cell.Top
intBottomBorder = cell.Top + cell.Height
‘ Выполнение вращения и перемещения фигур
Do
‘ Изменение положения каждой автофигуры
For i = 1 To 2
With ashShapes(i)
‘ Контроль достижения правой границы ячейки
If .Left + .Width + alngHorzSpeed(i) > intRightBorder Then
‘ Корректировка положения
.Left = intRightBorder — .Width
‘ Изменение направления горизонтальной скорости _
на противоположное
alngHorzSpeed(i) = -alngHorzSpeed(i)
End If
‘ Контроль достижения левой границы ячейки
If .Left + alngHorzSpeed(i) < intLeftBorder Then
‘ Корректировка положения
.Left = intLeftBorder
‘ Изменение направления горизонтальной скорости _
на противоположное
alngHorzSpeed(i) = -alngHorzSpeed(i)
End If
‘ Контроль достижения нижней границы ячейки
If .Top + .Height + alngVertSpeed(i) > intBottomBorder Then
‘ Корректировка положения
.Top = intBottomBorder — .Height
‘ Изменение направления вертикальной скорости _
на противоположное
alngVertSpeed(i) = -alngVertSpeed(i)
End If
‘ Контроль достижения верхней границы ячейки
If .Top + alngVertSpeed(i) < intTopBorder Then
‘ Корректировка положения
.Top = intTopBorder
‘ Изменение направления вертикальной скорости _
на противоположное
alngVertSpeed(i) = -alngVertSpeed(i)
End If
‘ Перемещение автофигуры
.Left = .Left + alngHorzSpeed(i)
.Top = .Top + alngVertSpeed(i)
‘ Вращение автофигуры (изменение направления вращения _
происходит каждый раз при изменении направления _
вертикального перемещения)
.IncrementRotation alngVertSpeed(i)
‘ Даем Excel команду обработать пользовательский ввод
DoEvents
End With
Next
Loop
End Sub
Вызов таблицы цветов
Листинг 3.80. Отображение таблицы цветов
Sub ShowColorTable()
Dim intColor As Integer
‘ Формирование заголовка таблицы
Range(«A1»).Value = «Цвет»
Range(«B1»).Value = «Значение свойства ColorIndex»
‘ Вывод таблицы
Range(«A2»).Select
For intColor = 1 To 56
‘ Окрашиваем ячейку столбца «A» в текущий цвет
With ActiveCell.Interior
.ColorIndex = intColor
.Pattern = xlSolid
.PatternColorIndex = xlAutomatic
End With
‘ В ячейку столбца «B» вносим индекс текущего цвета
ActiveCell.Offset(0, 1).Value = intColor
‘ Переходим на следующую строку
ActiveCell.Offset(1, 0).Activate
Next
‘ Покажем ячейку «A1» (начало таблицы)
Range(«A1»).Select
ActiveWindow.ScrollRow = 1
End Sub
Создание калькулятора
Листинг 3.81. Создание калькулятора
Sub SimpleCalculator()
Dim strExpr As String
‘ Ввод выражения
strExpr = InputBox(«Что будем считать?»)
‘ Подсчет и вывод результата
MsgBox strExpr & » = » & Application.Evaluate(strExpr)
End Sub
Склонение фамилии, имени и отчества
Листинг 3.85. Склонение ФИО
Public Sub PossessiveCase()
‘ Склоняем ФИО в родительный падеж
Dim strName1 As String, strName2 As String, strName3 As String
strName1 = dhGetName(ActiveCell, 1) ‘ Выделяем имя
strName2 = dhGetName(ActiveCell, 2) ‘ Выделяем фамилию
strName3 = dhGetName(ActiveCell, 3) ‘ Выделяем отчество
‘ Если в ячейке менее трех слов — закрытие процедуры
If strName1 = «» Or strName2 = «» Or strName3 = «» Then Exit Sub
‘ Склоняем
Cells(ActiveCell.Row, ActiveCell.Column) = dhPossessive( _
strName1, strName2, strName3)
End Sub
Public Sub DativeCase()
‘ Объявление переменных
Dim strName1 As String, strName2 As String, strName3 As String
strName1 = dhGetName(ActiveCell, 1)
strName2 = dhGetName(ActiveCell, 2)
strName3 = dhGetName(ActiveCell, 3)
‘ Если в ячейке менее трех слов — закрытие процедуры
If Len(strName1) = 0 Or Len(strName2) = 0 Or Len(strName3) = 0 _
Then Exit Sub
Cells(ActiveCell.Row, ActiveCell.Column) = dhDative( _
strName1, strName2, strName3)
End Sub
Function dhPossessive(strName1 As String, strName2 As String, _
strName3 As String) As String
Dim fMan As Boolean
‘ Определяем, мужские ФИО или женские
fMan = (Right(strName3, 1) = «ч»)
‘ Склонение фамилии в родительный падеж
If Len(strName1) > 0 Then
If fMan Then
‘ Склонение мужской фамилии
Select Case Right(strName1, 1)
Case «о», «и», «я», «а»
dhPossessive = strName1
Case «й»
dhPossessive = Mid(strName1, 1, Len(strName1) — 2) + «ого»
Case Else
dhPossessive = strName1 + «а»
End Select
Else
‘ Склонение женской фамилии
Select Case Right(strName1, 1)
Case «о», «и», «б», «в», «г», «д», «ж», «з», «к», «л», _
«м», «н», «п», «р», «с», «т», «ф», «х», «ц», «ч», _
«ш», «щ», «ь»
dhPossessive = strName1
Case «я»
dhPossessive = Mid(strName1, 1, Len(strName1) — 2) & «ой»
Case Else
dhPossessive = Mid(strName1, 1, Len(strName1) — 1) & «ой»
End Select
End If
dhPossessive = dhPossessive & » »
End If
‘ Склонение имени в родительный падеж
If Len(strName2) > 0 Then
If fMan Then
‘ Склонение мужского имени
Select Case Right(strName2, 1)
Case «й», «ь»
dhPossessive = dhPossessive & Mid(strName2, _
1, Len(strName2) — 1) & «я»
Case Else
dhPossessive = dhPossessive & strName2 & «а»
End Select
Else
‘ Склонение женского имени
Select Case Right(strName2, 1)
Case «а»
Select Case Mid(strName2, Len(strName2) — 1, 1)
Case «и», «г»
dhPossessive = dhPossessive & Mid( _
strName2, 1, Len(strName2) — 1) & «и»
Case Else
dhPossessive = dhPossessive & Mid(strName2, _
1, Len(strName2) — 1) & «ы»
End Select
Case «я»
If Mid(strName2, Len(strName2) — 1, 1) = «и» Then
dhPossessive = dhPossessive & Mid(strName2, _
1, Len(strName2) — 1) & «и»
Else
dhPossessive = dhPossessive & Mid(strName2, _
1, Len(strName2) — 1) & «и»
End If
Case «ь»
dhPossessive = dhPossessive & Mid(strName2, _
1, Len(strName2) — 1) & «и»
Case Else
dhPossessive = dhPossessive & strName2
End Select
End If
dhPossessive = dhPossessive & » »
End If
‘ Склонение отчества в родительный падеж
If Len(strName3) > 0 Then
If fMan Then
dhPossessive = dhPossessive & strName3 & «а»
Else
dhPossessive = dhPossessive & Mid(strName3, 1, _
Len(strName3) — 1) & «ы»
End If
End If
End Function
Function dhDative(strName1 As String, strName2 As String, _
strName3 As String) As String
Dim fMan As Boolean
‘ Определяем, мужские ФИО или женские
fMan = (Right(strName3, 1) = «ч»)
‘ Склонение фамилии в дательный падеж
If Len(strName1) > 0 Then
If fMan Then
‘ Склонение мужской фамилии
Select Case Right(strName1, 1)
Case «о», «и», «я», «а»
dhDative = strName1
Case «й»
dhDative = Mid(strName1, 1, Len(strName1) — 2) + «ому»
Case Else
dhDative = strName1 + «у»
End Select
Else
‘ Склонение женской фамилии
Select Case Right(strName1, 1)
Case «о», «и», «б», «в», «г», «д», «ж», «з», «к», «л», _
«м», «н», «п», «р», «с», «т», «ф», «х», «ц», «ч», «ш», _
«щ», «ь»
dhDative = strName1
Case «я»
dhDative = Mid(strName1, 1, Len(strName1) — 2) & «ой»
Case Else
dhDative = Mid(strName1, 1, Len(strName1) — 1) & «ой»
End Select
End If
dhDative = dhDative & » »
End If
‘ Склонение имени в дательный падеж
If Len(strName2) > 0 Then
If fMan Then
‘ Склонение мужского имени
Select Case Right(strName2, 1)
Case «й», «ь»
dhDative = dhDative & Mid(strName2, 1, _
Len(strName2) — 1) & «ю»
Case Else
dhDative = dhDative & strName2 & «у»
End Select
Else
‘ Склонение женского имени
Select Case Right(strName2, 1)
Case «а», «я»
If Mid(strName2, Len(strName2) — 1, 1) = «и» Then
dhDative = dhDative & Mid(strName2, 1, _
Len(strName2) — 1) & «и»
Else
dhDative = dhDative & Mid(strName2, 1, _
Len(strName2) — 1) & «е»
End If
Case «ь»
dhDative = dhDative & Mid(strName2, 1, _
Len(strName2) — 1) & «и»
Case Else
dhDative = dhDative & strName2
End Select
End If
dhDative = dhDative & » »
End If
‘ Склонение отчества в дательный падеж
If Len(strName3) > 0 Then
If fMan Then
dhDative = dhDative & strName3 & «у»
Else
dhDative = dhDative & Mid(strName3, 1, Len(strName3) — 1) & «е»
End If
End If
End Function
Function dhGetName(strString As String, intNum As Integer)
‘ Функция возвращает слово с номером intNum во входной строке _
strString
Dim strTemp As String
Dim intWord As Integer
Dim intSpace As Integer
‘ Удаление пробелов по краям строки
strTemp = Trim(strString)
‘ Просмотр строки (до слова с нужным номером)
For intWord = 1 To intNum — 1
‘ Поиск следующего пробела
intSpace = InStr(strTemp, » «)
If intSpace = 0 Then
‘ Строка закончилась
intSpace = Len(strTemp)
End If
‘ Строка strTemp теперь начинается со слова с номером intWord
strTemp = Trim(Right(strTemp, Len(strTemp) — intSpace))
Next intWord
‘ Выделение нужного слова (по пробелу после него)
intSpace = InStr(strTemp, » «)
If intSpace = 0 Then
intSpace = Len(strTemp)
End If
dhGetName = Trim(Left(strTemp, intSpace))
End Function
ГЛАВА 12. ДАТА И ВРЕМЯ
Вывод даты и времени_1
Sub Test()
Dim MyDate As Date
MyDate = DateValue(«6/1/72») + TimeValue(«10:10:12»)
MsgBox Str(Minute(MyDate))
MsgBox Str(Year(MyDate))
End Sub
Вывод даты и времени_2
Sub TimeAndDate()
Dim strDate As String, strTime As String
Dim strGreeting As String
Dim strUserName As String
Dim intSpacePos As Integer
strDate = Format(Date, «**** Date»)
strTime = Format(Time, «Medium Time»)
‘ Приветствие — в зависимости от времени суток
If Time < TimeValue(«12:00») Then
strGreeting = «Доброе утро, »
ElseIf Time < TimeValue(«17:00») Then
strGreeting = «Добрый день, »
Else
strGreeting = «Добрый вечер, »
End If
‘ В приветствие добавляется имя текущего пользователя
strUserName = Application.UserName
intSpacePos = InStr(1, strUserName, » «, 1)
‘ Управление ситуацией, когда в имени нет пробела
If intSpacePos = 0 Then intSpacePos = Len(strUserName)
strGreeting = strGreeting & Left(strUserName, intSpacePos)
‘ Вывод на экран информационного сообщения о дате и времени
MsgBox strDate & vbCrLf & strTime, vbOKOnly, strGreeting
End Sub
Получение системной даты
Извлечение даты и часов
Month(переменная типа Date)
Day(переменная типа Date)
Year(переменная типа Date)
Hour(переменная типа Date)
Minute(переменная типа Date)
Second(переменная типа Date)
WeekDay(переменная типа Date)
WeekDay это день недели, если Вам это нужно, то вы можете написать что-то типа этого.
Sub Test()
Dim MyDate As Date
MyDate = DateValue(«9/1/72»)
If (WeekDay(MyDate) = vbSunday) Then MsgBox («Sunday»)
End Sub
vbSunday это константа , есть еще vbMonday , ну дальше понятно.
Функция ДатаПолная
Function ДатаПолная(Ячейка)
‘ Получение данных в заданной ячейке в формате _
«dd mmmm yyyy»
Дата = Format(Ячейка, «dd mmmm yyyy»)
If IsDate(Ячейка) = True Or IsDate(Дата) = True Then
‘ Возврат строки с полной датой
ДатаПолная = StrConv(Дата, vbProperCase)
Else
‘ Данные в ячейке не являются датой
ДатаПолная = «<>»
End If
End Function
Excel VBA Examples for Beginners
Macros are your best friend when it comes to increasing productivity or saving time at your workplace. From small to big tasks, we can automate by using the VBA coding language. We know often you might have thought of some of the limitations Excel has but with VBA coding, you can eliminate all of those. If you struggled with VBA and are still a beginner in this article, we will give some useful examples of VBA Macro code in Excel.
Table of contents
- Excel VBA Examples for Beginners
- List of Top 19 Examples
- #1 – Print All Sheet Names
- #2 – Insert Different Color Index in VBA
- #3 – Insert Serial Number From Top
- #4 – Insert Serial Number From Bottom
- #5 – Insert Serial Number From 10 to 1
- #6 – Insert Worksheets as Much as You want
- #7 – Delete All Blank Worksheets From the Workbook
- #8 – Insert Blank Row After Every Other Row
- #9 – Highlight Spelling Mistake
- #10 – Change All To Upper Case Characters
- #11 – Change All To Lower Case Characters
- #12 – Highlight All the Commented Cells
- #13 – Highlight All the Blank Cells
- #14 – Hide All Sheets Except One Sheet
- #15 – Unhide All Sheets
- #16 – Delete All Files in the Folder
- #17 – Delete Entire Folder
- #18 – Find the Last Used Row in the Sheet
- #19 – Find the Last Used Column in the Sheet
- Recommended Articles
- List of Top 19 Examples
You are free to use this image on your website, templates, etc, Please provide us with an attribution linkArticle Link to be Hyperlinked
For eg:
Source: VBA Examples (wallstreetmojo.com)
List of Top 19 Examples
- Print All Sheet Names
- Insert Different Color Index in VBA
- Insert Serial Number From Top
- Insert Serial Number From Bottom
- Insert Serial Number From 10 to 1
- Insert Worksheets as Much as You want
- Delete All Blank Worksheets From the Workbook
- Insert Blank Row After Every Other Row
- Highlight Spelling Mistake
- Change All To Upper Case Characters
- Change All To Lower Case Characters
- Highlight All the Commented Cells
- Highlight All the Blank Cells
- Hide All Sheets Except One Sheet
- Unhide All Sheets
- Delete All Files in the Folder
- Delete Entire Folder
- Find the Last Used Row in the Sheet
- Find the Last Used Column in the Sheet
Let’s see each of these examples in detail.
You can download this VBA Examples Excel Template here – VBA Examples Excel Template
#1 – Print All Sheet Names
Code:
Sub Print_Sheet_Names() Dim i As Integer For i = 1 To Sheets.Count Cells(i, 1).Value = Sheets(i).Name Next i End Sub
It will extract all the sheet names to the active sheet.
#2 – Insert Different Color Index in VBA
Code:
Sub Insert_Different_Colours() Dim i As Integer For i = 1 To 56 Cells(i, 1).Value = i Cells(i, 2).Interior.ColorIndex = i Next End Sub
It will insert numbers from 1 to 56 and their color index in the next column.
#3 – Insert Serial Number From Top
Code:
Sub Insert_Numbers_From_Top() Dim i As Integer For i = 1 To 10 Cells(i, 1).Value = i Next i End Sub
It will insert serial numbers from 1 to 10 from the top.
#4 – Insert Serial Number From Bottom
Code:
Sub Insert_Numbers_From_Bottom() Dim i As Integer For i = 20 To 1 Step -1 Cells(i, 7).Value = i Next i End Sub
It will insert serial numbers from 1 to 20 from the bottom.
#5 – Insert Serial Number From 10 to 1
Code:
Sub Ten_To_One() Dim i As Integer Dim j As Integer j = 10 For i = 1 To 10 Range("A" & i).Value = j j = j - 1 Next i End Sub
It will insert serial numbers from 10 to 1 from the top.
#6 – Insert Worksheets as Much as You want
Code:
Sub AddSheets() Dim ShtCount As Integer, i As Integer ShtCount = Application.InputBox("How Many Sheets you would like to insert?", "Add Sheets", , , , , , 1) If ShtCount = False Then Exit Sub Else For i = 1 To ShtCount Worksheets.Add Next i End If End Sub
It will ask you to enter the number of worksheets you would like to insert. Just specify the number in the input box and click on “OK.” It will insert those many sheets immediately.
#7 – Delete All Blank Worksheets From the Workbook
Code:
Sub Delete_Blank_Sheets() Dim ws As Worksheet Application.DisplayAlerts = False Application.ScreenUpdating = False For Each ws In ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets If WorksheetFunction.CountA(ws.UsedRange) = 0 Then ws.Delete End If Next ws Application.DisplayAlerts = True Application.ScreenUpdating = True End Sub
It will delete all the blank worksheets from the workbook we are working on.
#8 – Insert Blank Row After Every Other Row
Code:
Sub Insert_Row_After_Every_Other_Row() Dim rng As Range Dim CountRow As Integer Dim i As Integer Set rng = Selection CountRow = rng.EntireRow.Count For i = 1 To CountRow ActiveCell.EntireRow.Insert ActiveCell.Offset(2, 0).Select Next i End Sub
For this, first, you need to select the range where you would like to insert alternative blank rows.
#9 – Highlight Spelling Mistake
Code:
Sub Chech_Spelling_Mistake() Dim MySelection As Range For Each MySelection In ActiveSheet.UsedRange If Not Application.CheckSpelling(Word:=MySelection.Text) Then MySelection.Interior.Color = vbRed End If Next MySelection End Sub
First, select the data and run the VBA codeVBA code refers to a set of instructions written by the user in the Visual Basic Applications programming language on a Visual Basic Editor (VBE) to perform a specific task.read more. It will highlight the cells which have spelling mistakes.
#10 – Change All To Upper Case Characters
Code:
Sub Change_All_To_UPPER_Case() Dim Rng As Range For Each Rng In Selection.Cells If Rng.HasFormula = False Then Rng.Value = UCase(Rng.Value) End If Next Rng End Sub
First, select the data and run the code. It will convert all the text values to upper case characters.
#11 – Change All To Lower Case Characters
Code:
Sub Change_All_To_LOWER_Case() Dim Rng As Range For Each Rng In Selection.Cells If Rng.HasFormula = False Then Rng.Value = LCase(Rng.Value) End If Next Rng End Sub
First, select the data and run the code. It will convert all the text values to lower case characters in excelThere are six methods to change lowercase in excel — Using the lower function to change case in excel, Using the VBA command button, VBA shortcut key, Using Flash Fill, Enter text in lower case only, Using Microsoft word.
read more.
Code:
Sub HighlightCellsWithCommentsInActiveWorksheet() ActiveSheet.UsedRange.SpecialCells(xlCellTypeComments).Interior.ColorIndex = 4 End Sub
Result:
#13 – Highlight All the Blank Cells
Code:
Sub Highlight_Blank_Cells() Dim DataSet As Range Set DataSet = Selection DataSet.Cells.SpecialCells(xlCellTypeBlanks).Interior.Color = vbGreen End Sub
First, select the data range and run the code. It will highlight all the blank cells with green color.
#14 – Hide All Sheets Except One Sheet
Code:
Sub Hide_All_Except_One() Dim Ws As Worksheet For Each Ws In ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets If Ws.Name <> "Main Sheet" Then Ws.Visible = xlSheetVeryHidden Next Ws End Sub
The above code hides all the sheets except the sheet named “Main Sheet.” You can change the worksheet name as per your wish.
#15 – Unhide All Sheets
Code:
Sub UnHide_All() Dim Ws As Worksheet For Each Ws In ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets Ws.Visible = xlSheetVisible Next Ws End Sub
It will unhide all the hidden sheets.
#16 – Delete All Files in the Folder
Code:
Sub Delete_All_Files() 'You can use this to delete all the files in the folder Test '' On Error Resume NextVBA On Error Resume Statement is an error-handling aspect used for ignoring the code line because of which the error occurred and continuing with the next line right after the code line with the error.read more Kill "C:UsersAdmin_2.Dell-PcDesktopDelete Folder*.*" On Error GoTo 0 End Sub
Change the folder path marked in red as per your folder deletion.
#17 – Delete Entire Folder
Code:
Sub Delete_Whole_Folder() 'You can use this to delete entire folder On Error Resume NextVBA On Error Resume Statement is an error-handling aspect used for ignoring the code line because of which the error occurred and continuing with the next line right after the code line with the error.read more Kill "C:UsersAdmin_2.Dell-PcDesktopDelete Folder*.*" 'Firstly it will delete all the files in the folder 'Then below code will delete the entire folder if it is empty RmDir "C:UsersAdmin_2.Dell-PcDesktopDelete Folder" 'Note: RmDir delete only a empty folder On Error GoTo 0 End Sub
Change the folder path marked in red as per your folder deletion.
#18 – Find the Last Used Row in the Sheet
Code:
Sub Last_Row() Dim LR As Long LR = Cells(Rows.Count, 1).End(xlUp).Row MsgBox LR End Sub
Here, we find the last used row in the sheet.
#19 – Find the Last Used Column in the Sheet
Code:
Sub Last_Column() Dim LC As Long LC = Cells(1, Columns.Count).End(xlToLeft).Column MsgBox LC End Sub
Here, we find the last used column in the sheet.
Recommended Articles
This article is a guide to VBA Examples. Here, we discuss the list of top 19 useful examples of VBA Macro code in Excel along with the downloadable template. Below are some useful articles related to Excel VBA: –
- VBA XLUP
- CDATE VBA Function
- VBA Tutorial
- VBA Randomize
Using Excel Macros can speed up work and save you a lot of time.
One way of getting the VBA code is to record the macro and take the code it generates. However, that code by macro recorder is often full of code that is not really needed. Also macro recorder has some limitations.
So it pays to have a collection of useful VBA macro codes that you can have in your back pocket and use it when needed.
While writing an Excel VBA macro code may take some time initially, once it’s done, you can keep it available as a reference and use it whenever you need it next.
In this massive article, I am going to list some useful Excel macro examples that I need often and keep stashed away in my private vault.
I will keep updating this tutorial with more macro examples. If you think something should be on the list, just leave a comment.
You can bookmark this page for future reference.
Now before I get into the Macro Example and give you the VBA code, let me first show you how to use these example codes.
Using the Code from Excel Macro Examples
Here are the steps you need to follow to use the code from any of the examples:
- Open the Workbook in which you want to use the macro.
- Hold the ALT key and press F11. This opens the VB Editor.
- Right-click on any of the objects in the project explorer.
- Go to Insert –> Module.
- Copy and Paste the code in the Module Code Window.
In case the example says that you need to paste the code in the worksheet code window, double click on the worksheet object and copy paste the code in the code window.
Once you have inserted the code in a workbook, you need to save it with a .XLSM or .XLS extension.
How to Run the Macro
Once you have copied the code in the VB Editor, here are the steps to run the macro:
- Go to the Developer tab.
- Click on Macros.
- In the Macro dialog box, select the macro you want to run.
- Click on Run button.
In case you can’t find the developer tab in the ribbon, read this tutorial to learn how to get it.
Related Tutorial: Different ways to run a macro in Excel.
In case the code is pasted in the worksheet code window, you don’t need to worry about running the code. It will automatically run when the specified action occurs.
Now, let’s get into the useful macro examples that can help you automate work and save time.
Note: You will find many instances of an apostrophe (‘) followed by a line or two. These are comments that are ignored while running the code and are placed as notes for self/reader.
In case you find any error in the article or the code, please be awesome and let me know.
Excel Macro Examples
Below macro examples are covered in this article:
Unhide All Worksheets at One Go
If you are working in a workbook that has multiple hidden sheets, you need to unhide these sheets one by one. This could take some time in case there are many hidden sheets.
Here is the code that will unhide all the worksheets in the workbook.
'This code will unhide all sheets in the workbook Sub UnhideAllWoksheets() Dim ws As Worksheet For Each ws In ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets ws.Visible = xlSheetVisible Next ws End Sub
The above code uses a VBA loop (For Each) to go through each worksheets in the workbook. It then changes the visible property of the worksheet to visible.
Here is a detailed tutorial on how to use various methods to unhide sheets in Excel.
Hide All Worksheets Except the Active Sheet
If you’re working on a report or dashboard and you want to hide all the worksheet except the one that has the report/dashboard, you can use this macro code.
'This macro will hide all the worksheet except the active sheet Sub HideAllExceptActiveSheet() Dim ws As Worksheet For Each ws In ThisWorkbook.Worksheets If ws.Name <> ActiveSheet.Name Then ws.Visible = xlSheetHidden Next ws End Sub
Sort Worksheets Alphabetically Using VBA
If you have a workbook with many worksheets and you want to sort these alphabetically, this macro code can come in really handy. This could be the case if you have sheet names as years or employee names or product names.
'This code will sort the worksheets alphabetically Sub SortSheetsTabName() Application.ScreenUpdating = False Dim ShCount As Integer, i As Integer, j As Integer ShCount = Sheets.Count For i = 1 To ShCount - 1 For j = i + 1 To ShCount If Sheets(j).Name < Sheets(i).Name Then Sheets(j).Move before:=Sheets(i) End If Next j Next i Application.ScreenUpdating = True End Sub
Protect All Worksheets At One Go
If you have a lot of worksheets in a workbook and you want to protect all the sheets, you can use this macro code.
It allows you to specify the password within the code. You will need this password to unprotect the worksheet.
'This code will protect all the sheets at one go Sub ProtectAllSheets() Dim ws As Worksheet Dim password As String password = "Test123" 'replace Test123 with the password you want For Each ws In Worksheets ws.Protect password:=password Next ws End Sub
Unprotect All Worksheets At One Go
If you have some or all of the worksheets protected, you can just use a slight modification of the code used to protect sheets to unprotect it.
'This code will protect all the sheets at one go Sub ProtectAllSheets() Dim ws As Worksheet Dim password As String password = "Test123" 'replace Test123 with the password you want For Each ws In Worksheets ws.Unprotect password:=password Next ws End Sub
Note that the password needs to the same that has been used to lock the worksheets. If it’s not, you will see an error.
Unhide All Rows and Columns
This macro code will unhide all the hidden rows and columns.
This could be really helpful if you get a file from someone else and want to be sure there are no hidden rows/columns.
'This code will unhide all the rows and columns in the Worksheet Sub UnhideRowsColumns() Columns.EntireColumn.Hidden = False Rows.EntireRow.Hidden = False End Sub
Unmerge All Merged Cells
It’s a common practice to merge cells to make it one. While it does the work, when cells are merged you will not be able to sort the data.
In case you are working with a worksheet with merged cells, use the code below to unmerge all the merged cells at one go.
'This code will unmerge all the merged cells Sub UnmergeAllCells() ActiveSheet.Cells.UnMerge End Sub
Note that instead of Merge and Center, I recommend using the Centre Across Selection option.
Save Workbook With TimeStamp in Its Name
A lot of time, you may need to create versions of your work. These are quite helpful in long projects where you work with a file over time.
A good practice is to save the file with timestamps.
Using timestamps will allow you to go back to a certain file to see what changes were made or what data was used.
Here is the code that will automatically save the workbook in the specified folder and add a timestamp whenever it’s saved.
'This code will Save the File With a Timestamp in its name Sub SaveWorkbookWithTimeStamp() Dim timestamp As String timestamp = Format(Date, "dd-mm-yyyy") & "_" & Format(Time, "hh-ss") ThisWorkbook.SaveAs "C:UsersUsernameDesktopWorkbookName" & timestamp End Sub
You need to specify the folder location and the file name.
In the above code, “C:UsersUsernameDesktop is the folder location I have used. You need to specify the folder location where you want to save the file. Also, I have used a generic name “WorkbookName” as the filename prefix. You can specify something related to your project or company.
Save Each Worksheet as a Separate PDF
If you work with data for different years or divisions or products, you may have the need to save different worksheets as PDF files.
While it could be a time-consuming process if done manually, VBA can really speed it up.
Here is a VBA code that will save each worksheet as a separate PDF.
'This code will save each worsheet as a separate PDF Sub SaveWorkshetAsPDF() Dim ws As Worksheet For Each ws In Worksheets ws.ExportAsFixedFormat xlTypePDF, "C:UsersSumitDesktopTest" & ws.Name & ".pdf" Next ws End Sub
In the above code, I have specified the address of the folder location in which I want to save the PDFs. Also, each PDF will get the same name as that of the worksheet. You will have to modify this folder location (unless your name is also Sumit and you’re saving it in a test folder on the desktop).
Note that this code works for worksheets only (and not chart sheets).
Save Each Worksheet as a Separate PDF
Here is the code that will save your entire workbook as a PDF in the specified folder.
'This code will save the entire workbook as PDF Sub SaveWorkshetAsPDF() ThisWorkbook.ExportAsFixedFormat xlTypePDF, "C:UsersSumitDesktopTest" & ThisWorkbook.Name & ".pdf" End Sub
You will have to change the folder location to use this code.
Convert All Formulas into Values
Use this code when you have a worksheet that contains a lot of formulas and you want to convert these formulas to values.
'This code will convert all formulas into values Sub ConvertToValues() With ActiveSheet.UsedRange .Value = .Value End With End Sub
This code automatically identifies cells are used and convert it into values.
Protect/Lock Cells with Formulas
You may want to lock cells with formulas when you have a lot of calculations and you don’t want to accidentally delete it or change it.
Here is the code that will lock all the cells that have formulas, while all the other cells are not locked.
'This macro code will lock all the cells with formulas Sub LockCellsWithFormulas() With ActiveSheet .Unprotect .Cells.Locked = False .Cells.SpecialCells(xlCellTypeFormulas).Locked = True .Protect AllowDeletingRows:=True End With End Sub
Related Tutorial: How to Lock Cells in Excel.
Protect All Worksheets in the Workbook
Use the below code to protect all the worksheets in a workbook at one go.
'This code will protect all sheets in the workbook Sub ProtectAllSheets() Dim ws As Worksheet For Each ws In Worksheets ws.Protect Next ws End Sub
This code will go through all the worksheets one by one and protect it.
In case you want to unprotect all the worksheets, use ws.Unprotect instead of ws.Protect in the code.
Insert A Row After Every Other Row in the Selection
Use this code when you want to insert a blank row after every row in the selected range.
'This code will insert a row after every row in the selection Sub InsertAlternateRows() Dim rng As Range Dim CountRow As Integer Dim i As Integer Set rng = Selection CountRow = rng.EntireRow.Count For i = 1 To CountRow ActiveCell.EntireRow.Insert ActiveCell.Offset(2, 0).Select Next i End Sub
Similarly, you can modify this code to insert a blank column after every column in the selected range.
Automatically Insert Date & Timestamp in the Adjacent Cell
A timestamp is something you use when you want to track activities.
For example, you may want to track activities such as when was a particular expense incurred, what time did the sale invoice was created, when was the data entry done in a cell, when was the report last updated, etc.
Use this code to insert a date and time stamp in the adjacent cell when an entry is made or the existing contents are edited.
'This code will insert a timestamp in the adjacent cell Private Sub Worksheet_Change(ByVal Target As Range) On Error GoTo Handler If Target.Column = 1 And Target.Value <> "" Then Application.EnableEvents = False Target.Offset(0, 1) = Format(Now(), "dd-mm-yyyy hh:mm:ss") Application.EnableEvents = True End If Handler: End Sub
Note that you need to insert this code in the worksheet code window (and not the in module code window as we have done in other Excel macro examples so far). To do this, in the VB Editor, double click on the sheet name on which you want this functionality. Then copy and paste this code in that sheet’s code window.
Also, this code is made to work when the data entry is done in Column A (note that the code has the line Target.Column = 1). You can change this accordingly.
Highlight Alternate Rows in the Selection
Highlighting alternate rows can increase the readability of your data tremendously. This can be useful when you need to take a print out and go through the data.
Here is a code that will instantly highlight alternate rows in the selection.
'This code would highlight alternate rows in the selection Sub HighlightAlternateRows() Dim Myrange As Range Dim Myrow As Range Set Myrange = Selection For Each Myrow In Myrange.Rows If Myrow.Row Mod 2 = 1 Then Myrow.Interior.Color = vbCyan End If Next Myrow End Sub
Note that I have specified the color as vbCyan in the code. You can specify other colors as well (such as vbRed, vbGreen, vbBlue).
Highlight Cells with Misspelled Words
Excel doesn’t have a spell check as it has in Word or PowerPoint. While you can run the spell check by hitting the F7 key, there is no visual cue when there is a spelling mistake.
Use this code to instantly highlight all the cells that have a spelling mistake in it.
'This code will highlight the cells that have misspelled words Sub HighlightMisspelledCells() Dim cl As Range For Each cl In ActiveSheet.UsedRange If Not Application.CheckSpelling(word:=cl.Text) Then cl.Interior.Color = vbRed End If Next cl End Sub
Note that the cells that are highlighted are those that have text that Excel considers as a spelling error. In many cases, it would also highlight names or brand terms that it doesn’t understand.
Refresh All Pivot Tables in the Workbook
If you have more than one Pivot Table in the workbook, you can use this code to refresh all these Pivot tables at once.
'This code will refresh all the Pivot Table in the Workbook Sub RefreshAllPivotTables() Dim PT As PivotTable For Each PT In ActiveSheet.PivotTables PT.RefreshTable Next PT End Sub
You can read more about refreshing Pivot Tables here.
Change the Letter Case of Selected Cells to Upper Case
While Excel has the formulas to change the letter case of the text, it makes you do that in another set of cells.
Use this code to instantly change the letter case of the text in the selected text.
'This code will change the Selection to Upper Case Sub ChangeCase() Dim Rng As Range For Each Rng In Selection.Cells If Rng.HasFormula = False Then Rng.Value = UCase(Rng.Value) End If Next Rng End Sub
Note that in this case, I have used UCase to make the text case Upper. You can use LCase for lower case.
Highlight All Cells With Comments
Use the below code to highlight all the cells that have comments in it.
'This code will highlight cells that have comments` Sub HighlightCellsWithComments() ActiveSheet.Cells.SpecialCells(xlCellTypeComments).Interior.Color = vbBlue End Sub
In this case, I have used vbBlue to give a blue color to the cells. You can change this to other colors if you want.
Highlight Blank Cells With VBA
While you can highlight blank cell with conditional formatting or using the Go to Special dialog box, if you have to do it quite often, it’s better to use a macro.
Once created, you can have this macro in the Quick Access Toolbar or save it in your personal macro workbook.
Here is the VBA macro code:
'This code will highlight all the blank cells in the dataset Sub HighlightBlankCells() Dim Dataset as Range Set Dataset = Selection Dataset.SpecialCells(xlCellTypeBlanks).Interior.Color = vbRed End Sub
In this code, I have specified the blank cells to be highlighted in the red color. You can choose other colors such as blue, yellow, cyan, etc.
How to Sort Data by Single Column
You can use the below code to sort data by the specified column.
Sub SortDataHeader()
Range("DataRange").Sort Key1:=Range("A1"), Order1:=xlAscending, Header:=xlYes
End Sub
Note that the I have created a named range with the name ‘DataRange’ and have used it instead of the cell references.
Also there are three key parameters that are used here:
- Key1 – This is the on which you want to sort the data set. In the above example code, the data will be sorted based on the values in column A.
- Order- Here you need to specify whether you want to sort the data in ascending or descending order.
- Header – Here you need to specify whether your data has headers or not.
Read more on how to sort data in Excel using VBA.
How to Sort Data by Multiple Columns
Suppose you have a dataset as shown below:
Below is the code that will sort the data based on multiple columns:
Sub SortMultipleColumns()
With ActiveSheet.Sort
.SortFields.Add Key:=Range("A1"), Order:=xlAscending
.SortFields.Add Key:=Range("B1"), Order:=xlAscending
.SetRange Range("A1:C13")
.Header = xlYes
.Apply
End With
End Sub
Note that here I have specified to first sort based on column A and then based on column B.
The output would be something as shown below:
How to Get Only the Numeric Part from a String in Excel
If you want to extract only the numeric part or only the text part from a string, you can create a custom function in VBA.
You can then use this VBA function in the worksheet (just like regular Excel functions) and it will extract only the numeric or text part from the string.
Something as shown below:
Below is the VBA code that will create a function to extract numeric part from a string:
'This VBA code will create a function to get the numeric part from a string Function GetNumeric(CellRef As String) Dim StringLength As Integer StringLength = Len(CellRef) For i = 1 To StringLength If IsNumeric(Mid(CellRef, i, 1)) Then Result = Result & Mid(CellRef, i, 1) Next i GetNumeric = Result End Function
You need place in code in a module, and then you can use the function =GetNumeric in the worksheet.
This function will take only one argument, which is the cell reference of the cell from which you want to get the numeric part.
Similarly, below is the function that will get you only the text part from a string in Excel:
'This VBA code will create a function to get the text part from a string Function GetText(CellRef As String) Dim StringLength As Integer StringLength = Len(CellRef) For i = 1 To StringLength If Not (IsNumeric(Mid(CellRef, i, 1))) Then Result = Result & Mid(CellRef, i, 1) Next i GetText = Result End Function
So these are some of the useful Excel macro codes that you can use in your day-to-day work to automate tasks and be a lot more productive.
Other Excel tutorials you may like:
- How to Delete Macros in Excel
- How to Enable Macros in Excel?
VBA Code Examples
AutoMacro: VBA Add-in with Hundreds of Ready-To-Use VBA Code Examples & much more!
Search the list below for free Excel VBA code examples complete with explanations.
Some include downloadable files as well. These Excel VBA Macros & Scripts are professionally developed and ready-to-use.
We hope you find this list useful!
Excel Macro Examples
Below you will find a list of basic macro examples for common Excel automation tasks.
Copy and Paste a Row from One Sheet to Another
This super simple macro will copy a row from one sheet to another.
Sub Paste_OneRow()
'Copy and Paste Row
Sheets("sheet1").Range("1:1").Copy Sheets("sheet2").Range("1:1")
Application.CutCopyMode = False
End SubSend Email
This useful macro will launch Outlook, draft an email, and attach the ActiveWorkbook.
Sub Send_Mail()
Dim OutApp As Object
Dim OutMail As Object
Set OutApp = CreateObject("Outlook.Application")
Set OutMail = OutApp.CreateItem(0)
With OutMail
.to = "test@test.com"
.Subject = "Test Email"
.Body = "Message Body"
.Attachments.Add ActiveWorkbook.FullName
.Display
End With
Set OutMail = Nothing
Set OutApp = Nothing
End SubList All Sheets in Workbook
This macro will list all sheets in a workbook.
Sub ListSheets()
Dim ws As Worksheet
Dim x As Integer
x = 1
ActiveSheet.Range("A:A").Clear
For Each ws In Worksheets
ActiveSheet.Cells(x, 1) = ws.Name
x = x + 1
Next ws
End SubUnhide All Worksheets
This macro will unhide all worksheets.
' Unhide All Worksheets
Sub UnhideAllWoksheets()
Dim ws As Worksheet
For Each ws In ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets
ws.Visible = xlSheetVisible
Next ws
End SubHide All Worksheets Except Active
This macro will hide all worksheets except the active worksheet.
' Hide All Sheets Except Active Sheet
Sub HideAllExceptActiveSheet()
Dim ws As Worksheet
For Each ws In ThisWorkbook.Worksheets
If ws.Name <> ActiveSheet.Name Then ws.Visible = xlSheetHidden
Next ws
End SubUnprotect All Worksheets
This macro example will unprotect all worksheets in a workbook.
' UnProtect All Worksheets
Sub UnProtectAllSheets()
Dim ws As Worksheet
For Each ws In Worksheets
ws.Unprotect "password"
Next ws
End SubProtect All Worksheets
This macro will protect all worksheets in a workbook.
' Protect All Worksheets
Sub ProtectAllSheets()
Dim ws As Worksheet
For Each ws In Worksheets
ws.protect "password"
Next ws
End SubDelete All Shapes
This macro will delete all shapes in a worksheet.
Sub DeleteAllShapes()
Dim GetShape As Shape
For Each GetShape In ActiveSheet.Shapes
GetShape.Delete
Next
End SubDelete All Blank Rows in Worksheet
This example macro will delete all blank rows in a worksheet.
Sub DeleteBlankRows()
Dim x As Long
With ActiveSheet
For x = .Cells.SpecialCells(xlCellTypeLastCell).Row To 1 Step -1
If WorksheetFunction.CountA(.Rows(x)) = 0 Then
ActiveSheet.Rows(x).Delete
End If
Next
End With
End SubHighlight Duplicate Values in Selection
Use this simple macro to highlight all duplicate values in a selection.
' Highlight Duplicate Values in Selection
Sub HighlightDuplicateValues()
Dim myRange As Range
Dim cell As Range
Set myRange = Selection
For Each cell In myRange
If WorksheetFunction.CountIf(myRange, cell.Value) > 1 Then
cell.Interior.ColorIndex = 36
End If
Next cell
End SubHighlight Negative Numbers
This macro automates the task of highlighting negative numbers.
' Highlight Negative Numbers
Sub HighlightNegativeNumbers()
Dim myRange As Range
Dim cell As Range
Set myRange = Selection
For Each cell In myRange
If cell.Value < 0 Then
cell.Interior.ColorIndex = 36
End If
Next cell
End SubHighlight Alternate Rows
This macro is useful to highlight alternate rows.
' Highlight Alternate Rows
Sub highlightAlternateRows()
Dim cell As Range
Dim myRange As Range
myRange = Selection
For Each cell In myRange.Rows
If cell.Row Mod 2 = 1 Then
cell.Interior.ColorIndex = 36
End If
Next cell
End SubHighlight Blank Cells in Selection
This basic macro highlights blank cells in a selection.
' Highlight all Blank Cells in Selection
Sub HighlightBlankCells()
Dim rng As Range
Set rng = Selection
rng.SpecialCells(xlCellTypeBlanks).Interior.Color = vbCyan
End SubExcel VBA Macros Examples – Free Download
We’ve created a free VBA (Macros) Code Examples add-in. The add-in contains over 100 ready-to-use macro examples, including the macro examples above!
Download Page
Excel Macro / VBA FAQs
How to write VBA code (Macros) in Excel?
To write VBA code in Excel open up the VBA Editor (ALT + F11). Type “Sub HelloWorld”, Press Enter, and you’ve created a Macro! OR Copy and paste one of the procedures listed on this page into the code window.
What is Excel VBA?
VBA is the programming language used to automate Excel.
How to use VBA to automate Excel?
You use VBA to automate Excel by creating Macros. Macros are blocks of code that complete certain tasks.
Practice VBA
You can practice VBA with our interactive VBA tutorial.