The System of Affixation in English refers to the process of attaching a group of letters to a word in order to change its meaning, number, state, or form.
There are two primary types of affixation: Prefixes and Suffixes
| Base word | Affixation | Word |
|---|---|---|
| determined | pre + determined | predetermined |
| play | play + er | player |
| weekly | bi + weekly | biweekly |
| follow | follow + ing | following |
Prefix
A prefix is a small group of letters that are affixed at the beginning of the word.
- Subsidiary
- Nonviolence
- Intolerance
Functions of Prefix
Indicate presence or absence
| amoral | without morals |
| injected | put into |
| congenital | present from birth |
Indicate position
| hypodermic | under the skin |
| circumnavigate | to sail around |
| antechamber | a chamber before another |
| Interstellar | between stars |
Indicate qualities, size, or number
| thermometer | heat measuring instrument |
| macrocosm | big world or universe |
| polyglot | someone who speaks many languages |
Indicates time, frequency, or order
| post dated | later than the stipulated date |
| redo | do again |
| primary | first |
Types of Prefixes
Negative Prefixes
| Prefix | Meaning | Usage |
|---|---|---|
| un- | not | uncomfortable, unbearable, unforgivable |
| in- | not | incomplete, indecisive, independent |
| dis- | opposite of | disinterested, disproportionate, displeasure |
| ir- | not | irresponsive, irresponsible, irrevocable |
| il- | not | illogical, illegitimate, illegible |
| im- | not | improbable, impossible, impenetrable |
| non- | not | nonviolent, nonchalant, non-invasive |
| mis- | wrong/wrongly | misinterpret, misunderstand, miscalculation |
| mis- | hate | misogynist, misogamist, misanthrope |
| mal- | bad/ badly | malfunction, malevolent, malediction, malnutrition |
| anti- | against | antinational, antibacterial, antibiotics |
| de- | down, reduce | descend, decry, deject, demote, decline |
| a- | without, not | asocial, amorphous, abiotic, atrophy |
| dis- | apart, off, away | disband, disturb, disburse, dismiss |
| dys- | bad | dystopia, dysfunctional, dyslexia |
Prefixes of Size
| Prefix | Meaning | Usage |
|---|---|---|
| semi- | half | semicircle, semiconductor, semi-active, semicolon |
| equi- | equal | equidistant, equivalent, equisonant |
| micro- | small, tiny | microscope, microorganism, microcosm, micromanage |
| macro- | big | macroeconomics, macrocosm, macrolevel |
| mega- | big | megalomaniac, megapolis, megapixel |
| mini- | small | minimum, minicomputer, miniature |
| maxi- | big | maximum, maximal, maxim |
| hemi- | half | hemisphere |
Prefixes of Position or Location
| Prefix | Meaning | Usage |
|---|---|---|
| inter- | between | interstellar, intermediate, interval, intervene |
| super- | over, above | superfluous, supersede, superintendent, supervisor |
| trans- | across | transfer, transport, transgress, transmit |
| ex- | out | exterior, external, extraneous, extract |
| in-/ im- | inside | internal, induce, imbibe, impregnate, influence |
| sub-, suc-, sus- | under | subterranean, susceptible, submit, submarine |
| sur- | over | surface, surfeit, surrender, survive, surcharge |
| circum- | around | circumspect, circumnavigate, circumscribe, circumvent |
| peri- | around | perimeter, periscope, perimortem |
| per- | through | percolate, pervade, perfect, perforated, perceive |
| infra- | below | infrared, infravision, infrarealism |
| ab- | away | abduct, abstain, abjure, abdicate |
| contra- | against | contravene, contradict, contralto, contrast |
| de- | down | descend, decline, demote, decrease |
| dia- | across | diagonal, diaphanous, diachronic, diagnosis |
| hyper- | over | hypertrophy, hyperactivity, hyperbole, hypertension |
| hypo- | under | hypothermia, hypothyroid |
| ob- | against | obloquy, obnoxious, object, obfuscate |
| pro- | for | prologue, provide, protect, project, procreate |
| syn-, sym- | together | synthesis, syndicate, sympathy |
| ultra- | beyond | ultraviolet, ultramodern, ultra-royalist, ultrasonic |
| under- | under | underground, underachiever, underestimate |
| meta- | beyond | metastasis, metabolize, metamorphic, metaphysics |
| mid- | between | midterm, middle, midday |
| by- | near | bypass, bygone, by-product |
| epi- | upon | epidermis, epilogue, epitaph |
| post- | back | postern, posterior |
Prefixes of time and sequence
| Prefix | Meaning | Usage |
|---|---|---|
| pre- | before | prevent, prepare, predict, premonition, prelude |
| ante- | before | antediluvian, antebellum |
| prime- | first | primary, primordial, prima donna, primate, primeval |
| post- | after | posterity, posthumous, postlude, post-marital |
| retro- | before | retrogression, retroflex, retrospect |
| pro- | before | progenitor, proceed, prologue, prophecy, prophylactic |
| re- | again | recur, recount, rethink |
| fore- | before | foretell, forestall, foresight |
| after- | after | after-effects, afterthought |
| chron- | time | chronology, chronicle |
Prefixes of numbers and amount
| Prefix | Meaning | Usage |
|---|---|---|
| mono- | one | monotheism, monologue, monochromatic, monarch |
| uni- | one | universe, unitary, union, unanimous, unity |
| bi- | two | bicentennial, biannual, bicycle, bigamous, bipolar |
| du-, di- | two | duo, dual, dicotyledon, dichromatic |
| tri- | three | trident, tricolor, triumvirate, trifecta, trilogy, tripod |
| quad- | four | quadruple, quadruplets, quadrilateral |
| tetra- | four | tetrapods, tetrameter |
| penta- | five | pentagram, pentacle, pentagon |
| quint- | five | quintuplets, quintal |
| hex- | six | hexagon, hexadecimal, hexameter |
| sex- | six | sextuplets, sextet |
| sept- | seven | septuagenarian, septuplets |
| hept- | seven | heptagonal, heptathlon |
| octa- | eight | octagon, October, octopus, octuplets |
| nov- | nine | novena, November |
| dec- | ten | decade, decimal, decathlon |
| hendeca- | eleven | hendecacolic, hendecagonal |
| dodeca- | twelve | dodecahedron, dodecaphony |
| triskaideka- | thirteen | triskaidekaphobia |
| cent- | hundred | century, century, centipede |
| hector- | thousand | hector, hectogram |
| kilo- | thousand | kilogram |
| mega- | million | megaton, megahertz |
| giga- | billion | gigabyte |
| multi- | many | multimillionaire, multipurpose |
| poly- | many | polynomial, polygon, polymath |
Miscellaneous Prefixes
| Prefix | Meaning | Usage |
|---|---|---|
| alb- | white | albino, albinism |
| ambi- | both | ambidextrous, ambivalent, ambiguous |
| amphi- | both | amphibian, amphitheatre |
| bio- | life | biology, biohazard, biosphere |
| auto- | self | automated, autonomous, autocrat |
| co-, com-, con- | together, joint | co-dependent, companion, congregation |
| en-, em- | make, become | engender, empower, endanger |
| eu- | good | euthanasia, eulogy, euphemism |
| cario- | heart | cardiovascular, cardiogram |
| hydr- | water | hydrogen, hydraulic, hydrophobia |
| ig- | bad | ignominy, ignoble, ignorant |
| bene- | good | benevolent, benediction, benign |
| bon- | good | bon voyage, bonhomie, bonafide |
| homo- | same | homonym, homophone, homeopathy |
| pan- | all | panacea, pan Asiatic, panorama |
| pseudo- | fake | pseudonym |
| neo-, nov- | new | neologism, novelty |
| amo-, ami | love | amorous, amicable, amiable |
| aqua- | water | aqueduct, aquatic |
Suffix
A suffix is a group of letters that are fixed to the end of a root word or a base word.
Functions of Suffix
Change the part of speech of the word
| meaning (n) | meaningful (adj) |
| beautiful (adj) | beautifully (adv) |
| subject (n) | subjecting (v) |
Indicate whether the number is singular or plural
| girl (singular noun) | girls (plural noun) |
| stratum (singular noun ) | strata (plural noun) |
| lifts (singular verb) | lift (plural verb) |
Indicate the tense of the verb
| hopped (past) | hopping (continuous) |
| steal (past) | stolen (past participle) |
Indicate the gender of a noun
| host (masculine) | hostess (feminine) |
| steward (masculine) | stewardess (feminine) |
| executor (masculine) | executrix (feminine) |
Types of Suffixes
Noun Suffixes
| Suffix | Usage | Example |
|---|---|---|
| -al | state | refusal, betrayal, perusal |
| -ance, -ence, -ancy, -ency | quality or state | militancy, performance |
| -tion | condition | condition, relation |
| -ice | condition | malice, novice, justice |
| -er/-or | doer | painter, trainer, actor |
| -graph | record | telegraph, phonograph, polygraph |
| -ism | belief | Hinduism, communism, fascism |
| -ist | doer | pacifist, pianist, altruist |
| -ian | someone who does | Gandhian, guardian, politician |
| -ing | name of an activity | reading, gardening, sleeping |
| -ity | state | continuity, annuity |
| -logy | the study | geology, neurology |
| -ship | state of | friendship, kinship, sportsmanship |
| -sion, -tion | the process of | expansion, determination, connection |
| -ory | place | dormitory, reformatory, laboratory |
| -orium, -arium | place | sanitarium, aquarium, crematorium |
| -mania | madness | monomania, bibliomania, egomani |
| -phobia | fear | hydrophobia, cynophobia, mysophobia |
| -ure | state | composure, exposure, leisure |
| -ment | state | abandonment, refinement, entertainment |
| -ness | state | happiness, completeness, fullness |
Suffixes of Verbs
| Suffix | Usage | Example |
|---|---|---|
| -able | to make | enable, disable |
| -ate | Latin origin verbs | recreate, abate, mediate |
| -ed | simple past or participle form | killed, toyed, booked |
| -en | verbs formed from adjectives | broken, frozen, sunken |
| -er | actions that have a repetitive quality | blabber, snicker, mutter |
| -fy | do | magnify, specify, rectify |
| -ing | action in continuation | hearing, yearning, making |
| -ise | to make/do | revolutionise, apologise, despise |
| -ish | become or do | flourish, banish, demolish |
| -nt | to do | prevent, augment, content |
| -s, -es | simple present tense form | criticises, runs, laughs |
Suffixes of Adjectives
| Suffix | Meaning | Usage |
|---|---|---|
| -able, -ible | having the quality of | flexible, available, eatable |
| -al | related to | ventral, global, musical |
| -ant | doing | dependent, buoyant, resilient |
| -ic | having the quality | terrific, generic, specific |
| -esque | like, having the quality | statuesque, picturesque |
| -er, -est | comparative and superlative qualities | fatter, tallest |
| -ose | full of | verbose, grandiose |
| -ful | full of | beautiful, boastful, grateful |
| -ing | participle form of an adjective | interesting, frustrating, sleeping |
| -istic | having the quality | realistic, artistic, surrealistic |
| -ive | having the nature of | pensive, aggressive, massive |
| -ous, -ious | full of | gaseous, spacious, gracious |
Suffixes of Adverbs
| Suffix | Meaning | Usage |
|---|---|---|
| -ably | with a quality | comfortably, admirably, disagreeably |
| -ibly | with a quality | audibly, horribly, negligibly |
| -s | shows time or place | backwards, always, forwards |
| -wise | shows manner or position | clockwise, otherwise, lengthwise |
Root Words and Base Words
The root word and the base words are the parts that contain the primary meaning of the word. Prefixes and suffixes are added to root and base words to create new words and ideas.
Root Word
- A root word cannot stand on its own as an independent word.
- It needs the addition of the prefix or the suffix for the completion of its meaning.
- For example, let us consider the words amphibian, regeneration and subtraction.
amphi- -bi- -an
prefix root suffix
re- -generat- -ion
prefix root suffix
sub- -tract- -ion
prefix root suffix
- In the above cases, the roots -bi-, -generat- and -tract- cannot stand alone as individual words.
- They are therefore known as root words.
Base Word
- A base word, unlike a root word, can stand on its own like an independent word.
- It does not need the addition of a prefix or suffix in order to function as a stand-alone word.
- For example, let us consider the words redone, nonviolent and unmoved.
re- done
prefix base word
non- violent
prefix base word
un- moved
prefix base word
In the above examples, done, violent, and moved can function as independent words.
You Asked, We Listened – List of All Grammar Chapters Updated 😍😍
Also, Read
Figures of Speech
Subject Verb Agreement
Degrees of Comparison
Time and Tense
Словообразование в английском языке: значения приставок и суффиксов
Словообразование (word formation) – это образование новых слов при помощи приставок, суффиксов, сложения основ и других способов. Если вы знаете, как устроено словообразование в английском языке, понимаете значение основных приставок и суффиксов, вам будет куда проще пополнять словарный запас, читать, понимать английскую речь, потому что значение огромного количества слов вы будете угадывать без словаря.
Кстати, если вам любопытно узнать, какой у вас словарный запас, рекомендую прочитать эту статью: “Как узнать, какой у вас словарный запас?” Из нее вы узнаете простые и интересные способы определения словарного запаса.
Есть несколько способов словообразования, наиболее важное практическое значение имеет образование слов с помощью суффиксов и приставок. На нем мы остановимся подробнее, остальные способы рассмотрим обзорно.
Содержание:
Пройдите тест на уровень английского:
Зачем нужно знать словообразование?
Главная польза в том, что знание значений приставок и суффиксов значительно увеличивает количество слов, которые вы узнаете при чтении и слушании (особенно при чтении). Иначе говоря, увеличивается пассивный словарный запас.
Возьмем, к примеру, глагол to use – использовать. С помощью суффиксов из него образуются:
- Прилагательное useful – полезный. Прилагательное useless – бесполезный. Существительное usage – использование.
Понимая значение суффиксов -ful, -less, -age, вы без труда поймете все три образованные от to use слова, даже если не знали их значение.
- -ful и -less указывают на наличие или отсутствие качества: от слова care (забота, ) careful – осторожный, careless – беззаботный. -age образует существительные от глаголов: leak (протекать) – leakage (утечка), pass (проходить) – passage (проход).
А почему пассивный словарный запас, почему не активный? Префиксы и суффиксы – это хорошие смысловые подсказки, но английская лексика так устроена (как и русская), что не к любому слову можно приделать любой аффикс.
Яркий пример – приставки in- и un-, имеющие значение отрицания: able – способный, unable – неспособный, stable – стабильный, instable – нестабильный. Приставки совершенно совпадают по смыслу, но вот когда какую нужно “приставлять” – это нужно запомнить. При чтении вы легко поймете смысл слов с inun-, но в речи можете и ошибиться.
Впрочем, это не так уж страшно. Уверен, что вас поймут, если вы скажете inable и unstable, перепутав приставки. Говоря по-русски, мы еще и не такие ошибки совершаем!
Как изучать словообразование в английском языке
Приставки и суффиксы (вместе их называют “аффиксы”) – это не тот случай, когда нужно садиться за учебники, зубрить правила, выполнять упражнения одно за другим. Вполне достаточно просто ознакомиться со значением основных приставок и суффиксов, посмотреть примеры.
В этом вам помогут таблицы и интеллект-карты (изображения-конспекты) ниже. В таблицах раскрывается значение приставок и суффиксов (насколько это возможно), примеры слов, а интеллект-карты – это своего рода конспект, шпаргалка, сделанная на основе таблиц.
Просмотрев материалы, вы заметите, что многие аффиксы похожи на русские и даже имеют схожее значение. Ничего удивительного, ведь они пришли в английский, русский и другие языки из латинского и греческого, особенно это касается аффиксов с научным оттенком: deactivate – деактивировать, antivirus – антивирус, counterbalance – противовес, idealism – идеализм. Благодаря этим сохранившимся связям между языками, слоовообразование в английском языке дается без особых проблем.
Как и в случае со словарным запасом и грамматикой, основательно, надежно знания закрепляются только с практикой в чтении, слушании, письме, речи. Подробнее о всех сторонах изучения языка читайте в главе “Формула языка” моей книги “Как выучить английский язык”.
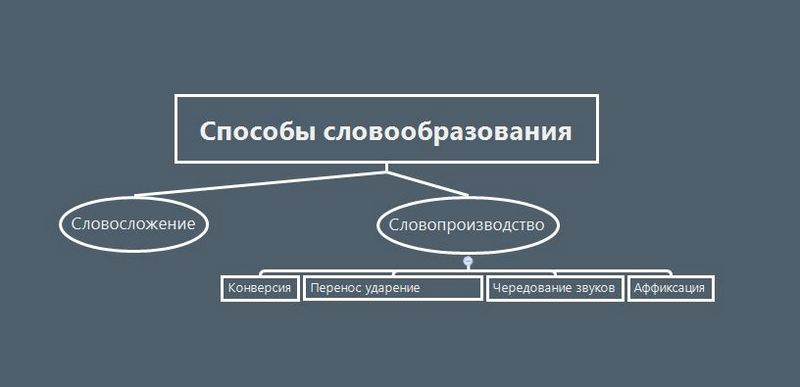
Способы словообразования в английском языке
Есть разные подходы к классификации способов словообразования, в русскоязычной литературе обычно выделяют два главных способа: словосложение и словопроизводство.
Словопроизводство, в свою очередь, бывает четырех видов: конверсия, изменение места ударение, чередование звуков и аффиксация (приставки и суффиксы).
Словосложение
Словосложение – это объединение в одно слово двух слов или основ. Получившиеся слова пишутся слитно или через дефис. В русском языке тоже есть такой способ и, кстати, само слово “словосложение” образовано словосложением.
- Глаголы: to blackmail (шантажировать), to broadcast (передавать по радио). Существительные: girlfriend (подруга), handbook (справочник), newspaper (газета). Прилагательные: dark-blue (темно-синий), kind-hearted (добросердечный). Наречия: nowhere (нигде), everywhere (везде). Местоимения: somebody (кто-нибудь), everyone (все).
Словопроизводство
Словопроизводство – это образование одного слова от других. Оно может происходить четырьмя способами:
- Конверсия.
- Изменение места ударения.
- Чередование звуков.
- Аффиксация.
Конверсия
Конверсия – это переход слова из одной части речи в другую без изменения написания и звучания. Выходит, что слово формально остается неизменным, но:
- оно превращается в другую часть речи, меняется его значение.
Конверсия – способ словообразования, характерный для английского языка, благодаря ему в английском множество слов, которые внешне и по звучанию не отличаются, но имеют значения разных частей речи.
К примеру, могут совпадать существительные и глаголы:
| Существительное | Глагол |
|---|---|
| answer (ответ) | to answer (отвечать) |
| hand (рука) | to hand (вручать) |
| place (место) | to place (помещать) |
| work (работа) | to work (работать) |
Или прилагательные и глаголы:
| Прилагательное | Глагол |
|---|---|
| clean (чистый) | to clean (чистить) |
| empty (пустой) | to empty (опустошать) |
| free (свободный) | to free (освобождать) |
Изменение места ударения
В этом случает существительные совпадают по форме с глаголами, но у них другое ударение. Обычно у глагола ударение падает на второй слог, а у существительного на первый.
| Существительное | Глагол |
|---|---|
| conflict (конфликт) | to conflict (конфликтовать) |
| export (экспорт) | to export (экспортировать) |
| record (запись) | to record (записывать) |
| suspect (подозреваемый) | to suspect (подозревать) |
Чередование звуков
В этом случае глаголы и существительные, образованные от одного корня, различаются чередованием последнего согласного звука. Обычно в глаголе он звонкий, а в существительном глухой.
| Существительное | Глагол |
|---|---|
| advice [əd’vaɪs] – совет | to advise [əd’vaɪz] – советовать |
| belief [bɪ’li:f] – вера | to believe [bɪ’li:v] – верить |
Аффиксация
Очень часто слова образуются с помощью присоединение приставок и суффиксов (вместе их называют аффиксами).
- Приставки (префиксы) изменяют значение слов, но само слово при этом не переходит в другую часть речи. Зная наиболее употребительные приставки, вы сможете угадывать значение образованных с их помощью слов, если, разумеется, знаете исходное слово. Суффиксы служат для образования одной части речи из другой. Зная какие суффиксы для какой речи характерны, вы будете легко понимать, какая перед вами часть речи, соответственно это облегчит понимание слова.
Приставки в английском языке
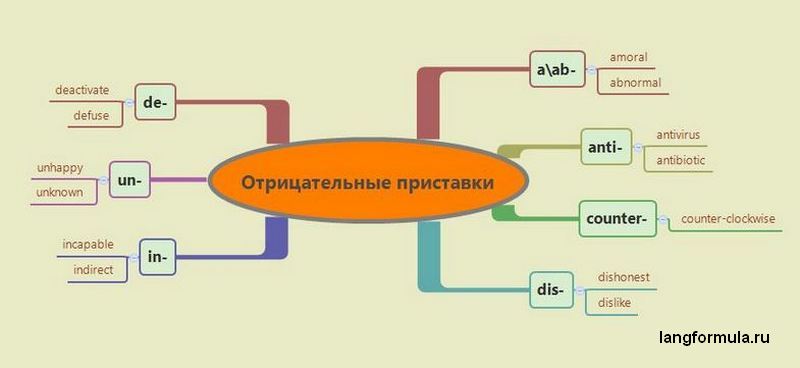
Приставки можно разделить на две группы: отрицательные и все остальные.
Наиболее употребительные отрицательные приставки: un-, in-, dis-. Нет никаких правил, регулирующих какая из этих приставок используется для придания слову отрицательного значения.
Однако, если говорить о пассивном словарном запасе, о понимании текста или речи, то это не так важно: если у слова есть одна из отрицательных приставок, значит его значение изменено на отрицательное или противоположное. В таблицах ниже приведены примеры слов с этими приставками.
Приставка un-
| comfortable – удобный | uncomfortable – неудобный |
| equal – равный | unequal – неравный |
| expected – ожидаемый | unexpected – неожиданный |
| happy – счастливый | unhappy – несчастный |
| important – важный | unimportant – неважный |
| known – известный | unknown – неизвестный |
| limited – ограниченный | unlimited – неограниченный |
| pleasant – приятный | unpleasant – неприятный |
Также un- присоединяется к глаголам, чтобы выразить противоположное действие.
| to dress – одеваться | to undress – раздеваться |
| to lock – запирать | to unlock – отпирать |
| to pack – упаковывать | to unpack – распаковывать |
Приставка in-
Нет правил, регулирующих, когда используется un-, а когда in-, хотя по смыслу эти приставки не отличаются. Важная разница в том, что in- НЕ используется в глаголах.
Примеры:
| ability – способность | inability – неспособность |
| adequate – достаточный | inadequate – недостаточный |
| capable – способный | incapable – неспособный |
| comparable – сравнимый | incomparable – несравнимый |
| complete – полный | incomplete – неполный |
| direct – прямой | indirect – непрямой |
| experienced – опытный | inexperienced – неопытный |
Приставка in– видоизменяется в некоторых случаях:
- перед l превращается в il- перед r превращается в ir- перед m и p превращается в im-
| legal – законный | illegal – незаконный |
| logical – логичный | illogical – нелогичный |
| regular – регулярный | irregular – нерегулярный |
| responsible – ответственный | irresponsible – безответственный |
| patient – терпеливый | impatient – нетерпеливый |
| possible – возможный | impossible – невозможный |
Приставка dis-
Dis- может выражать отрицание или противоположное действие.
| honest – честный | dishonest – бесчестный |
| to approve – одобрять | disapprove – не одобрять |
| to like – любить (I like – мне нравится) | to dislike – не любить (I dislike – мне не нравится) |
| to appear – появляться | to disappear – исчезать |
| to arm – вооружать | to disarm – разоружать |
| to connect – соединять | to disconnect – разъединять |
Другие отрицательные приставки
Среди прочих отрицательных приставок много международных, латинского и греческого происхождения, встречающихся и в русском языке.
- aab– (без-, не-, а-): abnormal – ненормальный, amoral – аморальный. anti- (анти-, противо-): antivirus – антивирус, antibiotic – антибиотик. counter- (контр-, противо-): counterstrike – контрудар, counter-clockwise – против часовой стрелки. de- (лишать, удалять): decode – раскодировать, deformation – расформирование. non- (отрицание, отсутствие): non-stop – безостановочный, non-alcoholic – безалкогольный.
Приставки с разными значениями
to overestimate – переоценивать
To underestimate – недооценивать
to overpay – переплатить
to underpay – недоплатить
post-revolutionary – послереволюционный
post-war – послевоенный
| Приставка re- (снова, заново, вновь) | |
|---|---|
| to appear – появиться | to reappear – снова появиться |
| to construct – построить | to reconstruct – перестроить |
| to read – прочитать | to reread – перечитать |
| to sell – продать | to resell – перепродать |
| Приставка mis- (неправильно, неверно) | |
| to hear – услышать | to mishear – ослышаться, неправильно услышать |
| to lead – вести | to mislead – ввести в заблуждение |
| to quote – цитировать | to misquote – неправильно цитировать |
| to understand – понимать | to misunderstand – неправильно понимать |
| Приставки over- (сверх, чрезмерно) и under- (недо-, недостаточно) | |
| to estimate – оценивать | |
| to pay – платить | |
| Приставки pre- (перед, ранее) и post- (пост-, после), часто пишутся через дефис | |
| revolutionary – революционный | |
| war – война | |
| Приставка co- (сотрудничество, общность действия), часто пишется через дефис | |
| author – автор | co-author – соавтор |
| existence – существование | co-existence – сосуществование |
| operation – операция | co-operation – кооперация, содействие |
| Приставка inter- (между, среди, взаимно) | |
| national – национальный | international – международный |
| action – действие | interaction – взаимодействие |
| town – город | intertown – междугородний |
| Приставка ex- (экс-, бывший), пишется через дефис | |
| husband – муж | ex-husband – бывший муж |
| president – президент | ex-president – экс-президент |
| Приставка sub- (суб-, под-) | |
| marine – морской | submarine – подводный |
| section – секция | subsection – подсекция |
| Приставка ultra- (ультра-, сверх-), пишется через дефис | |
| microscopic – микроскопический | ultramicroscopic – ультрамикроскопический |
| violet – фиолетовый | ultra-violet – ультрафиолетовый |
| Приставка en- (делать что-то) | |
| circle – круг | encircle – окружать (делать круг) |
| large – большой | enlarge – увеличивать (делать больше) |
| slave – раб | enslave – порабощать (делать рабом) |
Примечания:
- В современном английском языке есть слова с неотделяемыми приставками, в них входят приставки, перечисленные в таблице выше, но, отделив их, мы не получим самостоятельного слова. Например: re duce (сокращать), dis cuss (обсуждать), pre pare (готовить). На самом деле эти приставки – уже и не приставки вовсе. Когда-то давно они приросли к корням слов, ныне уже неупотребительным и видоизмененным, и постепенно сами вошли в состав корня слова. К примеру, в слове prepare (готовить) pre – это уже не приставка, а часть корня слова. В разговорной речи в ходу слово “ex” – оно в точности соответствует нашему “бывший, бывшая” и имеет значение “бывший мужпарень, бывшая женадевушка”: My ex texted me – Мой бывший написал мне СМС.
Суффиксы в английском языке
Суффиксы являются индикаторами частей речи в английском языке, соответственно их можно разделить на три группы: суффиксы существительных, прилагательных и глаголов. О наречиях рассказаывать особо нечего, в большинстве случаев они образуются с помощью только одного суффикса -ly (quick – quickly), о них есть небольшое примечание в конце статьи .
Суффиксы существительных
С помощью суффиксов образуются существительные, обозначающие лица, и отвлеченные существительные, обозначающие широкие или обобщенные понятия.
Словообразование в английском языке
О чем эта статья:
Словообразование английских слов — процесс невероятно увлекательный и чем-то похожий на сборку пазла. В английском языке есть два способа словообразования: словосложение и словопроизводство.
Словопроизводство включает аффиксы (то есть приставки и суффиксы), конверсию, чередование звуков и ударений, а также аббревиатуры и сокращения слов. Словосложение — это когда мы объединяем несколько слов в одно. А теперь чуть подробнее.
Словосложение
Начнем с самого простого и знакомого нам способа словообразования английский слов — словосложения. Даже само слово «словосложение» образовано с помощью словосложения. По-простому, это объединение основ или корней двух слов для того, чтобы получить новое слово.
В русском языке примером может служить множество слов разных частей речи: водоотталкивающий, паровоз, самовар.
В английском языке чаще всего таким способом образуются имена существительные (postman – почтальон), и в меньшей степени глаголы (oven-bake – готовить в духовке), прилагательные (heartbreaking – душераздирающий), наречия (nevertheless – тем не менее) и местоимения (someone – кто-то).
Словопроизводство
Словопроизводство включает в себя три категории:
- Аффиксы (сюда входят приставки и суффиксы)
- Конверсия
- Чередование звуков и ударения
Давайте разберем правила словообразования в английском языке для каждой из этих категорий.
Приставки, как способ словообразования в английском
Prefix, то есть приставка или префикс — это часть слова, которая стоит перед корнем. Приставки чаще всего используют для изменения значения слова и реже — для изменения части речи. Мы выделяем большую группу приставок, функцией которых является изменять значение слова на противоположное:
Un-
Выполнить противоположное действие
Im-, in-, il -,ir-
Эквивалент русской приставки не
Dis-
Выполнить противоположное действие
Mis
Неправильно что-то сделать
С ошибкой в слове
При использовании приставок im-, in-, il -,ir- вам необходимо выбрать, какая из них подходит к слову, которое вы хотите изменить.
Im— стоит только перед согласными b, p, m
Il— стоит только перед буквой l
Ir— стоит только перед r
Во всех остальных случаях выбирайте приставку in-.
Приставки с другим приставочным значением: существительные
Anti-
Auto-
Mid-
Post-
После какого-то события
Super-
Приставки с другим приставочным значением: глаголы
De-
Изменить на противоположное
Over-
Under-
Сделать что-то не до конца
Re-
En-, em-
Воплощать качества или состояния
Запомните, что приставка em- пишется перед звуками [b], [p], [m]. В остальных случаях — пишите en-.
Приставки с другим приставочным значением: прилагательные
Extra-
За пределами чего-то
Inter-
Суффиксы, как способ словообразования в английском
Suffix стоит после корня перед окончанием — по нему просто определить, к какой части речи принадлежит слово. Давайте посмотрим, как это происходит.
Подключайтесь к нашим онлайн урокам по английскому языку, для учеников 10-18 лет!
Словообразование существительных в английском языке с помощью суффикса
Суффиксы существительных можно разделить на две группы: суффиксы субъекта деятельности и суффиксы абстрактных существительных.
Субъект деятельности
-er/-or
Описывают роль занятий человека
-an, -ian
Указывает в названии профессии или страны происхождения
-ist
Указывает на принадлежность к соц. течению
-ant, -ent
Помогают образовать существительное от глагола
-ee
Помогают образовывать отглагольные существительные
-ess
Суффикс существительных женского рода
Абстрактные существительные
-ity
-ance, -ence, -ancy, -ency
Находиться в каком-то состоянии
-ion, -tion, -sion
-ism
-hood
-ure
Образует существительные от глаголов
-dom
-ment
Обозначает результат действия
-ness
-ship
Образует существительные от других существительных
Словообразование прилагательных в английском языке с помощью суффикса
-able/-ible
Указывает на возможность использования
-ful
Указывает на обладание каким-то качеством
-en
Указывает на качество или материал предмета
-ive
Обозначает наличие какого-либо качества
-less
Отрицает наличие чего-то
-ous
Владеющий чем-то, полный чего-то
-y
Используется для описания состояния чего-либо
Как образуются глаголы
-ate
-ify, -fy
-ise (в британском английском)
-ize (в американском английском)
-en
Как образуются наречия
-ly
Эквивалент русского окончания «о» у наречий
-wise
Для передачи движения, позиции, направления
Против часовой стрелки
По часовой стрелке
-ward(s)
По направлению к дому
Суффиксы: таблица словообразования по частям речи
После такого количества информации нужно закрепить выученное удобной табличкой. Пользуйтесь в удовольствие — сохраните на телефон в папку «английский» или распечатайте и храните в учебнике.
Объединение суффиксов и приставок: преобразование слов в английском языке
Замечательная характеристика словообразования — в том, что от одного корня и основы можно составить целую группу слов. Нанизывая приставки и суффиксы на основы мы можем получить различные формы слов в английском языке. Давайте посмотрим как свершается такая трансформация:
- Agree => disagree => disagreeable / disagreement. Соглашаться => не соглашаться => несогласный / несогласие.
- Laugh => laughter => laughable. Смеяться => смех => смехотворный.
- Body => embody => embodiment. Тело => воплощать => воплощение.
Конверсия: новые слова без внешних изменений
А теперь давайте рассмотрим конверсию — способ словообразования, при котором слова из одной части речи переходят в другую. Слова меняют свое значение, не меняя написания и звучания.
Существительное email появилось в английском задолго до глагола. Еще десятилетие назад единственным возможным вариантом было сказать: send an email (отправить имейл. Здесь email — существительное), в то время как сейчас мы можем просто email people («имейлить» людям. Здесь email является глаголом).
Наиболее продуктивной, то есть часто используемой, является конверсия существительных в глаголы:
- access – to access – доступ – получить доступ
- bottle – to bottle – бутылка – закупоривать в бутылку
- eye – to eye – глаз – внимательно рассматривать
- fiddle – to fiddle – скрипка – возиться
- fool – to fool – дурак – одурачить
- Google – to google – Гугл – гуглить
- host – to host – хозяин – принимать (гостей)
- knife – to knife – нож – ударить ножом
- microwave – to microwave – микроволновка – подогревать в микроволновке
- name – to name – имя – называть
- pocket – to pocket – карман – прикарманить
- salt – to salt – соль – солить
- shape – to shape – форма – придавать форму
- ship – to ship – корабль – отправлять по почте
- spear – to spear – копье – проткнуть копьем
- torch – to torch – факел– поджигать
Рассмотрим на примерах, как преобразовывать слова с помощью конверсии:
- She microwaved (глагол) her lunch. – Она «промикроволновила» свой ланч.
- She heated her lunch in the microwave (существительное). – Она подогрела свой ланч в микроволновке.
- The doctor eyed (глагол) my swollen eye (существительное). – Доктор внимательно осмотрел мой опухший глаз.
Менее продуктивной является обратная конверсия глаголов с существительные:
- to alert – alert – оповещать – тревога, оповещение
- to attack – attack – атаковать – атака
- to call – call – звонить – звонок
- to clone – clone – клонировать – клон
- to command – command – командовать – команда
- to cover – cover – укрывать – укрытие
- to cry – cry – плакать – плач
- to experience – experience – испытывать – опыт
Вот парочка примеров:
- The guard alerted (глагол) the general to the attack (существительное). – Караульный известил генерала об атаке.
- The enemy attacked (глагол) before an alert (существительное) could be sounded. – Враг атаковал до того, как прозвучала тревога.
- Sometimes one just needs a good cry (существительное). – Иногда просто стоит хорошо проплакаться.
- The baby cried (глагол) all night. – Малыш плакал всю ночь.
Другие части речи, такие как прилагательные, союзы и даже предлоги с междометиями тоже могут попадать под конверсию. Давайте посмотрим на примеры ниже.
Прилагательное в глагол
- green → to green (to make environmentally friendly) – зеленый → озеленять (в значении делать экологически благоприятным).
Предлог в существительное
- up, down → the ups and downs of life – вверх, вниз → взлеты и падения жизни.
Союз в существительное
- if, and, but → no ifs, ands, or buts – если, и, но → никаких если, и, но.
Междометие в существительное
- ho ho ho → I love the ho ho ho’s of Christmas time. – хо хо хо → Я люблю все эти хо хо хо в рождественское время.
Изменение места ударения
Образование слов в английском языке может происходить очень интересными способами. Сейчас мы вам расскажем историю о том, как одно ударение может изменить мир. Точнее, часть речи и значение слова. Вы наверняка слышали об одном таком примере, слово адрес – address. Поставив ударение на первом слоге AD-ress, вы получите существительное:
- Give me your postal AD-ress. – Дай мне свой почтовый адрес.
А если поставить ударение на втором слоге ad-RESS, у нас получается глагол в значении адресовать свои слова кому-то:
- Don’t you dare ad-RESS me this way! – Не смей ко мне так обращаться!
Вот еще парочка примеров:
Content – сущ. содержание/прил. умиротворенный
- The CON-tent of your essay is fine, but you need to rearrange the structure. – Содержание твоего эссе неплохое, но тебе надо переделать его структуру.
- She was reading a book, looking very con-TENT. – Читая книгу, она выглядела очень умиротворенно.
Desert – гл.дезертировать/сущ.пустыня
- I wouldn’t advise you to des-ERT the army, as it will get you into trouble. – Я бы не советовал тебе дезертировать из армии, так как это принесет проблемы.
- The army marched through the DES-ert. – Армия промаршировала через пустыню.
Лайфхак. Обычно у глагола ударение падает на второй слог, а у существительного — на первый. Зная это, вы никогда не перепутаете слова, которые выглядит один в один, а означают совсем разные вещи, как, например, OB-ject – объект и ob-JECT – возражать.
Чередование звуков
To advise (советовать) – advice (совет)
To believe (верить) – belief (вера)
Это примеры словообразования в английском языке, когда чередование последнего согласного звука меняет часть речи слова. Из глагола «советовать», мы получаем существительное «совет», и из глагола «верить», существительное «вера».
Заметьте, что в глаголе последний согласный звук звонкий (to advise – [адвайз]), а в существительном – глухой (advice – [адвайс]).
Аббревиатуры и сокращения слов
Знаете ли вы, что слово лазер является аббревиатурой? Да-да, это сложно себе представить, но такое уже бытовое слово LASER расшифровывается как light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation — «усиление света посредством вынужденного излучения».
Часто аббревиатуры можно встретить в интернет переписках и в различных мессенджерах. Ими заменяют часто используемые выражения, которые слишком долго писать целыми словами.
Друг поделился записью эфира его любимого комика, а вы ему отвечаете: LOL – laughing out loud («смеюсь вслух»). Или, вам срочно необходимо отлучиться, и из вежливости вы пишите собеседнику: BRB – be right back «(скоро вернусь»). Или вас спросили, что вы будете делать завтра вечером, а у вас еще нет планов и вы отвечаете: IDK – I don’t know («я не знаю»).
Кстати, англоговорящие жители этой планеты просто обожают сокращать слова. Особенно этим отличаются жители Англии, Австралии и Новой Зеландии. Для них, овощи — это vegos (вместо vegetables), кареты скорой помощи – ambos (вместо ambulances), возможно — probs (а не probably), а собака не dog, а милое doggo🐶
А вот еще парочка слов и их сокращений, которые используют по всему англоязычному миру:
Сello – violoncello (виолончель)
Flu – influenza (инфлюэнца)
Ad – advertisement (рекламное объявление)
Rhino – rhinoceros (носорог)
Telly – television (телевидение)
Bike – bicycle (велосипед)
Используйте их в речи и в переписке — и вы точно покажете себя как pro (сокращение от professional – «профессионал») в english!
Образование существительных в английском языке: суффиксы, приставки и др.
Приставки и суффиксы имен существительных в английском языке
Чтобы правильно выполнить задания 26 — 31 из раздела «Грамматика и лексика» на ЕГЭ по английскому языку, Вам необходимо знать наиболее употребляемые приставки и суффиксы имен существительных.
Хочу сразу сказать, статья будет длинной, поэтому наберитесь терпения и дочитайте её до конца.
Полезный совет:
Обязательно выучите все слова из этой статьи, так как они подобраны из реальных заданий прошлых лет, которые были предложены к выполнению на ЕГЭ по английскому языку.
Работайте отдельно с каждым блоком, прописывая слова, даже если они вам кажутся хорошо знакомыми.
Помните, что в заданиях 26 — 31 наряду с вашими умениями образовывать новые слова при помощи различных аффиксов, оцениваются ваши орфографические навыки!
1) Суффикс – er
Модель образования: Verb + er = Noun
При присоединении суффикса – er к глаголу или существительному, образуется имя существительное, обозначающее профессию, род занятий человека, а также названия некоторых предметов:
To write — writer, to sing — singer, to drive — driver, to teach — teacher, to examine — examiner, to learn — learner, to build — builder, to loaf (лодырничать) — loafer (лодырь)
Trumpet — trumpeter (трубач), bank — banker (банкир), finance — financier (финансист)
To contain — container (контейнер), to dust — duster (тряпка для вытирания пыли), to grate — grater (терка), to mix — mixer (миксер), to shake — shaker (шейкер), to blend — blender (блендер), to open — opener (консервный нож)
Mince (фарш) — mincer (мясорубка)
Исключение: to lie (лгать) — LIAR (лгун / лгунья)
2) Суффикс – or
Модель образования: Verb + or = Noun
При присоединении суффикса – or к глаголу образуется имя существительное, обозначающее профессию, род занятий человека (это преимущественно существительные имеющие латинское и французское происхождение):
To act — actor (актер), to advise — advisor /–er (советник, консультант), to animate — animator (аниматор), to conduct — conductor (проводник, дирижер), to create — creator (создатель), to decorate — decorator (декоратор, маляр, оклейщик обоев), to direct — director (директор, режиссер), to educate — educator (педагог), to illustrate — illustrator (иллюстратор), to invent — inventor (изобретатель), to invest — investor (инвестор, вкладчик), to instruct — instructor (инструктор), to translate — translator (переводчик), to sail — sailor (моряк), to visit — visitor (посетитель), to conquer — coqueror (завоеватель)
Вот еще несколько существительных с суффиксом –or, которые следует запомнить:
doctor, professor, sculptor, sponsor, ancestor (предок), tutor, mentor (наставник)
3) Суффикс — ist
Модель образования: Noun + ist = Noun
При присоединении суффикса -ist к существительному образуется имя существительное, обозначающее профессию, род занятий человека:
art — artist (художник), cello — cellist (виолончелист), chemistry — chemist (химик, аптекарь), drama — dramatist (драматург), ecology — ecologist (эколог), economics — economist (экономист), geology — geologist (геолог), genetics — geneticist (генетик), guitar — guitarist (гитарист), journal — journalist (журналист), medal — medalist (медалист), meteorology — meteorologist (метеоролог), optimism — optimist (оптимист), pessimism — pessimist (пессимист), phylology — phylologist (филолог), physics — physicist (физик), piano — pianist (пианист), speciality — specialist (специалист), science — scientist (ученый), terror — terrorist (террорист), zoology — zoologist (зоолог)
4) Суффикс – ment
Модель образования: Verb + ment = Noun
При присоединении к глаголу суффикса –ment образуется существительное, которое обозначает действие, процесс, средство или инструмент:
To agree — agreement (соглашение)
To arrange — arrangement (приведение в порядок, договоренность)
To assess — assessment (оценивание)
To advertise — advertisement (реклама)
To amuse — amusement (развлечение, забава)
To announce — announcement (объявление)
To appoint — appointment (назначение на должность)
To achieve — achievement (достижение)
To develop — development (развитие)
To entertain — entertainment (прием гостей, развлечение)
To equip — equipment (оборудование)
To establish — establishment (учреждение, заведение)
To excite — excitement (волнение, возбуждение)
To govern — government (правительство)
To punish — punishment (наказание)
To require — requirement (требование, потребность)
To state — statement (утверждение)
To settle — settlement (населенный пункт)
5) Суффикс – ness
Модель образования: Adjective + ness = Noun
При присоединении к прилагательному суффикса – ness образуется существительное, которое обозначает состояние или качество, выраженное прилагательным, от которого оно образовано:
Aware – awareness (сознание) Bald – baldness (облысение)
Bright – brightness (яркость) Careless – carelessness (небрежность)
Dark – darkness (темнота) Deaf – deafness (глухота)
Good – goodness (доброта) Great – greatness (величие)
Fair – fairness (справедливость) Foolish – foolishness (глупость)
Friendly – friendliness (дружелюбие) Happy – happiness (счастье)
Ill – illness (болезнь) Kind – kindness (доброта)
Lonely – loneliness (одиночество) Lazy – laziness (лень)
Mad – madness (безумие) Mean – meanness (подлость, скупость)
Quick – quickness (быстрота, сообразительность) Quiet – quietness (тишина)
Ready – readiness (готовность) Rich – richness (богатство)
Ripe – ripeness (спелость) Rude – rudeness (грубость)
Rough – roughness (неотесанность) Sad – sadness (грусть, тоска)
Sharp – sharpness (резкость) Serious – seriousness (серьезность)
Stuffy – stuffiness (духота) Tidy – tidiness (опрятность)
Weak – weakness (слабость) Wicked – wickedness (злой поступок)
Ugly – ugliness (уродство)
ВНИМАНИЕ! Если прилагательное оканчивается на согласную + y, то y меняется на i. Например: lonely + ness = loneliness. (Помните, что в разделе «Грамматика и лексика» при оценивании учитываются и орфографические ошибки!)
6) Суффикс – ship
Модель образования: Noun + ship = Noun
Суффикс — ship используется для образования существительных, которые имеют абстрактное или собирательное значение:
— указание на сообщество людей, которых объединяет какой-либо вид деятельности:
Membership – круг членов одной организации, Readership – круг читателей, Listenership – читательская аудитория, Partnership – партнерство
— указание на звание, должность человека, или его общественное положение:
Ambassadorship – полномочия посла, Chairmanship – председательство, Chancellorship – канцлерство, Clerkship – должность секретаря, Directorship – директорство, руководство, Professorship – профессорство, Captainship — капитанство, Statesmanship – управление государственными делами, Stewardship – должность управляющего, Apprenticeship – период обучения, ученичество
— указывает на абстрактные понятия:
Citizenship – гражданство, Censorship – цензура, Authorship – авторство, Ownership – владение,собственность, Scholarship – стипендия, эрудиция, Sponsorship – спонсорство, Leadership – руководство, лидерство, Hardship — невзгоды, Township — район
— указывает на умение, мастерство, искусство:
Draftsmanship – искусство черчения, Horsemanship – искусство верховой езды, Airmanship – летное мастерство, Sportsmanship – спортивное мастерство, Craftsmanship – мастерство, тонкая работа
— указывает на отношения:
Friendship – дружба, Companionship – общение, Fellowship – товарищество, содружество, Relationship – взаимоотношения, Courtship – ухаживание
7) Суффикс — ion
Модель образования: Verb + ion = Noun
При присоединении суффикса — ion к глаголу образуются существительные, которые могут обозначать качества, свойства, состояния, процесс либо абстрактные понятия:
to add — addition (добавление), to addopt — addoption (усыновление, принятие), to attract — attraction (достопримечательность, аттракцион), to assume — assumtion (предположение), to collect — collection (коллекция), to connect — connection (связь, соединение), to anticipate — anticipation (предвидение), to invent — invention (изобретение), to qualify — qualification (квалификация), to satisfy — satisfaction (удовлетворение), to admire — admiration (восхищение), to motivate — motivation (мотивация), to reduce — reduction (сокращение), to form — formation (образование), to preserve — preservation (сохранение), to subscribe — subscription (подписка), to relax — relaxation (расслабление, отдых), to invite — invitation (приглашение), to exaggerate — exaggeration (преувеличение)
to express — expression (выражение), to expand — expansion (расширение), to permit — permission (разрешение), to possess — possession (обладание), to tense — tension (напряжение), to impress — impression (впечатление), to confuse — confusion (смущение, путаница), to conclude — conclusion (заключение, вывод), to include — inclusion (включение), to persuade — persuasion (убеждение), to decide — decision (решение)
Суффиксы существительных в английском языке

Прежде чем говорить о суффиксах существительных, необходимо разобраться, что такое суффикс. Под данным термином понимается значимая часть слова, которая следует сразу после корня.
Иными словами, слово – это конструктор, состоящий из нескольких элементов, которые прочно соединены между собой и при надобности легко разъединяются. Суффикс – один из этих элементов. Его можно присоединить или наоборот – отъединить от слова.
При этом конструкция «слово» не разрушается, меняется только её форма – звучание, написание и лексическое значение:
- Школа – школьник – школьница (суффиксы -ник-, -ница-);
- Friend (друг) – friendship (дружба) – friendly (дружелюбный) (суффикс –ship, -ly).
Суффикс имеет две функции. Первая – формообразующая, которая участвует в образовании новых грамматических форм: clever (умный) – cleverest (умнейший) (суффикс –est участвует в образовании превосходной степени прилагательного). Вторая – словообразующая, необходимая для образования новых однокоренных лексических единиц: to write – writer (писать – писатель).
У имени существительного, как самостоятельной части речи, есть свои суффиксы. Они способствуют образованию новых слов. В таблице “Суффиксы существительных” в английском языке представлены самые продуктивные и их общее значение:
| Суффикс | Значение | Примеры |
| -ist (-an, -ian, -ean) | Национальная принадлежность, принадлежность к политической партии, течению) | Scientist (учёный), communist (коммунист), Russian (русский), historian (историк) |
| -er (-or, -eer, -ee, -ant, -ier, -ar) | Профессия, занятие, должность | Writer (писатель), speaker (оратор), inspector (инспектор), dreamer (мечтатель), employee (служащий), engineer (инженер) |
| -ism | Принадлежность к определённому учению или политической партии | Buddhism (буддизм), fascism (фашизм), nationalism(национализм) |
| -ment (-ade) | Итог работы, результат труда | development (развитие), punishment (наказание) |
| -hood (-ship, -cy) | Определённое состояние, уровень отношений | Boyhood (отрочество), orphanhood (сиротство), friendship (дружба), infancy (младенчество) |
| -ness (-dom, -y, -ancy, -ency, -ity, -ty) | Определённое состояние или качество | Boredom (тоска), Wisdom (мудрость), darkness (темнота), prettiness (привлекательность), clarity (ясность), gaiety (весёлость) |
| -al, -ation, -sion, -tion, -ition,-ance, -ence, -ing, -age | Очевидный результат, состояние, процесс | Regulation (регулирование), attention (внимание), barrage (заграждение), shortage (нехватка) |
| -ics | Раздел науки | Mathematics (математика), physics (физика) |
| -ry, -y | Место работы, занятия или состояние | Laboratory (лаборатория), observatory (обсерватория) |
| -ty, -ity, -y | Абстрактные понятия | Authority (власть),equality (равенство), |
| -ess, -ette | Женский род | Mistress (госпожа), poetess (поэтесса) |
В английском языке много суффиксов. Не обязательно их учить наизусть. Достаточно быть внимательным и проводить параллели между словами с одинаковыми суффиксами.
Сегодня были рассмотрены самые известные и продуктивные суффиксы существительных в английском языке. Основная их функция – образование новых однокоренных слов.
Будь в числе первых на доске почета
Образование существительных в английском языке с помощью суффиксов
Образование существительных в английском языке может происходить различными способами. В этой статье рассмотрим образование существительных в английском языке с помощью суффиксов. Суффикс в английском языке – это буква или несколько букв, которые добавляют к слову, чтобы образовать другую часть речи или другой тип слова.
Например, если добавить суффикс –ly к слову quick – быстрый (имя прилагательное в английском языке), мы получим слово quickly – быстро (наречие), если же мы добавим суффикс – еr к слову train – обучать, тренировать (глагол в английском), мы получим существительное и другой тип слова – trainer – тренер (имя существительное в английском языке).
Образование существительных в английском языке происходит от различных частей речи. Существуют группы суффиксов в английском языке, которые указывают на часть речи, к которой относится слово.
Суффиксы, которые указывают на принадлежность слова к такой части речи, как существительное:
-ation, -ion, -ness, -ship, -ity, -ism, -ist, -ence, -ment, -al, -er(-or), -hood, -ing, -th, -ant, -age, -ure(-ture, -sure), -ship, -ian, -ency, -ee, — ette, -ocracy, -ology, -phobe, -phobia, -ess, -ese
- -ation – указывает на состояние, процесс предмета. Зачастую это окончание добавляют к глаголу, чтобы образовать существительное:
inform – information (информировать – информация)
explore – exploration (исследовать – исследование)
starve – starvation (голодать, умирать от голода — голод; голодание)
She quitted those English courses because she was payed starvation wages — она уволилась с тех курсов английского языка, потому что ей платили нищенскую заработную плату
repeat – repetition (повторять – повторение)
Can you spell this English word? – Можешь сказать это английское слово по буквам?
- -ness – добавляют к прилагательному, чтобы образовать существительное:
happy – happiness (счастливый – счастье)
happiness takes no account of time — для счастливых время не существует
- Суффикс-ship в английском языке указывает на статус, состояние, свойство:
friend – friendship (друг – дружба)
director – directorship (директор — руководство, управление)
She has got a friend from Kiev – у нее есть друг из Киева
friendship cannot stand always on one side – дружба должна быть взаимной
- -ity – добавляют к прилагательному, чтобы образовать существительное в английском:
false – falsity (неправильный, ошибочный — ложность, неверность)
electric – electricity (электрический – электричество)
to lay on the electricity — подводить электричество
- -ism – добавление этого суффикса в английском языке характеризует многие верования, мнения, убеждения:
to combat manifestations of nationalism — бороться с проявлениями национализма
- -ist – этот суффикс в английском языке присоединяют к существительным, чтобы образовать от них производные, указывающие на профессионалов, сторонников общественного или научного направления:
This pianist is going to give a concert in Kiev – у этого пианиста будет концерт в Киеве в следующем месяце
- -ence – присоединяют к глаголу или существительному, существительное указывает на состояние или процесс:
reluctant – reluctance (делающий что-либо с большой неохотой — неохота, нежелание)
intelligent — intelligence (образованный – интеллект, рассудок, разум; умственные способности)
This scientist from Kiev is a person of considerable intelligence — этот ученый из Киева — человек большого ума
- -ment — присоединяют к глаголу для образования существительных в английском языке. Данный суффикс указывает на процесс, результат:
govern – government (править, управлять – правительство)
arrange – arrangement (приводить в порядок; расставлять — приведение в порядок; расположение; классификация; систематизация; обычно меры, мероприятия, приготовления)
But personal prejudices again interposed to prevent an arrangement so desirable — но личные предубеждения снова помешали достичь столь желаемого соглашения
All the arrangements were done. Now she is ready to open her own English language courses in Kiev – все приготовления были завершены. Теперь она готова открыть свои курсы английского языка в Киеве
- -al – присоединяют к глаголу для образования существительных в английском языке:
refuse – refusal (отвергать, отказывать; отклонять — отказ, непринятие)
I could not comprehend her refusal to help me with my English language project — я не мог понять, почему она отказалась помочь мне с моим проектом по английскому языку
- -er(-or) – этот суффикс служит для образования существительных в английском языке от глаголов. Существительное с такими суффиксами указывает на человека, который выполняет действие или устройство, производящее ту или иную операцию:
play – player (играть, забавляться – игрок, участник)
read – reader (читать – читатель)
mix – mixer (смешивать – смеситель, смешивающий аппарат, миксер)
edit – editor (редактировать, готовить к печати – редактор)
drive – driver (ездить; ехать – водитель)
write – writer (писать – писатель)
He is a famous English writer – он известный английский писатель
- -hood – образует существительное, которое указывает на состояние, положение, качество:
brother – brotherhood (брат – братство)
child – childhood (ребенок – детство)
She spent her childhood in Kiev – она провела свое детство в Киеве
- -ing – с помощью этого суффикса происходит образование существительных в английском языке от глаголов:
meet – meeting (встречать – встреча)
proceed – proceeding (продолжать (говорить) — акт, действие, поступок)
I have arranged a meeting with my English teacher – я назначил встречу с моим преподавателем по английскому языку
- -th – образует существительные со значением качества:
true – truth (правдивый – правда)
deep –depth (глубокий – глубина)
He started studying language in depth after he had signed up to take a course in English in Kiev— он начал глубоко (тщательно) изучать язык после того, как записался на курсы английского языка в Киеве
- -ant – образуют существительные, которые указывают на человека или вещество:
assist – assistant (ассистировать – ассистент)
He is an English teaching assistant — ассистент преподавателя английского языка
- -age – в английском языке этот суффикс присоединяют к глаголу. С его помощью образуются существительные с различными значениями:
marry – marriage (жениться, выходить замуж – женитьба)
break – breakage (ломать – поломка)
shrink – shrinkage (уменьшать, сокращать – сокращение, уменьшение)
shrinkage of fabric — усадка ткани
- -ure(-ture, -sure) – эти суффиксы служат для образования существительных в английском языке от глаголов, которые указывают на процесс:
press – pressure (давить – давление)
mix – mixture (смешивать – смешивание)
- -ship – присоединяют к существительному, которое указывает на статус, состояние, качество:
friend – friendship (друг – дружба)
leader – leadership (лидер – лидерство)
These newly opened English language courses in Kiev have taken over the leadership very quickly — эти курсы английского языка в Киеве быстро вышли в лидеры
- -ian – в английском языке существительное с таким суффиксом может указывать на национальность, звание, профессию (может выступать прилагательным):
She studied Italian at these courses in foreign languages in Kiev — она изучала итальянский язык на курсах иностранных языков в Киеве
- -ency – в английском языке существительное с такими суффиксами могут указывать на процесс, состояние. Они могут быть образованы от существительных или прилагательных:
president – presidency (президент – президентство)
independent – independency (независимый – независимость)
She has promised improvements during her presidency — она обещала добиться улучшения в период своего президентства.
- -ee – в английском языке существительные с такими суффиксами могут указывать на объект; образование существительных в английском в этом случае происходит от глаголов:
train – trainee (тренировать — практикант, стажёр)
employ – employee (нанимать на работу – наемный рабочий)
There are 200 employees working for our subsidiary in Kiev – 200 сотрудников работает в нашем дочернем предприятии в Киеве
- -ette – указывает на уменьшительное значение. Присоединяют к существительному (образование существительных в английском языке от других существительных):
kitchenette – кухонька, небольшая кухня (совмещенная с комнатой)
- -logy – указывает на принадлежность слова к науке, предмету (школьному):
He spent the following year at the same Institute where he studied Biology – следующий год он провел в в том же институте, где изучал биологию
- -phobe – указывает на то, что человек является трусом, ненавистником, либо боязливым, робким человеком:
Anglophobe – англофоб (человек, который боится или ненавидит Англию)
- -phobia – в английском языке этот суффикс указывает на раздражение или страх, боязнь чего-то (фобию):
arachnophobia – боязнь пауков
pantophobia — боязнь всего
ophidiophobia – патологическая боязнь змей
claustrophobia – клаустрофобия (патологическая боязнь замкнутого пространства)
- -ess – принадлежность к женскому полу (женская особь):
She worked as waitress in Kiev restaurant – она работала официанткой в ресторане Киева
- -ese – указывает на язык или национальность (может выступать прилагательным):
I studied English and Japanese at these courses in foreign languages in Kiev – я изучал английский и китайский на этих курсах иностранных языков в Киеве
На этом заканчиваем тему образования существительных в английском языке с помощью суффиксов, а образование прилагательных, наречий и глаголов при помощи различных суффиксов мы рассмотрим в одной из следующих статей.
Суффиксы существительных
Большинство существительных образуются от глаголов, от прилагательных или других существительных путём присоединение к их основе соответствующих суффиксов. Как правило, суффиксы безударны, но в отдельных случаях они получают главное ударение.
Суффиксы «er, or» присоединяются к глаголам для обозначения действующих лиц.
to buy – a buyer
покупать – покупатель
to translate – a translator
переводить – переводчик
Суффикс «ee» служит для обозначения лица, на которое направлено действие. Cуффикс «ee» получает главное ударение, а второстепенное ударение падает на первый слог:
to address – an address`ee
адресовать – адресат
to trust – a trust`ee
доверять – доверенное лицо
to employ – an employ`ee
нанимать на работу – служащий
Суффикс «ian» служит для обозначения национальной принадлежности:
Russia – russian
Россия – русский
Ukraine – ukrainian
Украина – украинец
Bulgaria – bulgarian
Болгария – болгарин
Для обозначения отвлечённых существительных используются суффиксы «dom, ness, hood, ship, ment, ure, age, ion«.
Суффикс «dom» образует существительные от прилагательных и существительных:
free – freedom
свободный – свобода
king – kingdom
король – королевство
Суффиксы «ness, (ance, ence)» образуют существительные от соответствующих прилагательных:
happy – happiness
счастливый – счастье
important – importance
важный – важность
different – difference
различный – различие
Суффиксы «ship, hood» образуют существительные от других существительных:
friend – friendship
друг – дружба
leader – leadership
вождь – руководство
child – childhood
ребёнок – детство
neighbour – neighbourhood
сосед – соседство
Суффиксы «ment, ure, age» образуют существительные от глаголов:
to govern – government
управлять – правительство
to develop – development
развивать – развитие
to depart – departure
уезжать – отъезд
to press – pressure
давить – давление
to marry – marriage
выходить замуж – замужество
to pass – passage
проходить – проход
Суффиксы «ion (tion, sion, ssion)» также образуют существительные от глаголов. При этом в некоторых случаях изменяется произношение, а иногда и написание слов:
to expect – expectation
ожидать – ожидание
to produce – production
производить – продукция
to exclude – exclusion
исключать – исключение
to permit – permission
разрешать – разрешение
Словообразование (использование префиксов и суффиксов). Видеоурок. Английский язык 5 Класс
Рис. 1. Части слова (Источник)
Приставка (prefix) – это буква или группа букв, которые добавляются к началу слова (at the beginning of the word) с целью образовать новое слово.
Prefix + Word
Un (prefix) + do (base/root word) = undo
Re (prefix) + write (base/root word) = rewrite
Суффикс (suffix) – это буква или группа букв, которые добавляются к концу слова (at the end of the word) с целью образовать новое слово.
Word + Suffix
Use (base/root word) + ful (suffix) = useful
Friend (base/root word) + ly (suffix) = friendly
Процесс образования новых слов с помощью префиксов (рис. 2) и суффиксов называется словообразованием. Зная значение приставок и суффиксов, всегда можно понять, какой частью речи является новое слово, и определить его значение.
Рис. 2. Приставка (Источник)
Приставки добавляются в начале слова и изменяют его значение. Однако слово остается той же частью речи, что и без приставки.
Приставки un-, im-, in-, mis-, dis- придают слову отрицательное значение, делают его противоположным по значению основному слову.
Comfortable (удобный) – uncomfortable (неудобный)
Polite (вежливый) – impolite (невежливый)
Active (активный) – inactive (неактивный)
Приставка re- имеет значение «заново», «снова».
Write (писать) – rewrite (переписать)
Do (делать) – redo (переделать)
Count (считать) – recount (пересчитать)
Prefixes!
Об английском с любовью
О любом человеке можно рассказать многое, и для этого есть много существительных. Во-первых, любому человеку можно “приписать” профессию или род занятий. Как правило, при этом мы отталкиваемся от глагола. Если человек выполняет какое-либо действие, то значит это и есть его род занятий или профессия.
Человек живет в социуме, который имеет “слои общества”, есть дворянство, а значит и титулы, передаваемые по наследству, крестьянство, рабы. Это не профессия и не род занятий. Человек всегда имеет статус “родства”.
Например, женщина может быть матерью, женой, сестрой, свекровью, дочерью, а человек мужского пола может быть мужем, зятем, сыном, отцом, холостяком и т.д.
Суффиксы “-HOOD”, “-SHIP” и “-DOM” образуют абстрактные существительные, которые могут указывать на статус человека в обществе, но не род занятий или профессию. Суффиксы “-HOOD”, “SHIP” и “DOM” во многом похожи по смыслу, но есть и различия, поэтому давайте рассмотрим их поочередно.
Суффикс “-HOOD” пришел в английский язык с немецкого языка и часто говорит о жизни человека, когда он проходит постепенно все фазы взросления от младенца до зрелого человека. Еще суффикс “-HOOD” может указывать на качества человека, которые не относятся к его роду деятельности.
Напишу несколько примеров существительных с суффиксом “-HOOD”.
BABY = ребенок, младенец + HOOD = BABYHOOD = младенчество;
BACHELOR (1) = холостяк + HOOD = BACHELORHOOD = холостяцкая жизнь;
BACHELOR (2) = бакалавр + HOOD = BACHELORHOOD = степень бакалавра;
BROTHER = брат, собрат, коллега, земляк + HOOD = BROTHERHOOD = братство, братские, дружеские отношения, люди одной профессии;
BOY = мальчик, школьник, парень, молодой человек, сын + HOOD = BOYHOOD = отрочество;
CHILD = ребенок, дитя, чадо, сын, дочь, отпрыск, потомок + HOOD = CHILDHOOD = детство;
FALSE = ложный, ошибочный, неправильный, фальшивый, вероломный, лживый, обманчивый + HOOD = FALSEHOOD = ложь, неправда, фальшь;
GENTLE = мягкий, добрый, тихий, спокойный, кроткий, родовитый, знатный + HOOD = GENTLEHOOD = знатность, благовоспитанность, любезность;
HARDY = смелый, отважный, дерзкий, закаленный, выносливый, стойкий + HOOD = HARDIHOOD = смелость, дерзость, наглость;
GIRL = девочка, девушка + HOOD = GIRLHOOD = девичество;
KNIGHT = рыцарь, витязь + HOOD = KNIGHTHOOD = рыцарство, рыцарское достоинство; дворянство;
LIVELY = живой (при описании), оживленный, веселый + HOOD = LIVELIHOOD = средства к жизни, пропитание;
Английские приставки-суффиксы

Опубликовано: 18 июля 2016
Чем полезны английские приставки и суффиксы? Может, «ну их»?Зачем тратить уйму времени на их запоминание? А вот и зря вы так думаете.
Умение применить подходящую приставку, суффикс или окончание выручит во время беседы с носителем, когда под рукой нет словаря и когда он, может, даже и есть, но заглядывать в него стыдно или неудобно.
Посмотрим, как можно выкрутиться на ходу.
Английские приставки, окончания и суффиксы в примерах
Начнём со слов (а таких, поверьте, немало), которые образуют новые варианты с помощью английских приставок, суффиксов и окончаний.
EMPLOY – нанимать, предоставлять работу
Employer – наниматель (типичный случай образования рода деятельности от глагола)
Employee – служащий, работающий по найму
Employment – служба, занятие, работа по найму
Employed – имеющий работу
Unemployed – безработный
Employable – трудоспособный
Employability – трудоспособность, возможность устроиться на работу
RELY – полагаться, надеяться
Reliable – надёжный, верный
Unreliable — ненадёжный
Reliability – надёжность, достоверность
FRIEND – друг
Friendly – дружелюбный
Unfriendly – недружелюбный
Friendless – одинокий, не имеющий друзей
Friendship – дружба
RETIRE – уходить в отставку
Retired – вышедший на пенсию
Retirement – отставка
ATTRACT – притягивать, привлекать (внимание)
Attractive – привлекательный, очаровательный
Unattractive – непривлекательный
Attraction — привлекательность, достопримечательность
Attracting – притягивающий
Attracted – привлекаемый
Зачем же нужны английские приставки-суффиксы?
Как видим, английские приставки и суффиксы помогли нам создать несколько слов от одной основы. Конечно, нельзя взять какой-нибудь префикс и лепить его абсолютно везде. Важно понимать его значение. Так, например, приставка un- в английском считается отрицательной.
Обратите внимание на значение слов: unemployed, unreliable, unfriendly и unattractive. Суффикс –ment поможет вам образовать существительное от глагола, как в наших примерах: retirement и employment.
Суффикс less- в английском языке незаменим, если нужно добавить противоположное значение к глаголу или существительному: useless (бесполезный), helpless (беспомощный), childless (бездетный) и friendless.
В моих примерах выше можно найти довольно частый случай образования лица от действия: to employ – employer. Таких слов много. Мы просто не обращаем на них внимание. Возьмём хотя бы самые популярные пары:
to teach – teacher
to speak – speaker
to dance – dancer
to manage – manager
Можно пользоваться и таким суффиксом, как –ion, если потребуется существительное от глагола: to attract – attraction. Именно таким образом появилось information (от глагола to inform).
Конечно, за один раз трудно усвоить все случаи употребления английских приставок и суффиксов, но практика творит чудеса. На уроках в школе Fluent English мы обращаем внимание на происхождение слов, что упрощает процесс их запоминания и приучает использовать нужный суффикс или приставку в похожем случае.
Будем рады видеть вас на пробном уроке!
You have no rights to post comments
Словообразование имен существительных в английском языке
Словообразование имен существительных в английском языке может выполняться разными способами, и все эти случаи встречаются довольно часто.
В процессе изучения языка эта тема может доставить довольно большую сложность, так как иногда те или иные правила создания слов выглядят вполне логично, а некоторые совершенно необъяснимы с точки зрения грамматики, и их приходится просто запоминать.
О том, как правильно образовать существительное, а также обо всех возможных способах словообразования далее и пойдет речь.
Принцип конверсии
В некоторых случаях для образования существительных не требуется использовать каких-либо дополнительных морфем или присоединять разные основы друг к другу.
Иногда существительные могут просто переходить в разряд noun от глаголов, когда форма verb остается неизменной, и пропадает лишь частица to. Полученные nouns могут быть самыми разными: это и concrete, и abstract nouns.
К сожалению, далеко не все слова могут формироваться по такому принципу, и вот некоторые из них:
to look – a look (смотреть – взгляд)
to face – a face (сталкиваться – лицо)
to set – a set (устанавливать – установка)
to ride – a ride (ехать верхом – поездка)
to love – love (любить – любовь)
Как видно из примеров, у этого способа образования существительных нет ничего сложного, достаточно лишь помнить слова, которые могут употребляться по такому принципу.
Принцип словосложения
Еще один прием, с помощью которого мы обычно образуем новые формы имён существительных, называется словосложение. Примеры этого принципа встречаются в языке довольно часто: берется две грамматические основы слов, причем совершенно необязательно, чтобы обе они были от nouns, и путем их соединения образуется новая форма.
У подобного образования имен существительных есть свои плюсы, так как в процессе не нужно менять местами какие-либо части основ или добавлять дополнительные элементы, достаточно просто объединить две структуры в одну. При этом смысл полученных конструкций далеко не всегда будут схож со значениями исходных форм.
Вот как выглядит такое образование существительных в английском языке и конструкции, образованные с их помощью:
school + bag = schoolbag (портфель)
boy + friend = boyfriend (парень, друг)
lady + bird = lady-bird (божья коровка)
rail + way = railway (железная дорога)
mother + in + law = mother-in-law (теща)
passer + by = passer-by (прохожий)
Как видно из некоторых примеров, иногда только одна основа образовывает общий смысл полученного слова, а, например, предлог его дополняет.
Аффиксальное образование nouns
Словообразование существительных английского языка с помощью аффиксального способа, то путем добавления дополнительных морфем (приставок и суффиксов) – это, вероятно, наиболее распространенный способ образования слов категории nouns.
Образование с помощью приставок
Приставочный способ позволяет получить новые значения, которые могут противоположными исходному слову (stress – antistress, legality — illegality), прошлое состояние (president – ex-president), суть взаимодействия (national – international) и пр. Кроме того, помимо nouns, приставочным способом могут образовываться и новые значения прилагательных в английском языке. Префиксальный принцип весьма распространен и часто используется в лексике.
Суффиксальное образование
Образование существительных с помощью суффиксов – способ, который может встретить практически в любом тексте. Дело в том, что суффиксы в английском языке не только могут передать различные значения (–less – отсутствие, –ful – наличие чего-либо, etc.). Существуют особенные морфемы, которые типичны исключительно для nouns.
Образовать те или иные nouns суффиксальным способом – значит присоединить к другому слову (это могут быть и глагольные структуры, и прилагательные, и другие nouns) особенный суффикс, типичный именно для объекта или явления, отвечающего на вопрос кто? или что? Вот некоторые примеры того, как выглядит суффиксальный способ на практике, и какие морфемы принято использовать в таких случаях:
inform – information
free – freedom
lead – leader
race – racism
active – activity
leader – leadership
press – pressure
move – movement
dark – darkness
strong – strength
Путем суффиксального способа можно образовать много новых значений, при этом нужно запоминать суффиксы, типичные для тех или иных слов.
Отглагольные существительные
Отглагольные существительные – это слова, которые часто путают с герундием из-за идентичного окончания –ing. Для таких nouns характерно образование от глагола, как видно из самого названия.
Переводится оно, как правило, как стандартное noun, то есть при помощи ответа на вопрос кто? или что? Кроме того, с такими словами, во многом схожими с глагольными формами из-за их внешнего сходства, может употребляться и суффиксы, например –al: to read («читать») – reading («чтение»), to arrive («прибывать») – arrival («прибытие») и т. д.
Разнообразие словообразовательных принципов делает необходимым тщательное изучение всех этих принципов и запоминание специфических случаев употребления тех или иных морфем. Зная вышеописанные случаи, образовывать новые nouns станет существенно проще.
Суффиксы в английском языке. Suffixes in English
Суффикс – это часть слова, которая добавляется в конце слова, иногда при этом изменяя его значение и часть речи.
Суффиксы в английских словах более распространены и гибки, чем приставки.
Как и в любом другом языке, в английском языке нужно запоминать, какой суффикс сочетается с конкретным словом. Однако, существует все же небольшой набор правил, которые стоит принять к сведению.
Существительные
Самый распространенный суффикс для существительных – это суффикс делателя.
Он превращает слова-действия в слова, обозначающие тех, кто делает это самое действие. То есть, говоря научным языком, из глаголов действия образуются существительные, обозначающие делателя.
teach – teacher (учить — учитель), build – builder (строить — строитель), catch – catcher (ловить — ловец), beg – beggar (просить — попрошайка), sail – sailor (плавать по морю — моряк).
Сюда же можно отнести слова: father, sister, daughter, хотя они имеют еще согласный перед –er.
Второй по распространенности – суффикс –ment. Он также превращает глаголы в существительное.
develop – development (развивать — развитие), depart – department (отделять – отделение (в магазине)), engage – engagement (увлекать, заинтересовывать – увлечение, интерес)
Для этой же цели служит суффикс – tion/-sion правда, французского происхождения.
Поэтому и слова с ним строго фиксированы и в некоторых случаях уже невозможно определить глагол, от которого они произошли.
revolve – revolution, act – action, abort – abortion, obsess — obsession; nation, fiction, aggression, complexion.
Не все глаголы становятся существительными при помощи суффиксов, иногда это происходит без всяких суффиксов, при помощи конверсии.
Чтобы образовать из прилагательного существительное, нужно употребить суффикс – ness.
busy – business (занятый, деловой – дело, занятие, бизнес)
crazy – craziness (cумашедший — сумашествие)
Как вы, вероятно, заметили, конечный y меняется на i. Иногда этот суффикс присоединяется к прилагательным, которые уже имеют суффикс (например, -y, как в предыдущих примерах, или –ful, -ish). В результате слово получается довольно-таки длинным:
fancy – воображение, причуда, fanciful – воображаемый, причудливый, fancifulness – выдумка, плод воображения, изощренность
tact – такт, tactful – тактичный, tacfulness – тактичность
self – эго, selfish – эгоистичный, selfishness – эгоизм
Прилагательные
Самый знакомый суффикс для прилагательного –
Вероятно, когда-то этот суффикс имел что-то общее со словом full – полный (full of…)
Во всяком случае, значение суффикса похоже на выражение full of:
beauty – beautiful (full of beauty): красота – красивый (исполненный красоты);
wonder – wonderful (full of wonders): чудо – чудесный (исполненный чудес);
Только не забывайте, что в отличие от full, суффикс –ful имеет только одну L.
Слова, заканчивающиеся на –y также часто (но не всегда!) являются прилагательными:
easy, busy, cozy, catchy, lucky.
Часто встречается также суффикс –able/ible
По-английски «able» — способный к чему-либо. Например, He is an able sportsman – Он способный спортсмен.
Такое же значение добавляет и суффикс –able/ible
work – workable (работать – рабочий, в рабочем состоянии)
read – readable (читать – читабельный, который можно прочитать)
eat – edible (есть — съедобный)
Не менее распространен суффикс латинский –al, который есть и в русском.
vocal – вокальный, cenral – центральный,
face – facial (лицевой, относящийся к лицу), например, facial expression
navy – naval (флот – морской, относящийся к морскому флоту), naval officer
А также –ive, который тоже есть в русском:
create – creative (создавать – способный создавать, креативный), sport – sportive (спорт — спортивный), offend – offensive (обвинять — обвинительный).
Стоит отметить –ish – суффикс, обозначающий качество, иногда употребляется как принадлежность к национальности.
child – childish (ребенок — детский), girl – girlish (девочка — девичий), Scotts – Scottish (шотландцы — шотландский), например childish behavoiur, girlish look.
а также суффикс, который делает прилагательное отрицательным –
price – priceless (цена — бесценный),
help – helpless (помощь — беспомощный)
Наречия
Наречия в английском языке образуются от прилагательных при помощи суффикса –ly.
happy – happily (счастливый — счастливо), even – evenly (ровный — ровно), beautiful – beautifully (красивый — красиво), quick – quickly (быстрый — быстро).
Некоторые слова, заканчивающиеся на –ly являются прилагательными, но это скорее исключения. Например, motherly (love) – материнская.
Некоторые наречия образуются не прибавлением суффикса –ly, а являются совершенно другим словом, некоторые остаются без изменения. Такие слова-исключения надо запомнить.
good – хороший, well – хорошо.
bad – плохой, bad – плохо, а вот badly – очень сильно.
Глаголы
Глаголы редко присоединяют суффиксы. Глагольных суффиксов мало, и они не очень распостранены. Вот несколько примеров:
emphasize – подчеркивать, делать ударение на
mystify — мистифицировать, terrify — ужасать, signify — означать
light — enlighten — просвещать, broad — broaden — расширять
источники:
http://skysmart.ru/articles/english/slovoobrazovanie-v-anglijskom-yazyke
http://crownenglishclub.ru/dlya-nachinayushhih/obrazovanie-sushhestvitelnyh-v-anglijskom-yazyke-suffiksy-pristavki-i-dr.html
Suffixes and Prefixes are described along with the definition, meaning, examples, list, rules, uses, etc. All the concepts will be cleared in this session. There are an ever-increasing number of words in the English language. In addition to enhancing your vocabulary, learning new words can be overwhelming. However, if you know English prefixes and suffixes, you will learn many new words and gain a greater understanding of language.
It’s like learning a code when you master common prefixes and suffixes. Having cracked the code, you can not only spell words more accurately, but also recognize and perhaps even define unfamiliar words as well. Let’s explore Suffixes and Prefixes!
Let’s try to understand the basics of suffix and prefixes with examples.
Suffix and Prefix Basics
The English vocabulary is vast! We all know that, don’t we? But without an extensive stock of vocabulary, how can you improve your skills with the language? Well, expanding your vocabulary is not an easy task; you need to read a lot before your stock of words will reach a certain level.
- But what if you get some tricks to not only effectively use the language but also expand your vocabulary rapidly?
- Sounds interesting?

Well, this is exactly what you can do with suffix and prefix. So what are they exactly, and how do they function?
The Function of Suffix and Prefix
This is exactly what this post is all about. Thanks to the nature of the English language, just adding two letters before or after a particular word can change the meaning of the original word and create a new word altogether. These extra letters that you can add before or after any particular words are called suffix and prefix. But can you add these letters for every word in the English language?
In this post, we are going to find out all these answers regarding suffix and prefix. Read on as we talk about the definition, rules, and examples of suffix and prefix and how you can use them to expand your vocabulary. So without any further ado, let’s get started.
A very nice course available on the internet for basic engineering course, which is highly rated & effective. You can available. Its not free but has a minimal charge.
What is The Definition Of Suffix And Prefix?
Well, before we move on to the definition of suffix and prefix, you need to understand where they occur in a word? Usually, the suffix and prefix will be added as per the root of every word. Now, the question arises what a root of a word is?
Well, to put it simply, a root of a word is nothing but the shortest base form of a word. For example, if we take the word ‘Video’, the root of the word is ‘vid’. The suffix and prefix will be added to the root of the word. This is how the meaning of the word will be determined after the change.
Suffix and Prefix with Examples
Let’s try to understand suffix and prefix with examples!

Let’s know about word formation before suffix and prefix.
Define Word Formation
A derivation and composition process results in words in a language. This is known as Word Formation.
Define Suffix: What is Suffix?
Suffixes form new words by adding a prefix to a root word, except they are added at the end of the root word. By adding a suffix to the root word, one can change the meaning of that word slightly, but only a little, not opposite or negative as prefixes do, instead, one can change the class of the word, as in making a verb an adjective.
Suffix refers to the group of letters that sits after the word and alters the meaning or qualifies the meaning of the original word. Like for example, ‘able’ is a suffix that can be used with the word ‘comfort’, and together they make ‘comfortable’, which qualifies the meaning of the original word.
So, comfort + able = comfortable.
Hence, ‘able’ is a suffix here.
Define Prefix: What is Prefix?
A prefix is a word that is added to the beginning of a root for the formation of a new word. There is no meaning to a prefix word on its own, but when added to a root word it changes its meaning. Prefixes make words negative, indicate opinions, or show repetition.
Prefix denotes the group of letters that sits before a word based on the root and alters or qualifies the meaning of the original word. For example, ‘de’ is a prefix that can be used with the word ‘code’, and together they form the opposite of the original word ‘decode’.
In case of uncomfortable, we see that un + comfortable = uncomfortable.
Here, ‘un’ is a prefix. Are you still not clear about the concept? Let’s take a look at some other examples.
Prefix Examples
Prefix examples are as follows,
- Non, un, im, in, il, ir = not, opposite = Nonsense, invalid, unhappy, unchanged.
- Re- = again = redo, replay, revisit.
- Mis = wrongly, not = misunderstand, misguide.
- De = reverse, remove = Deconstruct, destruct, detonate.
- Co, com, con = with, together = Compute, construct, contrive.
- Dis, dif, di = separation, away = Disbelief, Disown, Disorder, dissect.
Suffix Examples
Suffix examples are as follows,
- Er, or = showing comparison = Donner, teacher, cheater.
- Able, Ible = capable = Respectable, Formidable, Credible.
- D, ed = forming the past tense = Respected, Cheated, Fired, Aggravated.
- Ing = continuous tense = Running, Eating, Fighting, Working.
- Ment = State of result = Disappointment, Appointment.
- Ive = having the quality = Decisive, Creative, Divisive.
Check a NICE VIDEO from Shaw English Online,
Importance of Prefix & Suffix
You will be able to get through the Verbal Ability section of Competitive exams with ease if you are familiar with the usage of prefixes and suffixes in English. The English section of most government exams is considered a common and important part of the exam. To master the English section one needs to have a good grasp of English vocabulary and word formation.
It aims therefore to provide knowledge on the formation of words in the English language by using examples to illustrate how prefixes and suffixes work. Additionally, you will be able to download the list of prefixes and suffixes for your own reference.
Basic Rules for Suffix and Prefix
Always remember that neither suffix nor prefix can be used with every word. So before you use them, you need to keep in mind certain aspects. Below, I am listing them for your better understanding.
Suffix Rules
Rule#1: While using a suffix, you need to understand that sometimes they can have multiple meanings.
- For example, the suffix ‘er’. Sitting after the word, it can refer to the person who does the activity.
- Like ‘a dancer, a singer’. Sometimes, they can help establish a comparison as well, like ‘ faster, weaker, lower’.
Rule#2: When the suffix is used, sometimes, it can change the spelling of the word.
- For example, when the ‘ing’ suffix is used, the spelling of the word is bound to be changed.
- Like for ‘running. Swimming, fighting’. Another similar example can be ‘iness’ which is often applicable for words ending with ‘y’. In that case, ‘y’ is replaced by ‘I’.
Suffixes are also similar in meaning to many prefixes. In like manner with the suffix, ‘er’ indicates the action performed by a person when added to a word such as Teachers, gardeners, performers, etc. Comparative adjectives and adverbs are also modified by adding the suffix ‘er’. Fast is shortened to faster and soon becomes sooner, etc.
The spelling of the base word can change when a suffix is added. In general, these are the base words ending in y or e. For example, happy becomes happier, costly becomes costlier with the suffix ‘er’, manage become managing, make become making with the suffix ‘ing’.
Prefix Rules
Rule#1: Many prefixes also mean the same. Like for example, un-, in-, and non mean the same as ‘mis’ and ‘ir’.
Rule#2: Sometimes using the prefix changes the spelling by introducing double letters. Like for example, ‘unnatural’ ‘unnoticeable’.
Rule#3: Using the prefix will never alter the root of the original word. This is very important. Like for example, if you take the word ‘Live’ and add the prefix ‘re’, it will be ‘relive’, keeping the root of the word intact.
A hyphen (-) should be used when adding a prefix to a common noun. Examples include Pro-American or Anti-Religion.
After self- and ex-prefixes, hyphen must be used, for example, self-desirable, self-disciplined, ex-husband, ex-employee etc.
If you add a prefix, you should not change the spelling of the original word or root word; for example: undo, disappear, irrelevant, cooperation, irrational, etc.
When adding a prefix, letters can be repeated.
Prefixes that end with an ‘a’ are used as they are, like atypical, amoral, etc. With prefixes that end with a vowel, the base word will use it as it is.
Following point number 3 (don’t change spelling) is generally recommended even if it results in double consonants after adding the prefix.
The word Uncle begins with a prefix, but it does not have a prefix added to it.
There are many prefixes that can mean the same thing, such as ‘in’, ‘im’, ‘un’ all of these prefixes mean ‘opposite of’ or ‘not’.
List of Suffixes and Prefixes
Suffixes and prefixes lists are tabulated,
Prefixes List
| Prefix | Meaning | Examples |
| anti- | against, | antibiotic, |
| auto- | self | autobiography |
| co- | with | co-operation |
| de- | down | decrease |
| dis- | opposite of, | disagree, disapprove |
| ex- | former, | ex-president, |
| extra- | beyond, | extraordinary, |
| il-, | not | illegal, |
| im-, | not | impossible, |
| In- | not | indefinite |
| ir- | not | irresponsible, |
| in- | into | insert, |
| inter-, | between | interact, |
| micro- | small | microscope, |
| mis- | wrongly | mistake, |
| mono- | one, | monotone, |
| para- | beside | parachute, |
| post- | after | postpone, |
| pre- | before | prefix, |
| re- | again | react |
| semi- | half | semicircle, |
| super- | over | superfood, |
| therm- | heat | thermodynamics |
| trans- | across, | transport, |
| tri- | three | triangle |
| un- | against | unusual |
Suffixes List
| Suffix | Meaning | Examples |
| -al | Related or action | annual, criminal |
| -able | able to, | remarkable |
| -dom | state | freedom |
| -ence | quality | ambience |
| -er | in comparison | bigger, |
| -est | superlative | heaviest |
| -fy | make | justify |
| -ful | full of | houseful |
| -ible | to form adjective | terrible |
| -ily | To form adverb | happily, |
| -ing | action | driving |
| -ist | Person who acts | psychologist |
| -less | without, | Fearless, helpless |
| -ness | to express the state | hardness |
| -tion | state | position |
| -y | to express condition | noisy |
Why Do You Need To Learn And Practice Suffix And Prefix?
As mentioned earlier as well, learning suffixes and prefixes will not only help you understand the grammatical elements better but will also help you expand your vocabulary too.

Keep in mind that suffix and prefix can only be used for certain words. Hence, you need to practice regularly to master the concept. Plus, as for everything related to English grammar, the more you read, the more you will learn. The same can be said for suffix and prefix as well.
- So, from now on, whenever you will read something in English, try to locate the words that are using suffixes or prefixes.
- Firstly, it will help you understand the usage better and refer to the points I have mentioned above about using them.
- Apart from that, you can also note down the words in a copy. This can be a great practice to improve your vocabulary and learn new words.
Conclusion
So, what else would you like to know about suffix and prefix? Should you have any further queries about them, then reach out to us, and we will surely get back to you to the best of our knowledge. Further Study you can refer below:
| Refer Our Few Interesting Articles | |
| Rules to use preposition in | What is magnet for kids |
| Luminous and Illuminated Objects | Thirty Important tips to concentrate on Study |
| How does light interact with matters | Tips to build reading habit of kids |
| What is reflection of light | What is preposition |
| What is noun in english grammar | Types of Noun |
Below you will see a chart of English language word roots that
are common prefixes and suffixes to base words. (This list is similar
to that which appeared previously on this site.)
This list is a small portion of our 2,000 word root database which you can
search using our root search engine.
👉 Prefix Meaning
Prefix is a letter or a group of letters that appears at the beginning of a word and changes the word’s original meaning.
Prefix Meaning Translation
English  |
Prefix is a letter or a group of letters that appears at the beginning of a word and changes the word’s original meaning. |
Spanish |
El prefijo es una letra o un grupo de letras que aparece al principio de una palabra y cambia su significado original. |
French |
Le préfixe est une lettre ou un groupe de lettres qui apparaît au début d’un mot et qui en modifie le sens initial. |
Italian |
Il prefisso è una lettera o un gruppo di lettere che appare all’inizio di una parola e cambia il significato originale della parola. |
German |
Eine Vorsilbe ist ein Buchstabe oder eine Gruppe von Buchstaben, die am Anfang eines Wortes erscheint und die ursprüngliche Bedeutung des Wortes verändert. |
Portuguese |
Prefixo é uma letra ou um grupo de letras que aparece no início de uma palavra e altera o significado original da palavra. |
Russian |
Префикс – это буква или группа букв, которая появляется в начале слова и изменяет его исходное значение. |
Chinese |
前缀是指出现在单词开头的一个字母或一组字母,它改变了单词的本义。 |
Japanese |
接頭辞とは、単語の先頭に現れ、その単語の本来の意味を変える文字または文字群のことです。 |
Polish |
Przedrostek to litera lub grupa liter, która pojawia się na początku słowa i zmienia jego pierwotne znaczenie. |
| Hungarian | Az előtag olyan betű vagy betűcsoport, amely egy szó elején jelenik meg, és megváltoztatja a szó eredeti jelentését. |
| Swedish | Prefix är en bokstav eller en grupp av bokstäver som står i början av ett ord och ändrar ordets ursprungliga betydelse. |
👉 Suffix Meaning
What is the Suffix?
Suffix is a letter or a group of letters that is usually added onto the end of words, to change the way a word fits into a sentence grammatically.
Suffix Meaning Translation
English  |
Suffix is a letter or a group of letters that is usually added onto the end of words, to change the way a word fits into a sentence grammatically. |
Spanish |
El sufijo es una letra o un grupo de letras que se suele añadir al final de las palabras, para cambiar la forma en que una palabra encaja gramaticalmente en una frase. |
French |
Le suffixe est une lettre ou un groupe de lettres qui est généralement ajouté à la fin d’un mot, afin de modifier la façon dont ce mot s’intègre dans une phrase sur le plan grammatical. |
Italian |
Il suffisso è una lettera o un gruppo di lettere che di solito viene aggiunto alla fine delle parole, per cambiare il modo in cui una parola si inserisce grammaticalmente in una frase. |
German |
Ein Suffix ist ein Buchstabe oder eine Gruppe von Buchstaben, die normalerweise an das Ende von Wörtern angehängt wird, um die Art und Weise zu ändern, wie ein Wort grammatikalisch in einen Satz passt. |
Portuguese |
Sufixo é uma letra ou um grupo de letras que é normalmente adicionado no final das palavras, para alterar a forma como uma palavra se encaixa numa frase gramaticalmente. |
Russian |
Суффикс – это буква или группа букв, которые обычно добавляются в конец слова, чтобы изменить способ грамматического вставки слова в предложение. |
Chinese |
后缀是一个字母或一组字母,通常加在单词的末尾,以改变一个单词在语法上与句子的配合方式。 |
Japanese |
Suffix(サフィックス)とは、通常、単語の末尾に付加される文字または文字群のことで、文法的に単語が文に収まる方法を変えるためのものです。 |
Polish |
Sufiks to litera lub grupa liter, która jest zazwyczaj dodawana na końcu słowa, aby zmienić sposób, w jaki słowo pasuje do zdania pod względem gramatycznym. |
| Hungarian | Az utótag olyan betű vagy betűcsoport, amelyet általában a szavak végére illesztenek, hogy megváltoztassák a szó nyelvtani beilleszkedését a mondatba. |
| Swedish | Suffix är en bokstav eller en grupp av bokstäver som vanligtvis läggs till i slutet av ett ord för att ändra hur ett ord passar in i en mening rent grammatiskt. |
Suffix Meaning Translation
Nouns, verbs, adjectives and adverbs all tend to use different suffixes, so this makes it a little easier to remember! Collectively, prefixes and suffixes are known as ‘affixes’.
Prefix Definitions
A prefix is a letter or a group of letters that attaches to the beginning of a word and helps to indicate or modify its meaning. An easy example would be the word ‘prefix’ itself! It begins with the prefix pre-, which means ‘before’.
It is quite important to understand what different prefixes mean as they can help to understand the meanings of any new vocabulary that you learn. However, you do need to be careful, as sometimes a prefix can have more than one meaning!
An example would be im-, this can mean ‘not’ or ‘into’.
Here is a list of the most common prefixes
👉 Prefix Examples
| PREFIX | MEANING | EXAMPLES |
|---|---|---|
| ante- | before | antenatal, anteroom, antedate |
| anti- | against, opposing | antibiotic, antidepressant, antidote |
| circum- | around | circumstance, circumvent, circumnavigate |
| co- | with | co-worker, co-pilot, co-operation |
| de- | off, down, away from | devalue, defrost, derail, demotivate |
| dis- | opposite of, not | disagree, disappear, disintegrate, disapprove |
| em-, en- | cause to, put into | embrace, encode, embed, enclose, engulf |
| epi- | upon, close to, after | epicentre, episcope, epidermis |
| ex- | former, out of | ex-president, ex-boyfriend, exterminate |
| extra- | beyond, more than | extracurricular, extraordinary, extra-terrestrial |
| fore- | before | forecast, forehead, foresee, foreword, foremost |
| homo- | same | homosexual, homonuclear, homoplastic |
| hyper- | over, above | hyperactive, hyperventilate |
| il-, im-, in-, ir- | not | impossible, illegal, irresponsible, indefinite |
| im-, in- | into | insert, import, inside |
| infra- | beneath, below | infrastructure, infrared, infrasonic, infraspecific |
| inter-, intra- | between | interact, intermediate, intergalactic, intranet |
| macro- | large | macroeconomics, macromolecule |
| micro- | small | microscope, microbiology, microfilm, microwave |
| mid- | middle | midfielder, midway, midsummer |
| mis- | wrongly | misinterpret, misfire, mistake, misunderstand |
| mono- | one, singular | monotone, monobrow, monolithic |
| non- | not, without | nonsense, nonentity, nondescript |
| omni- | all, every | omnibus, omnivore, omnipotent |
| para- | beside | parachute, paramedic, paradox |
| post- | after | post-mortem, postpone, post-natal |
| pre- | before | prefix, predetermine, pre-intermediate |
| re- | again | return, rediscover, reiterate, reunite |
| semi- | half | semicircle, semi-final, semiconscious |
| sub- | under | submerge, submarine, sub-category, subtitle |
| super- | above, over | superfood, superstar, supernatural, superimpose |
| therm- | heat | thermometer, thermostat, thermodynamic |
| trans- | across, beyond | transport, transnational, transatlantic |
| tri- | three | triangle, tripod, tricycle |
| un- | not | unfinished, unfriendly, undone, unknown |
| uni- | one | unicycle, universal, unilateral, unanimous |
METRIC SYSTEM PREFIXES
|
nano- |
0. 000 000 001 |
|
milli- |
0. 001 |
|
centi- |
0. 01 |
|
kilo- |
1000 |
|
mega- |
1000 000 |
|
giga- |
1000 000 000 |
|
tera- |
1000 000 000 000 |
Prefix nano-
The prefix nano- is used in the metric system. The prefix denotes a factor of one billionth.
Example:
- Nanometer
Prefix milli-
The prefix milli- is used in the metric system. It has only one use and it is to denote a factor of one thousandth.
Example:
- Millimeter
Prefix centi-
Centi- is a unit prefix in the metric system. It denotes a factor of one hundredth.
Examples:
- Centimeter, centigram, centiliter, etc.
Prefix kilo-
The prefix kilo- is a decimal unit prefix in the metric system. It denotes a multiplication of one thousand.
Examples:
- Kilogram, kilometer, kilojoule, kilobyte, kilobit, kiloohm, kilosecond, etc.
Prefix mega-
The prefix mega- can be used in two ways. The first is as a unit prefix in the metric system, and it describes one million units. The second is as an add-on for words to make them present something large.
Examples for metric system
- Megapixel, megahertz, megabyte, megawatt, megadeath, megaton, megameter, etc.
Examples for add-on:
- Mega-mass, mega-man, mega-important, mega-dope, mega-sized, etc.
Prefix giga-
The prefix giga- is used in the metric system to denote a factor of a billion. It is also commonly hyphenated in colloquial speech to describe something of great size.
Examples:
- Gigahertz, gigabyte, gigabit, giga-shroom, giga-power, giga-hamburger, giga-sized, etc.
Prefix tera- / Prefix for trillion
The prefix for trillion is tera-. Tera- is a unit prefix in the metric system.
Examples:
- Terawatt, terabyte, teralitre, terameter, terasecond, etc.
MEDICAL, BIOLOGY, CHEMISTRY, AND SCIENCE PREFIXES
|
epi- |
Biology and medicine – meaning: up, upon, over, etc. |
|
para- |
Science and medicine – meaning: on the side of, beside, etc. |
|
endo- |
Biology and Medicine – meaning: within |
|
eu- |
Biology and chemistry – meaning: good, well |
|
intra- |
Medicine and biology – meaning: within |
|
hemi- |
Medicine and biology – meaning: half |
|
hetero- |
Biology and social science – meaning: different, other |
|
trans- |
Chemistry and astronomy – meaning: across, over, beyond, etc. |
|
sub- |
Chemistry and science – meaning: under, below, beneath, etc. |
|
poly- |
Chemistry, biology, and music theory – meaning: many, much, etc. |
|
tetra- |
Chemistry, math, and geometry – meaning: four |
|
iso- |
Chemistry – meaning: equal |
|
di- |
Chemistry – meaning: two, twice, double |
|
mono- |
Chemistry and biology – meaning: singular, alone, one |
|
hyper- |
Science and astrology – meaning: abundant, exaggerated, etc. |
|
hypo- |
Medicine and biology – meaning: under |
|
peri- |
Biology and geography – meaning: around, about, etc. |
Prefix epi-
The prefix epi- is of Greek origin. It describes something that is on, upon, over, near, at before, or after something else. It is used across many sciences and disciplines, and is most common in biology and medicine,
Examples:
- Epicenter, epiblast, epidemic, epicarp, epiderm, epidural, epigene, epistasis, epidermis, epitome, epigraph, epigram, epipod, etc.
Prefix para-
The prefix para- is most commonly attached to verbs, and verb phrases. It means at one side of, or on the side of, as well as meaning beside, side by side, beyond, past, or describes something defective or inactive. It is used commonly in sciences and medicine.
Examples:
- Paradigm, parabola, paradox, parasitic, parallax, parameter, paranoia, paranormal, paraphernalia, parapraxis, parasite, paralegal, etc.
Prefix endo-
Endo- is a very simple prefix, and it means within. It is commonly used in biology, medicine, and other sciences.
Examples:
- Endobiotic, endocarp, endocrine, endoderm, endogenous, endomitosis, endomorph, endorphin, endoplasm, endospore, endotherm, etc.
Prefix eu-
The prefix eu- stems from Greek. It means something good, or well. It is commonly used in biology, medicine, and chemistry.
Examples:
- Eulogy, eucalyptus, euchlorine, euglycemia, eukaryote, euthanasia, euglena, eupeptic, eupnea, euthyroid, euthropic, euploid, etc.
Prefix intra-
The prefix intra- simply means within, and it is often associated with the prefix inter-. It is used to form compound words. The prefix intra- is also commonly used in biology and medicine.
Examples:
- Intravenous, intradermal, intracranial, intrada, intracardiac, intraclonal, intracodon, intray, intraocular, intrauterine, intrahost, intrasient, intraset, etc.
Prefix hemi-
The prefix hemi- is a simple one, and it means half. It is most commonly used in medicine and biology.
Examples:
- Hemiparesis, hemiplegia, hemithorax, hemihelix, hemicarbonic, hemicerebral, hemicoronal, heminode, hemiparesis, etc.
Prefix hetero-
The prefix hetero- simply means different, or other. It’s most commonly encountered in medicine and biology, as well as sometimes in social sciences.
Examples:
- Heterocyclic, heteromorphism, heterosexual, heterozygous, heterodox, heterogene, heteropod, heterochromatic, heterolateral, heterodiagenic, etc.
Prefix trans-
The prefix trans- is originally from Latin, and it’s very versatile in its use. It means something across, over, beyond, through, or changing. It is also used in chemistry, and astronomy, to denote distance. It also refers to something on the other side of something, and is used to describe one’s gender if it doesn’t align with the biologically assigned sex.
Examples:
- Transgression, translucent, transaction, transfixed, transatlantic, transcontinental, trans-Martian, trans-Neptunian, transsexual, transgender, translation, etc.
Prefix sub-
The prefix sub- comes from Latin and it is very simple, but versatile. It means under, below, beneath, slightly, nearly, imperfect, secondary, or subordinate. It is also commonly used in chemistry and other sciences.
Examples:
- Subject, subtract, subjugate, subnitrate, suboxide, subchloride, subplot, subcommittee, subvert, submerge, submarine, subscribe, subtropical, etc.
Prefix poly-
The prefix poly- means many, much, or in great number. It is very common in chemistry and biology, as well as music theory.
Examples:
- Polyandrous, polyethylene, polymorphic, polyglot, polymer, polyester, polycaliber, polycentric, polytonal, polychord, polycratic, etc.
Prefix tetra-
Tetra- is a numeral prefix, and it means four. It is used to denote a thing that consists of four parts. It is commonly used in various sciences, especially chemistry, math, and geometry.
Examples:
- Tetrameter, tetragon, tetrahelix, tetrahydride, tetraionic, tetrachloride, tetracube, tetracycline, tetraethyl, tetranuclear, etc.
Prefix iso-
The prefix iso- means equal. It is commonly used in chemistry to describe isometric compounds. It is also used in the formation of various compound words.
Examples:
- Isometric, isotope, isocyanic, isoalkene, isolate, isontropic, isoclonal, isocurve, etc.
Prefix di-
The prefix di- comes from Greek, and it means two, twice, or double. It is used in the formation of various compound words. It is commonly seen in chemistry.
Examples:
- Dipolar, disulfide, diatomic, dioxide, dialogic, diazepine, dicobalt, diacarboxyl, dibasal, dibenzonate, etc.
Prefix mono-
The prefix mono- means something singular, alone, or simply one. It is commonly used in various sciences.
Examples:
- Mononucleosis, monophonic, monogamy, monorail, monopoly, monotheism, monolayer, monohydrate, monotonous, monotone, monoplan, etc.
Prefix hyper-
The prefix hyper- comes from Greek. It is used to describe something that is abundant, it means over and denotes something in excess or something being exaggerated. It is used commonly in sciences to denote mass or space.
Examples:
- Hyperbole, hyperthyroid, hyperventilate, hypermass, hyperinflation, hyperactive, hypercatabolic, hyperchloric, hypercritical, hyperchronic, hyperlink, etc.
Prefix hypo-
Hypo is a very simple prefix that comes from Greek. It means under. It is commonly used in medical terms, as well as generally in sciences and various researches.
Examples:
- Hypodermic, hypoglycemia, hypochondria, hypoallergenic, hypothesis, hypocritical, hypocrite, hypocorism, hypogean, hypocaust, etc.
Prefix peri-
The prefix peri- comes from Greek. It means around, about, enclosing, surrounding, or near. It is commonly used in biology and geography.
Examples:
- Periphery, periscope, pericranial, peridigital, perifacial, perimeter, peripatetic, perimorph, periodontal, periosteum, perihelion, etc.
Chemistry Prefixes
In chemistry prefixes are used to name various compounds. These prefixes denote the number of a given element within a compound.
Prefixes:
- 1 – mono, 2 – di, 3 – tri, 4 – tetra, 5 – penta, 6 – hexa, 7 – hepta, 8 – octa, 9 – nona, 10 – deca
Examples:
- Nitrogen trihydride, copper sulfate pentahydrate, bicarbon sulfate, etc.
GRAMMATICAL PREFIXES
|
de- |
Privation, removal, separation, etc. |
|
inter- |
In between, among, together, etc. |
|
pro- |
Affinity to something, advancing, etc. |
|
ex- |
Our of, from, without |
|
un- |
Not, opposite meaning of the original word |
|
re- |
Again, repeating, back, etc. |
|
mis- |
Mistaken, wrong, incorrect, etc. |
|
con- |
Together, joined, etc. |
|
pre- |
Before, prior to, in front of, etc. |
|
im- |
Change meaning to the negative form of the original |
|
ad- |
To, towards, joining, etc. |
|
anti- |
Against, in opposition of something, etc. |
|
auto- |
Self, same, spontaneous, etc. |
|
pan- |
All, union of branches |
|
dia- |
Through, completely, going apart, etc. |
|
neo- |
New, fresh, young, etc. |
|
post- |
Behind, after, later, etc. |
|
ab- |
Away from |
|
bi- |
Twice, two |
|
co- |
Together, jointly, mutually |
|
en- |
Confine something in a place, etc. |
|
fore- |
Before, in front, superior |
|
retro- |
Before, backwards |
|
tele- |
Distance, measuring distance |
|
be- |
To exist |
|
an- |
Without, lacking, not |
Prefix de-
The prefix de- is of Latin origin. It is used to indicate privation, removal, separation, negation, descent, reversal, or intensity. The prefix de- is also added to verbs in order for them to mean the opposite of what they originally mean.
Examples:
- Decide, dehumidify, degrade, detract, deduce, decompose, decentralize, desensitize, deconstruct, demoralize, defrost, destroy, etc.
Prefix inter-
The prefix inter- comes from Latin. It describes something that is between, among, in the midst of, mutual, reciprocated, together, or active during an event. The prefix can be used to modify various types of words.
Examples:
- Interact, intercede, interlude, intercept, intersect, intercom, interim, interject, intermediate, international, internet, interrupt, intertwine, interview, etc.
Prefix pro-
Pro- is a very versatile prefix. It is used to describe an affinity for something. It can also describe priority in space and time, as well as denoting advancing, or indicating substitution.
Examples:
- Pro-British, pro-Communist, proactive, provision, prologue, proceed, produce, protract, procrastinate, proactive, prohibit, provoke, pronounce, etc.
Prefix ex-
The prefix ex- is simple to use, because it is most commonly hyphenated. It means out of, from, utterly, thoroughly, not, or without, and can indicate a former status or title.
Examples:
- Ex-wife, ex-boyfriend, ex-girlfriend, ex-member, ex-president, ex-convict, exodus, exhume, ex-husband, ex-Christian, etc.
Prefix un-
The prefix un- is simple to use because it only means not. It can be attached to all forms of words in order for them to mean the opposite of what they originally do.
Examples:
- Unfair, unemployed, unseen, unfeeling, uninformed, undisputed, unheard, unrest, unable, unhappy, uncooked, unzip, etc.
Prefix re-
The prefix re- is originally from Latin. It means again, or describes something that is being repeated, and it can also mean back, or backwards to denote a regression.
Examples:
- Regenerate, refurbish, reimburse, revert, retract, retype, reconsider, revolt, renew, reveal, redistribute, reconcile, restock, etc.
Prefix mis-
Mis- is a very versatile prefix, and can be applied to many different types of words. It means ill, mistaken, wrong, incorrect, and in general has a negative context.
Examples:
- Mistake, mishap, misinformed, misaligned, misspell, misread, misuse, mispronounce, mishear, mistrial, misprint, mistrust, misbehavior, etc.
Prefix con-
The prefix con- is used with nouns, adjectives, and some verbs. It means together, joined, as well as denoting a group of people, ideas, or things.
Examples:
- Confirm, congregation, congenial, console, converge, consult, confederation, conjoined, conjecture, confluence, contingent, conflate, etc.
Prefix pre-
The prefix pre- stems from Latin, and it is applied to various different words. It means before, predating, prior to, in advance of, or in front of.
Examples:
- Prelude, preset, prevent, prepay, preschool, prewar, prefrontal, prenatal, predetermined, prehistoric, pretrial, preheat, precaution, etc.
Prefix im-
The prefix im- is a negative prefix, which means it is used to change the meaning of a word into a negative. It can be applied to many different types of words, most notably nouns and adjectives.
Examples:
- Impossible, impatient, imperfect, immature, impurity, impartially, immobilized, immaculate, impassive, imperil, etc.
Prefix ad-
The prefix ad- comes from Latin. It means towards, to, with regard to, or in relation to. It can also describe addition, or joining.
Examples:
- Administer, advertise, adhere, addition, adrenal, admonish, adgerminal, addental, adoral, adjoin, etc.
Prefix anti-
The prefix anti- means against, opposite of, or in opposition of something. It is used to form compound words that mean the opposite of their original meaning. It is also commonly hyphenated.
Examples:
- Antiseptic, anti-hero, antidote, antifreeze, antisocial, antiviral, antibiotic, antibody, antiwar, anti-government, antisocial, antiaircraft, etc.
Prefix auto-
The prefix auto- means self, same, spontaneous, or self-sufficient. It is used to create compound words, and can be used on various types of words.
Examples:
- Autobiography, automotive, autopilot, autograph, automobile, automatic, autonomy, autocratic, autocorrect, autodidact, etc.
Prefix pan-
The prefix pan- comes from Greek. It means all, and it implies the union of branches or groups. It is often hyphenated, and can be used to create various compound words.
Examples:
- Panacea, panoply, pantheism, pantonality, pan-Christian, pan-Slavic, panorama, pansexual, pan-African, etc.
Prefix dia-
The prefix dia- stems from Greek. It means passing through, thoroughly, completely, going apart, or opposed in the moment. It is a very diverse prefix and is used in different compound words.
Examples:
- Diabetes, dialect, diabolic, diagnosis, dialysis, diagram, diaspora, dialogue, diaper, diarrhea, diameter, diagonal, etc.
Prefix neo-
The prefix neo- comes from Greek. It means new, fresh, young, or recent. It is often hyphenated, and can be used to create various compound words.
Examples:
- Neolithic, neo-Baroque, neoformative, neonatal, neo-socialist, neoclassical, neoclassicism, neo-fascist, neoglacial, neo-Hellenic, neocosmic, etc.
Prefix post-
The prefix post- comes from Latin. It means behind, after, later, subsequent to. It is used in various compound words, and it can be often hyphenated.
Examples:
- Postdoctoral, postscript, postmodern, postgraduate, post-Victorian, postcolonial, post-coital, posthumous, postpone, postwar, post-Elizabethan, posterior, etc.
Prefix ab-
The prefix ab- comes from Latin. It is a simple prefix and it means away from. It’s used commonly in with various types of words.
Examples:
- Abdicate, absolve, absolute, absorb, abject, abhor, abjure, abort, absorb, abnormal, abrasive, abominable, ablation, etc.
Prefix bi-
The prefix bi- is very simple and it means twice, or two. It is used in various compound words.
Examples:
- Biracial, biceps, biannual, bilingual, bipedal, billion, binoculars, bicycle, bipartisan, bisect, bimonthly, bicarbonate, bifurcate, etc.
Prefix co-
The prefix co- means together, jointly, or mutually, and it is used with various nouns, adjectives, or verbs. It can also be hyphenated sometimes.
Examples:
- Cohabitation, coauthor, copilot, co-conspirator, co-manage, coexist, coaxial, co-captain, co-creator, co-anchor, etc.
Prefix en-
The prefix en- stems mainly from French. It means to confines something in a place, or to gather in a place, as well as to cause something or someone o be in a specific place. It is a very versatile prefix used in many different compound words.
Examples:
- Enslave, entrust, enthrone, entomb, enshrine, encircle, enclose, entwine, encapsulate, entangle, enable, endear, encase, etc.
Prefix fore-
The prefix fore- is fairly simple, and it means before, in front, or superior. It is used with various types of words.
Examples:
- Forehead, forefront, forecast, forefathers, foreman, foremost, foreground, foreshadow, foresee, foreword, forebode, etc.
Prefix retro-
The prefix retro- comes from Latin. It means before, or backwards. It is commonly used with various types of words.
Examples:
- Retroactive, retrograde, retrospective, retrogress, retrorocket, retroscape, retroglossal, retrogene, retrodiagnose, etc.
Prefix tele-
The prefix tele- means distant, or refers to a transmission over distance. It is most commonly used with nouns and adjectives.
Examples:
- Television, telesales, telephone, teleplay, telegraph, telemarketing, teleguide, telegram, telekinesis, telemonitor, etc.
Prefix be-
Be-, as a separate word, means to exist. Be- as a suffix comes from Old English, and has been used in the English language ever since. It was first used in the formation of verbs, but has since expanded in use.
Examples:
- Befriend, bewitch, besiege, beguile, become, berate, bejewel, bewail, bedazzle etc.
Prefix an-
An- is another Old English prefix. It is used to shift words into a negative meaning. This means that the words usually describe something without, lacking, or just simply means not.
Examples:
- Anoxia, anastral, anegoic, anethical, anhistorical, aniconic, anisomeric, anisotomic, anotia, anuria, etc.
YOUR QUESTIONS ANSWERED
What are the prefix words?
Prefixes are words that don’t mean anything on their own. They only serve to change the meaning of the word they are attached to. Prefixes, because of that, are not really words.
Prefixes are attached to the start of other words.
Example:
- DIS-
DISbelief, DISpleasure, DISconnect
DIS, by itself, does not mean anything. When it’s combined with another word it changes the meaning.
Some prefixed are words that have a meaning on their own, but they are short and can be attached to other words.
Words with the prefix for?
The prefix for is very old, and it comes from Scandinavian languages. It was adopted by the English language and has been used for ages. Usually, the prefix for is added to words when they are supposed to describe something that ends up being worse than it started.
Many words that have the prefix for are old, and are not used very commonly today.
Examples:
- Forbear, forbuy, forcut, fordo, forswearer, forgather, forhang, forlet, forlive, forset, forslow, forstop, fortear, fortread, forwarn, forwork, etc.
Other words are used in English regularly, and the prefix has been integrated into the word. In some words an E has been added between the suffix and the rest of the word. In other modern versions the prefix has remained the same
Examples:
- Forebode, forego, forefather, forbidden, forsake, foreshadow, foreskin, forsworn
Prefix Herbicide
Prefix herbicide is an American product that is manufactured in the US, and used to treat various types of grass. It is a selective herbicide and can be applied to different types of grassy terrain, as well as come crops. PREFIX is the name of manufacturer.
Are prefix allowed in scrabble?
Prefixes by themselves are not allowed in Scrabble. This means that just putting any prefix such as post-, pre-, neo-, eb-, or others, is not allowed.
However, you can use words that are built with prefixes. Only complete words are allowed in Scrabble. This means that you can use postmodernism, instead of just modernism.
Can prefix be a noun / verb / plural?
Prefixes as grammatical elements are not complete words. They cannot be any type of word except a prefix. Prefixes are used to change words and are always added to another type of words.
The only case when prefixes are complete words is when two or more words are hyphenated together. Some examples are jet-black, tar-runway, hot-blooded, and others. In this case, two full words are connected with a hyphen.
Prefix and Postfix
Prefix and postfix are terms used in programming and coding. They are connected to operators and operands. Each appears in a different situation, and achieves different results.
A prefix is an expression where the operator appears in the expression before the operands. This is then called a prefix expression.
A postfix appears in an expression when the operator appears in the expression after the operands. This is then called a postfix expression.
Prefix and postfix expressions are used in C++, Java, and C#.
Recommended for you:
Adverbs Of Frequency
Best English Grammar and Spelling Checkers Online
A suffix is a letter or a group of letters that is usually attached to the end of a word to form a new word, as well as alter the way it functions grammatically.
Words with Suffixes
Depending on whether it is a noun, verb, adjective or adverb, a different suffix would be required. For example, the verb read can be altered to become the noun reader by adding the suffix -er. The same verb can also be turned into the adjective readable by adding the suffix –able.
It is just as important to understand the definitions of suffixes as prefixes, because they too help us to deduce the meanings of any new words that we learn. I have listed some of the most common suffixes below:
👉 Suffix Examples
| SUFFIX | MEANING | EXAMPLE |
|---|---|---|
| NOUN SUFFIXES | ||
| -acy | state or quality | democracy, accuracy, lunacy |
| -al | the action or process of | remedial, denial, trial, criminal |
| -ance, -ence | state or quality of | nuisance, ambience, tolerance |
| -dom | place or state of being | freedom, stardom, boredom |
| -er, -or | person or object that does a specified action | reader, creator, interpreter, inventor, collaborator, teacher |
| -ism | doctrine, belief | Judaism, scepticism, escapism |
| -ist | person or object that does a specified action | Geologist, protagonist, sexist, scientist, theorist, communist |
| -ity, -ty | quality of | extremity, validity, enormity |
| -ment | condition | enchantment, argument |
| -ness | state of being | heaviness, highness, sickness |
| -ship | position held | friendship, hardship, internship |
| -sion, -tion | state of being | position, promotion, cohesion |
| VERB SUFFIXES | ||
| -ate | become | mediate, collaborate, create |
| -en | become | sharpen, strengthen, loosen |
| -ify, -fy | make or become | justify, simplify, magnify, satisfy |
| -ise, -ize | become | publicise, synthesise, hypnotise |
| ADJECTIVE SUFFIXES | ||
| -able, -ible | capable of being | edible, fallible, incredible, audible |
| -al | having the form or character of | fiscal, thermal, herbal, colonial |
| -esque | in a manner of or resembling | picturesque, burlesque, grotesque |
| -ful | notable for | handful, playful, hopeful, skilful |
| -ic, -ical | having the form or character of | psychological, hypocritical, methodical, nonsensical, musical |
| -ious, -ous | characterised by | pious, jealous, religious, ridiculous |
| -ish | having the quality of | squeamish, sheepish, childish |
| -ive | having the nature of | inquisitive, informative, attentive |
| -less | without | meaningless, hopeless, homeless |
| -y | characterised by | dainty, beauty, airy, jealousy |
| ADVERB SUFFIXES | ||
| -ly | related to or quality | softly, slowly, happily, crazily, madly |
| -ward, -wards | direction | towards, afterwards, backwards, inward |
| -wise | in relation to | otherwise, likewise, clockwise |
So as you can see, affixes can dramatically change the definitions of words. Knowing the various prefixes and suffixes along with their meanings can really help you to understand how words are used, and also how they should be spelled.
Although these groups of letters (affixes) are important and assist with forming words, they are not words in their own right and cannot stand alone in a sentence.
If they are printed or written alone, then they should have a hyphen before or after them to demonstrate that they are to be attached to other letters to form words (the way I have listed them in the above tables).
MEDICAL, BIOLOGY, CHEMISTRY, AND SCIENCE SUFFIXES:
|
-itis |
Medicine – meaning: infection, inflammation |
|
-pathy |
Medicine – meaning: have a condition |
|
-penia |
Medicine – meaning: deficiency |
|
-tomy/otomy |
Medicine and biology – meaning: condition, procedures, etc. |
|
-logy |
Science and medicine – meaning: various branches of science |
|
-lysis |
Biology and science – meaning: decomposition, loosening, etc. |
|
-osis |
Biology – meaning: infection, condition, state, etc. |
|
-centisis |
Medicine – meaning: surgical puncture |
|
suffixes for pain |
Medicine and biology |
Suffix -itis
The suffix –itis is commonly used in medicine. It describes a type of infection, condition, inflammation, or some medical diagnoses.
Examples:
- Appendicitis, arthritis, barotitis, bronchitis, cerebritis, colitis, conjunctivitis, encephalitis, gastritis, hepatitis, meningitis, etc.
Suffix -pathy
The suffix -pathy comes from Greek, and is commonly used in medicine. It means to suffer from a disease, or have a condition.
Examples:
- Biopathy, cerebropathy, colopathy, dyspathy, eupathy, genopathy, homeopathy, immunopathy, leucopathy, mazopathy, neuropathy, osteopathy, stomatopathy, etc.
Suffix -penia
The suffix -penia is common in medicine. It means to have a deficiency of something.
Examples:
- Calcipenia, cytopenia, enzymopenia, kaliopenia, lipopenia, neutropenia, sarcopenia, sideropenia, etc.
Suffix -tomy / -otomy
The suffixes -tomy or -otomy are often used in biology and medicine. They refer to medical conditions, diagnoses, procedures, or operations.
Examples:
- Anatomy, autotomy, craniotomy, episiotomy, hysterotomy, laparotomy, lobotomy, tracheotomy, polytomy, rumenotomy, tenotomy, uvulotomy, etc.
Suffix -logy
The suffix –logy is commonly used in sciences, and medicine. It refers to various branches of science, or to a body of knowledge. It can also denote collection of stories and discourses.
Examples:
- Trilogy, duology, mythology, archaeology, anthropology, theology, paleontology, toxicology, gynecology, biology, Egyptology, ethnology, neurology, etc.
Suffix -lysis
The suffix -lysis of common biology, various sciences, and academics in general. It refers to decomposition, loosening, breaking down, separation, or decomposition.
Examples:
- Analysis, adipolysis, dermolysis, biolysis, catalysis, dialysis, plasmolysis, radiolysis, tenolysis, sonolysis, virolysis, streptolysis, etc.
Suffix -osis
-Osis is a very common suffix in biology. -Osis means to be infected with something, or means a condition, state, abnormal process, and disease.
Examples:
- Asbestosis, cyanosis, fibrosis, hypnosis, ketosis, mitosis, neurosis, osteoporosis, psychosis, stenosis, thrombosis, tuberculosis, etc.
Suffix -centisis
General surgical punctures are described with the suffix -centisis. This suffix is used to denote that a specific part of the body has been surgically punctured. It can be used with almost any body part.
Examples:
- Abdominocentisis, paracentesis, arthrocentesis, celiocentesis, lumbarocentesis, thoracentesis, etc.
Suffixes for Pain
In order to describe pain through the use of a suffix you can use any medical suffix to present the condition. There is no specific suffix that denotes a type of pain. Instead, you can use a variety of suffixes to describe a specific type of condition, or pain in a specific area.
Suffix examples:
- -algia, -cardia, -emia, -itis, -lysis, -oma, -osis, -pathy, etc.
Word examples:
- Fibromyalgia, neuralgia, tachycardia, enamia, hypoglycemia, arthritis, meningitis, paralysis, blastoma, glaucoma, proctosis, neuropathy, etc.
LIST OF NAME SUFFIXES / SUFFIX OF A NAME
Names can have suffixes depending on the person’s academic honors, religious affiliation, political title, or family status.
Academic honors examples:
- Bachelor’s degree: John Doe, A.B, B.A., B.A., Hons, B.S., B.E., B.F.A., B.Tech., L.L.B, B.Sc., etc.
- Master’s degree: John Doe, M.A., M.S., M.F.A., LL.M, M.L.A., M.B.A., M.Sc., M.Eng etc.
- Professional doctorate: John Doe, J.D., M.D., D.O., Pharm.D., D.Min., etc.
- Academic doctorate: John Doe, Ph.D., Ed.D., D.Phil., D.B.A., LL.D, Eng.D., etc.
Political and religious title examples:
- Order of the British Empire: John Doe, O.B.E
- Knight Commander of the Order of the British Empire: John Doe, K.B.E
- Doctor of Divinity: John Doe, D.D.
- Esquire: John Doe, Esq.
- Attorney: John Doe, CSA
The suffix Jr. is used after names. It means that a person is the offspring of a father with the same name. Some famous examples are Martin Luther King Jr., Cuba Gooding Jr. Sammy Davis Jr., John F. Kennedy Jr. and others.
Family status examples:
- John Doe, Jr.
- John Doe, Sr.
GRAMMATICAL SUFFIXES:
|
-ism |
Practice, action, principle, etc. |
|
-ous |
Form of possession |
|
-al |
Kind of, pertaining to, etc. |
|
-ist |
Specific action, specific value, doctrine, etc. |
|
-able |
Capability, susceptible of, fit for, etc. |
|
-ic |
Something has a characteristic of something else |
|
-ion |
Action, condition |
|
-tion |
Action or result of something |
|
-ed |
Past tense, adjectives from nouns or verbs, compound verbs |
|
-ly |
Repeated in intervals |
|
-ment |
Actions, results |
|
-ness |
Quality, state |
|
-er |
Specific action, job, origin, etc. |
|
-ate |
Group of people, office, institution, etc. |
|
Pertaining to |
-as, -al, -ar, -ary. -ic, -ical, -ous, and -ile |
Suffix -ism
The -ism suffix comes from Ancient Greek. It is used to form action nouns from verbs. They mean some kind of practice, action, principles, doctrines, devotion, adherence, etc.
Examples:
- Baptism, aphorism, criticism, Lutherism, Protestantism, Palamism, atheism, fanaticism, capitalism, nationalism, romanticism, vegetarianism, Atticism, Americanism, racism, sexism, heterosexism, daturism, rheumatism, etc.
Suffix -ous
The suffix -ous is used for adjectives. It means that something is full, or a form of possession. It also means that something has a given quality.
Examples:
- Dangerous, famous, various, enormous, courageous, jealous, glorious, superfluous, obvious, hideous, tremendous, curious, etc.
Suffix -al
The suffix -al is commonly used to make adjectives out of nouns. It means kid of, pertaining to, having a form or character of something.
Examples:
- Seasonal, sensual, official, commercial, individual, spiritual, annual, essential, celestial, usual, racial, intellectual, financial, classical, etc.
Suffix -ist
The suffix –ist is used for nouns. It means a person who performs a specific action, produces something specific, plays a specific instrument, holds a specific value, has a specific doctrine, and others.
Examples:
- Archaeologist, activist, evangelist, anthropologist, capitalist, communist, Marxist, fascist, nationalist, conformist, machinist, novelist, cyclist, masochist, etc.
Suffix -able
The suffix -able is commonly used for adjectives. I refers to someone or something that is capable of something, susceptible of, fit for, tending or given to something.
Examples:
- Movable, amendable, breakable, flammable, amicable, pleasurable, impressionable, payable, reportable, detestable, capable, punishable, fashionable, taxable, etc.
Suffix -ic
The suffix -ic is used to create adjectives out of other words. It originally comes from Greek and Latin, and it means that something, or someone, has the characteristic of something else.
Examples:
- Acidic, episodic, comedic, melodic, nomadic, periodic, idiotic, psychotic, patriotic, athletic, poetic, magnetic, emphatic, kinetic, prosthetic, chaotic, narcotic, academic, economic, etc.
Suffix -ion
The suffix -ion is of Latin origin. It denotes and action or condition, and it is often used to form nouns out of adjectives.
Examples:
- Acceleration, devotion, religion, ration, concentration, communion, diffusion, delusion, illusion, fabrication, hydration, meditation, infusion, levitation, gestation, reaction, invigoration, etc.
Suffix -tion
The suffix –tion is used to form nouns. They mean an action of something, or the result of something.
Examples:
- Deletion, ignition, determination, resolution, action, justification, intersection, connection, gumption, communication, starvation, construction, relation, temptation, revolution, etc.
Suffix -ed
The suffix -ed is very versatile. It can be used in three different ways: 1) to form the past tense for weak verbs, 2) to form adjectives out of nouns or verbs to describe someone or something, 3) added to nouns or verbs in order to form compound adjectives that are hyphenated.
Examples:
- 1) Acted, danced, posted, lived, wanted, hated, played, tried, named, called, walked, talked, used, created, etc.
- 2) bearded, colored, angered, triggered, used, rugged, incorporated, incarcerated, floored, stoned, etc.
- 3) cone-shaped, green-tinted, loose-fitted, off-handed, amateur-produced, well-defined, etc.
Suffix -ly
The suffix -ly is added to various words depending on the purpose. It can be added to adverbs to form adjectives, or to nouns in order for them to mean something that is repeated in certain intervals.
Examples:
- Gladly, gradually, secondly, thirdly, essentially, boldly, bravely, carefully, generously, lowly, shortly, angrily, anxiously, suddenly, generally, etc.
- Hourly, daily, weekly, monthly, yearly
Suffix -ness
The suffix -ness is very common and is used often. It is used on adjectives and principles, in order to create abstract nouns that denote a quality or a state.
Examples:
- Happiness, kindness, darkness, preparedness, consciousness, effectiveness, callousness, laziness, loneliness, ugliness, fitness, dryness, baldness, etc.
Suffix -er
The suffix -er is used in many different ways, and is a common suffix in English. It can be attached to verbs in order to create an agent noun that describes a person doing a specific action. It can also be used to create nouns that describe a person’s job, location or origin, or a special characteristic.
Examples:
- Caterer, Icelander, southerner, villager, tattooer, cobbler, reader, rapper, creditor, auditor, editor, recruiter, rider, writer, educator, calculator, spectator, infiltrator, catcher, staffer, etc.
Suffix -ate
The suffix -ate is added often to nouns, adjective, and verbs. When it is added to nouns it denotes a group of people, an office or institution, or administrative region. When it is added to verbs it changes the verb to mean that something is caused to change. When added to adjectives it means that something is showing or full of something.
Examples:
- Electorate, caliphate, protectorate, consulate, magistrate, regulate, vacate, activate, disseminate, obfuscate, confiscate, passionate, considerate, obstinate, celibate, etc.
Suffixes that mean Pertaining To
There are multiple suffixes that mean something pertains to something else. These are: -as, -al, -ar, -ary. -ic, -ical, -ous, and -ile. Some words incorporate more than one suffix.
Examples:
- Clinical, surgical, conscious, versatile, necessary, sub-par, etc.
BANK ACCOUNT SUFFIX
What does Bank account Suffix mean?
Account numbers and card numbers are divided into sections. While the prefix denotes the bank issuing the card, the body is the account numbers, and the suffix is the account type.
The suffix is important because it lets the bank know which type of account is being used, and that way customers can’t access operations not approved for the type of account. The suffix is made up of two to three numbers.
Different numbers describe a different type of account. There are various types of accounts, and each has a unique number profile for a specific bank.
Examples:
- Cheque account – 00, Number 2 account – 02, Fixed account – 03, Savings account – 30, Credit card account – 40, Thrift club account – 50, Term deposit account – 81
Recommended for you:
How to Remember Rules of Grammar, Idioms and Vocabulary
Use of Modal Verbs in English Grammar
👉 Combining Forms
When you are learning the different types of prefixes, it is important to remember that not every word containing these combinations is a prefix. Sometimes words have ‘combining forms’, which look very similar to prefixes but work differently!
Let me explain….
As you know, a prefix is a letter or a group of letters that appears at the beginning of words, but it can also be removed from the base word, and the word would still be a word without it, even if the meaning changes.
For example, non- means ‘not’ or ‘without’, this is used in words such as ‘nonsense’. The word ‘sense‘ can be separated from the prefix and it would still be a word on its own, even if the meaning is different.
Combining forms are similar to prefixes, and are sometimes known as ‘chameleon prefixes’, because they act like them and appear at the beginning of words like them, BUT the combining form is intrinsic to the word, meaning it is a part of the word and cannot be removed.
They are called ‘chameleons’, because they change their spelling and physical form to suit the word they are attached to!
So, combining forms act as prefixes but are different, because the remaining letters cannot be separated to form an independent word.
Here are some examples of prefixes that are also ‘combining forms’:
| PREFIX | MEANING | EXAMPLE | COMBINING FORM | MEANING | EXAMPLE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| com-, con- | with, alongside | comprise, connote | com-, con- | with, jointly | companion, comrade, community |
| contra- | against | contraindicate | contra- | against | contraceptive, contradict |
| de- | opposite | devalue | de- | down, away | descend |
| ex- | former | ex-husband | ex- | out | exhort |
| a- | not, without | amoral | a-, an- | not, without | apathy, anaemic |
| in- | not | inconvenient | in- | into | inebriate, indulge |
| homo- | same | homograph, homophone | homo- | same | homogeneous |
| magn- | great | magnate | magn- | great | magnificent, magnanimous, magnitude, magnify |
| para- | beside | paragraph, paramedic | para- | beside | paradox |
| sub- | under | submarine | sub- | under | substitute |
| trans- | across | transnational, transparent | trans- | through, across | transmit, transcend |
| tri- | three | triangle, tripod | tri- | three | triceps, triathlon |
Recommended for you:
List of Words With 17 Silent Letters in English
Punctuation Marks – Quotation Marks – Question Mark
Prefix definition: an affix attached to the beginning of a word to modify its meaning.
Suffix definition: a particle attached to the end of a word to modify its meaning or change it into a different word class.
What is the Difference Between Prefixes and Suffixes?
In the English language, we often place prefixes and suffixes at the beginning and end, respectively, of a word in order to modify it.
The original word does have meaning in itself, but by adding a prefix or suffix to it, we change the word.

- Janet resubmitted her application after she was initially denied a loan.
Resubmitted includes the prefix re which means again.
What is a suffix? Suffixes are placed at the end of a word in order to alter its meaning or change the classification of the word.
- We work hard in order to ensure our children’s happiness.
Happiness includes the state of being suffix ness. By adding the suffix, we have changed our word from an adjective to a noun in order for it to fit grammatically in our sentence.

Prefix Examples:
- a-, an- = without; amoral, anemic
- ante- = before; antecedent
- co- = with; co-worker
- de- = off, remove; de-ice
- ex =out of, former; ex-boyfriend
- il = not; illegal
- inter = between; intergalactic
- post = after; postpone
- super = above; supersede
- un = not; unnatural
Let’s try using a prefix in a sentence.
- Craig was dissatisfied with the customer service he received at the store.
- Prefix = dis = negative
When to Hyphenate Prefixes

Proper nouns: when adding a prefix to a proper noun, you must add a hyphen:
- Not liking apple pie may be seen as un-American.
Same vowel: If the last letter of your prefix is the same as the first letter in the word, you need to add a hyphen:
- In order to be allowed re-entry to the amusement park, patrons must obtain a stamped ticket.
Special prefixes: Always use a hyphen when you use ex- and self-.
- Lisa was self-conscious about her body after having a baby.
- The ex-student body president trained the current officer on how to organize prom.
Clarification: Use a hyphen when a word may cause confusion or look odd in the sentence.
- The mother reminder the children to re-cover the sandbox after they were done playing.
We need the hyphen, so that readers don’t confuse re-cover with the word recover, which means to reinstate health or regain a lost possession.
What are Suffixes?

Suffix Examples:
- –al = having characteristics of; remedial, denial
- –ed = past-tense verbs; traveled, talked
- –en = made of, consisting of; wooden, golden
- –er, -est = comparative; stronger, strongest
- –tion, -ion = state of being, condition; completion, relation
- –ity = quality of; humility, enormity
- –less = without; hopeless, homeless
- –ly = characteristic of; brotherly, lovely
- –s, -es = more than one; apples, trenches
Let’s look at an example of a suffix used in a sentence:
- In government class, students will research the current election.
- Suffix = ion = act, process
When to Hyphenate Suffixes

Cumbersome words: an optional hyphen can be used when a word seems lengthy without one.
- community-wide
Exception words: -like, -type, -elect,
- scholarly-like
When last letter is same as first letter:
- graffiti-ism, past-tense
Summary
Define prefix: the definition of prefix is an element placed at the beginning of a word to alter or qualify its meaning.
Define suffix: the definition of suffix is a particle placed at the end of a word to alter its meaning or adjust its grammatical sense.
In summary,
- Prefixes and suffixes are added to words to change them.
- Prefixes are added to change the meaning of the root word.
- Suffixes are added so that the word will make grammatical sense in a sentence.
Here are a couple of final examples of how we use prefixes and suffixes.
- Many science fiction books include an intergalactic war.
- Prefix = inter = between
- The employee rushed to his car after work on Friday.
- Suffix = ed = past-tense verb
Contents
- 1 What is the Difference Between Prefixes and Suffixes?
- 2 What are Prefixes?
- 3 When to Hyphenate Prefixes
- 4 What are Suffixes?
- 5 When to Hyphenate Suffixes
- 6 Summary
Amazement, Quickly, Impossible, Intergalactic. What do all of these words have in common? The answer is that they all contain affixes. Read on to learn all about affixes in English, the different examples of affixes, and the affixation process.
Affixation Linguistics Definition
What is the definition of affixation? We see the meaning of affixation as a morphological process whereby a group of letters (the affix) is attached to a base or root word to form a new word. Sometimes the new word takes on a whole new meaning, and sometimes it simply gives us more grammatical information.
For example, adding the affix ‘-s’ to the end of the word ‘apple’ tells us there is more than one apple.
Morphological process — Changing or adding to a root word to create a more suitable word for the context.
Affixes are a type of bound morpheme — this means they cannot stand alone and must appear alongside a base word to get their meaning. Take a look at an example of affixes below:
On its own, the affix ‘-ing’ doesn’t really mean anything. However, placing it at the end of a base word, such as ‘walk’ to create the word ‘walking,’ lets us know that the action is progressive (ongoing).
Understanding the meaning and usage of affixes can help us ‘decipher’ the meaning of unknown words.
There are three types of affixes: prefixes, suffixes, and circumfixes. Let’s take a closer look at these now.

Types of Affixation
To begin, let’s look at the different types of affixes that we can add to a base word. The two main types of affixation are suffixes and prefixes, and the third, less common, are circumfixes. We have compiled some examples of affixation and their types for you to check out below!
Prefixes
Prefixes are affixes that go at the beginning of a base word. Prefixes are very common in the English language, and thousands of English words contain a prefix. Common English prefixes include in-, im-, un-, non-, and re-.
Prefixes are commonly used to make based words negative/positive (e.g., unhelpful) and to express relations of time (e.g., prehistoric), manner (e.g., underdeveloped), and place (e.g., extraterrestrial).
Here are some common English words with prefixes:
- impolite
- autobiography
- hyperactive
- irregular
- midnight
- outrun
- semicircle
A more complete list of all English prefixes can be found towards the end of this explanation!
Prefixes and Hyphens (-)
Unfortunately, there aren’t any set rules as to when you should use a hyphen (-) with a prefix; however, there are a few guidelines you can follow to help you decide when to use a hyphen.
- If the prefixed word can easily be confused with another existing word, e.g., re-pair and repair (to pair again and to fix something)
- If the prefix ends in a vowel and the base word begins with a vowel, e.g., anti-intellectual
- If the base word is a proper noun and should be capitalized, e.g., un-American
- When using dates and numbers, e.g., mid-century, pre-1940s
Suffixes
Whereas prefixes go at the beginning of a base word, suffixes go at the end. Common suffixes include -full, -less, -ed, -ing, -s, and -en.
When we add suffixes to base words, the affixation process is either derivational or inflectional. So, what exactly does that mean?
When the word’s meaning or the word class (e.g., noun, adjective, verb, etc.) completely changes, the process is derivational. For example, adding ‘-er’ to the end of the based word ‘teach’ changes the verb (teach) to a noun (teacher).
Derivational affixes are one the most common ways new words are formed in English!
Some examples of words with derivational suffixes include:
- laughable (changes the verb laugh to an adjective)
- joyous (changes the abstract noun joy to an adjective)
- quickly (changes the adjective quick to an adverb)

On the other hand, inflectional suffixes show a grammatical change within a word class — this means the word class always remains the same. For example, adding the suffix ‘-ed’ to the verb ‘talk’ to create the verb ‘talked’ shows us that the action happened in the past.
Some example words with inflectional suffixes include:
- walking (shows the progressive aspect)
- shoes (shows plurality)
- likes (shows 3rd person singular, e.g., he likes coffee)
- taller (a comparative adjective)
- tallest (a superlative adjective)
- eaten (shows the perfect aspect)
Circumfixes
In affixation, circumfixes are less common than prefixes and affixes and typically involve adding affixes to both the beginning and the end of a base word.
- enlighten
- unattainable
- incorrectly
- inappropriateness
Examples of Affixation
Here are several useful tables outlining examples of affixation, with some of English’s most common prefixes and suffixes:
Prefixes
| Prefix | Meaning | Examples |
| anti- | against or opposite | antibiotics, antiestablishment |
| de- | removal | de-iced, decaffeinated |
| dis- | negation or removal | disapprove, disloyal |
| hyper- | more than | hyperactive, hyperallergic |
| inter- | between | interracial, intergalactic |
| non- | absence or negation | nonessential, nonsense |
| post- | after a period of time | post-war |
| pre- | before a period of time | pre-war |
| re- | again | reapply, regrow, renew |
| semi- | half | semicircle, semi-funny |
Derivational Suffixes Forming Nouns
| Suffix | Original word | New word |
| -er | drive | driver |
| -cian | diet | dietician |
| -ness | happy | happiness |
| -ment | govern | government |
| -y | jealous | jealousy |
Derivational Suffixes Forming Adjectives
| Suffix | Original word | New word |
| -al | President | Presidential |
| -ary | exemplar | exemplary |
| -able | debate | debatable |
| -y | butter | buttery |
| -ful | resent | resentful |
Derivational Suffixes Forming Adverbs
| Suffix | Original word | New word |
| -ly | slow | slowly |
Derivational Suffixes Forming verbs
| Suffix | Original word | New word |
| -ize | apology | apologize |
| -ate | hyphen | hyphenate |
Rules for Affixation
There aren’t any rules for which words can go through the affixation process. Language is an ever-evolving and developing thing created by the people, and, as we previously mentioned, adding affixes is one of the most common ways new words enter the English dictionary.
However, there are few rules regarding the affixation process. Let’s take a look at some examples of affixation rules now.
The Affixation Process
What is the affixation process? When we add affixes to a base word, there are a few guidelines regarding spelling that should be followed. Most of these rules and examples of affixes apply to adding suffixes and making plurals (a type of suffix).
Suffixes
-
Double the final constant when it comes after and before a vowel, e.g., running, hopped, funny.
-
Drop the ‘e’ at the end of the base word if the suffix begins with a vowel, e.g., closable, using, adorable
-
Change a ‘y’ to an ‘i’ before adding the suffix if a consonant comes before the ‘y’, e.g., happy —> happiness.
-
Change ‘ie’ to ‘y’ when the suffix is ‘-ing,’ e.g., lie —> lying.
The most common way to show the plurality of nouns is to add the suffix ‘-s’; however, we add ‘-es’ when the base word ends in -s, -ss, -z, -ch, -sh, and -x, e.g., foxes, buses, lunches.
Remember that not all words will follow these rules — this is the English language, after all!
Why not have a go at affixation yourself? You never know; your new word could end up in The Oxford English Dictionary one day.
Affixation — Key Takeaways
- Affixation is a morphological process, meaning letters (affixes) are added to a base word to form a new word.
- Affixes are a type of bound morpheme — this means they cannot stand alone and must appear alongside a base word to get their meaning.
- The main types of affixes are prefixes, suffixes, and circumfixes.
- Prefixes go at the beginning of a base word, suffixes go at the end, and circumfixes go at the beginning and the end.
- Suffixes can be either derivational (meaning they create a new word class) or inflectional (meaning they express grammatical function).
What is word formation in grammar? and what are the methods of word formation? What are prefixes and suffixes?
Word formation definition:
Merriam Webster dictionary defines word formation as the formation of words in a language by the processes of derivation and composition.
We usually add a prefix or suffix to make new words. How are prefixes and suffixes alike? Both are a type of affix and both can change a word’s meaning.
Word formation prefixes and suffixes in English: Word formation examples lists
Word formation suffixes and prefixes (important word formation lists)
List of prefixes and suffixes
Generally, we use prefixes and suffixes to make new words. This post deals with words with prefixes and suffixes.
Word formation prefixes
Prefix meaning
A prefix is defined as a letter or group of letters that we add to the beginning of a word to form new words. Prefixes can be used to guess the meaning of words.
Below is a high-quality poster that can be printed out. The poster contains prefixes list, their meanings, and examples. Also, there is a link to an outstanding video on prefixes
Prefix examples
Look at the words tie, retie and untie. What do they have in common? ( prefix of tie)
They all include the word tie. So the word tie is the root word or base word. Adding a prefix changes the meaning of the root.
Adding a prefix changes the meaning of the root.
Here are lists of common prefixes and suffixes, along with their meanings and examples, that we use in word formation.
The word formation examples list below shows prefixes (word building prefixes)
What prefix means new? What is the prefix for new and recent?
The prefix meaning new and recent is neo-
The prefix of tie is un- (untie)
The prefix of look is over- (overlook which means fail to notice = misheed)
The prefix with present or potent is omni- (omnipresent, omnipotent)
The prefix of appeared is dis-. It means the opposite of. (disappeared is the opposite of appeared).
The prefix of able is un- or dis- (Examples: unable, disable)
The prefix of see is un- or for- (Examples: unsee, forsee)
The prefix of paid is under- (underpaid)
The prefix for potent is im- (impotent)
The prefix for tied is un- (untied)
The prefix of populated is un- (unpopulated which means uninhabited)
The prefix for the word trust is dis- , un- or mis- ( we can say distrust, untrust or mistrust. All of them mean lack of trust or confidence)
The prefix for accurate is in- (inaccurate which means not accurate or incorrect or wrong)
The prefix of use is mis- (misuse which means use in the wrong way or badly) (The prefix mis means wrongly or badly)
The prefix of necessary is un- (unnecessary)
The prefix that means recent is neo- (Words with prefix neo-)
The prefix for tie (tie prefix) is un- (untie)
The poster below shows over 10 examples of prefixes
The prefixes in-, im-, il-, ir-, un-, dis- have the same meaning. They mean ‘opposite of’ or ‘not’. When we add these prefixes to a word, they give its opposite.
Prefixes examples and prefixes rules and tips
-
im– is used before a word beginning with ‘m’ or ‘p’ {e.g. Immature, impatient…}
Adjectives beginning with c usually take the prefix in– {e.g. incorrect…}
-
il– is used before a word beginning with ‘l’ {e.g. illiterate, illegal…}
-
ir– is used before a word beginning with ‘r’ {e.g. irregular, irrelevant…} What does the prefix ir mean? The prefix ir means ‘opposite of’ or ‘not’
-
There are no rules for in– , un– and dis–
- We can also use the prefixes un– and dis– with verbs to form their opposites. (e.g. untie, unfasten, unpack, undo, unlock, undress, disagree, disappear, dislike, disqualify, disobey, disconnect etc.)
- dis meaning (with adjectives, adverbs and nouns): The prefix dis- in adjectives, adverbs and nouns mean ‘not’ or ‘opposite of’ (dishonest, disagreeably, disadvantage)
- in prefix meaning (meaning of the prefix in-) (in prefix): The prefix in means ‘not’ or ‘opposite of’ (in prefix words: incorrect (= not correct), infinite, inaccurate, inactive, inadequate, incapable, incoherent, incomplete, indirect…) (words with the prefix in)
- The prefix of able can be dis-, un– or en-. Here are some examples: disable (verb), unable (adjective), enable (verb).
Prefix video
-
Word formation suffixes
What is a suffix in English? /What does suffix mean? / Suffix meaning formation?
A suffix is the letters or syllables that we add to the end of a word to create new words. Using suffixes to form new words is a good way to enrich your vocabulary.
As we said before, we add prefix or suffix to make new words. Knowing the different suffixes can enable you to guess the meaning of new words and recognize whether the word is a verb, a noun, an adjective, an adverb, etc.
The suffix can change the spelling of the original word. For example, the -e ending of the verb ‘create’ and the adjective ‘wise’ is omitted when the suffix is added.
- Create → creation
- wise→ wisdom
Adding the suffixes change the spelling of the original word.
In the English language, not only do suffixes change the spelling of the original word but they also change the word’s part of speech. For example, the suffix ly changes adjectives to adverbs. (brave (adjective) → bravely (adverb), correct → correctly )
Here is a list of common suffixes (suffixes list/suffix examples)
Suffixes tips:
- The suffix less meaning (less definition): The suffix less means ‘without’.
- al suffix meaning: The suffix al in adjectives means ‘having the quality of’ or ‘connected with’. The suffix al in nouns means ‘the state or process of’
- able suffix meaning: The suffix able means ‘that can or must be’ or ‘having the quality of’
The table below displays more suffixes with meaning and examples (suffix words)
Very Important Related Posts:
How Are Prefixes and Suffixes Alike?
Important Prefixes and Suffixes Exercises with Answers pdf
Prefixes and Suffixes Exercises / Prefixes and suffixes worksheet (Word formation exercises)
In the exercises below, you should add prefixes and suffixes to the words in the sentences so that they are meaningful sentences.
A. Fill in the blanks with the correct prefix. Make any necessary changes
- He has never been to school. He is …………literate. He can’t write and read.
- Male students …………..number female students in rural areas.
- He is so ……..……honest that nobody trusts him.
- My father is ……..…..partial. He does not discriminate between his children.
- I’m sorry to …….…….pronounce your name.
- Children in some African countries are ………..fed. They suffer from hunger.
- China is an………..…populated country. It has over a billion people.
- It is ……….…responsible of some students not to prepare for their exams and resort to cheating.
- Big cities are usually ………………..crowded.
- It’s ………………moral to smoke in class and expose students to danger.
- Most workers are complaining that they are ………………paid.
B. Complete with the right suffixes. Make any necessary changes.
- Georgia is cap……………….of helping you with your problems. Why don’t you ask her to?
- Be care………………! A car is coming.
- The best treat………..……..for obesity is doing sport every day.
- Our factory has installed two video cameras for secure ………………reasons.
- An anonym………………person called me twice last night.
- The belief that things will improve is called optim……….., whereas the belief that things will get worse is called pessim……..
- The legs of these trousers are too long. Could you short…………..them for me, please?
- Don’t be pessimist……..…….. Everything will be all right.
- Could you simple ………..………..your instructions, please?
- Nobody can understand this sentence. It is meaning…………
- Criticize…………………is useful on condition that it is constructive.
- He does exercise every day so as to strength……………his muscles.
- The news of his best friend’s death sad……..….….him.
- I don’t see any similar…………….between the two presidents.
- She works very hard. She has the able…….………to succeed.
- For further inform………..….., contact me on this mobile number.
People who search for word formation, also search for prefixes and suffixes worksheets, prefixes and suffixes pdf, prefixes and suffixes examples, and prefixes and suffixes exercises.
Download prefixes and suffixes worksheet pdf here
Related Posts:
- Start online college today and earn an online degree
- The phrase check for me and other phrases
- Here is a list of words starting in ir (ir words)
- Words with au
- Words that end in i
What are the 10 examples of prefix?
| Prefix | Prefix meaning | Words with prefixes/ examples of prefixes/prefixes examples |
| en- | cause to be/make/put into | enrich, enlarge, encircle, enable, endanger… |
| re- | do again/back | rewrite, reread, resend, readmit, re-advertise, reaffirm… |
| pre- | before/earlier | prehistoric, preplan, pretest… |
| post- | after | postgraduate, post-war, post hoc, posthumous, postmodifier, postmortem… |
| non- | not/ not connected with | non-alcoholic, non-governmental, non-aligned, non-essential… |
| under- | too little/ not enough | undercooked, underpaid, undercharge, underdone, underfed… |
| mis- | wrongly/badly | misunderstand, misbehave, misapply, misdeed… |
| self- | by oneself | self-education, self-analysis, self-confidence, self-assured… |
| multi- | many / more than one | multinational, multimedia, multi-access, multicolored… |
| bi- | twice/ two/double | bilingual, biannual, bicameral, bicycle, biennial… |
| Neo– | Prefix meaning new/recent | neo-Georgian, neo-colonialism, neo-fascist, neoliberal, |
| Tri- | Prefix meaning three | Tricycle, triatomic, triacid, tri-band, tri-focused, tri-camera photography |
Words with Both Prefixes and Suffixes List
Here is a list of words with a prefix and suffix and a root.
- Unhelpful
- undoubtedly
- Unacceptable
- Uninteresting
- Unconsciousness
- Unsuccessful
- Unsuccessfully
- Impossibly
- Antidisestablishmentarianism
- Disrespectful
- Disrespectfully
- Distasteful
- Disconnected
- Disloyalty
- Ilogically
- Nonconformist
- Replacement
- Reappearance
- Immeasureable
Learn English online with Englishdotcom