Содержание
- POWER в Excel (формула, примеры) — Как использовать функцию POWER?
- СИЛА в Excel
- POWER Formula в Excel
- Как использовать функцию POWER в Excel?
- Пример № 1
- Пример № 2
- Пример № 3
- Функция POWER в VBA
- Что нужно помнить о функции POWER
- Рекомендуемые статьи
- POWER Function in Excel
- Power in Excel
- The Formula of POWER Function
- Explanation of POWER Function in Excel
- How to Use POWER Function in Excel
- POWER in Excel Example #1
- POWER in Excel Example #2
- POWER in Excel Example #3
- POWER in Excel Example #4
- Recommended Articles
POWER в Excel (формула, примеры) — Как использовать функцию POWER?
ВЛАСТЬ в Excel (Содержание)
- СИЛА в Excel
- POWER Formula в Excel
- Как использовать функцию POWER в Excel?
СИЛА в Excel
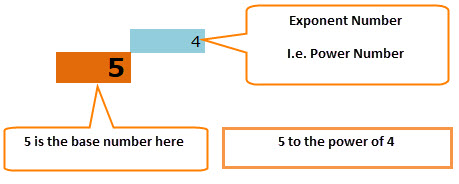
Я до сих пор помню дни, когда мой учитель математики почти каждый день бил меня за то, что я не помнил КВАДРАТНЫЙ КОРЕНЬ чисел. Я буквально плакал, когда наступил математический период. Есть много случаев, когда я занимался математикой только для того, чтобы избежать побоев со стороны моего учителя математики.
Хорошо, теперь мне не нужно запоминать все эти КВАДРАТНЫЕ КОРНИ, вместо этого я могу положиться на красивую функцию под названием POWER Function.
Функция POWER помогает поднять число в другое число раз до мощности.
Например: каково значение 5 на квадрат 3? Ответ 5 * 5 * 5 = 125 .
POWER Formula в Excel
Ниже приведена формула СИЛА:
Функция Power включает в себя два параметра, и оба являются обязательными аргументами.
Число: число, которое вам нужно для поднятия силы, т.е. базовое число любого действительного числа.
Мощность: сколько раз вам нужно поднять базовое число. Это показатель для поднятия базового числа.
Символ или оператор (оператор каретки) действует как показатель степени. Например: 6 2 = 36. Это не 6 умножается на 2, а 6 * 6 = 36. Шесть умножается на сам шесть дважды.
Простое уравнение 5 * 5 * 5 * 5 = 625
Как использовать функцию POWER в Excel?
Эта функция POWER очень проста в использовании. Давайте теперь посмотрим, как использовать функцию POWER с помощью нескольких примеров.
Вы можете скачать эту функцию POWER в шаблоне Excel здесь — функция POWER в шаблоне Excel
Пример № 1
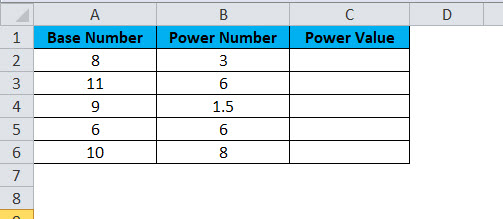
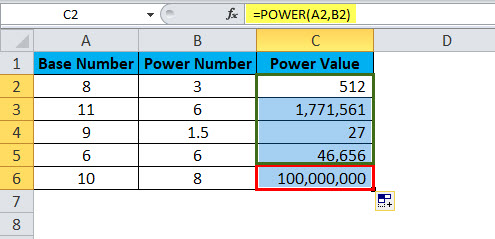
Предположим, у вас есть базовые числа из A2: A6 и степенное число (экспоненциальные числа) из B2: B6. Показать мощность значений в столбце A, используя числа питания в столбце B.
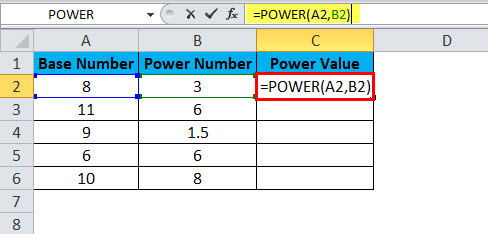
Применить формулу силы в ячейке C2
Перетащите формулу в другие ячейки.
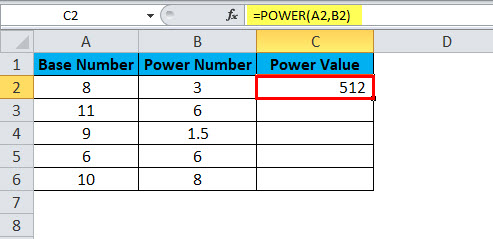
- Первое значение — это базовое число 8, возведенное в степень 3, то есть 8 куб. = 8 * 8 * 8 = 512.
Во-вторых, базовое число 11 повышается до степени 6, то есть 11 умножается в 6 раз на 11. = 11 * 11 * 11 * 11 * 11 * 11 = 17, 71 561. Точно так же все значения привели таким образом.
Пример № 2
Используйте те же данные из приведенного выше примера. Вместо использования функции POWER мы используем оператор каретки (^) для выполнения расчетов. Результаты будут такими же, хотя.
Примените формулу в ячейке H2
Перетащите формулу в другие ячейки.
Пример № 3
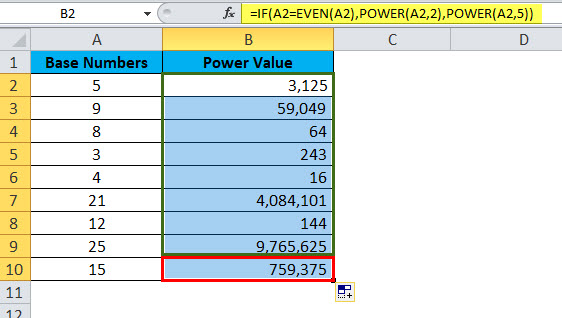
Использование функции POWER вместе с другими функциями. Из приведенных ниже данных увеличьте все четные числа на 2, если число не четное, то увеличьте значение на 5.
Здесь сначала нужно проверить, является ли число четным или нет. Если число найдено даже тогда, увеличьте мощность на 2, если не увеличьте мощность на 5.
Проблема такого типа может быть решена с помощью условия IF, чтобы проверить, является ли число четным или нет.
Примените формулу в ячейке B2.
Перетащите формулу в другие ячейки.
- Если условие IF проверяет, равно ли указанное число четному числу или нет. = ЕСЛИ (А2 = РАВ (А2),
- Если логика ПЧ истинна, функция POWER повысит мощность на 2. = POWER (A2, 2),
- Если логика ПЧ ложна, функция POWER увеличивает мощность на 5. = POWER (A2, 5),
Функция POWER в VBA
В VBA также мы можем использовать функцию POWER. Однако дело в том, что мы не видим многих из этих живых примеров в нашей повседневной жизни.
Шаг 1: Откройте редактор VBA (ALT + F11).
Шаг 2: Перейти, чтобы вставить и вставить модуль. Это мгновенно создаст новый модуль для написания нашего кода для функции POWER
Шаг 3: Скопируйте и вставьте приведенный ниже код в новый модуль.
Dim My_Result As String
My_Result = Application.WorksheetFunction.Power (6, 3)
Теперь ваше окно должно выглядеть так, как показано ниже.
Если вы запустите код, вы получите следующий результат.
Что нужно помнить о функции POWER
- Для лучшего понимания мы можем представить степенную функцию таким образом. POWER (X, Y) или POWER (X Y) оба одинаковы.
- Функция POWER применяется только для числовых значений. Что-нибудь кроме числовых значений, это вызовет ошибку как # ЗНАЧЕНИЕ! Если какой-либо из параметров содержит нечисловые значения, мы получим ошибку. На рисунке ниже показан пример ошибки.
Это покажет ошибку.
Рекомендуемые статьи
Это было руководство к функции питания. Здесь мы обсуждаем формулу POWER и как использовать функцию POWER вместе с практическими примерами и загружаемыми шаблонами Excel. Вы также можете просмотреть наши другие предлагаемые статьи —
- Как использовать функцию поиска в Excel?
- Функция Excel НЕ
- ТРАНСПОЗИРОВАТЬ функцию Excel
- LOOKUP в MS Excel
Источник
POWER Function in Excel
In mathematics, we had exponents, the power to a given base number. In Excel, we have a similar built-in function known as the POWER function, which is used to calculate the power of a given number or base. To use this function, we can use the keyword =POWER( in a cell and provide two arguments, one as the number and another as power.
For example, suppose the base number 4 is raised to the power number 3. i.e., 4 cube. =4*4*4 = 64.
Power in Excel
A POWER in Excel is a Math/Trigonometric function that computes and returns the result of a number raised to a power. The POWER Excel function takes two arguments: the base (any real number) and the exponent (power that signifies how many times the given number will be multiplied by itself). For example, 5 multiplied by a power of 2 is the same as 5 x5.
Table of contents
The Formula of POWER Function

Explanation of POWER Function in Excel
The POWER function in Excel takes both arguments as a numeric value. Hence, the arguments passed are of integer type where the number is the base number, and the POWER is the exponent. Both arguments are required and are not optional.


We can use the POWER function in Excel in many ways, like for mathematical operations. For example, we can use the POWER function equation to compute the relational algebraic functions.
How to Use POWER Function in Excel
The Excel POWER function is very simple and easy to use. Let us understand the working of POWER in Excel by some examples.
POWER in Excel Example #1
We have a POWER function equation y=x^n (x to the power n), where y is dependent on the value of x, and n is the exponent. We also want to draw the graph of this f(x, y) function for given values of x and n=2. For example, the values of x are:
So, in this case, since the value of y depends upon the nth power of x, we will calculate the value of Y using the POWER function in Excel.
- 1 st value of y will be 2^2 (=POWER(2,2)
- 2 nd value of y will be 4^2 (=POWER(4,2)
- ……………………………………………………………
- ……………………………………………………………
- 10 th value of y will be 10^2 (=POWER(10,2)
Now, selecting the values of x and y from range B4:K5, choose the graph (in this example, we have chosen the scatter graph with smooth lines) from the “Insert” tab.
So, we get a linear, exponential graph for the given POWER function equation.
POWER in Excel Example #2
In algebra, we have the quadratic POWER function equation, represented as ax2+bx+c=0, where x is unknown, and a, b and c are the coefficients. The solution of this POWER function equation gives the roots of the equation, which are the values of x.
The roots of the quadratic POWER function equation are computed by following mathematical formula:
- x = (-b+ (b 2 -4ac) 1/2 )/2a
- x = (-b- (b 2 -4ac) 1/2 )/2a
b2-4ac is called discriminant and describes a quadratic POWER function equation’s number of roots.
Now, we have a list of quadratic POWER function equations given in column A. But, first, we need to find the roots of the equations.
^ is the exponential operator used to represent the power (exponent). For example, X2 is the same as x^2.
We have five quadratic POWER function equations, and we will solve them using the formula with the help of the POWER function in Excel to find the roots.
In the first POWER function equation, a=4, b=56, and c = -96. If we mathematically solve them using the above formula, we have the roots -15.5 and 1.5.
To implement this in Excel formula, we will use the POWER function in Excel and the formula will be:
- =((-56+POWER(POWER(56,2)-(4*4*(-93)),1/2)))/(2*4) will give the first root and
- =((-56-POWER(POWER(56,2)-(4*4*(-93)),1/2)))/(2*4) will give the second root of the equation
So, the complete formula will be,
=”Roots of equations are”&” “&((-56+POWER(POWER(56,2)-(4*4*(-93)),1/2)))/(2*4)&” , “&((-56-POWER(POWER(56,2)-(4*4*(-93)),1/2)))/(2*4)
The formulas are concatenated with the string “Roots of equation are.”
Using the same formula for other POWER function equations, we have:
Output:
POWER in Excel Example #3
So, we can use the POWER function in Excel for different mathematical calculations.
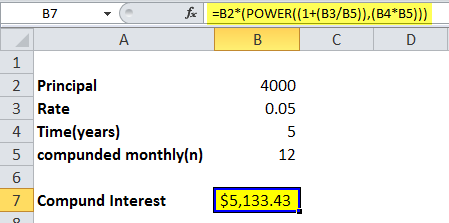
Amount = Principal (1 + r/n) nt
- Where r is the interest rate, n is the number of times interest is compounded per year, and t is the time.
- If an amount of $4,000 is deposited into an account (saving) at an interest rate of 5% annually, compounded monthly, the value of the investment after 5 years can be calculated using the above compound interest formula.
- When, Principal = $4000, rate = 5/100 that is 0.05, n =12 (compounded monthly), time =5 years.
We have the formula using the compound interest formula and implementing it into the Excel formula using the POWER function.
=B2*(POWER((1+(B3/B5)),(B4*B5)))
So, the investment balance after 5 years is $5.133.43.
POWER in Excel Example #4
According to Newton’s gravitation law, two bodies at a distance of r from their center of gravity attract each other in the universe according to a gravitational POWER Excel formula.
When F is the magnitude of the gravitational force, G is called the gravitational constant, M is the mass of the first body, m is the mass of the second body, and r is the distance between the bodies from their center of gravity.
Let us calculate the magnitude of gravitational force by which the sun pulls the earth.
- The mass of the sun is 1.98*10^30 kg.
- The mass of the earth is 5.97*10^24 kg.
- The distance between the sun and the earth is 1.496 x 10^11 meters.
- Gravitational constant value is 6.67*10^-11 m3kg-1s-2.
In Excel, if we want to calculate the gravitational force, we will again be using the POWER in Excel that can operate over big numeric values.
- So, we can convert the scientific notation values into the POWER Excel formula using the POWER in Excel.
- 1.98*10^30 will be represented as 1.98*Power(10,30), similarly to other values.
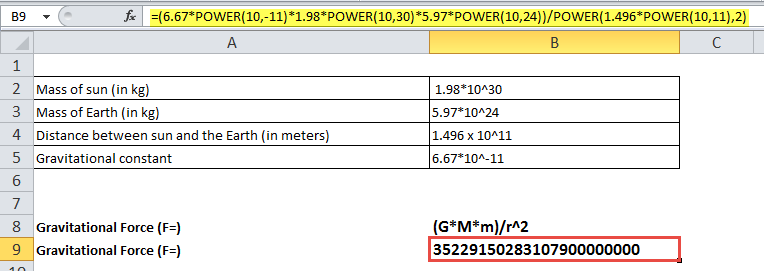
- So, the POWER Excel formula to calculate the force will be: = (6.67*POWER(10,-11)*1.98*POWER(10,30)*5.97*POWER(10,24))/POWER(1.496*POWER(10,11),2)
Output:
So, the sun pulls the earth with a force of magnitude 35229150283107900000000 Newton.
Recommended Articles
This article is a guide to the POWER Function in Excel. Here, we discuss the POWER formula in Excel and how to use the POWER Excel function, along with Excel examples and downloadable Excel templates. You may also look at these useful functions in Excel: –
Источник
Excel for Microsoft 365 Excel for Microsoft 365 for Mac Excel for the web Excel 2021 Excel 2021 for Mac Excel 2019 Excel 2019 for Mac Excel 2016 Excel 2016 for Mac Excel 2013 Excel 2010 Excel 2007 Excel for Mac 2011 Excel Starter 2010 More…Less
Let’s say you want to calculate an extremely small tolerance level for a machined part or the vast distance between two galaxies. To raise a number to a power, use the POWER function.
Description
Returns the result of a number raised to a power.
Syntax
POWER(number, power)
The POWER function syntax has the following arguments:
-
Number Required. The base number. It can be any real number.
-
Power Required. The exponent to which the base number is raised.
Remark
The «^» operator can be used instead of POWER to indicate to what power the base number is to be raised, such as in 5^2.
Example
Copy the example data in the following table, and paste it in cell A1 of a new Excel worksheet. For formulas to show results, select them, press F2, and then press Enter. If you need to, you can adjust the column widths to see all the data.
|
Formula |
Description |
R |
|
=POWER(5,2) |
5 squared. |
25 |
|
=POWER(98.6,3.2) |
98.6 raised to the power of 3.2. |
2401077.222 |
|
=POWER(4,5/4) |
4 raised to the power of 5/4. |
5.656854249 |
Need more help?
Want more options?
Explore subscription benefits, browse training courses, learn how to secure your device, and more.
Communities help you ask and answer questions, give feedback, and hear from experts with rich knowledge.
In mathematics, we had exponents, the power to a given base number. In Excel, we have a similar built-in function known as the POWER function, which is used to calculate the power of a given number or base. To use this function, we can use the keyword =POWER( in a cell and provide two arguments, one as the number and another as power.
For example, suppose the base number 4 is raised to the power number 3. i.e., 4 cube. =4*4*4 = 64.
A POWER in Excel is a Math/Trigonometric function that computes and returns the result of a number raised to a power. The POWER Excel function takes two arguments: the base (any real number) and the exponent (power that signifies how many times the given number will be multiplied by itself). For example, 5 multiplied by a power of 2 is the same as 5 x5.
Table of contents
- Power in Excel
- Formula of POWER Function
- Explanation of POWER Function in Excel
- How to Use POWER Function in Excel
- POWER in Excel Example #1
- POWER in Excel Example #2
- POWER in Excel Example #3
- POWER in Excel Example #4
- Recommended Articles
The Formula of POWER Function

Explanation of POWER Function in Excel
The POWER function in Excel takes both arguments as a numeric value. Hence, the arguments passed are of integer type where the number is the base number, and the POWER is the exponent. Both arguments are required and are not optional.
We can use the POWER function in Excel in many ways, like for mathematical operations. For example, we can use the POWER function equation to compute the relational algebraic functions.
How to Use POWER Function in Excel
The Excel POWER function is very simple and easy to use. Let us understand the working of POWER in Excel by some examples.
You can download this POWER Function Excel Template here – POWER Function Excel Template
POWER in Excel Example #1
We have a POWER function equation y=x^n (x to the power n), where y is dependent on the value of x, and n is the exponent. We also want to draw the graph of this f(x, y) function for given values of x and n=2. For example, the values of x are:
So, in this case, since the value of y depends upon the nth power of x, we will calculate the value of Y using the POWER function in Excel.
- 1st value of y will be 2^2 (=POWER(2,2)
- 2nd value of y will be 4^2 (=POWER(4,2)
- ……………………………………………………………
- ……………………………………………………………
- 10th value of y will be 10^2 (=POWER(10,2)
Now, selecting the values of x and y from range B4:K5, choose the graph (in this example, we have chosen the scatter graph with smooth lines) from the “Insert” tab.
So, we get a linear, exponential graph for the given POWER function equation.
POWER in Excel Example #2
In algebra, we have the quadratic POWER function equation, represented as ax2+bx+c=0, where x is unknown, and a, b and c are the coefficients. The solution of this POWER function equation gives the roots of the equation, which are the values of x.
The roots of the quadratic POWER function equation are computed by following mathematical formula:
- x = (-b+ (b2-4ac)1/2)/2a
- x = (-b- (b2-4ac)1/2)/2a
b2-4ac is called discriminant and describes a quadratic POWER function equation’s number of roots.
Now, we have a list of quadratic POWER function equations given in column A. But, first, we need to find the roots of the equations.
^ is the exponential operator used to represent the power (exponent). For example, X2 is the same as x^2.
We have five quadratic POWER function equations, and we will solve them using the formula with the help of the POWER function in Excel to find the roots.
In the first POWER function equation, a=4, b=56, and c = -96. If we mathematically solve them using the above formula, we have the roots -15.5 and 1.5.
To implement this in Excel formula, we will use the POWER function in Excel and the formula will be:
- =((-56+POWER(POWER(56,2)-(4*4*(-93)),1/2)))/(2*4) will give the first root and
- =((-56-POWER(POWER(56,2)-(4*4*(-93)),1/2)))/(2*4) will give the second root of the equation
So, the complete formula will be,
=”Roots of equations are”&” “&((-56+POWER(POWER(56,2)-(4*4*(-93)),1/2)))/(2*4)&” , “&((-56-POWER(POWER(56,2)-(4*4*(-93)),1/2)))/(2*4)
The formulas are concatenated with the string “Roots of equation are.”
Using the same formula for other POWER function equations, we have:
Output:
POWER in Excel Example #3
So, we can use the POWER function in Excel for different mathematical calculations.
Suppose we have to find out the compound interestCompound interest is the interest charged on the sum of the principal amount and the total interest amassed on it so far. It plays a crucial role in generating higher rewards from an investment.read more for which the formula is:
Amount = Principal (1 + r/n)nt
- Where r is the interest rate, n is the number of times interest is compounded per year, and t is the time.
- If an amount of $4,000 is deposited into an account (saving) at an interest rate of 5% annually, compounded monthly, the value of the investment after 5 years can be calculated using the above compound interest formula.
- When, Principal = $4000, rate = 5/100 that is 0.05, n =12 (compounded monthly), time =5 years.
We have the formula using the compound interest formula and implementing it into the Excel formula using the POWER function.
=B2*(POWER((1+(B3/B5)),(B4*B5)))
So, the investment balance after 5 years is $5.133.43.
POWER in Excel Example #4
According to Newton’s gravitation law, two bodies at a distance of r from their center of gravity attract each other in the universe according to a gravitational POWER Excel formula.
F = (G*M*m)/r2
When F is the magnitude of the gravitational force, G is called the gravitational constant, M is the mass of the first body, m is the mass of the second body, and r is the distance between the bodies from their center of gravity.
Let us calculate the magnitude of gravitational force by which the sun pulls the earth.
- The mass of the sun is 1.98*10^30 kg.
- The mass of the earth is 5.97*10^24 kg.
- The distance between the sun and the earth is 1.496 x 10^11 meters.
- Gravitational constant value is 6.67*10^-11 m3kg-1s-2.
In Excel, if we want to calculate the gravitational force, we will again be using the POWER in Excel that can operate over big numeric values.
- So, we can convert the scientific notation values into the POWER Excel formula using the POWER in Excel.
- 1.98*10^30 will be represented as 1.98*Power(10,30), similarly to other values.
- So, the POWER Excel formula to calculate the force will be: = (6.67*POWER(10,-11)*1.98*POWER(10,30)*5.97*POWER(10,24))/POWER(1.496*POWER(10,11),2)
Since the value obtained as force is a big number Excel expressed it scientific notationIn Excel, scientific notation is a specific style of writing numbers in scientific and exponential forms. Scientific notation compactly helps display values, allowing us to compare and use the same in calculations.read more. To change it into a fraction, change the format to the fraction.
Output:
So, the sun pulls the earth with a force of magnitude 35229150283107900000000 Newton.
Recommended Articles
This article is a guide to the POWER Function in Excel. Here, we discuss the POWER formula in Excel and how to use the POWER Excel function, along with Excel examples and downloadable Excel templates. You may also look at these useful functions in Excel: –
- Excel vs. AccessExcel and Access are two of Microsoft’s most powerful tools for data analysis and report generation, but there are some significant differences between them. Excel is an older product of Microsoft, whereas Access is the most advanced and complex product of Microsoft. Excel is very easy to create dashboards and formulas, whereas Access is very easy for databases and connections.read more
- GetPivotData in Excel
- NOT Function
POWER in Excel (Table of Contents)
- POWER in Excel
- POWER Formula in Excel
- How to Use POWER Function in Excel?
POWER in Excel
I still remember the days when my maths teacher beat me almost every day for not remembering the SQUARE ROOT of numbers. I literally cried when maths period is on the way. There are many instances where I bunked the math class just to get away from those beatings from my maths teacher.
Ok, now I need not to remember all those SQUARE ROOTS; instead, I can rely on a beautiful function called the POWER Function.
POWER function helps in raising the number to another number of times to the power.
For example: What is the value of 5 to the square of 3? The answer is 5*5*5 = 125.
POWER Formula in Excel
Below is the POWER Formula:
The Power Function includes two parameters, and both are required arguments.
- Number: The number you need to raise the power, i.e. the base number of any real number.
- Power: The number of times you need to raise the base number. It is the exponent to raise the base number.
The symbol or operator ^ (caret operator) acts as an exponent. For example: 6^2 = 36. This is not 6 is multiplied by 2 rather 6 * 6 = 36. Six is multiplied by the six itself twice.
The simple equation is 5 * 5 * 5 * 5 = 625
How to Use the POWER Function in Excel?
This POWER function is very simple easy to use. Let us now see how to use the POWER Function with the help of some examples.
You can download this POWER Function in Excel Template here – POWER Function in Excel Template
Example #1
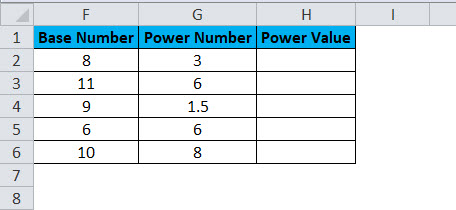
Assume you have base numbers from A2:A6 and the power number (exponential numbers) from B2:B6. Show the power of values in column A by using power numbers in column B.
Apply Power formula in the cell C2
The answer will be:
Drag and drop the formula to other cells.
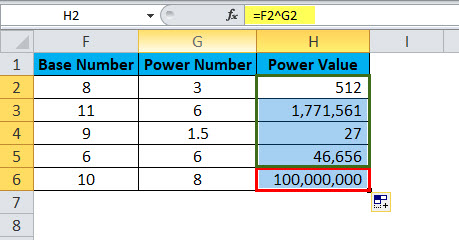
- The first value is base number 8 is raised to the power number 3. i.e. 8 cube. =8*8*8 = 512.
Secondly, base number 11 is raised to the power number 6, i.e. 11 is multiplied 6 times to the 11 itself. =11 * 11* 11* 11* 11* 11 = 17, 71,561. Similarly, all the values have resulted in that way.
Example #2
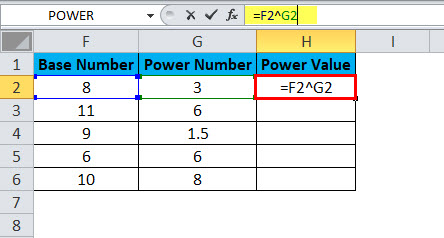
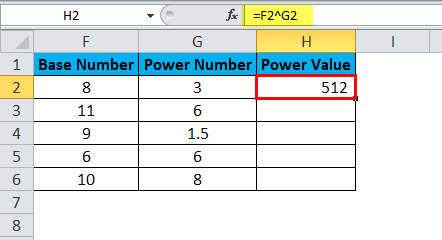
Use the same data from the above example. Instead of using the POWER Function, we use the caret operator (^) to do the calculation. The results will be the same, though.
Apply formula in the cell H2
The answer will be:
Drag and drop the formula to other cells.
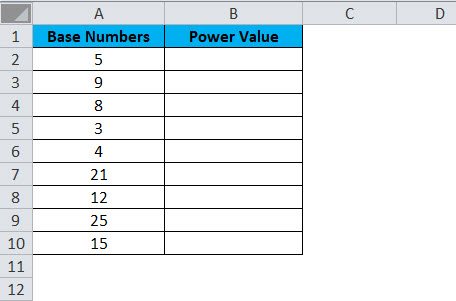
Example #3
Using POWER Function along with other functions. From the below data, raise all the even numbers power by 2; if the number is not even, then raise the power by 5.
Here, first, we need to test whether the number is even or not. If the number found, raise the power by 2; if not, raise the power by 5.
This type of problem can be addressed by using the IF condition to test whether the number is even or not.
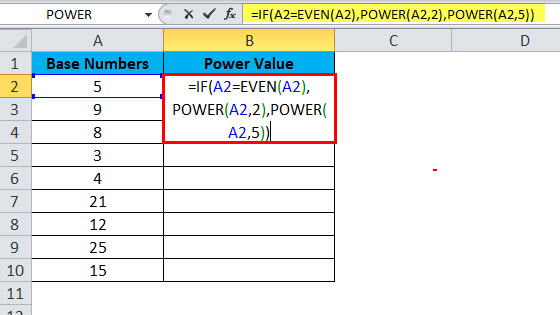
Apply formula in cell B2.
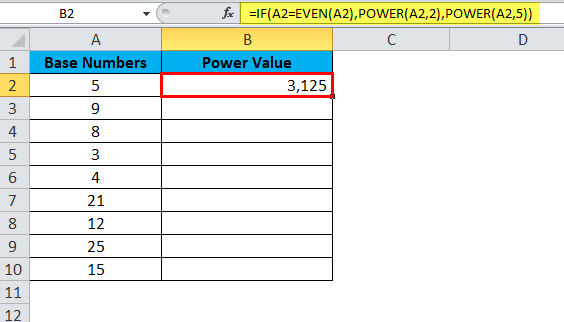
The answer will be:
Drag and drop the formula to other cells.
- IF condition tests whether the supplied number is equal to an even number or not. =IF(A2=EVEN(A2),
- If the IF logic is true then the POWER function will raise the power by 2. =POWER(A2,2),
- If the IF logic is false, then the POWER function will raise the power by 5. =POWER(A2,5),
POWER Function in VBA
In VBA, also we can use the POWER function. However, the thing is, we do not get to see many of these live examples in our day-to-day life.
Step 1: Open your VBA editor (ALT + F11).
Step 2: Go to insert and insert Module. This would instantly create a new module to write our code for the POWER function.
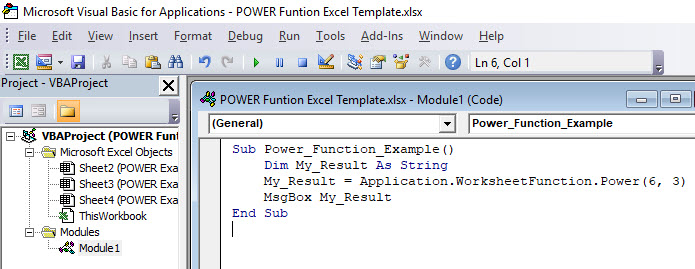
Step 3: Copy and paste the below code inside the new module.
Sub Power_Function_Example ()
Dim My_Result As String
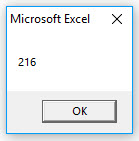
My_Result = Application.WorksheetFunction.Power(6, 3)
MsgBox My_Result
End Sub
Now your window should look like the one below one.
If you run the code, you will get the below result.
Things to Remember about POWER Function
- For a better understanding, we can represent the power function in this way. POWER(X, Y) or POWER(X^Y) both are the same only.
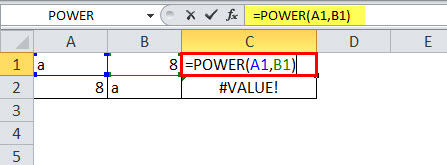
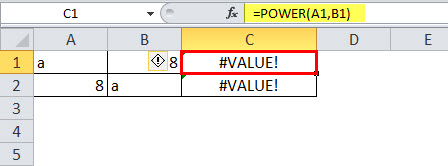
- The POWER function is applied only for numerical values. Anything other than numerical values, it will throw the error as #VALUE! If any one of the parameters contains non-numerical values, we will get the error. The below image shows an example of the error.
It will show an error.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to POWER Function. Here we discuss the POWER Formula and how to use the POWER Function along with practical examples and downloadable excel templates. You can also go through our other suggested articles –
- How to Use FIND Function in Excel?
- Excel NOT Function
- TRANSPOSE Excel Function
- LOOKUP in MS Excel
This Excel tutorial explains how to use the Excel POWER function with syntax and examples.
Description
The Microsoft Excel POWER function returns the result of a number raised to a given power.
The POWER function is a built-in function in Excel that is categorized as a Math/Trig Function. It can be used as a worksheet function (WS) in Excel. As a worksheet function, the POWER function can be entered as part of a formula in a cell of a worksheet.
Syntax
The syntax for the POWER function in Microsoft Excel is:
POWER( number, power )
Parameters or Arguments
- number
- It is the base number.
- power
- It is the exponent used to raise the base number to.
Returns
The POWER function returns a numeric value.
Applies To
- Excel for Office 365, Excel 2019, Excel 2016, Excel 2013, Excel 2011 for Mac, Excel 2010, Excel 2007, Excel 2003, Excel XP, Excel 2000
Type of Function
- Worksheet function (WS)
Example (as Worksheet Function)
Let’s look at some Excel POWER function examples and explore how to use the POWER function as a worksheet function in Microsoft Excel:
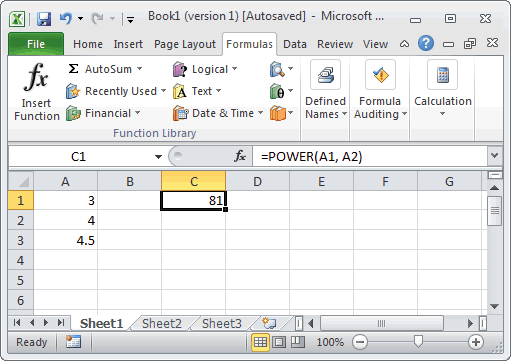
Based on the Excel spreadsheet above, the following POWER examples would return:
=POWER(A1, A2) Result: 81 =POWER(A1, A3) Result: 140.2961154 =POWER(A2, 2) Result: 16