Поиск номера последней заполненной строки с помощью кода VBA Excel для таблиц, расположенных как в верхнем левом углу, так и в любом месте рабочего листа.
Номер последней заполненной строки в таблице Excel обычно используется в коде VBA для определения следующей за ней первой пустой строки для добавления новой записи. А также для задания интервала для поиска и обработки информации с помощью цикла For… Next (указание границ обрабатываемого диапазона).
Переменную, которой присваивается номер последней строки, следует объявлять как Long или Variant, например: Dim PosStr As Long. В современных версиях Excel количество строк на рабочем листе превышает максимальное значение типа данных Integer.
Таблица в верхнем левом углу
В первую очередь рассмотрим все доступные варианты поиска номера последней заполненной строки для таблиц, расположенных в верхнем левом углу рабочего листа. Такие таблицы обычно представляют собой простые базы данных в Excel, или, как их еще называют, наборы записей.
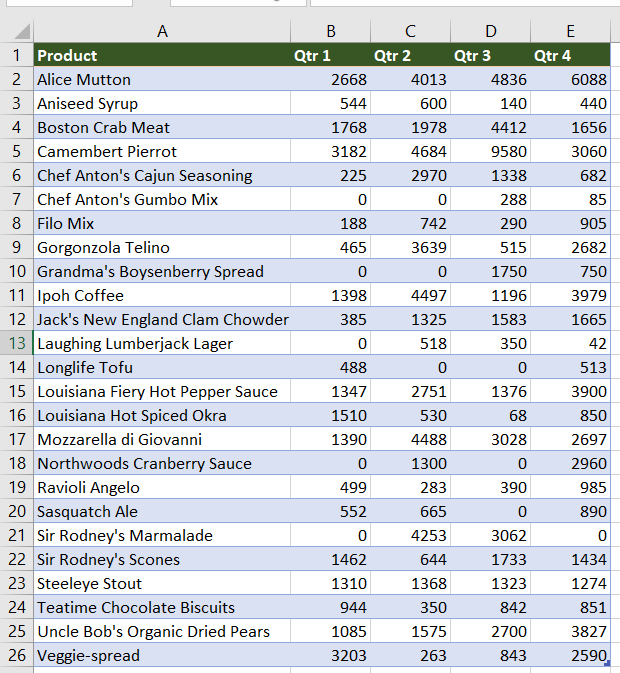
Пример таблицы с набором данных в Excel
Вариант 1
Основная формула для поиска последней строки в такой таблице, не требующая соблюдения каких-либо условий:
PosStr = Cells(1, 1).CurrentRegion.Rows.Count
Вариант 2
Ниже таблицы не должно быть никаких записей, в том числе ранее удаленных:
PosStr = ActiveSheet.UsedRange.Rows.Count
Вариант 3
В первом столбце таблицы не должно быть пропусков, а также в таблице должно быть не менее двух заполненных строк, включая строку заголовков:
PosStr = Cells(1, 1).End(xlDown).Row
Вариант 4
В первой колонке рабочего листа внутри таблицы не должно быть пропусков, а ниже таблицы в первой колонке не должно быть других заполненных ячеек:
PosStr = WorksheetFunction.CountA(Range("A:A"))
Вариант 5
Ниже таблицы не должно быть никаких записей:
PosStr = Cells.SpecialCells(xlLastCell).Row
Последняя строка любой таблицы
Последнюю заполненную строку для любой таблицы будем искать, отталкиваясь от ее верхней левой ячейки: Cells(a, b).
Вариант 1
Основная формула для поиска последней строки в любой таблице, не требующая соблюдения каких-либо условий:
PosStr = Cells(a, b).CurrentRegion.Cells(Cells(a, b).CurrentRegion.Cells.Count).Row
Вариант 2
Дополнительная формула с условием, что в первом столбце таблицы нет пустых ячеек:
PosStr = Cells(a, b).End(xlDown).Row
Если у вас на рабочем листе Excel есть записи вне таблиц, следите за тем, чтобы таблицы были окружены пустыми ячейками или пустыми ячейками и границами листа. Тогда не будет случайно внесенных заметок, примыкающих к таблицам, которые могут отрицательно повлиять на точность вычисления номера последней строки из кода VBA.
We use Range.SpecialCells() method in the below VBA Code to find and return details of last used row, column, and cell in a worksheet.
Sample Data:
Sample Data
Syntax:
expression.SpecialCells (Type, Value)
Eg: To return the last used cell address in an activesheet. ActiveSheet.Range(“A1”).SpecialCells(xlCellTypeLastCell).Address
VBA Code:
Declaring Variables:
| Variable | Data Type | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| LastRow | Long | Find and store last used row |
| LastCol | Long | store last used column |
| LastCell | String | store last used cell address |
'Variable Declaration Dim LastRow As Long, LastCol As Long, LastCell As String
Use SpecialCells function to find last used row/column/cell
'Find Last Used Row
LastRow = ActiveSheet.Range("A1").SpecialCells(xlCellTypeLastCell).Row
'Find Last Used Column
LastCol = ActiveSheet.Range("A1").SpecialCells(xlCellTypeLastCell).Column
'Find Last Used Cell
LastCell = ActiveSheet.Range("A1").SpecialCells(xlCellTypeLastCell).Address
Concatenate all three variables (LastRow/LastCol/LastCell), add a new line between variables use Chr(10). Show the final output in an Excel Message box.
'Display the last used row/column/cell MsgBox "Last Used Row : " & LastRow & Chr(10) & "Last Used Column : " & LastCol & Chr(10) & "Last Used Cell : " & LastCell
Implementation:
Follow the below steps to find the Last Used Row and Last Used Column in Excel VBA
Step 1: Add a shape (Find Last Row/Column/Cell) on your worksheet.
Step 2: Right-click on “Find Last Row/Column/Cell” and “Assign Macro..”
Step 3: Select “findLastUsedCell”, you can see a list of macros if available in your workbook
Step 4: Save your excel file as “Excel Macro-Enabled Workbook” *.xlsm
Step 5: Click “Find Last Row/Column/Cell” to execute the VBA code. Code will popup below output for the above given example (Output).
Output:
How can I determine the last row in an Excel sheet, including some blank lines in the middle?
With this function:
Function ultimaFilaBlanco(col As String) As Long
Dim lastRow As Long
With ActiveSheet
lastRow = ActiveSheet.Cells(ActiveSheet.Rows.Count, col).End(xlUp).row
End With
ultimaFilaBlanco = lastRow
End Function
And this data:
Row 1 : Value
Row 2 : Value
Row 3 : Value
Row 4 : Value
Row 5 : Value
Row 6 : White
Row 7 : Value
Row 8 : Value
Row 9 : Value
Row 10 : White
Row 11 : White
Row 12 : White
Row 13 : Value
Row 14 : White
The function returns 5, and I need 13. Any idea how to do it?
Paolo Stefan
10.1k5 gold badges48 silver badges64 bronze badges
asked Dec 3, 2012 at 15:49
4
The best way to get number of last row used is:
ActiveSheet.UsedRange.Rows.Count for the current sheet.
Worksheets("Sheet name").UsedRange.Rows.Count for a specific sheet.
To get number of the last column used:
ActiveSheet.UsedRange.Columns.Count for the current sheet.
Worksheets("Sheet name").UsedRange.Columns.Count for a specific sheet.
I hope this helps.
Abdo
answered Jun 12, 2013 at 14:19
3
ActiveSheet.UsedRange.Rows.Count + ActiveSheet.UsedRange.Rows(1).Row -1
Short. Safe. Fast. Will return the last non-empty row even if there are blank lines on top of the sheet, or anywhere else. Works also for an empty sheet (Excel reports 1 used row on an empty sheet so the expression will be 1). Tested and working on Excel 2002 and Excel 2010.
answered Dec 23, 2013 at 14:30
3
I use the following:
lastrow = ActiveSheet.Columns("A").Cells.Find("*", SearchOrder:=xlByRows, LookIn:=xlValues, SearchDirection:=xlPrevious).Row
It’ll find the last row in a specific column. If you want the last used row for any column then:
lastrow = ActiveSheet.Cells.Find("*", SearchOrder:=xlByRows, LookIn:=xlValues, SearchDirection:=xlPrevious).Row
answered Dec 3, 2012 at 17:24
Sid HollandSid Holland
2,8713 gold badges29 silver badges43 bronze badges
1
You’re really close. Try using a large row number with End(xlUp)
Function ultimaFilaBlanco(col As String) As Long
Dim lastRow As Long
With ActiveSheet
lastRow = ActiveSheet.Cells(1048576, col).End(xlUp).row
End With
ultimaFilaBlanco = lastRow
End Function
answered Dec 3, 2012 at 16:18
fbonettifbonetti
6,5823 gold badges33 silver badges32 bronze badges
2
LastRow = ActiveSheet.UsedRange.Rows.Count
CallumDA
12k6 gold badges30 silver badges52 bronze badges
answered Dec 3, 2012 at 16:19
2
The Problem is the «as string» in your function. Replace it with «as double» or «as long» to make it work. This way it even works if the last row is bigger than the «large number» proposed in the accepted answer.
So this should work
Function ultimaFilaBlanco(col As double) As Long
Dim lastRow As Long
With ActiveSheet
lastRow = ActiveSheet.Cells(ActiveSheet.Rows.Count, col).End(xlUp).row
End With
ultimaFilaBlanco = lastRow
End Function
answered Jun 14, 2013 at 12:03
user1965813user1965813
6715 silver badges16 bronze badges
If sheet contains unused area on the top, UsedRange.Rows.Count is not the maximum row.
This is the correct max row number.
maxrow = Sheets("..name..").UsedRange.Rows(Sheets("..name..").UsedRange.Rows.Count).Row
answered Jun 21, 2018 at 5:26
0
Well apart from all mentioned ones, there are several other ways to find the last row or column in a worksheet or specified range.
Function FindingLastRow(col As String) As Long
'PURPOSE: Various ways to find the last row in a column or a range
'ASSUMPTION: col is passed as column header name in string data type i.e. "B", "AZ" etc.
Dim wks As Worksheet
Dim lstRow As Long
Set wks = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Sheet1") 'Please change the sheet name
'Set wks = ActiveSheet 'or for your problem uncomment this line
'Method #1: By Finding Last used cell in the worksheet
lstRow = wks.Range("A1").SpecialCells(xlCellTypeLastCell).Row
'Method #2: Using Table Range
lstRow = wks.ListObjects("Table1").Range.Rows.Count
'Method #3 : Manual way of selecting last Row : Ctrl + Shift + End
lstRow = wks.Cells(wks.Rows.Count, col).End(xlUp).Row
'Method #4: By using UsedRange
wks.UsedRange 'Refresh UsedRange
lstRow = wks.UsedRange.Rows(wks.UsedRange.Rows.Count).Row
'Method #5: Using Named Range
lstRow = wks.Range("MyNamedRange").Rows.Count
'Method #6: Ctrl + Shift + Down (Range should be the first cell in data set)
lstRow = wks.Range("A1").CurrentRegion.Rows.Count
'Method #7: Using Range.Find method
lstRow = wks.Column(col).Cells.Find("*", SearchOrder:=xlByRows, LookIn:=xlValues, SearchDirection:=xlPrevious).Row
FindingLastRow = lstRow
End Function
Note: Please use only one of the above method as it justifies your problem statement.
Please pay attention to the fact that Find method does not see cell formatting but only data, hence look for xlCellTypeLastCell if only data is important and not formatting. Also, merged cells (which must be avoided) might give you unexpected results as it will give you the row number of the first cell and not the last cell in the merged cells.
answered Aug 5, 2017 at 17:23
jainashishjainashish
4,4425 gold badges38 silver badges48 bronze badges
1
ActiveSheet.UsedRange.Rows(ActiveSheet.UsedRange.Rows.count).row
ActiveSheet can be replaced with WorkSheets(1) or WorkSheets("name here")
answered Jan 29, 2018 at 21:48
18C18C
1,95410 silver badges16 bronze badges
here is my code to find the next empty row for example in first row ‘A’.
To use it for any other row just change cells(i,2 or 3 or 4 so on)
Sheets("Sheeet1").Select
for i=1 to 5000
if cells(i,1)="" then nextEmpty=i goto 20
next i
20 'continue your code here
enter code here
answered Sep 14, 2015 at 8:51
Better:
if cells(i,1)="" then
nextEmpty=i:
exit for
Vagish
2,50018 silver badges32 bronze badges
answered Dec 12, 2017 at 13:43
1
Dynamic VBA Code With Last Row/Column
Finding the Last Row or Last Column within your VBA code is key to ensuring your macro doesn’t break in the future.
Early on when I first began writing VBA macro code, I always needed to go back into the code and modify range references. I had created a bunch of macros to clean up and perform analysis on raw data exported from databases and the data never had the same amount of rows from one data pull to the next.
My coding skills dramatically changed the day I realized my VBA code could be dynamic and automatically determine the size of my raw data once executed. I soon came to realize the goal of coding a macro: to write it once and never touch it again.
Variability is also the greatest challenge for any VBA coder as you have to think of every possible change that could occur in the future. I have found writing VBA code that can automatically resize itself is one of the greatest things missing from most average macro user’s code.
In this article, I have compiled a list of the best methods you can use to accomplish finding the last row or column in your data range.
Prep Your Excel Data!
Keep in mind some of these methods may not give you the desired row or column number if you are not setting your spreadsheet up properly or using a well-formatted block of data.
What I mean by a “well-formatted block of data”, is a worksheet with data that starts in cell A1 and does not have any blank rows or columns in the middle of the data.
The below figure illustrates the difference.
An Example of a Poorly-Formatted Data Set
An Example of a Well-Formatted Data Set
In a data set starting in Row 4, you may need to add or subtract a numerical value depending on the method you use. If you are going to be coding for a data set that has blank rows or columns within it, always be sure to test out your code to make sure it is calculating properly.
Find the Last Cell In Spreadsheet With Data
Finding the last cell with a value in it is key to determining the last row or last column. There are a couple of different ways you can locate the last cell on your spreadsheet. Let’s take a look!
1. The Find Function Method (Best Method)
This line of VBA code will search all the cells on your sheet and return the row of the last cell with any sort of value stored in it. Because the Find function is set to search from the very bottom of the spreadsheet and upwards, this code can accommodate blank rows in your data.
Dim LastCell As Range
Set LastCell = ActiveSheet.Cells.Find(«*», SearchOrder:=xlByRows, SearchDirection:=xlPrevious)
This method ignores empty cells with formatting still in them, which is ideal if you are truly wanting the find the last cell with data in it, not necessarily the last cell that had any modifications done to it.
2. SpecialCells Method
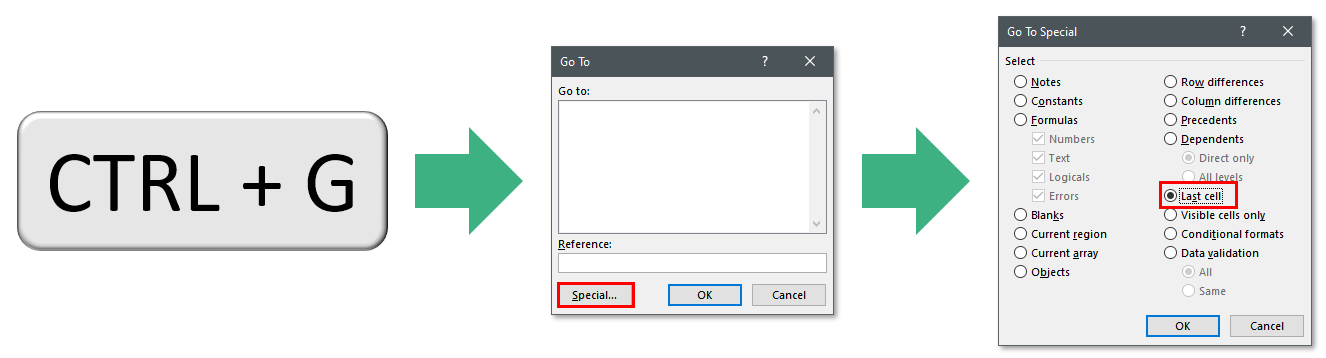
One of the best manual ways to do this is to utilize the Go To Special dialog box.
The Go To Special dialog box has a variety of actions that can be taken to select certain cells or objections on your spreadsheet. One of those options is to select the Last Cell on the active spreadsheet.
You can get to the Go To Special dialog box by using the keyboard shortcut Ctrl + G which will open the Go To dialog box. From there you can click the Special button and you’ll have arrived at the Go To Special dialog box.
In VBA, the select actions in the Go To Special dialog box are simply called SpecialCells. By calling the SpecialCells function in VBA, you gain the same actions, though they have slightly different names. The particular action you’ll want to call is named xlCellTypeLastCell.
The below VBA code stores the last cell found on the spreadsheet with a value in it to a range variable.
Dim LastCell As Range
Set LastCell = ActiveSheet.Cells.SpecialCells(xlCellTypeLastCell)
WARNING! This method could give you unintended results as this finds the last cell with any sort of data or formatting associated with it. This means it can return an empty cell that used to have data in it or simply has any formatting changes (like a yellow cell fill color).
7 Ways To Find The Last Row With VBA
There are actually quite a few ways to determine the last row of a data set in a spreadsheet. We will walk through a number of different ways in this article. I have marked specific methods with a “Best Method” tag as these coding practices are the most bullet-proof ways to determine the last row in your spreadsheet data.
1. The Find Function Method (Best Method)
This line of VBA code will search all the cells on your sheet and return the row of the last cell with any sort of value stored in it. Because the Find function is set to search from the very bottom of the spreadsheet and upwards, this code can accommodate blank rows within your data.
Dim LastRow As Long
LastRow = ActiveSheet.Cells.Find(«*», SearchOrder:=xlByRows, SearchDirection:=xlPrevious).Row
2. SpecialCells Method
SpecialCells is a function you can call in VBA that will allow you to pinpoint certain cells or a range of cells based on specific criteria. We can use the xlCellTypeLastCell action to find the last cell in the spreadsheet and call for the cell’s row number.
Dim LastRow As Long
LastRow = ActiveSheet.Cells.SpecialCells(xlCellTypeLastCell).Row
WARNING! This method could give you unintended results as this finds the last cell with any sort of data or formatting associated with it. This means it can return an empty cell that used to have data in it or simply has any formatting changes (like a yellow cell fill color).
3. Ctrl+Shift+End Method
This line of VBA code mimics the keyboard shortcut Ctrl + Shift + End and returns the numerical value of the last row in the range.
Dim LastRow As Long
LastRow = ActiveSheet.Cells(ActiveSheet.Rows.Count, «A»).End(xlUp).Row
4. UsedRange Method
The Used Range is something that Excel stores a reference to behind the scenes. It represents the area of the spreadsheet that has values in it. The Used Range can be referenced in VBA using the UsedRange object.
You must be careful with the Used Range though , as Excel does not always update the reference in real time. Sometimes when you delete cell content the Used Range will not readjust itself right away. For this reason, it is wise to force the UsedRange object to restructure itself with your VBA code. The below VBA code example calls this restructure/refresh prior to utilizing UsedRange to pull the last row.
Dim LastRow As Long
ActiveSheet.UsedRange ‘Refresh UsedRange
LastRow = ActiveSheet.UsedRange.Rows(ActiveSheet.UsedRange.Rows.Count).Row
5. Table Object Method (Best Method)
If you are using a Table Object to store your data, you can use the Table’s name in the below VBA code to return the numerical value of how many rows are in the table.
Dim LastRow As Long
LastRow = ActiveSheet.ListObjects(«Table1»).Range.Rows.Count
6. Named Range Method
If you are using a Named Range to reference your data’s location, you can use the Range name in the below VBA code to return the numerical value of how many rows are in the Named Range.
Dim LastRow As Long
LastRow = ActiveSheet.Range(«MyNamedRange»).Rows.Count
7. Ctrl+Shift+Down Method
Dim LastRow As Long
LastRow = ActiveSheet.Range(«A1»).CurrentRegion.Rows.Count
Expand Your Range To The Last Row
After you have determined the last row, how do you use it? The vast majority of the time you are going to want to store your entire data range to a Range variable. The following code shows you how to incorporate the last row number you calculated into a Range reference.
Dim DataRange As Range
Set DataRange = Range(«A1:M» & LastRow)
7 Ways To Find The Last Column With VBA
There are actually quite a few ways to determine the last column of a data set in a spreadsheet. We will walk through a number of different ways in this article. I have marked specific methods with a “Best Method” tag as these coding practices are the most bullet-proof ways to determine the last column in your spreadsheet data.
1. The Find Function Method (Best Method)
This line of VBA code will search all the cells on your sheet and return the column of the last cell with any sort of value stored in it. Because the Find function is set to search from the very far right of the spreadsheet and then leftward, this code can accommodate blank columns within your data.
Dim LastColumn As Long
LastColumn = ActiveSheet.Cells.Find(«*», SearchOrder:=xlByColumns, SearchDirection:=xlPrevious).Column
2. SpecialCells Method
SpecialCells is a function you can call in VBA that will allow you to pinpoint certain cells or a range of cells based on specific criteria. We can use the xlCellTypeLastCell action to find the last cell in the spreadsheet and call for the cell’s column number.
Dim LastColumn As Long
LastColumn = ActiveSheet.Cells.SpecialCells(xlCellTypeLastCell).Column
WARNING! This method could give you unintended results as this finds the last cell with any sort of data or formatting associated with it. This means it can return an empty cell that used to have data in it or simply has any formatting changes (like a yellow cell fill color).
3. Ctrl+Shift+End Method
Dim LastColumn As Long
LastColumn = ActiveSheet.Cells(1, ActiveSheet.Columns.Count).End(xlToLeft).Column
4. UsedRange Method
Dim LastColumn As Long
ActiveSheet.UsedRange ‘Refresh UsedRange
LastColumn = ActiveSheet.UsedRange.Columns(ActiveSheet.UsedRange.Columns.Count).Column
5. Table Object Method (Best Method)
If you are using a Table Object to store your data, you can use the Table’s name in the below VBA code to return the numerical value of how many columns are in the table.
Dim LastColumn As Long
LastColumn = ActiveSheet.ListObjects(«Table1»).Range.Columns.Count
6. Named Range Method
Dim LastColumn As Long
LastColumn = ActiveSheet.Range(«MyNamedRange»).Columns.Count
7. Ctrl+Shift+Right Method
Dim LastColumn As Long
LastColumn = ActiveSheet.Range(«A1»).CurrentRegion.Columns.Count
How To Expand Your Range To The Last Column
After you have determined the last column, how do you use it? The vast majority of the time you are going to want to store your entire data range to a Range variable. The following code shows you how to incorporate the last column number you calculated into a Range reference.
Dim DataRange As Range
Set DataRange = Range(Cells(1, 1), Cells(100, LastColumn))
VBA Function To Find Last Row or Column
Tim provided the inspiration for a function that can return either the last row or column number through a user-defined function for a given worksheet.
An example of how you could call this function to return the last row on the active worksheet would be written as: x = LastRowColumn(ActiveSheet, «Row»)
Function LastRowColumn(sht As Worksheet, RowColumn As String) As Long
‘PURPOSE: Function To Return the Last Row Or Column Number In the Active Spreadsheet
‘INPUT: «R» or «C» to determine which direction to search
Select Case LCase(Left(RowColumn, 1)) ‘If they put in ‘row’ or column instead of ‘r’ or ‘c’.
Case «c»
LastRowColumn = sht.Cells.Find(«*», LookIn:=xlFormulas, SearchOrder:=xlByColumns, _
SearchDirection:=xlPrevious).Column
Case «r»
LastRowColumn = sht.Cells.Find(«*», LookIn:=xlFormulas, SearchOrder:=xlByRows, _
SearchDirection:=xlPrevious).Row
Case Else
LastRowColumn = 1
End Select
End Function
What Can I Do With A LastRow Or LastColumn Variable?
There are many things you can do by calculating the last row or last column of a data set. Examples could be:
-
Resizing a Pivot Table range
-
Looping through cells in a column
-
Deleting only the raw data range
There are many, many more examples of this and I’m sure you can think of a few examples yourself.
Let me know in the comments section below how you use resizing a range in your macro code! Also, if you can think of any other ways to use VBA code to find the last row or last column, post your coding method in the comments section so we can improve the current list. I look forward to reading about your experiences.
I Hope This Excel Tutorial Helped!
Hopefully, I was able to explain how you can use VBA code to find the last row or last column of your range to add dynamic capabilities to your macros. If you have any questions about these techniques or suggestions on how to improve this article, please let me know in the comments section below.
About The Author
Hey there! I’m Chris and I run TheSpreadsheetGuru website in my spare time. By day, I’m actually a finance professional who relies on Microsoft Excel quite heavily in the corporate world. I love taking the things I learn in the “real world” and sharing them with everyone here on this site so that you too can become a spreadsheet guru at your company.
Through my years in the corporate world, I’ve been able to pick up on opportunities to make working with Excel better and have built a variety of Excel add-ins, from inserting tickmark symbols to automating copy/pasting from Excel to PowerPoint. If you’d like to keep up to date with the latest Excel news and directly get emailed the most meaningful Excel tips I’ve learned over the years, you can sign up for my free newsletters. I hope I was able to provide you with some value today and hope to see you back here soon! — Chris
Excel VBA Last Row
Finding the last row in a column is an important aspect in writing macro’s and making those dynamic. As we would not prefer to update the cell ranges every now and then when we are working with Excel cell references. As being a coder/developer, you would always prefer to write a dynamic code which can be used on any data and suffice your requirement. Moreover, it would always be great if you have the last row known of your data so that you can dynamically change the code as per your requirement.
I will just point out one example which iterates the importance of dynamic code.
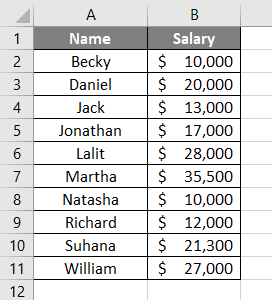
Suppose I have data as given below with employee and their salaries.
And look at the code given below:
Code:
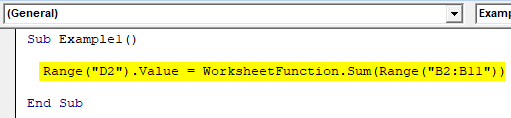
Sub Example1() Range("D2").Value = WorksheetFunction.Sum(Range("B2:B11")) End Sub
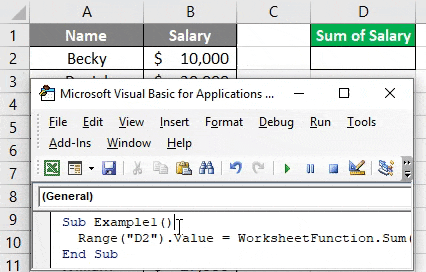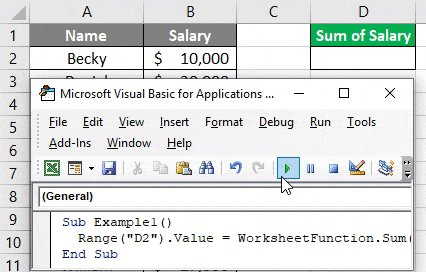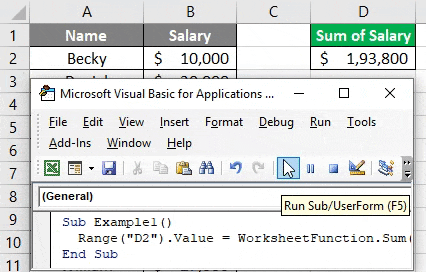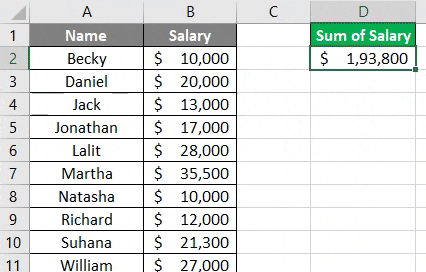
Here, this code prints the sum of salaries for all employees (cell B2:B11) in cell D2. See the image below:
Now, what if I add some cells to this data and run this code again?
Logically speaking, the above code will not sum up all the 14 rows from column B. Reason for the same is the range which we have updated under WorksheetFunction (which is B2:B11). This is the reason a dynamic code which can take the last filled row into consideration makes it more important for us.
In this article, I will introduce some methods which can be useful in finding out the last row for a given data set using VBA code.
How to Find Last used Row in Column Using VBA?
Below are the different examples with different methods to find the last used Row of a Column in Excel using VBA Code.
You can download this VBA Last Row Excel Template here – VBA Last Row Excel Template
Example #1 – Using Range.End() Method
Well, this method is as same as using the Ctrl + Down Arrow in Excel to go to the last non-empty row. On similar lines, follow the below steps for creating code in VBA to reach to the last non-empty row of a column in Excel.
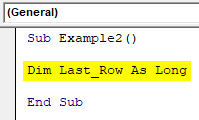
Step 1: Define a variable which can take value for the last non-empty row of the excel column.
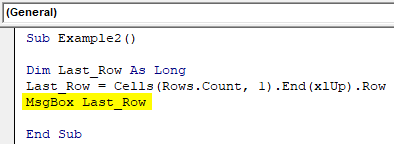
Code:
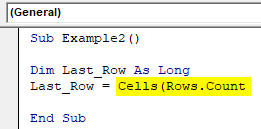
Sub Example2() Dim Last_Row As Long End Sub
Here, the variable Last_Row is defined as LONG just to make sure it can take any number of arguments.
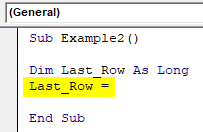
Step 2: Use the defined variable to hold the value of the last non-empty row.
Code:
Sub Example2() Dim Last_Row As Long Last_Row = End Sub
Step 3: Type the code starting with CELLS (Rows.Count in front of Last_Row =.
Code:
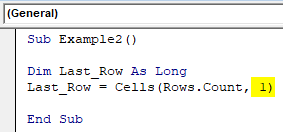
Sub Example2() Dim Last_Row As Long Last_Row = Cells(Rows.Count End Sub
Step 4: Mention 1 after a comma in the above-mentioned code. The value numeric 1 is synonyms to the first column in the excel sheet.
Code:
Sub Example2() Dim Last_Row As Long Last_Row = Cells(Rows.Count, 1) End Sub
This code allows VBA to find out the total number of (empty + non-empty) rows present in the first column of the excel worksheet. This means this code allows the system to go to the last cell of Excel.
Now, what if you are at the last cell of the excel and want to go up to the last non-empty row? You’ll use Ctrl + Up Arrow, right?
The same logic we are going to use in the next line of code.
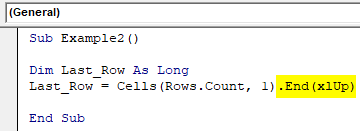
Step 5: Use a combination of End key and xlUp to go to the last non-empty row in excel.
Code:
Sub Example2() Dim Last_Row As Long Last_Row = Cells(Rows.Count, 1).End(xlUp) End Sub
This will take you to the last non-empty row in the excel. However, you wanted a row number for the same.
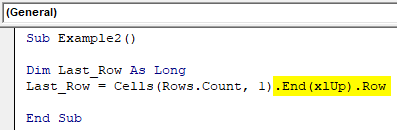
Step 6: Use ROW to get the row number of the last non-empty row.
Code:
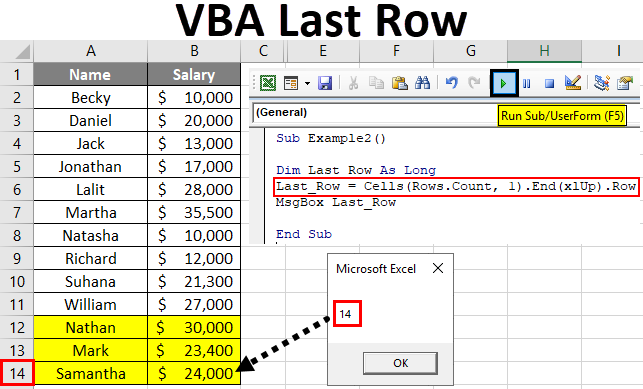
Sub Example2() Dim Last_Row As Long Last_Row = Cells(Rows.Count, 1).End(xlUp).Row End Sub
Step 7: Show the value of Last_Row, which contains the last non-empty row number using MsgBox.
Code:
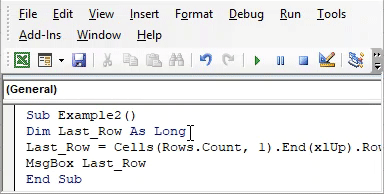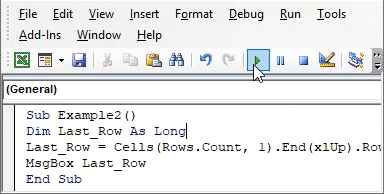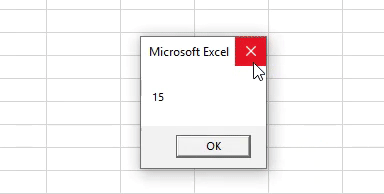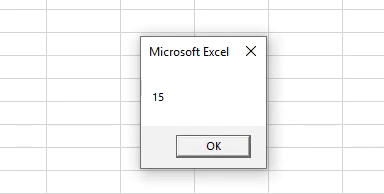
Sub Example2() Dim Last_Row As Long Last_Row = Cells(Rows.Count, 1).End(xlUp).Row MsgBox Last_Row End Sub
Step 8: Run the code using the Run button or hitting F5 and see the output.
Output:
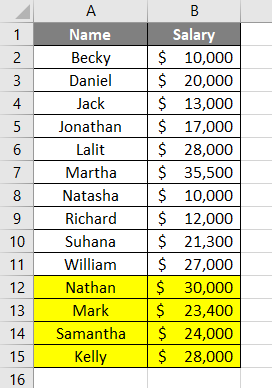
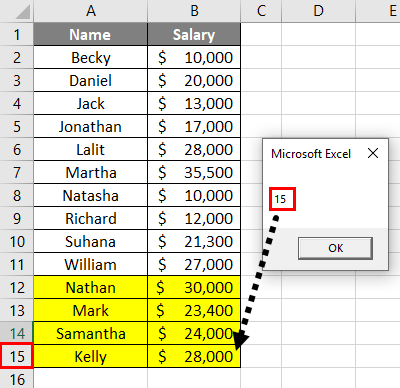
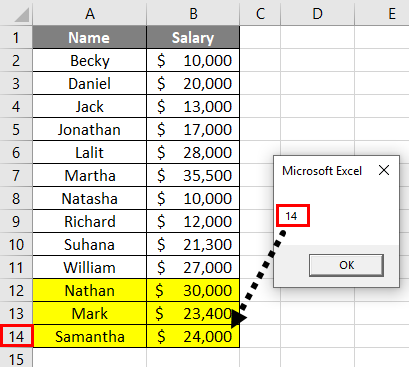
Step 9: Now, let’s delete one row and see if the code gives an accurate result or not. It will help us checking the dynamism of our code.
Example #2 – Using Range and SpecialCells
We can also use the Range and SepcialCells property of VBA to get the last non-empty row of the excel sheet.
Follow the below steps to get the last non-empty row in excel using VBA code:
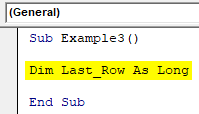
Step 1: Define a variable again as Long.
Code:
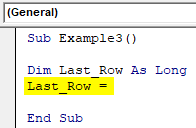
Sub Example3() Dim Last_Row As Long End Sub
Step 2: Start storing the value to the variable Last_Row using the assignment operator.
Code:
Sub Example3() Dim Last_Row As Long Last_Row = End Sub
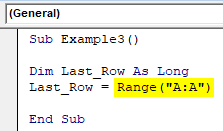
Step 3: Start Typing Range(“A:A”).
Code:
Sub Example3() Dim Last_Row As Long Last_Row = Range("A:A") End Sub
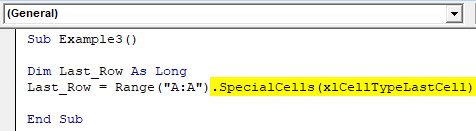
Step 4: Use the SpecialCells function to find out the last non-empty cell.
Code:
Sub Example3() Dim Last_Row As Long Last_Row = Range("A:A").SpecialCells(xlCellTypeLastCell) End Sub
This function SpecialCells selects the last cell from your excel as it is written in the parentheses (xlCellTypeLastCell allows you to select the last non-empty cell from your excel sheet).
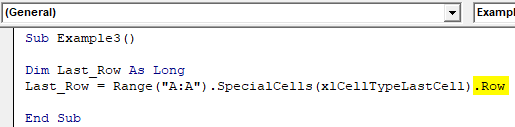
Step 5: Now, use ROW to get the last row from your excel sheet.
Code:
Sub Example3() Dim Last_Row As Long Last_Row = Range("A:A").SpecialCells(xlCellTypeLastCell).Row End Sub
This will return the last non-empty row for you from your excel.
Step 6: Now, assign this value of Last_Row to MsgBox so that we can see the last non-empty row number on the message box.
Code:
Sub Example3() Dim Last_Row As Long Last_Row = Range("A:A").SpecialCells(xlCellTypeLastCell).Row MsgBox Last_Row End Sub
Step 7: Run the code by hitting the F5 or Run button placed at the top of the left corner.
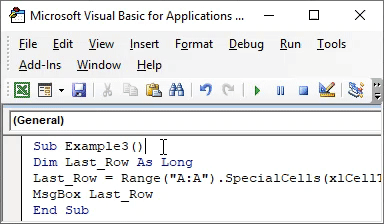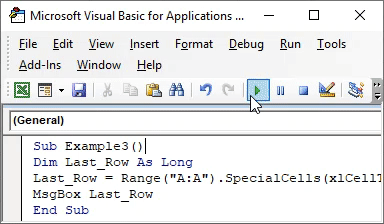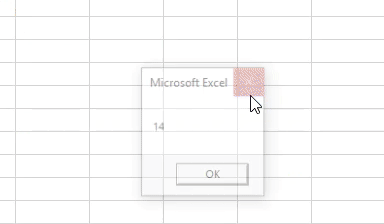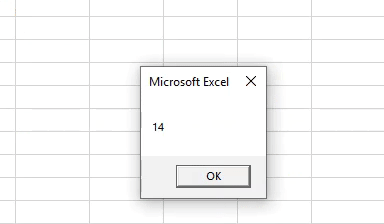
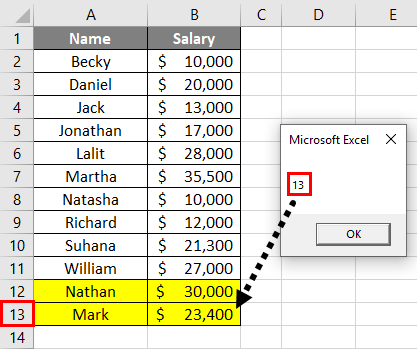
Output:
You can see that the last non-empty cell number is popped out through MsgBox with reference to the column A because we have mentioned the column A under the Range function while defining the variable formula.
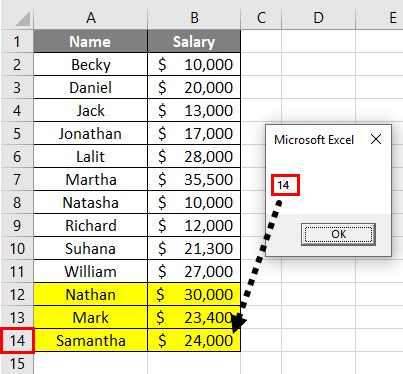
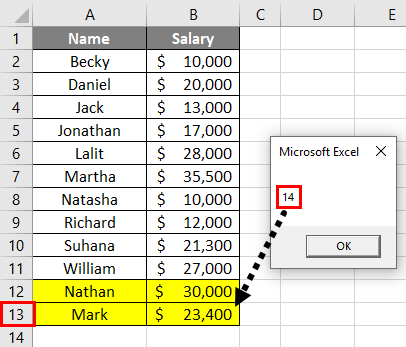
Step 8: If we delete a row and can run this formula. Let’s see what happens.
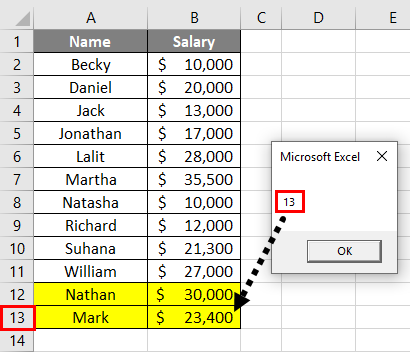
You can see the system has still given a row count of 14. Even though I have deleted a row and the actual row count is 13, the system has not captured the row count accurately. For the system to capture the actual row count, you need to save the worksheet and run the code again.
You can see the actual row count is showing in this screenshot now.
Example #3 – Using Range.Find()
Follow the below steps to get the last non-empty row in excel using VBA code:
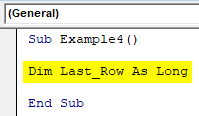
Step 1: Define a variable as long.
Code:
Sub Example4() Dim Last_Row As Long End Sub
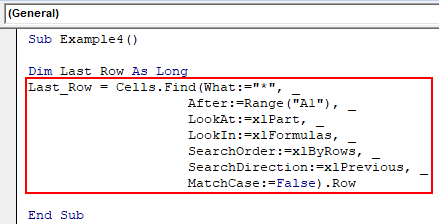
Step 2: Now, use the following code to see the last non-empty row.
Code:
Sub Example4() Dim Last_Row As Long Last_Row = Cells.Find(What:="*", _ After:=Range("A1"), _ LookAt:=xlPart, _ LookIn:=xlFormulas, _ SearchOrder:=xlByRows, _ SearchDirection:=xlPrevious, _ MatchCase:=False).Row End Sub
Here, the FIND function looks for the first non-blank cell. Asterisk (*) is a wildcard operator which helps in finding out the same.
Starting from cell A1, the system goes back to the last cell from the sheet and searches in a backward direction (xlPrevious). It moves from right to left (xlByRows) and loops up in the same sheet through all the rows on similar lines until it finds a non-blank row (see the .ROW at the end of the code).
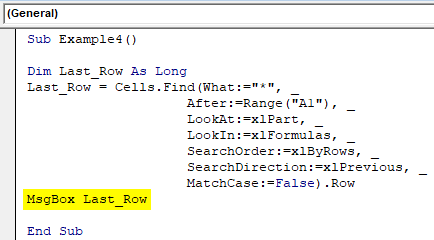
Step 3: Use MsgBox to store the value of the last non-empty row and see it as a pop-up box.
Code:
Sub Example4() Dim Last_Row As Long Last_Row = Cells.Find(What:="*", _ After:=Range("A1"), _ LookAt:=xlPart, _ LookIn:=xlFormulas, _ SearchOrder:=xlByRows, _ SearchDirection:=xlPrevious, _ MatchCase:=False).Row MsgBox Last_Row End Sub
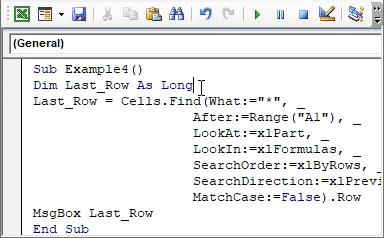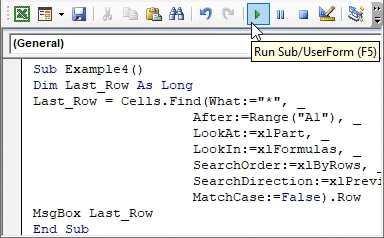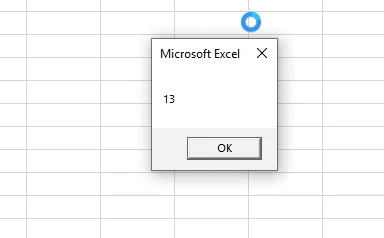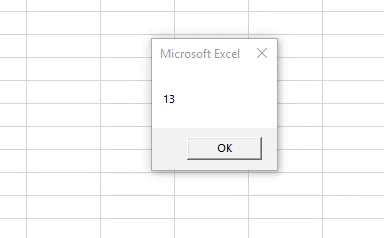
Step 4: Run the code and see the output as a pop-up box containing the last non-empty row number.
Output:
Things to Remember
- End (Example1) can be used to find out the first blank cell/row or last non-empty cell/row in a given column using the VBA code.
- The end works on a single column most of the time. If you have data in ranges, it would be difficult to decide which column should be used to find out the last non-empty row.
- Find (Example3) works on an entire range from the point of start and finds out the last non-empty cell/row in a given column using VBA code. It also can be used to find out the last non-empty column.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to VBA Last Row. Here we discuss how to find the last used row in a given column along with some practical examples and a downloadable excel template. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –
- VBA Insert Column
- VBA Range Cells
- VBA XML
- VBA XLUP