$header = ['c1.', 'c2', 'c3', 'c4', 'c5', 'c6', 'c7', 'c8', 'c9', 'c10', 'c11'];
header('Content-Disposition: attachment; filename="data'.date('d-m-y').'.xls"');
header("Content-Type: application/vnd.ms-excel");
$output = fopen('php://output', 'w');
fputcsv($output, $header , "t");
foreach ($Data as $value) {
$tmp_data = [];
array_push($tmp_data, $value['c1']);
array_push($tmp_data, $value['c2']);
array_push($tmp_data, $value['c3']);
array_push($tmp_data, $value['c4']);
array_push($tmp_data, $value['c5'] );
array_push($tmp_data, $value['c6']);
array_push($tmp_data, $value['c7']);
array_push($tmp_data, $value['c8']);
array_push($tmp_data, $value['c9']);
array_push($tmp_data, $value['c10']);
array_push($tmp_data, $value['c11']);
fputcsv($output, $tmp_data , "t" );
}
fclose($output);
Ребят, подскажите как такой массив:
Array ( [0] => 123-345 [1] => 999-257 [2] => 399-455 [3] => 846-313 [4] => 555-000 [5] => 766-765 [6] => 564-564 )
записать в Excel?
Чтобы в Exele было:
А1 = 123-345
А2= 999-257и т.д.
Использую PHPExcel
-
Вопрос заданболее года назад
-
568 просмотров
$array = [ '123-345', '999-257', '399-455', '846-313', '555-000', '766-765', '564-564' ];
// создаем excel объект
$objPHPExcel = new PHPExcel();
// устанавливаем свойства excel документа
$objPHPExcel->getProperties()->setCreator("Levandovskaya Marina")
->setLastModifiedBy("Levandovskaya Marina")
->setTitle("Doc Title")
->setSubject("Doc Subject")
->setDescription("Doc Description")
->setKeywords("Doc Keywords")
->setCategory("Doc Category");
$objPHPExcel->setActiveSheetIndex(0);
// добавляем данные из массива в документ
foreach ( $array as $key => $value ) {
$objPHPExcel->setActiveSheetIndex(0)->setCellValue( 'A' . $key, $value );
}
// сохраняем файл
$objWriter = PHPExcel_IOFactory::createWriter( $objPHPExcel, 'Excel2007' );
$objWriter->save( str_replace( '.php', '.xlsx', __FILE__ ) );Если нужно будет писать в строку A1, B1, C1 и т.д. используйте массив буквенных ключей
$letters = array();
for ( $x = 'A'; $x <= 'ZZ'; $x++ ) {
$letters[] = $x;
}Пригласить эксперта
PHPExcel больше не поддерживается, переходите на PhpOfficePhpSpreadsheet
<?php
namespace Enso;
use PhpOfficePhpSpreadsheet;
use InvalidArgumentException;
use DateTimeImmutable;
/**
* Класс для работы с xlsx файлами.
*/
class XlsxFile
{
private $dataDir;
private $path;
private $placeholders;
private $spreadsheet;
public function __construct(string $path)
{
$this->dataDir = realpath(__DIR__ . '/../data') . DIRECTORY_SEPARATOR;
$this->path = realpath($path);
// Загружает метки ячеек
$cacheFile = $this->dataDir . 'cache.json';
if (file_exists($cacheFile)) {
$this->placeholders = json_decode(file_get_contents($cacheFile), true);
} else {
$this->placeholders = $this->extractPlaceholders();
file_put_contents($cacheFile, json_encode($this->placeholders));
}
PhpSpreadsheetCalculationFunctions::setReturnDateType(
PhpSpreadsheetCalculationFunctions::RETURNDATE_PHP_OBJECT
);
// Загружает заполненный xlsx файл
$reader = new PhpSpreadsheetReaderXlsx();
$reader->setReadDataOnly(false);
$reader->setReadEmptyCells(true);
$this->spreadsheet = $reader->load($this->path);
}
/**
* Извлекает метки ячеек из пустой xlsx файла.
*/
private function extractPlaceholders(): array
{
$blankFile = $this->dataDir . 'dummy.xlsx';
$reader = new PhpSpreadsheetReaderXlsx();
$reader->setReadDataOnly(true);
$reader->setReadEmptyCells(false);
$spreadsheet = $reader->load($blankFile);
unset($reader);
$placeholders = [];
foreach ($spreadsheet->getAllSheets() as $sheetId => $sheet) {
foreach ($sheet->getRowIterator() as $row) {
$cells = $row->getCellIterator();
$cells->setIterateOnlyExistingCells(true);
foreach ($cells as $cell) {
$value = trim($cell->getValue());
if ($value[0] === '{' && $value[-1] === '}') {
$key = substr($value, 1, -1);
$placeholders[$key] = ['sheet' => $sheetId, 'cell' => $cell->getCoordinate()];
}
}
}
}
return $placeholders;
}
/**
* Проверяет наличие метки в шаблоне.
*/
public function hasPlaceholder(string $placeholder): bool
{
return isset($this->placeholders[$placeholder]);
}
/**
* Возвращает ячейку по её метке.
*/
public function getCell(string $placeholder)
{
if (!$this->hasPlaceholder($placeholder)) {
throw new InvalidArgumentException(
'Метка {' . $placeholder . '} не задана в файле ' . $this->dataDir . 'dummy.xlsx'
);
}
return $this->spreadsheet
->getSheet($this->placeholders[$placeholder]['sheet'])
->getCell($this->placeholders[$placeholder]['cell']);
}
/**
* Возвращает значение ячейки по её метке.
*/
public function getCellValue(string $placeholder)
{
return $this->getCell($placeholder)->getValue();
}
/**
* Задает значение ячейки по её метке.
*/
public function setCellValue(string $placeholder, $value)
{
if (is_bool($value)) {
$value = $value ? 'да' : 'нет';
} elseif (is_string($value)) {
$value = trim($value);
}
$this->getCell($placeholder)->setValue($value);
}
/**
* Задает значения ячеек колонки по её метке. Метка ставится в первую ячейку колонки.
*/
public function setColumnCellValues(string $placeholder, array $values)
{
$cell = $this->getCell($placeholder);
$cell->getWorksheet()->fromArray(array_chunk($values, 1), null, $cell->getCoordinate());
}
/**
* Задает значения ячеек колонок по их меткам.
*/
public function setColumnsCellValues(string $placeholderPrefix, array $values)
{
$keys = array_keys(current($values));
foreach ($keys as $key) {
$placeholder = $placeholderPrefix . $key;
if ($this->hasPlaceholder($placeholder)) {
$colValues = array_column($values, $key);
$this->setColumnCellValues($placeholder, $colValues);
}
}
}
/**
* Перезаписывает файл.
*/
public function save()
{
$writer = new PhpSpreadsheetWriterXlsx($this->spreadsheet);
$writer->save($this->path);
}
}-
Показать ещё
Загружается…
14 апр. 2023, в 14:45
20000 руб./за проект
14 апр. 2023, в 14:39
1500 руб./за проект
14 апр. 2023, в 14:21
1500 руб./за проект
Минуточку внимания
This tutorial will describe the usage of the PHPExcel library to generate an Excel file from a PHP array. Usage of PHPExcel library is very simple and easy. Just follow the below steps.
Similar Posts
CodeIgniter 4 – Export data to excel in CodeIgniter using PhpSpreadsheet
How to use PHPExcel with CodeIgniter?
1. First thing first – Download PHPExcel from – http://phpexcel.codeplex.com/
2. After downloading files Unzip the PHPExcel.zip files and we only need files and directories under the class directory. So just copy past the file from the class folder to your project folder. The below image shows that my folder structure.
3. Now include the PHPExcel.php file and create an object, just follow the comments.
setActiveSheetIndex(0);
// read data to active sheet
$doc->getActiveSheet()->fromArray($dataArray);
//save our workbook as this file name
$filename = 'just_some_random_name.xls';
//mime type
header('Content-Type: application/vnd.ms-excel');
//tell browser what's the file name
header('Content-Disposition: attachment;filename="' . $filename . '"');
header('Cache-Control: max-age=0'); //no cache
//save it to Excel5 format (excel 2003 .XLS file), change this to 'Excel2007' (and adjust the filename extension, also the header mime type)
//if you want to save it as .XLSX Excel 2007 format
$objWriter = PHPExcel_IOFactory::createWriter($doc, 'Excel5');
//force user to download the Excel file without writing it to server's HD
$objWriter->save('php://output');
?>
I hope you like this Post, Please feel free to comment below, your suggestion and problems if you face — we are here to solve your problems.
Accessing cells in a Spreadsheet should be pretty straightforward. This
topic lists some of the options to access a cell.
Setting a cell value by coordinate
Setting a cell value by coordinate can be done using the worksheet’s
setCellValue() method.
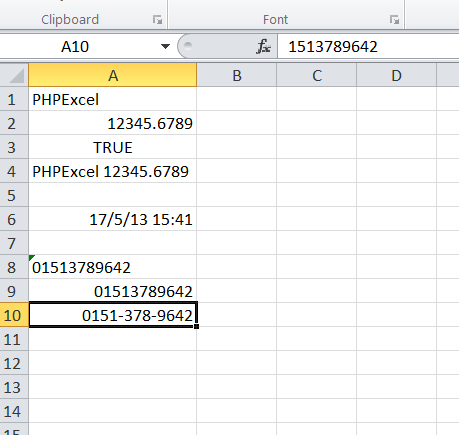
// Set cell A1 with a string value
$spreadsheet->getActiveSheet()->setCellValue('A1', 'PhpSpreadsheet');
// Set cell A2 with a numeric value
$spreadsheet->getActiveSheet()->setCellValue('A2', 12345.6789);
// Set cell A3 with a boolean value
$spreadsheet->getActiveSheet()->setCellValue('A3', TRUE);
// Set cell A4 with a formula
$spreadsheet->getActiveSheet()->setCellValue(
'A4',
'=IF(A3, CONCATENATE(A1, " ", A2), CONCATENATE(A2, " ", A1))'
);
Alternatively, you can retrieve the cell object, and then call the
cell’s setValue() method:
$spreadsheet->getActiveSheet()
->getCell('B8')
->setValue('Some value');
Creating a new Cell
If you make a call to getCell(), and the cell doesn’t already exist, then
PhpSpreadsheet will create that cell for you.
BEWARE: Cells assigned to variables as a Detached Reference
As an «in-memory» model, PHPSpreadsheet can be very demanding of memory,
particularly when working with large spreadsheets. One technique used to
reduce this memory overhead is cell caching, so cells are actually
maintained in a collection that may or may not be held in memory while you
are working with the spreadsheet. Because of this, a call to getCell()
(or any similar method) returns the cell data, and sets a cell pointer to that cell in the collection.
While this is not normally an issue, it can become significant
if you assign the result of a call to getCell() to a variable. Any
subsequent calls to retrieve other cells will change that pointer, although
the cell object will still retain its data values.
What does this mean? Consider the following code:
$spreadSheet = new Spreadsheet();
$workSheet = $spreadSheet->getActiveSheet();
// Set details for the formula that we want to evaluate, together with any data on which it depends
$workSheet->fromArray(
[1, 2, 3],
null,
'A1'
);
$cellC1 = $workSheet->getCell('C1');
echo 'Value: ', $cellC1->getValue(), '; Address: ', $cellC1->getCoordinate(), PHP_EOL;
$cellA1 = $workSheet->getCell('A1');
echo 'Value: ', $cellA1->getValue(), '; Address: ', $cellA1->getCoordinate(), PHP_EOL;
echo 'Value: ', $cellC1->getValue(), '; Address: ', $cellC1->getCoordinate(), PHP_EOL;
The call to getCell('C1') returns the cell at C1 containing its value (3),
together with its link to the collection (used to identify its
address/coordinate C1). The subsequent call to access cell A1
modifies the value of $cellC1, detaching its link to the collection.
So when we try to display the value and address a second time, we can display
its value, but trying to display its address/coordinate will throw an
exception because that link has been set to null.
Note: There are some internal methods that will fetch other cells from the
collection, and this too will detach the link to the collection from any cell
that you might have assigned to a variable.
Excel DataTypes
MS Excel supports 7 basic datatypes:
- string
- number
- boolean
- null
- formula
- error
- Inline (or rich text) string
By default, when you call the worksheet’s setCellValue() method or the
cell’s setValue() method, PhpSpreadsheet will use the appropriate
datatype for PHP nulls, booleans, floats or integers; or cast any string
data value that you pass to the method into the most appropriate
datatype, so numeric strings will be cast to numbers, while string
values beginning with = will be converted to a formula. Strings that
aren’t numeric, or that don’t begin with a leading = will be treated
as genuine string values.
Note that a numeric string that begins with a leading zero (that isn’t
immediately followed by a decimal separator) will not be converted to a
numeric, so values like phone numbers (e.g. `01615991375«will remain as
strings).
This «conversion» is handled by a cell «value binder», and you can write
custom «value binders» to change the behaviour of these «conversions».
The standard PhpSpreadsheet package also provides an «advanced value
binder» that handles a number of more complex conversions, such as
converting strings with a fractional format like «3/4» to a number value
(0.75 in this case) and setting an appropriate «fraction» number format
mask. Similarly, strings like «5%» will be converted to a value of 0.05,
and a percentage number format mask applied, and strings containing
values that look like dates will be converted to Excel serialized
datetimestamp values, and a corresponding mask applied. This is
particularly useful when loading data from csv files, or setting cell
values from a database.
Formats handled by the advanced value binder include:
- TRUE or FALSE (dependent on locale settings) are converted to booleans.
- Numeric strings identified as scientific (exponential) format are
converted to numbers. - Fractions and vulgar fractions are converted to numbers, and
an appropriate number format mask applied. - Percentages are converted
to numbers, divided by 100, and an appropriate number format mask
applied. - Dates and times are converted to Excel timestamp values
(numbers), and an appropriate number format mask applied. - When strings contain a newline character (
n), then the cell styling is
set to wrap.
Basically, it attempts to mimic the behaviour of the MS Excel GUI.
You can read more about value binders later in this section of the
documentation.
Setting a formula in a Cell
As stated above, if you store a string value with the first character an =
in a cell. PHPSpreadsheet will treat that value as a formula, and then you
can evaluate that formula by calling getCalculatedValue() against the cell.
There may be times though, when you wish to store a value beginning with =
as a string, and that you don’t want PHPSpreadsheet to evaluate as though it
was a formula.
To do this, you need to «escape» the value by setting it as «quoted text».
// Set cell A4 with a formula
$spreadsheet->getActiveSheet()->setCellValue(
'A4',
'=IF(A3, CONCATENATE(A1, " ", A2), CONCATENATE(A2, " ", A1))'
);
$spreadsheet->getActiveSheet()->getCell('A4')
->getStyle()->setQuotePrefix(true);
Then, even if you ask PHPSpreadsheet to return the calculated value for cell
A4, it will return =IF(A3, CONCATENATE(A1, " ", A2), CONCATENATE(A2, " ", A1))
as a string, and not try to evaluate the formula.
Setting a date and/or time value in a cell
Date or time values are held as timestamp in Excel (a simple floating
point value), and a number format mask is used to show how that value
should be formatted; so if we want to store a date in a cell, we need to
calculate the correct Excel timestamp, and set a number format mask.
// Get the current date/time and convert to an Excel date/time
$dateTimeNow = time();
$excelDateValue = PhpOfficePhpSpreadsheetSharedDate::PHPToExcel( $dateTimeNow );
// Set cell A6 with the Excel date/time value
$spreadsheet->getActiveSheet()->setCellValue(
'A6',
$excelDateValue
);
// Set the number format mask so that the excel timestamp will be displayed as a human-readable date/time
$spreadsheet->getActiveSheet()->getStyle('A6')
->getNumberFormat()
->setFormatCode(
PhpOfficePhpSpreadsheetStyleNumberFormat::FORMAT_DATE_DATETIME
);
Setting a number with leading zeroes
By default, PhpSpreadsheet will automatically detect the value type and
set it to the appropriate Excel numeric datatype. This type conversion
is handled by a value binder, as described in the section of this
document entitled «Using value binders to facilitate data entry».
Numbers don’t have leading zeroes, so if you try to set a numeric value
that does have leading zeroes (such as a telephone number) then these
will be normally be lost as the value is cast to a number, so
«01513789642» will be displayed as 1513789642.
There are two ways you can force PhpSpreadsheet to override this
behaviour.
Firstly, you can set the datatype explicitly as a string so that it is
not converted to a number.
// Set cell A8 with a numeric value, but tell PhpSpreadsheet it should be treated as a string
$spreadsheet->getActiveSheet()->setCellValueExplicit(
'A8',
"01513789642",
PhpOfficePhpSpreadsheetCellDataType::TYPE_STRING
);
Alternatively, you can use a number format mask to display the value
with leading zeroes.
// Set cell A9 with a numeric value
$spreadsheet->getActiveSheet()->setCellValue('A9', 1513789642);
// Set a number format mask to display the value as 11 digits with leading zeroes
$spreadsheet->getActiveSheet()->getStyle('A9')
->getNumberFormat()
->setFormatCode(
'00000000000'
);
With number format masking, you can even break up the digits into groups
to make the value more easily readable.
// Set cell A10 with a numeric value
$spreadsheet->getActiveSheet()->setCellValue('A10', 1513789642);
// Set a number format mask to display the value as 11 digits with leading zeroes
$spreadsheet->getActiveSheet()->getStyle('A10')
->getNumberFormat()
->setFormatCode(
'0000-000-0000'
);
Note: that not all complex format masks such as this one will work
when retrieving a formatted value to display «on screen», or for certain
writers such as HTML or PDF, but it will work with the true spreadsheet
writers (Xlsx and Xls).
Setting a range of cells from an array
It is also possible to set a range of cell values in a single call by
passing an array of values to the fromArray() method.
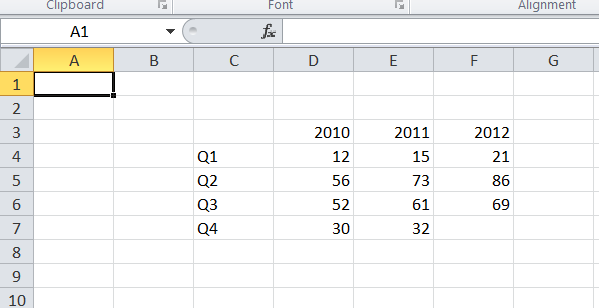
$arrayData = [
[NULL, 2010, 2011, 2012],
['Q1', 12, 15, 21],
['Q2', 56, 73, 86],
['Q3', 52, 61, 69],
['Q4', 30, 32, 0],
];
$spreadsheet->getActiveSheet()
->fromArray(
$arrayData, // The data to set
NULL, // Array values with this value will not be set
'C3' // Top left coordinate of the worksheet range where
// we want to set these values (default is A1)
);
If you pass a 2-d array, then this will be treated as a series of rows
and columns. A 1-d array will be treated as a single row, which is
particularly useful if you’re fetching an array of data from a database.
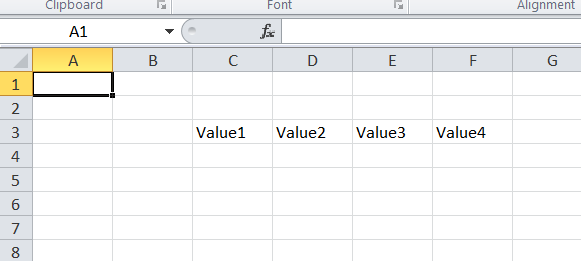
$rowArray = ['Value1', 'Value2', 'Value3', 'Value4'];
$spreadsheet->getActiveSheet()
->fromArray(
$rowArray, // The data to set
NULL, // Array values with this value will not be set
'C3' // Top left coordinate of the worksheet range where
// we want to set these values (default is A1)
);
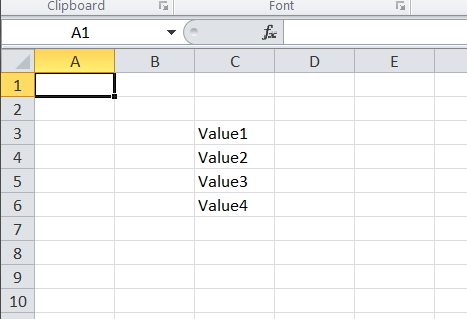
If you have a simple 1-d array, and want to write it as a column, then
the following will convert it into an appropriately structured 2-d array
that can be fed to the fromArray() method:
$rowArray = ['Value1', 'Value2', 'Value3', 'Value4'];
$columnArray = array_chunk($rowArray, 1);
$spreadsheet->getActiveSheet()
->fromArray(
$columnArray, // The data to set
NULL, // Array values with this value will not be set
'C3' // Top left coordinate of the worksheet range where
// we want to set these values (default is A1)
);
Retrieving a cell value by coordinate
To retrieve the value of a cell, the cell should first be retrieved from
the worksheet using the getCell() method. A cell’s value can be read
using the getValue() method.
// Get the value from cell A1
$cellValue = $spreadsheet->getActiveSheet()->getCell('A1')->getValue();
This will retrieve the raw, unformatted value contained in the cell.
If a cell contains a formula, and you need to retrieve the calculated
value rather than the formula itself, then use the cell’s
getCalculatedValue() method. This is further explained in
the calculation engine.
// Get the value from cell A4
$cellValue = $spreadsheet->getActiveSheet()->getCell('A4')->getCalculatedValue();
Alternatively, if you want to see the value with any cell formatting
applied (e.g. for a human-readable date or time value), then you can use
the cell’s getFormattedValue() method.
// Get the value from cell A6
$cellValue = $spreadsheet->getActiveSheet()->getCell('A6')->getFormattedValue();
Setting a cell value by column and row
Setting a cell value by coordinate can be done using the worksheet’s
setCellValueByColumnAndRow() method.
// Set cell A5 with a string value
$spreadsheet->getActiveSheet()->setCellValueByColumnAndRow(1, 5, 'PhpSpreadsheet');
Note: that column references start with 1 for column A.
Retrieving a cell value by column and row
To retrieve the value of a cell, the cell should first be retrieved from
the worksheet using the getCellByColumnAndRow() method. A cell’s value can
be read again using the following line of code:
// Get the value from cell B5
$cellValue = $spreadsheet->getActiveSheet()->getCellByColumnAndRow(2, 5)->getValue();
If you need the calculated value of a cell, use the following code. This
is further explained in the calculation engine.
// Get the value from cell A4
$cellValue = $spreadsheet->getActiveSheet()->getCellByColumnAndRow(1, 4)->getCalculatedValue();
Retrieving a range of cell values to an array
It is also possible to retrieve a range of cell values to an array in a
single call using the toArray(), rangeToArray() or
namedRangeToArray() methods.
$dataArray = $spreadsheet->getActiveSheet()
->rangeToArray(
'C3:E5', // The worksheet range that we want to retrieve
NULL, // Value that should be returned for empty cells
TRUE, // Should formulas be calculated (the equivalent of getCalculatedValue() for each cell)
TRUE, // Should values be formatted (the equivalent of getFormattedValue() for each cell)
TRUE // Should the array be indexed by cell row and cell column
);
These methods will all return a 2-d array of rows and columns. The
toArray() method will return the whole worksheet; rangeToArray()
will return a specified range or cells; while namedRangeToArray() will
return the cells within a defined named range.
Looping through cells
Looping through cells using iterators
The easiest way to loop cells is by using iterators. Using iterators,
one can use foreach to loop worksheets, rows within a worksheet, and
cells within a row.
Below is an example where we read all the values in a worksheet and
display them in a table.
$reader = PhpOfficePhpSpreadsheetIOFactory::createReader('Xlsx');
$reader->setReadDataOnly(TRUE);
$spreadsheet = $reader->load("test.xlsx");
$worksheet = $spreadsheet->getActiveSheet();
echo '<table>' . PHP_EOL;
foreach ($worksheet->getRowIterator() as $row) {
echo '<tr>' . PHP_EOL;
$cellIterator = $row->getCellIterator();
$cellIterator->setIterateOnlyExistingCells(FALSE); // This loops through all cells,
// even if a cell value is not set.
// For 'TRUE', we loop through cells
// only when their value is set.
// If this method is not called,
// the default value is 'false'.
foreach ($cellIterator as $cell) {
echo '<td>' .
$cell->getValue() .
'</td>' . PHP_EOL;
}
echo '</tr>' . PHP_EOL;
}
echo '</table>' . PHP_EOL;
Note that we have set the cell iterator’s setIterateOnlyExistingCells()
to FALSE. This makes the iterator loop all cells within the worksheet
range, even if they have not been set.
The cell iterator will create a new empty cell in the worksheet if it
doesn’t exist; return a null as the cell value if it is not set in
the worksheet; although we can also tell it to return a null value
rather than returning a new empty cell.
Setting the cell iterator’s setIterateOnlyExistingCells() to false
will loop all cells in the worksheet that can be available at that
moment. If this is then set to create new cells if required, then it
will likely increase memory usage!
Only use it if it is intended to loop all cells that are possibly
available; otherwise use the option to return a null value if a cell
doesn’t exist, or iterate only the cells that already exist.
It is also possible to call the Row object’s isEmpty() method to
determine whether you need to instantiate the Cell Iterator for that
Row.
Looping through cells using indexes
One can use the possibility to access cell values by column and row
index like [1, 1] instead of 'A1' for reading and writing cell values in
loops.
Note: In PhpSpreadsheet column index and row index are 1-based. That means 'A1' ~ [1, 1]
Below is an example where we read all the values in a worksheet and
display them in a table.
$reader = PhpOfficePhpSpreadsheetIOFactory::createReader('Xlsx');
$reader->setReadDataOnly(TRUE);
$spreadsheet = $reader->load("test.xlsx");
$worksheet = $spreadsheet->getActiveSheet();
// Get the highest row and column numbers referenced in the worksheet
$highestRow = $worksheet->getHighestRow(); // e.g. 10
$highestColumn = $worksheet->getHighestColumn(); // e.g 'F'
$highestColumnIndex = PhpOfficePhpSpreadsheetCellCoordinate::columnIndexFromString($highestColumn); // e.g. 5
echo '<table>' . "n";
for ($row = 1; $row <= $highestRow; ++$row) {
echo '<tr>' . PHP_EOL;
for ($col = 1; $col <= $highestColumnIndex; ++$col) {
$value = $worksheet->getCellByColumnAndRow($col, $row)->getValue();
echo '<td>' . $value . '</td>' . PHP_EOL;
}
echo '</tr>' . PHP_EOL;
}
echo '</table>' . PHP_EOL;
Alternatively, you can take advantage of PHP’s «Perl-style» character
incrementors to loop through the cells by coordinate:
$reader = PhpOfficePhpSpreadsheetIOFactory::createReader('Xlsx');
$reader->setReadDataOnly(TRUE);
$spreadsheet = $reader->load("test.xlsx");
$worksheet = $spreadsheet->getActiveSheet();
// Get the highest row number and column letter referenced in the worksheet
$highestRow = $worksheet->getHighestRow(); // e.g. 10
$highestColumn = $worksheet->getHighestColumn(); // e.g 'F'
// Increment the highest column letter
$highestColumn++;
echo '<table>' . "n";
for ($row = 1; $row <= $highestRow; ++$row) {
echo '<tr>' . PHP_EOL;
for ($col = 'A'; $col != $highestColumn; ++$col) {
echo '<td>' .
$worksheet->getCell($col . $row)
->getValue() .
'</td>' . PHP_EOL;
}
echo '</tr>' . PHP_EOL;
}
echo '</table>' . PHP_EOL;
Note that we can’t use a <= comparison here, because 'AA' would match
as <= 'B', so we increment the highest column letter and then loop
while $col != the incremented highest column.
Using value binders to facilitate data entry
Internally, PhpSpreadsheet uses a default
PhpOfficePhpSpreadsheetCellIValueBinder implementation
(PhpOfficePhpSpreadsheetCellDefaultValueBinder) to determine data
types of entered data using a cell’s setValue() method (the
setValueExplicit() method bypasses this check).
Optionally, the default behaviour of PhpSpreadsheet can be modified,
allowing easier data entry. For example, a
PhpOfficePhpSpreadsheetCellAdvancedValueBinder class is available.
It automatically converts percentages, numbers in scientific format, and
dates entered as strings to the correct format, also setting the cell’s
style information. The following example demonstrates how to set the
value binder in PhpSpreadsheet:
/** PhpSpreadsheet */
require_once 'src/Boostrap.php';
// Set value binder
PhpOfficePhpSpreadsheetCellCell::setValueBinder( new PhpOfficePhpSpreadsheetCellAdvancedValueBinder() );
// Create new Spreadsheet object
$spreadsheet = new PhpOfficePhpSpreadsheetSpreadsheet();
// ...
// Add some data, resembling some different data types
$spreadsheet->getActiveSheet()->setCellValue('A4', 'Percentage value:');
// Converts the string value to 0.1 and sets percentage cell style
$spreadsheet->getActiveSheet()->setCellValue('B4', '10%');
$spreadsheet->getActiveSheet()->setCellValue('A5', 'Date/time value:');
// Converts the string value to an Excel datestamp and sets the date format cell style
$spreadsheet->getActiveSheet()->setCellValue('B5', '21 December 1983');
Alternatively, a PhpOfficePhpSpreadsheetCellStringValueBinder class is available
if you want to preserve all content as strings. This might be appropriate if you
were loading a file containing values that could be interpreted as numbers (e.g. numbers
with leading sign such as international phone numbers like +441615579382), but that
should be retained as strings (non-international phone numbers with leading zeroes are
already maintained as strings).
By default, the StringValueBinder will cast any datatype passed to it into a string. However, there are a number of settings which allow you to specify that certain datatypes shouldn’t be cast to strings, but left «as is»:
// Set value binder
$stringValueBinder = new PhpOfficePhpSpreadsheetCellStringValueBinder();
$stringValueBinder->setNumericConversion(false)
->setBooleanConversion(false)
->setNullConversion(false)
->setFormulaConversion(false);
PhpOfficePhpSpreadsheetCellCell::setValueBinder( $stringValueBinder );
You can override the current binder when setting individual cell values by specifying a different Binder to use in the Cell’s setValue() or the Worksheet’s setCellValue() methods.
$spreadsheet = new Spreadsheet();
Cell::setValueBinder(new AdvancedValueBinder());
$value = '12.5%';
$cell = $spreadsheet->getActiveSheet()->getCell('A1');
// Value will be set as a number 0.125 with a format mask '0.00%'
$cell->setValue($value); // Using the Advanced Value Binder
$cell = $spreadsheet->getActiveSheet()->getCell('A2');
// Value will be set as a string '12.5%' with a format mask 'General'
$cell->setValue($value, new StringValueBinder()); // Overriding the Advanced Value Binder
Creating your own value binder
Creating your own value binder is relatively straightforward. When more specialised
value binding is required, you can implement the
PhpOfficePhpSpreadsheetCellIValueBinder interface or extend the existing
PhpOfficePhpSpreadsheetCellDefaultValueBinder or
PhpOfficePhpSpreadsheetCellAdvancedValueBinder classes.