Complete Guide to Pausing VBA Execution
Background Information and Explanation
All Microsoft Office applications run VBA code in the same thread as the main user interface. This means, as long as the VBA code doesn’t call DoEvents, code execution freezes the entire application (It will show as «not responding» in Task-Manager!). This includes calls to the Sleep API function. Once Sleep is called, there is no way of recovering from this state without waiting for the time to pass or force quitting the Application and restarting it.
The Excel-specific Application.Wait also suffers from this issue, except that the app will not show as not responding in Task Manager in this case. It will still be just as unresponsive to the user.
A way to circumvent this problem is calling DoEvents in a loop, as other people have already pointed out. However, this comes with another issue. Because the application will try to execute VBA code as fast as possible, DoEvents is called at the maximum achievable rate essentially saturating the CPU completely on that single thread, leading to high, unnecessary CPU and power usage and potentially slowing down other more important tasks in the UI.
This is why the best way of getting VBA to pause execution is a combination of both methods, using DoEvents to stay responsive and Sleep to avoid maximum CPU usage. An implementation of this is presented in the following.
Universal Solution
The following code implements a WaitSeconds Sub that will pause execution for a given amount of seconds while avoiding all of the above-mentioned issues.
It can be used like this:
Sub UsageExample()
WaitSeconds 3.5
End Sub
This will pause the macro for 3.5 seconds, without freezing the application or causing excessive CPU usage. For this to work, just copy the following code to the top of any standard code module.
#If Mac Then
#If VBA7 Then
Private Declare PtrSafe Sub USleep Lib "/usr/lib/libc.dylib" Alias "usleep" (ByVal dwMicroseconds As Long)
#Else
Private Declare Sub USleep Lib "/usr/lib/libc.dylib" Alias "usleep" (ByVal dwMicroseconds As Long)
#End If
#Else
#If VBA7 Then
Private Declare PtrSafe Sub MSleep Lib "kernel32" Alias "Sleep" (ByVal dwMilliseconds As Long)
#Else
Private Declare Sub MSleep Lib "kernel32" Alias "Sleep" (ByVal dwMilliseconds As Long)
#End If
#End If
'Sub providing a Sleep API consistent with Windows on Mac (argument in ms)
'Authors: Guido Witt-Dörring, https://stackoverflow.com/a/74262120/12287457
' Cristian Buse, https://stackoverflow.com/a/71176040/12287457
Public Sub Sleep(ByVal dwMilliseconds As Long)
#If Mac Then 'To avoid overflow issues for inputs > &HFFFFFFFF / 1000:
Do While dwMilliseconds And &H80000000
USleep &HFFFFFED8
If dwMilliseconds < (&H418937 Or &H80000000) Then
dwMilliseconds = &H7FBE76C9 + (dwMilliseconds - &H80000000)
Else: dwMilliseconds = dwMilliseconds - &H418937: End If
Loop
Do While dwMilliseconds > &H418937
USleep &HFFFFFED8: dwMilliseconds = dwMilliseconds - &H418937
Loop
If dwMilliseconds > &H20C49B Then
USleep (dwMilliseconds * 500& Or &H80000000) * 2&
Else: USleep dwMilliseconds * 1000&: End If
#Else
MSleep dwMilliseconds
#End If
End Sub
'Sub pausing code execution without freezing the app or causing high CPU usage
'Author: Guido Witt-Dörring, https://stackoverflow.com/a/74387976/12287457
Public Sub WaitSeconds(ByVal seconds As Single)
Dim currTime As Single: currTime = Timer()
Dim endTime As Single: endTime = currTime + seconds
Dim cacheTime As Single: cacheTime = currTime
Do While currTime < endTime
Sleep 15: DoEvents: currTime = Timer() 'Timer function resets at 00:00!
If currTime < cacheTime Then endTime = endTime - 86400! '<- sec per day
cacheTime = currTime
Loop
End Sub
[1] More information on the cross-platform Sleep included in the above code can be found here and here.
If application freezing is not an issue, e.g. for very short delays or if user interaction is undesired, the best solution is to call Sleep directly. This is why, in the above solution, it is also declared as Public. Note that Sleep takes its argument as milliseconds.
'Does freeze application
Sub UsageExample()
Sleep 3.5 * 1000
End Sub
Important Notes:
-
The time precision of the
Timer()function used in this solution is better on Windows, however, the claim in the documentation, that resolution on Mac is one second, is wrong. Even on Mac, the resolution is better than 0.1 seconds. Still, you shouldn’t expect a resolution much better than ~0.1seconds from this solution!WaitSeconds 1will wait around1.015 ± 0.02seconds on Windows. -
If you plan on using this to pause your code for long periods of time, or even in a case like OP is dealing with, you are most likely not using the correct tool for the job. If you are using Excel, consider looking into
Application.OnTime. (See the following section)
Alternatives to Pausing VBA Execution and Better Solution for OP
The question op has asked does not lead to the best solution for his problem. It’s an XY-Problem.
It is not actually necessary to have VBA code running non-stop in the background in order to recalculate a Workbook every second. This is a typical example of a task that can also be achieved with Application.OnTime.
A detailed guide including a copy-paste solution to recalculate any Range at any desired time interval ≥ 1s is available here.
The big advantage of using Application.OnTime for this is that it avoids a continuously running macro and hence allows the use of other macros or other features that are unavailable while macros are running.
Meta-Analysis of All Other Solutions in This Thread
The reason I even wrote this answer is that all other solutions presented in this thread (at the time this post was written) have at least one of the following two severe drawbacks:
- They freeze the calling application completely, causing it to no longer respond to user input, or
- They cause excessive CPU usage (100% on the calling application’s thread) by calling
DoEventsin a loop.
Additionally, many of the proposed solutions have other issues:
-
Some only work on Windows
-
Some only work in Excel
-
Some have an intrinsic imprecision of more than one second
-
Some have other problems or even bugs
The following table will give a short overview of all the solutions in this thread and their features
Legend
| Column | ✅ (Good) | ❌ (Bad) |
|---|---|---|
| App Responds | App stays responsive and usable | Freezes calling app completely |
| CPU Usage | Practically no CPU usage | 100% CPU usage in the single executing thread |
| Cross-App | Works outside Excel | Works only in Excel |
| Win/Mac | Works on both, Windows and Mac | Only works on Windows |
| Precise | Time precision < 0.1 seconds | Time precision > 0.1 seconds (usually about 1 second) |
| Other Issues | No other issues | Has some other issues described in the table below |
Overview
Other issues
| Solution by | Other issues |
|---|---|
| cyberpunk | This solution will sleep indefinitely if at the time of calling Timer() + vSeconds > 172800 (vSevonds is the input value). In practice, this shouldn’t be a big problem because Timer() is always ≤ 86400 so the input value needs to be bigger than 86400 which is one day. Such functions usually shouldn’t be called for such long times anyways. |
| Reverus | This solution doesn’t allow pausing for a specific amount of time at all! You just specify how often you want to call DoEvents before continuing. How long this is, depends on the speed of your system. On my PC, calling the function with the maximum value a Long can take (2147483647) (so the maximum time the function can pause) will pause for about 1434 seconds or about 24 minutes. Obviously, this is a terrible «solution». |
| Brian Burns | This solution will sleep indefinitely if at the time of calling Timer() + sngSecs > 86400 (sngSecs is the input value). Because Timer() can return values up to 86400, calling this function right before midnight can cause this bug even with very small input values. This is a severe bug and should be considered! |
| g t | This solution does not wait at all. If you consider its generalization, Application.Wait Second(Now) + dblInput, it will not wait at all for input values smaller than CDbl(Now) - 60# / 86400#, which is 44815 at the time of writing this, and for input values larger than that, it will wait for dblInput - CDbl(Now) - Second(Now) / 86400# days. While input values can be constructed that will make this wait for a reasonable amount of time, this is very difficult. A terrible «solution». |
| ITI | The comment describes this function as being able to cause delays of up to 99 seconds. This is wrong because input values where T Mod 100 > 60(T is the input parameter) will cause an error and hence stop execution indefinitely if the error is not handled by the calling code. You can confirm this by calling the function like this: Delay 61 |
| dave | This solution will work correctly but additionally sets Application.EnableEvents = True for no reason at all. If the calling code set this property to False and reasonably doesn’t expect a function that has nothing to do with this to set it to True, this can lead to severe bugs in the calling code. If that line is deleted, the solution is fine. |
Return to VBA Code Examples
In this Article
- Use of Application.Wait Method
- Wait 1 Second
- Wait Until
- Use of Sleep Method
- Using a Loop with Do Events
This tutorial will demonstrate how to pause / delay code using the Wait and Sleep functions in VBA.
When we create large VBA programs that perform a lot of calculations, or perhaps even call external program to run, we may require our VBA code to stop running for a specific length of time while the external process is taking place. VBA has a few methods available in order to achieve this.
Use of Application.Wait Method
If we need to pause our macro’s running for some time or until a specified time has been reached before executing the next step, we can use the Application.Wait method. This could be useful, for example, if we have automated a login process to a website and need to wait some seconds until the page is loaded before our macro continues running.
Wait 1 Second
Including this line below into your macro, its running will be paused for approximately 1 second:
Application.Wait (Now + TimeValue("0:00:01"))Wait Until
In some cases you will need to wait until a specific time. With this line below your macro will not proceed before 9am:
Application.Wait "09:00:00"Please note that the Application.Wait does not accept delays of less than 1 second.
Use of Sleep Method
If you need a more precise way of pausing your macro, you can use the Sleep method.
Sleep is a Windows API function, that is, it is not part of VBA. It can be accessed by using a special declaration statement.
If you are using the 64-bit version of Microsoft Office, you can insert the following statement into a new module or at the beginning of the module (not directly in the subroutine) you want to use the Sleep function in:
Public Declare PtrSafe Sub Sleep Lib "kernel32" (ByVal Milliseconds As LongPtr)With 32-bit version use this line:
Public Declare Sub Sleep Lib "kernel32" (ByVal Milliseconds As LongPtr)After declaring the Sleep function, you have access to it in you subroutines like this:
Sleep 10000With this line above your macro will be paused for 10,000 milliseconds, i.e., 10 seconds.
Using a Loop with Do Events
The big disadvantage of using the Wait and Sleep methods is that the user cannot do anything in Excel while waiting for the macro to continue. A user could think that Excel has stopped responding and while the user can then use Ctl+Break to interrupt the macro, this defeats the purpose of putting a pause in the macro to begin with.
To overcome this problem, we can use a loop with a method called DoEvents.
Public Sub Test()
Dim i As Long
For i = 1 To 20000
Range(“A1”).Value = i
DoEvents
Next i
End Sub
Now, while Excel is running the macro above, the user can continue to interact with Excel – we can change tabs or format cells for example – basically, the macro is continuing to run but the Excel screen is not frozen. We could use a similar loop to create a timer function in Excel and incorporate the DoEvents method in that to unfreeze the screen while the timer is running.
VBA Coding Made Easy
Stop searching for VBA code online. Learn more about AutoMacro — A VBA Code Builder that allows beginners to code procedures from scratch with minimal coding knowledge and with many time-saving features for all users!
Learn More!
Complete Guide to Pausing VBA Execution
Background Information and Explanation
All Microsoft Office applications run VBA code in the same thread as the main user interface. This means, as long as the VBA code doesn’t call DoEvents, code execution freezes the entire application (It will show as «not responding» in Task-Manager!). This includes calls to the Sleep API function. Once Sleep is called, there is no way of recovering from this state without waiting for the time to pass or force quitting the Application and restarting it.
The Excel-specific Application.Wait also suffers from this issue, except that the app will not show as not responding in Task Manager in this case. It will still be just as unresponsive to the user.
A way to circumvent this problem is calling DoEvents in a loop, as other people have already pointed out. However, this comes with another issue. Because the application will try to execute VBA code as fast as possible, DoEvents is called at the maximum achievable rate essentially saturating the CPU completely on that single thread, leading to high, unnecessary CPU and power usage and potentially slowing down other more important tasks in the UI.
This is why the best way of getting VBA to pause execution is a combination of both methods, using DoEvents to stay responsive and Sleep to avoid maximum CPU usage. An implementation of this is presented in the following.
Universal Solution
The following code implements a WaitSeconds Sub that will pause execution for a given amount of seconds while avoiding all of the above-mentioned issues.
It can be used like this:
Sub UsageExample()
WaitSeconds 3.5
End Sub
This will pause the macro for 3.5 seconds, without freezing the application or causing excessive CPU usage. For this to work, just copy the following code to the top of any standard code module.
#If Mac Then
#If VBA7 Then
Private Declare PtrSafe Sub USleep Lib "/usr/lib/libc.dylib" Alias "usleep" (ByVal dwMicroseconds As Long)
#Else
Private Declare Sub USleep Lib "/usr/lib/libc.dylib" Alias "usleep" (ByVal dwMicroseconds As Long)
#End If
#Else
#If VBA7 Then
Private Declare PtrSafe Sub MSleep Lib "kernel32" Alias "Sleep" (ByVal dwMilliseconds As Long)
#Else
Private Declare Sub MSleep Lib "kernel32" Alias "Sleep" (ByVal dwMilliseconds As Long)
#End If
#End If
'Sub providing a Sleep API consistent with Windows on Mac (argument in ms)
'Authors: Guido Witt-Dörring, https://stackoverflow.com/a/74262120/12287457
' Cristian Buse, https://stackoverflow.com/a/71176040/12287457
Public Sub Sleep(ByVal dwMilliseconds As Long)
#If Mac Then 'To avoid overflow issues for inputs > &HFFFFFFFF / 1000:
Do While dwMilliseconds And &H80000000
USleep &HFFFFFED8
If dwMilliseconds < (&H418937 Or &H80000000) Then
dwMilliseconds = &H7FBE76C9 + (dwMilliseconds - &H80000000)
Else: dwMilliseconds = dwMilliseconds - &H418937: End If
Loop
Do While dwMilliseconds > &H418937
USleep &HFFFFFED8: dwMilliseconds = dwMilliseconds - &H418937
Loop
If dwMilliseconds > &H20C49B Then
USleep (dwMilliseconds * 500& Or &H80000000) * 2&
Else: USleep dwMilliseconds * 1000&: End If
#Else
MSleep dwMilliseconds
#End If
End Sub
'Sub pausing code execution without freezing the app or causing high CPU usage
'Author: Guido Witt-Dörring, https://stackoverflow.com/a/74387976/12287457
Public Sub WaitSeconds(ByVal seconds As Single)
Dim currTime As Single: currTime = Timer()
Dim endTime As Single: endTime = currTime + seconds
Dim cacheTime As Single: cacheTime = currTime
Do While currTime < endTime
Sleep 15: DoEvents: currTime = Timer() 'Timer function resets at 00:00!
If currTime < cacheTime Then endTime = endTime - 86400! '<- sec per day
cacheTime = currTime
Loop
End Sub
[1] More information on the cross-platform Sleep included in the above code can be found here and here.
If application freezing is not an issue, e.g. for very short delays or if user interaction is undesired, the best solution is to call Sleep directly. This is why, in the above solution, it is also declared as Public. Note that Sleep takes its argument as milliseconds.
'Does freeze application
Sub UsageExample()
Sleep 3.5 * 1000
End Sub
Important Notes:
-
The time precision of the
Timer()function used in this solution is better on Windows, however, the claim in the documentation, that resolution on Mac is one second, is wrong. Even on Mac, the resolution is better than 0.1 seconds. Still, you shouldn’t expect a resolution much better than ~0.1seconds from this solution!WaitSeconds 1will wait around1.015 ± 0.02seconds on Windows. -
If you plan on using this to pause your code for long periods of time, or even in a case like OP is dealing with, you are most likely not using the correct tool for the job. If you are using Excel, consider looking into
Application.OnTime. (See the following section)
Alternatives to Pausing VBA Execution and Better Solution for OP
The question op has asked does not lead to the best solution for his problem. It’s an XY-Problem.
It is not actually necessary to have VBA code running non-stop in the background in order to recalculate a Workbook every second. This is a typical example of a task that can also be achieved with Application.OnTime.
A detailed guide including a copy-paste solution to recalculate any Range at any desired time interval ≥ 1s is available here.
The big advantage of using Application.OnTime for this is that it avoids a continuously running macro and hence allows the use of other macros or other features that are unavailable while macros are running.
Meta-Analysis of All Other Solutions in This Thread
The reason I even wrote this answer is that all other solutions presented in this thread (at the time this post was written) have at least one of the following two severe drawbacks:
- They freeze the calling application completely, causing it to no longer respond to user input, or
- They cause excessive CPU usage (100% on the calling application’s thread) by calling
DoEventsin a loop.
Additionally, many of the proposed solutions have other issues:
-
Some only work on Windows
-
Some only work in Excel
-
Some have an intrinsic imprecision of more than one second
-
Some have other problems or even bugs
The following table will give a short overview of all the solutions in this thread and their features
Legend
| Column | ✅ (Good) | ❌ (Bad) |
|---|---|---|
| App Responds | App stays responsive and usable | Freezes calling app completely |
| CPU Usage | Practically no CPU usage | 100% CPU usage in the single executing thread |
| Cross-App | Works outside Excel | Works only in Excel |
| Win/Mac | Works on both, Windows and Mac | Only works on Windows |
| Precise | Time precision < 0.1 seconds | Time precision > 0.1 seconds (usually about 1 second) |
| Other Issues | No other issues | Has some other issues described in the table below |
Overview
Other issues
| Solution by | Other issues |
|---|---|
| cyberpunk | This solution will sleep indefinitely if at the time of calling Timer() + vSeconds > 172800 (vSevonds is the input value). In practice, this shouldn’t be a big problem because Timer() is always ≤ 86400 so the input value needs to be bigger than 86400 which is one day. Such functions usually shouldn’t be called for such long times anyways. |
| Reverus | This solution doesn’t allow pausing for a specific amount of time at all! You just specify how often you want to call DoEvents before continuing. How long this is, depends on the speed of your system. On my PC, calling the function with the maximum value a Long can take (2147483647) (so the maximum time the function can pause) will pause for about 1434 seconds or about 24 minutes. Obviously, this is a terrible «solution». |
| Brian Burns | This solution will sleep indefinitely if at the time of calling Timer() + sngSecs > 86400 (sngSecs is the input value). Because Timer() can return values up to 86400, calling this function right before midnight can cause this bug even with very small input values. This is a severe bug and should be considered! |
| g t | This solution does not wait at all. If you consider its generalization, Application.Wait Second(Now) + dblInput, it will not wait at all for input values smaller than CDbl(Now) - 60# / 86400#, which is 44815 at the time of writing this, and for input values larger than that, it will wait for dblInput - CDbl(Now) - Second(Now) / 86400# days. While input values can be constructed that will make this wait for a reasonable amount of time, this is very difficult. A terrible «solution». |
| ITI | The comment describes this function as being able to cause delays of up to 99 seconds. This is wrong because input values where T Mod 100 > 60(T is the input parameter) will cause an error and hence stop execution indefinitely if the error is not handled by the calling code. You can confirm this by calling the function like this: Delay 61 |
| dave | This solution will work correctly but additionally sets Application.EnableEvents = True for no reason at all. If the calling code set this property to False and reasonably doesn’t expect a function that has nothing to do with this to set it to True, this can lead to severe bugs in the calling code. If that line is deleted, the solution is fine. |
Функция ожидания Excel VBA
VBA Подождите это встроенная функция для приостановки выполнения кода на указанное время. Это очень похоже на то, что мы делаем в команде Sleep. Чтобы приостановить код, мы используем метод Application.Wait.
Некоторым кодам требуется некоторое время, прежде чем перейти к следующей строке кода из-за выполнения других задач. В этих случаях нам нужно остановить выполнение кода, сделать паузу на некоторое время, а затем продолжить выполнение. Мы можем приостановить выполнение кода двумя способами: методом сна и методом ожидания. В нашей предыдущей статье обсуждалось, что «VBA SleepVBA SleepVBA Sleep — это функция Windows, присутствующая в файлах DLL Windows, которая приостанавливает выполнение программы на определенный период времени (даже в миллисекундах). Подробнее» для приостановки кода VBA. Pause The VBA CodeVBA Пауза помогает приостановить выполнение кода на определенный период. Вы можете приостановить код VBA на определенный период, используя две функции: «Ждать» и «Сон». Подробнее.
Оглавление
- Функция ожидания Excel VBA
- Примеры использования функции ожидания Excel VBA
- Пример №1
- Пример #2
- VBA Sleep против VBA Ожидание
- Рекомендуемые статьи
- Примеры использования функции ожидания Excel VBA
«Подождите», как следует из названия, будет удерживать код макроса, который должен быть выполнен до указанного периода времени. Используя этот метод, нам нужно указать, когда наш код должен приостанавливаться. Далее мы увидим примеры.
Синтаксис функции WAIT следующий.
Нам нужно указать количество времени, на которое наш код должен приостановиться. Как видите, в конце написано Boolean. Это означает, что он возвращает результат в виде логических значений: TRUE или FALSE.
Пока не наступит указанное время, он говорит FALSE. В тот момент, когда наступает указанное время, он возвращает TRUE.
Это не похоже на функцию SLEEP, потому что WAIT — это встроенная функция, где SLEEP — это функция Windows. Итак, прежде чем мы получим доступ к функции SLEEP, нам нужно упомянуть код ниже в верхней части модуля. Но WAIT этого не требует.
Код:
#If VBA7 Then Public Declare Sub Sleep Lib PtrSafe «kernel32» (ByVal dwMilliseconds As LongPtr) ‘Для 64-битных систем #Else Public Declare Sub Sleep Lib «kernel32» (ByVal dwMilliseconds As Long) ‘Для 32-битных систем End If
Примеры использования функции ожидания Excel VBA
.free_excel_div{фон:#d9d9d9;размер шрифта:16px;радиус границы:7px;позиция:относительная;margin:30px;padding:25px 25px 25px 45px}.free_excel_div:before{content:»»;фон:url(центр центр без повтора #207245;ширина:70px;высота:70px;позиция:абсолютная;верх:50%;margin-top:-35px;слева:-35px;граница:5px сплошная #fff;граница-радиус:50%} Вы можете скачать этот шаблон VBA Wait Excel здесь — Шаблон Excel ожидания VBA
Пример №1
Предположим, вы работаете в Excel в полдень в 14:30:00. Вы хотите, чтобы ваш код приостанавливался до тех пор, пока время не станет 14:40:00. Вы можете использовать приведенный ниже код.
Код:
Sub Wait_Example1() Application.Wait «14:40:00» End Sub
Код остановит работу вашего Excel до тех пор, пока время не достигнет 14:40:00 в вашей операционной системе. Предоставление такого времени опасно, потому что мы не всегда работаем с 14:30:00. Он все время меняется.
Скажем, всякий раз, когда вы запускаете код. Вы хотите подождать 2 минуты. Как вы ссылаетесь на это в своем коде?
Итак, мы можем использовать VBA NOWVBA NOWNOW — это функция даты и времени в VBA, которая используется для получения текущей системной даты и времени. Функция VBA Now не принимает никаких аргументов, и возвращаемым результатом для этой функции является функция date.read more с функцией TIME VALUE для ввода указанного времени из текущего времени.
Функция NOW () возвращает текущую дату и время для вашей компьютерной системы. Функция TIMEVALUE представляет время с 00:00:00 до 23:59:59, т.е. 23:59:59 в 24-часовом формате. Он преобразует строковое значение в значение времени.
Например, NOW () + TIMEVALUE (00:02:30) означает текущее время + 2 минуты 30 секунд.
Если текущее время 14:25:30, оно становится 14:28:00.
Вы можете использовать приведенный ниже код, чтобы остановить выполнение вашего кода с текущего времени до следующих 10 минут.
Код:
Sub Wait_Example2() Application.Wait (Now() + TimeValue(«00:10:00»)) End Sub
Важно использовать функцию СЕЙЧАС () для точных пауз. В противном случае есть вероятность, что ваша книга Excel будет приостановлена до полуночи. Однако мы можем выйти из метода паузы в любой момент времени, нажав кнопку Esc ключ или Разбить ключ.
Пример #2
Подождите 10 секунд каждый раз, когда цикл запускается
Можно использовать метод ожидания с циклами. Однако бывают ситуации, когда вам может потребоваться подождать 10 секунд каждый раз, когда цикл запускается. Например, посмотрите на данные ниже.
Чтобы рассчитать Прибыль = (Продажи — Стоимость), вы хотите создать цикл, и после каждого цикла вы хотите подождать 10 секунд, чтобы проверить, является ли результат точным или нет. Приведенный ниже код сделает это.
Код:
Sub Wait_Example3() Dim k As Integer For k = 2–9 Cells(k, 4).Value = Cells(k, 2) — Cells(k, 3) Application.Wait (Now() + TimeValue(«00:00) :10»)) Next k End Sub
Этот код будет вычислять столбец прибыли построчно. После завершения первой строки он будет ждать 10 секунд перед вычислением следующей строки.
VBA Sleep против VBA Ожидание
ВБА СОНПОДОЖДИТЕ VBAЭто не встроенная функция VBA. Для доступа к этой функции требуется специальный код. Это встроенная функция VBA, и для доступа к этой функции не требуется никакого специального кода. Для сна требуются миллисекунды в качестве временных рамок. Для ожидания требуются обычные временные рамки. код в миллисекундах. Мы можем задерживать только целые секунды.
Рекомендуемые статьи
Эта статья была руководством по функции ожидания VBA. Здесь мы обсудим, как использовать метод Wait для приостановки выполнения кода с помощью практических примеров и загружаемых листов Excel. Вы можете узнать больше о VBA из следующих статей:
- Пересечение VBA
- Разделить функцию в VBA
- Операторы в VBA
Pause VBA Code From Running
VBA Pause one may use to pause the code to execute for a specified amount of time and to pause a code in VBA. We use the application.wait method.
When we build large VBA projects after performing something, we may need to wait for some time to do other tasks. So, how do we pause the macro code to do our task in such scenarios? We can pause the VBA code for a specified period using two functions. Those functions are “Wait” and “Sleep.”
Table of contents
- Pause VBA Code From Running
- How to Pause Code using Wait Method?
- How to Pause the VBA Code using Sleep Method?
- Recommended Articles
You are free to use this image on your website, templates, etc, Please provide us with an attribution linkArticle Link to be Hyperlinked
For eg:
Source: VBA Pause (wallstreetmojo.com)
How to Pause Code using the Wait Method?
“Wait” is the function in VBAVBA functions serve the primary purpose to carry out specific calculations and to return a value. Therefore, in VBA, we use syntax to specify the parameters and data type while defining the function. Such functions are called user-defined functions.read more to hold the macro running for a specific amount of time. So, by applying this function, we need to know when our code should wait.
You can download this VBA Pause Excel Template here – VBA Pause Excel Template
For example, if executing the code at 13:00:00, if you supply the time as “13:15:00”, it will hold the Macro running for 15 minutes.
Now, look at the argument of the WAIT function in VBAThe In-built VBA Wait Function, also known as Application.Wait method, pauses the program execution for a particular time period (not less than 1 second).read more.
We must mention when our code should pause or wait in the time argument.
For example, look at the below VBA codeVBA code refers to a set of instructions written by the user in the Visual Basic Applications programming language on a Visual Basic Editor (VBE) to perform a specific task.read more.
Code:
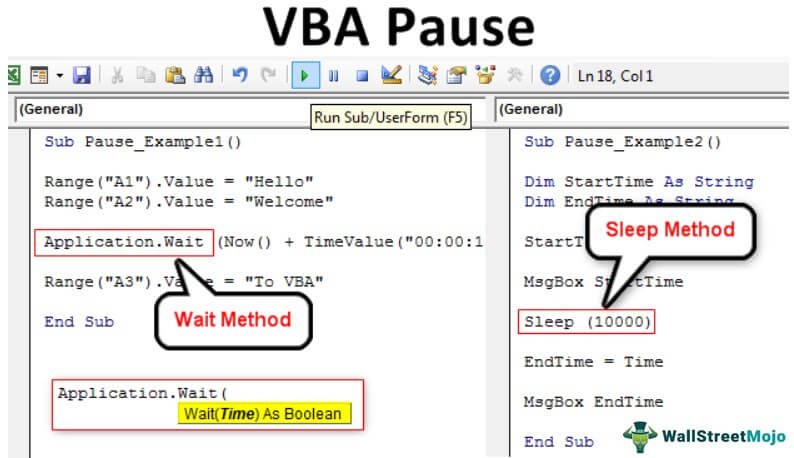
Sub Pause_Example1() Range("A1").Value = "Hello" Range("A2").Value = "Welcome" Application.Wait ("13:15:00") Range("A3").Value = "To VBA" End Sub
Remember, while running this code, my system time is 13:00:00. As soon as we run the code, it will execute the first two lines i.e.
Range("A1").Value = "Hello” &
Range("A2").Value = "Welcome"
But if you look at the next line, it says Application.Wait (“13:15:00”), so after executing those lines tasks, my Macro will be paused for 15 minutes, i.e., from 13:00:00, it will wait until my system time reaches 13:15:01.
Once my system reaches that time, it will execute the remaining lines of code.
Range("A3").Value = "To VBA"
However, this is not the best way of practicing the pause code. For example, let us say you are running the code at different times. Then we need to use the NOW VBA functionNOW is a date and time function in VBA which is used to get the current system date and time. VBA Now function does not takes any arguments and the return output for this function is date.read more with TIME VALUE function.
Now function returns the current date & time as per the system we are working on.
TIME Value function holds the time from 00:00:00 to 23:59:29.
Assume we need to pause the code for 10 minutes whenever we run the code. Then, we can use the below code.
Code:
Sub Pause_Example1() Range("A1").Value = "Hello" Range("A2").Value = "Welcome" Application.Wait (Now() + TimeValue("00:00:10")) Range("A3").Value = "To VBA" End Sub
It is similar to the previous code, but the only difference is we have added the NOW and TIME VALUE function.
Whenever we run this code, it will hold or pause the execution for 10 minutes.
How to Pause the VBA Code using the Sleep Method?
Sleep is a complicated function in VBA because it is not a built-in function. Since it is not built-in to make it available to use, we need to add the code below to the top of our module.
Code:
#If VBA7 Then Public Declare PtrSafe Sub Sleep Lib "kernel32" (ByVal dwMilliseconds As LongPtr) 'For 64 Bit Systems #Else Public Declare Sub Sleep Lib "kernel32" (ByVal dwMilliseconds As Long) #End If 'For 32 Bit Systems
You must copy the above code and paste it at the top of the module.
We need to add the above code because SLEEP is a VBA function presented in Windows DLL files, so we need to declare the nomenclature before we start the subprocedure.
Let us look at the example of the SLEEP function now.
Code:
Sub Pause_Example2() Dim StartTime As String Dim EndTime As String StartTime = Time MsgBox StartTime Sleep (10000) EndTime = Time MsgBox EndTime End Sub
First, we have declared two variables as String.
Dim StartTime As String Dim EndTime As String
Then we assigned the TIME excelTime is a time worksheet function in Excel that is used to calculate time based on the inputs provided by the user. The arguments can take the following formats: hours, minutes, and seconds.read more function to the StartTime variable. The TIME function returns the current time as per the system.
StartTime = Time
Then we have assigned the same to show in the message box.
MsgBox StartTime
Then, we applied the SLEEP function as Sleep (10000).
Here 10000 is milliseconds, which is equal to 10 seconds in VBA.
Then, we have finally assigned one more TIME function to the variable EndTime.
Now again, we have written a code to show the time.
EndTime = Time
It will show the difference between start time and end time.
We will now execute the code and see the start time.
When we execute the code, my system time is 13:40:48. Now, my code will sleep for 10 seconds. So, in the end, my time is as follows.
So, like this, we can pause the code from executing it for a specified time.
Recommended Articles
This article is a guide to the VBA Pause Method. Here, we discuss how to pause code from running using the SLEEP and WAIT for function in Excel VBA with examples and a downloadable Excel sheet. You can learn more about VBA from the following articles: –
- VBA InStr Function
- VBA COUNTIF
- VBA Val Function
- VBA Progress Bar