This article will demonstrate how to parse a string in VBA.
Often we will use Excel to import data from other files. Occasionally this data might be in a format that is not very user friendly, or that we need to amend to bring the information into Excel in a logical way. There are a number of string functions we can use in Excel VBA to extract the data correctly from the string that is brought in.
VBA Split Function
If the string comes into Excel as a delimited string (ie separated by commas, semi-colons, etc.), we can easily split the string into the individual values by using the Split function.
For example, say we have this string of names:
“John, Mary, Jack, Fred, Melanie, Steven, Paul, Robert”
Using the split function, we can return these names to Excel individually:
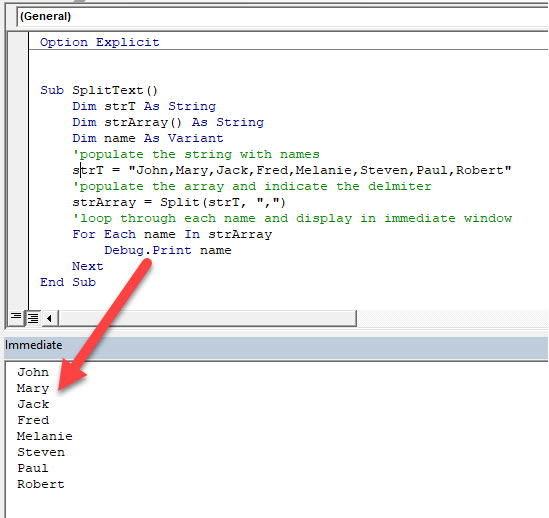
Sub SplitText()
Dim strT As String
Dim strArray() As String
Dim name As Variant
'populate the string with names
strT = "John,Mary,Jack,Fred,Melanie,Steven,Paul,Robert"
'populate the array and indicate the delmiter
strArray = Split(strT, ",")
'loop through each name and display in immediate window
For Each name In strArray
Debug.Print name
Next
End SubVBA Left, Right and Mid Functions
We can also extract data from strings by using the Left, Right and Mid functions. They are not as efficient as using the Split function to get multiple values from a string, but if you need to separate a line into specific areas, they can be useful.
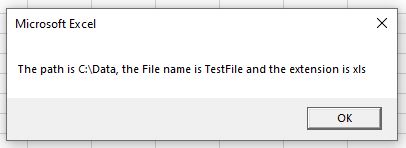
For example, say our file name is “C:DataTestFile.xls” . Now this includes the drive, the folder on the drive, the name of the file and the file extension.
To get the drive that the file is stored on we can use:
LEFT(“C:DataTestFile.xls”, 1) – which will return C.
To get the Path including the drive we can use:
LEFT(“C:DataTestFile.xls”, 7) – which will return C:Data.
To get the name of the file only, we can use MID:
MID(“C:DataTestFile.xls”, 9,8) – which will return TestFile
To get the extension of the file we can use:
RIGHT(“C:DataTestFile.xls”, 3)
Sub ExtractData()
Dim strData As String
Dim strLeft As String
Dim strRight As String
Dim strMid As String
'populate the string
strData = "C:DataTestFile.xls"
'break down the name
strLeft = Left(strData, 7)
strMid = Mid(strData, 9, 8)
strRight = Right(strData, 3)
'return the results
MsgBox "The path is " & strLeft & ", the File name is " & strMid & " and the extension is " & strRight
End SubThe result of which would be:
VBA Replace Function
Another useful string function to manipulate strings in Excel, is the Replace function. This can be used to remove anything from a string and replace it with something else. This is particularly useful if the string that you have brought into Excel has characters that your coding will not recognize, or will mess up your data.
For example:
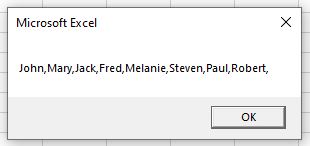
Consider the following string:
“John””Mary””Jack””Fred””Melanie””Steven””Paul””Robert”””
We can replace the double-quotes with commas using the Replace function.
Sub ExtractData()
Dim StrData As String
StrData = "John""Mary""Jack""Fred""Melanie""Steven""Paul""Robert"""
StrData = Replace(StrData, """", ",")
MsgBox StrData
End SubVBA Coding Made Easy
Stop searching for VBA code online. Learn more about AutoMacro — A VBA Code Builder that allows beginners to code procedures from scratch with minimal coding knowledge and with many time-saving features for all users!
Learn More!
I have a macro that send an XMLHTTP request to a server and it gets as response a plain text string, not a JSON format string or other standard formats (at least for what I know).
I would like to parse the output string in order to access the data in an structured approach in the same fashion as the parseJson subroutine in this link
My problem is I am not good with regular expressions and I am not able to modify the routine for my needs.
The string that I need to parse has the following structure:
- The string is a single line
- Each single parameter is defined by its parameter name the equal simbol, its value and ending with; «NID=3;» or «SID=Test;»
- Parameter can be collected in «structures» starts and end with the symbol | and they are identified with their name followed by ; such as |STEST;NID=3;SID=Test;|
- A structure can contain also other structures
An example of a output string is the following
|KC;|AD;PE=5;PF=3;|CD;PE=5;HP=test;|CD;PE=3;HP=abc;|
In this case there is a macro structure KC which contains a structure AD. The structure AD is composed by the parameters PE, PF and 2 structures CD. And finaly the structures CD have the parameters PE and HP
So I would like to parse the string to obtain an Object/Dictionary that reflects this structure, can you help me?
Adds after the first answers
Hi all, thank you for your help, but I think I should make more clear the output that I would like to get.
For the example string that I have, I would like to have an object with the following structure:
<KC>
<AD>
<PE>5</PE>
<PF>3</PF>
<CD>
<PE>5</PE>
<HP>test</HP>
</CD>
<CD>
<PE>3</PE>
<HP>abc</HP>
</CD>
</AD>
</KC>
So I started to wrote a possible working code base on some hint from @Nvj answer and the answer in this link
Option Explicit
Option Base 1
Sub Test()
Dim strContent As String
Dim strState As String
Dim varOutput As Variant
strContent = "|KC;|AD;PE=5;PF=3;|CD;PE=5;HP=test;|CD;PE=3;HP=abc;|"
Call ParseString(strContent, varOutput, strState)
End Sub
Sub ParseString(ByVal strContent As String, varOutput As Variant, strState As String)
' strContent - source string
' varOutput - created object or array to be returned as result
' strState - Object|Array|Error depending on processing to be returned as state
Dim objTokens As Object
Dim lngTokenId As Long
Dim objRegEx As Object
Dim bMatched As Boolean
Set objTokens = CreateObject("Scripting.Dictionary")
lngTokenId = 0
Set objRegEx = CreateObject("VBScript.RegExp")
With objRegEx
.Global = True
.MultiLine = True
.IgnoreCase = True
.Pattern = "|[A-Z]{2};" 'Pattern for the name of structures
Tokenize objTokens, objRegEx, strContent, lngTokenId, bMatched, "str"
.Pattern = "[A-Z]{2}=[^|=;]+;" 'Pattern for parameters name and values
Tokenize objTokens, objRegEx, strContent, lngTokenId, bMatched, "par"
End With
End Sub
Sub Tokenize(objTokens, objRegEx, strContent, lngTokenId, bMatched, strType)
Dim strKey As String
Dim strKeyPar As String
Dim strKeyVal As String
Dim strWork As String
Dim strPar As String
Dim strVal As String
Dim strLevel As String
Dim strRes As String
Dim lngCopyIndex As Long
Dim objMatch As Object
strRes = ""
lngCopyIndex = 1
With objRegEx
For Each objMatch In .Execute(strContent)
If strType = "str" Then
bMatched = True
With objMatch
strWork = Replace(.Value, "|", "")
strWork = Replace(strWork, ";", "")
strLevel = get_Level(strWork)
strKey = "<" & lngTokenId & strLevel & strType & ">"
objTokens(strKey) = strWork
strRes = strRes & Mid(strContent, lngCopyIndex, .FirstIndex - lngCopyIndex + 1) & strKey
lngCopyIndex = .FirstIndex + .Length + 1
End With
lngTokenId = lngTokenId + 1
ElseIf strType = "par" Then
strKeyPar = "<" & lngTokenId & "par>"
strKeyVal = "<" & lngTokenId & "val>"
strKey = strKeyPar & strKeyVal
bMatched = True
With objMatch
strWork = Replace(.Value, ";", "")
strPar = Split(strWork, "=")(0)
strVal = Split(strWork, "=")(1)
objTokens(strKeyPar) = strPar
objTokens(strKeyVal) = strVal
strRes = strRes & Mid(strContent, lngCopyIndex, .FirstIndex - lngCopyIndex + 1) & strKey
lngCopyIndex = .FirstIndex + .Length + 1
End With
lngTokenId = lngTokenId + 2
End If
Next
strContent = strRes & Mid(strContent, lngCopyIndex, Len(strContent) - lngCopyIndex + 1)
End With
End Sub
Function get_Level(strInput As String) As String
Select Case strInput
Case "KC"
get_Level = "L1"
Case "AD"
get_Level = "L2"
Case "CD"
get_Level = "L3"
Case Else
MsgBox ("Error")
End
End Select
End Function
This function creates a dictionary with an item for each structure name, parameter name and parameter value as shown in the figure
Thanks to the function get_Level the items associated to structures have a level that should help to preserve the original hierarchy of the data.
So what I am missing is a function to create an object that has the original structure of the input string. This is what the Retrieve function do in this answer link, but I do not know how to adapt it to my case
Если использовать тип Long, то файл ограничится размером в 2Гб, думаю тогда можно сделать тип Single. Встречал в интернете, что некоторым нужно было обрабатывать большие файлы, размером в 10Гб.
Размер буфера я пробовал менять от 100Кб до 10Мб, особой разницы я не заметил, зато при 10Мб требуется мегабайт 20 оперативки дополнительно. Величина в 512Кб вполне подходит и по скорости и по объему оперативки.
scripting.fso не использовал, т.к. посчитал что данный способ простой и вполне понятный, мне кажется это на скорость не повлияет, т.к. операций чтения файла происходит немного, и при этом эта библиотека все равно не имеет операторов, чтобы читать файл задом наперед построчно.
Обработку ошибок при открытии файла не писал, т.к. сроки поджимали, важно было сделать сам алгоритм
Модуль и вправду большой получился. Оформлять в виде класса идея хорошая, может и сделаю, пока не до этого.
Всем спасибо. Может кому пригодится.
|
Парсинг текстовой строки (обрезка строки) |
||||||||
Ответить |
||||||||
Ответить |
||||||||
Ответить |
||||||||
Ответить |
||||||||
Ответить |
||||||||
Ответить |
||||||||
Ответить |
||||||||
Ответить |
||||||||
Ответить |
||||||||
Ответить |
Пользовательские функции VBA Excel для парсинга сайтов, html-страниц и файлов, возвращающие их текстовое содержимое. Примеры записи текста в переменную.
Парсинг html-страниц (msxml2.xmlhttp)
Пользовательская функция GetHTML1 (VBA Excel) для извлечения (парсинга) текстового содержимого из html-страницы сайта по ее URL-адресу с помощью объекта «msxml2.xmlhttp»:
|
Function GetHTML1(ByVal myURL As String) As String On Error Resume Next With CreateObject(«msxml2.xmlhttp») .Open «GET», myURL, False .send Do: DoEvents: Loop Until .readyState = 4 GetHTML1 = .responseText End With End Function |
Парсинг сайтов (WinHttp.WinHttpRequest.5.1)
Пользовательская функция GetHTML2 (VBA Excel) для извлечения (парсинга) текстового содержимого из html-страницы сайта по ее URL-адресу с помощью объекта «WinHttp.WinHttpRequest.5.1»:
|
Function GetHTML2(ByVal myURL As String) As String On Error Resume Next With CreateObject(«WinHttp.WinHttpRequest.5.1») .Open «GET», myURL, False .send Do: DoEvents: Loop Until .readyState = 4 GetHTML2 = .responseText End With End Function |
Парсинг файлов (ADODB.Stream)
Пользовательская функция GetText (VBA Excel) для извлечения (парсинга) текстового содержимого из файла (.txt, .csv, .mhtml), сохраненного на диск компьютера, по его полному имени (адресу) с помощью объекта «ADODB.Stream»:
|
Function GetText(ByVal myFile As String) As String On Error Resume Next With CreateObject(«ADODB.Stream») .Charset = «utf-8» .Open .LoadFromFile myFile GetText = .ReadText .Close End With End Function |
Примеры записи текста в переменную
Общая формула записи текста, извлеченного с помощью пользовательских функций VBA Excel, в переменную:
|
Dim htmlText As String htmlText = GetHTML1(«Адрес сайта (html-страницы)») htmlText = GetHTML2(«Адрес сайта (html-страницы)») htmlText = GetText(«Полное имя файла») |
Конкретные примеры:
|
htmlText = GetHTML1(«https://internettovary.ru/nabor-dlya-vyrashchivaniya-veshenki/») htmlText = GetHTML2(«https://internettovary.ru/nabor-dlya-vyrashchivaniya-veshenki/») htmlText = GetText(«C:UsersEvgeniyDownloadsНовый текстовый документ.txt») htmlText = GetText(«C:UsersEvgeniyDownloadsИспользование msxml2.xmlhttp в Excel VBA.mhtml») |
В понятие «парсинг», кроме извлечения текстового содержимого сайтов, html-страниц или файлов, входит поиск и извлечение конкретных данных из всего полученного текстового содержимого.
Пример извлечения email-адресов из текста, присвоенного переменной, смотрите в последнем параграфе статьи: Регулярные выражения (объекты, свойства, методы).
Парсинг содержимого тегов
Извлечение содержимого тегов с помощью метода getElementsByTagName объекта HTMLFile:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 |
Sub Primer1() Dim myHtml As String, myFile As Object, myTag As Object, myTxt As String ‘Извлекаем содержимое html-страницы в переменную myHtml с помощью функции GetHTML1 myHtml = GetHTML1(«https://internettovary.ru/sadovaya-nozhovka-sinitsa/») ‘Создаем объект HTMLFile Set myFile = CreateObject(«HTMLFile») ‘Записываем в myFile текст из myHtml myFile.body.innerHTML = myHtml ‘Присваиваем переменной myTag коллекцию одноименных тегов, имя которого ‘указанно в качестве аргумента метода getElementsByTagName Set myTag = myFile.getElementsByTagName(«p») ‘Выбираем, содержимое какого тега по порядку, начинающегося с 0, нужно извлечь myTxt = myTag(5).innerText MsgBox myTxt ‘Большой текст может не уместиться в MsgBox, тогда для просмотра используйте окно Immediate ‘Debug.Print myTxt End Sub |
С помощью этого кода извлекается текст, расположенный между открывающим и закрывающим тегами. В примере — это текст 6-го абзаца (p) между 5-й (нумерация с 0) парой отрывающего <p> и закрывающего </p> тегов.
Примеры тегов, используемых в html: "p", "title", "h1", "h2", "table", "div", "script".
Пример извлечения содержимого тега "title":
|
Sub Primer2() Dim myHtml As String, myFile As Object, myTag As Object, myTxt As String myHtml = GetHTML1(«https://internettovary.ru/sadovaya-nozhovka-sinitsa/») Set myFile = CreateObject(«HTMLFile») myFile.body.innerHTML = myHtml Set myTag = myFile.getElementsByTagName(«title») myTxt = myTag(0).innerText MsgBox myTxt End Sub |
Парсинг содержимого Id
Извлечение текстового содержимого html-элементов, имеющих уникальный идентификатор — Id, с помощью метода getElementById объекта HTMLFile:
|
Sub Primer3() Dim myHtml As String, myFile As Object, myTag As Object, myTxt As String myHtml = GetHTML1(«https://internettovary.ru/sadovaya-nozhovka-sinitsa/») Set myFile = CreateObject(«HTMLFile») myFile.body.innerHTML = myHtml ‘Присваиваем переменной myTag html-элемент по указанному в скобках Id Set myTag = myFile.getElementById(«attachment_465») ‘Присваиваем переменной myTxt текстовое содержимое html-элемента с Id myTxt = myTag.innerText MsgBox myTxt ‘Большой текст может не уместиться в MsgBox, тогда для просмотра используйте окно Immediate ‘Debug.Print myTxt End Sub |
Для реализации представленных здесь примеров могут понадобиться дополнительные библиотеки. В настоящее время у меня подключены следующие (к данной теме могут относиться последние шесть):
- Visual Basic For Applications
- Microsoft Excel 16.0 Object Library
- OLE Automation
- Microsoft Office 16.0 Object Library
- Microsoft Forms 2.0 Object Library
- Ref Edit Control
- Microsoft Scripting Runtime
- Microsoft Word 16.0 Object Library
- Microsoft Windows Common Controls 6.0 (SP6)
- Microsoft ActiveX Data Objects 6.1 Library
- Microsoft ActiveX Data Objects Recordset 6.0 Library
- Microsoft HTML Object Library
- Microsoft Internet Controls
- Microsoft Shell Controls And Automation
- Microsoft XML, v6.0
С этим набором библиотек все примеры работают. Тестирование проводилось в VBA Excel 2016.