- Remove From My Forums
-
Вопрос
-
Используя OpenFileDialog надо открыть Excel файл чтоб бы в программе было в виде таблице с помощью DataGridView. Какой код нужен и куда написать его? За ответы благодарю.
Под кнопкой OpenFileDialog использовал код ниже
private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Stream myStream = null;
OpenFileDialog openFileDialog1 = new OpenFileDialog();openFileDialog1.InitialDirectory = «c:\»;
openFileDialog1.Filter = «All files (*.*)|*.*»;
openFileDialog1.FilterIndex = 2;
openFileDialog1.RestoreDirectory = true;if (openFileDialog1.ShowDialog() == DialogResult.OK)
{
try
{
if ((myStream = openFileDialog1.OpenFile()) != null)
{
using (myStream)
{
// Insert code to read the stream here.
}
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
MessageBox.Show(«Error: Could not read file from disk. Original error: » + ex.Message);
}-
Изменено
8 мая 2015 г. 5:02
-
Изменено
Ответы
-
Добрый день.
Если нужно открыть файл Excel для редактирования, чтобы там работали ввод, формулы, валидаторы и т.д., то лучше использовать не DataGridView, а какой нибудь существующий контрол. Например,
SpreadsheetGear. Если вам нужно просто показать данные из Excel-я, то можно считать данные через Ole и вывести их в DataGridView. Чтение в массив можете посмотреть
здесь, ну а показ массива уже дело не хитрое. Если на машине Excel не установлен, то чуть сложнее, работать придется через
OpenXML.А вот чтение через Stream, это очень сложно. И при наличии указанных выше возможностей — не целесообразно.
-
Я написал не вЫложите весь текст, а вЛожите текст листа Excel.
Вы просто должны сделать так:
1) считать данные с Excel;
2) создать DataTable;
3) записать данные в DataTable;
4) присвоить DataGrid (через Source) DataTable и все.
-
Предложено в качестве ответа
AlexFV
9 мая 2015 г. 13:10 -
Помечено в качестве ответа
Maksim MarinovMicrosoft contingent staff, Moderator
5 июня 2015 г. 6:47
-
Предложено в качестве ответа
Давайте научимся быстро и просто создавать и записывать файлы Excel с помощью visual studio c#. Наше самое простое приложение Windows Forms будет брать из текстбокса текст и заносить его в первую ячейку. Статья написана специально для Сергея =).
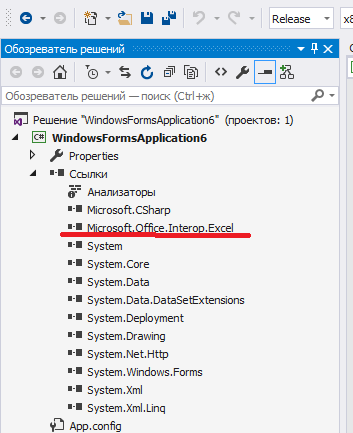
Начать необходимо с подключения библиотеки Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel. Выглядеть это должно так:
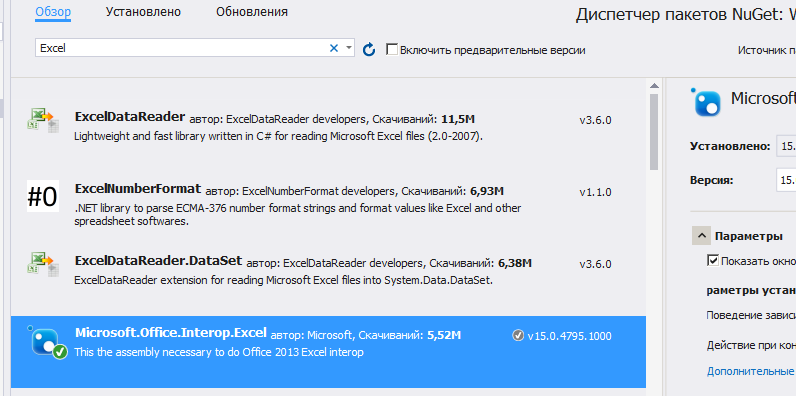
Если у вас при открытии обозревателя решений – Ссылки – правая кнопка – Добавить ссылку – Сборки – в списке нет Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel, то добавьте её через Nuget. Проект – управление пакетами NuGet – в строке поиска Excel:
Теперь создайте новый проект Windows Forms и на форму закиньте текстбокс и кнопку. На кнопки кликните два раза, откроется исходный код. В самом верху допишите следующее:
using Excel = Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel;
А в методе button1_Click замените так:
private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
string fileName = "D:\temp\test.xls";
try
{
var excel = new Excel.Application();
var workBooks = excel.Workbooks;
var workBook = workBooks.Add();
var workSheet = (Excel.Worksheet)excel.ActiveSheet;
workSheet.Cells[1, "A"] = textBox1.Text;
workBook.SaveAs(fileName);
workBook.Close();
}
catch (Exception ex) {
MessageBox.Show("Ошибка: "+ ex.ToString());
}
MessageBox.Show("Файл "+ Path.GetFileName (fileName) + " записан успешно!");
}
Вот, собственно говоря и все. Текст из текстбокса запишется в ячейку A1. Обратите внимание, что папка temp на диске уже должна существовать.
Дополнение. Прочитать первую ячейку
Это тоже просто:
string fileName = "D:\temp\test.xls"; Excel.Application xlApp = new Excel.Application(); Excel.Workbook xlWorkbook = xlApp.Workbooks.Open(fileName, 0, true, 5, "", "", true, Excel.XlPlatform.xlWindows, "t", false, false, 0, true, 1, 0); Excel._Worksheet xlWorksheet = (Excel._Worksheet)xlWorkbook.Sheets[1]; Excel.Range xlRange = xlWorksheet.UsedRange; string temp = (string)(xlRange.Cells[1, 1] as Excel.Range).Value2;// 1 1 - адрес 1-й ячейки MessageBox.Show(temp);
Автор этого материала — я — Пахолков Юрий. Я оказываю услуги по написанию программ на языках Java, C++, C# (а также консультирую по ним) и созданию сайтов. Работаю с сайтами на CMS OpenCart, WordPress, ModX и самописными. Кроме этого, работаю напрямую с JavaScript, PHP, CSS, HTML — то есть могу доработать ваш сайт или помочь с веб-программированием. Пишите сюда.
заметки, си шарп, excel
I am trying to convert some VBA code to C#. I am new to C#. Currently I am trying to open an Excel file from a folder and if it does not exist then create it. I am trying something like the following. How can I make it work?
Excel.Application objexcel;
Excel.Workbook wbexcel;
bool wbexists;
Excel.Worksheet objsht;
Excel.Range objrange;
objexcel = new Excel.Application();
if (Directory("C:\csharp\error report1.xls") = "")
{
wbexcel.NewSheet();
}
else
{
wbexcel.Open("C:\csharp\error report1.xls");
objsht = ("sheet1");
}
objsht.Activate();
abatishchev
97.3k85 gold badges297 silver badges432 bronze badges
asked Jan 21, 2009 at 11:25
4
You need to have installed Microsoft Visual Studio Tools for Office (VSTO).
VSTO can be selected in the Visual Studio installer under Workloads > Web & Cloud > Office/SharePoint Development.
After that create a generic .NET project and add a reference to Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel via ‘Add Reference… > Assemblies’ dialog.
Application excel = new Application();
Workbook wb = excel.Workbooks.Open(path);
Missing.Value is a special reflection struct for unnecessary parameters replacement
In newer versions, the assembly reference required is called Microsoft Excel 16.0 Object Library. If you do not have the latest version installed you might have Microsoft Excel 15.0 Object Library, or an older version, but it is the same process to include.
answered Jan 21, 2009 at 15:07
abatishchevabatishchev
97.3k85 gold badges297 silver badges432 bronze badges
13
FileInfo fi = new FileInfo("C:\test\report.xlsx");
if(fi.Exists)
{
System.Diagnostics.Process.Start(@"C:testreport.xlsx");
}
else
{
//file doesn't exist
}
answered Oct 18, 2011 at 21:49
MennanMennan
4,42112 gold badges53 silver badges86 bronze badges
4
private void btnChoose2_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
OpenFileDialog openfileDialog1 = new OpenFileDialog();
if (openfileDialog1.ShowDialog() == System.Windows.Forms.DialogResult.OK)
{
this.btnChoose2.Text = openfileDialog1.FileName;
String filename = DialogResult.ToString();
var excelApp = new Excel.Application();
excelApp.Visible = true;
excelApp.Workbooks.Open(btnChoose2.Text);
}
}
LarsTech
80.3k14 gold badges151 silver badges222 bronze badges
answered Jan 28, 2014 at 17:45
FlaneFlane
1111 silver badge3 bronze badges
1
Imports
using Excel= Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel;
using Microsoft.VisualStudio.Tools.Applications.Runtime;
Here is the code to open an excel sheet using C#.
Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel.Application excel = new Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel.Application();
Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel.Workbook wbv = excel.Workbooks.Open("C:\YourExcelSheet.xlsx");
Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel.Worksheet wx = excel.ActiveSheet as Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel.Worksheet;
wbv.Close(true, Type.Missing, Type.Missing);
excel.Quit();
Here is a video mate on how to open an excel worksheet using C# https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=O5Dnv0tfGv4
answered Aug 20, 2016 at 0:39
0
For opening a file, try this:
objexcel.Workbooks.Open(@"C:YourPathYourExcelFile.xls",
missing, missing, missing, missing, missing, missing, missing,
missing, missing, missing, missing, missing,missing, missing);
You must supply those stupid looking ‘missing’ arguments. If you were writing the same code in VB.Net you wouldn’t have needed them, but you can’t avoid them in C#.
answered Jan 21, 2009 at 11:39
2
you should open like this
Excel.Application xlApp ;
Excel.Workbook xlWorkBook ;
Excel.Worksheet xlWorkSheet ;
object misValue = System.Reflection.Missing.Value;
xlApp = new Excel.ApplicationClass();
xlWorkBook = xlApp.Workbooks.Open("csharp.net-informations.xls", 0, true, 5, "", "", true, Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel.XlPlatform.xlWindows, "t", false, false, 0, true, 1, 0);
xlWorkSheet = (Excel.Worksheet)xlWorkBook.Worksheets.get_Item(1);
source : http://csharp.net-informations.com/excel/csharp-open-excel.htm
ruden
answered Apr 17, 2013 at 6:23
0
It’s easier to help you if you say what’s wrong as well, or what fails when you run it.
But from a quick glance you’ve confused a few things.
The following doesn’t work because of a couple of issues.
if (Directory("C:\csharp\error report1.xls") = "")
What you are trying to do is creating a new Directory object that should point to a file and then check if there was any errors.
What you are actually doing is trying to call a function named Directory() and then assign a string to the result. This won’t work since 1/ you don’t have a function named Directory(string str) and you cannot assign to the result from a function (you can only assign a value to a variable).
What you should do (for this line at least) is the following
FileInfo fi = new FileInfo("C:\csharp\error report1.xls");
if(!fi.Exists)
{
// Create the xl file here
}
else
{
// Open file here
}
As to why the Excel code doesn’t work, you have to check the documentation for the Excel library which google should be able to provide for you.
answered Jan 21, 2009 at 14:57
Mats FredrikssonMats Fredriksson
19.6k6 gold badges36 silver badges57 bronze badges
Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel.Application excapp;
excapp = new Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel.Application();
object misval=System.Reflection.Missing.Value;
Workbook wrkbuk = new Workbook();
Worksheet wrksht = new Worksheet();
wrkbuk = excapp.Workbooks._Open(@"C:Users......_template_v1.0.xlsx", misval, misval,
misval, misval, misval, misval, misval, misval, misval, misval, misval, misval);
wrksht = (Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel.Worksheet)wrkbuk.Worksheets.get_Item(2);
RememberME
2,0823 gold badges37 silver badges62 bronze badges
answered Jul 15, 2011 at 10:50
Is this a commercial application or some hobbyist / open source software?
I’m asking this because in my experience, all free .NET Excel handling alternatives have serious problems, for different reasons. For hobbyist things, I usually end up porting jExcelApi from Java to C# and using it.
But if this is a commercial application, you would be better off by purchasing a third party library, like Aspose.Cells. Believe me, it totally worths it as it saves a lot of time and time ain’t free.
answered Jan 21, 2009 at 15:29
Tamas CzinegeTamas Czinege
118k40 gold badges148 silver badges175 bronze badges
Code :
private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
textBox1.Enabled=false;
OpenFileDialog ofd = new OpenFileDialog();
ofd.Filter = "Excell File |*.xlsx;*,xlsx";
if (ofd.ShowDialog() == DialogResult.OK)
{
string extn = Path.GetExtension(ofd.FileName);
if (extn.Equals(".xls") || extn.Equals(".xlsx"))
{
filename = ofd.FileName;
if (filename != "")
{
try
{
string excelfilename = Path.GetFileName(filename);
}
catch (Exception ew)
{
MessageBox.Show("Errror:" + ew.ToString());
}
}
}
}
answered Jan 12, 2015 at 6:54
For editing Excel files from within a C# application, I recently started using NPOI.
I’m very satisfied with it.
answered Apr 4, 2012 at 15:06
bvgheluwebvgheluwe
8537 silver badges25 bronze badges
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 238 239 240 241 242 243 244 245 246 247 248 249 250 251 252 253 254 255 256 257 258 259 260 261 262 263 264 265 266 267 268 269 270 271 272 273 274 275 276 277 278 279 280 281 282 283 284 285 286 287 288 289 290 291 292 293 294 295 296 297 298 299 300 301 302 303 304 305 306 307 308 309 310 311 312 313 314 315 316 317 318 319 320 321 322 323 324 325 326 327 328 329 330 331 332 333 334 335 336 337 338 339 340 341 342 343 344 345 346 347 348 349 350 351 352 353 354 355 356 357 358 359 360 361 362 363 364 365 |
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Diagnostics; using System.IO; using System.Windows.Forms; using Excel = Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel; namespace WindowsFormsApplication1 { public partial class Form1 : Form { List<char> ABC; //счетчик и "сбрасыватель" счетчика int abcIt = 0; int abc = 26; //26 букв в англ. алфавите ;) public Form1() { InitializeComponent(); } private void Form1_Load(object sender, EventArgs e) { ABC = new List<char>(); for (int i = 65; i < 91; i++) //ABCDEF... англ. алфавит { ABC.Add((char)i); } } private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) //Загружаем данные в dataGridView с Excel файла и вырисовываем dataGridView { bool Load = true; CloseExcel(); bool isSelected = false; openFileDialog1.InitialDirectory = "C:"; openFileDialog1.Title = "Выбрать файл"; openFileDialog1.FileName = ""; openFileDialog1.Filter = "Файлы xlsx|*.xlsx"; if (openFileDialog1.ShowDialog() == DialogResult.OK) { Prop.Path = openFileDialog1.FileName; isSelected = true; Prop.FileName = openFileDialog1.SafeFileName; } else { MessageBox.Show("Файл не выбран"); } if (isSelected) //Файл выбран, начинаем загрузку в dataGridView { this.Cursor = Cursors.AppStarting; //Меняем вид курсора пока происходит загрузка из файла на dataGridView. dataGridView1.RowHeadersWidth = 60; //Ширина столбца, заголовков строк abcIt = 0; abc = 26; Excel.Application xlApp; Excel.Workbook xlWorkBook; Excel.Worksheet xlWorkSheet; object misValue = System.Reflection.Missing.Value; xlApp = new Excel.Application(); var workbooks = xlApp.Workbooks; xlWorkBook = workbooks.Open(Prop.Path, 0, false, 5, "", "", true, Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel.XlPlatform.xlWindows, "t", false, false, 0, true, 1, 0); var worksheets = xlWorkBook.Worksheets; xlWorkSheet = (Excel.Worksheet)worksheets.get_Item(1); //Счетчики int NullRows = 0; int NullColums = 0; int index = 1; //Считаем сколько у нас заполненных строк и столбцов в excel файле. Считать будем по заголовкам. Все остальное в расчет не брал. //Количество строк. Подсчет ведется для создания количества строк на dataGridView. for (int x = 1; x < 256; x++) //То есть больше 256х256 он искать не будет. Но и лишние - пустые ячейки он считать не будет. { if (xlWorkSheet.Cells[x, index].Value == null) //Если ячейка пустая, то наш счетчик считает до 5 и выходит из цикла. (Вспомнилась считалочка, "Я считаю до пяти, не могу до десяти") { NullRows++; if (NullRows == 5) { Prop.X = x - 5; if (Prop.X > 0) //Проверка на вертикальные заголовки. Если есть текст, то загружаем его в dataGridView { break; } else { x = 0; NullRows = 0; //Обнуляем счетчики, для дальнейшего подсчета index++; //Увеличиваем индекс на 1, для просмотра строк, следующих пяти столбцов if (index == 5) //Если же 5 строк пяти столбцов оказались без текста, то... { MessageBox.Show("Файл либо пустой, либо поиск рассчитан на определенное расположение текста в Excel файле. Работа с данным файлом, в данное версии программы, прекращена"); index = 1; Load = false; break; } } } } else //Если же после пустых ячеек(до 5), есть еще заполненная ячейка, то "обнуляем" наш счетчик. { if (NullRows >= 1) { NullRows = 0; } } } //Количество столбцов. Подсчет ведется для создания количества столбцов на dataGridView. for (int y = 1; y < 256; y++) { if (xlWorkSheet.Cells[1, y].Value == null) { NullColums++; if (NullColums == 5) { Prop.Y = y - 5; if (Prop.Y > 0) //Проверка на вертикальные заголовки(надеюсь понятно, что это такое;)). Если есть текст, то загружаем его { break; } else { y = 0; NullColums = 0; index++; if (index == 5) { MessageBox.Show("Файл либо пустой, либо поиск рассчитан на определенное расположение текста в Excel файле. Работа с данным файлом, в данное версии программы, прекращена"); index = 1; Load = false; break; } } } } else { if (NullColums >= 1) { NullColums = 0; } } } if (Load) { //Рисуем dataGridView1 dataGridView1.RowCount = Prop.X; dataGridView1.ColumnCount = Prop.Y; //названия/имена "x" и "y" малость перепутаны ;) for (int x = 0; x < Prop.Y; x++) { if ((string)dataGridView1.Columns[x].HeaderCell.Value == "") //Если вместо "АА" "АВ" и тд. будет "", то... { //Если дойдем до "AZ", то после следующей "махинации", следующий заголовок столбца станет "BA"..."BZ","CA"..."CZ" и тд. if ((x - 26) == 26) { abcIt++; abc += 26; } dataGridView1.Columns[x].HeaderCell.Value = ABC[abcIt].ToString() + ABC[x - abc].ToString(); //Пишем в заголовки столбцов (AA AB AC AD.. DA DB... ZZ дальше ZZ выдаст ошибку, индекс за пределами массива. Если расчет верен, ZZ будет столбцом № 17602 в Excel файле) } for (int y = 0; y < Prop.X; y++) { if (dataGridView1.Rows[y].HeaderCell.Value == null) //проверка на null - чтобы лишний раз не записывать одно и то же число в одну и ту же ячейку { dataGridView1.Rows[y].HeaderCell.Value = (y + 1).ToString(); //Записываем в dataGridView, в строковые заголовки, значения от 1 до Prop.Y } //Записываем в dataGridView dataGridView1[x, y].Value = xlWorkSheet.Cells[y + 1, x + 1].Value; } } } //Закрываем документы xlWorkBook.Close(true, misValue, misValue); xlApp.Quit(); this.Cursor = Cursors.Default; //Меняем вид курсора в первоисходное положение } } private void button2_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) //Сохраняем в Excel файл { CloseExcel(); bool isSave = false; saveFileDialog1.InitialDirectory = "C:"; saveFileDialog1.Title = "Сохранить в файл"; saveFileDialog1.FileName = ""; saveFileDialog1.Filter = "Файлы xlsx|*.xlsx"; saveFileDialog1.FileName = Prop.FileName; if (saveFileDialog1.ShowDialog() == DialogResult.OK) { Prop.Path = saveFileDialog1.FileName; isSave = true; } else { MessageBox.Show("Файл не сохранен"); } if (isSave) { //Если файл не существует, то мы создадим его if (!File.Exists(Prop.Path)) { Excel.Application WorkExcel = new Excel.Application(); Excel.Workbook WorkBook = WorkExcel.Workbooks.Add(); // создаем книгу WorkBook.SaveAs(Prop.Path);//сохранить Excel файл WorkBook.Close(); WorkExcel.Quit(); } this.Cursor = Cursors.AppStarting; //Меняем вид курсора пока происходит сохранение в файл. Excel.Application xlApp; Excel.Workbook xlWorkBook; Excel.Worksheet xlWorkSheet; object misValue = System.Reflection.Missing.Value; xlApp = new Excel.Application(); var workbooks = xlApp.Workbooks; xlWorkBook = workbooks.Open(Prop.Path, 0, false, 5, "", "", true, Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel.XlPlatform.xlWindows, "t", false, false, 0, true, 1, 0); var worksheets = xlWorkBook.Worksheets; xlWorkSheet = (Excel.Worksheet)worksheets.get_Item(1); Prop.X = dataGridView1.Columns.Count; Prop.Y = dataGridView1.Rows.Count; //Сохраняем в Excel файл. for (int x = 0; x < Prop.X; x++) { for (int y = 0; y < Prop.Y; y++) { xlWorkSheet.Cells[y + 1, x + 1].Value = dataGridView1[x, y].Value; } } xlWorkBook.Save(); xlWorkBook.Close(true, misValue, misValue); xlApp.Quit(); this.Cursor = Cursors.Default; MessageBox.Show("Сохранено!"); } } void CloseExcel() { int proc = 0; bool OK = false; bool Cancel = false; foreach (Process item in Process.GetProcesses()) { if (item.ProcessName == "EXCEL") { proc++; if (proc > 0 && !Cancel) { //Чтобы не повторяться, то есть по несколько раз не выдавать одно и тоже сообщение if (!OK) { var result = MessageBox.Show("Для корректной работы программы процесс Microsoft Excel нужно завершить. При завершении все не сохраненные файлы будут потеряны. Прежде чем завершить работу процесса, сохраните данные. Все ровно завершить?", "Обнаружен включенный процесс Microsoft Excel", MessageBoxButtons.OKCancel, MessageBoxIcon.Warning); if (result == DialogResult.OK) { OK = true; } else { Cancel = true; } } if (OK) { item.Kill(); } } } if (Cancel) { break; } } } } } |
Microsoft Excel is powerful spreadsheet tool with lots of features for data visualization, analysis and documentation. Excel formats data in the form of rows and columns and cells. As a developer, many times you are required to read or write data into an Excel file. There are multiple ways to read and write data in excel programmatically i.e. by using COM Components and using third party components/SDKs.
This tutorial shows you how to Read and Write Excel files in Microsoft C#. We are going to use Microsoft COM Objects i.e. Excel 16 object in our application. Use the following sample C# source code for Excel reading and writing. There are multiple examples discussed in this tutorial to read Excel files using C# and write data back to Excel file.
Table of Contents
- Write data to Excel file
- Read data from Excel file
- Steps to read and write data from Excel using C#
- Step 1: Create a new C# project in Visual Studio
- Step 2: Add COM Component Reference i.e. Excel 14 Object
- Step 3: Import the namespaces in C# code
- Step 4: Write Data to Excel File
- Step 5: Read Data from Excel File
- Step 6: Run the C# Program
Write data to Excel file
The following C# code uses the Excel interop library to create a new Excel instance, open a specified workbook and write text to the first cell of the worksheet. It also includes cleanup code to release resources and ensure that the Excel process is fully closed.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 |
// Set cursor as hourglass Cursor.Current = Cursors.WaitCursor; Excel.Application xlApp = new Excel.Application(); Excel.Workbook xlWorkbook = xlApp.Workbooks.Open(FileName); Excel._Worksheet xlWorksheet = xlWorkbook.Sheets[1]; Excel.Range xlRange = xlWorksheet.UsedRange; xlWorksheet.Cells[1, 1] = txtWrite.Text; xlApp.Visible = false; xlApp.UserControl = false; xlWorkbook.Save(); //cleanup GC.Collect(); GC.WaitForPendingFinalizers(); //release com objects to fully kill excel process from running in the background Marshal.ReleaseComObject(xlRange); Marshal.ReleaseComObject(xlWorksheet); //close and release xlWorkbook.Close(); Marshal.ReleaseComObject(xlWorkbook); //quit and release xlApp.Quit(); Marshal.ReleaseComObject(xlApp); // Set cursor as default arrow Cursor.Current = Cursors.Default; |
Read data from Excel file
The following C# code also uses the same mechanism to read the data from an Excel sheet. First, it creates a new Excel instance, open a specified workbook and read value from the second cell of the worksheet. It also includes cleanup code to release resources and ensure that the Excel process is fully closed.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 |
// Set cursor as hourglass Cursor.Current = Cursors.WaitCursor; Excel.Application xlApp = new Excel.Application(); Excel.Workbook xlWorkbook = xlApp.Workbooks.Open(FileName); Excel._Worksheet xlWorksheet = xlWorkbook.Sheets[1]; Excel.Range xlRange = xlWorksheet.UsedRange; if (xlRange.Cells[1, 2] != null && xlRange.Cells[1, 2].Value2 != null) { txtRead.Text = xlRange.Cells[1, 2].Value2.ToString(); } //cleanup GC.Collect(); GC.WaitForPendingFinalizers(); //release com objects to fully kill excel process from running in the background Marshal.ReleaseComObject(xlRange); Marshal.ReleaseComObject(xlWorksheet); //close and release xlWorkbook.Close(); Marshal.ReleaseComObject(xlWorkbook); //quit and release xlApp.Quit(); Marshal.ReleaseComObject(xlApp); // Set cursor as default arrow Cursor.Current = Cursors.Default; |
Steps to read and write data from Excel using C#
In this tutorial, we are going to use Microsoft Visual Studio 2017 Community Edition.
Step 1: Create a new C# project in Visual Studio
Open up Visual Studio and create a new Windows Desktop application using Visual C#. You can choose any .NET Framework available in your computer. We are going to use .NET Framework 4.6.1.
Step 2: Add COM Component Reference i.e. Excel 14 Object
Next step is to right click on ExcelReaderWriter C# Project under Solution Explorer and choose Add->Reference.
Then choose COM->Type Libraries and select the desired COM Component for Excel. In our case we used Microsoft Excel 16.0 Object Library.
Step 3: Import the namespaces in C# code
Add the following namespaces to import into the code.
|
using System.Runtime.InteropServices; //Microsoft Excel 16 object in references-> COM tab using Excel = Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel; |
Also create a class variable to hold Excel File name i.e.
|
private string FileName = @«C:data.xlsx» |
Step 4: Write Data to Excel File
Add a Button and TextBox controls on the form. Then double click on the button to show up the code view and Visual Studio Automatically creates the button click event handler. Add the code to the handler so that it looks like below:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 |
private void btnWrite_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { // Set cursor as hourglass Cursor.Current = Cursors.WaitCursor; Excel.Application xlApp = new Excel.Application(); Excel.Workbook xlWorkbook = xlApp.Workbooks.Open(FileName); Excel._Worksheet xlWorksheet = xlWorkbook.Sheets[1]; Excel.Range xlRange = xlWorksheet.UsedRange; xlWorksheet.Cells[1, 1] = txtWrite.Text; xlApp.Visible = false; xlApp.UserControl = false; xlWorkbook.Save(); //cleanup GC.Collect(); GC.WaitForPendingFinalizers(); //release com objects to fully kill excel process from running in the background Marshal.ReleaseComObject(xlRange); Marshal.ReleaseComObject(xlWorksheet); //close and release xlWorkbook.Close(); Marshal.ReleaseComObject(xlWorkbook); //quit and release xlApp.Quit(); Marshal.ReleaseComObject(xlApp); // Set cursor as default arrow Cursor.Current = Cursors.Default; } |
Step 5: Read Data from Excel File
Create another Button and TextBox control to use for reading the data from Excel file. Add the following code to button click even handler.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 |
private void btnRead_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { // Set cursor as hourglass Cursor.Current = Cursors.WaitCursor; Excel.Application xlApp = new Excel.Application(); Excel.Workbook xlWorkbook = xlApp.Workbooks.Open(FileName); Excel._Worksheet xlWorksheet = xlWorkbook.Sheets[1]; Excel.Range xlRange = xlWorksheet.UsedRange; if (xlRange.Cells[1, 2] != null && xlRange.Cells[1, 2].Value2 != null) { txtRead.Text = xlRange.Cells[1, 2].Value2.ToString(); } //cleanup GC.Collect(); GC.WaitForPendingFinalizers(); //release com objects to fully kill excel process from running in the background Marshal.ReleaseComObject(xlRange); Marshal.ReleaseComObject(xlWorksheet); //close and release xlWorkbook.Close(); Marshal.ReleaseComObject(xlWorkbook); //quit and release xlApp.Quit(); Marshal.ReleaseComObject(xlApp); // Set cursor as default arrow Cursor.Current = Cursors.Default; } |
Step 6: Run the C# Program
Compile and run the program now. The output should be similar to the one showing below. Enter some data in first text box and click Write button. It will write data to already created Excel file C:data.xlsx. Similarly, you can click on Read button, which will read the data from same Excel file and show it in the second text file.
There are other third party libraries available, which you can use in your code to read and write Excel files. These libraries are available both under open source as well as commercially available. Few of them are:
- https://github.com/nissl-lab/npoi – Open Source, Apache 2.0 License
- https://github.com/EPPlusSoftware/EPPlus – Commercially Available
- https://github.com/JanKallman/EPPlus – Available under LGPL
- https://bytescout.com/products/developer/spreadsheetsdk/bytescoutspreadsheetsdk.html – Commercially Available