“John felt he was living the American dream….What is another word for American dream?
| good life | bed of roses |
|---|---|
| life of Riley | hog heaven |
| easy street | comfort |
| luxury | the good life |
| good fortune | well-being |
What is the American dream during the Great Depression?
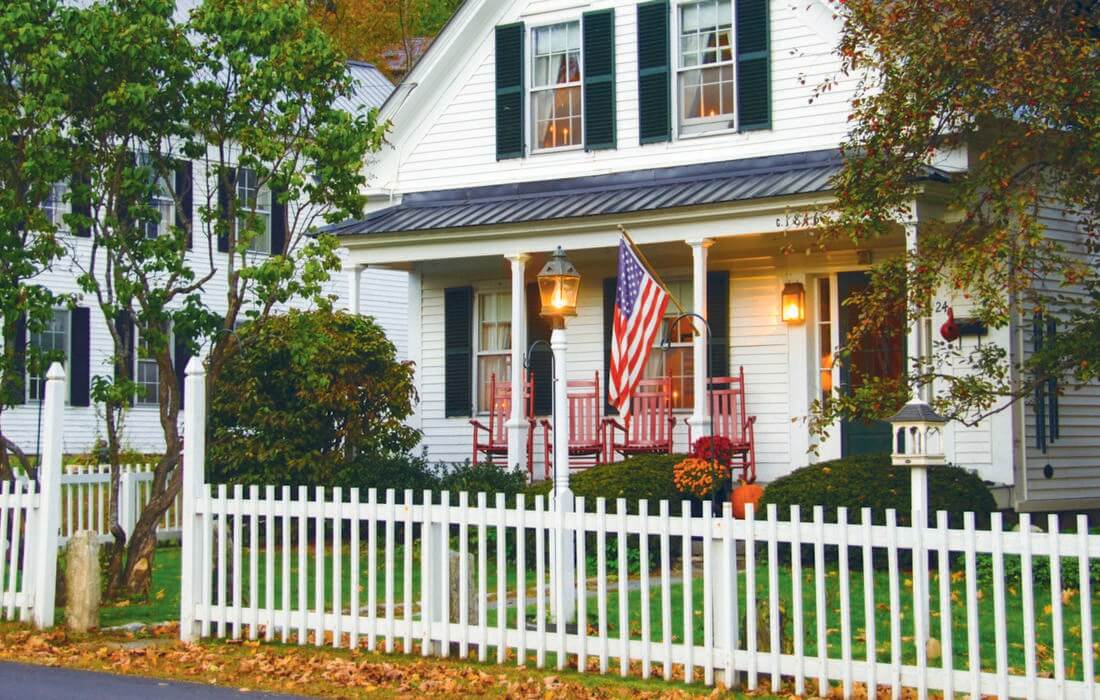
During the 1930’s, the ideal American Dream consisted of three criterions: two children, a marriage, and a three-bedroom house with the infamous white picket fence. The American Dream rose to its greatest fame during the 1930’s as a result of the on-going Great Depression from 1929 to 1939.
Is the American Dream a destructive or empowering force?
The American Dream is an empowering force because it allows lower than average people to become wealthy, however, it is a destructive force because it leads to greed, and blinds people from the facing reality because of their avid desire for greater amounts of wealth, and material goods.
What is the American Dream in a raisin in the sun?
The American dream in the ’50s was close to materialism. The ownership of consumer goods was believed to bring joy into a family’s life. This stereotypical view governs the dream of one of the main characters in Lorraine Hansberry’s play.
What is the biggest obstacle to reaching the American Dream essay?
While there are many reasons people struggle, poverty is the biggest obstacle to the American Dream. In fact, all four stories illustrate poverty. Cite Evidence: It is poverty that keeps Esperanza’s family from their dream house and Esperanza’s mother from her education.
In what ways did the American dream become a reality for immigrants to the US?
The American Dream did come true for immigrants in New York because they were able to get jobs and their lives improved. The American Dream did come true for immigrants because they were able to escape the problems in their homelands and have a new start.
What was the American dream in the 1920s?
During the 1920s, the perception of the American Dream was that an individual can achieve success in life regardless of family history or social status if they only work hard enough.
Is American dream available to everyone?
The American Dream can be broadly defined as the belief that anyone, regardless of where they were born or what class they were born into, can attain their own version of success in a society where upward mobility is possible for everyone.
What is American Ness?
“Americanness” is defined as “The quality of being American, of having and revealing American characteristics” (“American”). In 2008, that definition is updated and upgraded to full entry; the word is now defined as “The quality or fact of being American or having American characteristics” (“Americanness”).
What are the obstacles to achieving the American dream?
Lack of education and work opportunities, a depressed or recessionary economy, inadequate political direction and global factors are all seen by most Americans as significant obstacles to achieving the American Dream. Disadvantages are even more acute for recent immigrants although they apply to all demographics.
How is the American dream part of the American identity?
For many people the American Dream defines the American identity. The American dream means individualism, gaining control of one’s life, and the pursuit of happiness and upward mobility. However, the American Dream is not a universal concept that ensures success and equality.
When did the American dream become popular?
It was in that creed that the phrase the American dream was first used to articulate — not in 1931, when it was popularized, but when it first appeared in American political discourse, at the turn of the 20th century.
What is the American Dream in the Great Gatsby essay?
In The Great Gatsby by Scott Fitzgerald the power and drive the American Dream creates is present through wealth, social class, and the realities of the characters. The American Dream is defined as someone starting low on the economic, or social level, and working hard to achieve wealth and prosperity.
How do you live the American dream?
Part of the American dream is having the freedom to do things besides work to make a fuller, happier life for yourself. Spend time doing the things you love — this can mean hobbies, like writing, playing sports, and working on your car, but it can also mean simple pleasures like simply spending time with your family.
Why is the American dream so important?
The American Dream is the idea that the government should protect each person’s opportunity to pursue their idea of happiness. The government protects the rights of you and every other American citizen to find their path to economic prosperity.
Is the American dream a real term or attitude?
The American Dream can be considered as a real term and as an attitude. The idea of the American Dream is where qualities of hard work and ambition are shown. It’s defined as someone starting low on the economic or social level, and working hard towards fortune, prosperity and or fame.
What is the American Dream Oxford dictionary?
noun. /ði əˌmerɪkən ˈdriːm/ /ði əˌmerɪkən ˈdriːm/ [singular] the belief that America offers the opportunity to everyone of a good and successful life achieved through hard work.
Does the American Dream make you happy?
“The American Dream” most often conjures up images of opportunity, success, happiness. But these ideals have evolved since 1931 when the phrase was coined by the writer James Truslow Adams. Adams intended for the American Dream to signify idealism and freedom more than “material prosperity,” according to The Atlantic.
What are examples of the American dream?
Examples of the American Dream include owning your own house, starting a family, and having a stable job, or owning your own business.
as in la dolce vita
a life marked by material wealth and comfort
with the acquisition of a big house in the suburbs, they felt as though the American dream had indeed become a reality for them
Thesaurus Entries Near American dream
Cite this Entry
“American dream.” Merriam-Webster.com Thesaurus, Merriam-Webster, https://www.merriam-webster.com/thesaurus/American%20dream. Accessed 14 Apr. 2023.
Share
Subscribe to America’s largest dictionary and get thousands more definitions and advanced search—ad free!
Merriam-Webster unabridged
What is another word for American dream?good lifebed of rosesopulencerichdomsuccessgravy trainaffluenceexorbitanceeaseprosperousness118
What two words describe the United States?
Here is a list of words that describe society in the United States:African American.Ambitious.American dream.American Indian.Cajun.Colonial.Democratic.Hillbilly.
What are words to describe America?
There are many words that describe America, and almost all of them are good, such as freedom, full, grateful, pride and most of all, happy.
What is another word for American?
American Synonyms – WordHippo Thesaurus….What is another word for American?New WorlderUnited StatesianU.S. AmericanUnited StatesmanUSianUS’er5
Why is the US referred to as America?
The Western world was named after Amerigo Vespucci, which led to the continents being named “North America” and “South America”. When several states within North America all united to form a single government, they called themselves the “United States of America”.

What is the most common word used in America?
100 most common wordsWordParts of speechOEC ranktheArticle1beVerb2toPreposition3ofPreposition477
What is an act of patriotism?
Patriotism or national pride is the feeling of love, devotion, and sense of attachment to a homeland and alliance with other citizens who share the same sentiment. This attachment can be a combination of many different feelings relating to one’s own homeland, including ethnic, cultural, political or historical aspects.
What Is the American Dream?
The American dream is the belief that anyone, regardless of where they were born or what class they were born into, can attain their own version of success in a society in which upward mobility is possible for everyone.
The American dream is believed to be achieved through sacrifice, risk-taking, and hard work, rather than by chance.
Key Takeaways
- The term «American dream» was coined in a best-selling book in 1931 titled Epic of America.
- James Truslow Adams described it as «that dream of a land in which life should be better and richer and fuller for everyone, with opportunity for each according to ability or achievement.»
- The American dream was aided by a number of factors that gave the United States a competitive advantage over other countries.
- Homeownership and education are often seen as paths to achieving the American dream.
- Though the definition of the American Dream has changed to mean different things to different generations, it’s undoubtedly part of the American ethos, and likely always will be.
American Dream
Understanding the American Dream
The term was coined by writer and historian James Truslow Adams in his best-selling 1931 book Epic of America. He described it as «that dream of a land in which life should be better and richer and fuller for everyone, with opportunity for each according to ability or achievement.»
Adams went on to explain, «It is a difficult dream for the European upper classes to interpret adequately, and too many of us ourselves have grown weary and mistrustful of it. It is not a dream of motorcars and high wages merely, but a dream of social order in which each man and woman shall be able to attain to the fullest stature of which they are innately capable, and be recognized by others for what they are, regardless of the fortuitous circumstances of birth or position.»
The idea of the American dream has much deeper roots. Its tenets can be found in the Declaration of Independence, which states: “We hold these truths to be self-evident, that all men are created equal, that they are endowed by their Creator with certain unalienable Rights, that among these are Life, Liberty, and the pursuit of Happiness.”
In a society based on these principles, an individual can live life to its fullest as they define it. America also grew mostly as a nation of immigrants who created a nation where becoming an American—and passing that citizenship to your children—didn’t require being the child of an American.
Advantages and Disadvantages of the American Dream
Advantages
Achieving the American dream requires political and economic freedom, as well as rules of law and private property rights. Without them, individuals cannot make the choices that will permit them to attain success, nor can they have confidence that their achievements will not be taken away from them through arbitrary force.
The American dream promises freedom and equality. It offers the freedom to make both the large and small decisions that affect one’s life, the freedom to aspire to bigger and better things and the possibility of achieving them, the freedom to accumulate wealth, the opportunity to lead a dignified life, and the freedom to live in accordance with one’s values—even if those values are not widely held or accepted.
The books of post-Civil War writer Horatio Alger, in which impoverished but hardworking teenage boys rise to success through pluck, determination, and good fortune, came to personify realizing the Dream.
The American dream also offers the promise that the circumstances of someone’s birth—including whether they were born American citizens or immigrants—do not completely determine their future.
Disadvantages
Terming it a «dream» also carries with it the notion that these ideals aren’t necessarily what has played out in the lives of many actual Americans and those who hope to become Americans. The criticism that reality falls short of the American dream is at least as old as the idea itself. The spread of settlers into Native American lands, slavery, the limitation of the vote (originally) to white male landowners, and a long list of other injustices and challenges have undermined the realization of the dream for many who live in the United States.
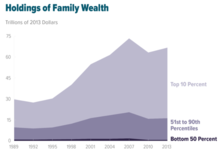
As income inequality has increased substantially since the 1970s, the American dream has begun to seem less attainable for those who aren’t already affluent or born into affluence. According to U.S. Census family income data, real family income began to grow much more among the top income group than among other segments of American society.
These realities, however, do not diminish the luster of the American dream as an ideal and a beacon to all nations.
Pros
-
The American dream promises freedom and equality.
-
The ideals of the American dream are motivating, including the freedom to be in charge of one’s own life.
Cons
-
The reality of the American dream often falls short of the idea itself.
-
As income inequality has increased, the American dream has seemed less attainable.
How to Measure the American Dream
Today, homeownership is frequently cited as an example of attaining the American dream. It is a symbol of financial success and independence, and it means the ability to control one’s own dwelling place instead of being subject to the whims of a landlord. Owning a business and being one’s own boss also represents the American dream fulfillment. In addition, access to education and healthcare have been cited as elements of the Dream.
Homeownership has steadily increased over time in the U.S., reflecting a key aspect of owning your own property as a sign of achieving the American Dream. For example, the homeownership rate at the end of 2020 was 65.8%, reflecting an increase of 0.7% higher than the previous year. Entrepreneurship has always been important to the U.S. economy too. In 2019, small businesses created 1.6 million net jobs alone.
Owning property, one’s own business, and carving a life of one’s own making is all part of the American dream, and the U.S. as a first-world country also offers the benefits of pursuing these passions, without having to worry about basics such as accessing good education and healthcare.
Special Considerations
In her book Spreading the American Dream: American Economic and Cultural Expansion, 1890-1945, sociologist Emily S. Rosenberg identifies five components of the American dream that have shown up in countries around the world. These include the following:
- The belief that other nations should replicate America’s development
- Faith in a free market economy
- Support for free trade agreements and foreign direct investment
- Promotion of a free flow of information and culture
- Acceptance of government protection of private enterprise
The American dream was aided by a number of factors that gave the United States a competitive advantage over other countries. For starters, it is relatively isolated geographically, compared to many other countries, and enjoys a temperate climate. It has a culturally diverse population that businesses use to foster innovation in a global landscape. Abundant natural resources—including oil, arable land, and long coastlines—generate food and income for the country and its residents.
“The American Dream” has always been about the prospect of success, but 100 years ago, the phrase meant the opposite of what it does now. The original “American Dream” was not a dream of individual wealth; it was a dream of equality, justice, and democracy for the nation used in the early 1900s The phrase was repurposed by each generation, until the Cold War, when it became an argument for a consumer capitalist version of democracy. Our ideas about the “American Dream” froze in the 1950s. Today, it doesn’t occur to anybody that it could mean anything else.
What Is the Original American Dream?
The phrase “American dream” was often used by Progressive-era reformers of the 1900s. Rather than exalting the pursuit of wealth, they sought to tame monopoly capitalism and protect workers and communities from robber barons. This concept was popularized by writer and historian James Truslow Adams in his best-selling 1931 book Epic of America. He described it as «that dream of a land in which life should be better and richer and fuller for everyone, with opportunity for each according to ability or achievement.»
What Are Examples of the American Dream?
Examples of the American Dream include owning your own house, starting a family, and having a stable job or owning your own business.
Is the American Dream Still Achievable?
It’s widely debated if the American Dream is still achievable, and what that achievement even entails. Indeed, today, many people wonder if they can keep up with rising housing costs and interest payments on loans needed to purchase things like homes and cars. Moreover, American’s need to save for their own retirement and pay large out-of-pocket costs for healthcare and higher education, which can leave families saddled with high-interest debt that is hard to crawl back from.
What Is the American Dream in Dr. Martin Luther King’s Speech?
Dr. Martin Luther King Jr.’s famous speech referenced the concept of the American dream by stating: «I have a dream that one day this nation will rise up and live out the true meaning of its creed: ‘We hold these truths to be self-evident; that all men are created equal.'» Since the early 1960s, Dr. King had pondered and preached about how African Americans didn’t get a chance to access the reality of the American dream because they were not truly equal to white men and women. Ultimately, Dr. King’s «American dream» was equality.
How Has the American Dream Changed?
Over time, the American dream has shifted from an ethos of equality and solidarity to one of individualistic competition to succeed materialistically, fueled by consumption. In the 1990s and early 2000s, mortgage company Fannie Mae began promulgating the notion that buying a home was a cornerstone of the American Dream, and use the term prominently in ads selling home loans. This ideology led to the housing boom and ultimate bubble that popped ultimately, leading to the 2008-09 financial crisis.
The Bottom Line
The concept of the American dream is still one of the most uniquely «American» ideals—the ultimate idea that any individual should be able to pursue their dreams and build the life they want if they put in the hard work. This motivating drive influences the economy with entrepreneurship and individual ambition, infusing a romantic notion to anyone trying to be successful in the United States. Though the definition of the American Dream has changed to mean different things to different generations, it’s undoubtedly part of the American ethos, and always will be.
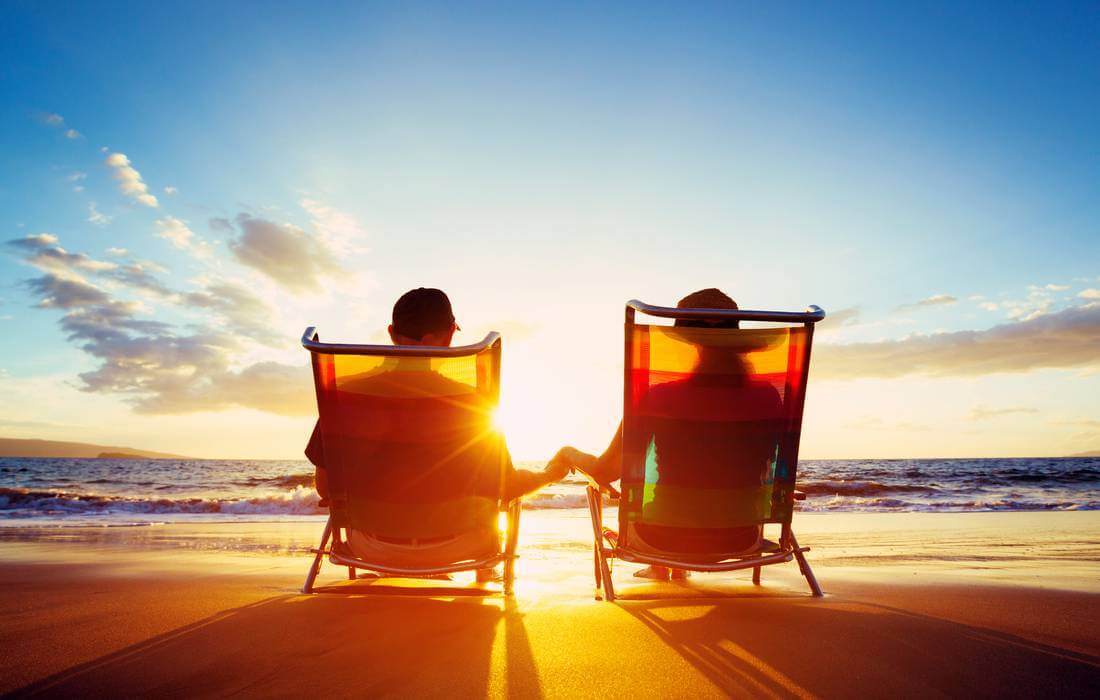
Who first started dreaming
Like any great idea, it all started in hard times.

In fact, the term «American dream» in this treatise is indicated quite indirectly — as the path to benefits and equality through labor. Practically, all the same was described in the Declaration of Independence of 1776, in our times Adams would be threatened with a court for plagiarism. But everything sounded rather pathetic and rather vague, so that the powers that be picked up the term and made a motivating motto of the generation.
Since the 1930s, no election campaign in the United States has managed without this phrase. It was used thousands of times in commercials and in sermons. If William Safire or Donald Trump talked about his greatness, then William Faulkner and Hunter Thompson smashed to smithereens. That is, its place in the culture, it has firmly taken.
How she looks like
The American dream is too abstract to give it a single definition. Historians, philosophers and culturologists have still not agreed on any of the interpretations. But during the existence of the term, a lot of social stereotypes and versions of its performance have been gathered, from which a certain picture can be folded.
As part of this concept is placed a whole complex of aspects:
- Values and ideals — politics, religion, social consciousness, etc.;
- Household life — that you need to have from the material;
- Relations in society — how to interact with other people.
We will understand in more detail the main points and the most important components — what needs to be done to make the dream come true.
What to think about
Since the foundation of the country, the main ideals of society have been freedom, democracy and the possibility of self-realization. Of course, not without reservations — women got the right to vote only in the 20s, and the tense situation with the African population subsided only by the 70th. The election of Barack Obama as president or the formation of Oprah Winfrey’s career is considered an unprecedented achievement even for such a deliberately democratic and tolerant country as the United States. But nevertheless, it is customary to think that it is the reliance on freedom and the concept of self-made (cultivating yourself as an intelligent person on your own) can create a miracle and turn anyone into a socially significant, open-minded person with a favorite and profitable job.
What to get
Stereotypical American life With a dream come true, it looks like this: a large bright house in the suburbs, a star-striped flag, a neat garden, a friendly family with two or more children are flying on the facade. After work on weekdays, family dinners and passive rest. Every Saturday — family holidays or barbecue in the courtyard, every Sunday — the church, most likely, Protestant. Food, clothing, car, money for entertainment, education and anything else — always in plenty, even a little in excess. And of course, it is assumed that all this will be earned by honest work and in proportion to the efforts.
Not that all this is not available in the apartment, the format itself is just changing. Material wealth should be as much as necessary to maintain a high quality of life. Well, maybe a little more. And a bit more. Until you get tired of their presence and need to spend.
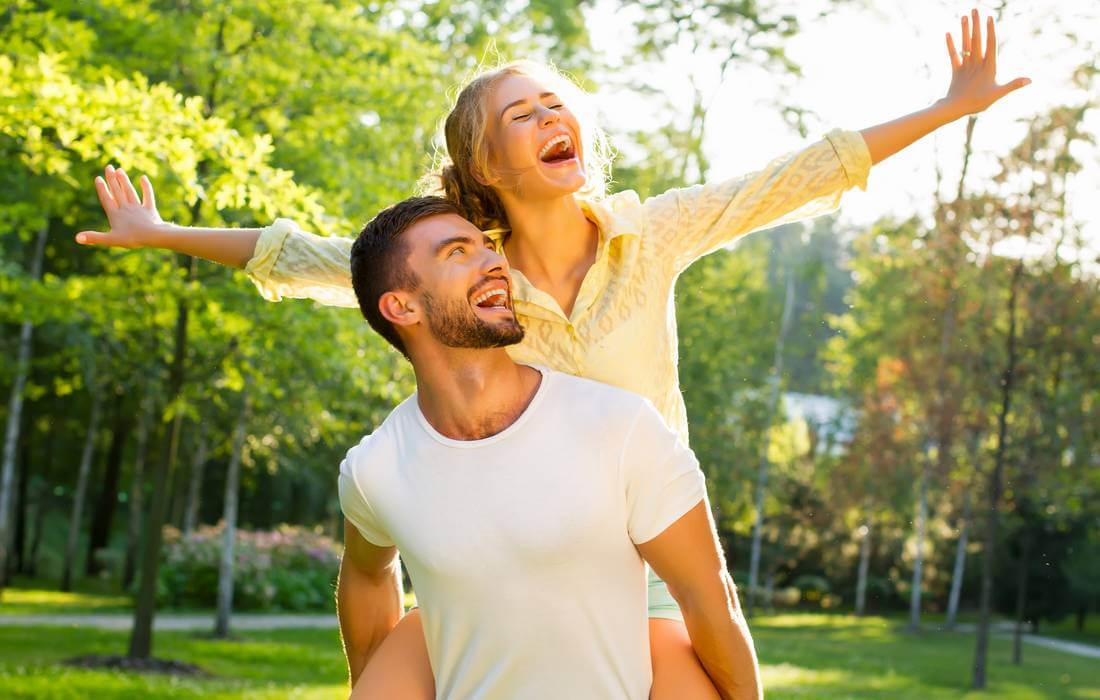
 Who and how to communicate
Who and how to communicate
You can communicate with everyone, but in different ways. The most important contacts are business. Here all means are good and there is no room for error. In second place is family and relatives, they will always understand and forgive. In the third — the image in society and maintaining the image of a confident and influential person. Even if this is not always the case, the brand is worth keeping. For the rest, only mutual respect and friendliness is required.
Nothing seems familiar? Almost the same concept of an ideal society, as in the USSR, only turned in a capitalist fashion. All the same rules of existence in order to feel good and find the approval of others. The American dream allows for individualism and encourages the accumulation of money as a resource for achieving happiness. Her Soviet sister loves to sentence «everything to the house» and does not love those who pop out. In fact, these are two utopias with one single difference. The first one even flashes on the horizon, even if it’s far away — there will always be a hero who wants to swim to it and really come out of the water by another person. The socialist paradise has not yet been discerned in any telescope.
It is always better to see once than read a hundred times. American Butler can help get as close to the American dream as possible. We organize the most interesting tours and help with the relocation and adaptation in the United States. Our customers are ordinary people from different countries, and you can get to America.
Сontact us via the chat window or any other available method, and consider that your journey has already begun.
Filters
Filter by Part of speech
phrase
noun
Suggest
If you know synonyms for American dream, then you can share it or put your rating in listed similar words.
Suggest synonym
Menu
American dream Thesaurus
Definitions of American dream
External Links
Other usefull sources with synonyms of this word:
Synonym.tech
Merriam-webster.com
Wiktionary.org
Image search results for American dream






Cite this Source
- APA
- MLA
- CMS
Synonyms for American dream. (2017). Retrieved 2023, April 14, from https://thesaurus.plus/synonyms/american_dream
Synonyms for American dream. N.p., 2017. Web. 14 Apr. 2023. <https://thesaurus.plus/synonyms/american_dream>.
Synonyms for American dream. 2017. Accessed April 14, 2023. https://thesaurus.plus/synonyms/american_dream.
During the mid-to-late 19th and early 20th-century of the United States, for many immigrants, the Statue of Liberty in New York Harbor was their first view of the country. In this role, it signified new opportunities for Americans and evolved into a symbol of the American Dream.
The American Dream is the national ethos of the United States, a set of ideals including representative democracy, rights, liberty, and equality, in which freedom is interpreted as the opportunity for individual prosperity and success, as well as upward social mobility for oneself and their children, achieved through hard work in a capitalist society with few barriers.
The term «American Dream» was coined by James Truslow Adams in 1931, saying that «life should be better and richer and fuller for everyone, with opportunity for each according to ability or achievement» regardless of social class or circumstances of birth.[1]
Proponents of the American Dream often claim that its tenets originate from the United States Declaration of Independence, which states that «all men are created equal» with the right to «life, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness».[2] The Preamble to the U.S. Constitution is used similarly. It states that the Constitution’s purpose is to, in part, «secure the Blessings of Liberty to ourselves and our Posterity».[a]
Throughout American history, there have been critics of its national ethos. Some critics point out that American focus on individualism and capital results in materialism, consumerism and a lack of worker solidarity.[3] In 2015, only 10.5 percent of American workers were members of a labor union.[4] The American Dream has also been criticized as a product of American exceptionalism, as it does not acknowledge the hardships many Americans face, namely in regards to the legacies of American slavery and Native American genocide, as well as other examples of discriminatory violence.[5]
Belief in the American Dream is often inversely associated with rates of national disillusionment. Evidence indicates that upward economic mobility has declined and income inequality has risen in the United States in recent decades.[6] In 2020, a poll found only 54 percent of US adults thought the American Dream was attainable for them, 28 percent believed it was unattainable for them personally, while 9 percent rejected the idea of the American Dream entirely. Younger generations were also less likely to believe in the American Dream than their older counterparts.[7]
History
|
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (November 2022) |
The meaning of the American Dream has changed over the course of history, and includes both personal components such as home ownership and upward mobility as well as a global vision for cultural hegemony and diplomacy.
18th century
Historically, the Dream originated in colonial mystique regarding frontier life. As John Murray, 4th Earl of Dunmore, the colonial Governor of Virginia, noted in 1774, the Americans «for ever imagine the Lands further off are still better than those upon which they are already settled». He added that, «if they attained Paradise, they would move on if they heard of a better place farther west».[8]
19th century
Many well-educated Germans who fled the failed 1848 revolution found the United States more politically free than their homeland, which they believed to be a hierarchical and aristocratic society that determined the ceiling for their aspirations. One of them claimed:
The German emigrant comes into a country free from the despotism, privileged orders and monopolies, intolerable taxes, and constraints in matters of belief and conscience. Everyone can travel and settle wherever he pleases. No passport is demanded, no police mingles in his affairs or hinders his movements … Fidelity and merit are the only sources of honor here. The rich stand on the same footing as the poor; the scholar is not a mug above the most humble mechanics; no German ought to be ashamed to pursue any occupation … [In America] wealth and possession of real estate confer not the least political right on its owner above what the poorest citizen has. Nor are there nobility, privileged orders, or standing armies to weaken the physical and moral power of the people, nor are there swarms of public functionaries to devour in idleness credit for. Above all, there are no princes and corrupt courts representing the so-called divine ‘right of birth’. In such a country the talents, energy and perseverance of a person … have far greater opportunity to display than in monarchies.[9]
The discovery of gold in California in 1849 brought in a hundred thousand men looking for their fortune overnight—and a few did find it. Thus was born the California Dream of instant success. Historian H. W. Brands noted that in the years after the Gold Rush, the California Dream spread across the nation:
The old American Dream … was the dream of the Puritans, of Benjamin Franklin’s «Poor Richard»… of men and women content to accumulate their modest fortunes a little at a time, year by year by year. The new dream was the dream of instant wealth, won in a twinkling by audacity and good luck. [This] golden dream … became a prominent part of the American psyche only after Sutter’s Mill.[10]
Historian Frederick Jackson Turner in 1893 advanced the frontier thesis, under which American democracy and the American Dream were formed by the American frontier. He stressed the process—the moving frontier line—and the impact it had on pioneers going through the process. He also stressed results; especially that American democracy was the primary result, along with egalitarianism, a lack of interest in high culture, and violence. «American democracy was born of no theorist’s dream; it was not carried in the Susan Constant to Virginia, nor in the Mayflower to Plymouth. It came out of the American forest, and it gained new strength each time it touched a new frontier,» said Turner.[11] In the thesis, the American frontier established liberty by releasing Americans from European mindsets and eroding old, dysfunctional customs. The frontier had no need for standing armies, established churches, aristocrats or nobles, nor for landed gentry who controlled most of the land and charged heavy rents. Frontier land was free for the taking. Turner first announced his thesis in a paper entitled «The Significance of the Frontier in American History», delivered to the American Historical Association in 1893 in Chicago. He won wide acclaim among historians and intellectuals. Turner elaborated on the theme in his advanced history lectures and in a series of essays published over the next 25 years, published along with his initial paper as The Frontier in American History.[12] Turner’s emphasis on the importance of the frontier in shaping American character influenced the interpretation found in thousands of scholarly histories. By the time Turner died in 1932, 60% of the leading history departments in the U.S. were teaching courses in frontier history along Turnerian lines.[13]
20th century
Freelance writer James Truslow Adams popularized the phrase «American Dream» in his 1931 book Epic of America:
But there has been also the American dream, that dream of a land in which life should be better and richer and fuller for every man, with opportunity for each according to his ability or achievement. It is a difficult dream for the European upper classes to interpret adequately, and too many of us ourselves have grown weary and mistrustful of it. It is not a dream of motor cars and high wages merely, but a dream of social order in which each man and each woman shall be able to attain to the fullest stature of which they are innately capable, and be recognized by others for what they are, regardless of the fortuitous circumstances of birth or position… The American dream, that has lured tens of millions of all nations to our shores in the past century has not been a dream of merely material plenty, though that has doubtlessly counted heavily. It has been much more than that. It has been a dream of being able to grow to fullest development as man and woman, unhampered by the barriers which had slowly been erected in the older civilizations, unrepressed by social orders which had developed for the benefit of classes rather than for the simple human being of any and every class.[citation needed]
Martin Luther King Jr., in his «Letter from a Birmingham Jail» (1963) rooted the civil rights movement in the African-American quest for the American Dream:[14]
We will win our freedom because the sacred heritage of our nation and the eternal will of God are embodied in our echoing demands … when these disinherited children of God sat down at lunch counters they were in reality standing up for what is best in the American dream and for the most sacred values in our Judeo-Christian heritage, thereby bringing our nation back to those great wells of democracy which were dug deep by the Founding Fathers in their formulation of the Constitution and the Declaration of Independence.
21st century
During the presidency of Donald Trump from 2017 to 2021, the American government instituted many immigration restrictions. Critics invoked the American Dream in their rhetoric. Congresswoman Alexandria Ocasio-Cortez responded to Trump’s immigrant wealth requirements by characterizing them as an attempt to turn the Dream into a «private club with a cover charge.»[15]
Literature
The concept of the American Dream has been used in popular discourse, and scholars have traced its use in American literature ranging from the Autobiography of Benjamin Franklin,[16] to Mark Twain’s Adventures of Huckleberry Finn (1884), Willa Cather’s My Ántonia,[17] F. Scott Fitzgerald’s The Great Gatsby (1925), Theodore Dreiser’s An American Tragedy (1925) and Toni Morrison’s Song of Solomon (1977).[18] Other writers who used the American Dream theme include Hunter S. Thompson, Edward Albee,[19] John Steinbeck,[20] Langston Hughes,[21] and Giannina Braschi.[22] The American Dream is also discussed in Arthur Miller’s Death of a Salesman as the play’s protagonist, Willy, is on a quest for the American Dream.
In 2006, Dr. Guiyou Huang from St. Thomas University in Florida wrote a
paper regarding the American Dream as a recurring theme in the fiction of Asian Americans.[23][24]
American ideals
Many American authors added American ideals to their work as a theme or other reoccurring idea, to get their point across.[25] There are many ideals that appear in American literature such as, but not limited to, all people are equal, United States of America is the Land of Opportunity, independence is valued, The American Dream is attainable, and everyone can succeed with hard work and determination. John Winthrop also wrote about this term called, American exceptionalism. This ideology refers to the idea that Americans are, as a nation, elect.[26]
European governments, worried that their best young people would leave for America, distributed posters like this to frighten them (this 1869 Swedish anti-emigration poster contrasts Per Svensson’s dream of the American idyll (left) and the reality of his life in the wilderness (right), where he is menaced by a mountain lion, a big snake and wild Indians who are scalping and disembowelling someone).[27]
The American Dream has been credited with helping to build a cohesive American experience, but has also been blamed for inflated expectations.[28] Some commentators have noted that despite deep-seated belief in the egalitarian American Dream, the modern American wealth structure still perpetuates racial and class inequalities between generations.[29] One sociologist notes that advantage and disadvantage are not always connected to individual successes or failures, but often to prior position in a social group.[29]
Since the 1920s, numerous authors, such as Sinclair Lewis in his 1922 novel Babbitt, and F. Scott Fitzgerald, in his 1925 classic, The Great Gatsby, satirized or ridiculed materialism in the chase for the American dream. For example, Jay Gatsby’s death mirrors the American Dream’s demise, reflecting the pessimism of modern-day Americans.[30] The American Dream is a main theme in the book by John Steinbeck, Of Mice and Men. The two friends George and Lennie dream of their own piece of land with a ranch, so they can «live off the fatta the lan'» and just enjoy a better life. The book later shows that not everyone can achieve the American Dream, although it is possible to achieve for a few. A lot of people follow the American Dream to achieve a greater chance of becoming rich. Some posit that the ease of achieving the American Dream changes with technological advances, availability of infrastructure and information, government regulations, state of the economy, and with the evolving cultural values of American demographics.
In 1949, Arthur Miller wrote Death of a Salesman, in which the American Dream is a fruitless pursuit. Similarly, in 1971 Hunter S. Thompson depicted in Fear and Loathing in Las Vegas: A Savage Journey Into the Heart of the American Dream a dark psychedelic reflection of the concept—successfully illustrated only in wasted pop-culture excess.[31]
The novel Requiem for a Dream by Hubert Selby Jr. is an exploration of the pursuit of American success as it turns delirious and lethal, told through the ensuing tailspin of its main characters. George Carlin famously wrote the joke «it’s called the American dream because you have to be asleep to believe it».[32] Carlin pointed to «the big wealthy business interests that control things and make all the important decisions» as having a greater influence than an individual’s choice.[32] Pulitzer Prize–winning journalist Chris Hedges echos this sentiment in his 2012 book Days of Destruction, Days of Revolt:[33]
The vaunted American dream, the idea that life will get better, that progress is inevitable if we obey the rules and work hard, that material prosperity is assured, has been replaced by a hard and bitter truth. The American dream, we now know, is a lie. We will all be sacrificed. The virus of corporate abuse—the perverted belief that only corporate profit matters—has spread to outsource our jobs, cut the budgets of our schools, close our libraries, and plague our communities with foreclosures and unemployment.
The American Dream, and the sometimes dark response to it, has been a long-standing theme in American film.[34] Many counterculture films of the 1960s and 1970s ridiculed the traditional quest for the American Dream. For example, Easy Rider (1969), directed by Dennis Hopper, shows the characters making a pilgrimage in search of «the true America» in terms of the hippie movement, drug use, and communal lifestyles.[35]
Political leaders
Scholars have explored the American Dream theme in the careers of numerous political leaders, including Henry Kissinger,[36] Hillary Clinton,[37] Benjamin Franklin, and Abraham Lincoln.[38] The theme has been used for many local leaders as well, such as José Antonio Navarro, the Tejano leader (1795–1871), who served in the legislatures of Coahuila y Texas, the Republic of Texas, and the State of Texas.[39]
In 2006 U.S. Senator Barack Obama wrote a memoir, The Audacity of Hope: Thoughts on Reclaiming the American Dream. It was this interpretation of the American Dream for a young black man that helped establish his statewide and national reputations.[40][41] The exact meaning of the Dream became for at least one commentator a partisan political issue in the 2008 and 2012 elections.[42]
Political conflicts, to some degree, have been ameliorated by the shared values of all parties in the expectation that the American Dream will resolve many difficulties and conflicts.[43]
Public opinion
The ethos today implies an opportunity for Americans to achieve prosperity through hard work. According to the Dream, this includes the opportunity for one’s children to grow up and receive a good education and career without artificial barriers. It is the opportunity to make individual choices without the prior restrictions that limited people according to their class, caste, religion, race, or ethnicity. Immigrants to the United States sponsored ethnic newspapers in their own language; the editors typically promoted the American Dream.[44] Lawrence Samuel argues:
For many in both the working class and the middle class, upward mobility has served as the heart and soul of the American Dream, the prospect of «betterment» and to «improve one’s lot» for oneself and one’s children much of what this country is all about. «Work hard, save a little, send the kids to college so they can do better than you did, and retire happily to a warmer climate» has been the script we have all been handed.[45]
A key element of the American Dream is promoting opportunity for one’s children, Johnson interviewing parents says, «This was one of the most salient features of the interview data: parents—regardless of background—relied heavily on the American Dream to understand the possibilities for children, especially their own children».[46] Rank et al. argue, «The hopes and optimism that Americans possess pertain not only to their own lives, but to their children’s lives as well. A fundamental aspect of the American Dream has always been the expectation that the next generation should do better than the previous generation.»[47]
«A lot of Americans think the U.S. has more social mobility than other western industrialized countries. This [study using medians instead of averages] makes it abundantly clear that we have less. Your circumstances at birth—specifically, what your parents do for a living—are an even bigger factor in how far you get in life than we had previously realized. Generations of Americans considered the United States to be a land of opportunity. This research raises some sobering questions about that image.»
Michael Hout, Professor of Sociology at New York University, 2018[48]
Hanson and Zogby (2010) report on numerous public opinion polls that since the 1980s have explored the meaning of the concept for Americans, and their expectations for its future. In these polls, a majority of Americans consistently reported that for their family, the American Dream is more about spiritual happiness than material goods. Majorities state that working hard is the most important element for getting ahead. However, an increasing minority stated that hard work and determination does not guarantee success. Most Americans predict that achieving the Dream with fair means will become increasingly difficult for future generations. They are increasingly pessimistic about the opportunity for the working class to get ahead; on the other hand, they are increasingly optimistic about the opportunities available to poor people and to new immigrants. Furthermore, most support programs make special efforts to help minorities get ahead.[49]
In a 2013 poll by YouGov, 41% of responders said it is impossible for most to achieve the American Dream, while 38% said it is still possible.[50] Most Americans perceive a college education as the ticket to the American Dream.[51] Some recent observers warn that soaring student loan debt crisis and shortages of good jobs may undermine this ticket.[52] The point was illustrated in The Fallen American Dream,[53] a documentary film that details the concept of the American Dream from its historical origins to its current perception.
Research published in 2013 shows that the US provides, alongside the United Kingdom and Spain, the least economic mobility of any of 13 rich, democratic countries in the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development.[55][56] Prior research suggested that the United States shows roughly average levels of occupational upward mobility and shows lower rates of income mobility than comparable societies.[57][58] Blanden et al. report, «the idea of the US as ‘the land of opportunity’ persists; and clearly seems misplaced.»[59] According to these studies, «by international standards, the United States has an unusually low level of intergenerational mobility: our parents’ income is highly predictive of our incomes as adults. Intergenerational mobility in the United States is lower than in France, Germany, Sweden, Canada, Finland, Norway and Denmark. Research in 2006 found that among high-income countries for which comparable estimates are available, only the United Kingdom had a lower rate of mobility than the United States.»[60] Economist Isabel Sawhill concluded that «this challenges the notion of America as the land of opportunity».[61][62][63] Several public figures and commentators, from David Frum to Richard G. Wilkinson, have noted that the American dream is better realized in Denmark, which is ranked as having the highest social mobility in the OECD.[64][65][66][67][68] In the U.S., 50% of a father’s income position is inherited by his son. In contrast, the amount in Norway or Canada is less than 20%. Moreover, in the U.S. 8% of children raised in the bottom 20% of the climbed to the top 20% as adult, while the figure in Denmark is nearly double at 15%.[69][70][71] In 2015, economist Joseph Stiglitz stated, «Maybe we should be calling the American Dream the Scandinavian Dream.»[72]
In the United States, home ownership is sometimes used as a proxy for achieving the promised prosperity; home ownership has been a status symbol separating the middle classes from the poor.[73]
Sometimes the Dream is identified with success in sports or how working class immigrants seek to join the American way of life.[74]
According to a 2020 American Journal of Political Science study, Americans become less likely to believe in the attainability of the American dream as income inequality increases.[75] A 2022 study in the same journal found that exposure to «rags-to-riches» TV narratives makes Americans more likely to believe in upward mobility.[6]
Four dreams of consumerism
Ownby (1999) identifies four American Dreams that the new consumer culture addressed. The first was the «Dream of Abundance» offering a cornucopia of material goods to all Americans, making them proud to be the richest society on earth. The second was the «Dream of a Democracy of Goods» whereby everyone had access to the same products regardless of race, gender, ethnicity, or class, thereby challenging the aristocratic norms of the rest of the world whereby only the rich or well-connected are granted access to luxury. The «Dream of Freedom of Choice» with its ever-expanding variety of good allowed people to fashion their own particular lifestyle. Finally, the «Dream of Novelty», in which ever-changing fashions, new models, and unexpected new products broadened the consumer experience in terms of purchasing skills and awareness of the market, and challenged the conservatism of traditional society and culture, and even politics. Ownby acknowledges that the dreams of the new consumer culture radiated out from the major cities, but notes that they quickly penetrated the most rural and most isolated areas, such as rural Mississippi. With the arrival of the model T after 1910, consumers in rural America were no longer locked into local general stores with their limited merchandise and high prices in comparison to shops in towns and cities. Ownby demonstrates that poor black Mississippians shared in the new consumer culture, both inside Mississippi, and it motivated the more ambitious to move to Memphis or Chicago.[76][77]
Other parts of the world
The aspirations of the «American Dream» in the broad sense of upward mobility have been systematically spread to other nations since the 1890s as American missionaries and businessmen consciously sought to spread the Dream, says Rosenberg. Looking at American business, religious missionaries, philanthropies, Hollywood, labor unions and Washington agencies, she says they saw their mission not in catering to foreign elites but instead reaching the world’s masses in democratic fashion. «They linked mass production, mass marketing, and technological improvement to an enlightened democratic spirit … In the emerging litany of the American dream what historian Daniel Boorstin later termed a ‘democracy of things’ would disprove both Malthus’s predictions of scarcity and Marx’s of class conflict.» It was, she says «a vision of global social progress».[78] Rosenberg calls the overseas version of the American Dream «liberal-developmentalism» and identified five critical components:
(1) belief that other nations could and should replicate America’s own developmental experience; (2) faith in private free enterprise; (3) support for free or open access for trade and investment; (4) promotion of free flow of information and culture; and (5) growing acceptance of [U.S.] governmental activity to protect private enterprise and to stimulate and regulate American participation in international economic and cultural exchange.[79]
Knights and McCabe argued American management gurus have taken the lead in exporting the ideas: «By the latter half of the twentieth century they were truly global and through them the American Dream continues to be transmitted, repackaged and sold by an infantry of consultants and academics backed up by an artillery of books and videos».[80]
After World War II
In West Germany after World War II, says Reiner Pommerin, «the most intense motive was the longing for a better life, more or less identical with the American dream, which also became a German dream».[81] Cassamagnaghi argues that to women in Italy after 1945, films and magazine stories about American life offered an «American dream». New York City especially represented a sort of utopia where every sort of dream and desire could become true. Italian women saw a model for their own emancipation from second class status in their patriarchal society.[82]
Britain
The American dream regarding home ownership had little resonance before the 1980s.[83] In the 1980s, British Prime Minister Margaret Thatcher worked to create a similar dream, by selling public-housing units to their tenants. Her Conservative Party called for more home ownership: «HOMES OF OUR OWN: To most people ownership means first and foremost a home of their own … We should like in time to improve on existing legislation with a realistic grants scheme to assist first-time buyers of cheaper homes.»[84] Guest calls this Thatcher’s approach to the American Dream.[85] Knights and McCabe argue that, «a reflection and reinforcement of the American Dream has been the emphasis on individualism as extolled by Margaret Thatcher and epitomized by the ‘enterprise’ culture.»[86]
Russia
Since the fall of communism in the Soviet Union in 1991, the American Dream has fascinated Russians.[87] The first post-Communist leader Boris Yeltsin embraced the «American way» and teamed up with Harvard University free market economists Jeffrey Sachs and Robert Allison to give Russia economic shock therapy in the 1990s. The newly independent Russian media idealized America and endorsed shock therapy for the economy.[88] In 2008 Russian President Dmitry Medvedev lamented the fact that 77% of Russia’s 142 million people live «cooped up» in apartment buildings. In 2010 his administration announced a plan for widespread home ownership: «Call it the Russian dream», said Alexander Braverman, the Director of the Federal Fund for the Promotion of Housing Construction Development. Russian Prime Minister Vladimir Putin, worried about his nation’s very low birth rate, said he hoped home ownership will inspire Russians «to have more babies».[89]
China
The Chinese Dream describes a set of ideals in the People’s Republic of China. It is used by journalists, government officials and activists to describe the aspiration of individual self-improvement in Chinese society. Although the phrase has been used previously by Western journalists and scholars,[90][91] a translation of a New York Times article written by the American journalist Thomas Friedman, «China Needs Its Own Dream», has been credited with popularizing the concept in China.[91] He attributes the term to Peggy Liu and the environmental NGO JUCCCE’s China Dream project,[92][93] which defines the Chinese Dream as sustainable development.[93] In 2013, China’s new paramount leader Xi Jinping began promoting the phrase as a slogan, leading to its widespread use in the Chinese media.[94]
The concept of Chinese Dream is very similar to the idea of «American Dream». It stresses entrepreneurship and glorifies a generation of self-made men and women in post-reform China, such as rural immigrants who moved to the urban centers and achieve magnificent improvement in terms of their living standards, and social life. Chinese Dream can be interpreted as the collective consciousness of Chinese people during the era of social transformation and economic progress. The idea was put forward by Chinese Communist Party new General Secretary Xi Jinping on November 29, 2012. The government hoped to revitalize China, while promoting innovation and technology to boost the international prestige of China. In this light, the Chinese Dream, like American exceptionalism, is a nationalistic concept as well.
According to Ellen Brown, writing in 2019, over 90% of Chinese families own their own homes, giving the country one of the highest rates of home ownership in the world.[95]
See also
- Achievement ideology
- Center for a New American Dream
- Empire of Liberty
- American way
Notes
- ^ «Posterity» is a now-archaic term referring to one’s descendants.
References
- ^ «Lesson Plan: The American Dream». Library of Congress. Retrieved October 30, 2020.
- ^ Kamp, David (April 2009). «Rethinking the American Dream». Vanity Fair. Archived from the original on May 30, 2009. Retrieved June 20, 2009.
- ^ «Global education and the ‘American Dream’«. University World News. Retrieved November 14, 2022.
- ^ McCarthy, Niall. «Which Countries Have The Highest Levels Of Labor Union Membership? [Infographic]». Forbes. Retrieved November 14, 2022.
- ^ «Perspective | The big problem with the American Dream». Washington Post. ISSN 0190-8286. Retrieved November 14, 2022.
- ^ a b Kim, Eunji (2022). «Entertaining Beliefs in Economic Mobility». American Journal of Political Science. 67: 39–54. doi:10.1111/ajps.12702. ISSN 0092-5853. S2CID 247443342.
- ^ «In 2020, do people see the American Dream as attainable? | YouGov». today.yougov.com. Retrieved November 14, 2022.
- ^ Lord Dunmore to Lord Dartmouth, December 24, 1774, quoted in John Miller, Origins of the American Revolution (1944) p. 77
- ^ F. W. Bogen, The German in America (Boston, 1851), quoted in Stephen Ozment, A Mighty Fortress: A New History of the German People (2004) pp. 170–71
- ^ H. W. Brands, The age of gold: the California Gold Rush and the new American dream (2003) p. 442.
- ^ Turner, Frederick Jackson (1920). «The Significance of the Frontier in American History». The Frontier in American History. p. 293.
- ^ Turner, The Frontier in American History (1920) chapter 1
- ^ Bogue, Allan G. (1994). «Frederick Jackson Turner Reconsidered». The History Teacher. 27 (2). p. 195. doi:10.2307/494720. JSTOR 494720.
- ^ Quoted in James T. Kloppenberg, The Virtues of Liberalism (1998). p. 147
- ^ Twitter https://twitter.com/aoc/status/1221883795672129540. Retrieved November 14, 2022.
- ^ J. A. Leo Lemay, «Franklin’s Autobiography and the American Dream», in J. A. Leo Lemay and P. M. Zall, eds. Benjamin Franklin’s Autobiography (Norton Critical Editions, 1986) pp. 349–360
- ^ James E. Miller, Jr., «My Antonia and the American Dream» Prairie Schooner 48, no. 2 (Summer 1974) pp. 112–123.
- ^ Harold Bloom and Blake Hobby, eds. The American Dream (2009)
- ^ Nicholas Canaday, Jr., «Albee’s The American Dream and the Existential Vacuum». South Central Bulletin Vol. 26, No. 4 (Winter 1966) pp. 28–34
- ^ Hayley Haugen, ed., The American Dream in John Steinbeck’s of Mice and Men (2010)
- ^ Lloyd W. Brown, «The American Dream and the Legacy of Revolution in the Poetry of Langston Hughes» Studies in Black Literature (Spring 1976) pp. 16–18.
- ^ Riofio, John (2015). «Fractured Dreams: Life and Debt in United States of Banana» (PDF). Biennial Conference on Latina/o Utopias Literatures: «Latina/o Utopias: Futures, Forms, and the Will of Literature».
Braschi’s novel is a scathing critique…of over-wrought concepts of Liberty and the American Dream….(It) connects the dots between 9/11, the suppression of individual liberties, and the fragmentation of the individuals and communities in favor of a collective worship of the larger dictates of the market and the economy.
- ^ anupama jain (2011). How to Be South Asian in America: Narratives of Ambivalence and Belonging. Temple University Press. ISBN 978-1439903032. Retrieved November 27, 2018.
- ^ Guiyou Huang, The Columbia guide to Asian American literature since 1945 (2006), pp 44, 67, 85, 94.
- ^ Neumann, Henry. Teaching American Ideals through Literature. Washington: Government Printing Office, 1918. Print.
- ^ Symposium: The Role of the Judge in the Twenty-first Century. Boston: Boston U Law School, 2006. Print.
- ^ The pictures originally illustrated a cautionary tale published in 1869 in the Swedish periodical Läsning för folket, the organ of the Society for the Propagation of Useful Knowledge (Sällskapet för nyttiga kunskapers spridande). H. Arnold Barton, A Folk Divided: Homeland Swedes and Swedish Americans, 152547256425264562564562462654666 FILS DE (Uppsala, 1994) p. 71.
- ^ Greider, William. The Nation, May 6, 2009. The Future of the American Dream
- ^ a b Johnson, 2006, pp. 6–10. «The crucial point is not that inequalities exist, but that they are being perpetuated in recurrent patterns—they are not always the result of individual success or failure, nor are they randomly distributed throughout the population. In the contemporary United States, the structure of wealth systematically transmits race and class inequalities through generations despite deep-rooted belief otherwise.»
- ^ Dalton Gross and MaryJean Gross, Understanding The Great Gatsby (1998) p. 5
- ^ Stephen E. Ambrose, Douglas Brinkley, Witness to America (1999) p. 518
- ^ a b Smith, Mark A. (2010) The Mobilization and Influence of Business Interests in L. Sandy Maisel, Jeffrey M. Berry (2010) The Oxford Handbook of American Political Parties and Interest Groups p. 460; see also: Video: George Carlin «It’s called the American Dream because you have to be asleep to believe it.» The Progressive, June 24, 2008.
- ^ Chris Hedges and Joe Sacco (2012). Days of Destruction, Days of Revolt. pp. 226–227. Nation Books. ISBN 1568586434
- ^ Gordon B. Arnold. Projecting the End of the American Dream: Hollywood’s Vision of U.S. Decline. Santa Barbara, CA: Praeger, 2013.
- ^ Barbara Klinger, «The Road to Dystopia: Landscaping the Nation in Easy Rider» in Steven Cohan, ed. The Road Movie Book (1997).
- ^ Jeremi Suri, «Henry Kissinger, the American Dream, and the Jewish Immigrant Experience in the Cold War», Diplomatic History, Nov 2008, Vol. 32 Issue 5, pp. 719–747
- ^ Dan Dervin, «The Dream-Life of Hillary Clinton», Journal of Psychohistory, Fall 2008, Vol. 36 Issue 2, pp. 157–162
- ^ Edward J. Blum, «Lincoln’s American Dream: Clashing Political Perspectives», Journal of the Abraham Lincoln Association, Summer 2007, Vol. 28 Issue 2, pp. 90–93
- ^ David McDonald, Jose Antonio Navarro: In Search of the American Dream in Nineteenth-Century Texas (Texas State Historical Association, 2011)
- ^ Deborah F. Atwater, «Senator Barack Obama: The Rhetoric of Hope and the American Dream», Journal of Black Studies, Nov 2007, Vol. 38 Issue 2, pp. 121–129
- ^ Willie J. Harrell, «‘The Reality of American Life Has Strayed From Its Myths'», Journal of Black Studies, Sep 2010, Vol. 41 Issue 1, pp. 164–183 online
- ^ Matthias Maass, «Which Way to Take the American Dream: The U.S. Elections of 2008 and 2010 as a Struggle for Political Ownership of the American Dream», Australasian Journal of American Studies (July 2012), vol 31 pp. 25–41.
- ^ James Laxer and Robert Laxer, The Liberal Idea of Canada: Pierre Trudeau and the Question of Canada’s Survival (1977) pp. 83–85
- ^ Leara D. Rhodes, The Ethnic Press: Shaping the American Dream (Peter Lang Publishing; 2010)
- ^ Lawrence R. Samuel (2012). The American Dream: A Cultural History. Syracuse UP. p. 7. ISBN 978-0815651871.
- ^ Heather Beth Johnson (2014). American Dream and Power Wealth. Routledge. p. 43. ISBN 978-1134728794.
- ^ Mark Robert Rank; et al. (2014). Chasing the American Dream: Understanding What Shapes Our Fortunes. Oxford U.P. p. 61. ISBN 978-0195377910.
- ^ «Lack of social mobility more of an ‘occupational hazard’ than previously known».
- ^ Sandra L. Hanson, and John Zogby, «The Polls – Trends», Public Opinion Quarterly, Sept 2010, Vol. 74 Issue 3, pp. 570–584
- ^ Henderson, Ben. «American Dream Slipping Away, But Hope Intact». YouGov. Retrieved August 8, 2013.
- ^ Americans View Higher Education as Key to American Dream Public Agenda – May 2000
- ^ Donald L. Barlett; James B. Steele (2012). The Betrayal of the American Dream. PublicAffairs. pp. 125–126. ISBN 978-1586489700.
- ^ The Fallen American Dream Archived June 30, 2013, at archive.today
- ^ «Trends in Family Wealth, 1989 to 2013». Congressional Budget Office. August 18, 2016.
- ^ Autor, David (May 23, 2014), «Skills, education, and the rise of earnings inequality among the «other 99 percent»«, Science Magazine, vol. 344, no. 6186, pp. 843–851, Bibcode:2014Sci…344..843A, doi:10.1126/science.1251868, hdl:1721.1/96768, PMID 24855259, S2CID 5622764
- ^ Corak M (2013). «Inequality from Generation to Generation: The United States in Comparison». In Rycroft RS (ed.). The Economics of Inequality, Poverty, and Discrimination in the 21st Century. ABC-CLIO. p. 111. ISBN 978-0313396922.
- ^ Beller, Emily; Hout, Michael (2006). «Intergenerational Social Mobility: The United States in Comparative Perspective». The Future of Children. 16 (2): 19–36. doi:10.1353/foc.2006.0012. JSTOR 3844789. PMID 17036544. S2CID 26362679.
- ^ Miles Corak, «How to Slide Down the ‘Great Gatsby Curve’: Inequality, Life Chances, and Public Policy in the United States», December 2012, Center for American Progress.
- ^ Jo Blanden; Paul Gregg; Stephen Machin (April 2005). «Intergenerational Mobility in Europe and North America» (PDF). The Sutton Trust. Archived from the original (PDF) on January 20, 2013.
- ^ CAP: Understanding Mobility in America – April 26, 2006
- ^ Economic Mobility: Is the American Dream Alive and Well? Archived May 3, 2012, at the Wayback Machine Economic Mobility Project – May 2007
- ^ Obstacles to social mobility weaken equal opportunities and economic growth, says OECD study, Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), Economics Department, February 10, 2010.
- ^ Harder for Americans to Rise From Lower Rungs | By Jason DeParle | January 4, 2012
- ^ David Frum (October 19, 2011). The American Dream moves to Denmark. The Week. Retrieved December 12, 2014.
- ^ Wilkinson, Richard (Oct 2011). How economic inequality harms societies (transcript). TED. (Quote featured on his personal profile on the TED website). Retrieved December 13, 2014.
- ^ Diane Roberts (January 17, 2012). Want to get ahead? Move to Denmark. The Guardian. Retrieved December 13, 2014.
- ^ Kerry Trueman (October 7, 2011). Looking for the American Dream? Try Denmark. The Huffington Post. Retrieved December 13, 2014.
- ^ Matt O’Brien (August 3, 2016). This country has figured out the only way to save the American Dream. The Washington Post. Retrieved September 18, 2016.
- ^ Rank, Mark R; Eppard, Lawrence M (March 13, 2021). «The American Dream of upward mobility is broken. Look at the numbers». The Guardian.
- ^ «Comparing Economic Mobility». archive.nytimes.com. Retrieved October 20, 2022.
- ^ «American Exceptionalism in a New Light: A Comparison of Intergenerational Earnings Mobility in the Nordic Countries, the United Kingdom and the United States». www.iza.org. Retrieved October 20, 2022.
- ^ ‘Scandinavian Dream’ is true fix for America’s income inequality. CNN Money. June 3, 2015.
- ^ William M. Rohe and Harry L. Watson, Chasing the American Dream: New Perspectives on Affordable Homeownership (2007)
- ^ Thomas M. Tarapacki, Chasing the American Dream: Polish Americans in Sports (1995); Steve Wilson. The Boys from Little Mexico: A Season Chasing the American Dream (2010) is a true story of immigrant boys on a high school soccer team who struggle not only in their quest to win the state championship, but also in their desire to adapt as strangers in a new land.
- ^ Wolak, Jennifer; Peterson, David A. M. (2020). «The Dynamic American Dream». American Journal of Political Science. 64 (4): 968–981. doi:10.1111/ajps.12522. ISSN 1540-5907. S2CID 219100278.
- ^ Ted Ownby, American Dreams in Mississippi: Consumers, Poverty, and Culture 1830–1998 (University of North Carolina Press, 1999)
- ^ Christopher Morris, «Shopping for America in Mississippi, or How I Learn to Stop Complaining and Love the Pemberton Mall», Reviews in American History» March 2001 v.29#1 103–110
- ^ Emily S. Rosenberg, Spreading the American Dream: American Economic and Cultural Expansion 1890–1945 (1982) pp. 22–23
- ^ Rosenberg, Spreading the American Dream p. 7
- ^ David Knights and Darren McCabe, Organization and Innovation: Guru Schemes and American Dreams (2003) p 35
- ^ Reiner Pommerin (1997). The American Impact on Postwar Germany. Berghahn Books. p. 84. ISBN 978-1571810953.
- ^ Cassamagnaghi, Silvia. «New York nella stampa femminile italiana del secondo dopoguerra [«New York in the Italian women’s press after World War II»]». Storia Urbana (Dec. 2005): 91–111.
- ^ Niall Ferguson, The Ascent of Money: A Financial History of the World (2009) p .252
- ^ See «Conservative manifesto, 1979 Archived May 22, 2013, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ David E. Guest, «Human Resource Management and the American Dream», Journal of Management Studies (1990) 27#4 pp. 377–397, reprinted in Michael Poole, Human Resource Management: Origins, Developments and Critical Analyses (1999) p. 159
- ^ Knights and McCabe, Organization and Innovation (2003) p. 4
- ^ Richard M. Ryan et al., «The American Dream in Russia: Extrinsic Aspirations and Well-Being in Two Cultures», Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin, (Dec. 1999) vol. 25 no. 12 pp. 1509–1524, shows the Russian ideology converging toward the American one, especially among men.
- ^ Donald J. Raleigh (2011). Soviet Baby Boomers: An Oral History of Russia’s Cold War Generation. Oxford U.P. p. 331. ISBN 978-0199744343.
- ^ Anastasia Ustinova, «Building the New Russian Dream, One Home at a Time», Bloomberg Business Week, June 28 – July 4, 2010, pp. 7–8
- ^ Fallows, James (May 3, 2013). «Today’s China Notes: Dreams, Obstacles». The Atlantic.
- ^ a b «The role of Thomas Friedman». The Economist. May 6, 2013.
- ^ Fish, Isaac Stone (May 3, 2013). «Thomas Friedman: I only deserve partial credit for coining the ‘Chinese dream’«. Foreign Policy.
- ^ a b «China Dream». JUCCCE.
- ^ Xi Jinping and the Chinese Dream The Economist May 4, 2013, p. 11
- ^ Brown, Ellen (June 13, 2019). «The American Dream Is Alive and Well – in China». Truthdig. Retrieved June 15, 2019.
Further reading
- Adams, James Truslow. (1931). The Epic of America (Little, Brown, and Co. 1931)
- Brueggemann, John. Rich, Free, and Miserable: The Failure of Success in America (Rowman & Littlefield; 2010) 233 pages; links discontent among middle-class Americans to the extension of market thinking into every aspect of life.
- Chomsky, Noam. Requiem for the American Dream: The 10 Principles of Concentration of Wealth & Power. Seven Stories Press, 2017. ISBN 978-1609807368
- Chua, Chen Lok. «Two Chinese Versions of the American Dream: The Golden Mountain in Lin Yutang and Maxine Hong Kingston», MELUS Vol. 8, No. 4, The Ethnic American Dream (Winter, 1981), pp. 61–70 in JSTOR
- Churchwell, Sarah. Behold, America: The Entangled History of ‘America First’ and ‘the American Dream’ (2018). 368 pp. online review
- Cullen, Jim. The American dream: a short history of an idea that shaped a nation, Oxford University Press US, 2004. ISBN 0195173252
- Hanson, Sandra L., and John Zogby, «The Polls – Trends», Public Opinion Quarterly, Sept 2010, Vol. 74, Issue 3, pp. 570–584
- Hanson, Sandra L. and John Kenneth White, ed. The American Dream in the 21st Century (Temple University Press; 2011); 168 pages; essays by sociologists and other scholars how on the American Dream relates to politics, religion, race, gender, and generation.
- Hopper, Kenneth, and William Hopper. The Puritan Gift: Reclaiming the American Dream Amidst Global Financial Chaos (2009), argues the Dream was devised by British entrepreneurs who build the American economy
- Johnson, Heather Beth. The American dream and the power of wealth: choosing schools and inheriting inequality in the land of opportunity, CRC Press, 2006. ISBN 0415952395
- Levinson, Julie. The American Success Myth on Film (Palgrave Macmillan; 2012) 220 pages
- Lieu, Nhi T. The American Dream in Vietnamese (U. of Minnesota Press, 2011) 186 pages ISBN 978-0816665709
- Ownby, Ted. American Dreams in Mississippi: Consumers, Poverty, and Culture 1830–1998 (University of North Carolina Press, 1999)
- Samuel, Lawrence R. The American Dream: A Cultural History (Syracuse University Press; 2012) 241 pages; identifies six distinct eras since the phrase was coined in 1931.
External links
- American culture at Curlie
- For a 1951 radio drama about the American Dream see «Russell Thomas Story», a presentation from Destination Freedom


 Who and how to communicate
Who and how to communicate