| title | description | ms.date | ms.topic | dev_langs | helpviewer_keywords | author | ms.author | manager | ms.technology | ms.workload | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Excel Object model overview |
Learn that you can interact with the objects provided by the Excel object model to develop solutions that use Microsoft Office Excel. |
08/14/2019 |
conceptual |
|
|
John-Hart |
johnhart |
jmartens |
office-development |
office |
Excel object model overview
[!INCLUDE Visual Studio]
To develop solutions that use Microsoft Office Excel, you can interact with the objects provided by the Excel object model. This topic introduces the most important objects:
-
xref:Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel.Application
-
xref:Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel.Workbook
-
xref:Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel.Worksheet
-
xref:Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel.Range
[!INCLUDEappliesto_xlalldocapp]
[!includeAdd-ins note]
The object model closely follows the user interface. The xref:Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel.Application object represents the entire application, and each xref:Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel.Workbook object contains a collection of Worksheet objects. From there, the major abstraction that represents cells is the xref:Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel.Range object, which enables you to work with individual cells or groups of cells.
In addition to the Excel object model, Office projects in Visual Studio provide host items and host controls that extend some objects in the Excel object model. Host items and host controls behave like the Excel objects they extend, but they also have additional functionality such as data-binding capabilities and extra events. For more information, see Automate Excel by using extended objects and Host items and host controls overview.
This topic provides a brief overview of the Excel object model. For resources where you can learn more about the entire Excel object model, see Use the Excel object model documentation.
Access objects in an Excel project
When you create a new VSTO Add-in project for Excel, Visual Studio automatically creates a ThisAddIn.vb or ThisAddIn.cs code file. You can access the Application object by using Me.Application or this.Application.
When you create a new document-level project for Excel, you have the option of creating a new Excel Workbook or Excel Template project. Visual Studio automatically creates the following code files in your new Excel project for both workbook and template projects.
| Visual Basic | C# |
|---|---|
| ThisWorkbook.vb | ThisWorkbook.cs |
| Sheet1.vb | Sheet1.cs |
| Sheet2.vb | Sheet2.cs |
| Sheet3.vb | Sheet3.cs |
You can use the Globals class in your project to access ThisWorkbook, Sheet1, Sheet2, or Sheet3 from outside of the respective class. For more information, see Global access to objects in Office projects. The following example calls the xref:Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel._Worksheet.PrintPreview%2A method of Sheet1 regardless of whether the code is placed in one of the Sheetn classes or the ThisWorkbook class.
C#
:::code language=»csharp» source=»../vsto/codesnippet/CSharp/Trin_VstcoreExcelAutomationCS/Sheet1.cs» id=»Snippet82″:::
VB
:::code language=»vb» source=»../vsto/codesnippet/VisualBasic/Trin_VstcoreExcelAutomation/Sheet1.vb» id=»Snippet82″:::
Because the data in an Excel document is highly structured, the object model is hierarchical and straightforward. Excel provides hundreds of objects with which you might want to interact, but you can get a good start on the object model by focusing on a small subset of the available objects. These objects include the following four:
-
Application
-
Workbook
-
Worksheet
-
Range
Much of the work done with Excel centers around these four objects and their members.
Application object
The Excel xref:Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel.Application object represents the Excel application itself. The xref:Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel.Application object exposes a great deal of information about the running application, the options applied to that instance, and the current user objects open within the instance.
[!NOTE]
You should not set the xref:Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel.ApplicationClass.EnableEvents%2A property of the xref:Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel.Application object in Excel to false. Setting this property to false prevents Excel from raising any events, including the events of host controls.
Workbook object
The xref:Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel.Workbook object represents a single workbook within the Excel application.
The Office development tools in Visual Studio extend the xref:Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel.Workbook object by providing the xref:Microsoft.Office.Tools.Excel.Workbook type. This type gives you access to all features of a xref:Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel.Workbook object. For more information, see Workbook host item.
Worksheet object
The xref:Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel.Worksheet object is a member of the xref:Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel.Worksheets collection. Many of the properties, methods, and events of the xref:Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel.Worksheet are identical or similar to members provided by the xref:Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel.Application or xref:Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel.Workbook objects.
Excel provides a xref:Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel.Sheets collection as a property of a xref:Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel.Workbook object. Each member of the xref:Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel.Sheets collection is either a xref:Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel.Worksheet or a xref:Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel.Chart object.
The Office development tools in Visual Studio extend the xref:Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel.Worksheet object by providing the xref:Microsoft.Office.Tools.Excel.Worksheet type. This type gives you access to all features of a xref:Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel.Worksheet object, as well as new features such as the ability to host managed controls and handle new events. For more information, see Worksheet host item.
Range object
The xref:Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel.Range object is the object you will use most within your Excel applications. Before you can manipulate any region within Excel, you must express it as a xref:Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel.Range object and work with methods and properties of that range. A xref:Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel.Range object represents a cell, a row, a column, a selection of cells that contains one or more blocks of cells, which might or might not be contiguous, or even a group of cells on multiple sheets.
Visual Studio extends the xref:Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel.Range object by providing the xref:Microsoft.Office.Tools.Excel.NamedRange and xref:Microsoft.Office.Tools.Excel.XmlMappedRange types. These types have most of the same features as a xref:Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel.Range object, as well as new features such as the data binding capability and new events. For more information, see NamedRange control and XmlMappedRange control.
Use the Excel object model documentation
For complete information about the Excel object model, you can refer to the Excel primary interop assembly (PIA) reference and the VBA object model reference.
Primary interop assembly reference
The Excel PIA reference documentation describes the types in the primary interop assembly for Excel. This documentation is available from the following location: Excel 2010 primary interop assembly reference.
For more information about the design of the Excel PIA, such as the differences between classes and interfaces in the PIA and how events in the PIA are implemented, see Overview of classes and interfaces in the Office primary interop assemblies.
VBA object model reference
The VBA object model reference documents the Excel object model as it is exposed to Visual Basic for Applications (VBA) code. For more information, see Excel 2010 object model reference.
All of the objects and members in the VBA object model reference correspond to types and members in the Excel PIA. For example, the Worksheet object in the VBA object model reference corresponds to the xref:Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel.Worksheet object in the Excel PIA. Although the VBA object model reference provides code examples for most properties, methods, and events, you must translate the VBA code in this reference to Visual Basic or Visual C# if you want to use them in an Excel project that you create by using Visual Studio.
Related topics
| Title | Description |
|---|---|
| Excel solutions | Explains how you can create document-level customizations and VSTO Add-ins for Microsoft Office Excel. |
| Work with ranges | Provides examples that show how to perform common tasks with ranges. |
| Work with worksheets | Provides examples that show how to perform common tasks with worksheets. |
| Work with workbooks | Provides examples that show how to perform common tasks with workbooks. |
Аннотация: Лекция посвящена описанию объектной модели MS Excel и подробному описанию методов, свойств и событий Application.
13.1. Особенности программирования для MS Excel
Microsoft Office Excel — это популярные электронные таблицы. Обычно, программируя для этой программы, преследуют такие цели:
- Автоматизация вычислений.
- Автоматизация ввода и обработки информации.
- Работа с базами данных — вывод, ввод, анализ, визуализация информации.
- Анализ финансовой и другой информации.
- Создание систем для организации автоматизированного ввода данных
- Математическое моделирование.
В общем виде программирование в Excel похоже на работу с Microsoft Word. Однако одно из главных отличий заключается в том, что в Excel рабочая область листа разбита на ячейки, каждая из которых имеет собственное имя. Имена ячеек могут быть двух видов.
- Первый вид (стиль A1) — это имя, состоящее из буквенного имени столбца и номера строки. Например, A1 — ячейка, находящаяся на пересечении столбца А (первого) и первой строки.
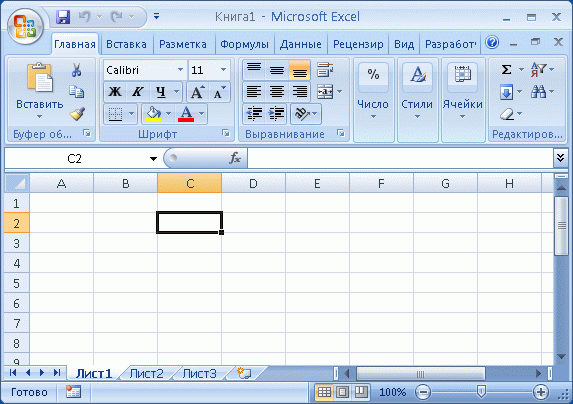
- Другой вид — это индексы ячеек (стиль именования R1C1 ). Для адресации ячейки в таком стиле указывают номер строки (R — Row — строка) и номер столбца (C — Column — столбец), на пересечении которых расположена ячейка. Строки изначально пронумерованы, а номера столбцов начинаются с 1 — первому столбцу соответствует столбец A, второму — В и т.д. Например, (2, 3) — это адрес ячейки, находящийся на пересечении второй строки и третьего столбца, то есть, если переложить это на стиль A1 — получим ячейку С2 (рис. 13.1.)
Рис.
13.1.
Ячейка C2 на листе MS Excel
Для выполнения большинства операций в MS Excel применяются следующие объекты.
- Excel.Application (Приложение) — объект, представляющий приложение Microsoft Excel, аналогичен Word.Application.
- Workbook (Рабочая книга) — представляет рабочую книгу — аналог документа Microsoft Word. Однако, в Word мы работаем с данными, расположенными в документе, а в Excel на пути к данным есть еще один объект — рабочий лист.
- Worksheet (Рабочий лист) — книга в MS Excel разбита на рабочие листы. Именно на листе расположены ячейки, которые могут хранить информацию и формулы.
- Range (Диапазон) — может быть представлен в виде одной ячейки или группы ячеек. Этот объект заменяет множество объектов для работы с элементами документов ( character, word и т.д.), которые применяются в Microsoft Word. В результате работа с листом становится очень четкой и удобной — чтобы работать с какой-либо ячейкой, надо знать лишь ее имя (в формате A1) или адрес ( R1C1 ).
- QueryTable (Таблица запросов) — этот объект используют для импорта в Microsoft Excel информации из баз данных. Подключение к базе данных, запрос информации и т.д. производятся средствами объекта, а итоги запроса выгружаются на лист MS Excel в виде обычной таблицы.
- PivotTable (Сводная таблица) — это особый вид электронной таблицы Excel — она позволяет в интерактивном режиме обобщать и анализировать большие объемы информации, в частности, взятой из базы данных.
- Chart (Диаграмма) — представляет собой диаграмму. Обычно их используют для визуализации данных.
Давайте начнем рассмотрение объектной модели MS Excel с объекта Application.
13.2. Объект Application
13-01-Excel Application.xlsm — пример к п. 13.2.
Принципы работы с объектом Application в MS Excel очень похожи на таковые в MS Word.
Рассмотрим пример. Откроем MS Excel, добавим на рабочий лист кнопку, добавим в обработчик щелчка по кнопке такой код (листинг 13.1.).
MsgBox Excel.Application.Name
Листинг
13.1.
Вывести имя приложения
После выполнения программы в окне сообщения отобразится имя приложения — в данном случае — Microsoft Excel. Очевидно, что свойство Name объекта Application возвращает имя приложения.
Теперь рассмотрим наиболее важные методы и свойства Application. Некоторые из них похожи на таковые в MS Word. Например, метод Quit точно так же, как в Word, закрывает приложение, свойство Visible отвечает за видимость окна программы и т.д.
13.3. Методы Application
13.3.1. Calculate — принудительный пересчет
Этот метод, вызываемый для объекта Application, позволяет пересчитать все открытия книги. Его же можно вызывать для отдельных книг (объект Workbook ) листов ( Worksheet ), ячеек и их диапазонов ( Range ). Например, код из листинга 13.2. позволяет пересчитать все открытые книги.
Application.Calculate
Листинг
13.2.
Пересчитать все открытые книги
13.3.2. GoTo — переход в ячейку
13-02-Excel GoTo.xlsm — пример к п. 13.3.2.
Позволяет выделить любой диапазон ячеек в любой книге, причем, если книга не активна — она будет активирована. Так же метод может запускать макросы Microsoft Excel.
Полный вызов метода выглядит так:
Goto(Reference, Scroll)
В качестве параметра Reference используется ссылка на ячейку или диапазон ячеек, которые должны быть выделены после вызова метода. Так же здесь может быть использовано имя макроса — тогда он будет запущен.
Параметр Scroll отвечает за «перемотку» листа Excel к выделенным ячейкам — так, чтобы левый верхний угол выделения совпадал бы с левым верхним углом отображаемой области листа. Если Scroll установлен в True — лист перематывается, если в False — нет.
Например, такой вызов (листинг 13.3.) позволяет выделить ячейку H500 на активном листе.
Application.Goto _
Reference:=ActiveSheet.Range("H500"), _
Scroll:=True
Листинг
13.3.
Выделить ячейку H500
Как видите, обращение к активному листу очень напоминает обращение к активному документу в MS Word. Обратите внимание на то, что мы используем полное обращение к методу — Application.GoTo — как вы знаете, обычно свойства и методы объекта Application можно использовать в коде, не указывая этого объекта. Однако, если в этом случае не указать Application, то вместо метода GoTo программа попытается выполнить оператор безусловного перехода GoTo.
13.3.3. SendKeys — имитация нажатий на клавиши клавиатуры
13-03-Excel SendKeys.xlsm — пример к п. 13.3.3.
Очень интересный метод — позволяет передавать в активное окно приложения нажатия клавиш. Полный вызов метода выглядит так:
SendKeys(Keys, Wait)
Параметр Keys позволяет задавать клавиши, нажатия которых будут переданы приложению. Метод поддерживает эмуляцию как алфавитно-цифровых, так и управляющих клавиш, для которых применяется специальная кодировка. Алфавитно-цифровые клавиши указываются при вызове в своем обычном виде Например, для передачи символа «Ф» нужно указать его при вызове метода и т.д.
Чтобы передать приложению нажатия клавиши Backspace — используйте код {BS}. Для передачи нажатия кнопки Enter используйте значок ~ (тильда), для клавиши Del — код {DEL}.
Для передачи приложению нажатий клавиш Shift, Ctrl или Alt, можно воспользоваться следующими кодами этих клавиш:
- SHIFT — + (знак плюс)
- CTRL — ^ (крышка)
- ALT — % (знак процента)
Параметр Wait может принимать значения True или False. Если он будет установлен в True — макрос подождет, пока приложение обработает введенные с «клавитуры» данные, после чего продолжит выполнение. Если в False — макрос ждать не будет.
Рассмотрим пример. С помощью метода SendKeys введем в ячейку A1 текст «Сейчас закрою программу!», после чего попытаемся закрыть программу, «нажав» сначала Alt, потом Ф (для открытия главного меню Office), и потом — Ы — для выхода из программы. Подразумевается, что при запуске макроса (листинг 13.4.) указанная ячейка активна — в ней находится рамка выделения.
Application.SendKeys ("Сейчас закрою программу!")
Application.SendKeys ("%ФЫ")
Листинг
13.4.
Имитация нажатий клавиш клавиатуры
После выполнения этого кода вы увидите окно со стандартным вопросом о сохранении документа.
13.3.4. Wait — пауза при выполнении макроса
13-04-Excel Wait.xlsm — пример к п. 13.3.4.
Позволяет сделать паузу в выполнении макроса. Пауза может быть нужна для того, чтобы пользователь успел что-то рассмотреть или для того, чтобы на время освободить вычислительные ресурсы системы.
При вызове этого метода указывается время, на которое должно быть приостановлено выполнение макроса. После того, как истекает время, заданное при вызове метода, он возвращает True и выполнение программы продолжается. Например, в листинге 13.5. так можно остановить выполнение прораммы на 7 секуд, после чего — вывести сообщение.
If Application.Wait(Now + TimeValue("0:00:7")) Then
MsgBox "Семь секунд прошло!"
End If
Листинг
13.5.
Приостановка выполнения программы
Здесь мы получаем значение типа Date с помощью функции TimeValue. После того, как пройдут 7 секунд, выполнение макроса возобновится, метод возвратит True, будет выполнено условие и выведено сообщение.

One of the concepts that keep coming up, and will continue to come up in future tutorials, is that of objects. The main reason for this is simple:
VBA is (loosely) based on Object Oriented Programming. At a basic level, this (roughly) means that the VBA paradigm mostly relies on working with (or manipulates) objects.
As a consequence of the above, if you want to really master Excel macros and Visual Basic for Applications, you must have a good understanding of the following 3 topics:
- Objects.
- How to manipulate VBA objects.
- Excel’s VBA object model.
My 2 main purposes when writing this VBA tutorial are to:
- Explain the main characteristics of Excel’s VBA object model.
- Illustrate how you construct VBA object references when working with Visual Basic for Applications. This allows you to identify the Excel VBA object you want to work with and manipulate.
More precisely, in this macro tutorial I explain the following topics:
I’ll say from the start that the topics of Excel’s VBA object model and building VBA object references are not particularly simple. However…
Your knowledge and understanding of Excel’s VBA object model and object references will improve as you continue to study, and work with, Visual Basic for Applications. Therefore, don’t worry if, after reading this VBA tutorial things are not absolutely clear. This guide should provide you with a solid base and, with some work I’m sure you’ll master this topic and know all you need about Excel VBA objects.
Let’s begin by answering the first question that you probably have regarding the introduction I’ve made above by understanding…
Why Excel’s VBA Object Model Is Important
Visual Basic for Applications is included in most products that are part of Microsoft Office. In addition to Excel, the list of applications that have VBA includes PowerPoint, Word and Access.
This underscores one of the great advantaged of learning VBA:
Once you know Visual Basic for Applications, you can immediately start writing macros for the other products that use VBA. In fact, you’ll be able to create macros that work across all of those different applications.
One of the main topics you need to master in order to reach those levels of expertise is objects. At a basic level, VBA manipulates objects.
Each individual Application that works with VBA (for example, Excel, Word, PowerPoint, Outlook) has its own unique object model. Having a good understanding of the principles behind objects and object models helps you work with VBA in these different Applications.
OK. So Excel’s VBA object model is clearly important. The next question you may have is…
What Is Excel’s VBA Object Model
At a basic level, the Excel VBA Object Model is a hierarchy of the objects you can use when working with Excel VBA.
Among other advantages, this hierarchy makes VBA objects easier to reference. Therefore, let’s take a closer look at…
Excel’s VBA Object Hierarchy
An object hierarchy looks as follows:
- Level #1: At the very top, you have one single object.
- Level #2: The object at the top of the hierarchy contains some objects.
- Level #3: In turn, the object in the second level of the hierarchy, may contain other objects.
- Level #4: The objects in level 3 may contain other objects.
- …
- You probably get the idea… Objects may contain other objects. The process repeats itself until you reach objects that don’t contain any other objects.
When you’re working with a particular software application, the first object to consider is the application itself (the Application object). Generally, the application is at the top of the hierarchy.
In the case of Excel, the Application object is Excel itself.
Since Visual Basic for Applications can communicate with other applications and programs beyond Excel, this isn’t strictly speaking the top level of the hierarchy. However, you’ll usually see most people referring to the Application object itself as being the top of Excel’s VBA object hierarchy. That’s the convention I use in this macro tutorial.
The Application object contains other VBA objects. Some of the VBA objects contained by the Excel Application object are the following:
- Add-Ins, which contains all Add-In objects.
- Windows, which (at this level) contains all Window objects in the application.
- Workbooks, which contains all Workbook objects.
Each of these VBA objects, in turn, is capable of containing other objects. For example, some of the VBA objects that can be contained within a Workbook object are the following:
- Charts, which contains Chart objects.
- Names, which contains Name objects.
- VBProjects, which represents open projects.
- Windows, which (at this level) contains Window objects in the specified Excel workbook.
- Worksheets, which contains Worksheet objects.
Again, these VBA objects can contain other objects. Continuing with the example above, a Worksheet object can contain the following VBA objects:
- ChartObjects, which contains ChartObject objects.
- Comment, which represents a cell comment.
- Hyperlink, which represents a hyperlink.
- Name, which represents a defined name for a particular cell range.
- PageSetup, which is used to store printing information.
- PivotTables, which contains PivotTable objects.
- Range, which represents cells, rows, columns, selections of cells with contiguous blocks of cells, or 3-D ranges.
- As I explain here, the Range object is one of the most important (and most frequently used) objects.
Graphically, the portion of Excel’s VBA object hierarchy described above looks roughly as follows:
The image above illustrates only a very small portion of Excel’s VBA object hierarchy. The Excel Object Model has a very large number of objects. A full diagram of Excel’s VBA object hierarchy exceeds the scope of this Excel VBA Object Model Tutorial.
What can you do about this?
You can definitely master Visual Basic for Applications despite the huge amount of Excel VBA objects. There are several reasons for this, including the following:
- In practice, you’ll usually deal with a limited amount of VBA objects. There are some objects that you’re unlikely to ever need (or will very rarely need).
- If you’re stuck when working on a particular problem, you can use certain strategies for purposes of finding out which Excel VBA objects to use. You can, for example, use the macro recorder to discover VBA objects.
Additionally, as you continue working with Visual Basic for Applications, you’ll start noticing the logic behind the structure of the Excel VBA object hierarchy.
Object Collections
Collections are defined by 2 main characteristics:
- They are themselves objects.
- Their main purpose is to group and manage VBA objects of the same class.
In other words, collections are VBA objects that are used to group and manage other objects (which are related).
The fact you can group and manage several VBA objects by using collections is extremely useful in some situations. Imagine, for example, that you want to do something with or to a particular group of objects. If all of these objects are part of the same collection, you can structure your VBA code to go through each of the members of the collection and carry out the desired actions. As you can imagine, this structure is simpler than, for example, having to list each of the collection members individually.
In other words, collections allow you to work with a complete group of VBA objects at the same time, instead of working with each single object.
The following are examples of common collections:
- Workbooks, which is a collection of all the Excel workbooks that are currently open.
- Worksheets, the collection of all the Excel worksheets within a particular Workbook.
- Charts, which groups all chart sheets that are inside a particular Workbook.
- Sheets, which is a collection of all the sheets within a particular Workbook. In this case, it doesn’t matter the type of sheet. Therefore, this collection includes both worksheets and charts sheets.
In fact, if you go back up to the explanation of Excel’s VBA object hierarchy, you’ll find several other examples of collections. Basically, any VBA object which is listed there as containing other objects is a collection.
By now you probably have a firm grasp of what an object and a collection are. So let’s get into the actual practice. Let’s look at how you can start referencing VBA objects with Visual Basic for Applications:
Introduction To VBA Object References
Knowing how to refer to objects when writing VBA code is essential. The reason for this is that, obviously, when you want to start working with a particular VBA object, you must identify it.
The question is, how do you do it? How do you refer to an object in Visual Basic for Applications?
Let’s take a look at some of the most common and basic situations. The purpose of this section is to serve as an introduction to VBA object references. There are many other more advanced cases. For example, I explain several ways to refer to VBA’s Range object in Excel VBA Object Model And Object References: The Essential Guide which you can find in the Archives.
Object References: Fully Qualified References And Connecting VBA Objects
Let’s start by taking a look at how to refer to an object by going through the whole hierarchy of Excel VBA objects. This is known as a fully qualified reference because you tell Excel exactly what VBA object you want to work with by referencing all of its parents.
As I explain in the following sections, you can usually simplify fully qualified references. However, you must learn how fully qualified references work. They are the basis of VBA object references and, in practice, you’ll use them most of the time. Additionally, they’re quite useful for purposes of understanding better the VBA code behind your macros.
You already know that the object at the top of the Excel VBA object hierarchy is Application. Referring to this object is very easy. In the Visual Basic Editor, you refer to Application by typing:
Application
From there on, you need to start moving along the hierarchy by using the dot (.) operator. In other words, you connect each VBA object to the previous one (the object parent) by using a dot (.). Those dots (.) are used to connect and reference members of Excel’s VBA object model from the top down.
To see this in practice, let’s go back to the example of the Excel VBA object hierarchy that I display above. Assume that you want to refer to a Range object. As shown in the graph displayed below, this object is at the bottom of the pyramid used in the example. There are 2 VBA objects and 3 steps between the Application and the Range object, as shown by the image below:
You already know that you simply need to connect the different objects with a dot (.) while you’re going down the Excel VBA object hierarchy. In other words, you know that, in very general terms, you can refer to a Range object using the following basic structure:
Application.Workbooks.Worksheets.Range
Graphically:
Easy, right?
This is, however, just a basic framework. You’ll notice that this very basic structure is not actually identifying an individual VBA object. You may be wondering:
- If there are several workbooks or worksheets how does Excel know to which one I’m referring to?
- How does Excel know what is the range I want to work with?
These questions can be summarized by the following:
How do you refer to a particular object within a collection?
Let’s answer this question so that you can complete the fully qualified reference above.
VBA Object References: An Object From A Collection
It is likely that, most of the time, you’ll be working with a particular VBA object from a collection. This is in contrast with the collection as a whole.
Note that you can also work with a collection as a whole. In fact, the ability to do this is one of the advantages of collections.
However, let’s focus for now on how you can reference an object from a collection. For these purposes, you can use either of the following 2 options:
Option #1: Using The VBA Object Name.
In this case, the syntax that you must use to refer to an object is “Collection_name(“Object_name”)”. In other words:
- #1: The name of the relevant collection (collection_name) goes first.
- #2: Collection_name is followed by parentheses ().
- #3: Within the parentheses, you have the name of the individual VBA object (Object_name).
- #4: The VBA object name is within quotations (“”).
- If you fail to include the quotation marks, Excel understands that the VBA object name is a variable name. Therefore, it won’t be able to identify the object you want.
- In other words, don’t forget the quotations when using this VBA object reference method.
For example, if you’re working with an Excel Workbook that has 3 worksheets and you want to work with Sheet1, you can use either of the following:
Worksheets("Sheet1")
or
Sheets("Sheet1")
Option #2: Using Index Number.
If you choose to use this option, you refer to a VBA object using “Collection_name(Index_number)”. This structure is substantially the same as that above with the following 2 differences:
- Instead of using the VBA object name, you refer to it by using its index number.
- You don’t use double quotes within the parentheses, just a number.
Going back to the example above, where you’re want to work with Sheet1, you can use either of the following 2 options:
Worksheets(1)
or
Sheets(1)
Now that you know how to refer to an individual VBA object within a collection, let’s go back to the fully qualified reference that I used as an example in the section above:
Application.Workbooks.Worksheets.Range
How can you complete this, assuming that the object you want to work with is cell A1 from Worksheet Sheet1 within Workbook Book1?
If you’re using the object name to refer to each of the individual VBA objects (option #1 above), the fully qualified reference for this cell is:
Application.Workbooks("Book1.xlsx").Worksheets("Sheet1").Range("A1")
As you may guess, if you had to reference each and every single object using a fully qualified reference, your VBA code would get quite long very fast. From a typing perspective, this may get a little bit annoying. Additionally, and perhaps more importantly, these very long pieces of VBA code can be difficult to read.
There are some ways in which you can simplify object references, making the VBA code much shorter. Let’s take a look at some of the methods that you can apply for these purposes…
Simplifying Fully Qualified Object References
The ability to simplify a VBA object reference has several advantages. Mainly, this allows you to shorten your VBA code and make it easier to read.
The main reason why you can simplify fully qualified object references is because Excel’s VBA object model has some default objects. These default objects are assumed by Excel unless you enter something different. This leads me to a very important point, which is that…
Simplifying fully qualified object references is not without dangers. In particular, the second simplification method described below relies on you correctly identifying the current active Workbook and Worksheet. If you make a mistake by for example, thinking that the current active Worksheet is Sheet1 when in reality its Sheet2, you’ll face problems. The most likely issues you’ll encounter in these cases are:
- Excel returns an error.
- Excel returns an erroneous result.
- Excel executes an erroneous action that you can’t undo.
Another possible disadvantage of simplifying fully qualified object references is related to execution speed. This happens, for example, if you’re working with a particular macro that works with several Excel worksheets. In that case, you have to go through all of them to activate them. Needless to say, this isn’t very efficient.
Considering the above, ensure that you’re only using these simplification methods when appropriate. Perhaps more importantly, remember that you shouldn’t blindly simplify fully qualified references all the time.
In fact, you should probably (as a general rule):
- Fully qualify VBA object references; and
- Avoid relying on default objects, with a few exceptions.
- One of these main exceptions, as I explain below, is relying on the Application default object. This particular VBA object is seldom included in VBA code, although there are some cases in which you must reference the Application.
In other words, having a deep knowledge of Excel’s VBA object model and using fully qualified references has 2 main advantages:
- Reliability.
- Accuracy.
An alternative to the extremes of fully qualifying references or simplifying them is using With… End With statements. These statements simplify macro syntax by executing several statements which refer to the same VBA object. At the same time, due to their structure, they allow you to maintain fully qualified object references.
You can see a very simple example of a With…End With statement in this macro that deletes rows based on whether a cell in a given range is blank.
With the warning above in mind, let’s take a look at the methods you can use to simplify fully qualified object references:
Simplification #1: The Application Object.
The main default VBA object is the Application object. As a general rule:
- This object is always assumed; and
- It doesn’t matter where the VBA code is located.
When creating macros, it is assumed that you’ll be working with Excel. In other words, Excel assumes that you’re working with the Application object. Therefore, as you may expect, you can generally omit this Excel VBA object from your object references.
Explicitly referring to (entering) the Application object makes sense in only a few cases.
Applying this shortcut to the statement referring to cell A1 in Sheet1 within Book1 that has been used as an example simplifies the reference as follows:
Workbooks("Book1.xlsx").Worksheets("Sheet1").Range("A1")
Simplification #2: The Active Workbook and Worksheet.
The second group of default objects you can use to simplify fully qualified object references applies when you’re working inside a standard module. Within the Visual Basic Editor, you can usually find standard modules in the Project Window under the Modules node:
In these cases, in addition to assuming that you’re working with the Application object, Excel also assumes that you’re working with the active Workbook.
Therefore, if you know that the current active Excel workbook is the Workbook you want to work with, you can omit that part of the VBA object reference. Continuing with the example above, the statement can then be shortened to the following:
Worksheets("Sheet1").Range("A1")
Finally, if you’re sure that the Excel worksheet you want to work with is the current active Worksheet, you can also omit that part of the VBA object reference. The statement above can then be shortened even further:
Range("A1")
In addition to the dangers of using this simplification that I explain at the beginning of this section, there is a further aspect you must consider. The 2 assumptions that I’ve listed in Simplification #2 above only work as long as you’re in a standard module. Therefore, you must avoid relying on these assumptions when working in another type of module. For example:
Conclusion
Excel’s VBA object model is extremely important. You can’t ignore this topic if you really want to become a master in Excel macros and Visual Basic for Applications.
Excel’s VBA object model is not the simplest topic to understand but, if you practice and study, you’ll eventually master the topic. Then, you’ll be on your way to creating powerful macros that increase your productivity and efficiency when working with Excel.
If you’ve studied this particular VBA tutorial, you not only have a good understanding of what is Excel’s VBA object model, but also know how to start building object references in Visual Basic for Applications. This ability to create appropriate VBA object references is what allows you to tell Excel which object you want to work with and manipulate. This is an essential skill that you now have in your VBA knowledge-box.
Due to the complexity and extensiveness of Excel’s VBA object model, this is a topic that we’re all constantly studying and learning about.
VB
и VBA
не одно и то же. VB
представляет собой язык для разработки
программного обеспечения, которое
используется отдельно от MS
Office.
VBA
входит в состав пакета MS
Office.
Устанавливая его, вы получаете доступ
к VBA.
Он необходим для управления данными MS
Office.
Язык VBA
поддерживает все базовые элементы
любого другого языка программ.:
1)переменные 2)массивы 3)подпрограммы
4)управляющие структуры 5)возможность
создания пользоват. типов данных и т.д.
VBA
явл. языком визуального и событийно
управляемого программирования. В нем
есть возможность создания форм с
управляющими элементами, написания
процедур, обрабатывающих события. VBA
позволяет работать с огромным набором
объектов. VBA
поддерживается такими приложениями,
как Access,
PowerPoint,
Word
и др. В каждом из приложений свой набор
объектов. В Access:формы,
запросы, отчеты, таблицы; в Word:абзац,
сноска; в PowerPoint
слайд. Каждая программа поддерживает
свою версию VBA.
VBA
отличается от других языков программирования
тем, что предоставляет возможность
непосредственно работать со всеми
объектами MS
Office.
Он имеет графическую инструментальную
среду, позволяющую создать экранные
формы и управляющие элементы.
Объектная модель
Excel
является основой структуры программы.
Без создания иерархической структуры
объектов программы, нельзя использовать
VBA
в Еexcel.
Все элементы Excel
– объекты, с которыми приходится работать
в программе. Чаще всего используются
такие объекты, как рабочие книги
WorkBooks,
рабочие листы WorkSheets,
диапазоны Range.
Объект WorkSheets
имеет свойство Name,
только объект Range
не имеет ярко выраженной коллекции.
Выступает как коллекция и как объект.
Чаще исп. В программном коде, обладает
огромными возможностями.
2. Объектная модель Excel: понятие объекта, метода, свойства, события.
Объектная модель
Excel
является основой структуры программы.
Без создания иерархической структуры
объектов программы, нельзя использовать
VBA
в Еexcel.
Все элементы Excel
– объекты, с которыми приходится работать
в программе. Чаще всего используются
такие объекты, как рабочие книги
WorkBooks,
рабочие листы WorkSheets,
диапазоны ячеек Range
ckarts.
Свойства определяют
внешний вид и состояние объекта. Для
определения свойства его нужно указать
справа от имени объекта через точку.
Range(“A1”).Value
– свойство описывает содержимое ячейки
А1. Существует 2 вида опереций при работе
со свойствами: 1)присваивание свойству
значения. Объект.Свойство=<значение>
Range(“A1”).Value=
«Отчет о командировке». 2)полученное
свойство присваивается переменной.
Переменная=Объект.Свойство
Var=
Range(“A1”).Value
Методы объекта
открывают задачи, которые может выполнять
объект. Объект.Метод – когда у метода
нет параметров. Range(“A1”).CleanContenst
– очищает диапазон, но сохраняет
форматирование. Если метод имеет
аргументы, то они перечисляются через
, после названия метода.
Событие представляет
собой действие, распознаваемое объектом,
для которого можно запрограммировать
отклик. Суть программирования в VBA
заключается в 2 понятиях: событие и
отклик на него.
Свойства и методы
могут быть связаны между собой: выполнение
метода приводит к изменению свойства
объекта, а изменение некоторого свойства
может вызвать наступление события.
3. редактор VB.
Окно проекта. Окно редактирования кода.
Окно редактирования формы. Панель
элементов. Окно свойств. Окно просмотра
объектов. Окна Immediate,
Watch.
Редактор
VB=Visual
Basic
Editor.
Редактора VBA
не бывает! Для запуска этого редактора
нужно открыть приложение Excel
и выполнить команду Сервис/Макрос/Редактор
VB
или Alt+F11.
Чтобы вернуться в Excel,
нужно повторно нажать Alt+F11.
В открывшемся окне VBA:
строка заголовка, меню, панели инструментов
и несколько окон.
По умолчанию в
верхнем левом углу находится окно
проекта.
Вывести его можно командой View/Project
Explorer.
Это окно содержит список всех открытых
проектов и список всех их компонентов.
В проекте всегда располагаются 3
модуля(на каждом листе) и модуль книги.
Все модули делятся на: 1) стандартные –
добавляются к проекту Insert/Module.
Они содержат макросы, функции и процедуры.
2) модули объектов – модули, связанные
с рабочими книгами, раблчими листами и
формами. Проект VBA
состоит из объектов, имеющих иерархическую
структуру, и включает: объекты Excel,
формы, стандартные модули и модули
классов. Окно
редактирования кода. В
окне проекта выделяете объект, для
которого будет введен программный код.
Затем выполнить команду View/Code.
Откроется окно, в которое нужно ввести
программный код. Окно
редактирования формы.
Для вывода формы: Insert/User
Form.
На экране появится форма. Окно
свойств. Для
открытия: View/Properties
Window.
В левой части окна перечислены свойства
объекта, в правой – значения свойств,
которые можно изменять. Окно
просмотра объектов. View/Object
Browser
или F2.
В верхнем левом углу открывшегося окна
– список библиотек объектной модели
Excel.
Оно дает спраку о всех объектах Excel,
их свойствах и методах.
Панель
элементов (View/Dwbug)
в стандартном
варианте включает различные классы
управляющих элементов: CommandButton
(командная кнопка), TextBox,
Label
и др. Существует возможность дополнить
панель с помощью команды Tools/Additional
Controls.
Окно Immediate
– один из инструментов отладки.
Предназначено для непосредственного
ввода команд. Окно Watch
– порядок выполнения программы и
отслеживание ошибок.
4. Создание
простой программы на примере приложения
«Информация о продажах по регионам».
Задача:
создать программу, которая будет
отслеживать продажи в каждом регионе.
Для каждого региона отразить сообщение
с количеством месяцев, когда продажи
превышали заданный объем, введенный
пользователем. Порядок выполнения:
открыть Excel
и на первом листе создать список
следующего вида:
|
А |
В |
С |
… |
G |
|
месяц |
Регион1 |
Регион2 |
Регион3 |
|
|
Янв2005 |
||||
|
…. |
||||
|
Дек2006 |
Отформатировать
столбцы(1 – дата, остальные – формат
денежный). Заполнить список. Затем
выделить диапазон ячеек B2:G25
и присвоить ему имя SalesRange.
Перейти в редактор вба: Alt+F11
или Сервис/Макрос/Редактор Вб. Если окна
нет, выполнить команду View/Project
Explorer.
Далее выполнить Insort/Module,
откроется окно редактора. Ввести
следующий программный код:
Sub
CountHighSales()
Dim
i As Integer, j As Integer, ks As Integer, s As Currency
s = InputBox(«Введите
цену для сравнения», «окно для ввода
критерия»)
For
i = 1 To 6
ks
= 0
For
j = 1 To 24
If
Range(«SalesRange»).Cells(j, i) >= s Then
ks
= ks + 1
End
If
Next j
MsgBox «в регионе
» & i & » объем продаж превышал
» & s & » в » & ks & » месяцах»
Next i
End Sub
Запустить программу
на выполнение: F5
или Run/Run
Sub.
На экране появится окно InputBox. Запуск
программы с помощью кнопки, расположенной
на рабочем листе. Находясь
на рабочем листе, выполнить команду
Вид/Панели инструментов/Формы. В
появившемся окне выбрать элемент Кнопка
и нарисовать на рабочий лист. Откроется
окно, в котором предлагается создать
макрос, выбрать название CountHighSales
и закрыть. Дать свое название кнопке.
Для запуска программы щелкнуть на этой
кнопке.
Создать программу
можно и другим способом, начиная с
размещения кнопки. Появляется окно
«Назначить макрос объекту». Нажать на
кнопку Создать. Запустится редактор
VBE
и откроется окно редактирования кода
макроса. Ввести программный код.
5. Стандартные
элементы управления VB:
понятия, свойства, методы, события общие
для этих элементов.
Краткая
характеристика элементов управления.
Элементы управления — это объекты,
которые можно разместить на форме. Как
и все объекты, они имеют свойства, методы
и события. Свойства определяют внешний
вид и поведение. Изменять свойства можно
как во время проектирования (через окно
свойств), так и в программном коде. Общие
свойства: name
– имя, которое используется для ссылок
на элементы управления в программном
коде. Left,
Top
– левый верхний угол элемента. Width,
height
– ширина, высота элемента. Visible
– будет ли виден на экране. Методы: Move
– перемещение элемента на форме. Drag
– перетаскивание. События: Set
Focus,
click,
dblclick.
Элемент управления Командная кнопка
(CommandButton).
Свойства: Caption
— текст на кнопке Picture-
определяет рисунок на кнопке. Picture
Position
— определяет позицию рисунка на кнопке.
Событие: Click
— возникает при нажатии пользователем
кнопки Мышью, DblClick-
двойной щелчок, когда возникает нажатие.
Элемент управления счетчик SpinButton
— позволяет уменьшать или увеличивать
числовое значение в результате щелчка
стрелки. Элемент управления полоса
прокрутки ScrollBar.
Позволяет выбрать значение из заданного
диапазона с помощью мыли. Щелчком мыши
на концах полосы прокрутки или на самой
полосе путем перетаскивания бегунка.
Важнейшие свойства SpinButton
и ScrollBar:
max-
максимальное значение, выдаваемое
полосой прокрутки или счетчиком (всегда
положителен) min-
минимальное значение выдаваемое этими
элементами. CmalChange-
отрицательное или положительное целое
число равное шагу изменения значения
этих элементов в тот момент,
когдыапроизводится щелчок. событие
Change
происходит при смене значений этих
элементов. С помощью свойства Value
в некоторой переменной можно запомнить
текущее значение этого счетчика. Элемент
управления рамка (Frame)
Она является контейнером и служит для
объединения других элементов в группу.
После чего помещенными в нее объектами
можно управлять как единым целым (либо
переключатели, либо флажки обычно в нее
помещаются) Свойства: Caption-
задает текст, который выводится в левом
верхнем углу рамки; Appearance-
2 значения: 0- Flat
(простая рамка), 1- 3D
объемная. Элемент управления текстовое
поле. Он
обеспечивает возможность ввода текста
пользователем во время работы приложения
или отображение информации, задаваемой
свойством Text.
Свойства: text-
текстовое поле, характеризуется еще
свойствами, позволяющими использовать
этот элемент при создании полей,
предназначенных для ввода пароля.
PasswordChar
задает символ отображаемый в поле вместо
возможных символов. Maxlength-
максимальное количество символов,
вводимых в поле. Элемент управления
Метка (надпись) он используется в форме
для размещения статичного текста.
Свойства: Caption-
текст который размещается на этом
элементе, размер не более 1024 байт. Font-
внешний вид шрифта.
6. Типы подпрограмм
и их определения: определение и виды
процедур. Примеры процедур разных видов.
Логические
фрагменты кода, которые выполняют
определенную задачу, называются
подпрограммами. В вба подпрограммами
называют макросы, процедуры и даже
функции.
Можно создать
основную процедуру и вызвать из нее
остальные процедуры. В этом случае набор
совместно работающих процедур наз.
приложением. Существуют следующие виды
процедур: 1)обработки событий 2) макросов
3) пользователей. Процедура обработки
события всегда связана с каким-либо
объектом.
Private
Sub
ИмяОбъекта_Событие()
<тело
процедуры обрабатываемого события>
End
Sub
Пример:
Private Sub CommandButton_Click()
Ипотека.Show
End
Sub
Процедура
обработки макроса имеет следующий
синтаксис:
Sub
ИмяМакроса ()
<Тело
макроса>
End
Sub
Для вызова макроса
из главной процедуры используется
оператор Call
ИмяМакроса. При условии, что все процедуры,
в том числе и главная, расположены в
одном модуле.
Пример:
Sub
MainProcedure()
Call
GetProblemSize
Call
Initialize
Exit
Sub
End Sub
Sub
GetProblemSize()
Ncities =
Range(«DistMatrix»).Rows.Count
ReDim
Visited(Ncities)
ReDim
Route(Ncities + 1)
End Sub
Sub
Initialize()
Dim I As
Integer
Route(1) = 1
Route(Ncities + 1) = 1
Visited(1) = True
For
I = 2 To Ncities
Visited(I) = False
Next
TotDist = 0
End Sub
Синтаксис процедуры
пользователя:
[Private/Public]
Sub ИмяПроцедуры
(Параметры)
<Тело процедуры>
End
Sub
Элементы списка
параметров имеют следующий вид:
ИмяЭлемента As
ТипДанных
7. Типы подпрограмм
и их определения: определение и виды
процедур. Примеры процедур разных видов.
Логические
фрагменты кода, которые выполняют
определенную задачу, называются
подпрограммами. В вба подпрограммами
называют макросы, процедуры и даже
функции. Функция – это подпрограмма,
которая действует в пределах своего
блока и возвращает только одно значение.
Функции: 1)ф. пользователя 2) ф. модулей
классов. Функция имеет следующий
синтаксис:
[Private/Public]
Function
Имя функции(список параметров) As
ТипДанных
<тело функции>
End
Function
Тип данных для
функции предназначен для определения
типа и возвращения функцией зн-я
Чтобы создать
функцию пользователя, надо: 1. если нет
модуля Insert/Module
2. Insert/Procedure
3. в открывшемся окне выбрать переключатель
“Function”,
в поле Name
ввести имя функции («Доход») 4. в этом же
окне установить переключатель «общие»,
чтобы был тип – Public
5. Ок. Откроется окно редактора. Ввести
параметры функции и код.
Option
explicit
Option
Base 1
Function
Doxod (procent as double, platezh as variant, god as variant) as
double
Dim
i, j, n as integer, s as double
n=platezh.rows.count
s=0
for
i=1 to n
s=s+platezh(i)/(1+procent)^((god(i)-god(1))/365)
next
i
doxod=s
end
fuction
Не закрывая окна
View/Object
Browser.
Откроется окно просмотра объектов. В
левом верхнем углу выбрать VBAProject
и в окне Классы отобрать элементы
текущего проекта. Выбрать модуль, в
котором ваша функция. Затем в окне
Компоненты отобрать все элементы, в том
числе и функцию Доход. Щелкнуть правой
кнопкой мыши на Доход и выбрать значение
Свойства. Откроется окно «Параметры
компонента», в нем ввести описание(назначение)
функции. Закрыть окно и после этого ваша
функция попадет в библиотеку стандартных
функций Excel.
Соседние файлы в предмете [НЕСОРТИРОВАННОЕ]
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #