Note: The screen shots in this article were taken in Excel 2016. If you have a different version your view might be slightly different, but unless otherwise noted, the functionality is the same.
Add page numbers on a single worksheet
-
Click the worksheet for which you want to insert page numbers.
-
On the Insert tab, in the Text group, click Header & Footer.
Excel displays the worksheet in Page Layout view. You can also click Page Layout
on the status bar to display this view.
-
On the worksheet, click Click to add header or Click to add footer.
This displays the Header & Footer Tools, adding the Design tab.
-
To specify where in the header or footer you want the page number to appear, click inside the Left section, Center section, or Right section box of the header or footer.
-
On the Design tab, in the Header & Footer Elements group, click Page Number.
The placeholder &[Page] appears in the selected section.
If want to add the total number of pages, type a space after &[Page], type the word of followed by a space and then, in the Header & Footer Elements group, click Number of Pages.
The placeholder &[Page] of &[Pages] appears in the selected section
-
Click anywhere outside the header or footer area to display the actual page numbers in Page Layout view.
-
After you have completed working in Page Layout view, on the View tab, in the Workbook Views group, click Normal.
You can also click Normal
on the status bar.
You can insert page numbers for a worksheet in Page Layout view, where you can see them, or you can use the Page Setup dialog box if you want to insert page numbers for more than one worksheet at the same time. For other sheet types, such as chart sheets, you can insert page numbers only by using the Page Setup dialog box.
Add page numbers in multiple worksheets
You can insert page numbers on multiple worksheets in your workbook by using the Page Setup dialog box. For example, if your workbook contains two worksheets that are both two pages long, the first worksheet will contain two pages numbered 1 and 2. The second worksheet will also contain two pages numbered 1 and 2.
Tip: To add page numbers to all worksheets in a workbook sequentially, you must change the number that each worksheet starts with. For more information, see Set a different number for the starting page.
-
Click the worksheets or chart sheets to which you want to add page numbers.
|
To select |
Do this |
|---|---|
|
A single sheet |
Click the sheet tab.
If you don’t see the tab that you want, click the tab scrolling buttons to display the tab, and then click the tab.
|
|
Two or more adjacent sheets |
Click the tab for the first sheet. Then hold down Shift while you click the tab for the last sheet that you want to select. |
|
Two or more nonadjacent sheets |
Click the tab for the first sheet. Then hold down Ctrl while you click the tabs of the other sheets that you want to select. |
|
All sheets in a workbook |
Right-click a sheet tab, and then click Select All Sheets on the shortcut menu. |
Tip: When multiple worksheets are selected, [Group] appears in the title bar at the top of the worksheet. To cancel a selection of multiple worksheets in a workbook, click any unselected worksheet. If no unselected sheet is visible, right-click the tab of a selected sheet, and then click Ungroup Sheets.
-
On the Page Layout tab, in the Page Setup group, click the Dialog Box Launcher
next to Page Setup.
-
In the Page Setup dialog box, on the Header/Footer tab, click Custom Header or Custom Footer.
-
To specify where in the header or footer you want the page number to appear, click inside the Left section, Center section, or Right section box.
-
To insert numbers, click the Insert Page Number button
.
The placeholder &[Page] appears in the selected section.
Notes:
-
If you want to add the total number of pages, type a space after &[Page], type the word of followed by a space, and then click the Insert Number of Pages button
.
-
The placeholder &[Page] of &[Pages] appears in the selected section.
-
Set a different number for the starting page
To number all of the worksheet pages in a workbook sequentially, first add page numbers to all worksheets in a workbook, and then use the following procedure to begin the page number for each worksheet with the appropriate number. For example, if your workbook contains two worksheets that with both be printed as two pages, you would use this procedure to begin the page numbering for the second worksheet with the number 3.
-
On the Page Layout tab, in the Page Setup group, click the Dialog Box Launcher
next to Page Setup.
-
On the Page tab, in the First page number box, type the number that you want to use for the first page.
To use the default numbering system, type Auto in the First page number box.
Change the order in which pages are numbered
By default, Excel numbers and prints pages from the top down and then left to right on the worksheet, but you can change the direction to number and print pages from left to right and then from the top down.
-
Click the worksheet for which you want to change the numbering order.
-
On the Page Layout tab, in the Page Setup group, click the Dialog Box Launcher
next to Page Setup.
-
On the Sheet tab, under Page order, click Down, then over or Over, then down.
The direction of each option is displayed in the preview box.
Delete page numbers
-
Click the worksheets or chart sheets for which you want to remove page numbers.
|
To select |
Do this |
|---|---|
|
A single sheet |
Click the sheet tab.
If you don’t see the tab that you want, click the tab scrolling buttons to display the tab, and then click the tab.
|
|
Two or more adjacent sheets |
Click the tab for the first sheet. Then hold down Shift while you click the tab for the last sheet that you want to select. |
|
Two or more nonadjacent sheets |
Click the tab for the first sheet. Then hold down Ctrl while you click the tabs of the other sheets that you want to select. |
|
All sheets in a workbook |
Right-click a sheet tab, and then click Select All Sheets on the shortcut menu. |
Tip: When multiple worksheets are selected, [Group] appears in the title bar at the top of the worksheet. To cancel a selection of multiple worksheets in a workbook, click any unselected worksheet. If no unselected sheet is visible, right-click the tab of a selected sheet, and then click Ungroup Sheets on the shortcut menu.
-
On the Page Layout tab, in the Page Setup group, click the Dialog Box Launcher
next to Page Setup.
-
On the Header/Footer tab, in the Header or Footer drop-down box, click (none).
Note: You may have to scroll to the top of the list to click (none).
Add page numbers
-
On the Insert tab, click Header & Footer.
Excel automatically changes to Page Layout view.
-
On Header & Footer tab, click either the Header or Footer, and then select the page number format you want.
Header page numbers appear at the top of the printed page, and footer page numbers appear at the bottom.
-
When you’re done, you can either stay in Page Layout view, or you can switch to Normal view by clicking Normal on the View tab.
Set a different number for the starting page
You can make the first printed sheet start with a page number other than 1. This is helpful if there are other printed pages that will come before the sheet. For example, you might print a 2-page Word document that will account for pages 1 and 2, and your Excel sheet would then start on page 3.
-
On the Page Layout tab, click Page Setup.
-
On the Page tab, in the First page number box, type the number you want for the first page number. For example, if you wanted the first page number to be 3, you’d type the number 3.
-
Click OK.
If you are using a page number format that counts the total pages, for example: Page 3 of 7, you’ll need to make an adjustment to the second number. This adjustment ensures you don’t end up with something like this: Page 10 of 7.
-
In Page Setup, click the Header/Footer tab, and then click either Custom Header or Custom Footer.
-
After Page &[Page] of &[Pages], type the plus sign (+), and then type the number of pages that come before your first page number.
For example, if 3 is your first page number, you need to include 2 pages in the total page count. So you’d type a +2 at the end: Page &[Page] of &[Pages]+2 and then click OK.
-
Click OK again.
Change the order that pages are numbered
-
On the Page Layout tab, click Page Setup, and then click Sheet.
-
Under Page order, select the page numbering order that you want.
Remove page numbers
-
On the Page Layout tab, click Page Setup, and then click Header/Footer.
-
Under Header or Footer, select (none).
You might have to scroll to find (none) at the top of the list.
Add page numbers
-
On the Layout tab, under Page Setup, click Header & Footer.
-
On pop-up menu under Header or Footer, select the page number format that you want to add.
Header formats appear at the top of the printed page, and footer formats appear at the bottom.
Tips:
-
You can see how your page numbers will appear by viewing your sheet in preview mode. On the Layout tab, under Print, click Preview.
-
To add page numbers to multiple sheets in your workbook at the same time, select the sheets you want before clicking Header & Footer. The page number format you choose will be applied to all selected sheets.
-
You can create a completely custom header or footer with page numbers by clicking Customize Header or Customize Footer, and following the instructions given.
-
Set a different number for the starting page
-
On the Layout tab, under Page Setup, click Header & Footer.
-
Add page numbers in the format that you want.
-
Click Customize Header or Customize Footer, depending on where the page numbers appear.
-
Look for the page number code &[Page], and click immediately after it to move the insertion point to this location.
-
Type a plus sign (+), and then type the number of pages by which you want to advance the starting page. For example, to start on page 4, you are increasing the starting page number by three pages, so you type +3. The code now appears as &[Page]+3.
-
Click OK.
In the Header or Footer box, the new first page header or footer is shown.
Note: If you want to use a page number format that includes the total number of pages, such as Page 4 of 7, make sure that you also add the plus sign (+) and page number increase to the total pages code, &[Pages].
Change the order that pages are numbered
-
On the Layout tab, under Page Setup, click Header & Footer.
-
On the Sheet tab, under Page order, select the page numbering order that you want.
Remove page numbers
-
On the Layout tab, under Page Setup, click Header & Footer.
-
On pop-up menu under Header or Footer, select (none).
Excel Numbering (Table of Contents)
- Numbering in Excel
- How to Add Serial Number in Excel?
Numbering in Excel
There are various ways of numbering in excel, which are Fill Handle, Fill Series, Row Function mainly. By Fill Handle, we can drag already written 2-3 numbers in sequence until the limit we want. By Fill Series, which is available in the Home menu tab and select the Series option, select the lowest and highest numbers. And if we select the Row function for numbering, then also we can create a number in the sequence.
How to Add Serial Number in Excel?
To add a serial number in Excel is very simple and easy. Let’s understand the working of adding a serial number in Excel by some methods with its example.
You can download this Numbering Excel Template here – Numbering Excel Template
Example #1 – Fill Handle Method
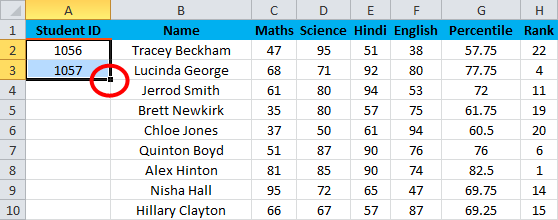
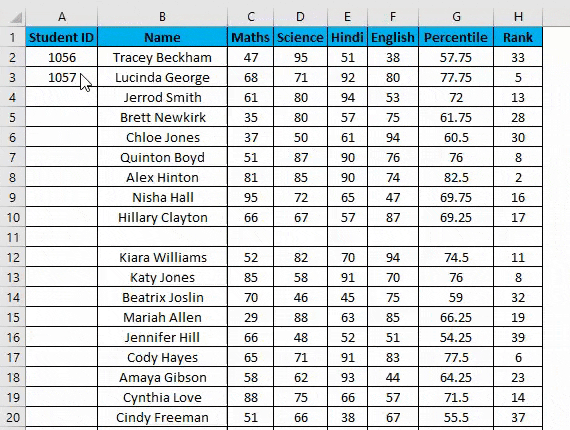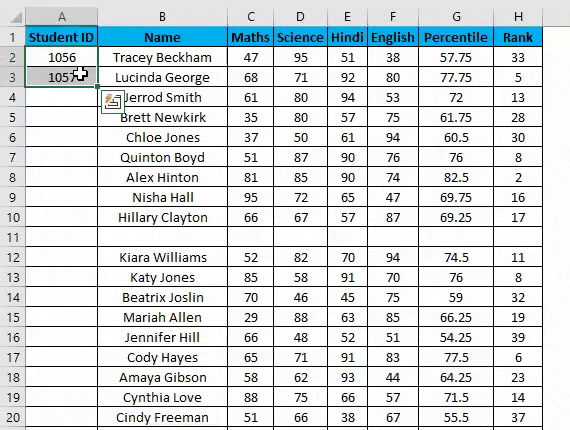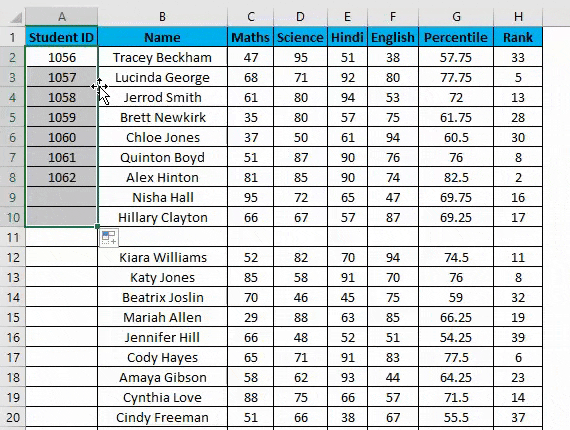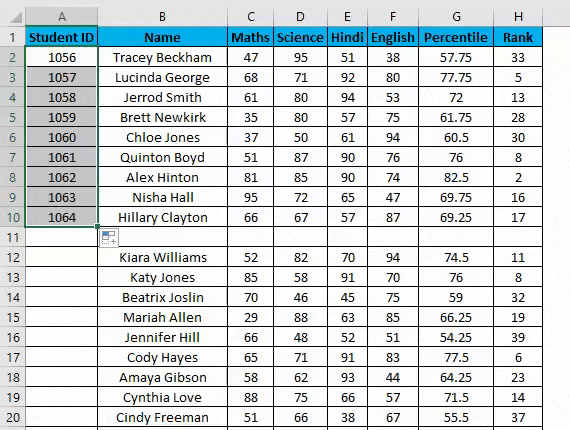
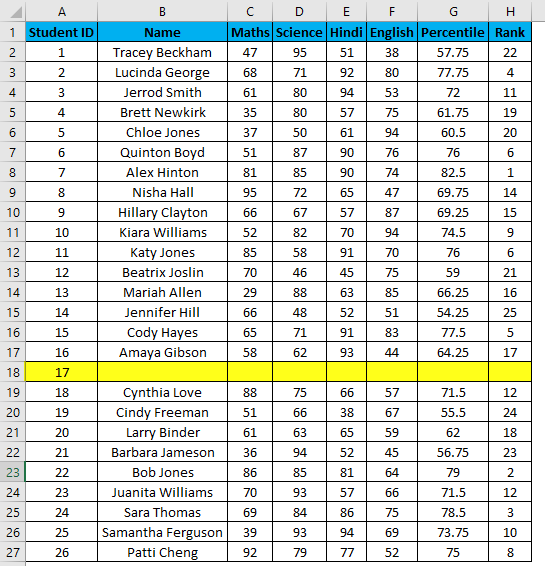
Suppose you have the following dataset. And you have to give a Student ID to each entry. Student ID there will be the same as a serial number of each row entry.
You can use the fill handle method here.
For example, you want to give Student ID 1056 to the first student, and after it should be numerically increasing, 1056, 1057,1058, and so on…
Steps to number rows in Excel:
- Enter 1056 in cell A2 and 1057 in cell A3.
- Select both cells.
- Now you can notice a square at the bottom-right of selected cells.
- Move your cursor to this square; now, it will be changed to the small plus sign.
- Now double click this plus icon, and it will automatically fill the series till the end of the dataset.
Key Point:
- It identifies a pattern from a few filled cells and quickly fills the entire selected column.
- It would only work till the last contiguous non-blank row. Viz. If you have any blank row(s) between your dataset. It will not detect them, so it’s not recommended to use the fill method.
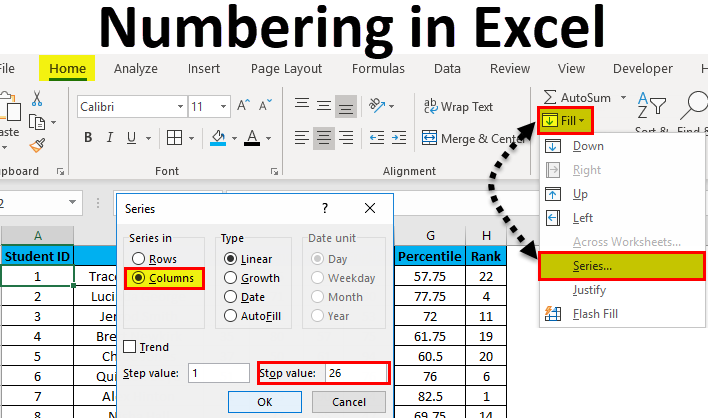
Example #2 – Fill Series Method
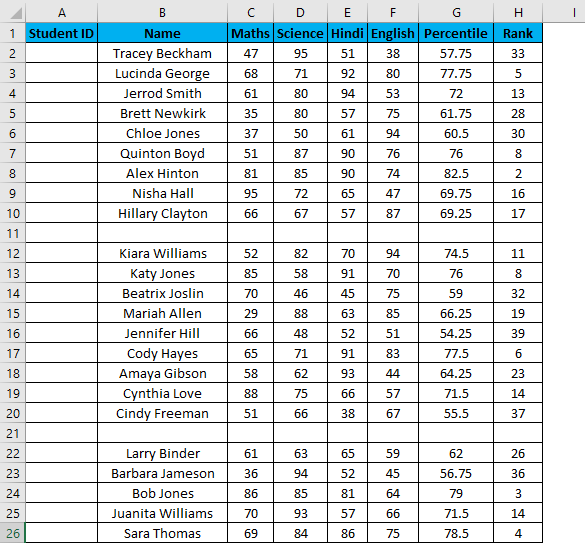
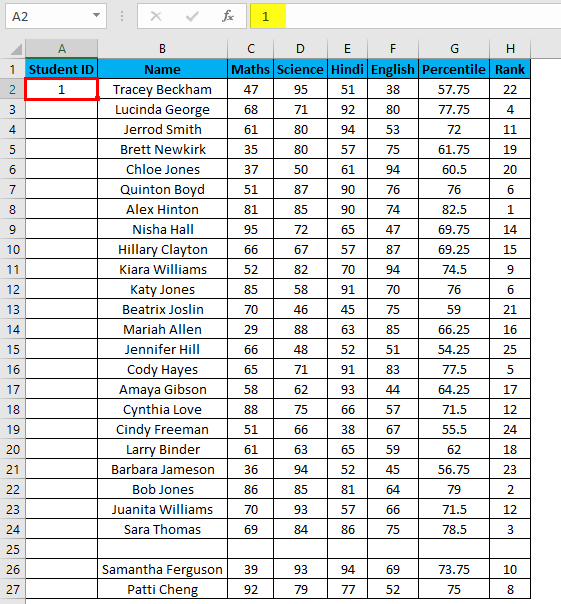
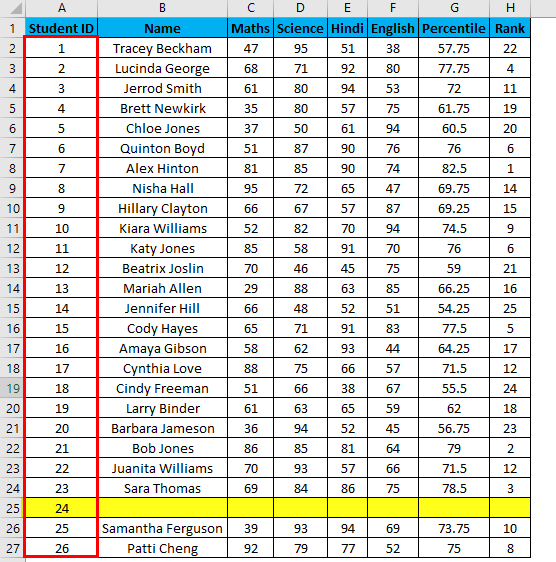
Suppose now we have the following dataset (same as above, now entries are only 26.).
Steps to use the Fill Series method:
- Enter 1 in cell A2.
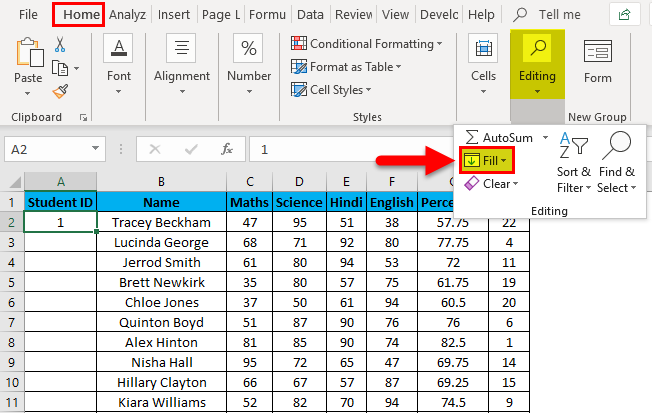
- Go to the Home tab.
- In the Editing group, click on the Fill drop-down.
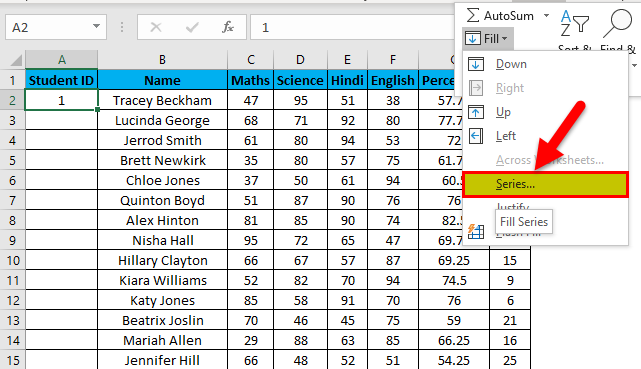
- From the drop-down, select Series.
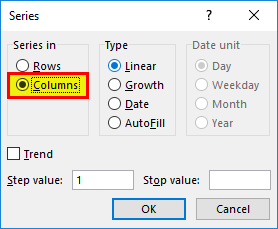
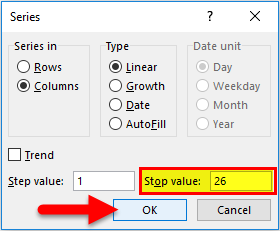
- In the Series dialog box, select Columns in the ” Series in ” option.
- Specify the Stop value. Here we can enter 26 and then click Ok.
- If you don’t enter any value, Fill Series will not work.
Hotkey to use fill series: ALT key+ H+ FI+ S
You can notice, it overcomes the drawback of the previous method. But then it has its own drawback that if we have blank rows in between of the dataset, Fill Series would still fill the number for that row.
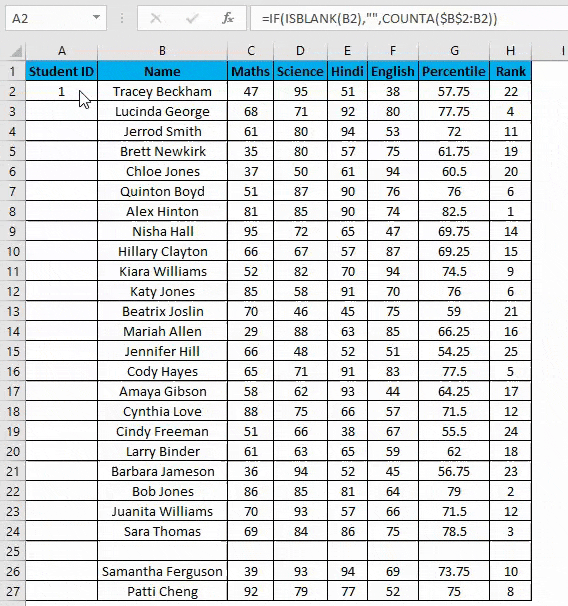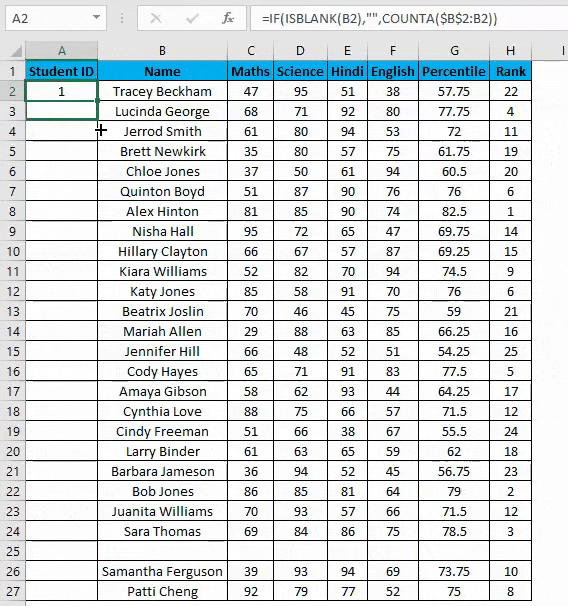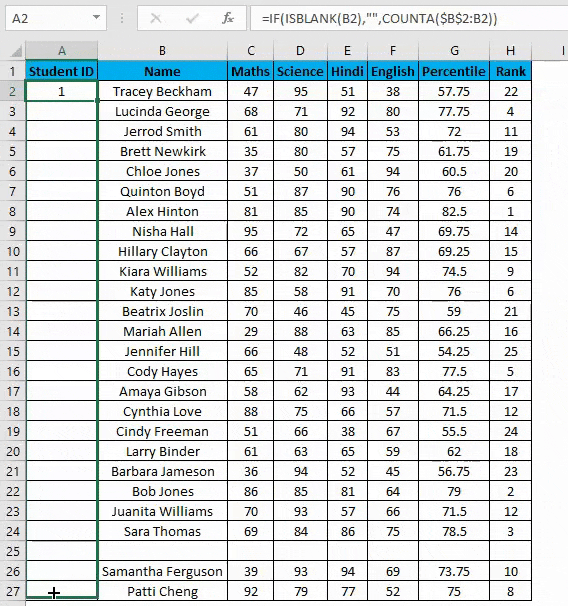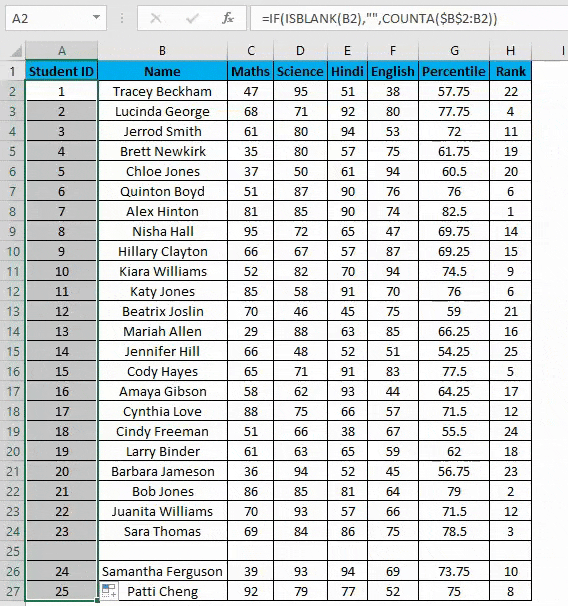
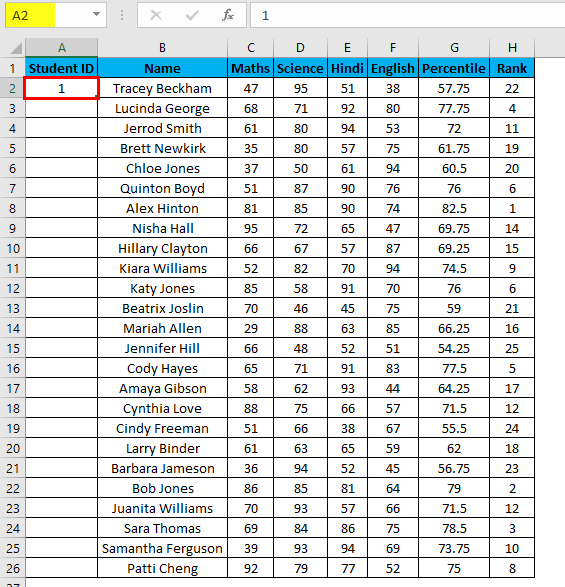
Example #3 – COUNTA Function
Suppose you have the same data set as above, now if you want to number rows in excel only which are filled Viz. Overcoming the shortcomings of the above 2 methods. You can use a COUNTA function here.
Steps to use a COUNTA Function:
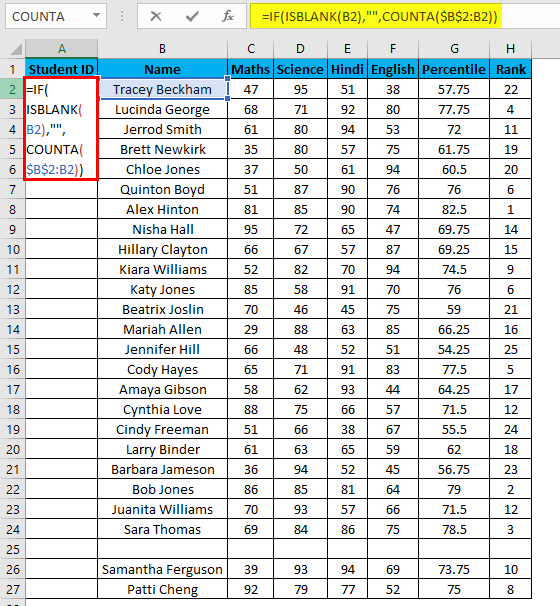
- Now enter the formula in the cell A2 i.e. =IF(ISBLANK(B2),””,COUNTA($B$2:B2))
- Drag it down till the last row of your data set.
- In the above formula, the IF function will check if cell B2 is empty or not. If found empty, it returns a blank, but it returns the count of all the filled cells till that cell if it’s not.
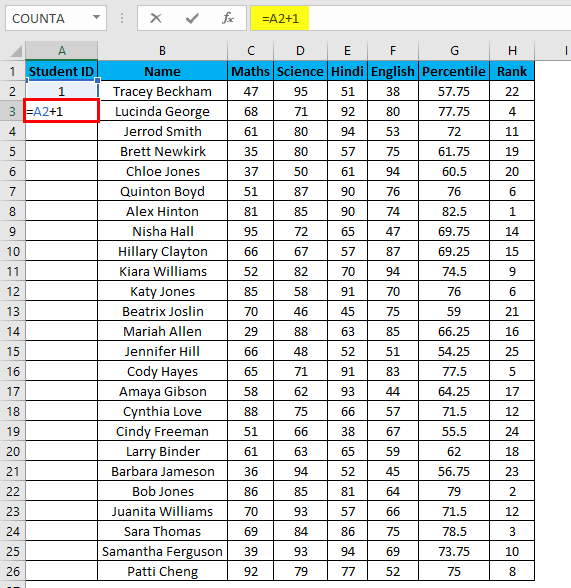
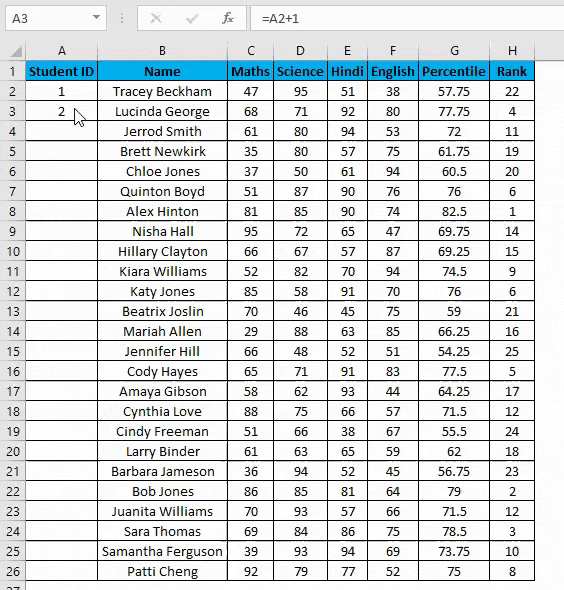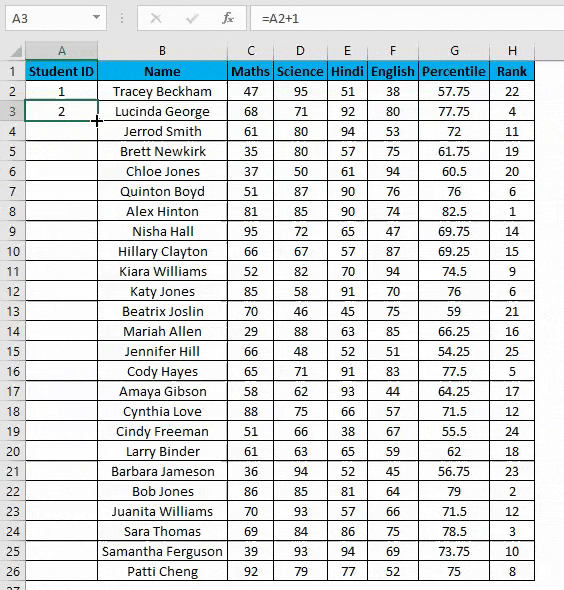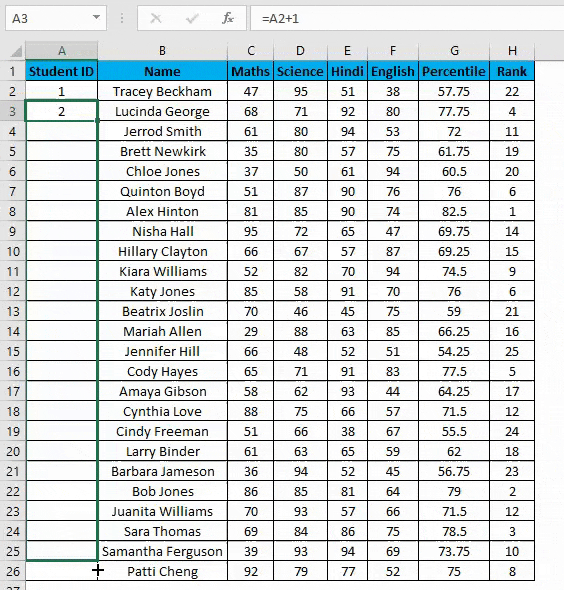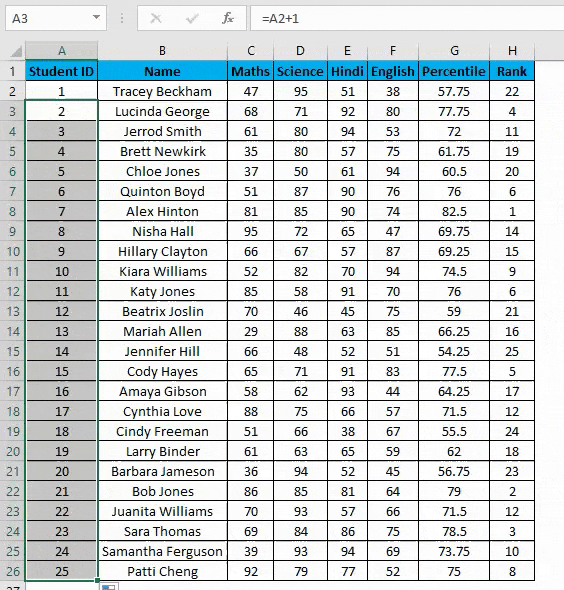
Example #4 – Increment Previous Row Number
This is a very simple method. The main method is to add 1 to the previous row number simply.
Suppose you again have the same dataset.
- In the first row, manually enter 1 or any number from where you want to start numbering all rows in excel. In our case. Enter 1 in cell A2.
- Now in cell A3, simply enter the formula=A2+1.
- Drag this formula until the last row, and it will be increased by 1 in each following row.
Example #5 – Row Function
We can even use a row function to give serial numbers to rows in our columns. In above all methods, the serial number inserted is fixed values. But what if a row is moved or you cut and paste data somewhere else in the worksheet?
The above problem can be resolved by using the ROW function. To number the rows in a given dataset using the ROW function.
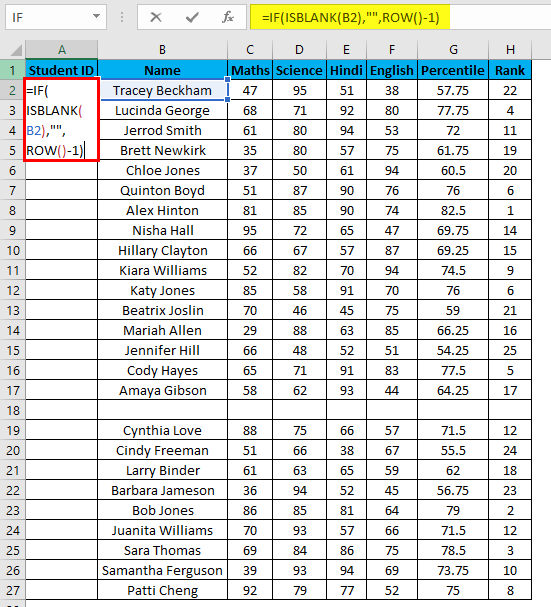
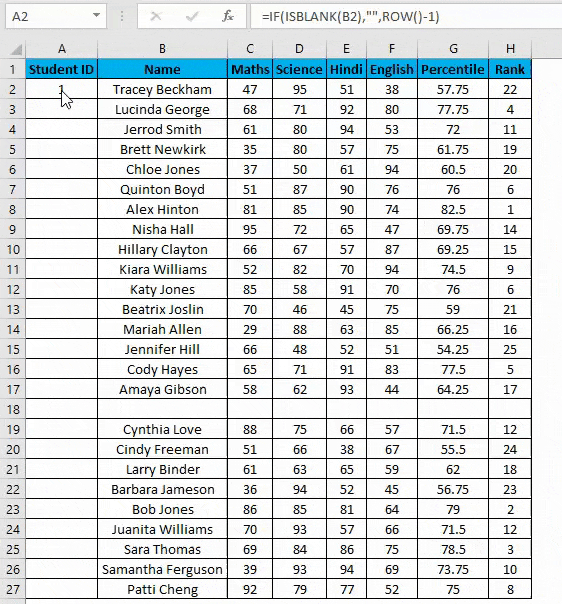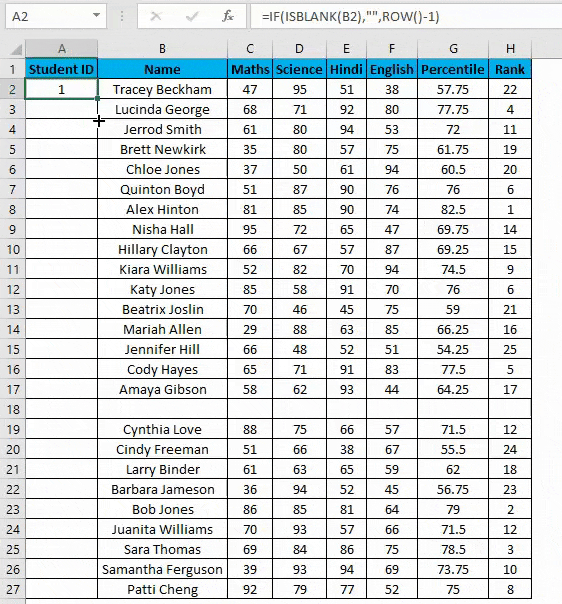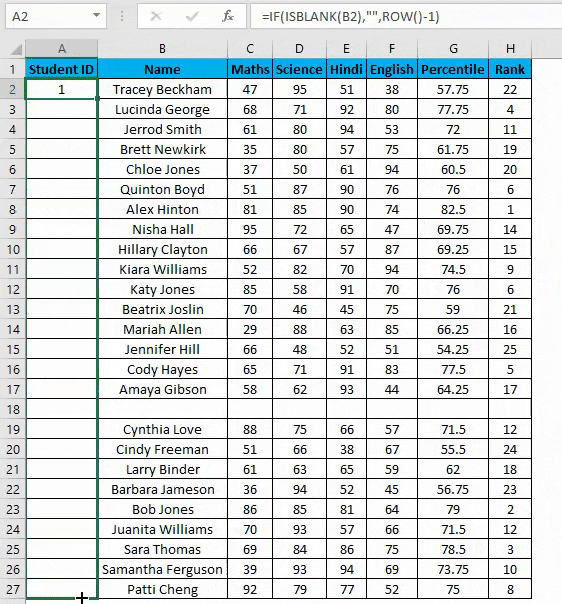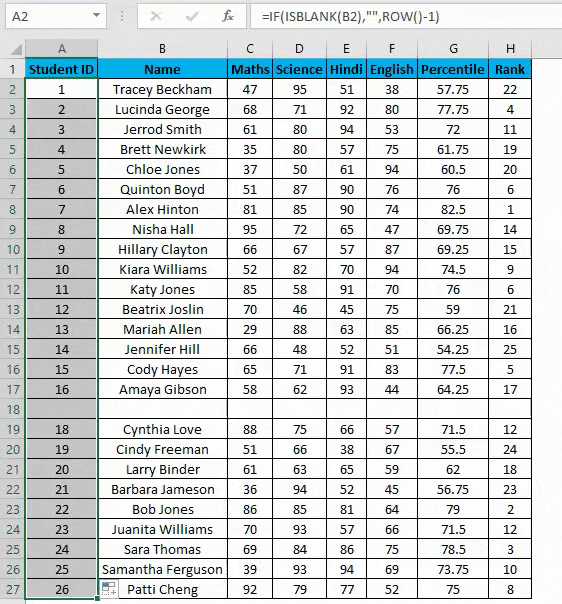
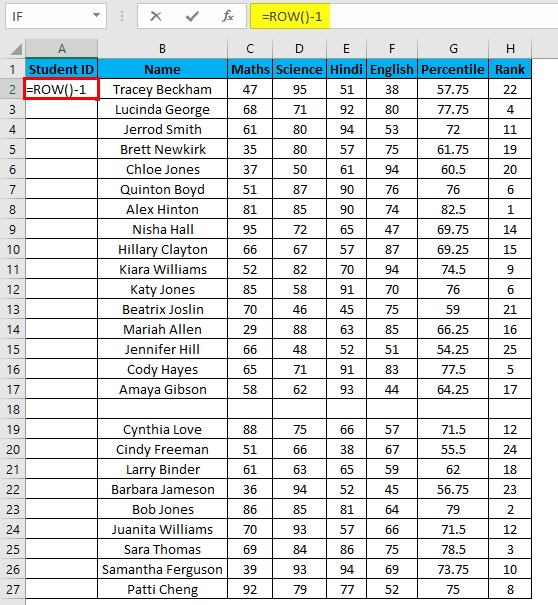
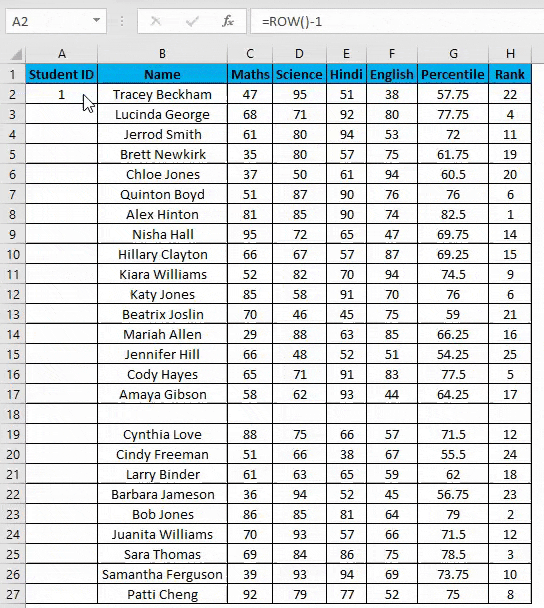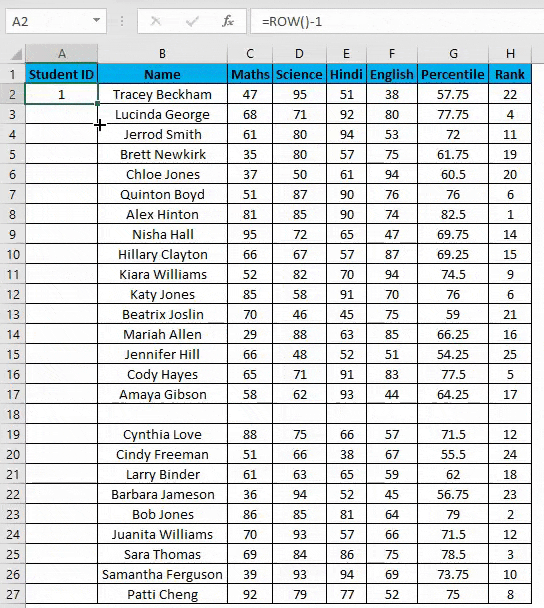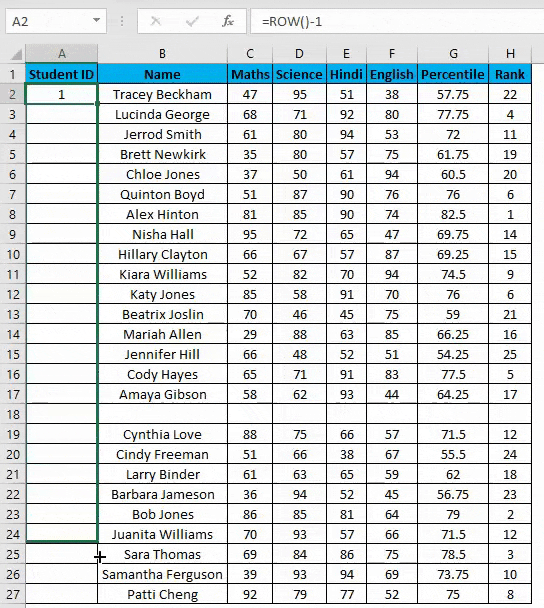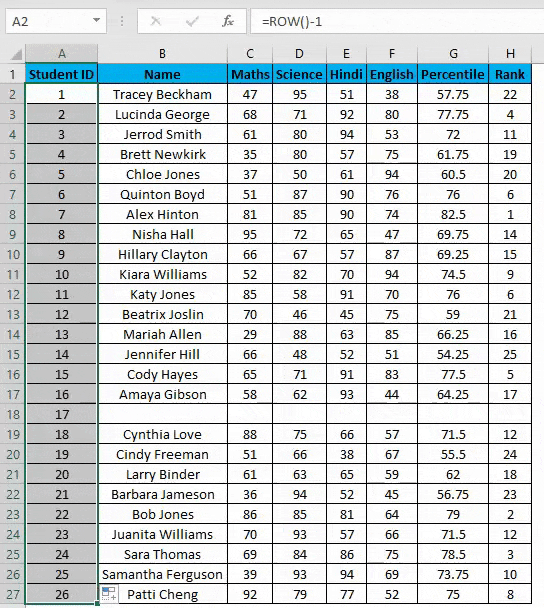
- Enter the formula in the first cell i.e. =IF(ISBLANK(B2),””,ROW()-1)
- Drag this formula until the last row.
- In the above formula IF function will check if the adjacent cell B is blank or not. If it’s found blank, it will return space, and if non-blank, then row function will come into the picture. ROW() function will give us the row number since the first row in Excel consists of our dataset. So we don’t need to count it. To eliminate the first row, I have subtracted 1 from the returned value of the above function.
- But it will not still adjust the row number, and a blank row will still have a serial number assigned to it. Though it is not shown, look at the below screenshot.
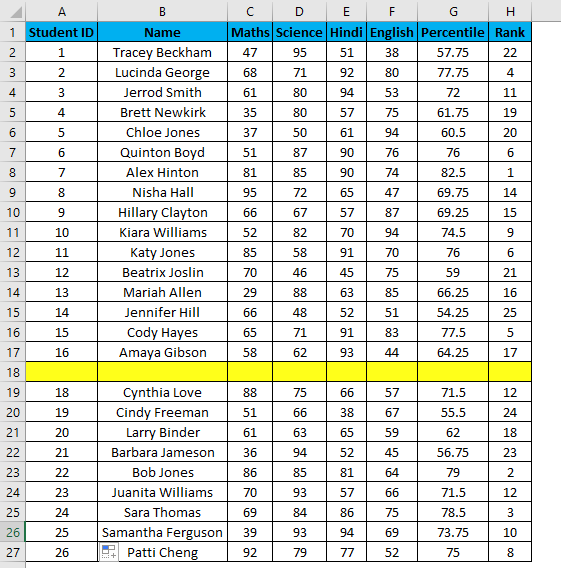
- You can overcome the above issue with this formula, i.e.=ROW()-1
- Drag this formula until the last row.
- But now, it will consider the blank rows in the dataset and will number them as well. Consider the below screenshot.
The main advantage of using this method is even if you delete one or more entries in your dataset. You don’t need to struggle with the numbering of rows each and every time, and it will be corrected automatically in excel.
So by now, I have discussed 5 unique methods to give serial numbers to row in a dataset stored in Excel. Although there are numerous methods to do the same, above five are the most common and easy to use method which can be implemented in different scenarios.
Things to Remember About Numbering in Excel
- While storing data in Excel, we often need to give serial numbers to each row in our data set.
- Entering a serial number to each and every row in the huge dataset can be time-consuming and prone to error.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to Numbering in Excel. Here we discuss how to add serial Numbers using different methods in excel along with practical examples and a downloadable excel template. You can also go through our other suggested articles –
- ISNUMBER Excel Function
- Negative Numbers in Excel
- Excel ISNUMBER Formula
- VBA Number Format
Numbering in Excel means providing a cell with numbers like serial numbers to some table. We can also do it manually by filling the first two cells with numbers and dragging them down to the end of the table, which Excel will automatically load the series. Else, we can use the =ROW() formula to insert a row number as the serial number in the data or table.
When working with Excel, some small tasks need to be done repeatedly. However, if we know the right way to do it, they can save a lot of time. For example, generating the numbers in Excel is a task that is often used while working. Serial numbers play a very important role in Excel. It defines a unique identity for each record of your data.
One of the ways is to add the serial numbers manually in Excel. But it can be a pain if you have the data of hundreds or thousands of rows and must enter the row number for them.
This article will cover the different ways to do it.
Table of contents
- Numbering in Excel
- How to Add Serial Number in Excel Automatically?
- #1 – Using Fill Handle
- #2 – Using Fill Series
- #3 – Using the ROW Function
- Things to Remember about Numbering in Excel
- Recommended Articles
How to Add Serial Number in Excel Automatically?
There are many ways to generate the number of rows in Excel.
You can download this Numbering in Excel Template here – Numbering in Excel Template
- Using Fill Handle
- Using Fill Series
- Using ROW Function
#1 – Using Fill Handle
It identifies a pattern from a few already filled cells and then quickly uses that pattern to fill the entire column.
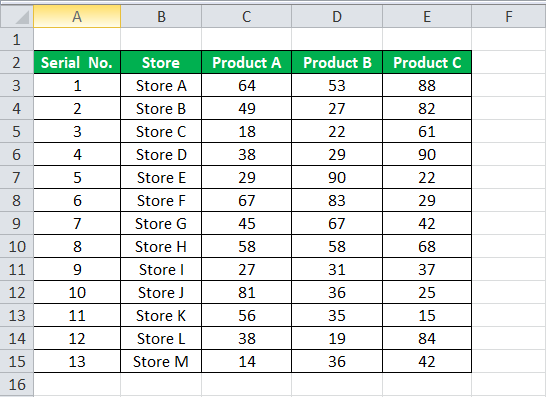
For example, let us take the below dataset.
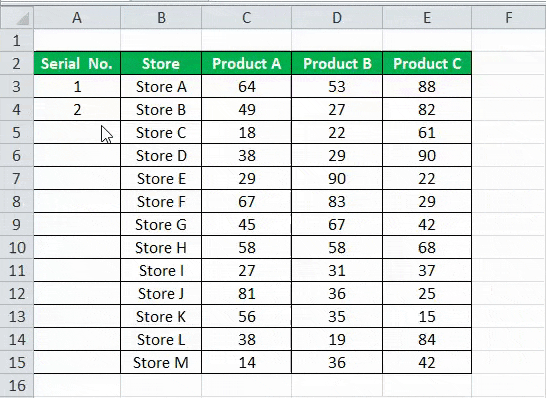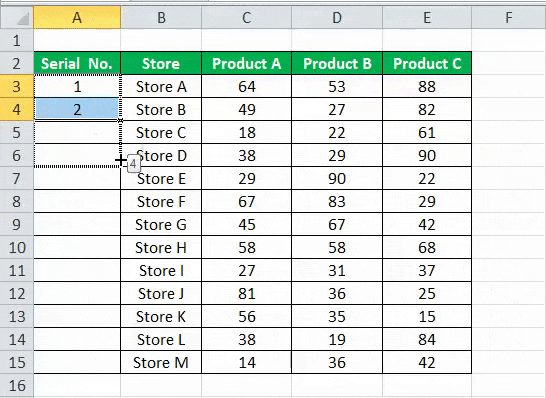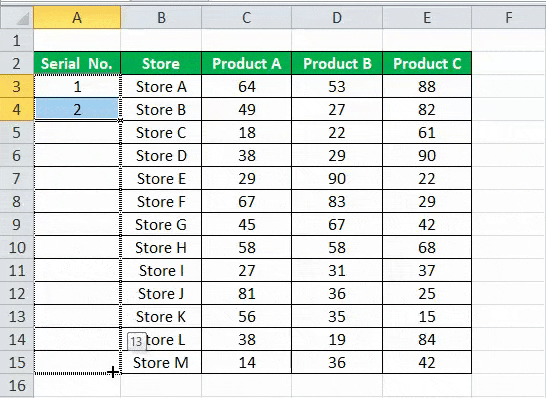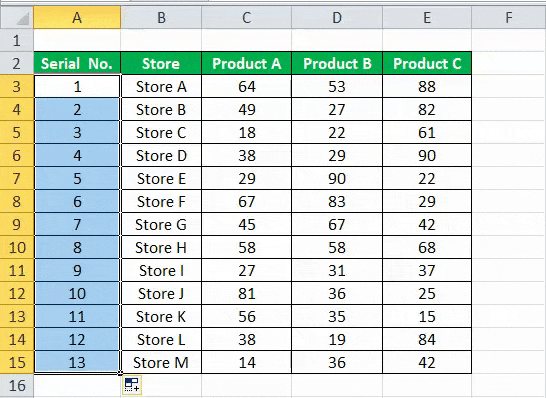
For the above dataset, we have to fill the serial no record-wise. Follow the below steps:
- First, we must enter 1 in cell A3 and insert 2 in cell A4.
- Then, select both the cells as per the below screenshot.
As we can see, a small square is shown in the above screenshot, which is rounded by a red color called “Fill Handle” in Excel.
Place the mouse cursor on this square and double-click on the fill handle.
- It will automatically fill all the cells until the end of the dataset. For example, refer to the below screenshot.
As the fill handle identifies the pattern, fill the individual cells with that pattern.
If you have any blank row in the dataset, the fill handle would only work until the last contiguous non-blank row.
#2 – Using Fill Series
It gives more control over data on how the serial numbers are entered into Excel.
For example, suppose you have below the score of students subject-wise.
Follow the below steps to fill series in the Excel:
- We must first insert 1 in cell A3.
- Then, go to the “HOME” tab. Next, click on the “Fill” option under the “Editing” section, as shown in the below screenshot.
- Click on the “Fill” dropdown. It has many options. Click on “Series,” as shown in the below screenshot.
- It will open a dialog box, as shown below screenshot.
- Click on “Columns” under the “Series in” section. Then, refer to the below screenshot.
- Insert the value under the “Stop value” field. In this case, we have 10 records; enter 10. If we skip this value, the Fill “Series” option may not work.
- Enter “OK.” It will fill rows with serial numbers from 1 to 10. Refer to the below screenshot.
#3 – Using the ROW Function
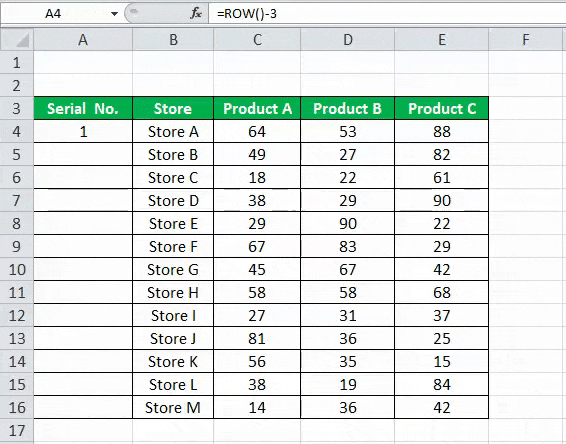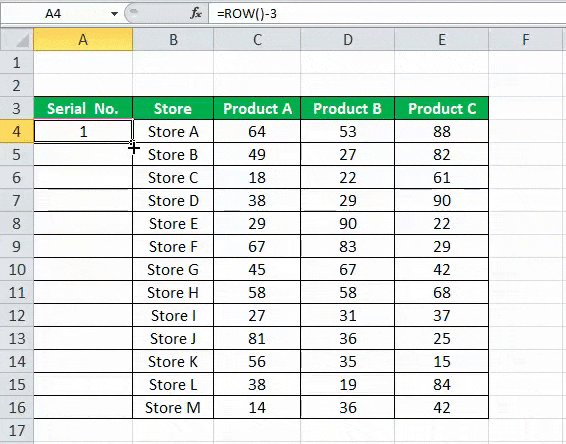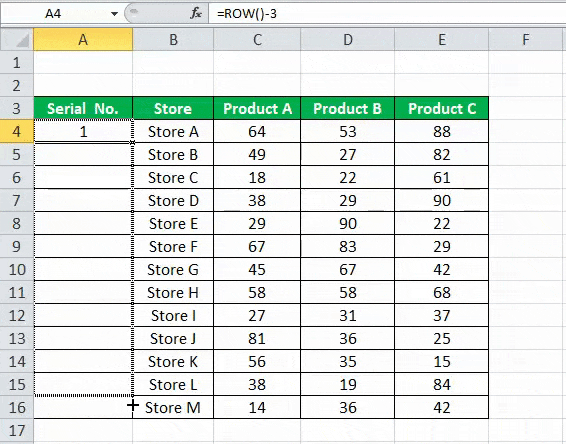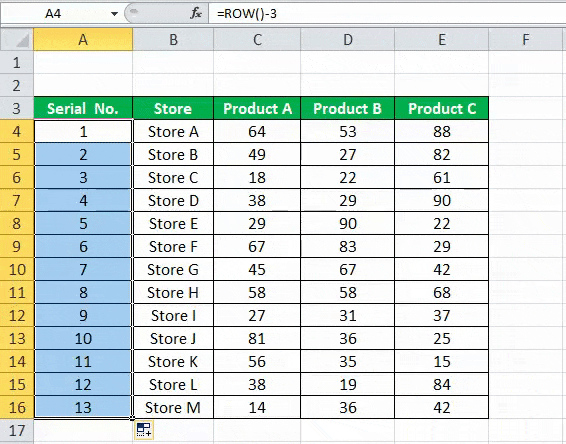
Excel has a built-in function, which also can be used to number the rows in Excel. To get the Excel row numbering, we must enter the following formula in the first cell shown below:
- The ROW function gives the Excel row number of the current row. We have subtracted 3 from it as we started the data from the 4th. If the data starts from the 2nd row, we must remove 1 from it.
- See the below screenshot. Using =ROW()-3 formula.
Drag this formula for the rest of the rows. The final result is shown below.
Using this formula for numbering will not damage the numbers if we delete a record in the dataset. Furthermore, since the ROW function does not reference cell addresses, it will automatically adjust to give the correct row number.
Things to Remember about Numbering in Excel
- The “Fill Handle” and “Fill Series” options are static. Therefore, if we move or delete any record or row in the dataset, the row number will not change accordingly.
- The ROW function gives the exact numbering if we cut and copy the data in Excel.
Recommended Articles
This article is a guide to Numbering in Excel. We discuss how to automatically add serial numbers in Excel using the fill handle, fill series, and ROW function, along with examples and downloadable templates. You may learn more about Excel functions from the following articles: –
- Auto Numbering in ExcelThere are two approaches for auto numbering. To begin, fill the first two cells with the series you wish to insert and drag it to the table’s end. Second, use the =ROW() formula to get the number, and then drag it to the table’s end.read more
- Row Limit in Excel
- Excel Negative NumberIn Excel, negative numbers, i.e. numbers less than 0 in value, are displayed with minus symbols by default.read more
- IsNumber FunctionISNUMBER function in excel is an information function that checks if the referred cell value is numeric or non-numeric.read more
- Null in ExcelNull is a type of error in Excel that occurs when two or more cell references provided in formulas are wrong, or when their position is incorrect. Using space in formulas between two cell references, for example, will result in a null error.read more
Reader Interactions
If your work involves printing your excel worksheets, it’s a good idea to insert page numbers in it.
Inserting page numbers in Excel takes a little more work as compared with other Microsoft applications such as Word or PowerPoint.
Watch Video – How to Insert Page Numbers in Excel
How to Insert Page Numbers in Excel
In this tutorial, you’ll learn how to insert page numbers in Excel worksheets.
- How to Insert Page Numbers in Excel using the using the Page Layout View.
- Insert Page Numbers in Excel Using the Page Setup Dialogue Box.
- Start Page Numbering with the Desired Number.
- Change the Order in which pages are numbered.
- Remove Page Numbers from the Excel Worksheets.
Insert Page Numbers in Excel: Page Layout View
If you want to insert page numbers in all the pages of a worksheet, using the page layout view is the fastest way to do it.
Here is how to do this:
Note that these page numbers are visible only in the Page Layout view. You would not see it when you go back to the normal view. If you print the worksheet, the page numbers also get printed.
Have a Different First Page Footer
You may want to have a different text in the footer on the first page, and regular page numbers of other pages. For example, on the first page, you may want to have Company’s name/website or copyright info along with the page number.
Here is how to do this:
Now, whatever you have entered in the first page would only be visible on the first page and rest all the pages would show page numbers.
Have Different Odd and Even Pages Footer
If you want to have different page numbers for odd and even pages, you can easily do this using the inbuilt settings.
For example, you may not want to show page numbers on even pages.
Here is how to do this:
Insert Page Numbers in Excel: Page Setup Dialogue Box
You can also insert page numbers in Excel using the page setup dialogue box.
Here is how to do this:
This will instantly insert page numbers in Excel. If you want to insert page numbers in on the active worksheet only, follow the above steps. If you want to insert page numbers in multiple worksheets, select all the worksheets (hold the SHIFT key and select the worksheet tabs) and then follow the above steps.
Start Page Numbering with the Desired Number
If you are printing a report which is a continuation of some other report, or which is a part of some the overall report, you may want to begin page numbers with a different number (instead of 1).
To do this:
Change the Page Order while Numbering
If you have a large data set, by default, Excel would first insert page numbers to the all the sheets going down, and then move to the right and then number those sheets.
If you want to change the order, you can do this by following the below steps:
Remove Page Numbers
To remove page numbers:
- Go to View and select the Page Layout view.
- Scroll down and select the footer where you see the page numbers.
- You would notice that as soon as you click on the box with the page number, it would change into a code. Delete that code.
- Click anywhere else on the worksheet.
You may also like the following Excel tutorials:
- Insert Page Numbers in Excel Worksheets – MS Help.
- How to Insert a Check Mark (Tick ✓) Symbol in Excel
- How to Quickly Insert Date and Timestamp in Excel
- How to Insert a Watermark in Excel
- How to Print Excel Sheet on One Page
- How to Insert Page Breaks in Excel (& Remove, Delete Page Breaks)
Bottom Line: Learn 4 different techniques for creating a list of numbers in Excel. These include both static and dynamic lists that change when items are added or deleted from the list.
Skill Level: Beginner
Watch the Tutorial
Download the Excel File
You can download the worksheet that I use in the video here:
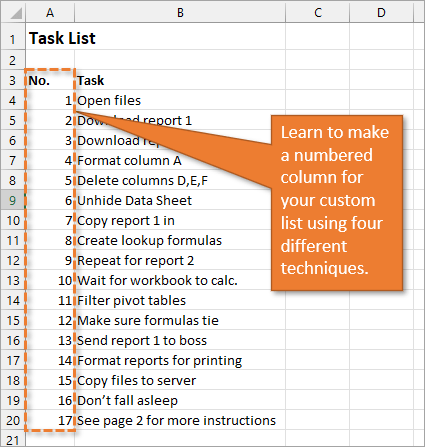
If you have a list of items in Excel and you’d like to insert a column that numbers the items, there are several ways to accomplish this. Let’s look at four of those ways.
1. Create a Static List Using Auto-Fill
The first way to number a list is really easy. Start by filling in the first two numbers of your list, select those two numbers, and then hover over the bottom right corner of your selection until your cursor turns into a plus symbol. This is the fill handle.
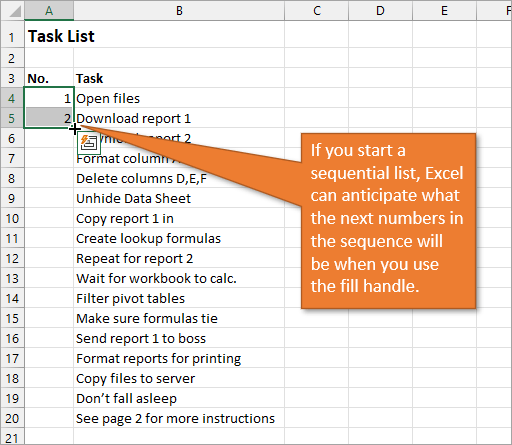
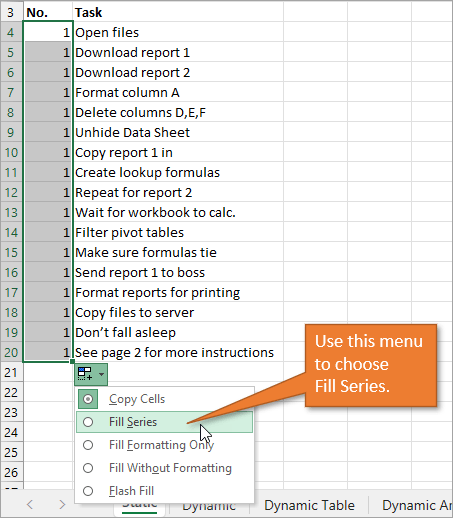
When you double-click on that fill handle (or drag it down to the end of your list), Excel will fill in the blanks with the next numbers in the sequence.
An alternate way to create this same numbered list is to type a 1 in the first cell and then double-click the fill handle. Because Excel doesn’t have a second number to identify a sequence or pattern, it will fill down the columns with 1s. But you will notice that a menu is available at the end of your column, and from that menu, you can select the option to Fill Series. This will change the 1s to a sequential list of numbers.
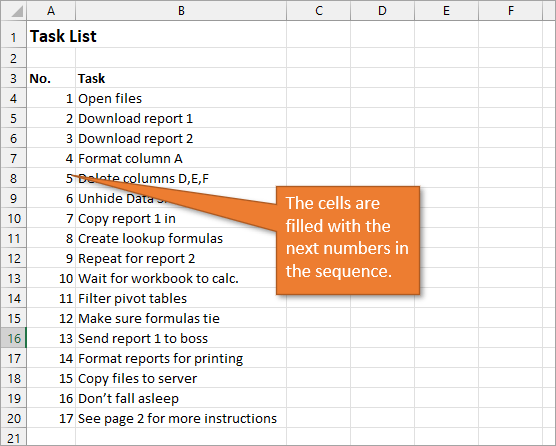
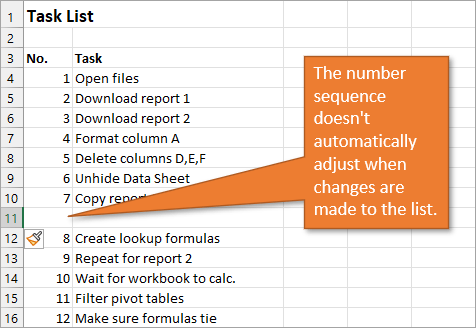
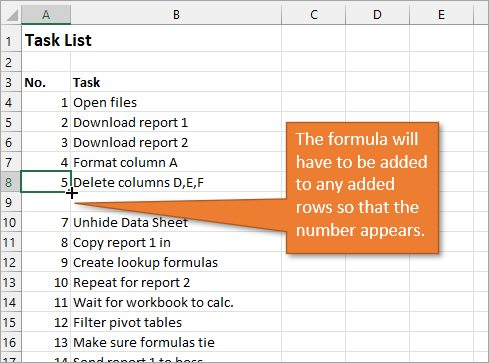
The numbered column we’ve created in both instances is static. This means it doesn’t change when you make additions or deletions to the corresponding list of items. For example, if I insert a new row in order to add another task, there is a break in the numbered column as well, and I would have to repeat the same steps to correct the list.
So, unless we want the numbers to always remain as they are, a better option would be to create a dynamic list.
2. Create a Dynamic List Using a Formula
We can use formulas to create a dynamic list where the numbers update when we add or delete rows from the list.
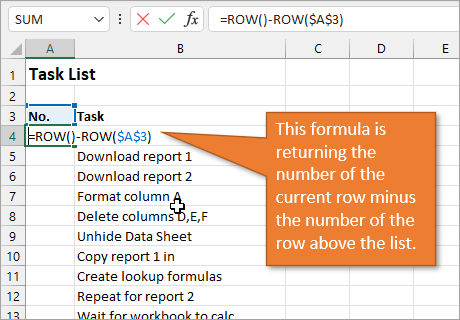
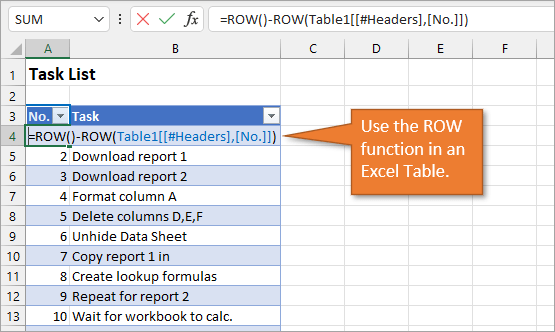
To use a formula for creating a dynamic number list, we can use the ROW function. The ROW function returns the row number of a cell. If we don’t specify a cell for ROW, it just returns the current row number of whatever is selected.
In our example, the first cell in our list doesn’t start on Row 1. It starts on Row 4. But we don’t want our list to start at 4; we want it to start at 1. To subtract the extra 3, our formula will include a minus sign and then the ROW function again, but this time pointed to the cell above our formula (which is in Row 3).
We use the absolute values (dollar signs) in our cell selection because we don’t want that number to change as we copy the formula down the list. In other words, we always want to subtract 3 from the row number to give us our list number.
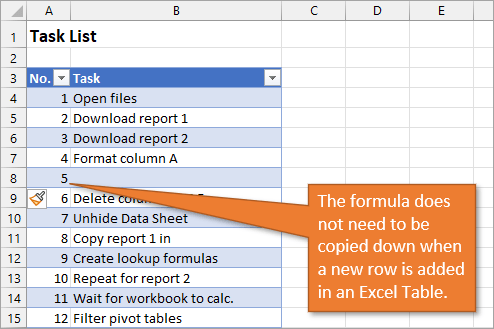
When we copy down the formula, we have a numbered list that will adjust when we add or delete rows. However, when adding a row, we will have to copy the formula into the newly inserted cell.
This additional step of copying the formula into new rows can be avoided if we use Excel Tables.
3. Create a Dynamic List Using a Formula in an Excel Table
If we write the same formula but we use an Excel table, the only difference we will make in the formula is that we reference the column header instead of the absolute cell value.
Because we are using an Excel Table, the formula automatically fills down to the other rows. When we add a row to the table, the formula will automatically populate in the new cell.
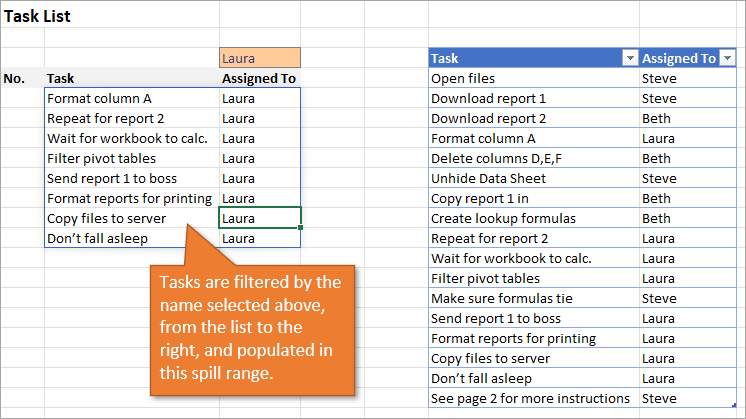
4. Create a Dynamic List Using Dynamic Array Formulas
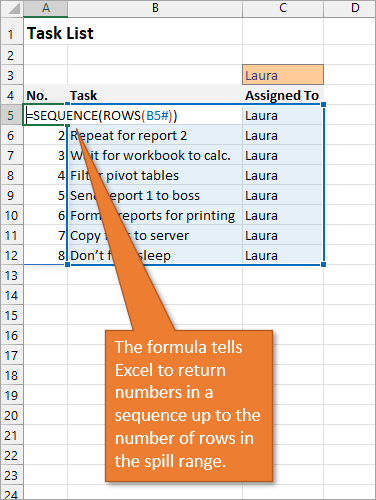
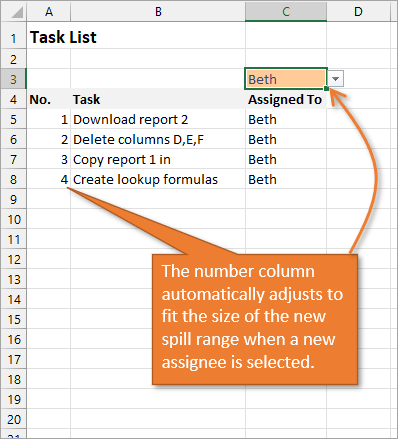
Below, I have a table that is populated using Dynamic Array Formulas. The FILTER formula spills a range of results based on whatever name is selected in the orange cell.
The Dynamic Array formula we will use is SEQUENCE. This will return a sequence for the number of rows we identify in the formula. To tell Excel how many rows there are, we will use the ROW function as the argument for sequence. The argument for ROW is just the spill range. The way to notate the spill range is to simply place a hashtag after the name of the first cell in the range. So our formula looks like this:
=SEQUENCE(ROWS(B5#))
Once we complete our formula and hit Enter, the list will be numbered.
With this formula in place, if the size of the range changes when a new name is selected, the numbered column for the list will automatically adjust as well.
Bonus Tip: Formatting Your Numbered List
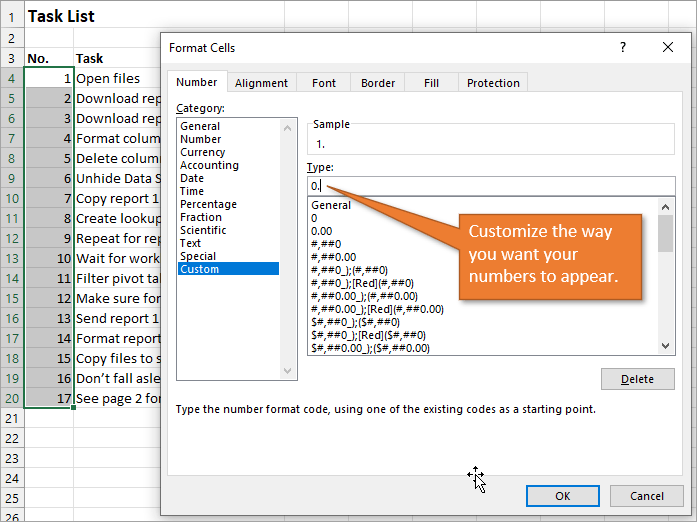
If you want to add periods or other punctuation to your numbered list:
- Select the entire list and right-click to choose Format Cells. Or use the keyboard shortcut Ctrl + 1.
- Choose the Custom option on the Number tab.
- Then in the Type field, type in the number 0 with whatever punctuation you would like to surround your number.
Here, I’ve just added a period.
When you hit OK, you will have formatted the entire selection.
Related Posts
Here are a few similar posts that may interest you.
- Excel Tables Tutorial Video – Beginners Guide for Windows & Mac
- New Excel Features: Dynamic Array Formulas & Spill Ranges
- How to Prevent Excel from Freezing or Taking A Long Time when Deleting Rows
Conclusion
I hope these four ways to create ordered lists are helpful for you. If you have questions or feedback, I would love to hear them in the comments. Have a great week!
Whether it’s for preparing revenues or customer lists, continuous numbering improves the clarity of Excel tables. Although Excel does not provide a button for automatic numbering, it’s easy to automatically number rows once you know how to. The following guide explains how to use Excel’s simple options to add numbering.
Auto numbering in Excel – what are the options?
Excel provides two options for automatic numbering to help make tables easier to read. On the one hand, you have the option to create continuous or user-defined number sequences with the fill box. On the other, the ROW function lets you define numbering as part of a formula.
Excel with Microsoft 365 and IONOS!
Use Excel to create spreadsheets and organize your data — included in all Microsoft 365 packages!
Office Online
OneDrive with 1TB
24/7 support
Method 1: Auto numbering with fill boxes
The fill box or auto-fill box can be found at the bottom right edge of a cell when you move your mouse cursor over it. To select multiple cells, click on the area inside a cell and drag the box down – without clicking on the little fill box at the bottom right edge.
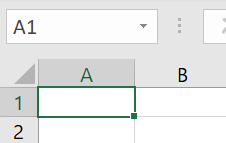
The fill box is the easiest way to add auto numbering to rows in your Excel table. Here, you have the option to set the sequence the numbering should adopt.
Step 1: If you prefer ascending numbering (1, 2, 3, 4, …), simply enter “1” and “2” in the first two cells of the column. Excel always needs 2 or 3 numbers to automatically detect and continue a desired sequence. Select the range with the numbers. When you select the range, make sure you don’t click on the little green square at the bottom right of the cell. Instead, click in the cell and drag the frame to the end of the corresponding cell.
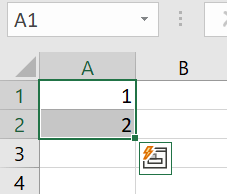
Step 2: Now, move the cursor to the little green box in the bottom right edge of the cell. Drag this down to the end of the area in which you’d like numbering to appear.
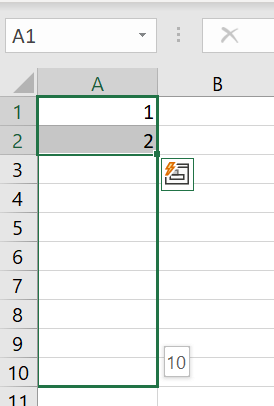
Step 3: Excel will now complete the continuous number sequence.
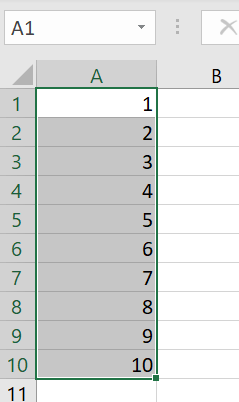
You can also insert numbering for odd numbers or in steps of 10, 20, or 100, for example. To do this, simply enter the number sequence you wish to use. Excel will take care of the rest.
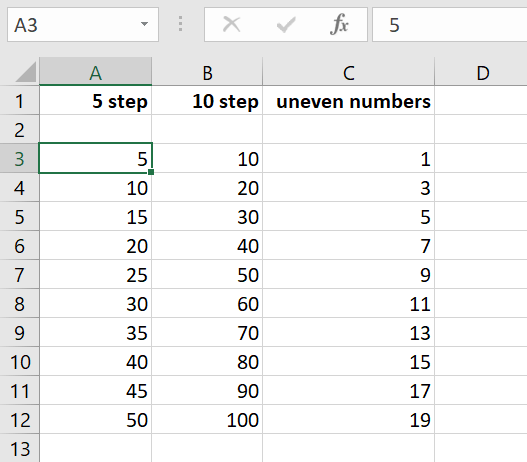
Tip
You can also use auto numbering to auto-complete date entries or times, for example. But you always need to provide the first 3 to 3 numbers for Excel to recognize a number sequence or pattern. Only then does the program automatically detect the sequence.
Method 2: Add numbering with the ROW function
As an alternative to the fill box, you can use the ROW function to add automatic numbering in Excel. The ROW function syntax is as follows:
The ROW function returns the row number of the reference, which is entered in brackets “()”. Add “B5” into the formula, for example.
Now press [Enter]. The function will return “5,” since it refers to row 5 in column B.
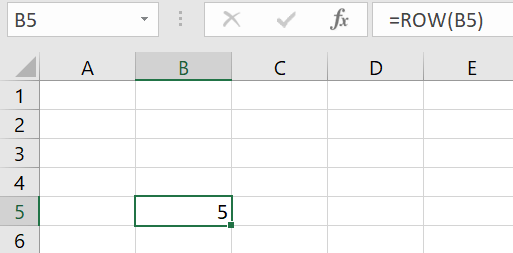
Note
Remember that you define the cell reference. If you leave the reference empty, the ROW function will automatically output the number of the cell that contains the formula.
Now, you can use the ROW function to insert automatic numbering.
Step 1: In the first cell, enter the ROW function with the starting cell reference. If you begin automatic numbering in cell A1, enter “=ROW(A1)”.
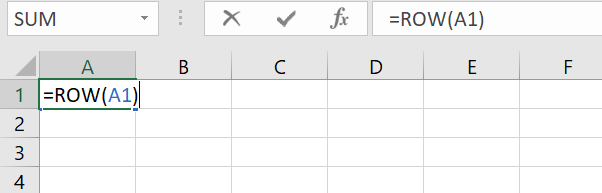
Press [Enter]. A “1” will now appear in cell A1.
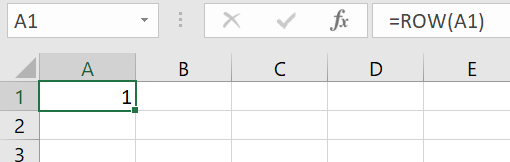
Step 2: Now drag the fill box to the end of the desired area. The ROW function will then insert continuous numbering.
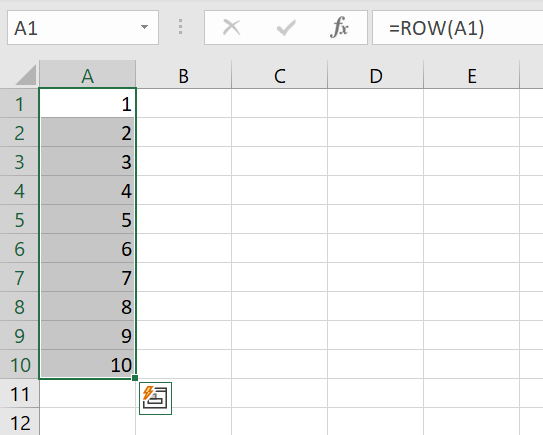
Note
If you change the data or move or delete rows after adding the ROW function, the numbering may be interrupted. To update it, select two of the existing numbers of the numbering sequence and drag the fill box across the interrupted area.
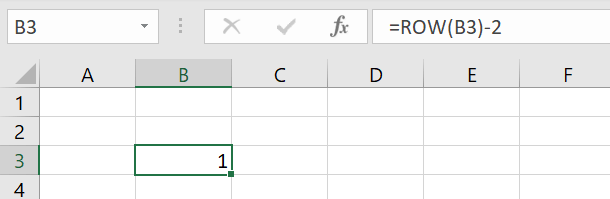
Step 3: Would you like the ROW function with number 1 to begin in a different row? This is easy to do: Click on the cell where numbering should start, e.g. B3. Enter the ROW function and then subtract the rows that remain empty above the start of the numbering sequence. The syntax is as follows:
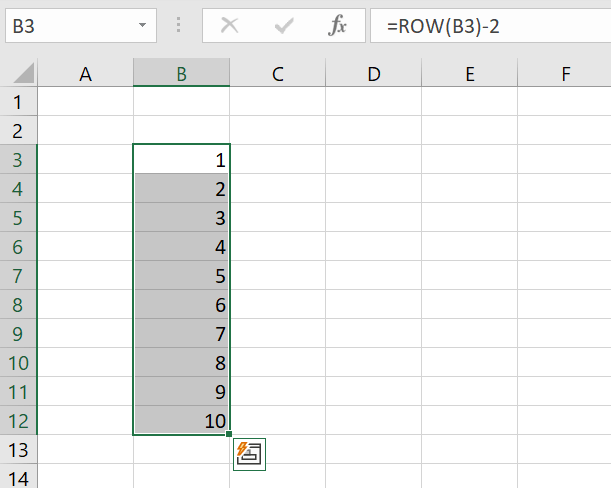
=ROW([CELL REFERENCE])-[NUMBER OF CELLS]The ROW function will now start your numbering sequence with “1” in row B3, since B1 and B2 are subtracted from the numbering:
Drag the fill box down again. The ROW function will insert the numbering automatically.
Microsoft 365 with IONOS!
Experience powerful Exchange email and the latest versions of your favorite Office apps including Word, Excel and PowerPoint on any device!
Office Online
OneDrive with 1TB
24/7 support

How to create graphs in Excel
Long sequences of numbers can be off-putting and rarely provide quick overviews. But by creating a graph in Excel, you can ensure that everyone will immediately understand the relationships and trends you’re presenting. The Microsoft Excel spreadsheet application allows you to create many different types of charts and customize them exactly to your needs.
How to create graphs in Excel

Excel: ROUNDDOWN – an explanation of this handy function
When performing complex calculations in tables, you can quickly produce values that are not fit for everyday use because they have far too many decimal places. The ROUNDDOWN function in Excel can help with this. It uses a simple formula to simplify your workflow. You can use it to round down any number to the desired number of decimal places.
Excel: ROUNDDOWN – an explanation of this handy function

How to use the Excel COUNT function
Analyses and calculations in Excel can be highly complex. Excel’s worksheets let you create huge tables, but sometimes you just want to answer a very simple question: How many cells in the table contain a number? In big worksheets, it can be virtually impossible to check the whole thing manually. The COUNT function in Excel was created specifically to solve this problem.
How to use the Excel COUNT function

Excel: working with dates
Many countries have their own unique way of displaying dates and times. To be able to switch seamlessly between date and time formats, the information must first be stored in a universal format. You can use the DATE function in Excel for this purpose. In this article, you’ll learn how to work with the Excel DATE formula.
Excel: working with dates
See all How-To Articles
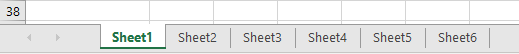
This tutorial demonstrates how to count the number of worksheets in an Excel file.
Count Number of Worksheets
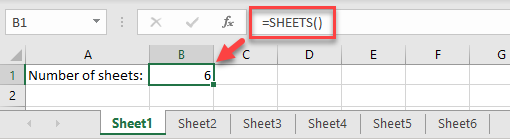
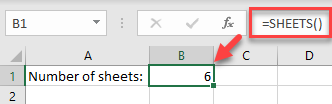
The easiest way to count the number of worksheets in your workbook is to use the SHEETS Function. Say your Excel file has six worksheets.
In any cell on any of the sheets, enter the formula:
=SHEETS()As you can see, this function without arguments returns the total number of sheets in the current workbook (including hidden sheets).
Numbering cells is a task often you’ll often perform in Excel. But writing the number manually in each cell takes a lot of time.
Fortunately, there are methods that help you add numbers automatically. And in this article, I’ll show you two methods of doing so: the first is a simple method, and the second lets you have dynamically numbered cells. So let’s get started.
How to Auto-Number Cells with a Regular Pattern
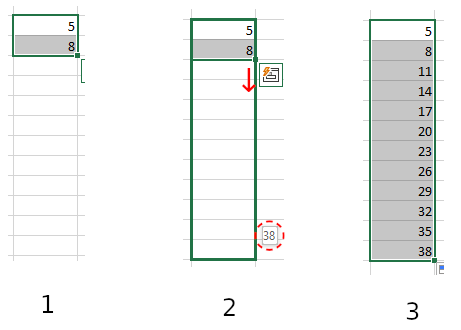
For this method, you set your starting number in one cell and the next number in the series in the next cell.
Once you have two adjacent cells filled with your two starting numbers, you can select those two cells, click on the handle in the bottom right corner of the green outline, and drag to select all the cells that you want to follow your pattern.
A useful tooltip appears near the bottom right corner of the green outline to show what the last number in the series would be if you released at that point.
So, if you want to start with the number 5 and increment by 3 until 38, you would write 5 in your first cell, and 8 in the next cell. You would then select the cells containing the 5 and the 8, click on the handle, and drag to select the other cells until you see 38 appear in the tooltip. Then you can release, and the numbers will be filled in automatically.
The numbers can also be formatted in descending order: if you start with 7 and then enter 5, the pattern will continue with 3, 1, -1, and so on.
You can also do the same with rows instead of columns. Fill in two consecutive cells in a row with the start of your pattern, then select them and drag the outline horizontally across those cells that you want to continue that pattern. It’ll automatically fill in those numbers.
You can also do the same going upward – fill two cells, select them, click the handle and drag upward to fill the cells above your two starting cells.
Note: this will always add numbers that are evenly spaced in the pattern you’ve started. It won’t work with other kinds of number progressions.
How to Auto-Number Cells Using the ROW() Function
If you have data that can be sorted in different ways (say, a list of names — alphabetically, etc), it’s annoying if the numbering of your lines gets scrambled when you’re sorting other data.
To avoid that, you can dynamically number your rows using the ROW() function.
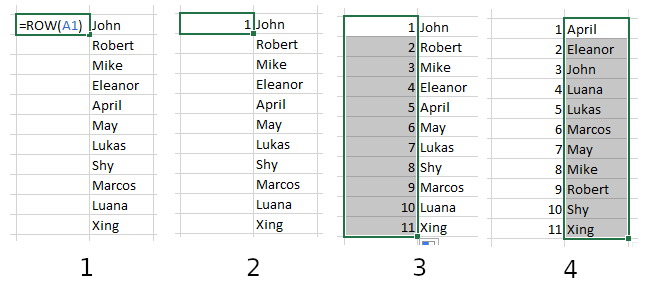
In the cell where you want the numbering to start, write =ROW(A1). This will produce the number 1 in the cell.
Select the cell and drag the outline from the handle in the corner to populate the same formula in the rest of the cells (or, if you are adding the line numbers near a block of data already present, you can just double-click on the handle on the corner of the selection).
=ROW(A1) in your first cell, 2) It will appear as the number1, 3) Click and drag or double-click to fill all other cells. 4) Now if you sort the data, the line numbers will stay in order.
If you want to have a different regular pattern, you can use a bit of math: to have numbers spaced by 2, you can write =ROW(A1) * 2 in the first cell, and then proceed with the same steps as above. This will produce the numbers 2, 4, 6…and so on.
If you want to change the starting point of the pattern – to maybe have only odd numbers, for example – you can subtract one: =ROW(A1) * 2 - 1, this will produce the numbers 1, 3, 5, 7…
As a general formula, to get any pattern you can write =ROW(A1) * a + b. a is used to determine the step, and b (it can be either a positive or negative number) is used to change the starting point of the pattern.
If you want to number your columns, you can use the COLUMN() function in the same way as the ROW(). Just fill in your first cell with =COLUMN(A1) , select the cell, then expand the selection to the rest of the cells you want your numbers to be in.
Note: if you add or delete rows, you will need to set the auto-numbering again by selecting the first cell and dragging or double-clicking again to restore the pattern.
Conclusion
Writing numbers in cells is a task often performed in Excel, and here we have seen two simple methods that let us save time. The first method just involves writing numbers in two cells, and then a couple of clicks. And the other just requires writing a formula in one cell, and then a couple of clicks.
There are a few other methods for numbering cells in Excel, but these are the most straightforward.
Learn to code for free. freeCodeCamp’s open source curriculum has helped more than 40,000 people get jobs as developers. Get started
/Excel Tips /Formula To Count The Number Of Sheets In The Excel

In fact, MS Excel doesn’t have any Straight Formula to Count the Number of Sheets in the Workbook. But, we have Indirect Way to Count the same.
HOW?
First we need to “Define Name” by Referring to =GET.WORKBOOK(1)&T(NOW())
Then, Use the below Formula to Count the Number of Sheets
=COUNTA(INDEX(DEFINED NAME,0))
Step By Step?
2003 and Below excel versions
1. Click ”Ctrl+F3′, then ‘Define Name’ Box appears
2. Enter ‘Names in workbook’ as CountSheets (Your choice)
3. Enter ‘Refers To’ as =GET.WORKBOOK(1)&T(NOW())
4. Click OK
5. Come to the Cell, where you want to enter the Formula
6. Enter the Formula as =COUNTA(INDEX(CountSheets,0))
7. Click Enter
2007 and above Excel Versions
1. Click ‘Ctrl+F3’, then ‘Name Manager’ Box Appears
2. Click ‘New’ (use shortcut key Alt+N)
3. Then, ‘New name’ box appears
4. Enter ‘Name’ as “CountSheets“(Your choice)
5. Enter ‘Refer To’ as =GET.WORKBOOK(1)&T(NOW())
6. Click OK
7. It takes you to the ‘Name Manager’ box again (you can find the Defined Name in the list)
8. Click ‘Close’
9. Come to the Cell, where you want to enter the Formula
10. Enter the Formula as =COUNTA(INDEX(CountSheets,0))
11. Click Enter
If you google on this, you can find alternative solutions with VBA code. Without using VBA, I think this is the easy way to Count Number of Sheets.
Don’t forget to give comment below, if you find any alternative solution, or if you have any questions.
Also read
- How to Count Number of Rows in a Word Table?
- Why INDEX-MATCH Is Far Better Than VLOOKUP or HLOOKUP in Excel
Courtesy: lostinexcel.blogspot.in

 on the status bar to display this view.
on the status bar to display this view.
 on the status bar.
on the status bar.
 next to Page Setup.
next to Page Setup.
 .
. .
.