способность,
inability
неспособность;
disability
нетрудоспособность
способный, умелый
unable
неспособный
disabled
искалеченный; инвалид
дать возможность
disable
делать неспособным, калечить
умело, искусно
абсурдность
абсурдный
приемлемость
приемлемый
unacceptable
неприемлемый
принимать, соглашаться
доступ
accessibility
доступность
доступный
доступно
случай, случайность
случайный
нечаянно, случайно
действие
actor
актер
actress
актриса
activity
активность
activities
деятельность
acting
представление
активный
acting
действующий, работающей
действовать
активно
достижение
достигать
привычка, приверженность, увлеченность
addict
увлеченный человек, имеющий стойкую привычку
способный вызывать привычку
увлекаться, предаваться
восхищение
восхитительный
восхищаться
восхитительно
совет
рекомендуемый
советовать
притворство, искусственность
affection
привязанность, любовь
притворный
affectionate
любящий
affective
эмоциональный
воздействовать, влиять; притворяться
соглашение, согласие
disagreement
разногласие, несогласие
соответствующий, приятный
соглашаться
disagree
не соглашаться
соответственно
агрессия
aggressor
агрессору зачинщик
агрессивный
нападать
агрессивно
цель
бесцельный
целиться, намереваться
бесцельно
то, что может быть позволено
unaffordable
то, что невозможно себе позволить
позволять себе
развлечение
приятно изумленный
amusing
забавный
развлекать, забавлять
изумленно
внешность; появление
disappearance
исчезновение
появляться
disappear
исчезать
назначение; деловая встреча
disappointment
разочарование, досада
назначенный
disappointed
огорченный
disappointing
разочаровывающий
назначать
disappoint
разочаровывать
одобрение
одобренный
approving
одобрительный
одобрять
одобрительно
соглашение; расположение
приведенный в порядок
приводить в порядок, организовывать
аргумент, довод
argumentation
аргументация
доказуемый (в споре)
argumentative
спорный, конфликтный
утверждать, спорить, ссориться
доказательно
присвоение; ассигнование
подходящий, соответствующий
inappropriate
несоответствущий, неуместный
присваивать, предназначать
соответственно, подходяще
прибытие
прибывать, приезжать
притяжение, привлекательность
привлеченный
attractive
привлекательный
привлекать
привлекательно
избежание, отмена
то, чего можно избежать
unavoidable
неизбежный
избегать
неизбежно
красота; красавица
красивый
украшать
красиво
роды
сносный, допустимый
unbearable
невыносимый
носить; терпеть
невыносимо
вера
вероятный, правдоподобный
unbelievable
невероятный
верить
выгода
выгодный
получать выгоду
зануда
boredom
скука
испытывающий скуку
boring
скучный, надоедливый
надоедать
скучно
дыхание, дуновение
breathing
дыхание
breather
короткая передышка
дышащий
breathless
бездыханный
дышать
затаив дыхание
дело
businessman
деловой мужчина
businesswoman
деловая женщина
занятой
businesslike
деловой, практичный
занимать делом
деловито, по-деловому
забота, уход
заботливый
careless
небрежный
заботиться, любить
заботливо
carelessly
небрежно
празднование
celebrity
знаменитость
знаменитый, прославленный
праздновать, прославлять
определенность
uncertainty
неопределенность, неуверенность
определенный
uncertain
неопределенный
определенно, уверенно
изменение; мелочь, сдача
изменчивый
changed
изменившийся
changeless
неизменный
unchanged
не изменившийся
менять; обменивать(ся)
неизменно
характер
характерный, типичный
характеризовать
выбор
разборчивый
выбирать
ребенок
children
дети
детский; ребяческий
очистка; устранение препятствий
четкий, ясный
очищать, расчищать
четко, ясно
облако
облачный
cloudless
безоблачный
собрание; коллекция
collector
сборщик
коллективный, совокупный
собирать; коллекционировать
колония
колониальный
колонизировать
цвет
цветной
colourless
бесцветный
multi-coloured
разноцветный
раскрашивать
комфорт; утешение
discomfort
беспокойство; неудобство
удобный, комфортабельный
uncomfortable
неудобный
утешать, успокаивать
удобно
uncomfortably
неудобно
община, общество
общественный, коллективный
сообщение
communicator
коммуникатор, переговорщик
использующийся в общении; коммуникативный
сообщать; общаться
сравнение
сравниваемый
comparative
сравнительный
сравнивать
сравнительно, относительно
соревнование; конкуренция
competitor
конкурент, соперник
соревновательный
соревноваться, конкурировать
в форме соревнования, конкуренции
завершение, окончание
законченный
complete
полный, завершенный
incomplete
неполный, назавершенный
заканчивать, завершать
полностью
поздравление
поздравлять
соединение, объединение
связанный, соединенный
соединять
disconnect
разъединять
внимание; рассмотрение, обсуждение
значительный
considerate
внимательный, деликатный, тактичный
inconsiderate
неосмотрительный; невнимательный к другим
считать, полагать; рассматривать
значительно
совесть
совестливый, добросовестный
conscientiousless
бессовестный
добросовестно
сознание
осознающий
unconscious
без сознания
сознательно, осознанно
консультация
consultant
консультант
консультирующий
консультировать
вместилище, контейнер
содержащий
содержать, вмещать
непрерывность
продолжающийся, длящийся
продолжать
непрерывно
управление, руководство
поддающийся управлению
uncontrollable
неподдающийся управлению
controlled
управляемый
uncontrolled
неуправляемый
управлять, регулировать
бесконтрольно
убеждение
убедительный
convinced
убежденный
убеждать
убедительно
повар
cooker
плита, духовка
переваренный
under-cooked
недоваренный
готовить еду
исправление
corrector
корректор
правильный
incorrect
неправильный
исправлять
правильно
прилавок
discount
скидка
accountant
бухгалтер
исчисляемый
uncountable
неисчисляемый
считать
немеряно, без счета
храбрость
храбрый
encouraged
воодушевленный
encouraging
подбадривающий
discouraged
обескураженный
приободрять, поддерживать
discourage
отговаривать, обескураживать
смело, храбро
создание
creativity
творчество
creator
творец, создатель
creature
творение; живое существо
творческий
создавать, творить
творчески
вера, доверие
вероятный, заслуживающий доверия
incredible
невероятный
вероятно
incredibly
невероятно
критик
criticism
критика
критический; переломный; рискованный
критиковать
критично, критически
культивация, обработка
культивированный, обработанный
обрабатывать
культура
культурный, воспитанный
cultural
культурный (как часть культуры)
культурно
лекарство; лечение
излечимый
incurable
неизлечимый
вылечивать, исцелять
неизлечимо
опасность
опасный
угрожать
опасно
день
ежедневный
ежедневно
обман, заблуждение
обманчивый
deceitful
обманчивый, лживый
обманывать
обманчиво, предательски
решение
определенный, явный
undecided
нерешительный, неясный
decisive
решительный, убежденный, убедительный
решать, принимать решение
решительно, определенно
определение
четкий, определенный
indefinite
неопределенный
определять, давать определение
определенно, ясно
indefinitely
нечетко, неопределенно
восторг, наслаждение
восхитительный
delighted
польщенный
восхищаться
с восторгом
доставка, поставка
доставленный
доставлять
зависимость
independence
независимость
зависимый
independent
независимый
зависеть
независимо
депрессия, подавленность
депрессивный, вызывающий депрессию
depressed
подавленный
подавлять
описание
описательный, наглядный
описывать
проект, дизайн
designer
дизайнер, проектировщик
проектировать
желание, стремление
желательный, желаемый
undesirable
нежелательный
желать, стремиться
желательно
разрушение
разрушенный
разрушать, уничтожать
решительность; определение
решительный
решать, определять
развитие
developer
разработчик
развитой
developing
развивающийся
undeveloped
неразвитый
развивать(ся)
умирающий
умирать
разница, различие
indifference
безразличие
другой, отличающийся
indifferent
безразличный
отличаться
по-другому
indifferently
с безразличием
тревога, беспокойство; нарушение тишины, порядка
обеспокоенный
disturbing
беспокоящий
беспокоить, мешать
сомнение
сомнительный
doubtless
несомненный
undoubted
бесспорный
сомневаться
с сомнением
doubtlessly
не сомневаясь
undoubtedly
без сомнения
легкость, свобода
disease
болезнь
легкий
uneasy
неловкий, тревожный
облегчать, ослаблять
легко
uneasily
неловко
хозяйство
экономический
economical
экономный
экономить
экономически; экономно
воспитатель, педагог
education
образование
образованный
uneducated
необразованный
educative
образовательный
воспитывать, давать образование
следствие, результат
effectiveness
эффективность
эффективный, действующий
производить, выполнять
эффективно, действенно
электричество
electrician
электрик
электрический
электрифицировать
империя
empiror
император
имперский
empiric / empirical
исходящий из опыта, эмпирический
служба, работа
unemployment
безработица
employer
наниматель, работодатель
employee
работающий по найму
нанятый, занятый
unemployed
безработный
нанимать
конец, окончание
бесконечный
unending
нескончаемый
конец, окончание
бесконечно
окружающая среда
природный
развлечение
развлекательный
развлекать
энтузиазм, восторг
enthusiast
энтузиаст, восторженный человек
восторженный
с восторгом
оборудование
снаряженный, оборудованный
снаряжать
сущность
главный, основной
главным образом
экзамен; медосмотр
проэкзаменованный; осмотренный врачом
экзаменовать; осматривать
возбуждение, волнение
возбуждающий
excitable
возбудимый
excited
возбужденный, взволнованный
возбуждать, волновать
взволнованно, возбужденно
ожидание, предчувствие
ожидаемый
unexpected
неожиданный
ожидать, предчувствовать
расход(ы), затраты
дорогой
inexpensive
недорогой
тратить, расходовать
дорого
опыт, опытность
inexperience
неопытность
experiment
эксперимент
опытный
inexperienced
неопытный
experimental
эспериментальный
испытывать
взрыв
explosive
взрывчатое вещество
взрывчатый
взрываться
выражение
выразительный
выражать
выразительно
пространство, степень
длительный,обширный
extensive
обширный
простираться, тянуться
обширно, протяженно
крайняя степень, крайность
крайний, чрезвычайный
крайне
очарование, обаяние
чарующий
fascinated
очарованный
очаровывать
справедливость; порядочность
порядочный, справедливый
unfair
несправедливый
справедливо, честно; довольно-таки
финансы
финансовый
финансировать
финансово
твердость
твердый
утверждать
твердо
физическая форма, физическое состояние
находящийся в хорошей форме; подходящий
unfit
неподходящий
подгонять, подстраивать
следующий
следовать
глупыш, дурак
глупый
обманывать
глупо
забываемый
unforgettable
незабываемый
forgetful
забывчивый
forgotten
забытый
забывать
прощение
прощающий
forgivable
простительный
unforgivable
непростительный
прощать
с прощением
судьба, счастье; богатство, состояние
счастливый
unfortunate
несчастный
к счастью
unfortunately
к сожалению
свобода
свободный; бесплатный
свободно
частота
частый
часто посещать
часто
друг
friendship
дружба
friendliness
дружелюбие
дружеский, дружелюбный
unfriendly
недружеский
дружелюбно
страх, испуг
страшный
frightened
испуганный
frightening
пугающий
пугать, устрашать
страшно; испуганно
щедрость
щедрый
щедро
джентльмен
мягкий, нежный
мягко, нежно
привидение, призрак
похожий на привидение
трава
травяной
привычка, обычай
habitant
обитатель
habitat
естественная среда
habitation
жилище, обиталище
привычный
приучать
обычно
рука; рабочий
handful
горсть
удобный (для использования)
handmade
изготовленный вручную
вручать
счастье
unhappiness
несчастье
счастливый
unhappy
несчастный
счастливо
unhappily
несчастливо
вред
вредный
harmless
безвредный
повредить, навредить
вредно
здоровье
здоровый
unhealthy
нездоровый
дом, жилище
бездомный
честь
почетный
почитать, чтить
почетно
надежда
hopefulness
оптимизм, надежда
надеющийся
hopeless
безнадежный
надеяться
с надеждой
человечество
человеческий
humane
гуманный
inhuman
бесчеловечный
humanitarian
гуманитарный
юмор
юмористический
с юмором
спешка
торопливый, спешащий
hurried
торопливый
торопиться
торопливо
лед
ледяной
важность
важный
unimportant
незначительный
важно
впечатление
впечатленный
impressive
впечатляющий
unimpressed
безучастный
производить впечатление
впечатляюще
улучшение
улучшенный
улучшать
толчок, побуждение
импульсивный
импульсивно
несчастный случай; конфликт, инцидент
случайный
случайно
рост, увеличение
растущий
увеличивать(ся)
с ростом
промышленность
промышленный
industrious
трудолюбивый. усердный
индустриализовать
в промышленном отношении
сообщение, информация
informant
осведомитель
formality
формальность
осведомленный
well-informed
знающий, хорошо информированный
misinformed
неверно информированный
formal
формальный, официальный
informal
неофициальный
информировать
misinform
неверно сообщать; дезинформировать
информационно
интенсивность
интенсивный
интенсифицировать
интенсивно
интерес
заинтересованный
interesting
интересный
интересовать
изобретатель
invention
изобретение
изобретательный
изобретать
изобретательно
приглашение
приглашенный
приглашать
вдохновение
вдохновленный
inspiring
вдохновляющий
вдохновлять
знание
acknowledgement
признание; расписка
признанный
признавать, подтверждать
законность, легальность
юридический, законный
illegal
незаконный, подпольный
легализовать
законно
illegally
незаконно
сходство, подобие
приятный
unlike
непохожий
like
аналогичный
относиться хорошо
dislike
относиться отрицательно
вероятно
unlikely
невероятно
unlike
в отличие
жизнь
living
жизнь
оживленный, веселый
live
актуальный, реальный
жить
оживленно
литература
буквальный
literary
литературный
literate
грамотный
illiterate
неграмотный
буквально
место, поселение
местный
размещать
в определенном месте
одиночество
одинокий; один
удача
удачливый
unlucky
неудачливый, неудачный
к счастью
роскошь
шикарный
большинство
главный, основной
управляющий, руководитель
управленческий
управлять; справляться
женитьба
женатый / замужняя
unmarried
неженатый / незамужняя
жениться
встреча; собрание
встречать, знакомиться
память
memorial
мемориал
памятный
заучивать наизусть
нищета
нищенский, ничтожный
месяц
ежемесячный
ежемесячно
движение
неподвижный
показывать жестом
тайна, загадка
таинственный, загадочный
таинственно, загадочно
необходимость
необходимый
unnecessary
ненужный
необходимо
нерв
нервный
нервировать
нервно
число; количество
многочисленный
numerate
умеющий считать
innumerate
неумеющий считать
обозначать цифрами
объект, предмет
objective
цель; возражение
объективный
возражать
объективно
упрямый
упрямо
случай, происшествие
происходить
операция; оперирование, приведение в действие
управлять, действовать
возможность
opportunist
оппортунист
своевременный, подходящий
оппозиция, противостояние
opponent
оппонент, противник
напротив
opposed
противоположный
противопосталять
владелец, хозяин
собственный
владеть
боль
болезненный
painless
безболезненный
болезненно
painlessly
безболезненно
терпение
impatience
нетерпение
patient
пациент
терпеливый
impatient
нетерпеливый
терпеливо
impatiently
нетерпеливо
участник
participation
участие
участвующий
принимать участие
подробности
особенный
особенно
совершенство
совершенный, идеальный
imperfect
несовершенный
совершенствовать, улучшать
отлично, безупречно
период, срок
периодический
периодически
представление; исполнение
performer
исполнитель
исполнять, выполнять, совершать
мир, спокойствие
мирный
мирно
разрешение
permissiveness
вседозволенность
permit
пропуск
позволяющий
позволять
с позволением
удовольствие
приятный
pleased
довольный
displeased
недовольный
доставлять удовольствие
приятно
точка; пункт
остроконечный, нацеленный
pointful
уместный, удачный
pointless
бесцельный
указывать, направлять
остро, по существу
вежливость
вежливый
impolite
невежливый
вежливо
популярность
популярный
unpopular
непопулярный
популяризировать
владение, собственность
possessor
обладатель, владелец
собственнический
владеть, обладать
вероятность, возможность
возможный
impossible
невозможный
возможно
сила, мощь
мощный
powerless
бессильный
уполномочивать
предпочтение
предпочтительный
preferential
пользующийся препочтением
предпочитать
предпочтительно
подготовка
подготовленный
unprepared
неподготовленный
подготовить
с готовностью
престиж
престижный
престижно
профессия
профессиональный
профессионально
выгода
выгодный
unprofitable
не приносящий выгоды
получать выгоду
выгодно
прогресс, продвижение
прогрессивный
продвигаться вперед
постепенно, продвигаясь вперед
предложение
предложенный
делать предложение
процветание
процветающий
процветать
процветающе
общественность
общественный
разглашать
открыто, публично
быстрота
быстрый
убыстрять
быстро
реальность
realization
реализация, осуществление
реальный, настоящий
unreal
нереальный
реализовать, осуществлять
действительно, в самом деле
признание, узнавание
признанный
узнавать; признавать
снижение, понижение
уменьшенный; сниженный
снижать; сбавлять
отдых, расслабление
расслабленный
relaxing
отдыхающий; расслабляющий
отдыхать, расслабляться
расслабленно
надежность
надежный
unreliable
ненадежный
доверять, полагаться
надежно
религия
религиозный
нежелание, неохота
неохотный
неохотно
регулярность
irregularity
нерегулярность
регулярный, правильный
irregular
неправильный; нестандартный
регулировать
регулярно
замечание
замечательный
замечать, отмечать
замечательно
представление
representative
представитель
представительный
представлять
упрек
безупречный
упрекать
с упреком
репутация
имеющий хорошую репутацию, почтенный
disreputable
имеющий плохую репутацию
давать репутацию
disrepute
компрометироватъ
сопротивление
ударопрочный;
irresistible
неотразимый
resistant
прочный
сопротивляться
неотразимо
уважение
уважительный
уважать
с уважением
отдых
беспокойный
отдыхать
беспокойно
награда
стоящий награды
unrewarded
невознагражденный
награждать
богатства
richness
богатство
богатый
обогащать
богато
риск
рискованный
рисковать
грусть
грустный
огорчать
грустно
сейф
safety
безопасность
безопасный
unsafe
опасный
спасать; экономить
безопасно
удовлетворение
dissatisfaction
неудовлетворенность; недовольство
довольный
dissatisfied
недовольный
satisfactory
удовлетворительный
unsatisfactory
неудовлетворительный
удовлетворять
dissatisfy
разочаровывать; огорчать
исследование
искать, осуществлять поиск
безопасность
безопасный
insecure
находящийся в опасности
охранять, гарантировать
безопасно
серьезность
серьезный
серьезно
наука
scientist
ученый
научный
научно
чувство
insensibility
отсутствие чувствительности
чувствительный
insensitive
несочувствующий
sensible
разумный
insensible
нечувствительный, неосознающий
ощущать
чувствительно
sensibly
разумно
услуга, обслуживание
servant
слуга
обслуженный; поданный на стол
служить, обслуживать, подавать на стол
значительный
insignificant
незначительный
иметь значение
значительно
сходство, похожесть
похожий, подобный
похоже, подобно
искренность
искренний
insincere
неискренний
искренне
шорты
короткий
укорачивать
кратко
сон
sleeper
спящий; спальный вагон
спящий
sleepless
бессонный
спать
без сна
решение; раствор
решенный; растворенный
решать; находить выход; растворять
специальность; фирменное блюдо
specialty
особенность
особенный; специальный
specific
специфический
точно определять
specialize
специализировать(ся)
специально
specifically
специфично
сила
сильный
укреплять
сильно
стресс
стрессовый
ударять, ставить ударение
в состоянии стресса
успех
успешный
unsuccessful
безуспешный
преуспевать
успешно
достаточность
insufñcience
недостаточность
достаточный
insufficient
недостаточный
быть достаточным
достаточно
подходящий
unsuitable
неподходящий
подходить, устраивать
предложение
предлагать
подозреваемый
подозрительный
подозревать
подозрительно
пловец
swimming
плавание
плавающий, плавательный
плавать
сочувствие, понимание
сочувствующий
сочувствовать
с пониманием; сочувственно
уверенность
уверенный
unsure
неуверенный
assured
обеспеченный; уверенный
self-assured
уверенный в себе
обеспечивать; гарантировать
assure
уверять, обеспечивать
конечно; уверенно
assuredly
с уверенностью
окружение
окруженный
окружать
беседа, разговор
разговорчивый
беседовать
вкус
distaste
отсуствие вкуса
сделанный со вкусом; обладающий вкусом
tasteless
безвкусный
пробовать
со вкусом
tastelessly
без вкуса
террор
terrorist
террорист
ужасный
terrific
потрясающий
terrifying
ужасающий
terrified
напуганный
ужасать
ужасно
terrifically
потрясающе
жажда
испытывать жажду
колготки
плотный, тесный
сжимать, натягивать
тесно, плотно
мысль
задумчивый
thoughtless
бездумный
думать, иметь мнение
задумчиво
трагедия
трагичный
tragical
трагический
трагично
путешествие
traveller
путешественник
путешествующий
путешествовать
правда
untruth
неправда
правильный; настоящий
untrue
неверный, не соответствующий действительности
truthful
правдивый
по-настоящему, искренне
truthfully
правдиво
ценность
ценимый
valuable
ценный
ценить, оценивать
разнообразие
variability
изменчивость, непостоянство
изменяемый
invariable
неизменный
менять, разнообразить
неизменно
год
ежегодный
ежегодно
понимание
misunderstanding
непонимание; недоразумение
понятный
понимать
польза
misuse
неправильное использование;
usage
использование
полезный
useless
бесполезный
used
использованный
unused
неиспользованный
использовать, пользоваться
полезно
uselessly
бесполезно
неделя
еженедельный
еженедельно
ширина
широкий
расширять
широко
воля, желание; завещание
жаждущий, желающий
unwilling
не желающий
проявлять волю, желать
охотно, с удовольствием
unwillingly
неохотно
ветер
ветренный
windless
безветренный
мудрость
мудрый
unwise
неблагоразумный
мудро
unwisely
неблагоразумно
стоимость, ценность
достойный
worthless
не имеющий ценности
Содержание
- Имя существительное
- Имя прилагательное
- Глагол
- Наречие
- Местоимение
- Числительные
- Cоюз
- Предлоги
- Артикли
- Частицы
- Междометия
- Сводная таблица частей речи в английском языке
Так уж сложилось, что издавна во всех языках словообразование играло одну из первостепенных ролей. Обозначение разных частей речи и их название стало неким этапом в эволюции языка и языкознания.
Также как и в современном русском языке, каждое слово в английском принадлежит определенной части речи (part of speech), то есть категории слов, обладающих своими характерными признаками.
Part of speech — one of the grammatical groups, such as noun, verb, and adjective, into which words are divided depending on their use
Английские части речи классифицируются по синтаксической функции, грамматическому значению и форме. Следовательно, существуют самостоятельные (notional) и служебные (functional) части речи. Но в отличие от русского языка, в английском есть «переходные зоны» между частями речи. То есть одно и то же слово может выступать в роли разных частей речи. И в данном случае опорой служит сам контекст, а не форма слова.
Распознавание или предугадывание частей речи по контексту очень важный навык, если вы готовитесь к сдаче ЕГЭ или международных экзаменов. Понимание частей речи, безусловно, облегчит выполнение заданий в разы, а хорошая система подготовки определенно сыграет свою роль. В качестве помощи команда онлайн-школы Инглиш Шоу разработала курсы по подготовке к разнообразным экзаменам, начиная с ЕГЭ и заканчивая TOEFL или IELTS. Узнать, как это работает очень просто – стоит только записаться на бесплатный пробный урок и проверить эффективность обучения с преподавателем на себе!
Самостоятельные части речи в английском языке
Если у слова есть свое собственное лексическое значение, то его без сомнений можно отнести к самостоятельным частям речи. Произнося его, сразу становится понятен смысл слова. К самостоятельным частям речи в английском языке относятся:
Имя существительное (Noun)
Грамматика и теория русского языка даёт нам следующее определение существительного: оно называет людей, животных, места, абстрактные понятия, предметы. И для него характерно отвечать на вопросы: «Кто?» или «Что?».
В английском существительные бывают разные:
-
Common – нарицательные
Например: person – человек, teacher – учитель, log – бревно -
Proper – собственные
Например: Stephen, Italy, America, Saturn -
Compound – составные (состоящими из двух корней)
Например: post office – почтовое отделение, car park – парковка, textbook – учебник, bookcase – книжный шкаф -
Abstract – абстрактные
Например: beauty – красота, intelligence – ум, democracy – демократия -
Collective – собирательные
Например: family – семья, flock — стая, herd – стадо
Кроме этого, в английском есть четкое разделение на исчисляемые (countable) и неисчисляемые (uncountable). Исчисляемые они потому что их можно посчитать поштучно и все они имеют форму как единственного, так и множественного числа. И перед существительным в единственном числе мы ставим артикль (a/an).
Например:
-
I have got an orange and a banana.
У меня есть апельсин и банан. -
There are a lot of cookies in this bowl.
В этой тарелке много печенья.
Стоит отметить, что к неисчисляемым существительным в основном относятся жидкости, сыпучие продукты, абстрактные понятия или те, которые существуют либо только в единственном, либо во множественном числе.
Например:
-
I don’t have much money.
У меня немного денег. -
I like listening rock music.
Я люблю слушать рок музыку. -
There is some rice in the bowl.
В тарелке есть немного риса. -
Give me some information upon this case.
Предоставь мне информацию по этому случаю.
Существительные в английском образуются с помощью определенных суффиксов, по которым вы легко сможете определить эту часть речи:
- ance: disturbance, relevance
- ence: reference, occurrence
- ity: complexity, scarcity
- ment: disappointment, achievement
- acy/cy: accuracy
- age: percentage, breakage
- an: Russian, American
- dom: kingdom, freedom
- hood: motherhood, brotherhood
В предложении эта часть речи может выполнять функции как подлежащего (subject), дополнения (object) или функцию complement (дополнения) внутри именного сказуемого.
Например:
-
We have accepted the invitation for the party.
(We – subject; invitation – object)
Мы приняли приглашение на вечеринку.
Вне всяких сомнений, существует ещё множество других нюансов, которые необходимо знать о существительных. Например, важно правильно образовывать множественное число. Об этом мы рассказывали в ролике:
Имя прилагательное (Adjective)
Мы используем прилагательные для описания существительных, то есть они характеризуют признаки предмета, человека или события. И отвечают на вопросы: «Какая?», «Какие?» и т.д.
В английском прилагательные подразделяются по степеням сравнения и бывают:
- Положительной степени (Positive form)
- Сравнительной степени (Comparative form)
- Превосходной степени (Superlative form)
Например:
-
large – larger – the largest
большой – больше – самый большой
Более подробно со всеми правилами эта тема разобрана в нашей статье 👉 Степени сравнения прилагательных
Очень часто в предложении можно встретить описание из нескольких прилагательных, в таком случае они расположены в определенном порядке:
judgement – size – shape – age – colour – origin – material – purpose – noun
суждение – размер – форма – возраст – цвет – происхождение – материал – цель – существительное
💡 Чтобы было легче запомнить, ловите подсказку: чем прилагательное субъективнее, тем дальше оно от самого существительного.
Например:
-
There is a small, old, blue, plastic table.
Это маленький, старый, голубой, пластиковый стол. -
I am a short, young, blue-eyed person.
Я молодой человек среднего роста с голубыми глазами.
Глагол (Verb)
Как мы помним со школьной скамьи, глагол – это слово «действие», которое характеризуется вопросами: «Что делать?», «Что сделать?» и так далее.
Вместе с подлежащим он представляет главные члены предложения и образует грамматическую основу.
Классификация глаголов в английском:
- Semi-auxiliary – служебные
- Auxiliary — вспомогательные
- Notional – смысловые
Также очень важным моментом является то, что в английском глаголы подразделяют на:
-
Transitive – переходные (за которым следует объект или дополнение)
She is cooking the dinner.
Она готовит обед. -
Intransitive – непереходные (которые не требуют после себя какого-либо дополнения, они просто характеризуют само действие)
He slept late this morning.
Он спал допоздна этим утром.
Ну и конечно же глаголы могут быть разных форм:
-
Infinitive – инфинитив или неопределенная форма глагола, в английском используется с частичкой to. Если без неё, то это будет форма bare infinitive (голый инфинитив).
Например: to go – идти, to cry – плакать, to unearth – раскопать
- Base form – первоначальная форма, это тот же инфинитив, но используемый уже без частички to.
-
Past Simple form – форма прошедшего времени
И здесь стоит сказать, что существуют правильные (regular) и неправильные (irregular) глаголы.
Неправильные глаголы собраны в таблицу и их просто нужно выучить для правильного употребления в речи. А правильные глаголы образуют форму прошедшего времени путем добавления -ed.
-
Past Participle – причастие прошедшего времени, это третий столбик в таблице неправильных глаголов.
Примеры: beaten – побитый, broken — сломанный
Или если глагол правильный, то он образует вторую и третью формы с помощью окончания -ed.
Примеры: play — played, study — studied, watch — watched
-
Present Participle – причастие настоящего времени, это глагол с -ing или как его ещё называют — герундий.
Например: hoping- надеющийся, studying – обучающийся
Наречие (Adverb)
В целом, наречия в отличие от прилагательных характеризуют действия или глаголы и отвечают на вопросы: «Как?», «Где?», «Когда?», «Почему?», «Каким образом?».
Классификация наречий:
-
Manner – наречие образа действия:
Well – хорошо, slowly — медленно -
Place – места:
Above – над, here – здесь -
Time – времени:
Now – сейчас, then – тогда, soon – вскоре -
Degree – степени:
Very – очень, really – реально, quite – достаточно -
Frequency – частоты:
Once – однажды, twice – дважды
В основном наречия образуются с помощью суффикса -ly, который так сказать «определитель» для этой части речи, но, как вы заметили, исключения всегда имеют место быть.
Местоимение (Pronoun)
Судя по названию, местоимения мы используем вместо имён, то есть вместо имён собственных, предметов или качеств предмета.
В английском языке существуют следующие классы местоимений:
-
Object pronouns – личные, выступающие в роли объекта: me, him, her, it, us, you, them
He met me at the park yesterday.
Он встретил меня вчера в парке. -
Subject pronouns – личные, выступающие в роли субъекта: I, he, you, she, we, it, they
They used to play tennis 10 years ago.
Они имели обыкновение играть в теннис 10 лет назад. -
Reflexive pronouns – возвратные: himself, herself, ourselves, myself
We decided to do it by ourselves.
Мы решили это сделать сами. -
Demonstrative pronouns – указательные: those, this, that, these
These are your pieces of equipment.
Вот это твоё оборудование. -
Possessive pronouns – притяжательные: hers, his, mine, yours
These shoes are mine!
Это мои туфли! -
Relative pronouns – относительные: who, which, that, whose
This was the man who stole your wallet.
Это тот мужчина, который украл у тебя кошелёк.
Числительные (Numerals)
Числительные показывают порядок предметов при счете и их количество. Для них характерными являются вопросы: «Сколько?» или «Который по счету?». Также, как и в русском языке, они бывают:
-
Cardinal numbers – количественными:
one, six, thirty, one hundred -
Ordinal numbers – порядковыми:
first – первый, second – второй, third – третий, fourth – четвертый
Образование порядковых числительных происходит с помощью окончания -th, начиная с числа 4, а первые три числа нужно просто запомнить.
Служебные части речи в английском языке
Исходя из названия можно догадаться, что служебные части речи выполняют вспомогательную функцию и, так сказать, служат самостоятельным частям речи.
Служебных частей речи не так уж много:
- Article – артикль
- Conjunction – союз
- Preposition – предлог
- Paticles — частицы
- Interjections — междометия
Cоюз (Сonjunction)
Союзы служат соединительными словами-связками, это своего рода взаимодействие однородных членов предложения. Или же они выполняют роль соединения предложений между собой.
-
Conjunctions for words of the same class (Союзы для однородных частей речи):
and, but, or, nor, yet -
Conjunctions for clauses of sentences (Союзы для частей предложения):
as soon as, before, since, until, when, because, although, unless, so, where
Предлоги (Prepositions)
Как правило, предлоги показывают отношение существительного или местоимения к другим словам в предложении. Существуют такие категории, как:
-
Place – предлоги места:
in, at, on, by, above, over -
Movement – предлоги движения:
from, to, in, into, on, onto, by, out, through -
Time – предлоги времени:
at, on, by, before, in, from, since, during, until
Сложность выбора предлогов заключается в том, что нет строгой однозначности в их использовании. Поэтому хорошим советом здесь будет: Practise, practise & practise! Подробнее про предлоги места и времени читайте в нашей статье: predlogi-mesta-i-vremeni
Артикли (Аrticles)
В английском существует всего лишь два типа артиклей, по сравнению с другими романо-германскими языками, в которых их гораздо больше.
-
Definite article – определенный артикль – the
Используется в том случае, если субъект или объект являются определенными по ситуации или единственными в своем роде.
Например:
The football is blue.
Мячик является голубым. (Именно конкретный мячик)The sun is shining brightly.
Солнце ярко светит. (Единственное в своем роде – the sun) -
Indefinite article – неопределенный артикль – a/an
Данный артикль может употребляться только с исчисляемыми существительными и в единственном числе. То есть он просто служит неким обозначением предмета в единственном числе. Поэтому нужно быть предельно внимательными при его использовании.
Например:
A lotus is a flower.
Лотус – это цветок.
Более подробно про артикли читайте в нашей следующей статье: artikli-v-anglijskom-jazyke
Частицы (Paticles)
Частицы имеют свойство придавать словам дополнительные оттенки, значение. Они не имеют грамматических категорий, а также не являются членами предложения. Давайте посмотрим, какие же существуют классификации частиц:
-
Limiting — выделительно-ограничительные:
even, only, merely, solely, just, but, alone -
Intensifying particles – усилительные:
simply, just, all, still, yet -
Negative particle — отрицательная частица:
not -
Additive particle — дополняющая частица:
else
Междометия (Interjections)
Междометия на самом деле не относятся ни к самостоятельным, ни к служебным частям речи, так как они не имеют особого смысла. Они лишь передают наши чувства и эмоции.
Например:
oh, eh, alas, er, hey, uhm
Сводная таблица частей речи в английском языке
| PARTS OF SPEECH | DESCRIPTION | EXAMPLES |
|---|---|---|
| NOUNS | Name people, animals, places, things | Chair, sparrow, school, Greece |
| VERBS | Name action or activity | Be, seem, smell, jump |
| ADJECTIVES | Describe nouns such as people or things | Clean/dirty, expensive/cheap, light/dark |
| ADVERBS | Describe verbs (actions) | Well, quickly, sometimes |
| PRONOUNS | Used instead of nouns | He, we, they, their, my |
| NUMERALS | Name numbers | Fifty, eighty, thirty-first |
| CONJUNCTIONS | Join words or clauses of sentence | And, but, as soon as, unless, although |
| PREPOSITIONS | Show the relationship between a noun and other words | At, on, by, before, since |
| ARTICLES | Show if the noun is definite or indefinite | The, a/an |
| PARTICLES | Give additional meaning to words | Not, yet, else |
| INTERJECTIONS | Describe feelings and emotions | Oh, eh, alas, er, hey, uhm |
Эта таблица поможет вам определять части речи. Также, используя русско-английский словарь, вы можете посмотреть принадлежность слова к той или иной части речи. Но, чтобы начать лучше разбираться в грамматических аспектах, лучше начать изучение последовательно, к примеру, с глаголов и потом постепенно переходить к другим самостоятельным или служебным частям речи. Тогда вы сможете с легкостью выдохнуть — у вас не будет никакой каши в голове и сложностей в использовании на практике.
Также не стоит забывать, что построение английского предложения начинается с прямого порядка слов, о чем многие забывают при переключении с русского на английский. Как раз для подобного рода практики команда Инглиш Шоу разработала курс Разговорный Марафон. Каждый день на протяжении нескольких месяцев вы отрабатываете основные навыки, разговаривая на повседневные темы с разными преподавателями. Но это ещё не все! В течение курса вас ждёт масса сюрпризов и лайфхаков, так что после курса можете с уверенностью собираться заграницу! Записывайтесь на бесплатный пробный урок и узнайте все подробности самостоятельно.
Learning a language is like learning the most important aspect of a nation. There are many, many reasons why learning a new language is a good idea. It allows you to communicate with new people. It helps you to see things from a different perspective, or get a deeper understanding of another culture. It helps you to become a better listener and so on. So, for all these purpose you have to learn English.
What are tenses?
Tenses is the most essential part of English Grammar.
However, tenses are used to classify time reference with reference to the moment of speaking. Tenses are used to classify the time of your speech, that is, present, future and past. Thus, there are many tense less sentences which are used in different languages like Chinese.
Moreover, tenses are used to express time related to moment of speaking.
Uses of Tenses
However, Tense is understood as a category that expresses time reference, using grammatical means places a state or action in time.
Moreover, Tense is normally indicated by the use of a particular verb form either an inflected form of the main verb, or a multi-word construction, or both in combination.
Thus, Tenses are used in sentences to indicate a particular time whether it is past, present or future.
Types of Tenses
However, There are three main types of tenses. They are: Present tense, past tense, future tense.
You must read: Tense Chart in Hindi with Rules
1. Present Tense
In Present tense, we generally make sentences which refers to present situation.
For examples:
- Ram is eating his dinner.
- Priya is dancing.
- Rahul is playing.
2. Past tense
In past tense, we generally make sentences which refers to past situation or the things which already took place.
For example:
- He ate his icecream.
- Sheena went home.
- Garv had fish yesterday.
3. Future Tense
In future tense, we generally make sentences which refers to future situation or the things which will take place in future.
For example:
- Riya will come tomorrow.
- I will eat pizza tomorrow.
- We will go to grandmother’s home next week.
Some examples of tenses are:
- She is watching television.
- He is watching a football match.
- She will go Goa tomorrow.
- He had been playing football.
- She has won five matches so far.
- I got a call yesterday.
- I am suffering from fever.
- She had a fight yesterday.
- We are playing cricket.
- He will give you his book next week.
Tenses are very essential in English Grammar as one can make sentences with the help of them easily.
English tense chart with formula and example, tense chart, tense rules, tense examples, tense sentences list and tense chart with rules and examples find here.
The word “Tense” is origin from the Latin word which means “Time”. Tense is a form of verb which is used to indicate the time of an action or state in relation to the time of speaking.
For Example:
- I go to college.
- I went to college.
- I will go to college.
Example of Tenses
- Present Tense
- Past Tense
- Future Tense
1. Present Tense: Present Tense refers to an activity which is currently happening or going on or necessarily to be performed.
For Example:
- I go to school.
- The sun rises in the East.
- I jump in the lake every Saturday.
2. Past Tense: Past Tense refers to an activity which has been performed earlier or happened earlier or in past.
For Example:
- I went to school.
- It rained yesterday.
- I had completed my homework.
3. Future Tense: Future Tense refers to an activity which will performed in future or it not yet happened.
For Example:
- I will go to school.
- I’ll see you tomorrow.
- I will complete my homework.
Tense Table: Chart of Tenses in English with Examples
1. Present Simple (Indefinite) Tense Examples
- I eat Dal Chapati.
- We eat Dal Chapati.
- You eat Dal Chapati.
- He eats Dal Chapati.
- She eats Dal Chapati.
- It eats Dal Chapati.
- They eat Dal Chapati.
2. Past Simple Tense Examples
- I ate Malai Kofta.
- We ate Malai Kofta.
- You ate Malai Kofta.
- He ate Malai Kofta.
- She ate Malai Kofta.
- It ate Malai Kofta.
- They ate Malai Kofta.
3. Future Simple Tense Examples
- I shall travel to Washington.
- We shall travel to Washington.
- You will travel to Washington.
- He will travel to Washington.
- She will travel to Washington.
- It will travel to Washington.
- They will travel to Washington.
4. Present Continuous Tense
- I am eating a tomato.
- We are eating tomatoes.
- You are eating tomatoes.
- He is eating a tomato.
- She is eating a tomato.
- It is eating a tomato.
- They are eating tomatoes.
5. Past Continuous Tense
- I was eating a carrot.
- We were eating carrots.
- You were eating carrots.
- He was eating a carrot.
- She was eating a carrot.
- It was eating a carrot.
- They were eating carrots.
6. Future Continuous Tense
- I shall be eating pomegranate.
- We shall be eating pomegranates.
- You will be eating pomegranate.
- He will be eating pomegranate.
- She will be eating pomegranate.
- It will be eating pomegranate.
- They will be eating pomegranate.
7. Present Perfect Tense
- I have eaten a pomegranate.
- We have eaten pomegranates.
- You have eaten pomegranates.
- He has eaten a pomegranate.
- She has eaten a pomegranate.
- It has eaten a pomegranate.
- They have eaten pomegranates.
8. Past Perfect Tense
- I had eaten Dal Chapati.
- We had eaten Dal Chapati.
- You had eaten Dal Chapati.
- He had eaten Dal Chapati.
- She had eaten Dal Chapati.
- It had eaten Dal Chapati.
- They had eaten Dal Chapati.
9. Future Perfect Tense
- I shall have eaten Dal Chapati.
- We shall have eaten Dal Chapati.
- You will have eaten Dal Chapati.
- Ha will have eaten Dal Chapati.
- She will have eaten Dal Chapati.
- It will have eaten Dal Chapati.
- They will have eaten Dal Chapati.
10. Present Perfect Continuous Tense
- I have been eating Dal Chapati.
- We have been eating Dal Chapati.
- You have been eating Dal Chapati.
- He has been eating Dal Chapati.
- She has been eating Dal Chapati.
- It has been eating Dal Chapati.
- They have been eating Dal Chapati.
11. Past Perfect Continuous Tense
- I had been eating Dal Chapati.
- We had been eating Dal Chapati.
- You had been eating Dal Chapati.
- He had been eating Dal Chapati.
- She had been eating Dal Chapati.
- It had been eating Dal Chapati.
- They had been eating Dal Chapati.
12. Future Perfect Continuous Tense
- I shall have been eating Dal Chapati.
- We shall have been eating Dal Chapati.
- You will have been eating Dal Chapati.
- He will have been eating Dal Chapati.
- She will have been eating Dal Chapati.
- It will have been eating Dal Chapati.
- They will have been eating Dal Chapati.
Present Tense Chart | Definition | Uses | Examples
What is present tense?
Tenses is the most important part of English Grammar. Present tense is a part of Tenses.
However, tenses are used to classify time reference with reference to the moment of speaking.
Moreover, it is one of the type of Tenses.
However, the present tense is used for actions which are happening right now. Its principle function is to locate a situation or event in present time. In order to understand present tense, it is important to use time as a tool on which present, past and future tense are positioned.
Moreover, it describes a current event or a state of being.
Uses of present tense
Mostly, present tense is used to frame a sentence on a present situation.
- It is used to give instructions and directions. For example: You walk for ten meters, then you turn right.
- It is also used to express fixed arrangements present or future. For example: Your race starts at 10:00.
- To express general truths, habits, repeated actions or unchanging situations, emotions and wishes. For example: I drink tea (habit), I work in Australia (unchanging situations), California is an IT hub (general truth).
- It is also used to express future time after some conjunctions such as; as soon as, after, when, until. For example: She’ll give it to you when you come next Friday.
Ways to form simple present tense
However, There are certain ways from which we can form its sentences.
do/does + [subject] + [root form of verb]
For singular:
- First-person singular: I read.
- Second-person singular: You read
- Third-person singular: He/she/it reads (note the -s)
For plural:
- First-person plural: We read.
- Second-person plural: You read.
- Third-person plural: They read.
Types of Present tense
There are four types of present tense in English Grammar. They are as follows:
- Simple present: It is used to express habits and general truths.
- Present Continuous: It is used to express an action which is taking place now.
- Present Perfect: This form of tense is used for repeated actions, actions where time doesn’t has importance and actions that begin in the past and are not finished yet.
- Present perfect continuous: Here process and result both are important. It is used to talk about ongoing actions.
Examples of Present tense
- I am eating icecream.
- She is cooking pizza for me.
- He is reading my book.
- She is coming here.
- Complete your dinner.
- Wear your shoes.
- Ram is playing cricket.
- Riya is studying.
- Bring my bag.
Moreover, it is very useful in English Grammar. It can be used while framing sentences.
Present continuous tense | Definition | Uses | Examples
What is present continuous tense?
It is an essential part of present tense. It is generally used for action happening right now or for actions which are unfinished and can also be used when the action is temporary.
However, It indicated that the action is happening frequently, and may continue in the future.
Some examples of present continuous tense are:
- She is swimming.
- He is crying.
- The girl is sleeping in her room.
- He is eating his meal.
- We are visiting the hotel in the evening.
Uses of present continuous tense
- Present continuous tense is used to describe an action that is going on at this moment. For example: You are studying math, You are using my comb.
- It is used to describe a temporary event or a situation. For example: He usually speaks in English but he is speaking in Hindi today.
- It can also be used to show that something will or will not happen in the near future. For example: She is not going to the school today.
- Present continuous tense is used to describe an event of the future which is already planned and prepared. For example: I am meeting my best friend tonight.
- Present continuous tense can be used in questions as well. For example: Is she laughing?, Are we going?, etc.
- It can be used while we speak about current trends. For example: Online shopping is growing in popularity nowadays.
- This tense is also important since it is a simple sentence structure that can show actions or events that are happening right now, either in the planned future, or even in the past.
Some examples of present continuous tense are
- She is playing guitar.
- What are you wearing tonight?
- We are going to the museum.
- He is playing with his basketball.
Hence, The above mentioned part of present tense is very useful in framing sentences in English Grammar.
Present Perfect Tense Chart | Definition | Uses | Examples
What is present perfect tense?
The present perfect tense is used to indicate a link between the present and the past. It is often used to describe about an past event that has present consequences. It is used in everyday conversation, in the news, on the radio, and when writing letters.
While using present perfect tense, you require an auxiliary verb that helps your main verb to function. The main verb is always in a past participle form.
Uses of present perfect tense
- The present perfect tense is used to describe an action or situation that started in the past and continues in the present.
- It is used to describe an action that was completed in the very recent past. For example: I have just finished my dinner.
- It is also used to describe an action that has not finished yet. For example: It has rained a lot this month.
- To describe an event where time is not an important aspect. For example: He has lost his wedding ring.
- To express a repeated action in an unspecified period between the past and now. For example: We have visited London several times.
Importance of Present perfect tense
It is used while talking about past experiences or about a change or situation that has happened in the past and still continues in the present. It states that the actions or events of the past has ab direct effect on present. That is why it is an important part of English Grammar.
Examples of Present perfect tense
- I have lived in Jaipur.
- I have lost my bag.
- He has broken his hand.
- There has been an accident.
- We haven’t seen him today.
- The children have made mess in the drawing room.
Hence, Present perfect tense holds a very important place in tenses. It can be used in framing sentences.
Affirmative: Subject+have/has+past participle
For Example: 1. I have tired sushi
2. My father is just gone to bed.
3. I have already ironed the shirts.
Negative Affirmative: Subject+have not (haven’t)/has not (hasn’t)+ past participle
For Example: 1. I have not tried sushi.
2.She has never studied Chinese.
3.We have not been to New York.
Interrogative Affirmative: Have/has + subject + past participle
For Example: 1. Have you tried sushi?
2. Have you lived here all your life?
3. Has there ever been a war in united states?
Present perfect continuous tense | Definition | Uses | Structure | Examples
What is Present Perfect Tense?
The present perfect tense is expressed when an action or event begins in past and continues in present or has recently stopped. It states an ongoing action that started at some point in the past.
It refers to an unspecified time between ‘before now’ and ‘now’. The process may still be going on, or may have just finished.
‘Since’ and ‘for’ are the words used in sentences to show the time of action. Since is the word used for exact starting time. For is used to express the amount of time.
Present Perfect Tense Uses
It is used for actions that started in the past and continue in the present. For example: She has been waiting for you all day, They have been travelling since January.
Present perfect tense is used when the actions have just finished. But we are interested in the results. For example: It’s been raining, She has been sleeping since last night.
Structure of sentence
Main verb: Present participle(Base form+ ing)
Auxiliary verb: has been, have been, etc.
Positive sentences
They include Subject+ auxiliary verb+ main verb + time reference.
For example:
- He has been living in Australia since 1999.
- She has been listening to music from last two hours.
- He has been playing cricket from last two hours.
- She has been sleeping for five hours.
Negative sentences
They include Subject+ Auxiliary verb+ main verb+ time-reference.
For example:
- She has not been studying her books for five days.
- I have not been sleeping for three days.
- I have not been meeting him since a month.
- Kids have not playing games for three hours.
Examples of Present perfect continuous tense
- He has been waiting for you all day.
- Someone’s been eating my chocolates.
- It’s been raining.
- Has he been using her car for three years?
Hence, these are some of the examples of Present perfect continuous tense.
Simple past tense | Definition | Uses | Structure | Examples
What is Simple past tense?
Simple past tense is called preterite. This term is used for completed actions. Or the action and events that has already taken place in the past. It is the basic form of past tense in English Grammar.
The time of the action can be in recent past or distant past as the action duration is not considered important in this.
Uses of Simple past tense
Simple past tense can be used in following ways:
You can use it when an action occurred just a little while ago. For example: I ate an mango.
It can be used for an action that occurred on regular basis in past. For example: He worked in a shop.
We use it sentences to associate with certain past time experiences. For example: I often bought my lunch to collage.
Structure of the sentence
Main verb: Past simple form (2nd form of the form).
Auxiliary verb: Did.
Positive sentences
Subject+ main verb+ Object.
Subject+ Past simple form (2nd form of the verb) + object
For example:
- I bought a mobile.
- She met me in the park.
- She laughed to see the circus.
- He applied for an exam.
Negative sentences
Subject+ Auxiliary verb + NOT + main verb + Object.
Subject+ Did + NOT + Base form(1st form of verb) + Object.
For example:
- He did not buy a scooter.
- Riya did not help me.
- He did not find any home.
- She did not come here.
Some examples of simple past tense are:
- Rishabh sailed to Europe in 1999.
- My friend died last year.
- He lived in Australia in 1980.
- We crossed the bridge yesterday.
Moreover, here some of the examples of simple past tense are mentioned which will help you in framing sentences.
- Simple Past Tense chart, sentence, examples, rules, formula, worksheet find here.
- Simple Past Tense chart, sentence, examples, rules, formula, worksheet find here.
Simple past tense: Simple past tense refers to the activity or action which had happened before or exist in past.
For example: 1. I saw a movie yesterday.
2. I didn’t see a play yesterday.
3. Last year, I traveled to Japan.
Simple Past Tense Affirmative
Subject + VII + object ( H.V (Did) is not used)
Example:
- Ram went to school.
- They played football
- You wrote a letter
- He drank milk
Simple Past Tense Negative
Subject + (did) not + VI + object
(VI is always used with ‘did’)
Example:
- Ram did not go to school.
- They did not play football
- You didn’t write a letter
- He did not drink milk
Simple Past Tense Interrogative
Did + subject + VI + object?
Example:
- Did ram go to school?
- Did they play football?
- Did you write a letter?
- Did he drink milk?
Simple Past Tense Negative Interrogative
Did + subject + not + VI + object?
- Did ram not go to school?
- Did they not play football?
- Did you not write a letter?
- Did he not drink milk?
Simple Past Tense Interrogative with “Who -word”
“who-word” + did + subject + VI+ object?
Example:
- When did ram go to school?
- What did they play football?
- What did you write a letter?
- What did he drink milk?
Note: In “who-word” interrogative sentences “who-word” comes first then we put H.V “did” .
But if the “who-word” is “who” then direct main verb is used (only in affirmative)
Example:
- Where did you learn English?
- Who taught you English?
- Who did not play cricket?
Past continuous tense | Definition | Uses | Sentences | Examples
What is Past continuous tense?
Past continuous tense is also known as past progressive tense. It refers to an continuing action or for a state or event that was happening at some point in the past.
However, it can also be used to describe an action that was continuously happening in the past and an another action interrupted it. It is used to describe conditions that existed in the past.
Basically, The past continuous can shed light on what was happening at a precise or particular time in the past.
Past Continuous Tense Uses
- It is used to describe the background of a story written in the past tense. For example: The sun was shining and birds were flying as the lion came out of the jungle.
- Past continuous tense is used to describe the change in mind. For example: I was going Hawaii in my holidays but now I’ve decided to go London instead.
- It can also be used to describe an unfinished action or event that was interrupted by another event or action. For example: I was having a wonderful dream when the alarm clock rang.
Positive sentences
Subject + Auxiliary verb + main verb + Object
Subject+ Were/Was + Present participle + (Verb+ing)+ An object.
For example:
- She was waiting for you.
- He was writing a letter.
- Rahul was driving his car.
- I was planning about my future.
Negative sentences
Subject + Auxiliary verb + NOT + main verb + object.
A subject + were/was + NOT + Present participle + Object
For example:
- She was not sleeping.
- I was not walking alone.
- She was not reading the book.
- The kids were not playing in the park.
Some examples of past continuous tense:
- They were waiting for the ambulance when the accident happened.
- Sunny was skiing when she broke her leg.
- When we arrived he was having a bath.
- When the fire started I was listening radio.
Moreover, These are some of the examples of Past continuous tense which we can use while framing sentences.
Past perfect tense | Definition | Uses | Sentences | Examples
What is past perfect tense?
Past perfect tense indicates that an action was completed at some point in the past before something else happened.
However, It is used to express two types of actions which occurred or took place in the past. It gives a sense of completion of an activity in past. Past perfect tense can also be used to state an action that occurred somewhere in the past.
Example:
- I had walked for two miles.
- She had slept.
- He had sent me his picture a year ago.
- I had lost my phone.
The past perfect formula
The past perfect tense formula is had+ [past participle]. The formula doesn’t change no matter the subject is singular or plural.
Structure of sentence
Main verb: Past participle (3rd form of the form) e.g. gone, written, etc.
Auxiliary verb: Had
Positive sentences
Subject + Auxiliary verb + Main verb+ Object.
Subject + Had +Past participle + (3rd form of verb)+ Object.
For example:
- She had cooked a cake.
- He had bought a new mobile.
- They had shifted to a new place.
- I had lost my pen.
Negative sentences
Subject + Auxiliary verb + NOT + main verb + Object.
Subject + Had + Not + Past Participle + Object.
For example:
- She had not finished her homework.
- I had not visited him.
- They had not cleaned their room.
- He had not informed me about his pain.
Interrogative sentences
Auxiliary verb + Subject + main verb + Object
Had+ Subject + Past participle + Object.
For example:
- Had you completed your homework?
- Had you thought about your future?
- Has she appeared for her exams?
- Has he waited for you?
However, These are some of the examples of past continuous tense. You can use these rules while framing sentences.
Past Perfect Continuous Tense | Definition | Uses | Sentences | Examples
What is past perfect continuous tense?
Past perfect continuous tense is also known as past perfect progressive tense. It indicated that an action which started in the past continued up until another time in the past.
The formula for past perfect continuous tense is had been + the verb’s present participle (root + -ing).
It states an action or event that started in the past, continued up in the past and also ended at some definite point in the past.
The sentence include time-reference to show that when the action started in the past or for how long the action was continued in past. Two specific words are used for time reference. They are ‘since’ and ‘for’.
Structure of the sentence
Main verb: Present participle(base form verb+ ing). Ex. waiting, cooking, etc.
Auxiliary verb: Had been.
Positive sentences
Subject+ Auxiliary verb+ main verb+ Object+ time-reference.
Subject+ had been+ present participle( base form of verb+ing)+ Object+ time- reference.
For example:
- They were playing cricket since 10:00 am.
- I had been applying for jobs since January 2017.
- She had been watching the movie for three hours.
- I had been waiting for you since two hours.
Negative sentences
Subject+ Auxiliary verb+ main verb+ Object+ time-reference.
Subject+ had not been+ present participle+ Object+ time-reference.
For example:
- She had not been eating vegetables for three years.
- Kid had not been drinking milk for two hours.
- You had not been reading this book for two months.
- He had not been playing badminton since 3 O’ clock.
Interrogative sentences
Had+ subject+ been+ Present participle+ Object+ Time-reference.
For example:
- Had he been using the same mobile since 2014?
- Had he been working on the same project since 2017?
- Had she been doing her homework since last night?
- Had you been helping your parents for three years?
Hence, These are some of the examples of Past perfect continuous tense. We can use them while framing sentences.
Future tense | Definition | Uses | Type
What is future tense?
There are three types of tenses , that is, Present tense, Past tense, Future tense. Here, we will discuss Future Tense.
Future tense is a type of Tenses. It generally marks the event described by the verb that will happen in future and has not happened yet.
Moreover, it expresses a future event or a future state of being. The future expressed byit generally means the future related to the moment of speaking.
Uses of Future tense
- The most important use of it is to describe the events of Future or to talk about things that has not happened yet.
- We can use the it to talk about an action or condition that will begin and end in the future.
- We can use it to discuss about future plans or plan something which will take place in future.
- It can also be used to ask about any event that will happen in future.
Types of Future Tense
- Simple future tense: It is used for an action or an event that will happen or occur in future. For example: She will go, I will celebrate my birthday by flying to London.
- Future progressive tense: The future progressive tense is used for an on-going action that will occur in the future. For example: She will be going, I will be dancing for next two hours.
- Future perfect tense: It is used to describe an action that will have been completed at some point in the future. For example: She will have gone, By the time you arrive, we will have finished the practice.
- Future perfect progressive: Future perfect progressive is used for an on-going action that will be completed at some specific time in future. For example: She will have been going, In August next week, you will have been studying for five years.
Simple Future Tense | Definition | Uses | Sentences | Examples
What is simple future tense?
Simple future tense indicates an action or event that will occur or happen in the future. It describes an action that will happen in near or far future after said by the speaker.
It also refers to a time later than now, and expresses facts or certainty. There is no attitude in this case.
Structure of the sentence
Main verb: Base or 1st form of verb.
Auxiliary verb: “will”
The formula for simple future tense is will + [root form of verb]. It doesn’t matter if the subject is singular or plural, the formula for the simple future tense doesn’t change.
Uses of simple future tense
- It is used to express willingness. For example: She’ll do the washing up.
- To predict a future event. For example: I will go school tomorrow.
- With you, to give orders. For example: You will do exactly what she says.
- It is also used with I or We, to express a spontaneous decision. For example: I’ll pay for the laptop by credit card.
- Simple future tense is also used in a negative form to express unwillingness. For example: The gill won’t eat her sandwich.
Positive sentences
Subject+ Auxiliary verb+ main verb + Object.
Subject+ will+ Base or 1st form of verb+ Object.
For example:
- She will come here tomorrow.
- He will send me a mail.
- He will marry her next year.
- I will give her a nice gift.
Negative sentences
Subject+ Auxiliary verb+ NOT+ main verb+ Object.
Subject+ will+ NOT+ base form of verb+ Object.
For example:
- They will not play football.
- He will not help you.
- She will not come to college.
- I will not study this book.
Hence, These are some of the examples of Simple future tense. You can use this information mentioned above while framing sentences.
Future Progressive Tense | Definition | Uses | Sentences | Examples
What is Future progressive tense?
Future progressive tense is used to indicate a continuing action that will occur at some point in the future. It is a English verb tense. It expresses that something will be in progress at a particular moment in future.
However, It is also called future continuous tense.
For example:
- I will be studying.
- She will be reading.
- I will be leaving.
Uses of future progressive tense
- Future progressive tense is used to indicate that something will happen or take place in near future. For example: You will be hearing from us in the coming months.
- It is also used to talk about future events which are fixed or decided. Personnel intentions are not suggested here. For example: I will be seeing her one of these days.
- It can also be used to predict the present. For example: Don’t call him now, he will be having shower.
- The future progressive tense can also be used to make polite inquiries about people’s plan. For example: Will you be singing till the night.
- Whenever we want to know listener’s plan, future progressive tense is used. For example: Are you coming to my house this Sunday?
Structure
It follows a specific structure or standard formula which is as follows:
It is created with “to be” verb conjugation” and the present participle of a verb (with an –ing ending).
We use Subject + will be + present participle of verbs to form the future progressive.
Some examples of future progressive tense:
- I will be eating your chocolate.
- I will be reading this newspaper.
- She will be bargaining.
- I will be seeing you soon.
- Will you be coming at my place?
These are some of the examples which can be used while framing sentences.
Future Perfect Tense | Definition | Structure | Formula | Examples
What is future perfect tense?
Future perfect tense is a verb form which indicates an action or event that is expected or planned to happen before a time of reference in the future. It reflects that an action will have been completed at some point in the future. It gives a sense of completion.
Moreover, The construction of future perfect tense consists of Auxiliary verbs(will or shall) to mark the future.
Form of the Sentence
The form of Future perfect tense is composed of two elements, that is, the simple future of the verb “to have” (will have) + the past participle of the main verb.
For example: She will have finished.
Structure of the sentence
Main verb: Past participle(3rd form of the verb).
Auxiliary verb: Will have.
Positive Sentences
- Subject + Auxiliary verb + Main verb + Object.
- Subject + will have + Past participle (3rd form of the verb) + Object.
For example:
- She will have started a new job.
- Teacher will have taken the test.
- The kids will have played cricket in the school.
- I will have taken my dinner.
Negative Sentences
- Subject + Auxiliary verb + Main verb+ Object.
- Subject+ WILL NOT have+ past participle + Object.
For example:
- He will have not come here.
- They will have not seen us.
- She will have not reached her home.
- The kids will have not eaten their food.
Interrogative sentences
Will + Subject + Have + Past participle + Object.
For example:
- Will he have helped his siblings?
- Will she have started her journey?
- Would they have constructed a new house?
- Will she have decided her decision?
However, they are some of the examples of future perfect tense. You can use the above mentioned formulas while framing sentences for future perfect tense.
Future Perfect Progressive Tense | Meaning | Structure | Sentences | Examples
What is future perfect progressive tense?
Future perfect progressive tense is also known as future perfect continuous tense. It is a verb form that indicates a continuous action that will be completed at some point in the future.
The future perfect progressive tense consists of certain elements such as will + have + been + the verb’s present participle (verb root + -ing).
In future perfect progressive tense, when we describe an action, we are projecting ourselves forward in time and looking back at the duration of the activity.
However, progressive forms occur only with what are called dynamic verbs and not with stative verbs. The action is assumed to be continued for a specific time in future.
In this verb form, a time reference is used to show the starting point of the sentence or for how long the action continues.
Since and for are the two specific words used in the sentences for ‘time reference’.
Structure of the Sentence
Main verb: Present participle( Base or 1st form of the verb+ing) Example: going, leaving, working.
Auxiliary verb: Will have been.
Positive Sentences
Subject + Auxiliary verb + Main verb + Object + Time reference.
Subject+ will have been+ Present participle(1st form of the verb+ing)+ Object+ time-reference.
For example:
- She will have been reading this book since Friday.
- They will have been writing blogs for three hours.
- The girl will have been sleeping since 11 pm.
- He will have been singing songs for two hours.
Negative Sentences
Subject + Auxiliary verb + Main verb + Object + Time-reference.
Subject+ WILL NOT have been+ present participle(1st form of the verb+ ing)+ Object+ time-reference.
For example:
- She will not have been dancing for three hours.
- He will not have been using my car anymore.
- He will not have been playing games since November 2016.
- I will not have been waiting for you anymore.
Hence, these are some of the rules and formulas which you can use while framing sentences.
Learn 8 Parts of Speech in English
| Name | Functions | Words | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Verb | Action/State | do, have, be, to be, can, must, work, like | This is a blog. I like EnglishGrammar10.com. |
| Noun | Name of thing, person, object | USA, Taylor Swift, Pencil, Cow, River, Name, Village | This is my village. She lives in USA. We read in books. |
| Adjective | attribute of a noun or pronoun | sweet, small, interesting, blue | My shirt is blue. I like sweet mangoes. |
| Determiner | a modifying word «determines» | Few, Little, A, An, The, Many, Some, Much | I have two cows and some buffaloes. |
| Adverb | describes a verb, adjective or adverb | well, badly, quickly, silently, very, really | My cat eats quickly. When child is very hungry, she eats really quickly. |
| Pronoun | replaces a noun | It, I, we, you, he, she | Laro is Italian. He is handsome. |
| Preposition | links a noun to another word | at, to, in, after, on, into | They go to school on Tuesday. |
| Conjunction | linking words | and, but, when | They like cows and they like buffaloes. They like cows and buffaloes. They like cows but I don’t like buffaloes. |
| Interjection | Joy, feelings, exclamation | well done!, oh!, ouch!, hurrah! uh-huh! | Ouch! That struck! uh-huh! Well, I know. hurrah! we won. |
A complete parts of speech and their
examples are giving here so it can understand easily. Online study
better for all who are like to read and search latest parts of speech
questions answers, exercise, quiz and test series free.
Adjective: Definition and Examples
Definition –Adjective is a word whose main
role is to modify and describe a noun. Its making your writing and
speaking. Adjective is the one of the main part of speeches and English
language. Its change information by the noun.
Use –
Adjectives use for identify and quantify individual people and unique
things. Usually positioned before noun and pronoun that they modify same
sentences contain.
Type – 2 types of adjectives:
- Descriptive Adjective
- Limiting Adjective
Descriptive Adjective
1 Attributive Adjective –
Generally more straightforward than their counterparts. Most
adjectives used in two positions. When they are used before the noun
they describe, they are called Attributive Adjectives. Attributive
Adjective are- black, English, fast etc.
Examples –
- It is an English Rose.
- A black dog.
- A fast journey.
- A White cow.
2 Predicate Adjective
When they are use after a verb such as be, become look, grow and
seem, they are called Predicate Adjective. It is contrasts with an
attribute adjective. Its part of the predicate hence. They modify the
subject of sentences. Its part of the predicate hence. They modify the
subject of sentences. Predicate Adjectives are- Gloomy, black, sweet
etc.
Examples –
- Fruit is sweet.
- The dog was black.
- They were growing tired.
- A future looks gloomy,.
Limiting Adjective
1 Possessive Adjective
Its show possession of describe whom thing belongs. And ownership of
something while we use then when we refer to people. Possessive
Adjective are- your, her, him, my etc.
Examples –
- She loves your hat.
- This is my phone.
- The dog is sitting on its tail.
- The shopkeeper sold her favorite thing.
2 Demonstrative Adjective
Its describes which noun and pronoun you are referring. That are used
to modify noun. Its helpful for make it clear which thing of person you
would like to talk. Whether person is far and near or singular and
plural. Demonstrative Adjectives are- these, that, those, this etc.
Examples-
- My parents preferred those plates.
- She lives in this house.
- That cat is so adorable.
- This is boring.
3 Indefinite Adjective
Its used to describe to noun. Its type of adjective. Adjective
depending on context. Its singular or plural. Singular Indefinite
Adjective are- each, enough, either, everybody etc. and Plural
Indefinite Adjective are- both, few, many, other etc.
Examples-
- Both are beautiful.
- Everybody come here.
- Each state is under world.
- Anybody seen this movie.
4 Interrogative Adjective
Its used with noun for ask the questions. Its used to modify
interrogative sentences. Its part of adjective.Similar use with noun and
pronoun. Interrogative Adjective are- what, which, why, who, where etc.
Examples-
- Where do you live?
- What is your favorite subject?
- Why are you laughing?
- Which is your dress?
- Where is Riya’s mother?
5 Cardinal Adjective
Adjective that modify the noun by numbers. Its sentences use with
numbers. Similar use with nouns and pronouns but simple use with
numerical sentences. Cardinal Adjectives are- one, two, three etc.
Examples-
- She is no. one girl.
- They are two brothers.
- Fifteen students are absent.
- Total five family member in their home.
- Three parrots are flying in the sky.
6 Ordinal Adjective
Its indicate the position of a noun in a series. Words are
representing the position of rank in a sequential order. The order may
be of size and importance etc. Ordinal Adjectives are- first, second,
third etc.
Examples-
- She comes on the first date.
- Third month is wonderful for me.
- He is sitting on third row.
- She is born in second month.
- Just once read it.
7 Proper Adjective
Adjective drive from proper name and sentence who is called proper
adjective. We are easily recognized. Its modified with nouns and
pronouns. Its alternative ending with each sentences. Proper Adjectives
are- Indian, Australian, American etc.
Examples-
- Italian food.
- Russian opera.
- I love Indian culture.
- I like Japanese dress.
ADJECTIVE
Definition of Adjective
Adjectives
are those words that are used to describe or modify nouns or pronouns.
Examples of Adjective
- They live in a beautiful house
- Riya is wearing the sleeveless dress today.
- She wears a beautiful dress.
- She writes meaningless messages.
- This shop is much nicer.
- Sappy is an adorable baby.
- Deepika’s hair is gorgeous
- This glass is breakable.
There are 7 Types of Adjective
Types of ADJECTIVE
In Adjective
there are 7 Types of adjectives are present in English Grammar.
- Descriptive
Adjective - Quantitative
Adjective - Demonstrative
Adjective - Possesive
Adjective - Interrogative
Adjective - Distributive
Adjective - Articles
Descriptive Adjectives Examples List
1 Descriptive Adjective
Definition of
Descriptive Adjective
Descriptive
adjectives are used to describe nouns and pronouns.
Examples
of Descriptive Adjective
- Rishi is a nice person.
- He is a cricketer.
- I bought a genuine kajal.
- I am a self reliant woman.
- She has a beautiful daughter.
- She is a clever girl.
- I have an old touring car.
- She want to buy a diamond ring.
- We ate some delicious food.
- She loves golden jars.
2 Quantitative Adjective
Definition of Quantitative
Adjective
Quantitative Adjectives describe the quantity of something.
Examples
of Quantitative Adjective
- She has 40 horses.
- The forest has 2125 animals.
- The second world war still hunts some peoples.
- She ate half of my apple.
- Most people are people in this world.
- Kartik has many pencils in his bag.
- He is doing it for 66th times now.
- The fourth boy became first in the final exam.
- There are 30 girls and 32 boy in this class.
- Rohan completed the whole task.
3 Demostrative Adjective
Definition of Demonstrative Adjective
A demonstrative adjective describes “which” noun or pronoun you’re referring to.
Examples
of Demonstrative Adjective
- Give me that pink water bottle.
- This time I won’t fail you.
- I want those gorgeous marbles.
- I wanted to propose you that day.
- These mangoes are rotating.
- I can’t forget that accident
- I cannot give you money at this time.
- That building is stronger than this hut.
- Those people were mean to her.
- Those rascals are back in the town.
4 Possessive Adjective
Definition of Possessive
Adjective
Possessive Adjective show possession. They describe to whom a
thing belongs. Some of the most common possessive adjective.
Examples of Possessive Adjective
- My computer is not working properly.
- Your cycle has been stolen yesterday.
- We are concerned about his performance.
- Your child is not doing well in the school.
- I could not understand her intentions.
- Stop messing with my hair.
- Her nails are so pretty.
- I cannot believe that you are broke my glasses.
- Her thoughts are too complex.
- I don’t want to see his shadow again.
5 Interrogative Adjective
Definition of Interrogative
Adjective
Interrogative adjective, meaning that they ask a question. These
adjectives are always followed by noun or pronoun, and are used to form
questions.
Examples
of Interrogative Adjective
- Whose book is this?
- Which pen do you like?
- Which song is your favourite ?
- What books are you buying today?
- Whose dress did you wear today?
- What product did you order from there?
- Which is Rohan’s bat?
- What recipe did you choose from the recipe book?
- Which player did get a fifty yesterday?
- Whose phone is this?
6 Distributive Adjective
Definition of Distributive
Adjective
Distributive Adjective describe specific members out of a
group. These adjectives are used to single out one or more individual items or
people.
Examples
of Distributive Adjective
- Each book was written with a pen or a brush.
- Every day there is much work to be done.
- Either situation might be the case.
- Neither of them had a clue what was on her mind.
- It’s not a decision or a wish any more.
- We know each other from last 10 years.
- He was strong and ready for every duty.
- I don’t like either the one or the other.
- He heard neither the clock nor the birds.
- Call me if there’s any change.
7 Article
Definition of Article
There are only three article in the English Grammar: A, An, The.
Articles can be difficult for English learners to use correctly.
Articles are their own parts of speech.
Examples
of Article
- There was a tree.
- He has been
here about an hour. - The horse did
not stir. - She tell me
I walked the day I was a year
old. - He wanted
needed an answer - Ritika
walks on the air all right. - I suppose
they are both a little
artificial. - I was not an easy decision.
- I like the black color dress.
- A warm hand
rested on her waist.
Antonyms Examples List
Antonyms
A word that has the exact opposite meaning of another word its antonym.
Examples of Antonyms
| Accurate | Inaccurate | Evening | Morning |
| Achieve | Fail | Evil | Good |
| Add | Subtract | Excited | Bored |
| Admit | Deny | Exhale | Inhale |
| Admit | Reject | Expand | Shrink |
| Adore | Hate | Expensive | Cheap |
| Against | For | Export | Import |
| Agree | Disagree | Exterior | Interior |
| Ahead | Behind | External | Internal |
| Alive | Dead | Fake | Real |
| All | None | Fall | Rise |
| Allow | Forbid | Famous | Unknown |
| Alone | Together | Fast | Slow |
| Always | Never | Fat | Skinny |
| Amateur | Professional | Fat | Thin |
| Amuse | Depart | Few | Many |
| Ancient | Modern | First | Last |
| Answer | Question | Float | Sink |
| Authentic | Imitation | Foolish | Wise |
| Back | Front | Forget | Remember |
| Bad | Good | Forgive | Blame |
| Beautiful | Ugly | Forward | Backward |
| Before | After | Friend | Enemy |
| Beg | Offer | Funny | Sad |
| Begin | End | Generous | Stingy |
| Beginning | Conclusion | Gentle | Rough |
| Behind |
In Front of |
Giant | Tiny |
| Beneath | Above | Give | Take |
| Best | Worst | Guilty | Innocent |
| Better | Worse | Harmful | Harmless |
| Big | Little | Harsh | Mild |
| Birth | Death | Healthy | Sick |
| Bitter | Sweet | Heavy | Light |
| Black | White | Hero | Coward |
| Blunt | Sharp | Hide | Show |
| Boring | Interesting | High | Low |
| Borrow | Lend | Hungry | Full |
| Bottom | Top | Husband | Wife |
| Boy | Girl | Identical | Different |
| Buy | Sell | Ignorant | Educated |
| Calm | Windy | Important | Trivial |
| Capable | Incapable | Imprison | Free |
| Capture | Release | In | Out |
| Carefull | Careless | Incomplete | Complete |
| Catch | Throw | Increase | Decrease |
| Change | Remain | Inside | Outside |
| Child | Adult | Interesting | Boring |
| Chilly | Warm | Junior | Senior |
| Chreeful | Sad | Justice |
In Justice |
| Clean | Dirty | Kind | Mean |
| Clever | Foolish | Large | Small |
| Clever | Stupid | Laugh | Cry |
| Close | Open | Lazy | Dilligent |
| Cold | Hot | Lead | Follow |
| Combine | Separate | Leave | Stay |
| Comedy | Tragedy | Left | Right |
| Complex | Simple | Legal | Illegal |
| Conceal | Reveal | Like | Dislike |
| Conquer | Fail | Live | Die |
| Continue | Interrupt | Lock | Unlock |
| Cool | Warm | Long | Short |
| Correct | Incorrect | Loose | Tight |
| Correct | Wrong | Love | Hate |
| Crazy | Sane | Lowful | Unlowful |
| Create | Destroy | Loyal | Disloyal |
| Cruel | Kind | Mature | Immature |
| Dangerous | Safe | Merry | Sad |
| Dark | Bright | Narrow | Broad |
| Dark | Light | Near | Messy |
| Dawn | Sunset | Noisy | Silent |
| Deep | Shallow | Notice | Overlock |
| Demand | Supply | Obedient | Disobediant |
| Despair | Hope | Reward | Punishment |
| Different | Same | Right | Wrong |
| Difficult | Easy | Rough | Smooth |
| Discomfort | Comfort | Small | Big |
| Doubt | Trust | Soft | Hard |
| Downwards | Upwards | Spend | Save |
| Drunk | Sober | Start | Finish |
| Dry | Wet | Stay | Go |
| Dusk | Dawn | Straight | Crooked |
| Early | Late | Strengthen | Weaken |
| Easy | Hard | Strong | Weak |
| Effective | Ineffective | Sweet | Sour |
| Enter | Exit | Tall | Short |
A An The Articles
According to Dictionary “ARTICLES” refers to a particular item or object.
According to Grammar: Definition
1. The words A, An and The are called Articles (according to primary students).
2. Articles refers to the word which is used before noun in which
defines whether something is specific or unspecific and it is
type of adjectives (according to secondary students).
For Example: The Moon , The Earth , An Apple, A Boy etc.
Types of Articles
- Definite Article
- Indefinite Article
1. Definite Articles
Definite Article refers to “The“. It defines the noun which is specific or particularly one.
For Example:
- The Earth is third planet in the solar System.
- The cat is black.
- The book is heavy.
2. Indefinite Article
Indefinite Article refers to “A and An“. It defines the noun which is unspecific or one thing, it is not used with non-countable nouns.
For Example:
- Ram is a good boy.
- I have a sports bike.
- That is an excellent book.
- I think this is an animal.
How to use Articles
The Use of “AN” – Before a singular noun beginning with a vowel sound.
For Example:
- We are looking for an apartment.
- An Apple
The Use of “A” – Before a singular noun beginning with a consonant sound.
For Example:
- That man is a scoundrel.
- A girl
The Use of “THE” – Before a singular or plural noun which is specific or particularly one in the World.
For Example:
- The theory of relativity.
- The Taj Mahal
Conjunction
Conjunctions are words that link other words, phrases, or clauses
together. Conjunctions are considered to be invariable grammar particle,
and they may or may not stand between items they conjoin.
In other words, Conjunction is a word that join words or sentences.
Here, join means to connect two or more words or two or more sentences.
Example:-
Lavina and Ravina are sisters.
Here, and is a connector between two words Lavina and Ravina (It is the example of joining two words)
Janvi is a good girl. Vini is a good girl.
Janvi and Vini are good girls.
Here, and is used to joining two sentences.
And, but, for, nor, or, so, and yet — are the seven coordinating conjunctions. To remember them, the acronym FANBOYS can be used.
- F = for
- A = and
- N = nor
- B = but
- O = or
- Y = yet
- S = so
TYPES OF CONJUNCTIONS
There are three types of conjunctions.
- Coordinating conjunctions
- Subordinating conjunctions
- Correlative conjunctions
1. Coordinating conjunctions:- Coordinating conjunction
is to join two words, phrases, or independent clauses, which are
parallel in structure. There are seven coordinating conjunctions which
are by far the most common conjunctions: and, but, for, nor, or, so, yet.
It joins the following:-
- Word+Word
- Phrase+Phrase
- Clause+Clause
Examples:-
- I’ve just eaten dinner so, I’m not hungry.
- She needs to be home for her kids.
- She is neither tall nor fat.
- I want to go to bed, so I am brushing my teeth.
2. Subordinating conjunctions:– A subordinating conjunction is a word or phrase that links a dependent clause to an independent clause.
A subordinating conjunction is also called subordinator.
It joins the following:-
- Main clause+Subordinate clause
- Subordinate clause+Main clause
A main clause is a group of words having a subject and a verb. It can
stand alone as a sentence because it can give complete meaning. But, A
subordinate clause can’t stand alone as a sentence because it can’t give
complete meaning. The subordinate clause is completely depend on main
clause to give a specific meaning.The subordinate clause with
subordinate conjunction.
Example:-
- I need to finish the homework before the mother arrives from Market.
- She inspires me always because she believes in me.
- My mother believes that I should be a doctor.
- I started cooking when I was eleven.
3. Correlative conjunctions:-Correlative
conjunctions are paired words. Correlative conjunction is a phrase that
joins together two other words, phrases, or clauses.
The common correlatives conjunctions are as follows:-
- Either….or
- Neither….nor
- Whether….or
- Both….and
- Not only….but also
Examples:-
- Both the red and the black dress are beautiful.
- She is not only intelligent, but also very funny.
- Either I drive to the airport or I get a taxi.
- This book is neither interesting nor useful.
- I don’t know whether he will come or not.
Interjection
Interjection meaning according to the dictionary : an abrupt remark, especially as an aside or interruption.
Interjection refers to those words which are added in sentence to
express strong feeling and sudden emotions or sentiments such as
surprise, disgust, joy, excitement, pain, sorrow , attention , calling
etc.
Note: It is not related grammatically related with
any part of sentence.It is used to express feeling or emotions. an
interjection followed by an exclamation mark will be followed by an
exclamatory sentence in an sentence.
Use: The words are generally used in sentences are as follows: Oh! , Wow, Ouch, Oops, Aha, Yahoo, Eww etc.
For Example:
- Wow! We won the match
- You think this is good???-Eww
- Oh! I am so sorry
- Ouch!! You hurt me.
Types of interjections
Interjections has been divided in to many types which are greeting, joy, surprise, approval, sorrow, attention, and calling.
Why do we use interjections?
Interjections is the part of speech.It is generally used in informal
manner or language. It gives an identification to our emotions and
feelings.
It is necessary to use interjections?
It is not necessary to use interjections in a sentence. It generally
use to convey the speaker or individual feeling and emotions.However if
it use , it shows an expression of feeling or sentiment in message
which makes your message more reliable.
We hope that this matter will help you a lot in knowing
Interjections. For more grammar notes you can visit our website daily.
Thank you!!!!
Noun
The simplest definition of a noun is a thing and nouns are the basic building blocks of sentences. These
things can represent a person, animal, place, idea, emotion – almost
anything. A noun is a part of speech, and parts of speech simply refer
to types of words.
| What is a Noun? | What is a Noun for Kids? |
| Types of Nouns | Classifying Noun |
| Possessive Nouns | Collective Nouns |
| Irregular Plural Nouns | Singular and Plural Nouns |
| Common and Proper Noun | Common Proper Noun Worksheet |
The simple definition is: a person, place or thing. Here are some examples:
- person: man, woman, teacher, John, Mary
- place: home, office, town, countryside, America
- thing: table, car, banana, money, music, love, dog, monkey.
In other words, a noun is a word of a person, animal, thing or a place which contains a special meaning.
“We can touch and feel is a noun.”
Types of Noun
There are five types of noun:-
- Common noun
- Proper noun
- Collective noun
- Material noun
- Abstract noun
1. Common noun – A common noun is a name which can
be used commonly for persons, animals, places or things. It represents a
whole class of its kind. Example:-
- Boy
- Girl
- Dog
- Cow
- Pen
- Ball
- Delhi
- Jaipur
2. Proper noun:- A proper noun is the particular
name of the person, place, animal or thing. Proper nouns like Rajasthan,
Rajesh or Ball are capitalized to show their distinction from common
nouns, such as “state,” “man” or “thing.” Example:-
- Boy – Shivam
- Girl – Neha
- Place – Chittorgarh
- Thing – Table
3. Collective noun:- A collective noun is the name
given to a collection of common noun considered as common noun. It refer
to a group of something in particular. Examples:-
- An army of soldiers
- A band of musicians
- A heap of stones
- A group of people
- A jury of judges
4. Material noun:- A material noun is a thing which
is extracted from the earth or is used to make other things. It refers
to materials or substances from which things are made. Example:-
- Cotton
- Wheat
- Sugar
- Copper
- Wheat
5. Abstract noun:- An abstract noun is the name of
some quality, action, state, feeling, or idea. It something which we can
feel or think about, but cannot touch it. Example:-
- Bravery
- Goodness
- Strength
- Freedom
- Sickness
Noun, Definition, Noun Types
Definition
Of Noun
A noun is a
word that identify the name, place or thing.
| NAME | PLACE | THING |
| Riya | Jodhpur | Table |
| Priya | Mumbai | Spoon |
| Reeta | Hydrabad | Cap |
| Kajal | Jaipur | Tap |
| Divya | Kolkata | Bag |
| Poonam | Nepal | Box |
| Rinky | Delhi | Pen |
| Kavita | Japan | Car |
| Ravi | Agra | Chair |
There are 8 type of Noun in English Grammar.
1. Common Noun
Definition of Common Noun
A common noun that is the name of a group of similar things.
Examples
of Common Noun
- Watch
- Nail
- Foot
- Shoe
- Train
- Mouse
- Wallet
- Dress
- Waterfall
- Pillow
2. Proper Noun
Definition of Proper Noun
A Proper
Noun is the name of a particular name, place or thing. Proper Noun is always
start with capital letter.
Examples of Proper Noun
- 1.Virat Kohli is the best cricket player.
- 2. Riya was born in India.
- 3. Her friend name is Kavita.
- 4. Harbhajan Singh plays for Mumbai Indian in IPL.
- 5. She has a dog named Poppy.
3. Concrete Noun
Definition of Concrete
Noun
Concrete
nouns are that we can experience with our touch, feel, sight, hearing or smell.
Examples of Concrete
Noun
Apple, Ambulace, Ball, Chair, Hat, Lamp, Man, Paper, Pencil, Purse,
Restaurant, Shampoo, Suit, Table, Water, Oil, Rose, Mall, Library,
Jacket, Hen, Gift, Ears, Eyes, Nose, Hair, Nail, Tea, Coffee, Rice.
4. Abstract Noun
Definition of Abstract
Noun.
Abstract
Noun refer to intangible things, like actions, feelings, ideals, concepts and
qualities.
Examples of Abstract
Noun
Beauty, Bravery, Charity, Ego, Goodness, Kindness, Honor, Hope,
Loyalty, Jealousy, Sensitivity, Weakness, Trust, Maturity, Patience,
Love, Pain, Death, Idea.
5. Collective Noun
Definition of Collective
Noun
A collective
noun is a type of noun that identifies the groups of people and things.
Examples of Collective
Noun
- A group of Girls: Giggle
- A group of Boys: Rascal
- A group of cats: Clutter
- A group of musicians: Band
- A group of singers: Choir
- A group of players: Team
- A group of students: Class
- A group of flowers: Bouquet
- A group of trees: Forest
- A group of stars: Galaxy
6. Compound Noun
Definition of Compound
Noun
A compound noun is a noun that is made with two or more words. A
compound noun word is usually made with noun+ noun or noun + adjective.
Examples
of Compound Noun
Any + More = Anymore
Birth + Day = Birthday
Every + Day = Everyday
Foot + Print = Footprint
Girl + Friend = Girlfriend
Heart + Beat = Heartbeat
Ear + Rings = Earings
Butter + Fly = Butterfly
7. Countable Noun
Definition of Countable
Noun
Countable noun is a noun that can be in singular or plural form, or we can count easily.
Examples of Countable
Noun
Restaurants, Café, Books, Glass, Mobile, Laptop, Elephant, School,
College, Table, Chapters, Car, Calender, Computer, Apple, Chocolates,
Egg, Tomato, Girl, Boy.
8. Uncountable Noun
Definition of Uncountable
Noun
An
uncountable noun is noun that can not count, only we can touch or feel.
Examples of Uncountable
Noun
Water, Petrol, Oil, Ghee, Cheese, Information, Garbage, Juice, Gas, Milk, Coffee, Tea, Salt, Hairs, Time, Honey
English Pronoun Chart | Rules | Types | Examples
Words which are use instead of noun are known as pronoun. However, in
grammar it is being defined as the word or the phase which are
substituted in place of the noun. Thus, words which can be replaced in
known as the pronoun’s antecedent. Moreover, the work performed by the
noun can also be done by this as well. So, it can easily act as
a subject, direct object, indirect object, object of the preposition and
more. Thus, there are various words which are of very short words.
Example:
- He
- She
- They
- It
- We
- Who
Examples of Pronoun:
- I have lost my pen. Buy a new pen for me.
- We are getting bored. Let us go for a movie.
- She sang very well. Everyone clapped for her.
- Look at Mary she is dancing.
- They are glad to see her.
- Ann and Lily have come to see her.
- This is her pen.
- The girl who is simple is respected by all.
- He is going home.
- We are going on vacation.
Rules of Pronoun:
However, there are few important rules for using this. So, go through
them read the examples and notice how the rules are followed. So, that
you can learn the way to use this.
- Use subject in the sentence. Example: We did a great job.
- However, you must also use subject to rename the subject. Example: It was she who decided we should go to Hawaii.
- Moreover,
the Indefinite pronouns don’t have antecedents. As they are capable
enough of standing on their own. For example: No one likes the sound of
fingernails on a chalkboard. - They are also capable of Object
pronouns are used as direct objects, indirect objects, and objects of
prepositions. These include: you, me, him, her, us, them, and it.
Example: David talked to her about the mistake. - Moreover, the Possessive pronouns show ownership. Thus, they do not need apostrophes. Example: The cat washed its whiskers.
Types of Pronoun:
However, this can be divided into numerous categories. Thus, these are:
-
Personal Pronoun.
- Reflexive Pronoun.
- Indefinite/Distributive Pronoun.
- Demonstrative Pronoun.
- Possessive Pronoun.
- Relative Pronoun.
- Interrogative Pronoun.
- Reciprocal Pronoun.
You study about pronoun that pronoun can do everything that noun do, right! Pronoun can take place of noun.
Surprise to Know about Types of Pronoun
In our books, there are 8 types of pronouns, but it may be 9. So
which counting is correct? Don’t think. It is an old English and modern
English game. Generally there are 8 types of pronouns. If you can clear,
please.
Definition of Pronoun
Pronoun is a word which used in place of a noun.
There are 3 kinds of Pronouns.
-
Personal Pronoun
- Interrogative Pronoun
- Relative Pronoun
1 PERSONAL PRONOUN
Definition of Personal Pronoun
These pronouns are used for person.
These are 3 kinds:
-
First Person
- Second Person
- Third Person
First Person: In a Sentence, a person who talks is first person. Example- I, We
Second Person: To whom, the person talks is second person. Ex- you
Third Person: About whom, the person talks is third person. Ex- He, She , it, they
- First person- I, We जो बोल रहा है
- Second Person-you जो सुन रहा है
- Third Person- He, She, it, they जिसके बारे में बात की जा रही रही है
2 Interrogative Pronoun
Definition of Interrogative Pronoun
These are also call “ Question Words” or wh-words”. In interrogative
sentences, helping verb used after wh-words. Question Mark? Is put up
after interrogative sentence
| Word | Meaning in Interrogative Pronoun | Meaning in relative pronoun |
| Who (living person) | कौन | जो |
| What ( idea or non living person) | क्या | जो |
| Where (place) | कहाँ | वहाँ, जहाँ |
| Why (reason) | क्यों | इसलिए |
| When (time) | कब | ज़ब |
| How (manner of work) | कैसे | जैसे |
| How many (plural, in numbers) | कितने | उतने, जितने |
| How much (singular, quantity) | कितना | उतना, जितना |
| Which (slection) | कौनसा | जो |
| Whom (indirect object) | किसकों | जिसको |
| Whose (possession) | किसका, किसकी | जिसका, जिसकी |
3 Relative Pronoun
Definition of Relative Pronoun
Relative Pronoun is used to connect two sentences.
When “wh-word” are used in the middle of sentence, they perform as a “ Relative Pronoun”.
Example of relative pronoun
- What are you doing?
In the above sentences “what” is performing as “interrogative pronoun”.
- I don’t know what are you doing?
In the above sentence “what” is performating as “relative pronoun” because it connects two sentences.
Verb, Types, Exercises, Verb List
Definition: Verbs are the action words in a sentence that describe what the subject is doing. Verbs are doing words. A verb can express a physical action, a mental action, or a state of being.
In other words, verbs are action words that describes the action o the state of the subject.
Different Types of Verbs
- Non-finite verbs
- Finite verbs
- Action verbs
- Linking verbs
- Auxiliary verbs
- Modal verbs
1. Finite verbs:- They are the actual verbs which are called the roots of sentences A finite verb is a verb which has a subject and shows tense. In short, it is a verb being a verb (i.e., a doing word) as opposed to a verbal (which is another part of speech formed from a verb).
Example:-
- He is excited to see the amusement park.
- The water level is rising day by day and it is alarming.
- He painted all the walls.
2. Non-finite verbs:- They are not the actual verbs. A non-finite verb (also known as a verbal) is the term used to describe a verb that is not showing tense.
In other words, it a verb form that does not act like a verb (or, at least, the type of verb you need to form a sentence). Therefore, a non-finite verb is never the main verb in a sentence.
Example:-
- We are ready to play.
- Sleeping in the afternoon is not healthy.
- We ate a lot of roasted meat.
- I respect the working disabled people.
3. Action verbs:- An action verb is a verb that expresses physical or mental action. The action verb tells us what the subject of our clause or sentence is doing-physically or mentally.
Examples:-
- He hit a home run at the last game.
- They bought a new house.
- I just want to sit down and relax.
- He is throwing the football.
Action Verb can be of two types
- Transitive verbs.
- Intransitive verbs.
1. Transitive verbs:- A transitive verb is a verb that can take a direct object. In other words, the action of a transitive verb is done to someone or something. Most verbs are transitive. A transitive verb contrasts with an intransitive verb, which is a verb that does not take a direct object.
Example:-
- He painted the car. (The verb ‘paint’ demands an object to be painted)
- He is reading the newspaper. (The verb ‘read’ asks the question “what is she reading?” – the answer is the object)
2. Intransitive verbs:- An intransitive verb is simply defined as a verb
that does not take a direct object. That means there’s no word in the
sentence that tells who or what received the action of the verb. Intransitive verbs are complete without a direct object.
Example:-
- He smiled. (The verb ‘smile’ cannot have any object since the action of ‘smiling’ does not fall upon anything/anyone)
- He wake up at 4 AM. (No object is needed for this verb)
4. Linking verbs:- Action verbs are verbs that specifically describe what the subject of the sentence is doing. These types of verbs carry a great deal of information in a sentence and serve to make the sentence complete.
Example:-
- Banana tastes delicious.
- She appears upset about the announcement.
- He became suspicious.
- Building the house proves difficult for them
5. Auxiliary verbs:- Auxiliary verbs are also called helping verbs. An auxiliary verb extends the main verb by helping to show time, tense, and possibility. A verb used in forming the tenses, moods, and voices of other verbs. The primary auxiliary verbs in English are be, do, and have ; the modal auxiliaries are can, could, may, might, must, shall, should, will, and would.
Examples:-
- She is writing a message to her mother.
- Didn’t I waste a lot of planned trips?
- She had planned it another way.
- Does he play volleyball?
6. Modal verbs:- A modal verb is a kind of an auxiliary verb. It assists the main verb to indicate possibility, potentiality, ability, permission, expectation, and obligation.
The modal verbs are can, could, must, may, might, ought to, shall, should, will, would.
Example:-
- I can speak English.
- You must not smoke in the hospital.
- It may rain tomorrow.
- He will go there.
Linking Verbs. Definition, Examples And Exercise
Definition: Unlike action verbs, linking verbs show a
relationship between the subject of the sentence and a noun or
adjective being linked to it.
I am putty in his hand.
Dream come true when we believe in them.
- The most common linking verbs are forms of the verb to be: am, is, are, was, were, being, been.
- Other common linking verbs include: appear, become, feel, grow, look, remain, seem, smell, sound, stay, taste, and turn.
Your plans for the wedding sound nice.
You look exhausted after studying all night.
To check if these are being used as linking verbs, try replacing them with the correct form of to be. If they make sense and have almost the same meaning, they are linking verbs.
- Anthony has been a dream the last few weeks.
- Building the house proves difficult for them.
Find out linking verbs from the examples for exercise:
- William is excited about his promotion.
- She appears upset about the announcement.
- He went red after tripping on the rug.
- Tom acted nervous when the teacher found the note.
- The crowd stayed calm in spite of the imminent threat.
- Bob felt sleepy after eating the whole pizza.
- The cinnamon rolls taste heavenly.
- All the children seem satisfied with the bouncy castle.
- All the kittens were playful.
- Your friend might be disappointed if you don’t go.
Active and Passive Voice, Definition, Examples, Exercise
There are
two kinds of voices
- Active Voice
- Passive Voice
Active Voice
When subject itself is achieve in sentences then it is called
Active Voice or is in Active Form.
Passive Voice
When object is active in a sentence or object works like
subjct than the sentence is in Passive Voice.
Only those verbs be converted into passive which have objects
or verbs have effect on subject. Those verbs are called transitive verbs.
Rules for
Converting Voices:
-
Objects are put at the place of subjects and subjects are put in the place of objects.
- VIII form of verb is used with helping verbs.
- Only transitive verbs can be changed into passive.
| Subject | Object |
| I | Me |
| We | Us |
| You | You |
| They | Them |
| She | Her |
| He | His |
| It | It |
- The forms of Be- is, are am, was, were, be, being,
been.
(Be, being, been) are used first after helping verbs.
- ‘by’ or any other preposition is used for passive.
Definition: If you are active, you are doing something. In a sentence
written in active voice, the subject of the sentence is doing the verb.
Harry ate six shrimp at dinner.
We are going to watch a movie tonight.
Definition: If you are passive, something is done to you. In a
sentence written in passive voice, the subject of the sentence is having
the action of the verb done to it by something else.
At dinner, six shrimp were eaten by harry.
A movie going to be watched by us tonight.
- When you write sentences with active voice, you can use more interesting verbs and your writing seems to move more quickly.
I ran the obstacle course in record time.
- When you write sentences with passive voice, you end up using
more helping verbs, but it can be effective if you want to slow down the
action of your writing and focus on a scene. The obstacle course was run by me in record time.
Find out active and passive voice from the examples for exercise:
- 1. Some people raise sugar cane in Hawaii.(active)
- Sugar cane is raised by some people in Hawaii. (passive)
- 2. The kangaroo carried her baby in her pouch. (active)
- The baby was carried by the kangaroo in her pouch. (passive)
- 3. The team will celebrate their victory tomorrow. (active)
- The victory will be celebrated by the team tomorrow. (passive)
- 4. The director will give you instructions. (active)
- Instructions will be given to you by the director. (passive)
- 5. Alex posted the video on Facebook. (active)
- The video was posted on Facebook by Alex. (passive)
- 6. Who ate the last cookie? (active)
- The last cookie was eaten by whom? (passive)
- 7. The science class viewed the comet. (active)
- The comet was viewed by the science class. (passive)
- 8. Susan will bake two dozen cupcakes for the bake sale. (active)
- For the bake sale, two dozen cookies will be baked by Susan. (passive)
- 9. The wedding planner is making all the reservations. (active)
- All the reservation will be made by the wedding planner. (passive)
- 10. The two kings are signing the treaty. (active)
- The treaty is being signed by the two kings. (passive)
Preposition
A preposition is a word. Its show direction and time and location or
introduce an object. Preposition is followed by many objects as like
noun, pronoun. A preposition may appear at the end of a clause or
sentence. but only when its object comes earlier.
A preposition is a word which is to link the nouns, pronouns or
phrases to other words within a sentence. Here link means to provide
relationship between noun and other words in any sentence that makes the
sentence complete (these other words may be noun, verb or adjective).
They act to connect the people, objects, time and locations of a
sentence Prepositions are usually short words, and they are normally
placed directly in front of nouns. In some cases, you’ll find
prepositions in front of gerund verbs. Example:-
The dog is sitting near the car.
Here, near(preposition) is used to link the car
which is a noun and sitting placement of the dog. If we do not use the
near and write the same it is like:- The dog is sitting the car.
We are not able to get what is the relationship between the sitting of
the dog and the car. By using, near we are confirmed that the dog is sitting near the car. Hence, near is a preposition here.
Some more examples of preposition:-
- There is some milk in the fridge.
- He sat on the chair.
- The car went through the tunnel.
- I walked down the streets.
- I prefer to read in he library.
- He swam across the pool.
- Take your sister with you.
TYPES OF PREPOSITION
There are three types of prepositions, including time prepositions, place prepositions, and direction prepositions.
- Preposition of time
- Preposition of place
- Preposition of movement
1. Preposition of time:- The preposition which describes when an event happened are defined as Preposition of time. On, at, in, from, to, for, since, ago, before, till/until, by, etc. are the most common preposition of time. Example:-
- He started sleeping at 9 PM.
- The company called meeting on 13 March.
- There is a meeting on Saturday.
- She has been ill since Wednesday.
Preposition of Time usage
It show the relationship of time between the nouns to the other parts of a sentence.
Common preposition of time: On, at, in, from, to, for, since, ago, before, till/until, by, etc. are the most common.
At
At always indicates an exact and specific time.
Example:
- I started sleeping at 11 PM.
- The meeting starts at 9 AM.
- The mall opens at 11 AM.
Note: Exceptions are that we say – at the weekend, at night, at Christmas, at Easter, at the moment, etc.
On
On generally indicates a fixed date or a day.
Example:
- I’ll see him on Monday.
- She broke a glass on Sunday evening.
- She has a meeting on 11 March.
In
In generally indicates an indefinite and unspecific time of months, seasons, years, centuries, etc.
Example:
- I will get a new mobile phone in February.
- She was born in 1999.
- I love watching TV in night
Note: Some very common exceptions are – in the
morning, in the evening, in the afternoon, in five minutes, in six days,
in two years, etc.
From – To
From….to indicates a fixed time-span with the beginning and the end.
Example:
- I worked there from 10 AM to 6PM.
- I usually sleep from 10 PM to 6 AM.
- I will stay there from 10 AM to 6 PM.
Until/Till
Until/till indicates a specific or unspecific time/event up to a point.
Example:
- He will not return until Monday.
- Stop for me until I came back
- He does not give up until he is succeeded.
- I will be stayed there until March.
Since
Since indicates a time-span beginning in a time in the past and still continuing in the present (now).
Example:
- Raghav has been in the flat since night.
- She has been reading from book since morning.
- Ram and Shyam have been enemies since childhood.
For
For indicates a period of time (amount of time) in the past, present or future.
Example:
- She stayed there for fifteen days.
- He will be staying there for two years.
- They will work with them for two days.
- She was staying there for a long time.
Before
Before indicates a prior event/ period of time from a point.
Example:
- Nandini was very happy before the marriage.
- He want to leave before the dinner.
- Children should not get out before the tea break.
- Before going, close all the door.
After
After indicates a following event/period of time from a point. This preposition is the exact opposite of before.
Example:
- She felt unhappy after the defeat.
- I want to leave after dinner.
- After playing football, we went home.
During
During indicates a period of time throughout the course or duration of any event or action.
Example:
- Shanaya was sleeping during the study.
- He don’t talk during working.
- Taniya doesn’t usually eat during sleeping time.
By
By means ‘within the extent or period of; during’ something.
Example:
- He will not complete the project by Monday.
- She will return by 2 PM.
- They will submit the assignment by 6 PM.
2. Preposition of place:- The preposition that describes where anything is in context to other are defined as preposition of place.Example:-
- He is at home.
- He came from England.
Preposition of place usage
In
In indicates something to be present in a
place or enclosure. It does not say particularly where but gives an
enclosure to the noun it connects with.
Example:
- Dheeraj works in that mall.
- She lives in Mumbai.
- Your Dress is in the Wardrobe. (Does not indicate an exact place)
- The dogs are in the kennel.
AT
At indicates an exact place.
Example:
- They are at the terrace.
- We can meet at the crossroads.
- She is at home.
- We will meet at the airport.
On
On indicates a position above but touching the object.
Example:
- The sculpture hangs on the wall
- She is on the tenth floor.
- The images are on the page.
- The cat is on the table.
Above
Above indicates a much higher position than the preposition on does. It also indicates something out of reach.
Example:
- Hold your hands above your head.
- Stars are above the sky.
- There’s a mirror above the sink.
- She waved the letter excitedly above his head.
- He’s rented a room above a shop.
Over
Over means a position between on and above which is not touching.
Example:
- What are you doing over here?
- He is famous all over the world.
- My House is over that mall.
- You see it all over the Internet.
Under
Under is the opposite of on and means ‘below the surface of’ something.
Example:
- He was sleeping under the tree.
- I had everything under control.
- I work better under pressure.
- I hid under the table.
- She’s still under age.
Below
Below indicates something at a slightly lower position than what under indicates.
Example:
- I have a scar just below my right eye.
- Your work is below average.
- Please, don’t write below this line.
- It’s six degrees below zero.
- Their price is below ours.
3. Preposition of movement:- Preposition of movement
are those to understand as they are less abstract than prepositions of
place and time. They describe how something or someone moves from one
place to another.
Preparation of movement
To
To indicates a motion in the direction of a place.
Example:
- Theye went to college.
- She has gone on vacation to France.
- He walked from the farm to the beach.
- They will go to bed when they are tired.
- They will go to the zoo if they finish their errands.
Through
Through indicates a motion in the middle of something.
Example:
- They drove through the tunnel.
- We came through a forest.
- She came through a wedding gate.
- He led his armies through many countries.
Across
Across means going to the other side of a river or road or something straight.
Example:
- She went across the river.
- I walked across the road.
- She was sitting at a table across and down from them.
- I couldn’t get my idea across to the class.
Up
Up means a motion towards a higher place or position.
Example:
- He picked up his coffee.
- She stared up at him.
- What’s going on up there?
- Climb up the tree.
- She didn’t look up.
Into
Into indicates a motion towards/going inside something. It has many uses.
Example:
- Go into the lab.
- The police broke into the bar.
- She walked into the garden.
- The little fellow ran into the street.
Down
Down indicates the opposite meaning of up. It means a motion towards a lower place or position.
Example:
- He bent down and picked up a rock.
- They sat down at the table.
- Go down the stairs.
- She sat down on the bed
From
From indicates the point of place at which a motion, journey, or action starts.
Example:
- Get away from here.
- They walked from the beach to the farm.
- Keep away from me.
- He leaped from his horse.
- I am from Brazil.
Synonyms Examples List
A synonyms is a word that means exactly or nearby the same as another word or phrase in the same language.
| Amazing | surprising, Outstanding, Stunings |
| Bad | awful, terrible, horrible |
| Beautiful | attractive, pretty, stunning |
| Benefit | profit, revenue, yield |
| Big | large, huge, giant |
| Brave | courageous, valiant, heroic |
| Cold: | chilly, freezing, forsty |
| Comparioion | connection, illustration, relation |
| Criteria | foundation, rule, law |
| Cunning | keen, sharp, Slick |
| Display | unfolding, front, presentation |
| Easy | simple, effortless, straightforward |
| Explanation | details, information, answer |
| Fair | just, objective, impartial |
| Fertile | fruitful, abudant, productive |
| Gauge | meter, rule, thickness |
| Guide | advice, leader, inspiration |
| Happy | content, joyful, mirthful |
| Hardworking | determined, industrious, enterprising |
| Honest | honourable, fair, sincere |
| Hot | burining, fiery, boiling, |
| Hungry | empty, ravenous, starved |
| Ideal | goal, standard,patern |
| Illustration | clarification, representative, sample |
| Instance | occurrence, sample, particular |
| Intelligent | brillant, clever, smart |
| Kind | considerate, amirable, gracious |
| Lazy | idle, lethargic, indolent |
| Lead | advance, point, direction |
| Light | angle, condition, education |
| Lucky | auspicious, fortunate |
| Materializaion |
inclusion, externalization, structure |
| Mean | unfriendly, unpleasant, difficult |
| Measure | scale, type, method |
| Objectification | collection, formation, symbol |
| Old | elderly, aged, senior |
| Organisation | association, institution, management |
| Pacify | appease, placate |
| Panoply | arrangement, exposure, shine |
| Partner | associate, colleauge, companion |
| Personalization | inclusion, realization, conformation |
| Piece | fragment, section, segment |
| Polite | courteous, cordial, gracious |
| Portion | piece, part, segment |
| Positive | optimistic, cheerful, sanguine |
| Problem | teaser, twister, illustration |
| Rich | affluent, wealthy, well-off |
| Risky | dangerous, perilous, treacherous |
| Senseless | absurd, illogical, unreasonable |
| Sleepy | drowsy, listless, sluggish |
| Small | Tiny, little, mini |
| Standard | mean, requirement, measure |
| Strong | stable, secure, solid, tough |
| True | genuine, factual, accurate, correct, real |
| Unhappy | sad, depressed, melancholy, miserable |
| Vacant | empty, deserted, uninhabited |
| Valid | authorized, legitimate |
| Warning | intimation, lesson, prediction |
| Weak | frail, infirm, puny, fragil |
| Wet | damp, moist, soggy |
| Yardstick | guide, meter, indicator |
| Young | budding, fledging, tenderfoot |
Word | Definition | Meaning | Examples
A collection or group of letters with some meaning, called as ‘word’. The definition of a word is a letter or groups of letters that has meaning when spoken or written.
Example:-
- A dog
- A boy
- A girl
- A cat
- A ball
- An apple
- A car
A word is a speech sound or a combination of sounds, or its representation in writing, that symbolizes and communicates a meaning.
English has four major word classes: nouns, verbs, adjectives and adverbs. They have many thousands of members, and new nouns, verbs, adjectives and adverbs are often created. Nouns are the most common type of word, followed by verbs. Adjectives are less common and adverbs are even less common.
TYPES OF WORDS
All types of words is known as ‘word classes’ or ‘part of speech’.
There are two types of classes
- Open classes
- Closed classes
Open classes
These are classes of word which are always open to change: new words are formed, while old ones drop out of use. The open classes are: noun, verbs, adjectives, and adverbs.
It is also known as ‘content’ or ‘lexical’ words.
Example:- 1. Bad – badly. 2. Happy – happily
Closed classes
On the other hand, pronouns, determines, prepositions, conjunctions are closed classes because there are no such additions to or deletions from them.
These words contain ‘structural’ words that contribute to the grammatical structure of the sentences.
Example:- 1. He – H(no meaning) 2. She – Sh(no meaning)
Sentence | Definition | Meaning | Examples
A sentence is a group of words that are put together to mean something. A sentence is the basic unit of language which expresses a complete thought.
In simple words, a sentence is a set of words that contain a subject and a predicate.
- A subject ( what the sentence is about, the topic of the sentence).
- A predicate ( what is said about the subject).
There are three important characteristics of a sentence:-
It expresses a complete thought or idea.
Example:- green tree is the (it is a group of words but it is not a sentence because it is meaningless)
The Tree is green (it is a sentence because it is meaningful)
2. It must have a subject and a verb. Sometimes, subject is not given but it is understandable.
Example:- Put the pen there (in this subject is not given but you is implied subject here)
3. It is the most important characteristic of sentence. The meaning of any sentence is different based on different expression. This expression may be of a statement, a question, a command or any exclamation.
TYPES OF SENTENCES
- Declarative sentence
- Interrogative sentence
- Imperative sentence
- Exclamatory sentence
1. Declarative sentence:- Declarative sentences are those to tell information about anything. They end with a period. Example:-
He is a handsome boy. (Here we are defining the beauty of a girl). They all are end with a period.
2. Interrogative sentences:-Interrogative sentences are used to ask a question. They are end with a question mark. They starts with Wh words Like- who, where, whom, what, when,why and so on. Whenever we ask a question we use Interrogative sentences. For example:-
- Where are you?
- Whose pencil is this?
- What are you doing?
- When it happens?
3. Imperative sentences:-Imperative sentences are those which are gives command or instruction and ask for request. They end with period and exclamation mark depending on how forcefully say any sentence. If sentence is spoken more forcefully and the exclamation mark is used otherwise a period is used. Example:-
- Shut the front door
- Wait for me!
Whenever we are giving a command and asking for the request these sentences(Imperative) are used.
4. Exclamatory sentences:-Exclamatory sentences are used to express strong feelings and emotions ( end with a exclamation mark). When we are happy, angry or surprised we are used exclamation to express out our emotion. Example:-
- What a beautiful dress.
- She is a such a nice girl.
English Sentences We Use in Our Daily Life
English Sentences We Use in Our Daily Life:There are many words and sentences, we use daily. Our communication will incomplete without words and sentences.
Some special words and sentences are used in our daily life. It can know as daily routine words.
| in Hindi | in English |
| सीधे खड़े रहो, झुको नहीं | |
Stand upright, don’t bend. |
| आमदनी से ज्यादा खर्च न करो | | Don’t spend more than you earn. |
| हिसाब साफ़ रखो | | Keep the accounts clear. |
| मेरे पास नकद रुपया नहीं है | | I don’t have any cash. |
| रूपये की कमी है | | There is shortage of funds/ cash. |
| मैं पैसो का भूखा नहीं हूँ | | I am not after money. |
| क्या आप मुझे 100 रुपया उधार देंगे? | Can you lend me 100 Rupees? |
| यह खोटा सिक्का नहीं है | | This is not the base coin. |
| सब रुपये खर्च हो गए हैं | | All the money has been spent. |
| अपनी आदतें सुधारो | |
Mend your ways. |
| जितना हो सके साफ़ लिखो | | Write as neatly as you can. |
| मेहनत की आदत डालो| |
Cultivate the habit of hard working. |
| मुझे यह जानकार दुःख हुआ| | I was sorry / pained to hear this. |
| मैं आपसे माफ़ी चाहता हूँ | | I beg your pardon. |
| माफ़ी मत मांगिये , कोई बात नहीं| |
Don’t apologize, it does not matter. |
| आप आपे से बाहर क्यों हो रहे हो ? | Why are you losing your temper? |
|
सावधान| यह दोबारा मुंह से न निकालना| |
Beware! Don’t utter it again. |
| तुम बड़े चिडचिडे स्वभाव के हो| | You are very short-tempered. |
| उसमे मेरी नाक में दम कर रखा हैं | | He has got on my nerves. |
| जो हो सो हो| | Come what may! |
| मैंने तुम्हारा क्या बिगाड़ा है ? |
What harm/ wrong have I done to you? |
| तुम्हे अपने आप को सुधारना पड़ेगा | | You will have to mend your ways. |
|
क्यों इससे व्यर्थ में झगडा मोल लेते हो ? |
Why do you quarrel with him unnecessarily? |
| आवेश में न आओ | | Don’t get worked up or excited. |
| अब किसी न किसी तरह बात को निपटाओ | | Now settle the matter somehow. |
| क्या आपके होश ठिकाने हैं ? | Are you in your senses? |
| मेरी आँखों से दूर हो जाओ | | Get out of my sight. |
| आपका हमारी बातों से क्या सम्बन्ध ? |
How are you concerned with our affairs? |
| बात को अधिक न बढाओ| | Don’t stretch the matter further. |
| भाड में जाओ | | Go to hell. |
| झगडे का फैसला हो गया | | The quarrel is settled. |
| आप बुरा न माने| | Please don’t mind. |
| मैं तो मज़ाक कर रहा था| | I was just kidding. |
| माफ़ कीजिए, मैं समय पर नहीं आ सका| | I am sorry, I got late. |
| कोई हर्ज़ नहीं | | That’s all right. |
| चुल्लूभर पानी में डूब मरो | |
Shame on you or you should be ashamed of yourself. |
| तुम बड़े चालू आदमी हो | | You are an extremely cunning man. |
| तुम बड़े नीच / धूर्त हो | | You are a mean/ cunning fellow. |
| बक बक मत करो | |
Don’t talk none sense. or Stop Yapping. |
|
मैं तुम्हारी सूरत नहीं देखना चाहता | |
I don’t want to see your face. |
| यह सब तुम्हारे कारण हुआ | | It’s all because of you. |
| तुम इससे बच नहीं सकते | | You can’t escape from this. |
| तुम्हे कभी माफ़ नहीं किया जा सकता | | You can never be forgiven. |
| इसके ज़िम्मेदार तुम हो| | You are responsible for this. |
| मैं हूँ जो हूँ | | I am who I am. |
| जल्दी काजिये | | Make it quick. |
| मुंह मत बनाओ | | Don’t make faces. |
| हमें किसी चीज़ की कमी नहीं है | | We lack nothing. |
| यह मुफ्त का है| | It’s for free. |
| मुझ पर हमला किया गया | | I was assaulted. |
| क्यों गला फाड़ के चिल्ला रहे हो ? |
Why are you shouting at the top of your voice. |
| मैं वैसे ही चला गया| | I dropped in casually. |
| मुझे बहुत सी बातें करनी है | | I have a lot to talk about. |
| कल मिलेंगे । | See you tomorrow. |
| बैठ जाओ । | Sit down. |
| खड़े हो जाओ । | Stand up. |
| दूर ले जाओ । | Take away. |
| ध्यान रखना । | Take care. |
| यह लो । | Take it. |
| भगवान का लाख लाख शुक्र है । | Thank God. |
| पक्ष लेने के लिये धन्यवाद । | Thanks for the favour. |
| इस सम्मान के लिये धन्यवाद । | Thanks for the honour. |
| बहुत है । | That is much. |
| बहुत ज्यादा है । | That is too much. |
| बस काफी है । | That’s enough. |
| कहीं नजर ना लगे! | Touch wood! |
| अच्छी बात है । | Very good. |
| बहुत अच्छा । | Very well. |
| बाहर इंतज़ार करो । | Wait outside. |
| आइए ! | Welcome! |
| क्यों नही? | Why not? |
| हां जरूर (सभी तरह से) | Yes, by all means. |
| हां | Yes/Yep |
| दूर जाओ । | Go away. |
| सीधे जाओ । | Go straight. |
| वहां जाओ । | Go there. |
| अच्छा चलते है! | Goodbye! |
| बहुत है । | It’s too much. |
| मैं अभी आ रहा हूँ । | Just coming. |
| चुप रहो । | Keep mum. |
| चुप रहो । | Keep quiet. |
| कभी नही । | Never. |
| कोई बात नही । | No problem. |
| नही, कभी नही । | No, not at all. |
| थोड़ा सा भी नही । | Not a bit. |
| जरा सा भी नहीं! | Not the least! |
| और कुछ नही । | Nothing else. |
| कोई खास बात नही | Nothing special. |
| अच्छा । | O.K. |
| बेशक/हां, हां । | Of course. |
| बन्द करो/समेटो । | Pack up. |
| भरोसा रखें । | Rest Assured. |
| फिर मिलेंगे । | See you again. |
| एकदम/बिल्कुल | Absolutely |
| और कुछ? | Anything else? |
| जैसी आपकी मर्जी । | As you please/As you like. |
| जैसा आप चाहे । | As you wish. |
| सावधान रहो । | Be careful / Be cautious. |
| गंभीर बनो । | Be serious. |
| आपको विदा! | Bye bye! |
| हां जरूर | Certainly |
| शांत रहिये | Chill please. |
| इसे साफ करो । | Clear it. |
| यहां आओ । | Come here. |
| पास आओ । | Come near. |
| अब चाहे जो हो! | Come what may! |
| कोई बात नही । | Doesn’t matter. |
| शरारती मत बनो । | Don’t be naughty. |
| अच्छी बात है । | Fine. |
| उतर जाओ । | Get off |
| निकल जाओ । | Get out |
| तैयार हो जाओ । | Get ready/Be ready |
| तुरन्त जाओ । | Go at once. |
| मुद्देपरआओ | Come to the point. |
| अपने काम पर ध्यान दो | Mind your own business |
| जगह खाली करो | Vacate your place. |
| जैसी आपकी मर्ज़ी | As you wish. |
| कृपया बैठिए | Please be seated. |
| कृपया थोड़ा सा इंतज़ार करें | Please wait for a bit. |
| बकवास मत करो | Do not talk nonsense. |
| खाली मत बैठो | Do not Seat idle. |
| दूसरों पर मत हंसो | Do not laugh at others. |
| कृपया यहाँ हस्ताक्षर कीजिये | Please sign here. |
| बाद में वापस आता हूँ | Be back later |
| अभी वापस आता हूँ | Be right back. |
| वैसे | By the way. |
| मुझे नहीं पता | I don’t know. |
| मेरी राय में | In my opinion. |
| बाद में बात करते हैं | Talk to you later. |
| असल ज़िन्दगी में | In real life. |
Do you need to know about daily use sentences and words that make your communication fluent and easy?
We collect 1000 words and sentences. It can find on our englishgrammar10.Com blog.
We hope that this matter will help you a lot in knowing English Grammar Topics. For more grammar notes you can visit our website daily.
Thank you!
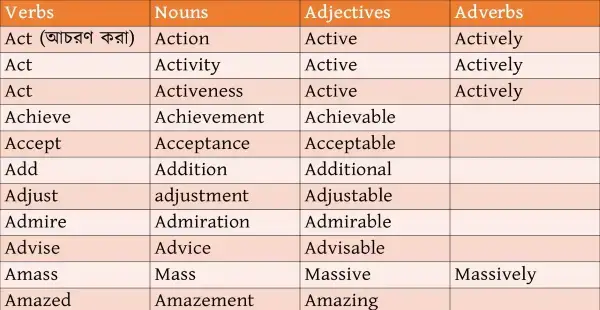
See the vedio of full article on the list of nouns, verbs adjectives & adverbs
Noun : The name of something is called noun. Generally it may be person,place,things or idea. Noun can be singular or plural . Noun is often used with article (a,an,the) but not in all time. Proper Noun begins with Capital letter. Suppose – The Amazon river is the biggest river of the world. Some examples of Noun: Newyork, Justine, Sundarbans etc.
Pronoun : Pronoun is a word that is the substitute of noun. Pronoun is used in replace of noun or noun phrase. Pronoun are 9 in types: Personal Pronoun– he,they we. Demonstrative Pronoun– this,that,these. Interrrogative pronoun– who,which,whose .Indefinite pronoun– None,several, any . Possessive Pronoun– ours,their,my,his . Reciprocal Pronoun– each other,one another . Relative Pronoun– Who,which,that . Reflexive Pronoun– itself,himself,ourselves. Intensive Pronoun– Mainly Intensive pronouns are used to emphasize their antecedent .Like I myself do this task.
Verb: Verb indicates the action. The action of something is called verb. Sometimes the main verb takes helping verbs. He can do the job. Here ‘can’ is a helping verb. Verbs are 3 types: Action verbs, helping verbs and Linking verbs. Action verbs: eat, go, make etc. Helping verbs: The verb that helps the main verb. Jessika could learn to drive car. Linking Verbs: The verbs that mainly works as a connector between subject and object as a same thing. Austin became an entrepreneur.
Adjectives: Adjective is the word that modifies noun or pronouns. Examples- The nice girl is dancing on the stage.
Adverbs: The word that modify verbs, adjectives or another adverb. Generally, adverbs give the answer of the question where, how, when or under which condition.
Preposition: Preposition is a word that place before noun or pronoun. Example- The dog jumped out of the moving train. With, at, in, on, before, without etc.
Conjunctions: The word Conjunctions make joining between two or more sentences or phrases. Example- and, but, or etc.
Interjection: The word interjection is used to express emotion. Example- oh!… wow! oops!
| Verbs | Nouns | Adjectives | Adverbs |
| Act (আচরণকরা) |
Action | Active | Actively |
| Act | Activity | Active | Actively |
| Act | Activeness | Active | Actively |
| Achieve | Achievement | Achievable | |
| Accept | Acceptance | Acceptable | |
| Add | Addition | Additional | |
| Adjust | adjustment | Adjustable | |
| Admire | Admiration | Admirable | |
| Advise | Advice | Advisable | |
| Amass | Mass | Massive | Massively |
| Amazed | Amazement | Amazing |
| Verbs | Nouns | Adjectives | Adverbs |
| Amuse | Amusement | Amazing | |
| Annoy | Annoyance | Annoying | |
| Approach | Approach | Approachable | |
| Attend | Attention | Attentive | |
| Attract | Attraction | Attractive | |
| avoid | Avoidance | Avoidable | |
| Believe | Belief | Believable | |
| Blacken | Blackness | Black | |
| Bleed | Blood | Bloody | |
| Bore | Boredom | Boring | |
| Bother-বিরকত | Botheration | Bothering |
nouns,verbs, adjectives, adverbs
| Verbs | Nouns | Adjectives | Adverbs |
| Breathe | Breath | Breathing | |
| Bury | Burial | Buried | |
| Care | Care | Careful | Carefully |
| Chase | Chase | Chasing | |
| Choose | Choice | Chosen | |
| Cheer | Cheerfulness | Cheerful | Cheerfully |
| Challenge | Challenge | Challenging | |
| Clear | Clarity | Clear | Clearly |
| Collect | Collection | Collective | Collectively |
| Comfort | Comfort | Comfortable | Comfortably |
| Complex | Complexity | Complex |
| Verbs | Nouns | Adjectives | Adverbs |
| Consider | Consideration | Considerable | Considerably |
| Confuse | Confusion | Confused | |
| Console | Consolation | Consoled | |
| Continue | Continuity | Continuous | Continuously |
| Craze | Craze | Crazy | Crazily |
| Create | Creation | Creative | Creatively |
| Cure | Cure | Curable | |
| Credit | Credit | Creditable | Creditably |
| Curse | Curse | Cursed | |
| Decide | Decision | Decisive | |
| Delight | Delight | Delightful | Delightfully |
| Verbs | Nouns | Adjectives | Adverbs |
| Damage | Damage | Damaged | |
| Deafen | Deafness | Deaf | |
| Decorate | Decoration | Decorative | |
| Demand | Demand | Demanding | |
| Deserve | Deserve | Deserving | |
| Derive | Derivation | Derivative | |
| Develop | Development | Developing | |
| Destroy | Destruction | Destructive | Destructively |
| Die | Death | Dead | |
| Distrub | Disturbance | Disturbing | |
| Dust | Dust | Dusty |
| Verbs | Nouns | Adjectives | Adverbs |
| Empower | Power | Powerful | |
| Embarrass | Embarrassment | Embarrassing | |
| Educate | Education | Educative | |
| Empty | Emptiness | Empty | |
| Encourage | Courage | Courageous | Courageously |
| Encircle | Circle | Circular | Circularly |
| Endanger | Danger | Dangerous | Dangerously |
| Enumerate | Number | Numberable | |
| Enthuse | Enthusiasm | Enthusiastic | |
| Evaporate | Evaporation | Evaporating | |
| Envy | Envy | Envious | Enviously |
| Verbs | Nouns | Adjectives | Adverbs |
| Explain | Explanation | Explainable | |
| Expect | Expectation | Expected | Expectedly |
| Explore | Exploration | Exploring | |
| Firm | Firmness | Firm | Firmly |
| Feed | Food | ||
| Fly | Flight | Flying | |
| Force | Force | Forceful | Forcefully |
| Grow | Growth | Growing | Growingly |
| Glorify | Glory | Glorious | Gloriously |
| Hate | Hatred | Hateful | Hatefully |
| Harm | Harm | Harmful | Harmfully |
| Verbs | Nouns | Adjectives | Adverbs |
| Hope | Hope | Hopeful | Hopefully |
| Heal | Health | Healthy | Healthily |
| Identify | Identity | Identifying | |
| Indentify | Identification | Identified | |
| Imitate | Imitation | Imitative | Imitatively |
| Impress | Impression | Impressive | Impressively |
| Indicate | Indication | Indicative | Indicatively |
| inhabit | Habitat | Inhabitant | |
| include | Inclusion | Inclusive | Inclusively |
| Inform | Information | Informative | |
| Injure | Injury | Injurious |
| Verbs | Nouns | Adjectives | Adverbs |
| Instruct | Instruction | Instructive | |
| Inquire | Inquiry | Inquiring | |
| Intent | Intention | Intentional | Intentionally |
| Insult | Insult | Insulting | Insultingly |
| Introduce | Introduction | Introductory | |
| Interfere | Interference | Interfering | |
| Irritate | Irritation | Irritating | |
| Invent | Invention | Inventive | |
| Lose | Loss | Lost | |
| Lead | Leadership | Leading | Leadingly |
| Live | Life | alive | livingly |
| Verbs | Nouns | Adjectives | Adverbs |
| Live | Life | Lively | Livingly |
| Live | Liveliness | Lively | Livingly |
| Migrate | Migration | Migrating | |
| Madden | Madness | Mad | Madly |
| Modernise | Modernity | Modern | |
| Monotonies | Monotony | Monotonous | Monotonously |
| Moisten | Moisture | Moistures | |
| Move | Movement | Movable | Movingly |
| Nationalise | Nationality | National | Nationwide |
| Narrow | Narrowness | Narrow | |
| Own | ownership | Own |
| Verbs | Nouns | Adjectives | Adverbs |
| Permit | Permission | Permissible | |
| Please | Pleasure | Pleasant | |
| Perform | Performance | Performing | |
| Persuade | Persuasion | Persuasive | |
| Popularise | popularity | Popular | |
| Quicken | Quickness | Quick | Quickly |
| Redden | Redness | Red | |
| Secure | Security | Secured | Securely |
| Sadden | Sadness | Sad | Sadly |
| Speed | Speed | Speedy | Speedily |
| See | Scene | Scenic |
| Verbs | Nouns | Adjectives | Adverbs |
| See | Sight | Seen | |
| Whiten | Whiteness | White |
Above these are the list of nouns,verbs, adjectives, adverbs
Parts of Speech: Nouns, Verbs, Adjectives, and Adverbs
https://schooltutoring.com/help/wp-content/uploads/sites/2/2019/02/e7aeff85f4e66b14d1098dc84ec3-1458231.png
1200
1200
Teaching Staff
Teaching Staff
https://secure.gravatar.com/avatar/d96b825901af08f4b20fdfa2d056868f?s=96&d=mm&r=g
February 28, 2019
February 28, 2019
There are several different parts of speech, which are categories of types of words. We are going to talk about four of the main eight parts of speech, which are nouns, verbs, adjectives, and adverbs. Understanding the parts of speech will teach you to use words properly in a sentence and become a better writer.
Nouns
A noun is a person, place, or thing
Some examples of a person are: sister, friend, Alex, Stephanie, you, me, dog
Examples of places are: house, beach, New York, playground, the store
Things (can be physical things or ideas): chair, pencil, thoughts, memories, and knowledge.
Verbs
Verbs are action words! They are used to describe things that nouns do!
An example of a verb would be “run”. Run is a word to describe someone or something who is moving faster than a walking speed.
Other examples of verbs include: sing, watch, play, sleep, study, walk, and think.
Adjectives
Adjectives are describing words. They are used to describe nouns.
An example of an adjective would be “beautiful”. Beautiful is a word to describe someone or something. For example, the sky is beautiful. Since the sky is a noun, and beautiful is used to describe it, that makes beautiful an adjective.
Other examples of adjectives are: blue, dark, warm, happy, good, and fast.
Adverbs
Adverbs are words that describe verbs.
For example, quickly is an adverb because if you say you walk quickly, walk is the verb, and quickly is describing how you walk. Therefore, quickly is an adverb. An easy way to spot an adverb is by their ending, since they often end in the letters ly, like quickly.
Other examples of adverbs include: nicely, proudly, slowly, and firmly.
Some words can be used as either a noun, verb, adjective, or an adverb. Usually though, you’ll have to change the endings of the words depending on how you want to use them. The following chart has some examples of words that you can change to be different parts of speech.
| Noun | Verb | Adjective | Adverb |
| decision | decide | decisive | decisively |
| creation | create | creative | creatively |
| sadness | sadden | sad | sadly |
| action | act | active | actively |
| quickness | quicken | quick | quickly |
| heal | health | healthy | healthily |
SchoolTutoring Academy is the premier educational services company for K-12 and college students. We offer tutoring programs for students in K-12, AP classes, and college. To learn more about how we help parents and students in Columbus, Ohio visit: Tutoring in Columbus, Ohio.




