Excel for Microsoft 365 Excel for Microsoft 365 for Mac Excel for the web Excel 2021 Excel 2021 for Mac Excel 2019 Excel 2019 for Mac Excel 2016 Excel 2016 for Mac Excel 2013 Excel 2010 Excel 2007 Excel for Mac 2011 Excel Starter 2010 More…Less
Use the NOT function, one of the logical functions, when you want to make sure one value is not equal to another.
Example
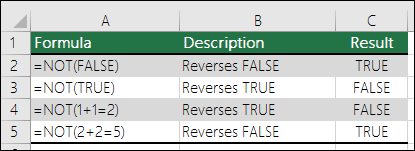
The NOT function reverses the value of its argument.
One common use for the NOT function is to expand the usefulness of other functions that perform logical tests. For example, the IF function performs a logical test and then returns one value if the test evaluates to TRUE and another value if the test evaluates to FALSE. By using the NOT function as the logical_test argument of the IF function, you can test many different conditions instead of just one.
Syntax
NOT(logical)
The NOT function syntax has the following arguments:
-
Logical Required. A value or expression that can be evaluated to TRUE or FALSE.
Remarks
If logical is FALSE, NOT returns TRUE; if logical is TRUE, NOT returns FALSE.
Examples
Here are some general examples of using NOT by itself, and in conjunction with IF, AND and OR.
|
Formula |
Description |
|---|---|
|
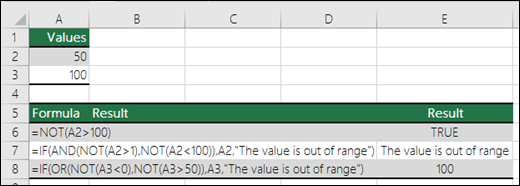
=NOT(A2>100) |
A2 is NOT greater than 100 |
|
=IF(AND(NOT(A2>1),NOT(A2<100)),A2,»The value is out of range») |
50 is greater than 1 (TRUE), AND 50 is less than 100 (TRUE), so NOT reverses both arguments to FALSE. AND requires both arguments to be TRUE, so it returns the result if FALSE. |
|
=IF(OR(NOT(A3<0),NOT(A3>50)),A3,»The value is out of range») |
100 is not less than 0 (FALSE), and 100 is greater than 50 (TRUE), so NOT reverses the arguments to TRUE/FALSE. OR only requires one argument to be TRUE, so it returns the result if TRUE. |
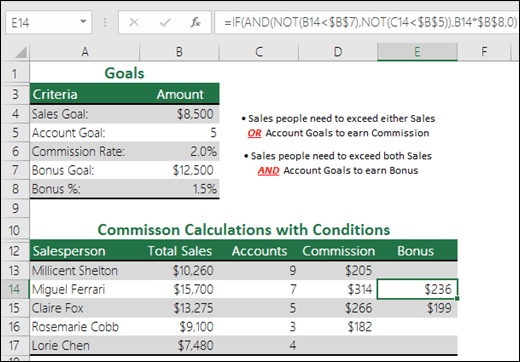
Sales Commission Calculation
Here is a fairly common scenario where we need to calculate if sales people qualify for a bonus using NOT with IF and AND.
-
=IF(AND(NOT(B14<$B$7),NOT(C14<$B$5)),B14*$B$8,0)— IF Total Sales is NOT less than Sales Goal, AND Accounts are NOT less than the Account Goal, then multiply Total Sales by the Commission %, otherwise return 0.
Need more help?
You can always ask an expert in the Excel Tech Community or get support in the Answers community.
Related Topics
Video: Advanced IF functions
Learn how to use nested functions in a formula
IF function
AND function
OR function
Overview of formulas in Excel
How to avoid broken formulas
Use error checking to detect errors in formulas
Keyboard shortcuts in Excel
Logical functions (reference)
Excel functions (alphabetical)
Excel functions (by category)
Need more help?
Want more options?
Explore subscription benefits, browse training courses, learn how to secure your device, and more.
Communities help you ask and answer questions, give feedback, and hear from experts with rich knowledge.
NOT in Excel
NOT function is an inbuilt function that is categorized under the Logical Function; the logical function operates under a logical test. It is also called Boolean logic or function. Boolean functions are most commonly used along with or in conjunction with other functions, specifically along with conditional test functions (“IF’’ FUNCTION), to create formulas that can evaluate multiple parameters or criteria and produce desired results depending on that criteria. It is used as an individual function or part of the formula and other excel functions in a cell. E.G. with AND, IF & OR function. It returns the opposite value of a given logical value in the formula, NOT function is used to reverse a logical value. If the argument is FALSE, then TRUE is returned and vice versa.
Note: Use NOT function when you want to make sure a value is not equal to one Specific or particular value
It’s a worksheet function; it is also used as part of the formula in a cell along with other excel function
- If given with the value TRUE, the Not function returns FALSE
- If given with the value FALSE, the Not function returns TRUE
NOT Formula in Excel
Below is the NOT Formula in excel:
=NOT (logical) logical – A value that can be evaluated to TRUE or FALSE
The only parameter in the NOT function is a logical value.
The logical test or argument can be either entered directly, or it can be entered as a reference to a cell that contains a logical value, and it always returns the Boolean value (“TRUE” OR “FALSE”) only.
How to Use the NOT Function in Excel?
NOT Function in Excel is very simple and easy to use. Let us now see how to use the NOT function in excel with the help of some examples.
You can download this NOT function Excel Template here – NOT function Excel Template
Example #1 – Excel NOT Function
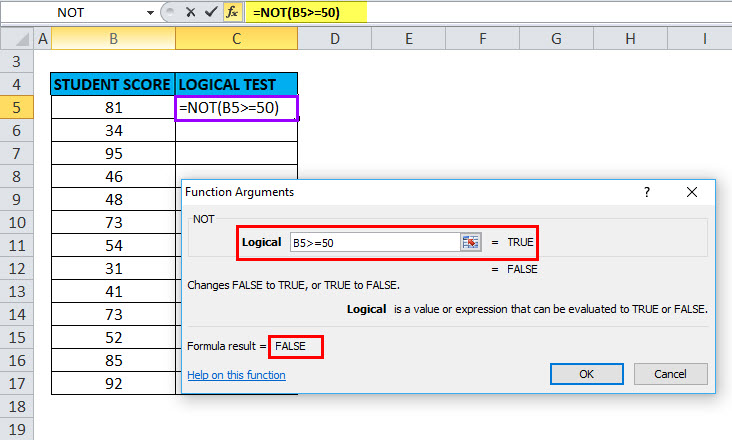
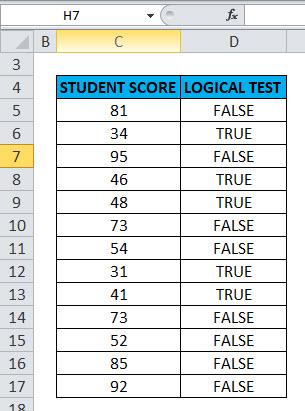
Here a logical test is performed on the given set of values (Student score) by using the NOT function. Here, we will check which value is greater than or equal to 50.
In the table, we have 2 columns, the first column contains student score & the second column is the logical test column, where the NOT function is performed.
Result: It will return the reverse value if the value is greater than or equal to 50, then it will return FALSE and if the lesser than or equal to 50, it will return TRUE as output.
The result will be as given below:
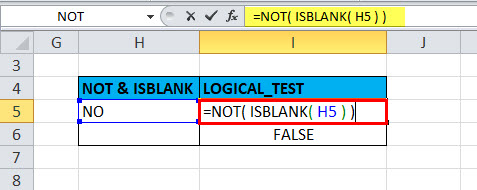
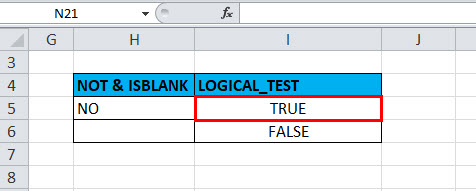
Example #2 – Using NOT Function with ISBLANK
the logical test is performed on the H5 & H6 Cells by using the NOT Function along with ISBLANK function; here will check if cells H5 & H6 is blank OR not using NOT function along with ISBLANK in excel
OUTPUT will be TRUE.
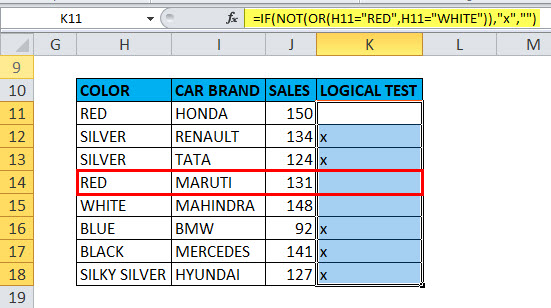
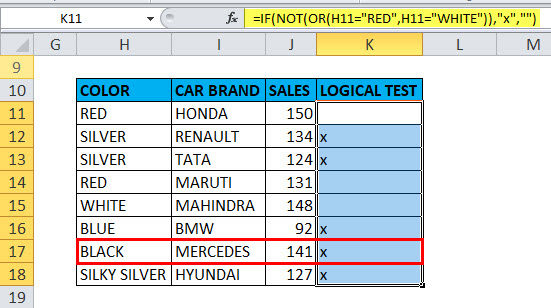
Example #3 – NOT Function along with “IF” and “OR” Function
Here the color check is performed for the cars in the below-mentioned table by using NOT Function along with “if” and “or” function
Here we have to sort out color “WHITE” or “RED” from the given set of data
=IF(NOT(OR(H11=”RED”,H11=”WHITE”)),”x”,””) formula is used
This logical condition is applied on a Color column containing any car with color “RED” or “WHITE”,
if the condition is true, then it will return blank as output,
if not true, then it will return x as output
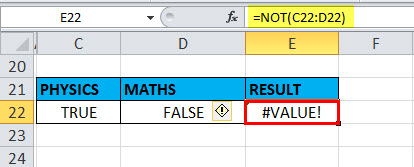
Example #4 – VALUE! Error
It Occurs when the supplied argument is not a logical or numeric value.
Suppose, if we give a range in the logical argument
Selected the range C22:D22 in the logical argument, i.e. =NOT (C22:D22)
a function returns a #VALUE error because the NOT function does not allow any range and can take only a logical test or argument or one condition.
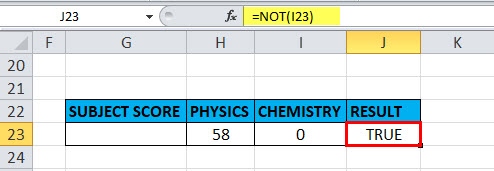
Example #5 – NOT Function for an empty cell or blank or “0”
An empty cell or blank or “0” are treated as false, therefore “NOT” function returns TRUE
Here in the cell “I23”, the stored value is “0” suppose if I apply the “NOT” function with logical argument or value as “0” or “I23”, Output will be TRUE.
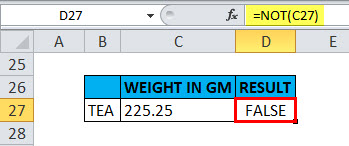
Example #6 – NOT Function for Decimals
When the value is decimal in a cell
Suppose if we take the argument as decimals, i.e. suppose if I apply the “NOT” function with logical argument or value as “225.25” or “c27”, Output will be FALSE.
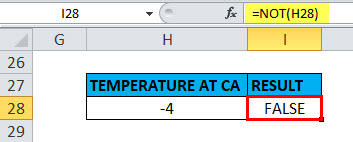
Example #7 – NOT Function for Negative Number
When the value is a negative number in a cell
Suppose if we take the argument as a negative number, i.e. suppose if I apply the “NOT” function with logical argument or value as “-4” or “H27”, Output will be FALSE.
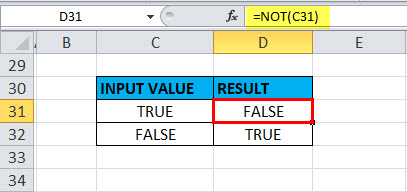
Example #8 – When the value or Reference is Boolean Input in NOT Function
When the value or reference is Boolean input (“TRUE” OR “FALSE”) in a cell.
Here in the cell “C31”, the stored value is “TRUE” suppose if I apply the “NOT” function with logical argument or value as “C31” or “TRUE”, Output will be FALSE. It will be vice versa if the logical argument is “FALSE”, i.e. the NOT function returns the “TRUE” value as output.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to NOT Function. Here we discuss the NOT Formula and how to use the NOT function along with practical examples and downloadable excel templates. You can also go through our other suggested articles –
- FV Function in Excel
- LOOKUP in Excel
- MINVERSE in Excel
- Write Formula in Excel
The NOT Excel function is a logical function in Excel called the negation function. It negates the value returned through a function or a value from another logical function. This built-in function in Excel takes a single argument: the logic, which can be a formula or a logical value.
For example, suppose we inserted the Excel NOT function in the dataset and conducted the logical test. As a result, it may return the opposite of a given logical or Boolean value. Suppose one value is TRUE, NOT function returns as FALSE. And when the given value is FALSE, NOT function may return TRUE. The NOT function can reverse a logical value.
Table of contents
- NOT Function in Excel
- Syntax
- Compulsory Parameter:
- Examples
- Example #1
- Example #2
- Example #3
- Example #4
- Recommended Articles
- Syntax
Syntax
Compulsory Parameter:
- Logical: The numeric value 0 is considered “False,” and the rest of the values are considered “True.” Logical is an expression that either calculates the TRUE or FALSE if it returns TRUE if the expression is FALSE and returns FALSE if the expression is TRUE.
Examples
You can download this NOT Function Excel Template here – NOT Function Excel Template
Example #1
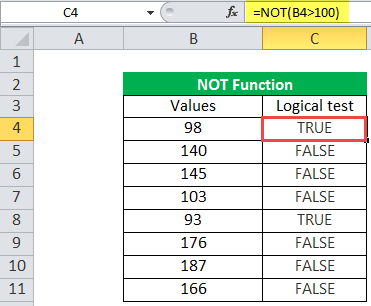
We must check which value is greater than 100; then, we can use the NOT function in the Logical testA logical test in Excel results in an analytical output, either true or false. The equals to operator, “=,” is the most commonly used logical test.read more column. It will return the reverse return if the value is greater than 100, then it will return FALSE, and if the value is less than or equal to 100, it will return the TRUE as output.
Example #2
Let us consider another example wherein we must exclude the color combination red and blue from the toy data set. Then, we can use the NOT function to filter out this combination. But, again, the output will be TRUE because the color is red here.
Example #3
Let us take the employee data wherein we must find the bonus amount for employees who did the extra task and no bonus for those who did not perform the additional task, and employees get ₹100 for each extra task.
The output will be = ₹7500 as it will first check for a blank entry in a cell. If not empty, it will multiply the extra task and 100 to calculate the bonus unlocked by the employee.
Example #4
Suppose we have to check colors, such as for the example below, we have to filter out the toy name with the color blue or red from the given data set.
First, this will check the condition if the color column contains any toy with blue or red if the condition is TRUE, then it will return blank as output; if not TRUE, it will return x as output.
Recommended Articles
This article is a guide to NOT Function in Excel. We discuss using the NOT Excel function, examples, and downloadable Excel templates. You may also look at these useful functions in Excel: –
- VBA Not FunctionThe VBA NOT function in MS Office Excel VBA is a built-in logical function. If a condition is FALSE, it yields TRUE; otherwise, it returns FALSE. It works as an inverse function.read more
- Excel Mathematical FunctionMathematical functions in excel refer to the different expressions used to apply various forms of calculation. The seven frequently used mathematical functions in MS excel are SUM, AVERAGE, AVERAGEIF, COUNTA, COUNTIF, MOD, and ROUND.read more
- Error Handling in VBAVBA error handling refers to troubleshooting various kinds of errors encountered while working with VBA. read more
- Excel Recording MacrosRecording macros is a method whereby excel stores the tasks performed by the user. Every time a macro is run, these exact actions are performed automatically. Macros are created in either the View tab (under the “macros” drop-down) or the Developer tab of Excel.
read more - Hide Formula in ExcelHiding formula in excel is used when we do not want the formula to be displayed in the formula bar when we click on a cell with formulas. We can format the cells, check the hidden checkbox, and protect the worksheet.read more
Функция NOT (НЕ) в Excel используется для изменения логического выражения TRUE (Истина) / FALSE (Ложь).
Содержание
- Что возвращает функция
- Синтаксис
- Аргументы функции
- Дополнительная информация
- Примеры использования функции NOT (НЕ) в Excel
- Пример 1. Конвертируем значение TRUE (Истина) в FALSE (Ложь), и наоборот.
- Пример 2. Используем функцию NOT (НЕ) с результатом формулы
- Пример 3. Используем функцию NOT (НЕ) с числовыми значениями
Что возвращает функция
Логический аргумент, который является обратным логическому аргументу, используемому в функции NOT. Например, =NOT(TRUE) возвращает FALSE (Ложь) и =NOT(FALSE) возвращает TRUE(Истина).
Синтаксис
=NOT (logical) — английская версия
=НЕ(логическое_значение) — русская версия
Аргументы функции
- logical (логическое значение) — значение или выражение, которое может быть логически оценено как TRUE (Истина) или FALSE (Ложь)
Дополнительная информация
С помощью функции NOT (НЕ) в Excel вы можете проверить выражение, которое принимает значение TRUE или FALSE. Например, =NOT(1 + 1 = 2) вернет FALSE.

Примеры использования функции NOT (НЕ) в Excel
Пример 1. Конвертируем значение TRUE (Истина) в FALSE (Ложь), и наоборот.
Функция преобразует TRUE (Истина) в FALSE (Ложь) и FALSE (Ложь) в TRUE (Истина). Аргумент внутри функции также может быть результатом другой функции, результатом которой являются TRUE / FALSE.
Пример 2. Используем функцию NOT (НЕ) с результатом формулы
Если вы используете функцию с результатом какой-либо формулы (которая возвращает значения TRUE или FALSE), то она конвертирует результат TRUE в FALSE и наоборот. На примере выше, значение в ячейке А2 сравнивается с числом. По результату вычисления, при совпадении условий формулы, NOT (НЕ) выдаст FALSE, или отразит TRUE, если значение не совпадает с условиями.
Пример 3. Используем функцию NOT (НЕ) с числовыми значениями
В Excel, по умолчанию принято, что цифровое значение “0” (ноль) принимается за FALSE, а любое положительное значение — TRUE. Функция NOT (НЕ) при использовании с числами конвертирует “0” (ноль) в TRUE (Истина) и любое позитивное значение или отрицательное в FALSE (Ложь).
The Excel NOT function is categorized as a logical function. According to MS Excel, «The NOT function changes FALSE to TRUE, or TRUE to FALSE».
What we’re saying is that the function results in the opposite outcome of its fed parameters. The NOT function is beneficial in the cases where we wish to verify if a specific condition was not met.
We see the NOT function going way back to 2003 where it made its place in the Excel world with its other logical function friends.
Syntax
The unfussy syntax of the NOT function is as follows:
=NOT(logical)
Arguments:
logical – The value or condition to be tested.
Important Characteristics of NOT Function in Excel
- NOT function returns either «TRUE» or «FALSE» and can evaluate up to 255 conditions.
- If an argument is the number 0, the result will be «TRUE». Excel processes 0 as FALSE. The NOT function changes FALSE to TRUE.
- If no logical values are found in the formula, the function returns a #VALUE! error.
- If the formula has any typos or misspelling, the function returns a #NAME?
- The arguments can be numbers, cell references, defined names, formulas, functions, or text.
Examples of NOT Function
The talk is better when practically put to the test. So let’s see some examples to understand why the NOT function does the opposite of what it’s told.
Example 1 – Super Duper Basic NOT Function
Riddle time.
Question – What is not TRUE?
Answer: FALSE
Question – What is not FALSE?
Answer: TRUE
See how easy that was? That wasn’t even in Excel language. Working with Boolean parameters, bringing out this function’s ability could not get simpler than this:
=NOT(TRUE) //returns "FALSE"
=NOT(FALSE) //returns "TRUE"
We’re making the NOT function’s life too easy. We can make it work harder.
Example 2 – Plain Vanilla Version of NOT Function
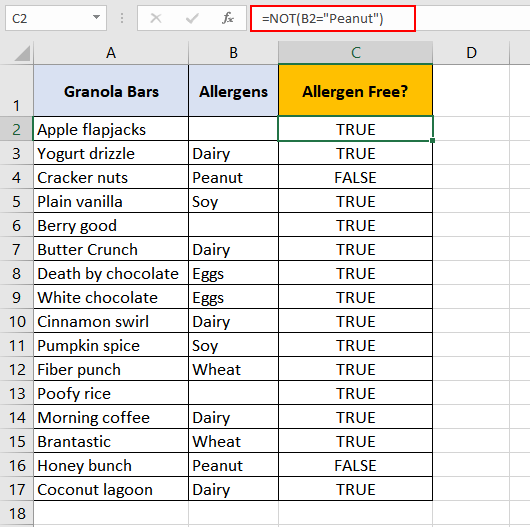
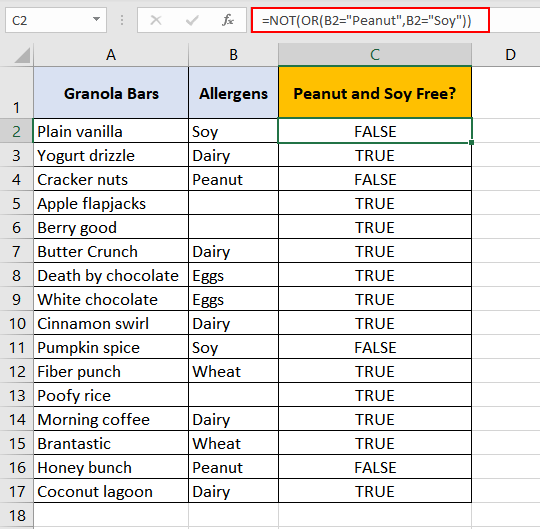
Let’s say Gina loves granola. We have granola bars enlisted with allergens that they contain since Gina has a severe peanut allergy.
Our objective here is to pick out the bars that contain peanuts so Gina can steer clear of them. That’s achievable with this formula:
=NOT(B2 = "Peanut")
What this formula is doing is looking up column B for the word «Peanut». Since the command is for the cell to not contain «Peanut», if the word «Peanut» is found, the result would be «FALSE». If it is not found, the result will be «TRUE».
- Cell «C2» asks cell «B2» ‘NOT Peanut?’. «B2» is blank, it’s TRUE, «B2» is ‘NOT Peanut’.
- Cell «C4» asks cell «B4» ‘NOT Peanut?’. «B4» is «Peanut», it’s FALSE.
Gina has to keep away from the «FALSE» results. Luckily, she has a lot of peanut-free options.
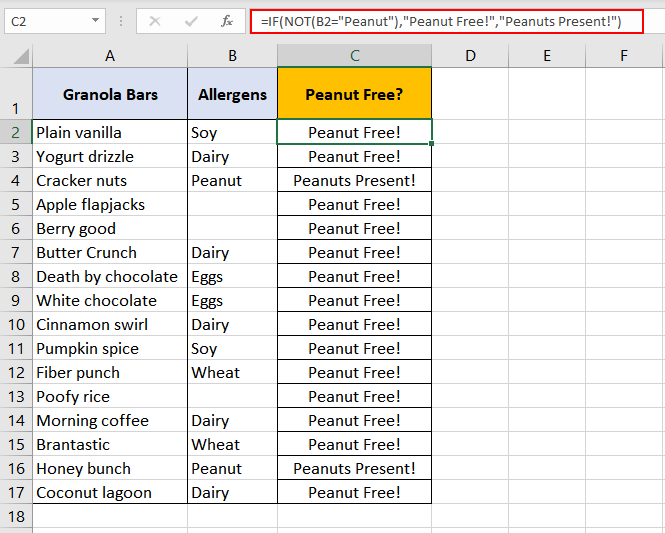
Example 3 – Use of NOT Function with IF Function
The role of an IF function is to return a value based on a stated condition. Bringing forward the example from above, we take a look at how the 2 functions go together.
The plus point here of using the NOT function within the IF function is that we can get:
- «Peanut Free!» instead of «TRUE» and
- «Peanuts Present!» instead of «FALSE»
as a result.
We use the following formula:
=IF(NOT(B2 = "Peanut"), "Peanut Free!", "Peanuts Present!")
Firstly, the NOT function starts its work, looks up the «B2» cell to check whether it contains «Peanut». NOT function finds «B2» cell blank, which implies «B2» is «NOT» equal to «Peanut». And thus, the result of the NOT function is «TRUE».
The result is passed onto the IF function where the corresponding value for TRUE is «Peanut Free!». Hence the IF function returns «Peanut Free!» as a result.
Example 4 – NOT «X» OR «Y»
The OR function can be used to evaluate an array of values and determine whether the condition specified is met in at least one value or not. Let’s carry forward the example above.
It turns out Gina isn’t as lucky as we thought; she is also allergic to soy! Which means her favorite granola bars need to be peanut and soy-free. Let’s help her.
We need to find granola bars that do not contain peanuts or soy. To find these two allergens, the formula we’ve applied is:
=NOT(OR(B2 = "Peanut", B2 = "Soy"))
The OR function has been asked to check cells from B2 to B17 and see whether they contain
- «Peanut» or
- «Soy».
The OR function finds «B2» contains «Soy». Since one argument of the function is fulfilled, the result is «TRUE». This result is passed onto the NOT function.
The NOT function flips «TRUE» to «FALSE».
The core purpose of having the NOT function here anyway is to find out whether «B2» is NOT «Peanut» OR «Soy». So as the greater picture, the result is also «FALSE» and that is the result returned in C2.
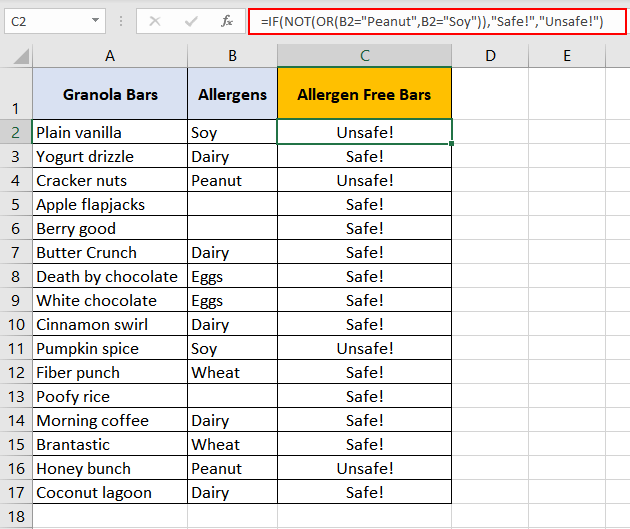
IF NOT «x» OR «y»
To attain the same customized result seen in Example 3, we can easily incorporate the IF function by this formula:
=IF(NOT(OR(B2 = "Peanut", B2 = "Soy")),"Safe!","Unsafe!")
The results are in column C. Adding the IF function has customized the results into:
- «Safe!» instead of «TRUE» and
- «Unsafe!» instead of «FALSE».
That would be it. NOT the last you hear from us. Since we talked so much about granola bars, you know what else you can do on Excel?
You can make a pie chart of your favorite bars.
And a bar graph of your favorite pies.
We’ll be back with more… functions, not jokes.
Purpose
Reverse arguments or results
Usage notes
The NOT function returns the opposite of a given logical or Boolean value. Use the NOT function to reverse a Boolean value or the result of a logical expression.
- When given FALSE, NOT returns TRUE.
- When given TRUE, NOT returns FALSE.
Example #1 — not green or red
In the example shown, the formula in C5, copied down, is:
=NOT(OR(B5="green",B5="red"))
The literal translation of this formula is «NOT green or red». At each row, the formula returns TRUE if the color in column B is not green or red, and FALSE if the color is green or red.
Example #2 — Not blank
A common use case for the NOT function is to reverse the behavior of another function. For example, If cell A1 is blank (empty), the ISBLANK function will return TRUE:
=ISBLANK(A1) // TRUE if A1 is empty
To reverse this behavior, wrap the NOT function around the ISBLANK function:
=NOT(ISBLANK(A1)) // TRUE if A1 is NOT empty
By adding NOT the output from ISBLANK is reversed. This formula will return TRUE when A1 is not empty and FALSE when A1 is empty. You might use this kind of test to only run a calculation if there is a value in A1:
=IF(NOT(ISBLANK(A1)),B1/A1,"")
Translation: if A1 is not blank, divide B1 by A1, otherwise return an empty string («»). This is an example of nesting one function inside another.
The TRUE function in Excel is intended to indicate a logical true value and returns it as a result of calculations.
The FALSE function in Excel is used to specify a logical false value and returns it accordingly.
The NOT function in Excel returns the opposite of the specified logical value. For example, writing = NOT (TRUE) will return the result FALSE.
Examples of using the logical functions true, false and not in Excel
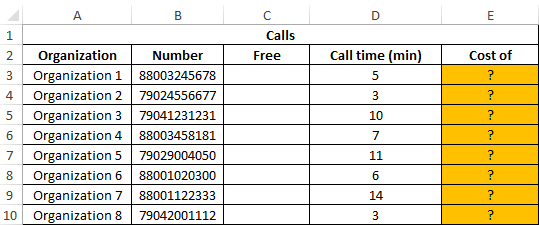
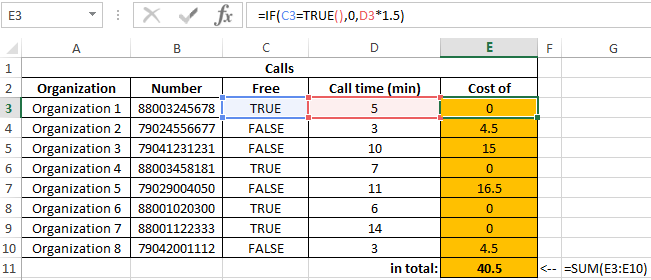
Example 1. The Excel spreadsheet stores the phone numbers of various organizations. Calls to some of them are free of charge (code 8800), while the rest are charged at the rate of 1.5 rubles per minute. Determine the cost of calls made.
Data table:
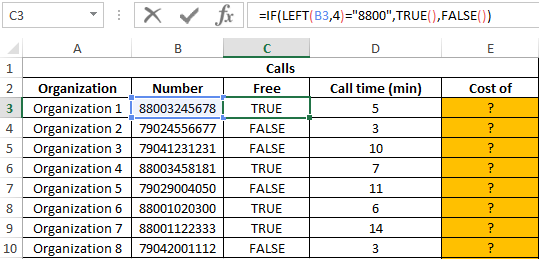
In the “Free” column we display the logical values TRUE or FALSE according to the following condition: is the phone number code equal to “8800”? We introduce the formula in cell C3:
Argument Description:
- LEFT (B3; 4) = «8800» — condition for checking the equality of the first four characters of the string to the specified value («8800»).
- If the condition is met, the TRUE () function will return a true logical value;
- If the condition is not fulfilled, the FALSE () function will return a false logical value.
Similarly, we determine whether the call is free for other rooms. Result:
To calculate the cost, we use the following formula:
Argument Description:
- C3 = TRUE () — checking the condition «is the value stored in cell C3 equal to the value returned by the function (logical truth)?».
- 0- call cost, if the condition is met.
- D3 * 1.5 — the cost of the call, if the condition is not met.
Calculation results:
We received the total cost of all calls made by all organizations.
How to calculate the average value of the condition in Excel
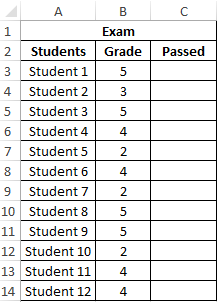
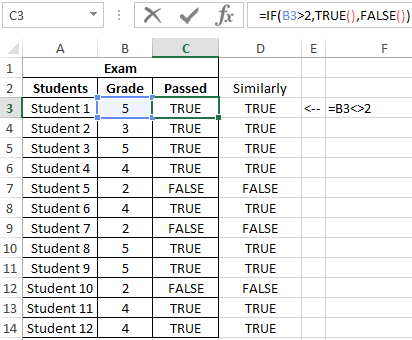
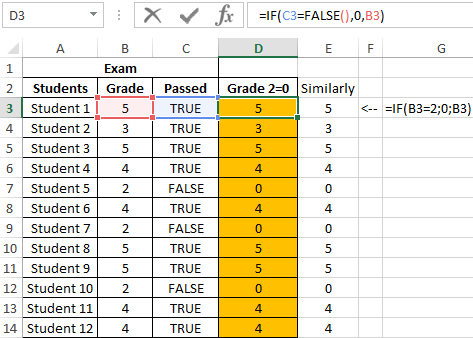
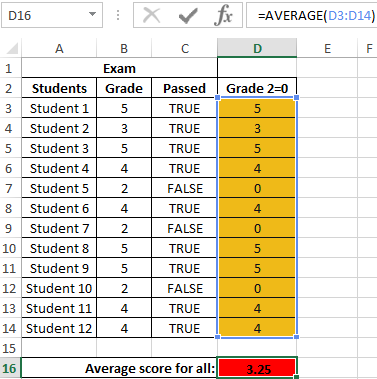
Example 2. Determine the average score for the exam for a group of students, in the composition of which there are students who have failed. It is also necessary to obtain an average assessment of performance only for those students who have passed the exam. The grade of the student who did not pass the exam must be counted as 0 (zero) in the formula for the calculation.
Data table:
To fill in the “Passed” column, use the formula:
Result of calculations:
Create a new column in which we rewrite the estimates, provided that grade 2 is interpreted as 0 using the formula:
Result of calculations:
We determine the average score by the formula:
=AVERAGE(D3:D14)
Result:
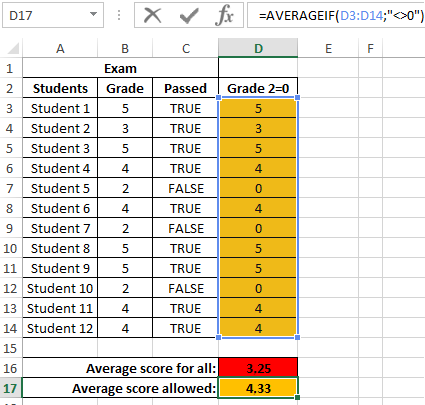
Now we get the average grade point for students who are admitted to the next exams. To do this, we use another logical function AVERAGEIF:
How to get the value module numbers without using the abs function
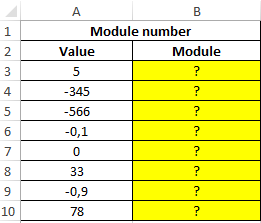
Example 3. Implement an algorithm for determining the value of the modulus of a number (absolute value), that is, an alternative for the ABS function.
Data table:
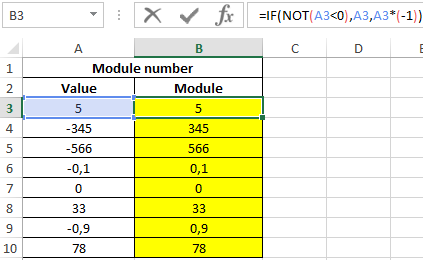
To solve, we use the array formula:
=IF(NOT(A3<0),A3,A3*(-1))
Argument Description:
- NOT (A3: A10 <0) — checking the condition “does the number belong to a range of positive values or is it 0 (zero)?”. Without the use of the function, a longer version of the OR record would not be required (A3: A10 = 0, A3: A10> 0);
- A3: A10 — the returned number (the corresponding element from the range), if the condition is met;
- A3: A10 * (- 1) — the returned number, if the condition is not met (that is, the initial value belongs to the range of negative numbers, to obtain the module, multiply by -1).
Result:
Note: as a rule, the logical values and the functions themselves (TRUE (), FALSE ()) are not explicitly indicated in the expressions, as is done in examples 1 and 2. For example, to avoid intermediate calculations in Example 2, you could use the formula = IF B3 = 2, 0, B3), and also = B3 <> 2.
At the same time, Excel automatically determines the result of calculating the expression B3 <> 2 or B3 = 2, 0, B3 in the arguments of the IF function (logical comparison) and on its basis performs the corresponding action prescribed by the second or third arguments of the IF function.
Features of use of functions true, false, not in Excel
In functions TRUE and FALSE Arguments are absent.
The function does NOT have the following syntax notation:
=NOT( logical value )
Argument Description:
- logical is a required argument characterizing one of two possible values: TRUE or FALSE.
Notes:
- If the argument logical value of the function is NOT used the number 0 or 1, they are automatically converted to logical values FALSE and TRUE, respectively. For example, the function = NOT (0) returns TRUE, = NOT (1) returns FALSE.
- If any numeric value> 0 is used as an argument, the function will NOT return FALSE.
- If the only argument of the function is NOT a text string, the function will return the error code #VALUE !.
- In computing, a special logical data type is used (in programming, it has the name “Boolean” type or Boolean in honor of the famous mathematician George Boole). This data type operates with only two values: 1 and 0 (TRUE, FALSE).
- In Excel, the true logical value also corresponds to the number 1, and the false logical value also corresponds to the numerical value 0 (zero).
- The functions TRUE () and FALSE () can be entered in any cell or used in the formula and will be interpreted as logical values, respectively.
- Both of the above functions are necessary to ensure compatibility with other software products designed for working with tables.
- The function does NOT allow you to expand the capabilities of functions intended to perform a logical test. For example, when using this function as an argument to log_expression of an IF function, you can check several conditions at once.
Download examples of formulas TRUE FALSE and NOT
Excel NOT Function (Example + Video)
When to use Excel NOT Function
It can be used when you want to reverse the value of a logical argument (TRUE/FALSE).
What it Returns
It returns a logical argument which is the reverse of the logical argument used within the NOT function. For example, =NOT(TRUE) returns FALSE and =NOT(FALSE) returns TRUE.
Syntax
=NOT(logical)
Input Arguments
- logical – A value or expression that can be evaluated to TRUE or FALSE.
Additional Notes:
- You can check expression with NOT function that evaluates to TRUE or FALSE.
- For example, =NOT(1+1=2) would return FALSE.
Examples – Using Excel NOT Function
Here are three example of using the Excel NOT Function:
#1 Converting TRUE to FALSE / FALSE to TRUE
It converts TRUE to FALSE and FALSE to TRUE. The argument within the function can also be a result of some other function(s) that results in TRUE/FALSE.
#2 Using with Formula Result
If used with a formula result (that returns TRUE/FALSE), it converts TRUE to FALSE and FALSE to TRUE. In the above example, the value is A2 is compared with a number (that returns TRUE if the condition is met, else FALSE), and NOT function is used on the result of the comparison.
#3 Using with Numbers
In Excel, 0 denotes FALSE and any other number denotes TRUE. Excel NOT function converts 0 (which is FALSE) to TRUE and any other number to FALSE.
Excel NOT Function – Video Tutorial
Related Excel Functions:
- Excel AND Function.
- Excel OR Function.
- Excel IF Function.
- Excel IFS Function.
- Excel IFERROR Function.
- Excel FALSE Function.
- Excel TRUE Function.