- Размер: 288 Кб
- Количество слайдов: 26























![2. [ '_ '_ ]. The accentual type is commonly realized in compound words, most 2. [ '_ '_ ]. The accentual type is commonly realized in compound words, most](https://present5.com/docs//english_phonetics_lecture_5_images/english_phonetics_lecture_5_23.jpg)
![4. [ ˌ _'___]. The accentual type marks a great number of simple words and some 4. [ ˌ _'___]. The accentual type marks a great number of simple words and some](https://present5.com/docs//english_phonetics_lecture_5_images/english_phonetics_lecture_5_24.jpg)

Lecture 5
Изображение слайда
General Notes on Word Stress.
Types of Word Stress.
Degrees of Word Stress.
Placement of Word Stress.
Common Rules of Word Stress in English.
Functions of Word Stress.
Изображение слайда
3
Слайд 3: The Nature of Word Stress
Изображение слайда
4
Слайд 4: The Nature of Word Stress
Word Stress
is a greater degree of prominence of a syllable or syllables as compared to the other syllables of the word
Изображение слайда
5
Слайд 5: The Nature of Word Stress
Scientists about Word Stress:
D. Jones: Word Stress is the degree of force, which is accompanied by a strong force of exhalation and gives an impression of loudness.
A. C. Gimson: English word stress or accent is a complex phenomenon, marked by the variations in force, pitch, quality and quantity.
Изображение слайда
6
Слайд 6: The Nature of Word Stress
Scientists about Word Stress:
B. A. Bogoroditsky : Stress as an increase of energy, accompanied by an increase of expiratory and articulatory activity.
S. F. Leontyeva : Word stress can be defined as the singling out of one or more syllables in a word, which is accompanied by the change of the force of utterance, pitch of the voice, qualitative and quantitative characteristics of the sound which is usually a vowel.
Изображение слайда
7
Слайд 7: The Nature of Word Stress
The effect of prominence of the stressed syllable is achieved by a number of phonetic parameters:
Pitch
Loudness
Length
Vowel Quality
These 4 factors usually work together in combination, but they are not equally important. The strongest effect is produced by pitch and length.
Изображение слайда
8
Слайд 8: The Nature of Word Stress
In the stressed syllable:
the force of utterance is greater, which is connected with more energetic articulation;
the pitch of the voice is higher, which is connected with stronger tenseness of the vocal cords and the walls of resonance cavity;
the quantity of the vowel is greater, the vowel becomes longer;
the quality of the vowel is different (in unstressed syllables it is usually narrow).
Изображение слайда
9
Слайд 9: The Nature of Word Stress
Word Stress
is singling out of one or more syllables in a word, which is accompanied by the change of the force of utterance, pitch of the voice, qualitative and quantitative characteristics of the sound, which is usually a vowel.
Изображение слайда
10
Слайд 10: Types of Word Stress
Изображение слайда
11
Слайд 11: Types of Word Stress
We distinguish the following types of Word Stress:
dynamic (force) stress is achieved by greater force with which the syllable is pronounced (Russian, English, French, German);
musical (tonic) stress is achieved through the change of pitch/musical tone (Japanese, Korean);
quantitative stress is achieved through the changes in the quantity of the vowels, which are longer in the stressed syllables (Russian);
qualitative stress is achieved through the changes in the quality of the vowel (Russian).
Изображение слайда
12
Слайд 12: Types of Word Stress
English Word Stress
is traditionally defined as dynamic, but in fact, the special prominence of the stressed syllables is manifested not only through the increase of intensity, but also through the changes in the vowel quantity, consonant and vowel quality and pitch of the voice.
Изображение слайда
13
Слайд 13: Degrees of Word Stress
Изображение слайда
14
Слайд 14: Degrees of Word Stress
The syllables in a word are characterized by different degrees of prominence. There are as many degrees of stress in a word as there are syllables.
In English there are 3 degrees of stress :
primary (strong, main, principal);
secondary (half-stressed, half-strong);
weak (unstressed).
Изображение слайда
15
Слайд 15: Degrees of Word Stress
In American English there are 4 degrees of stress :
primary (strong, main, principal);
secondary (half-stressed, half-strong);
tertiary (on the last but one syllable in the words with suffixes -ary, -ory, -ony : ´ dictio ˏ nary.
weak (unstressed).
Изображение слайда
16
Слайд 16: Degrees of Word Stress
In transcription stress is indicated by placing the stress mark before the symbol of the first sound of the stressed syllable.
Primary stress is marked by a raised short vertical stroke and secondary stress is marked by a lowered one:
examination [ɪg ˏ zᴂmɪ ´ neɪʃ(ǝ)n]
Изображение слайда
17
Слайд 17: Placement of Word Stress
Изображение слайда
18
Слайд 18: Placement of Word Stress
According to its placement in a word,
stress can be:
fixed
free
shifting
Изображение слайда
19
Слайд 19: Placement of Word Stress
Fixed
(the position of the word stress is always the same,
it is restricted to a particular syllable):
in French (the last syllable),
in Finnish and Czech (the first syllable),
in Polish (the last but one syllable).
Изображение слайда
20
Слайд 20: Placement of Word Stress
Free
(the location of the word stress is not
confined to a specific position,
it can fall on any syllable of the word):
English, Russian, Italian, Greek, Spanish, etc.
Изображение слайда
21
Слайд 21: Placement of Word Stress
Shifting
(the word stress can change
its position in different forms
of the word and its derivatives):
´ music — mu ´ sician
Изображение слайда
22
Слайд 22: Placement of Word Stress
To define the position of word stress
it is necessary to take into account
a number of factors :
phonological structure of the syllable;
the number of syllables in a word;
morphological factor;
the part of speech the word belongs to;
the semantic factor.
Изображение слайда
23
Слайд 23: Placement of Word Stress
The phonological structure of the syllable is related to the status of a particular syllables in terms of the degree of sonority.
The sounds that possess a greater degree of sonority contribute to the greater prominence of the syllable. A syllable is strong when it contains a long vowel or a diphthong or a short vowel followed by two consonants:
a ´ rrive — de ´ velop
Изображение слайда
24
Слайд 24: Placement of Word Stress
The number of syllables in a word influences the number of stresses and the position of stress.
There are stress patterns typical of two-syllable words, three-syllable words and so on.
In multi-syllable words there appears secondary stress.
Изображение слайда
25
Слайд 25: Placement of Word Stress
Morphological factor shows that in complex words the placement of stress depends on the type of suffix.
Suffixes are divided into:
stress-neutral (which do not affect the stress placement in the stem);
stress-fixing (which influence stress in the stem);
stress-attracting (which carry stress themselves).
Изображение слайда
26
Слайд 26: Placement of Word Stress
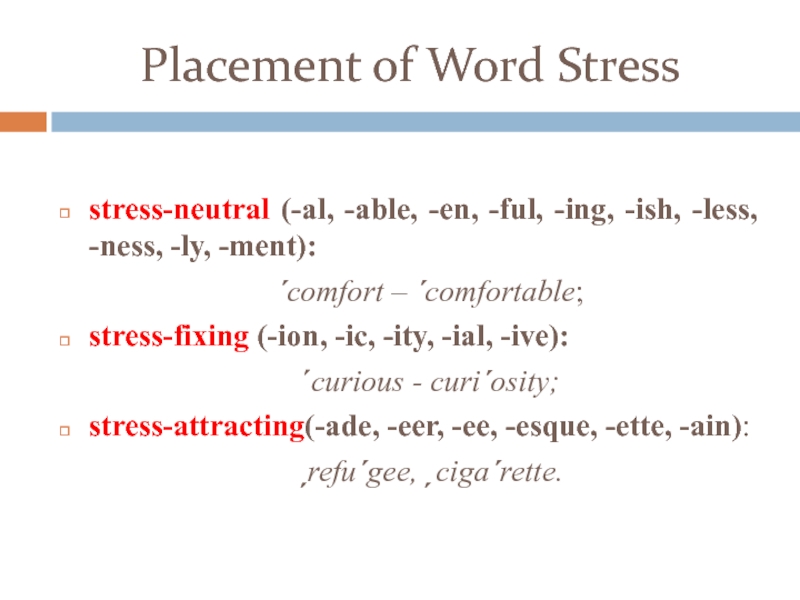
stress-neutral (-al, -able, -en, — ful, — ing, — ish, -less, — ness, — ly, — ment ):
´ comfort – ´ comfortable ;
stress-fixing (-ion, — ic, — ity, — ial, — ive ):
´ curious — curi ´ osity ;
stress-attracting (- ade, — eer, — ee, — esque, — ette, — ain ) :
ˏ refu ´ gee, ˏ ciga ´ rette.
Изображение слайда
27
Слайд 27: Placement of Word Stress
The grammatical category the word belongs to:
´contrast – to con´trast
´habit – ha´bitual
´music – mu´sician
´insult – to in´sult
´record – to re´cord
´present – to pre´sent
Изображение слайда
28
Слайд 28: Placement of Word Stress
The semantic factor (for compound words and words with the so-called separable prefixes).
The majority of such words have two equally strong stresses, both stressed parts are considered to be of equal semantic importance:
compound adjectives: ´ hard- ´ working, ´ blue- ´ eyed,
verbs with post positions : ´ sit ´ down, ´ take ´ off,
numerals from 13 to 19: ´ four ´ teen, ´ six ´ teen.
Изображение слайда
29
Слайд 29: Common Rules of Word Stress
Изображение слайда
30
Слайд 30: Common Rules of Word Stress
Two-syllable words (verbs, adjectives, adverbs):
the second syllable is stressed if it contains a long vowel or a diphthong, or if it ends with more than one consonant: a ´ pply, a ´ ssist. But! ´ hone st.
the first syllable is stressed if the final syllable contains a short vowel and one (or no) final consonant: ´ enter, ´ open.
Two-syllable words (nouns):
the first syllable is stressed if the second syllable contains a short vowel: ´ money ;
the second syllable is stressed if the second syllable contains a long vowel or a diphthong : es ´ tate.
Изображение слайда
31
Слайд 31: Common Rules of Word Stress
Three-syllable words (verbs):
the last but one syllable is stressed if the last syllable contains a short vowel and ends with one consonant: de ´ termine.
the final syllable is stressed if it contains a long vowel or a diphthong, or ends with more than one consonant: enter´tain.
Изображение слайда
32
Слайд 32: Common Rules of Word Stress
Three-syllable words (nouns, adjectives):
the middle syllable is stressed if the syllable preceding the final syllable contains a long vowel or a diphthong, or if it ends with more than one consonant:
di ´ saster ;
the first syllable is stressed if the final syllable contains a short vowel and the middle syllable contains a short vowel and ends with not more than one consonant:
´ cinema
´insolent
Изображение слайда
33
Слайд 33: Common Rules of Word Stress
Words with prefixes:
in words with prefixes the primary stress typically falls on the syllable following the prefix:
im ´ possible, re ´ call ;
in words with prefixes with their own meaning, the place of secondary stress is on the prefix:
ˏ ex- ´ minister.
in prefixal verbs which are distinguished from similarly spelt nouns and adjectives, the second syllable is stressed:
to in ´ crease – ´ increase.
Изображение слайда
34
Слайд 34: Common Rules of Word Stress
Words with suffixes:
suffixes -esce, -esque, -ate, -ize, -fy, -ette, -ique, -ee, -eer, — ade have stress on themselves or the preceding syllable:
ˏ mari ´ nade, ˏ specia ´ lize ;
suffixes -ical, -ic, -ion, -ity, -ial, -cient, -iency, -eous,-ual, -uous, -ety, -itous, -ive, -ative, -itude, -ident, -inal, -wards have stress on the preceding syllable:
eco ´ nomic, ma ´ jority.
Изображение слайда
35
Слайд 35: Common Rules of Word Stress
Words of 4 or more syllables:
The stress is on the antepenultimate syllable (third from the end):
e ´ mergency
his ´ torical
Изображение слайда
36
Слайд 36: Common Rules of Word Stress
Compound words:
The first element is stressed when:
Compounds are written as one word : ´ bedroom.
Nouns are compounded of a verb and an adv.: ´ make-up.
The second element is stressed when:
Food items have the first element which is of a material used in manufacturing the whole : ˏ apple ´ tart.
Parts of the house are implied : ˏ front ´ door.
Изображение слайда
37
Слайд 37: Common Rules of Word Stress
Compound words:
The first element is stressed when:
Adjectives with past participle characterize people :
ˏ thick- ´ skinned.
Nouns ending in -er, -ing are followed by adverbs :
ˏ passer ´ by.
The first element of compounds is a number:
second- ´ class, three — ´ wheeler.
Compound function as an adverb :
head- ´ first.
Изображение слайда
38
Слайд 38: Common Rules of Word Stress
The most common types of English stress pattern
´_ _ (´after)
_´_ (be´fore)
´_ _ _ (´family)
_´_ _ (im´portance)
Some words have 2 variants of stress:
ki ´ lometer – ´ kilometer
Изображение слайда
39
Слайд 39: Functions of Word Stress
Изображение слайда
Изображение слайда
41
Слайд 41: Functions of Word Stress
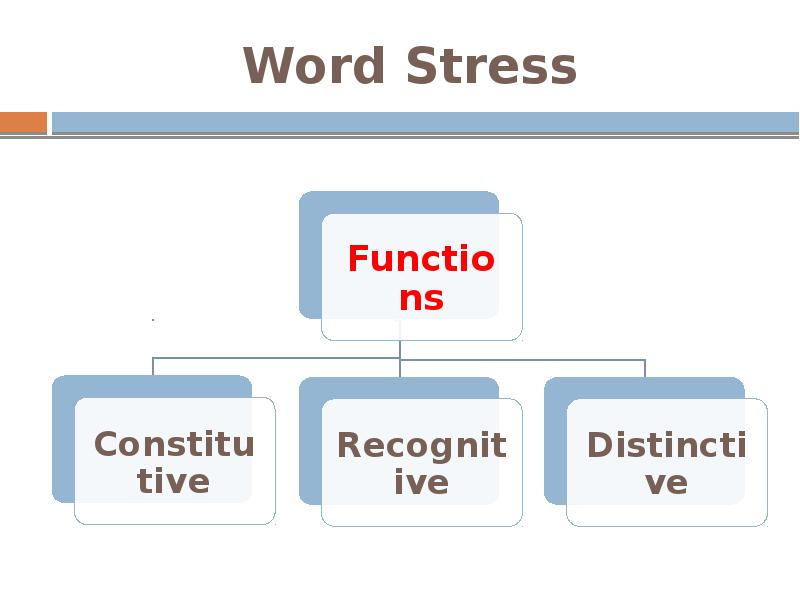
The constitutive function:
word stress organizes the syllables into a word
The recognitive ( identicatory ) function:
word stress makes it possible to identify and recognize a word in the chain of speech.
The distinctive function:
word stress is capable of differentiating the meaning of words or their forms: ´ import — im ´ port.
Изображение слайда
What is WORD STRESS?
What types of word stress do you know?
How does stress perform constitutive, distinctive and recognitive function?
What is the terminology suggested by different authors to distinguish between different degrees of word stress?
What factors determine the place of word stress?
Изображение слайда
Леонтьева С.Ф. Теоретическая фонетика современного английского языка (на англ. яз.) /С.Ф. Леонтьева.- М., 2002. – 336 с.
Соколова М.А. Практическая фонетика английского языка /М.А. Соколова. – М.: Гуманит. изд. центр ВЛАДОС, 1997. – 384 с.
O’Connor L.D. Phonetics /L.D. O’Connor. Penguin, 1977.
Sokolova M.A. English Phonetics. A theoretical course /M.A. Sokolova. M., 1996. – 286 p.
Vassilyev V.A. English Phonetics: A theoretical Course /V.A. Vassilyev. M., 1980. – 323 p.
Изображение слайда
44
Последний слайд презентации: Word Stress: Thank you for your attention!
Изображение слайда
Слайды презентации
English. The
Degrees of Stress.
•
The Functions and Tendencies of
the
English Stress.
•
The Typology of Accentual Structures.
Слайд 2
The syllable or syllables which are uttered with
more prominence
than the other syllables of
the word are said
to be stressed or accented .
Stress in the isolated
word is termed word
stress ; stress in connected speech is termed
sentence stress .
Слайд 3
Word stress can be defned as the singling out of
one or more syllables in a word, which is
accompanied by the change of the force of
utterance, pitch
of the voice, qualitative and
quantitative characteristics of the sound , which is
usually a vowel.
In diferent languages one of the factors
constituting word stress is usually more
signifcant than the others.
Слайд 4
If special prominence in a stressed syllable
or syllables is
achieved mainly through the
intensity of articulation, such type
of stress
is called dynamic, or force stress .
Слайд 5
If special prominence in a stressed syllable is
achieved mainly
through the change of pitch,
or musical tone, such
accent is called
musical, or tonic . It is characteristic
of the
Japanese, Korean and other oriental
languages.
Слайд 6
If special prominence in a stressed syllable is
achieved through
the changes in the quantity of the
vowels, which
are longer in the stressed syllables
than in the unstressed
ones, such type of stress is
called quantitative .
Qualitative type of stress is achieved through
the changes in the quality of the vowel under
stress.
Слайд 7
The traditional classifcation of languages
concerning place of stress in
a word is into those
with a fixed stress
and those with a free stress .
In languages with a
fied stress the
occurrence of the word stress is limited to a
particular syllable in a polysyllabic word.
In languages with a free stress its place is not
confned to a specifc position in the word.
E.g.
‘appetite — be’ginning — ba’lloon
Слайд 8
The word stress in English is not only free but
it
may also be shifting , performing the semantic
function of diferentiating leiical units, parts of
speech, grammatical forms.
E.g. ‘contrast — con’trast; ‘music — mu’sician.
Слайд 9
There are actually as many degrees of
stress in a
word as there are syllables. eiamination
ɪɡ . ˌzæm .
ɪ . ˈneɪʃ . Ə
n
3 2
4 1 5Degrees of Word Stress
Слайд 10
The primary stress is the strongest, it is
marked by
number 1, the secondary
stress is the second strongest
marked by 2.
All the other degrees are termed weak
stress . Unstressed syllables are supposed
to have weak stress.
Слайд 11
American linguists distinguish four degrees of
word stress and term
them: primary stress,
secondary stress, tertiary stress and weak
stress . The diference between the secondary
and tertiary stresses
is very subtle and seems
subjective.
Слайд 12
The second pretonic syllables of such words as libe’ration, recog’nition
are marked by secondary
stress in BrE, in AmE
they are said to have tertiary
stress.
In AmE tertiary
stress also afects the sufies
-ory,
-ary, -ony
of nouns and the sufies –ate, -ize, -y of
verbs, which are considered unstressed in BrE, e.g.
‘territory, ‘ceremony, ‘dictionary; ‘demonstrate,
‘organize, ‘simplify.
Слайд 13
Word stress in a language performs three
functions.Functions of Word
Stress
Слайд 14
Word stress constitutes a word, it
organizes the syllables of
a word into a
language unit having a defnite
accentual
structure, that is a pattern of relationship
among the
syllables; a word does not eiist
without the word stress. Constitutive function
Слайд 15
Word stress enables a person to
identify a succession of
syllables as a
defnite accentual pattern of a word.
Identificatory /
recognitive function
Слайд 16
Word stress alone is capable of diferentiating
the meaning of
words or their forms.
The accentual patterns of words or
the
degrees of word stress and their positions
form oppositions:
E.g. ‘import — im’port, ‘billow — be’low.Distinctive /
contrastive function
Слайд 17
According to Prof. V.O. Vasyliev
(V.A.Vassilyev), the distinctive function
makes
word accent a suprasegmental
phonological unit which performs a
sense-
diferentiating function . He calls it
accenteme .
Слайд 18
According to Prof. V.O. Vasyliev (V.A. Vassilyev) ,
they are:
The
recessive tendency
The rhythmic tendency
The retentive tendency
The semantic factor Word
Stress
Tendencies
Слайд 19
In Germanic languages the word stress originally
fell on the
initial syllable or the second syllable, the
root syllable
in the English words with prefies.
Unrestricted recessive tendency is
observed in
the native English words having no prefi, e.g. mother, daughter, brother, swallow,
in assimilated
French borrowings, e.g.
reason, colour, restaurant.
Restricted recessive tendency marks English
words with prefies which have no referential
meaning now,
e.g. foresee, begin, withdraw, apart. The recessive
tendency
Слайд 20
The rhythm of alternating stressed and
unstressed syllables gave birth
to this
tendency in the present-day English which
caused
the appearance of the secondary
stress in the multisyllabic French
borrowings,
e.g. ˌrevo’lution, ˌorgani’sation, aˌssimi’lation,
etc.
It also eiplains the placement of primary
stress on the third syllable from the end in
three- and four-syllable words, e.g.
‘cinema,
‘situate, ar’ticulate. The rhythmic
tendency
Слайд 21
A third tendency was traced in the
instability of the
accentual structure of English
word stress: a derivative often
retains the
stress of the original or parent word ,
E.g. ‘person — ‘personal — ˌperso’nality,
‘similar
— as’similate,
recom’mend
— recommen ‘dation.The retentive
tendency
Слайд 22
It determines the stress in compound words and
words with
so-called separable prefies .
The majority of such words have
two equally
strong stresses, both stressed parts are
considered to
be of equal semantic importance ,
with semantic factor thus canceling the
rhythmic tendency in word stressing, e.g.
Compound adjectives : hard-working, blue-eyed;
Verbs with postpositions : sit down, take of;
Numerals from 13 to 19 : fourteen, siiteen. The semantic factor
Слайд 23
G.P. Torsuyev classifes the accentual types
according to the number
of stressed syllables,
their degree or character (the main
and the
secondary stress).
The most widely spread accentual types are:
1.
[‘___]. This accentual type marks both
simple and compound words. The accentual
structures of this type may include two and
more syllables, e.g. ‘father, ‘possibly, ‘mother-
in-law, ‘gas-pipe. The Typology of Accentual
Structure
Слайд 24
2. [ ‘_ ‘_ ]. The accentual type is
commonly
realized in compound words,
most of them are with
separable prefies,
e.g. ‘radio-‘active, ‘re’write, ‘diso’bey.
3. [‘_
ˌ ___]. The
type is realized both in
simple and compound words, very
common among compound words, e.g.
‘hair-,dresser, ‘substructure.
Слайд 25
4. [ˌ _’___]. The accentual type marks a
great number
of simple words and some
compound words as well.
In simple words the
stresses fall onto:
the prefi and the
root:
ˌmaga’zine;
the root and the sufi:
ˌhospi’tality;
the prefi and the sufi
.
Слайд 26
The variability of the word accentual structure is
multiplied in
connected speech. The accentual
structure of words may be
altered under the
infuence of rhythm , e.g. An ‘unpolished
‘stone
but:
The ‘stone was un’polished.
The tempo of speech may infuence the
accentual pattern of words . With the quickening
of the speed the carefulness of articulation is
diminished, the vowels are reduced or elided,
the secondary stress may be dropped, e.g.
The
‘whole organi’zation of the ‘meeting was ‘faulty.
Чтобы скачать презентацию — поделитесь ей с друзьями с помощью
социальных кнопок.
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 1
Описание слайда:
Word Stress
Lecture 5
Слайд 2
Описание слайда:
Plan
General Notes on Word Stress.
Types of Word Stress.
Degrees of Word Stress.
Placement of Word Stress.
Common Rules of Word Stress in English.
Functions of Word Stress.
Слайд 3
Описание слайда:
The Nature of Word Stress
Слайд 4
Описание слайда:
The Nature of Word Stress
Word Stress
is a greater degree of prominence of a syllable or syllables as compared to the other syllables of the word
Слайд 5
Описание слайда:
The Nature of Word Stress
Scientists about Word Stress:
D. Jones: Word Stress is the degree of force, which is accompanied by a strong force of exhalation and gives an impression of loudness.
A. C. Gimson: English word stress or accent is a complex phenomenon, marked by the variations in force, pitch, quality and quantity.
Слайд 6
Описание слайда:
The Nature of Word Stress
Scientists about Word Stress:
B. A. Bogoroditsky: Stress as an increase of energy, accompanied by an increase of expiratory and articulatory activity.
S. F. Leontyeva: Word stress can be defined as the singling out of one or more syllables in a word, which is accompanied by the change of the force of utterance, pitch of the voice, qualitative and quantitative characteristics of the sound which is usually a vowel.
Слайд 7
Описание слайда:
The Nature of Word Stress
The effect of prominence of the stressed syllable is achieved by a number of phonetic parameters:
Pitch
Loudness
Length
Vowel Quality
These 4 factors usually work together in combination, but they are not equally important. The strongest effect is produced by pitch and length.
Слайд 8
Описание слайда:
The Nature of Word Stress
In the stressed syllable:
the force of utterance is greater, which is connected with more energetic articulation;
the pitch of the voice is higher, which is connected with stronger tenseness of the vocal cords and the walls of resonance cavity;
the quantity of the vowel is greater, the vowel becomes longer;
the quality of the vowel is different (in unstressed syllables it is usually narrow).
Слайд 9
Описание слайда:
The Nature of Word Stress
Word Stress
is singling out of one or more syllables in a word, which is accompanied by the change of the force of utterance, pitch of the voice, qualitative and quantitative characteristics of the sound, which is usually a vowel.
Слайд 10
Описание слайда:
Types of Word Stress
Слайд 11
Описание слайда:
Types of Word Stress
We distinguish the following types of Word Stress:
dynamic (force) stress is achieved by greater force with which the syllable is pronounced (Russian, English, French, German);
musical (tonic) stress is achieved through the change of pitch/musical tone (Japanese, Korean);
quantitative stress is achieved through the changes in the quantity of the vowels, which are longer in the stressed syllables (Russian);
qualitative stress is achieved through the changes in the quality of the vowel (Russian).
Слайд 12
Описание слайда:
Types of Word Stress
English Word Stress
is traditionally defined as dynamic, but in fact, the special prominence of the stressed syllables is manifested not only through the increase of intensity, but also through the changes in the vowel quantity, consonant and vowel quality and pitch of the voice.
Слайд 13
Описание слайда:
Degrees of Word Stress
Слайд 14
Описание слайда:
Degrees of Word Stress
The syllables in a word are characterized by different degrees of prominence. There are as many degrees of stress in a word as there are syllables.
In English there are 3 degrees of stress:
primary (strong, main, principal);
secondary (half-stressed, half-strong);
weak (unstressed).
Слайд 15
Описание слайда:
Degrees of Word Stress
In American English there are 4 degrees of stress:
primary (strong, main, principal);
secondary (half-stressed, half-strong);
tertiary (on the last but one syllable in the words with suffixes -ary, -ory, -ony: ´dictioˏnary.
weak (unstressed).
Слайд 16
Описание слайда:
Degrees of Word Stress
In transcription stress is indicated by placing the stress mark before the symbol of the first sound of the stressed syllable.
Primary stress is marked by a raised short vertical stroke and secondary stress is marked by a lowered one:
examination [ɪgˏzᴂmɪ´neɪʃ(ǝ)n]
Слайд 17
Описание слайда:
Placement of Word Stress
Слайд 18
Описание слайда:
Placement of Word Stress
According to its placement in a word,
stress can be:
fixed
free
shifting
Слайд 19
Описание слайда:
Placement of Word Stress
Fixed
(the position of the word stress is always the same,
it is restricted to a particular syllable):
in French (the last syllable),
in Finnish and Czech (the first syllable),
in Polish (the last but one syllable).
Слайд 20
Описание слайда:
Placement of Word Stress
Free
(the location of the word stress is not
confined to a specific position,
it can fall on any syllable of the word):
English, Russian, Italian, Greek, Spanish, etc.
Слайд 21
Описание слайда:
Placement of Word Stress
Shifting
(the word stress can change
its position in different forms
of the word and its derivatives):
´music — mu´sician
Слайд 22
Описание слайда:
Placement of Word Stress
To define the position of word stress
it is necessary to take into account
a number of factors:
phonological structure of the syllable;
the number of syllables in a word;
morphological factor;
the part of speech the word belongs to;
the semantic factor.
Слайд 23
Описание слайда:
Placement of Word Stress
The phonological structure of the syllable is related to the status of a particular syllables in terms of the degree of sonority.
The sounds that possess a greater degree of sonority contribute to the greater prominence of the syllable. A syllable is strong when it contains a long vowel or a diphthong or a short vowel followed by two consonants:
a´rrive — de´velop
Слайд 24
Описание слайда:
Placement of Word Stress
The number of syllables in a word influences the number of stresses and the position of stress.
There are stress patterns typical of two-syllable words, three-syllable words and so on.
In multi-syllable words there appears secondary stress.
Слайд 25
Описание слайда:
Placement of Word Stress
Morphological factor shows that in complex words the placement of stress depends on the type of suffix.
Suffixes are divided into:
stress-neutral (which do not affect the stress placement in the stem);
stress-fixing (which influence stress in the stem);
stress-attracting (which carry stress themselves).
Слайд 26
Описание слайда:
Placement of Word Stress
stress-neutral (-al, -able, -en, -ful, -ing, -ish, -less, -ness, -ly, -ment):
´comfort – ´comfortable;
stress-fixing (-ion, -ic, -ity, -ial, -ive):
´curious — curi´osity;
stress-attracting(-ade, -eer, -ee, -esque, -ette, -ain):
ˏrefu´gee, ˏciga´rette.
Слайд 27
Описание слайда:
Placement of Word Stress
The grammatical category the word belongs to:
´contrast – to con´trast
´habit – ha´bitual
´music – mu´sician
´insult – to in´sult
´record – to re´cord
´present – to pre´sent
Слайд 28
Описание слайда:
Placement of Word Stress
The semantic factor (for compound words and words with the so-called separable prefixes).
The majority of such words have two equally strong stresses, both stressed parts are considered to be of equal semantic importance:
compound adjectives: ´hard-´working, ´blue-´eyed,
verbs with post positions : ´sit´down, ´take´off,
numerals from 13 to 19: ´ four´teen, ´six´teen.
Слайд 29
Описание слайда:
Common Rules of Word Stress
Слайд 30
Описание слайда:
Common Rules of Word Stress
Two-syllable words (verbs, adjectives, adverbs):
the second syllable is stressed if it contains a long vowel or a diphthong, or if it ends with more than one consonant: a´pply, a´ssist. But! ´honest.
the first syllable is stressed if the final syllable contains a short vowel and one (or no) final consonant: ´enter, ´open.
Two-syllable words (nouns):
the first syllable is stressed if the second syllable contains a short vowel: ´money;
the second syllable is stressed if the second syllable contains a long vowel or a diphthong: es´tate.
Слайд 31
Описание слайда:
Common Rules of Word Stress
Three-syllable words (verbs):
the last but one syllable is stressed if the last syllable contains a short vowel and ends with one consonant: de´termine.
the final syllable is stressed if it contains a long vowel or a diphthong, or ends with more than one consonant: enter´tain.
Слайд 32
Описание слайда:
Common Rules of Word Stress
Three-syllable words (nouns, adjectives):
the middle syllable is stressed if the syllable preceding the final syllable contains a long vowel or a diphthong, or if it ends with more than one consonant:
di´saster;
the first syllable is stressed if the final syllable contains a short vowel and the middle syllable contains a short vowel and ends with not more than one consonant:
´cinema
´insolent
Слайд 33
Описание слайда:
Common Rules of Word Stress
Words with prefixes:
in words with prefixes the primary stress typically falls on the syllable following the prefix:
im´possible, re´call ;
in words with prefixes with their own meaning, the place of secondary stress is on the prefix:
ˏex-´minister.
in prefixal verbs which are distinguished from similarly spelt nouns and adjectives, the second syllable is stressed:
to in´crease – ´increase.
Слайд 34
Описание слайда:
Common Rules of Word Stress
Words with suffixes:
suffixes -esce, -esque, -ate, -ize, -fy, -ette, -ique, -ee, -eer, — ade have stress on themselves or the preceding syllable:
ˏmari´nade, ˏspecia´lize;
suffixes -ical, -ic, -ion, -ity, -ial, -cient, -iency, -eous,-ual, -uous, -ety, -itous, -ive, -ative, -itude, -ident, -inal, -wards have stress on the preceding syllable:
eco´nomic, ma´jority.
Слайд 35
Описание слайда:
Common Rules of Word Stress
Words of 4 or more syllables:
The stress is on the antepenultimate syllable (third from the end):
e´mergency
his´torical
Слайд 36
Описание слайда:
Common Rules of Word Stress
Compound words:
The first element is stressed when:
Compounds are written as one word: ´bedroom.
Nouns are compounded of a verb and an adv.:´make-up.
The second element is stressed when:
Food items have the first element which is of a material used in manufacturing the whole: ˏapple ´tart.
Parts of the house are implied: ˏfront ´door.
Слайд 37
Описание слайда:
Common Rules of Word Stress
Compound words:
The first element is stressed when:
Adjectives with past participle characterize people:
ˏthick-´skinned.
Nouns ending in -er, -ing are followed by adverbs:
ˏpasser´by.
The first element of compounds is a number:
second-´class, three -´wheeler.
Compound function as an adverb:
head-´first.
Слайд 38
Описание слайда:
Common Rules of Word Stress
The most common types of English stress pattern
´_ _ (´after)
_´_ (be´fore)
´_ _ _ (´family)
_´_ _ (im´portance)
Some words have 2 variants of stress:
ki´lometer – ´kilometer
Слайд 39
Описание слайда:
Functions of Word Stress
Слайд 40
Описание слайда:
Word Stress
Слайд 41
Описание слайда:
Functions of Word Stress
The constitutive function:
word stress organizes the syllables into a word
The recognitive (identicatory) function:
word stress makes it possible to identify and recognize a word in the chain of speech.
The distinctive function:
word stress is capable of differentiating the meaning of words or their forms: ´import — im´port.
Слайд 42
Описание слайда:
Questions:
What is WORD STRESS?
What types of word stress do you know?
How does stress perform constitutive, distinctive and recognitive function?
What is the terminology suggested by different authors to distinguish between different degrees of word stress?
What factors determine the place of word stress?
Слайд 43
Описание слайда:
Literature
Леонтьева С.Ф. Теоретическая фонетика современного английского языка (на англ. яз.) /С.Ф. Леонтьева.- М., 2002. – 336 с.
Соколова М.А. Практическая фонетика английского языка /М.А. Соколова. – М.: Гуманит. изд. центр ВЛАДОС, 1997. – 384 с.
O’Connor L.D. Phonetics /L.D. O’Connor. Penguin, 1977.
Sokolova M.A. English Phonetics. A theoretical course /M.A. Sokolova. M., 1996. – 286 p.
Vassilyev V.A. English Phonetics: A theoretical Course /V.A. Vassilyev. M., 1980. – 323 p.
Слайд 44
Описание слайда:
Thank you for your attention!
Слайд 2Plan
General Notes on Word Stress.
Types of Word Stress.
Degrees of Word
Stress.
Placement of Word Stress.
Common Rules of Word Stress in English.
Functions
of Word Stress.

Слайд 4The Nature of Word Stress
Word Stress
is a greater degree of
prominence of a syllable or syllables as compared to the
other syllables of the word

Слайд 5The Nature of Word Stress
Scientists about Word Stress:
D. Jones: Word
Stress is the degree of force, which is accompanied by
a strong force of exhalation and gives an impression of loudness.
A. C. Gimson: English word stress or accent is a complex phenomenon, marked by the variations in force, pitch, quality and quantity.

Слайд 6The Nature of Word Stress
Scientists about Word Stress:
B. A. Bogoroditsky:
Stress as an increase of energy, accompanied by an increase
of expiratory and articulatory activity.
S. F. Leontyeva: Word stress can be defined as the singling out of one or more syllables in a word, which is accompanied by the change of the force of utterance, pitch of the voice, qualitative and quantitative characteristics of the sound which is usually a vowel.

Слайд 7The Nature of Word Stress
The effect of prominence of the
stressed syllable is achieved by a number of phonetic parameters:
Pitch
Loudness
Length
Vowel
Quality
These 4 factors usually work together in combination, but they are not equally important. The strongest effect is produced by pitch and length.

Слайд 8The Nature of Word Stress
In the stressed syllable:
the force of
utterance is greater, which is connected with more energetic articulation;
the
pitch of the voice is higher, which is connected with stronger tenseness of the vocal cords and the walls of resonance cavity;
the quantity of the vowel is greater, the vowel becomes longer;
the quality of the vowel is different (in unstressed syllables it is usually narrow).

Слайд 9The Nature of Word Stress
Word Stress
is singling out
of one or more syllables in a word, which is
accompanied by the change of the force of utterance, pitch of the voice, qualitative and quantitative characteristics of the sound, which is usually a vowel.

Слайд 11Types of Word Stress
We distinguish the following types of Word
Stress:
dynamic (force) stress is achieved by greater force with which
the syllable is pronounced (Russian, English, French, German);
musical (tonic) stress is achieved through the change of pitch/musical tone (Japanese, Korean);
quantitative stress is achieved through the changes in the quantity of the vowels, which are longer in the stressed syllables (Russian);
qualitative stress is achieved through the changes in the quality of the vowel (Russian).

Слайд 12Types of Word Stress
English Word Stress
is traditionally
defined as dynamic, but in fact, the special prominence of
the stressed syllables is manifested not only through the increase of intensity, but also through the changes in the vowel quantity, consonant and vowel quality and pitch of the voice.

Слайд 14Degrees of Word Stress
The syllables in a word are characterized
by different degrees of prominence. There are as many degrees
of stress in a word as there are syllables.
In English there are 3 degrees of stress:
primary (strong, main, principal);
secondary (half-stressed, half-strong);
weak (unstressed).

Слайд 15Degrees of Word Stress
In American English there are 4 degrees
of stress:
primary (strong, main, principal);
secondary (half-stressed, half-strong);
tertiary (on the last
but one syllable in the words with suffixes -ary, -ory, -ony: ´dictioˏnary.
weak (unstressed).

Слайд 16Degrees of Word Stress
In transcription stress is indicated by placing
the stress mark before the symbol of the first sound
of the stressed syllable.
Primary stress is marked by a raised short vertical stroke and secondary stress is marked by a lowered one:
examination [ɪgˏzᴂmɪ´neɪʃ(ǝ)n]

Слайд 18Placement of Word Stress
According to its placement in a word,
stress can be:
fixed
free
shifting

Слайд 19Placement of Word Stress
Fixed
(the position of the word stress is
always the same,
it is restricted to a particular syllable):
in French (the last syllable),
in Finnish and Czech (the first syllable),
in Polish (the last but one syllable).

Слайд 20Placement of Word Stress
Free
(the location of the word stress is
not
confined to a specific position,
it can fall on
any syllable of the word):
English, Russian, Italian, Greek, Spanish, etc.

Слайд 21Placement of Word Stress
Shifting
(the word stress can change
its position
in different forms
of the word and its derivatives):
´music
— mu´sician

Слайд 22Placement of Word Stress
To define the position of word stress
it is necessary to take into account
a number of
factors:
phonological structure of the syllable;
the number of syllables in a word;
morphological factor;
the part of speech the word belongs to;
the semantic factor.

Слайд 23Placement of Word Stress
The phonological structure of the syllable is
related to the status of a particular syllables in terms
of the degree of sonority.
The sounds that possess a greater degree of sonority contribute to the greater prominence of the syllable. A syllable is strong when it contains a long vowel or a diphthong or a short vowel followed by two consonants:
a´rrive — de´velop

Слайд 24Placement of Word Stress
The number of syllables in a word
influences the number of stresses and the position of stress.
There
are stress patterns typical of two-syllable words, three-syllable words and so on.
In multi-syllable words there appears secondary stress.

Слайд 25Placement of Word Stress
Morphological factor shows that in complex words
the placement of stress depends on the type of suffix.
Suffixes
are divided into:
stress-neutral (which do not affect the stress placement in the stem);
stress-fixing (which influence stress in the stem);
stress-attracting (which carry stress themselves).

Слайд 26Placement of Word Stress
stress-neutral (-al, -able, -en, -ful, -ing, -ish,
-less, -ness, -ly, -ment):
´comfort – ´comfortable;
stress-fixing (-ion, -ic, -ity,
-ial, -ive):
´curious — curi´osity;
stress-attracting(-ade, -eer, -ee, -esque, -ette, -ain):
ˏrefu´gee, ˏciga´rette.
Слайд 27Placement of Word Stress
The grammatical category the word belongs to:
´contrast
– to con´trast
´habit – ha´bitual
´music – mu´sician
´insult – to in´sult
´record
– to re´cord
´present – to pre´sent

Слайд 28Placement of Word Stress
The semantic factor (for compound words and
words with the so-called separable prefixes).
The majority of such
words have two equally strong stresses, both stressed parts are considered to be of equal semantic importance:
compound adjectives: ´hard-´working, ´blue-´eyed,
verbs with post positions : ´sit´down, ´take´off,
numerals from 13 to 19: ´ four´teen, ´six´teen.

Слайд 30
Common Rules of Word Stress
Two-syllable words (verbs, adjectives, adverbs):
the second
syllable is stressed if it contains a long vowel or
a diphthong, or if it ends with more than one consonant: a´pply, a´ssist. But! ´honest.
the first syllable is stressed if the final syllable contains a short vowel and one (or no) final consonant: ´enter, ´open.
Two-syllable words (nouns):
the first syllable is stressed if the second syllable contains a short vowel: ´money;
the second syllable is stressed if the second syllable contains a long vowel or a diphthong: es´tate.

Слайд 31
Common Rules of Word Stress
Three-syllable words (verbs):
the last but one
syllable is stressed if the last syllable contains a short
vowel and ends with one consonant: de´termine.
the final syllable is stressed if it contains a long vowel or a diphthong, or ends with more than one consonant: enter´tain.

Слайд 32
Common Rules of Word Stress
Three-syllable words (nouns, adjectives):
the middle syllable
is stressed if the syllable preceding the final syllable contains
a long vowel or a diphthong, or if it ends with more than one consonant:
di´saster;
the first syllable is stressed if the final syllable contains a short vowel and the middle syllable contains a short vowel and ends with not more than one consonant:
´cinema
´insolent

Слайд 33
Common Rules of Word Stress
Words with prefixes:
in words with prefixes
the primary stress typically falls on the syllable following the
prefix:
im´possible, re´call ;
in words with prefixes with their own meaning, the place of secondary stress is on the prefix:
ˏex-´minister.
in prefixal verbs which are distinguished from similarly spelt nouns and adjectives, the second syllable is stressed:
to in´crease – ´increase.

Слайд 34
Common Rules of Word Stress
Words with suffixes:
suffixes -esce, -esque, -ate,
-ize, -fy, -ette, -ique, -ee, -eer, — ade have stress
on themselves or the preceding syllable:
ˏmari´nade, ˏspecia´lize;
suffixes -ical, -ic, -ion, -ity, -ial, -cient, -iency, -eous,-ual, -uous, -ety, -itous, -ive, -ative, -itude, -ident, -inal, -wards have stress on the preceding syllable:
eco´nomic, ma´jority.

Слайд 35
Common Rules of Word Stress
Words of 4 or more syllables:
The
stress is on the antepenultimate syllable (third from the end):
e´mergency
his´torical

Слайд 36
Common Rules of Word Stress
Compound words:
The first element is stressed
when:
Compounds are written as one word: ´bedroom.
Nouns are compounded of
a verb and an adv.:´make-up.
The second element is stressed when:
Food items have the first element which is of a material used in manufacturing the whole: ˏapple ´tart.
Parts of the house are implied: ˏfront ´door.

Слайд 37
Common Rules of Word Stress
Compound words:
The first element is stressed
when:
Adjectives with past participle characterize people:
ˏthick-´skinned.
Nouns ending in -er, -ing
are followed by adverbs:
ˏpasser´by.
The first element of compounds is a number:
second-´class, three -´wheeler.
Compound function as an adverb:
head-´first.

Слайд 38
Common Rules of Word Stress
The most common types of English
stress pattern
´_ _ (´after)
_´_ (be´fore)
´_ _ _ (´family)
_´_ _ (im´portance)
Some words have 2 variants of stress:
ki´lometer – ´kilometer

Слайд 41
Functions of Word Stress
The constitutive function:
word stress organizes the
syllables into a word
The recognitive (identicatory) function:
word stress makes it
possible to identify and recognize a word in the chain of speech.
The distinctive function:
word stress is capable of differentiating the meaning of words or their forms: ´import — im´port.

Слайд 42Questions:
What is WORD STRESS?
What types of word stress do
you know?
How does stress perform constitutive, distinctive and recognitive function?
What
is the terminology suggested by different authors to distinguish between different degrees of word stress?
What factors determine the place of word stress?

Слайд 43
Literature
Леонтьева С.Ф. Теоретическая фонетика современного английского языка (на
англ. яз.) /С.Ф. Леонтьева.- М., 2002. – 336 с.
Соколова
М.А. Практическая фонетика английского языка /М.А. Соколова. – М.: Гуманит. изд. центр ВЛАДОС, 1997. – 384 с.
O’Connor L.D. Phonetics /L.D. O’Connor. Penguin, 1977.
Sokolova M.A. English Phonetics. A theoretical course /M.A. Sokolova. M., 1996. – 286 p.
Vassilyev V.A. English Phonetics: A theoretical Course /V.A. Vassilyev. M., 1980. – 323 p.




































































![Презентация, доклад на тему The Nature of Word Stress 2. [ '_ '_ ]. The accentual type is commonly realized 2. [ '_ '_ ]. The accentual type is commonly realized in compound words, most](https://slaidy.com/files/161/160621/page-24.jpg)
![Презентация, доклад на тему The Nature of Word Stress 4. [ˌ _'___]. The accentual type marks a great number of 4. [ˌ _'___]. The accentual type marks a great number of simple words and some](https://slaidy.com/files/161/160621/page-25.jpg)















![Degrees of Word Stress
In transcription stress is indicated by placing the stress mark before the symbol of the first sound of the stressed syllable.
Primary stress is marked by a raised short vertical stroke and secondary stress is marked by a lowered one:
examination [ɪgˏzᴂmɪ´neɪʃ(ǝ)n]](https://myslide.ru/documents_7/36592529c536c90e3814b98ded49d489/img15.jpg)