Excel for Microsoft 365 Excel 2021 Excel 2019 Excel 2016 Excel 2013 Excel 2010 Excel 2007 Excel Starter 2010 More…Less
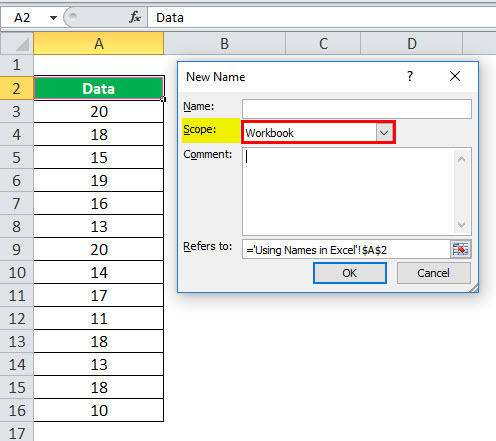
You can quickly create a named range by using a selection of cells in the worksheet.
Note: Named ranges that are created from selecting cells have a workbook-level scope.
-
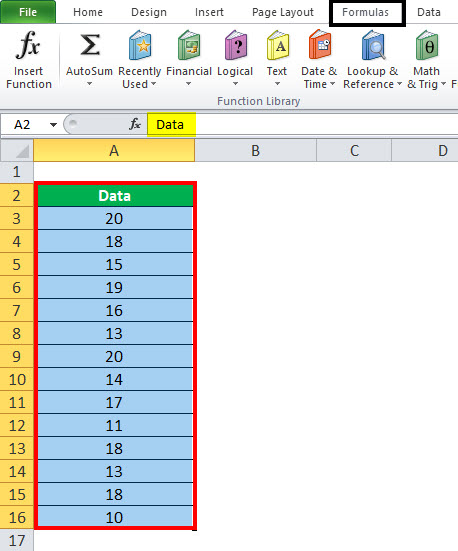
Select the range you want to name, including the row or column labels.
-
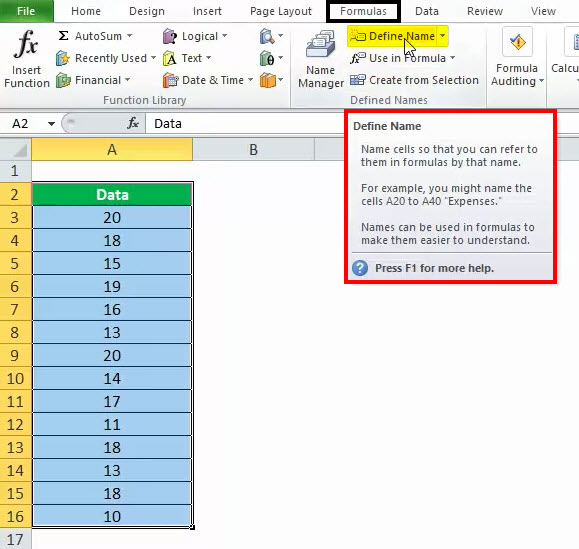
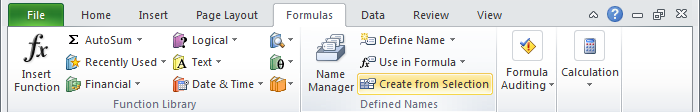
Click Formulas > Create from Selection.
-
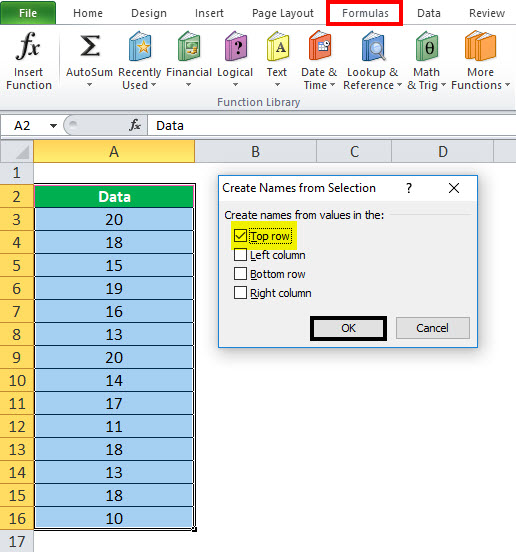
In the Create Names from Selection dialog box, select the checkbox (es) depending on the location of your row/column header. If you have only a header row at the top of the table, then just select Top row. Suppose you have a top row and left column header, then select Top row and Left column options, and so on.
-
Click OK.
Need more help?
You can always ask an expert in the Excel Tech Community or get support in the Answers community.
Need more help?
Want more options?
Explore subscription benefits, browse training courses, learn how to secure your device, and more.
Communities help you ask and answer questions, give feedback, and hear from experts with rich knowledge.
What’s in the name?
If you are working with Excel spreadsheets, it could mean a lot of time saving and efficiency.
In this tutorial, you’ll learn how to create Named Ranges in Excel and how to use it to save time.
Named Ranges in Excel – An Introduction
If someone has to call me or refer to me, they will use my name (instead of saying a male is staying in so and so place with so and so height and weight).
Right?
Similarly, in Excel, you can give a name to a cell or a range of cells.
Now, instead of using the cell reference (such as A1 or A1:A10), you can simply use the name that you assigned to it.
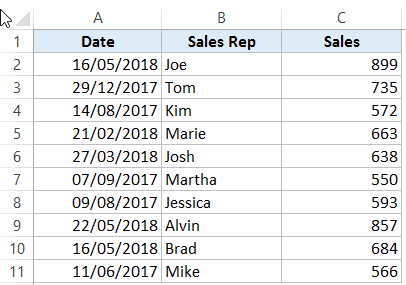
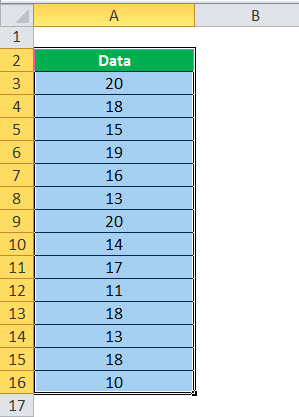
For example, suppose you have a data set as shown below:
In this data set, if you have to refer to the range that has the Date, you will have to use A2:A11 in formulas. Similarly, for Sales Rep and Sales, you will have to use B2:B11 and C2:C11.
While it’s alright when you only have a couple of data points, but in case you huge complex data sets, using cell references to refer to data could be time-consuming.
Excel Named Ranges makes it easy to refer to data sets in Excel.
You can create a named range in Excel for each data category, and then use that name instead of the cell references. For example, dates can be named ‘Date’, Sales Rep data can be named ‘SalesRep’ and sales data can be named ‘Sales’.
You can also create a name for a single cell. For example, if you have the sales commission percentage in a cell, you can name that cell as ‘Commission’.
Benefits of Creating Named Ranges in Excel
Here are the benefits of using named ranges in Excel.
Use Names instead of Cell References
When you create Named Ranges in Excel, you can use these names instead of the cell references.
For example, you can use =SUM(SALES) instead of =SUM(C2:C11) for the above data set.
Have a look at ṭhe formulas listed below. Instead of using cell references, I have used the Named Ranges.
- Number of sales with value more than 500: =COUNTIF(Sales,”>500″)
- Sum of all the sales done by Tom: =SUMIF(SalesRep,”Tom”,Sales)
- Commission earned by Joe (sales by Joe multiplied by commission percentage):
=SUMIF(SalesRep,”Joe”,Sales)*Commission
You would agree that these formulas are easy to create and easy to understand (especially when you share it with someone else or revisit it yourself.
No Need to Go Back to the Dataset to Select Cells
Another significant benefit of using Named Ranges in Excel is that you don’t need to go back and select the cell ranges.
You can just type a couple of alphabets of that named range and Excel will show the matching named ranges (as shown below):
Named Ranges Make Formulas Dynamic
By using Named Ranges in Excel, you can make Excel formulas dynamic.
For example, in the case of sales commission, instead of using the value 2.5%, you can use the Named Range.
Now, if your company later decides to increase the commission to 3%, you can simply update the Named Range, and all the calculation would automatically update to reflect the new commission.
How to Create Named Ranges in Excel
Here are three ways to create Named Ranges in Excel:
Method #1 – Using Define Name
Here are the steps to create Named Ranges in Excel using Define Name:
This will create a Named Range SALESREP.
Method #2: Using the Name Box
- Select the range for which you want to create a name (do not select headers).
- Go to the Name Box on the left of Formula bar and Type the name of the with which you want to create the Named Range.
- Note that the Name created here will be available for the entire Workbook. If you wish to restrict it to a worksheet, use Method 1.
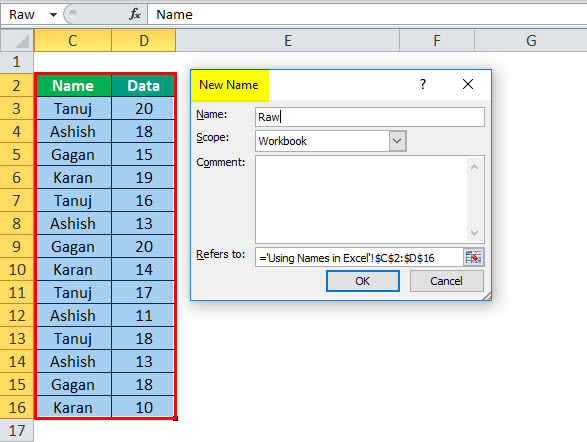
Method #3: Using Create From Selection Option
This is the recommended way when you have data in tabular form, and you want to create named range for each column/row.
For example, in the dataset below, if you want to quickly create three named ranges (Date, Sales_Rep, and Sales), then you can use the method shown below.
Here are the steps to quickly create named ranges from a dataset:
This will create three Named Ranges – Date, Sales_Rep, and Sales.
Note that it automatically picks up names from the headers. If there are any space between words, it inserts an underscore (as you can’t have spaces in named ranges).
Naming Convention for Named Ranges in Excel
There are certain naming rules you need to know while creating Named Ranges in Excel:
- The first character of a Named Range should be a letter and underscore character(_), or a backslash(). If it’s anything else, it will show an error. The remaining characters can be letters, numbers, special characters, period, or underscore.
- You can not use names that also represent cell references in Excel. For example, you can’t use AB1 as it is also a cell reference.
- You can’t use spaces while creating named ranges. For example, you can’t have Sales Rep as a named range. If you want to combine two words and create a Named Range, use an underscore, period or uppercase characters to create it. For example, you can have Sales_Rep, SalesRep, or SalesRep.
- While creating named ranges, Excel treats uppercase and lowercase the same way. For example, if you create a named range SALES, then you will not be able to create another named range such as ‘sales’ or ‘Sales’.
- A Named Range can be up to 255 characters long.
Too Many Named Ranges in Excel? Don’t Worry
Sometimes in large data sets and complex models, you may end up creating a lot of Named Ranges in Excel.
What if you don’t remember the name of the Named Range you created?
Don’t worry – here are some useful tips.
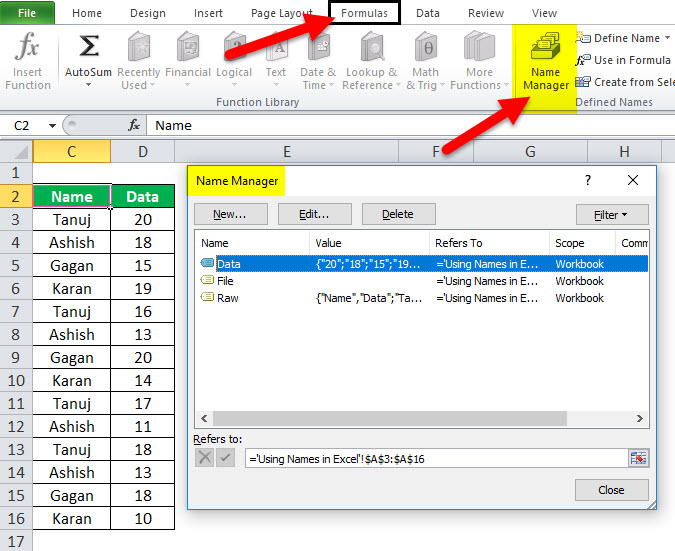
Getting the Names of All the Named Ranges
Here are the steps to get a list of all the named ranges you created:
This will give you a list of all the Named Ranges in that workbook. To use a named range (in formulas or a cell), double click on it.
Displaying the Matching Named Ranges
- If you have some idea about the Name, type a few initial characters, and Excel will show a drop down of the matching names.
How to Edit Named Ranges in Excel
If you have already created a Named Range, you can edit it using the following steps:
Useful Named Range Shortcuts (the Power of F3)
Here are some useful keyboard shortcuts that will come handy when you are working with Named Ranges in Excel:
- To get a list of all the Named Ranges and pasting it in Formula: F3
- To create new name using Name Manager Dialogue Box: Control + F3
- To create Named Ranges from Selection: Control + Shift + F3
Creating Dynamic Named Ranges in Excel
So far in this tutorial, we have created static Named Ranges.
This means that these Named Ranges would always refer to the same dataset.
For example, if A1:A10 has been named as ‘Sales’, it would always refer to A1:A10.
If you add more sales data, then you would have to manually go and update the reference in the named range.
In the world of ever-expanding data sets, this may end up taking up a lot of your time. Every time you get new data, you may have to update the Named Ranges in Excel.
To tackle this issue, we can create Dynamic Named Ranges in Excel that would automatically account for additional data and include it in the existing Named Range.
For example, For example, if I add two additional sales data points, a dynamic named range would automatically refer to A1:A12.
This kind of Dynamic Named Range can be created by using Excel INDEX function. Instead of specifying the cell references while creating the Named Range, we specify the formula. The formula automatically updated when the data is added or deleted.
Let’s see how to create Dynamic Named Ranges in Excel.
Suppose we have the sales data in cell A2:A11.
Here are the steps to create Dynamic Named Ranges in Excel:
-
- Go to the Formula tab and click on Define Name.
- In the New Name dialogue box type the following:
- Name: Sales
- Scope: Workbook
- Refers to: =$A$2:INDEX($A$2:$A$100,COUNTIF($A$2:$A$100,”<>”&””))
- Click OK.
- Go to the Formula tab and click on Define Name.
Done!
You now have a dynamic named range with the name ‘Sales’. This would automatically update whenever you add data to it or remove data from it.
How does Dynamic Named Ranges Work?
To explain how this work, you need to know a bit more about Excel INDEX function.
Most people use INDEX to return a value from a list based on the row and column number.
But the INDEX function also has another side to it.
It can be used to return a cell reference when it is used as a part of a cell reference.
For example, here is the formula that we have used to create a dynamic named range:
=$A$2:INDEX($A$2:$A$100,COUNTIF($A$2:$A$100,"<>"&""))
INDEX($A$2:$A$100,COUNTIF($A$2:$A$100,”<>”&””) –> This part of the formula is expected to return a value (which would be the 10th value from the list, considering there are ten items).
However, when used in front of a reference (=$A$2:INDEX($A$2:$A$100,COUNTIF($A$2:$A$100,”<>”&””))) it returns the reference to the cell instead of the value.
Hence, here it returns =$A$2:$A$11
If we add two additional values to the sales column, it would then return =$A$2:$A$13
When you add new data to the list, Excel COUNTIF function returns the number of non-blank cells in the data. This number is used by the INDEX function to fetch the cell reference of the last item in the list.
Note:
- This would only work if there are no blank cells in the data.
- In the example taken above, I have assigned a large number of cells (A2:A100) for the Named Range formula. You can adjust this based on your data set.
You can also use OFFSET function to create a Dynamic Named Ranges in Excel, however, since OFFSET function is volatile, it may lead a slow Excel workbook. INDEX, on the other hand, is semi-volatile, which makes it a better choice to create Dynamic Named Ranges in Excel.
You may also like the following Excel resources:
- Free Excel Templates.
- Free Online Excel Training (7-Part Online Video Course).
- Useful Excel Macro Code Examples.
- 10 Advanced Excel VLOOKUP Examples.
- Creating a Drop Down List in Excel.
- Creating a Named Range in Google Sheets.
- How to Reference Another Sheet or Workbook in Excel
- How to Delete Named Range in Excel?
What is Name Range in Excel?
The name range in Excel is the range that has been given a name for future reference. To make a range as a named range, select the range of data and then insert a table. Then, we put a name to the range from the Name Box on the left-hand side of the window. After this, we can refer to the range by its name in any formula.
The name range in Excel makes it much cooler to keep track of things, especially when using formulas. You can assign a name to a range. No problem with any change in that range; you need to update the range from the Name Manager in ExcelThe name manager in Excel is used to create, edit, and delete named ranges. For example, we sometimes use names instead of giving cell references. By using the name manager, we can create a new reference, edit it, or delete it.read more. You do not need to update every formula manually. Similarly, you can create a name for a formula. Then, if you want to use that formula in another formula or another location, refer to it by name.
- The name ranges are significant because you can put any names in your formulas without considering cell references/addresses. Furthermore, you can assign the range with any name.
- Create a named range for any data or a named constant and use these names in your formulas in place of data references. In this way, you can make your formulas easier to comprehend better. A named range is just a human-understandable name for a range of cells in Excel.
- Using the name range in Excel, you can simplify and comprehend your formulas better. For example, you can assign a name for a range in an excel sheet for a function, a constant, or table data. Once you start using the names in your Excel sheet, you can easily understand these names.
Table of contents
- What is Name Range in Excel?
- Define Names For a Selected Range
- Excel names the cells based on the labels in the range you designated.
- Update named ranges in the Name Manager (Control + F3)
- How to Use Name Range in Excel?
- Example #1 Create a name by using the Define Name option
- Example #2 Make a named range by using Excel Name Manager
- Name Range using VBA.
- Things to Remember
- Recommended Articles
- Define Names For a Selected Range
Define Names For a Selected Range
- Select the data range you want to assign a name, then select formulas and create from the selection.
- Click on the “Create Names from Selection,” then select the “Top row,” “Left column,” “Bottom row,” or “Right column” checkbox and select “OK.”
Excel names the cells based on the labels in the range you designated.
- Use names in formulas, then select a cell and enter a formula.
- Place the cursor where you want to use the name range formula.
- Type the first letter of the name, and select the name from the list that appears.
- Or, select “Formulas,” then use in formula and select the name you want to use.
- Press the “Enter” key.
Update named ranges in the Name Manager (Control + F3)
You can update the name from the Name Manager. Press “Ctrl” and “F3” to update the name. Select the name you want to change, then change the reference range directly.
How to Use Name Range in Excel?
Let us understand the working of conditional formatting by simple Excel examples.
You can download this Using Names in Excel Template here – Using Names in Excel Template
Example #1 Create a name by using the Define Name option
Below are the steps to create a name by using the “Define Name” option:
- First, select the cell(s).
- On the “Formulas” tab, click the “Define Name” in the “Defined Names” group.
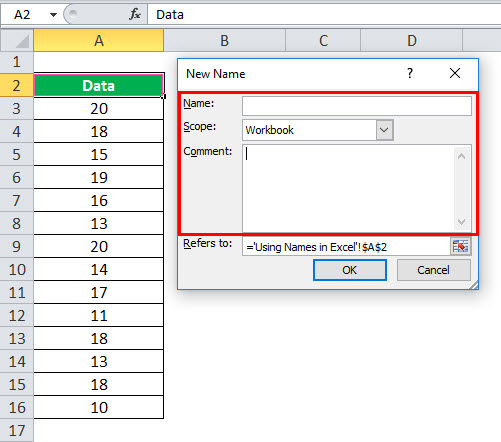
- In the “New Name” dialog box, specify three things:
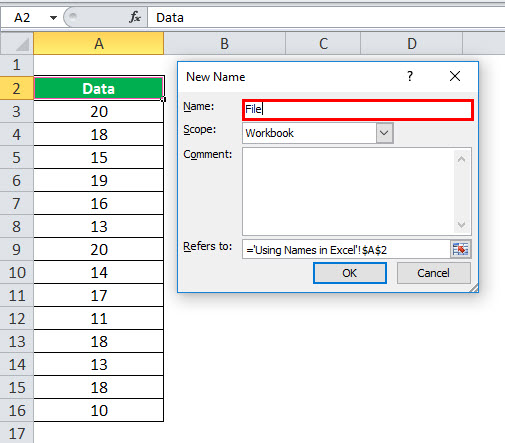
- First, in the “Name” box, type the range name.
- In the “Scope” drop-down, set the name scope (Workbook by default).
- In the “Refers to” box, check the reference and correct it if needed. Finally, click “OK” to save the changes and close the dialog box.
Example #2 Make a named range by using Excel Name Manager
- Go to the “Formulas” tab, then the “Defined Names” group, and click the “Name Manager” or press “Ctrl + F3” (the preferred way).
- In the top left-hand corner of the “Name Manager” dialog window, click the “New… button:”
Name Range using VBA.
We can apply the naming in VBA; here is the example as follows:
Sub sbNameRange()
‘Adding a Name
Names.Add Name:=”myData”, RefersTo:=”=Sheet1!$A$1:$A$10″
‘OR
‘You can use Name property of a Range.
Sheet1.Range(“$A$1:$A$10”).Name = “myData”
End Sub
Things to Remember
We must follow the below instruction while using the name range.
- The names can start with a letter, backslash (), or an underscore (_).
- The name should be under 255 characters long.
- The names must be continuous and cannot contain spaces and most punctuation characters.
- There must be no conflict with cell references in names using in excelCell reference in excel is referring the other cells to a cell to use its values or properties. For instance, if we have data in cell A2 and want to use that in cell A1, use =A2 in cell A1, and this will copy the A2 value in A1.read more.
- We can use single letters as names, but the letters “r” and “c” are reserved in Excel.
- The names are not case-sensitive – “Tanuj”, “TANUJ”, and “TaNuJ” are all the same in Excel.
Recommended Articles
This article is a guide to the Name Range in Excel. We discuss using names in Excel, practical examples, and downloadable Excel templates here. You also may look at these useful functions in Excel: –
- VBA RangeRange is a property in VBA that helps specify a particular cell, a range of cells, a row, a column, or a three-dimensional range. In the context of the Excel worksheet, the VBA range object includes a single cell or multiple cells spread across various rows and columns.read more
- Data Tables ExcelA data table in excel is a type of what-if analysis tool that allows you to compare variables and see how they impact the result and overall data. It can be found under the data tab in the what-if analysis section.read more
- Data Validation using ExcelThe data validation in excel helps control the kind of input entered by a user in the worksheet.read more
- Paste SpecialPaste special in Excel allows you to paste partial aspects of the data copied. There are several ways to paste special in Excel, including right-clicking on the target cell and selecting paste special, or using a shortcut such as CTRL+ALT+V or ALT+E+S.read more
Named ranges are one of these crusty old features in Excel that few users understand. New users may find them weird and scary, and even old hands may avoid them because they seem pointless and complex.
But named ranges are actually a pretty cool feature. They can make formulas *a lot* easier to create, read, and maintain. And as a bonus, they make formulas easier to reuse (more portable).
In fact, I use named ranges all the time when testing and prototyping formulas. They help me get formulas working faster. I also use named ranges because I’m lazy, and don’t like typing in complex references 
The basics of named ranges in Excel
What is a named range?
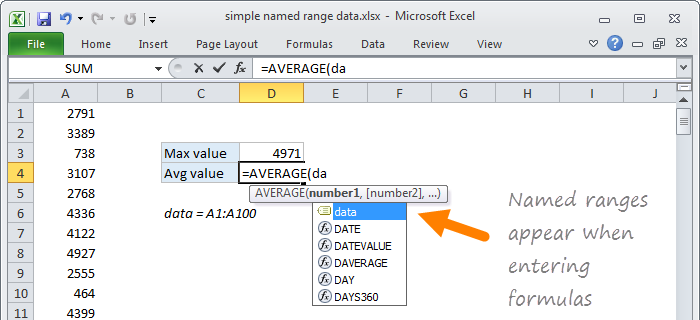
A named range is just a human-readable name for a range of cells in Excel. For example, if I name the range A1:A100 «data», I can use MAX to get the maximum value with a simple formula:
=MAX(data) // max value
The beauty of named ranges is that you can use meaningful names in your formulas without thinking about cell references. Once you have a named range, just use it just like a cell reference. All of these formulas are valid with the named range «data»:
=MAX(data) // max value
=MIN(data) // min value
=COUNT(data) // total values
=AVERAGE(data) // min value
Video: How to create a named range
Creating a named range is easy
Creating a named range is fast and easy. Just select a range of cells, and type a name into the name box. When you press return, the name is created:
To quickly test the new range, choose the new name in the dropdown next to the name box. Excel will select the range on the worksheet.
Excel can create names automatically (ctrl + shift + F3)
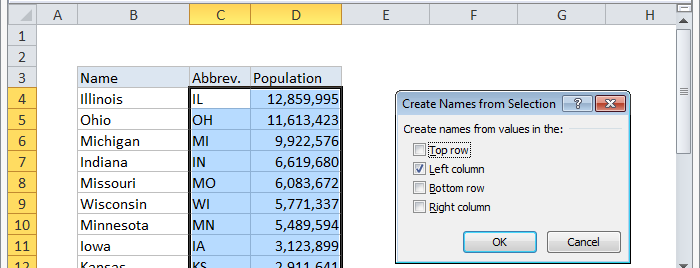
If you have well structured data with labels, you can have Excel create named ranges for you. Just select the data, along with the labels, and use the «Create from Selection» command on the Formulas tab of the ribbon:
You can also use the keyboard shortcut control + shift + F3.
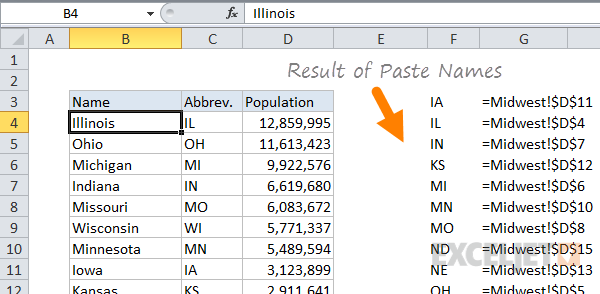
Using this feature, we can create named ranges for the population of 12 states in one step:
When you click OK, the names are created. You’ll find all newly created names in the drop down menu next to the name box:
With names created, you can use them in formulas like this
=SUM(MN,WI,MI)
Update named ranges in the Name Manager (Control + F3)
Once you create a named range, use the Name Manager (Control + F3) to update as needed. Select the name you want to work with, then change the reference directly (i.e. edit «refers to»), or click the button at right and select a new range.
There’s no need to click the Edit button to update a reference. When you click Close, the range name will be updated.
Note: if you select an entire named range on a worksheet, you can drag to a new location and the reference will be updated automatically. However, I don’t know a way to adjust range references by clicking and dragging directly on the worksheet. If you know a way to do this, chime in below!
See all named ranges (control + F3)
To quickly see all named ranges in a workbook, use the dropdown menu next to the name box.
If you want to see more detail, open the Name Manager (Control + F3), which lists all names with references, and provides a filter as well:
Note: in older versions of Excel on the Mac, there is no Name Manager, and you’ll see the Define Name dialog instead.
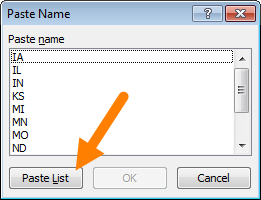
Copy and paste all named ranges (F3)
If you want a more persistent record of named ranges in a workbook, you can paste the full list of names anywhere you like. Go to Formulas > Use in Formula (or use the shortcut F3), then choose Paste names > Paste List:
When you click the Paste List button, you’ll see the names and references pasted into the worksheet:
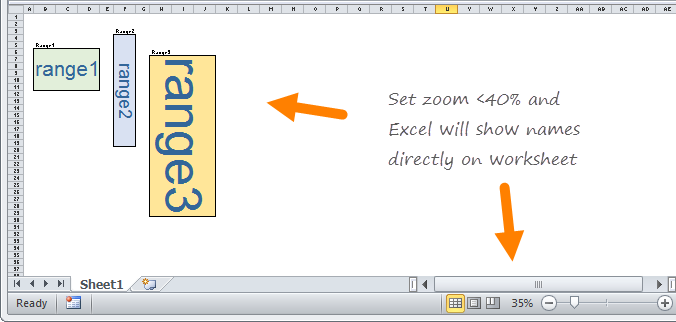
See names directly on the worksheet
If you set the zoom level to less than 40%, Excel will show range names directly on the worksheet:
Thanks for this tip, Felipe!
Names have rules
When creating named ranges, follow these rules:
- Names must begin with a letter, an underscore (_), or a backslash ()
- Names can’t contain spaces and most punctuation characters.
- Names can’t conflict with cell references – you can’t name a range «A1» or «Z100».
- Single letters are OK for names («a», «b», «x», etc.), but the letters «r» and «c» are reserved.
- Names are not case-sensitive – «home», «HOME», and «HoMe» are all the same to Excel.
Named ranges in formulas
Named ranges are easy to use in formulas
For example, lets say you name a cell in your workbook «updated». The idea is you can put the current date in the cell (Ctrl + 
The formula in B8 looks like this:
="Updated: "& TEXT(updated, "ddd, mmmm d, yyyy")
You can paste this formula anywhere in the workbook and it will display correctly. Whenever you change the date in «updated», the message will update wherever the formula is used. See this page for more examples.
Named ranges appear when typing a formula
Once you’ve created a named range, it will appear automatically in formulas when you type the first letter of the name. Press the tab key to enter the name when you have a match and want Excel to enter the name.
Named ranges can work like constants
Because named ranges are created in a central location, you can use them like constants without a cell reference. For example, you can create names like «MPG» (miles per gallon) and «CPG» (cost per gallon) with and assign fixed values:
Then you can use these names anywhere you like in formulas, and update their value in one central location.
Named ranges are absolute by default
By default, named ranges behave like absolute references. For example, in this worksheet, the formula to calculate fuel would be:
=C5/$D$2
The reference to D2 is absolute (locked) so the formula can be copied down without D2 changing.
If we name D2 «MPG» the formula becomes:
=C5/MPG
Since MPG is absolute by default, the formula can be copied down column D as-is.
Named ranges can also be relative
Although named ranges are absolute by default, they can also be relative. A relative named range refers to a range that is relative to the position of the active cell at the time the range is created. As a result, relative named ranges are useful building generic formulas that work wherever they are moved.
For example, you can create a generic «CellAbove» named range like this:
- Select cell A2
- Control + F3 to open Name Manager
- Tab into ‘Refers to’ section, then type: =A1
CellAbove will now retrieve the value from the cell above wherever it is it used.
Important: make sure the active cell is at the correct location before creating the name.
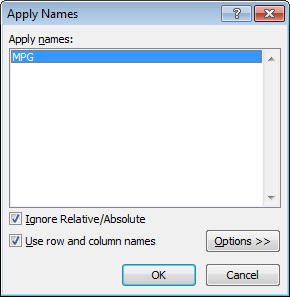
Apply named ranges to existing formulas
If you have existing formulas that don’t use named ranges, you can ask Excel to apply the named ranges in the formulas for you. Start by selecting the cells that contain formulas you want to update. Then run Formulas > Define Names > Apply Names.
Excel will then replace references that have a corresponding named range with the name itself.
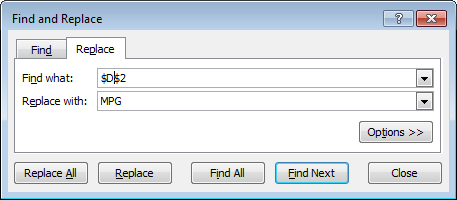
You can also apply names with find and replace:
Important: Save a backup of your worksheet, and select just the cells you want to change before using find and replace on formulas.
Key benefits of named ranges
Named ranges make formulas easier to read
The biggest single benefit to named ranges is they make formulas easier to read and maintain. This is because they replace cryptic references with meaningful names. For example, consider this worksheet with data on planets in our solar system. Without named ranges, a VLOOKUP formula to fetch «Position» from the table is quite cryptic:
=VLOOKUP($H$4,$B$3:$E$11,2,0)
However, with B3:E11 named «data», and H4 named «planet», we can write formulas like this:
=VLOOKUP(planet,data,2,0) // position
=VLOOKUP(planet,data,3,0) // diameter
=VLOOKUP(planet,data,4,0) // satellites
At a glance, you can see the only difference in these formulas in the column index.
Named ranges make formulas portable and reusable
Named ranges can make it much easier to reuse a formula in a different worksheet. If you define names ahead of time in a worksheet, you can paste in a formula that uses these names and it will «just work». This is a great way to quickly get a formula working.
For example, this formula counts unique values in a range of numeric data:
=SUM(--(FREQUENCY(data,data)>0))
To quickly «port» this formula to your own worksheet, name a range «data» and paste the formula into the worksheet. As long as «data» contains numeric values, the formula will work straightway.
Tip: I recommend that you create the needed range names *first* in the destination workbook, then copy in the formula as text only (i.e. don’t copy the cell that contains the formula in another worksheet, just copy the text of the formula). This stops Excel from creating names on-the-fly and lets you to fully control the name creation process. To copy only formula text, copy text from the formula bar, or copy via another application (i.e. browser, text editor, etc.).
Named ranges can be used for navigation
Named ranges are great for quick navigation. Just select the dropdown menu next to the name box, and choose a name. When you release the mouse, the range will be selected. When a named range exists on another sheet, you’ll be taken to that sheet automatically.
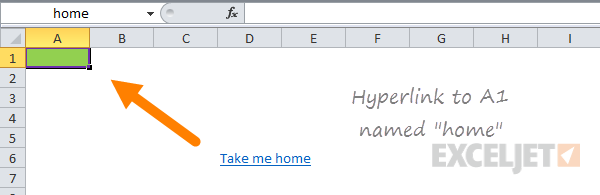
Named ranges work well with hyperlinks
Named ranges make hyperlinks easy. For example, if you name A1 in Sheet1 «home», you can create a hyperlink somewhere else that takes you back there.
To use a named range inside the HYPERLINK function, add a hash (#) in front of the named range:
=HYPERLINK("#home","take me home")
You can use this same syntax to create a hyperlink to a table:
=HYPERLINK("#Table1","Go to Table1")Note: in older versions of Excel you can’t link to a table like this. However, you can define a name equal to a table (i.e. =Table1) and hyperlink to that.
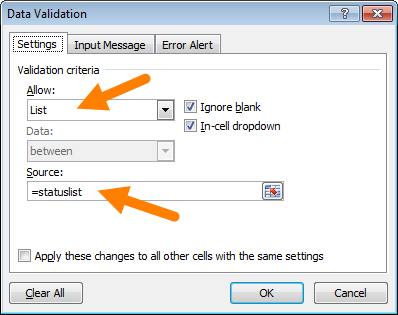
Named ranges for data validation
Names ranges work well for data validation, since they let you use a logically named reference to validate input with a drop down menu. Below, the range G4:G8 is named «statuslist», then apply data validation with a List linked like this:
The result is a dropdown menu in column E that only allows values in the named range:
Dynamic Named Ranges
Names ranges are extremely useful when they automatically adjust to new data in a worksheet. A range set up this way is referred to as a «dynamic named range». There are two ways to make a range dynamic: formulas and tables.
Dynamic named range with a Table
A Table is the easiest way to create a dynamic named range. Select any cell in the data, then use the shortcut Control + T:
When you create an Excel Table, a name is automatically created (e.g. Table1), but you can rename the table as you like. Once you have created a table, it will expand automatically when data is added.
Dynamic named range with a formula
You can also create a dynamic named range with formulas, using functions like OFFSET and INDEX. Although these formulas are moderately complex, they provide a lightweight solution when you don’t want to use a table. The links below provide examples with full explanations:
- Example of dynamic range formula with INDEX
- Example of dynamic range formula with OFFSET
Table names in data validation
Since Excel Tables provide an automatic dynamic range, they would seem to be a natural fit for data validation rules, where the goal is to validate against a list that may be always changing. However, one problem with tables is that you can’t use structured references directly to create data validation or conditional formatting rules. In other words, you can’t use a table name in conditional formatting or data validation input areas.
However, as a workaround, you can define named a named range that points to a table, and then use the named range for data validation or conditional formatting. The video below runs through this approach in detail.
Video: How to use named ranges with tables
Deleting named ranges
Note: If you have formulas that refer to named ranges, you may want to update the formulas first before removing names. Otherwise, you’ll see #NAME? errors in formulas that still refer to deleted names. Always save your worksheet before removing named ranges in case you have problems and need to revert to the original.
Named ranges adjust when deleting and inserting cells
When you delete *part* of a named range, or if insert cells/rows/columns inside a named range, the range reference will adjust accordingly and remain valid. However, if you delete all of the cells that enclose a named range, the named range will lose the reference and display a #REF error. For example, if I name A1 «test», then delete column A, the name manager will show «refers to» as:
=Sheet1!#REF!
Delete names with Name Manager
To remove named ranges from a workbook manually, open the name manager, select a range, and click the Delete button. If you want to remove more than one name at the same time, you can Shift + Click or Ctrl + Click to select multiple names, then delete in one step.
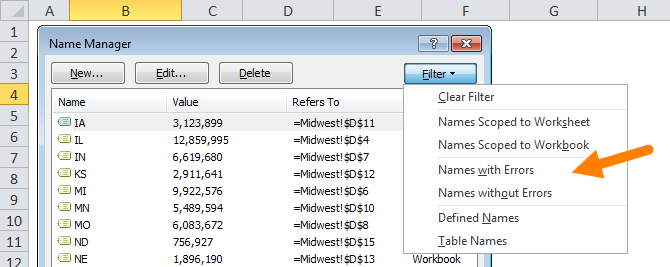
Delete names with errors
If you have a lot of names with reference errors, you can use the filter button in the name manager to filter on names with errors:
Then shift+click to select all names and delete.
Named ranges and Scope
Named ranges in Excel have something called «scope», which determines whether a named range is local to a given worksheet, or global across the entire workbook. Global names have a scope of «workbook», and local names have a scope equal to the sheet name they exist on. For example, the scope for a local name might be «Sheet2».
The purpose of scope
Named ranges with a global scope are useful when you want all sheets in a workbook to have access to certain data, variables, or constants. For example, you might use a global named range a tax rate assumption used in several worksheets.
Local scope
Local scope means a name is works only on the sheet it was created on. This means you can have multiple worksheets in the same workbook that all use the same name. For example, perhaps you have a workbook with monthly tracking sheets (one per month) that use named ranges with the same name, all scoped locally. This might allow you to reuse the same formulas in different sheets. The local scope allows the names in each sheet to work correctly without colliding with names in the other sheets.
To refer to a name with a local scope, you can prefix the sheet name to the range name:
Sheet1!total_revenue
Sheet2!total_revenue
Sheet3!total_revenue
Range names created with the name box automatically have global scope. To override this behavior, add the sheet name when defining the name:
Sheet3!my_new_name
Global scope
Global scope means a name will work anywhere in a workbook. For example, you could name a cell «last_update», enter a date in the cell. Then you can use the formula below to display the date last updated in any worksheet.
=last_update
Global names must be unique within a workbook.
Local scope
Locally scoped named ranges make sense for worksheets that use named ranges for local assumptions only. For example, perhaps you have a workbook with monthly tracking sheets (one per month) that use named ranges with the same name, all scoped locally. The local scope allows the names in each sheet to work correctly without colliding with names in the other sheets.
Managing named range scope
By default, new names created with the namebox are global, and you can’t edit the scope of a named range after it’s created. However, as a workaround, you can delete and recreate a name with the desired scope.
If you want to change several names at once from global to local, sometimes it makes sense to copy the sheet that contains the names. When you duplicate a worksheet that contains named ranges, Excel copies the named ranges to the second sheet, changing the scope to local at the same time. After you have the second sheet with locally scoped names, you can optionally delete the first sheet.
Jan Karel Pieterse and Charles Williams have developed a utility called the Name Manager that provides many useful operations for named ranges. You can download the Name Manager utility here.
How to Name a Range in Excel: Step-by-Step (+ Name Manager)
Excel is all about storing data and doing something with it. And to make data storage and manipulation easier, Excel allows users to name their data.
You can name different ranges (or arrays) in Excel and the Excel Name Manager will store them for you. Once saved, you can refer to that range of cells simply by using its name.
So instead of referencing a range like this =SUM($A$2:$C$250), write the name you gave it, which could be something like this =SUM(Prices).
Looks much easier, right? 💡
Practicing something in real-time can make you 10x faster at it. And you can master naming ranges in Excel with our sample workbook for free. Grab it here.
How to name a range in excel
A named range can save you a lot of time and confusion. And if you haven’t used it before, take my word for it – it’s very easy to create a named range.
It literally takes less than five seconds – unless, of course, the name you assign is extremely long 😅
Let’s see a simple example of naming a range below.
We have the following data.

I want to name the range A2:A10 as ‘Tableof5’.
For that:
- Select the range.

- Click in the Name Box

- Assign a name to the cell range.
- Press Ok.

The selected range has now been named.
Excel will show you the name of the range when you select it.
Important note:
Note that the name of a range cannot contain space. If you add space in the Name Box, Excel will show an error prompt:

Similarly, the first character of the name cannot be a digit. And names cannot have any other symbol other than period, backslash, and underscore character. Also, the name must not exceed 255 characters.
How to use a named range in a formula
Named ranges make writing formulas easier and quicker. Usually, you would type a formula, select all the cell references and then press Enter.
But with named ranges, you just need to enter the name of the range in place of the arguments. And it’s done 🤓
Let’s see how to use a named range in the formula below.
We will use our previous data set for this example.
We want to calculate the AVERAGE of the values of the sample data. For that:
- Name the range you want to use in the formula.
- In a cell, type in the formula.

- Enter the named range in place of the argument.

As evident, the formula immediately picks up the named range.
Note that Excel only shows the name of the range when you select the entire range. If you simply select a single cell from that range, it will show the selected cell’s reference. And not the name of the range.
- Press Enter.

Excel returns the AVERAGE of the named range.
Pretty easy, no? 😃
How to use the name manager in excel
Using names for ranges can be really useful – especially when working with an exceptionally large worksheet.
But it can be equally confusing too.
You can’t possibly readily remember the names of 32 ranges and their exact location. And figuring it out manually will leave you with no time.
Luckily, we have the Name Manager in Excel for this purpose.
As evident from the name, the Excel Name Manager is like the index page where all named ranges and cells are stored. You can also find the location of all named ranges in your Excel worksheet.
Let’s understand the Name Manager’s work in more detail below.
To open it:
- Go to the Formulas Tab.
- Select Name Manager from the Defined Names group.

- The Name Manager dialog box appears.

The Name Manager shows our previously created named range. It also shows which cells the named range refers to.
PRO TIP!
You can open the Excel Name Manager in seconds using the shortcut ALT + M + N. Cool, no? 😎
You can find all your named ranges in one place, thanks to the Name Manager. This makes it extremely useful, especially if you have plenty of named ranges.
There’s also a Filter button at the top right corner of the dialog box. It offers a menu of options that you can choose to perform different operations.
Edit named ranges
Just like adding and deleting named ranges, you can edit them too. You can access the Edit feature from the Name Manager dialog box.

You can edit the name of the range, change its reference, and even add comments.
Say, we want to change our named range ‘Tableof5’ to ‘Multiplesof5’.
For that:
- Click Edit from the Name Manager dialog box.
- The Edit Name dialog box appears.

- Click in the Name box and enter the desired name.
- Press Ok.

You can also change the references if you want to add or delete a field from the ‘Refers to’ box. It is at the bottom of the Edit Name dialog box.
Or you could do it directly from the Name Manager dialog box to save a click or two.

And that’s all about Editing named ranges in Excel 🤓
How to delete named ranges in Excel
Deleting named ranges is as simple as creating one. To delete it:
- Open the Name Manager dialog box.
- Select the named range you want to delete.
- Press the Delete button at the top.

- Excel will show a warning prompt.
- Press Ok.

The selected named range will be deleted.

That’s it – Now what?
In this article, we learned how to create named ranges in Excel. We also saw what purpose the Name Manager serves and how to edit and delete named ranges.
The named range is a very powerful and resourceful tool of Excel, especially when you have to store tons of data and refer to it several times. It lets you specify a name for each range and this makes working so convenient.
Instead of adding cell references of a range, you can simply use the name of the range in the argument. It is not only faster but easier too.
But to use named ranges in formulas, you need to know the functions first 😅 Worry not, we’ve got a solution to that as well.
Good functions to pair with named ranges are VLOOKUP, IF, and SUMIF. You can learn them for free in my 30-minute Excel course – delivered right to your inbox.
Other resources
In addition to ranges, you can also name data tables in Excel. And although naming a group of cells is easy, people often make errors while using them.
Most importantly, if you misspell the name of the named range while entering it in a function, you’d get a #NAME error. How do you fix that? Check our tutorial!
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can. Simply select a range of cells. Click the Name box at the left of the formula bar. Type in the name. Press Enter. And it’s done.
The name box is located to the left of the formula bar in the Excel sheet. It shows cell addresses, range names, and more.
You use a named range in a formula just like other arguments – if it requires one. Just type in the formula, and enter the range name instead of the cell references in the argument. Excel will apply the formula to that specific range.
Kasper Langmann2023-02-23T15:01:57+00:00
Page load link