In this Article
- VBA MsgBox Function
- VBA YesNo Message Box
- VBA Message Box Options
- Syntax of MsgBox Function
- Customize Message Box Title and Prompt
- MessageBox LineBreaks
- MsgBox Icons
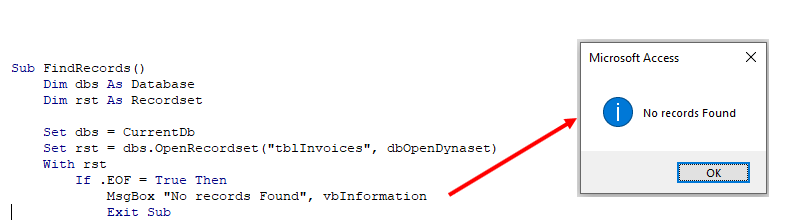
- MsgBox Icons – Information
- MsgBox Icons – Critical
- MsgBox Icons – Question
- MsgBox Icons – Exclamation
- MsgBox Variables
- OK Message Box – vbOKOnly
- OK Cancel Message Box – vbOKCancel
- Yes No Message Box – vbYesNo
- Yes No Cancel Message Box – vbYesNoCancel
- Abort Retry Ignore Message Box – vbAbortRetryIgnore
- Retry Cancel Message Box – vbRetryCancel
- VBA MessageBox Examples
- Message Box Confirmation Before Running Macro
- Yes / No Message Box – Exit Sub
- VBA Message Box in Access VBA
This tutorial will cover how to use the VBA MsgBox Function to display messageboxes to users (including the YesNo Messagebox). You might also be interested in our article on InputBoxes.
VBA MsgBox Function
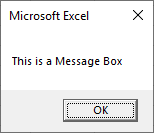
In VBA, it’s easy to display a simple MsgBox:
MsgBox "This is a Message Box"However you can do a lot more than display a simple OK message box. Let’s quickly look at complicated example before we dive into specifics…
VBA YesNo Message Box
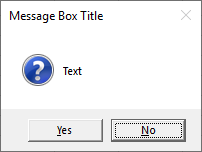
Below we will create a message box with:
- A title “Message Box Title” and prompt “Text”
- A question mark icon
- Yes / No options instead of a simple “OK”
- Default button = ‘No’
Dim answer As Integer
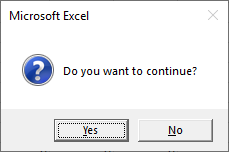
answer = MsgBox("Text", vbQuestion + vbYesNo + vbDefaultButton2, "Message Box Title")The messagebox will return vbYes or vbNo depending on the user’s choice. You can then then perform different actions based on the choice:
If answer = vbYes Then
MsgBox "Yes"
Else
MsgBox "No"
End IfIn the next section we will show you all of the options available to you when creating message boxes. Then we will introduce you to the syntax of the MsgBox Function and finally go over other message box examples.
VBA Message Box Options
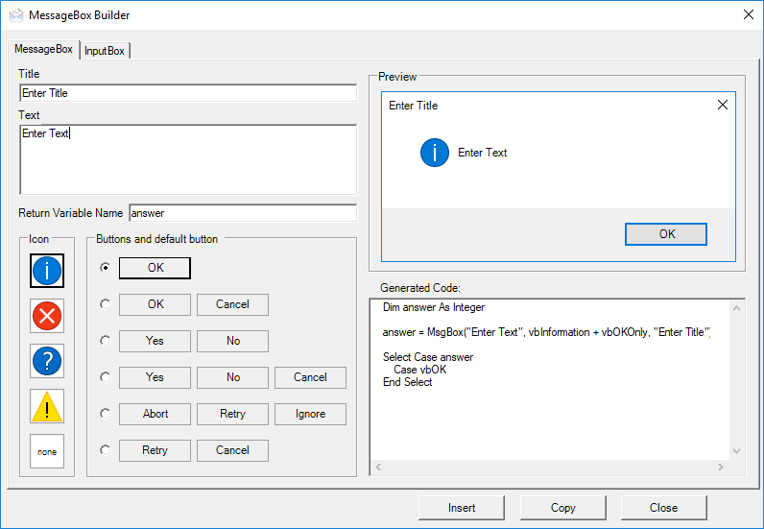
Take a look at the image below. Here you will see (almost) all of the options available to you when creating message boxes. Take notice of the icons and the different buttons.
This is a screenshot of the “MessageBox Builder” from our Premium VBA Add-in: AutoMacro. The MessageBox Builder allows you to quickly design your desired messagebox and insert the code into your code module. It also contains many other code builders, an extensive VBA code library, and an assortment of coding tools. It’s a must-have for any VBA developer.
Syntax of MsgBox Function
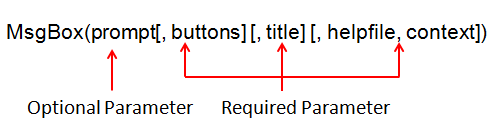
MsgBox( prompt [, buttons ] [, title ] [, helpfile, context ] )
prompt (Required) – This is the primary message box text.
buttons – Choose which buttons to display. If omitted, ‘OKonly’. Here you can also specify what icon to show and the default button.
title – The title at the top of the message box. If omitted, the name of the current application is displayed (ex. Microsoft Excel).
helpfile – Specify help file that can be accessed when user clicks on the ‘Help’ button. If specified, then you must also add context (below)
context – Numeric expression representing the Help context number assigned to the appropriate Help topic.
You can probably ignore the helpfile and context arguments. I’ve never seen them used.
Customize Message Box Title and Prompt
The MsgBox function allows you to customize the title and prompt messages like so:
Msgbox "Prompt",,"Title"Another example:
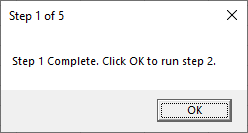
Sub MsgBoxPromptTitle()
MsgBox "Step 1 Complete. Click OK to run step 2.",, "Step 1 of 5"
End SubImportant! You must remember to surround your text with quotations.
MessageBox LineBreaks
You can also add line breaks to your message box prompts with ‘vbNewLine’.
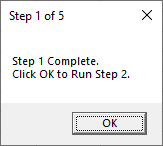
Sub MsgBoxPromptTitle_NewLine()
MsgBox "Step 1 Complete." & vbNewLine & "Click OK to Run Step 2.", , "Step 1 of 5"
End SubNotice we use the & symbol to join text together. You can learn more about using & with text and other options for inserting linebreaks in our article on joining text.
VBA Coding Made Easy
Stop searching for VBA code online. Learn more about AutoMacro — A VBA Code Builder that allows beginners to code procedures from scratch with minimal coding knowledge and with many time-saving features for all users!
Learn More
MsgBox Icons
VBA gives you the ability to add one of four pre-built icons to your message boxes:
| Icon Constant | Icon |
|---|---|
| vbInformation | |
| vbCritical | |
| vbQuestion | |
| vbExclamation |
The Icon constant should be placed within the button argument:
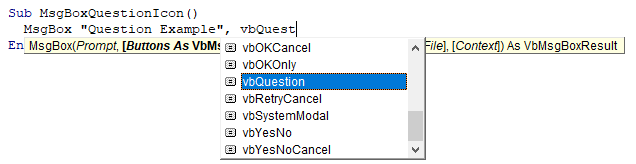
Sub MsgBoxQuestionIcon()
MsgBox "Question Example", vbQuestion
End SubThis will generate the default ‘OK’ message box with the Question icon:
Notice how when you type, the VBA Editor will show you the options available to you:
This is helpful because you don’t need to remember the exact syntax or names of icons or buttons.
Now we will demo each message box icon:
MsgBox Icons – Information
Sub MsgBoxInformationIcon()
MsgBox "Information Example", vbInformation
End SubMsgBox Icons – Critical
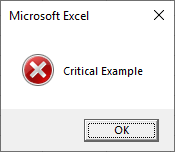
Sub MsgBoxCriticalIcon()
MsgBox "Critical Example", vbCritical
End SubVBA Programming | Code Generator does work for you!
MsgBox Icons – Question
Sub MsgBoxQuestionIcon()
MsgBox "Question Example", vbQuestion
End SubMsgBox Icons – Exclamation
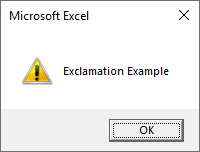
Sub MsgBoxExclamationIcon()
MsgBox "Exclamation Example", vbExclamation
End SubBelow we will talk about generating message boxes with different button layouts. If you do choose a different message box type, you will need to append the icon type after the buttons using a “+”:
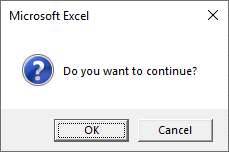
Sub MsgBoxQuestionIcon()
MsgBox "Do you want to continue?", vbOKCancel + vbQuestion
End SubMsgBox Variables
So far we have worked primarily with the default ‘OK’ message box. The OK message box only has one option: Pressing ‘OK’ allows the code to continue. However, you can also specify other button groupings: OK / Cancel, Yes / No, etc.
In which case you will want to perform different actions based on which button is pressed. Let’s look at an example.
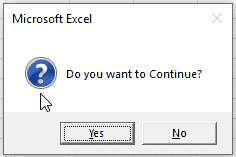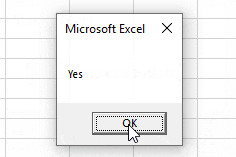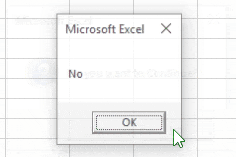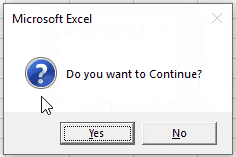
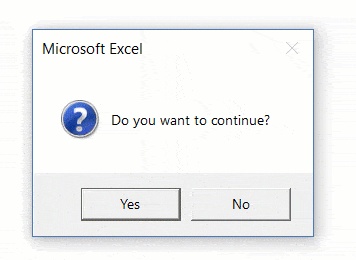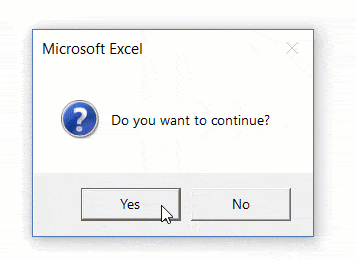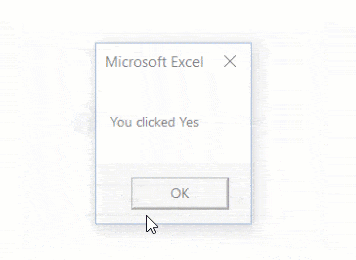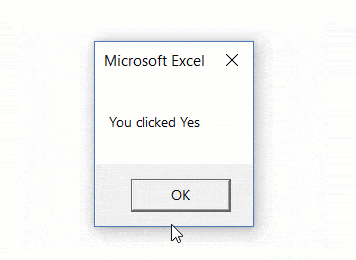
Here is the message box we will generate:
This is the entire code (we will break it down next):
Sub MsgBoxVariable()
Dim answer As Integer
answer = MsgBox("Do you want to Continue?", vbQuestion + vbYesNo)
If answer = vbYes Then
MsgBox "Yes"
Else
MsgBox "No"
End If
End SubFirst we assign the messagebox output to an integer variable.
Dim answer As Integer
answer = MsgBox("Do you want to Continue?", vbQuestion + vbYesNo)Next we use an If-Else to determine what to do based on which button is pressed:
If answer = vbYes Then
MsgBox "Yes"
Else
MsgBox "No"
End IfThe MsgBox function returns an integer value (between 1-7) so we define the variable as an integer type. However, instead of referring to the integer number, you can refer to a constant (ex. vbOK, vbCancel, etc.). Look at this table to see all of the options:
| Button | Constant | Value |
|---|---|---|
| OK | vbOK | 1 |
| Cancel | vbCancel | 2 |
| Abort | vbAbort | 3 |
| Retry | vbRetry | 4 |
| Ignore | vbIgnore | 5 |
| Yes | vbYes | 6 |
| No | vbNo | 7 |
Now we will demo each button grouping:
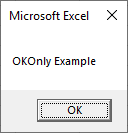
OK Message Box – vbOKOnly
This is the standard VBA messagebox.
Sub MsgBox_OKOnly()
Dim answer As Integer
answer = MsgBox("OKOnly Example", vbOKOnly)
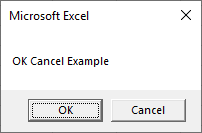
End SubOK Cancel Message Box – vbOKCancel
Sub MsgBox_OKCancel()
Dim answer As Integer
answer = MsgBox("OK Cancel Example", vbOKCancel)
If answer = vbOK Then
MsgBox "OK"
Else
MsgBox "Cancel"
End If
End SubAutoMacro | Ultimate VBA Add-in | Click for Free Trial!
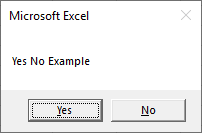
Yes No Message Box – vbYesNo
Sub MsgBox_YesNo()
Dim answer As Integer
answer = MsgBox("Yes No Example", vbYesNo)
If answer = vbYes Then
MsgBox "Yes"
Else
MsgBox "No"
End If
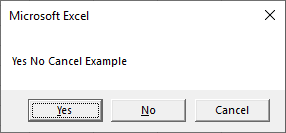
End SubYes No Cancel Message Box – vbYesNoCancel
Sub MsgBox_YesNoCancel()
Dim answer As Integer
answer = MsgBox("Yes No Cancel Example", vbYesNoCancel)
If answer = vbYes Then
MsgBox "Yes"
ElseIf answer = vbNo Then
MsgBox "No"
Else
MsgBox "Cancel"
End If
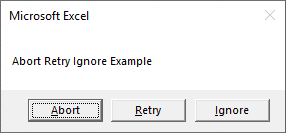
End SubAbort Retry Ignore Message Box – vbAbortRetryIgnore
Sub MsgBox_AbortRetryIgnore()
Dim answer As Integer
answer = MsgBox("Abort Retry Ignore Example", vbAbortRetryIgnore)
If answer = vbAbort Then
MsgBox "Abort"
ElseIf answer = vbRetry Then
MsgBox "Retry"
Else
MsgBox "Ignore"
End If
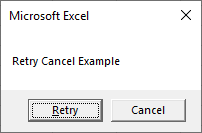
End SubRetry Cancel Message Box – vbRetryCancel
Sub MsgBox_RetryCancel()
Dim answer As Integer
answer = MsgBox("Retry Cancel Example", vbRetryCancel)
If answer = vbRetry Then
MsgBox "Retry"
Else
MsgBox "Cancel"
End If
End SubAutoMacro | Ultimate VBA Add-in | Click for Free Trial!
VBA MessageBox Examples
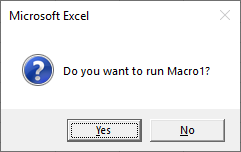
Message Box Confirmation Before Running Macro
This code will display a Yes No Message box before calling a macro. If Yes is clicked the macro is called, if No is clicked, the Macro does not run.
Sub Msgbox_BeforeRunning()
Dim answer As Integer
answer = MsgBox("Do you want to run Macro1?", vbQuestion + vbYesNo)
If answer = vbYes Then Call Macro1
End SubYes / No Message Box – Exit Sub
Here we will confirm with the user whether to continue running a macro. If No is clicked, the code will exit the sub, otherwise the procedure will continue.
Sub Msgbox_BeforeRunning()
Dim answer As Integer
answer = MsgBox("Do you want to continue?", vbQuestion + vbYesNo)
If answer = vbNo Then Exit Sub
'Some Code
End SubVBA Message Box in Access VBA
All of the above examples work exactly the same in Access VBA as in Excel VBA.
На чтение 10 мин. Просмотров 38.4k.
В Excel VBA вы можете использовать функцию MsgBox для отображения окна сообщения (как показано ниже):
MsgBox — это не что иное, как диалоговое окно, которое вы можете использовать для информирования своих пользователей, показывая пользовательское сообщение или получая некоторые основные входные данные (такие как Да / Нет или OK / Отмена).
Пока отображается диалоговое окно MsgBox, ваш код VBA останавливается. Вам нужно нажать любую из кнопок в MsgBox, чтобы запустить оставшийся код VBA.
Примечание: в этом уроке я буду использовать слова «окно сообщения» и MsgBox взаимозаменяемо. При работе с Excel VBA вам всегда нужно использовать MsgBox.
Содержание
- Анатомия VBA MsgBox в Excel
- Синтаксис функции VBA MsgBox
- Константы кнопки Excel VBA MsgBox (примеры)
- Константы значков Excel VBA MsgBox (примеры)
- Настройка заголовка и приглашения в MsgBox
- Присвоение значения MsgBox переменной
Анатомия VBA MsgBox в Excel
Окно сообщения состоит из следующих частей:
- Title — заголовок: обычно используется для отображения содержания окна сообщения. Если вы ничего не указали, отображается имя приложения, в данном случае Microsoft Excel.
- Prompt — подсказка: это сообщение, которое вы хотите отобразить. Вы можете использовать это пространство, чтобы написать пару строк или даже отобразить таблицы / данные здесь.
- Button(s) — кнопка(-и): хотя кнопка «ОК» является кнопкой по умолчанию, ее можно настроить таким образом, чтобы отображать такие кнопки, как «Да / Нет»; «Да / Нет / Отмена», «Повторить» / «Пропустить» и т.д.
- Close Icon — значок закрытия: Вы можете закрыть окно сообщения, нажав на значок закрытия.
Синтаксис функции VBA MsgBox
Как я уже упоминал, MsgBox является функцией и имеет синтаксис, аналогичный другим функциям VBA.
MsgBox( prompt [, buttons ] [, title ] [, helpfile, context ] )
- prompt — это обязательный аргумент. Он отображает сообщение, которое вы видите в MsgBox. В нашем примере текст «Это образец MsgBox» — это «подсказка». В приглашении можно использовать до 1024 символов, а также использовать его для отображения значений переменных. Если вы хотите показать подсказку, состоящую из нескольких строк, вы можете сделать это также (подробнее об этом позже в этом руководстве).
- [buttons ] — определяет, какие кнопки и значки отображаются в MsgBox. Например, если я использую vbOkOnly, на нем будет отображаться только кнопка OK, а если я использую vbOKCancel, на нем будут отображаться кнопки OK и Отмена. Я расскажу о различных видах кнопок позже в этом уроке.
- [title] — здесь вы можете указать заголовок в диалоговом окне сообщения. Отображается в строке заголовка MsgBox. Если вы ничего не укажете, будет показано название приложения.
- [helpfile] — вы можете указать файл справки, к которому можно получить доступ, когда пользователь нажимает кнопку «Справка». Кнопка справки появится только тогда, когда вы используете для нее код кнопки. Если вы используете файл справки, вам также необходимо указать аргумент context.
- [context] — это числовое выражение, которое является номером контекста справки, назначенным соответствующему разделу справки.
Если вы новичок в концепции Msgbox, не стесняйтесь игнорировать аргументы [helpfile] и [context]. Они редко используются.
Примечание. Все аргументы в квадратных скобках являются необязательными. Только аргумент «подсказка» является обязательным.
Константы кнопки Excel VBA MsgBox (примеры)
В этом разделе я расскажу о различных типах кнопок, которые вы можете использовать с VBA MsgBox.
Прежде чем я покажу вам код VBA для него и то, как выглядит MsgBox, вот таблица, в которой перечислены все различные константы кнопок, которые вы можете использовать.
| Константа кнопки | Описание |
| vbOKOnly | Показывает только кнопку ОК |
| vbOKCancel | Показывает кнопки ОК и Отмена |
| vbAbortRetryIgnore | Показывает кнопки «Прервать», «Повторить» и «Игнорировать» |
| vbYesNo | Показывает кнопки Да и Нет |
| vbYesNoCancel | Показывает кнопки Да, Нет и Отмена |
| vbRetryCancel | Показывает кнопки «Повторить» и «Отменить» |
| vbMsgBoxHelpButton | Показывает кнопку справки. Чтобы это работало, вам нужно использовать аргументы справки и контекста в функции MsgBox |
| vbDefaultButton1 | Делает первую кнопку по умолчанию. Вы можете изменить номер, чтобы изменить кнопку по умолчанию. Например, vbDefaultButton2 делает вторую кнопку по умолчанию |
Примечание. Просматривая примеры создания различных кнопок, вы можете задаться вопросом, какой смысл использовать эти кнопки, если они не влияют на код.
Влияют! В зависимости от выбора вы можете кодировать то, что вы хотите, чтобы код делал. Например, если вы выберете «ОК», код должен продолжиться, а если вы нажмете «Отмена», код должен прекратиться. Это можно сделать с помощью переменных и присвоения значения окна сообщения переменной. Мы рассмотрим это в последующих разделах этого урока.
Теперь давайте рассмотрим несколько примеров того, как различные кнопки могут отображаться в MsgBox и как они выглядят.
Кнопки MsgBox — vbOKOnly (по умолчанию)
Если вы используете только приглашение и не указываете ни один из аргументов, вы получите окно сообщения по умолчанию, как показано ниже:
Ниже приведен код, который выдаст это окно сообщения:
Sub DefaultMsgBox() MsgBox "This is a sample box" End Sub
Обратите внимание, что текстовая строка должна быть в двойных кавычках.
Вы также можете использовать постоянную кнопку vbOKOnly, но даже если вы ничего не указали, она используется по умолчанию.
Кнопки MsgBox — ОК и Отмена
Если вы хотите показать только ОК и кнопку Отмена, вам нужно использовать константу vbOKCancel
Sub MsgBoxOKCancel() MsgBox "Want to Continue?", vbOKCancel End Sub
Кнопки MsgBox — Отмена, Повтор и Игнорирование
Вы можете использовать константу vbAbortRetryIgnore для отображения кнопок «Отмена», «Повторить» и «Игнорировать».
Sub MsgBoxAbortRetryIgnore() MsgBox "What do you want to do?", vbAbortRetryIgnore End Sub
Кнопки MsgBox — Да и Нет
Вы можете использовать константу vbYesNo для отображения кнопок Да и Нет.
Sub MsgBoxYesNo() MsgBox "Should we stop?", vbYesNo End Sub
Кнопки MsgBox — Да, Нет и Отмена
Вы можете использовать константу vbYesNoCancel для отображения кнопок «Да», «Нет» и «Отмена».
Sub MsgBoxYesNoCancel() MsgBox "Should we stop?", vbYesNoCancel End Sub
Кнопки MsgBox — повторить попытку и отменить
Вы можете использовать константу vbRetryCancel для отображения кнопок «Повторить» и «Отмена».
Sub MsgBoxRetryCancel() MsgBox "What do you want to do next?", vbRetryCancel End Sub
Кнопки MsgBox — Кнопка справки
Вы можете использовать константу vbMsgBoxHelpButton для отображения кнопки справки. Вы можете использовать его с другими константами кнопок.
Sub MsgBoxRetryHelp() MsgBox "What do you want to do next?", vbRetryCancel + vbMsgBoxHelpButton End Sub
Обратите внимание, что в этом коде мы объединили две разные константы кнопки (vbRetryCancel + vbMsgBoxHelpButton). Первая часть показывает кнопки «Повторить» и «Отмена», а вторая часть показывает кнопку «Справка».
MsgBox Buttons — Настройка кнопки по умолчанию
Вы можете использовать константу vbDefaultButton1 для установки первой кнопки по умолчанию. Это означает, что кнопка уже выбрана, и если вы нажмете Enter, она выполнит эту кнопку.
Ниже приведен код, который установит в качестве кнопки по умолчанию вторую кнопку (кнопка «Нет»).
Sub MsgBoxOKCancel() MsgBox "What do you want to do next?", vbYesNoCancel + vbDefaultButton2 End Sub
В большинстве случаев крайняя левая кнопка является кнопкой по умолчанию. Вы можете выбрать другие кнопки, используя vbDefaultButton2, vbDefaultButton3 и vbDefaultButton4.
Константы значков Excel VBA MsgBox (примеры)
Помимо кнопок, вы также можете настроить значки, отображаемые в диалоговом окне MsgBox. Например, у вас может быть красный критический значок или синий информационный значок.
Ниже приведена таблица со списком кода, который будет отображать соответствующий значок.
| Константа значка | Описание |
| vbCritical | Показывает значок критического сообщения |
| vbQuestion | Показывает значок вопроса |
| vbExclamation | Показывает значок предупреждения |
| vbInformation | Показывает значок информации |
Иконки MsgBox — Критические
Если вы хотите показать критический значок в своем MsgBox, используйте константу vbCritical. Вы можете использовать ее вместе с другими константами кнопки (поставив знак + между кодами).
Например, ниже приведен код, который будет показывать кнопку ОК по умолчанию с критическим значком.
Sub MsgBoxCriticalIcon() MsgBox "This is a sample box", vbCritical End Sub
Если вы хотите показать критический значок с кнопками Да и Нет, используйте следующий код:
Sub MsgBoxCriticalIcon() MsgBox "This is a sample box", vbYesNo + vbCritical End Sub
Иконки MsgBox — Вопрос
Если вы хотите показать иконку вопроса в своем MsgBox, используйте константу vbQuestion.
Sub MsgBoxQuestionIcon() MsgBox "This is a sample box", vbYesNo + vbQuestion End Sub
Иконки MsgBox — Восклицательный знак
Если вы хотите показать восклицательный значок в вашем MsgBox, используйте константу vbExclamation.
Sub MsgBoxExclamationIcon() MsgBox "This is a sample box", vbYesNo + vbExclamation End Sub
Иконки MsgBox — Информация
Если вы хотите отобразить информационный значок в вашем MsgBox, используйте константу vbInformation.
Sub MsgBoxInformationIcon() MsgBox "This is a sample box", vbYesNo + vbInformation End Sub
Настройка заголовка и приглашения в MsgBox
При использовании MsgBox вы можете настроить заголовок и сообщения подсказок.
До сих пор в примерах, которые мы видели, использовался Microsoft Excel в качестве заголовка. Если вы не указали аргумент title, MsgBox автоматически использует заголовок приложения (в данном случае это был Microsoft Excel).
Вы можете настроить заголовок, указав его в коде, как показано ниже:
Sub MsgBoxInformationIcon() MsgBox "Do you want to continue?", vbYesNo + vbQuestion, "Step 1 of 3" End Sub
Точно так же вы также можете настроить сообщение подсказки.
Вы также можете добавить разрывы строк в сообщении подсказки.
В приведенном ниже коде я добавил разрыв строки, используя «vbNewLine».
Sub MsgBoxInformationIcon() MsgBox "Do you want to continue?" & vbNewLine & "Click Yes to Continue", vbYesNo + vbQuestion, "Step 1 of 3" End Sub
Вы также можете использовать символ возврата каретки — Chr (13) или перевод строки — Chr (10), чтобы вставить новую строку в сообщение с подсказкой.
Обратите внимание, что вы можете добавить новую строку только к сообщению, а не к заголовку.
Присвоение значения MsgBox переменной
До сих пор мы видели примеры, где мы создавали окна сообщений и настраивали кнопки, значки, заголовок и приглашение.
Однако нажатие кнопки ничего не сделало.
С помощью функции MsgBox в Excel вы можете решить, что вы хотите делать, когда пользователь нажимает определенную кнопку. И это возможно, поскольку каждая кнопка имеет значение, связанное с ней.
Поэтому, если я нажимаю кнопку «Да», функция MsgBox возвращает значение (6 или константа vbYes), которое я могу использовать в своем коде. Аналогично, если пользователь выбирает кнопку «Нет», он возвращает другое значение ((7 или константа vbNo)), которое я могу использовать в коде.
Ниже приведена таблица, которая показывает точные значения и константу, возвращаемую функцией MsgBox. Вам не нужно запоминать их, просто помните об этом, и вы можете использовать константы, которые проще в использовании.
| При нажатии кнопки | Константа | Значение |
| Ok | vbOk | 1 |
| Cancel | vbCancel | 2 |
| Abort | vbAbort | 3 |
| Retry | vbRetry | 4 |
| Ignore | vbIgnore | 5 |
| Yes | vbYes | 6 |
| No | vbNo | 7 |
Теперь давайте посмотрим, как мы можем контролировать макрос-код VBA в зависимости от того, на какую кнопку нажимает пользователь.
В приведенном ниже коде, если пользователь нажимает кнопку «Да», отображается сообщение «Вы нажали кнопку «Да», а если пользователь нажимает кнопку «Нет», отображается сообщение «Вы нажали кнопку «Нет»».
Sub MsgBoxInformationIcon()
Result = MsgBox("Do you want to continue?", vbYesNo + vbQuestion)
If Result = vbYes Then
MsgBox "You clicked Yes"
Else: MsgBox "You clicked No"
End If
End Sub
В приведенном выше коде я присвоил значение функции MsgBox переменной Result. Когда вы нажимаете кнопку «Да», переменная Result получает константу vbYes (или число 6), а когда вы нажимаете «Нет», переменная Result получает константу vbNo (или число 7).
Затем я использовал конструкцию If Then Else, чтобы проверить, содержит ли переменная Result значение vbYes. Если это так, отображается запрос «Вы нажали Да», в противном случае — «Вы нажали Нет».
Вы можете использовать ту же концепцию для запуска кода, если пользователь нажимает Да, и выход из подпрограммы, когда он нажимает Нет.
Примечание. Когда вы присваиваете выход MsgBox переменной, вы должны поместить аргументы функции MsgBox в круглые скобки. Например, в строке Result = MsgBox («Хотите продолжить?», VbYesNo + vbQuestion) вы можете видеть, что аргументы находятся в скобках.
Если вы хотите в дальнейшем углубиться в функцию Message Box, вот официальный документ по ней.
Использование функции MsgBox в VBA Excel, ее синтаксис и параметры. Значения, возвращаемые функцией MsgBox. Примеры использования.
Функция MsgBox предназначена в VBA Excel для вывода сообщения в диалоговом окне, ожидания нажатия кнопки и возврата значения типа Integer, указывающего на то, какая кнопка была нажата. Для упрощения восприятия информации, в этой статье не рассматриваются параметры, связанные с контекстной справкой и модальностью диалогового окна MsgBox.
Синтаксис функции
MsgBox ( Prompt [, Buttons ] [, Title ])
Обязательным параметром функции MsgBox является Prompt, если Buttons и Title явно не указаны, используются их значения по умолчанию. Кроме того, если необязательные параметры не указаны и возвращаемое значение не присваивается переменной, сообщение не заключается в скобки:
Пример 1
|
Sub Test1() MsgBox «Очень важное сообщение!» End Sub |
Параметры функции
| Параметр | Описание | Значение по умолчанию |
|---|---|---|
| Prompt* | Обязательный параметр. Выражение типа String, отображаемое в диалоговом окне в виде сообщения. Разделить на строки можно с помощью константы vbNewLine. | Нет |
| Buttons | Необязательный параметр. Числовое выражение, которое представляет собой сумму значений, задающих номер и тип отображаемых кнопок, стиль используемого значка, тип кнопки по умолчанию. | 0 |
| Title | Необязательный параметр. Выражение типа String, отображаемое в заголовке диалогового окна. | Имя приложения** |
*Максимальная длина параметра Prompt составляет примерно 1024 знака и зависит от их ширины.
**В Excel по умолчанию в заголовке MsgBox выводится надпись «Microsoft Excel».
Константы параметра «Buttons»
Тип и количество кнопок
| Константа | Описание | Значение |
|---|---|---|
| vbOKOnly | Отображается только кнопка OK. | 0 |
| vbOKCancel | Отображаются кнопки OK и Cancel (Отмена). | 1 |
| vbAbortRetryIgnore | Отображаются кнопки Abort (Прервать), Retry (Повторить) и Ignore (Пропустить). | 2 |
| vbYesNoCancel | Отображаются кнопки Yes (Да), No (Нет) и Cancel (Отмена). | 3 |
| vbYesNo | Отображаются кнопки Yes (Да) и No (Нет). | 4 |
| vbRetryCancel | Отображаются кнопки Retry (Повторить) и Cancel (Отмена). | 5 |
Стиль значка
| Константа | Описание | Значение |
|---|---|---|
| vbCritical | Отображается значок Critical — Критичное сообщение, сообщение об ошибке. | 16 |
| vbQuestion | Отображается значок Question — Сообщение с вопросом. | 32 |
| vbExclamation | Отображается значок Exclamation — Предупреждающее сообщение. | 48 |
| vbInformation | Отображается значок Information — Информационное сообщение. | 64 |
Для просмотра отображаемых значков, скопируйте код в свой модуль и запустите на выполнение:
Пример 2
|
Sub Test2() Dim a As Integer a = MsgBox(«Критичное сообщение, сообщение об ошибке», 16) a = MsgBox(«Сообщение с вопросом», 32) a = MsgBox(«Предупреждающее сообщение», 48) a = MsgBox(«Информационное сообщение», 64) End Sub |
Кнопка по умолчанию
| Константа | Описание | Значение |
|---|---|---|
| vbDefaultButton1 | По умолчанию активна первая кнопка. | 0 |
| vbDefaultButton2 | По умолчанию активна вторая кнопка. | 256 |
| vbDefaultButton3 | По умолчанию активна третья кнопка. | 512 |
Возвращаемые значения
| Константа | Кнопка | Значение |
|---|---|---|
| vbOK | OK | 1 |
| vbCancel | Отмена | 2 |
| vbAbort | Прервать | 3 |
| vbRetry | Повторить | 4 |
| vbIgnore | Пропустить | 5 |
| vbYes | Да | 6 |
| vbNo | Нет | 7 |
Значение, возвращаемое функцией MsgBox, используется для выбора дальнейших действий исполняемой программы в зависимости от нажатой кнопки.
Для третьего примера зададим следующие параметры первой функции MsgBox:
- Prompt = «Выберите кнопку!»
- Buttons = 323 (3 (vbYesNoCancel) + 64 (vbInformation) + 256 (vbDefaultButton2))
- Title = «Выбор кнопки»
Вторая функция MsgBox используется как простое информационное сообщение с параметрами по умолчанию.
Пример 3
|
Sub Test3() Dim a As Integer a = MsgBox(«Выберите кнопку!», 323, «Выбор кнопки») If a = 6 Then MsgBox «Вы нажали кнопку: Да» ElseIf a = 7 Then MsgBox «Вы нажали кнопку: Нет» Else MsgBox «Вы нажали кнопку: Отмена» End If End Sub |
В этом примере, в зависимости от нажатой кнопки в первом диалоговом окне, во втором сообщении выводится название нажатой кнопки. Обратите внимание, что вторая кнопка в открывшемся первом окне MsgBox выделена по умолчанию и срабатывает при нажатии клавиши «Enter».
А что будет, если первое диалоговое окно из третьего примера закрыть крестиком? Проверьте сами.
VBA MsgBox Excel Examples – 100+ Message Box Macros
The MsgBox in VBA is a popup message box to display message in Excel VBA, Access VBA and other MS Office Applications. Excel VBA MsgBox shows Message Box using VBA Macro Programming with verity of Options and Types.
Message Box (MsgBox) VBA Macros explained with syntax. Use MsgBox in VBA to show vbYes, No and Cancel, vbexclamation, vbcritical, vbinformation message boxes and other advanced popup messages box models to display with icons and command buttons.
VBA MsgBox Function
VBA MsgBox is one of the most frequently used functions in VBA Application Development. We can use MsgBox Function in Microsoft Word, Excel, Access and PowerPoint VBA Programming. Excel VBA Message Box function displays a message, optional icon and selected set of command buttons in a dialog box. It waits for the user to click a button, and returns an Integer indicating the button which user clicked. Here is the syntax and different kinds of Message Boxes in VBA.
VBA MsgBox – Syntax:
Here is the syntax of VBA MsgBox Function. This is same in Excel, Word, Access, PowerPoint and VBScript.
MsgBox(prompt
[, buttons] [, title] [, helpfile, context])
Where
- Prompt: It Contains String expression displayed as the message in the dialog box. The Maximum length of Prompt is 1024 Characters. You can use carriage return Character,If prompt consists more than one line.
- buttons:It Contains Numeric value specifying the number and type of buttons to display.The default button value is 0.
- title:It Contains String expression displayed in the title bar of the dialog box.
VBA MsgBox in Excel VBA – Example Cases:
Here is a short video to show you VBA Message Box with different types of options:
Here are the different types of Message Boxes available in Excel VBA. You can click on each link to see the respective examples, Screenshots of output and explanation.
VBA MsgBox arguments
VBA MsgBox will take the following parameters: These options will change the appearance of the Message Box. You can change the model of the Message Box by combining different option of MsgBox Function.
- MsgBox Prompt: This is the message text which you want to show/prompt
- MsgBox Buttons Style: This is the type of message box which you want to show, like Yes No buttons with Information Icon
- MsgBox Title: This is the title of the message box window
- MsgBox Help File, and Context: These are the other optional parameters which we use in very rare
Here is the Hello World MsgBox Function example with Parameters.
MsgBox “Hello World!”, vbYesNo + vbInformation, “VBA Hello World Message Box Example Title”
The above MsgBox will show you Yes No Type message box with information icon and title.
VBA MessageBox Options and Uses
Let us see the different options and usage of Message Box Function. We can create verity of Message Boxes in VBA to handle different scenarios.
VBA MsgBox Styles
In Most cases we use vbYesNo Message Box and get the result to a variable. Let us see vbYesNo Syntax, arguments, parameters, yes no default buttons, yes no prompt and yes no examples. yes no if syntax helps us to decide based on the user input. We can check If yes no return, yes no answer.
MsgBox “This is the example Yes No Syntax”, vbYesNo
We can also create MsgBox with Yes No and Cancel values, and get the user yes, no or cancel responses. Instead of adding the strings in MsgBox Parameters. We can create variable string and pass as a string. We can use the variable for MsgBox Prompt or Title. Combining Yes No Button Types with different option, we can display yes no critical, yes no warning, yes no exclamation, yes no question type Msg Box. below arr syntax to change button caption, button labels, button names.
Here is the Example with Yes, No, Cancel and Exclamation Icon.
MsgBox “This is the example Yes No Cancel Syntax”, vbYesNoCancel + vbExclamation
We can use Userforms to create customized Message Boxes: MsgBox Without OK button, without buttons, no buttons to show prompt. We can use command buttons, radio buttons in UserForm. We can fortmat the text, Font Size, Font Color and set Bold text in MsgBox.
We can pass variable value or variable text create a string and use as MsgBox variable input for Prompt and Titles. Different buttons and icons of MsgBox are created for different purposes.
We can have multiple lines, access custom buttons, access new line, access carriage return, variable type, variable, error handling, on error goto, error message dialog box, display array, two lines, access multiple lines.
Excel VBA MsgBox Yes No Syntax
The following is the simple Example on VBA MsgBox Yes No Prompt Type. We can use this to receive the acceptance of user to certain criteria. And decide the further process.
MsgBox “This is the example Yes No Syntax”, vbYesNo
Check the below example, it will check if user clicked on Yes or No button. We can also show the Help when user pressing F1 button or Help button.
If MsgBox("Do you want to see know the current Time", vbYesNo) = vbYes Then
MsgBox Format(Now(), "HH:MM:SS AMPM"), vbInformation, "Current Time"
End If
VBA MsgBox Yes No If
The following example on vba msgbox yes no if to show the different messages boxes based on the selected option. If then and exit sub syntax helps terminate the sub procedure based on the certain condition.
Sub sbKnowingUserInput()
intUserOption = MsgBox("Press Yes or No Button", vbYesNo)
If vbOption = 6 Then
MsgBox "You Pressed YES Option"
ElseIf vbOption = 7 Then
MsgBox "You Pressed NO Option"
Else
MsgBox "Nothing!"
End If
End Sub
VBA Message Box New line,carriage return, two lines, multiple line
We can use vbCr to split the message box text into a new line and add carriage return to make into two lines. We can use & vbCr to split the message into multiple lines.
MsgBox “Hello, This is Line ONE” & vbCr & “This is Line TWO”
VBA MsgBox Yes No Cancel Return
The below example on vba msgbox yes no cancel return to access the response of MsgBox. This will help us to access,store and input the msgbox response or string in variable value. We can use this variable text in the further programming.
Dim msgValue
msgValue = MsgBox("Hello, Are you a graduate? Choos:" _
& vbCr & "Yes: if you are a graduate" _
& vbCr & "Yes: if you are Not a graduate" _
& vbCr & "Yes: if you are Not Intrested" _
, vbYesNoCancel + vbQuestion)
If msgValue = vbYes Then
MsgBox "You are eligible for applying for this Job"
ElseIf msgValue = vbNo Then
MsgBox "You are NOT eligible for applying for this Job"
ElseIf msgValue = vbCancel Then
MsgBox "No Problems, We will find suitable job for you"
End If
VBA If Then MsgBox and Exit Sub
Some times we may want to ask user to continue further, other wise skip the execution of next program. The below example on VBA if then msgbox and exit sub will help you to do this:
Sub sbPressYesToExitSub()
If MsgBox("Would you like to continue...?", vbQuestion + vbYesNo) <> vbYes Then
Exit Sub
End If
'The below statements will not be executed when your press Yes button.
'You can write the next programming steps here... This will execute if user selects No in the above prompt.
MsgBox "You have not pressed Yes button"
End Sub
VBA On Error GoTo Message Box for Error Handling
MsgBox is also useful in error handling. We can tell VBA error message on error. Or we can go to a label and show message box with error number and description. The below code will execute the code and show the error number and description if there is any run-time error.
Sub sbShowing_Error_MessageBox() On Erro GoTo ErrorHanMsg1 'Your code goes here.... Exit Sub 'This comes before End Sub or End Function Statement ErrorHanMsg1: MsgBox Err.Number & vbCr & Err.Description End Sub
VBA MsgBox Styles
Here are the list of styles and models of Message Box Function in VBA. We combine different options to display a message box with desired options.
- vbOKOnly: Displays the message box with OK button
- vbOKCancel: This option will show you two buttons, OK and Cancel button to the user.
- vbAbortRetryIgnore: MsgBox with three buttons, Abort, Retry and Ignore buttons.
- vbYesNoCancelShows 3 buttons: Yes, No and Cancel.
- vbYesNo: Shows both Yes, No buttons
- vbRetryCancel: Helps to display Retry and Cancel buttons
- vbCritical: Adds Critical Warning Icon to message box
- vbQuestion: Question mark Icon will be added to message box
- vbExclamation: Exclamation mark will be added to the MsgBox
- vbInformation: Information symbol can show on message box
- vbDefaultButton1: To set the focus on the first button
- vbDefaultButton2: You can set the focus on the second button
- vbDefaultButton3: To set the focus on the third button
- vbDefaultButton4: You can set the focus on the fourth button
- vbApplicationModal: Close MsgBox to access to Current applications
- vbSystemModal: Close MsgBox to access to All applications
- vbMsgBoxHelpButton:Shows Help Button on the message box
- VbMsgBoxSetForeground:Set MsgBox Foreground
- vbMsgBoxRight: Text aligned to right.
- vbMsgBoxRtlReading: RTL support
- Custom Message Box in Excel VBA: Using UserForms.
- Message Box Constants in Excel VBA
- Message Box Return Constants and Enumerations in Excel VBA
VBA MsgBox:vbOKOnly
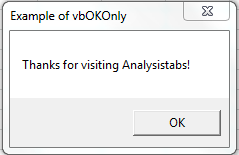
Please find the following code and output. It will Display OK button only. When we click OK button, It will return value 1 as a output.
Code:
Sub MessageBox_vbOKOnly()
'Variable Declaration
Dim OutPut As Integer
'Example of vbOKOnly
OutPut = MsgBox("Thanks for visiting Analysistabs!", vbOKOnly, "Example of vbOKOnly")
End Sub
Output:
Top
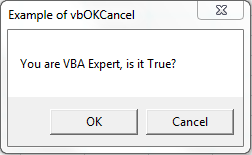
VBA MsgBox: vbOKCancel MessageBox
Please find the following code and output. It will Display OK and Cancel buttons. When we click OK button, It will return value 1 as a output.And When we click Cancel button, It will return value 2 as a output.
Code:
Sub MessageBox_vbOKCancel()
'Variable Declaration
Dim OutPut As Integer
'Example of vbOKCancel
OutPut = MsgBox("You are VBA Expert, is it True?", vbOKCancel, "Example of vbOKCancel")
If OutPut = 1 Then
'Output = 1(Ok)
MsgBox "Grate! You are VBA Expert, You can learn Advanced Our VBA!", , "Ok - 1"
Else
'Output = 2(Cancel)
MsgBox "You can Star Learning from Basics!", , "Cancel - 2"
End If
End Sub
Output:
Top
VBA MsgBox: vbAbortRetryIgnore
Please find the following code and output. It will Display Abort, Retry, and Ignore buttons. When we click Abort button, It will return value 3 as a output. When we click Retry button, It will return value 4 as a output.And When we click Ignore button, It will return value 5 as a output.
Code:
Sub MessageBox_vbAbortRetryIgnore()
'Variable Declaration
Dim OutPut As Integer
'Example of vbAbortRetryIgnore
OutPut = MsgBox("The Connection has failed. Do you want to Continue?", vbAbortRetryIgnore, "Example of vbAbortRetryIgnore")
If OutPut = 3 Then
'Output = 1(Abort)
MsgBox "Abort!", , "Abort - 3"
ElseIf OutPut = 4 Then
'Output = 4(Retry)
MsgBox "Retry!", , "Retry - 4"
Else
'Output = 5(Ignore)
MsgBox "Ignore!", , "Ignore - 5"
End If
End Sub
Output:
Top
VBA MsgBox in Excel: vbYesNoCancel MessageBox
Please find the following code and output. It will Display Yes, No, and Cancel buttons. When we click Yes button, It will return value 6 as a output. When we click No button, It will return value 7 as a output.And When we click Cancel button, It will return value 2 as a output.
Code:
Sub MessageBox_vbYesNoCancel()
'Variable Declaration
Dim OutPut As Integer
'Example of vbYesNoCancel
OutPut = MsgBox("File already exists. Do you want to replace?", vbYesNoCancel, "Example of vbYesNoCancel")
If OutPut = 6 Then
'Output = 6(Yes)
MsgBox "Yes!", vbInformation, "Yes - 6"
ElseIf OutPut = 7 Then
'Output = 7(No)
MsgBox "No!", vbInformation, "No - 7"
Else
'Output = 2(Cancel)
MsgBox "Cancel!", vbInformation, "Cancel - 2"
End If
End Sub
Output:
Top
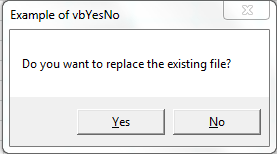
VBA MsgBox: vbYesNo
Please find the following code and output.It will display Display Yes and No buttons. When we click Yes button, It will return value 6 as a output.And, When we click No button, It will return value 7 as a output.
Code:
Sub MessageBox_vbYesNo()
'Variable Declaration
Dim OutPut As Integer
'Example of vbYesNo
OutPut = MsgBox("Do you want to replace the existing file?", vbYesNo, "Example of vbYesNo")
If OutPut = 6 Then
'Output = 6(Yes)
MsgBox "Yes! Replace the file", vbInformation, "Yes - 6"
Else
'Output = 7(No)
MsgBox "No! Don't replace the file", , "No - 7"
End If
End Sub
Output:
Top
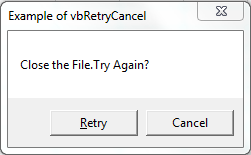
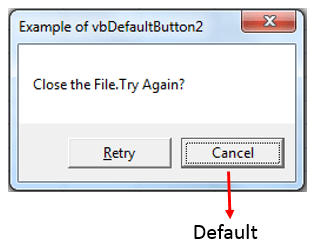
MsgBox in Excel VBA: vbRetryCancel MessageBox
Please find the following code and output. It will Display Retry and Cancel buttons.When we click Retry button, It will return value 4 as a output.And, When we click Cancel button, It will return value 2 as a output.
Code:
Sub MessageBox_vbRetryCancel()
'Variable Declaration
Dim OutPut As Integer
'MsgBox VBA Example of vbRetryCancel
OutPut = MsgBox("Close the File.Try Again?", vbRetryCancel + vbDefaultButton2, "Example of vbRetryCancel")
If OutPut = 4 Then
'Output = 4(Retry)
MsgBox "Retry!", , "Retry - 4"
Else
'Output = 2(Cancel)
MsgBox "Cancel It!", , "Cancel - 2"
End If
End Sub
Output:
Top
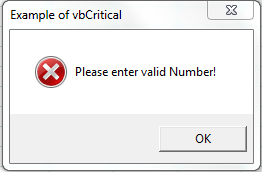
VBA MsgBox: vbCritical
Please find the following code and output. When we click Ok button, It will return value 1 as a output. And, It will display critical Message Icon.
Code:
Sub MessageBox_vbCritical()
'Variable Declaration
Dim OutPut As Integer
'Example of vbCritical
OutPut = MsgBox("Please enter valid Number!", vbCritical, "Example of vbCritical")
End Sub
Output:
Top
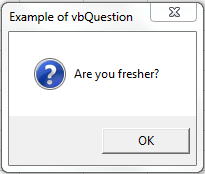
VBA MsgBox: vbQuestion
Please find the following code and output.When we click Ok button, It will return value 1 as a output. And, It will display Warning Query icon.
Code:
Sub MessageBox_vbQuestion()
'Variable Declaration
Dim OutPut As Integer
'Example of vbQuestion
OutPut = MsgBox("Are you fresher?", vbQuestion, "Example of vbQuestion")
End Sub
Output:
Top
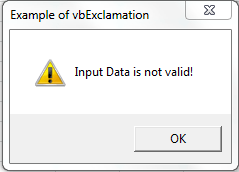
VBA MsgBox: vbExclamation
Please find the following code and output.When we click Ok button, It will return value 1 as a output. And, It will display Warning Message icon.
Code:
Sub MessageBox_vbExclamation()
'Variable Declaration
Dim OutPut As Integer
'Example of vbExclamation
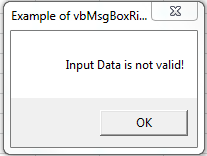
OutPut = MsgBox("Input Data is not valid!", vbExclamation, "Example of vbExclamation")
End Sub
Output:
Top
VBA MsgBox: vbInformation
Please find the following code and output.When we click Ok button, It will return value 1 as a output. And, It will display Information Message icon.
Code:
Sub MessageBox_vbInformation()
'Variable Declaration
Dim OutPut As Integer
'Example of vbInformation
OutPut = MsgBox("Succesessfully Completed the Task.", vbInformation, "Example of vbInformation")
End Sub
Output:
Top
VBA MsgBox: vbDefaultButton1
Please find the following code and output. By Default it will focus on first (Retry) Button. When we press enter it will result the value of Retry button as 4.
Code:
Sub MessageBox_vbDefaultButton1()
'Variable Declaration
Dim OutPut As Integer
'Example of vbDefaultButton1
OutPut = MsgBox("Close the File.Try Again?", vbRetryCancel + vbDefaultButton1, "Example of vbDefaultButton1")
End Sub
Output:
Top
VBA MsgBox: vbDefaultButton2
Please find the following code and output.By Default it will focus on Second(Cancel) Button. When we press enter it will result the value of Retry button as 2.
Code:
Sub MessageBox_vbDefaultButton2()
'Variable Declaration
Dim OutPut As Integer
'Example of vbDefaultButton2
OutPut = MsgBox("Close the File.Try Again?", vbRetryCancel + vbDefaultButton2, "Example of vbDefaultButton2")
End Sub
Output:
Top
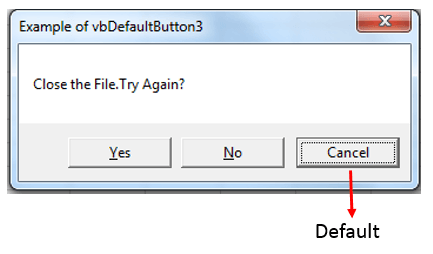
VBA MsgBox: vbDefaultButton3
Please find the following code and output.By Default it will focus on Third(Cancel) Button. When we press enter it will result the value of Retry button as 2.
Code:
Sub MessageBox_vbDefaultButton3()
'Variable Declaration
Dim OutPut As Integer
'Example of vbDefaultButton2
OutPut = MsgBox("Close the File.Try Again?", vbYesNoCancel + vbDefaultButton3, "Example of vbDefaultButton3")
End Sub
Output:
Top
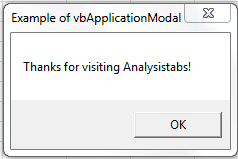
VBA MsgBox: vbApplicationModal
Please find the following code and output.The user must respond to the message box before continuing work in the current application.
Code:
Sub MessageBox_vbApplicationModal()
'Variable Declaration
Dim OutPut As Integer
'Example of vbApplicationModal
OutPut = MsgBox("Thanks for visiting Analysistabs!", vbApplicationModal, "Example of vbApplicationModal")
End Sub
Output:
Top
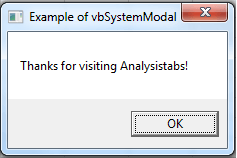
VBA MsgBox: vbSystemModal
Please find the following code and output.All applications are suspended until the user responds to the message box.
Code:
Sub MessageBox_vbSystemModal()
'Variable Declaration
Dim OutPut As Integer
'Example of vbSystemModal
OutPut = MsgBox("Thanks for visiting Analysistabs!", vbSystemModal, "Example of vbSystemModal")
End Sub
Output:
Top
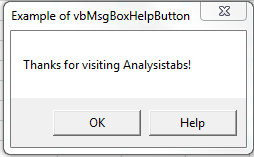
VBA MsgBox: vbMsgBoxHelpButton
Please find the following code and output.Adds Help button to the message box.
Code:
Sub MessageBox_vbMsgBoxHelpButton()
'Variable Declaration
Dim OutPut As Integer
'Example of vbMsgBoxHelpButton
OutPut = MsgBox("Thanks for visiting Analysistabs!", vbMsgBoxHelpButton, "Example of vbMsgBoxHelpButton")
End Sub
Output:
Top
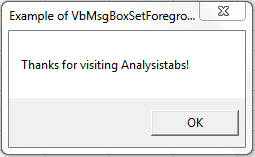
VBA MsgBox: VbMsgBoxSetForeground
Please find the following code and output.Specifies the message box window as the foreground window.
Code:
Sub MessageBox_VbMsgBoxSetForeground()
'Variable Declaration
Dim OutPut As Integer
'Example of VbMsgBoxSetForeground
OutPut = MsgBox("Thanks for visiting Analysistabs!", vbMsgBoxSetForeground, "Example of VbMsgBoxSetForeground")
End Sub
Output:
Top
VBA MsgBox: vbMsgBoxRight
Please find the following code and output.Here text is right aligned.
Code:
Sub MessageBox_vbMsgBoxRight()
'Variable Declaration
Dim OutPut As Integer
'Example of vbMsgBoxRight
OutPut = MsgBox("Input Data is not valid!", vbMsgBoxRight, "Example of vbMsgBoxRight")
End Sub
Output:
Top
VBA MsgBox: vbMsgBoxRtlReading
Please find the following code and output.It Specifies text should appear as right-to-left reading on Hebrew and Arabic systems.
Code:
Sub MessageBox_vbMsgBoxRtlReading()
'Variable Declaration
Dim OutPut As Integer
'Example of vbMsgBoxRtlReading
OutPut = MsgBox("Thanks for visiting Analysistabs!", vbMsgBoxRtlReading, "Example of vbMsgBoxRtlReading")
End Sub
Output:
Instructions:
- Open an excel workbook
- Press Alt+F11 to open VBA Editor
- Double click on ThisWorkbook from Project Explorer
- Copy the above code and Paste in the code window
- Press F5
- You should see the above output
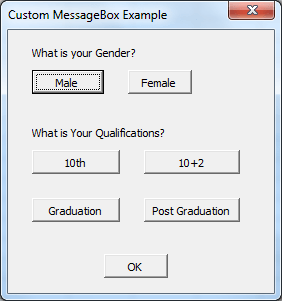
Custom Message Box in Excel VBA:
What if your requirement is not achievable with the available types of MessageBox. You Can create your own MessageBox using Forms in Excel VBA. You can design your own custom MessageBox using Form Controls.
Here is the example Custom MessageBox.
Top
MessageBox Constants in Excel VBA:
Please find the following table for button argument values:
| Constant | Value | Description |
| vbOKOnly | 0 | It Display’s OK button only. |
| vbOKCancel | 1 | It Display’s OK and Cancel buttons. |
| vbAbortRetryIgnore | 2 | It Display’s Abort, Retry, and Ignore buttons. |
| vbYesNoCancel | 3 | It Display’s Yes, No, and Cancel buttons. |
| vbYesNo | 4 | It Display’s Yes and No buttons. |
| vbRetryCancel | 5 | It Display’s Retry and Cancel buttons. |
| vbCritical | 16 | It Display’s Critical Message icon. |
| vbQuestion | 32 | It Display’s Warning Query icon. |
| vbExclamation | 48 | It Display’s Warning Message icon. |
| vbInformation | 64 | It Display’s Information Message icon. |
| vbDefaultButton1 | 0 | Here first button is default. |
| vbDefaultButton2 | 256 | Here second button is default. |
| vbDefaultButton3 | 512 | Here third button is default. |
| vbDefaultButton4 | 768 | Here fourth button is default. |
| vbApplicationModal | 0 | Application modal. The user must respond to the message box before continuing work in the current application. |
| vbSystemModal | 4096 | System modal. In this case all applications are suspended until the user responds to the message box. |
| vbMsgBoxHelpButton | 16384 | Adds Help button to the message box. |
| VbMsgBoxSetForeground | 65536 | Specifies the message box window as the foreground window. |
| vbMsgBoxRight | 524288 | Text is right aligned. |
| vbMsgBoxRtlReading | 1048576 | Specifies text should appear as right-to-left reading on Hebrew and Arabic systems. |
Top
Message Box Return Constants and Enumerations in Excel VBA:
| Constant | Value | Description |
| vbOK | 1 | OK |
| vbCancel | 2 | Cancel |
| vbAbort | 3 | Abort |
| vbRetry | 4 | Retry |
| vbIgnore | 5 | Ignore |
| vbYes | 6 | Yes |
| vbNo | 7 | No |
Top
Recommended Resource
- VBA Open File DialogBox Macros
- VBA InputBox Macros
- VBA ComboBox
- VBA ListBox
- VBA CheckBox
- VBA CommandButton
- VBA TextBox
- VBA Userform CheckBox
- VBA Userform ComboBox
- VBA Userform CommandButton
- VBA Userform Image
- VBA Userform Label
- VBA Userform ListBox
- VBA Userform OptionButton
- VBA Userform TextBox
A Powerful & Multi-purpose Templates for project management. Now seamlessly manage your projects, tasks, meetings, presentations, teams, customers, stakeholders and time. This page describes all the amazing new features and options that come with our premium templates.
Save Up to 85% LIMITED TIME OFFER

All-in-One Pack
120+ Project Management Templates
Essential Pack
50+ Project Management Templates
Excel Pack
50+ Excel PM Templates
PowerPoint Pack
50+ Excel PM Templates
MS Word Pack
25+ Word PM Templates
Ultimate Project Management Template
Ultimate Resource Management Template
Project Portfolio Management Templates
Related Posts
- VBA MsgBox Function
- VBA MsgBox – Syntax:
- VBA MsgBox in Excel VBA – Example Cases:
- VBA MsgBox arguments
- VBA MessageBox Options and Uses
-
- VBA MsgBox Styles
-
- Excel VBA MsgBox Yes No Syntax
- VBA MsgBox Yes No If
- VBA Message Box New line,carriage return, two lines, multiple line
- VBA MsgBox Yes No Cancel Return
- VBA If Then MsgBox and Exit Sub
- VBA On Error GoTo Message Box for Error Handling
- VBA MsgBox Styles
- VBA MsgBox:vbOKOnly
- VBA MsgBox: vbOKCancel MessageBox
- VBA MsgBox: vbAbortRetryIgnore
- VBA MsgBox in Excel: vbYesNoCancel MessageBox
- VBA MsgBox: vbYesNo
- MsgBox in Excel VBA: vbRetryCancel MessageBox
- VBA MsgBox: vbCritical
- VBA MsgBox: vbQuestion
- VBA MsgBox: vbExclamation
- VBA MsgBox: vbInformation
- VBA MsgBox: vbDefaultButton1
- VBA MsgBox: vbDefaultButton2
- VBA MsgBox: vbDefaultButton3
- VBA MsgBox: vbApplicationModal
- VBA MsgBox: vbSystemModal
- VBA MsgBox: vbMsgBoxHelpButton
- VBA MsgBox: VbMsgBoxSetForeground
- VBA MsgBox: vbMsgBoxRight
- VBA MsgBox: vbMsgBoxRtlReading
- Custom Message Box in Excel VBA:
- MessageBox Constants in Excel VBA:
- Message Box Return Constants and Enumerations in Excel VBA:
- Recommended Resource
- Message Box Return Constants and Enumerations in Excel VBA:
VBA Reference
Effortlessly
Manage Your Projects
120+ Project Management Templates
Seamlessly manage your projects with our powerful & multi-purpose templates for project management.
120+ PM Templates Includes:
19 Comments
-
Shady Mohsen
January 21, 2014 at 11:02 PM — ReplyThanks friend. It helped me a lot.I appreciate your efforts on creating useful VBA codes.
-
ramana
January 31, 2015 at 11:57 PM — Replynice post..
is there any suggestion how to display message box from the statement ‘For – Next’ , but the message itself does not appear repeatedly based on that ‘For-Next’ values? -
PNRao
February 3, 2015 at 10:14 PM — ReplyHi Ramana,
You can use a Boolean variable to do this:Sub ShowMsgOnceInForLoop() Dim msgFlag As Boolean msgFlag = False For iCntr = 1 To 100 If msgFlag = False Then MsgBox "This is MSGBox" msgFlag = True End If Next End Sub
Instead of this flag, you may use any other condition when you want to show the Message box.
Thanks-PNRao!
-
Dilip
March 4, 2015 at 1:46 PM — Replyi want to replace MsgBox appearing for Data Validation – Input & Error Message. I want to skip Help Button in Excel Default Message and add our own Message Title. Is there any way to do this ? Pl. provide VBA code only. Don’t waste your time in explaining how this can be done through Ribbon Menu pl. I will be highly obliged if i get the solution asap.If you require further information pl. let me know asap.
-
PNRao
March 7, 2015 at 7:34 PM — ReplyHi Dilip,
Please see the below VBA example code for Data validation and Custom mesagebox.
Sub sbCustomDatavalidation() With Range("A1:A5").Validation .Delete .Add Type:=xlValidateWholeNumber, AlertStyle:=xlValidAlertStop, _ Operator:=xlBetween, Formula1:="1", Formula2:="5" .IgnoreBlank = True .InCellDropdown = True .InputTitle = "Enter #Items" .InputMessage = "Enter an value between 1 to 5" .ErrorTitle = "My Message Box title" .ErrorMessage = "My Message Box Description" .ShowInput = True .ShowError = True End With End SubThanks-PNRao!
-
Paul
April 14, 2015 at 11:43 PM — ReplyHey Valli, Great article!
I was wondering … I’d like a box to pop up for one second (or other time period), then dismiss itself without user interaction.
Can msgbox be made to do this, or is there a different command that could do this?
Thanks -
pratyush
December 26, 2015 at 9:10 PM — ReplyI learned so many things from all above.Thanks and please stay-Tuned.
All the VBA beginners like me are refering all these and its very helpful.Thanks Again. .
-
Csaba
March 2, 2016 at 6:01 PM — ReplyHow I can stop the “X” button from the upper right corner to close the msgbox, practically force the user to respond with assigned buttons. Something similar with UserForm_QueryClose(Cancel As Integer, CloseMode As Integer), cancel = false, and post a message.
-
Stephen Nzai
September 6, 2016 at 7:40 PM — ReplyCan someone tell me how to put the displaced value on a message box on a cell. Lets say the message box displays integer 5, how do I get it on a cell without typing it?
-
sambit
September 15, 2016 at 10:56 AM — Replyi need VBA code so that i can get an alert when a cell in excel exceeds certain specified number which is automatically populated by the server
-
Bob
November 8, 2016 at 2:25 AM — ReplyFunny everyone illustrates how to add a help button, but no one will attempt to demonstrate how to get the help button to display help. The help button example above works great and pops up an empty help file. However if you add the next parameter, the help file path, vbscript complains – “Invalid procedure call or arguments: MsgBox”. The “.chm” file I tested with works great if you click on the file directly. Does this mean that not all .chm help files are windows compatible or is MsgBox broken.
-
ParismaX
February 14, 2017 at 6:03 PM — ReplyI was wondering if I could make a message box display the user’s name.
I know it is possible to do this but how would I go about it? -
Gregory Feeney
May 27, 2017 at 8:29 PM — ReplyPrivate Sub Workbook_SheetChange(ByVal Sh As Object, ByVal Target As Range)
Dim MyValue As String
‘Set MyValue to whatever you want
MyValue = 1‘Set the Range to what ever cell you want to monitor changes
If Range(“A1”) > MyValue Then
MsgBox “Alert Box Appears”
End IfEnd Sub
-
Sub DisplayUserName()
msgBox “The User Name is: ” & Environ(“UserName”),vbInformation,”User Name”
End Sub -
Colin Riddington
June 17, 2017 at 3:30 AM — ReplyYou can use the Environ function to get the logged on user name
e.g. MsgBox “Hello ” & Environ(“UserName”),vbExclamation,”MsgBox Title”
However the user name may not give the person’s forename.
Otherwise use DLookup to find the forename in a table.
e.g. If you have a table tblUsers with logged user info including a field called Forename and UserID stored as a string strUserID, you could use DLookup something like this:MsgBox “Hello ” & DLookup(“Forename”,”tblUsers”,”UserID”= ‘” & strUserID & “‘”),vbExclamation,”MsgBox Title”
-
Ariful Romadhon
August 5, 2017 at 3:54 PM — ReplyCould you help me please?
I want to make message box for validating surveys.
the message box contain the message because error of stuffingI want my message box keep showing, so i can click the sheets which contain error of stuffing without closing the message box.
So, the message box will guide me to fix the error in that sheets
This is my previous code:
Dim error As String
error = ”If (vehicle = True) And (gasoline_month = 0) Then
error = error & “- the expenditure of gasoline should not be empty” & Chr(10)
End IfIf error = “” Then msgbox “clean”, vbInformation Else MsgBox error, vbCritical
End SubThank you, I hope anyone can help me,,
(sorry for my bad english) -
rathy
August 12, 2017 at 10:23 PM — ReplyDim msgValue
msgValue = MsgBox(“Hello, Are you a graduate? Choos:” _
& vbCr & “Yes: if you are a graduate” _
& vbCr & “Yes: if you are Not a graduate” _
& vbCr & “Yes: if you are Not Intrested” _
, vbYesNoCancel + vbQuestion)I think the above incorrect right, it should be
Dim msgValue
msgValue = MsgBox(“Hello, Are you a graduate? Choos:” _
& vbCr & “Yes: if you are a graduate” _
& vbCr & “No: if you are Not a graduate” _
& vbCr & “Cancel: if you are Not Intrested” _
, vbYesNoCancel + vbQuestion).
-
Mike
September 4, 2017 at 7:26 PM — ReplyVery helpful. Perfect Macros. Thanks you.
-
ajay
October 10, 2020 at 8:20 PM — Replycan give msg box button a person name.. just like yes no or ok cancel
thanks
Effectively Manage Your
Projects and Resources
ANALYSISTABS.COM provides free and premium project management tools, templates and dashboards for effectively managing the projects and analyzing the data.
We’re a crew of professionals expertise in Excel VBA, Business Analysis, Project Management. We’re Sharing our map to Project success with innovative tools, templates, tutorials and tips.
Project Management
Excel VBA
Download Free Excel 2007, 2010, 2013 Add-in for Creating Innovative Dashboards, Tools for Data Mining, Analysis, Visualization. Learn VBA for MS Excel, Word, PowerPoint, Access, Outlook to develop applications for retail, insurance, banking, finance, telecom, healthcare domains.
Page load link
Go to Top
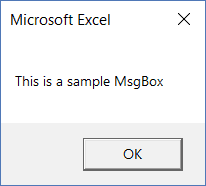
In Excel VBA, you can use the MsgBox function to display a message box (as shown below):
A MsgBox is nothing but a dialog box that you can use to inform your users by showing a custom message or get some basic inputs (such as Yes/No or OK/Cancel).
While the MsgBox dialog box is displayed, your VBA code is halted. You need to click any of the buttons in the MsgBox to run the remaining VBA code.
Note: In this tutorial, I will be using the words message box and MsgBox interchangeably. When working with Excel VBA, you always need to use MsgBox.
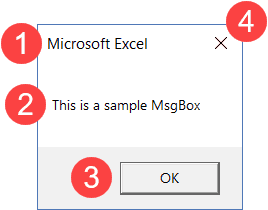
Anatomy of a VBA MsgBox in Excel
A message box has the following parts:
- Title: This is typically used to display what the message box is about. If you don’t specify anything, it displays the application name – which is Microsoft Excel in this case.
- Prompt: This is the message that you want to display. You can use this space to write a couple of lines or even display tables/data here.
- Button(s): While OK is the default button, you can customize it to show buttons such as Yes/No, Yes/No/Cancel, Retry/Ignore, etc.
- Close Icon: You can close the message box by clicking on the close icon.
Syntax of the VBA MsgBox Function
As I mentioned, MsgBox is a function and has a syntax similar to other VBA functions.
MsgBox( prompt [, buttons ] [, title ] [, helpfile, context ] )
- prompt – This is a required argument. It displays the message that you see in the MsgBox. In our example, the text “This is a sample MsgBox” is the ‘prompt’. You can use up to 1024 characters in the prompt, and can also use it to display the values of variables. In case you want to show a prompt that has multiple lines, you can do that as well (more on this later in this tutorial).
- [buttons] – It determines what buttons and icons are displayed in the MsgBox. For example, if I use vbOkOnly, it will show only the OK button, and if I use vbOKCancel, it will show both the OK and Cancel buttons. I will cover different kinds of buttons later in this tutorial.
- [title] – Here you can specify what caption you want in the message dialog box. This is displayed in the title bar of the MsgBox. If you don’t specify anything, it will show the name of the application.
- [helpfile] – You can specify a help file that can be accessed when a user clicks on the Help button. The help button would appear only when you use the button code for it. If you’re using a help file, you also need to also specify the context argument.
- [context] – It is a numeric expression that is the Help context number assigned to the appropriate Help topic.
If you’re new to the concept of Msgbox, feel free to ignore the [helpfile] and [context] arguments. I have rarely seen these being used.
Note: All the arguments in square brackets are optional. Only the ‘prompt’ argument is mandatory.
Excel VBA MsgBox Button Constants (Examples)
In this section, I will cover the different types of buttons that you can use with a VBA MsgBox.
Before I show you the VBA code for it and how the MsgBox looks, here is a table that lists all the different button constants you can use.
| Button Constant | Description |
| vbOKOnly | Shows only the OK button |
| vbOKCancel | Shows the OK and Cancel buttons |
| vbAbortRetryIgnore | Shows the Abort, Retry, and Ignore buttons |
| vbYesNo | Shows the Yes and No buttons |
| vbYesNoCancel | Shows the Yes, No, and Cancel buttons |
| vbRetryCancel | Shows the Retry and Cancel buttons |
| vbMsgBoxHelpButton | Shows the Help button. For this to work, you need to use the help and context arguments in the MsgBox function |
| vbDefaultButton1 | Makes the first button default. You can change the number to change the default button. For example, vbDefaultButton2 makes the second button as the default |
Note: While going through the examples of creating different buttons, you may wonder what’s the point of having these buttons if it doesn’t have any impact on the code.
It does! Based on the selection, you can code what you want the code to do. For example, if you select OK, the code should continue, and if you click Cancel, the code should stop. This can be done by using variables and assigning the value of the Message Box to a variable. We will cover this in the later sections of this tutorial.
Now let’s have a look at some examples of how the different buttons can be displayed in a MsgBox and how it looks.
MsgBox Buttons – vbOKOnly (Default)
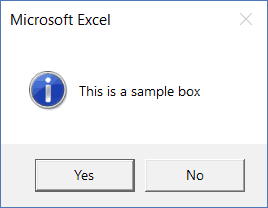
If you only use the prompt and don’t specify any of the arguments, you will get the default message box as shown below:
Below is the code that will give this message box:
Sub DefaultMsgBox() MsgBox "This is a sample box" End Sub
Note that the text string needs to be in double quotes.
You can also use the button constant vbOKOnly, but even if you don’t specify anything, it’s taken as default.
MsgBox Buttons – OK & Cancel
If you only want to show the OK and the Cancel button, you need to use the vbOKCancel constant.
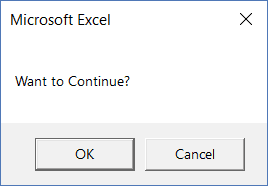
Sub MsgBoxOKCancel() MsgBox "Want to Continue?", vbOKCancel End Sub
MsgBox Buttons – Abort, Retry, and Ignore
You can use the ‘vbAbortRetryIgnore’ constant to show the Abort, Retry, and the Ignore buttons.
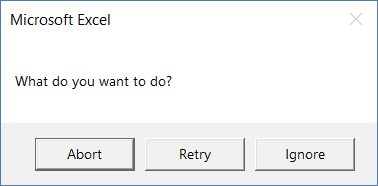
Sub MsgBoxAbortRetryIgnore() MsgBox "What do you want to do?", vbAbortRetryIgnore End Sub
MsgBox Buttons – Yes and No
You can use the ‘vbYesNo’ constant to show the Yes and No buttons.
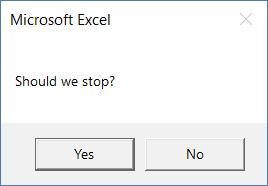
Sub MsgBoxYesNo() MsgBox "Should we stop?", vbYesNo End Sub
MsgBox Buttons – Yes, No and Cancel
You can use the ‘vbYesNoCancel’ constant to show the Yes, No, and Cancel buttons.
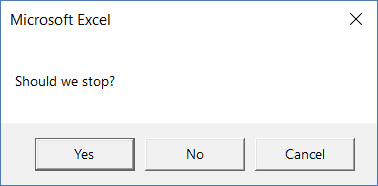
Sub MsgBoxYesNoCancel() MsgBox "Should we stop?", vbYesNoCancel End Sub
MsgBox Buttons – Retry and Cancel
You can use the ‘vbRetryCancel’ constant to show the Retry and Cancel buttons.
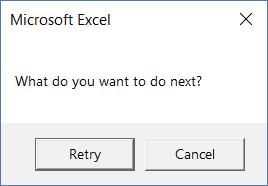
Sub MsgBoxRetryCancel() MsgBox "What do you want to do next?", vbRetryCancel End Sub
MsgBox Buttons – Help Button
You can use the ‘vbMsgBoxHelpButton’ constant to show the help button. You can use it with other button constants.
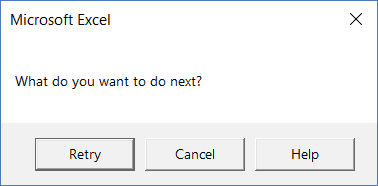
Sub MsgBoxRetryHelp() MsgBox "What do you want to do next?", vbRetryCancel + vbMsgBoxHelpButton End Sub
Note that in this code, we have combined two different button constants (vbRetryCancel + vbMsgBoxHelpButton). The first part shows the Retry and Cancel buttons and the second part shows the Help button.
MsgBox Buttons – Setting a Default Button
You can use the ‘vbDefaultButton1’ constant to set the first button as default. This means that the button is already selected and if you press enter, it executes that button.
Below is the code that will set the second button (the ‘No’ button) as the default.
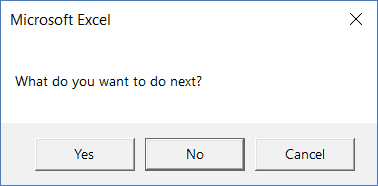
Sub MsgBoxOKCancel() MsgBox "What do you want to do next?", vbYesNoCancel + vbDefaultButton2 End Sub
In most cases, the left-most button is the default button. You can choose other buttons using vbDefaultButton2, vbDefaultButton3, and vbDefaultButton4.
Excel VBA MsgBox Icon Constants (Examples)
Apart from the buttons, you can also customize the icons that are displayed in the MsgBox dialog box. For example, you can have a red critical icon or a blue information icon.
Below is a table that lists the code that will show the corresponding icon.
| Icon Constant | Description |
| vbCritical | Shows the critical message icon |
| vbQuestion | Shows the question icon |
| vbExclamation | Shows the warning message icon |
| vbInformation | Shows the information icon |
MsgBox Icons – Critical
If you want to show a critical icon in your MsgBox, use the vbCritical constant. You can use this along with other button constants (by putting a + sign in between the codes).
For example, below is a code that will show the default OK button with a critical icon.
Sub MsgBoxCriticalIcon() MsgBox "This is a sample box", vbCritical End Sub
If you want to show the critical icon with Yes and No buttons, use the following code:
Sub MsgBoxCriticalIcon() MsgBox "This is a sample box", vbYesNo + vbCritical End Sub
MsgBox Icons – Question
If you want to show a critical icon in your MsgBox, use the vbQuestion constant.
Sub MsgBoxQuestionIcon() MsgBox "This is a sample box", vbYesNo + vbQuestion End Sub
MsgBox Icons – Exclamation
If you want to show an exclamation icon in your MsgBox, use the vbExclamation constant.
Sub MsgBoxExclamationIcon() MsgBox "This is a sample box", vbYesNo + vbExclamation End Sub
MsgBox Icons – Information
If you want to show an information icon in your MsgBox, use the vbInformation constant.
Sub MsgBoxInformationIcon() MsgBox "This is a sample box", vbYesNo + vbInformation End Sub
Customizing Title and Prompt in the MsgBox
When using MsgBox, you can customize the title and the prompt messages.
So far, the example we have seen have used Microsoft Excel as the title. In case you don’t specify the title argument, MsgBox automatically uses the title of the application (which has been Microsoft Excel in this case).
You can customize the title by specifying it in the code as shown below:
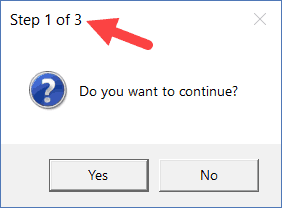
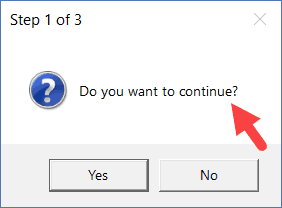
Sub MsgBoxInformationIcon() MsgBox "Do you want to continue?", vbYesNo + vbQuestion, "Step 1 of 3" End Sub
Similarly, you can also customize the prompt message.
You can also add line breaks in the prompt message.
In the below code, I have added a line break using ‘vbNewLine’.
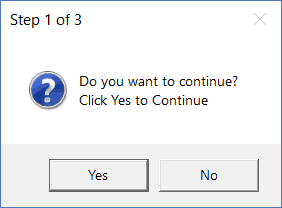
Sub MsgBoxInformationIcon() MsgBox "Do you want to continue?" & vbNewLine & "Click Yes to Continue", vbYesNo + vbQuestion, "Step 1 of 3" End Sub
You can also use the carriage return character – Chr(13) – or line feed – Chr(10) to insert a new line in the prompt message.
Note that you can add a new line to the prompt message only and not the title.
Assigning MsgBox Value to a Variable
So far, we have seen the examples where we have created message boxes and customized the buttons, icons, title, and prompt.
However, clicking a button has done nothing.
With MsgBox function in Excel, you can decide what you want to do when a user clicks a specific button. And this is possible as every button has a value associated to it.
So if I click on the Yes button, the MsgBox function returns a value (6 or the constant vbYes) which I can use in my code. Similarly, is the user selects the No button, it returns a different value ((7 or the constant vbNo)) that I can use in the code.
Below is a table that shows the exact values and the constant returned by the MsgBox function. You don’t need to memorize these, just be aware of it and you can use the constants which are easier to use.
| Button Clicked | Constant | Value |
| Ok | vbOk | 1 |
| Cancel | vbCancel | 2 |
| Abort | vbAbort | 3 |
| Retry | vbRetry | 4 |
| Ignore | vbIgnore | 5 |
| Yes | vbYes | 6 |
| No | vbNo | 7 |
Now let’s see how we can control the VBA macro code based on what button a user clicks.
In the below code, if the user clicks Yes, it displays the message “You Clicked Yes”, and if the user clicks No, it displays, “You clicked No”.
Sub MsgBoxInformationIcon()
Result = MsgBox("Do you want to continue?", vbYesNo + vbQuestion)
If Result = vbYes Then
MsgBox "You clicked Yes"
Else: MsgBox "You clicked No"
End If
End Sub
In the above code, I have assigned the value of the MsgBox function to the Result variable. When you click Yes button, the Result variable gets the vbYes constant (or the number 6) and when you click No, the Result variable gets the vbNo constant (or the number 7).
Then I used an If Then Else construct to check if the Result variable holds the value vbYes. If it does, it shows the prompt “You Clicked Yes”, else it shows “You clicked No”.
You can use the same concept to run a code if a user clicks Yes and exit the sub when he/she clicks No.
Note: When you assign the MsgBox output to a variable, you need to put the arguments of MsgBox function in parenthesis. For example, in the line Result = MsgBox(“Do you want to continue?”, vbYesNo + vbQuestion), you can see that the arguments are within parenthesis.
If you want to further dig into the Message Box function, here is the official document on it.
You May Also Like the Following Excel VBA Tutorials:
- Excel VBA Split Function.
- Excel VBA InStr Function.
- Working with Cells and Ranges in Excel VBA.
- Working with Worksheets in VBA.
- Working with Workbooks in VBA.
- Using Loops in Excel VBA.
- Understanding Excel VBA Data Types (Variables and Constants)
- How to Create and Use Personal Macro Workbook in Excel.
- Useful Excel Macro Code Examples.
- Using For Next Loop in Excel VBA.
- Excel VBA Events – An Easy (and Complete) Guide.
- How to Run a Macro in Excel – A Complete Step-by-Step Guide.
- How to Create and Use an Excel Add-in.
- Using Active Cell in VBA in Excel (Examples)