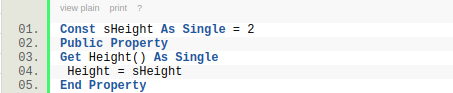Хитрости »
1 Август 2013 63756 просмотров
Работа с модулями классов
Многие наверняка слышали про модули классов, но не все их используют. На самом деле довольно многие программирующие на VBA за все время программирования прекрасно обходятся без применения модулей классов. Т.к. VBA не является языком объектно-ориентированного программирования(ООП) в строгом смысле слова, то пользовательские классы здесь не обязательны и как следствие не так уж и часто используются при разработке. Это не значит, что VBA не содержит модулей классов: модули книги, листов, пользовательские формы — все это модули классов. Многие, кстати, используют их даже не зная того, что используют именно модули классов. Т.к. модуль листа, книги и формы — это модуль класса, то почти каждый, кто работал с формой работал с модулем класса. В чем их большая польза — с их помощью можно отслеживать различные события объектов. Для форм это события самой формы или любого её элемента — например CommandButton_Click или TextBox_Change. Но мы сейчас рассмотрим лишь тот тип модулей, который в VBA обычно называют модулем класса — Class Module.
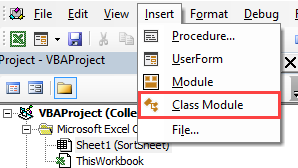
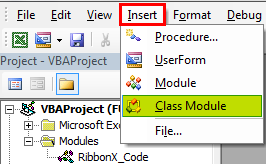
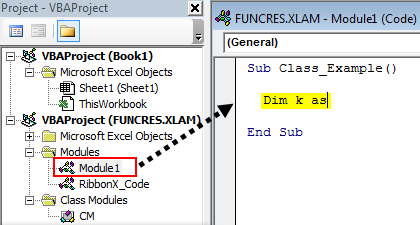
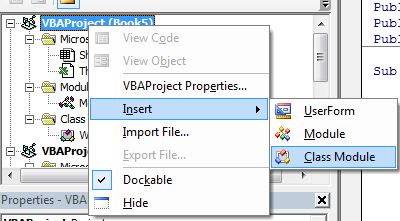
Модуль класса(Class Module) – это модуль, содержащий программные коды, которые реализуют работу пользовательских классов. В подавляющем большинстве случаев создается специально для отслеживания событий различных объектов. Создается так же, как и любой другой объект проекта: в окне проводника объектов щелкаем правой кнопкой мыши на нужном проекте-Insert—Class Module
Но прежде чем создать модуль, необходимо понять, что мы будем в нем хранить и для чего он нам. Возьмем для примера самую распространенную проблему: на форме создано несколько ТекстБоксов и необходимо отследить событие ввода данных в эти ТекстБоксы. Обычно делается все просто — для каждого ТекстБокса прописывается отслеживание события:
Private Sub TextBox1_Change() MsgBox "Изменено значение TextBox1" End Sub Private Sub TextBox2_Change() MsgBox "Изменено значение TextBox2" End Sub Private Sub TextBox3_Change() MsgBox "Изменено значение TextBox3" End Sub 'и т.д.
С одной стороны — все верно. А с другой: что если таких текстбоксов у нас не 3, а 43? Не очень удобно для каждого событие прописывать. Да и читабельность такой «портянки» кода тоже значительно падает.
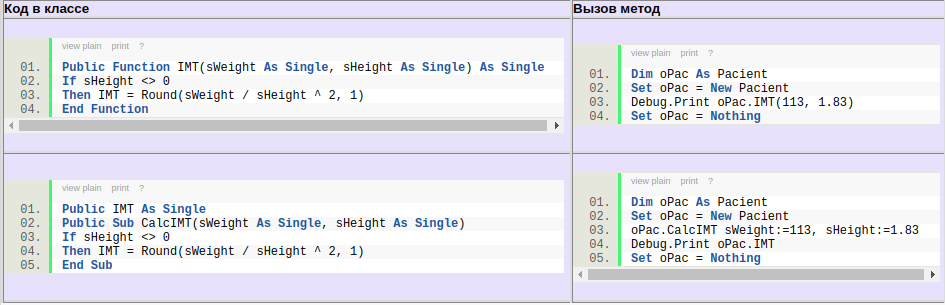
Или другая ситуация — необходимо «на ходу» создать ТекстБоксы на форме и в дальнейшем отслеживать их события. Как тут быть? Ведь раз ТексБоксов еще нет — то и события в форме для них не создать. Создание для них кодов обработки событий заранее ничего не даст — они не будут связаны с самими объектами, поэтому и пытаться даже не стоит. Почему так — при создании элемента вручную VBE делает за нас всю грязную работу — он сам ассоциирует созданный объект с событиями, предназначенные для него заранее. Если же создать объект программно — то часть грязной работы придется делать самим. И создание модуля класса, с описанием в нем объекта ТекстБокс и его событий, как раз очень даже подойдет.
Рассмотрим сразу оба случая. Что нам для этого потребуется:
- для начала создать модуль класса с именем clsmTxtBxes(Insert—Class Module)
- создать стандартный модуль с именем mMain(Insert—Module)
- ну и сама форма тоже не лишняя(Insert—UserForm). У меня форма называется frmTest.
- очень желательно наличие у вас опыта написания хотя бы простейших процедур. Иначе может показаться все очень сложным и непонятным.
Чтобы было проще вникать советую скачать файл с готовыми кодами:

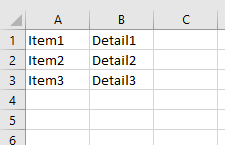
Для начала создадим на нашей форме frmTest 4 ТекстБокса, не меняя их имена(по умолчанию они будут TextBox1, TextBox2, TextBox3, TextBox4). Это для того, чтобы понять как применить модули класса к уже созданным ранее на форме элементам.
Далее в стандартный модуль mMain поместим следующий код:
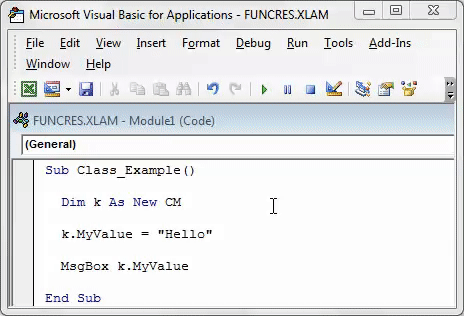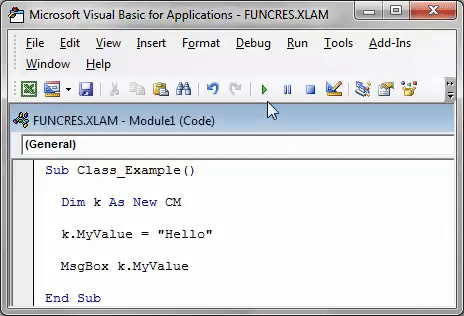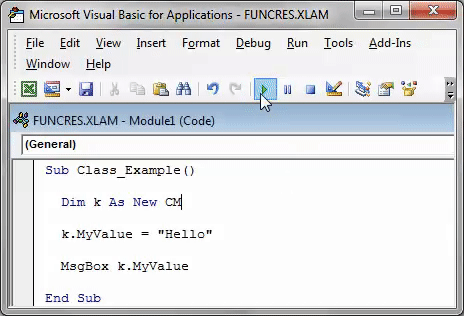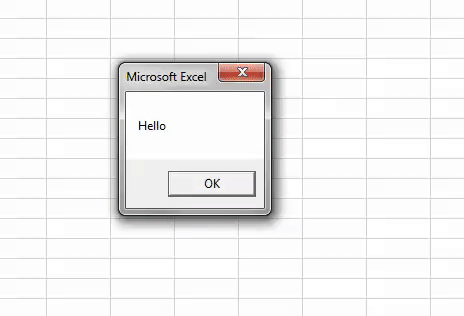
Option Explicit Public aoTxtBxes(1 To 8) As New clsmTxtBxes Sub Show_Form() frmTest.Show End Sub
aoTxtBxes — массив, который будет содержать до 8 ТекстБоксов. Объявляется как Public (чтобы был доступен из любого модуля проекта. Подробнее в статье: Что такое переменная и как правильно её объявить?). Обращаю внимание, что данный массив объявлен как созданный нами модуль класса — As clsmTxtBxes. Это обязательное условие. Если у вас модуль класса называется ClassModule1, то и объявлять aoTxtBxes следует соответственно:
Public aoTxtBxes(1 To 8) As New ClassModule1
но я не приветствую подобный подход, т.к. имя ClassModule1 ни о чем нам не говорит, в то время как clsmTxtBxes сразу дает понять, что там мы обрабатываем ТекстБоксы. Хотя это дело вкуса. Если в одном модуле класса собраны различные событийные процедуры для разных типов(TextBox, ComboBox, ListBox и т.д.) — то конечно, имя лучше дать более общее.
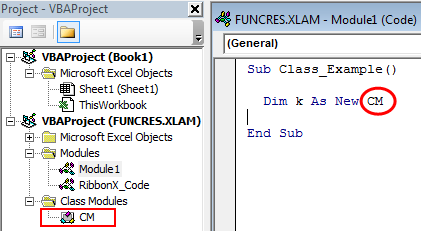
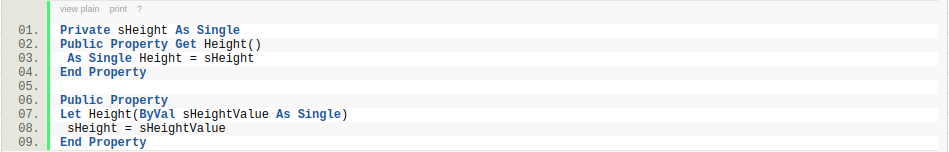
Теперь в созданный модуль класса clsmTxtBxes запишем создание объекта и код, который хотим применить для всех наших ТекстБоксов:
Option Explicit Public WithEvents oTxtBx As MSForms.TextBox 'событие изменения текста в TextBox-ах Private Sub oTxtBx_Change() MsgBox "Вы изменили значение " & oTxtBx.Name, vbInformation, "Информационное окно" End Sub
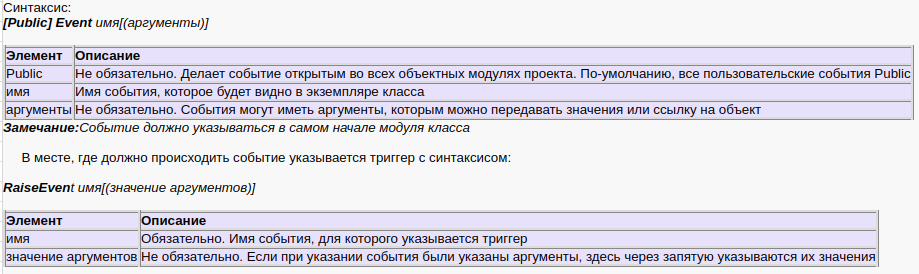
Public WithEvents oTxtBx As MSForms.TextBox — создаем объект типа ТекстБокс с отслеживанием его событий. Идентификатором объекта с отслеживанием событий служит оператор WithEvents (может применяться только в модулях классов).
Если необходимо отследить изменения не TextBox, а ComboBox, то соответственно объявляем объект нужного типа:
Public WithEvents oCmbBx As MSForms.ComboBox
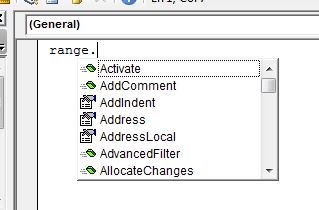
Сами события для контролов не берутся из головы и не пишутся вручную — они уже есть и следует использовать именно те, которые доступны. Чтобы для конкретного элемента создать событие, необходимо перейти в модуль класса, вверху в левой части выбрать из списка нужный объект(в нашем случае это oTxtBx) и после этого в правом списке выбрать событие(в этом списке перечисляются все процедуры, доступные для выбранного объекта):
Для выбранного события в модуле будет автоматически создана новая процедура.
Процедуры, события для которых уже созданы, выделяются в списке жирным шрифтом и при выборе их из списка происходит переход в процедуру выбранного события.
Завершающий этап — создаем код в модуле формы frmTest, который создаст недостающие ТекстБоксы и свяжет их и ранее созданные с модулем класса:
Option Explicit Private Sub UserForm_Initialize() Dim i As Integer 'Присваиваем последовательно значениям массива aoTxtBxes значения объектов, существующих на форме For i = 1 To 4 Set aoTxtBxes(i).oTxtBx = Me.Controls("TextBox" & i) Next i 'создаем 4 своих TrxtBox-а помимо имеющихся на форме и так же заносим в массив aoTxtBxes For i = 5 To 8 Set aoTxtBxes(i).oTxtBx = Me.Controls.Add("Forms.TextBox.1", "TextBox" & i) 'задаем позицию нового TextBox aoTxtBxes(i).oTxtBx.Left = 100 aoTxtBxes(i).oTxtBx.Top = Me.Controls("TextBox" & i - 4).Top Next i End Sub
Кратко описать, что делает эта процедура, можно так:
- при запуске формы в массив aoTxtBxes запоминаются сначала те ТекстБоксы, которые мы предусмотрительно заранее создали на форме
- затем создаются еще 4 новых ТекстБокса, которые также записываются в массив aoTxtBxes
- Т.к. массив aoTxtBxes у нас является новым экземпляром класса, то обращаться к его содержимому мы можем только по законам работы с классами, т.е. только к тем объектам и методам, которые в классе прописаны. А у нас там пока только один объект прописан — oTxtBx(Public WithEvents oTxtBx As MSForms.TextBox). Его и используем. Ничего другого использовать VBE нам и не позволит
- т.к. класс мы создали, событие объекта прописали, объектам значения ТекстБоксов присвоили — остается только наслаждаться. Теперь любое изменение в любом из ТекстБоксов будет обработано и появится сообщение — «Вы изменили значение » + имя ТекстБокса
Если необходимо больше ТекстБоксов обработать — увеличиваем верхнюю границу массива aoTxtBxes(если хотим вместить 20 текстбоксов — Public aoTxtBxes(1 To 20) As New clsmTxtBxes). Если заранее неизвестно количество — либо задаем с запасом, либо объявляем aoTxtBxes как динамический массив(Public aoTxtBxes() As New clsmTxtBxes), а границы определяем в процессе(посредством ReDim Preserve). Но это уже совершенно другая тема.
Конечно, здесь я привел лишь маленький пример показа сообщения при изменении ТекстБокса. Но ведь можно таким образом отследить практически любое доступное событие. И не просто сообщение показывать, а запретить ввод букв, делать проверку введенного значения на соответствие шаблону и пр. Все зависит от конкретной задачи.
Так же дополню, что подобным образом можно создавать и отслеживать и иные элементы форм. Для этого необходимо лишь изменить тип элемента здесь:
Me.Controls.Add("Forms.TextBox.1", "TextBox" & i)
и соответственно изменить/добавить тип переменной в модуле класса:
Public WithEvents oCmbBx As MSForms.ComboBox
Всего для создания доступно 11 встроенных типов контролов:
ComboBox — MSForms.ComboBox
CheckBox — MSForms.CheckBox
CommandButton — MSForms.CommandButton
Frame — MSForms.Frame
Image — MSForms.Image
Label — MSForms.Label
ListBox — MSForms.ListBox
MultiPage — MSForms.MultiPage
SpinButton — MSForms.SpinButton
TabStrip — MSForms.TabStrip
ToggleButton — MSForms.ToggleButton
И небольшая ложка дегтя: из модулей классов доступны не все события. Например, для TextBox-ов нет события Exit. Это порой расстраивает. И никак это не исправить — нет его и все…
Скачать пример:

Также см.:
Что такое модуль? Какие бывают модули?
Что такое переменная и как правильно её объявить?
Variable not defined или что такое Option Explicit и зачем оно нужно?
Статья помогла? Поделись ссылкой с друзьями!
Видеоуроки
Поиск по меткам
Access
apple watch
Multex
Power Query и Power BI
VBA управление кодами
Бесплатные надстройки
Дата и время
Записки
ИП
Надстройки
Печать
Политика Конфиденциальности
Почта
Программы
Работа с приложениями
Разработка приложений
Росстат
Тренинги и вебинары
Финансовые
Форматирование
Функции Excel
акции MulTEx
ссылки
статистика
“Classes struggle, some classes triumph, others are eliminated. Such is history” – Chairman Mao
A Quick Guide to the VBA Class Module
| Item | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Class Module | Allows the user to create their own objects. |
| Method | A public function or sub in the class module. |
| Member variable | A variable declared in the class module. |
| Property | Special function/subs that behave like variables when used |
| Property types | Get, Set and Let. |
| Event — Initialize | Sub that automatically runs when the class module object is created. |
| Event — Terminate | Sub that automatically runs when the class module object is deleted. |
| Declaring and Creating — Static |
Dim o As New Class1 |
| Declaring and Creating — Dynamic | Dim o As Class1 Set o = New Class1 |
| Calling a class module sub | o.WriteValues Total |
| Calling a class module function | Amount = o.Calculate() |
| Using a class module property | o.Amount = 1 Total = o.Amount |
The Webinar
Members of the Webinar Archives can access the webinar for this article by clicking on the image below.
(Note: Archive members have access to the webinar archive.)
Introduction
VBA Class Modules allow the user to create their own objects. If you are not familiar with objects then I would highly recommend that you first check out my previous post VBA Objects – The Ultimate Guide.
In languages such as C# and Java, classes are used to create objects. Class Modules are the VBA equivalent of these classes. The major difference is that VBA Class Modules have a very limited type of Inheritance* compared to classes in the other languages. In VBA, Inheritance works in a similar way to Interfaces** in C#Java.
In VBA we have built-in objects such as the Collection, Workbook, Worksheet and so on. The purpose of VBA Class Modules is to allow us to custom build our own objects.
Let’s start this post by looking at why we use objects in the first place.
*Inheritance is using an existing class to build a new class.
**Interfaces are a form of Inheritance that forces a class to implement specifics procedures or properties.
Download the Source Code
Why Do We Use Objects
Using objects allows us to build our applications like we are using building blocks.
The idea is that the code of each object is self-contained. It is completely independent of any other code in our application.
This is similar to how things are built using Lego® bricks. There are many different types of Lego® components used. For example, a block, steering wheel, and laser are different items. They behave completely independently of each other. The wheel spins, the laser rotates etc. Yet we can connect them together to create a building, vehicle, space station and so on.
If you are still not clear about this then don’t worry. We’ll be breaking it all down into simple terms in the rest of this post.
Advantages of Using Objects
Treating parts of our code as blocks provide us with a lot of great advantages
- It allows us to build an application one block at a time.
- It is much easier to test individual parts of an application.
- Updating code won’t cause problems in other parts of the application.
- It is easy to add objects between applications.
Not a good look for your code © BigStockPhoto.com
Disadvantages of Using Objects
With most things in life there are pros and cons. Using VBA class modules is no different. The following are the disadvantages of using class module to create objects
- It takes more time initially to build applications*.
- It is not always easy to clearly define what an object is.
- People new to classes and objects can find them difficult to understand at first.
*If you create an application using objects it will take longer to create it initially as you have to spend more time planning and designing it. However, in the long run it will save you a huge amount of time. Your code will be easier to manage, update and reuse.
Creating a Simple Class Module
If you would like to see working examples of this code you can download the source code from the top of this post.
Let’s look at a very simple example of creating a class module and using it in our code.
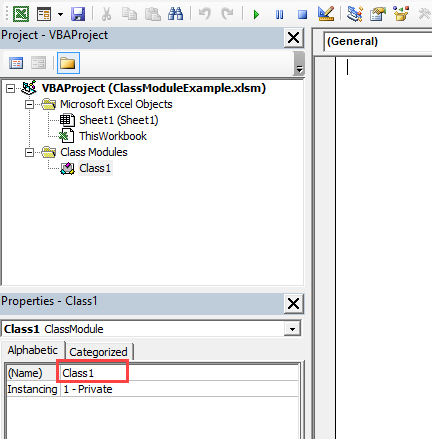
To create a class module we right-click in the Project window and then select Insert and Class Module
Adding a Class Module
Our new class is called Class1. We can change the name in the Properties window as the following screenshot shows:
Let’s change the name of the class module to clsCustomer. Then we will add a variable to the class module like this:
Public Name As String
We can now use this class module in any module(standard or class) in our workbook. For example
' Create the object from the class module Dim oCustomer As New clsCustomer ' Set the customer name oCustomer.Name = "John" ' Print the name to the Immediate Window(Ctrl + G) Debug.Print oCustomer.Name
Class Module versus Objects
People who are new to using classes and VBA class modules, often get confused between what is a class and what is an object.
Let’s look at a real world example. Think of a mass produced item like a coffee mug. A design of the mug is created first. Then, thousands of coffee mugs are created from this design.
This is similar to how class modules and objects work.
The class module can be thought of as the design.
The object can be thought of as the item that is created from the design.
The New keyword in VBA is what we use to create an object from a class module. For example:
' Creating objects using new Dim oItem As New Class1 Dim oCustomer1 As New clsCustomer Dim coll As New Collection
Note: We don’t use New with items such as Workbooks and Worksheets. See When New is not required for more information.
VBA Class Modules Versus VBA Normal Modules
Writing code in a class module is almost the same as writing code in a normal module. We can use the same code we use in normal modules. It’s how this code is used which is very different.
Let’s look at the two main differences between the class and the normal module. These often cause confusion among new users.
Difference 1 – How the modules are used
If you want to use a sub/function etc. from a class module you must create the object first.
For example, imagine we have two identical PrintCustomer subs. One is in a class module and one is in a normal module…
' CLASS MODULE CODE - clsCustomer Public Sub PrintCustomer() Debug.Print "Sample Output" End Sub
' NORMAL MODULE CODE Public Sub PrintCustomer() Debug.Print "Sample Output" End Sub
You will notice the code for both is exactly the same.
To use the PrintCustomer sub from the class module, you must first create an object of that type
' Other Module ' https://excelmacromastery.com/ Sub UseCustomer() Dim oCust As New clsCustomer oCust.PrintCustomer End Sub
To use PrintCustomer from the normal module you can call it directly
' Other Module ' https://excelmacromastery.com/ Sub UseCustomer() PrintCustomer End Sub
Difference 2 – Number of copies
When you create a variable in a normal module there is only one copy of it. For a class module, there is one copy of the variable for each object you create.
For example, imagine we create a variable StudentName in both a class and normal module:
' NORMAL MODULE Public StudentName As String
' CLASS MODULE called clsStudent Public StudentName As String
For the normal module variable there will only be one copy of this variable in our application.
StudentName = "John"
For the class module, a new copy of the variable StudentName is created each time a new object is created.
Dim student1 As New clsStudent Dim student2 As New clsStudent student1.StudentName = "Bill" student2.StudentName = "Ted"
When you fully understand VBA class modules, these differences will seem obvious.
The Parts of a Class Module
There are four different items in a class module. These are
- Methods – functions/subs.
- Member variables – variables.
- Properties– types of functions/subs that behave like variables.
- Events – subs that are triggered by an event.
You can see they are all either functions, subs or variables.
Let’s have a quick look at class that has examples of each of these:
' CLASS MODULE CODE from clsAccount ' https://excelmacromastery.com/vba-class-modules/ ' Member variable Private m_balance As Double ' Properties Property Get Balance() As Double Balance = m_balance End Property Property Let Balance(value As Double) m_balance = value End Property ' Event - triggered when class created Private Sub Class_Initialize() m_balance = 100 End Sub ' Methods Public Sub Withdraw(amount As Double) m_balance = m_balance - amount End Sub Public Sub Deposit(amount As Double) m_balance = m_balance + amount End Sub
The following code demonstrates how this class could be used:
' This sub uses the clsAccount class ' The results are printed to the Immediate Window(Ctrl + G) ' https://excelmacromastery.com/vba-class-modules/ Sub Demo_clsAccount() Dim oAccount As New clsAccount ' Print the balance Debug.Print "Starting balance is: " & oAccount.Balance ' Deposit money oAccount.Deposit 25 ' Print the balance Debug.Print "Balance after deposit is: " & oAccount.Balance ' Withdraw Money oAccount.Withdraw 100 ' Print the balance Debug.Print "Balance after withdrawl is: " & oAccount.Balance End Sub
If we run the code we will get the following:
Starting balance is: 100
Balance after deposit is: 125
Balance after withdrawl is: 25
Now that we have seen examples, let’s take a look at each of these in turn.
Class Module Methods
Methods refer to the procedures of the class. In VBA procedures are subs and functions. Like member variables they can be Public or Private.
Let’s look at an example:
' CLASS MODULE CODE for clsExample ' https://excelmacromastery.com/vba-class-modules/ ' Public procedures can be called from outside the object Public Sub PrintText(text As String) Debug.Print text End Sub Public Function Calculate(amount As Double) As Double Calculate = amount - GetDeduction End Function ' private procedures can only be called from within the Class Module Private Function GetDeduction() As Double GetDeduction = 2.78 End Function
We can use the clsExample class module like this:
' Sub used to demonstrate Class clsExample ' https://excelmacromastery.com/vba-class-modules/ Public Sub ClassMembers() Dim oSimple As New clsExample oSimple.PrintText "Hello" Dim total As Double total = oSimple.Calculate(22.44) Debug.Print total End Sub
Class Module Member Variables
The member variable is very similar to the normal variable we use in VBA. The difference is we use Public or Private instead of Dim.
' CLASS MODULE CODE Private Balance As Double Public AccountID As String
Note: Dim and Private do exactly the same thing but the convention is to use Dim in sub/functions and to use Private outside sub/functions.
The Public keyword means the variable can be accessed from outside the class module. For example:
' This code will give an ERROR!! Sub Demo_BankAccount() Dim oAccount As New clsBankAccount ' Valid - AccountID is public oAccount.AccountID = "499789" ' ERROR - Balance is private oAccount.Balance = 678.9 End Sub
In the above example, we cannot access Balance because it is declared as Private. We can only use a Private variable within the class module. We can use in a function/sub in the class module e.g.
' CLASS MODULE CODE ' https://excelmacromastery.com/ Private Balance As Double Public Sub SetBalance() Balance = 100 Debug.Print Balance End Sub
It is considered poor practice to have public member variables. This is because you are allowing code outside the object to interfere with how the class works. The purpose of the using classes is so that we hide what is happening from the caller.
To avoid the user directly talking to our member variables we use Properties.
Class Module Properties
- Get – returns an object or value from the class
- Let – sets a value in the class
- Set – sets an object in the class
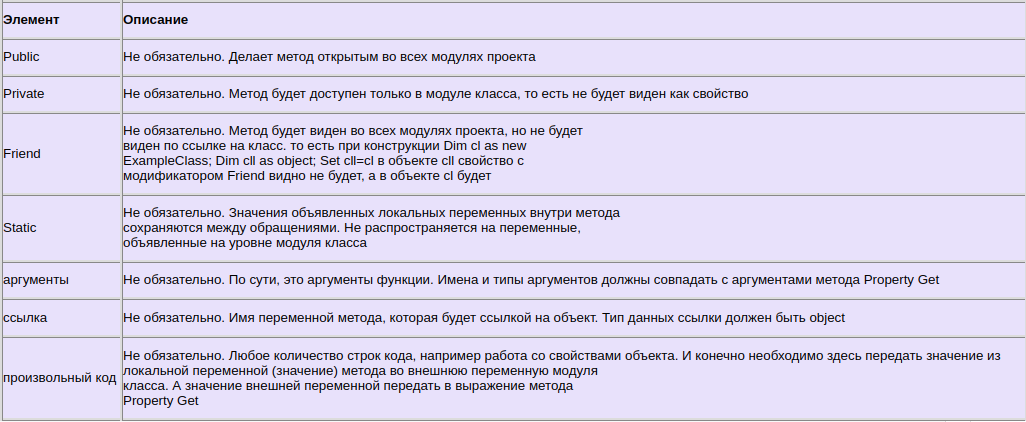
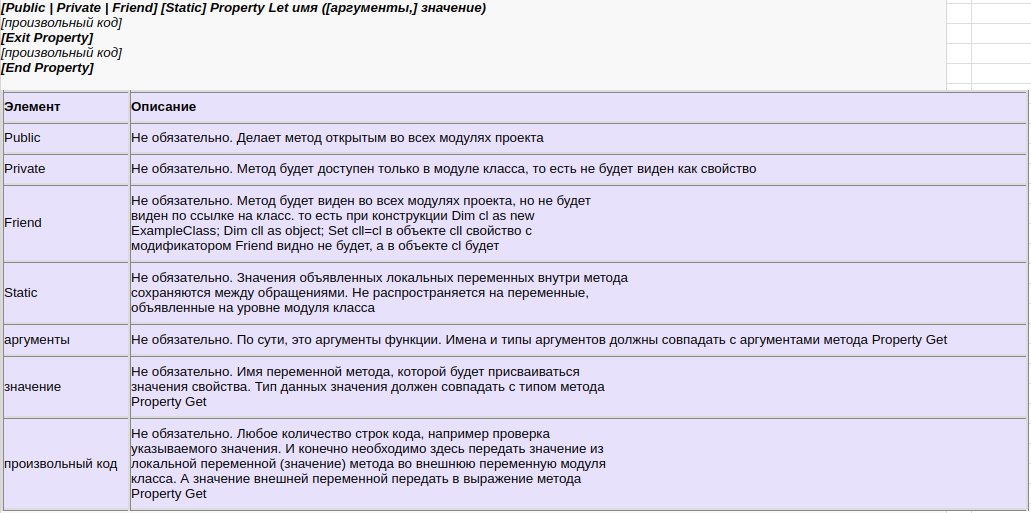
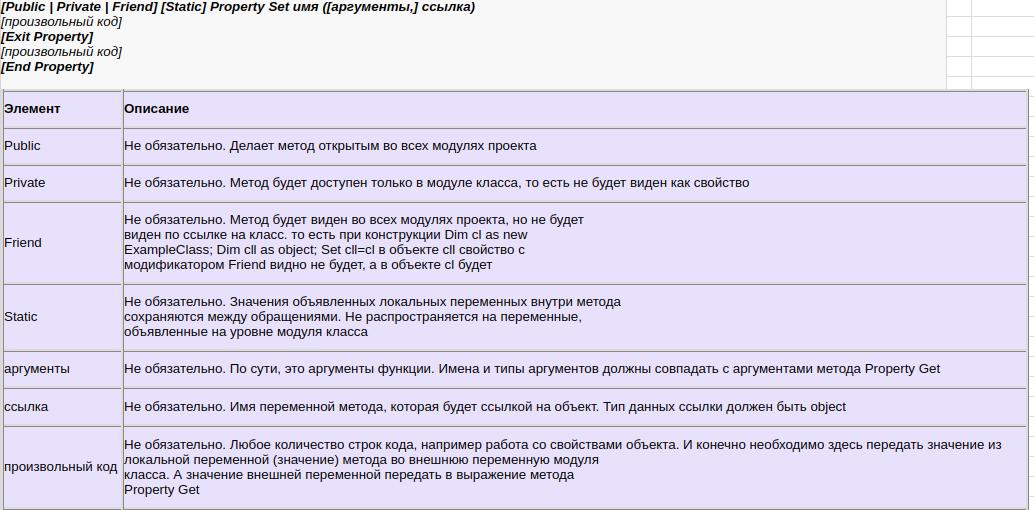
Format of VBA Property
The normal format for the properties are as follows:
Public Property Get () As Type End Property Public Property Let (varname As Type ) End Property Public Property Set (varname As Type ) End Property
We have seen already that the Property is simply a type of sub. The purpose of the Property is to allow the caller to get and set values.
Why we use Properties
Why can’t we just make the variables Public and use them directly?
Let’s explain with some examples. Imagine we have a class that maintains a list of Countries. We could store the list as an array
' Use array to store countries ' https://excelmacromastery.com/ Public arrCountries As Variant ' Set size of array when class is initialized ' https://excelmacromastery.com/ Private Sub Class_Initialize() ReDim arrCountries(1 To 1000) End Sub
When the user wants to get the number of countries in the list they could do this:
' NORMAL MODULE CODE Dim oCountry As New clsCountry ' Get the number of items NumCountries = UBound(oCountry.arrCountries) - LBound(oCountry.arrCountries) + 1
There are two major problems with the above code:
- To get the number of countries you need to know how the list is stored e.g. Array.
- If we change the Array to a Collection, we need to change all code that reference the array directly.
To solve these problems we can create a function to return the number of countries
' CLASS MODULE CODE - clsCountryList ' Array Private arrCountries() As String Public Function Count() As Long Count = UBound(arrCountries) + 1 End Function
We then use it like this:
' MODULE CODE Dim oCountries As New clsCountries Debug.Print "Number of countries is " & oCountries.Count
This code solves the two problems we listed above. We can change our Array to a Collection and the caller code will still work e.g.
' CLASS MODULE CODE ' Collection ' https://excelmacromastery.com/ Private collCountries() As Collection Public Function Count() As Long Count = collCountries.Count End Function
The caller is oblivious to how the countries are stored. All the caller needs to know is that the Count function will return the number of countries.
As we have just seen, a sub or function provides a solution to the above problems. However, using a Property can provide a more elegant solution.
Using a Property instead of a Function/Sub
Instead of the creating a Count Function we can create a Count Property. As you can see below they are very similar:
' Replace this Public Function Count() As Long Count = UBound(m_countries) - LBound(m_countries) + 1 End Function ' With this Property Get Count() As Long Count = UBound(m_countries) - LBound(m_countries) + 1 End Property
In this scenario, there is not a lot of difference between using the Property and using a function. However, there are differences. We normally create a Get and Let property like this:
' https://excelmacromastery.com/vba-class-modules/ Private m_totalCost As Double Property Get totalCost() As Long totalCost = m_totalCost End Property Property Let totalCost(value As Long) m_totalCost = value End Property
Using Let allows us to treat the property like a variable. So we can do this
oAccount.TotalCost = 6
The second difference is that using Let and Get allows us to use the same name when referencing the Get or Let property. So we can use the property like a variable. This is the purpose of using Properties over a sub and function.
oAccount.TotalCost = 6 value = oAccount.TotalCost
If we used a function and a sub then we cannot get the behaviour of a variable. Instead we have to call two different procedures e.g.
oAccount.SetTotalCost 6 value = oAccount.GetTotalCost
You can also see that when we used Let we can assign the value like a variable. When we use SetTotalCost , we had to pass it as a parameter.
The Property in a Nutshell
- The Property hides the details of the implementation from the caller.
- The Property allows us to provide the same behaviour as a variable.
Types of VBA Property
There are three types of Properties. We have seen Get and Let already. The one we haven’t looked at is Set.
Set is similar to Let but it is used for an object(see Assigning VBA Objects for more detail about this).
Originally in Visual Basic, the Let keyword was used to assign a variable. In fact, we can still use it if we like.
' These line are equivalent Let a = 7 a = 7
So we use Let to assign a value to a variable and we use Set to assign an object to an object variable.
' Using Let Dim a As Long Let a = 7 ' Using Set Dim coll1 As Collection, coll2 As Collection Set coll1 = New Collection Set coll2 = coll1
- Let is used to assign a value to a basic variable type.
- Set is used to assign an object to an object variable.
In the following example, we use Get and Let properties for a string variable:
' CLASS MODULE CODE for clsPerson ' https://excelmacromastery.com/vba-class-modules/ ' SET/LET PROPERTIES for a variable Private m_name As String ' Get/Let Properties Property Get name() As String name = m_name End Property Property Let name(name As String) m_name = name End Property
We can then use the name properties like this:
' Testing Let and Set for the clsPerson Class ' https://excelmacromastery.com/vba-class-modules/ Sub TestLetSet() Dim name As String Dim oPerson As New clsPerson ' Let Property oPerson.name = "Bill" ' Get Property name = oPerson.name End Sub
In the next example, we use Get and Set properties for an object variable:
' CLASS MODULE CODE for clsCurrency ' https://excelmacromastery.com/vba-class-modules/ Private m_Prices As Collection ' Get/Set Properties Property Get Prices() As Collection Set Prices = m_Prices End Property Property Set Prices(newPrices As Collection) Set m_Prices = newPrices End Property
We can then use the properties like this:
' The code below demonstrates how to use the LetSet properties with a class. ' ' 1. The sub creates a collection and adds value. ' 2. We then add it to the clsCurrency class object using the Set Property. ' 3. We then read it from the class object usiing the Get property. ' ' https://excelmacromastery.com/vba-class-modules/ Sub TestLetSet() ' Create a collection and add prices Dim Prices As New Collection Prices.Add 21.23 Prices.Add 22.12 Prices.Add 20.12 Dim oCurrency As New clsCurrency ' Uses the Set property of clsCurrency to ' add the collection to the class Set oCurrency.Prices = Prices Dim PricesCopy As Collection ' Uses the Get property of clsCurrency ' to read the collection from the class Set PricesCopy = oCurrency.Prices ' Print the results to the Immediate Window(Ctrl + G) PrintCollection Prices, "Prices" PrintCollection PricesCopy, "Copy" End Sub ' Print the contents of a Collection to the Immediate Window(Ctrl + G) Sub PrintCollection(c As Collection, name As String) Debug.Print vbNewLine & "Printing " & name & ":" Dim item As Variant For Each item In c Debug.Print item Next item End Sub
We use the Get property to return the values for both items. Notice that even though we use the Get Property to return the Collection, we still need to use the Set keyword to assign it.
One very important thing to understand is that when we use Set we are still referencing the same collection. Set is not creating a copy of the collection. You can read more about this here
Class Module Events
If you to see working examples of this code you can download the source code from the top of this post.
A class module has two events
- Initialize – occurs when a new object of the class is created.
- Terminate – occurrs when the class object is deleted.
In Object-Oriented languages like C++, these events are referred to as the Constructor and the Destructor. In most languages, you can pass parameters to a constructor but in VBA you cannot. We can use a Class Factory to get around this issue as we will see below.
Initialize
Let’s create a very simple class module called clsSimple with Initialize and Terminate events:
' CLASS MODULE CODE ' https://excelmacromastery.com/ Private Sub Class_Initialize() MsgBox "Class is being initialized" End Sub Private Sub Class_Terminate() MsgBox "Class is being terminated" End Sub Public Sub PrintHello() Debug.Print "Hello" End Sub
In the following example, we use Dim and New to create the object.
In this case, oSimple is not created until we reference it for the first time e.g.
' https://excelmacromastery.com/ Sub ClassEventsInit2() Dim oSimple As New clsSimple ' Initialize occurs here oSimple.PrintHello End Sub
When we use Set and New together the behaviour is different. In this case the object is created when Set is used e.g.
' https://excelmacromastery.com/ Sub ClassEventsInit() Dim oSimple As clsSimple ' Initialize occurs here Set oSimple = New clsSimple oSimple.PrintHello End Sub
Note: For more information about the different between using New with Dim and using New with Set see Subtle Differences of Dim Versus Set
As I said earlier, you cannot pass a parameter to Initialize. If you need to do this you need a function to create the object first
' CLASS MODULE - clsSimple ' https://excelmacromastery.com/ Public Sub Init(Price As Double) End Sub ' NORMAL MODULE Public Sub Test() ' Use CreateSimpleObject function Dim oSimple As clsSimple Set oSimple = CreateSimpleObject(199.99) End Sub Public Function CreateSimpleObject(Price As Double) As clsSimple Dim oSimple As New clsSimple oSimple.Init Price Set CreateSimpleObject = oSimple End Function
We will expand on this CreateSimpleObject in Example 2 to create a Class Factory.
Terminate
The Terminate event occurs when the class is deleted. This happens when we set it to Nothing
' https://excelmacromastery.com/ Sub ClassEventsTerm() Dim oSimple As clsSimple Set oSimple = New clsSimple ' Terminate occurs here Set oSimple = Nothing End Sub
If we don’t set the object to Nothing then VBA will automatically delete it when it goes out of scope.
What this means is that if we create an object in a procedure, when that procedure ends VBA will delete any objects that were created.
' https://excelmacromastery.com/ Sub ClassEventsTerm2() Dim oSimple As New clsSimple ' Initialize occurs here oSimple.PrintHello ' oSimple is deleted when we exit this Sub calling Terminate End Sub
Class Module Example 1
In this example, we are going to look at a very common use of a Class module.
Imagine we have the following data
We want to read the Albums based on a range of years and then create various reports.
We could use a 2D Array for this or a Collection of collections e.g.
' https://excelmacromastery.com/ For i = 2 To rg.Rows.Count Year = rg.Cells(i, 3) If startYear <= Year And endYear >= Year Then ' Create a new collection for each row Set rowColl = New Collect ' Add artist rowColl.Add rg.Cells(i, 1).Value ' Add Title rowColl.Add rg.Cells(i, 2).Value ' and so on ' Add row collection to main collection coll.Add rowColl End If Next i
As you can imagine this code would get messy very quickly.
© BigStockPhoto.com
Lucky for us we have VBA class modules to make our life easier. We can create a class module to store the items.
' clsAlbum class module Private m_sArtist As String Private m_sTitle As String Private m_sYear As String Private m_sGenre As String Private m_sSales As String ' Properties ' https://excelmacromastery.com/ Public Property Get Artist() As String Artist = m_sArtist End Property Public Property Let Artist(ByVal sArtist As String) m_sArtist = sArtist End Property ' etc
Each time we want to add a record we can do it as follows:
' Declare the Variable Dim oAlbum As clsAlbum ' Create new album Set oAlbum = New clsAlbum ' Add the details oAlbum.Artist = rg.Cells(i, 1) oAlbum.Title = rg.Cells(i, 2) oAlbum.Year = rg.Cells(i, 3) oAlbum.Genre = rg.Cells(i, 4) oAlbum.Sales = rg.Cells(i, 5) ' Add the album object to the collection coll.Add oAlbum
You can see that this makes our code much more readable. It is clear what Artist, Title etc. are being used for.
We can then easily use this data to create reports, write to files etc.
' https://excelmacromastery.com/ Sub PrintAlbum(coll As Collection) Dim oAlbum As clsAlbum For Each oAlbum In coll ' Print out the title and artist for each album Debug.Print oAlbum.Title, oAlbum.Artist Next End Sub
Below is the full code for this example:
' https://excelmacromastery.com/ Sub CreateReport() Dim coll As Collection ' read the data Set coll = ReadAlbums(1990, 2001) ' Print the album details PrintAlbum coll ' Print the total sales PrintTotalSales coll End Sub Function ReadAlbums(startYear As Long, endYear As Long) _ As Collection Dim rg As Range Set rg = Sheet1.Range("A1").CurrentRegion ' Create a collection to store the albums Dim coll As New Collection Dim oAlbum As clsAlbum Dim i As Long, Year As Long For i = 2 To rg.Rows.Count Year = rg.Cells(i, 3) If startYear <= Year And endYear >= Year Then ' Create new album Set oAlbum = New clsAlbum ' Add the details oAlbum.Artist = rg.Cells(i, 1) oAlbum.Title = rg.Cells(i, 2) oAlbum.Year = Year oAlbum.Genre = rg.Cells(i, 4) oAlbum.sales = rg.Cells(i, 5) ' Add the album objecdt to the collection coll.Add oAlbum End If Next i Set ReadAlbums = coll End Function Sub PrintAlbum(coll As Collection) Dim oAlbum As clsAlbum For Each oAlbum In coll Debug.Print oAlbum.Title, oAlbum.Artist Next End Sub Sub PrintTotalSales(coll As Collection) Dim oAlbum As clsAlbum, sales As Double For Each oAlbum In coll sales = sales + oAlbum.sales Next Debug.Print "Total number sales is " & sales End Sub
Class Module Example 2
In this example, we’re going to take things a bit further. We’re going to look at some neat tricks when using objects.
Imagine you have a list of products like in the image below.
The products have different fields so we need to use a different class module for each product type. One type for a Book row, one type for a Film row.
We’ll create our class modules first. As you can imagine the are very similar for both product types
' CLASS MODULE - clsBook ' https://excelmacromastery.com/ ' Member variables Private m_Title As String Private m_Year As Long ' Properties Property Get ItemType() As String ItemType = "Book" End Property Property Get Title() As String Title = m_Title End Property Property Get Year() As Long Year = m_Year End Property ' Methods Public Sub Init(rg As Range) m_Title = rg.Cells(1, 2) m_Year = CLng(rg.Cells(1, 4)) End Sub Public Sub PrintToImmediate() Debug.Print ItemType, m_Title, m_Year End Sub
' CLASS MODULE - clsFilm ' https://excelmacromastery.com/ ' Member variables Private m_Title As String Private m_Year As Long ' Properties Property Get ItemType() As String ItemType = "Film" End Property Property Get Title() As String Title = m_Title End Property Property Get Year() As Long Year = m_Year End Property ' Methods Sub Init(rg As Range) m_Title = rg.Cells(1, 2) m_Year = CLng(rg.Cells(1, 5)) End Sub Public Sub PrintToImmediate() Debug.Print ItemType, m_Title, m_Year End Sub
As you can see, the only real difference is the Init sub.
When we read each record we need to determine if it is a Book or Film. Then we create the appropriate object. You would imagine we would have to create a variable for each type e.g.
' One variable required for each type Dim oBook As clsBook Dim oFilm As clsFilm ' If book do this Set oBook = New clsBook ' Else If film do this Set oFilm = New clsFilm
If we had lots of different types this would get very messy indeed. The good news is we only need to use one variable!
In VBA we can declare a variable as a Variant. When we use a Variant we are essentially saying “We will decide the type of variable when the code is running”.
This is very useful when dealing with objects and allows us to get away with using one variable e.g.
' Only one variable required Dim oItem As Variant ' If book set type to clsBook Set oItem = New clsBook ' Else If film set type to clsFilm Set oItem = New clsFilm
This is really useful as we only need one variable no matter how many objects we have.
A second advantage of using a Variant is this. If each Class Module has a sub/function with the same name and parameters, we can use the same variable to call it
So imagine clsBook has a function called InitBook and clsFilm has a function called InitFilm. We would need to do this:
' If clsBook If Type = "Book" Then oItem.InitBook ElseIf Type = "Film" Then oItem.InitFilm
However, if they have the same name, e.g. Init, we can replace the IfElseIf lines of code with one line:
' this will call the Init sub of whatever type oItem is set to
oItem.Init
We can now create a function to create the appropriate object. In Object Oriented Programming, we have what is called a Class Factory. This is simply a function that creates an object based on a given type.
We saw earlier that the Initialize event does not take parameters. We can call Init in the Class Factory to get around this issue.
The full code for the ClassFactory function is here:
' https://excelmacromastery.com/ Function ClassFactory(rg As Range) As Variant ' Get product type Dim sType As String sType = rg.Cells(1, 1) ' Create an object based on the type Dim oItem As Variant Select Case sType Case "Book": Set oItem = New clsBook Case "Film": Set oItem = New clsFilm Case Else MsgBox "Invalid type" End Select ' Parse the fields to the correct class variables oItem.Init rg ' Return the product object Set ClassFactory = oItem End Function
This following is our starting sub. In this sub, we read through the worksheet and pass the range to ClassFactory.
It creates the object, passes the range to the object Parse method. Then it returns the object which we add to our Collection.
' https://excelmacromastery.com/ Sub ReadProducts() ' Create the collection Dim coll As New Collection Dim product As Variant Dim rg As Range ' Read products from the worksheet Dim i As Long For i = 1 To 2 Set rg = Sheet1.Range("A" & i & ":E" & i) Set product = ClassFactory(rg) coll.Add product Next ' Print the product details to the Immediate Window(Ctrl + G) PrintCollection coll End Sub
We can also use the variant object to print the items. As long as both objects have a sub with the same name and parameters(e.g PrintToImmediate) we can call it using a Variant type.
' https://excelmacromastery.com/ Public Sub PrintCollection(ByRef coll As Collection) Dim v As Variant For Each v In coll ' Print items v.PrintToImmediate Next End Sub
The source code for this post also includes this example using Inheritance(i.e. class interfaces). You can download the code here:
Conclusion
That concludes my post on the VBA Class Modules. In this post, we have looked at the parts of the VBA Class Module and two example cases where you would use them.
It’s important to understand that Classes and Objects is a vast topic. There are countless types of objects you can create and ways you can use them.
If you plan to use Class Modules then my advice is to start simple and get familiar with how to create a simple one. Once you have mastered the basics it will be much easier to move onto more challenging scenarios.
What’s Next?
Free VBA Tutorial If you are new to VBA or you want to sharpen your existing VBA skills then why not try out the The Ultimate VBA Tutorial.
Related Training: Get full access to the Excel VBA training webinars and all the tutorials.
(NOTE: Planning to build or manage a VBA Application? Learn how to build 10 Excel VBA applications from scratch.)
На чтение 24 мин. Просмотров 22.7k.

Председатель Мао
Классовая борьба, одни классы побеждают, другие исключаются. Такова история
Содержание
- Краткое руководство по VBA Class Module
- Введение
- Почему мы используем объекты
- Преимущества использования объектов
- Недостатки использования объектов
- Создание простого Class Module
- Class Module VBA против обычных модулей VBA
- Части Class Module
- События Class Module
- Class Module. Пример 1
- Class Module. Пример 2
- Заключение
Краткое руководство по VBA Class Module
| Пункт | Пояснение |
| Class Module | Позволяет пользователю создавать свои собственные объекты. |
| Метод | Открытая функция или подпрограмма в Class Module . |
| Переменная | Переменная, объявленная в Class Module. |
| Свойство | Специальная функция / подпрограммы, которые ведут себя как переменные при использовании |
| Типы свойств | Get, Let и Set. |
| Событие — инициализация | Sub, который автоматически запускается при создании объекта Class Module. |
| Событие — завершение | Sub, который автоматически запускается при удалении объекта Class Module. |
| Объявление и создание — статический |
Dim o As New Class1 |
| Объявление и создание — динамический |
Dim o As Class1 Set o = New Class1 |
| Вызов подпрограммы Class Module |
o.WriteValues Total |
| Вызов функции Class Module | Amount = o.Calculate() |
| Использование свойства Class Module |
o.Amount = 1 Total = o.Amount |
Введение
Class Module VBA позволяют пользователю создавать свои собственные объекты. Если вы не знакомы с объектами, я настоятельно рекомендую вам сначала ознакомиться с моей статьей Все об объектах VBA Objects.
В таких языках, как C # и Java, классы используются для создания объектов. Class Module являются VBA-эквивалентом этих классов. Основное отличие состоит в том, что Class Module VBA имеют очень ограниченный тип наследования * по сравнению с классами на других языках. В VBA наследование работает аналогично интерфейсам ** в C # Java.
В VBA у нас есть встроенные объекты, такие как Collection, Workbook, Worksheet и так далее. Целью Class Module VBA является предоставление нам возможности создавать собственные объекты.
Давайте начнем эту статью с рассмотрения того, почему мы используем объекты в первую очередь.
*Наследование использует существующий класс для создания нового класса.
**Интерфейсы — это форма наследования, которая заставляет класс реализовывать специфические процедуры или свойства.
Почему мы используем объекты
Использование объектов позволяет нам создавать наши приложения так же, как мы используем строительные блоки.
Идея состоит в том, что код каждого объекта является автономным. Он полностью независим от любого другого кода в нашем приложении.
Это похоже на то, как все строится с использованием кирпичей Lego. Существует много различных типов компонентов Lego. Например, блок, руль и лазер — это разные вещи. Они ведут себя совершенно независимо друг от друга. Но мы можем соединить их вместе, чтобы создать здание, транспортное средство, космическую станцию и так далее.
Если вам все еще неясно, не волнуйтесь. В остальной части этой статьи мы разберем все это на простые термины.
Преимущества использования объектов
Рассматривая части нашего кода как блоки, мы получаем много больших преимуществ.
- Это позволяет нам создавать приложения по одному блоку за раз.
- Намного проще протестировать отдельные части приложения.
- Обновление кода не вызовет проблем в других частях приложения.
- Легко добавлять объекты между приложениями.
Недостатки использования объектов
У большинства вещей в жизни есть свои плюсы и минусы. Использование Class Module VBA ничем не отличается. Ниже приведены недостатки использования Class Module для создания объектов.
- Первоначально для создания приложений требуется больше времени *.
- Не всегда легко четко определить, что такое объект.
- Люди, плохо знакомые с классами и предметами, могут сначала найти их трудными для понимания.
*Если вы создаете приложение с использованием объектов, на его создание уйдет больше времени, поскольку вам придется тратить больше времени на планирование и проектирование. Однако в долгосрочной перспективе это сэкономит вам огромное количество времени. Вашим кодом будет легче управлять, обновлять и использовать повторно.
Создание простого Class Module
Давайте рассмотрим очень простой пример создания Class Module и использования его в нашем коде.
Чтобы создать Class Module, мы щелкаем правой кнопкой мыши в окне Project и затем выбираем Insert и Class Module.
Наш новый класс называется Class1. Мы можем изменить имя в окне свойств, как показано на следующем скриншоте.
Давайте изменим имя модуля класса на clsCustomer. Затем мы добавим переменную в Class Module следующим образом.
Теперь мы можем использовать этот Class Module в любом модуле (стандартном или классе) в нашей рабочей книге. Например:
' Создать объект из Class Module Dim oCustomer As New clsCustomer ' Установите имя клиента oCustomer.Name = "Иван" ' Напечатайте имя в Immediate Window(Ctrl + G) Debug.Print oCustomer.Name
Class Module против Объектов
Люди, которые плохо знакомы с использованием классов и модулей классов VBA, часто путаются между тем, что такое класс и что является объектом.
Давайте посмотрим на пример из реального мира. Думайте о предмете массового производства как кофейная кружка. Дизайн кружки создается в первую очередь. Затем тысячи кофейных кружек создаются из этого дизайна.
Это похоже на работу Class Module и объектов.
Class Module можно рассматривать как дизайн.
Объект можно рассматривать как элемент, созданный из дизайна.
Ключевое слово New в VBA — это то, что мы используем для создания объекта из Class Module. Например:
' Создание объектов с использованием New Dim oItem As New Class1 Dim oCustomer1 As New clsCustomer Dim coll As New Collection
Примечание. Мы не используем New для таких элементов, как Workbooks и Worksheets. См. Когда New не требуется для получения дополнительной информации.
Class Module VBA против обычных модулей VBA
Написание кода в Class Module почти такое же, как написание кода в обычном модуле. Мы можем использовать тот же код, который мы используем в обычных модулях. То, как этот код используется, сильно отличается.
Давайте посмотрим на два основных различия между классом и обычным модулем. Это часто вызывает путаницу у новых пользователей.
Разница 1 — Как используются модули
Если вы хотите использовать подпрограмму / функцию и т.д. Из
Class Module, вы должны сначала создать объект.
Например, представьте, что у нас есть два идентичных Sub PrintCustomer. Один находится в Class Module, а другой — в обычном модуле…
' CLASS MODULE Код - clsCustomer
Public Sub PrintCustomer()
Debug.Print "Пример вывода"
End Sub
' Код обычного модуля
Public Sub PrintCustomer()
Debug.Print "Пример вывода"
End Sub
Вы заметите, что коды абсолютно одинаковые.
Чтобы использовать подпрограмму PrintCustomer из Class Module, вы должны сначала создать объект этого типа
' Другой модуль
Sub UseCustomer()
Dim oCust As New clsCustomer
oCust.PrintCustomer
End Sub
Чтобы использовать PrintCustomer из обычного модуля, вы можете вызвать его напрямую
' Другой модуль
Sub UseCustomer()
PrintCustomer
End Sub
Разница 2 — Количество копий
Когда вы создаете переменную в обычном модуле, существует только одна ее копия. Для Class Module существует одна копия переменной для каждого создаваемого вами объекта.
Например, представьте, что мы создаем переменную StudentName как в классе, так и в обычном модуле.
' Обычный модуль Public StudentName As String
' CLASS MODULE Public StudentName As String
Для обычной переменной модуля в нашем приложении будет только одна копия этой переменной.
Для Class Module новая копия переменной StudentName создается каждый раз, когда создается новый объект.
Dim student1 As New clsStudent Dim student2 As New clsStudent student1.StudentName = "Петр" student2.StudentName = "Василий"
Когда вы полностью поймете Class Module VBA, эти различия будут казаться очевидными.
Части Class Module
В Class Module есть четыре разных предмета. Это:
- Методы — функции / подводные лодки.
- Переменные-члены — переменные.
- Свойства — типы функций / подпрограмм, которые ведут себя как переменные.
- События — подводные лодки, которые запускаются событием
Вы можете видеть, что они все или функции, подпрограммы или переменные.
Давайте кратко рассмотрим некоторые примеры, прежде чем разбираться с ними по очереди.
' CLASS MODULE Код
' Переменная
Private dBalance As Double
' Свойства
Property Get Balance() As Double
Balance = dBalance
End Property
Property Let Balance(dValue As Double)
dBalance = dValue
End Property
' Событие - срабатывает при создании класса
Private Sub Class_Initialize()
dBalance = 100
End Sub
' Методы
Public Sub Withdraw(dAmount As Double)
dBalance = dBalance - dAmount
End Sub
Public Sub Deposit(dAmount As Double)
dBalance = dBalance + dAmount
End Sub
Теперь, когда мы увидели примеры, давайте рассмотрим каждый из них по очереди.
Методы Class Module
Методы относятся к процедурам класса. В VBA есть процедуры и функции. Как и переменные-члены, они могут быть Public или Private.
Давайте посмотрим на пример:
' CLASS MODULE Код
' Имя класса: clsSimple
' Публичные процедуры могут быть вызваны извне объекта
Public Sub PrintText(sText As String)
Debug.Print sText
End Sub
Public Function Calculate(dAmount As Double) As Double
Calculate = dAmount - GetDeduction
End Function
' частные процедуры могут быть вызваны только из Class Module
Private Function GetDeduction() As Double
GetDeduction = 2.78
End Function
Мы можем использовать Class Module clsSimple следующим образом
Sub ClassMembers()
Dim oSimple As New clsSimple
oSimple.PrintText "Hello"
Dim dTotal As Double
dTotal = oSimple.Calculate(22.44)
Debug.Print dTotal
End Sub
Переменные-члены Class Module
Переменная-член очень похожа на обычную переменную, которую мы используем в VBA. Разница в том, что мы используем Public или Private вместо Dim.
' CLASS MODULE Код Private Balance As Double Public AccountID As String
Примечание: Dim и Private делают одно и то же, но соглашение заключается в том, чтобы использовать Dim в sub / functions и использовать Private за пределами sub / functions.
Ключевое слово Public означает, что переменная может быть доступна вне Class Module. Например:
Dim oAccount As New clsAccount ' Действительный - AccountID открыт oAccount.AccountID = "499789" ' Ошибка - Баланс является частным oAccount.Balance = 678.90
В приведенном выше примере мы не можем получить доступ к Балансу, потому что он объявлен, как Частный. Мы можем использовать только приватную переменную внутри Class Module. Мы можем использовать функцию / подпрограмму в Class Module, например:
' CLASS MODULE Код
Private Balance As Double
Public Sub SetBalance()
Balance = 100
Debug.Print Balance
End Sub
Считается плохой практикой иметь публичные переменные-члены. Это потому, что вы позволяете коду вне объекта мешать работе класса. Цель использования классов состоит в том, чтобы скрыть происходящее от вызывающего.
Чтобы пользователь не общался напрямую с нашими переменными-членами, мы используем Свойства.
Свойства Class Module
- Get — возвращает объект или значение из класса
- Let — устанавливает значение в классе
- Set — устанавливает объект в классе
Формат свойств VBA
Обычный формат для свойств выглядит следующим образом:
Public Property Get () As Type End Property Public Property Let (varname As Type ) End Property Public Property Set (varname As Type ) End Property
Мы уже видели, что свойство это просто тип sub. Назначение свойства — позволить вызывающей стороне получать и устанавливать значения.
Почему мы используем свойства
Почему мы не можем просто сделать переменные общедоступными и использовать их напрямую?
Давайте объясним с некоторыми примерами. Представьте, что у нас есть класс, который ведет список стран. Мы могли бы сохранить список в виде массива:
' Использовать массив для хранения стран
Public arrCountries As Variant
' Установить размер массива при инициализации класса
Private Sub Class_Initialize()
ReDim arrCountries(1 To 1000)
End Sub
Когда пользователь хочет получить количество стран в списке, он может сделать это:
' Код обычного модуля Dim oCountry As New clsCountry ' Получить количество элементов NumCountries = UBound(oCountry.arrCountries) + 1
С приведенным выше кодом есть две основные проблемы
- Чтобы узнать количество стран, вам необходимо знать, как хранится список, например, Массив.
- Если мы изменим массив на коллекцию, нам нужно будет изменить весь код, который напрямую ссылается на массив
Для решения этих проблем мы можем создать функцию, возвращающую количество стран:
' CLASS MODULE Код - clsCountryList
' Массив
Private arrCountries() As String
Public Function Count() As Long
Count = UBound(arrCountries) + 1
End Function
Затем мы используем это так
' Код модуля Dim oCountries As New clsCountries Debug.Print "Количество стран " & oCountries.Count
Этот код решает две проблемы, которые мы перечислили выше. Мы можем изменить наш массив на коллекцию, и код вызывающего абонента все равно будет работать. Например:
' CLASS MODULE Код
' Коллекция
Private collCountries() As Collection
Public Function Count() As Long
Count = collCountries.Count
End Function
Вызывающий не замечает, как хранятся страны. Все, что нужно знать вызывающему — это то, что функция Count будет возвращать количество стран.
Как мы только что видели, подпрограмма или функция обеспечивает решение вышеуказанных проблем. Однако использование свойства может обеспечить более элегантное решение.
Использование свойства вместо Function/Sub
Вместо создания функции Count мы можем создать свойство Count. Как вы можете видеть ниже, они очень похожи:
' Замени это
Public Function Count() As Long
Count = UBound(arrCountries) + 1
End Function
' На это
Property Get Count() As Long
Count = UBound(arrCountries) + 1
End Function
В этом сценарии нет большой разницы между использованием свойства и использованием функции. Тем не менее, есть различия. Обычно мы создаем свойство Get и Let так:
' CLASS MODULE Код - clsAccount
Private dTotalCost As Double
Property Get TotalCost() As Long
TotalCost= dTotalCost
End Property
Property Let TotalCost(dValue As Long)
dTotalCost = dValue
End Property
Использование Let позволяет нам рассматривать свойство, как переменную. Таким образом, мы можем сделать это:
Второе отличие состоит в том, что использование Let и Get позволяет нам использовать одно и то же имя при обращении к свойству Get или Let. Таким образом, мы можем использовать свойство, как переменную. Это цель использования свойств над подпрограммой и функцией.
oAccount.TotalCost = 6 dValue = oAccount.TotalCost
Если мы использовали функцию и подпрограмму, то мы не можем получить поведение переменной. Вместо этого мы должны вызвать две разные процедуры, например:
oAccount.SetTotalCost 6 dValue = oAccount.GetTotalCost
Вы также можете видеть, что когда мы использовали Let, мы можем присвоить значение, как переменную. Когда мы используем SetTotalCost, мы должны были передать его в качестве параметра.
О Свойствах в двух словах
- Свойство скрывает детали реализации от вызывающей стороны.
- Свойство позволяет нам обеспечивать то же поведение, что и переменная.
Типы свойств VBA
Есть три типа свойств. Мы уже видели Get и Let. Но мы еще не рассмотрели Set.
Set похож на Let, но он используется для объекта (подробнее об этом см. Назначение объектов VBA).
Первоначально в Visual Basic ключевое слово Let использовалось для назначения переменной. На самом деле, мы можем использовать его, как захотим.
' Эти строки эквивалентны Let a = 7 a = 7
Поэтому мы используем Let, чтобы присвоить значение переменной, и мы используем Set, чтобы назначить объект переменной объекта.
' Используем Let Dim a As Long Let a = 7 ' Используем Set Dim coll1 As Collection, coll2 As Collection Set coll1 = New Collection Set coll2 = coll1
- Let используется для присвоения значения базовому типу переменной.
- Set используется для назначения объекта переменной объекта
В следующем примере мы используем свойства Get и Let для строковой переменной
' CLASS MODULE Код
' Свойства SET/LET для переменной
Private m_sName As String
' свойства Get/Let
Property Get Name() As String
Name = m_sName
End Property
Property Let Name(sName As String)
m_sName = sName
End Property
Затем мы можем использовать свойства Name так:
Sub TestLetSet()
Dim sName As String
Dim coll As New Collection
Dim oCurrency As New clsCurrency
' Свойство Let
oCurrency.Name = "USD"
' Свойство Get
sName = oCurrency.Name
End Sub
В следующем примере мы используем свойства Get и Set для переменной объекта
' CLASS MODULE Код
Private m_collPrices As Collection
' Свойства Get/Set
Property Get Prices() As Collection
Set Prices = m_collPrices
End Property
Property Set Prices(collPrices As Collection)
Set m_collPrices = collPrices
End Property
Затем мы можем использовать свойства так:
Sub TestLetSet()
Dim coll1 As New Collection
Dim oCurrency As New clsCurrency
' Свойство Set
Set oCurrency.Prices = coll1
' Свойство Get
Dim coll2 As Collection
Set Coll2 = oCurrency.Prices
End Sub
Мы используем свойство Get, чтобы вернуть значения для обоих элементов. Обратите внимание, что даже если мы используем свойство Get для возврата коллекции, нам все равно нужно использовать ключевое слово Set для его назначения.
События Class Module
Class Module имеет два события:
- Инициализировать — происходит при создании нового объекта класса.
- Завершить — происходит, когда объект класса удален.
В объектно-ориентированных языках, таких как C ++, эти события называются Конструктором и Деструктором. В большинстве языков вы можете передавать параметры конструктору, но не в VBA. Мы можем использовать Class Factory, чтобы обойти эту проблему, как показано ниже.
Инициализация
Давайте создадим очень простой Class Module с именем clsSimple с событиями Initialize и Terminate.
' CLASS MODULE Код
Private Sub Class_Initialize()
MsgBox "Класс инициализируется"
End Sub
Private Sub Class_Terminate()
MsgBox "Класс прекращается"
End Sub
Public Sub PrintHello()
Debug.Print "Привет"
End Sub
В следующем примере мы используем Dim и New для создания объекта.
В этом случае oSimple не создается, пока мы не ссылаемся на него в первый раз, например:
Sub ClassEventsInit2()
Dim oSimple As New clsSimple
' Инициализация происходит здесь
oSimple.PrintHello
End Sub
Когда мы используем Set и New вместе, поведение отличается. В этом случае объект создается при использовании Set, например:
Sub ClassEventsInit()
Dim oSimple As clsSimple
' Инициализация происходит здесь
Set oSimple = New clsSimple
oSimple.PrintHello
End Sub
Примечание: Для получения дополнительной информации о различиях между использованием New с Dim и использованием New с Set см. Тонкие различия Dim и Set
Как я уже говорил ранее, вы не можете передать параметр в Initialize. Если вам нужно сделать это, вам нужна функция, чтобы сначала создать объект.
' CLASS MODULE - clsSimple
Public Sub Init(Price As Double)
End Sub
' обычный модуль
Public Sub Test()
' использование функции CreateSimpleObject
Dim oSimple As clsSimple
Set oSimple = CreateSimpleObject(199.99)
End Sub
Public Function CreateSimpleObject(Price As Double) As clsSimple
Dim oSimple As New clsSimple
oSimple.Init Price
Set CreateSimpleObject = oSimple
End Function
Мы расширим CreateSimpleObject в Примере 2, чтобы создать фабрику классов.
Завершение
Событие Terminate наступает при удалении класса. Это происходит, когда мы устанавливаем значение Nothing.
Sub ClassEventsTerm()
Dim oSimple As clsSimple
Set oSimple = New clsSimple
' Завершение происходит здесь
Set oSimple = Nothing
End Sub
Если мы не установим объект в Nothing, VBA автоматически удалит его, когда он выйдет из области видимости.
Это означает, что если мы создадим объект в процедуре, когда эта процедура завершится, VBA удалит все созданные объекты.
Sub ClassEventsTerm2()
Dim oSimple As New clsSimple
' Инициализация происходит здесь
oSimple.PrintHello
' oSimple удаляется, когда мы выходим из этого Sub-вызова Terminate
End Sub
Class Module. Пример 1
В этом примере мы рассмотрим очень распространенное использование Class Module.
Представьте, что у нас есть следующие данные:
Мы хотим читать альбомы по разным годам, а затем создавать различные отчеты.
Мы могли бы использовать для этого 2D-массив или коллекцию коллекций, например:
For i = 2 To rg.Rows.Count
Year = rg.Cells(i, 3)
If startYear <= Year And endYear >= Year Then
' Создать новую коллекцию для каждой строки
Set rowColl = New Collect
' Добавить исполнителя
rowColl.Add rg.Cells(i, 1).Value
' Добавить заголовок
rowColl.Add rg.Cells(i, 2).Value
' и так далее
' Добавить коллекцию строк в основную коллекцию
coll.Add rowColl
End If
Next i
Как вы можете себе представить, этот код очень быстро запутался.
К счастью для нас, у нас есть Class Module VBA, чтобы сделать нашу жизнь проще. Мы можем создать Class Module для хранения элементов.
' clsAlbum class module
Private m_sArtist As String
Private m_sTitle As String
Private m_sYear As String
Private m_sGenre As String
Private m_sSales As String
' Свойства
Public Property Get Artist() As String
Artist = m_sArtist
End Property
Public Property Let Artist(ByVal sArtist As String)
m_sArtist = sArtist
End Property
' и т.д.
Каждый раз, когда мы хотим добавить запись, мы можем сделать это следующим образом:
' Объявить переменную Dim oAlbum As clsAlbum ' Создать новый альбом Set oAlbum = New clsAlbum ' Добавить детали oAlbum.Artist = rg.Cells(i, 1) oAlbum.Title = rg.Cells(i, 2) oAlbum.Year = rg.Cells(i, 3) oAlbum.Genre = rg.Cells(i, 4) oAlbum.Sales = rg.Cells(i, 5) ' Добавить объект альбома в коллекцию coll.Add oAlbum
Как видите, это делает наш код более читабельным. Понятно, для чего используются Artist, Title и т.д.
Затем мы можем легко использовать эти данные для создания отчетов, записи в файлы и т.д.
Sub PrintAlbum(coll As Collection)
Dim oAlbum As clsAlbum
For Each oAlbum In coll
' Распечатайте название и исполнителя для каждого альбома
Debug.Print oAlbum.Title, oAlbum.Artist
Next
End Sub
Ниже приведен полный код для этого примера
Sub CreateReport()
Dim coll As Collection
' читать данные
Set coll = ReadAlbums(1990, 2001)
' Распечатать информацию об альбоме
PrintAlbum coll
' Распечатать общий объем продаж
PrintTotalSales coll
End Sub
Function ReadAlbums(startYear As Long, endYear As Long) _
As Collection
Dim rg As Range
Set rg = Sheet1.Range("A1").CurrentRegion
' Создать коллекцию для хранения альбомов
Dim coll As New Collection
Dim oAlbum As clsAlbum
Dim i As Long, Year As Long
For i = 2 To rg.Rows.Count
Year = rg.Cells(i, 3)
If startYear <= Year And endYear >= Year Then
' Создать новый альбом
Set oAlbum = New clsAlbum
' Добавить детали
oAlbum.Artist = rg.Cells(i, 1)
oAlbum.Title = rg.Cells(i, 2)
oAlbum.Year = Year
oAlbum.Genre = rg.Cells(i, 4)
oAlbum.sales = rg.Cells(i, 5)
' Добавить объект альбома в коллекцию
coll.Add oAlbum
End If
Next i
Set ReadAlbums = coll
End Function
Sub PrintAlbum(coll As Collection)
Dim oAlbum As clsAlbum
For Each oAlbum In coll
Debug.Print oAlbum.Title, oAlbum.Artist
Next
End Sub
Sub PrintTotalSales(coll As Collection)
Dim oAlbum As clsAlbum, sales As Double
For Each oAlbum In coll
sales = sales + oAlbum.sales
Next
Debug.Print "Общее количество продаж составляет " & sales
End Sub
Class Module. Пример 2
В этом примере мы пойдем дальше. Мы собираемся взглянуть на некоторые хитрые приемы при использовании объектов.
Представьте, что у вас есть список продуктов, как на картинке ниже.
Продукты имеют разные поля, поэтому нам нужно использовать разные модули классов для каждого типа продуктов. Один тип для строки Книги, один тип для строки Фильмы.
Сначала мы создадим наши модули классов. Они очень похожи для обоих типов продуктов.
' CLASS MODULE - clsBook
' Переменные
Private m_Title As String
Private m_Year As Long
' Свойства
Property Get ItemType() As String
ItemType = "Book"
End Property
Property Get Title() As String
Title = m_Title
End Property
Property Get Year() As Long
Year = m_Year
End Property
' Методы
Public Sub Init(rg As Range)
m_Title = rg.Cells(1, 2)
m_Year = CLng(rg.Cells(1, 4))
End Sub
Public Sub PrintToImmediate()
Debug.Print ItemType, m_Title, m_Year
End Sub
' CLASS MODULE - clsFilm
' Переменные
Private m_Title As String
Private m_Year As Long
' Свойства
Property Get ItemType() As String
ItemType = "Film"
End Property
Property Get Title() As String
Title = m_Title
End Property
Property Get Year() As Long
Year = m_Year
End Property
' Методы
Sub Init(rg As Range)
m_Title = rg.Cells(1, 2)
m_Year = CLng(rg.Cells(1, 5))
End Sub
Public Sub PrintToImmediate()
Debug.Print ItemType, m_Title, m_Year
End Sub
Как видите, единственная реальная разница — это инициализация.
Когда мы читаем каждую запись, нам нужно определить, книга это или фильм. Затем мы создаем соответствующий объект. Представьте, что нам нужно создать переменную для каждого типа, например:
' Для каждого типа требуется одна переменная Dim oBook As clsBook Dim oFilm As clsFilm ' Если Книга сделать это Set oBook = New clsBook ' Если фильм сделать это Set oFilm = New clsFilm
Если бы у нас было много разных типов, это было бы действительно очень грязно. Хорошей новостью является то, что нам нужно использовать только одну переменную!
В VBA мы можем объявить переменную как вариант. Когда мы используем Variant, мы, по сути, говорим: «Мы определим тип переменной во время выполнения кода».
Это очень полезно при работе с объектами и позволяет нам избежать использования одной переменной, например:
' Требуется только одна переменная Dim oItem As Variant ' Если книга, указать тип clsBook Set oItem = New clsBook ' Если фильм, указать тип clsFilm Set oItem = New clsFilm
Это действительно полезно, так как нам нужна только одна переменная, независимо от того, сколько у нас объектов.
Второе преимущество использования Variant заключается в следующем. Если у каждого Class Module есть подпрограмма / функция с одинаковым именем и параметрами, мы можем использовать одну и ту же переменную для ее вызова.
Представьте, что в clsBook есть функция InitBook, а в clsFilm есть функция InitFilm. Нам нужно сделать это:
' Если clsBook
If Type = "Book" Then
oItem.InitBook
ElseIf Type = "Film" Then
oItem.InitFilm
Однако, если они имеют одинаковое имя, например, Init, мы можем заменить строки кода If ElseIf одной строкой:
' это вызовет подпрограмму Init любого типа oItem, установленного в
oItem.Init
Теперь мы можем создать функцию для создания соответствующего объекта. В объектно-ориентированном программировании мы имеем то, что называется фабрикой классов. Это просто функция, которая создает объект на основе заданного типа.
Ранее мы видели, что событие Initialize не принимает параметры. Мы можем позвонить в Init на фабрике классов, чтобы обойти эту проблему.
Полный код для функции ClassFactory здесь:
Function ClassFactory(rg As Range) As Variant
' Получить тип продукта
Dim sType As String
sType = rg.Cells(1, 1)
' Создать объект на основе типа
Dim oItem As Variant
Select Case sType
Case "Book":
Set oItem = New clsBook
Case "Film":
Set oItem = New clsFilm
Case Else
MsgBox "Invalid type"
End Select
' Разобрать поля на правильные переменные класса
oItem.Init rg
' Вернуть объект продукта
Set ClassFactory = oItem
End Function
Это следующее наше начало. В этом разделе мы читаем таблицу и передаем диапазон в ClassFactory.
Создает объект, передает диапазон в метод Parse объекта. Затем он возвращает объект, который мы добавляем в нашу коллекцию.
Sub ReadProducts()
' Создать коллекцию
Dim coll As New Collection
Dim product As Variant
Dim rg As Range
' Читайте продукты с листа
Dim i As Long
For i = 1 To 2
Set rg = Sheet1.Range("A" & i & ":E" & i)
Set product = ClassFactory(rg)
coll.Add product
Next
' Распечатать информацию о продукте в Immediate Window(Ctrl + G)
PrintCollection coll
End Sub
Мы также можем использовать вариант объекта для печати элементов. Пока оба объекта имеют подпрограмму с одинаковым именем и параметрами (например, PrintToImmediate), мы можем вызывать ее, используя тип Variant.
Public Sub PrintCollection(ByRef coll As Collection)
Dim v As Variant
For Each v In coll
' Печать элементов
v.PrintToImmediate
Next
End Sub
Заключение
На этом я заканчиваю свою статью о Class Module VBA. В этой статье мы рассмотрели части Class Module VBA и два примера, в которых вы могли бы их использовать.
Важно понимать, что классы и объекты — это обширная тема. Существует множество типов объектов, которые вы можете создавать, и способы их использования.
Если вы планируете использовать Class Module, то я советую начать с основ и ознакомиться с тем, как создать простой. Как только вы освоите основы, вам будет намного легче переходить к более сложным сценариям.
In this Article
- VBA Class Modules – Introduction
- Class Modules vs. Modules
- Advantages of Using Class Modules
- Disadvantages of Using Class Modules
- Inserting a Class Module
- Creating an Object Item
- Creating a Collection
- Using Your New Object
- Summary of Creating an Object Using a Class Module
- Using a Class Module to Create a Variable Repository
- Turning Your Object into an Add-In
This tutorial will teach you about Class Modules in VBA. You’ll learn what they are and how to use them.
VBA Class Modules – Introduction
When you insert modules into the Visual Basic Editor (VBE) in order to enter your code, you may have noticed that you can also insert what is called a ‘Class Module’.
Class Modules vs. Modules
The class modules work in a very different way to the ordinary modules in that they facilitate creating a Component Object Model (COM) which can then be used within your normal VBA code
Effectively, you create an object which works in the same way as a built in Excel object such as ‘Worksheets’. In the Worksheets Object, you have a number of properties and methods which allow you to get the number of worksheets within a workbook or each individual name of a worksheet, or numerous other information
When you create a new Object in this way, you are creating a building block which can be used anywhere within VBA. The Object has a number of properties and methods that can be accessed by your VBA code from anywhere within the workbook without having to keep re-writing the code over again.
As well as referring to your new object from a standard VBA module, you can also use it in the code behind a UserForm that is part of your custom application
You can also use it where you have placed Active X controls onto a worksheet, such as a command button or a drop down. These controls all use VBA, and your new object can easily be incorporated into the event code for these controls.
You can also turn your object into an Excel add-in. Your object will automatically be available to other users who have that add-in loaded. This adds your own multi-tier architecture to your Excel application
Excel is a multi-tiered application. There is the client services layer, which drives the actual worksheet window that that the user is familiar with. The Excel object model is the next layer underneath. Press F2 in a VBA module and you will be able to see the huge number of objects and members of those objects that are the engine of Excel. Note that your new object will also be displayed here.
Finally, underneath all of this, you have the data services layer which holds all the data that you have entered into the worksheets and cells. Excel accesses this using the Excel Object model.
Creating a Class Module allows you to extend the Excel Object Module with your own custom objects and members
This article explains to you how you to create a simple hierarchy of objects using Class Modules.
Advantages of Using Class Modules
- You can develop a robust building block which can be used in any number of different Excel applications
- Once it is thoroughly tested, then is can be relied on to always produce the correct results in the same way as the built-in Excel objects
- If updates are made to code elsewhere in the application, the new object will still continue to work in the same way
- You can use your new object in other Excel applications as an add-in
- The objects can be re-used in other applications and helps in debugging
Disadvantages of Using Class Modules
- They can be difficult to create and understand.
- Naming conventions are very important because this is what you will see when use your object within a normal module.
- If you have not created a class module before, they can be difficult to understand and there is a steep learning curve
- Impossible to make changes at run-time – you have to re-set the project.
- If Properties and Private Variables have the same name then infinite loops can occur resulting in errors
Inserting a Class Module
Select Insert | Class Module from the VBE (Visual Basic Editor) menu. The new Class Module will automatically be called ‘Class 1’, but this needs to be changed immediately to the name that you are going to use for your object
You change the name in the Properties window where the arrow is pointing. You simply type in your new name, and this will change in the Class Modules collection
If the Properties window is not visible, then select View | Properties on the VBE menu or press F4
Call your new class module ‘MyItem’ and double click the name in the tree-view in the Project Explorer to display the code window for it.
Creating an Object Item
This example will create a top-level object called ‘MyItems’ with a member object below it called ‘MyItem’ which will hold the individual data for each item. Once created it will work in the same way as a built in Excel Object. For example, there is an object called ‘Worksheets’ which is a collection of each worksheet within your workbook. There is also an object called ‘Sheet’ which represents each individual worksheet within your workbook, and holds all the properties and methods for each worksheet. This object relates to the ‘Worksheets’ collection object.
You can iterate through the ‘Worksheets’ collection, viewing each ‘Sheet’ in turn. In the same way you will be able to iterate through the ‘MyItems’ collection viewing the properties that you created in the ‘Myitem’ member.
The first thing to do is to create the sub object for the member level which will hold the actual items within the collection of the top-level object. This is the equivalent of the members (e.g. name, visible, count) within the ‘Sheet’ object in Excel. This code is entered into the class module called ‘MyItem’
Class modules have Properties and Methods. Properties are effectively like variables, in that they hold values of data like variables, and Methods are like sub routines or functions.
In the sub object we are going to create two properties for the object – Item and Detail
Initially two string variables need to be declared to hold the values for the properties:
Private mItem As String
Private mDetail As String
These need to be declared in the Declarations section at the top of the code for the class module so that they can be used in all sub routines throughout the module
They need to be given unique names to make them different from the properties that we are going to create, so an ‘m’ (for member) has been put in front of each name.
The variables are declared as Private so they cannot be seen by anyone using the object. They are working variables for use within the object code and are not there as part of the final object.
The next step is to set up code to give access to the two properties. You do this by means of a Property Let and a Property Get statement for each property. These must be Public otherwise the top-level object will not have any visible properties
Public Property Let Item(vdata As String)
mItem = vdata
End Property
Public Property Get Item () As String
Item = mItem
End Property
Public Property Let Detail (vdata As String)
mDetail = vdata
End Property
Public Property Get Detail () As String
Detail = mDetail
End Property
This code creates the means to read and write values to the two properties (Item and Detail) using the two private variables that were defined in the declarations section of the module.
The ‘vdata’ parameter is used to pass data to the property concerned.
It is important that each property has a ‘Let’ and ‘Get’ statement and that the property name is the same in each case. You could end up with two different properties if miss-spelt – one that you can read from and one that you can write to!
To help with creating this code, you can use Insert | Procedure on the VBE menu to create a code skeleton which will create the initial code for the ‘Get’ and ‘Let’ properties for a given property name
This will display a pop-up window where you type the property name in and select ‘Property’ on the radio buttons:
Click ‘OK’ and the skeleton code will be added into the class module:
Public Property Get MyProperty() As Variant
End Property
Public Property Let MyProperty(ByVal vNewValue As Variant)
End Property
This prevents any mistakes over names of properties. You simply add your code in between the ‘Public Property’ and ‘End Property’ statements.
You now have an object called ‘MyItem’ which will hold all the data for this exercise.
VBA Coding Made Easy
Stop searching for VBA code online. Learn more about AutoMacro — A VBA Code Builder that allows beginners to code procedures from scratch with minimal coding knowledge and with many time-saving features for all users!
Learn More
Creating a Collection
The next stage is to create a top-level object as a Collection object to give access to the properties that you have set up in the ‘MyItem’ object
Again, you need to define a working object to act as the collection object in the same way that you defined the two string variables in the ‘MyItem’ object.
Private mItems As CollectionAgain, this this has to have a unique name which is why there is an ‘m’ (member object) in front of the name, and it is also declared as ‘Private’ so that it does not appear when the new object is being used
Next, you need to populate the Class_Initialize code. This runs when you first use the object within your code, and it determines what values will be loaded into the object
You can access this sub routine by selecting ‘Class’ in the first drop down and ‘Initialize’ in the second drop down of the module window
Private Sub Class_Initialize()
Dim objItem As MyItem
Set mItems = New Collection
For n = 1 To 3
Set objItem = New MyItem
objItem.Item = Worksheets("Sheet1").Range("a" & n).Value
objItem.Detail = Worksheets("Sheet1").Range("b" & n).Value
mItems.Add objItem
Next n
End Sub
The code sets up an object called ‘objItem’ using the definition of ‘MyItem’ which we built as a class module earlier on.
It then creates a new Collection based on the ‘mItems’ object defined earlier
It iterates through values held on Sheet1 of the workbook and puts them into the properties that we created for the ‘MyItem’ object. Note that when you use ‘objitem’, a drop down appears showing the two properties, exactly as if you were using a built-in Excel object.
The item object is then added into the collection object which now holds all the data in the property values.
The input data does not have to be taken from a worksheet. It could be static values, or it could come from a connection to a database such as Microsoft Access or SQL Server, or it could come from another worksheet.
You then need to add a public function called ‘Item’
Public Function Item(index As Integer) As MyItem
Set Item = mItems.Item(index)
End Function
This allows you to refer to individual objects within the collection object by their index number. This function provides a ‘mirror’ of what is going on in the ‘mMyItems’ collection in the background.
You will also need to add a property called ‘Count’ so that your code can establish how many ‘MyItem’ objects are in the ‘MyItems’ collection, should you wish to iterate through it.
Public Property Get Count() As Long
Count = mItems.Count
End Property
In this case you only need a ‘Get’ property because it is read-only. It uses the mItems collection because this already has a count property built into it.
You now have an object (MyItems) with a full hierarchy defined by the object ‘MyItem’
To make the whole thing work, you now need to populate a worksheet (Sheet1) with data so that the Class Initialize routine can collect this into the object
Your spreadsheet should look like this:
Using Your New Object
You can now use your Collection object (MyItems) within a standard Excel VBA module. Enter the following code:
Sub test_object()
Dim MyClass As New MyItems, n As Integer
MsgBox MyClass.Count
For n = 1 To MyClass.Count
MsgBox MyClass.Item(n).Item
MsgBox MyClass.Item(n).Detail
Next n
End Sub
This code creates an object called ‘MyClass’ based on the collection object that you created called ‘MyItems’. This fire off the ‘Initialize’ routine that extracts all the data from the worksheet into the object.
It displays the number of items in the collection and then iterates through the collection showing the ‘Item’ text and the ‘Detail’ text. You will notice that when you refer to the ‘MyClass’ object in your code, you will see a list of the two member properties which helps in adding the correct property.
If you change the value of a cell in the input data on the spreadsheet, this will automatically be updated in the collection when you run the above code again, since when you dimension the object, the initialize routine runs and picks up all the new data
If you use the word ‘Static’ instead of ‘Dim’ the initialise routine does not run and the old values are kept, so long as the code is continuously running. If the data on the spreadsheet changes this will not be reflected in the object
Sub Test_Static()
Static Myclass As New MyItems, n As Integer
For n = 1 To Myclass.Count
MsgBox Myclass.Item(n).Item
MsgBox Myclass.Item(n).Detail
Next n
End Sub
Summary of Creating an Object Using a Class Module
As you have seen, creating a hierarchy of class modules to use as an object is quite a complicated business, even for a structure as simple as the example provided here. The scope for making mistakes is enormous!
However, it does have huge advantages in making your code more elegant and easier to read. It is also easier to share with other Excel applications and developers by turning it into an Add-In.
In this example of how to create an object to hold data, it would be a normal approach to create a multi-dimensional array to hold the multi-column spreadsheet data, and you would write a line of code to update or read each element in the array. This would probably end up being quite messy, and mistakes could easily be made in addressing the various elements.
With your new object, you can simply refer to it and the members that you have created below it to hold the data.
Also, if the data changes in the spreadsheet (or in a linked database if you have used this as a data source within your class module) whenever you use the ‘Dim’ statement the initialize routine will be called and the data will be instantly updated. No need to write code to re-populate your array.
VBA Programming | Code Generator does work for you!
Using a Class Module to Create a Variable Repository
When you write VBA code you use variables all over the place, all with different scopes. Some may only be defined for a particular procedure, some for a particular module, and some may be global variables that can be used all over the application
You can create a class module that will hold a large number of variables, and because it is an object, it can be used anywhere within your code, even on a user form or in an Active X control that you have placed on a worksheet.
The added advantage is that when you refer to your variable object, you will see a list of all the variable names held in the object sorted into ascending order.
To create a repository, you need to insert a new class module. You do this by using Insert | Class Module from the VB Editor menu
Change the name to ‘MyVariables’ using the same methodology as previously discussed in this article.
Enter the following code:
Private mV As Variant
Public Property Get Variable1() As Variant
Variable1 = mV
End Property
Public Property Let Variable1(ByVal vNewValue As Variant)
mV = vNewValue
End Property
Public Property Get Variable2() As Variant
Variable1 = mV
End Property
Public Property Let Variable2(ByVal vNewValue As Variant)
mV = vNewValue
End Property
This code sets up ‘Let’ and ‘Get’ properties for two variables (‘Variable1’ and ‘Variable2’). The Let and Get properties are required for each of your variables so that they are read / write
You can use your own names for the variables instead of the sample ones in this code, and you can add further variables, making sure that each new variable has a ‘Let’ and ‘Get’ statement.
The private declaration of the variable ‘mV’ is to create a working variable that is only used within the class module to transfer values.
To use the variable repository, enter the following code into a standard module:
Global VarRepo As New MyVariables
Sub TestVariableRepository()
MsgBox VarRepo.Variable1
VarRepo.Variable1 = 10
MsgBox VarRepo.Variable1
End Sub
This code creates a global instance of your ‘MyVariables’ object that you created. You only need to do this declaration once from anywhere within your code.
The code first displays the value of ‘Variable1’ to show that it is empty.
A value of 10 is assigned to ‘Variable1’ and the new value within the object is then displayed to show that this property now holds this value.
Because the instance of the ‘MyVariables’ object has been defined globally, you can refer to any of the defined variables within the object from anywhere within your code.
This has a huge advantage in that if you want to use your variables anywhere in your code, you only need to define one global variable, and from that instance, all the variables can be freely accessed and modified throughout your code.
Turning Your Object into an Add-In
So far, the code for the object creation is within your workbook application. However, if you want to be able to share your object with other developers or in other Excel applications of your own, you can turn it into an Add-In
To do this, all that needs to happen is to save the file as an Add-In. Select File | Save As and a browser window will appear
Select the file type as Add-In (.xlam) from the file type drop down and click OK. The file will be saved to the Add-In folder by default, but you can change the location.
You can then incorporate the add-in file into your Excel applications, giving you the flexibility to make use of your new object
To include your new Add-In into Excel, click on File on the Excel ribbon, and then click on Options at the bottom of the left-hand pane
Click on ‘Add-Ins’ in the left-hand pane in the pop-up window that appears. At the bottom of the window is a button marked ‘Go’
Click on this and an ‘Add-In’ pop-up window will appear. Click on ‘Browse’ and then locate your Add-In file. You will then be able to refer to your object in your code.
When we use VBA we use the properties and attributes defined in VBA but what happens when we want to create our own properties and methods and attributes, that is when we use a class module in VBA so that we can have it user-defined, a class module has its own set of codes defined for functions, properties, and objects by the user.
Class Modules are used to create an object. When we say items, even though it is a variable, those are small programs. While writing the code, we usually write in modules. Essential modules are where we write our principles to do the job. We also use User Form to create Graphic User Interfaces.
But if you look at the above image, you can see “Class Module.” I know for sure you have not touched that until you are reading this post. You must be wondering what is this VBA classVBA Class allows us to create our Object function to add any features, command line, function type. When created, they act like totally an independent object function but are connected.read more module is when all the job can be done by using our regular Module itself.
Table of contents
- Excel VBA Class Modules
- What is the Class Module?
- Example
- Class Module vs. Objects
- Recommended Articles
What is the Class Module?
Class Modules allow a user to create their object just like how we have built-in items in standard modules like “Worksheets,” “Workbooks,” “Range,” and so on.
Like this using a class module, we can create custom objects.
The class has a direct relationship with objects. For example, you have a machine diagram to build a machine but remember it is not a machine yet and using this machine diagram, and we can make many machines like that.
For example, if you want to list various machine brands to list the characteristics of multiple models.
In the machine, we have a brand name, series number, machine power, color of the device, number of motors involved in it, motor fuel type, etc.… In technical language, these are called “properties.”
Concerning the properties of the machine, we can start, we can turn off, we can increase the speed of the motor, we can pause, etc… And these are called “Methods.”
Example
You can download this VBA Class Template here – VBA Class Template
Let’s start the ball rolling because it is always the boring thing to read out the theoretical part. To insert a class module, go to the insert option in a basic visual editor.
Now we can see a class module like the below.
This looks similar to the one we have above as a regular module. Change the name of the class module in the properties window. To see the properties window, press the F4 key.
Now declare the variable as a string.
Without creating a subprocedure in VBASUB in VBA is a procedure which contains all the code which automatically gives the statement of end sub and the middle portion is used for coding. Sub statement can be both public and private and the name of the subprocedure is mandatory in VBA.read more, we need to declare the variable and use the word “Public” not “Dim.”
Now we can access this variable in any module and class module.
Now go to a regular module and name the variable.
After declaring the variable, we need to assign the data type in VBA; instead of setting the data type, we can give the name of the class module, i.e., CM.
Using the variable “k,” we can access the public variableIn VBA, «public variables» are variables that are declared to be used publicly for all macros written in the same module as well as macros written in different modules. As a result, variables declared at the start of any macro are referred to as «Public Variables» or «Global Variables.»read more we have defined in the class module, i.e., “My Value.”
As we can see in the above picture, it is showing the option of variable name from the class module to assign the value to it.
Now show the value of the assigned variable in the VBA message boxVBA MsgBox function is an output function which displays the generalized message provided by the developer. This statement has no arguments and the personalized messages in this function are written under the double quotes while for the values the variable reference is provided.read more.
Code:
Sub Class_Example() Dim k As New CM k.MyValue = "Hello" MsgBox k.MyValue End Sub
Run this code using the F5 key or manually to show the result.
Class Module vs. Objects
At the initial stage of the class module, everybody gets confused with what class is and what an object is.
To understand this, recollect our earlier example of a machine diagram. The first thing we need to produce a machine is we need to design the machine first, and then several copies can be replicated with that design.
Now relate this to our class module.
- Here Class Module is a Design. And Object is the copy created by the Design.
- One more interesting thing is we need to use the word “new” to create an object from the class module.
Below is an example of the same.
One more thing when we use built-in objects like worksheets, workbooks, and range objects, we don’t use the word “new.”
To start off the proceedings with the Class Module, these basic things you should know. In the coming articles, we will see the next level examples.
It seems difficult to understand this; the more time you spend with a class module, you will get used to it.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to VBA Class Module. Here we learn how to create and use a class module in VBA and also the difference between the class module and object along with examples & downloadable excel templates. Below are some useful articles related to Excel VBA –
- Pause VBA Code
- List of VBA Worksheet Function
- VBA On Error Methods
- VBA IsEmpty
What is a Class in VBA?
A class is a blueprint for an object to be created. A class itself does nothing but using classes you can create multiple identical objects that can perform operations or can be used as a data resource.
In real life, the model (design and functionalities) of a car is a class and the car itself is an object of that class. In the class, we define what the car has in it and what it can do. For example, a car has 4 wheels, 5 gears, steering wheel, etc. These are attributes/properties. We also define what a car can do, like moving forward, backward, turn, etc. These are functions of the car class. A car object created using car class, will have all these properties. If you define a car that has 5 wheels than a car created using this class will have 5 wheels. You get the point.
Enough of theory, now let’s see how you can use a class module in VBA.
Using Excel VBA class module
While working in VBA, you must have used Range(«A1»).select. The Range is pre-defined class in VBA. The select is one of the functions of Range class that select the specified range. Similarly, Debug is class in VBA and print and assert are it’s methods. Worksheets, Workbooks, Range, etc. all are VBA classes that we use in our subs.
Create your own class
First, we need to add a class module in VBA
Press ALT+F11 key combination to open excel VBA editor.
-
- Right-click on project explorer. Move the cursor to Insert—> Class module. Click on it. The same thing can be done from the Insert menu.
-
- The class will be added to the folder «Class module». The default name is like class1, class2, and so on. You can change the class name from the property window. Let’s name our class «Welcome».
- Now let’s create add some attributes to our class. Since I want these attributes to be available to the public, I have use accessibility operator public.
Public name As String Public var1 As Integer Public var2 As Integer
- Now let’s add a function to this class. I want a function that says Hi! to the user. To do so add a sub and name it sayHiTo.
Sub sayHiTo(user As String) name = user MsgBox ("Hi! " & name) End Sub - Now let’s use class in a module. Insert a new module if you don’t have any. Write a sub. I have named my sub Test.
Sub test() Dim wc As New Welcome 'Declared and initialized Welcome object wc.sayHiTo ("Jack") 'used sayHiTo method of Welcome Object. End Sub
- Run this sub Test using F5 key. It will prompt «Hi! Jack» on excel workbook.
How does it work?
In sub Test, we have created is an object «wc» of Welcome class. An object is created in VBA in two methods. we run the code, Test sub creates an object wc of the Welcome class. This object has all the properties of the Welcome class. We use the sayHiTo method of the Welcome class to say hi to the user.
Object Creation in Excel VBA
-
- Instant creation
In Instant creation, we create an object while declaring the object with the «new» key. In our example above, we have used instant creation.
Dim wc As New Welcome
2. Delayed creation
In delayed creation, we first declare the object only. We don’t use the «new» keyword. In order to use the object, we need to initialize it with the «new» keyword.
Sub test() Dim wc As Welcome 'wc.sayHiTo ("Jack") 'generates error since wc is not initialised yet 'initialising object Set wc = New Welcome wc.sayHiTo ("Cory") 'this will work. End Sub
Accessing Variables of a Class
In the above examples, we have used public variables for class but it is wrong to practice. We should avoid using public variables in a class. Now the question is how would we access variables of the class. Earlier, we used subroutine to access name but VBA classes provide properties that are used to systematically update and retrieve private variable values of the class. The properties are more elegant than sub or function for updating and accessing private variables. Let’s see how.
Syntax of class property
Private name As String Private var1 As Integer Private var2 As Integer Property Let MyName(nm As String) name = nm End Property Property Get MyName() As String MyName = name End Property
Let’s use them in a module.
Sub test() 'creating class object Dim wc As New Welcome Dim wc1 As New Welcome 'using properties wc.MyName = "Exceltip.com" wc1.MyName = "ExcelForum.com" Debug.Print wc.MyName Debug.Print wc1.MyName End Sub
When you will run this test sub, you will get two names printed for two objects of the «Welcome» class.
How properties are different from sub and functions
In the above example, notice that we have used MyName property as a variable. We initialized the value of «Name» variable just by writing wc.MyName=»assdf». This line of command called the property called Property Get MyName() As String. We didn’t pass any value in parenthesis as we did in the beginning.
Similarly, to print the values of «Name» variable we used command Debug.Print wc.MyName. Isn’t it as simple as normal variable initialization? The only difference is that you can do a whole lot in the property segment. You put data validation, calculation, communication, etc. and user will only see the result.
Another difference is that we can use same name of the property to let and get part. This makes it easier and less confusing.
So yeah guys, this was a simple example of a class module in Excel VBA. This is just the tip of the iceberg, there’s a lot of juice in this topic that we will explore in later articles. We will explore each of them one by one in the easiest way possible. I hope I was explanatory enough to make you understand this. If you have any doubts regarding this topic or any other excel VBA topic, mention it in the comments section below.
Related Articles:
Import a module from a file using VBA in Microsoft Excel | Learn how to import entire module from another file using VBA.
Create a new module using VBA in Microsoft Excel | You can use a module to create another model in VBA. This can help you minimize the additional overhead work.
Add a procedure to a module using VBA in Microsoft Excel | To add procedures to modules automatically use this VBA code.
Popular Articles:
50 Excel Shortcuts to Increase Your Productivity | Get faster at your task. These 50 shortcuts will make you work even faster on Excel.
The VLOOKUP Function in Excel | This is one of the most used and popular functions of excel that is used to lookup value from different ranges and sheets.
COUNTIF in Excel 2016 | Count values with conditions using this amazing function. You don’t need filter your data to count specific value. Countif function is essential to prepare your dashboard.
How to Use SUMIF Function in Excel | This is another dashboard essential function. This helps you sum up values on specific conditions.
Создание приложения на vba путем написания процедур и функций стоит называть процедурным программированием. Написание участков кода, называемых процедурами и функциями, которые описывают какое-либо действие, и последующее последовательное исполнение этих кодов, является основным методом программирования на vba. При этом используется доступ к объектной модели Excel или других приложений. Данные и подпрограммы (функции и процедуры) функционально не связаны между собой. Это значит, что объявляя переменную «длина хвоста» на уровне модуля, нельзя задать ей различные значения для двух процедур.
При объектно-ориентированном программировании (
ООП) подход иной. Данные и подпрограммы связаны между собой и описываются в классе. Класс – сложный тип данных, в котором описывается структура объекта. Объект – основной строительный материал для написания программ. Отличные представители объектов – форма, лист, книга, диаграмма. Объект, созданный на основе класса, можно называть экземпляром класса.
Класс имеет следующую структуру:
Поле – элемент класса для хранения данных, Свойство – элемент класса для хранения данных с возможностью их обработки, Метод – аналог процедуры или функции, Событие – сигнал при изменении состояния объекта, например исполнения метода или изменения данных.
Из всех принципов ООП в vba реализуемы только два:
Абстрагирование и инкапсуляция. Инкапсуляция позволяет скрыть механизм работы класса, оставив открытыми для других процедур только необходимые для работы с экземпляром класса.
Абстракция позволяет создать объект, наиболее приближенный к некомпьютерному прототипу. Например, создать объект «Кошка» со свойствами «количество лап» и «цвет хвоста».
Создание класса
Для создания класса в vba редакторе выберите в меню Insert строку Class Module. Назовите созданный класс путем переименования созданного модуля. В файле с примером он называется ExampleClass. А модуль, демонстрирующий использование этого класса называется ExClassManagement. В свойствах класса, кроме имени так же есть параметр Instancing. Указывается, будет ли виден класс из другой книги при установке ссылки на данную книгу. При установке Private (по умолчанию) класс виден только в данной книге, при установке PublicNotCreatable, класс не будет доступен из другой книги, однако экземпляр класса доступен будет, если он создан в данной книге.
Создание экземпляра класса
Класс — это всего лишь описание объекта. Для использования возможностей класса, необходимо создать экземпляр класса (объект). Существует несколько способов: Способ 1:
Private Sub TestClass()
Dim cl As ExampleClass
Set cl = New ExampleClass End Sub
Данный способ корректен абсолютно Способ 2:
Dim cl As ExampleClass
Private Sub TestClass()
Set cl = New ExampleClass End Sub
Этот способ отличается от первого способа тем, что экземпляр класса объявляется вне процедуры и работать с ним можно во всех процедурах модуля. При замене Dim на Public экземпляр класса доступен во всем проекте, если объявляется вне объектного модуля. Способ 3:
Dim cl WithEvents As ExampleClass
Private Sub TestClass()
Set cl = New ExampleClass End Sub
Экземпляр класса объявляется с событиями, и если в классе описаны события объекта, они будут доступны. Работает только при объявлении в объектном модуле (модуль класса, формы, листа, книги)
Способ 4:
Private Sub TestClass()
Dim cl As New ExampleClass
End Sub
Так называемый неявный метод создания экземпляра класса. В этом случае объект создается при первом обращении к переменной cl. Наверное, предпочтительнее сначала объявлять переменную (выделяется память), а затем явно создавать объект.
Уничтожение экземпляра класса
Естественно, после использования экземпляра класса, необходимо очистить память. Делается это одним способом:
Set cl = Nothing
Если не деинициализировать экземпляр класс, то ничего глобально страшного происходить в современных офисных пакетах не будет. Но делать это нужно.
Создание полей класса
Созданный класс ExampleClass не имеет полей, свойств, методов, событий, поэтому и созданный на его основе объект (экземпляр класса) cl, так же бесполезен.
Поля это переменные класса, объявленные в его модуле. Поля бывают закрытые и открытые. Доступ к закрытым полям возможен только внутри модуля класса. Открытое поле, по сути – свойство класса, и при создании экземпляра класса оно будет доступно.
Создание закрытого поля:
Dim sBody As String
или
Private sBody As String
Создание открытого поля:
Public Head As String
И теперь свойство Head доступно у экземпляра класса cl.
В него можно записать
cl.Head = «FHead»
и прочитать
Debug.Print cl.Head
Создать поле с пользовательским типом данных не удастся.
Поля используются для хранения данных в объекте. Данные будут доступны, пока объект существует. Однако нельзя указать значение по-умолчанию для поля и нельзя сделать поле только для чтения.
Создание свойства класса
Свойство это способ доступа к данным внутри объекта. Выглядят как поля, однако, это функции (назовем их методами). Называются они Property Get для чтения данных из объекта, и Property Let для записи данных в объект. Есть еще третье Property Set для установки ссылки на другой объект. Но это можно сделать и при помощи Property Let, поэтому Property Set вещь бесполезная.
Синтаксис
Property Get
[Public | Private | Friend] [Static] Property Get имя [(аргументы)] [As тип]
[произвольный код]
[имя=выражение]
[Exit Property]
[произвольный код]
[имя=выражение]
[End Property]
|
Элемент |
Описание |
|
Public |
Не обязательно. Делает метод открытым во всех модулях проекта |
|
Private |
Не обязательно. Метод будет доступен только в модуле класса, то есть не будет виден как свойство |
|
Friend |
Не обязательно. Метод будет виден во всех модулях проекта, но не будет |
|
Static |
Не обязательно. Значения объявленных локальных переменных внутри метода |
|
имя |
Обязательно. Имя метода будет являться и именем свойства. при этом оно |
|
аргументы |
Не обязательно. По сути, это аргументы функции. Имена и типы аргументов должны совпадать с аргументами метода Property Let |
|
тип |
Не обязательно. Тип данных, возвращаемый функцией может быть Byte, |
|
произвольный код |
Не обязательно. Любое количество строк кода, например математические операции с возвращаемым значением |
|
выражение |
Значение, возвращаемое методом Property Get. Если не указать, метод |
Замечания:
— Элемент Exit Property означает выход из метода, и по сути аналог Exit Function. В методе их может быть несколько.
— Внутри метода Property Get может быть сколько угодно процедур и
функций, но сам метод не может входить в состав других процедур и
функций, одноименных методов Property Get в модуле класса быть не может.
Синтаксис
Property Let [Public | Private | Friend] [Static] Property Let имя ([аргументы,] значение)
[произвольный код]
[Exit Property]
[произвольный код]
[End Property]
|
Элемент |
Описание |
|
Public |
Не обязательно. Делает метод открытым во всех модулях проекта |
|
Private |
Не обязательно. Метод будет доступен только в модуле класса, то есть не будет виден как свойство |
|
Friend |
Не обязательно. Метод будет виден во всех модулях проекта, но не будет |
|
Static |
Не обязательно. Значения объявленных локальных переменных внутри метода |
|
аргументы |
Не обязательно. По сути, это аргументы функции. Имена и типы аргументов должны совпадать с аргументами метода Property Get |
|
значение |
Не обязательно. Имя переменной метода, которой будет присваиваться |
|
произвольный код |
Не обязательно. Любое количество строк кода, например проверка |
Замечание:
— Аналогично методу Property Get
Синтаксис
Property Set[Public | Private | Friend] [Static] Property Set имя ([аргументы,] ссылка)
[произвольный код]
[Exit Property]
[произвольный код]
[End Property]
|
Элемент |
Описание |
|
Public |
Не обязательно. Делает метод открытым во всех модулях проекта |
|
Private |
Не обязательно. Метод будет доступен только в модуле класса, то есть не будет виден как свойство |
|
Friend |
Не обязательно. Метод будет виден во всех модулях проекта, но не будет |
|
Static |
Не обязательно. Значения объявленных локальных переменных внутри метода |
|
аргументы |
Не обязательно. По сути, это аргументы функции. Имена и типы аргументов должны совпадать с аргументами метода Property Get |
|
ссылка |
Не обязательно. Имя переменной метода, которая будет ссылкой на объект. Тип данных ссылки должен быть object |
|
произвольный код |
Не обязательно. Любое количество строк кода, например работа со свойствами объекта. И конечно необходимо здесь передать значение из |
Замечание:
— Не забывайте, передача ссылки на объект происходит при помощи Set.
Примеры создания свойства в модуле класса Pacient:
Private sHeight As Single
Public Property Get Height()
As Single Height = sHeight
End Property
Public Property
Let Height(ByVal sHeightValue As Single)
sHeight = sHeightValue
End Property
Свойство Height доступно для чтения и записи. при этом при записи и чтении никаких модификаций с данными не производится, то есть такая конструкция аналогична открытому полю (Public Height as Single), а потому создание ее смысла не имеет. Просто лишний код.
Private sHeight As Single
Public Property Get Height() As Single
Height = sHeight
End Property
Свойство доступно только для чтения. Метод
Property Let не создавался. Предполагается, что данные переменной sHeight заданы в какой-либо процедуре модуля класса.
Const sHeight As Single = 2
Public Property
Get Height() As Single
Height = sHeight
End Property
Свойство доступно только для чтения и содержит константу. Единственный способ открытия константы из объектного модуля. Конструкция
Public Const sHeight As Single = 2 работать не будет.
Private sHeight As Single
Public Property
Let Height(ByVal sHeightValue As Single)
sHeight = sHeightValue
End Property
Свойство только для записи. при попытке его прочитать, появится ошибка.
Private sHeight As Single
Public Property
Get Height() As Single
Height = sHeight
End Property
Public Property
Let Height(ByVal sHeightValue As Single)
Select Case sHeightValue
Case Is > 250
sHeight = 250
Case Is < 50
sHeight = 50
Case Else
sHeight = sHeightValue
End Select End Property
Происходит проверка данных при записи значения.
Private sHeight As Single
Public Property
Get Height() As Single
Height = sHeight / 100
End Property
Public Property
Let Height(ByVal sHeightValue As Single)
sHeight =
sHeightValue
End Property
Пример произвольного кода в методе Property Get. В свойство Height записывается значение в сантиметрах, а читается в метрах.
Private sHeight As Single
Public Property Get Height(ByVal Scales As Integer) As Single
Select Case Scales
Case 1
Height = sHeight
Case 2
Height = sHeight / 10
Case 3 Height = sHeight / 1000
End Select
End Property
Public Property Let Height(ByVal Scales As Integer, ByVal sHeightValue As Single)
Select Case Scales
Case 1
sHeight = sHeightValue
Case 2
sHeight = sHeightValue * 10
Case 3 sHeight = sHeightValue * 1000
End Select
End Property
Свойство со аргументом. Аргумент Scales указывает, в каких единицах измерения записывается рост, а в каких читается.
Private sHeight As Single
Private sWeight As Single
Public Property Let Height(ByVal sHeightValue As Single)
sHeight = sHeightValue
End Property
Public Property Let Weight(ByVal sWeightValue As Single)
sWeight = sWeightValue
End Property
Property Get IMT() As Single
If sHeight <> 0
Then IMT = Round(sWeight / sHeight ^ 2, 1)
End Property
Свойства Height и Weight только для записи, свойство IMT только для чтения и содержит индекс массы тела, рассчитанный на основе веса и роста. Расчет происходит всякий раз при обращении к свойству IMT.
Методы класса
В созданном классе можно создавать процедуры и функции. Они будут видны в экземпляре класса как методы, если указаны как Public и не видны, если указаны как Private. Все процедуры и функции, которые не планируется использовать как методы, должны быть Private. Этого требует принцип инкапсуляции.
Их создание ничем не отличается от создания процедур и функций в обычном модуле. Процедуры, как и функции, могут содержать обязательные и не обязательные аргументы. Однако вызов их отличается.
|
Код в классе |
Вызов метод |
|
Public Function IMT(sWeight As Single, sHeight As Single) As Single If sHeight <> 0 Then IMT = Round(sWeight / sHeight ^ 2, 1) End Function |
Dim oPac As Pacient Set oPac = New Pacient Debug.Print oPac.IMT(113, 1.83) Set oPac = Nothing |
|
Public IMT As Single Public Sub CalcIMT(sWeight As Single, sHeight As Single) If sHeight <> 0 Then IMT = Round(sWeight / sHeight ^ 2, 1) End Sub |
Dim oPac As Pacient Set oPac = New Pacient oPac.CalcIMT sWeight:=113, sHeight:=1.83 Debug.Print oPac.IMT Set oPac = Nothing |
В первом случае значение индекса массы тела возвращает функция, во втором открытое поле IMT.
Классический вариант:
|
Код в классе |
Вызов метод |
|
Private sHeight As Single Private sWeight As Single Private sIMT As Single Public Property Get Height() As Single Height = sHeight End Property Public Property Let Height(ByVal sHeightValue As Single) sHeight = sHeightValue End Property Public Property Get Weight() As Single Weight = sWeight End Property Public Property Let Weight(ByVal sWeightValue As Single) sWeight = sWeightValue End Property Public Property Get IMT() As Single IMT = sIMT End Property Public Sub CalcIMT() If sHeight <> 0 Then sIMT = Round(sWeight / sHeight ^ 2, 1) End Sub |
Dim oPac As Pacient Set oPac = New Pacient oPac.Height = 1.83 oPac.Weight = 113 oPac.CalcIMT Debug.Print oPac.IMT Set oPac = Nothing |
Свойства Height и Weight для чтения и записи, свойство IMT только для чтения. Индекс массы тела рассчитывается методом CalcIMT.
События класса
Созданный класс уже имеет два скрытых события:
Class_Initialize — Происходит при создании экземпляра класса. В этом событии удобно указывать значения свойств и переменных по-умолчанию.
Class_Terminate — Происходит при уничтожении экземпляра класса. Экземпляр класса уничтожается, когда процедура, в которой он был объявлен, завершает свою работу. Или после явной деинициализации экземпляра класса:
Set oPac=Nothing
Добавление собственных событий в класс, которые будут происходить при определенных условиях, не составляет особых сложностей. Единственное условие – экземпляр класса с событиями должен (может) быть объявлен только в объектном модуле (модуль класса, формы, листа, книги) на уровне модуля.
Private WithEvents
oPac As Pacient
А в самом модуле класса указывается событие:
Синтаксис:
[Public] Event имя[(аргументы)]
|
Элемент |
Описание |
|
Public |
Не обязательно. Делает событие открытым во всех объектных модулях проекта. По-умолчанию, все пользовательские события Public |
|
имя |
Имя события, которое будет видно в экземпляре класса |
|
аргументы |
Не обязательно. События могут иметь аргументы, которым можно передавать значения или ссылку на объект |
Замечание:Событие должно указываться в самом начале модуля класса
В месте, где должно происходить событие указывается триггер с синтаксисом:
RaiseEvent имя[(значение аргументов)]
|
Элемент |
Описание |
|
имя |
Обязательно. Имя события, для которого указывается триггер |
|
значение аргументов |
Не обязательно. Если при указании события были указаны аргументы, здесь через запятую указываются их значения |
Вот пример кода расчета индекса массы тела в форме. Код в классе:
Public Event IMTCalculated(IMTValue As Single)
Private sHeight As Single
Private sWeight As Single
Private sIMT As Single
Public Property Get Height() As Single
Height = sHeight
End Property
Public Property Let Height(ByVal sHeightValue As Single)
sHeight = sHeightValue
End Property
Public Property Get Weight() As Single
Weight = sWeight
End Property
Public Property Let Weight(ByVal sWeightValue As Single)
sWeight = sWeightValue
End Property
Public Sub CalcIMT()
If sHeight <> 0 Then sIMT = Round(sWeight / sHeight ^ 2, 1)
RaiseEvent IMTCalculated(sIMT)
End Sub
Вызов метода в форме:
Private WithEvents oPac As Pacient
Private Sub CommandButton1_Click()
Set oPac = New Pacient
oPac.Height = 1.83
oPac.Weight = 113
oPac.CalcIMT
End Sub
Private Sub oPac_IMTCalculated(IMTValue As Single)
Me.Label1.Caption = IMTValue
End Sub
Событие IMTCalculated срабатывает после расчета индекса массы тела, и в форме значение аргумента IMTValue присваивается надписи. Таким образом, отпадает необходимость в создании отдельного свойства IMT.
Практическое применение модулей классов
Большинство разработчиков никогда не используют модули классов в своих программах. Но есть задачи, которые нельзя решить без написания пользовательских классов:
|
Задача |
Пример файла |
|
Выполнение одной процедуры несколькими контролами формы |
|
|
Управление событиями на уровне приложения |
|
Есть случаи, когда использовать пользовательские классы удобнее, чем процедуры и функции:
|
Задача |
Пример файла |
|
Сокрытие деталей реализации компонента для упрощения работы с ним и |
|
|
|
Желаю успехов в разработке
ratboy
ondister@gmail.com
Макросы – это полноценная программа, просто она выполняется на базе другого приложения. Следовательно, все принципы программирования соблюдаются. А все языки программирования разделяются на две категории: процедурные и объектно-ориентированные.
Макросы разрабатываются на базе языка VBA, который является скорее процедурным с возможностью обращения к отдельным объектам. Недостатком такого подхода есть то, что одна процедура не связана тесно с другой.
Объектно-ориентированный подход имеет некоторые принципиальные отличия от процедурного. Сейчас этот тип программирования является наиболее популярным. Поэтому его нужно рассмотреть более детально применительно к макросам Excel.
Содержание
- Общие сведения и определения
- Как создать класс в VBA
- Способы создания экземпляра класса
- Способ №1
- Способ №2
- Способ №3
- Способ №4
- Как удалить экземпляр класса?
- Как создать поля класса
- Процесс определения свойств класса
- Пример создания свойства в модуле класса
- Методы класса
- События класса
- Выводы
Общие сведения и определения
Все подпрограммы, которые есть в объектно-ориентированном программировании, тесно связаны между собой. Основное понятие, которое нужно знать на этом этапе – это класс.
Под классом подразумевается тот тип данных, в котором приводится описание структуры объекта. Все программы, написанные с помощью объектно-ориентированных языков, основываются на объектах. В случае с Excel такими служат формы, лист, книги, диаграммы и другие. Класс может объединять в себя целую кучу объектов, каждый из которых является своеобразной его копией с некоторыми доработками.
Выражаясь проще, класс – это шаблон, по которому генерируется объект.
Структура класса:
- Поле. Это такой элемент класса, в котором непосредственно содержатся данные.
- Свойство. Это составная часть класса, в которой также хранятся данные, которые в дальнейшем могут быть обработаны.
- Метод. По сути та же процедура или функция, просто в рамках класса. Методы – одно из главных понятий любого объектно-ориентированного языка программирования.
- Событие. Это ситуация, при которой активируется метод. Это может быть изменение содержимого ячеек или выполнение другого метода.
VBA не является полноценным объектно-ориентированным языком программирования, поскольку в нем есть только два принципа:
- Абстракция. С помощью этого метода можно создать объект, который больше всего напоминает некомпьютерный. Например, можно создать объект «собака», в котором будут такие свойства, как «количество ушей», «длина шерсти» и другие.
- Инкапсуляция. Она дает возможность спрятать класс от других процедур, которые не используют его в своей работе. Но этот принцип допускает использование отдельных свойств класса другими процедурами, если это требуется.
Как создать класс в VBA
Переходим к практическим аспектам использования классов в языке программирования VBA. Чтобы создать класс, в редакторе нужно нажать на пункт «Class Module», который можно найти в меню «Insert». Далее нужно классу дать определенное имя. Это можно сделать только одним способом – изменить имя, сгенерированное автоматически.
VBA предусматривает возможность спрятать класс от другой книги, если она ссылается на эту. За эту возможность отвечает свойство Instancing. Если его значение выставлено на Private, то этот класс будет обнаруживаться только той книгой, в которой макрос открыт. Если такой макрос открыт на нескольких документах, то класс будет доступен только той книге, к которой он привязан. Если же установить параметр PublicNotCreateable, то класс будет обнаруживаться в том случае, если он создан в книге, но все равно не будет доступен для других книг.
Способы создания экземпляра класса
Итак, под классом подразумевается описание объекта, но не сам объект. Чтобы на основе класса его создать, необходимо воспользоваться одним из доступных способов.
Способ №1
Вот строка кода, которая демонстрирует первый способ создания объекта на основе существующего класса.
Private Sub TestClass()
Dim cl As ExampleClass
Set cl = New ExampleClass End Sub
Способ №2
Dim cl As ExampleClass
Private Sub TestClass()
Set cl = New ExampleClass End Sub
В этом случае объявление класса осуществляется за пределами процедуры, поэтому работа с ним возможна со всех имеющихся внутри модуля процедур. Если же заменить оператор Dim на Public, то объект будет доступен любой процедуре, которая выполняется в рамках проекта при условии, что объявление осуществляется за пределами объектного модуля.
Способ №3
Dim cl WithEvents As ExampleClass
Private Sub TestClass()
Set cl = New ExampleClass End Sub
В данном примере объект создается с событиями, и только в связи с ними они становятся доступными. Этот метод имеет ограниченную сферу использования, его можно применять лишь в рамках объектного модуля (например, листа или книги).
Способ №4
Private Sub TestClass()
Dim cl As New ExampleClass
End Sub
Этот метод не является самым популярным, и многие про него вообще не знают. В этом случае создание объекта осуществляется через переменную cl. Этот метод несколько хуже, потому что сначала лучше выделить память под определенную переменную, и только потом создавать объект, который будет встроен в эту переменную.
Как удалить экземпляр класса?
Хорошая привычка – очистить выделенную память, если этот объект уже не нужен. Это позволит значительно увеличить быстродействие макроса. Особенно это важно, если он будет использоваться на слабом компьютере.
Чтобы это сделать, нужно воспользоваться следующей строкой кода.
Set cl = Nothing
Конечно, современные версии офисных пакетов (равно как и компьютеры) устроены так, что если проигнорировать эту рекомендацию и не удалять класс, то ничего страшного не случится. Тем не менее, настоятельно рекомендуется это делать на случай, если придется запускать макрос на слабом компьютере (особенно сейчас, когда популярность стал набирать класс устройств, который называется смартбуками).
Как создать поля класса
Созданный нами ранее класс не содержит ничего, ни полей, ни свойств, ни других описанных выше элементов. Следовательно, от него никакой пользы. Поэтому давайте начнем с создания полей класса. Это переменные, которые используются для хранения данных.
Поля бывают двух типов: открытые и закрытые. Основная характеристика последних заключается в том, что они являются недоступными для других процедур, которые не находятся внутри этого модуля. Доступ к открытым может иметь любой модуль и в этом аспекте они не отличаются принципиально от свойств.
Но отличаются другим – невозможно указать значение, которое будет отображаться в поле по умолчанию, а также невозможно запретить средствами VBA его редактирование. Информация в поле хранится до того момента, как она не будет перезаписана или же пока существует соответствующая переменная.
Чтобы создать поле, необходимо выполнить такой код.
Dim sBody As String
Также можно воспользоваться таким вариантом кода, который выдает тот же результат.
Private sBody As String
Оба описанных случая позволяют создать поле закрытого типа. Чтобы создать открытое поле, необходимо написать такую строчку.
Public Head As String
После этих манипуляций становится возможным использование свойства Head у объекта. С ним можно выполнять разные операции, включая запись:
cl.Head = «FHead»
и чтение
Debug.Print cl.Head
Тип данных для поля строго определен. Поэтому нельзя изменить его на числовой или формат числа с плавающей точкой.
Процесс определения свойств класса
Под свойством подразумевается также элемент, через который можно записывать и читать информацию объекта, но отличие заключается в том, что это функции, а не переменные.
Для чтения данных используется функция Property Get, а для записи – Property Let. Конечно, языком предусмотрена еще и третья конструкция –– Property Set, но на практике она используется редко из-за того, что ссылку на другой объект (а именно для этого и нужна указанная функция) можно записать и с помощью процедуры Property Let.
Давайте детальнее опишем синтаксис всех описанных функций. Итак, вот скриншот, описывающий синтаксис функции Property Get.
А вот таблица, в которой детально описываются элементы свойств класса.
При чтении свойства класса нужно учитывать такие нюансы:
- С помощью элемента Exit Property осуществляется выход из метода. Допустимо использование сразу нескольких подобных элементов в рамках одного метода. Это может быть полезным, например, если используются циклы и условные операторы.
- Несмотря на то, что сама функция Property Get может содержать неограниченное количество процедур внутри, она сама не может быть составной частью других функций.
Теперь давайте более подробно рассмотрим синтаксис функции Property Let. Он виден на этом скриншоте.
Этой функции касаются все замечания, рассмотренные выше.
Ну и наконец, как выглядит синтаксис функции Property Set. Несмотря на то, что она считается бесполезной, знать, как с ней работать нужно хотя бы потому, что другой человек может использовать именно ее. И нужно уметь читать чужой код. Сам синтаксис приводится на этом скриншоте.
Пример создания свойства в модуле класса
А теперь давайте детальнее рассмотрим некоторые практические примеры. Будем приводить фрагменты кода с краткими пояснениями.
В данном случае мы можем использовать свойство Height как для чтения, так и для того, чтобы редактировать информацию, которая там указана. Простыми словами, мы имеем фактически открытое поле, потому что имеет все его характеристики. Просто образуется оно немного другим методом – через функцию, а не переменную с процедурой.
Теперь давайте взглянем немного на другой фрагмент кода.
В этом случае мы не можем вносить никаких изменений в свойство, поскольку был открыт доступ только для чтения. По умолчанию берется идея, что значение переменной sHeight уже указано в другой процедуре, которая есть в данном модуле.
В этом примере свойство не может быть отредактировано, и в нем содержится постоянное значение (константа). Ее можно открыть только из модуля, который находится в данном объекте. Если мы попробуем использовать конструкцию Public Const sHeight As Single = 2, то у нас ничего не получится.
Существует еще множество примеров, но они уже более глубокого уровня и не подходят для новичков. Поэтому давайте сейчас рассмотрим особенности создания методов и событий класса.
Методы класса
В рамках класса можно создавать как процедуры, так и функции. Все они суммарно называются методами, но лишь при одном условии. Чтобы функция считалась методом, она должна быть открыта для других классов. Если же не требуется таких прав для подпрограмм, то нужно обязательно их делать приватными. Это обязательное правило, которое соответствует принципу инкапсуляции.
В целом, процедура создания методов ничем не отличается от того, как создаются процедуры и функции. В них могут содержаться любые аргументы как те, которые нужно обязательно указывать, так и те, в которых смысла нет. При этом отличается вызов. Внимательнее посмотрите на следующий пример.
События класса
Внутри каждого класса содержится уже несколько событий:
- Class_Initialize. Событие, которое осуществляется в момент создания класса. Здесь можно легко настроить значения переменных и свойств, которые будут использоваться всегда, если не указано обратное.
- Class_Terminate. Это событие происходит, когда объект удаляется. Это происходит в двух случаях. Первый – деинициализация объекта. Второй – прекращение работы той процедуры, в рамках которой был объявлен класс.
Как правило, не возникает никаких проблем с тем, чтобы добавлять новые события. При этом есть одно требование. Важно убедиться в том, что объект, к которому привязывается событие, объявлялся только в рамках одного модуля на этом же уровне.
Само же событие указывается в рамках самого модуля.
Синтаксис конструкции, с помощью которой происходит объявление события, следующий.
Выводы
Конечно, это нелегкая тема для понимания. Но это всего лишь два принципа объектно-ориентированного программирования. В случае же с другими языками все еще сложнее. VBA вообще-то считается очень легким языком. Поэтому если приложить должное упорство, все должно получиться. Успехов.
Оцените качество статьи. Нам важно ваше мнение: