Home / VBA / VBA IF And (Test Multiple Conditions)
You can use the AND operator with the VBA IF statement to test multiple conditions, and when you use it allows you to test two conditions simultaneously and get true if both of those conditions are true. And, if any of the conditions is false it returns false in the result.
Combining IF AND
- First, start the IF statement with the “IF” keyword.
- After that, specify the first condition that you want to test.
- Next, use the AND keyword to specify the second condition
- In the end, specify the second condition that you want to test.

To have a better understanding let’s see an example.
Sub myMacro()
If 1 = 1 And 2 > 1 Then
MsgBox "Both of the conditions are true."
Else
MsgBox "Maybe one or both of the conditions are true."
End If
End Sub
If you look at the above example, we have specified two conditions one if (1 = 1) and the second is (2 > 1) and here both of the conditions are true, and that’s why it has executes the line of code that we have specified if the result is true.

Now lets if one of these two conditions is false, let me use the different code here.
Sub myMacro1()
If 1 = 1 And 2 < 1 Then
MsgBox "Both of the conditions are true."
Else
MsgBox "Maybe one or both of the conditions are true."
End If
End Sub
In the above code, the second condition is false (2 < 1) and when you run this macro it executes the line of code that we have specified if the result is false.

In the same way, you can also test more than two conditions at the same time. Let’s continue the above example and add the third condition to it.
Sub myMacro2()
If 1 = 1 And 2 > 1 And 1 - 1 = 0 Then
MsgBox "All the conditions are true."
Else
MsgBox "Some conditions are false."
End If
End Sub
Now we have three conditions to test and we have used the AND after the second condition to specify the third condition. As you learned above that when you use AND, all the conditions need to be true to get true in the result.
When you run this code, it executes the line of code that we have specified for the true.

And if any of the conditions is false, just like you have in the following code, it returns false.
Sub myMacro3()
If 1 = 1 And 2 < 1 And 1 + 1 = 0 Then
MsgBox "All the conditions are true."
Else
MsgBox "Some conditions are false."
End If
End Sub
Return to VBA Code Examples
This tutorial will show you how to use nested If statements in VBA.
If statements allow you to test for a single condition in VBA to see if the condition is True or False, and depending on the answer, the code will move in the direction of the true statement or the false statement.
A Single IF statement
Sub TestIf
Dim x as Integer
x = 10
If x = 10 then
'if x is 10, the condition is true
MsgBox x is 10"
Else
'if x is not 10, the condition is false
Msgbox "x is not 10"
End If
End SubNested IFs Explained
A Nested If allows you to put multiple conditions INSIDE each of the True and/or False statements of the original If.
Sub TestNestedIf()
Dim x as Integer
Dim y as Integer
Dim z as Integer
x = 10
y = 9
z = 8
If x = 10 Then
'if x is 10, the condition is true so test for y
If y = 9 Then
MsgBox "y is 9"
Else
'if y is not 9, the condition is false
Msgbox "y is not 9"
End If
Else
'if x is not 10 then the condition is false, so lets' test for z
If z = 8 Then
MsgBox "z is 8"
Else
'if z is not 8, the condition is false
Msgbox "z is not 8"
End If
'another End If is needed to close the original if
End If
End SubIndenting your code when you write it always good practice as it makes the code easy to read and follow when you have to come back to it at some stage, or when another programmer has to read it.
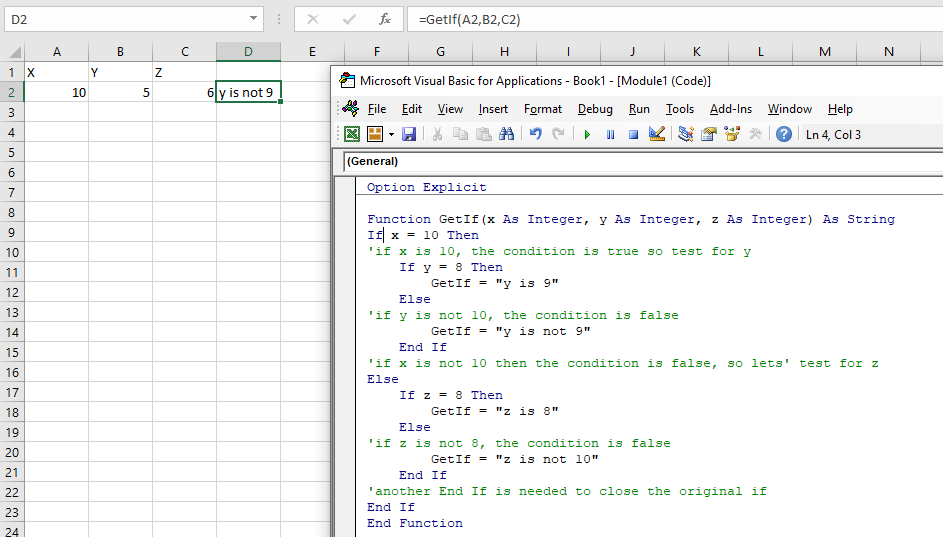
We could also create a user designed function (UDF) and call the values of some cells from Excel into the function using parameters.
Function GetIf(x as Integer, y as Integer, z as Integer) as String
If x = 10 Then
'if x is 10, the condition is true so test for y
If y = 9 Then
GetIf= "y is 9"
Else
'if y is not 9, the condition is false
GetIf="y is not 9"
End If
Else
'if x is not 10 then the condition is false, so lets' test for z
If z = 8 then
GetIf="z is 8"
Else
'if z is not 8, the condition is false
GetIf="z is not 8"
End If
'another End If is needed to close the original if
End If
End FunctionNested If Practical Example
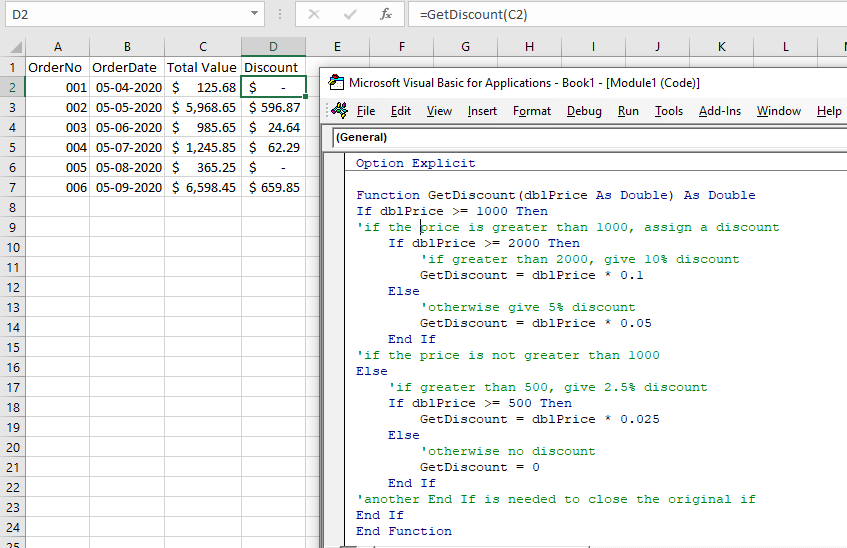
Consider the following function:
Function GetDiscount(dblPrice As Double) As Double
If dblPrice >= 1000 Then
'if the price is greater than 1000, assign a discount
If dblPrice >= 2000 Then
'if greater than 2000, give 10% discount
GetDiscount = dblPrice * 0.1
Else
'otherwise give 5% discount
GetDiscount = dblPrice * 0.05
End If
'if the price is not greater than 1000
Else
'if greater than 500, give 2.5% discount
If dblPrice >= 500 Then
GetDiscount = dblPrice * 0.025
Else
'otherwise no discount
GetDiscount = 0
End If
'another End If is needed to close the original if
End If
End FunctionUsing this Function in an Excel sheet, we can test to see the total price for an order, and apply different discounts depending on that total.
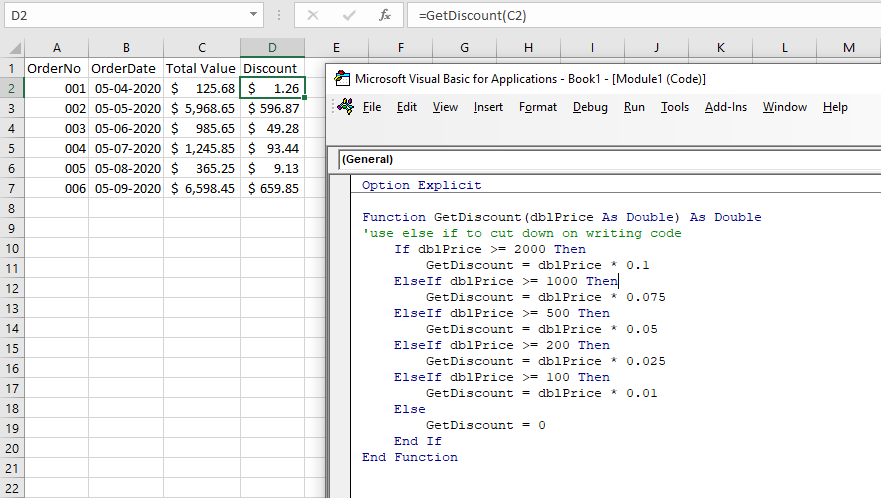
Using ElseIf
ElseIf enables us to simplify your code as it only moved down to the second if statement if the first one returns a false.
Function GetDiscount(dblPrice As Double) As Double
'use else if to cut down on writing code
If dblPrice >= 2000 Then
GetDiscount = dblPrice * 0.1
ElseIf dblPrice >= 1000 Then
GetDiscount = dblPrice * 0.075
ElseIf dblPrice >= 500 Then
GetDiscount = dblPrice * 0.05
ElseIf dblPrice >= 200 Then
GetDiscount = dblPrice * 0.025
ElseIf dblPrice >= 100 Then
GetDiscount = dblPrice * 0.01
Else
GetDiscount = 0
End If
End FunctionUsing a Case Statement
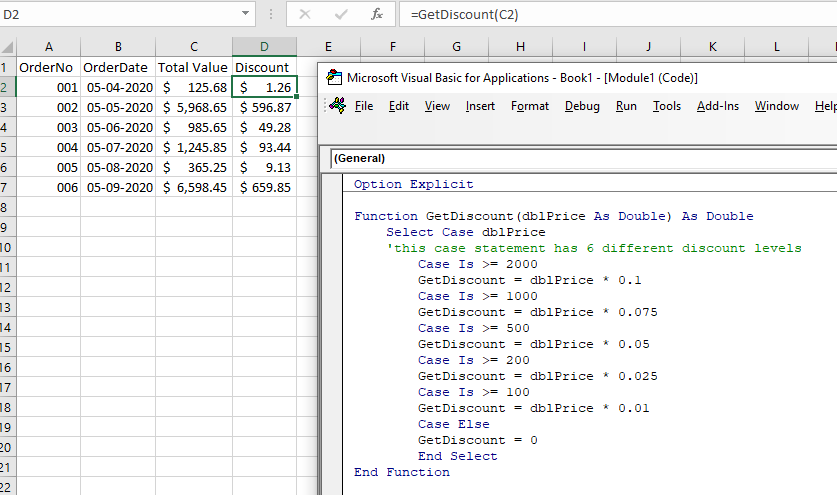
We can also use a Case Statement to achieve the same effect.
Function GetDiscount(dblPrice As Double) As Double
Select Case dblPrice
'this case statement has 6 different discount levels
Case Is >= 2000
GetDiscount = dblPrice * 0.1
Case Is >= 1000
GetDiscount = dblPrice * 0.075
Case Is >= 500
GetDiscount = dblPrice * 0.05
Case Is >= 200
GetDiscount = dblPrice * 0.025
Case Is >= 100
GetDiscount = dblPrice * 0.01
Case Else
GetDiscount = 0
End Select
End FunctionVBA Coding Made Easy
Stop searching for VBA code online. Learn more about AutoMacro — A VBA Code Builder that allows beginners to code procedures from scratch with minimal coding knowledge and with many time-saving features for all users!
Learn More!
katealex
Пользователь
Сообщений: 23
Регистрация: 17.08.2016
Это часть большого макроса для расчета, задать формулой получилось( очень большой), при записи макрорекордером формулы, excel виснет,поэтому решила применить конструкцию If..then..else, и вообще теперь не получается.
Рассчитать тариф(согласно зонам), т.е. если тариф равен : 420(1 зона),470(2зона),570(3 зона),700(4 зона), то если в графе надбавка пусто, тариф расчетный = 420, если 10, то 470, если 50,то 570, если 100, то 700, если нет, проверяется следующий тариф 500(1зона),500(2зона),700(3зона),700(4зона), если да,то если в графе надбавка пусто, тариф 500, если 10, то 500, если 50, то 700, если 100, то 700, нет — след.тариф 620(1 зона),670(2 зона),720(3 зона), 780(4 зона) и аналогично, если в графе надбавка пусто, то 620, если 10,то 670, если 50, то 720, если 100, то 780. Если тариф равен просто числу, то,соответственно, тариф расчетный = тарифу.
Однострочная и многострочная конструкции оператора If…Then…Else и функция IIf, используемые в коде VBA Excel — синтаксис, компоненты, примеры.
Оператор If…Then…Else предназначен для передачи управления одному из блоков операторов в зависимости от результатов проверяемых условий.
Однострочная конструкция
Оператор If…Then…Else может использоваться в однострочной конструкции без ключевых слов Else, End If.
Синтаксис однострочной конструкции If…Then…
|
If [условие] Then [операторы] |
Компоненты однострочной конструкции If…Then…
- условие — числовое или строковое выражение, возвращающее логическое значение True или False;
- операторы — блок операторов кода VBA Excel, который выполняется, если компонент условие возвращает значение True.
Если компонент условие возвращает значение False, блок операторов конструкции If…Then… пропускается и управление программой передается следующей строке кода.
Пример 1
|
Sub Primer1() Dim d As Integer, a As String d = InputBox(«Введите число от 1 до 20», «Пример 1», 1) If d > 10 Then a = «Число « & d & » больше 10″ MsgBox a End Sub |
Многострочная конструкция
Синтаксис многострочной конструкции If…Then…Else
|
If [условие] Then [операторы] ElseIf [условие] Then [операторы] ———————— Else [операторы] End If |
Компоненты многострочной конструкции If…Then…Else:
- условие — числовое или строковое выражение, следующее за ключевым словом If или ElseIf и возвращающее логическое значение True или False;
- операторы — блок операторов кода VBA Excel, который выполняется, если компонент условие возвращает значение True;
- пунктирная линия обозначает дополнительные структурные блоки из строки
ElseIf [условие] Thenи строки[операторы].
Если компонент условие возвращает значение False, следующий за ним блок операторов конструкции If…Then…Else пропускается и управление программой передается следующей строке кода.
Самый простой вариант многострочной конструкции If…Then…Else:
|
If [условие] Then [операторы] Else [операторы] End If |
Пример 2
|
Sub Primer2() Dim d As Integer, a As String d = InputBox(«Введите число от 1 до 40», «Пример 2», 1) If d < 11 Then a = «Число « & d & » входит в первую десятку» ElseIf d > 10 And d < 21 Then a = «Число « & d & » входит во вторую десятку» ElseIf d > 20 And d < 31 Then a = «Число « & d & » входит в третью десятку» Else a = «Число « & d & » входит в четвертую десятку» End If MsgBox a End Sub |
Функция IIf
Функция IIf проверяет заданное условие и возвращает значение в зависимости от результата проверки.
Синтаксис функции
|
IIf([условие], [если True], [если False]) |
Компоненты функции IIf
- условие — числовое или строковое выражение, возвращающее логическое значение True или False;
- если True — значение, которое возвращает функция IIf, если условие возвратило значение True;
- если False — значение, которое возвращает функция IIf, если условие возвратило значение False.
Компоненты если True и если False могут быть выражениями, значения которых будут вычислены и возвращены.
Пример 3
|
Sub Primer3() Dim d As Integer, a As String Instr: On Error Resume Next d = InputBox(«Введите число от 1 до 20 и нажмите OK», «Пример 3», 1) If d > 20 Then GoTo Instr a = IIf(d < 10, d & » — число однозначное», d & » — число двузначное») MsgBox a End Sub |
Пример 4
Стоит отметить, что не зависимо от того, выполняется условие или нет, функция IIf вычислит оба выражения в параметрах если True и если False:
|
Sub Primer4() On Error GoTo Instr Dim x, y x = 10 y = 5 MsgBox IIf(x = 10, x + 5, y + 10) MsgBox IIf(x = 10, x + 5, y / 0) Exit Sub Instr: MsgBox «Произошла ошибка: « & Err.Description End Sub |
При нажатии кнопки «Cancel» или закрытии крестиком диалогового окна InputBox из первых двух примеров, генерируется ошибка, так как в этих случаях функция InputBox возвращает пустую строку. Присвоение пустой строки переменной d типа Integer вызывает ошибку. При нажатии кнопки «OK» диалогового окна, числа, вписанные в поле ввода в текстовом формате, VBA Excel автоматически преобразует в числовой формат переменной d. В третьем примере есть обработчик ошибок.
Improve Article
Save Article
Like Article
Improve Article
Save Article
Like Article
VBA in Excel stands for Visual Basic for Applications which is Microsoft’s programming language. To optimize the performance and reduce the time in Excel we need Macros and VBA is the tool used in the backend.
Some helpful links to get more insights about Macros, VBA in Excel :
- Record Macros in Excel.
- How to Create a Macro in Excel?
In this article, we are going to use how to use the Nested If statement in Excel VBA.
Implementation :
In the Microsoft Excel tabs, select the Developer Tab. Initially, the Developer Tab may not be available.
The Developer Tab can be enabled easily by a two-step process :
- Right-click on any of the existing tabs at the top of the Excel window.
- Now select Customize the Ribbon from the pop-down menu.
- In the Excel Options Box, check the box Developer to enable it and click on OK.
- Now, the Developer Tab is visible.
- Now click on the Visual Basic option in the Developer tab and make a new module to write the program using the Select Case statement.
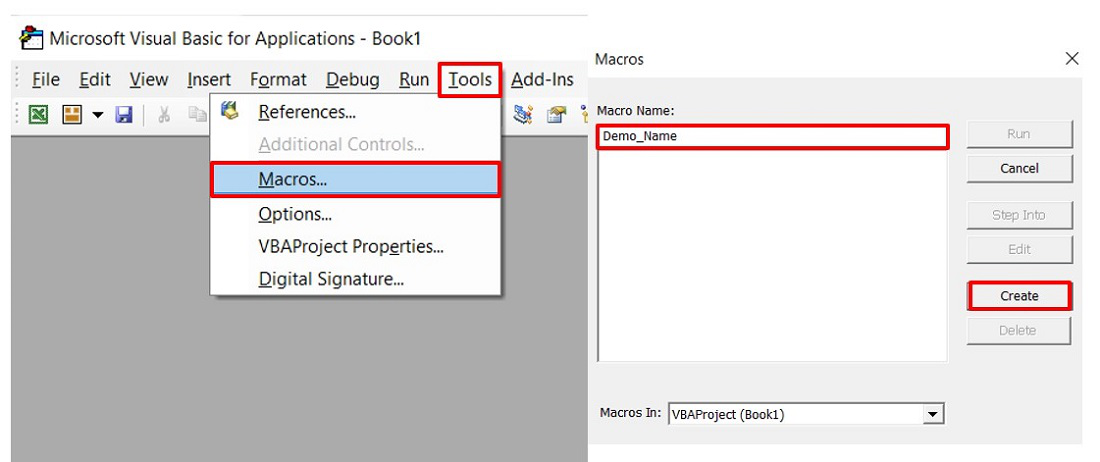
Developer -> Visual Basic -> Tools -> Macros
- Now create a Macro and give any suitable name.
- This will open the Editor window where can write the code.
The syntax for the If statement in Excel is :
If condition/expression Then
Code Block for True
Else
Code Block for False
End If
Nested IF:
The structure of Nested If statement in Excel is :
If condition/expression Then
Code Block 1
Else If condition/expression Then
Code Block 2
Else If condition/expression Then
Code Block 3
Else
Code Block 4
Else
Code Block 5
End If
Some important keywords used in Excel are as follows :
- InputBox : To take input from the user.
- MsgBox : To display output to the user.
Example: Consider a grading system where grading is based on the marks obtained in the exam. For example, If a student obtained 95 marks the grade obtained by the student is S grade and so on.
Code :
Sub Nested_If_Grade()
'Declaring the variable marks
Dim marks As Integer
'Asking marks from the user
marks = InputBox("Enter Your Marks:")
If marks >= 90 Then
MsgBox "You got S grade"
Else
If marks >= 80 Then
MsgBox "You got A grade"
Else
If marks >= 70 Then
MsgBox "You got B grade"
Else
If marks >= 60 Then
MsgBox "You got C grade"
Else
If marks >= 50 Then
MsgBox "You got D grade"
Else
If marks >= 40 Then
MsgBox "You got E grade"
Else
MsgBox "You have failed in the exam"
End If
End If
End If
End If
End If
End If
End Sub
Result :
Like Article
Save Article