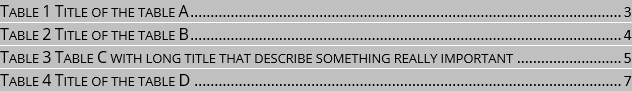Word can generate a list of all the tables in a document. Like a Table of Contents, this list of tables or Table of tables can include page references or links to each table.
A Table of tables can be useful for creating a proper appendix or reference within more formal documentation. It can be handy to have a list of all the tables used in a document either for publication or just for ‘in-house’ reference use during writing.
Before you can add a Table of tables to your document, you must add captions to all the tables in your document, as described in Adding Captions in Word. Yes, there is an alternative way making the list from styles but captions works better because each table gets a individual label.
Two Tables in Word
Before we begin, lets try to sort out a linguistic mess. Word has two features both called ‘tables’.
Table – a list of captions etc within a document e.g. Table of Contents, Table of Figures etc.
table – a grid of boxes or cells placed in a Word document from Insert | Table.
Normally the two are separate and it’s clear from the context which one we’re talking about.
For this article we’ll try to make it clear which ‘table’ we’re talking about by using the term ‘list’ but mostly with a capital letter ‘Table’ for the list and lower case ‘table’ for the grid. E.g. a Table of tables.
Slightly less confused? Good, let’s get on with it.
Making a simple Table of tables
Once you have some tables captioned in the document you can make a reference Table of them.
Click where you want the Table to appear (most likely as an appendix or close to your Table of Contents).
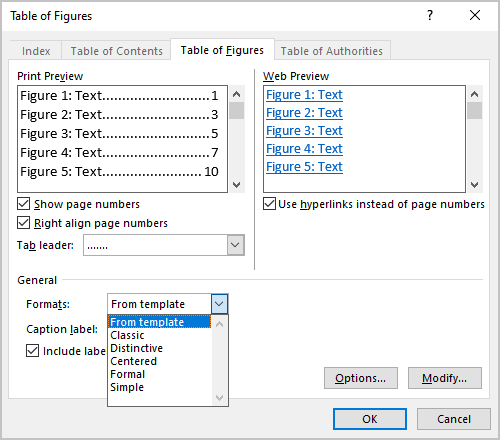
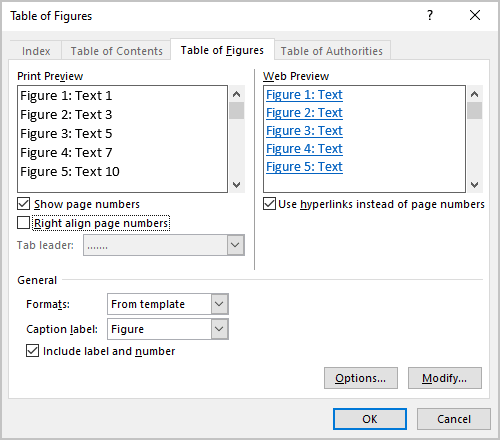
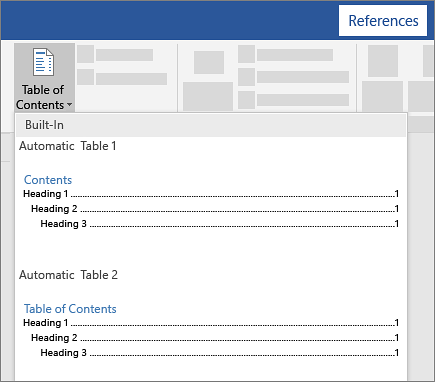
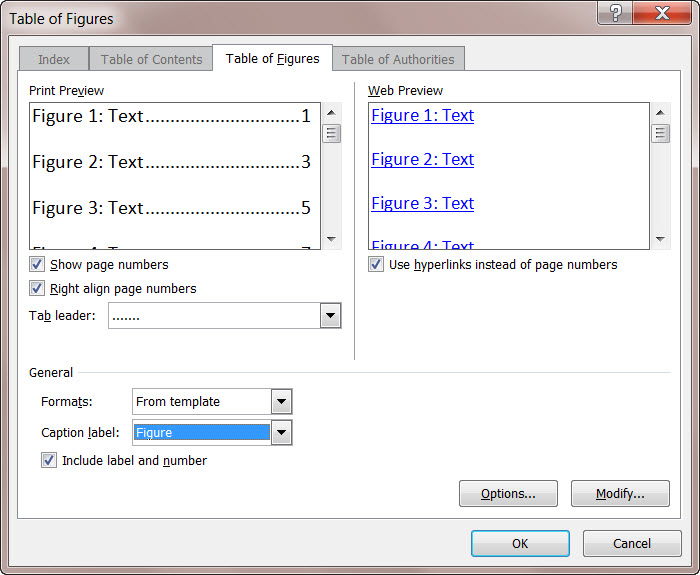
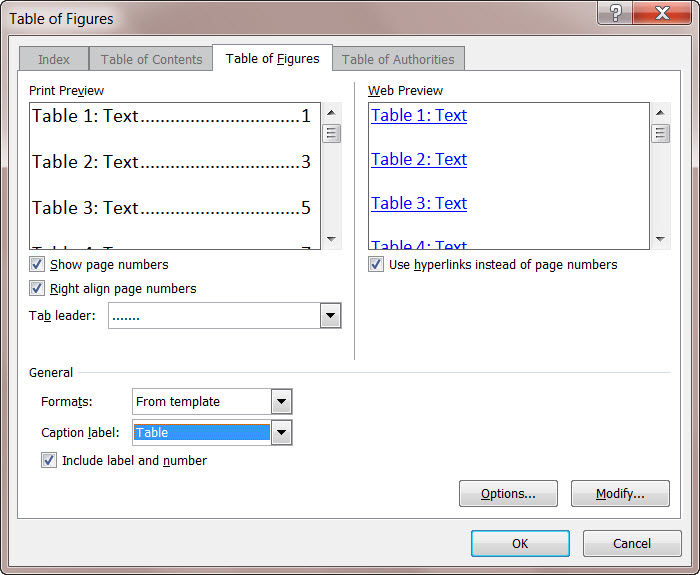
Go to References | Captions | Insert Table of Figures (yes, ‘Figures’) to bring up the “Table of Figures” dialog.
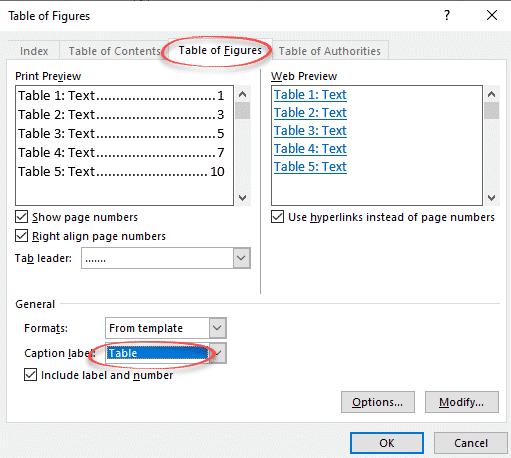
First thing to do is change the Caption Label from Figures to table. And lo! you have a Table of tables!
The “Print Preview” and “Web Preview” panes show how the Table will appear. By default, page numbers are displayed and aligned to the right, although you can change this by deselecting the appropriate checkboxes.
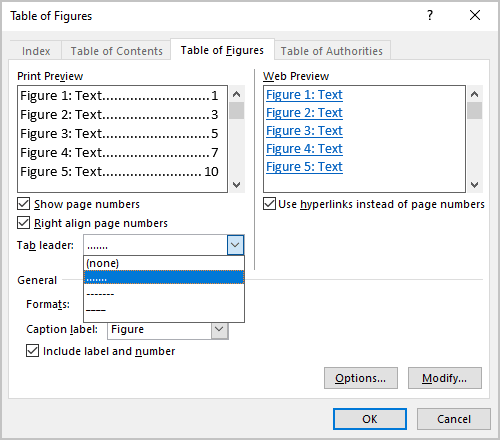
The “Tab leader” dropdown changes what appears between the text and the right-aligned page numbers.
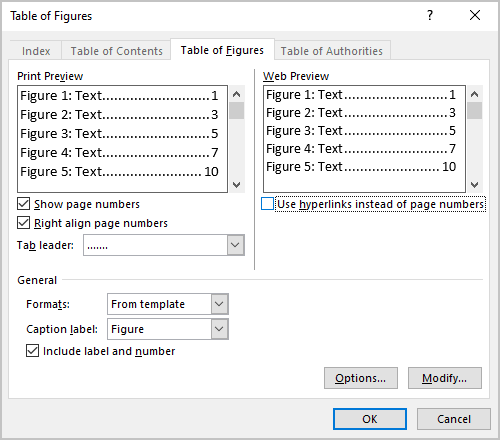
“Use hyperlinks instead of page numbers” for the web preview gives you a clickable table with links to each table in the Word document.
Table Formats
The “Formats” drop-down list directly affects the appearance of the Table of tables. The available options are:
- From template
- Classic
- Distinctive
- Centered
- Formal
- Simple
Select a format to see how it will look in the preview panes. Most people use ‘From template’ because that will match the font etc in the current document or template.
To design a custom Table of tables layout, select “From template” and click the “Modify” button to create your own style.
When you are happy with the layout, click “OK” to build your Table of tables. Word will search for the captions, sort them by number, and display the Table of tables in the document.
Word déjà vu
If all this seems familiar, that’s because it’s almost exactly the same as the ‘Table of Contents’ and Table of Figure options. In fact, a Table of tables uses the same underlying Word technology as Table of Contents (the {TOC } field).
All Word’s Table of Contents options
Four Word tricks to shrink a Table of Contents
Table of Contents basics in Word

We will also look at how to update the list as you add, move, or delete tables or figures.
Terminology Note: This tutorial uses the terms list of tables and list of figures, which are common terms in the publishing industry. However, Word refers to a list of tables or figures as a table of figures.
This tutorial is also available as a YouTube video showing all the steps in real time.
Watch more than 200 other writing-related software tutorials on my YouTube channel.
The images below are from Word in Microsoft 365 (formerly Office 365). The steps are the same in Word 2021, Word 2019, Word 2016, and Word 2013. However, your interface may look different in those older versions of the software.
Remember that these steps will only work if you used Word’s caption tool to number your tables or figures before creating the list.
- Insert your cursor where you want to place your list.
- Select the References tab in the ribbon.
- Select Insert Table of Figures from the Captions group.
- Select a visual style from the Formats menu in the Table of Figures dialog box. (The From Template option is based on the styles established in your current template.)
- Select Figure or Table from the Caption label menu. (There is no option for listing figures and tables together.)
- Ensure that Include label and number is checked if you want the label (i.e., Figure or Table) and the number to be included in the list. (Recommended)
- (Optional Step) Select additional options concerning page numbers and the tab leaders, which are the dots, dashes, or lines that appear before the page numbers.
Pro Tip: The Web Preview section shows how your list will look if you convert your Word file to a web page.
- Select the OK button.
- Manually type a title above your list.
- Save your file to save your changes.
The next section shows how to update a list of tables or figures.
How to Update a List of Tables or Figures
Word will not automatically update your list as you add or delete tables or figures. Instead, you can manually trigger updates, as necessary.
- Right-click the list and select Update Field from the shortcut menu.
- Select Update entire table from the Update Table of Figures dialog box.
- Select the OK button.
Your updates should appear immediately.
- Save your file to save your changes.
Important Note: Word’s caption tool, which inserts table titles and figure captions, will automatically number new tables and figures as you add titles and captions (e.g., Table 1, Table 2, Table 3). However, Word will not automatically update the numbering if you move or delete tables or figures.
See “How to Update Table and Figure Numbers in Microsoft Word” to learn how to force an update after moving or deleting a table or figure.
Related Resources
How to Create and Customize Charts in Microsoft Word
How to Insert and Modify Images in Microsoft Word
Three Ways to Insert Tables in Microsoft Word
How to Change the Style of Table Titles and Figure Captions in Microsoft Word
How to Cross-Reference Tables and Figures in Microsoft Word
How to Reference Tables and Figures in Text
Updated December 14, 2022
Some requirements demand listing figures, tables, and other visual objects at the end of a document. They are named List of Figures and List of Tables. Microsoft Word offers the functionality named Table of Figures that helps generate and update a list of the captions for pictures, charts, graphs, diagrams, slides, photos, or other illustrations of the document, along with the numbers of the pages on which the captions appear.
Table of Figures pretty much like Table of Content:
- Is helping readers and reviewers navigate to the visual objects in the document,
- Is generated from the figure and table captions or other object captions. All captions you need to include in the appropriate Table of Figures should be added using the Caption functionality.
Depending on the selected type of objects (captions label), the list generated by Table of Figures may contain:
- List of figures (see How to create automatic numbers and captions for figures: images, pictures):

- List of tables (see How to create automatic numbers and titles for tables):

- List of custom objects, labeled in the Caption functionality as a separate item. E.g., a List of photographs (see How to insert numbers, captions, and cutlines for photographs):
Note: See how to transform captions and titles for including or excluding different text parts to the Table of Figures.
Prepare items for a List of Tables or Figures
Before starting a Table of Figures functionality in Word, ensure that all visual objects have captions (or at least style you will use for creating a list). These allow Word to recognize and include them in the appropriate list.
You can create a list of objects and add a caption to the missed object later. Don’t forget to update caption numbering and already created lists!
Create a List of Figures or Tables in Word
To create a list of some objects in a Word document, position the cursor to insert the list. Then, on the Reference tab, in the Captions group, click the Insert Table of Figures button:
In the Table of Figures dialog box, on the Table of Figures tab (is displayed by default, all other tabs are grayed):
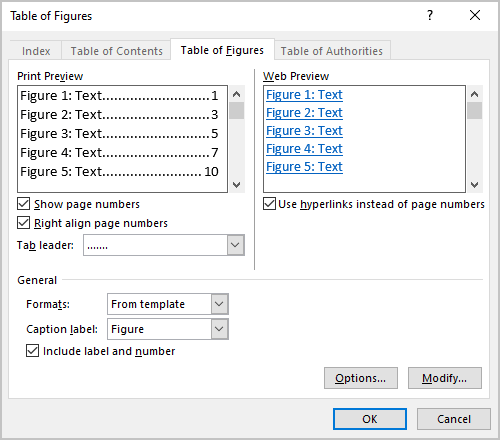
- In the General section (we recommend starting from this section because its options can change the selected parameters in other sections):
- From the Format dropdown list, select a visual format:
- From template is based on the styles established in the current template
- Classic
- Distinctive
- Centered
- Formal
- Simple
Note: Choose any proposed formats and see how the new list will look in the Print Preview section. E.g., the Formal format:
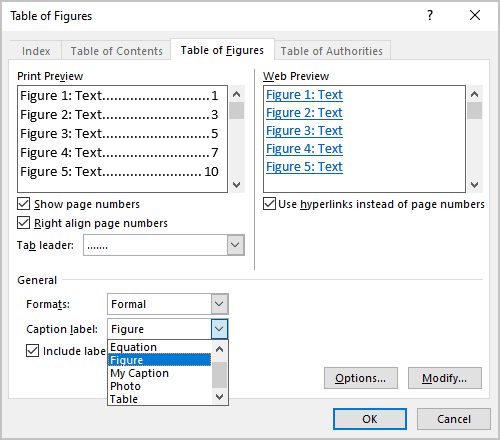
- From the Caption label dropdown list, select the type of items you want to include in the Table of Figures:
- (none)
- Figure (selected by default) – see how to create captions for figures,
- Equation – see how to create captions for equations,
- Table – see how to create captions for tables,
- Any other label (in this example, My Caption, Photo) was created using the New Label… button of the Caption dialog box. E.g., see how to create captions for photographs.
Note: There is no option for listing different labels in that list, such as figures and tables together. See how to create a list of all captions in the document below.
- Ensure that the Include label and number check box is selected if you want the label (i.e., Figure or Table) and the number to be included in the list. E.g.:
- With the selected Include label and number check box, the list displays the entire captions:
- With unselected Include label and number check box, the list displays only text from captions:
- From the Format dropdown list, select a visual format:
See all the changes and choices in the Print Preview and Web Preview sections:
- In the Print Preview section (all changes in that section can be changed by the selected options in the General section):
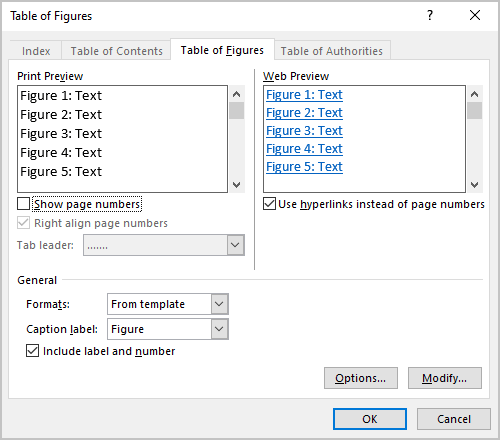
- Clear the Show page numbers check box if you prefer to hide page numbers from the list:
If you deselect this option, all other options in the Print Preview section will disappear.
- Clear the Right align page numbers check box to display page numbers right after items text:
If you deselect this option, you can’t choose the tab leader for page numbers.
- From the Tab leader dropdown list, select the tab leader you need. You can select dots, dashes, or lines that appear before the page numbers:
- Clear the Show page numbers check box if you prefer to hide page numbers from the list:
- In the Web Preview section (shows how your list will look if you convert your Word file to a web page):
- Clear the Use hyperlinks instead of page numbers check box if you prefer to see the same view as in Print Preview:
Create a list for the style or Table entry fields
In the Table of Figures dialog box, on the Table of Figures tab:
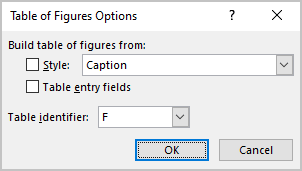
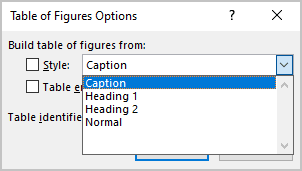
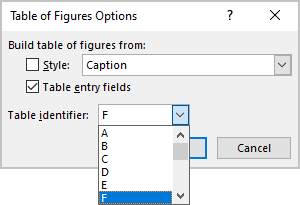
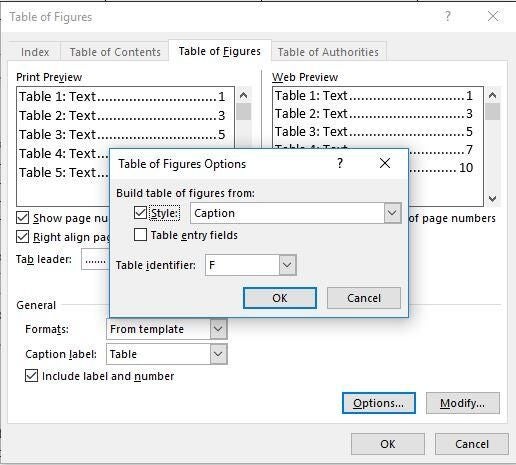
- Click the Options… button to use styles and Table entry fields for the Table of Figures instead of caption labels:
In the Table of Figures Options dialog box:
- Select the Style from the dropdown list (check box will be selected automatically) to add all text with the selected style in a Table of Figures:
Note: The Style dropdown list contains all styles already used in the Word document.
So, Word creates a list of all text blocks in a document with that style. E.g., if you select the Caption style, you will see all captions in a List:
Note: You can create a custom style for some titles or blocks of text and include them in the list. See some examples below.
- Select the Table entry fields check box to insert Table of Contents entries (see how to create and use the Table of Contents Entries):
For example, if you have the table titles in the separate line of the label and number, you can create the Table entry fields for such tables:
***
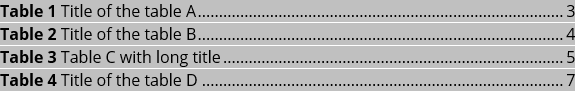
So, the List of Table will display specified titles:
Note: The issue of this example can also be solved using the transformation of the captions and titles.
- Select the Style from the dropdown list (check box will be selected automatically) to add all text with the selected style in a Table of Figures:
Customize the Table of Figures style
In the Table of Figures dialog box, on the Table of Figures tab:
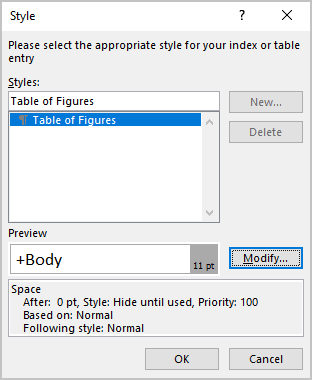
- Click the Modify… button to modify a predefined style for a Table for Figures.
In the Style dialog box:
- In the Styles list, is selected a style that Word will use for a created Table,
- In the Preview field, check how the style looks,
- Under Preview, the main options for the style are listed:
- Click the Modify… button to change the style.
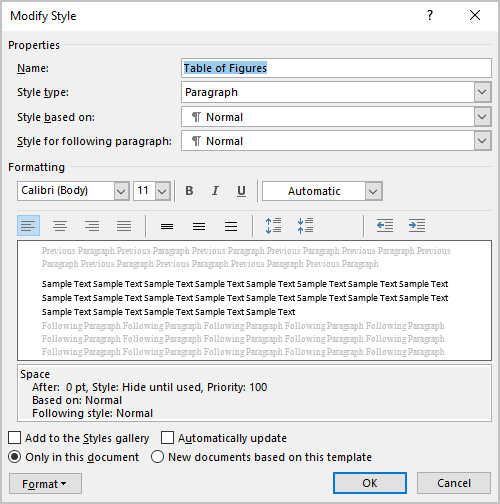
In the Modify Style dialog box, make changes you need, then click the OK button:
For example, the Table of Figures with double spacing and indentation for the long captions:
See how to customize the Table of Figure style for more details.
Add a title to the custom Table of Figures
After inserting a new Table of Figures, manually type a title above the list. E.g.:

Attention! We highly recommend checking the formatting requirements, accepted by your college, university, company, or established on the project, etc. For example:

See also how to customize the Table of Figures style.
Empty Table of Figures or Table of Tables
After creating a Table of Figures, Word can create a message “No table of figures entries found”:
The leading cause for this message is that Word could not find the text with the Caption style for the selected caption label (e.g., Figures, Tables, etc.).
To solve that problem, check the style for items captions such as figures and tables which you want to be displayed in the Table of Figures.
Don’t forget to update captions and any related items in a document!
Update a List of Tables or Figures
Microsoft Word inserts Table of Figures as a field:
So, you can change the TOC field using switches.
Word will not automatically update any Table of Figures after adding, deleting, or modifying included items and pages. To manually update them, follow the next steps:
1. Click on the list and do one of the following:
- On the References tab, in the Captions group, click the Update Table button:
Note: Only if your cursor is positioned on any of the generated Tables (Table of Figures, Table of Content, etc.), that button is not grayed.
- Right-click the list and select Update Field from the shortcut menu:
2. In the Update Table of Figures dialog box, select elements you need to update:
We recommend selecting the Update entire table option always.
3. Click the OK button to start updating.
Note: See how to turn on or turn off highlighting of fields in a Word document to display all fields in a document with a gray background.
Edit an existing Table of Figures or Table of Tables
If you need to modify an existing Table of Figures, you can:
- Delete existing Table of Figures and create a new one,
- Edit an existing field.
To edit the existing Table of Figures, follow the next steps:
1. Do one of the following:
- Click anywhere on the Table, then on the References tab, in the Captions group, click the Insert Table of Figures button.
- Select all the lines of the Table, then right-click on the selection and choose Edit Field… in the popup menu:
In the Field dialog box, click the Table of Contents… button:
Note: The button is visible only if you have selected all the existing Table of Figures lines.
2. In the Table of Figures dialog box, on the Table of Figures tab, select the options you need.
Be careful! Word opens the Table of Figures dialog box with default options. All the options selected for the existing Table disappear.
Delete a Table of Figures
To delete a List of Figures (List of Tables, or List of any objects), select all the lines of a Table of Figures and press Delete.
When you add several tables and figures or any other objects in your report, it is a best practice to create a list of tables and figures or lists of other objects in the report’s preface. In academic writing, this is a must-have section of your report. Like the table of contents, you can also generate a list of tables and figures or any other objects in Microsoft Word.
Table of Contents
Step 01: Add captions to tables and figures
The lists of tables and figures or lists of any other objects are generated from the captions you added for those objects in your report. If you haven’t added captions yet, you can learn how to add captions in Microsoft Word fro the following post.
How to add Captions in Microsoft Word
Step 02: Insert list of tables and figures
After you add a few captions to tables or figures in your document, you generate a list of those objects.
To generate a list of tables and figures or any other objects;
- Place the cursor where you want to add the list.
- Go to the References tab
- Click Insert Table of Figures in the Caption group
- In the Table of the Figures dialog box select the relevant Caption Label (Table, Figure, & Equation, etc…)
- Do the necessary formatting using the available options in the Table of Figures dialog box,
- Click OK.
The following animation demonstrates the above steps for creating a list of tables and figures.
Updating the lists
You need to update these lists in order to include the tables and figures or other objects you added later in the report. To update these lists,
- Click anywhere in the middle of the list to be updated
- Go to the References tab
- In the Caption group, click Update Table
- In the Update Table of Figures dialog box select the Update Entire Table option
- Click OK.
Insert a table of contents
A table of contents in Word is based on the headings in your document.
Create the table of contents
-
Put your cursor where you want to add the table of contents.
-
Go to References > Table of Contents. and choose an automatic style.
-
If you make changes to your document that affect the table of contents, update the table of contents by right-clicking the table of contents and choosing Update Field.
To update your table of contents manually, see Update a table of contents.
If you have missing entries
Missing entries often happen because headings aren’t formatted as headings.
-
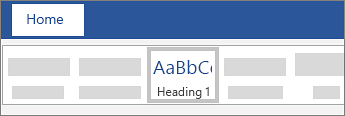
For each heading that you want in the table of contents, select the heading text.
-
Go to Home > Styles, and then choose Heading 1.
-
Update your table of contents.
To update your table of contents manually, see Update a table of contents.
Create the table of contents
Word uses the headings in your document to build an automatic table of contents that can be updated when you change the heading text, sequence, or level.
-
Click where you want to insert the table of contents – usually near the beginning of a document.
-
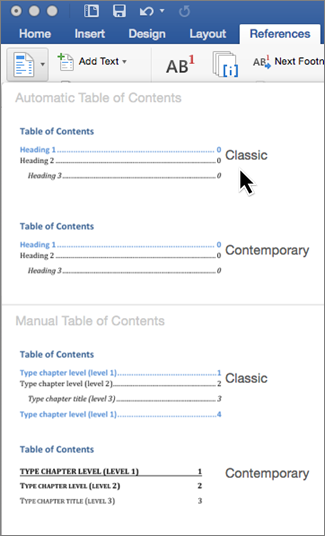
Click References > Table of Contents and then choose an Automatic Table of Contents style from the list.
Note: If you use a Manual Table of Contents style, Word won’t use your headings to create a table of contents and won’t be able to update it automatically. Instead, Word will use placeholder text to create the look of a table of contents so you can manually type each entry into the table of contents. To update your manual table of contents, see Update a table of contents.
If you want to Format or customize your table of contents, you can. For example, you can change the font, the number of heading levels, and whether to show dotted lines between entries and page numbers.
If you have missing entries
Missing entries often happen because headings aren’t formatted as headings.
-
For each heading that you want in the table of contents, select the heading text.
-
Go to Home > Styles, and then choose Heading 1.
-
Update your table of contents.
To update your table of contents manually, see Update a table of contents.
Word uses the headings in your document to build an automatic table of contents that can be updated when you change the heading text, sequence, or level.
-
Click where you want to insert the table of contents—usually near the beginning of the document.
-
On the toolbar ribbon, select References.
-
Near the left end, select Insert Table of Contents. (Or select Table of Contents > Insert Table of Contents.
The table of contents is inserted, showing the headings and page numbering in your document.
If you make changes to your document that affect the table of contents, you can update it by right-clicking the table and selecting Update Table of Contents.
Get the learning guide
For a hands-on guide that steps you through the process of creating a table of contents, download our Table of Contents tutorial. Or, in desktop Word, go to File > New, and search for table of contents.
See Also
Update a table of contents
Need more help?
Want more options?
Explore subscription benefits, browse training courses, learn how to secure your device, and more.
Communities help you ask and answer questions, give feedback, and hear from experts with rich knowledge.

Highlights
- Before adding a list of tables in your Word document, you need to add captions to them.
- You can add a list of tables in Word from the references ribbon.
- The method of adding a list of tables in an MS Word document is the same as adding a list of Figures.
Working on a report and want to add a list of tables to it? If you want to know how to add list of tables in Word, read this article.
If you are searching how do I automatically insert a list of tables in word, here is the answer. This is a quick guide on how to insert a list of tables in MS word documents.
If your Microsoft Word document has many tables and figures in the appendices, you need to create a separate list of tables and figures in it. This how-to will make creating lists of tables less time-consuming.

Before adding a list of tables in a Word document, make sure you have given appropriate captions to them. But if you haven’t, follow the below steps to add captions to tables.
Firstly, click on the table and then click on REFERENCES.
Then in the REFERENCES tab, click on the Insert caption.
Repeat this process for all the tables in your Word document. After captioning all the tables, you are ready to insert a list of tables into it.
Steps To Insert List Of Tables In Word
- Type the heading List of Tables, assign the Heading 1 style, and click where you want to insert the list.
- Click on REFERENCES and then click List of figures.
- In the resulting dialog, choose Table from the Caption Label dropdown.
- Uncheck the Use Hyperlinks Instead Of Page Numbers option.
- Click OK.

You will see that the list of tables has been added successfully.
How To Update List of tables In Word
If you add, delete, change, or move captions, use Update Table so the list of tables reflects your changes.
- Click on the list of tables in your document. This will highlight the entire list.
- Click References > Update Table.
- Note: Update Table becomes an option only when you click the table of figures in your document. You can also press F9 to modify your list of tables.
- Select an Update in the in the Update Table of Figures dialog box.
- Select Update page numbers if you need to adjust the page numbers.
- Select Update entire table if you have moved tables or altered captions.
- Click OK.
Back to top button

John A Trax Jr, Getty Images/iStockphoto
If you have a lot of tables, chances are you’ll want to document them. You can do so with minimal effort thanks to Word’s referencing feature. By giving your tables captions, you can easily generate a list of tables (and figures). The captions serve as descriptive titles, and you can use them to generate a list anywhere in the document, as easily as you would a table of contents.
There’s a monkey wrench though: The default settings rely on built-in captions for each table, and each caption displays a sequential number. That’s great if that’s what you want–but if it’s not, you’ll have to work a bit harder. In this article, I’ll show you how to generate both lists: one displaying the same caption and sequential numbers and one containing unique names and no sequential numbers. You can also apply both techniques to a list of figures.
I’m using Word 2016 on a Windows 10 64-bit system, but this technique works in older versions. The browser version will display the list, but the features needed to generate the list aren’t available. You can work with your own Word document or download the demonstration .docx or .doc file.
LEARN MORE: Office 365 Consumer pricing and features
The easy way
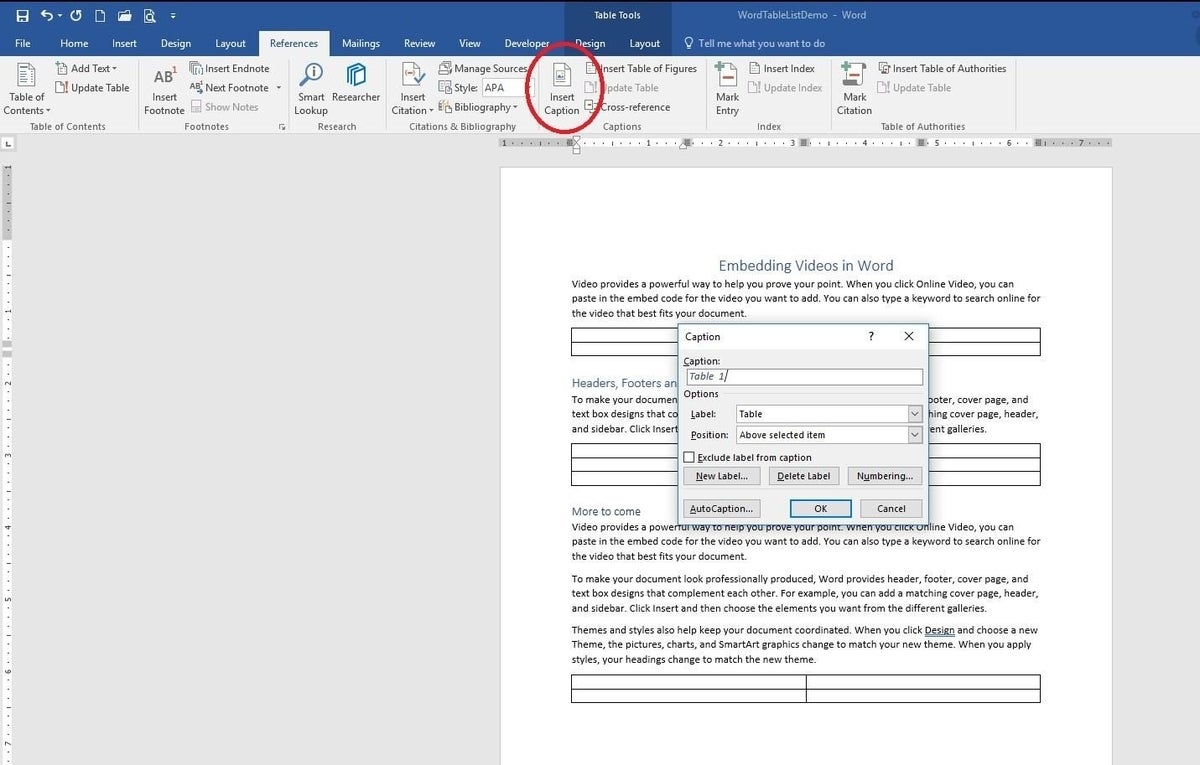
The easiest technique generates a list of built-in captions and sequential numbers. With a little work, you can add custom captions and remove the numbers. The only thing you must do either way is give each table a title using the Caption property. Let’s work through a simple document with a few tables. To add a caption, click anywhere inside the first table and then do the following:
- Click the References tab.
- In the Captions group, click Insert Caption.
- To retain the default settings (Figure A) click OK. As you can see in Figure B, Word adds the default caption–Table 1–above the table.
Figure A
Retain the default settings.
Figure B
Word displays a caption above the table.
Repeat this process for the remaining tables. When you’re done, you’re ready to add the list of tables to your document. You can put the list anywhere you like. In a technical document, a list of tables usually follows the table of contents. For this example, we’ll generate the list at the end of the document, as follows:
- Double-click at the end of the document.
- Click the References tab.
- In the Captions group, click Insert Table Of Figures.
- In the resulting dialog, choose Table from the Caption Label dropdown (Figure C).
- Uncheck the Use Hyperlinks Instead Of Page Numbers option.
- Click OK to return the document and the list shown in Figure D.
Figure C
You want to list tables.
Figure D
With almost no work, you can generate a list of tables.
Using the default settings, this feature quickly creates a list of tables, but the captions are limited. They aren’t descriptive and they include a sequential number. You might want something more meaningful.
SEE: 30 things you should never do in Microsoft Office (free PDF) (TechRepublic)
http://www.techrepublic.com/videos/video-how-to-rotate-text-in-microsoft-word/
Add meaning
Fortunately, adding custom captions and removing the sequential numbers requires only a few additional steps. First, if you’re actually working the example, remove the captions you added in the last section. Simply select and delete them or close and reopen the document without saving it. Next, click anywhere inside the first table, click the References tab, and then click Insert Caption, as before. To add the custom caption, do the following:
- Click New Label.
- In the resulting dialog, enter the text (Figure E).
- Click OK.
- Make sure the Position setting is correct–most likely you’ll want to use Above Selected Item. When you choose New Label, Word switches the position.
- Click OK to return to the document.
Figure E
Add a custom caption.
As you can see in Figure F, the caption displays the custom text and a sequential number. To remove the number, select it and delete it–it’s that simple. Figure G shows all three tables with custom captions and no sequential numbers. If you add all three captions and then go back to remove the values, you’ll notice that each caption is numbered 1. That’s because each caption is unique. As a result, the values aren’t functional.
Figure F
The caption is more meaningful, but it still includes the sequential number.
Figure G
Remove the sequential numbers from each caption.
Try to generate a list of tables as you did before. Notice that the Caption labels option now offers your custom labels. Because your captions are unique, choosing one of them will list only that table. Be sure to choose Table as you did before. Oops… you probably weren’t expecting to see the error shown in Figure H, were you? Adding custom captions is only half of the solution.
Figure H
This error means Word can’t find any table captions to list.
Luckily, the fix involves only a few extra clicks. Once again, use the Insert Table Of Figures option to display the Table Of Figures dialog (Figure C). Choose Table and uncheck the Use Hyperlinks Instead Of Page Numbers option as before. Instead of clicking OK, click Options. In the resulting dialog, check the Style option, as shown in Figure I, and click OK twice (and confirm to replace the existing list if prompted) . Figure J shows the results.
SEE: Microsoft Office: Full version comes to the Windows Store (TechRepublic)
Figure I
Use a table style instead of the caption labels to generate the list .
Figure J
The list displays meaningful names and no values.
Choosing this option changes the list element from labels to styles–specifically, Word’s built-in Caption style. You can use both techniques to generate a list of figures.
Send me your question about Office
I answer readers’ questions when I can, but there’s no guarantee. Don’t send files unless requested; initial requests for help that arrive with attached files will be deleted unread. You can send screenshots of your data to help clarify your question. When contacting me, be as specific as possible. For example, “Please troubleshoot my workbook and fix what’s wrong” probably won’t get a response, but “Can you tell me why this formula isn’t returning the expected results?” might. Please mention the app and version that you’re using. I’m not reimbursed by TechRepublic for my time or expertise when helping readers, nor do I ask for a fee from readers I help. You can contact me at susansalesharkins@gmail.com.
Follow these steps…
(1) Give all your tables a caption.
(2) Click your cursor at where you’d like to place your List of Tables.
Its traditional location in a technical document is right after the Table of Contents (if any) and after the “List of Figures” (if any).
(3) Select the References tab from the main menu. Then click Insert Table of Figures to display the Table of Figures dialog box:
(4) Clear the “Use hyperlinks instead of page numbers” check-box if you do not want to jump to a HTML destination accidentally.
(5) Select the “Show page numbers” check-box. Select the “Right align page numbers” check-box. Select a Tab Leader from the drop-down list.
(6) Select “Table” from the Caption Label drop-down list to display table captions in the Print Preview box. Then select the related “Include name and number” check-box:
(7) Select a template from the Formats drop-down list.
(8) Click OK to display your List of Tables at where your cursor is.
Insert and Edit a Table with Multiple Columns and Rows in Word
by Avantix Learning Team | Updated August 23, 2022
Applies to: Microsoft® Word® 2013, 2016, 2019, 2021 and 365 (Windows)
You can create a table in a Word document in 4 easy ways using the Ribbon. A table is a grid made up of columns and rows that intersect to form cells. You can insert text, numbers and images in a table. Once you have inserted a table, you can easily add and resize columns and rows and change table formatting.
It’s best to avoid using Draw Table to create a table since the table may not be created in a consistent way.
Note: Buttons and Ribbon tabs may display in a different way (with or without text) depending on your version of Word, the size of your screen and your Control Panel settings. For newer versions of Word, Ribbon tabs may appear with different names. For example, the Table Design tab may appear as Table Tools Design.
In the following example, a table with 4 columns and 5 rows has been inserted in a Word document:
Recommended article: 10 Microsoft Word Shortcuts for Moving Around in Tables
Do you want to learn more about Microsoft Word? Check out our virtual classroom or in-person classroom Word courses >
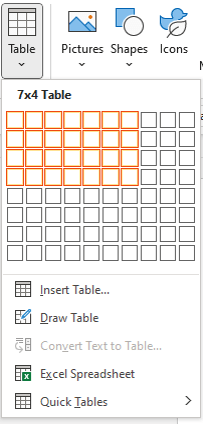
Create a table using the Table Grid
To insert a table using Insert Table and select columns and rows in the Table Grid:
- Click in the Word document where you want to insert a table.
- Click the Insert tab in the Ribbon.
- Click Table in the Tables group. A drop-down menu appears with a Table Grid.
- Hover over the grid until the number of columns and rows you want is selected.
- Click in the highlighted area of the grid to insert a table.
To insert a table, select cells in the Table Grid as follows:
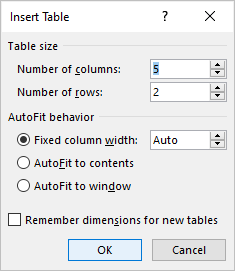
Create a table using the Insert Table dialog box
To insert a table using the Insert Table dialog box:
- Click in the Word document where you want to insert a table.
- Click the Insert tab in the Ribbon.
- Click Table in the Tables group. A drop-down menu appears.
- Select Insert Table. A dialog box appears.
- Enter the number of columns and rows you want to create.
- Select the desired options below AutoFit behavior (typically Fixed column width: Auto).
- Click OK.
The Insert Table dialog box appears with options to select the number of columns and rows:
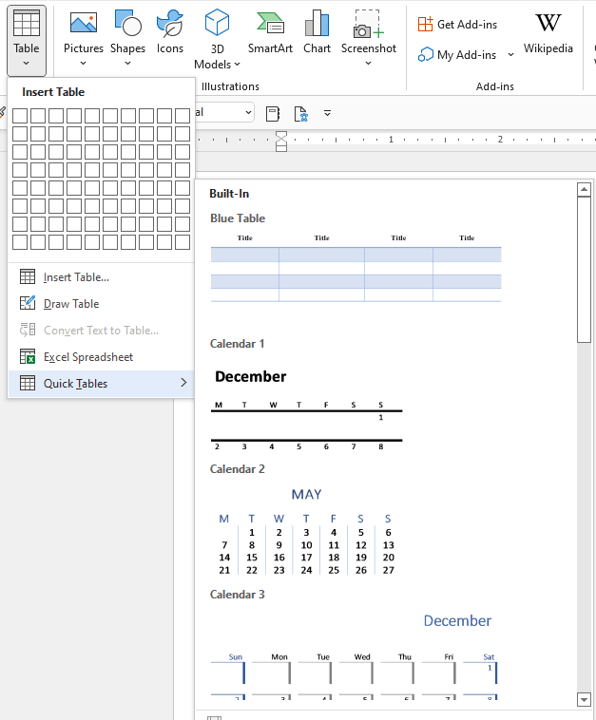
Create a table using Quick Tables
To insert a table using Quick Tables:
- Click in the Word document where you want to insert a table.
- Click the Insert tab in the Ribbon.
- Click Table in the Tables group. A drop-down menu appears.
- Select Quick Tables. A gallery appears.
- Click the table you want to insert.
Quick Tables appear in the Table drop-down menu:
Create a table by converting text to a table
If you have used tabs or other delimiters in paragraphs, you can convert the data into a table (if the delimiters are entered consistently). Wherever you have pressed Enter or Return to create a new paragraph, Word will create a new table row. You can use various delimiters to separate data but the most common are tabs, spaces or commas.
To convert delimited data to a table:
- Select the text that you want to convert.
- Click the Insert tab in the Ribbon.
- Click Table in the Tables group. A drop-down menu appears.
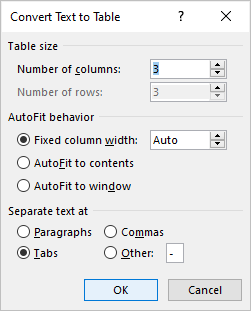
- Select Convert Text to Table. A dialog box appears.
- Enter the number of columns if necessary and ensure a delimiter is selected in the Separate text at area.
- Under AutoFit behavior, choose how you want your table to appear. Word chooses a width for the table columns by default. If you want a different column width, choose AutoFit to contents or AutoFit to window.
- Click OK.
In the Convert Text to Table dialog box, enter the number of columns as well as the delimiter:
Show table gridlines
Gridlines show the cell boundaries of a table on screen if table borders are not applied. Gridlines appear only on the screen and are not printed.
Gridlines are not visible when you view a document in a Web browser or in Print Preview.
To show table gridlines in a Word document:
- Click in a table.
- Click the Table Layout or Table Tools Layout tab in the Ribbon.
- In the Table group, check View Gridlines.
View Gridlines appears on the Table Tools Layout or Table Layout tab in the Ribbon:
Move around in a table
You can use the following keys to move from one cell to another in a table:
- Tab to move to the next cell to the right.
- Shift-Tab to move to the cell to left.
- Ctrl-Tab to tab within a cell.
Add a row or a column
To add a row in a table:
- Click in a cell that is located above or below where you want to add a row.
- Click the Table Layout or Table Tools Layout tab in the Ribbon.
- To add a row above the cell you clicked in, click Insert Above in the Rows and Columns group. To add a row below the cell you clicked in, in the Rows and Columns group, click Insert Below.
The commands to insert rows or columns appear on the Table Tools Layout or Table Layout tab in the Ribbon:
You can also right-click in a row and choose Insert from the drop-down menu and insert options from the sub-menu.
If you click in the last cell in a table and press Tab, Word will automatically add a row.
To add a column in a table:
- Click in a cell that is located to the right or left of where you want to add a column.
- Click the Table Layout or Table Tools Layout tab in the Ribbon.
- To add a column to the left of the cell you clicked in, click Insert Left in the Rows and Columns group. To add a column to the right of the cell you clicked in, in the Rows and Columns group, click Insert Right.
You can also right-click in a row and choose Insert from the drop-down menu and insert options from the sub-menu.
Delete a column or row
To delete a row or column:
- Select the row or column (drag over the cells or click to the left of a row or above a column when the arrow appears).
- Click the Table Layout or Table Tools Layout tab in the Ribbon.
- In the Rows & Columns group, click Delete. A drop-down menu applears.
- Click Delete Rows or Delete Columns as appropriate.
You can also right-click in a row or column and choose Delete from the drop-down menu and delete options from the sub-menu.
Change column width
To change column width:
- Select the column or columns you want to change.
- Click the Table Layout or Table Tools Layout tab in the Ribbon.
- Click Properties in the Table group. You can also right-click and choose Properties from the drop-down menu. A dialog box appears.
- Click the Column tab.
- Check Preferred Width.
- Type the new measurement for the column width. For example, typer 1.0″ or click the up and down arrows.
- Click OK.
The Table Properties dialog box appears as follows with the Column tab selected:
You can also drag the right line of a column to resize it.
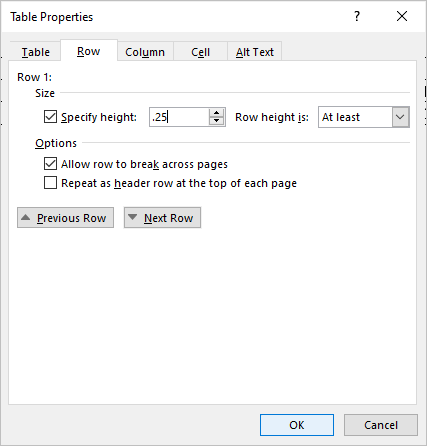
Change row height
To change row height:
- Select the row or rows you want to change.
- Click the Table Layout or Table Tools Layout tab in the Ribbon.
- Click Properties in the Table group. You can also right-click and choose Properties from the drop-down menu. A dialog box appears.
- Click the Row tab.
- Check Specify Height.
- Type the new measurement for the row height. For example, type 1.0″ or click the up and down arrows.
- Specify row height as At Least or Exactly.
- Click OK.
The Table Properties dialog box appears as follows with the Row tab selected:
You can also drag the bottom line of a row to resize it.
Distribute rows and columns evenly
To distribute rows and columns evenly:
- Select the entire table by clicking the four-arrows that appear on the top left of the table.
- Click the Table Layout or Table Tools Layout tab in the Ribbon.
- Click Distribute Rows and / or Distribute Columns in the Cell Size group.
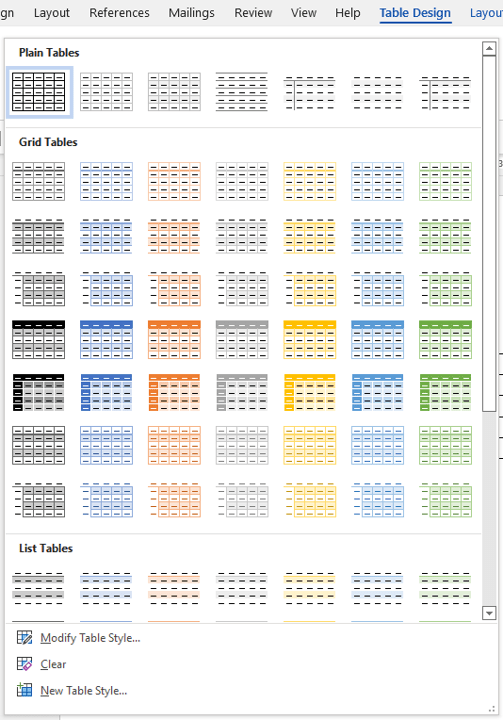
Apply a table style
To apply a table style:
- Click in the table.
- Click the Table Design or Table Tools Design tab in the Ribbon.
- Click a table style or click the More arrow to display the Table Styles gallery and click a style.
Table Styles gallery appears on the Table Tools Design or Table Design tab in the Ribbon:
To learn more about working with table styles, check out the article How to Format Microsoft Word Tables Using Table Styles (Ultimate Guide).
Subscribe to get more articles like this one
Did you find this article helpful? If you would like to receive new articles, JOIN our email list.
More resources
4 Ways to Delete a Table in Word
How to Make Columns in Word (Newspaper-style)
How to Insert Formulas and Functions in Word Tables
How to Keep a Microsoft Word Table Together on One Page
How to Delete a Page in Word (Remove Blank or Extra Pages)
Related courses
Microsoft Word: Intermediate / Advanced
Microsoft Excel: Intermediate / Advanced
Microsoft PowerPoint: Intermediate / Advanced
Microsoft Word: Long Documents Master Class
Microsoft Word: Styles, Templates and Tables of Contents
Microsoft Word: Designing Dynamic Word Documents Using Fields
VIEW MORE COURSES >
Our instructor-led courses are delivered in virtual classroom format or at our downtown Toronto location at 18 King Street East, Suite 1400, Toronto, Ontario, Canada (some in-person classroom courses may also be delivered at an alternate downtown Toronto location). Contact us at info@avantixlearning.ca if you’d like to arrange custom instructor-led virtual classroom or onsite training on a date that’s convenient for you.
Copyright 2023 Avantix® Learning
Microsoft, the Microsoft logo, Microsoft Office and related Microsoft applications and logos are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation in Canada, US and other countries. All other trademarks are the property of the registered owners.
Avantix Learning |18 King Street East, Suite 1400, Toronto, Ontario, Canada M5C 1C4 | Contact us at info@avantixlearning.ca
Creating tables in Microsoft Word used to be so annoying that most people just did it in Excel, then imported it into Word. It’s worth giving Word 2013’s table tools a try, though, because the process is easier, and there are some new graphical options.
Seven ways to create tables
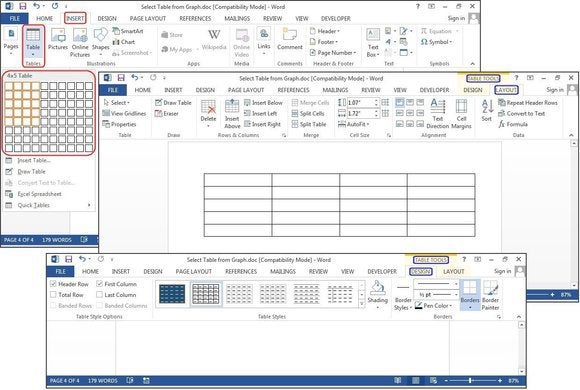
Microsoft now provides five different methods for creating tables: the Graphic Grid, Insert Table, Draw Table, insert a new or existing Excel Spreadsheet table, and Quick Tables, plus an option for converting existing text into a table. To start, open a blank Word document from the Home/New page. Position your cursor in the document where you want the table inserted.
Graphic Grid/Select Table from Graph
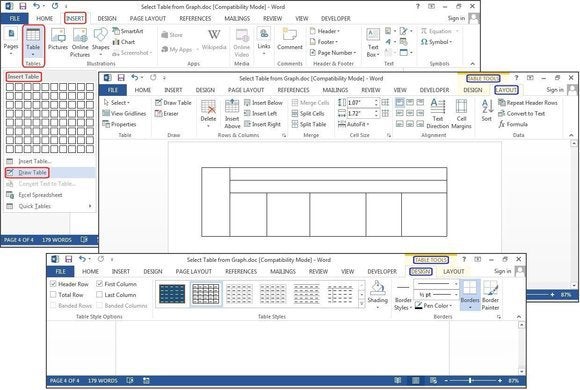
Under the Insert tab, click the Table button. The Insert Table dialog box will open, showing a basic grid pattern as well as traditional menu options below it. Place your cursor on the first cell in the grid and slide it down and over until you highlight (for this example) four columns and five rows, then click once.
Notice that once the table is created, a new option called Table Tools appears on the Ribbon bar with two new tabs: Design and Layout. See the Layout and Design section below for details regarding these options.
Create a new table using the graphical grid.
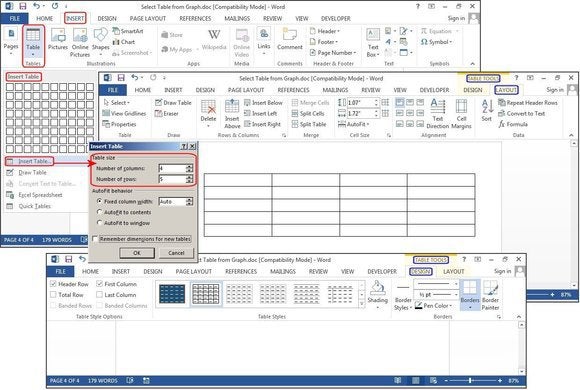
Insert Table
Click Insert > Tables > Insert Table from the dropdown menu. In the Insert Table dialog box, enter the number of columns and rows you want in this table (four columns and five rows). In the AutoFit Behavior panel, select Auto, or click the down arrow to choose a specific size. You can also choose AutoFit to Contents (produces narrow columns that expand as you add data) or AutoFit to Window (expands the table to fit the document size). Check the Remember Dimensions for New Tables box if you want the sizes you’re entering now to become your defaults for future tables.
Create a new table using Insert Table.
Draw Table
Click Insert> Tables > Draw Table. The cursor turns into a pencil, which you drag down and across to draw a box. Don’t worry about the exact dimensions; you can modify it any time.
Once the box is created, position the cursor inside the box and draw lines over and down for the columns and rows (one at a time). Don’t worry about crooked lines, either—Word straightens them as you draw.
To add or remove columns and/or rows later, click anywhere inside the table, then select the Design tab under Table Tools. Click the Draw Table button to add or continue drawing lines with your pencil cursor, or click the Eraser button to remove lines with the eraser cursor. To remove a line, just touch the line with the eraser cursor, and the line disappears.
Create a new table using Draw Table.
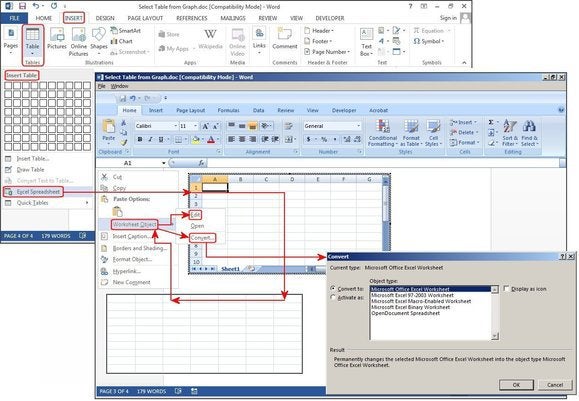
Excel Spreadsheet (create In Word)
Click Insert > Tables > Excel Spreadsheet. An Excel spreadsheet inserts at your cursor location. You can continue using Excel and its menus and commands, but after you enter your data it converts to a non-editable graphic.
If you want to add, delete, or modify the spreadsheet, right-click anywhere inside the worksheet graphic, select Worksheet Object from the dropdown menu, then click Edit. The original spreadsheet reappears for editing. Notice the top menu has changed to an Excel menu for edits.
Also from the Worksheet Object dropdown menu, you can click Open to open the spreadsheet in Excel, so you can manipulate it in that program. Or click Convert to view a Windows dialog box that lists file-conversion options.
Create a new table using Excel Spreadsheet.
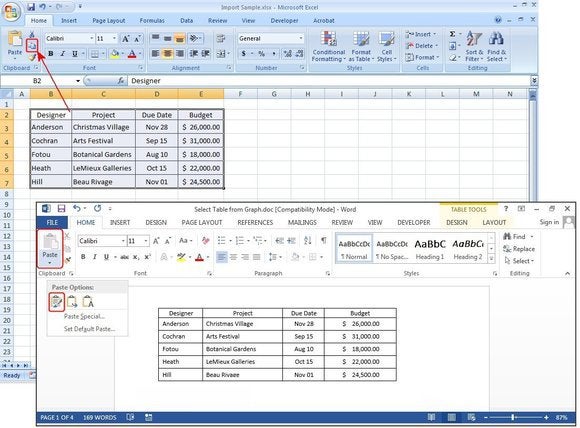
Excel Spreadsheet (copy and paste existing worksheet)
In the old days, Excel spreadsheets had to be imported into Word. Now you can just copy and paste. Open Excel, highlight the spreadsheet, and copy it. Then open Word, position your cursor at the desired location, and select Paste > Keep Source Formatting.
The other options on the Paste dialog menu are Merge Formatting, which changes the text format to match the file into which you pasted the spreadsheet, and Keep Text Only, which pastes the text without the Excel grid, meaning you will likely have to realign your columns with tabs.
Copy and paste an existing table from Excel.
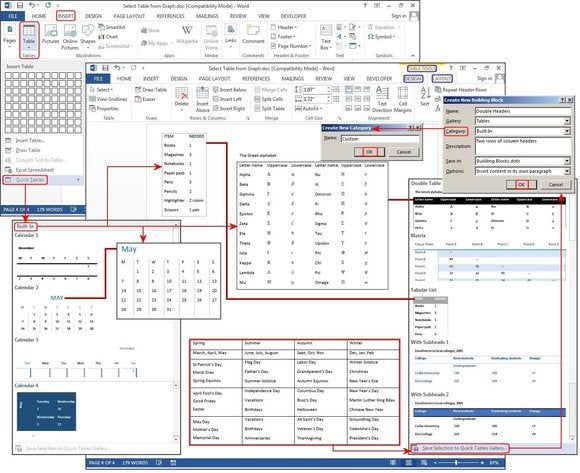
Quick Tables
Quick Tables are Word’s table templates. In addition to the nine templates provided, you can create your own designs and save them to the Quick Tables Gallery to use later. Click Insert > Tables > Quick Tables. Select a table template from the Quick Tables menu, then modify it to fit your project.
Create a new table using Quick Tables.
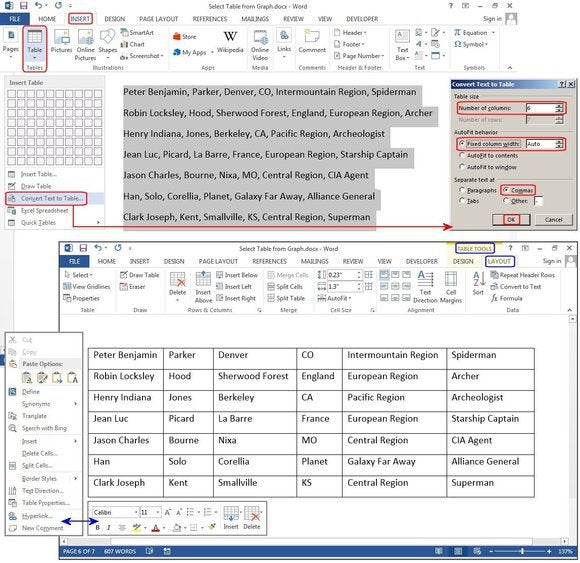
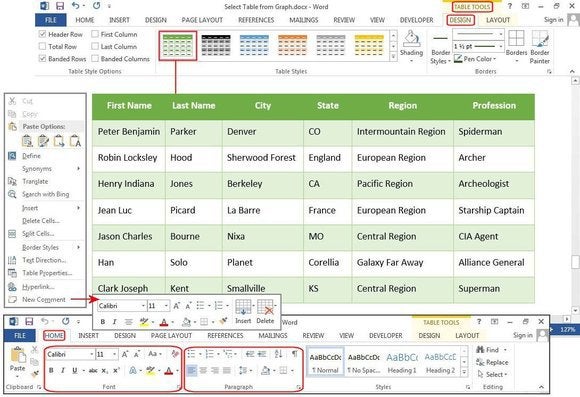
Convert Text to Table
The table tools can also make lists a lot easier to customize and even reorganize later. For our example, we’ll turn a classic contact list into a table, using a list of names—first, middle, last—plus the city, state, region, and profession of each person on the list.
For eons, people have used tabs to separate the fields, adding a tab or two to accommodate longer strings of data. But if you do this, when you convert the table to text, it misplaces all the data.
With the Convert Text to Table feature, you can separate the fields (Name, City, State, etc.) with paragraphs, tabs, commas, or other separator character, but use only one separator between each field.
Convert an existing block of text to a table.
Layout and Design
There are three options to modify and/or decorate tables:
1. Use the Table Tools > Design—or—Table Tools > Layout commands on the Ribbon menu.
2. Right-click and use the Shortcut popup menus.
3. Use the keyboard shortcuts, which become visible when you press the ALT key on your keyboard.
All of these methods are fast and easy, but using a combination of all three will always be quicker. For example, use your mouse to highlight, then right-click to copy with your right hand; then arrow down to the new location and press CTRL-V to paste with your left hand.
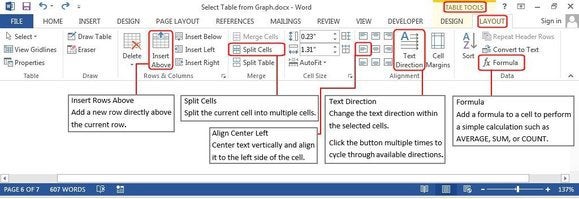
Layout tab
The Layout tab lets you modify the structure of the table. The menu is fairly self-explanatory, and you can roll your cursor over a feature to get further clarification.
Roll your mouse over each button to view how each feature works.
The dialog boxes below also illustrate each feature. Click Table Tools > Layout > Insert or Delete (from Rows and Columns group) to add or remove them; Merge or Split Cells or Split a Table (from the Merge group); or Text Direction (from the alignment group) to rotate the text inside the table.
Menu options to modify a table structure.
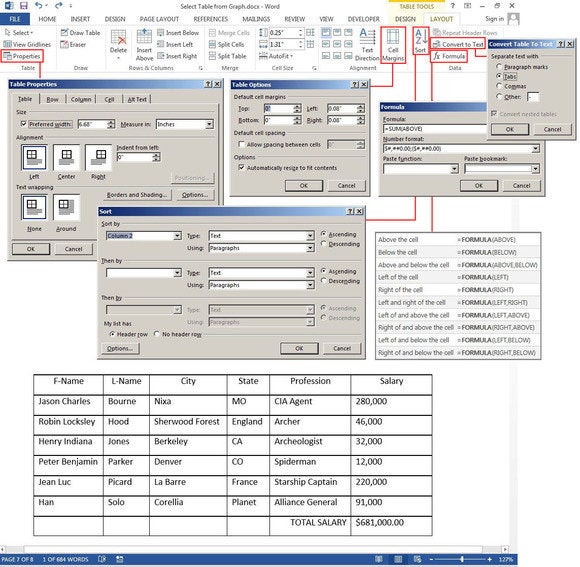
Other features include Table Properties, which provides several options for aligning the table with the text or wrapping text around your table. Select Cell Margins to change the margins inside each cell. With the table still highlighted, click Table Tools > Layout > Data > Sort to sort the table data alphabetically or numerically, just like in Excel. You can sort by column numbers or by column headers, and it provides two sort levels. For example, you can sort by Last Name, then by First Name. The table below is sorted by Last Name.
You can also convert your table back to a text block. Just choose the separator you prefer, so when the table grid disappears, the data isn’t all jumbled together.
You can even insert formulas to calculate your numeric data. I added a Salary column to the table below and entered some dollars, plus a new row at the bottom for the salary totals. To calculate the total salaries, position your cursor in the last row and the last column cell, and click the Formula button under the Data group. In the Formula dialog box type the SUM() formula [or Count() or Average()] in the Formula field box. If you are unfamiliar with the formulas Word provides, click the down arrow under the Paste Function field, and choose a formula from the list.
Type Above between the parentheses, choose a format under Number Format such as dollars, percent, or general, then click OK. Word calculates the column of numbers and places the calculation in the target cell (where your cursor resides). Review the Formula Format table in the graphic below for the correct commands that tell Word which direction to calculate (these go inside the parentheses).
Wrap text around a table, change cell margins, convert table back to text, sort the table data, and/or add formulas.
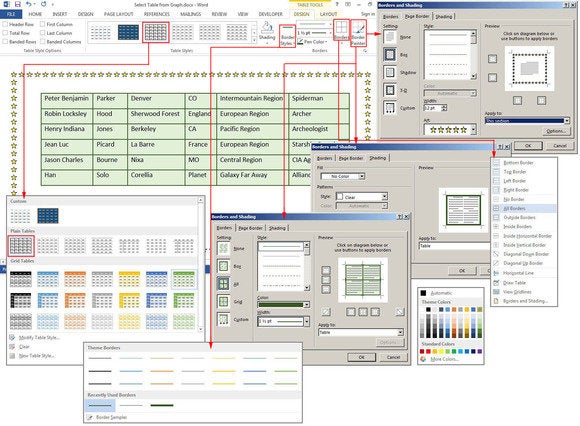
Design tab
The Design tab is for adding borders, shading, styles, and customizing the header columns and rows. Highlight your table, then select Table Tools > Design> Table Styles, Shading, Border Styles, Borders, or Border Painter (see the graphic below for ideas). There’s no learning curve, just play with the features and see what happens. If you don’t like a feature you’ve added, just click the Undo button or press CTRL-Z.
There’s also an option to add artwork borders to your pages. Select Table Tools > Design > Borders > Border Painter, and click the Page Border tab in the Borders and Shading dialog box. Click the down arrow in the field box under Art, then choose a border—mostly simple clip art—from the list.
Make your table pop with Table Styles, Shading, Border Styles, Borders, or Border Painter.
The table below uses one of the many preset styles that comes with Word. Select Table Tools > Design > Table Styles, then scroll through the gallery of styles. If you want to change the font or customize the paragraphs inside the table, use the Format Shortcut menu. Right-click anywhere inside the table, and this small menu pops up adjacent to the longer Table Options menu. If the formatting feature you need is not on the Shortcut menu (which is fairly limited), click the Home Tab and select the features you need from the Font or Paragraph group. All of the buttons and groups on the Home tab are available for formatting tables as well as documents. The options are endless.
Choose a Table Style with Banded Rows (i.e., every other row is different for easier viewing), then customize the fonts and paragraph spacing.
Stay tuned for more articles on getting the most out of Word 2013.