| title | description | ms.date | ms.topic | dev_langs | helpviewer_keywords | author | ms.author | manager | ms.technology | ms.workload | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
How to: Programmatically create Word tables |
Learn how to use the Add method of the Tables collection to add a table at the specified range in a Microsoft Word document. |
02/02/2017 |
how-to |
|
|
John-Hart |
johnhart |
jmartens |
office-development |
office |
How to: Programmatically create Word tables
[!INCLUDE Visual Studio]
The xref:Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word.Tables collection is a member of the xref:Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word.Document, xref:Microsoft.Office.Tools.Word.Document, xref:Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word.Selection, and xref:Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word.Range classes, which means that you can create a table in any of those contexts. You use the xref:Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word.Tables.Add%2A method of the xref:Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word.Tables collection to add a table at the specified range.
[!INCLUDEappliesto_wdalldocapp]
Create tables in document-level customizations
To add a table to a document
-
Use the xref:Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word.Tables.Add%2A method to add a table consisting of three rows and four columns at the beginning of the document.
To use the following code example, run it from the
ThisDocumentclass in your project.C#
:::code language=»csharp» source=»../vsto/codesnippet/CSharp/Trin_VstcoreWordAutomationCS/ThisDocument.cs» id=»Snippet86″:::
VB
:::code language=»vb» source=»../vsto/codesnippet/VisualBasic/Trin_VstcoreWordAutomationVB/ThisDocument.vb» id=»Snippet86″:::
When you create a table, it is automatically added to the xref:Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word.Tables collection of the xref:Microsoft.Office.Tools.Word.Document host item. You can then refer to the table by its item number by using the xref:Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word.Tables.Item%2A property, as shown in the following code.
To refer to a table by item number
-
Use the xref:Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word.Tables.Item%2A property and supply the item number of the table that you want to refer to.
To use the following code example, run it from the
ThisDocumentclass in your project.C#
:::code language=»csharp» source=»../vsto/codesnippet/CSharp/Trin_VstcoreWordAutomationCS/ThisDocument.cs» id=»Snippet87″:::
VB
:::code language=»vb» source=»../vsto/codesnippet/VisualBasic/Trin_VstcoreWordAutomationVB/ThisDocument.vb» id=»Snippet87″:::
Each xref:Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word.Table object also has a xref:Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word.Table.Range%2A property that enables you to set formatting attributes.
To apply a style to a table
-
Use the xref:Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word.Table.Style%2A property to apply one of the Word built-in styles to a table.
To use the following code example, run it from the
ThisDocumentclass in your project.C#
:::code language=»csharp» source=»../vsto/codesnippet/CSharp/Trin_VstcoreWordAutomationCS/ThisDocument.cs» id=»Snippet88″:::
VB
:::code language=»vb» source=»../vsto/codesnippet/VisualBasic/Trin_VstcoreWordAutomationVB/ThisDocument.vb» id=»Snippet88″:::
Create tables in VSTO Add-ins
To add a table to a document
-
Use the xref:Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word.Tables.Add%2A method to add a table consisting of three rows and four columns at the beginning of the document.
The following code example adds a table to the active document. To use this example, run it from the
ThisAddInclass in your project.C#
:::code language=»csharp» source=»../vsto/codesnippet/CSharp/Trin_VstcoreWordAutomationAddIn/ThisAddIn.cs» id=»Snippet86″:::
VB
:::code language=»vb» source=»../vsto/codesnippet/VisualBasic/Trin_VstcoreWordAutomationAddIn/ThisAddIn.vb» id=»Snippet86″:::
When you create a table, it is automatically added to the xref:Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word.Tables collection of the xref:Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word.Document. You can then refer to the table by its item number by using the xref:Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word.Tables.Item%2A property, as shown in the following code.
To refer to a table by item number
-
Use the xref:Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word.Tables.Item%2A property and supply the item number of the table that you want to refer to.
The following code example uses the active document. To use this example, run it from the
ThisAddInclass in your project.C#
:::code language=»csharp» source=»../vsto/codesnippet/CSharp/Trin_VstcoreWordAutomationAddIn/ThisAddIn.cs» id=»Snippet87″:::
VB
:::code language=»vb» source=»../vsto/codesnippet/VisualBasic/Trin_VstcoreWordAutomationAddIn/ThisAddIn.vb» id=»Snippet87″:::
Each xref:Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word.Table object also has a xref:Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word.Table.Range%2A property that enables you to set formatting attributes.
To apply a style to a table
-
Use the xref:Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word.Table.Style%2A property to apply one of the Word built-in styles to a table.
The following code example uses the active document. To use this example, run it from the
ThisAddInclass in your project.C#
:::code language=»csharp» source=»../vsto/codesnippet/CSharp/Trin_VstcoreWordAutomationAddIn/ThisAddIn.cs» id=»Snippet88″:::
VB
:::code language=»vb» source=»../vsto/codesnippet/VisualBasic/Trin_VstcoreWordAutomationAddIn/ThisAddIn.vb» id=»Snippet88″:::
See also
- How to: Programmatically add text and formatting to cells in Word tables
- How to: Programmatically add rows and columns to Word tables
- How to: Programmatically populate Word tables with document properties
- Optional parameters in Office solutions
You can try my method to export data to Word (*.docx) , it’s easy to use and works 100% with any DataGridView , just add Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word reference and copy the following code :
using Word = Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word;
public void Export_Data_To_Word(DataGridView DGV, string filename)
{
if (DGV.Rows.Count != 0)
{
int RowCount = DGV.Rows.Count;
int ColumnCount = DGV.Columns.Count;
Object[,] DataArray = new object[RowCount + 1, ColumnCount + 1];
//add rows
int r = 0;
for (int c = 0; c <= ColumnCount - 1; c++)
{
for (r = 0; r <= RowCount - 1; r++)
{
DataArray[r, c] = DGV.Rows[r].Cells[c].Value;
} //end row loop
} //end column loop
Word.Document oDoc = new Word.Document();
oDoc.Application.Visible = true;
//page orintation
oDoc.PageSetup.Orientation = Word.WdOrientation.wdOrientLandscape;
dynamic oRange = oDoc.Content.Application.Selection.Range;
string oTemp = "";
for (r = 0; r <= RowCount - 1; r++)
{
for (int c = 0; c <= ColumnCount - 1; c++)
{
oTemp = oTemp + DataArray[r, c] + "t";
}
}
//table format
oRange.Text = oTemp;
object Separator = Word.WdTableFieldSeparator.wdSeparateByTabs;
object ApplyBorders = true;
object AutoFit = true;
object AutoFitBehavior = Word.WdAutoFitBehavior.wdAutoFitContent;
oRange.ConvertToTable(ref Separator, ref RowCount, ref ColumnCount,
Type.Missing, Type.Missing, ref ApplyBorders,
Type.Missing, Type.Missing, Type.Missing,
Type.Missing, Type.Missing, Type.Missing,
Type.Missing, ref AutoFit, ref AutoFitBehavior, Type.Missing);
oRange.Select();
oDoc.Application.Selection.Tables[1].Select();
oDoc.Application.Selection.Tables[1].Rows.AllowBreakAcrossPages = 0;
oDoc.Application.Selection.Tables[1].Rows.Alignment = 0;
oDoc.Application.Selection.Tables[1].Rows[1].Select();
oDoc.Application.Selection.InsertRowsAbove(1);
oDoc.Application.Selection.Tables[1].Rows[1].Select();
//header row style
oDoc.Application.Selection.Tables[1].Rows[1].Range.Bold = 1;
oDoc.Application.Selection.Tables[1].Rows[1].Range.Font.Name = "Tahoma";
oDoc.Application.Selection.Tables[1].Rows[1].Range.Font.Size = 14;
//add header row manually
for (int c = 0; c <= ColumnCount - 1; c++)
{
oDoc.Application.Selection.Tables[1].Cell(1, c + 1).Range.Text = DGV.Columns[c].HeaderText;
}
//table style
oDoc.Application.Selection.Tables[1].set_Style("Grid Table 4 - Accent 5");
oDoc.Application.Selection.Tables[1].Rows[1].Select();
oDoc.Application.Selection.Cells.VerticalAlignment = Word.WdCellVerticalAlignment.wdCellAlignVerticalCenter;
//header text
foreach (Word.Section section in oDoc.Application.ActiveDocument.Sections)
{
Word.Range headerRange = section.Headers[Word.WdHeaderFooterIndex.wdHeaderFooterPrimary].Range;
headerRange.Fields.Add(headerRange, Word.WdFieldType.wdFieldPage);
headerRange.Text = "your header text";
headerRange.Font.Size = 16;
headerRange.ParagraphFormat.Alignment = Word.WdParagraphAlignment.wdAlignParagraphCenter;
}
//save the file
oDoc.SaveAs2(filename);
//NASSIM LOUCHANI
}
}
private void button_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
SaveFileDialog sfd = new SaveFileDialog();
sfd.Filter = "Word Documents (*.docx)|*.docx";
sfd.FileName = "export.docx";
if (sfd.ShowDialog() == DialogResult.OK)
{
Export_Data_To_Word(dataGridView1, sfd.FileName);
}
}
Thank you.
Большинству операций, выполняемых программным способом, есть эквиваленты в пользовательском интерфейсе (UI), доступные как команды в меню и на панелях инструментов. Также существует нижележащая архитектура, обеспечивающая поддержку команд, выбираемых из UI. Всякий раз, когда вы создаете новый документ Word, он базируется на каком-либо шаблоне; расширение файлов шаблонов «.dot», а файлы документов – «.doc». Шаблон Word может содержать текст, код, стили, панели инструментов, элементы автотекста, комбинации клавиш для быстрого доступа к командам. Новый документ связывается с шаблоном и получает полный доступ к его элементам. Если вы не указываете конкретный шаблон, новый документ создается на основе стандартного шаблона «Normal.dot», который устанавливается при установке Word).
Шаблон Normal.dot является глобальным, он доступен любому документу, который вы создаете. Вы могли бы при желании поместить весь свой код в Normal.dot и создавать все документы в своей среде на основе собственного шаблона Normal (Обычный). Но тогда его файл мог бы стать чрезмерно большим, поэтому более эффективное решение для многих разработчиков — создание собственных шаблонов для конкретных приложений. В документах, создаваемых на основе вашего шаблона, код из стандартного шаблона Normal по-прежнему будет доступен. При необходимости можно связывать документ с несколькими шаблонами в дополнение к шаблону Normal.
Для работы с приложением Microsoft Word в .NET, используется объект Application, который является предком всех остальных объектов. Получив на него ссылку, вы можете работать с его методами и свойствами. Этот объект предоставляет большой набор методов и свойств, позволяющих программным путем управлять Microsoft Word. Код инициализации нового объекта Application, представлен ниже.
Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word.Application winword = new Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word.Application();
Чтобы открыть существующий документ или создать новый, необходимо создать новый объект Document.
object missing = System.Reflection.Missing.Value;
Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word.Document document =
winword.Documents.Add(ref missing, ref missing, ref missing, ref missing);
Выполняя какую-либо операцию в пользовательском интерфейсе Word (например, добавляя верхний колонтитул), вы выделяете соответствующую секцию, используя объект «Selection», определяющий текущую позицию «невидимого» курсора и применяете к ней новый параметр форматирования с использованием объекта «Range». Данный объект представляет область в документе и может включать в себя все что угодно — от пары символов, до таблиц, закладок и много другого. Вы не ограничены одним объектом «Range» — в одном документе можно определить сразу несколько таких объектов.
//Добавление верхнего колонтитула
foreach (Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word.Section section in document.Sections)
{
Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word.Range headerRange =
section.Headers[Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word.WdHeaderFooterIndex.wdHeaderFooterPrimary].Range;
headerRange.Fields.Add(headerRange, Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word.WdFieldType.wdFieldPage);
headerRange.ParagraphFormat.Alignment =
Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word.WdParagraphAlignment.wdAlignParagraphCenter;
headerRange.Font.ColorIndex = Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word.WdColorIndex.wdBlue;
headerRange.Font.Size = 10;
headerRange.Text = "Верхний колонтитул" + Environment.NewLine + "www.CSharpCoderR.com";
}
//Добавление нижнего колонтитула
foreach (Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word.Section wordSection in document.Sections)
{
Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word.Range footerRange =
wordSection.Footers[Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word.WdHeaderFooterIndex.wdHeaderFooterPrimary].Range;
footerRange.Font.ColorIndex = Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word.WdColorIndex.wdDarkRed;
footerRange.Font.Size = 10;
footerRange.ParagraphFormat.Alignment =
Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word.WdParagraphAlignment.wdAlignParagraphCenter;
footerRange.Text = "Нижний колонтитул" + Environment.NewLine + "www.CSharpCoderR.com";
}
Чтобы добавить текст в документ, необходимо указать позицию для вставки и сам текст.
//Добавление текста в документ document.Content.SetRange(0, 0); document.Content.Text = "www.CSharpCoderR.com" + Environment.NewLine;
Так же вы можете применить к тексту определенный стиль.
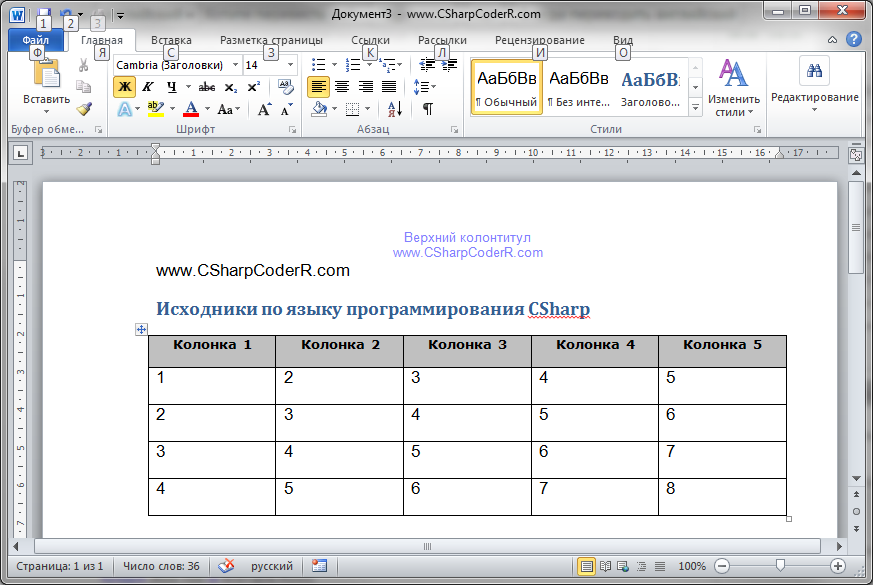
//Добавление текста со стилем Заголовок 1 Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word.Paragraph para1 = document.Content.Paragraphs.Add(ref missing); object styleHeading1 = "Заголовок 1"; para1.Range.set_Style(styleHeading1); para1.Range.Text = "Исходники по языку программирования CSharp"; para1.Range.InsertParagraphAfter();
В классе Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word.Document, присутствует коллекция «Tables», которая позволяет добавить таблицу в документ с использованием метода Add.
//Создание таблицы 5х5
Table firstTable = document.Tables.Add(para1.Range, 5, 5, ref missing, ref missing);
firstTable.Borders.Enable = 1;
foreach (Row row in firstTable.Rows)
{
foreach (Cell cell in row.Cells)
{
//Заголовок таблицы
if (cell.RowIndex == 1)
{
cell.Range.Text = "Колонка " + cell.ColumnIndex.ToString();
cell.Range.Font.Bold = 1;
//Задаем шрифт и размер текста
cell.Range.Font.Name = "verdana";
cell.Range.Font.Size = 10;
cell.Shading.BackgroundPatternColor = WdColor.wdColorGray25;
//Выравнивание текста в заголовках столбцов по центру
cell.VerticalAlignment =
WdCellVerticalAlignment.wdCellAlignVerticalCenter;
cell.Range.ParagraphFormat.Alignment =
WdParagraphAlignment.wdAlignParagraphCenter;
}
//Значения ячеек
else
{
cell.Range.Text = (cell.RowIndex - 2 + cell.ColumnIndex).ToString();
}
}
}
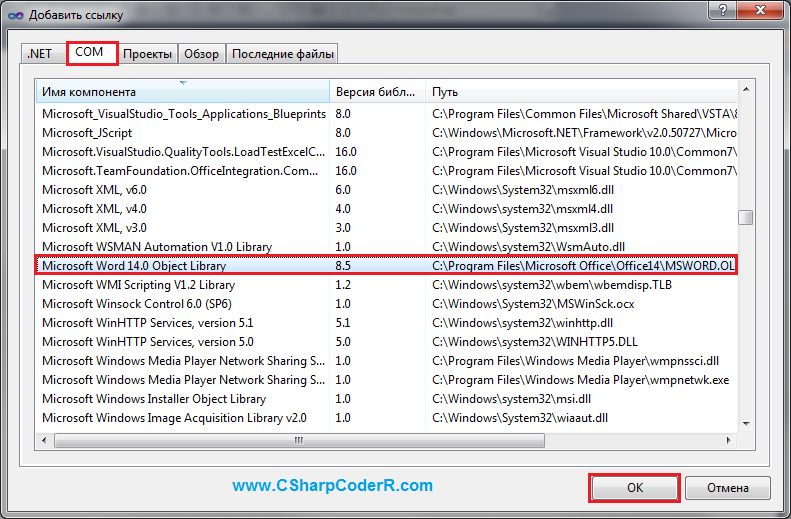
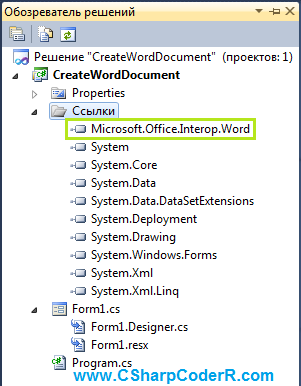
Для функционирования описанного выше кода, необходимо добавить к текущему проекту объектную библиотеку MS Word. Перейдите в меню «Проект» и выберете команду «Добавить ссылку» или в обозревателе решений, найдите пункт «Ссылки» и сделайте клик правой клавишей мыши по нему, из появившегося контекстного меню выберете соответствующий пункт.
В открывшемся окне «Добавить ссылку», перейдите на вкладку «COM» и выберете «Microsoft Word 14.0 Object Library» из предложенного списка библиотек.
В обозревателе решений у вас появится ссылка на данную библиотеку.
Перейдите в конструктор главной формы и добавьте из панели элементов, командную кнопку «Button». Данный элемент необходим для запуска процесса создания документа и вызов MS Word для отображения.
Сделайте двойной клик левой клавишей мыши по элементу «Button» и вы перейдете в автоматически созданный метод события «button1_Click». Добавьте в него приведенный ниже код.
try
{
Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word.Application winword =
new Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word.Application();
winword.Visible = false;
//Заголовок документа
winword.Documents.Application.Caption = "www.CSharpCoderR.com";
object missing = System.Reflection.Missing.Value;
//Создание нового документа
Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word.Document document =
winword.Documents.Add(ref missing, ref missing, ref missing, ref missing);
//добавление новой страницы
//winword.Selection.InsertNewPage();
//Добавление верхнего колонтитула
foreach (Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word.Section section in document.Sections)
{
Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word.Range headerRange = section.Headers[
Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word.WdHeaderFooterIndex.wdHeaderFooterPrimary].Range;
headerRange.Fields.Add(
headerRange, Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word.WdFieldType.wdFieldPage);
headerRange.ParagraphFormat.Alignment =
Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word.WdParagraphAlignment.wdAlignParagraphCenter;
headerRange.Font.ColorIndex =
Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word.WdColorIndex.wdBlue;
headerRange.Font.Size = 10;
headerRange.Text = "Верхний колонтитул" + Environment.NewLine + "www.CSharpCoderR.com";
}
//Добавление нижнего колонтитула
foreach (Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word.Section wordSection in document.Sections)
{
//
Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word.Range footerRange =
wordSection.Footers[Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word.WdHeaderFooterIndex.wdHeaderFooterPrimary].Range;
//Установка цвета текста
footerRange.Font.ColorIndex = Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word.WdColorIndex.wdDarkRed;
//Размер
footerRange.Font.Size = 10;
//Установка расположения по центру
footerRange.ParagraphFormat.Alignment =
Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word.WdParagraphAlignment.wdAlignParagraphCenter;
//Установка текста для вывода в нижнем колонтитуле
footerRange.Text = "Нижний колонтитул" + Environment.NewLine + "www.CSharpCoderR.com";
}
//Добавление текста в документ
document.Content.SetRange(0, 0);
document.Content.Text = "www.CSharpCoderR.com" + Environment.NewLine;
//Добавление текста со стилем Заголовок 1
Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word.Paragraph para1 = document.Content.Paragraphs.Add(ref missing);
object styleHeading1 = "Заголовок 1";
para1.Range.set_Style(styleHeading1);
para1.Range.Text = "Исходники по языку программирования CSharp";
para1.Range.InsertParagraphAfter();
//Создание таблицы 5х5
Table firstTable = document.Tables.Add(para1.Range, 5, 5, ref missing, ref missing);
firstTable.Borders.Enable = 1;
foreach (Row row in firstTable.Rows)
{
foreach (Cell cell in row.Cells)
{
//Заголовок таблицы
if (cell.RowIndex == 1)
{
cell.Range.Text = "Колонка " + cell.ColumnIndex.ToString();
cell.Range.Font.Bold = 1;
//Задаем шрифт и размер текста
cell.Range.Font.Name = "verdana";
cell.Range.Font.Size = 10;
cell.Shading.BackgroundPatternColor = WdColor.wdColorGray25;
//Выравнивание текста в заголовках столбцов по центру
cell.VerticalAlignment =
WdCellVerticalAlignment.wdCellAlignVerticalCenter;
cell.Range.ParagraphFormat.Alignment =
WdParagraphAlignment.wdAlignParagraphCenter;
}
//Значения ячеек
else
{
cell.Range.Text = (cell.RowIndex - 2 + cell.ColumnIndex).ToString();
}
}
}
winword.Visible = true;
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
MessageBox.Show(ex.Message);
}
Запустите ваш проект, нажав на клавиатуре, клавишу «F5». Нажмите на единственную кнопку, расположенную на главной форме вашего проекта. У вас автоматически откроется документ Microsoft Word с заполненным верхним и нижним колонтитулом, обычным и с применением стиля текстом, а так же заполненной таблицей.
Для сохранения документа в определенной директории, добавьте приведенный ниже код, после строки «winword.Visible = true;».
//Сохранение документа object filename = @"d:temp1.docx"; document.SaveAs(ref filename); //Закрытие текущего документа document.Close(ref missing, ref missing, ref missing); document = null; //Закрытие приложения Word winword.Quit(ref missing, ref missing, ref missing); winword = null;
При работе с приложением Word в памяти компьютера создается отдельный процесс, если его не закрыть или не вывести созданный документ на экран, то он будет работать до выключения компьютера. Так же при постоянной работе с такими документами, их процессы будут накапливаться незаметно для пользователя, что может привести к зависанию компьютера или другим последствиям.
Выбрать уже существующую таблицу внутри документа можно по ее порядковому номеру (начиная с 1 и начала документа) можно через интерфейс Tables. При этом мы получим объект типа Table
Word.Table _table = _document.Tables[tableNumber];
Новая вставляется методом Tables.Add (предполагается что мы уже получили диапазон _currentRange того места в документе, куда будем ее вставлять):
_table = _document.Tables.Add(_currentRange, numRows, numColumns, ref _missingObj, ref _missingObj);
и добавить к ней строки
_table.Rows.Add(ref _missingObj);
Тип границ для таблицы можно задать так:
_table.Borders.OutsideLineStyle = Word.WdLineStyle.wdLineStyleDouble; _table.Borders.InsideLineStyle = Word.WdLineStyle.wdLineStyleDouble;
Имея таблицу мы можем получить диапазон для конкретной ячейки по номеру строки/колонки через интерфейс Cell и делать с ним все описанное в предыдущих статьях:
_currentRange = _table.Cell(rowIndex, columnIndex).Range;
В том числе задать вертикальное выравнивание через перечисление WdCellVerticalAlignment
_table.Cell(rowIndex, columnIndex).VerticalAlignment = Word.WdCellVerticalAlignment.wdCellAlignVerticalTop;
Слить несколько ячеек в одну
_table.Rows[cellOneRowIndex].Cells[cellOneColIndex]. Merge(_table.Rows[cellTwoRowIndex].Cells[cellTwoColIndex]);
Или объединить все ячейки для строки
Word.Row row = _table.Rows[rowNum];
Word.Cell firstCell =row.Cells[1];
foreach(Word.Cell currCell in row.Cells)
{
if(currCell.ColumnIndex != firstCell.ColumnIndex)
{
firstCell.Merge(currCell);
}
}
- Работаем с MS Word из C#, часть 0, класс и тестовый проект-пример WinForms
- Работаем с MS Word из C#, часть 1. Открываем шаблон, ищем текст внутри документа
- Работаем с MS Word из C#, часть 2. Вставляем текст на закладку и форматируем
- Работаем с MS Word из C#, часть 3. Работа с таблицами
- Работаем с MS Word из C#, часть 4. Обьединяем несколько файлов в один, считаем количество страниц
- Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word Namespace
- Range Interface
- Rows Interface
|
1 / 1 / 0 Регистрация: 27.05.2019 Сообщений: 108 |
|
|
1 |
|
|
17.12.2021, 21:46. Показов 1742. Ответов 3
Добрый день! Помогите решить задачу используя именно Interop.Word На вход подается две DataTable и мне требуется объединить их в одну, при этом сделать шапку для каждой из таблиц. Разделение будет в виде объединенных 3-х ячеек и жирным текстом внутри «Первый блок» и «Второй блок» жирным текстом.
0 |
|
sfumatori 147 / 91 / 56 Регистрация: 03.02.2021 Сообщений: 274 |
||||
|
23.12.2021, 10:16 |
2 |
|||
|
Как-то так:
}
1 |
|
8927 / 4839 / 1885 Регистрация: 11.02.2013 Сообщений: 10,246 |
|
|
23.12.2021, 15:19 |
3 |
|
Как-то так: Зачем же использовать ActiveDocument, когда ссылка на документ уже находится в объекте doc?
0 |
|
147 / 91 / 56 Регистрация: 03.02.2021 Сообщений: 274 |
|
|
24.12.2021, 11:45 |
4 |
|
Это вы верно отметили, я начало кода дернул из проекта, который писал предыдущий программист
0 |