xlswrite
(Not recommended) Write Microsoft Excel spreadsheet file
Syntax
Description
example
xlswrite(filename,A)
writes matrix A to the first worksheet in the Microsoft®
Excel® spreadsheet workbook filename starting at cell
A1.
xlswrite(filename,A,sheet)
writes to the specified worksheet.
xlswrite(filename,A,xlRange)
writes to the rectangular region specified by xlRange in the
first worksheet of the workbook. Use Excel range syntax, such as 'A1:C3'.
example
xlswrite(filename,A,sheet,xlRange)
writes to the specified worksheet and range.
status = xlswrite(___)
returns the status of the write operation, using any of the input arguments in
previous syntaxes. When the operation is successful, status is
1. Otherwise, status is 0.
[status,message]
= xlswrite(___)
additionally returns any warning or error message generated by the write
operation in structure message.
Examples
collapse all
Write Vector to Spreadsheet
Write a 7-element vector to an Excel® file.
filename = 'testdata.xlsx';
A = [12.7 5.02 -98 63.9 0 -.2 56];
xlswrite(filename,A)
Write to Specific Sheet and Range in Spreadsheet
Write mixed text and numeric data to an Excel® file starting at cell E1 of Sheet2.
filename = 'testdata.xlsx'; A = {'Time','Temperature'; 12,98; 13,99; 14,97}; sheet = 2; xlRange = 'E1'; xlswrite(filename,A,sheet,xlRange)
Input Arguments
collapse all
filename — File name
character vector | string
File name, specified as a character vector or a string.
If filename does not exist, xlswrite
creates a file, determining the format based on the specified extension. To
create a file compatible with Excel 97-2003 software, specify an extension of
.xls. To create files in Excel 2007 formats, specify an extension of
.xlsx, .xlsb, or
.xlsm. If you do not specify an extension,
xlswrite uses the default,
.xls.
Example: 'myFile.xlsx' or
"myFile.xlsx"
Example: 'C:myFoldermyFile.xlsx'
Example: 'myFile.csv'
Data Types: char | string
A — Input matrix
matrix
Input matrix, specified as a two-dimensional numeric, character array, or
string array, or, if each cell contains a single element, a cell
array.
If A is a cell array containing something other than a
scalar numeric or text, then xlswrite silently leaves the
corresponding cell in the spreadsheet empty.
The maximum size of array A depends on the associated
Excel version. For more information on Excel specifications and limits, see the Excel help.
Example: [10,2,45;-32,478,50]
Example: {92.0,'Yes',45.9,'No'}
Example: "ABCDEF"
Data Types: single | double | int8 | int16 | int32 | int64 | uint8 | uint16 | uint32 | uint64 | logical | char | string | cell
sheet — Worksheet name
character vector | string | positive integer
Worksheet name, specified as one of the following:
-
Character vector or string that contains the worksheet name. The
name cannot contain a colon (:). To determine the
names of the sheets in a spreadsheet file, use
xlsfinfo. -
Positive integer that indicates the worksheet index.
If sheet does not exist, xlswrite
adds a new sheet at the end of the worksheet collection. If
sheet is an index larger than the number of
worksheets, xlswrite appends empty sheets until the
number of worksheets in the workbook equals sheet. In
either case, xlswrite generates a warning indicating that
it has added a new worksheet.
Data Types: char | string | single | double | int8 | int16 | int32 | int64 | uint8 | uint16 | uint32 | uint64
xlRange — Rectangular range
character vector | string
Rectangular range, specified as a character vector or a string.
Specify xlRange using two opposing corners that define
the region to write. For example, 'D2:H4' represents the
3-by-5 rectangular region between the two corners D2 and
H4 on the worksheet. The xlRange
input is not case sensitive, and uses Excel A1 reference style (see Excel help). xlswrite does not recognize named
ranges.
-
If you do not specify
sheet, then
xlRangemust include both corners and a colon
character, even for a single cell (such as
'D2:D2'). Otherwise,
xlswriteinterprets the input as a worksheet
name (such as'D2'). -
If you specify
sheet, then
xlRangecan specify only the first cell (such
as'D2').xlswritewrites
input arrayAbeginning at this cell. -
If
xlRangeis larger than the size of input
arrayA, Excel software fills the remainder of the region with
#N/A. IfxlRangeis
smaller than the size ofA, then
xlswritewrites only the subset that fits
intoxlRangeto the file.
Data Types: char | string
Output Arguments
collapse all
status — Status of the write operation
1 | 0
Status of the write operation, returned as either 1
(true) or 0
(false). When the write operation is successful,
status is 1. Otherwise,
status is 0.
message — Error or warning generated during the write operation
structure array
Error or warning generated during the write operation, returned as a
structure array containing two fields:
message |
Text of the warning or error message. |
identifier |
Message identifier. |
Limitations
-
The
xlswritefunction does not support writing cell arrays
that contain different data types when attempting to write CSV files. -
If your computer does not have Excel for Windows® or you are using MATLAB®
Online™, then thexlswritefunction:-
Writes array
Ato a text file in
comma-separated value (CSV) format.Amust be a
numeric matrix. -
Ignores the
sheetand
xlRangearguments.
This limitation also applies when the COM server (part of the
typical installation of Excel) is not available. -
Tips
-
If your computer has Microsoft Office 2003 software, but you want to create a file in an
Excel 2007 format, install the Office 2007 Compatibility Pack. -
Excel and MATLAB can store dates as text that represents those dates (such as
'10/31/96') or serial date numbers (such as
729329). If your array includes serial date numbers,
convert these dates to their text representation usingdatestrbefore calling
xlswrite. -
To write data to Excel files with custom formats (such as fonts or colors), access the
Windows COM server directly usingactxserverrather than
xlswrite. For example, this MathWorks Support Answer usesactxserverto
establish a connection between MATLAB and Excel, writes data to a worksheet, and specifies the colors of the
cells.
Algorithms
Excel converts Inf values to 65535.
MATLAB converts NaN values to empty cells.
Version History
Introduced before R2006a
expand all
R2019a: xlswrite is not recommended
xlswrite is not recommended. Use writetable, writematrix, or writecell instead. There are no plans to remove
xlswrite.
Starting in R2019a, use writetable,
writematrix, or writecell instead. The
writetable, writematrix, and
writecell functions have better cross-platform support and
performance over the xlswrite function.
This table shows typical usages of xlswrite and how to update
your code to use writetable, writematrix, or
writecell instead.
|
Not Recommended |
Recommended |
|---|---|
xlswrite(filename,M) |
To write tabular data to spreadsheets, use one of these Write a writetable(T,filename) Write writematrix(M,filename) Write writecell(C,filename) |
Write Tabular Data to Spreadsheet File
To export a table in the workspace to a Microsoft® Excel® spreadsheet file, use the writetable function. You can export data from the workspace to any worksheet in the file, and to any location within that worksheet. By default, writetable writes your table data to the first worksheet in the file, starting at cell A1.
For example, create a sample table of column-oriented data and display the first five rows.
load patients.mat
T = table(LastName,Age,Weight,Smoker);
T(1:5,:)
ans=5×4 table
LastName Age Weight Smoker
____________ ___ ______ ______
{'Smith' } 38 176 true
{'Johnson' } 43 163 false
{'Williams'} 38 131 false
{'Jones' } 40 133 false
{'Brown' } 49 119 false
Write table T to the first sheet in a new spreadsheet file named patientdata.xlsx, starting at cell D1. To specify the portion of the worksheet you want to write to, use the Range name-value pair argument. By default, writetable writes the table variable names as column headings in the spreadsheet file.
filename = 'patientdata.xlsx'; writetable(T,filename,'Sheet',1,'Range','D1')
Write the table T without the variable names to a new sheet called 'MyNewSheet'. To write the data without the variable names, specify the name-value pair WriteVariableNames as false.
writetable(T,filename,'Sheet','MyNewSheet','WriteVariableNames',false);
Write Numeric and Text Data to Spreadsheet File
To export a numeric array and a cell array to a Microsoft®
Excel® spreadsheet file, use the writematrix or
writecell functions. You can export data in individual
numeric and text workspace variables to any worksheet in the file, and to any
location within that worksheet. By default, the import functions write your
matrix data to the first worksheet in the file, starting at cell
A1.
For example, create a sample array of numeric data, A,
and a sample cell array of text and numeric data,
C.
A = magic(5)
C = {'Time', 'Temp'; 12 98; 13 'x'; 14 97}
A =
17 24 1 8 15
23 5 7 14 16
4 6 13 20 22
10 12 19 21 3
11 18 25 2 9
C =
'Time' 'Temp'
[ 12] [ 98]
[ 13] 'x'
[ 14] [ 97]
Write array A to the 5-by-5 rectangular region,
E1:I5, on the first sheet in a new spreadsheet file
named testdata.xlsx.
filename = 'testdata.xlsx'; writematrix(A,filename,'Sheet',1,'Range','E1:I5')
Write cell array C to a rectangular region that starts
at cell B2 on a worksheet named
Temperatures. You can specify range using only the
first cell.
writecell(C,filename,'Sheet','Temperatures','Range','B2');
writecell displays a warning because the worksheet,
Temperatures, did not previously exist, but you can
disable this warning.
Disable Warning When Adding New Worksheet
If the target worksheet does not exist in the file, then the
writetable and writecell functions display
this warning:
Warning: Added specified worksheet.
For information on how to suppress warning messages, see Suppress Warnings.
Format Cells in Excel Files
To write data to Excel files on Windows® systems with custom formats (such as fonts or colors), access the COM
server directly using actxserver rather than
writetable, writetimetable,
writematrix, or writecell. For example,
Technical Solution 1-QLD4K uses actxserver to
establish a connection between MATLAB® and Excel, write data to a worksheet, and specify the colors of the
cells.
For more information, see Get Started with COM.
See Also
writematrix | writecell | writetable
MATLAB provides options to write a table, array, or matrix to Microsoft Excel spreadsheets. The function available to do so is the writetable () function. The general syntax for this function is:
Syntax:
writetable(<data>, <filename>, <optional_values>)
Now, in the following sections, we shall see how to write a table, an array, and a matrix into a spreadsheet.
Writing a Table to Excel Spreadsheet:
Firstly, we shall create a table and then write the same to an excel spreadsheet with the help of writetable function.
Example 1:
Matlab
tab = magic(5);
tab = array2table(tab,"VariableNames",
["R1" "R2" "R3" "R4" "R5"]);
disp(tab)
writetable(tab,'new.xls','FileType','spreadsheet')
The output of the above code will create a new excel sheet in the current folder.
In the above code, we create a table from magic with the variable names or table headers passed as a vector. Then, in the writetable function, we pass the table, and the file name to be used (if present then, it’ll overwrite the data. If not, then it will create a new file and then, it’ll create a new file). The next argument is a field type that decides the file type and the argument following it is the value for the same field; spreadsheet in this case.
Writing a Matrix to Excel Spreadsheet
In the above section, we discussed how to add a table to an excel sheet. In this section, we shall explore the writetable further by adding a matrix at specified cells in a spreadsheet. Let us see the same with the help of an example.
To write numeric data into an excel sheet, we need can use the writetable function. We have to use another function, the writematrix function.
writematrix(<data>, <filename>, <optional_values>)
The syntax is the same as the writetable just the datatype changes to double, float, or int.
Example 2:
Matlab
tab = magic(5);
writematrix(tab,'new.xls','Sheet',2,'Range','C1')
Output:
In this code, we write the magic square matrix to an excel spreadsheet named new.xls. The following arguments define the sheet number and the starting cell where we want to write our matrix-formed data.
Writing a cell array (array of multiple data types) to an excel spreadsheet
To write an array with both numeric and text data, we use the writecell() function. The syntax of the same is similar to writematrix and writetable however, the data type then changes to a cell array.
writecell(<data>, <filename>, <optional_values>)
In the following example, we will write a cell array to a new sheet in our new.xls spreadsheet.
Example 3:
Matlab
arr = {'cell', 'array'; 1, 2; 23, 31};
writecell(arr,'new.xls','Sheet',3,'Range','C1:E2')
Output:
In this code, we are writing a 3×3 cell array to the spreadsheet in sheet 3 from a range of cells C1 to E2, this means that only as many elements as are specified in the range C1:E2.
(Не рекомендуемый) файл электронной таблицы Write Microsoft Excel
Синтаксис
Описание
пример
xlswrite( матрица записей filename,A)A к первому рабочему листу в Microsoft® Excel® рабочая книга электронной таблицы filename запуск в ячейке A1.
xlswrite( записи к заданному рабочему листу.filename,A,sheet)
xlswrite( записи в прямоугольную область заданы filename,A,xlRange)xlRange в первом рабочем листе рабочей книги. Используйте синтаксис области значений Excel, такой как 'A1:C3'.
пример
xlswrite( записи к заданному рабочему листу и области значений.filename,A,sheet,xlRange)
status = xlswrite(___)1. В противном случае состоянием является 0.
[ дополнительно возвращает любое предупреждающее сообщение или сообщение об ошибке, сгенерированное операцией записи в структуре status,message]
= xlswrite(___)message.
Примеры
свернуть все
Запись вектора в электронную таблицу
Запишите вектор с 7 элементами в файл Excel®.
filename = 'testdata.xlsx';
A = [12.7 5.02 -98 63.9 0 -.2 56];
xlswrite(filename,A)
Запись в определенный лист и область значений в электронной таблице
Запишите смешанные текстовые и числовые данные в файл Excel®, запускающийся в ячейке E1 из Sheet2.
filename = 'testdata.xlsx'; A = {'Time','Temperature'; 12,98; 13,99; 14,97}; sheet = 2; xlRange = 'E1'; xlswrite(filename,A,sheet,xlRange)
Входные параметры
свернуть все
filename FileName
вектор символов | строка
Имя файла в виде вектора символов или строки.
Если filename не существует, xlswrite создает файл, определяя формат на основе заданного расширения. Чтобы создать файл, совместимый с программным обеспечением Excel 97-2003, задайте расширение .xls. Чтобы создать файлы в форматах Excel 2007, задайте расширение .xlsx, .xlsb, или .xlsm. Если вы не задаете расширение, xlswrite использует значение по умолчанию, .xls.
Пример: 'myFile.xlsx' или "myFile.xlsx"
Пример: 'C:myFoldermyFile.xlsx'
Пример: 'myFile.csv'
Типы данных: char | string
A — Введите матрицу
матрица
Введите матрицу в виде двумерного числового, символьного массива или массива строк, или, если каждая ячейка содержит один элемент, массив ячеек.
Если A массив ячеек, содержащий что-то другое, чем числовой скаляр или текст, затем xlswrite тихо оставляет соответствующую ячейку в электронной таблице пустой.
Максимальный размер массива A зависит от связанной версии Excel. Для получения дополнительной информации о технических требованиях Excel и пределах, смотрите справку Excel.
Пример: [10,2,45;-32,478,50]
Пример: {92.0,'Yes',45.9,'No'}
Пример: "ABCDEF"
Типы данных: single | double | int8 | int16 | int32 | int64 | uint8 | uint16 | uint32 | uint64 | logical | char | string | cell
sheet — Имя рабочего листа
вектор символов | представляет в виде строки | положительное целое число
Имя рабочего листа в виде одного из следующего:
-
Вектор символов или строка, которая содержит имя рабочего листа. Имя не может содержать двоеточие (
:). Чтобы определить имена листов в файле электронной таблицы, используйтеxlsfinfo. -
Положительное целое число, которое указывает на индекс рабочего листа.
Если sheet не существует, xlswrite добавляет новый лист в конце набора рабочего листа. Если sheet индекс, больше, чем количество рабочих листов, xlswrite добавляет пустые листы, пока количество рабочих листов в рабочей книге не равняется sheet. В любом случае, xlswrite генерирует предупреждение, указывающее, что оно добавило новый рабочий лист.
Типы данных: char | string | single | double | int8 | int16 | int32 | int64 | uint8 | uint16 | uint32 | uint64
xlRange — Прямоугольная область значений
вектор символов | строка
Прямоугольная область значений в виде вектора символов или строки.
Задайте xlRange использование двух противостоящих углов, которые задают область, чтобы записать. Например, 'D2:H4' представляет прямоугольную область 3 на 5 между этими двумя углами D2 и H4 на рабочем листе. xlRange вход не является чувствительным к регистру, и использует стиль ссылки Excel A1 (см. справку Excel). xlswrite не распознает названные области значений.
-
Если вы не задаете
sheet, затемxlRangeдолжен включать оба угла и символ двоеточия, даже для отдельной ячейки (такие как'D2:D2'). В противном случае,xlswriteинтерпретирует вход как имя рабочего листа (такое как'D2'). -
Если вы задаете
sheet, затемxlRangeможет задать только первую ячейку (такую как'D2'xlswriteвходной массив записейAначало в этой ячейке. -
Если
xlRangeбольше, чем размер входного массиваA, Программное обеспечение Excel заполняет остаток от области с#N/A. ЕслиxlRangeменьше, чем размерA, затемxlswriteзаписи только подмножество, которое помещаетсяв xlRangeк файлу.
Типы данных: char | string
Выходные аргументы
свернуть все
status — Состояние операции записи
1
Состояние операции записи, возвращенной как любой 1 TRUE) или 0 ложь). Когда операция записи успешна, status 1. В противном случае, status 0.
message — Ошибка или предупреждение сгенерированного во время операции записи
массив структур
Ошибка или предупреждение сгенерированного во время операции записи, возвращенной как массив структур, содержащий два поля:
message |
Текст предупреждающего сообщения или сообщения об ошибке. |
identifier |
Идентификатор сообщения. |
Ограничения
-
xlswriteфункция не поддерживает массивы ячеек записи, которые содержат различные типы данных при попытке записать файлы CSV. -
Если ваш компьютер не имеет Excel для Windows® или вы используете MATLAB® Online™, затем
xlswriteфункция:-
Массив записей
Aк текстовому файлу в формате разделенного от запятой значения (CSV).Aдолжна быть числовая матрица. -
Игнорирует
sheetиxlRangeаргументы.
Это ограничение также применяется, когда сервер COM (часть типовой установки Excel) не доступен.
-
Советы
-
Если ваш компьютер имеет программное обеспечение Microsoft Office 2003, но вы хотите создать файл в формате Excel 2007, установить Пакет Совместимости Office 2007.
-
Excel и MATLAB могут сохранить даты как текст, который представляет те даты (такие как
'10/31/96') или последовательные числа даты (такие как729329). Если ваш массив включает последовательные числа даты, преобразуйте эти даты в их текстовое использование представленияdatestrпрежде, чем вызватьxlswrite. -
Чтобы записать данные к файлам Excel с пользовательскими форматами (такими как шрифты или цвета), получите доступ к серверу Windows COM непосредственно с помощью
actxserverвместоxlswrite. Например, этот MathWorks Support Answer используетactxserverустановить связь между MATLAB и Excel, записывает данные к рабочему листу и задает цвета ячеек.
Алгоритмы
Excel преобразует Inf значения к 65535. MATLAB преобразует NaN значения к пустым ячейкам.
Вопросы совместимости
развернуть все
xlswrite не рекомендуется
Не рекомендуемый запуск в R2019a
xlswrite не рекомендуется. Использование writetable, writematrix, или writecell вместо этого. Нет никаких планов удалить xlswrite.
При запуске в R2019a используйте writetable, writematrix, или writecell вместо этого. writetable, writematrix, и writecell функции имеют лучшую кросс-платформенную поддержку и эффективность по xlswrite функция.
Эта таблица показывает типичные использования xlswrite и как обновить ваш код, чтобы использовать writetable, writematrix, или writecell вместо этого.
|
Не рекомендуемый |
Рекомендуемый |
|---|---|
xlswrite(filename,M) |
Чтобы записать табличные данные в электронные таблицы, используйте одну из этих опций вместо этого. Запишите таблицу: writetable(T,filename) Запишите матрицу: writematrix(M,filename) Запишите массив ячеек: writecell(C,filename) |
Представлено до R2006a
Introduction to Matlab xlswrite
Xls command is basically used for excel file operations, and xlswrite is used to write or interprets an excel file. Along with the command, we can give the file name whatever we want and decide or select which sheet we want for writing. There is one more parameter range that decides the limit of rows and columns which is to be used. In this topic, we are going to learn about Matlab xlswrite.
Syntax:
- xlswrite(filename, A)
- xlswrite(filename, A, sheet, xlRange )
How Does Xlswrite Functions Work in Matlab?
To write data on a Microsoft Excel worksheet, we use an xlswrite statement. A filename statement is used for the unique identification of the file. After the identification of the file, the data will be written to the Microsoft Excel worksheet with the help of the ‘xlswrite’ function.
The steps for writing data on Microsoft Excel worksheet using an xlswrite statement:-
Step 1: First, identify the file using the ‘filename’ statement.
Step 2: Then, we take input data into a variable
Step 3: Then, we use an xlswrite statement with proper syntax for writing data to Microsoft
Excel worksheet
Step 4: After executing the code in Matlab, the data is stored in a Microsoft Excel worksheet
Examples of Matlab xlswrite
Given below are the examples of Matlab xlswrite:
Example #1
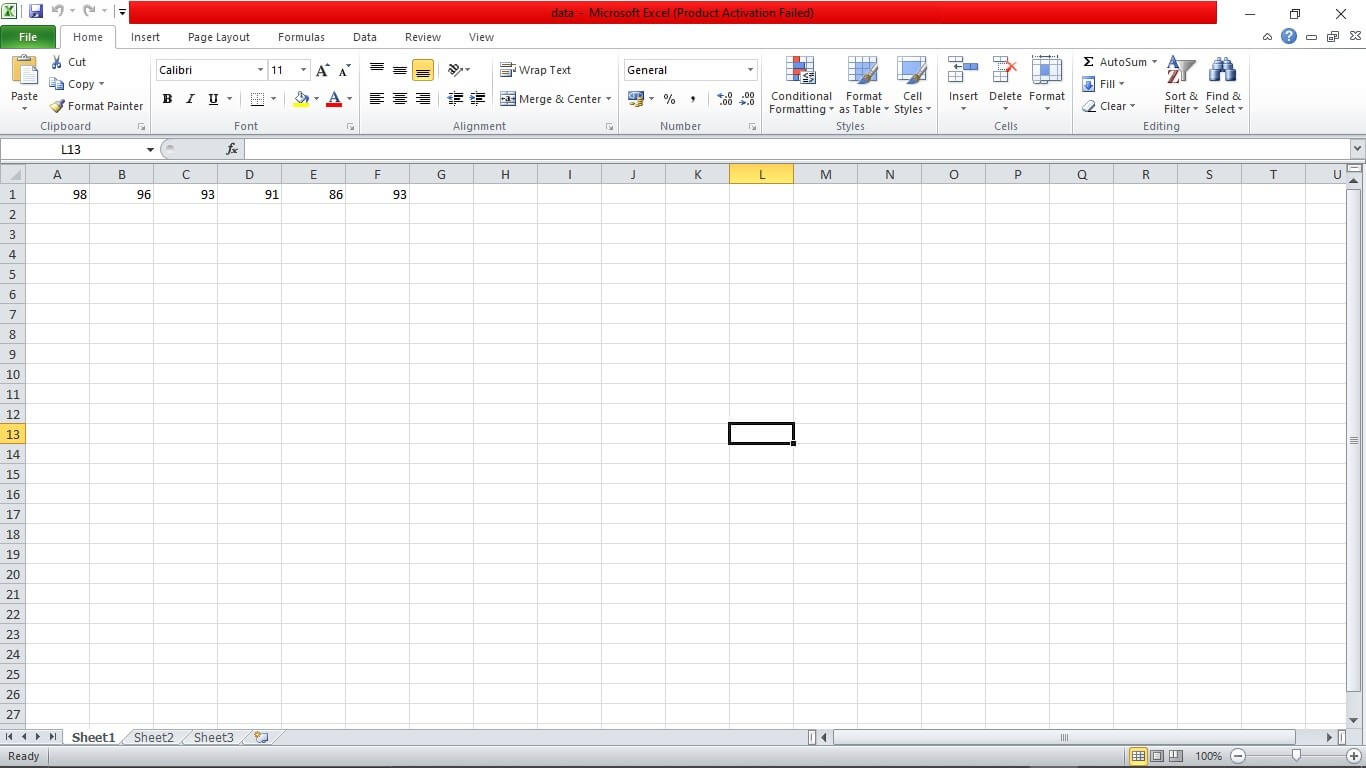
Let us see a simple example of the xlswrite statement. Basically, xlswrite is used to write data to the Microsoft Excel worksheet. For writing data on the Microsoft Excel worksheet, we use an xlswrite statement with proper syntax. A filename statement is used for the unique identification of the file. We use “filename = ‘data.xlsx’” to identification of the ‘data.xlsx’ file. The file with the ‘xlsx’ extension is nothing but a Microsoft Excel worksheet. We create a Microsoft Excel file with the name ‘data.xlsx’. Then we take a variable to store the input arguments. So we take a variable, namely D, and the input arguments are loaded into the variable. D = [98 96 93 91 86 93] it assign the input values to the variable D. Now, we can write the data into the Microsoft Excel worksheet. To write the data, we use the xlswrite function. For the writing into the Excel file, “xlswrite(filename, D)” syntax is used. After executing the file, the input data is written into the Microsoft Excel worksheet.
Code:
clc;
clear all;
close all;
filename = 'data.xlsx';
D = [98 96 93 91 86 93 ];
xlswrite(filename,D)
Output:
Command window:
Example #2
Let us see another example of the xlswrite statement. As we know, the xlswrite is used to write data to the Microsoft Excel worksheet. In this example, we can write the data to the specific address and the specific sheet also. In this example, we take readings for the voltage and frequency of the signal. Here ‘filename’ statement is used to the unique identification of the file. We use “filename = ‘readings.xlsx’ ” to identification of the ‘readings.xlsx’ file. The file with the ‘xlsx’ extension is nothing but a Microsoft Excel worksheet. We create a Microsoft Excel file with the name ‘data.xlsx’. Then we take a variable to store the input arguments. So we take a variable, namely G, and the input arguments are loaded into the variableG = {‘VOLTAGE’, ‘FREQUENCY’; 200,98; 225,99; 223,97} it assigns the input values to the variable G. Now, we can select the sheet by using the syntax. Here we used a simple syntax “sheet = 2;” to select the second sheet. The xlRange function is used to give a specific location for the start of writing. Now we can write the data into the Microsoft Excel worksheet. To write the data, we use the xlswrite function. “xlswrite(filename, G, sheet,xlRange)“ this line is used to write the input data to the Microsoft Excel worksheet. After executing the file, the readings are written into the given Microsoft Excel worksheet.
Code:
clc;
clear all;
close all;
filename = 'readings.xlsx';
G = {'VOLTAGE','FREQUENCY'; 200,98; 225,99; 223,97};
sheet = 2;
xlRange = 'D1';
xlswrite(filename,G,sheet,xlRange)
Output:
Command window:
Example #3
Let us see one more example of an xlswrite statement. In this example, we can write the data of the variable to the Microsoft Excel worksheet. In this example, we use the path to identify the file. Here we directly identify the Excel file. So first, we take one variable, namely b. Random data is stored into the variable b. After that, we use the xlswrite statement to write the data to the Excel file.
xlswrite(‘C:Userswin-10Desktoptemp.xlsx’,b,’ D5:m15′) is used to write the data stored into the variable b to the specified Excel file that is “temp.xlsx”. D5 and m15 are the starting and ending points for writing the data. After executing the code, the data into the variable b is written into the given Microsoft Excel worksheet with specified starting and ending points.
Code:
clc;
clear all;
close all;
b= rand(10);
xlswrite('C:Userswin-10Desktoptemp.xlsx',b,'D5:m15');
Output:
Command window:
Conclusion
In this article, we have seen the concept of xlswrite; basically, xlswrite is used to write data to the Microsoft Excel worksheet file along with customized parameters and default parameters. Then we saw syntax related to xlswrite statements to generate a database in Matlab code.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Matlab xlswrite. Here we discuss How Does Xlswrite Functions Work in Matlab and Examples along with the codes and outputs. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –
- Matlab fopen
- Strcmp Matlab
- Matlab trapz()
- Low Pass Filter Matlab