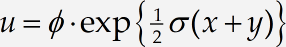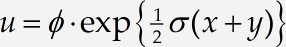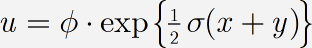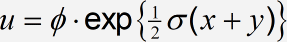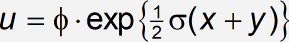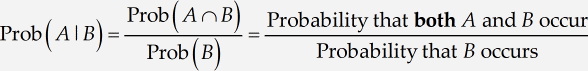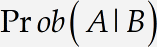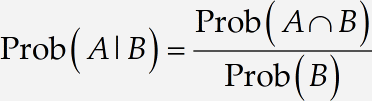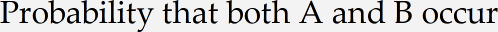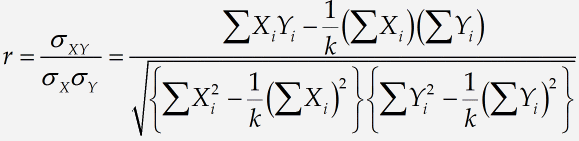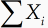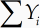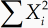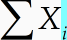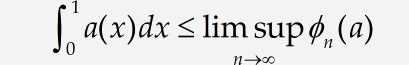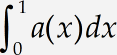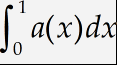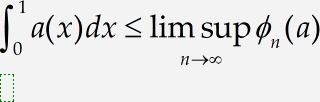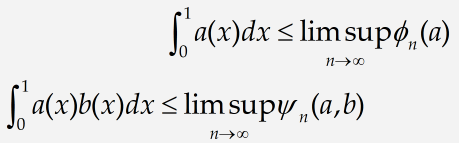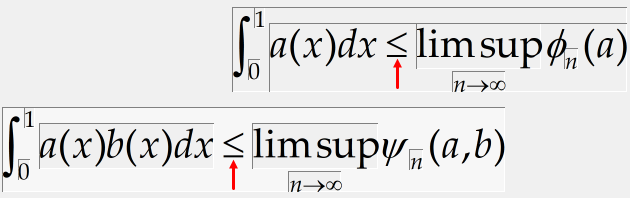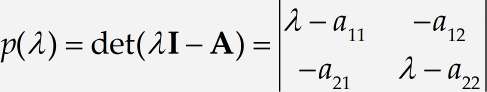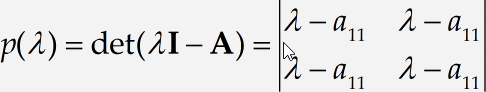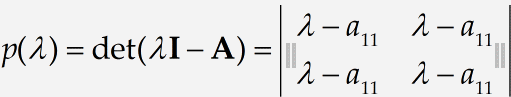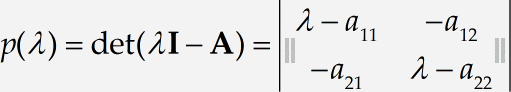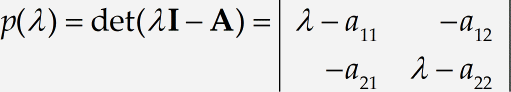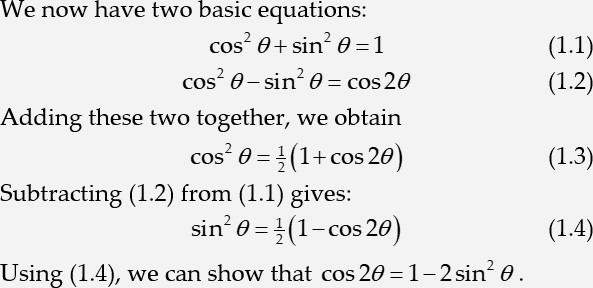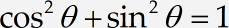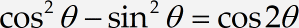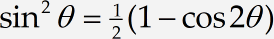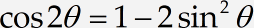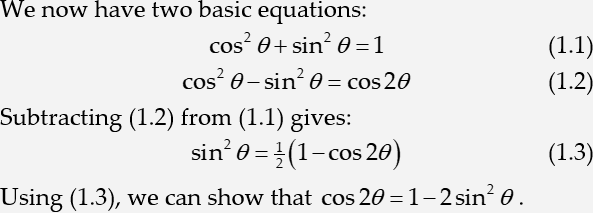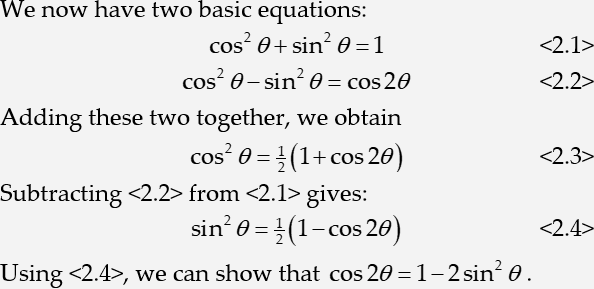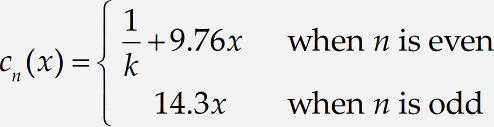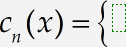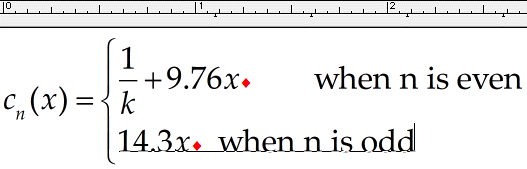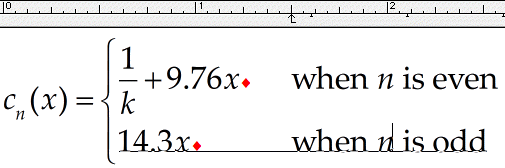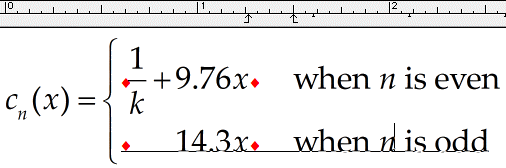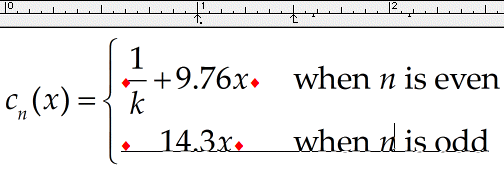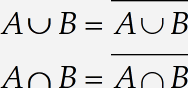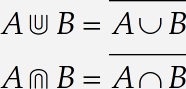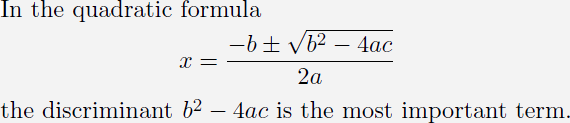Визуальные редакторы
Команды в этом меню назначают размер текущему выделению или последующим типизированным символам.
Текущий размер или размер выделенного фрагмента (если все они одного размера) отображается в Строке состояния (в разделе Size).
Full — Полный. — Назначает полный размер выбранным символам или символам, которые вы вводите впоследствии.
Subscript — Назначает размер подстрочного индекса выбранным символам или символам, которые вы вводите впоследствии.
Sub-subscript — Назначает размер подстрочного типа либо выбранным символам, либо символам, которые вы вводите впоследствии.
Symbol — Назначает размер типа символа выбранным символам или символам, которые вы вводите впоследствии.
Sub-symbol – Назначает мелкий размер символа либо выбранных символов или символы, которые вы вводите в дальнейшем.
User 1 (Пользовательский 1) — Размер yазначается пользователем для выбранных символов, либо для символов, которые вы вводите впоследствии.
User 2 (Пользовательский 2) — Размер yазначается пользователем для выбранных символов, либо для символов, которые вы вводите впоследствии.
Other — Другое. — открывает диалоговое окно другого размера, в котором можно ввести определенный размер шрифта в пунктах.
Smaller — Уменьшить. Ctrl + Shift + < / ⌘+Shift + < — уменьшает размер выделенных символов на 1 пункт (этот шаг можно изменить в диалоговом окне определения размеров).
Larger — Увеличить. Ctrl + Shift + > / ⌘+Shift+> — увеличивает размер выделенных символов на 1 пункт (этот шаг можно изменить в диалоговом окне определения размеров).
Reset Smaller/Larger . Сброс Уменьшить / Увеличить. — Сброс размера выбранных символов до их исходного размера. Отмена эффекта от использования команд Smaller или Larger .
Define — эта команда открывает диалоговое окно определения размеров, позволяющее изменить определенный размер точек, назначенный каждому размеру для всего уравнения или для новых уравнений.
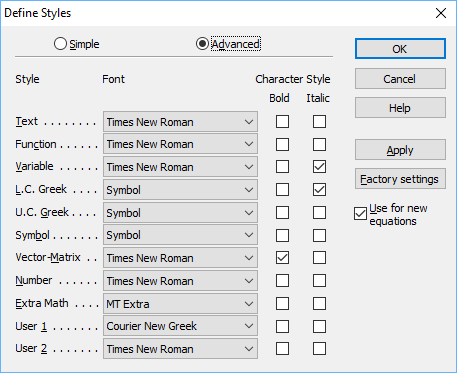
Define Sizes (Окно определения размеров)
Это диалоговое окно используется для просмотра и/или изменения абсолютных или относительных размеров, назначенных типизациям для всего выражения или для новых выражений.
Щелкните одно из значений typesize, чтобы просмотреть описательное изображение справа, которое дает представление о том, где конкретный размер будет использоваться в уравнениях.
Изменение основного размера шрифта уравнений
Основной размер шрифта уравнения — это размер точки, используемый для большей части уравнения, в отличие от размера, используемого для индексов и больших символов, таких как знаки суммирования и интегралы. В системе, набранных в mathtype из typesizes, основной размер шрифта называется Full size — Полный размер.
Чтобы упростить изменение размера шрифта уравнений в целом без изменения пропорций между различными размерами, MathType позволяет определить все остальные типы в процентах от полного размера.
Таким образом, чтобы изменить размер уравнения в целом, вы можете просто ввести новый размер точки для полного размера, и все остальные типы будут изменены относительно него.
Если вы хотите назначить размеры, которые не относятся к полному размеру, вы можете назначить absolute sizes — абсолютные размеры для любого или всех типов в дюймах, сантиметрах, точках или пик.
Use for new equations Использовать для новых уравнений
Если этот флажок установлен, размеры будут изменены как для текущего уравнения, так и для новых уравнений, создаваемых с этого момента (см. New Equation Preferences ). Если этот флажок снят, параметры размера будут влиять только на текущее уравнение.
Default Settings настройка по умолчанию
Нажмите эту кнопку, чтобы восстановить значения по умолчанию для размеров в этом диалоговом окне.
Exponenta.ru
1. Изменяем размер шрифта в первой из формул
2. Закрываем окно программы с формулой и сохраняем изменения
3. Далее в панели инструментов находим вкладку “MathType” и выбираем там “Format Equations…”.
4. Выбираем по картинке ниже
5. В итоге получаем обновление данных во всех формулах в документе 
Как выровнять формулы в Word?
Написан текст, и вставлена формула через Mathtype. Как сделать так, что бы буквы и символы в этой формуле примерно были размером как весь основной текст? В основном это приходится делать «тянув» за уголок формулы, что уменьшить ее. но есть ли другой способ?
У пользователей программы Microsoft Word при работе с формулами чаще всего бывают 2 проблемы:
1) Несовпадение шрифтов самой формулы и основного текста.
2) При нумерации формул нужно, чтобы формула была выровнена по центру, а номер — по правому краю.
В элементах MathType используется шрифт Cambria Math, поэтому изначально печатаемые формулы имеют немного другой внешний вид по сравнению с основным текстом.
Чтобы сделать внешний вид формул и текста примерно одинаковым, нужно изменить шрифт и его размер в самой формуле.
Например, в последних версиях Ворда это можно сделать в меню объекта MathType — раздел «Размер» -> «Определить». Откроется окно, где вы можете указать нужный вам размер всех элементов формулы.
Кроме того, нередко требуется нумеровать формулы так, чтобы сама формула была по центру, а номер был выравнен по правому краю. Подобное выравнивание формул можно сделать разными способами:
1) Можно использовать табуляцию и дополнительные пробелы.
2) Также есть вариант с таблицей, имеющей невидимые границы и опцию «Автоподбор по ширине окна». В ней должно быть 3 столбца — 1 столбец пустой, в центральном столбце пишем формулу и выравниваем её по центру, в правом столбце пишем номер формулы и делаем выравнивание по правому краю.
Fonts and styles
This tutorial introduces MathType system of styles. We will demonstrate how to change the fonts in your equations by changing style definitions. Using styles will allow you to achieve the formatting you want quickly and easily and enable you to create equations with a consistent appearance. See the Style menu for more information about styles, fonts and sizes.
In the following steps, we will create the equation
and experiment with changing the look of the equation by using different style definitions. This animation shows a summary of what you’ll be doing in this tutorial:
Make sure you’re in Math style
Verify the Status Bar’s Style panel displays «Math». If it doesn’t, choose Math from the Style menu. If MathType current style isn’t Math , its automatic style assignment will not be in effect, and the rest of this tutorial will not make much sense.
Create the equation
Create the equation, using the reduced-size fraction template for the fraction and inserting ϕ and σ by choosing them from the lowercase Greek palette, or by using the Ctrl+G / Command+G shortcut. (If you use the shortcut, remember after pressing the initial shortcut – Ctrl+G / Command+G – you must then press the letter associated with the Greek symbol you want). In this case, that’s either f or s, respectively.) The • operator is located on the 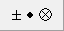
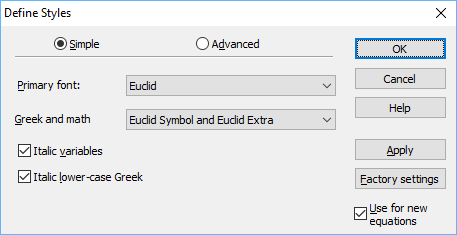
Define the styles
From the Style menu, choose Define. If necessary, click the Simple button to display this dialogue:
Change the «Primary font» to Euclid, change the «Greek and math fonts» to Euclid Symbol and Euclid Extra, as shown in the dialogue above, and click Apply. On-screen, your equation will now look like this:
The Euclid fonts supplied with MathType are based on the Computer Modern fonts typically used with TeX, so they give your documents a TeX-like appearance that you might prefer for some types of work. Another benefit of the Euclid fonts is that their regular and Greek characters are consistent, whereas Times and Symbol are mismatched. Of course, if you use the Euclid fonts in your equations, you will probably want to use Euclid as the primary body font in your word processing document, too.
Caution
We’ve included a MathType Preference File named TeXLook.eqp contains font and spacing settings that make MathType equations look like TeX. It’s in the Preferences folder inside your MathType folder. See the Preferences menu for more details on using preference files.
Return to Default Settings
If the Define Styles dialogue isn’t still open, open it. Click Default Settings (some versions: «Defaults»; others, «Factory settings») to return to using the Times New Roman and Symbol fonts.
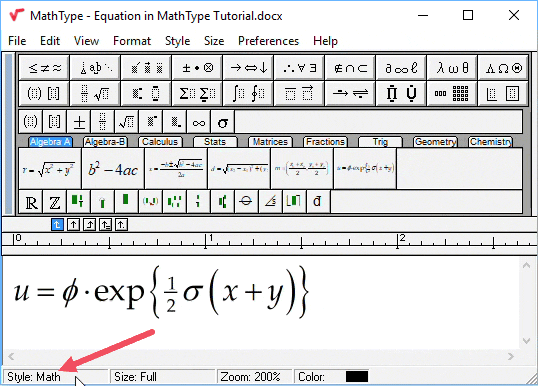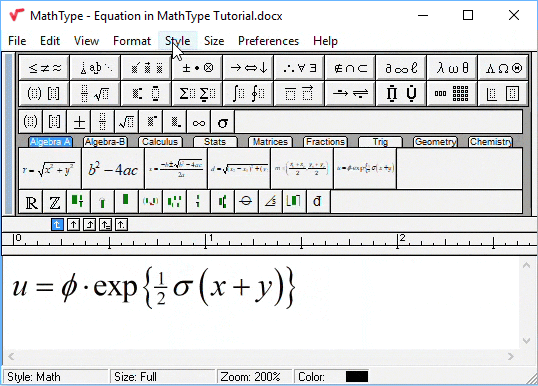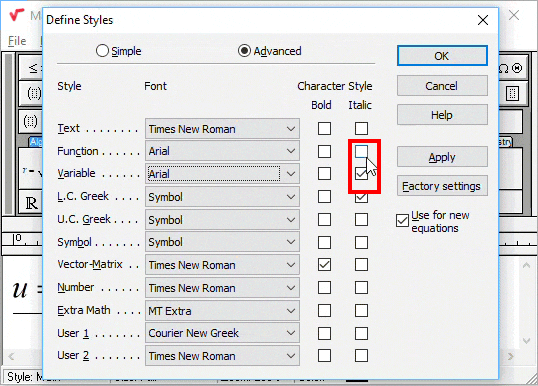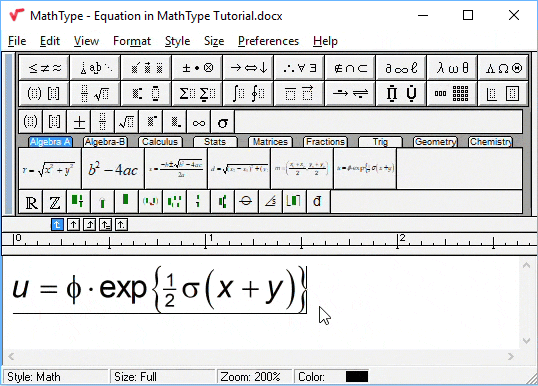
Advanced settings
Click the Advanced button to display a more extensive form of the Define Styles dialogue:
Tip
The changes you make in this dialogue apply to the current equation. Check «Use for new equations» to use the settings for new equations as well.
The names of the eleven styles are listed in the dialogue box, and the font and character style are assigned to each. The equation you have created uses the Function, Variable, L.C. Greek, Number, and Symbol styles. The letters «exp» are recognized as the abbreviation for the exponential function and are assigned the Function style; u, x, and y are treated as variables and assigned the Variable style; φ and σ being lowercase Greek letters, are assigned the L.C. (lowercase) Greek style, and the numbers in the fraction use the Number style. The symbols =, •, (, ), and + use the Symbol style. (The fraction bar is internal to MathType and does not use a style.) These styles are applied automatically as you create the equation because you use the Math style. This automatic style assignment is the advantage you gain by using the Math style when making equations.
Caution
The subject of MathType styles is covered in more detail in the Style menu.
We will change some of the styles to understand how they affect an equation’s appearance. You usually wouldn’t work this way; you’d change fonts using the Simple version of this dialogue.
Set font for Function style
The Function style is currently defined to use Times New Roman font. Click the arrow to the right of the font name in the Function row and choose a different font. You will want to select a font that looks noticeably different from Times New Roman, so the effect of the change will be noticeable. A good choice would be a sans serif font such as Arial.
See the effect of the style change
Choose the OK button. Your equation will be redisplayed using the new Function style definition. Your equation should look like this if you chose Arial font for Function style:
The function abbreviation exp is displayed using the new font. Of course, you probably wouldn’t want your equation to look like this – we’re simply demonstrating the effect of changing the Function style definition.
The Variable style definition is used for all ordinary alphabetic characters except for function abbreviations. In the current equation, this includes u, x, and y. Very often, according to the convention, the only difference you want between the Variable and Function styles is for the Variable style to be defined as italic. Let’s redefine the Variable style to be consistent with the new Function style definition.
Caution
Choosing fonts
A fast way to select a font is to click the list and then type the first letter of the name. You can also use the scroll bar in the list to move around quickly.
Set other styles
Once again, choose Define from the Style menu. In the Define Styles dialogue box, click the arrow next to the font name for Variable style, and choose the same font assigned to the Function style. Check that the italic character style is checked for Variable, but not for Function.
Let’s also change the Number style to use the same font as Function and Variable. You will find that this makes the equation look better. Finally, turn off the italic character style for the L.C. Greek style by removing the check in the Character Style column. Lowercase Greek letters are usually italicized, but let’s experiment with this.
Note
You can only assign fonts with the same encoding (arrangement of characters) as the Symbol font for the Symbol style. This typically restricts your choice to the Symbol font, the Euclid Symbol font, or some other similar font.
See the effect of the style change
Click OK. Your equation will be redisplayed using the new style definitions. If you are using the fonts we’ve recommended, the equation should now look like this:
The «variables» u, x, and y, and the numbers in the fraction ½ now use the new font definitions, and the lower-case Greek letters φ and σ are no longer italicized. You may want to use style definitions such as these for equations in a document in which the text is written in Arial.
To reset the style definitions, open the Define Styles dialogue and click «Default settings» (some versions: «Factory settings»).
Tip
You can also double-click or right-click in the Style panel of the Status Bar to make the Style menu appear.
While working through this tutorial, you have probably noticed that each style is also listed as a command on the Style menu. This allows you to assign a particular style to selected or subsequently-typed characters explicitly. The Other command on the Style menu can be used to assign any font available on your computer to selected or subsequently-typed characters. See Style menu for further details.
Including text in an equation
The following tutorial shows you how to enter words and phrases in an equation and how to handle function name abbreviations that MathType does not recognize. We are going to create the following equation:
Begin the equation
First, open a new MathType window using one of the methods you’ve already learned. Then type Prob(A|B). The result will be
MathType has used its built-in table of function names to recognize Pr as an abbreviation for «probability» and set it in the Function style. At the same time, o and b are regarded as variables. In this tutorial, we want to use Prob, rather than just Pr, as our abbreviation for «probability». You might think that you can fix the problem by making the o and b non-italic, but we don’t recommend this. If you remove the italicization, MathType will still regard o and b as variables, which we do not intend. The right approach is to select Prob and choose Function from the Style menu. This will remove the italics, but it also tells MathType that Prob is the name of a function, which will affect spacing and translation into languages such as LaTeX and MathML.
Caution
Controlling italics
To assign regular (non-italic) style to function names, use Function on the Style menu, rather than just removing the italics.
Create a fraction
Create the fraction in the middle term of the equation. You can copy and paste Prob(A|B) and modify it for re-use in the numerator and denominator. You can find ∩, the set intersection symbol on the 
Caution
Copying and dragging
To re-use part of an existing equation, select the part and then use Copy and Paste or drag and drop. Pressing and holding Ctrl (Mac: Option ) when dragging makes a copy of the selection.
Create another fraction
Construct the fraction on the right side of the equation by using the 
Caution
Typing text
Before typing everyday words and phrases, choose Text from the Style menu.
Choose Text style
If you just start typing characters into the numerator slot, MathType will assume that they are variables to be italicized, and any spaces you type will be ignored. To type ordinary words and phrases, you should first choose Text from the Style menu. Then type Probability that both A and B occur. The numerator of our fraction will look like this:
This is what we want, except the word «both» should be bold, and the A and B should be italic.
Change both to bold
Select the word «both», and choose Other from the Style menu. The Other Style dialogue will appear, letting you directly change the font and style (bold & italic) of selected characters. Click Bold, and then OK.
Make A and B italic
Next, we want to make the variables A and B italic. We could do this directly by using Other from the Style menu again, but this would not convey the correct meaning. A better approach is to select variable A, choose Math from the Style menu, and then repeat for variable B. This makes the A and B italic and tells MathType to treat them as mathematical variables.
Type the denominator
Enter the fraction’s denominator using the same technique we used for the numerator.
This completes the equation, but we can illustrate a few more of MathType capabilities.
Caution
New function names
You can customize the list of functions that MathType automatically recognizes.
Use the abbreviation «Prob» for probability regularly. You’ll get tired of manually changing it to Function style all the time, and you’ll want MathType to do this for you automatically. From the Preferences menu, choose Functions Recognized. Type Prob as the name of a new function, and click the Add button. Also, if you don’t want MathType to recognize Pr as an abbreviation for «probability», you can select Pr in the list of recognized functions and click the Remove button.
Now try recreating this same equation to see how much easier it is.
Using MathType‘s toolbar
In the previous tutorials, we saw two very similar formulas in the sense that they had many terms in common. This is typical of many branches of mathematics. For example, consider these formulas from elementary statistics:
Many statistical formulae use the symbols μ and σ, and they often involve various combinations of terms like 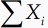
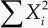
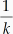
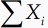
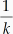
Caution
Toolbar icon sizes
Using the Workspace Preferences command on the Preferences menu you can alter the size of the toolbar icons.
Here’s how to add those symbols and expressions to the customizable toolbar:
Toolbars should be visible
Before we start, make sure that MathType toolbar is visible and that the Small Bar and the Small and Large Tabbed Bars are visible. Use the commands in the View menu to make them visible if necessary.
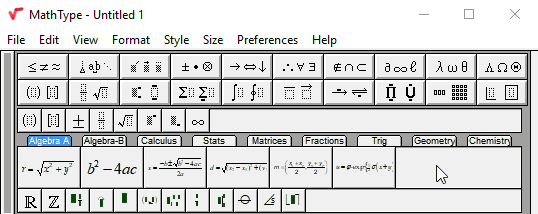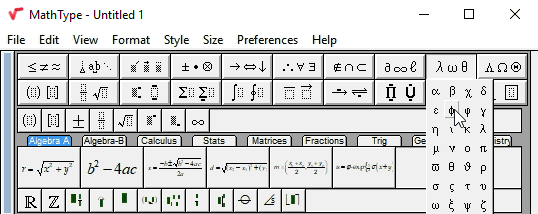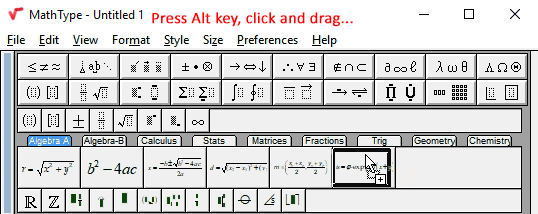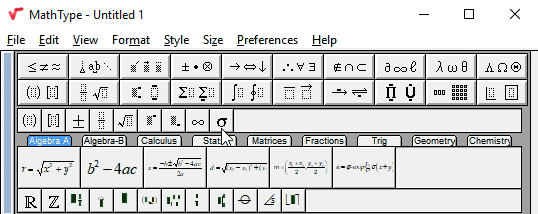
Open the Greek characters (lowercase) palette
Click the 
Add σ to the Small Bar
Now hold down Alt ( Command on the Mac), click σ and, keeping the left mouse button down, drag it over the Small Bar. You’ll see the mouse pointer change shape as it passes over different areas of the toolbar. When the pointer looks like this 

The symbol will be added to the end of the bar. To insert this symbol into an equation, you only need to click it in the Small Bar instead of hunting for it in the palettes. The Small Bar is a good location for frequently used symbols as it is always available and can contain many items.
Caution
Adding new symbols
You can add any symbol from any font on your computer to the toolbar. Enter it into the equation area, select it, and drag it to the taskbar. Use the Insert Symbol dialogue (on the Edit menu – see Inserting symbols that aren’t in the palettes for details) to locate the symbol, hold down the Alt key and drag the symbol to the toolbar. As a result, MathType has access to a virtually limitless supply of symbols.
Add an expression to the Large Tabbed Bar
Next, we’re going to add 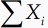
Create the expression
Delete the current contents of the MathType window, and create 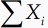
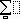
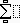
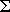
Caution
Editing toolbar expressions
You can edit a toolbar expression by double-clicking if you’re on Windows. Alternatively, on either Windows or Mac, you can edit a toolbar expression by right-clicking and choosing Edit (Windows) or Edit Expression (Mac). A new MathType window will open containing the expression. Make your changes, close the window, save the changes, and update the toolbar.
Select and drag expression to Large Tabbed Bar
To add this expression to the toolbar, select it and drag it to the Large Tabbed Bar. When you release the mouse you’ll see the expression appear in the bar.
Add fraction to Small Tabbed Bar
Create 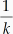
Tips and reminders
Creating this formula doesn’t require any new techniques, so we’re not going to give you the usual step-by-step instructions. Here are a few helpful hints and reminders:
-
You can insert σ by clicking on it in the Small Bar, which is much faster than the
palette.
-
You can insert the
by clicking it in the Large Tabbed Bar.
-
A fast way to create
is to insert
, drag across the X to select it, and type Y to replace it.
-
You can create
by inserting
and replacing the subscript template with a sub/superscript template. To do this, select the entire subscript slot (not simply the subscript itself; see inset note below), and hold down Ctrl as you choose
from the Subscript and Superscript templates palette. The Ctrl ( Option on Mac) key causes the new template to replace the selected one instead of wrapping around it. Then type 2 in the superscript slot.
Note
If your selection looks like this, it will not work: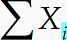
-
Note that the two terms inside curly brackets on the bottom line of the formula are identical except that one involves X and the other involves Y. To create the second term, duplicate the first one and replace the Xs with Ys.
-
You can duplicate a term by selecting it, holding down Ctrl (Option on Mac) and dragging it to the desired location (without Ctrl / Option, the term is moved).
Caution
Rearranging the toolbar MathType toolbar is initially filled with expressions useful for many of the various fields in mathematics. However, you can rename or delete the existing tabs and rearrange or remove any of the symbols or expressions in the default toolbar. You can also modify any expressions if they’re not quite suitable for your particular use.
To move a symbol or expression within the toolbar, hold Alt (Mac: Command ) and drag the item to its new location. You can insert an object between two others by dropping it between them.
Try it
Try this by dragging σ from the Small Bar (Step 3 above) to the Small Tabbed Bar. The choice of where to place an item is entirely up to you; a symbol or expression can be placed in any of the bars.
Now let’s delete σ from the Small Tabbed Bar.
Deleting symbols and expressions from the toolbar
Right-click σ and select Delete from the context menu that appears. You may also want to delete the other expressions you added to the tabbed bars.
Caution
Deleting toolbar items (Windows only)
Another way to delete an item in MathType for Windows is to Alt+drag it from the bar and release the mouse over an invalid target, e.g., outside the MathType window.
Change the names of the tabs
You can also change the names of the tabs to suit your particular situation. Double-click the Statistics tab to open the Tab Properties dialogue, where you can edit the tab’s name and change its keyboard shortcut.
If you prefer typing to use the mouse, you may use the toolbar’s keyboard interface. You can give the keyboard focus to a toolbar component using the following keyboard commands:
|
Palette or Bar |
Windows |
Mac |
|---|---|---|
|
Symbol Palette |
F5 |
Command+F5 |
|
Template Palette |
F6 |
Command+F6 |
|
Small Bar |
F7 |
Command+F7 |
|
Large Tabbed Bar |
F8 |
Command+F8 |
|
Small Tabbed Bar |
F9 |
Command+F6 |
Once a bar has the focus, you can use ← and → move the selection and Enter to insert the selected item (or open its corresponding menu). Esc closes a menu or returns the focus to the equation area. You can switch tabs by typing Ctrl+F10 ( Command+F10 on Mac), n where n is the number of the tab to activate. For example, typing Ctrl+F10 , 2 starts the second tab.
Deciding what to place in the toolbar
Some symbols and templates are used so frequently that you may not need to place them in the toolbar. You probably will have memorized the keyboard shortcuts for inserting them, so there’s not much to be gained by having them occupy valuable space in the toolbar. Greek symbols in particular fall into this category; once you’ve learned that you can insert a β by pressing Ctrl+G or Command+G followed by b (referred to as Ctrl+G, B on Windows or Command+G, B on Mac), you probably won’t need to add these characters to the toolbar.
However, it may make sense to add characters from any unique fonts you may have to the toolbar. The easiest method is to use the Insert Symbol dialogue (choose the Insert Symbol command on the Edit menu), a potent tool for viewing the characters in a font. You can also Alt+drag or Command+drag characters from this dialogue to the toolbar. You can add as many characters from your fonts to the toolbar as you will fit. Then you can enter these characters at any time into your equations, regardless of your current style definitions.
That does it for Using MathType Toolbar, so choose Select All ( Ctrl +A/ Command +A) from the Edit menu and press Backspace or Delete to clear the window for the following tutorial.
Spacing and alignment
In our following example, we introduce some of MathType facilities for controlling spacing and alignment in equations and other expressions. We are going to create the next pair of inequalities:
Note these expressions are arranged, so they’re less than or equal to signs are vertically aligned, and they both contain a «lim sup» construction of a type we have not used before.
Caution
Expanding integrals Integral signs are usually a constant size. You can create an expanding integral by holding down Shift while choosing an integral template from the integrals palette.
You can create these expressions like the one that follows.
Insert a definite integral
Insert a definite integral template by clicking 
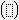
Add a thin space
To improve the appearance of our expression, we should insert a thin space (one-sixth of an em) in-between a(x) and dx in the integrand. MathType can not do this automatically, so we provide you with a convenient way of manually entering a space of the correct size.
Caution
Parentheses template
You may prefer to use the template instead of typing ( and ). Using the template can give your document a more consistent look. The template also includes more space around it, so you may not need to add the narrow space as shown here. We’re trying to teach you the different ways to create expressions; obviously, the final choice is up to you!
The 
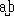
Move out of the integrand
Move the insertion point out of the integrand slot, into the position shown below. You must do this for the alignment commands to work properly. Don’t create the rest of the expression within the integrand slot.
Caution
Show Nesting
The Show Nesting command on the View menu shows the different slots and can help you avoid making mistakes.
Inequality symbol
Click ≤ in the Small Bar.
Enable the underscript
Now we want to build the «lim sup» structure. We begin by clicking the 
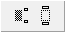
Type lim sup
The insertion point is positioned in the upper slot to type limsup. MathType will use your «Function» style (probably a plain style) for these characters and will insert a thin space between the «lim» and the «sup».
Note
lim sup is not a defined function in MathType but lim and sup individually are defined functions, so the appearance will still be correct.
Type the underscript
Move the insertion point down into the lower slot by clicking inside it or by pressing the Tab key, and enter n→∞. The → and ∞ symbols are very common in mathematics, so they’ve been added to MathType default Small Bar. They’re also available in the Symbol Palettes, of course. Following typesetting conventions (as always), MathType will not create any spacing around the → symbol, since it is in an underscript, but you can insert spaces if you want to.
Move out of the underscript
Press Tab to move the insertion point out of the lower slot, and type the rest of this first expression. The speedy way to do this is to just type Ctrl+G f Ctrl+L n Tab ( a ). If you like the Ctrl+G shortcut, you may be interested to know there are a few others that work in a similar fashion. If you press Ctrl+U , for example, the next character you type will be assigned the User 1 style you have defined with the Define command on the Style menu. In this way, you can access any character in any font with just two keystrokes, even if it’s not present in the Symbol Palettes.
Create a pile
Press Enter . This will create a new line directly beneath the first expression, so now you have a «pile» consisting of two lines. It should look like this:
Caution
Selecting a slot
You can double-click in a slot to select its contents or type Ctrl+Shift +S.
Copy-paste within MathType
To save time, we’re going to create the second expression by modifying a copy of the first one. Select the entire first expression by double-clicking somewhere near its ≤ sign, copy it to the clipboard, and then paste it into the new empty slot. You should now have two identical copies of the first expression, one directly beneath the other. Now just edit the lower copy to produce the second expression. To change ϕto ψ, select ϕ and press Ctrl+G / Command+G followed by y.
Different alignments
Finally, we’re going to experiment with different ways of aligning the two expressions. You can centre or right-justify them using the Align Center and Align Right commands on the Format menu. Give this a try, just to see how it looks.
Align at =
You will probably want to align these two expressions, so their ≤ signs are directly above one another. We choose the Align at = command from the Format menu to do this. It will work even though we have ≤ signs rather than = signs. You can align the expressions in other ways by using alignment symbols. You insert an alignment symbol in each expression at the two points you’d like to have aligned. (However, note alignment symbols inserted into template slots will not work.) Placing an alignment symbol to the right of each of the two ≤ signs would give the same results as using the Align at = command, for instance. The icon in the Symbol Palettes represents the alignment symbol — it’s located in the 
Caution
What if the inequalities still aren’t aligned?
If this happens, there’s a good chance you didn’t carefully follow the steps above, specifically step 3. In MathType View menu, select Show Nesting. We mentioned this in step 3, but there’s a real advantage to using it here; it lets you see the structure of the expressions. In this one, notice the first inequality has the ≤ symbol within the integrand, while the second one doesn’t (zoomed a bit for clarity):
Move the expression parts outside the integrand that don’t belong there, and the inequalities should be aligned.
Adjust line spacing
You may also want to adjust the line spacing, or leading, (i.e., the amount of vertical space between the two expressions). You can do this by placing the insertion point somewhere in the outermost slot of the second expression (not within a template), or by selecting the second expression, and choosing the Line Spacing command from the Format menu. When you’ve arranged them to your liking, the expressions are complete.
Now we’re done with these expressions, so it’s time to choose Select All from the Edit menu and press Backspace to clear your window for the next tutorial.
A simple matrix
The following tutorial illustrates MathType powerful capabilities for laying out matrices. We will construct the following matrix equation:
The matrix is a relatively simple one, and we’ll be able to create it very easily by using a matrix template. If you need more flexible formatting capabilities for matrices and tabular layouts, you should use tabs, as illustrated in Formatting with tabs.
Begin the equation
Type the first few terms of the equation to the second equals sign. MathType will recognize that «det» is an abbreviation for the determinant function and automatically set it in plain Roman type, so you don’t have to fiddle with it. The quick way to get λ is to press Ctrl+G / Command+G followed by a letter l (lower-case L). Also, note the I and the A represent matrices in our equation, so we have assigned them the Vector-Matrix style. This causes them to appear in bold type. The Ctrl+B shortcut will assign the Vector-Matrix style to the next character, so you can press Ctrl+B followed by I to get the I and Ctrl+B followed by A for the A. Alternatively, you can just type all the characters first and then select them and change their styles using the commands on the Style menu. Either way, your equation should end up looking like this:
Vertical bars
Type the second = sign and insert a vertical bar template by choosing the 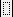
Insert 2×2 matrix
Insert a 2×2 matrix template inside the vertical bars by choosing the 

Begin entering matrix contents
The insertion point will be in the top left slot of the 2×2 matrix, so enter the expression λ – a11 there.
Copy-paste matrix elements
We’re feeling lazy, so we’re going to create the other entries in the matrix by cutting and pasting. Select the λ – a11 by double-clicking it, copying it to the clipboard, and pasting it into the other three slots in the matrix. The result should be as shown below; it’s not correct, of course, but we’re going to fix it up in a few moments.
Caution
Drag and drop
You can also drag the term and drop it in the other slots. Remember to hold down the Ctrl / Command key as you drag to copy the term.
Add some padding
Next, we’re going to put a little extra space between the vertical bars and the elements of the matrix. This is purely a matter of taste, so you can skip this part if you’d prefer to keep your matrix looking the way it does at present. Before we enter the spaces, we need to position the insertion point so that it’s inside the vertical bars but to the left of and outside the matrix. You can do this by clicking somewhere near the position indicated by the arrow pointer in the preceding picture. Then just enter one or two thin spaces by pressing Ctrl+Spacebar / Command+Spacebar . Do the same on the right side of the matrix. If you choose the Show All command from the View menu, you’ll be able to see your spaces. They should look like this:
Correct the pasted entries
After the brief digression in Step 6, it’s now time to correct the entries in our matrix. First, delete the λ from the upper right slot. The quickest way to do this is to place the insertion point to the right of it and press Backspace . Do the same with λ in the lower-left slot. Notice MathType adjusts the spacing after the minus signs to reflect the fact that they are now unary operators rather than binary operators (negation rather than subtraction).
Continue correcting the entries
Change all the subscripts in the matrix to their desired values. The «11» in the upper left slot is correct already, but we should have «12» in the upper right slot, «21» in the lower left, and «22» in the lower right. You can double-click the existing subscripts to select them, and then type the correct values over them, just as you would in a word processor. Your equation should now look like this:
Caution
Modifying a matrix
The Matrix submenu on the Format menu contains commands for adding and deleting rows and columns.
Nearly finished…
The equation is now essentially complete, although you may want to try out a few more formatting options. First, you might want to shift the entire matrix down to align its top row with the rest of the equation. To do this, place the insertion point anywhere in the matrix and choose Align at Top from the Format menu. Also, it might be nice to right justify the entries in each column. To do this, place the insertion point somewhere in the matrix, choose the Change Matrix command from the Matrix submenu on the Format menu, and click the button labelled «Right» in the dialogue box.
Finally, if you object to MathType tightened the spacing after the unary minus signs, you can put the spaces back in again. However, this would mean deviating from standard typesetting conventions. They should be thick spaces (one-third of an em). The vast area is the middle one in the second row of the spaces and ellipses palette. If you prefer to use the keyboard, you can insert a thick space by pressing Ctrl+Shift+Space / Command+Shift+Space . Alternatively, since a vast space is the same width as two narrow spaces, you can get the same results by pressing Ctrl-Space+ / Command-Space+ twice.
If you elected to make all of the modifications suggested in this step, your equation should look something like this:
If you’re going on to the following tutorial, press Ctrl+A / Command+A to select all, then press Backspace or Delete to clear your screen.
Equation numbering in Microsoft Word
Basic equation numbering & referencing
This tutorial describes how to use the MathType commands for numbering equations in Microsoft Word documents. Although Word has its own method for numbering equations (captions), Word places captions above or below an item, not to the side, typically how equations are numbered. Using the MathType commands added to Word, you can enter inline, display and numbered display equations with just one click.
Caution
Same Windows and Mac
Note the process described here is the same on both Windows and Mac platforms. Look on the MathType tab in Word’s ribbon for the commands we describe below unless you use Word 2011 for Mac. In that version, you can find the icons on the floating MathType toolbar and the commands in the MathType menu on Word’s menu bar. Also, if you’re using Word 2011, please see our warning about MathType and Office 2011.
We will create the following portion of a document to illustrate the equation numbering commands.
However, we’re going to create it in a slightly unrealistic sequence to illustrate the power and flexibility of the numbering commands.
Begin a new document
Run Microsoft Word and create a new document. Enter the following text: We now have two basic equations:
Insert a right-numbered display equation
Click the 
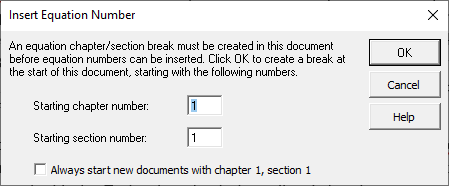
Beginning chapter/section break
A dialogue will appear asking if you want to create a new chapter/section break at the start of this document. We’ll explain the meaning of this later in the tutorial. For now, just click OK.
Caution
Word styles used
The equation’s line is formatted with Word’s MTDisplayEquation style, which you can modify to affect all display equations in your document.
Create the first equation
In the MathType window that opens, type this equation:
Close the MathType window. In your Word document, notice that the equation is centred and the equation number is aligned with the right margin.
Create another numbered equation
Repeat step 3 and insert the following equation into your Word document:
Add text
Enter the following text at the start of the next line: Subtracting
Insert an equation reference
Now let’s insert a reference to the second display equation. Click the Insert Reference button on the MathType tab:
The Insert Equation Reference dialogue will appear, displaying brief instructions about inserting an equation number reference. Once you are familiar with the process you can click the Don’t show me again box. For now, click OK, then double-click the equation number (1.2). You’ll see the number (1.2) is inserted into your sentence.
Caution
Equation references
You can jump to an equation in your document quickly by double-clicking on any of its references. Then press Shift+F5 to jump back to the reference.
In large documents try splitting your window into two panes (search for split in Word’s Help). Insert the references in one pane and scroll and double-click the equation numbers in the other.
You can place equation number references in footnotes and endnotes.
Continue the reference
Type from and then enter a reference to equation (1.1) using the method described in the previous step. You may want to enter a space before and after the reference.
Continue with another numbered equation
Type gives and insert the following numbered display equation:
More text and another reference
At the start of the following line, type Using and insert a reference to equation (1.3). Complete the line by typing we can show that
Inline equation
Click the 
Notice how this equation is inserted in the line of text (hence the name inline equation). Word also aligns the equation with the baseline of the text. Your document should now look like this:
Now we’ll insert another equation in the middle of this example to demonstrate automatic renumbering.
More text
Place the insertion point before the word Subtracting, and enter the following text (it’s not necessary to press Enter ): Adding these two together, we obtain
Another numbered equation
Insert this numbered display equation:
You’ll see the new equation is numbered (1.3), and the following equation number and its reference have been renumbered to (1.4). Your document should now look like the example at the start of this tutorial.
Caution
Equation numbers
If you’ve already inserted a display equation without the number, you can insert just the number using the Insert Equation Number command.
Caution
If updating is slow
If updating takes too long, uncheck «Update equation numbers automatically» in the Format Equation Numbers dialogue. Then use the Update Equation Numbers command to update the numbers manually.
Whenever you insert an equation number or an equation reference, all numbers in the document are updated. However, if you move or delete an equation number, you must use the Update Equation Numbers command on the MathType tab to regenerate the number sequence. It’s located here:
Also, be aware that deleting an equation number does not automatically delete any of its references; you’ll have to do this yourself. You can find them by using the Update Equation Numbers command, which will cause Word to display an error message in place of each reference. You can then delete them.
Caution
Equation number formats
You can also control the format of the equation numbers. Notice the «Format» command in the previous screenshot.
Whole document
To change the format of existing equation numbers, you must check the Whole Document checkbox. Otherwise, you’re only setting the format for the following number(s) you insert.
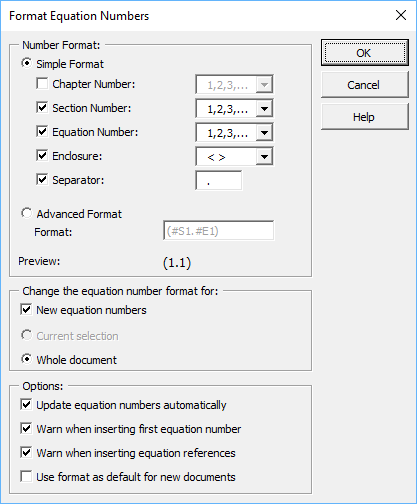
Formatting equation numbers
Choose the Format Equation Numbers command (shown above). Check the Whole Document checkbox (to change the existing numbers) and change the Enclosure option to <> (angle brackets). The preview shows you the result of your settings. Click OK, and you’ll see the equation numbers and references change to the new format. You may want to experiment with some of the settings – there are many possible combinations.
Chapter/Section Breaks
Section Numbers. If you don’t want section numbers included, you can turn them off in the Format Equation Numbers dialogue.
The default equation number format includes a section number and an equation number, e.g., (1.1). You can also include a chapter number if needed. The chapter and section numbers are determined by the nearest preceding Chapter/Section Break in your document. You insert and modify these breaks using Word commands on the MathType 7 tab. We already inserted one at the start of this document to insert the first equation number. Now we’ll change its value.
Caution
Show Chapter/Section Breaks
You can show and hide chapter/section breaks by clicking on the 
Change section number to 2
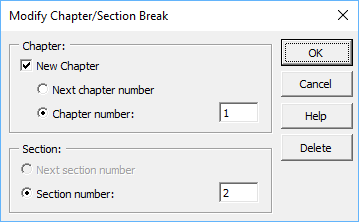
Choose the Modify Break command on the MathType tab. It’s located here:
The location of the section break will be highlighted and the Modify Chapter/Section Break dialogue will open. Let’s assume we’re working on Section 2 of a book, so we want the section number to be 2 and the equation number to be 1. Choose the «Section number:» button and enter 2. The «Next» option can be useful if your document contains several sections and you want them numbered sequentially. (Remember that there’s no link between Word’s sections and MathType chapter/section breaks. It’s up to you to associate them by placing the breaks in the appropriate places in your document). Now click OK. The chapter/section break will be hidden, and the equation numbers in the document will all start with 2.
If you’ve followed these steps your document should look something like this:
MathType equation numbering commands can also support three levels of numbering, e.g., chapter, section, and equation numbers. You can also control the format of the numbers and create your own custom formats. The next tutorial shows you how to do this; we’ll use the document we created in this tutorial so don’t delete it!
Advanced equation numbering
The simple equation numbering example shown in the previous tutorial is sufficient for many documents, but sometimes you may need to create a third level of numbers. For instance, your document may require chapter, section, and equation numbers. Or you may find that the built-in number formats don’t match your needs, and you’d like to create a custom number format. This tutorial shows you how to accomplish both tasks.
Open previous document
Open the document you created in the previous tutorial. If you didn’t save it, download ours and use it for this tutorial.
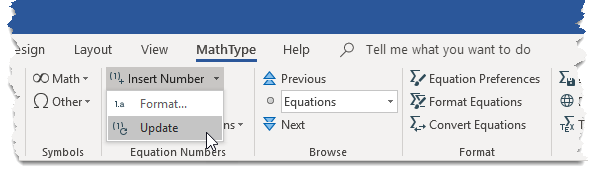
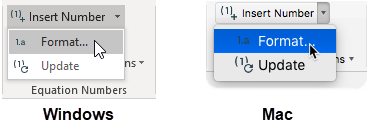
Open Format Equation Numbers dialogue
Open the Format Equation Numbers dialogue. This is on the MathType tab in Word, in the Equation Numbers group. Click the downward-pointing triangle to the right of Insert Number, and choose Format. (If you are using Word 2011 for Mac, the Format Equation Numbers command is in the MathType menu in Word. Use caution to not choose the similarly-named command Format Equations.)
The dialogue will open:
Enable Chapter Number
The settings should appear as shown above. The top group of items controls the number format. We want to add a chapter number, so check the «Chapter Number» checkbox. Notice how the preview changes to <1.1.1>.
Enable Whole document
Make sure «Whole document» is selected so the changes we make will be applied to existing equation numbers. Then click OK.
You’ll notice the document has changed, and the equation numbers now read <1.2.1>, <1.2.2> etc. This is because the chapter/section break at the start of the document sets the chapter number to 1. This was added to the document when we inserted the first equation number. Let’s pretend we want to set this to be Chapter 2.
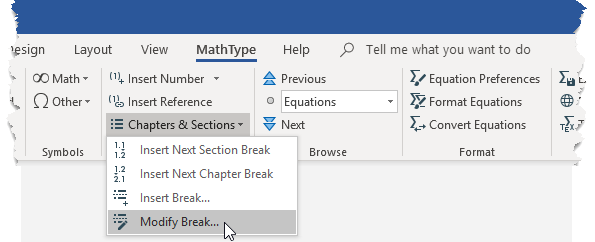
Open the Modify Break dialogue
Choose the Modify Break command on the MathType tab. It’s located here:
You’ll see the break itself has also been made visible in the Word document. Here’s the dialogue:
Change chapter number
Change the Chapter number value to 2 and click OK. The numbers in the document should now read <2.2.1>, <2.2.2> etc.
Now let’s try changing the format of the numbers more dramatically. We’ll set the format so the numbers read Equation 2.2.1, Equation 2.2.2 etc.
Advanced formatting
Choose the Format Equation Numbers command as described in step 2 above. Select the Advanced Format radio button, and enter Equation #C1.#S1.#E1 in the Format: box. You’ll see how the Preview changes.
Make sure «Whole document» is selected, and click OK. The equation numbers in the document should be updated.
You can experiment with different custom formats in this manner. The syntax used for the formats is very simple: all characters are used literally except for the constructs #Cx, #Sx, and #Ex, where x indicates the numeric representation and can be one of 1, a, A, i, I.
A fast way of learning how to control the formatting is to select the Simple Format button, and then change the various options. The Advanced Format text is still visible, and it updates every time you make a change to the built-in formats. Full details are in the Help for this dialogue.
Equation numbering in long documents
The previous two tutorials covered the information you’ll need to know for this tutorial to be most helpful. If you haven’t worked through those tutorials yet, we recommend doing so now unless you use numbered equations often and are familiar with the concepts already.
The scenario we’ll cover in this tutorial assumes you’re working on a manuscript with several chapters, each chapter contained in a separate document. Your equations are numbered with the chapter number and equation number, and without section numbers or enclosing symbols such as parentheses – such as this example equation:
Open the sample documents
For this tutorial, we’ve created three Word documents which will be chapters 1-3 of our manuscript. Open this file and unzip it to a convenient location on your computer.
Chapter 1 – Format equation numbers
Open our sample document Chapter 1.docx and on Word’s MathType tab, open the Format Equation Numbers dialogue. (Recall this is nested inside the Insert Number command on the MathType tab.) Configure your equation numbers like the one in the example above – include the chapter number, don’t include section number or enclosure, and use a single dash (hyphen) as a separator. Verify the Change the equation number format for options applies to New equation numbers and Whole document.
Note
If you’re creating these documents yourself, you’ll probably want to set the option at the bottom of the dialogue to Use format as default for new documents. Otherwise, you’ll have to go through this process for each chapter in your manuscript.
Note
We’ve already set the equation format for the three sample chapters you downloaded for this tutorial for Chapter 2 and Chapter 3. You won’t need to do this again in this tutorial.
Chapter 1 – Insert numbered equations
In Chapter 1.docx,
-
Insert a right-numbered equation (of your own choosing) immediately after the 2nd paragraph. Remember, you don’t have to insert a linefeed first; MathType will do that for you.
-
In the Insert Equation Number dialogue, verify the settings, beginning with Chapter 1 and Section 1 (though the section number won’t matter).
-
Now insert another right-numbered equation immediately after the first one. Your document should look similar to this, with your equations, of course, in place of ours:
Caution
For numbered equations not centred between margins, your style guide may specify an equation position other than the centre. Maybe you’re not working with a style guide, but you prefer the look of an equation indented 2 cm from the left margin. Whatever your reason for not wanting your equations to be centred on the line, please don’t position them manually. There’s a much more accessible, more elegant way to do it. The right way to do it is to modify Word’s MTDisplayEquation style. We have an article describing this style and showing how to change it. Please see this article for more information.
Equation formatting
When you insert MathType equation numbers, the formatting of the numbers will match the formatting of Word’s Normal style for your document. If you have modified the text — font, size, colour, etc. — by using the buttons on the Home tab in Word, rather than by using styles, results will be unpredictable, and the style of your equation numbers may not match the style of your document’s text. We recommend always using styles for formatting.
By contrast, when you insert MathType equations, they will be styled according to your settings in MathType Style and Size menus (by using the Define command in both menus). You must explicitly set the style of your equations to whatever you want them to be.
Chapter 2 – Insert equation chapter break
Now open Chapter 2.docx. Let’s insert a right-numbered equation after the first paragraph. When you click 
Set the Starting chapter number to 2. Since we’re not using section numbers, that entry won’t matter so let’s leave it at 1. Once you click OK, MathType will insert a number into the document and MathType will open for you to create the equation. Your document should look something like this:
If this is starting to seem routine, keep reading; we have some important points to make.
Chapter 3 – Insert numbered equation
Open Chapter 3.docx and without doing anything else, insert a numbered equation after the first paragraph. What did you notice that was different from inserting the equation into Chapter 2? You didn’t see the Insert Equation Number dialogue, did you? That’s because we had already inserted the chapter break into the document. You probably won’t be inserting the chapter break separately, but you can, and sometimes you’ll need to. Such would be the case if you already had equations in a document and you decided to split it into multiple chapters and/or sections and wanted the equations numbered accordingly. In that case, there’s no need to delete and re-insert the equation numbers. Just insert breaks where you need them.
Here’s how we inserted the break into Chapter 3…
-
Click to place the insertion point (cursor) at the beginning of the chapter title. It’s not necessary for it to be at that exact spot. All that’s necessary is for it to appear prior to the first numbered equation in the chapter or section. We recommend getting into the habit of placing the break at the beginning of the title. By doing so, you eliminate problems generated when you insert the break at some random spot, then insert another numbered equation before the break. If you place the break at the beginning of the title, this will never happen.
-
On the MathType tab in Word, click Chapters & Sections in the Equation Numbers group.
-
Click Insert Break.
-
Tick the box next to New Chapter, click the radio button next to Chapter number and type 3 into the box.
-
Click OK.
When you do that, you’ll see some things happening rather quickly, but if you pay close attention, you’ll probably see some red text inserted before the chapter title, then it will disappear. Let’s see what that hidden text consists of. On Word’s Home tab, click the Show/Hide button: 
Combining the chapters into a single document
Now it’s time to combine the multiple documents of our manuscript into a single document. We can do it with copy & paste, but there’s more to it than that.
-
We’ll follow the good practice of not working with the original, so create a new Word document. If your manuscript uses a particular template, naturally, you’ll want to use the same template for combining the documents. In the case of our sample documents, they’re all based on the Normal template, so just clicking File > New (or using the shortcut) should suffice.
-
If you click Show/Hide in the previous section, it’s probably still enabled, and you should see a paragraph mark (pilcrow) in the document. If you don’t see that, click Show/Hide.
-
Open Chapter 1 if it’s not still available. If you don’t see the hidden marks and text, click Show/Hide. It should look similar to this:
-
Select the entire contents of the document. The easiest and best way is to use the shortcut, Ctrl+A (Windows) or Command+A (Mac).
-
Copy the selected text.
-
Switch to the new document you created in step 1, and paste the copied text into that document. Don’t move the insertion point (cursor). It should remain to flash just before the final pilcrow at the end of the document.
-
Repeat steps 3 through 6 for Chapter 2 and Chapter 3.
-
If you prefer the formatting marks turned off, you can click Show/Hide to hide them. Your combined document should now include chapters 1 through 3, with the equations appropriately numbered sequentially.
Setting up a Microsoft Word document
When creating a Microsoft Word document containing equations, there are several considerations you should keep in mind. You’ll probably want the body text to match the equations in terms of fonts and sizes, and you’ll typically want all equations in the document to use consistent formatting, i.e. the same font and size settings, as well as any other unique settings you may have made in MathType
Notice
Word’s styles If you’re not familiar with Word’s styles, we urge you to take a few minutes to learn how to use them. In Word’s Help, search for styles.
Although Word and MathType allow you to select text and change their fonts and sizes directly, we strongly recommend you make use of styles instead. Both programs use this approach because it makes modifying the look of a document or equation very easy. You simply change the definition of a style (e.g., from Times New Roman to Arial, or from 12 pt plain to 10 pt italic), and your document or equation is immediately reformatted with the new settings.
Let’s assume you’re required to produce a document where the body font is 10pt Times New Roman. The first step is to define MathType settings to match the Word document.
Open MathType‘s Define Styles dialogue
In MathType, open the Define Styles dialogue and set the main font to Times New Roman using either the Simple or Advanced pane. Make sure the «Use for new equations» box is checked, and click OK.
Caution
Factory Settings
Click «Factory settings» to reset the values to Times New Roman font, 12pt.
Open MathType‘s Define Sizes dialogue
Open the Define Sizes dialogue, and set the Full size to 10 pt. As the other dimensions are by default expressed as percentages, MathType will calculate them for you. Again, check the «Use for new equations» option, and click OK.
Caution
Equation Preferences
The definitions of all the styles, sizes and spacing used in an equation are collectively referred to as «equation preferences». See Equation Preferences sub-menu for more details.
Attach Equation Preferences to the Word document
Back in Word, choose the Equation Preferences command in the Format group on the MathType tab. Make sure the MathType ‘New Equation’ preferences» option is selected. This means that whenever you create a new equation using the commands on the Insert Equations group, the settings MathType is currently set to use for new equations are the ones that will be used. Click OK to close this dialogue.
Note
You may not always want to rely on MathType ‘New Equation’ preferences. If you tend to change MathType size and style definitions quite often, you may want to create a MathType preference file, and then choose this file in the Set Equation Preferences dialogue. This will copy the file’s preferences into your Word document, so that no matter what changes you make to MathType equations created in your document will always use these preferences.
Create a new style
Now we’ll quickly create a Word style for the document’s body. If you’re using a Mac, see below, but if you’re using Windows, click the Dialog Box Launcher in the lower right corner of the Styles group on the Home tab:
In the lower-left corner of the Styles dialogue, click New Style:
If you’re using a Mac, click Styles Pane on the Home tab: 
Both Windows and Mac: in the Create New Style from Formatting (Mac: New Style) dialogue, name the new style «body». You’ll probably base it on Word’s built-in Normal style. Set the unique style’s font to Times New Roman 10pt by making the appropriate selections in the Formatting section of the dialogue. Don’t click OK yet.
Paragraph specs
Open the Format list in the lower-left corner of the dialogue. Choose Paragraph. On the dialogue’s Indents and Spacing tab, change the Line Spacing option to Single. Click OK to close the dialogue.
Close the dialogues
Click OK to close the New Style dialogue, and then click the X (Windows) or red «stoplight» (Mac) to complete the Styles dialogue if undocked or click the X to close the Styles pane if docked.
You’ve now configured Word and MathType to use the same font and size definitions, which will make equations closely match the look of the rest of the document. Go ahead and enter a line or two of text and insert a simple equation.
Now let’s suppose you have to change the document’s font to Garamond. Keeping this example simple won’t change the point size, but you’d follow the same steps if this were the case.
These are the changes we need to make:
-
Modify Word’s «body» style to use Garamond instead of Times New Roman.
-
Modify MathType styles to use Garamond instead of Times New Roman.
-
Update the existing equations in the document to use the new font.
The first two steps are very similar to how we created the styles and added them to the Word document to go through them in detail. The first step involves using Word’s Style dialogue (right-click Body in the Styles group, and choose Modify); the second step requires MathType Define Styles dialogue.
The third step involves the Format Equations command on the MathType tab in Word’s ribbon.
Open Format Equations dialogue
Choose the Format Equations command, and the Format Equations dialogue will appear. This dialogue allows you to reformat the equations in your document, and provides you with several ways to determine the equation preferences that are applied. The choices are:
-
The equation preferences are already stored in this document.
-
MathType current equation preferences for new equations.
-
The equation preferences contained in a MathType equation you’ve copied to the clipboard.
-
The equation preferences are contained in a MathType preference file.
Click the MathType ‘New Equation’ preferences» button for this example. You can click Preview to get a list of the actual preferences.
See Set Equation Preferences dialogue for more details on the other options.
Begin the equation formatting
Click OK, and the formatting process will start. This can take anywhere from a few seconds to several minutes, depending on the speed of your computer and the number of equations in your document. The command’s progress is shown in Word’s status bar. When the operation has finished, verify the equations were updated.
Formatting with tabs
In this example, we show you how MathType system of tabs provides extra flexibility for formatting equations. We’re going to create the equation:
and then format it several different ways. We proceed as follows:
Create the left side of the equation
Create the expression on the left side of the equals sign. As you know by now, you can choose the 
Add a single left brace
Choose the 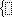

Enter «piece» #1
Enter the top expression in the brace, up to and including the x, and then press Ctrl+Tab (press the Tab key while holding down the Ctrl key, Mac or Windows). If you press the Tab key alone, this will move the insertion point, rather than insert a tab character.
Caution
Choosing styles
Another way to choose a style is to right-click in the Style panel of the status bar and select the style from the context menu that appears.
Type the first condition
Choose the Text style from the Style menu and type when n is even. While you’re using the Text style, the spacebar is active, so you may type spaces just as you would in a word processor. Choose Show All from the View menu, if it’s not already checked, so you can see your tab character, which is displayed as a small diamond. Also, choose Ruler from the View menu if it’s not already checked. Your equation should look like this:
Note the tab character causes the phrase «when n is even» to line up beneath the first default tab stop to the right of the x. The default tab stops (indicated by small inverted Ts along the ruler scale) are positioned at half-inch intervals starting at the left side of the current slot. Since we are currently within the central slot of the 
Caution
Ruler units
Default units for ruler graduations are inches. If you prefer to work in centimetres, points, or picas, double-click the ruler pane to bring up the Ruler Units dialogue. Make your choice of ruler units and click OK.
Type the second piece of the function
Press Enter to start a new line underneath the first one and type in its contents. It would be best to switch back to the Math style to enter 14.3x. Insert a tab character ( Ctrl+Tab ) after the x, as in the first line. Now switch back to Text again to type when n is odd. Now we have:
Again, the text phrase aligns with the first default tab stop to the right of the x. Note that you have created a two-line pile within the 
Change n to Math style
Select n in the first line and choose Math from the Style menu. This makes MathType interpret n as a mathematical quantity (i.e., a variable), and will therefore apply the Variable style (typically italic). Do the same to the n in the second line.
Set the tab stop
Place the insertion point somewhere within one of the two lines on the right-hand side of the equation, click the 
If this is how we want the equation formatted, then our work is finished. However, there are several other options that are worth exploring.
Align the two lines at x
First, we’re going to align x in the two lines. Insert a tab character ( Ctrl+Tab ) at the start of each of the two lines. This will cause each line to be shifted, so its left side aligns with the left tab stop. The text phrase in each line, since another tab character separates it, will align with the first available default tab stop to the right of the x.
Align the variable x
Next, click the 
You can now change the formatting easily by just dragging the tab stops around on the Tab Well pane of the ruler.
Align the two lines at decimal points
Now we’re going to align the two decimal points. To prepare for this, first, remove the 
That’s it for this tutorial, so delete your equation to be ready for the following tutorial.
Inserting symbols that aren’t in the palettes
In this tutorial, you’ll learn how to use MathType Insert Symbol dialogue to locate and use symbols that are not readily available in the built-in palettes. Suppose, for example, you will be writing a document about some newly-invented operations on sets that are analogous to conventional union and intersection. You will want to find symbols to represent your new set operations, and it would be nice if these were similar to the traditional ∪ and ∩ symbols. Your first attempt might be to use bold versions of the conventional symbols to represent your new operations, like this:
Unfortunately, the bold symbols look too much like the regular ones, so we’ll try to find a better solution.
Create the equations
Create the equations as shown above.
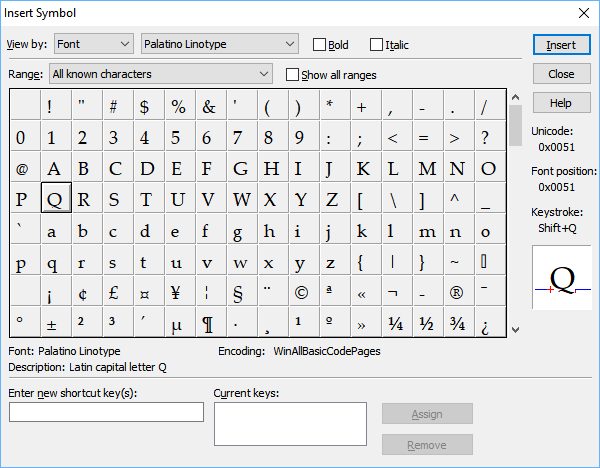
Open the Insert Symbol dialogue
From MathType Edit menu, choose Insert Symbol. The following dialogue will appear:
This dialogue is somewhat similar to Microsoft Word, the Windows Character Map app, and the Mac Character Viewer, at least one of which you may already know how to use.
You can use the Insert Symbol dialogue to browse all the fonts available on your computer and investigate MathType knowledge of them. Precisely, you can:
-
Insert a specific character or mathematical symbol into your equation.
-
Add a frequently used symbol to the toolbar.
-
Add a keyboard shortcut for a frequently used symbol.
-
Find a symbol by matching words in its description.
Symbol font
The first place to look for usable symbols is the Symbol font, so select Symbol from the list of fonts near the top of the Insert Symbol dialogue. A quick way to locate a font is to click on the list and type the first letter or two of the font’s name. Once you select the font you want, you can scroll through the large grid of characters in the centre of the dialogue, looking for likely prospects.
Caution
Larger symbol display
To enlarge the characters in the Insert Symbol dialogue, choose Workspace Preferences from MathType Preferences menu, and set Toolbar size to Medium or Large.
Other symbol fonts
You might also look in the Euclid Symbol and Wingdings fonts. The Insert Symbol dialogue tells you that Symbol and Euclid Symbol have the same «encoding» (arrangement of characters). So, if you don’t find the characters you need in one of these two fonts, you won’t find them in the other, either.
Search for a symbol
The Insert Symbol dialogue provides a more intelligent way to search for the characters you need, rather than just browsing through fonts. In the View by field, choose Description. Click the New Search button, type the word union, and select OK. The grid of characters will now show you several union-like symbols.
When there are too many to show
In the Insert Symbol dialogue, uncheck «Show one of each» to see all the characters on your computer that MathType knows about and which have the word «union» in their names. There may be a few dozen such characters depending on which fonts you have installed. If you are overwhelmed by the vast array of characters shown, click «Show one of each» to reduce the number. This causes the dialogue to display only one character (from the first font that contains it) for each description matched by the search criteria.
Look for a suitable symbol for union
Click a few of the promising-looking union characters, to see what MathType can tell you about them. Among other things, MathType will give you a description of the character, the font in which it was found, and the corresponding keystroke.
Try the double union symbol
One of the characters you should see is 
Now a suitable symbol for intersection
Using the techniques outlined above, search for symbols with «intersection» in their names. You should find 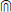
Switch fonts
In the «View by» list, choose Font, and select Euclid Math Two from the list of fonts near the top of the Insert Symbol dialogue. Scroll down to the bottom of the character grid until you see the 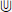
Caution
Keyboard shortcuts
The Insert Symbol dialogue allows you to assign a keyboard shortcut to any character in any font.
Save the new symbols to the toolbar
You can click Insert to insert symbols directly from the Insert Symbol dialogue. However, if you’re going to be using them repeatedly, you’ll want to place them on one of the MathType bars for easier access. Press and hold Alt (Mac: Command ) and drag the 
Now use the new symbols
Edit your equations to use the new symbols:
MathType knows all about the Euclid Math Two font, so it realizes the 
Customizing the keyboard
MathType has built-in keyboard shortcuts for its commands and the most commonly used symbols and templates. However, you can change any of the MathType shortcuts, and you can also assign your shortcuts for any items you place on the toolbar. See Keyboard shortcuts for a complete list of the built-in shortcuts.
Caution
Watch the Status Bar As you move the mouse over items in the palettes, MathType status bar – that’s the very bottom of the MathType window – displays a brief description of the current item, including its keyboard shortcut if one has been defined.
We’ll define a shortcut for a template that doesn’t already have one.
Using the same template several times
Let’s assume that you have to create several equations that include the 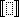
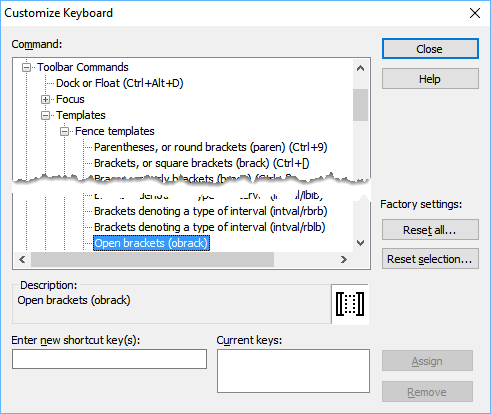
Customize Keyboard dialog
The Customize Keyboard dialogue will appear. The panel titled Command: contains a hierarchical list of all the MathType commands that can be assigned keyboard shortcuts. We want to assign one to a toolbar item, so click on the + next to the Toolbar Commands category. An indented list will appear underneath Toolbar Commands. Click on the + next to Templates in this list, and then on the + next to Fence Templates.
Find Open brackets
Select Open brackets (obrack) from the list (you may have to scroll the list down a little for this item to appear).
The template 
Shortcuts
Click inside the text box labelled «Enter new shortcut key(s)».
Create a shortcut
Type Ctrl+T , followed by [. Notice a message below the box indicating that this shortcut is already assigned to the Left Bracket command. If we assign this combination to the Open Brackets template, it would be removed from the Left Bracket command. When assigning new shortcuts, always check that you don’t accidentally overwrite an existing shortcut.
Caution
Multiple shortcuts
You can assign more than one shortcut for the same symbol, template, or menu command if you desire.
Assign a different shortcut
Press backspace once, and then type Alt+[. This time there’s no current assignment. Now click the Assign button, and you’ll see the shortcut appear in the Current Keys list, as well as being appended to the Open Brackets item in the list of commands.
Try the shortcut
Click Close to close the dialogue, then type Ctrl+T followed by Alt+[. You’ll see the open brackets template appear in the equation window.
Caution
Customize Keyboard
The Customize Keyboard dialogue lets you reset a command’s shortcut to its default setting by selecting it and clicking Reset Selection. Click Reset All to reset every command’s shortcuts to their original settings.
Since there are so many commands available in MathType, both one-key and two-key shortcuts are supported. MathType defines shortcuts for many templates using the form Ctrl+T followed by another character, which is why we used this particular combination. Of course, you’re free to define your own schemes as you see fit.
Two-key shortcuts
When MathType displays a two-key shortcut, it will be in the form of the first key, a comma, the second key. For the shortcut created in Step 7 above, we’d show that as Ctrl+T , Alt+[. Other common two-key shortcuts are Greek letters: Ctrl+G , A for a lower-case alpha or Ctrl+G , Shift + S for a capital Sigma, for example. When you release the first key or key combination, you have four seconds to press the second key or key combination.
Assigning a shortcut to a toolbar expression
Custom toolbar items
Make sure the Small Tabbed Bar is visible, and click the Algebra tab. We will assign a shortcut to the 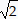
Expression Properties dialogue
Right-click the item and choose the Properties command (Mac: Expression Properties) from the context menu that appears. In the Expression Properties dialogue (Mac: Template Properties) that opens, you’ll see the same keyboard shortcut items we saw in the Customize Keyboard dialogue.
Enter the shortcut
Enter the shortcut Alt+R for this expression and close the dialogue.
Try the shortcut
Type Alt+R and 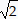
We could have assigned a shortcut for this expression using the Customize Keyboard dialogue, but locating the command would have involved clicking on Toolbar Commands, Tabs, Tab 1, Small Bar, Expression 14. Right-clicking the expression directly is a lot faster!
Working with TeX, LaTeX, & MathML
This tutorial teaches you how to convert MathType equations into textual markup languages, such as TeX, LaTeX, and MathML. Our primary focus will be on LaTeX, but techniques for other languages are very similar.
In creating your LaTeX document, we assume you will be running MathType simultaneously as your usual TeX system.
Caution
Not a TeX processor nor a TeX/MathML editor
MathType uses a system of translators to convert the MathType equation into TeX/LaTeX/MathML code. It does not create a complete TeX document, nor is it natively a TeX or MathML editor. Just as with spoken languages, any time translation is involved, there is the risk of something being translated not optimally, or perhaps even incorrectly. If you come across cases of this, please let us know by emailing our Tech Support department.
Suppose you want to create the following paragraph in your LaTeX document:
Here’s how to do it:
Begin the document
Type In the quadratic formula in your text editor or TeX system.
Open MathType
Run MathType by choosing it from the Start menu, Programs menu, Applications folder, etc. (In other words, don’t run it by opening it from Word, Pages, or another application.)
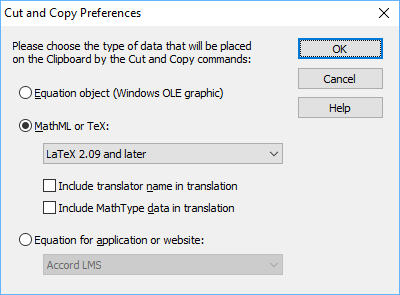
Cut and Copy Preferences dialogue
From MathType Preferences menu, choose Cut and Copy Preferences. In the dialogue that appears, set the options as shown below, and then select OK.
Type formula
Create the quadratic formula in MathType
Copy it
From MathType Edit menu (or using shortcuts), choose Select All and then Copy.
Paste into the TeX document
Switch back to your text editor, and choose Paste. This will insert the following text into your document:
%%[ x = frac- bpm sqrt {b^{2} - 4ac}2a ]%%
If you are familiar with LaTeX, you will recognize this as the LaTeX source code for the quadratic formula.
Resume typing the document text
Continue typing the discriminant, then switch back to MathType
Another MathType expression
Create the discriminant term 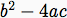
Inline Equation
In MathType Format menu, choose Inline Equation. MathType generates the appropriate LaTeX code for an inline equation.
Copy and paste into the document
Copy the expression from step 8, paste it into your text document, and then type the most important term. Your document should now look something like this:
In the quadratic formula
[x = frac{{ - bpm sqrt {b^{2} - 4ac} }}{{2a}}]
the discriminant $ {b^{2} - 4ac} $ is the most important term.
Translator options
In many situations, it is helpful to be able to transfer old equations from a TeX document back into MathType for editing or reuse. This is generally possible, whether the equations were initially created in MathType or not. However, if you are creating TeX equations with MathType and there’s a chance you or someone else may need to translate them back into MathType in the future, it’s helpful to be familiar with the translator options.
To understand the approach, choose Cut and Copy Preferences from MathType Preferences menu, and check the box labelled «Include MathType data in translation». Now create the quadratic formula again and copy & paste it into your text document. This time, the resulting text will be
% MathType!MTEF!2!1!+-
% feaaguart1ev2aaatCvAUfeBSjuyZL2yd9gzLbvyNv2CaerbuLwBLn
% hiov2DGi1BTfMBaeXatLxBI9gBaerbd9wDYLwzYbItLDharqqtubsr
% 4rNCHbGeaGqiVu0Je9sqqrpepC0xbbL8F4rqqrFfpeea0xe9Lq-Jc9
% vqaqpepm0xbba9pwe9Q8fs0-yqaqpepae9pg0FirpepeKkFr0xfr-x
% fr-xb9adbaqaaeGaciGaaiaabeqaamaabaabaaGcbaGaamiEaiabg2
% da9maalaaabaGaeyOeI0IaamOyaiabgglaXoaakaaabaGaamOyamaa
% CaaaleqabaGaaGOmaaaakiabgkHiTiaaisdacaWGHbGaam4yaaWcbe
% aaaOqaaiaaikdacaWGHbaaaaaa!42E1!
[x = frac{{ - b pm sqrt {{b^2} - 4ac} }}{{2a}}]
The first nine lines of text (the ones starting with a % sign) are a TeX comment containing MathType own private representation of your equation. When you paste it back into MathType , you must select this comment so it will be converted precisely back into a regular MathType equation. If you change the comment in any way, the transfer back to MathType will not work. TeX comments are ignored during the typesetting process not to affect your final output.
What’s not included in the translation?
Note that if you copy only the TeX code and paste it into MathType (without the MathType data), the equation will usually appear just fine. But let’s say you copied this equation from a Word document to translate into TeX, and now you want to paste it back into MathType to use in PowerPoint. MathType allows many adjustments to the appearance of the equation that isn’t carried over to the TeX translation. If you had made adjustments to the colour of the equation, the font face, the font size, or some spacing adjustments, these would not appear in the TeX code, but they will be retained in the MathType code. Therefore, keeping the MathType code with the equation ensures you will be able to paste the equation back into MathType precisely as it was when you initially created it.
MathType Cut and Copy Preferences dialogue also provides the «Include translator name in translation» option, which helps to delineate and identify equations in your documents. This might be useful if you want to write programs that search your TeX source files looking for equations and process them in some way.
Other translators
MathType includes translators for several dialects of TeX (Plain TeX, AMS-TeX, LaTeX, and AMS-LaTeX). These dialects correspond to various packages of TeX macros, which you must load before you typeset your document. For example, to typeset AMS-LaTeX code, you must include the commands documentclass{amsart} or usepackage{amsmath}, or some equivalent somewhere in the preamble of your document. Please consult your TeX or LaTeX documentation for more details.
Wikipedia and many other blogs, wikis, and websites represent math in a language called Texvc, which is essentially a subset of TeX math. MathType includes a Texvc translator tuned for use with Wikipedia and a second generic Texvc translator that works with many other sites that use TeX. Because Texvc is somewhat more straightforward than different TeX dialects, one of these translators is often a good choice if you edit the equation further by hand. MathType has a Toggle TeX feature that allows you to toggle back and forth between Texvc and MathType views of an equation in Microsoft Word.
MathType also includes translators for using MathType with several other applications and websites, including Maple, Mathematica, Physics Forum, Wikipedia, and Wolfram|Alpha. Look for these applications by name in the Equation for application or website section of the dialogue.
The list of available translators is constantly growing. See Using MathType with Applications and Websites for more information.
MathML
We also supply translators for MathML, a markup language based on XML (eXtensible Markup Language) for encoding mathematics. The current version of MathML is MathML 3.0, but MathType doesn’t yet have translators for the additional capability provided by MathML 3. MathType comes with three MathML 2.0 translators that only differ in the namespace in which the MathML is placed. Which one you should pick is determined by the MathML renderer you use – either an added rendering tool (such as MathJax) or a browser with built-in MathML support (Firefox and, to a lesser extent, Safari, and perhaps others).
Creating and modifying translators
If our standard translators do not meet your needs, you may want to modify one of them or write a new one of your own. Each translator is driven by a translation file written in our Translator Definition Language (TDL). You will find several TDL files in the MathType Translators folder, and you can edit these to suit your needs or write completely new ones.
Exporting equations in Microsoft Word
This tutorial shows you how to export all the equations in a Word document to individual graphics files. You can export them as GIF, EPS, WMF, PICT (Mac), or PDF (Mac) files, and you can control the location and naming of the files. You also have the option to replace each equation with the name of its corresponding file. This feature can be helpful when importing Word documents into desktop publishing programs. Some software doesn’t import embedded equations very well, preferring individual equation files. The Export Equations command makes this process much more manageable.
Launch Microsoft Word
Launch Word and create a document containing a couple of equations.
Export Equations dialogue
Choose the Export Equations command on Word’s MathType menu or in the Publish group on Word’s MathType tab. The Export Equations dialogue will appear.
Where to save the images?
Enter a location in the Folder field. You can either type the name of a folder or click the Browse button and select a folder. If you enter the name of a folder that doesn’t exist, you will be asked if you want to create it. Check the «Delete all files of the same type in folder» checkbox if you wish all files with the same extension deleted from this folder before exporting. Be careful if you select this option; if you export as GIF files to the folder C:My Documents, every GIF file in this folder will be deleted. It’s usually safest to create a new folder for each set of exported equation files.
Which image format?
Select the format of the exported equation files. You can also set the filename pattern and the starting number. The above example will create the files Eqn001.gif, Eqn002.gif etc. Setting the pattern to «PhysIntro###» and the first number to 50 will create the files PhysIntro050.eps, PhysIntro051.eps, etc. You may want to experiment with different patterns and numbers.
Replace equation with file name
Check the «Replace equation with file name» checkbox if you want to replace each equation exported from the document with the corresponding file name. For example, the above settings would insert the text <<Eqn001.gif>> in place of the first exported equation. Clear this checkbox if you want to leave the equations in the document unmodified.
«Whole document»?
Choose the «Whole document» option to export all equations in the document. The «Current selection» option is enabled only when selecting a portion of the document before running the Export Equations command.
Export the equations
Click OK to start the exporting process. When the process has finished, a dialogue appears showing how many equations were exported.
Simplifying rational expressions by dividing common factors
In mathematics, it’s often necessary to mark through a term in an expression to show borrowing in a subtraction problem, to divide out common factors in a rational expression, etc. It’s a trivial matter with a pencil and paper to perform such a «strike-through», but it’s a different matter when writing a document in your word processor. This tutorial will show how to make such annotations with MathType We’ll assume you’re preparing a worksheet showing how to simplify a rational expression:
We want to show students how to divide out the common factors, so we’ll use MathType strike-through templates.
Begin the equation
Create the first fraction shown above, then type = and insert the second fraction template:
Strike-through templates
Before typing the numerator, choose the «Strike-through (bottom-left to upper-right)» template from the «Underbar and overbar» templates palette:
Type the expression inside the strike-through template
Inside the strike-through template, type the first factor in the numerator. Press Tab to exit the strike-through template, then type the second factor:
Caution
Strike-through thickness
If the strike-through line isn’t distinct enough when you print or project it, you can increase its thickness. From the Format menu, choose Define Spacing. Scroll down near the bottom of the list until you find Strike-through consistency. Increase the thickness to a value that will make the strike-through more vivid. It’s unnecessary to click Apply before clicking OK, but doing so allows you to try out different thickness values before choosing the one you like best.
Repeat for the denominator
Repeat these steps for the denominator.
Caution
Strike-throughs in colour
An excellent way to draw attention to a part of an expression is to create contrasting colours. If you’re printing your worksheet in colour or inserting a strike-through into a PowerPoint presentation, choose the strike-through colour before choosing the template, then select the strike-through template. If you want the contents to be black, switch back to black before typing the contents.
Type the second line to complete
If you want to complete the solution steps, press Enter when you’re finished with the second fraction. Type another =, then type the final fraction in simplified form. To align the two lines at the = symbols, choose the Align at = command from the Format menu. The last problem solution should look like this:
Caution
Length of the strike-through
If it looks to you like the strike-throughs are too long, you can adjust the length in a way similar to the way we described adjusting the strike-through thickness above. Scroll down for the «Radical gap (vertical)» value in the Define Spacing dialogue. A smaller value for this parameter will result in a shorter strike-through. Be aware, though, and it will also have the apparent additional effect, which may not be desired. (That is, it will also affect the vertical distance between a radicand and the radical stroke above it.)
What to do next
This concludes the last of our tutorials. We certainly haven’t covered everything MathType can do, but if all went well then you’ve grasped the basic principles. Using MathType with applications and websitescontains additional information about using MathType with other applications. Creating web pages with MathPage introduces MathType MathPage technology, and shows how you can generate great-looking web pages from Word documents.
The Style menu section covers MathType styles and advanced formatting. It’s not necessary to read these sections immediately, but once you’ve progressed beyond creating simple equations you’ll find them worth reading. If you get stuck, please get in touch with us – our contact information is listed on our website.
MathType — профессиональный инструмент для набора формул и уравнений в документах. Применяется совместно с любым текстовым редактором, презентационной или полиграфической программой. Работает с более чем 350 приложениями и интернет-ресурсами, такими как: Microsoft Office, MATLAB, Wikipedia, Mathematica, Gmail, Maple, Google Docs, OpenOffice, Mathcad, Adobe InDesign.
Содержит огромную коллекцию математических выражений и символов, которые позволят без труда написать даже самое сложное уравнение (более 500 математических символов и шаблонов: дроби, радикалы, суммы, интегралы, произведения, матрицы, различные виды квадратных и фигурных скобок).
Особенности:
- Автоматический выбор шрифтов, стиля, интервала и расположения во время набора уравнения.
- Ввод выражений вручную. Эта функция доступна в системе Windows 7, в которой встроена функция распознавания рукописного текста.
- Полученные уравнения автоматически вставляются в виде рисунка, что позволяет просматривать их на любом компьютере, даже там, где MathType не установлен.
- Вкладка с программой может быть встроена в пользовательские интерфейсы приложений Word и PowerPoint.
- Поддержка редактирования уже вставленных формул доступна любому пользователю, у которого установлен MathType.
- Ввод выражений на языке TeX, LaTeX и MathML.
- Изменение цвета формул.
После окончания срока бесплатного использования, программа начнет запускаться в Lite-режиме. Это стандартный Редактор уравнений (Equation Editor), только с бонусами в виде шрифтов и символов, доступных в MathType.
Вот конкретные шаги.
Шаг 1: Сначала запустите MathType, нажмите команду «Определить» в меню «Размер», а в китайском варианте «Размер» — «Определение».

Нажмите «Размер» — «Определить»
Шаг 2: Откройте диалоговое окно «Определить размеры», мы можем отрегулировать размер шрифта в поле ввода после «Полный» (например, если шрифт слова маленький пять, соответствующий размер формулы устанавливается на 9 пунктов). Другие элементы в формуле автоматически корректируются соответствующим образом, поэтому, как правило, никаких других изменений не требуется. Нажмите кнопку «ОК», чтобы закрыть диалоговое окно. В открывшемся диалоговом окне «Определить размер» вы можете ввести размер шрифта, который нужно настроить после «Полный», и нажать «ОК».

диалоговое окно определения размеров
Шаг 3: Размер шрифта Word2003 и таблица сравнения PT Mathtype6.0 word, таблица сравнения размеров шрифта выглядит следующим образом.

Таблица сравнения размеров шрифта
Шаг 4: Нажмите команду «Настройки уравнения → Сохранить в файл» в меню «Настройки», чтобы сохранить выбранные нами параметры в файле с суффиксом «eqp». Нажмите кнопку «Параметр» — «Параметр формулы» — «Сохранить в файл» в меню основного интерфейса, чтобы сохранить предыдущие настройки в виде файла формата «.eqp». (В установочном каталоге MathType ../ mathtype / preferences / file.eqp).

Нажмите «Настройки уравнения → Сохранить в файл» в меню «Настройки»
Шаг 5. Это формат сохранения. Мы откроем его позже в WORD. Это ключевой файл для настройки размера формулы.)

Сохранить интерфейс
Шаг 6: Затем вернитесь в среду Word и нажмите команду «Уравнения формата» в меню «MathType» (возможно, многие знакомые сталкивались с тем, что строка меню не отображает параметр mathtype, см. Решение ниже).

Нажмите MathType —— Уравнения формата
Шаг 7: Откройте диалоговое окно «Уравнения формата».

Диалог форматирования уравнений
Шаг 8: Затем выберите опцию «Файл предпочтений MathType» в открывшемся диалоговом окне «Уравнения формата» и нажмите кнопку «Обзор». Найдите файл text.eqp, который мы сохранили, и дважды щелкните его. Затем выберите опцию «Весь документ» в пункте «Диапазон» ниже, нажмите кнопку «ОК» и подождите некоторое время, вы увидите, что все формулы были настроены в соответствии с указанным размером шрифта.

Нажмите кнопку Обзор, чтобы найти соответствующий файл
Шаг 9: На следующем рисунке показан эффект после настройки. Это удобно?

Модифицированный тест по математике
Выше показано, как MathType регулирует размер формул в документах Word в пакетах. Шаги просты и понятны. С помощью описанных выше шагов вы можете завершить пакетную модификацию шрифтов и размеров формул в редакторе формул MathType.Редактор формул 6.0 скачатьВы можете скачать последнюю версию MathType 6.9b.