Программное создание границ ячеек произвольного диапазона с помощью кода VBA Excel. Свойство Borders объекта Range. Создание границ одной ячейки. Код макроса.
Программное создание границ ячеек
Если записать макрос добавления границ к ячейкам какого-нибудь диапазона, то в тексте макроса будет сгенерировано очень много строк с указанием различных параметров. Создать сетку из границ ячеек с параметрами «по умолчанию» можно гораздо проще.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 |
‘Для этого необходима всего одна строка: Range(«A1:G7»).Borders.LineStyle = True ‘Вместо ключевого слова True можно ‘использовать константу xlContinuous: Range(«A1:G7»).Borders.LineStyle = xlContinuous ‘Кроме того, для создания границ ячеек можно ‘использовать единственную строку с указанием ‘какого-нибудь параметра, например, ‘для создания сетки из синих границ: Range(«A1:G7»).Borders.Color = vbBlue ‘или для создания сетки из границ в виде двойных линий: Range(«A1:G7»).Borders.LineStyle = xlDouble ‘Чтобы применить при создании границ два ‘параметра, придется использовать уже две ‘строки кода, например, для создания сетки ‘из границ в виде жирных красных линий: Range(«A1:G7»).Borders.Weight = xlThick Range(«A1:G7»).Borders.Color = vbRed ‘Удалить границы можно с помощью строки: Range(«A1:G7»).Borders.LineStyle = False ‘Вместо ключевого слова False можно ‘использовать константу xlNone: Range(«A1:G7»).Borders.LineStyle = xlNone |
Создание границ одной ячейки
Создать границы ячейки (только для одной ячейки) в VBA Excel можно следующим образом:
|
Range(«A5»).Borders.LineStyle = True Cells(2, 8).Borders.Color = vbBlue ActiveCell.Borders.LineStyle = xlDouble ‘Удаление границ: ActiveCell.Borders.LineStyle = False |
Пример кода записанного макроса
Запись макроса: включаем запись, выбираем диапазон «A1:E9», на панели инструментов выбираем значок «Все границы», останавливаем запись. И это все наши выполненные действия, а в результате получаем следующий код:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 |
Sub Макрос1() Range(«A1:E9»).Select ‘Отображается левая граница диапазона With Selection.Borders(xlEdgeLeft) .LineStyle = xlContinuous .ColorIndex = 0 .TintAndShade = 0 .Weight = xlThin End With ‘Отображается верхняя граница диапазона With Selection.Borders(xlEdgeTop) .LineStyle = xlContinuous .ColorIndex = 0 .TintAndShade = 0 .Weight = xlThin End With ‘Отображается нижняя граница диапазона With Selection.Borders(xlEdgeBottom) .LineStyle = xlContinuous .ColorIndex = 0 .TintAndShade = 0 .Weight = xlThin End With ‘Отображается правая граница диапазона With Selection.Borders(xlEdgeRight) .LineStyle = xlContinuous .ColorIndex = 0 .TintAndShade = 0 .Weight = xlThin End With ‘Отображаются внутренние вертикальные линии With Selection.Borders(xlInsideVertical) .LineStyle = xlContinuous .ColorIndex = 0 .TintAndShade = 0 .Weight = xlThin End With ‘Отображаются внутренние горизонтальные линии With Selection.Borders(xlInsideHorizontal) .LineStyle = xlContinuous .ColorIndex = 0 .TintAndShade = 0 .Weight = xlThin End With End Sub |
Конечно, можно использовать в своих программах код, сгенерированный при записи макроса, который будет прекрасно работать. Вот только нужны ли в самописном коде такие нагромождения лишних строк?
Макросы можно и нужно использовать, когда вы не знаете название нужного свойства или его значения, а после записи макроса открываете модуль и все перед глазами. Это касается не только создания границ ячеек, но и всех остальных случаев, когда предполагаемые действия можно записать с помощью макроса.
Создание и удаление диагональных линий
Диагональные линии не относятся к границам ячеек, но принцип работы с ними тот же. Отличие заключается в том, что для отображения и удаления диагональных линий, их необходимо указывать явно:
|
‘Создание диагональных линий: Range(«A1:G7»).Borders(xlDiagonalDown).LineStyle = True Range(«A1:G7»).Borders(xlDiagonalUp).LineStyle = True ‘Удаление диагональных линий: Range(«A1:G7»).Borders(xlDiagonalDown).LineStyle = xlNone Range(«A1:G7»).Borders(xlDiagonalUp).LineStyle = xlNone |
Расположение границ ячеек и диапазонов
Расположение границ по краям и внутри ячеек и диапазонов описывают константы из коллекции XlBordersIndex.
Список констант XlBordersIndex:
| Константа | Значение | Описание |
|---|---|---|
| xlDiagonalDown | 5 | Диагональная линия от верхнего левого угла к нижнему правому углу в каждой ячейке диапазона. |
| xlDiagonalUp | 6 | Диагональная линия от нижнего левого угла к правому верхнему углу в каждой ячейке диапазона. |
| xlEdgeBottom | 9 | Граница по нижнему краю диапазона. |
| xlEdgeLeft | 7 | Граница по левому краю диапазона. |
| xlEdgeRight | 10 | Граница по правому краю диапазона. |
| xlEdgeTop | 8 | Граница по верхнему краю диапазона. |
| xlInsideHorizontal | 12 | Горизонтальные границы для всех ячеек в диапазоне, за исключением внешних границ диапазона. |
| xlInsideVertical | 11 | Вертикальные границы для всех ячеек в диапазоне, за исключением внешних границ диапазона. |
|
‘Отображаем у выделенной ячейки нижнюю границу с толщиной и стилем по умолчанию (xlThin и xlContinuous) ActiveCell.Borders(xlEdgeBottom).LineStyle = True ActiveCell.Borders(xlEdgeBottom).LineStyle = 1 |
Толщина границ ячеек и диапазонов
Толщину границ по краям и внутри ячеек и диапазонов описывают константы из коллекции XlBorderWeight.
Список констант XlBorderWeight:
| Константа | Значение | Описание |
|---|---|---|
| xlHairline | 1 | Очень тонкая граница |
| xlThin | 2 | Тонкая граница (по умолчанию) |
| xlMedium | -4138 | 3* | Граница средней толщины |
| xlThick | 4 | Толстая граница |
* У меня, в Excel 2016, константе xlMedium соответствует не только числовое значение -4138, но и 3.
|
‘Отображаем у выделенной ячейки нижнюю границу в виде толстой линии ActiveCell.Borders(xlEdgeBottom).Weight = xlThick |
Стили границ (типы линий)
Стили границ по краям и внутри ячеек и диапазонов описывают константы из коллекции XlLineStyle.
Список констант XlLineStyle:
| Константа | Значение | Описание |
|---|---|---|
| xlContinuous | 1 | Непрерывная линия |
| xlDash | -4115 | Штриховая линия |
| xlDashDot | 4 | Чередование точек и тире |
| xlDashDotDot | 5 | Чередование двух точек и тире |
| xlDot | -4118 | Пунктирная линия |
| xlDouble | -4119 | Двойная линия |
| xlLineStyleNone | -4142 | Нет границы (удаление границы) |
| xlSlantDashDot | 13 | Линия, разрезанная двойными слешами |
Применяем разные типы линий к разным сторонам выделенного диапазона:
|
Sub Primer() With Selection .Borders(xlEdgeTop).LineStyle = xlDash .Borders(xlEdgeTop).Weight = xlMedium .Borders(xlEdgeRight).LineStyle = xlDouble .Borders(xlEdgeBottom).LineStyle = xlDot .Borders(xlEdgeLeft).LineStyle = xlDashDot End With End Sub |
Какие могут быть границы в сочетаниях типа линии и ее толщины, вы можете видеть в диалоговом окне «Формат ячеек» на вкладке «Граница».
Рисовать границы для разных ячеек вручную – это потребует много драгоценного времени и сил. Лучше применить специальный макрос, который сам поставит границы с разными типами и цветами линий для объединенных и необъединенных ячеек. Он автоматически определит положение объединенных ячеек и сам присвоит им линии границ в соответствии со всеми пожеланиями пользователя.
Как изменить границы макросом в ячейках таблицы Excel
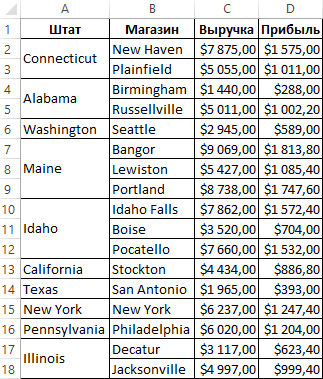
У нас иметься отчет по продажам в магазинах целой ритейловской сети, которые разделены на группы городов по отдельным штатам. В таблице отчета имеются объединенные ячейки:
Нам необходимо:
- Отформатировать ячейки таблицы таким образом, чтобы были установленные границы с толстой линией только для диапазонов каждого отдельного штата. А внутри группы городов каждого штата необходимо установить ячейкам границы с тонкой линией.
- Таким же образом хотим форматировать ячейки в объединенных диапазонах, охватывающих несколько столбцов. А, столбцы с показателями продаж и выручки необходимо отделить тонкими линиями. Дополнительно целая таблица должна иметь самую толстую линию для внешней границы по периметру.
- Если объединенная ячейка охватывает несколько строк, то границы ячеек, отделяющие эти строки, будут иметь тоненькие линии. По аналогичному принципу будут определены границы столбцов которых охватывает объединенная ячейка.
Напишем свой макрос, который сам автоматически выполнит весь этот объем работы для любой таблицы. Откройте редактор Visual Basic (ALT+F11):
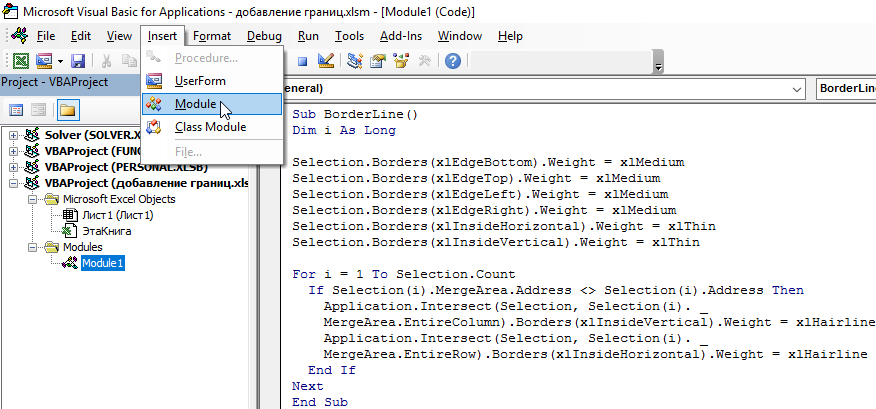
А затем создайте новый модуль с помощью инструмента: «Insert»-«Module». А потом введите в него следующий VBA-код:
Sub BorderLine()
Dim i As Long
Selection.Borders(xlEdgeBottom).Weight = xlMedium
Selection.Borders(xlEdgeTop).Weight = xlMedium
Selection.Borders(xlEdgeLeft).Weight = xlMedium
Selection.Borders(xlEdgeRight).Weight = xlMedium
Selection.Borders(xlInsideHorizontal).Weight = xlThin
Selection.Borders(xlInsideVertical).Weight = xlThin
For i = 1 To Selection.Count
If Selection(i).MergeArea.Address <> Selection(i).Address Then
Application.Intersect(Selection, Selection(i).MergeArea.EntireColumn).Borders(xlInsideVertical).Weight = xlHairline
Application.Intersect(Selection, Selection(i).MergeArea.EntireRow).Borders(xlInsideHorizontal).Weight = xlHairline
End If
Next
End Sub
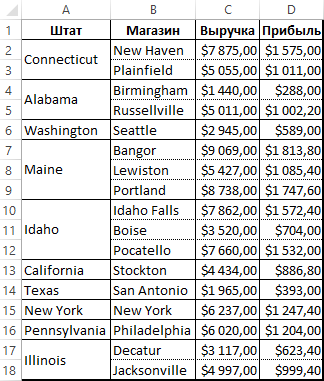
Теперь если мы хотим автоматически форматировать целую таблицу в один клик мышки, выделите диапазон A1:D18. А потом просто выберите инструмент: «РАЗРАБОТЧИК»-«Код»-«Макросы»-«BorderLine»-«Выполнить».
Чтобы группы данных по строкам и столбцам на против объединенных ячеек были экспонированы границами пользовательской толщены, сначала кода присваиваем линию увеличенной толщины для внешних границ выделенного диапазона. А внутренним границам присваивается линия со стандартной толщиной. Далее с помощью цикла выполняется проход по каждой ячейке выделенного диапазона и все они проверяются. Если ячейка является объединенной, то ей присваивается соответственная граница. Конечно же изменения границ касаются только для ячеек внутри выделенного диапазона.
С помощью свойства Weight можно установить 4 типа толщины линии для границ ячеек:
- xlThink – наиболее толстая линия.
- xlMedium – просто толстая граница.
- xlThin – стандартная толщина линии для границ.
- xlHairLine – свойство для самой тонкой границы ячейки.
Внимание! Если перед использованием макроса некоторые ячейки уже имели свои линии границ в другом цвете кроме черного или их лини были в другом стиле, тогда после запуска макроса некоторые ячейки могут получить другой цвет или стиль обводки. Чтобы перестраховаться от таких ошибок, в начале кода макроса, после строки декларации переменной i, вставим еще 2 строки с кодом:
Selection.Borders.Color = vbBlack
Selection.Borders.Color = xlContinuous
Полная версия макроса, работающего безошибочно при любых условиях и форматах для исходной таблицы:
Sub BorderLine()
Dim i As Long
Selection.Borders.Color = vbBlack
Selection.Borders.Color = xlContinuous
Selection.Borders(xlEdgeBottom).Weight = xlMedium
Selection.Borders(xlEdgeTop).Weight = xlMedium
Selection.Borders(xlEdgeLeft).Weight = xlMedium
Selection.Borders(xlEdgeRight).Weight = xlMedium
Selection.Borders(xlInsideHorizontal).Weight = xlThin
Selection.Borders(xlInsideVertical).Weight = xlThin
For i = 1 To Selection.Count
If Selection(i).MergeArea.Address <> Selection(i).Address Then
Application.Intersect(Selection, Selection(i).MergeArea.EntireColumn).Borders(xlInsideVertical).Weight = xlHairline
Application.Intersect(Selection, Selection(i).MergeArea.EntireRow).Borders(xlInsideHorizontal).Weight = xlHairline
End If
Next
End Sub
Теперь можно уверенно и быстро красиво форматировать большие таблицы по одному клику мышкой или нажатию комбинации горячих клавиш для вызова соответственного макроса.
To apply borders to a cell using VBA in Excel, you can use two different ways. The first is the “Borders“ property and the second is the “BorderAround” method. The only difference between these two ways is in the “Borders” property you can even apply the border to one side of the cell and in the border around it applies to the cell completely.
In this tutorial, we will explore both ways and look at what are the different ways to add the border.
VBA Border Property
- First, you need to specify the range or the cell where you wish to apply the border using the range object.
- After that, type a dot (.) and then select the “Borders” property from the list of properties and methods.
- Next, specify the border index from the contants avaiable. Here I’m using “xlEdgeBottom” to apply border only to the bottom of the cell.
- From here, specify the line style using the “LineStyle”. I’m using the “xlContinuonus” as the line style.
Sub vba_borders()
Range("A1") _
.Borders(xlEdgeBottom) _
.LineStyle = XlLineStyle.xlContinuous
End SubNow when you run this code, it will add a border to the bottom of the cell A1.

Using Different Colors with Color Index/Color
Just like you normally choose the color for the border when you do it manually. In the border property, you can further use the color index and color property to use a color other than the default color.
Consider the below code.
With Range("A1").Borders(xlEdgeBottom)
.LineStyle = XlLineStyle.xlContinuous
.Color = RGB(255, 0, 0)
End WithWhen you run this macro, it adds a border to the bottom of the cell with a red color.

Or if you want to use the colorindex property then the code would be like.
With Range("A1").Borders(xlEdgeBottom)
.LineStyle = XlLineStyle.xlContinuous
.ColorIndex = 7
End With
Related: VBA With Statement
Add Border Inside a Cell
If you want to apply a border inside a cell, in that case, you need to use “xlDiagonalUp” and “xlDiagonalDown” as the xlBorderIndex.
With Range("A1").Borders(xlDiagonalUp)
.LineStyle = XlLineStyle.xlDashDotDot
.Color = RGB(255, 0, 0)
End With
With Range("A1").Borders(xlDiagonalDown)
.LineStyle = XlLineStyle.xlDashDotDot
.Color = RGB(255, 0, 0)
End With
When you run the above code, it adds a border inside the cell upward and downward.
VBA BorderAround Method
In VBA’s BorderAround property you have 5 arguments to which are optional but two need to be specified to apply the border to a cell in the right way.

The following code applies the border around the range A1:A3 when you run the macro.
Range("A1:A3").BorderAround _
LineStyle:=xlContinuous, _
Weight:=xlThin
Add Border to Each Cell in the Range
The following code loops through all the cells in the range and applies the border to each cell one by one.
Sub vba_borders()
Dim iRange As Range
Dim iCells As Range
Set iRange = Range("A1:A10")
For Each iCells In iRange
iCells.BorderAround _
LineStyle:=xlContinuous, _
Weight:=xlThin
Next iCells
End Sub
Apply Border to All the Cells with Text
The following code uses a FOR LOOP, USED RANGE, IFEMPTY, and IF STATEMENT to apply borders to the only cells where you have value.
Dim iRange As Range
Dim iCells As Range
Set iRange = ThisWorkbook.ActiveSheet.UsedRange
For Each iCells In iRange
If Not IsEmpty(iCells) Then
iCells.BorderAround _
LineStyle:=xlContinuous, _
Weight:=xlThin
End If
Next iCellsRemove Borders
You just need to use line style “xlNone”.
Range("A1").Borders(xlDiagonalDown).LineStyle = xlNoneAnd if you want to remove the border from all the cells in a worksheet where you have a value, consider the following code.
Dim iRange As Range
Dim iCells As Range
Set iRange = ThisWorkbook.ActiveSheet.UsedRange
For Each iCells In iRange
If Not IsEmpty(iCells) Then
iCells.Borders(xlDiagonalDown).LineStyle = xlNone
End If
Next iCellsMore Tutorials
- Count Rows using VBA in Excel
- Excel VBA Font (Color, Size, Type, and Bold)
- Excel VBA Hide and Unhide a Column or a Row
- Excel VBA Range – Working with Range and Cells in VBA
- Find Last Row, Column, and Cell using VBA in Excel
- Insert a Row using VBA in Excel
- Merge Cells in Excel using a VBA Code
- Select a Range/Cell using VBA in Excel
- SELECT ALL the Cells in a Worksheet using a VBA Code
- ActiveCell in VBA in Excel
- Special Cells Method in VBA in Excel
- UsedRange Property in VBA in Excel
- VBA AutoFit (Rows, Column, or the Entire Worksheet)
- VBA ClearContents (from a Cell, Range, or Entire Worksheet)
- VBA Copy Range to Another Sheet + Workbook
- VBA Enter Value in a Cell (Set, Get and Change)
- VBA Insert Column (Single and Multiple)
- VBA Named Range | (Static + from Selection + Dynamic)
- VBA Range Offset
- VBA Sort Range | (Descending, Multiple Columns, Sort Orientation
- VBA Wrap Text (Cell, Range, and Entire Worksheet)
- VBA Check IF a Cell is Empty + Multiple Cells
⇠ Back to What is VBA in Excel
Helpful Links – Developer Tab – Visual Basic Editor – Run a Macro – Personal Macro Workbook – Excel Macro Recorder – VBA Interview Questions – VBA Codes
Borders in VBA Excel
We use borders in Excel to highlight our data. In any dashboard, it is a very important skill to represent the important data, and borders do it. Borders are a property in VBA that we can access using the Range method and giving the appropriate border style as we know there are different border styles.
If you are good at formatting in excelFormatting is a useful feature in Excel that allows you to change the appearance of the data in a worksheet. Formatting can be done in a variety of ways. For example, we can use the styles and format tab on the home tab to change the font of a cell or a table.read more, you can call yourself an “Excel Beautician.” Formatting is vital in making the reports look appealing to the end-user or readers. We hope you are well aware of the formatting techniques in the regular worksheet. Formatting through VBA codingConditional formatting is also possible in Excel VBA programming by using the ‘Format Conditions Collection’ macro/procedure. A conditional format is one that is applied only to cells that meet certain criteria, such as values above a certain threshold, positive or negative values, or values with a specific formula, and so on.read more requires a considerable amount of VBA coding languageVBA code refers to a set of instructions written by the user in the Visual Basic Applications programming language on a Visual Basic Editor (VBE) to perform a specific task.read more. This article will show you one of the most underrated formatting techniques, i.e., applying Excel VBA borders.
Table of contents
- Borders in VBA Excel
- Examples of Borders in VBA
- Example #1 – Apply VBA Borders with Coding
- Example #2 – Change the Border Using VBA Borders Around Method
- Recommended Articles
- Examples of Borders in VBA
You are free to use this image on your website, templates, etc, Please provide us with an attribution linkArticle Link to be Hyperlinked
For eg:
Source: VBA Borders (wallstreetmojo.com)
Examples of Borders in VBA
Let us take a look at some examples to understand this in a better manner.
You can download this VBA Borders Excel Template here – VBA Borders Excel Template
Example #1 – Apply VBA Borders with Coding
Creating a macro to apply Excel VBA borders with different styles, making them available as an add-on to the excelAn add-in is an extension that adds more features and options to the existing Microsoft Excel.read more ribbon, makes the job easier whenever we want to apply VBA borders.
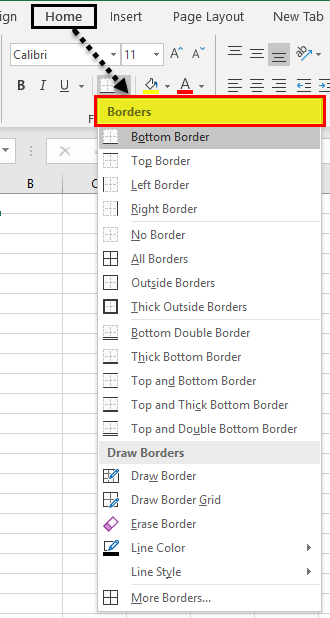
Every cell in a worksheet has borders and background colors. By default, every cell has no border and background color.
In the worksheet under the HOME tab, we have a border option. In addition, we have various options if you click on the drop-down list in excelA drop-down list in excel is a pre-defined list of inputs that allows users to select an option.read more.
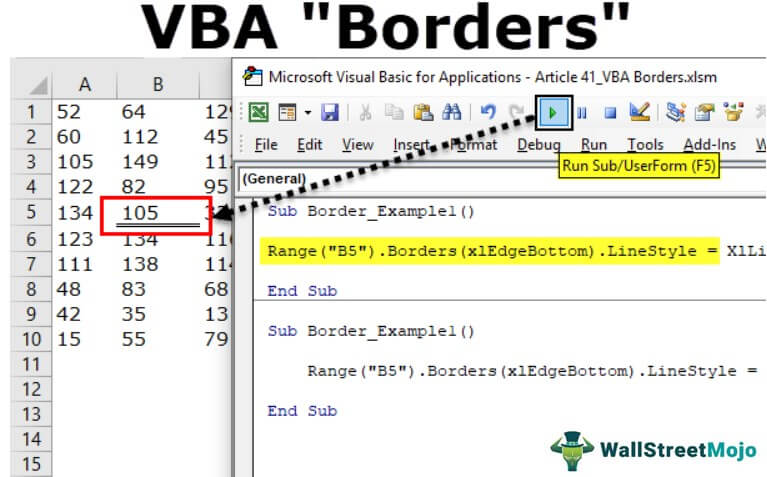
But in VBA, first, we must decide on the cell or range of cells. Then, we will apply the Excel VBA borders formatting styles. So, we can refer to the range of cells or cells using VBA RANGEThe range property of VBA is used to refer to any data, cells, or selection. It is an inbuilt property that allows us to access any part of the worksheet. Using the range property for a single cell-like range is referred to as range cells.read more object. So, for example, if you want to change the border of cell B5, then you can write the code like this.
Range(“B5”)
Then, we need to access the “Borders” property.
Code:
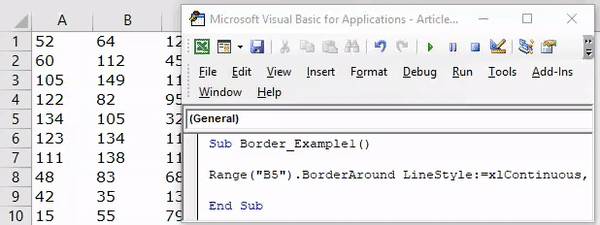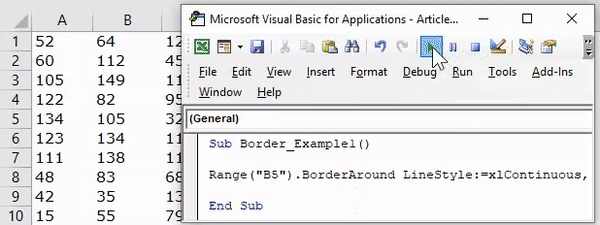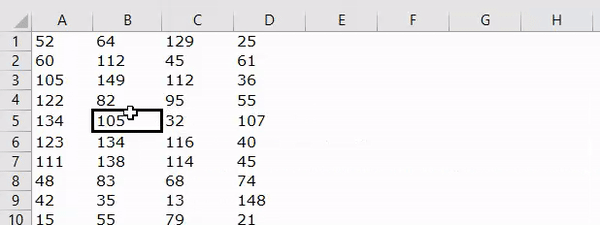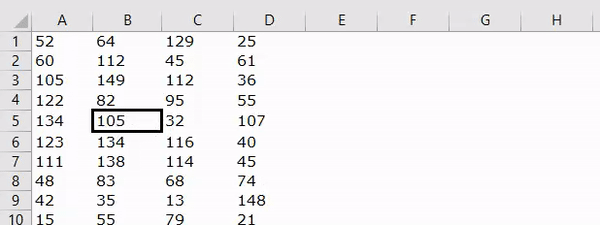
Sub Border_Example1() Range("B5").Bo End Sub
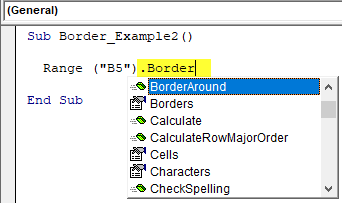
After applying the Excel VBA “Borders” property, we must open parenthesis to see all border formatting options..
Code:
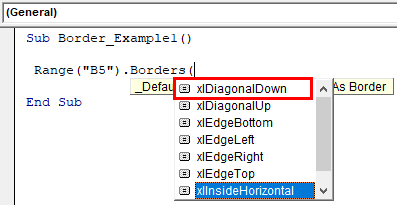
Sub Border_Example1() Range("B5").Borders( End Sub
Here, we have xlDiagonalDown, xlDiagonalUp, xlEdgeBottom, xlEdgeLeft, xlEdgeRight, xlEdgeTop, xlInsideHorizontal, and xlInsideVertical.
After selecting the border style, we need to select the characteristic we want to work with. One of the characters we need to use here is “LineStyle,” so select the “LineStyle” property.
Code:
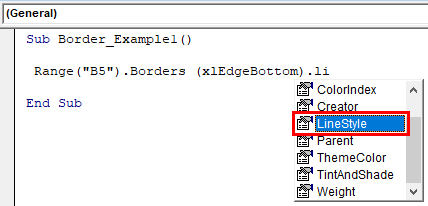
Sub Border_Example1() Range("B5").Borders (xlEdgeBottom).li End Sub
Once the line style property is selected, we need to set the line style type of line or type of borders we will apply in VBA.
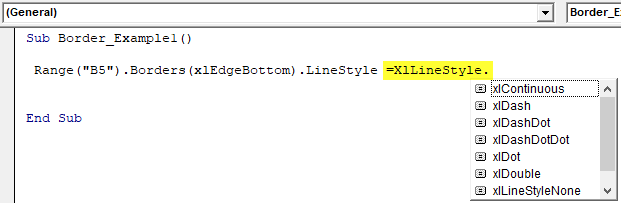
Put an equal sign and select “XlLineStyle” enumeration.
Code:
Sub Border_Example1() Range("B5").Borders(xlEdgeBottom).LineStyle =XlLineStyle. End Sub
Put a dot to see all the available border styles.
Code:
We have many options here. xlContinuous, xldash, xlDashDot, xlDashDotDot, xlDot, xlDouble, XlLineStyleNone, and xlSlantDashDot.
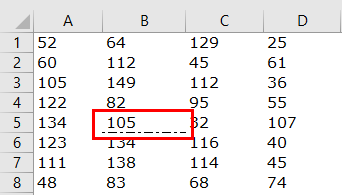
Now, we have selected the option of “xlDouble.”
Code:
Sub Border_Example1() Range("B5").Borders(xlEdgeBottom).LineStyle = XlLineStyle.xlDouble End Sub
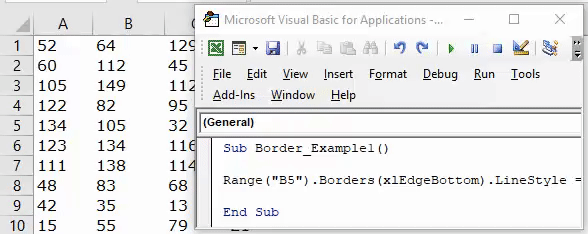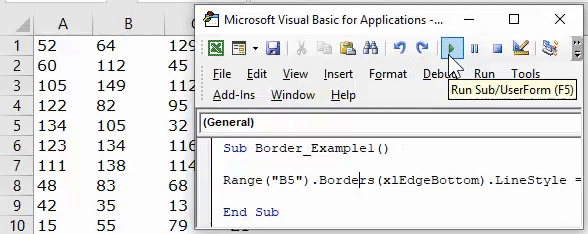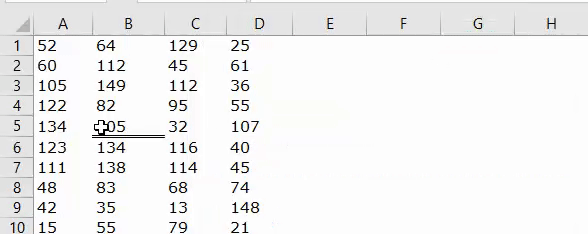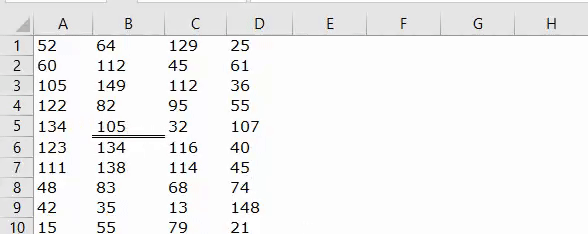
Now, if I run the code, it will apply the Double line to the bottom of cell B5.
Line Type: “xlContinuous”.
Code:
Sub Border_Example1() Range("B5").Borders(xlEdgeBottom).LineStyle = XlLineStyle.xlContinuous End Sub
Result:
Line Type: “clash.”
Code:
Sub Border_Example1() Range("B5").Borders(xlEdgeBottom).LineStyle = XlLineStyle.xlDash End Sub
Result:
Line Type: “xlDashDot.”
Code:
Sub Border_Example1() Range("B5").Borders(xlEdgeBottom).LineStyle = XlLineStyle.xlDashDot End Sub
Result:
Line Type: “xlDashDotDot”.
Code:
Sub Border_Example1() Range("B5").Borders(xlEdgeBottom).LineStyle = XlLineStyle.xlDashDotDot End Sub
Result:
Line Type: “xlDot.”
Code:
Sub Border_Example1() Range("B5").Borders(xlEdgeBottom).LineStyle = XlLineStyle.xlDot End Sub
Result:
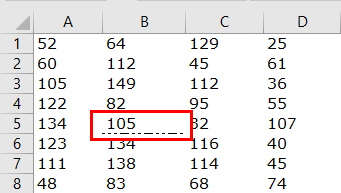
Line Type: “xlLineStyleNone”.
Code:
Sub Border_Example1() Range("B5").Borders(xlEdgeBottom).LineStyle = XlLineStyle.xlLineStyleNone End Sub
Result:
It will remove the border of the specified cell.
Line Type: “xlSlantDashDot”.
Code:
Sub Border_Example1() Range("B5").Borders(xlEdgeBottom).LineStyle = XlLineStyle.xlSlantDashDot End Sub
Result:
Example #2 – Change the Border Using VBA Borders Around Method
We can also change the cell’s borders using the VBA Borders Around method. Once we mention the range of cells or cells, we need to access the VBA Borders Around method.
Open parenthesis to see all the parameters.
Range(“B5”).BorderAround([Line Style], [Weight as xlBorderWeight], [ColorIndex], [Color], [Theme Color])
We can mention the line style, color, border weight, and many more things we can do with this method.
Code:
Sub Border_Example1() Range("B5").BorderAround LineStyle:=xlContinuous, Weight:=xlThick End Sub
It will change the Line Style to xlContinuous.
LineStyle:=xlContinuous
The weight of the Border is thick.
Weight:=xlThick
And the result of this code is as below.
Like this, using Excel VBA Borders and Border Around property and method, we can change the border and elements of borders through VBA coding.
Recommended Articles
This article has been a guide to VBA Borders. Here, we learn how to set borders with Excel VBA coding, practical examples, and downloadable code templates. You may also have a look at other articles related to Excel VBA: –
- What are Global Variables in Excel VBA?
- Examples to Create a Pivot Table in VBA
- Excel VBA End
- Conditional Formatting for Blank Cells
You can add border to any range in a very dynamic way by using the AddBorder and GetCurrentRegionStartingGivenCell function in Xatocode as follows:
' First you may define a worksheet level named range in starting cell and name it as rngData
Sub BorderExample()
Dim rngData As Range ' Range to sort
Set rngData = GetCurrentRegionStartingGivenCell(shtData.Range("rngData"))
Call AddBorder(rngData, EdgeLeft)
Call AddBorder(rngData, EdgeTop)
Call AddBorder(rngData, EdgeRight)
Call AddBorder(rngData, EdgeBottom)
Call AddBorder(rngData, InsideVertical)
Call AddBorder(rngData, InsideHorizontal)
Call AddBorder(rngData, DiagonalUp)
Call AddBorder(rngData, DiagonalDown)
Call ClearBorder(rngData)
Call AddBorder(rngData, Box)
Call AddBorder(rngData, AllBorder)
Call AddBorder(rngData, AllBorder, xlDot) ' Linestyle
Call AddBorder(rngData, AllBorder, , xlMedium) ' Thickness
Call AddBorder(rngData, AllBorder, , , vbRed) ' Color
End Sub
You can read the complete article here