What are the Different Types of Verbs?
Looking for a verbs list? Fret not. Here’s a quick guide on the list of verbs with illustrative examples. But before we get down to the list of verbs, let’s quickly brush through the definition of a verb.
A verb in the simplest sense is a word that describes an action, an event or a state. It tells you what the subject of a sentence is doing. The verbs (like those in the verb list below) are usually the main words in a sentence and without them a sentence is incomplete. Having said that, how do you recognize a verb in a sentence?
Well, verbs (like those in the verbs list below) are typically used after a noun or a pronoun. The nouns or pronouns in such cases, are referred to as subjects.
For example:
- Anthony went to the market.
In this case the action of Anthony physically having went to the market is the verb.
In this guide, verbs are categorized into a few different lists:
- action verbs list
- linking verbs list
- helping verbs list
- irregular verbs list
Except for the linking verb list, the other categories break down into different types. The next list of verbs can be physical or mental. The list of helping verbs can be auxiliary or modal. The list of irregular verbs shows verbs in different tenses.
Learning the words in each verb list can help you develop your English-speaking skills. To make comprehension easier, example sentences have been provided in the verb list sections.
List of Action Verbs
In an action verbs list, each verb can be used to state a subject’s action in a sentence. There are two types of action words you’ll find in this list of action verbs.
Type 1: Physical
The physical verb list features action words. In other words, the words within a physical action verb list usually describe an action that someone or something physically does. In a nutshell, a particular motion made using one’s body or a tool to complete an action is referred to as an action verb. For example, let’s start with a short list of action verbs:
- Walk
- Open
- Speak
All of the words on this short action verb list describe physical actions. The verb list below is a much longer list of action verbs that are useful to know.
Physical Action Verb List:
| Act | Answer | Approve | Arrange |
| Break | Build | Buy | Coach |
| Color | Cough | Create | Complete |
| Cry | Dance | Describe | Draw |
| Drink | Eat | Edit | Enter |
| Exit | Imitate | Invent | Jump |
| Laugh | Lie | Listen | Paint |
| Plan | Play | Read | Replace |
| Run | Scream | See | Shop |
| Shout | Sing | Skip | Sleep |
| Sneeze | Solve | Study | Teach |
| Touch | Turn | Walk | Win |
| Write | Whistle | Yank | Zip |
Hopefully you already recognized a few (or all) of the words on this action verbs list. They are all very useful! If you think you’ll need it, feel free to print this action verbs list for future reference.
Before moving on from the physical action verb list and looking at the mental verbs list below, consider reading these resources explaining MLA format and APA format. They could help you understand how to format your next writing assignment. Or, if you’re ready, let’s move on to the next list of action verbs.
Type 2: Mental
The second type of action verbs list is for mental action words. Mental action words describe intellectual processes that don’t happen physically, but rather take place in your mind. Examples of mental action words (that are part of the action verb list below) include think, feel, and want.
List of Verbs Describing Mental Action:
| Concern | Decide | Dislike |
| Doubt | Feel | Forget |
| Hate | Hear | Hope |
| Impress | Know | Learn |
| Like | Look | Love |
| Mind | Notice | Own |
| Perceive | Realize | Recognize |
| Remember | See | Smell |
| Surprise | Please | Prefer |
| Promise | Think | Understand |
It’s important to understand that some mental action words on this action verbs list don’t refer to the literal use of the word. For instance, the mental list of verbs includes the words see, look, hear, and smell. These words could also be included on a list of action verbs describing physical motion. When you don’t use these words in the literal sense, they become mental action words. In other words, these words could be found on both a physical and mental action verbs list.
Here are some examples showing the difference:
- Action: I can see Paul jumping up and down.
In this example , you can literally see Paul jumping around.
- Mental: Frank returned from Europe yesterday? I see.
However, in the above example you can’t literally see Frank returning from Europe. Instead, “I see” means to understand. Therefore, ‘see ’used in this context is a mental word.
- Action: These roses smell wonderful.
This example refers to the physical action of smelling flowers and comments on their scent.
- Mental: Something smells funny about this situation.
On the other hand, in this example, nothing literally smells funny. Instead, it means that there’s something strange and unusual about the situation.
To summarize, there are hundreds of words that could go on an action verbs list. The physical verbs list and the mental list of verbs only include a few basic words of each type. There are many more to learn and they’re all fun to use. In order to expand your vocabulary, it’s helpful to study another list of action verbs. For a PDF list of action verbs, visit this site.
The next verbs list is a list of linking verbs. Even if you don’t know what they are yet, these words are very important! Pay close attention to the list of linking verbs below. You never know when a list of linking verbs might come in handy.
Linking Verbs List
There’s a list of verbs that do not describe any action. Instead, these words explain a state of being such as a condition or relationship.They are also commonly known as linking verbs, and they make up the linking verb list below.
The words in the linking verbs list are words that connect the subject of a sentence to specific information about the subject. In other words, linking verbs connect the subject to a predicate noun or a predicate adjective.
A list of linking verbs could also be called a ‘being verbs list.’ This is because the words within a linking verbs list show a state of being. You’ll notice that most verbs on the being verbs list are forms of ‘to be’. Other verbs like ‘become’ and ‘seem’ also belong on a being verbs list.
These ‘being’ verbs (see the list of linking verbs/being verbs list below for examples) are used with subjects that are both in past and present tense. Being verbs like ‘was/were’ should be used instead of ’be’ in the past tense, and ‘is/am/are’ in the present tense. For instance:
- Amy was being cynical.
- We are being noisy.
- Andrew was afraid of Luna.
- You appear to be scared.
The being/linking words in the sentences above are included in the being verbs list below. You can use words in the linking verbs list to connect the subject with other words in a sentence. There aren’t as many words on a linking verb list as there are on a verb list for mental and physical action words, but each word in the list of linking verbs is nonetheless important.
Linking Verbs List / Being Verbs List:
| Am | Appear | Are |
| Be | Become | Been |
| Being | Feel | Grow |
| Is | Look | Remain |
| Seem | Smell | Sound |
| Stay | Taste | Turn |
| Was | Were |
As you can see on the linking verbs list above, all forms of to be are important linking words. It would be difficult to have a conversation about yourself without using any of the words on this linking verbs list. Want to remember all of these? Feel free to print and save this linking verb list for reference. You could also look for another linking verb list and examples to study.
Now that you’re well-versed with action words, and the linking verb list, let’s move on to helping words.
Helping Verbs List
Now that we’ve gone over the list of linking verbs let’s talk about helping verbs. A helping verb ‘helps’ or supports the main verb. There are two types of words within the helping verbs list: auxiliaries and modals.
Both auxiliaries and modals add more meaning to the main action or the being word. They can also describe the period of a physical or mental action taking place. They can also add emphasis to your sentences and indicate an event happening.
Auxiliaries (like those in our helping verb list below) extend the main verb and help show time, tense or possibility.
Examples of auxiliary verbs:
- Matthew is going out for lunch.
- I have finished my homework.
Modals indicate possibility, ability or expectation. A list of helping verbs that are modal are further down this page, but let’s start with a few example sentences; they’ll help us understand how they’re used.
Examples of modals:
- Wilson may want to talk to you again.
- Alexa must go to work today.
If you want to learn how to create complex sentences, then it’s important to study a helping verbs list. Here’s your first list of helping verbs.
List of Helping Verbs, Auxiliaries
| Auxiliary Word | And all its forms… |
|---|---|
| To Be | Am, Are, Is, Was, Were, Be, Been |
| To Have | Have, Has, Had |
| To Do | Do, Does, Did |
So, how do you know that the words in this auxiliary helping verbs list are actually ‘helpful’ or act as standalone words? Simply look for other verbs (action or being words) in the sentence. If you notice any form of ‘to be’, ‘to have’, or ‘to do’ before another action or being word, then you’re looking at a sentence with an auxiliary.
Using the previous auxiliary helping verbs list, can you figure out which word is the auxiliary in the examples below?
- Charlie’s mother is cooking breakfast for us tomorrow.
- Tina hasn’t exercised today.
Both modals and auxiliaries can be found on a list of helping verbs. Modals are usually followed by the infinitive of another verb. Just like the list of linking verbs, the list of modals within the list of helping verbs is also small and therefore easy to remember. A verbs list with modal verbs is given below.
List of Helping Verbs, Modals
| Can | Could | May |
| Might | Must | Ought to |
| Shall | Should | Will |
| Would |
Here are some examples of how modals, from the above list of verbs, explain uncertainty, obligation, and possibility.
- I must go to school today.
There’s an obligation to go to school.
- You could go to school today.
In this sentence, it’s possible that you will not go to school today.
- Jennifer’s not sick and should go to school today.
And in this sentence, it’s possible that Jennifer doesn’t go to school.
- If Tommy feels better tonight, he might go to school tomorrow.
Whereas in this sentence there’s a chance that Tommy may or may not go to school.
Now that you are well versed with a linking verbs list, a list of verbs that are ‘helpful,’ and a verbs list for action words, let’s move on to the next section: a list of irregular verbs.
Irregular Verbs List
The next verbs list you’ll look at is the list of action verbs that are irregular, thus they are part of the irregular verbs list. So what exactly are irregular verbs? Well, verbs that do not follow the normal rules for conjugation fall into the irregular verbs list.
Basically, most ‘normal’ words in the past tense have an -ed at the end. Examples include jumped, skipped, and leaped.
- jump → jumped
- skip → skipped
- leap → leaped
- walk → walked
This conjugation pattern applies to most words. However, irregular verbs — like those in the irregular verbs list below — don’t follow this normal pattern. For example:
- Draw → drew, drawn
These verbs shift tenses according to its own set of rules, and thus belong on our list of irregular verbs.
The words in the list of irregular verbs below are shown with their past simple and past participle versions. You could say, that it is also an irregular past tense verbs list.
An irregular past tense verbs list generally includes words like brought, were, became, etc. The irregular past tense verbs list below presents English past tense verbs.
Irregular Past Tense Verbs List:
| BASE FORM | PAST SIMPLE | PAST PARTICIPLE |
|---|---|---|
| Be | Was or Were | Been |
| Become | Became | Become |
| Bring | Brought | Brought |
| Build | Built | Built |
| Catch | Caught | Caught |
| Draw | Drew | Drawn |
| Fly | Flew | Flown |
| Get | Got | Got |
| Go | Went | Gone |
| Grow | Grew | Grown |
| Hold | Held | Held |
| Learn | Learnt/Learned | Learnt/Learned |
| Smell | Smelt | Smelt |
Did you come across any new verbs in this irregular verbs list? There are many other words that could be added to this irregular past tense verbs list, but this list of verbs is a good start. Hopefully, this list of irregular verbs (or irregular past tense verbs list) will help you write your assignments with greater precision. Once you’re done studying the list of irregular verbs, visit this informative site for further learning.
Congratulations on reviewing many verb list types! Now that you have finished reading a comprehensive linking verbs list and studied a helpful list of verbs along with an irregular verbs list, why not get some help on your next English assignment? The paper checker from Citation Machine Plus lets you make citations in APA format and more citation styles. Try it out today!
Published March 5, 2019. Updated April 16, 2020.
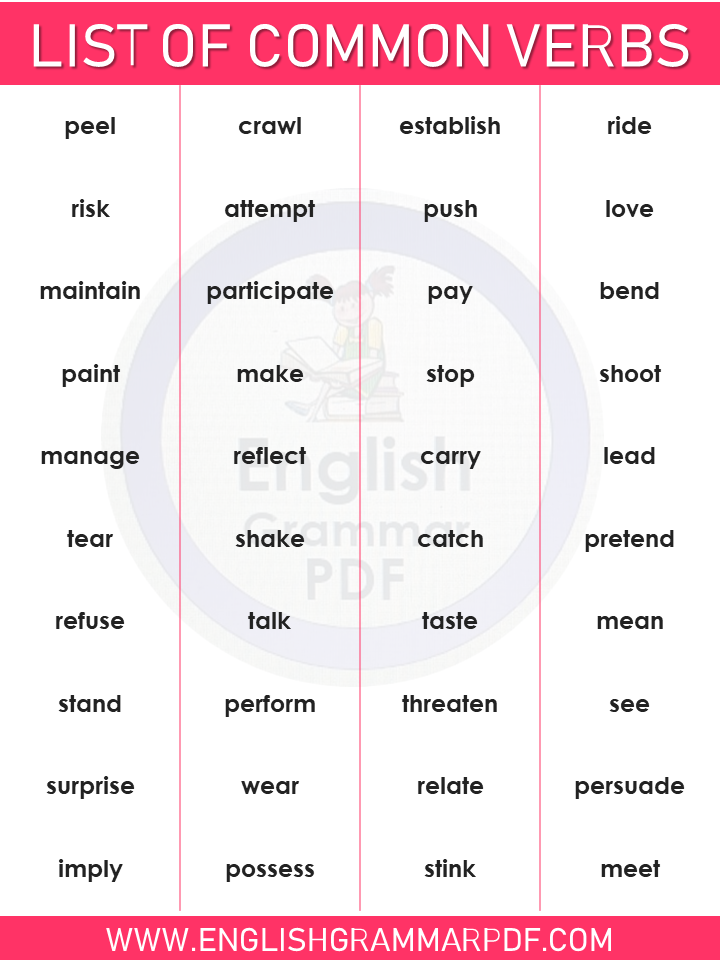
List of Common Verbs in English!
Table of Contents
What are the Verb in English Grammar?
A verb is a word or a combination of words that indicates action or a state of being or condition. Verbs have traditionally been defined as words that show action or state of being. A sentence may either have a main verb, a helping verb or both.
Examples
- Participate
- Pay
- Bend
- Paint
- Make
- Stop
- Shoot
- Manage
- Reflect
- Carry
- Lead
- Tear
- Shake
- Catch
- Pretend
- Refuse
- Talk
- Taste
- Mean
List of Common Verbs in English
- Peel
- Crawl
- Establish
- Ride
- Risk
- Attempt
- Push
- Love
- Maintain
- Participate
- Pay
- Bend
- Paint
- Make
- Stop
- Shoot
- Manage
- Reflect
- Carry
- Lead
- Tear
- Shake
- Catch
- Pretend
- Refuse
- Talk
- Taste
- Mean
- Stand
- Perform
- Threaten
- See
- Surprise
- Wear
- Relate
- Persuade
- Imply
- Possess
- Stink
- Meet
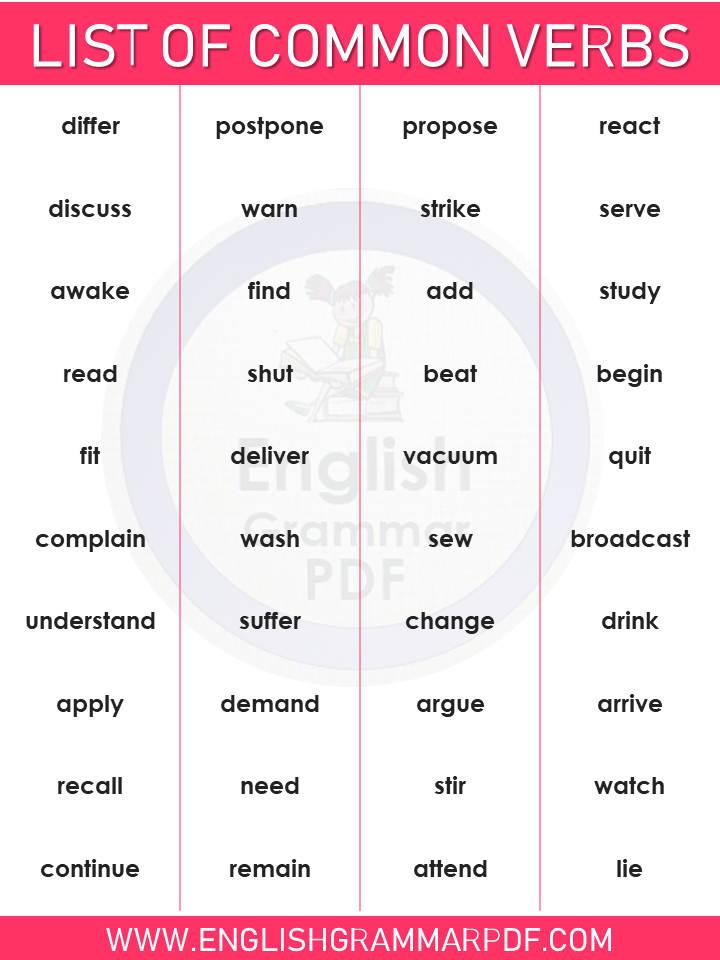
- Differ
- Postpone
- Propose
- React
- Discuss
- Warn
- Strike
- Serve
- Awake
- Find
- Add
- Study
- Read
- Shut
- Beat
- Begin
- Fit
- Deliver
- Vacuum
- Quit
- Complain
- Wash
- Sew
- Broadcast
- Understand
- Suffer
- Change
- Drink
- Apply
- Demand
- Argue
- Arrive
- Recall
- Need
- Stir
- Watch
- Continue
- Remain
- Attend
- Lie
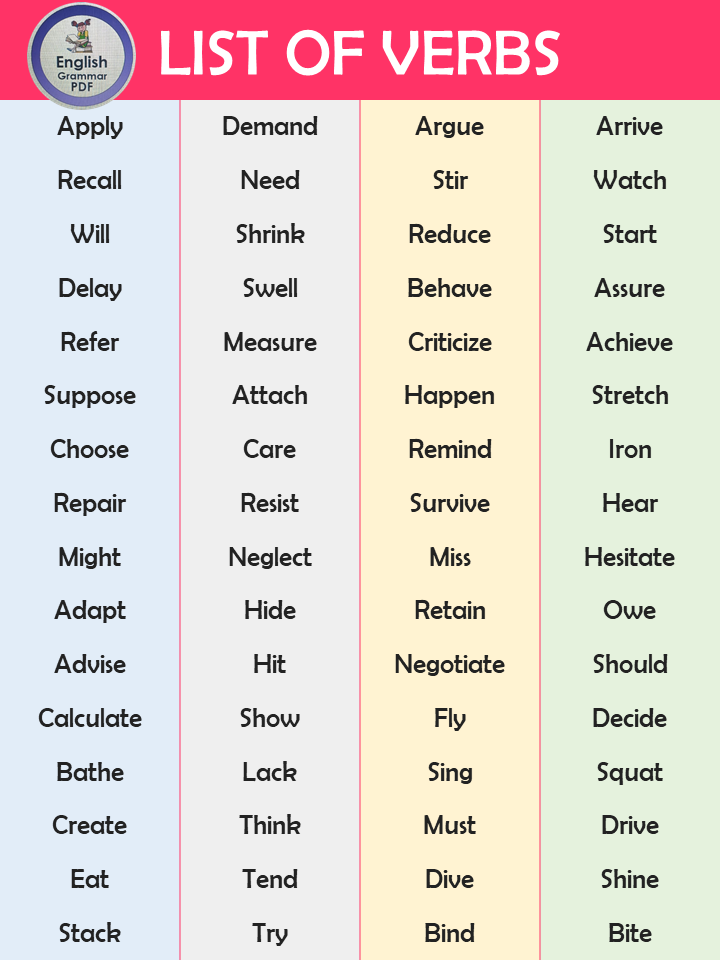
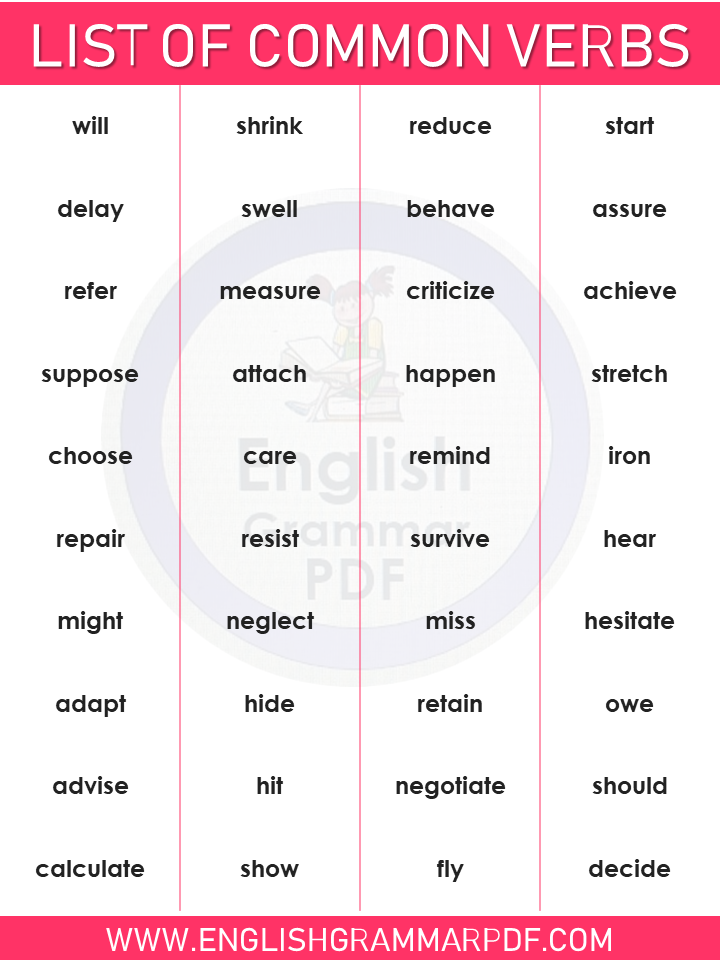
- Will
- Shrink
- Reduce
- Start
- Delay
- Swell
- Behave
- Assure
- Refer
- Measure
- Criticize
- Achieve
- Suppose
- Attach
- Happen
- Stretch
- Choose
- Care
- Remind
- Iron
- Repair
- Resist
- Survive
- Hear
- Might
- Neglect
- Miss
- Hesitate
- Adapt
- Hide
- Retain
- Owe
- Advise
- Hit
- Negotiate
- Should
- Calculate
- Show
- Fly
- Decide
- Bathe
- Lack
- Sing
- Squat
- Create
- Think
- Must
- Drive
- Eat
- Tend
- Dive
- Shine
- Stack
- Try
- Bind
- Bite
- Set
- Wave
- Enjoy
- Seem
- Bring
- Pinch
- Lie (in bed)
- Justify
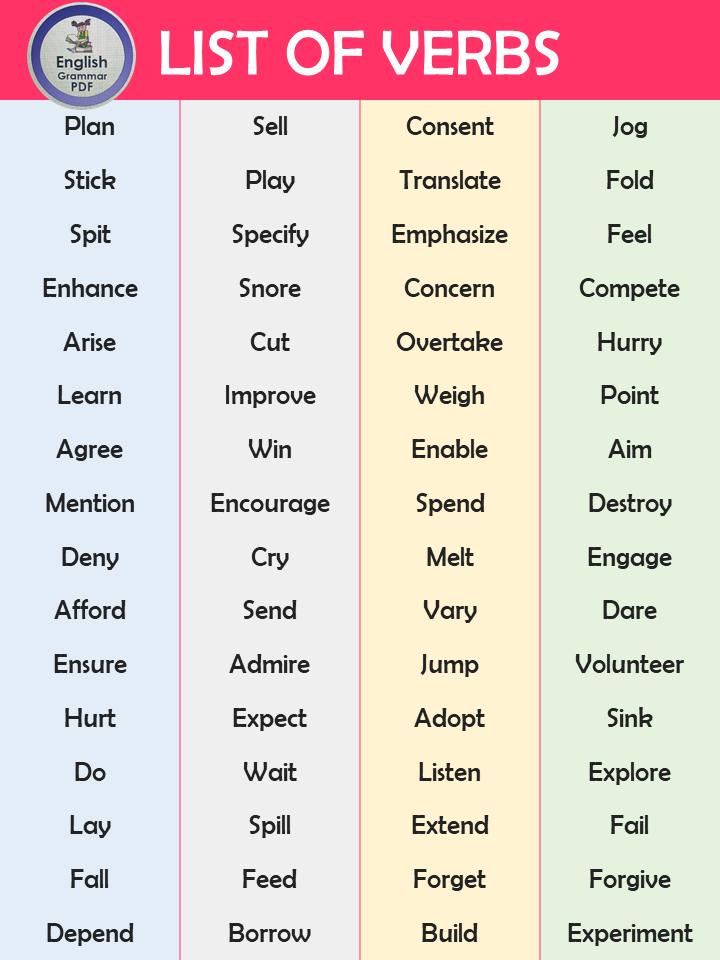
- Plan
- Sell
- Consent
- Jog
- Stick
- Play
- Translate
- Fold
- Spit
- Specify
- Emphasize
- Feel
- Enhance
- Snore
- Concern
- Compete
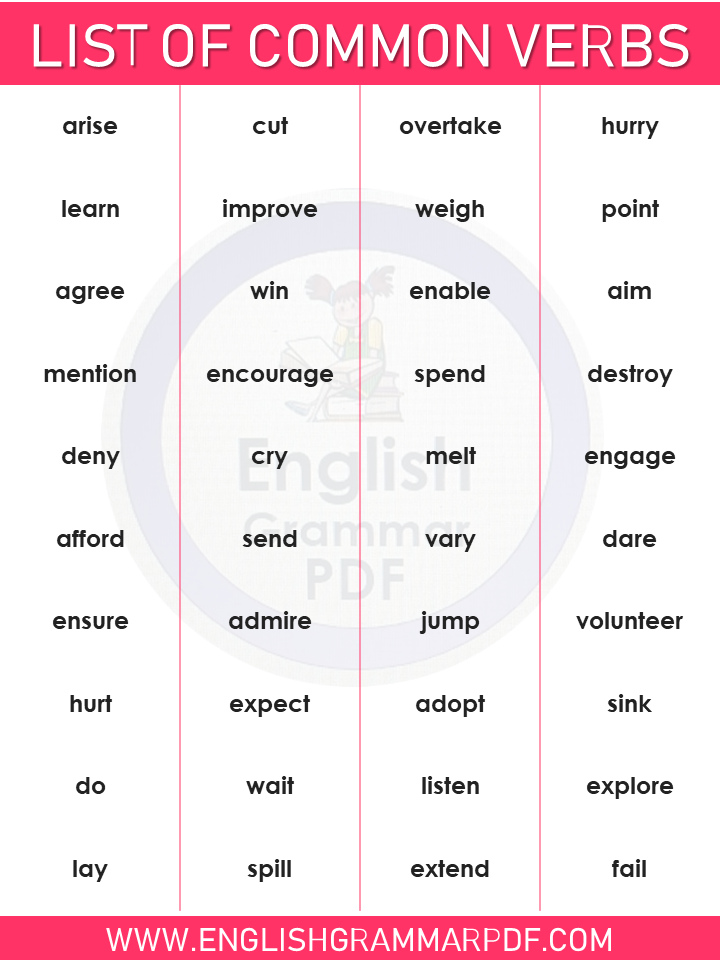
- Arise
- Cut
- Overtake
- Hurry
- Learn
- Improve
- Weigh
Must Learn: A List of Irregular Verbs
- Point
- Agree
- Win
- Enable
- Aim
- Mention
- Encourage
- Spend
- Destroy
- Deny
- Cry
- Melt
- Engage
- Afford
- Send
- Vary
- Dare
- Ensure
- Admire
- Jump
- Volunteer
- Hurt
- Expect
- Adopt
- Sink
- Do
- Wait
- Listen
- Explore
- Lay
- Spill
- Extend
- Fail
- Fall
- Feed
- Forget
- Forgive
- Depend
- Borrow
- Build
- Experiment
- Freeze
- Bounce
- Incorporate
- Organize
- Apologize
- Drop
- Fry
- Impress
- Ring
- Rise
- Adore
- Lose
- Be
- Would
- Roast
- Run
- Sanction
- Satisfy
- Pour
- Bow
- Value
- Matter
- Break
- May
- Practice
- Become
- Breed
- Qualify
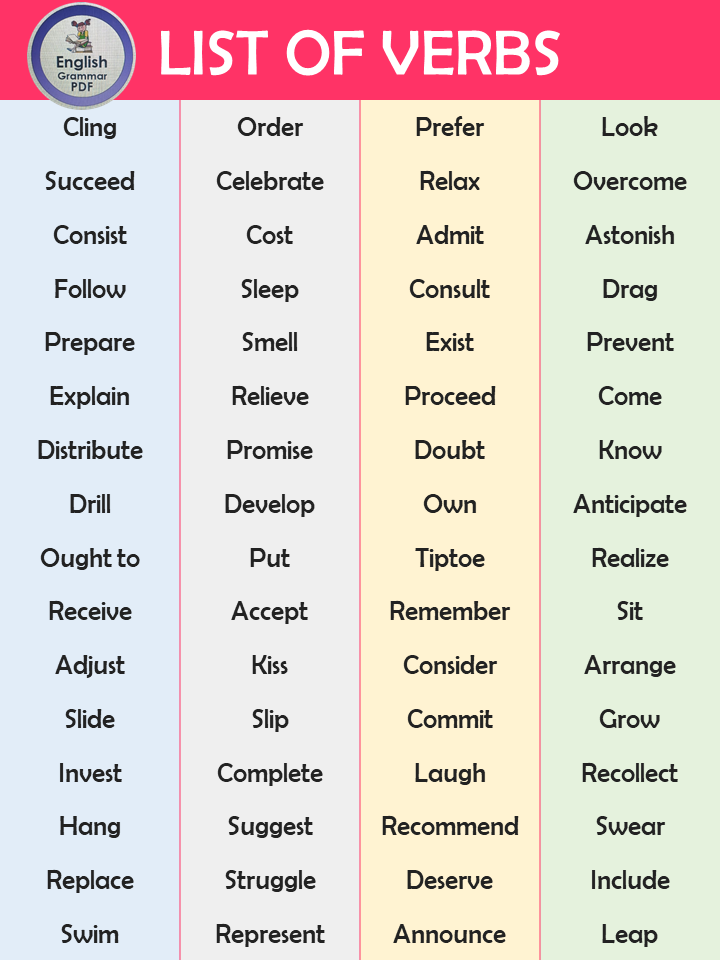
- Cling
- Order
- Prefer
- Look
- Succeed
- Celebrate
- Relax
- Overcome
- Consist
- Cost
- Admit
- Astonish
- Follow
- Sleep
- Consult
- Drag
- Prepare
- Smell
- Exist
- Prevent
- Explain
- Relieve
- Proceed
- Come
- Distribute
- Promise
- Doubt
- Know
- Regret
- explain
- Cook
- Rely
- Drill
- Develop
- Own
- Anticipate
- Ought to
- Put
- Tiptoe
- Realize
- Receive
- Accept
- Remember
- Sit
- Adjust
- Kiss
- Consider
- Arrange
- Slide
- Slip
- Commit
- Grow
- Invest
- Complete
- Laugh
- Recollect
- Hang
- Suggest
- Recommend
- Swear
- Replace
- Struggle
- Deserve
- Include
- Swim
- Represent
- Announce
- Leap
- Require
- Chop
- Blow
- Kick
- Hate
- Resent
- Appreciate
- Install
- Have
- Ski
- Steal
- Inform
- Lend
- Supply
- Pull
- Lift
- Mow
- Count
- Shed
- Wish
- Defer
- Tolerate
- Settle
- Indicate
- Whip
- Light
- Hold
- Claim
- Tell
- Hop
- Like
- Desire
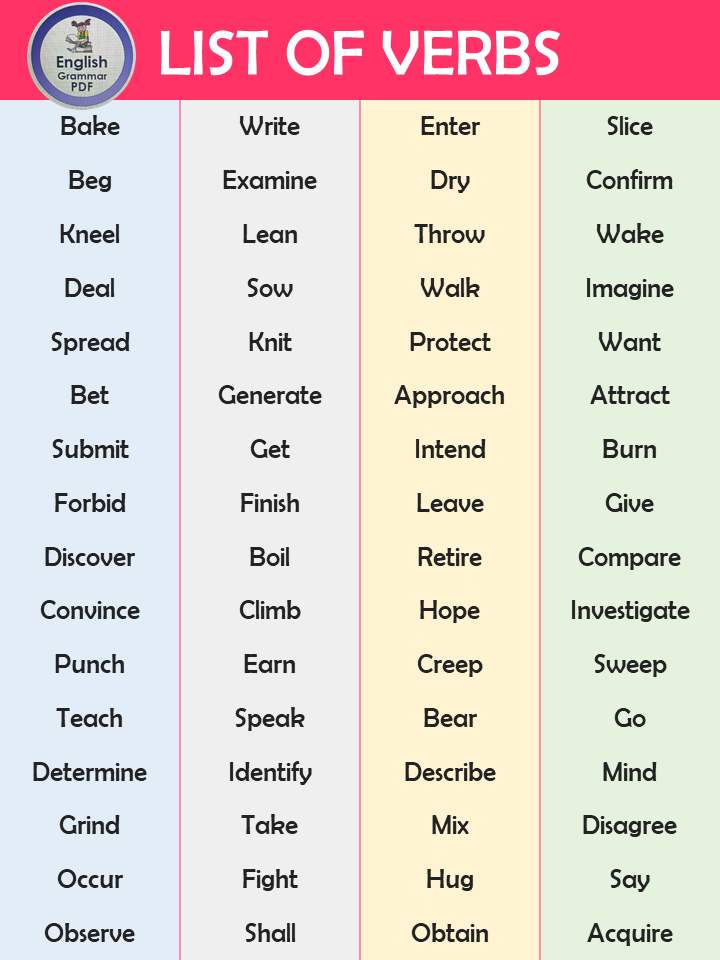
- Bake
- Write
- Enter
- Slice
- Beg
- Examine
- Dry
- Confirm
- Kneel
- Lean
- Throw
- Wake
- Deal
- Sow
- Walk
- Imagine
- Spread
- Knit
- Protect
- Want
- Bet
- Generate
- Approach
- Attract
- Submit
- Get
- Intend
- Burn
- Forbid
- Finish
- Leave
- Give
- Discover
- Boil
- Retire
- Compare
- Convince
- Climb
- Hope
- Investigate
- Punch
- Earn
- Creep
- Sweep
- Teach
- Speak
- Bear
- Go
- Determine
- Identify
- Describe
- Mind
- Grind
- Take
- Mix
- Disagree
- Occur
- Fight
- Hug
- Say
- Observe
- Shall
- Obtain
- Acquire
- Offer
- Prove
- Expand
- Contain
- Belong
- Rid
- Open
- Assume
- Burst
- Sting
- Insist
- Illustrate
- Approve
- Operate
- Avoid
- Solve
- Allow
- Can/Could
- Dream
- Entail
- Communicate
- Keep
Must Learn: Three Forms of Verb in English Grammar
- Scrub
- Pursue
- Appear
- Dance
- Weep
- Involve
- Ignore
- Ask
- Introduce
- Accuse
- Believe
- Dislike
- Spell
- Swing
- Buy
- Acknowledge
Related: Different Types of Verbs in English
Infographics (List of Common Verbs in English )
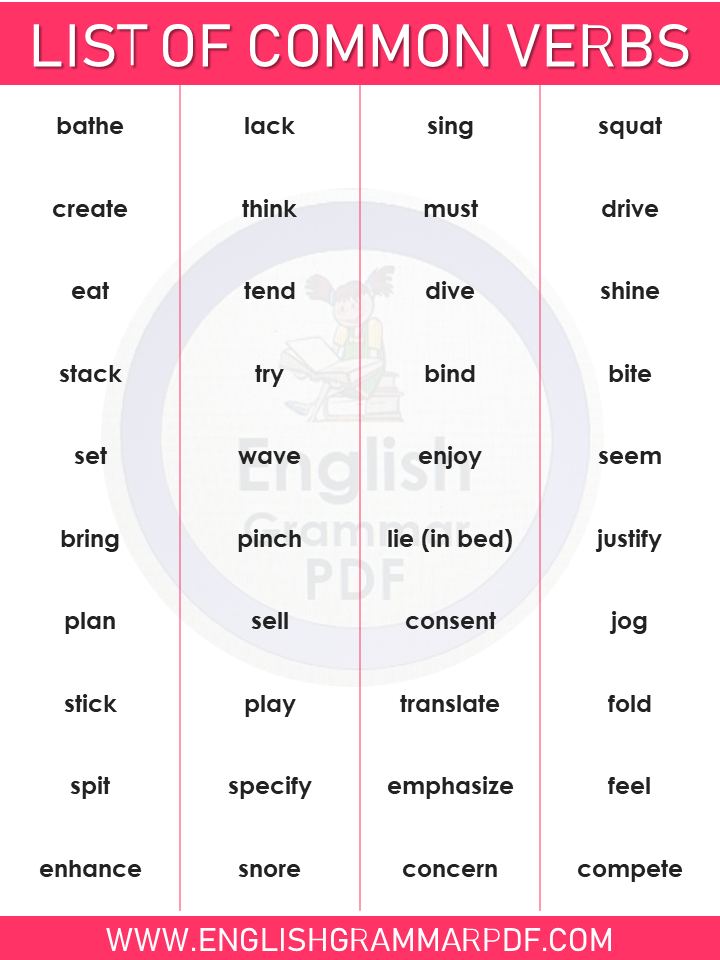
Download this lesson of list of common verbs in english grammar Pdf (Download Here)
List of Verbs! Useful list of over 200 verbs that are commonly used in English with example sentences and printable infographics. Learn these types of verbs with verb definition to improve your grammar in English.
Verb Definition and Types of Verbs
A verb is a kind of word (part of speech) that tells about an action or a state. It is the main part of a sentence: every sentence has a verb. In English, verbs are the only kind of word that changes to show past or present tense.
There are many types of verbs as below:
- Action Verbs
- Transitive Verbs
- Intransitive verbs
- Auxiliary verbs
- Stative verbs
- Modal verbs
- Phrasal verbs
- Irregular verbs
- Regular verbs
Here is a common list of verbs for you to expand your vocabulary:
| Accept | Guess |
| Achieve | Harass |
| Add | Hate |
| Admire | Hear |
| Admit | Help |
| Adopt | Hit |
| Advise | Hope |
| Agree | Identify |
| Allow | Interrupt |
| Announce | Introduce |
| Appreciate | Irritate |
| Approve | Jump |
| Argue | Keep |
| Arrive | Kick |
| Ask | Kiss |
| Assist | Laugh |
| Attack | Learn |
| Bake | Leave |
| Bathe | Lend |
| Be | Lie |
| Beat | Like |
| Become | Listen |
| Beg | Lose |
| Behave | Love |
| Bet | Make |
| Boast | Marry |
| Boil | Measure |
| Borrow | Meet |
| Breathe | Move |
| Bring | Murder |
| Build | Obey |
| Burn | Offend |
| Bury | Offer |
| Buy | Open |
| Call | Paint |
| Catch | Pay |
| Challenge | Pick |
| Change | Play |
| Cheat | Pray |
| Chew | |
| Choose | Pull |
| Clap | Punch |
| Clean | Punish |
| Collect | Purchase |
| Compare | Push |
| Complain | Quit |
| Confess | Race |
| Confuse | Read |
| Construct | Relax |
| Control | Remember |
| Copy | Reply |
| Count | Retire |
| Create | Rub |
| Cry | See |
| Damage | Select |
| Dance | Sell |
| Deliver | Send |
| Destroy | Sing |
| Disagree | Snore |
| Drag | Stand |
| Drive | Stare |
| Drop | Start |
| Earn | Stink |
| Eat | Study |
| Employ | Sweep |
| Encourage | Swim |
| Enjoy | Take |
| Establish | Talk |
| Estimate | Teach |
| Exercise | Tear |
| Expand | Tell |
| Explain | Thank |
| Fear | Travel |
| Feel | Type |
| Fight | Understand |
| Find | Use |
| Fly | Visit |
| Forget | Wait |
| Forgive | Walk |
| Fry | Want |
| Gather | Warn |
| Get | Wed |
| Give | Weep |
| Glow | Wink |
| Greet | Worry |
| Grow | Write |
| Yell |
Common Verb List | Infographic



When learning to write and read English, having a common verb list on hand can help you identify verbs and use them effectively.
The English language is full of interesting words, and verbs are the part of a sentence that shows the action or state of being. Understanding the English common verb list will help you identify these in your writing and use them more effectively, even when they have irregular conjugations.
The English language has thousands of potential verbs, but for those learning the language for the first time, identifying and using the more common verbs is helpful.
Whether you are an ESL student looking to brush up on your English verbs or are a writer who is trying to vary your writing and avoid using overly common words, this common verbs list will help you.
Best Grammar Checker
Grammarly
Grammarly is a top spelling, grammar and plagiarism checker. It’ll help you find and fix errors fast, and it works everywhere. It’s trusted by millions of writers for a reason.
Become a Writer Today is reader-supported. When you buy through links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission.
Contents
- Common Verb List With Example Sentences
- A Final Word on Common Verbs List
- FAQs about a Common Verb List
- Author
Common Verb List With Example Sentences
Do you want to learn some common verbs used in the English language? This list has the 20 most common verbs, along with examples of them used properly. It includes auxiliary verbs, irregular verbs, and regular verbs for those learning English to study.
1. To Be
To be is a common auxiliary verb, and it can also show an overall state of being. This is one of the most important and most common verbs, and it often shows up as a helping verb alongside another verb. The conjugations are:
- Simple past: was/were
- Present tense: is/are
- Future tense: will be
- Past participle: had been
- Gerund:
Examples:
- He was ready to leave early.
- He had been preparing for several hours.
- You are a great friend.
2. To Have
This is another of the irregular verbs in English that show up as a helping or auxiliary verb. Its conjugations are:
- Simple past: had
- Present tense: have/has
- Future tense: will have
- Past participle: had
- Gerund:
Examples:
- I will have a good time attending the concert.
- He has been going to that school to learn English for several years.
3. To Do
To do something requires action. This is part of this list of verbs because it is so common in English grammar. It is also one of the common irregular verbs with the following conjugation:
- Simple past: did
- Present tense: do/does
- Future tense: will do
- Past participle: done
- Gerund: doing
Examples:
- He did well on the examination.
- Does the trolley make a stop at the capital?
4. To Say
To say is the infinitive form of the verb that means to speak or convey meaning. This is yet another irregular verb with the following verb tenses:
- Simple past: said
- Present tense: say/says
- Future tense: will say
- Past participle: said
- Gerund: Saying
Examples:
- He says that he loves her, but his behavior is saying something different.
- The principal said it was time for the high school students to settle down.
5. To Go
To go means to move from one place to another. This verb has the following forms:
- Simple past: went
- Present tense: go/goes
- Future tense: will go
- Past participle: gone
- Gerund: going
Examples:
- I had gone to my new apartment, only to find the key didn’t work.
- We will go out for ice cream after the concert.
6. To Get
To get means to receive something. This is an irregular verb and can often be used as a helping verb.
- Simple past: got
- Present tense: get/gets
- Future tense: will get
- Past participle: got/gotten
- Gerund: getting
Examples:
- Getting ready for the day took all of her energy.
- The team members get approval when they exceed the coach’s expectations.
7. To Make
To make means to form or cause something. This commonly used verb is an irregular verb with these conjugations:
- Simple past: made
- Present tense: make/makes
- Future tense: will make
- Past participle: made
- Gerund: making
Examples:
- He will make a mess with all of that scrap paper.
- We make friends easily when we smile at others.
8. To Think
This verb refers to the act of having an opinion or thought. This verb can get confusing because some forms can be used as other parts of speech, like nouns. In verb form, its conjugations include:
- Simple past: thought
- Present tense: think/thinks
- Future tense: will think
- Past participle: thought
- Gerund: thinking
Examples:
- The girl thought it was a good idea to grab a snack before heading to play practice.
- I will think about it before making a decision.
9. To Take
To take means to remove or lay hold on something. This is a very common verb because of the many ways it gets used in sentences. Its conjugations are:
- Simple past: took
- Present tense: take/takes
- Future tense: will take
- Past participle: taken
- Gerund: taking
Examples:
- The photographer will take your school picture at lunchtime.
- She took her time getting ready for the dance number.
10. To See
This verb means to use your eyes to take in information about the world around you visually. Its conjugations are irregular:
- Simple past: saw
- Present tense: see/sees
- Future tense: will see
- Past participle: seen
- Gerund: seeing
Examples:
- The cat saw the dog in the neighbor’s yard and ran.
- Can you see the danger approaching?
11. To Come
To come means to move or travel toward a new place. This verb can also mean to take place. Conjugations include:
- Simple past: came
- Present tense: come
- Future tense: will come
- Past participle: come
- Gerund: coming
Examples:
- Will you please come here, so I can show you the picture?
- I came quickly when I heard the news.
12. To Want
This verb means to desire or crave something. It can also mean lack. It is one of the first regular verbs on the list with these conjugations:
- Simple past: wanted
- Present tense: want/wants
- Future tense: will want
- Past participle: wanted
- Gerund: wanting
Examples:
- The little boy wanted more of the dessert.
- We want for nothing in our affluent society.
13. To Know
This verb means to have knowledge or understanding of a thing. It has the following irregular conjugations:
- Simple past: knew
- Present tense: know/knows
- Future tense: will know
- Past participle: known
- Gerund: knowing
Examples:
- Even though she knew she was wrong, she made the statement anyway.
- You will know the truth in time.
14. To Look
This verb means to turn your gaze toward something or to think of something in a specific way. It has these conjugations:
- Simple past: looked
- Present tense: look/looks
- Future tense: will look
- Past participle: looked
- Gerund: looking
Examples:
- Look at the idea from a different point of view, and you may change your opinion.
- When the dog looked at his owner, the owner knew he wanted some breakfast.
15. To Use
To use is the base form of the verb that means to take or consume something. It has these conjugations:
- Simple past: used
- Present tense: use/uses
- Future tense: will use
- Past participle: used
- Gerund: using
Examples:
- The executive will use the correct terminology when referring to his brand.
- We used up all the milk when we made cookies.
16. To Find
This verb means to locate or discover something. It has the following irregular conjugations:
- Simple past: found
- Present tense: find/finds
- Future tense: will find
- Past participle: found
- Gerund: finding
Examples:
- The children found the presents under the tree on Christmas morning.
- We will find a way to succeed in life.
17. To Give
This verb means to provide or offer something to another person. Its conjugations are:
- Simple past: gave
- Present tense: give/gives
- Future tense: will give
- Past participle: given
- Gerund: giving
Examples:
- Every holiday season, we give thanks for our blessings.
- She gives her all in everything she does.
18. To Tell
To tell means to communicate information. It can also mean to decide something. It conjugates like this:
- Simple past: told
- Present tense: tell/tells
- Future tense: will tell
- Past participle: told
- Gerund: telling
Examples:
- Can you tell by our sunburns that we spent the weekend in the sun?
- The supervisor told his team that they would get the holiday off with pay.
19. To Work
This verb means to engage in physical or mental activities. When referring to a machine or system it can mean to operate properly. Conjugation examples include:
- Simple past: worked
- Present tense: work/works
- Future tense: will work
- Past participle: worked
- Gerund: working
Examples:
- The public transit system worked well to get us to our destination.
- Dad will work late during the company’s busy season.
20. To Call
To call means to cry out or to give someone a name. This is a regular verb with the following conjugations:
- Simple past: called
- Present tense: call/calls
- Future tense: will call
- Past participle: called
- Gerund: calling
Examples:
- The doctor called with the test results.
- She calls her child’s name when it’s time to eat dinner.
21. To Try
To try is a verb that means to make an attempt. It is a regular verb but does have a spelling change when adding an ending that starts with “e.” Here is how it conjugates:
- Simple past: tried
- Present tense: try/tries
- Future tense: will try
- Past participle: tried
- Gerund: trying
Examples:
- He tried to explain his feelings, but his attempt fell short.
- The little boy tries every day to make his father proud.
22. To Ask
The verb to ask means to make a request or petition. It is a regular verb with the following conjugations:
- Simple past: asked
- Present tense: ask/asks
- Future tense: will ask
- Past participle: asked
- Gerund: asking
Examples:
- The student will ask for permission before changing his research paper topic.
- They asked you to please dress up for the concert.
23. To Need
To need is another regular verb that means to require something. Needing implies that without the item, the person cannot survive or have success. The conjugations are:
- Simple past: needed
- Present tense: need/needs
- Future tense: will need
- Past participle: needed
- Gerund: needing
Examples:
- You will need a permission slip in order to go on the trip.
- The singer needed a drink to soothe her throat during the intermission.
24. To Feel
This verb can mean to handle or touch in order to experience the texture of something. It can also mean to think or to believe something. This irregular verb has these conjugations:
- Simple past: felt
- Present tense: feel/feels
- Future tense: will feel
- Past participle: felt
- Gerund: feeling
Examples:
- She will feel bad when she finds out how much her words hurt her best friend.
- The jacket felt warm and cozy on the cold fall evening.
25. To Become
This irregular verb means to come into existence or to undergo a change. It is an irregular verb with these conjugations:
- Simple past: became
- Present tense: become/becomes
- Future tense: will become
- Past participle: become
- Gerund: becoming
Examples:
- Becoming a teacher was the best decision I made.
- It becomes apparent that today’s youth is more tech-savvy than their parents.
26. To Leave
This verb means to depart or get away from. It can also mean to quit. It has these irregular conjugations:
- Simple past: left
- Present tense: leave/leaves
- Future tense: will leave
- Past participle: left
- Gerund: leaving
Examples:
- The argument left a bad taste in her mouth as she tried to decide what to do next.
- We will leave after the encore.
27. To Put
To put means to place or set down. It can be literal or figurative, such as “to put down roots.” This verb is unique because it barely changes with its conjugations.
- Simple past: put
- Present tense: put/puts
- Future tense: will put
- Past participle: put
- Gerund: putting
Examples:
- We will put out our best effort to impress the new client.
- Savannah put her hat on top of the coat rack before heading into the restaurant.
28. To Mean
This verb means to represent an idea or to be an indication of something. It is irregular and has these conjugations:
- Simple past: meant
- Present tense: mean/means
- Future tense: will mean
- Past participle: meant
- Gerund: meaning
Examples:
- Please say what you mean, not what you think I want to hear.
- The sign meant that we had to use the back door instead of the front door.
29. To Keep
To keep means to have or retain possession of something. it can also mean to continue in a specific course of action. The irregular conjugations are:
- Simple past: kept
- Present tense: keep/keeps
- Future tense: will keep
- Past participle: kept
- Gerund: keeping
Examples:
- To keep watch, the soldier paced in order to stay awake.
- They keep looking over here like we are doing something wrong.
30. To Let
This final verb on the list means to allow or give permission to something. It is an irregular verb that changes little in its conjugations.
- Simple past: let
- Present tense: let/lets
- Future tense: will let
- Past participle: let
- Gerund: letting
Examples:
- They let a few more people in to use the standing room only section during the concert.
- When you RSVP, it lets us know how many people to plan for as we order food.
A Final Word on Common Verbs List
People who are learning English must know how to identify verbs in order to use them well. This common verbs list will make that easier.
By taking the time to study these verbs and their basic combinations, you will be better prepared to read, write and understand English writing.
FAQs about a Common Verb List
What are the 10 most common verbs?
The 10 most common verbs are:
1. To be
2. To have
3. To do
4. To say
5. To go
6. To get
7. To make
8. To know
9. To think
10. To take
What are the common linking verbs?
1. am
2. is
3. are
4. was
5. were
6. be
7. being
8. been
Join over 15,000 writers today
Get a FREE book of writing prompts and learn how to make more money from your writing.
Основные глаголы (main verb) противопоставляются структурным глаголам (т.е. вспомогательным, модальным и аспектным глаголам).
Термин «основной глагол» обычно употребляется по отношению к глаголам входящих в состав синтаксических форм глагола:
-
She doesn’t dance. – Она не танцует. (основной глагол «dance» является смыслообразующим, а вспомогательный глагол «do» образует его отрицательную форму «doesn’t dance»).
Если сказуемое состоит из одного глагола, то обычно говорят о полнозначном или полузначном глаголе (см. ниже).
-
She dances. – Она танцует. (говорить здесь о глаголе «dances» как об основном, не имеет смысла, так как он единственный в сказуемом).
По лексическому значению среди основных глаголов выделяют полнозначные и полузначные:
-
Полнозначные глаголы (также смысловые глаголы или знаменательные глаголы (lexical verbs / full meaning verbs / notional verbs)) — это глаголы, называющие действия или состояния самостоятельно:
-
She learns to dance – Она учится танцевать. (в этом предложении два полнозначных глагола: «learns» и «to dance», второй глагол употребляется в функции дополнения к первому.)
-
-
Полузначные глаголы (semi-lexical verbs / semi-notional verbs) — это неполноценные в лексическом значении глаголы, так как смысловое значение выражений с этими глаголами определяется дополнением (см. основную статью: Полузначные глаголы):
-
She did a dance I never saw before. – Она исполнила танец, которого я никогда раньше не видел.
-
Некоторые глаголы могут употребляться в качестве как смыслового, так и вспомогательного или модального глагола:
-
I am home. – Я дома. (глагол «be» употребляемый в качестве полнозначного)
-
I am watching TV. – Я смотрю телевизор. («be» в качестве вспомогательного глагола)
-
I am to go. – Я должен идти. («be» употребляемый в качестве модального глагола)