ABS function
Math and trigonometry: Returns the absolute value of a number
ACCRINT function
Financial: Returns the accrued interest for a security that pays periodic interest
ACCRINTM function
Financial: Returns the accrued interest for a security that pays interest at maturity
ACOS function
Math and trigonometry: Returns the arccosine of a number
ACOSH function
Math and trigonometry: Returns the inverse hyperbolic cosine of a number
ACOT function

Math and trigonometry: Returns the arccotangent of a number
ACOTH function

Math and trigonometry: Returns the hyperbolic arccotangent of a number
AGGREGATE function
Math and trigonometry: Returns an aggregate in a list or database
ADDRESS function
Lookup and reference: Returns a reference as text to a single cell in a worksheet
AMORDEGRC function
Financial: Returns the depreciation for each accounting period by using a depreciation coefficient
AMORLINC function
Financial: Returns the depreciation for each accounting period
AND function
Logical: Returns TRUE if all of its arguments are TRUE
ARABIC function

Math and trigonometry: Converts a Roman number to Arabic, as a number
AREAS function
Lookup and reference: Returns the number of areas in a reference
ARRAYTOTEXT function

Text: Returns an array of text values from any specified range
ASC function
Text: Changes full-width (double-byte) English letters or katakana within a character string to half-width (single-byte) characters
ASIN function
Math and trigonometry: Returns the arcsine of a number
ASINH function
Math and trigonometry: Returns the inverse hyperbolic sine of a number
ATAN function
Math and trigonometry: Returns the arctangent of a number
ATAN2 function
Math and trigonometry: Returns the arctangent from x- and y-coordinates
ATANH function
Math and trigonometry: Returns the inverse hyperbolic tangent of a number
AVEDEV function
Statistical: Returns the average of the absolute deviations of data points from their mean
AVERAGE function
Statistical: Returns the average of its arguments
AVERAGEA function
Statistical: Returns the average of its arguments, including numbers, text, and logical values
AVERAGEIF function
Statistical: Returns the average (arithmetic mean) of all the cells in a range that meet a given criteria
AVERAGEIFS function
Statistical: Returns the average (arithmetic mean) of all cells that meet multiple criteria.
BAHTTEXT function
Text: Converts a number to text, using the ß (baht) currency format
BASE function
Math and trigonometry: Converts a number into a text representation with the given radix (base)
BESSELI function
Engineering: Returns the modified Bessel function In(x)
BESSELJ function
Engineering: Returns the Bessel function Jn(x)
BESSELK function
Engineering: Returns the modified Bessel function Kn(x)
BESSELY function
Engineering: Returns the Bessel function Yn(x)
BETADIST function
Compatibility: Returns the beta cumulative distribution function
In Excel 2007, this is a Statistical function.
BETA.DIST function

Statistical: Returns the beta cumulative distribution function
BETAINV function
Compatibility: Returns the inverse of the cumulative distribution function for a specified beta distribution
In Excel 2007, this is a Statistical function.
BETA.INV function

Statistical: Returns the inverse of the cumulative distribution function for a specified beta distribution
BIN2DEC function
Engineering: Converts a binary number to decimal
BIN2HEX function
Engineering: Converts a binary number to hexadecimal
BIN2OCT function
Engineering: Converts a binary number to octal
BINOMDIST function
Compatibility: Returns the individual term binomial distribution probability
In Excel 2007, this is a Statistical function.
BINOM.DIST function

Statistical: Returns the individual term binomial distribution probability
BINOM.DIST.RANGE function

Statistical: Returns the probability of a trial result using a binomial distribution
BINOM.INV function

Statistical: Returns the smallest value for which the cumulative binomial distribution is less than or equal to a criterion value
BITAND function

Engineering: Returns a ‘Bitwise And’ of two numbers
BITLSHIFT function

Engineering: Returns a value number shifted left by shift_amount bits
BITOR function

Engineering: Returns a bitwise OR of 2 numbers
BITRSHIFT function

Engineering: Returns a value number shifted right by shift_amount bits
BITXOR function

Engineering: Returns a bitwise ‘Exclusive Or’ of two numbers
BYCOL

Logical: Applies a LAMBDA to each column and returns an array of the results
BYROW

Logical: Applies a LAMBDA to each row and returns an array of the results
CALL function
Add-in and Automation: Calls a procedure in a dynamic link library or code resource
CEILING function
Compatibility: Rounds a number to the nearest integer or to the nearest multiple of significance
CEILING.MATH function

Math and trigonometry: Rounds a number up, to the nearest integer or to the nearest multiple of significance
CEILING.PRECISE function
Math and trigonometry: Rounds a number the nearest integer or to the nearest multiple of significance. Regardless of the sign of the number, the number is rounded up.
CELL function
Information: Returns information about the formatting, location, or contents of a cell
This function is not available in Excel for the web.
CHAR function
Text: Returns the character specified by the code number
CHIDIST function
Compatibility: Returns the one-tailed probability of the chi-squared distribution
Note: In Excel 2007, this is a Statistical function.
CHIINV function
Compatibility: Returns the inverse of the one-tailed probability of the chi-squared distribution
Note: In Excel 2007, this is a Statistical function.
CHITEST function
Compatibility: Returns the test for independence
Note: In Excel 2007, this is a Statistical function.
CHISQ.DIST function

Statistical: Returns the cumulative beta probability density function
CHISQ.DIST.RT function

Statistical: Returns the one-tailed probability of the chi-squared distribution
CHISQ.INV function

Statistical: Returns the cumulative beta probability density function
CHISQ.INV.RT function

Statistical: Returns the inverse of the one-tailed probability of the chi-squared distribution
CHISQ.TEST function

Statistical: Returns the test for independence
CHOOSE function
Lookup and reference: Chooses a value from a list of values
CHOOSECOLS

Lookup and reference: Returns the specified columns from an array
CHOOSEROWS

Lookup and reference: Returns the specified rows from an array
CLEAN function
Text: Removes all nonprintable characters from text
CODE function
Text: Returns a numeric code for the first character in a text string
COLUMN function
Lookup and reference: Returns the column number of a reference
COLUMNS function
Lookup and reference: Returns the number of columns in a reference
COMBIN function
Math and trigonometry: Returns the number of combinations for a given number of objects
COMBINA function

Math and trigonometry:
Returns the number of combinations with repetitions for a given number of items
COMPLEX function
Engineering: Converts real and imaginary coefficients into a complex number
CONCAT function

Text: Combines the text from multiple ranges and/or strings, but it doesn’t provide the delimiter or IgnoreEmpty arguments.
CONCATENATE function
Text: Joins several text items into one text item
CONFIDENCE function
Compatibility: Returns the confidence interval for a population mean
In Excel 2007, this is a Statistical function.
CONFIDENCE.NORM function

Statistical: Returns the confidence interval for a population mean
CONFIDENCE.T function

Statistical: Returns the confidence interval for a population mean, using a Student’s t distribution
CONVERT function
Engineering: Converts a number from one measurement system to another
CORREL function
Statistical: Returns the correlation coefficient between two data sets
COS function
Math and trigonometry: Returns the cosine of a number
COSH function
Math and trigonometry: Returns the hyperbolic cosine of a number
COT function

Math and trigonometry: Returns the hyperbolic cosine of a number
COTH function

Math and trigonometry: Returns the cotangent of an angle
COUNT function
Statistical: Counts how many numbers are in the list of arguments
COUNTA function
Statistical: Counts how many values are in the list of arguments
COUNTBLANK function
Statistical: Counts the number of blank cells within a range
COUNTIF function
Statistical: Counts the number of cells within a range that meet the given criteria
COUNTIFS function
Statistical: Counts the number of cells within a range that meet multiple criteria
COUPDAYBS function
Financial: Returns the number of days from the beginning of the coupon period to the settlement date
COUPDAYS function
Financial: Returns the number of days in the coupon period that contains the settlement date
COUPDAYSNC function
Financial: Returns the number of days from the settlement date to the next coupon date
COUPNCD function
Financial: Returns the next coupon date after the settlement date
COUPNUM function
Financial: Returns the number of coupons payable between the settlement date and maturity date
COUPPCD function
Financial: Returns the previous coupon date before the settlement date
COVAR function
Compatibility: Returns covariance, the average of the products of paired deviations
In Excel 2007, this is a Statistical function.
COVARIANCE.P function

Statistical: Returns covariance, the average of the products of paired deviations
COVARIANCE.S function

Statistical: Returns the sample covariance, the average of the products deviations for each data point pair in two data sets
CRITBINOM function
Compatibility: Returns the smallest value for which the cumulative binomial distribution is less than or equal to a criterion value
In Excel 2007, this is a Statistical function.
CSC function

Math and trigonometry: Returns the cosecant of an angle
CSCH function

Math and trigonometry: Returns the hyperbolic cosecant of an angle
CUBEKPIMEMBER function
Cube: Returns a key performance indicator (KPI) name, property, and measure, and displays the name and property in the cell. A KPI is a quantifiable measurement, such as monthly gross profit or quarterly employee turnover, used to monitor an organization’s performance.
CUBEMEMBER function
Cube: Returns a member or tuple in a cube hierarchy. Use to validate that the member or tuple exists in the cube.
CUBEMEMBERPROPERTY function
Cube: Returns the value of a member property in the cube. Use to validate that a member name exists within the cube and to return the specified property for this member.
CUBERANKEDMEMBER function
Cube: Returns the nth, or ranked, member in a set. Use to return one or more elements in a set, such as the top sales performer or top 10 students.
CUBESET function
Cube: Defines a calculated set of members or tuples by sending a set expression to the cube on the server, which creates the set, and then returns that set to Microsoft Office Excel.
CUBESETCOUNT function
Cube: Returns the number of items in a set.
CUBEVALUE function
Cube: Returns an aggregated value from a cube.
CUMIPMT function
Financial: Returns the cumulative interest paid between two periods
CUMPRINC function
Financial: Returns the cumulative principal paid on a loan between two periods
DATE function
Date and time: Returns the serial number of a particular date
DATEDIF function
Date and time: Calculates the number of days, months, or years between two dates. This function is useful in formulas where you need to calculate an age.
DATEVALUE function
Date and time: Converts a date in the form of text to a serial number
DAVERAGE function
Database: Returns the average of selected database entries
DAY function
Date and time: Converts a serial number to a day of the month
DAYS function

Date and time: Returns the number of days between two dates
DAYS360 function
Date and time: Calculates the number of days between two dates based on a 360-day year
DB function
Financial: Returns the depreciation of an asset for a specified period by using the fixed-declining balance method
DBCS function

Text: Changes half-width (single-byte) English letters or katakana within a character string to full-width (double-byte) characters
DCOUNT function
Database: Counts the cells that contain numbers in a database
DCOUNTA function
Database: Counts nonblank cells in a database
DDB function
Financial: Returns the depreciation of an asset for a specified period by using the double-declining balance method or some other method that you specify
DEC2BIN function
Engineering: Converts a decimal number to binary
DEC2HEX function
Engineering: Converts a decimal number to hexadecimal
DEC2OCT function
Engineering: Converts a decimal number to octal
DECIMAL function

Math and trigonometry: Converts a text representation of a number in a given base into a decimal number
DEGREES function
Math and trigonometry: Converts radians to degrees
DELTA function
Engineering: Tests whether two values are equal
DEVSQ function
Statistical: Returns the sum of squares of deviations
DGET function
Database: Extracts from a database a single record that matches the specified criteria
DISC function
Financial: Returns the discount rate for a security
DMAX function
Database: Returns the maximum value from selected database entries
DMIN function
Database: Returns the minimum value from selected database entries
DOLLAR function
Text: Converts a number to text, using the $ (dollar) currency format
DOLLARDE function
Financial: Converts a dollar price, expressed as a fraction, into a dollar price, expressed as a decimal number
DOLLARFR function
Financial: Converts a dollar price, expressed as a decimal number, into a dollar price, expressed as a fraction
DPRODUCT function
Database: Multiplies the values in a particular field of records that match the criteria in a database
DROP

Lookup and reference: Excludes a specified number of rows or columns from the start or end of an array
DSTDEV function
Database: Estimates the standard deviation based on a sample of selected database entries
DSTDEVP function
Database: Calculates the standard deviation based on the entire population of selected database entries
DSUM function
Database: Adds the numbers in the field column of records in the database that match the criteria
DURATION function
Financial: Returns the annual duration of a security with periodic interest payments
DVAR function
Database: Estimates variance based on a sample from selected database entries
DVARP function
Database: Calculates variance based on the entire population of selected database entries
EDATE function
Date and time: Returns the serial number of the date that is the indicated number of months before or after the start date
EFFECT function
Financial: Returns the effective annual interest rate
ENCODEURL function

Web: Returns a URL-encoded string
This function is not available in Excel for the web.
EOMONTH function
Date and time: Returns the serial number of the last day of the month before or after a specified number of months
ERF function
Engineering: Returns the error function
ERF.PRECISE function

Engineering: Returns the error function
ERFC function
Engineering: Returns the complementary error function
ERFC.PRECISE function

Engineering: Returns the complementary ERF function integrated between x and infinity
ERROR.TYPE function
Information: Returns a number corresponding to an error type
EUROCONVERT function
Add-in and Automation: Converts a number to euros, converts a number from euros to a euro member currency, or converts a number from one euro member currency to another by using the euro as an intermediary (triangulation).
EVEN function
Math and trigonometry: Rounds a number up to the nearest even integer
EXACT function
Text: Checks to see if two text values are identical
EXP function
Math and trigonometry: Returns e raised to the power of a given number
EXPAND

Lookup and reference: Expands or pads an array to specified row and column dimensions
EXPON.DIST function

Statistical: Returns the exponential distribution
EXPONDIST function
Compatibility: Returns the exponential distribution
In Excel 2007, this is a Statistical function.
FACT function
Math and trigonometry: Returns the factorial of a number
FACTDOUBLE function
Math and trigonometry: Returns the double factorial of a number
FALSE function
Logical: Returns the logical value FALSE
F.DIST function

Statistical: Returns the F probability distribution
FDIST function
Compatibility: Returns the F probability distribution
In Excel 2007, this is a Statistical function.
F.DIST.RT function

Statistical: Returns the F probability distribution
FILTER function

Lookup and reference: Filters a range of data based on criteria you define
FILTERXML function

Web: Returns specific data from the XML content by using the specified XPath
This function is not available in Excel for the web.
FIND, FINDB functions
Text: Finds one text value within another (case-sensitive)
F.INV function

Statistical: Returns the inverse of the F probability distribution
F.INV.RT function

Statistical: Returns the inverse of the F probability distribution
FINV function
Compatibility: Returns the inverse of the F probability distribution
In Excel 2007this is a Statistical function.
FISHER function
Statistical: Returns the Fisher transformation
FISHERINV function
Statistical: Returns the inverse of the Fisher transformation
FIXED function
Text: Formats a number as text with a fixed number of decimals
FLOOR function
Compatibility: Rounds a number down, toward zero
In Excel 2007 and Excel 2010, this is a Math and trigonometry function.
FLOOR.MATH function

Math and trigonometry: Rounds a number down, to the nearest integer or to the nearest multiple of significance
FLOOR.PRECISE function
Math and trigonometry: Rounds a number the nearest integer or to the nearest multiple of significance. Regardless of the sign of the number, the number is rounded up.
FORECAST function
Statistical: Returns a value along a linear trend
In Excel 2016, this function is replaced with FORECAST.LINEAR as part of the new Forecasting functions, but it’s still available for compatibility with earlier versions.
FORECAST.ETS function

Statistical: Returns a future value based on existing (historical) values by using the AAA version of the Exponential Smoothing (ETS) algorithm
FORECAST.ETS.CONFINT function

Statistical: Returns a confidence interval for the forecast value at the specified target date
FORECAST.ETS.SEASONALITY function

Statistical: Returns the length of the repetitive pattern Excel detects for the specified time series
FORECAST.ETS.STAT function

Statistical: Returns a statistical value as a result of time series forecasting
FORECAST.LINEAR function

Statistical: Returns a future value based on existing values
FORMULATEXT function

Lookup and reference: Returns the formula at the given reference as text
FREQUENCY function
Statistical: Returns a frequency distribution as a vertical array
F.TEST function

Statistical: Returns the result of an F-test
FTEST function
Compatibility: Returns the result of an F-test
In Excel 2007, this is a Statistical function.
FV function
Financial: Returns the future value of an investment
FVSCHEDULE function
Financial: Returns the future value of an initial principal after applying a series of compound interest rates
GAMMA function

Statistical: Returns the Gamma function value
GAMMA.DIST function

Statistical: Returns the gamma distribution
GAMMADIST function
Compatibility: Returns the gamma distribution
In Excel 2007, this is a Statistical function.
GAMMA.INV function

Statistical: Returns the inverse of the gamma cumulative distribution
GAMMAINV function
Compatibility: Returns the inverse of the gamma cumulative distribution
In Excel 2007, this is a Statistical function.
GAMMALN function
Statistical: Returns the natural logarithm of the gamma function, Γ(x)
GAMMALN.PRECISE function

Statistical: Returns the natural logarithm of the gamma function, Γ(x)
GAUSS function

Statistical: Returns 0.5 less than the standard normal cumulative distribution
GCD function
Math and trigonometry: Returns the greatest common divisor
GEOMEAN function
Statistical: Returns the geometric mean
GESTEP function
Engineering: Tests whether a number is greater than a threshold value
GETPIVOTDATA function
Lookup and reference: Returns data stored in a PivotTable report
GROWTH function
Statistical: Returns values along an exponential trend
HARMEAN function
Statistical: Returns the harmonic mean
HEX2BIN function
Engineering: Converts a hexadecimal number to binary
HEX2DEC function
Engineering: Converts a hexadecimal number to decimal
HEX2OCT function
Engineering: Converts a hexadecimal number to octal
HLOOKUP function
Lookup and reference: Looks in the top row of an array and returns the value of the indicated cell
HOUR function
Date and time: Converts a serial number to an hour
HSTACK

Lookup and reference: Appends arrays horizontally and in sequence to return a larger array
HYPERLINK function
Lookup and reference: Creates a shortcut or jump that opens a document stored on a network server, an intranet, or the Internet
HYPGEOM.DIST function
Statistical: Returns the hypergeometric distribution
HYPGEOMDIST function
Compatibility: Returns the hypergeometric distribution
In Excel 2007, this is a Statistical function.
IF function
Logical: Specifies a logical test to perform
IFERROR function
Logical: Returns a value you specify if a formula evaluates to an error; otherwise, returns the result of the formula
IFNA function

Logical: Returns the value you specify if the expression resolves to #N/A, otherwise returns the result of the expression
IFS function

Logical: Checks whether one or more conditions are met and returns a value that corresponds to the first TRUE condition.
IMABS function
Engineering: Returns the absolute value (modulus) of a complex number
IMAGINARY function
Engineering: Returns the imaginary coefficient of a complex number
IMARGUMENT function
Engineering: Returns the argument theta, an angle expressed in radians
IMCONJUGATE function
Engineering: Returns the complex conjugate of a complex number
IMCOS function
Engineering: Returns the cosine of a complex number
IMCOSH function

Engineering: Returns the hyperbolic cosine of a complex number
IMCOT function

Engineering: Returns the cotangent of a complex number
IMCSC function

Engineering: Returns the cosecant of a complex number
IMCSCH function

Engineering: Returns the hyperbolic cosecant of a complex number
IMDIV function
Engineering: Returns the quotient of two complex numbers
IMEXP function
Engineering: Returns the exponential of a complex number
IMLN function
Engineering: Returns the natural logarithm of a complex number
IMLOG10 function
Engineering: Returns the base-10 logarithm of a complex number
IMLOG2 function
Engineering: Returns the base-2 logarithm of a complex number
IMPOWER function
Engineering: Returns a complex number raised to an integer power
IMPRODUCT function
Engineering: Returns the product of complex numbers
IMREAL function
Engineering: Returns the real coefficient of a complex number
IMSEC function

Engineering: Returns the secant of a complex number
IMSECH function

Engineering: Returns the hyperbolic secant of a complex number
IMSIN function
Engineering: Returns the sine of a complex number
IMSINH function

Engineering: Returns the hyperbolic sine of a complex number
IMSQRT function
Engineering: Returns the square root of a complex number
IMSUB function
Engineering: Returns the difference between two complex numbers
IMSUM function
Engineering: Returns the sum of complex numbers
IMTAN function

Engineering: Returns the tangent of a complex number
INDEX function
Lookup and reference: Uses an index to choose a value from a reference or array
INDIRECT function
Lookup and reference: Returns a reference indicated by a text value
INFO function
Information: Returns information about the current operating environment
This function is not available in Excel for the web.
INT function
Math and trigonometry: Rounds a number down to the nearest integer
INTERCEPT function
Statistical: Returns the intercept of the linear regression line
INTRATE function
Financial: Returns the interest rate for a fully invested security
IPMT function
Financial: Returns the interest payment for an investment for a given period
IRR function
Financial: Returns the internal rate of return for a series of cash flows
ISBLANK function
Information: Returns TRUE if the value is blank
ISERR function
Information: Returns TRUE if the value is any error value except #N/A
ISERROR function
Information: Returns TRUE if the value is any error value
ISEVEN function
Information: Returns TRUE if the number is even
ISFORMULA function

Information: Returns TRUE if there is a reference to a cell that contains a formula
ISLOGICAL function
Information: Returns TRUE if the value is a logical value
ISNA function
Information: Returns TRUE if the value is the #N/A error value
ISNONTEXT function
Information: Returns TRUE if the value is not text
ISNUMBER function
Information: Returns TRUE if the value is a number
ISODD function
Information: Returns TRUE if the number is odd
ISOMITTED

Information: Checks whether the value in a LAMBDA is missing and returns TRUE or FALSE
ISREF function
Information: Returns TRUE if the value is a reference
ISTEXT function
Information: Returns TRUE if the value is text
ISO.CEILING function

Math and trigonometry: Returns a number that is rounded up to the nearest integer or to the nearest multiple of significance
ISOWEEKNUM function

Date and time: Returns the number of the ISO week number of the year for a given date
ISPMT function
Financial: Calculates the interest paid during a specific period of an investment
JIS function
Text: Changes half-width (single-byte) characters within a string to full-width (double-byte) characters
KURT function
Statistical: Returns the kurtosis of a data set
LAMBDA

Logical: Create custom, reusable functions and call them by a friendly name
LARGE function
Statistical: Returns the k-th largest value in a data set
LCM function
Math and trigonometry: Returns the least common multiple
LEFT, LEFTB functions
Text: Returns the leftmost characters from a text value
LEN, LENB functions
Text: Returns the number of characters in a text string
LET

Logical: Assigns names to calculation results
LINEST function
Statistical: Returns the parameters of a linear trend
LN function
Math and trigonometry: Returns the natural logarithm of a number
LOG function
Math and trigonometry: Returns the logarithm of a number to a specified base
LOG10 function
Math and trigonometry: Returns the base-10 logarithm of a number
LOGEST function
Statistical: Returns the parameters of an exponential trend
LOGINV function
Compatibility: Returns the inverse of the lognormal cumulative distribution
LOGNORM.DIST function

Statistical: Returns the cumulative lognormal distribution
LOGNORMDIST function
Compatibility: Returns the cumulative lognormal distribution
LOGNORM.INV function

Statistical: Returns the inverse of the lognormal cumulative distribution
LOOKUP function
Lookup and reference: Looks up values in a vector or array
LOWER function
Text: Converts text to lowercase
MAKEARRAY

Logical: Returns a calculated array of a specified row and column size, by applying a LAMBDA
MAP

Logical: Returns an array formed by mapping each value in the array(s) to a new value by applying a LAMBDA to create a new value
MATCH function
Lookup and reference: Looks up values in a reference or array
MAX function
Statistical: Returns the maximum value in a list of arguments
MAXA function
Statistical: Returns the maximum value in a list of arguments, including numbers, text, and logical values
MAXIFS function

Statistical: Returns the maximum value among cells specified by a given set of conditions or criteria
MDETERM function
Math and trigonometry: Returns the matrix determinant of an array
MDURATION function
Financial: Returns the Macauley modified duration for a security with an assumed par value of $100
MEDIAN function
Statistical: Returns the median of the given numbers
MID, MIDB functions
Text: Returns a specific number of characters from a text string starting at the position you specify
MIN function
Statistical: Returns the minimum value in a list of arguments
MINIFS function

Statistical: Returns the minimum value among cells specified by a given set of conditions or criteria.
MINA function
Statistical: Returns the smallest value in a list of arguments, including numbers, text, and logical values
MINUTE function
Date and time: Converts a serial number to a minute
MINVERSE function
Math and trigonometry: Returns the matrix inverse of an array
MIRR function
Financial: Returns the internal rate of return where positive and negative cash flows are financed at different rates
MMULT function
Math and trigonometry: Returns the matrix product of two arrays
MOD function
Math and trigonometry: Returns the remainder from division
MODE function
Compatibility: Returns the most common value in a data set
In Excel 2007, this is a Statistical function.
MODE.MULT function

Statistical: Returns a vertical array of the most frequently occurring, or repetitive values in an array or range of data
MODE.SNGL function

Statistical: Returns the most common value in a data set
MONTH function
Date and time: Converts a serial number to a month
MROUND function
Math and trigonometry: Returns a number rounded to the desired multiple
MULTINOMIAL function
Math and trigonometry: Returns the multinomial of a set of numbers
MUNIT function

Math and trigonometry: Returns the unit matrix or the specified dimension
N function
Information: Returns a value converted to a number
NA function
Information: Returns the error value #N/A
NEGBINOM.DIST function

Statistical: Returns the negative binomial distribution
NEGBINOMDIST function
Compatibility: Returns the negative binomial distribution
In Excel 2007, this is a Statistical function.
NETWORKDAYS function
Date and time: Returns the number of whole workdays between two dates
NETWORKDAYS.INTL function

Date and time: Returns the number of whole workdays between two dates using parameters to indicate which and how many days are weekend days
NOMINAL function
Financial: Returns the annual nominal interest rate
NORM.DIST function

Statistical: Returns the normal cumulative distribution
NORMDIST function
Compatibility: Returns the normal cumulative distribution
In Excel 2007, this is a Statistical function.
NORMINV function
Statistical: Returns the inverse of the normal cumulative distribution
NORM.INV function

Compatibility: Returns the inverse of the normal cumulative distribution
Note: In Excel 2007, this is a Statistical function.
NORM.S.DIST function

Statistical: Returns the standard normal cumulative distribution
NORMSDIST function
Compatibility: Returns the standard normal cumulative distribution
In Excel 2007, this is a Statistical function.
NORM.S.INV function

Statistical: Returns the inverse of the standard normal cumulative distribution
NORMSINV function
Compatibility: Returns the inverse of the standard normal cumulative distribution
In Excel 2007, this is a Statistical function.
NOT function
Logical: Reverses the logic of its argument
NOW function
Date and time: Returns the serial number of the current date and time
NPER function
Financial: Returns the number of periods for an investment
NPV function
Financial: Returns the net present value of an investment based on a series of periodic cash flows and a discount rate
NUMBERVALUE function

Text: Converts text to number in a locale-independent manner
OCT2BIN function
Engineering: Converts an octal number to binary
OCT2DEC function
Engineering: Converts an octal number to decimal
OCT2HEX function
Engineering: Converts an octal number to hexadecimal
ODD function
Math and trigonometry: Rounds a number up to the nearest odd integer
ODDFPRICE function
Financial: Returns the price per $100 face value of a security with an odd first period
ODDFYIELD function
Financial: Returns the yield of a security with an odd first period
ODDLPRICE function
Financial: Returns the price per $100 face value of a security with an odd last period
ODDLYIELD function
Financial: Returns the yield of a security with an odd last period
OFFSET function
Lookup and reference: Returns a reference offset from a given reference
OR function
Logical: Returns TRUE if any argument is TRUE
PDURATION function

Financial: Returns the number of periods required by an investment to reach a specified value
PEARSON function
Statistical: Returns the Pearson product moment correlation coefficient
PERCENTILE.EXC function

Statistical: Returns the k-th percentile of values in a range, where k is in the range 0..1, exclusive
PERCENTILE.INC function

Statistical: Returns the k-th percentile of values in a range
PERCENTILE function
Compatibility: Returns the k-th percentile of values in a range
In Excel 2007, this is a Statistical function.
PERCENTRANK.EXC function

Statistical: Returns the rank of a value in a data set as a percentage (0..1, exclusive) of the data set
PERCENTRANK.INC function

Statistical: Returns the percentage rank of a value in a data set
PERCENTRANK function
Compatibility: Returns the percentage rank of a value in a data set
In Excel 2007, this is a Statistical function.
PERMUT function
Statistical: Returns the number of permutations for a given number of objects
PERMUTATIONA function

Statistical: Returns the number of permutations for a given number of objects (with repetitions) that can be selected from the total objects
PHI function

Statistical: Returns the value of the density function for a standard normal distribution
PHONETIC function
Text: Extracts the phonetic (furigana) characters from a text string
PI function
Math and trigonometry: Returns the value of pi
PMT function
Financial: Returns the periodic payment for an annuity
POISSON.DIST function

Statistical: Returns the Poisson distribution
POISSON function
Compatibility: Returns the Poisson distribution
In Excel 2007, this is a Statistical function.
POWER function
Math and trigonometry: Returns the result of a number raised to a power
PPMT function
Financial: Returns the payment on the principal for an investment for a given period
PRICE function
Financial: Returns the price per $100 face value of a security that pays periodic interest
PRICEDISC function
Financial: Returns the price per $100 face value of a discounted security
PRICEMAT function
Financial: Returns the price per $100 face value of a security that pays interest at maturity
PROB function
Statistical: Returns the probability that values in a range are between two limits
PRODUCT function
Math and trigonometry: Multiplies its arguments
PROPER function
Text: Capitalizes the first letter in each word of a text value
PV function
Financial: Returns the present value of an investment
QUARTILE function
Compatibility: Returns the quartile of a data set
In Excel 2007, this is a Statistical function.
QUARTILE.EXC function

Statistical: Returns the quartile of the data set, based on percentile values from 0..1, exclusive
QUARTILE.INC function

Statistical: Returns the quartile of a data set
QUOTIENT function
Math and trigonometry: Returns the integer portion of a division
RADIANS function
Math and trigonometry: Converts degrees to radians
RAND function
Math and trigonometry: Returns a random number between 0 and 1
RANDARRAY function

Math and trigonometry: Returns an array of random numbers between 0 and 1. However, you can specify the number of rows and columns to fill, minimum and maximum values, and whether to return whole numbers or decimal values.
RANDBETWEEN function
Math and trigonometry: Returns a random number between the numbers you specify
RANK.AVG function

Statistical: Returns the rank of a number in a list of numbers
RANK.EQ function

Statistical: Returns the rank of a number in a list of numbers
RANK function
Compatibility: Returns the rank of a number in a list of numbers
In Excel 2007, this is a Statistical function.
RATE function
Financial: Returns the interest rate per period of an annuity
RECEIVED function
Financial: Returns the amount received at maturity for a fully invested security
REDUCE

Logical: Reduces an array to an accumulated value by applying a LAMBDA to each value and returning the total value in the accumulator
REGISTER.ID function
Add-in and Automation: Returns the register ID of the specified dynamic link library (DLL) or code resource that has been previously registered
REPLACE, REPLACEB functions
Text: Replaces characters within text
REPT function
Text: Repeats text a given number of times
RIGHT, RIGHTB functions
Text: Returns the rightmost characters from a text value
ROMAN function
Math and trigonometry: Converts an arabic numeral to roman, as text
ROUND function
Math and trigonometry: Rounds a number to a specified number of digits
ROUNDDOWN function
Math and trigonometry: Rounds a number down, toward zero
ROUNDUP function
Math and trigonometry: Rounds a number up, away from zero
ROW function
Lookup and reference: Returns the row number of a reference
ROWS function
Lookup and reference: Returns the number of rows in a reference
RRI function

Financial: Returns an equivalent interest rate for the growth of an investment
RSQ function
Statistical: Returns the square of the Pearson product moment correlation coefficient
RTD function
Lookup and reference: Retrieves real-time data from a program that supports COM automation
SCAN

Logical: Scans an array by applying a LAMBDA to each value and returns an array that has each intermediate value
SEARCH, SEARCHB functions
Text: Finds one text value within another (not case-sensitive)
SEC function

Math and trigonometry: Returns the secant of an angle
SECH function

Math and trigonometry: Returns the hyperbolic secant of an angle
SECOND function
Date and time: Converts a serial number to a second
SEQUENCE function

Math and trigonometry: Generates a list of sequential numbers in an array, such as 1, 2, 3, 4
SERIESSUM function
Math and trigonometry: Returns the sum of a power series based on the formula
SHEET function

Information: Returns the sheet number of the referenced sheet
SHEETS function

Information: Returns the number of sheets in a reference
SIGN function
Math and trigonometry: Returns the sign of a number
SIN function
Math and trigonometry: Returns the sine of the given angle
SINH function
Math and trigonometry: Returns the hyperbolic sine of a number
SKEW function
Statistical: Returns the skewness of a distribution
SKEW.P function

Statistical: Returns the skewness of a distribution based on a population: a characterization of the degree of asymmetry of a distribution around its mean
SLN function
Financial: Returns the straight-line depreciation of an asset for one period
SLOPE function
Statistical: Returns the slope of the linear regression line
SMALL function
Statistical: Returns the k-th smallest value in a data set
SORT function

Lookup and reference: Sorts the contents of a range or array
SORTBY function

Lookup and reference: Sorts the contents of a range or array based on the values in a corresponding range or array
SQRT function
Math and trigonometry: Returns a positive square root
SQRTPI function
Math and trigonometry: Returns the square root of (number * pi)
STANDARDIZE function
Statistical: Returns a normalized value
STOCKHISTORY function
Financial: Retrieves historical data about a financial instrument
STDEV function
Compatibility: Estimates standard deviation based on a sample
STDEV.P function

Statistical: Calculates standard deviation based on the entire population
STDEV.S function

Statistical: Estimates standard deviation based on a sample
STDEVA function
Statistical: Estimates standard deviation based on a sample, including numbers, text, and logical values
STDEVP function
Compatibility: Calculates standard deviation based on the entire population
In Excel 2007, this is a Statistical function.
STDEVPA function
Statistical: Calculates standard deviation based on the entire population, including numbers, text, and logical values
STEYX function
Statistical: Returns the standard error of the predicted y-value for each x in the regression
SUBSTITUTE function
Text: Substitutes new text for old text in a text string
SUBTOTAL function
Math and trigonometry: Returns a subtotal in a list or database
SUM function
Math and trigonometry: Adds its arguments
SUMIF function
Math and trigonometry: Adds the cells specified by a given criteria
SUMIFS function
Math and trigonometry: Adds the cells in a range that meet multiple criteria
SUMPRODUCT function
Math and trigonometry: Returns the sum of the products of corresponding array components
SUMSQ function
Math and trigonometry: Returns the sum of the squares of the arguments
SUMX2MY2 function
Math and trigonometry: Returns the sum of the difference of squares of corresponding values in two arrays
SUMX2PY2 function
Math and trigonometry: Returns the sum of the sum of squares of corresponding values in two arrays
SUMXMY2 function
Math and trigonometry: Returns the sum of squares of differences of corresponding values in two arrays
SWITCH function

Logical: Evaluates an expression against a list of values and returns the result corresponding to the first matching value. If there is no match, an optional default value may be returned.
SYD function
Financial: Returns the sum-of-years’ digits depreciation of an asset for a specified period
T function
Text: Converts its arguments to text
TAN function
Math and trigonometry: Returns the tangent of a number
TANH function
Math and trigonometry: Returns the hyperbolic tangent of a number
TAKE

Lookup and reference: Returns a specified number of contiguous rows or columns from the start or end of an array
TBILLEQ function
Financial: Returns the bond-equivalent yield for a Treasury bill
TBILLPRICE function
Financial: Returns the price per $100 face value for a Treasury bill
TBILLYIELD function
Financial: Returns the yield for a Treasury bill
T.DIST function

Statistical: Returns the Percentage Points (probability) for the Student t-distribution
T.DIST.2T function

Statistical: Returns the Percentage Points (probability) for the Student t-distribution
T.DIST.RT function

Statistical: Returns the Student’s t-distribution
TDIST function
Compatibility: Returns the Student’s t-distribution
TEXT function
Text: Formats a number and converts it to text
TEXTAFTER

Text: Returns text that occurs after given character or string
TEXTBEFORE

Text: Returns text that occurs before a given character or string
TEXTJOIN

Text: Combines the text from multiple ranges and/or strings
TEXTSPLIT

Text: Splits text strings by using column and row delimiters
TIME function
Date and time: Returns the serial number of a particular time
TIMEVALUE function
Date and time: Converts a time in the form of text to a serial number
T.INV function

Statistical: Returns the t-value of the Student’s t-distribution as a function of the probability and the degrees of freedom
T.INV.2T function

Statistical: Returns the inverse of the Student’s t-distribution
TINV function
Compatibility: Returns the inverse of the Student’s t-distribution
TOCOL

Lookup and reference: Returns the array in a single column
TOROW

Lookup and reference: Returns the array in a single row
TODAY function
Date and time: Returns the serial number of today’s date
TRANSPOSE function
Lookup and reference: Returns the transpose of an array
TREND function
Statistical: Returns values along a linear trend
TRIM function
Text: Removes spaces from text
TRIMMEAN function
Statistical: Returns the mean of the interior of a data set
TRUE function
Logical: Returns the logical value TRUE
TRUNC function
Math and trigonometry: Truncates a number to an integer
T.TEST function

Statistical: Returns the probability associated with a Student’s t-test
TTEST function
Compatibility: Returns the probability associated with a Student’s t-test
In Excel 2007, this is a Statistical function.
TYPE function
Information: Returns a number indicating the data type of a value
UNICHAR function

Text: Returns the Unicode character that is references by the given numeric value
UNICODE function

Text: Returns the number (code point) that corresponds to the first character of the text
UNIQUE function

Lookup and reference: Returns a list of unique values in a list or range
UPPER function
Text: Converts text to uppercase
VALUE function
Text: Converts a text argument to a number
VALUETOTEXT

Text: Returns text from any specified value
VAR function
Compatibility: Estimates variance based on a sample
In Excel 2007, this is a Statistical function.
VAR.P function

Statistical: Calculates variance based on the entire population
VAR.S function

Statistical: Estimates variance based on a sample
VARA function
Statistical: Estimates variance based on a sample, including numbers, text, and logical values
VARP function
Compatibility: Calculates variance based on the entire population
In Excel 2007, this is a Statistical function.
VARPA function
Statistical: Calculates variance based on the entire population, including numbers, text, and logical values
VDB function
Financial: Returns the depreciation of an asset for a specified or partial period by using a declining balance method
VLOOKUP function
Lookup and reference: Looks in the first column of an array and moves across the row to return the value of a cell
VSTACK

Look and reference: Appends arrays vertically and in sequence to return a larger array
WEBSERVICE function

Web: Returns data from a web service.
This function is not available in Excel for the web.
WEEKDAY function
Date and time: Converts a serial number to a day of the week
WEEKNUM function
Date and time: Converts a serial number to a number representing where the week falls numerically with a year
WEIBULL function
Compatibility: Calculates variance based on the entire population, including numbers, text, and logical values
In Excel 2007, this is a Statistical function.
WEIBULL.DIST function

Statistical: Returns the Weibull distribution
WORKDAY function
Date and time: Returns the serial number of the date before or after a specified number of workdays
WORKDAY.INTL function

Date and time: Returns the serial number of the date before or after a specified number of workdays using parameters to indicate which and how many days are weekend days
WRAPCOLS

Look and reference: Wraps the provided row or column of values by columns after a specified number of elements
WRAPROWS

Look and reference: Wraps the provided row or column of values by rows after a specified number of elements
XIRR function
Financial: Returns the internal rate of return for a schedule of cash flows that is not necessarily periodic
XLOOKUP function

Lookup and reference: Searches a range or an array, and returns an item corresponding to the first match it finds. If a match doesn’t exist, then XLOOKUP can return the closest (approximate) match.
XMATCH function

Lookup and reference: Returns the relative position of an item in an array or range of cells.
XNPV function
Financial: Returns the net present value for a schedule of cash flows that is not necessarily periodic
XOR function

Logical: Returns a logical exclusive OR of all arguments
YEAR function
Date and time: Converts a serial number to a year
YEARFRAC function
Date and time: Returns the year fraction representing the number of whole days between start_date and end_date
YIELD function
Financial: Returns the yield on a security that pays periodic interest
YIELDDISC function
Financial: Returns the annual yield for a discounted security; for example, a Treasury bill
YIELDMAT function
Financial: Returns the annual yield of a security that pays interest at maturity
Z.TEST function

Statistical: Returns the one-tailed probability-value of a z-test
ZTEST function
Compatibility: Returns the one-tailed probability-value of a z-test
In Excel 2007, this is a Statistical function.
Below is a brief overview of about 100 important Excel functions you should know, with links to detailed examples. We also have a large list of example formulas, a more complete list of Excel functions, and video training. If you are new to Excel formulas, see this introduction.
Note: Excel now includes Dynamic Array formulas, which offer important new functions.
Date and Time Functions
Excel provides many functions to work with dates and times.
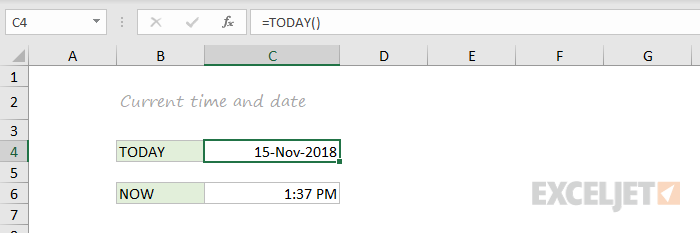
NOW and TODAY
You can get the current date with the TODAY function and the current date and time with the NOW Function. Technically, the NOW function returns the current date and time, but you can format as time only, as seen below:
TODAY() // returns current date
NOW() // returns current time
Note: these are volatile functions and will recalculate with every worksheet change. If you want a static value, use date and time shortcuts.
DAY, MONTH, YEAR, and DATE
You can use the DAY, MONTH, and YEAR functions to disassemble any date into its raw components, and the DATE function to put things back together again.
=DAY("14-Nov-2018") // returns 14
=MONTH("14-Nov-2018") // returns 11
=YEAR("14-Nov-2018") // returns 2018
=DATE(2018,11,14) // returns 14-Nov-2018
HOUR, MINUTE, SECOND, and TIME
Excel provides a set of parallel functions for times. You can use the HOUR, MINUTE, and SECOND functions to extract pieces of a time, and you can assemble a TIME from individual components with the TIME function.
=HOUR("10:30") // returns 10
=MINUTE("10:30") // returns 30
=SECOND("10:30") // returns 0
=TIME(10,30,0) // returns 10:30
DATEDIF and YEARFRAC
You can use the DATEDIF function to get time between dates in years, months, or days. DATEDIF can also be configured to get total time in «normalized» denominations, i.e. «2 years and 6 months and 27 days».
Use YEARFRAC to get fractional years:
=YEARFRAC("14-Nov-2018","10-Jun-2021") // returns 2.57
EDATE and EOMONTH
A common task with dates is to shift a date forward (or backward) by a given number of months. You can use the EDATE and EOMONTH functions for this. EDATE moves by month and retains the day. EOMONTH works the same way, but always returns the last day of the month.
EDATE(date,6) // 6 months forward
EOMONTH(date,6) // 6 months forward (end of month)
WORKDAY and NETWORKDAYS
To figure out a date n working days in the future, you can use the WORKDAY function. To calculate the number of workdays between two dates, you can use NETWORKDAYS.
WORKDAY(start,n,holidays) // date n workdays in future
Video: How to calculate due dates with WORKDAY
NETWORKDAYS(start,end,holidays) // number of workdays between dates
Note: Both functions automatically skip weekends (Saturday and Sunday) and will also skip holidays, if provided. If you need more flexibility on what days are considered weekends, see the WORKDAY.INTL function and NETWORKDAYS.INTL function.
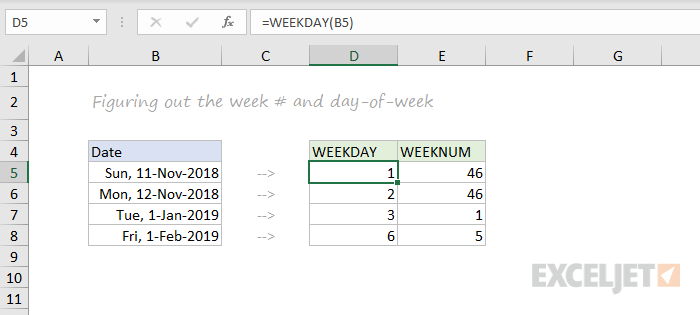
WEEKDAY and WEEKNUM
To figure out the day of week from a date, Excel provides the WEEKDAY function. WEEKDAY returns a number between 1-7 that indicates Sunday, Monday, Tuesday, etc. Use the WEEKNUM function to get the week number in a given year.
=WEEKDAY(date) // returns a number 1-7
=WEEKNUM(date) // returns week number in year
Engineering
CONVERT
Most Engineering functions are pretty technical…you’ll find a lot of functions for complex numbers in this section. However, the CONVERT function is quite useful for everyday unit conversions. You can use CONVERT to change units for distance, weight, temperature, and much more.
=CONVERT(72,"F","C") // returns 22.2
Information Functions
ISBLANK, ISERROR, ISNUMBER, and ISFORMULA
Excel provides many functions for checking the value in a cell, including ISNUMBER, ISTEXT, ISLOGICAL, ISBLANK, ISERROR, and ISFORMULA These functions are sometimes called the «IS» functions, and they all return TRUE or FALSE based on a cell’s contents.
Excel also has ISODD and ISEVEN functions that will test a number to see if it’s even or odd.
By the way, the green fill in the screenshot above is applied automatically with a conditional formatting formula.
Logical Functions
Excel’s logical functions are a key building block of many advanced formulas. Logical functions return the boolean values TRUE or FALSE. If you need a primer on logical formulas, this video goes through many examples.
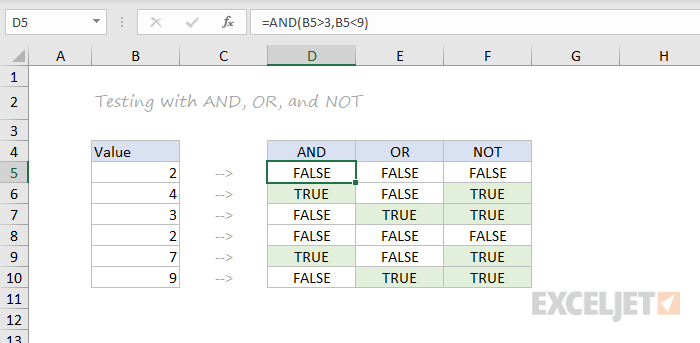
AND, OR and NOT
The core of Excel’s logical functions are the AND function, the OR function, and the NOT function. In the screen below, each of these function is used to run a simple test on the values in column B:
=AND(B5>3,B5<9)
=OR(B5=3,B5=9)
=NOT(B5=2)
- Video: How to build logical formulas
- Guide: 50 examples of formula criteria
IFERROR and IFNA
The IFERROR function and IFNA function can be used as a simple way to trap and handle errors. In the screen below, VLOOKUP is used to retrieve cost from a menu item. Column F contains just a VLOOKUP function, with no error handling. Column G shows how to use IFNA with VLOOKUP to display a custom message when an unrecognized item is entered.
=VLOOKUP(E5,menu,2,0) // no error trapping
=IFNA(VLOOKUP(E5,menu,2,0),"Not found") // catch errors
Whereas IFNA only catches an #N/A error, the IFERROR function will catch any formula error.
IF and IFS functions
The IF function is one of the most used functions in Excel. In the screen below, IF checks test scores and assigns «pass» or «fail»:
Multiple IF functions can be nested together to perform more complex logical tests.
New in Excel 2019 and Excel 365, the IFS function can run multiple logical tests without nesting IFs.
=IFS(C5<60,"F",C5<70,"D",C5<80,"C",C5<90,"B",C5>=90,"A")
Lookup and Reference Functions
VLOOKUP and HLOOKUP
Excel offers a number of functions to lookup and retrieve data. Most famous of all is VLOOKUP:
=VLOOKUP(C5,$F$5:$G$7,2,TRUE)
More: 23 things to know about VLOOKUP.
HLOOKUP works like VLOOKUP, but expects data arranged horizontally:
=HLOOKUP(C5,$G$4:$I$5,2,TRUE)
INDEX and MATCH
For more complicated lookups, INDEX and MATCH offers more flexibility and power:
=INDEX(C5:E12,MATCH(H4,B5:B12,0),MATCH(H5,C4:E4,0))
Both the INDEX function and the MATCH function are powerhouse functions that turn up in all kinds of formulas.
More: How to use INDEX and MATCH
LOOKUP
The LOOKUP function has default behaviors that make it useful when solving certain problems. LOOKUP assumes values are sorted in ascending order and always performs an approximate match. When LOOKUP can’t find a match, it will match the next smallest value. In the example below we are using LOOKUP to find the last entry in a column:
ROW and COLUMN
You can use the ROW function and COLUMN function to find row and column numbers on a worksheet. Notice both ROW and COLUMN return values for the current cell if no reference is supplied:
The row function also shows up often in advanced formulas that process data with relative row numbers.
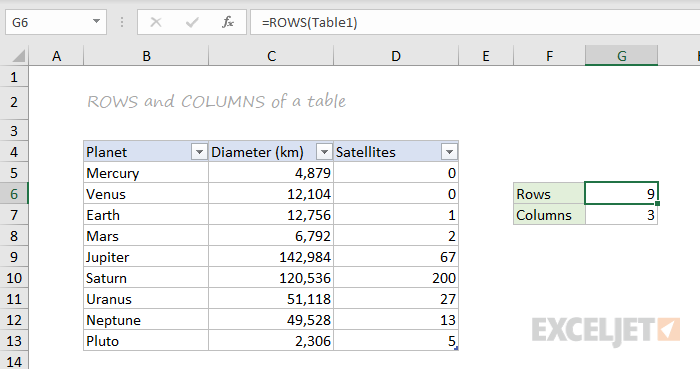
ROWS and COLUMNS
The ROWS function and COLUMNS function provide a count of rows in a reference. In the screen below, we are counting rows and columns in an Excel Table named «Table1».
Note ROWS returns a count of data rows in a table, excluding the header row. By the way, here are 23 things to know about Excel Tables.
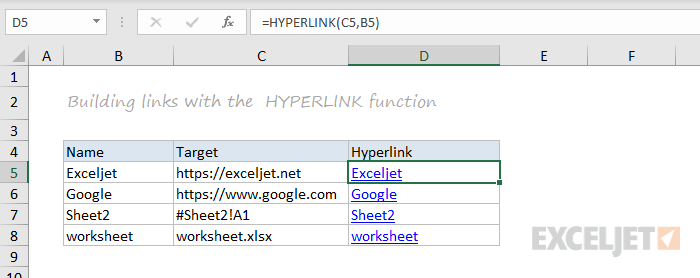
HYPERLINK
You can use the HYPERLINK function to construct a link with a formula. Note HYPERLINK lets you build both external links and internal links:
=HYPERLINK(C5,B5)
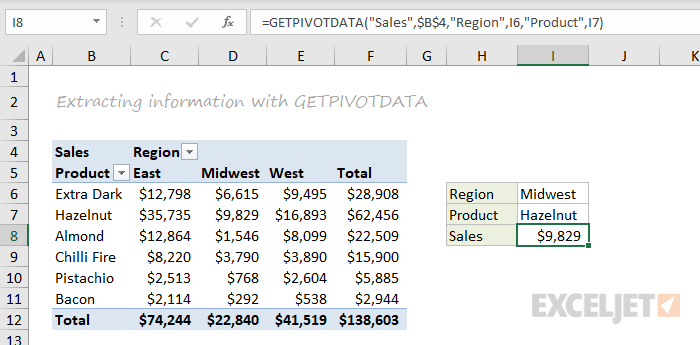
GETPIVOTDATA
The GETPIVOTDATA function is useful for retrieving information from existing pivot tables.
=GETPIVOTDATA("Sales",$B$4,"Region",I6,"Product",I7)
CHOOSE
The CHOOSE function is handy any time you need to make a choice based on a number:
=CHOOSE(2,"red","blue","green") // returns "blue"
Video: How to use the CHOOSE function
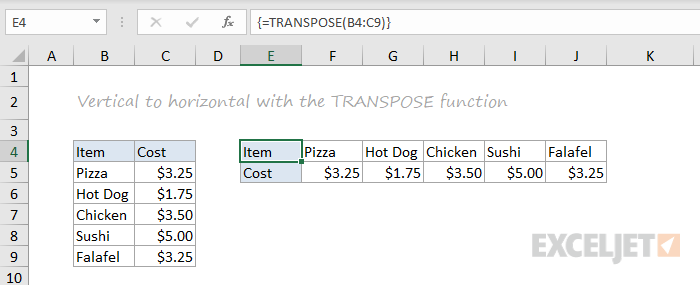
TRANSPOSE
The TRANSPOSE function gives you an easy way to transpose vertical data to horizontal, and vice versa.
{=TRANSPOSE(B4:C9)}
Note: TRANSPOSE is a formula and is, therefore, dynamic. If you just need to do a one-time transpose operation, use Paste Special instead.
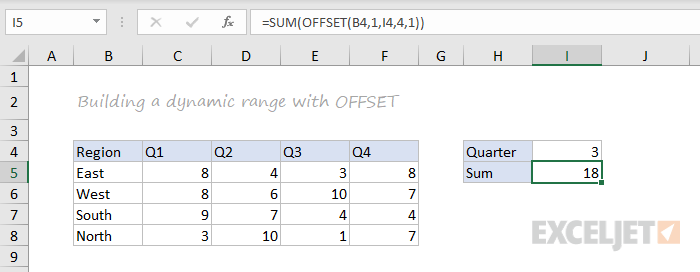
OFFSET
The OFFSET function is useful for all kinds of dynamic ranges. From a starting location, it lets you specify row and column offsets, and also the final row and column size. The result is a range that can respond dynamically to changing conditions and inputs. You can feed this range to other functions, as in the screen below, where OFFSET builds a range that is fed to the SUM function:
=SUM(OFFSET(B4,1,I4,4,1)) // sum of Q3
INDIRECT
The INDIRECT function allows you to build references as text. This concept is a bit tricky to understand at first, but it can be useful in many situations. Below, we are using INDIRECT to get values from cell A1 in 5 different worksheets. Each reference is dynamic. If a sheet name changes, the reference will update.
=INDIRECT(B5&"!A1") // =Sheet1!A1
The INDIRECT function is also used to «lock» references so they won’t change, when rows or columns are added or deleted. For more details, see linked examples at the bottom of the INDIRECT function page.
Caution: both OFFSET and INDIRECT are volatile functions and can slow down large or complicated spreadsheets.
STATISTICAL Functions
COUNT and COUNTA
You can count numbers with the COUNT function and non-empty cells with COUNTA. You can count blank cells with COUNTBLANK, but in the screen below we are counting blank cells with COUNTIF, which is more generally useful.
=COUNT(B5:F5) // count numbers
=COUNTA(B5:F5) // count numbers and text
=COUNTIF(B5:F5,"") // count blanks
COUNTIF and COUNTIFS
For conditional counts, the COUNTIF function can apply one criteria. The COUNTIFS function can apply multiple criteria at the same time:
=COUNTIF(C5:C12,"red") // count red
=COUNTIF(F5:F12,">50") // count total > 50
=COUNTIFS(C5:C12,"red",D5:D12,"TX") // red and tx
=COUNTIFS(C5:C12,"blue",F5:F12,">50") // blue > 50
Video: How to use the COUNTIF function
SUM, SUMIF, SUMIFS
To sum everything, use the SUM function. To sum conditionally, use SUMIF or SUMIFS. Following the same pattern as the counting functions, the SUMIF function can apply only one criteria while the SUMIFS function can apply multiple criteria.
=SUM(F5:F12) // everything
=SUMIF(C5:C12,"red",F5:F12) // red only
=SUMIF(F5:F12,">50") // over 50
=SUMIFS(F5:F12,C5:C12,"red",D5:D12,"tx") // red & tx
=SUMIFS(F5:F12,C5:C12,"blue",F5:F12,">50") // blue & >50
Video: How to use the SUMIF function
AVERAGE, AVERAGEIF, and AVERAGEIFS
Following the same pattern, you can calculate an average with AVERAGE, AVERAGEIF, and AVERAGEIFS.
=AVERAGE(F5:F12) // all
=AVERAGEIF(C5:C12,"red",F5:F12) // red only
=AVERAGEIFS(F5:F12,C5:C12,"red",D5:D12,"tx") // red and tx
MIN, MAX, LARGE, SMALL
You can find largest and smallest values with MAX and MIN, and nth largest and smallest values with LARGE and SMALL. In the screen below, data is the named range C5:C13, used in all formulas.
=MAX(data) // largest
=MIN(data) // smallest
=LARGE(data,1) // 1st largest
=LARGE(data,2) // 2nd largest
=LARGE(data,3) // 3rd largest
=SMALL(data,1) // 1st smallest
=SMALL(data,2) // 2nd smallest
=SMALL(data,3) // 3rd smallest
Video: How to find the nth smallest or largest value
MINIFS, MAXIFS
The MINIFS and MAXIFS. These functions let you find minimum and maximum values with conditions:
=MAXIFS(D5:D15,C5:C15,"female") // highest female
=MAXIFS(D5:D15,C5:C15,"male") // highest male
=MINIFS(D5:D15,C5:C15,"female") // lowest female
=MINIFS(D5:D15,C5:C15,"male") // lowest male
Note: MINIFS and MAXIFS are new in Excel via Office 365 and Excel 2019.
MODE
The MODE function returns the most commonly occurring number in a range:
=MODE(B5:G5) // returns 1
RANK
To rank values largest to smallest, or smallest to largest, use the RANK function:
Video: How to rank values with the RANK function
MATH Functions
ABS
To change negative values to positive use the ABS function.
=ABS(-134.50) // returns 134.50
RAND and RANDBETWEEN
Both the RAND function and RANDBETWEEN function can generate random numbers on the fly. RAND creates long decimal numbers between zero and 1. RANDBETWEEN generates random integers between two given numbers.
=RAND() // between zero and 1
=RANDBETWEEN(1,100) // between 1 and 100
ROUND, ROUNDUP, ROUNDDOWN, INT
To round values up or down, use the ROUND function. To force rounding up to a given number of digits, use ROUNDUP. To force rounding down, use ROUNDDOWN. To discard the decimal part of a number altogether, use the INT function.
=ROUND(11.777,1) // returns 11.8
=ROUNDUP(11.777) // returns 11.8
=ROUNDDOWN(11.777,1) // returns 11.7
=INT(11.777) // returns 11
MROUND, CEILING, FLOOR
To round values to the nearest multiple use the MROUND function. The FLOOR function and CEILING function also round to a given multiple. FLOOR forces rounding down, and CEILING forces rounding up.
=MROUND(13.85,.25) // returns 13.75
=CEILING(13.85,.25) // returns 14
=FLOOR(13.85,.25) // returns 13.75
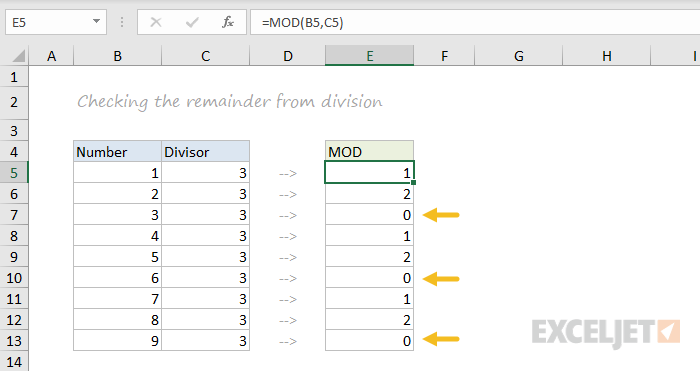
MOD
The MOD function returns the remainder after division. This sounds boring and geeky, but MOD turns up in all kinds of formulas, especially formulas that need to do something «every nth time». In the screen below, you can see how MOD returns zero every third number when the divisor is 3:
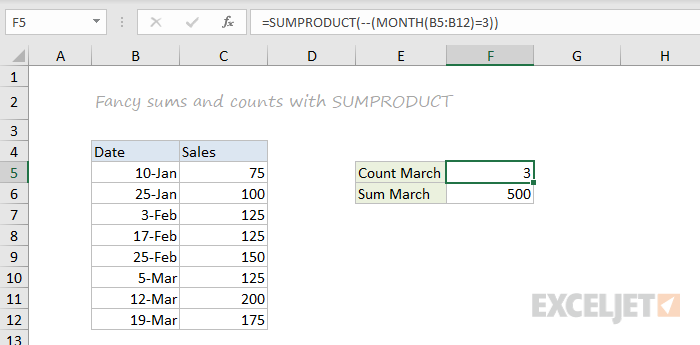
SUMPRODUCT
The SUMPRODUCT function is a powerful and versatile tool when dealing with all kinds of data. You can use SUMPRODUCT to easily count and sum based on criteria, and you can use it in elegant ways that just don’t work with COUNTIFS and SUMIFS. In the screen below, we are using SUMPRODUCT to count and sum orders in March. See the SUMPRODUCT page for details and links to many examples.
=SUMPRODUCT(--(MONTH(B5:B12)=3)) // count March
=SUMPRODUCT(--(MONTH(B5:B12)=3),C5:C12) // sum March
SUBTOTAL
The SUBTOTAL function is an «aggregate function» that can perform a number of operations on a set of data. All told, SUBTOTAL can perform 11 operations, including SUM, AVERAGE, COUNT, MAX, MIN, etc. (see this page for the full list). The key feature of SUBTOTAL is that it will ignore rows that have been «filtered out» of an Excel Table, and, optionally, rows that have been manually hidden. In the screen below, SUBTOTAL is used to count and sum only the 7 visible rows in the table:
=SUBTOTAL(3,B5:B14) // returns 7
=SUBTOTAL(9,F5:F14) // returns 9.54
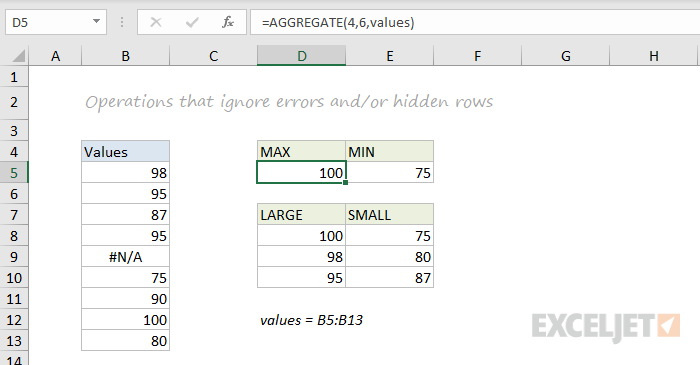
AGGREGATE
Like SUBTOTAL, the AGGREGATE function can also run a number of aggregate operations on a set of data and can optionally ignore hidden rows. The key differences are that AGGREGATE can run more operations (19 total) and can also ignore errors.
In the screen below, AGGREGATE is used to perform MIN, MAX, LARGE and SMALL operations while ignoring errors. Normally, the error in cell B9 would prevent these functions from returning a result. See this page for a full list of operations AGGREGATE can perform.
=AGGREGATE(4,6,values) // MAX ignore errors, returns 100
=AGGREGATE(5,6,values) // MIN ignore errors, returns 75
TEXT Functions
LEFT, RIGHT, MID
To extract characters from the left, right, or middle of text, use LEFT, RIGHT, and MID functions:
=LEFT("ABC-1234-RED",3) // returns "ABC"
=MID("ABC-1234-RED",5,4) // returns "1234"
=RIGHT("ABC-1234-RED",3) // returns "RED"
LEN
The LEN function will return the length of a text string. LEN shows up in a lot of formulas that count words or characters.
FIND, SEARCH
To look for specific text in a cell, use the FIND function or SEARCH function. These functions return the numeric position of matching text, but SEARCH allows wildcards and FIND is case-sensitive. Both functions will throw an error when text is not found, so wrap in the ISNUMBER function to return TRUE or FALSE (example here).
=FIND("Better the devil you know","devil") // returns 12
=SEARCH("This is not my beautiful wife","bea*") // returns 12
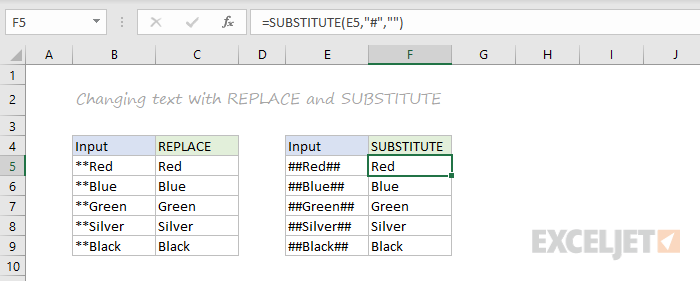
REPLACE, SUBSTITUTE
To replace text by position, use the REPLACE function. To replace text by matching, use the SUBSTITUTE function. In the first example, REPLACE removes the two asterisks (**) by replacing the first two characters with an empty string («»). In the second example, SUBSTITUTE removes all hash characters (#) by replacing «#» with «».
=REPLACE("**Red",1,2,"") // returns "Red"
=SUBSTITUTE("##Red##","#","") // returns "Red"
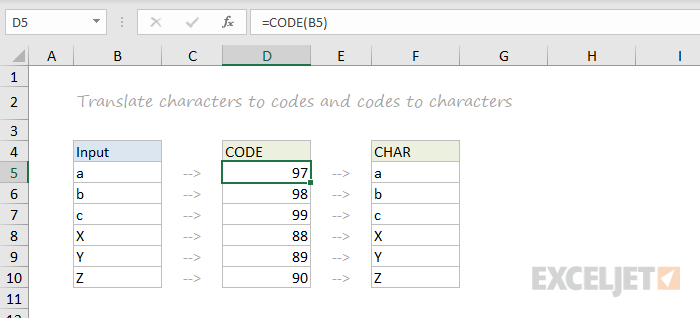
CODE, CHAR
To figure out the numeric code for a character, use the CODE function. To translate the numeric code back to a character, use the CHAR function. In the example below, CODE translates each character in column B to its corresponding code. In column F, CHAR translates the code back to a character.
=CODE("a") // returns 97
=CHAR(97) // returns "a"
Video: How to use the CODE and CHAR functions
TRIM, CLEAN
To get rid of extra space in text, use the TRIM function. To remove line breaks and other non-printing characters, use CLEAN.
=TRIM(A1) // remove extra space
=CLEAN(A1) // remove line breaks
Video: How to clean text with TRIM and CLEAN
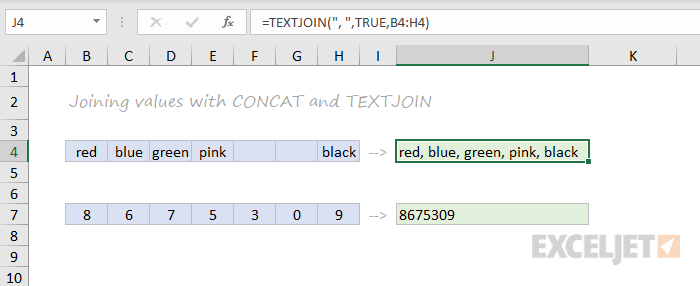
CONCAT, TEXTJOIN, CONCATENATE
New in Excel via Office 365 are CONCAT and TEXTJOIN. The CONCAT function lets you concatenate (join) multiple values, including a range of values without a delimiter. The TEXTJOIN function does the same thing, but allows you to specify a delimiter and can also ignore empty values.
=TEXTJOIN(",",TRUE,B4:H4) // returns "red,blue,green,pink,black"
=CONCAT(B7:H7) // returns "8675309"
Excel also provides the CONCATENATE function, but it doesn’t offer special features. I wouldn’t bother with it and would instead concatenate directly with the ampersand (&) character in a formula.
EXACT
The EXACT function allows you to compare two text strings in a case-sensitive manner.
UPPER, LOWER, PROPER
To change the case of text, use the UPPER, LOWER, and PROPER function
=UPPER("Sue BROWN") // returns "SUE BROWN"
=LOWER("Sue BROWN") // returns "sue brown"
=PROPER("Sue BROWN") // returns "Sue Brown"
Video: How to change case with formulas
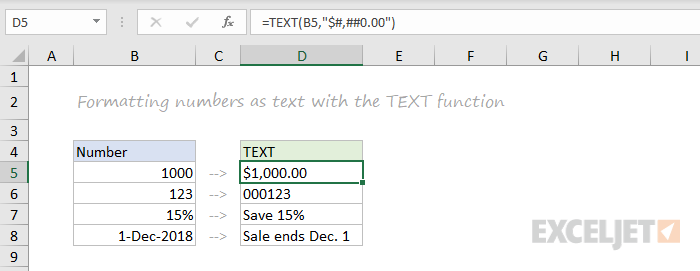
TEXT
Last but definitely not least is the TEXT function. The text function lets you apply number formatting to numbers (including dates, times, etc.) as text. This is especially useful when you need to embed a formatted number in a message, like «Sale ends on [date]».
=TEXT(B5,"$#,##0.00")
=TEXT(B6,"000000")
="Save "&TEXT(B7,"0%")
="Sale ends "&TEXT(B8,"mmm d")
More: Detailed examples of custom number formatting.
Dynamic Array functions
Dynamic arrays are new in Excel 365, and are a major upgrade to Excel’s formula engine. As part of the dynamic array update, Excel includes new functions which directly leverage dynamic arrays to solve problems that are traditionally hard to solve with conventional formulas. If you are using Excel 365, make sure you are aware of these new functions:
| Function | Purpose |
|---|---|
| FILTER | Filter data and return matching records |
| RANDARRAY | Generate array of random numbers |
| SEQUENCE | Generate array of sequential numbers |
| SORT | Sort range by column |
| SORTBY | Sort range by another range or array |
| UNIQUE | Extract unique values from a list or range |
| XLOOKUP | Modern replacement for VLOOKUP |
| XMATCH | Modern replacement for the MATCH function |
Video: New dynamic array functions in Excel (about 3 minutes).
Quick navigation
ABS, AGGREGATE, AND, AVERAGE, AVERAGEIF, AVERAGEIFS, CEILING, CHAR, CHOOSE, CLEAN, CODE, COLUMN, COLUMNS, CONCAT, CONCATENATE, CONVERT, COUNT, COUNTA, COUNTBLANK, COUNTIF, COUNTIFS, DATE, DATEDIF, DAY, EDATE, EOMONTH, EXACT, FIND, FLOOR, GETPIVOTDATA, HLOOKUP, HOUR, HYPERLINK, IF, IFERROR, IFNA, IFS, INDEX, INDIRECT, INT, ISBLANK, ISERROR, ISEVEN, ISFORMULA, ISLOGICAL, ISNUMBER, ISODD, ISTEXT, LARGE, LEFT, LEN, LOOKUP, LOWER, MATCH, MAX, MAXIFS, MID, MIN, MINIFS, MINUTE, MOD, MODE, MONTH, MROUND, NETWORKDAYS, NOT, NOW, OFFSET, OR, PROPER, RAND, RANDBETWEEN, RANK, REPLACE, RIGHT, ROUND, ROUNDDOWN, ROUNDUP, ROW, ROWS, SEARCH, SECOND, SMALL, SUBSTITUTE, SUBTOTAL, SUM, SUMIF, SUMIFS, SUMPRODUCT, TEXT, TEXTJOIN, TIME, TODAY, TRANSPOSE, TRIM, UPPER, VLOOKUP, WEEKDAY, WEEKNUM, WORKDAY, YEAR, YEARFRAC
The most frequently used functions in Excel are:
- AutoSum;
- IF function;
- LOOKUP function;
- VLOOKUP function;
- HLOOKUP function;
- MATCH function;
- CHOOSE function;
- DATE function;
Contents
- 1 What are the 5 functions in Excel?
- 2 What are the 10 functions in Excel?
- 3 What are the 4 major functions of Excel?
- 4 What are the 20 Excel functions?
- 5 How many functions are there in Excel?
- 6 What are the most used functions in Excel?
- 7 How many types of functions do you know?
- 8 What is function in Excel with example?
- 9 What are the six functions of MS Excel?
- 10 Is there a for function in Excel?
- 11 What are the 3 common uses for Excel?
- 12 What are the 12 types of functions?
- 13 What are the 4 types of functions?
- 14 What are the 8 types of functions?
- 15 What are spreadsheet functions?
- 16 Which is an example of a function?
- 17 What are the new functions in Excel?
- 18 How do you use functions in Excel?
- 19 How do you use the OR function in Excel?
- 20 What are the types of functions in Excel?
5 Functions of Excel/Sheets That Every Professional Should Know
- VLookup Formula.
- Concatenate Formula.
- Text to Columns.
- Remove Duplicates.
- Pivot Tables.
What are the 10 functions in Excel?
10 Excel Functions Every Marketer Should Know
- Table Formatting. What it does: transforms your data into an interactive database.
- Pivot Tables. What it does: summarizes data and finds unique values.
- Charting.
- COUNTIFS.
- SUMIFS.
- IF Statements.
- CONCATENATE.
- VLOOKUP.
What are the 4 major functions of Excel?
To help you get started, here are 5 important Excel functions you should learn today.
- The SUM Function. The sum function is the most used function when it comes to computing data on Excel.
- The TEXT Function.
- The VLOOKUP Function.
- The AVERAGE Function.
- The CONCATENATE Function.
What are the 20 Excel functions?
- Sum. “Sum” is probably the easiest and the most important Excel function at the same time.
- Average. Another very important function.
- If. Another must-use formula.
- Sumif. Sumif is another very useful Excel formula.
- Countif. Countif is a very useful function that works like a sumif.
- Counta.
- Vlookup.
- Left, Right, Mid.
How many functions are there in Excel?
Though every Excel feature has a use case, no single person uses every Excel feature themselves. Cut through the 500+ functions, and you’re left with 100 or so truly useful functions and features for the majority of modern knowledge workers.
What are the most used functions in Excel?
SUM functions. Probably the most frequently used function in Excel (or any other spreadsheet program), =SUM does just that: It sums a column, row, or range of numbers—but it doesn’t just sum. It also subtracts, multiplies, divides, and uses any of the comparison operators to return a result of 1 (true) or 0 (false).
How many types of functions do you know?
There are three different forms of representation of functions. The functions need to be represented to showcase the domain values and the range values and the relationship between them.
What is function in Excel with example?
Functions are predefined formulas and are already available in Excel. For example, cell A3 below contains a formula which adds the value of cell A2 to the value of cell A1. For example, cell A3 below contains the SUM function which calculates the sum of the range A1:A2.
What are the six functions of MS Excel?
The six functions are CONCAT, TEXTJOIN, IFS, SWITCH, MAXIFS, and MINIFS. The new chart type is a funnel chart. At least two of these calculation functions are vast improvements over existing functionality.
Is there a for function in Excel?
The FOR… NEXT statement is a built-in function in Excel that is categorized as a Logical Function. It can be used as a VBA function (VBA) in Excel. As a VBA function, you can use this function in macro code that is entered through the Microsoft Visual Basic Editor.
What are the 3 common uses for Excel?
The three most common general uses for spreadsheet software are to create budgets, produce graphs and charts, and for storing and sorting data. Within business spreadsheet software is used to forecast future performance, calculate tax, completing basic payroll, producing charts and calculating revenues.
What are the 12 types of functions?
Terms in this set (12)
- Quadratic. f(x)=x^2. D: -∞,∞ R: 0,∞
- Reciprocal. f(x)=1/x. D: -∞,0 U 0,∞ R: -∞,0 U 0,∞ Odd.
- Exponential. f(x)=e^x. D: -∞,∞ R: 0,∞
- Sine. f(x)=SINx. D: -∞,∞ R: -1,1. Odd.
- Greatest Integer. f(x)= [[x]] D: -∞,∞ R: {All Integers} Neither.
- Absolute Value. f(x)= I x I. D: -∞,∞ R: 0,∞
- Linear. f(x)=x. Odd.
- Cubic. f(x)=x^3. Odd.
What are the 4 types of functions?
The various types of functions are as follows:
- Many to one function.
- One to one function.
- Onto function.
- One and onto function.
- Constant function.
- Identity function.
- Quadratic function.
- Polynomial function.
What are the 8 types of functions?
The eight types are linear, power, quadratic, polynomial, rational, exponential, logarithmic, and sinusoidal.
What are spreadsheet functions?
A function is a predefined formula that performs calculations using specific values in a particular order. All spreadsheet programs include common functions that can be used for quickly finding the sum, average, count, maximum value, and minimum value for a range of cells.
Which is an example of a function?
The formula for the area of a circle is an example of a polynomial function.The graph of the function then consists of the points with coordinates (x, y) where y = f(x). For example, the graph of the cubic equation f(x) = x3 − 3x + 2 is shown in the figure.
What are the new functions in Excel?
New functions
- CONCAT. This new function is like CONCATENATE, but better.
- IFS. Tired of typing complicated, nested IF functions?
- MAXIFS. This function returns the largest number in a range, that meets a single or multiple criteria.
- MINIFS.
- SWITCH.
- TEXTJOIN.
How do you use functions in Excel?
Enter a formula that contains a built-in function
- Select an empty cell.
- Type an equal sign = and then type a function. For example, =SUM for getting the total sales.
- Type an opening parenthesis (.
- Select the range of cells, and then type a closing parenthesis).
- Press Enter to get the result.
How do you use the OR function in Excel?
The OR function is a logical function to test multiple conditions at the same time. OR returns either TRUE or FALSE. For example, to test A1 for either “x” or “y”, use =OR(A1=”x”,A1=”y”).
What are the types of functions in Excel?
Seven Basic Excel Formulas For Your Workflow
- SUM. The SUM function. The function will sum up cells that are supplied as multiple arguments.
- AVERAGE. The AVERAGE function.
- COUNT. The COUNT function.
- COUNTA. Like the COUNT function, COUNTA.
- IF. The IF function.
- TRIM. The TRIM function.
- MAX & MIN. The MAX.
Below is the list of the most important 100+ Excel functions and their formula usage. These Excel functions are subdivided into the following:
- Financial Functions
- Logical Functions
- Text Functions
- Date and Time Functions
- Lookup & Reference Functions
- Math Functions
- Statistical Functions
- Information Functions
Financial Functions in Excel
| FV in ExcelThe FV function in Excel is a built-in financial function that can also be referred to as the future value function. This function is very useful in calculating the future value of any investment made by anyone. It has some dependent arguments, which are the constant interest, periods, and payments.read more | Calculate the future value of an investment at a specified rate of interest |
rate nper pmt pv type |
| IPMTThe IPMT function calculates the interest to be paid on a given loan with constant interest and periodic payments. It is a financial function that computes the interest portion of a payment for a given period.read more | Calculate the interest of an investment for a specific period. |
rate per nper pv fv type |
| IRR | This excel function is simply the Internal Rate of Return for your investment in a series of cash flows. |
values guess |
| MIRR in ExcelMIRR or (modified internal rate of return) in excel is an in-build financial function to calculate the MIRR for the cash flows supplied with a period. It takes the initial investment, interest rate and the interest earned from the earned amount and returns the MIRR.read more | It is the Modified Internal Rate of Return, which returns the percentage by considering both the finance and reinvestment rates. |
values finance_rate reinvest_rate |
| NPERNPER, commonly known as the number of payment periods for a loan, is a financial term and an inbuilt financial function in Excel that can be used to calculate NPER for any loan. This formula takes rate, payment made, present value and future value as input from a user.read more | The number of installments or EMIs required to clear off the loan. |
rate pmt pv fv type |
| NPV | Net Present Value is the value of future cash inflows and outflows by considering the current discount rate. |
rate value1 value2 |
| PMTPMT function is an advanced financial function to calculate the monthly payment against the simple loan amount. You have to provide basic information, including loan amount, interest rate, and duration of payment, and the function will calculate the payment as a result.read more | This Excel function returns the per month payment required to repay the loan. |
rate nper pv fv type |
| PPMT in ExcelThe PPMT function in Excel is a financial function that calculates the payment for a given principal and returns an integer result. This function can be used to calculate the principal amount of an installment for any period.read more | It returns only the principal amount for an investment or loan |
per nper pv fv type |
| PRICE in ExcelThe price function in Excel is a financial function that calculates the original value or face value of a stock for per 100 dollars, assuming interest is paid periodically.read more | It returns the redemption value per 100 face value. |
settlement maturity rate yld redemption frequency basis |
| PV in ExcelPV, or present value, is a function that is used to calculate the current present value of any investment. It is determined by the investment rate and the number of payment periods, with the future value as an input.read more | It gives the present value of an investment by considering constant interest rates and payments |
rate nper pmt fv type |
| RATE in ExcelRate function in excel is used to calculate the rate levied on a period of a loan. The required inputs for this function are number of payment periods, pmt, present value and future value.read more | It returns the interest rate for an investment or loan. |
nper pmt pv fv type guess |
| XIRRThe XIRR function, also known as the Extended Internal Rate of Return function in Excel, is used to calculate returns based on multiple investments made for a series of non-periodic cash flows.read more | It returns the internal rate of return without any specific periodic period. |
values dates guess |
| YIELD | It estimates the amount earned on investment security over some time. |
Logical Functions in Excel
| AND | If all the supplied conditions are true, it will return TRUE or else FALSE. |
logical1 logical2 |
| IF | This tests the logic given; it the condition is true, then we can get whatever the result we want if FALSE also we can other than the TRUE result value. |
logical_test value_if_true value_if_false |
| IFERROR in ExcelThe IFERROR function in Excel checks a formula (or a cell) for errors and returns a specified value in place of the error.read more | This returns the specific value if the applied formula returns an error result. |
value value_if_error |
| NOT | This works indirectly, if the value is TRUE, it will result in FLASE, and if the result is FALSE, it will return TRUE. |
logical |
| OR in ExcelThe OR function in Excel is used to test various conditions, allowing you to compare two values or statements in Excel. If at least one of the arguments or conditions evaluates to TRUE, it will return TRUE. Similarly, if all of the arguments or conditions are FALSE, it will return FASLE.read more | This is just like the AND function in excel, but if anyone of the supplied is true, it will return TRUE. |
logical1 logical2 |
| TRUE | This is the formula to get TRUE value without manual typing |
– |
Text Functions in Excel
| CHAR | This excel function converts numbers to characters based on the American Standard Code For Information Interchange (ASCII). |
number |
| CLEAN | It removes only non-printable values. |
text |
| CODEIn Excel, the Code Function is used to determine the code of a character in a string. It only finds the code for the first character, thus if we use this formula as =Code(“Anand”) and =Code(“An”), the result will be 65, because the code for character A is 65.read more | This returns the numerical code for an alphabetic word. |
text |
| EXACT in ExcelThe exact function is a logical function in excel used to compare two strings or data with each other, and it gives us the result whether the both data are an exact match or not. This function is a logical function, so it provides true or false as a result.read more | This tests two cell values, whether they are exact, are not. |
text1 text2 |
| LEFT | This will get the value from the left-hand side of a string based on the number of characters we specify. |
text num_chars |
| LEN in ExcelThe Len function returns the length of a given string. It calculates the number of characters in a given string as input. It is a text function in Excel as well as an inbuilt function that can be accessed by typing =LEN( and entering a string as input.read more | This excel function returns the numbers of characters in a cell. Space is also a character. |
text |
| MID in ExcelThe mid function in Excel is a text function that finds strings and returns them from any mid-part of the spreadsheet. read more | This can fetch the data from the middle of the supplied value. |
text start_num num_chars |
| PROPER | This will arrange the text properly by changing the first character to an uppercase letter. |
text |
| REPLACE | This excel function replaces the text with new text from the specified position |
old_text start_num num_chars new_text |
| REPT | This will repeat the supplied character based on the number we specify. |
text number_times |
| RIGHT in ExcelRight function is a text function which gives the number of characters from the end from the string which is from right to left. For example, if we use this function as =RIGHT ( “ANAND”,2) this will give us ND as the result.read more | This will get the value from the right-hand side of a string based on the number of characters we specify. |
text num_chars |
| SEARCH in ExcelSearch function gives the position of a substring in a given string when we give a parameter of the position to search from. As a result, this formula requires three arguments. The first is the substring, the second is the string itself, and the last is the position to start the search.read more | This will return the position of the supplied character in the specific value. |
find_text within_text start_num |
| SUBSTITUTE in ExcelSubstitute function in excel is a very useful function which is used to replace or substitute a given text with another text in a given cell, this function is widely used when we send massive emails or messages in a bulk, instead of creating separate text for every user we use substitute function to replace the information.read more | This excel function substitutes the existing character with a new character. |
text old_text new_text instance_num |
| TEXT | This will convert the value to text based on the format we specify. |
value format_text |
| TRIM in ExcelThe Trim function in Excel does exactly what its name implies: it trims some part of any string. The function of this formula is to remove any space in a given string. It does not remove a single space between two words, but it does remove any other unwanted spaces.read more | This eliminates unnecessary spaces or trailing spaces. |
text |
| VALUE in ExcelIn Excel, the value function returns the value of a text representing a number. So, if we have a text with the value $5, we can use the value formula to get 5 as a result, so this function gives us the numerical value represented by a text.read more | This will convert the numerical values, which are in text format to number format. |
text |
Date and Time Functions in Excel
| DATE | This excel function requires three elements, year, month, and day. It will format the supplied numbers as a date. |
year month day |
| DAY | It extracts the day number from the supplied date. |
serial_number |
| EDATE in ExcelEDATE is a date and time function in excel which adds a given number of months into a date and gives us a date in a numerical format of date. It takes dates and integers as input, the output returned by this function is also a date value. read more | It is used to get a date on the same day of the month, x months in the past or future. |
start_date months |
| EOMONTHEOMONTH is a worksheet date function in excel which calculates the end of the month for the given date by adding a specified number of months to the arguments. This function takes two arguments: the date and another as integer, and the output is in the date format.read more | This excel function returns the end of the month for the supplied date. |
start_date months |
| NOW in ExcelIn an excel worksheet, the NOW function is used to display the current system date and time. The syntax for using this function is quite simple =NOW ().read more | It returns the current date and time. |
– |
| TIME in ExcelTime is a time worksheet function in Excel that is used to calculate time based on the inputs provided by the user. The arguments can take the following formats: hours, minutes, and seconds.read more | It requires three elements, hour, minute, and second. |
hour minute second |
| TODAY in ExcelToday function is a date and time function that is used to find out the current system date and time in excel. This function does not take any arguments and auto-updates anytime the worksheet is reopened. This function just reflects the current system date, not the time.read more | It gives the current date. |
– |
| WEEKDAY in ExcelThe WEEKDAY function in excel returns the day corresponding to a specified date. The date is supplied as an argument to this function. read more | It returns the weekday of the supplied date. |
serial_number return_type |
| WORKDAY in ExcelThe WORKDAY function returns the forthcoming work day after a given number of days from the start date. It has an optional argument for holidays that, if not provided, automatically considers weekends (Saturdays and Sundays) to be holidays.read more | This excel function returns the date from the supplied date based on the number of days we specify. |
start_date days holidays |
| YEAR in ExcelThe year function in excel is a date function to calculate the year from a given date. This function takes a serial number as an argument and returns a four-digit numeric value representing the year of the given date, formula = year (serial number)read more | This function extracts the year from the supplied date. |
serial_number |
Lookup & Reference Functions in Excel
| ADDRESS | This will create the cell reference or address of the cell as a text value. |
row_num column_num abs_num a1 sheet_text |
| CHOOSE | This excel function chooses the value from various values. |
index_num value1 value2 |
| COLUMN | This function returns the selected column number |
reference |
| COLUMNS in ExcelThe COLUMNS function returns the total number of columns in the given array or collection of references.read more | It will return how many columns are selected |
array |
| GETPIVOTDATAThe GetPivotData function in Excel is a query function that fetches values from a pivot table based on specific criteria such as the pivot table’s structure or the reference provided to the function.read more | It extracts data from the pivot tableA Pivot Table is an Excel tool that allows you to extract data in a preferred format (dashboard/reports) from large data sets contained within a worksheet. It can summarize, sort, group, and reorganize data, as well as execute other complex calculations on it.read more from the specified row and from the specified column |
data_field pivot_table field1 item1 |
| HLOOKUPHlookup is a referencing worksheet function that finds and matches the value from a row rather than a column using a reference. Hlookup stands for horizontal lookup, in which we search for data in rows horizontally.read more | It extracts data which is there horizontally based on the lookup value. |
lookup_value table_array row_index_num range_lookup |
| HYPERLINKA hyperlink is an inbuilt function in excel used to create hyperlinks for a particular cell. When the hyperlink is created, it redirects to a specific webpage. The hyperlink formula has two arguments, one is the URL while the other is the name we provide to the URL.read more | This creates a URL to open the data, which is where your PC or laptop. |
link_location friendly_name |
| INDEX | It returns the value from the lookup value. |
array row_num column_num area_num |
| INDIRECT Function in ExcelThe INDIRECT excel function is used to indirectly refer to cells, cell ranges, worksheets, and workbooks.read more | This indirectly refers to the other cell from a different cell. |
ref_text a1 |
| LOOKUP in ExcelThe LOOKUP excel function searches a value in a range (single row or single column) and returns a corresponding match from the same position of another range (single row or single column). The corresponding match is a piece of information associated with the value being searched. read more |
It looks for a value in one row and one column |
lookup_value lookup_vector result_vector |
| MATCHThe MATCH function looks for a specific value and returns its relative position in a given range of cells. The output is the first position found for the given value. Being a lookup and reference function, it works for both an exact and approximate match. For example, if the range A11:A15 consists of the numbers 2, 9, 8, 14, 32, the formula “MATCH(8,A11:A15,0)” returns 3. This is because the number 8 is at the third position. read more |
This returns the row number of a lookup value from the array. |
lookup_value lookup_array match_type |
| OFFSET in ExcelThe OFFSET function in excel returns the value of a cell or a range (of adjacent cells) which is a particular number of rows and columns from the reference point. read more | This function returns a reference to a range. |
reference rows cols height width |
| ROW | Returns the first-row number in the reference provided |
reference |
| Transpose in ExcelThe TRANSPOSE function in excel helps rotate (switch) the values from rows to columns and vice versa. Being a part of the Excel lookup and reference functions, its purpose is to organize the data in the desired format. To execute the formula, the exact size of the range to be transposed is selected and the CSE key (“Control+Shift+Enter”) is pressed. read more |
This function is used to switch cells between rows and columns. |
array |
| VLOOKUPThe VLOOKUP excel function searches for a particular value and returns a corresponding match based on a unique identifier. A unique identifier is uniquely associated with all the records of the database. For instance, employee ID, student roll number, customer contact number, seller email address, etc., are unique identifiers. read more |
This excel function returns the value of a lookup value from another table, which is there vertically. |
lookup_value table_array col_index_num range_lookup |
Math Functions in Excel
| ABS | This function converts all the negative numbers to positive numbers. |
number |
| AGGREGATE | This excel function supplies some of the important formulas like Average, Count, Max, Min, and many other functions by ignoring error values |
function_num options array k |
| CEILING Excel FunctionThe CEILING function is very similar to the FLOOR function in terms of functionality. However, the result is the polar opposite, with the floor function giving a less significant result. The ceiling formula, on the other hand, gives result with a higher significance.read more | Returns a rounded number based on a multiple significance. |
number significance mode |
| COMBIN Excel FunctionCOMBIN function in excel is the combination function to calculate possible combinations for two given numbers. This function takes two arguments. One is the number and number chosen. If the number is 5 and the number chosen is 1, then there are 5 combinations and 5 as a result.read more | This function returns the number of combinations for a specified number of items. |
number number_chosen |
| EVEN | This excel function converts all the odd numbers to even numbers. |
number |
| EXP Excel FunctionExponential Excel function(EXP) is an inbuilt function in excel used to calculate the exponent raised to the power of any number you provide. In this function the exponent is constant and is also known as the base of the natural algorithm.read more | It raises the supplied number to the power of e. |
number |
| INT in ExcelINT or integer function in excel returns the nearest integer of a given number and is used when we have many data sets and each data in a different format.read more | This function is responsible for returning a number’s integer portion. |
number |
| LN ExcelLN function calculates the logarithm of a given number which takes a single number as the argument and gives the result as the logarithm.read more | This function is used to calculate the natural logarithm of a number. |
number |
| LOG in ExcelThe LOG function returns the logarithm of a given number. The number’s base, on the other hand, is supposed to be provided by the user.read more | It returns the logarithm of a number to the base user gives |
number base |
| ODD in ExcelODD Function is an inbuilt function in excel as the name suggests it rounds any given number to its odd value, the number can be both negative or positive.read more | This function converts all the even numbers to ODD numbers. |
number |
| POWER in ExcelPOWER function calculates the power of a given number or base. To use this function you can use the keyword =POWER( in a cell and provide two arguments one as number and another as power.read more | This function raises the base number to a different number of times at the top of the base. |
number power |
| PRODUCT in ExcelProduct excel function is an inbuilt mathematical function which is used to calculate the product or multiplication of the given numbers. If you provide this formula arguments as 2 and 3 as =PRODUCT(2,3) then the result displayed is 6.read more | This function simply does the multiplication of two supplied numbers. |
number1 number2 |
| RAND in ExcelThe RAND function in Excel, also known as the random function, generates a random value greater than 0 but less than 1, with an even distribution among those numbers when used on multiple cells. read more | It returns values that are greater than zero but less than 1. This is a volatile function. |
– |
| ROUND | It either rounds up or rounds down to a specified number of decimals. |
number num_digits |
| ROUNDUP in ExcelThe ROUNDUP excel function calculates the rounded value of the number to the upward side or the higher side. In other words, it rounds the number away from zero. Being an inbuilt function of Excel, it accepts two arguments–the “number” and the “num_of _digits.” For example, “=ROUNDUP(0.40,1)” returns 0.4. read more |
This excel function rounds the given floating-point number to a number of decimal places provided. |
number num_digits |
| ROUNDDOWN in ExcelROUNDDOWN function is a built-in function in Microsoft Excel. It is used to round off the given number.read more | To round off the given number, this function is used. |
number num_digits |
| SIGN | This function calculates the sign of a supplied number. |
number |
| SIN in ExcelSIN Excel function is an inbuilt trigonometric function in excel which is used to calculate the sine value of given number or in terms of trigonometry the sine value of a given angle, here the angle is a number in excel and this function takes only a single argument which is the input number provided.read more | This function calculates the SIN of an angle |
number |
| SQRT in ExcelThe Square Root function is an arithmetic function built into Excel that is used to determine the square root of a given number. To use this function, type the term =SQRT and hit the tab key, which will bring up the SQRT function. Moreover, this function accepts a single argument.read more | Find a number of positive square roots |
number |
| SUBTOTAL in ExcelThe SUBTOTAL excel function performs different arithmetic operations like average, product, sum, standard deviation, variance etc., on a defined range.read more | This function ignores all the hidden rows and gives the calculation only for the visible rows. |
function_num ref1 |
| SUMThe SUM function in excel adds the numerical values in a range of cells. Being categorized under the Math and Trigonometry function, it is entered by typing “=SUM” followed by the values to be summed. The values supplied to the function can be numbers, cell references or ranges.read more | This excel function adds all the numerical values which are there in the range. |
number1 number2 |
| SUMIF in ExcelThe SUMIF Excel function calculates the sum of a range of cells based on given criteria. The criteria can include dates, numbers, and text. For example, the formula “=SUMIF(B1:B5, “<=12”)” adds the values in the cell range B1:B5, which are less than or equal to 12. read more |
This function adds the numbers based on the single criteria given by the user. |
range criteria sum_range |
| TAN | This function simultaneously does the summation as well as multiplication corresponding to the values. |
array1 array2 array3 |
| TAN in ExcelThe TAN Excel function is a trigonometric function built into Excel that is used to calculate the cosine value of a given number or, in terms of trigonometry, the cosine value of a given angle. In this case, the angle is a number in Excel, and this function accepts only one argument, which is the input number.read more | This function returns the tangent of an angle. |
number |
| TANH in ExcelIn trigonometry we have a term called hyperbolic tangent which is the ratio of the hyperbolic sine and cosine functions, to calculate this mathematical operation in excel we have an inbuilt trigonometric function known as TANH and it takes single argument as an input. read more |
TANH function gives the hyperbolic tangent of a given number, and the number is considered as an angle to radians. |
number |
Statistical Functions in Excel
| AVERAGE | This excel function returns the average value of the supplied numbers. |
number1 number2 |
| CORREL Excel FunctionCORREL function is a statistical function in Excel. The CORREL formula finds out the coefficient between two variables and returns the coefficient of array1 and array2. The correlation coefficient determines the relationship between the two properties.read more | This is nothing but a correlation between two data sets. |
array1 array2 |
| COUNT | This function counts all the numerical values in the supplied range. |
value1 value2 |
| COUNTIFThe COUNTIF function in Excel counts the number of cells within a range based on pre-defined criteria. It is used to count cells that include dates, numbers, or text. For example, COUNTIF(A1:A10,”Trump”) will count the number of cells within the range A1:A10 that contain the text “Trump” read more |
This excel function counts only the value w specify |
range criteria |
| F.TEST in ExcelF-test in excel is a statistical tool that helps us decide whether the variances of two populations having normal distribution are equal or not. F-test is an essential part of the analysis of variance (ANOVA) model.read more | This function is used to decide if two populations having normal distributionNormal Distribution is a bell-shaped frequency distribution curve which helps describe all the possible values a random variable can take within a given range with most of the distribution area is in the middle and few are in the tails, at the extremes. This distribution has two key parameters: the mean (µ) and the standard deviation (σ) which plays a key role in assets return calculation and in risk management strategy.read more have similar variances or the standard deviation. |
array1 array2 |
| FORECAST Excel FormulaThe FORECAST function in Excel is used to calculate or predict the future value based on existing values and the statistical value of the forecast. If we know the past data, we may use the function to forecast the future value.read more | This function calculates or estimates the sales values based on previous trends. |
x known_ys known_xs |
| FREQUENCY in ExcelThe FREQUENCY function in Excel calculates the number of times a data values occurs within a given range of values and returns a vertical array of numbers corresponding to each value’s frequency within a range.read more | This excel function shows how often a certain value is occurring in an array |
data_array bins_array |
| GROWTH | It calculates the exponential growthExponential Growth refers to the increase due to compounding of the data over time and follows a curve representing an exponential function. Exponential growth formula: Final value = Initial value * (1 + Annual Growth Rate/No of Compounding ) No. of years * No. of compoundingread more of given numbers based on two data sets. |
known_ys known_xs new_xs const |
| LARGE | It is responsible for returning the nth largest value from a given set of values in the spreadsheet. |
array k |
| LINEST ExcelThe built-in LINEST Function in Excel calculates statistics for a line by the least-squares regression method & returns an array that defines the line proving to be well-suited for the given data. read more | It is used to calculate a line’s stats. |
known_ys known_xs const stats |
| MAX in ExcelThe MAX Formula in Excel is used to calculate the maximum value from a set of data/array. It counts numbers but ignores empty cells, text, the logical values TRUE and FALSE, and text values.read more | This function is given the maximum value from the supplied numbers. |
number2 |
| MEDIAN | This function returns the middle value of the supplied numbers. |
number1 number2 |
| MIN in ExcelIn Excel, the MIN function is categorized as a statistical function. It finds and returns the minimum value from a given set of data/array.read more | This function is given the minimum value from the supplied numbers. |
number1 number2 |
| MODE | This excel function returns the MODE for each set of data. |
number1 number2 |
| NORMDISTNORMDIST or normal distribution is an inbuilt statistical function of excel that calculates the normal distribution of a data set with mean and standard deviation provided.read more | It estimates the probability of the variables plotting below or above a certain value. |
x mean standard_dev cumulative |
| NORM.S.INVThe NORM.S.INV function determines the inverse of the normal distribution. For this function, the mean of the data set is always zero and the standard deviation is always one.read more | This is the inverse of standard normal cumulative distribution. |
Probability |
| PERCENTILE in ExcelThe PERCENTILE function is responsible for returning the nth percentile from a supplied set of values. read more | This function returns the nth percentile of the set of values supplied. |
array k |
| QUARTILE in ExcelQuartile functions are used to find the various quartiles of a data set and are part of Excel’s statistical functions. There are three quartiles; the first quartile (Q1) is the middle number between the smallest value and the median value of a data set. The second quartile (Q2) is the median of the data. The third quartile (Q3) is the middle value between the median of the data set and the highest value.read more | This function in excel is used to find the different quartiles of a data set. |
array quart |
| SLOPE in ExcelThe Slope function returns the slope of a regression line based on the data points recognized by known _y values and known _x values.read more | This function calculates how steep the line is |
known_ys known_xs |
| SMALL in ExcelThe SMALL Function in Excel returns the nth smallest value from a set of values. For example, 2nd smallest value, 3rd smallest value and so on.read more | This function returns the nth smallest value of the set of values supplied. |
array k |
| STDEV.SThe standard deviation shows the variability of the data values from the mean (average). In Excel, the STDEV and STDEV.S calculate sample standard deviation while STDEVP and STDEV.P calculate population standard deviation. STDEV is available in Excel 2007 and the previous versions. However, STDEV.P and STDEV.S are only available in Excel 2010 and subsequent versions. read more |
SD shows how data spread outs among data points. |
number1 number2 |
| T.TEST | This function in excel calculates the probability associated with the T-testA T-test is a method to identify whether the means of two groups differ from one another significantly. It is an inferential statistics approach that facilitates the hypothesis testing.read more of the student. |
array1 array2 tails type |
| TREND | This function calculates the linear trend according to the given linear data set. |
known_ys known_xs new_xs const |
Information Functions in Excel
The complete Excel Functions list includes lookup, logic, date and time, text, information, and math functions with examples. Excel Functions are built-in presets, so Excel functions are hard-coded formulas with short, user-friendly names.
The list contains 300+ built-in Excel functions. Furthermore, look at the library of useful advanced functions (UDFs). If you want to jump to a specific category, use the list below; else, use the Search box for the latest tutorials.
- User-defined functions (must-have)
- Logical
- Text
- Lookup
- Date and Time
- Dynamic array
- Information
- Math
- Statistical
- Financial
Excel Function List
Logical
The functions below use logical tests and logical operators to evaluate a formula. Learn more about Boolean expressions.
LOOKUP
Here is the list of lookup functions in Excel. Of course, we already know that XLOOKUP changes everything. But it is worth keeping in mind the older lookup functions too.
User-defined functions
UDFs are advanced functions.
Date and Time
Date and Time functions help you create calculations based on dates and times.
Text
Text functions in Excel enable you to perform various calculations using strings.
Dynamic Array
Dynamic Arrays are resizable arrays. From now, Excel calculates the array automatically and returns values into multiple cells based on a formula entered in a single cell.
Information
Take a quick overview of information functions in Excel.
Math
Math Functions are great.
Math – Part 2
Financial
Use financial functions if you want.
Financial – Part 2
Statistical
Statistical – Part 2
Trigonometry
Engineering
Database
How to use Excel Functions?
To use a function, type an equal sign (=) in the formula bar or the cell to enter a function you want to use. After that, enter the function’s name and the arguments. There are custom functions in Excel, user-defined functions. If you want to learn more about how to solve complex tasks using UDFs, read our guide.