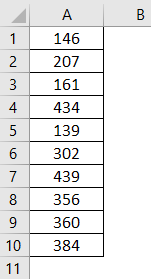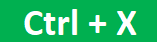Microsoft Excel Features
Almost all the professionals use this spreadsheet tool. MS Excel is the universal language that speaks in practically all the offices. However, as a starter or intermediate-level user, you need to know some of the important features of MS Excel. This article will show you the features of MS Excel.
Table of contents
- Microsoft Excel Features
- Top 9 Main Features of Microsoft Excel with Examples
- #1 – You Can Insert a New Worksheets at Will
- #2 – Time Saving Shortcut Keys
- #3 – Get Quick Sum of Numbers
- #4 – Filtering Data
- #5 – Paste Special Feature
- #6 – Insert Random Numbers
- #7 – Insert Random Fraction Numbers
- #8 – Goal Seek Analysis Tool
- #9 – Insert Serial Numbers
- Things to Remember about Features of MS Excel
- Recommended Articles
- Top 9 Main Features of Microsoft Excel with Examples
You are free to use this image on your website, templates, etc, Please provide us with an attribution linkArticle Link to be Hyperlinked
For eg:
Source: Features of MS Excel (wallstreetmojo.com)
Top 9 Main Features of Microsoft Excel with Examples
Now, we shall discuss the 9 different features of Microsoft Excel with examples which are as follows:
You can download this Features of MS Excel Template here – Features of MS Excel Template
#1 – You Can Insert a New Worksheets at Will
You might have seen one to three default worksheets while opening the new workbook (the number of worksheets may vary depending on the settings).
You can insert a new worksheet in excelTo add a new worksheet, go to the bottom of the screen and press the ‘+’ button. You can also navigate to ‘Home’, ‘Insert,’ and then ‘Insert Sheet’ to add a new sheet.read more and delete the same at any time. First, press the “+” icon key to insert any new worksheet available at the bottom.
Now, click on this button to insert a new worksheet.
We can also insert a new worksheet by pressing the shortcut key “Shift + F11.“
#2 – Time Saving Shortcut Keys
The time on Excel can be reduced drastically by masterful Excel shortcut keys. Apart from universal “Ctrl + C, Ctrl + X, and Ctrl + V,” we can use many other abundant shortcut keys in excelAn Excel shortcut is a technique of performing a manual task in a quicker way.read more.
Shortcut key for Copy:
Shortcut key for Cut:
Shortcut key for Paste:
You can refer to our article on “Excel Shortcut Keys” to learn some of the important shortcut keys.
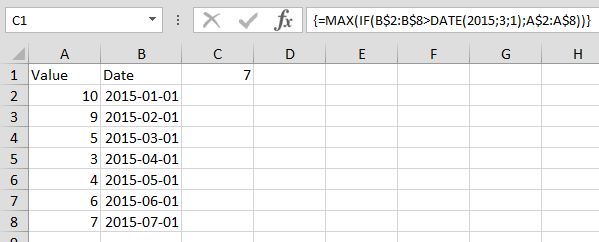
#3 – Get Quick Sum of Numbers
If we have serial numbers or any numerical data, we can quickly get the sum of these numbers with simple shortcut keys.
Assume we have numbers in 10 cells, and imagine how long it will take us to get the total of these numbers.
I can say less than a second!!!!
Yes, you hear it right less than a second.
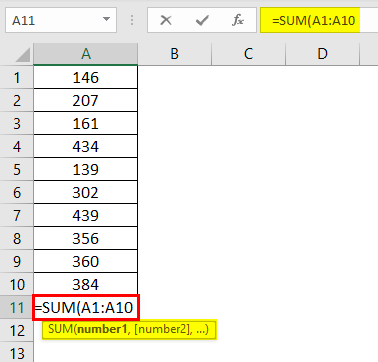
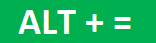
Select the cell where we need to get the total of these numbers and press the shortcut key “ALT + =” to get the AutoSum.
We get the following result.
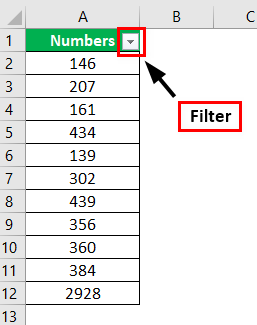
#4 – Filtering Data
Filtering the excel dataThe filter in excel helps display relevant data by eliminating the irrelevant entries temporarily from the view. The data is filtered as per the given criteria. The purpose of filtering is to focus on the crucial areas of a dataset. For example, the city-wise sales data of an organization can be filtered by the location. Hence, the user can view the sales of selected cities at a given time.
read more is one of the important features of Microsoft Excel. We can filter any data available under the “Filter” section.
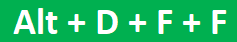
We can use more advanced techniques to filter the data. For example, to insert a short filter, we can press the shortcut key “Ctrl + Shift + L” or “Alt + D + F + F.”
Shortcut key to Insert the Filter:
or
For example,
#5 – Paste Special Feature
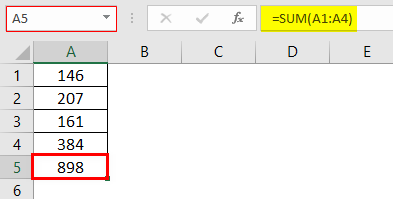
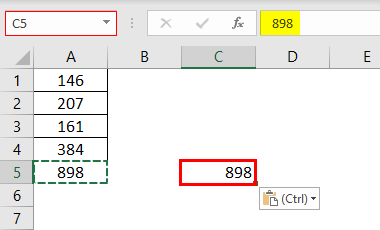
We love paste specialPaste special in Excel allows you to paste partial aspects of the data copied. There are several ways to paste special in Excel, including right-clicking on the target cell and selecting paste special, or using a shortcut such as CTRL+ALT+V or ALT+E+S.read more because it gives us more edge to increase workplace productivity. For example, look at the below data.
In the A5 cell, we have a formula that takes the range of cells from A1 to 4. So, the A5 cell is dependent on the above cells. So, if we copy and paste this cell to other cells, we may get this formula only, not value.
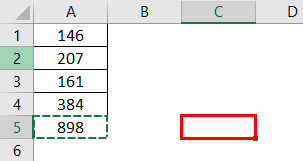
So, we can use the Paste Special technique to paste as only values. Therefore, we must copy cell A5 and place a cursor on the cell where we need to paste.
I have copied the cell A5 and placed the cursor on the C5 cell.
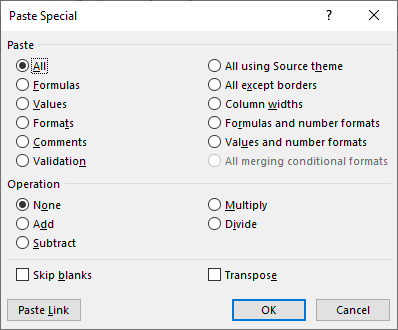
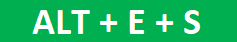
Now, press the “ALT + E + S” shortcut key and open the “Special” dialog box.
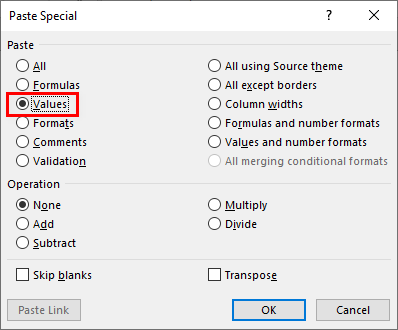
We have plenty of options under “Paste Special” features. However, we want to paste only the value in this example, so we must select the “Values” option to paste as the only value.
So this will paste only the value from A5 cell to C5 cell.
Like this, under “Paste Special,” we can use other available techniques like “Formulas,” “Formats,” etc.
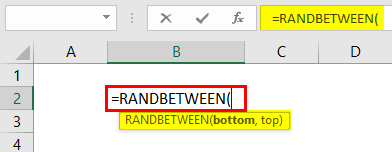
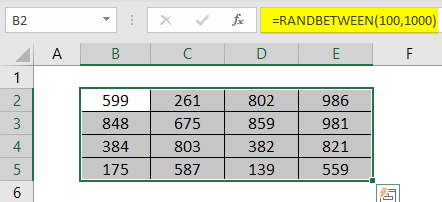
#6 – Insert Random Numbers
Excel has plenty of formulas and functions in its arsenal. For example, if we want to insert random numbers with an Excel worksheet, we can use a built-in function called“RANDBETWEENRANDBETWEEN excel formula determine random numbers between two extreme variables (bottom and top numbers). The user needs to fill in the bottom and top numbers in the syntax =RANDBETWEEN (bottom, top) to acquire the random integer.read more.”
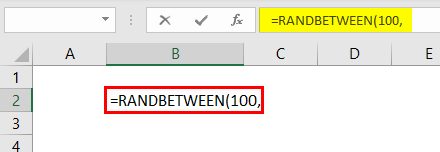
For the first argument, supply the least number that you want to insert.
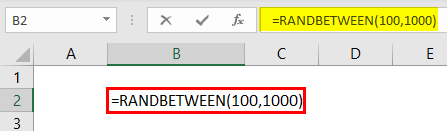
For the last argument, we must enter the highest number that we want to insert.
So, now, the RANDBETWEEN function inserts numbers from 100 to 1,000.
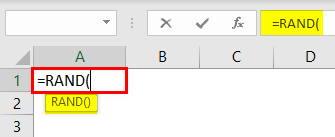
#7 – Insert Random Fraction Numbers
As seen above, we can insert random numbers. Now, we will see how we can insert random fraction numbers.
We must use the RAND functionThe RAND function in Excel, also known as the random function, generates a random value greater than 0 but less than 1, with an even distribution among those numbers when used on multiple cells. read more to insert random fraction numbers greater than 0 and less than 1.
The RAND function does not have any parameters, so we must close the bracket and insert the function.
Note:
Both RAND and RANDBETWEEN are volatile functions and keeps varying whenever we make any changes in the workbook.
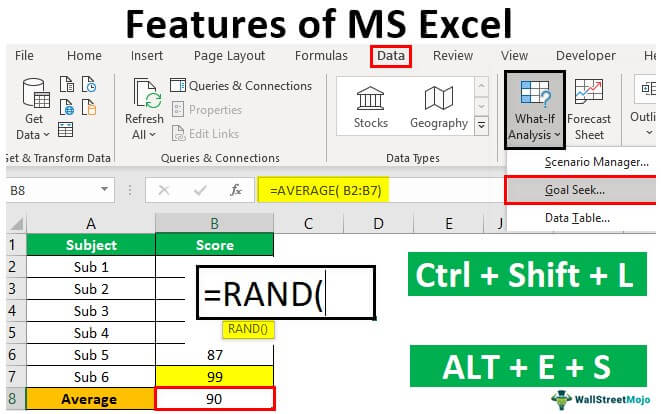
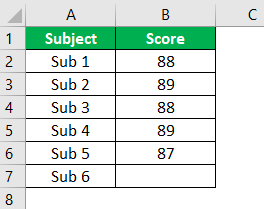
#8 – Goal Seek Analysis Tool
The Goal Seek analysisThe Goal Seek in excel is a “what-if-analysis” tool that calculates the value of the input cell (variable) with respect to the desired outcome. In other words, the tool helps answer the question, “what should be the value of the input in order to attain the given output?”
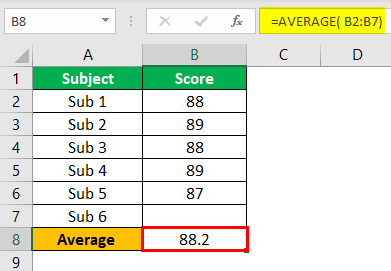
read more tool is extremely useful for determining what needs to be done to achieve the desired goal. For example, Mr. A wants to get an overall average score of 90 in 6 subjects. However, Mr. A has already attended five exams. Below are his anticipated scores.
Now, Mr. A is left with only one examination. He wants to know how much he must score in the final examination to get an overall average of 90.
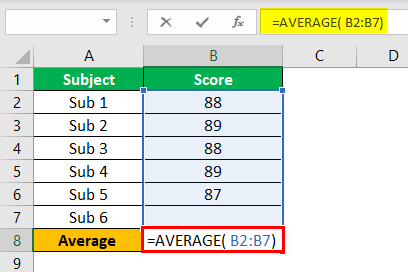
So, first, we must apply the AVERAGE function for the first five exams.
We get the following result.
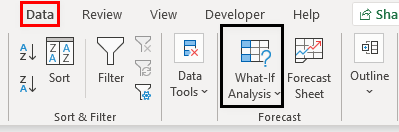
Now go to the DATA tab and click on the What-If AnalysisWhat-If Analysis in Excel is a tool for creating various models, scenarios, and data tables. It enables one to examine how a change in values influences the outcomes in the sheet. The three components of What-If analysis are Scenario Manager, Goal Seek in Excel, and Data Table in Excel.read more tool to open the “Goal Seek” tool.
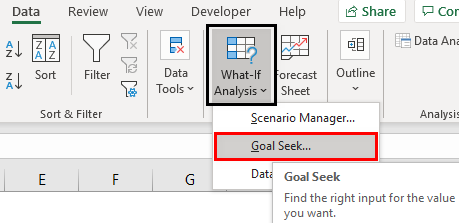
In the Goal Seek window, we can see three options.
We must select “Goal Seek.” Then, we may get the following options: “Set cell,” “To value,” and “By changing cell.”
The average function applies to the cell for the “Set cell,” the B8 cell.
In the “To value,” the cell enters the value as 90.
The “Changing cell” gives the cell reference to the B7 cell.
Now, we must click on “OK.” As a result, the “Goal Seek” analysis tool will help Mr. A to know how much he needs to score in the final examination to get the overall average of 90.
Mr. A has to score 99 on his final examination to get an overall average of 90.
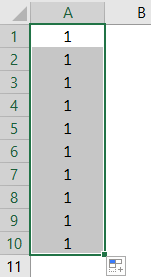
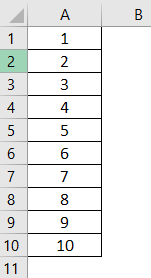
#9 – Insert Serial Numbers
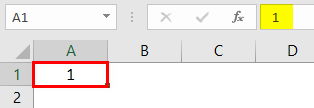
If we want to insert serial numbers incremented by 1, we can do this by the “Fill Series” option. Then, enter the value 1 in any of the cells.
Using the Excel FILL HandleThe fill handle in Excel allows you to avoid copying and pasting each value into cells and instead use patterns to fill out the information. This tiny cross is a versatile tool in the Excel suite that can be used for data entry, data transformation, and many other applications.read more function, we must drag until the cell where we want to insert serial numbers
Now, click on the “AutoFill” option and choose “Fill Series” to get the serial numbers incremented by 1.
We get the following result.
Things to Remember about Features of MS Excel
- These are some of the basic and cool features of Excel.
- We have so many uses that other features will also cover incoming topics.
- We must use the shortcut keys to use an excellent spreadsheet tool skillfully.
- We must first learn the basic formulas to get started with functions.
Recommended Articles
This article is a guide to the features of MS Excel. Here, we discuss the top 9 features of Microsoft Excel, including “Time Saving Shortcut Keys,” “Get Quick Sum of Numbers,” “Filtering Data,” “Paste Special” feature, etc., along with examples and a downloadable Excel template. You may learn more about Excel from the following articles: –
- Bullet Chart in Excel
- Formula in Excel Not Working
- SUM Shortcut in Excel
- “Save As” Excel Shortcut
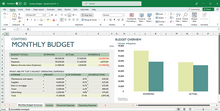
Features of Excel

Features of Excel made the Excel as most widely using application. Excel is the very popular application because of its wide range of features and powerful tools. Microsoft added many features in each release of Excel 2007, 2010, 2013, 2016 and Office Online 365. Here are the main features of the Microsoft Excel.
Main Features of Excel
We can divide the Main features of the Excel into Graphical, Data Base and Functional Features:
Graphical Features of Excel
Excel have verity of the graphical features to represent the data in Charts and pictorial format.
- Charts: We can use charts to represent the data in rich visualized graphical representation.
- Shapes: We can create verity of shapes to represent the data in shapes and info-graphics. We can draw any shape with the free form feature in Excel.
- SmartArts: We can use the SmartArts to align the data in a creative designs and visually communicate the information.
- Clip Arts: We can add the ready to use clip arts to convey our message in pictorial representation.
- Pictures: We can insert any image to enhance the objects. Example backgrounds of Worksheets, Shapes and Charts.
Data Base Features of Excel
Excel can be used as data base and perform of verity of data operations.
- PivotTables: We can use the Summarize the data and create powerful cross tables.
- Slicers: Slicers are introduced in Excel 2010, this will helps us to connect the multiple pivot tables and filter the data with buttons.
- Tables. We can create the tables in the data in records and fields format. This will be helpful to quickly perform further analysis.
- Sparklines: Introduced in Excel 2010, we can insert the light weight charts into the cells.
- Database: We can use Excel as Data base to store the 1 million records. We can connect to verity of the data bases and import the data into Excel.
- Sorting: We can sort the data in Excel. We can sort Ascending or Descending with on or more columns.
- Filtering: We can Filter the data in Excel. We can set verity of the options to filter with required options. Excel has the Advanced Filtering option to perform the more complex filters.
- Data validations: Data Validation Feature helps to restrict the cell to accept certain type of the data. We can also provide the drop-down to choose from the pre-defined list.
- Grouping: We can group the rows and columns with parent and child records.
Functional Features of Excel
Excel Tools and Functions will help to perform powerful calculations and enhance the Excel Application Features.
- Functions: There are more than 300 built-in formulas to use in the Excel Cells. Verity of the formulas (Text, Date, String, Maths,etc) will help to perform verity of calculations.
- VBA Macros: Excel comes with VBA Programming. We can use Macros feature to automate the repetitive tasks.
- Add-ins: We can develop the Excel Add-ins with VBA or .NET to enhance the Excel Functionality.
- Hyperlinks: We can add hyperlinks in the Excel to quickly navigate the different parts of the Excel Workbook.
- Conditional Format: We can format the data based on certain conditions. This helps to highlight the significant data range.
- SpellCheck: Built-in spell check feature helps us to avoid the spelling and grammatical errors in the data.
- Protection: Excel provides Workbook, Worksheet and VBA Protection options.
- Excel Provides, verity of the Add-ins for Data analysis and ETL process.
We can use Excel for wide range of applications. Here are the uses of MS Excel.. Excel has introduced ribbon menu in Office 2007 and added verity of the features in each release:
Features of Excel 2007
The main new feature in Excel 2007 is Excel Ribbon Menu. And many more useful features:
- Ribbon Menu: Excel introduced ribbon menu in 2007, the look and feel of the Excel is more modern
- Open XML: Introduced Open XML File structure
- More Rows and Columns: This addition allows to store more records and fields in each spreadsheet
- Themes and Styles: This feature helps to easily switch from one color schema to another
- Improvements and added features in Formulas, Charts and PivotTables
Features of Excel 2010
Main New features in Excel 2010 is Slicers and Sparklines:
- Slicers: Excel Slicers for PivotTable helps to filter the multiple PivotTable with one button Click
- Sparklines: Now you can create dashboards with graphs in Cells with Sparkline feature
- Mobile Excel for Windows 7 and many more Performance Features added in Excel 2010
Features of Excel 2013
Excel was MDI(Multple Document Interface) till Excel 2010, now it is Single Document Application. Smart and Modern look and feel of the Application, and many more performance features introduced in Excel 2013.
- New Start Screen is introduce in Excel 2013
- Ribbon menu is enhanced, now its similar to Windows 8/10 application menu
- Quick tools for Charts
- Quick Data analysis Tools introduced in Excel 2013
- Enhanced Graphics and Picture Quality in Excel 2013.
- Added many more color schema xml files.
Features of Excel 2016
Excel 2016 is almost looks like Excel 2013.
- Tell me what you want to do?: New tool to quickly search commands
- New Charts: Sunburst,Waterfall , Histograms and Pareto charts
- Scalable Vector Graphics: Now we can insert SVGs in Excel
- Icons: New command to browse the office icons and insert the ready to use vector icons
- Pen is added to draw the shapes
Features of Excel Online
Microsoft is developing many tools and fastening its Online Version of the MS Office. Most of the features works in the Excel Online version except the VBA Macros.
© Copyright 2012 – 2020 | Excelx.com | All Rights Reserved
Page load link
Содержание
- Features of MS Excel
- Microsoft Excel Features
- Top 9 Main Features of Microsoft Excel with Examples
- #1 – You Can Insert a New Worksheets at Will
- #2 – Time Saving Shortcut Keys
- #3 – Get Quick Sum of Numbers
- #4 – Filtering Data
- #5 – Paste Special Feature
- #6 – Insert Random Numbers
- #7 – Insert Random Fraction Numbers
- #8 – Goal Seek Analysis Tool
- #9 – Insert Serial Numbers
- Things to Remember about Features of MS Excel
- Recommended Articles
- What’s new in Excel 2021 for Windows
- Co-authoring
- Better collaboration with modern comments
- Know who’s in your workbook
- Visual refresh
- Look left, look right… XLOOKUP is here!
- LET function
- Dynamic arrays
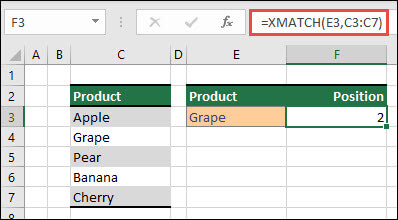
- XMATCH function
- Sheet views
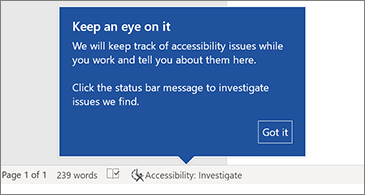
- A new way to reach the Accessibility tools
- Increase the reach of your content
- Performance improvements
- Unhide many sheets at the same time
- See what’s new in stock media
- Find what you need with Microsoft Search
- Save your changes as they happen
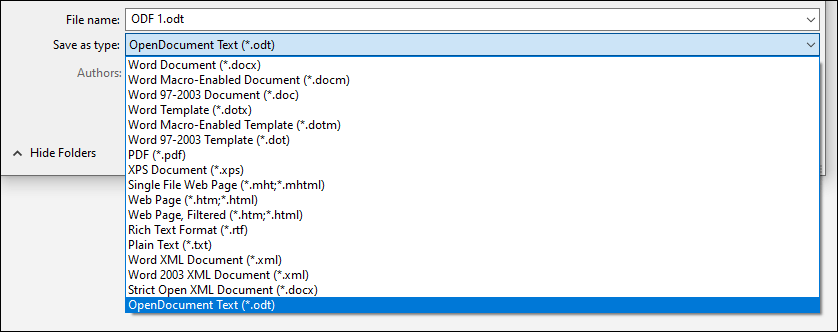
- Support for OpenDocument format (ODF) 1.3
- Updated Draw tab
- Get a quick summary of what’s in your workbook
- Pick the perfect color
- Try the Sketched style outline
Features of MS Excel
Microsoft Excel Features
Almost all the professionals use this spreadsheet tool. MS Excel is the universal language that speaks in practically all the offices. However, as a starter or intermediate-level user, you need to know some of the important features of MS Excel. This article will show you the features of MS Excel.
Table of contents
You are free to use this image on your website, templates, etc., Please provide us with an attribution link How to Provide Attribution? Article Link to be Hyperlinked
For eg:
Source: Features of MS Excel (wallstreetmojo.com)
Top 9 Main Features of Microsoft Excel with Examples
Now, we shall discuss the 9 different features of Microsoft Excel with examples which are as follows:
#1 – You Can Insert a New Worksheets at Will
You might have seen one to three default worksheets while opening the new workbook (the number of worksheets may vary depending on the settings).
Now, click on this button to insert a new worksheet.
We can also insert a new worksheet by pressing the shortcut key “Shift + F11.“
#2 – Time Saving Shortcut Keys
The time on Excel can be reduced drastically by masterful Excel shortcut keys. Apart from universal “Ctrl + C, Ctrl + X, and Ctrl + V,” we can use many other abundant shortcut keys in excel Shortcut Keys In Excel An Excel shortcut is a technique of performing a manual task in a quicker way. read more .
Shortcut key for Copy:
Shortcut key for Cut:
Shortcut key for Paste:
You can refer to our article on “Excel Shortcut Keys” to learn some of the important shortcut keys.
#3 – Get Quick Sum of Numbers
If we have serial numbers or any numerical data, we can quickly get the sum of these numbers with simple shortcut keys.
Assume we have numbers in 10 cells, and imagine how long it will take us to get the total of these numbers.
I can say less than a second.
Yes, you hear it right less than a second.
Select the cell where we need to get the total of these numbers and press the shortcut key “ALT + =” to get the AutoSum.
We get the following result.
#4 – Filtering Data
We can use more advanced techniques to filter the data. For example, to insert a short filter, we can press the shortcut key “Ctrl + Shift + L” or “Alt + D + F + F.”
Shortcut key to Insert the F ilter:
#5 – Paste Special Feature
In the A5 cell, we have a formula that takes the range of cells from A1 to 4. So, the A5 cell is dependent on the above cells. So, if we copy and paste this cell to other cells, we may get this formula only, not value.
So, we can use the Paste Special technique to paste as only values. Therefore, we must copy cell A5 and place a cursor on the cell where we need to paste.
I have copied the cell A5 and placed the cursor on the C5 cell.
Now, press the “ALT + E + S” shortcut key and open the “Special” dialog box.
We have plenty of options under “Paste Special” features. However, we want to paste only the value in this example, so we must select the “Values” option to paste as the only value.
So this will paste only the value from A5 cell to C5 cell.
Like this, under “Paste Special,” we can use other available techniques like “Formulas,” “Formats,” etc.
#6 – Insert Random Numbers
For the first argument, supply the least number that you want to insert.
For the last argument, we must enter the highest number that we want to insert.
So, now, the RANDBETWEEN function inserts numbers from 100 to 1,000.
#7 – Insert Random Fraction Numbers
As seen above, we can insert random numbers. Now, we will see how we can insert random fraction numbers.
The RAND function does not have any parameters, so we must close the bracket and insert the function.
Note:
Both RAND and RANDBETWEEN are volatile functions and keeps varying whenever we make any changes in the workbook.
#8 – Goal Seek Analysis Tool
The Goal Seek analysis Goal Seek Analysis The Goal Seek in excel is a “what-if-analysis” tool that calculates the value of the input cell (variable) with respect to the desired outcome. In other words, the tool helps answer the question, “what should be the value of the input in order to attain the given output?” read more tool is extremely useful for determining what needs to be done to achieve the desired goal. For example, Mr. A wants to get an overall average score of 90 in 6 subjects. However, Mr. A has already attended five exams. Below are his anticipated scores.
Now, Mr. A is left with only one examination. He wants to know how much he must score in the final examination to get an overall average of 90.
So, first, we must apply the AVERAGE function for the first five exams.
We get the following result.
In the Goal Seek window, we can see three options.
We must select “Goal Seek.” Then, we may get the following options: “Set cell,” “To value,” and “By changing cell.”
The average function applies to the cell for the “Set cell,” the B8 cell.
In the “To value,” the cell enters the value as 90.
The “Changing cell” gives the cell reference to the B7 cell.
Now, we must click on “OK.” As a result, the “Goal Seek” analysis tool will help Mr. A to know how much he needs to score in the final examination to get the overall average of 90.
Mr. A has to score 99 on his final examination to get an overall average of 90.
#9 – Insert Serial Numbers
If we want to insert serial numbers incremented by 1, we can do this by the “Fill Series” option. Then, enter the value 1 in any of the cells.
Now, click on the “AutoFill” option and choose “Fill Series” to get the serial numbers incremented by 1.
We get the following result.
Things to Remember about Features of MS Excel
- These are some of the basic and cool features of Excel.
- We have so many uses that other features will also cover incoming topics.
- We must use the shortcut keys to use an excellent spreadsheet tool skillfully.
- We must first learn the basic formulas to get started with functions.
Recommended Articles
This article is a guide to the features of MS Excel. Here, we discuss the top 9 features of Microsoft Excel, including “Time Saving Shortcut Keys,” “Get Quick Sum of Numbers,” “Filtering Data,” “Paste Special” feature, etc., along with examples and a downloadable Excel template. You may learn more about Excel from the following articles: –
Источник
What’s new in Excel 2021 for Windows
Excel 2021 for Windows allows you to collaboratively work with others and analyze data easily with new Excel capabilities including co-authoring, Dynamic Arrays, XLOOKUP, and LET functions.
Note: Some features listed below are not included in Excel LTSC 2021 for commercial customers. Each of those features is noted if it does not apply to Excel LTSC 2021 for commercial customers.
You and your colleagues can open and work on the same Excel workbook. This is called co-authoring. When you co-author, you can see each other’s changes quickly — in a matter of seconds.
Note: Co-authoring is not available in Excel LTSC 2021.
Have control of when you send comments to your co-authors and be productive with a consistent commenting experience in your workbooks and other Office apps.
Note: Modern comments is not available in Excel LTSC 2021.
Know who’s in your workbook
See who else is working along with you and where they are in the workbook.
Note: This feature is not available in Excel LTSC 2021.
Visual refresh
Work with a modernized Start experience and newly refreshed tabs in the ribbon. Experience a clean, clear style with monoline iconography, neutral color palette, and softer window corners. These updates communicate action and provide features with simple visuals.
Note: Visual refresh is not available in Excel LTSC 2021.
Look left, look right… XLOOKUP is here!
Row by row, find anything you need in a table or range with XLOOKUP.
Return exact matches by default—there’s no need to specify.
LET function
The LET function assigns names to calculation results. This allows storing intermediate calculations, values, or defining names inside a formula. These names only apply within the scope of the LET function.
Similar to variables in programming, LET is accomplished through Excel’s native formula syntax.
Dynamic arrays
Write one formula and return an array of values. Expedite calculations and insights with six
more new functions: FILTER, SORT, SORTBY, UNIQUE, SEQUENCE, and RANDARRAY.
XMATCH function
The XMATCH function searches for a specified item in an array or range of cells, and then returns the item’s relative position.
You can also use XMATCH to return a value in an array.
Sheet views
Create customized views in an Excel worksheet without disrupting others.
Note: Sheet views are not available in Excel LTSC 2021.
The Accessibility ribbon puts all the tools you need to create accessible content in one place.
Note: The Accessibility ribbon is not available in Excel LTSC 2021.
Increase the reach of your content
Accessibility Checker keeps an eye on your documents and tells you in the status bar when it finds something you should look at. Try it by clicking Review > Check Accessibility.
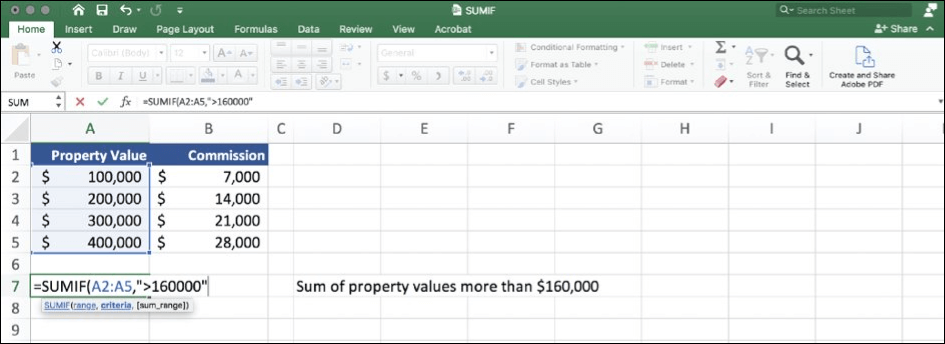
Performance improvements
Experience improved performance, stability, and speed across Excel.
Get faster calculations from common Excel functions like SUMIF, COUNTIF, and AVERAGEIF.
Unhide many sheets at the same time
No need to unhide one sheet at a time anymore—unhide multiple hidden sheets at once.
We’re constantly adding more rich media content to the Office Premium Creative Content collection that helps you express yourself, such as a curated library of stock images, icons, and more.
Find what you need with Microsoft Search
At the top of your Microsoft Office apps on Windows, you’ll find the new Microsoft Search box. This powerful tool helps you quickly find what you’re looking for, such as text, commands, help, and more.
Save your changes as they happen
Upload your files to OneDrive, OneDrive for Business, or SharePoint Online to make sure all your updates are saved automatically.
Note: AutoSave is not available in Excel LTSC 2021.
Support for OpenDocument format (ODF) 1.3
We now include support for the OpenDocument format (ODF) 1.3. The ODF 1.3 specification adds support for many new features.
Updated Draw tab
Quickly access and change the color of all your inking tools, all in one place.
Simplify how you work with ink using new Draw tab additions: Point Eraser, Ruler, and Lasso.
Get a quick summary of what’s in your workbook
Wondering how big your worksheet or workbook is getting? Excel provides workbook statistics to help you.
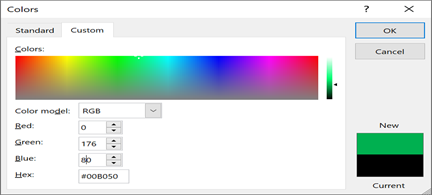
Pick the perfect color
Based on your feedback, we’ve added a new input field in the Colors dialog for Hex color values. No need to convert Hex color values into RGB values.
For any property where you can define a color, you can now enter a Hex color value in the Hex box, for example, #0F4C81 or 444.
Try the Sketched style outline
You can give a casual, hand-drawn look to shapes in your workbook with the Sketched style outline.
Try out the Curved, Freehand, or Scribble options under Format Shape > Line > Sketched style.
Источник
MS Excel is a commonly used Microsoft Office application. It is a spreadsheet program which is used to save and analyse numerical data.
In this article, we bring to you the important features of MS Excel, along with an overview of how to use the program, its benefits and other important elements. A few sample MS Excel question and answers are also given further below in this article for the reference of Government exam aspirants.
To learn more about the other programs under Microsoft Office, visit the linked article.
Computer Awareness is an integral part of the syllabus for major competitive exams and questions from MS Excel may also be asked in these exams. To get the detailed syllabus for Computer Knowledge, candidates can visit the linked article.
Basics of MS Excel
What is MS Excel?
MS Excel is a spreadsheet program where one can record data in the form of tables. It is easy to analyse data in an Excel spreadsheet. The image given below represents how an Excel spreadsheet looks like:
How to open MS Excel?
To open MS Excel on your computer, follow the steps given below:
- Click on Start
- Then All Programs
- Next step is to click on MS Office
- Then finally, choose the MS-Excel option
Alternatively, you can also click on the Start button and type MS Excel in the search option available.
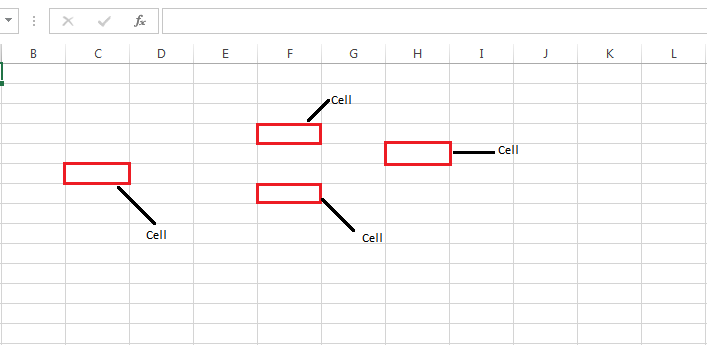
What is a cell?
A spreadsheet is in the form of a table comprising rows and columns. The rectangular box at the intersection point between rows and columns forms a cell. Given below is an image of a cell:
What is Cell Address?
The cell address is the name by which is cell can be addressed. For example, if row 7 is interested in column G, then the cell address is G7.
Features of MS Excel
Various editing and formatting can be done on an Excel spreadsheet. Discussed below are the various features of MS Excel.
The image below shows the composition of features in MS Excel:
- Home
- Comprises options like font size, font styles, font colour, background colour, alignment, formatting options and styles, insertion and deletion of cells and editing options
- Insert
- Comprises options like table format and style, inserting images and figures, adding graphs, charts and sparklines, header and footer option, equation and symbols
- Page Layout
- Themes, orientation and page setup options are available under the page layout option
- Formulas
- Since tables with a large amount of data can be created in MS excel, under this feature, you can add formulas to your table and get quicker solutions
- Data
- Adding external data (from the web), filtering options and data tools are available under this category
- Review
- Proofreading can be done for an excel sheet (like spell check) in the review category and a reader can add comments in this part
- View
- Different views in which we want the spreadsheet to be displayed can be edited here. Options to zoom in and out and pane arrangement are available under this category
For those willing to learn more about MS Excel, can refer to the video given below and understand every small aspect of this program in detail.
Benefits of Using MS Excel
MS Excel is widely used for various purposes because the data is easy to save, and information can be added and removed without any discomfort and less hard work.
Given below are a few important benefits of using MS Excel:
- Easy To Store Data: Since there is no limit to the amount of information that can be saved in a spreadsheet, MS Excel is widely used to save data or to analyse data. Filtering information in Excel is easy and convenient.
- Easy To Recover Data: If the information is written on a piece of paper, finding it may take longer, however, this is not the case with excel spreadsheets. Finding and recovering data is easy.
- Application of Mathematical Formulas: Doing calculations has become easier and less time-taking with the formulas option in MS excel
- More Secure: These spreadsheets can be password secured in a laptop or personal computer and the probability of losing them is way lesser in comparison to data written in registers or piece of paper.
- Data at One Place: Earlier, data was to be kept in different files and registers when the paperwork was done. Now, this has become convenient as more than one worksheet can be added in a single MS Excel file.
- Neater and Clearer Visibility of Information: When the data is saved in the form of a table, analysing it becomes easier. Thus, information is a spreadsheet that is more readable and understandable.
Competitive exam aspirants must also be aware of other subjects which are a part of the Government exam syllabus. To review and analyse the same, refer to the links below:
MS Excel – Points To Remember
There are certain things which one must know with respect to MS Excel, its applications and usage:
- An MS Excel file is saved with an extension of .xls
- Companies with large staff and workers use MS Excel as saving employee information becomes easier
- Excel spreadsheets are also used in hospitals where the information of patients can be saved more easily and can be removed conveniently once their medical history is cleared
- The sheet on which you work is called a Worksheet
- Multiple worksheets can be added in a single Excel file
- This is a data processing application
Aspirants can also prepare themselves by regularly solving mock tests and question papers to analyse the standard of examination and excelling in them. Refer to the links below, for the same:
MS Excel Questions and Answers
Given below are a few sample questions based on MS Excel which will help candidates preparing for competitive exams to score more in the Computer Awareness section.
Q 1. The address that is obtained by the combination of the Row number and the Column alphabet is called ________.
- Worksheet
- Cell
- Workbox
- Cell Address
- Column Address
Answer: (4) Cell Address
Q 2. Where is the option for page border given in the MS Excel spreadsheet?
- Home
- Insert
- Format
- View
- Page Border cannot be added in excel worksheet
Answer: (5) Page Border cannot be added in excel worksheet
Q 3. Excel workbook is a collection of _______ and _______.
- Worksheet and charts
- Graphs and images
- Sheets and images
- Video and audio
- None of the above
Answer: (1) Worksheet and charts
Q 4. What type of chart is useful for comparing values over categories?
- Bar Graph
- Column Chart
- Pie Chart
- Line Graph
- Such charts cannot be created in Excel
Answer: (2) Column Chart
Q 5. There is an option to add comments in an Excel worksheet, what are the cells called in which comments can be added?
- Cell Tip
- Comment Tip
- Smart Tip
- Point Tip
- Query Tip
Answer: (1) Cell Tip
Q 6. Which of the following symbols needs to be added in the formula bar, before adding a formula?
- *
- $
- %
- +
- =
Answer: (5) =
Q 7. Which keyboard key is used for Help in MS Excel?
- ctrl+H
- F2
- F1
- shift+H
- Alt+ctrl+home
Answer: (3) F1
Q 8. How can you activate a cell in MS Excel?
- By clicking on it
- By pressing the arrow keys
- By pressing Tab key
- All of the above
- None of the above
Answer: (4) All of the above
The questions given above are just for candidate’s reference and similar questions may be asked in the final exams. Aspirants can also get a detailed study plan at the Preparation Strategy for Competitive Exams page and based on it, can start their exam preparation.
A topic like MS Excel is important for everyone using computer devices to know and learn as it can be extremely useful in the various fields.
One must understand the information given in this article as it will not only help with exam preparation but also help with a better understanding as to how the program must be used.
For any further assistance related to the various exams conducted in the country, study material or preparation tips, you can turn to BYJU’S for help.
Frequently Asked Questions on Basics of MS Excel
Q1
Q 1. What is the definition of MS Excel?
Ans. MS Excel is a spreadsheet program where one can record data in the form of tables. This gives the user a more systematic display of data.
Q2
Q 2. What are the main features of Microsoft Excel?
Ans. The main features of MS Excel include inserting a pivot table, sorting of tabulated data, adding formulas to the sheet, and calculating large data.
Q3
Q 3. What are the common MS Excel formulas?
Ans. Given below are the common calculations which can be done using MS Excel:
- Addition
- Subtraction
- Average
- Maximum and Minimum
- Concatenate
- Count
Q4
Q 4. What is a cell in Microsoft Excel?
Ans. MS Excel comprises a spreadsheet is in the form of a table comprising rows and columns. The rectangular box at the intersection point between rows and columns forms a cell.
Q5
Q 5. Can multiple sheets be added to a single spreadsheet?
Ans. Yes, MS Excel gives an option to add multiple worksheets to a single spreadsheet. The user can rename each of these worksheets as per their requirements.
Microsoft Excel is a spreadsheet developed by Microsoft for Windows, macOS, Android, iOS and iPadOS. It features calculation or computation capabilities, graphing tools, pivot tables, and a macro programming language called Visual Basic for Applications (VBA). Excel forms part of the Microsoft 365 suite of software.
 |
|
A simple bar graph being created in Excel, running on Windows 11 |
|
| Developer(s) | Microsoft |
|---|---|
| Initial release | November 19, 1987; 35 years ago |
| Stable release |
2103 (16.0.13901.20400) |
| Written in | C++ (back-end)[2] |
| Operating system | Microsoft Windows |
| Type | Spreadsheet |
| License | Trialware[3] |
| Website | microsoft.com/en-us/microsoft-365/excel |
Excel for Mac (version 16.67), running on macOS Big Sur 11.5.2 |
|
| Developer(s) | Microsoft |
|---|---|
| Initial release | September 30, 1985; 37 years ago |
| Stable release |
16.70 (Build 23021201) |
| Written in | C++ (back-end), Objective-C (API/UI)[2] |
| Operating system | macOS |
| Type | Spreadsheet |
| License | Proprietary commercial software |
| Website | products.office.com/mac |

Excel for Android running on Android 13 |
|
| Developer(s) | Microsoft Corporation |
|---|---|
| Stable release |
16.0.14729.20146 |
| Operating system | Android Oreo and later |
| Type | Spreadsheet |
| License | Proprietary commercial software |
| Website | products.office.com/en-us/excel |
| Developer(s) | Microsoft Corporation |
|---|---|
| Stable release |
2.70.1 |
| Operating system | iOS 15 or later iPadOS 15 or later |
| Type | Spreadsheet |
| License | Proprietary commercial software |
| Website | products.office.com/en-us/excel |
Features
Basic operation
Microsoft Excel has the basic features of all spreadsheets,[7] using a grid of cells arranged in numbered rows and letter-named columns to organize data manipulations like arithmetic operations. It has a battery of supplied functions to answer statistical, engineering, and financial needs. In addition, it can display data as line graphs, histograms and charts, and with a very limited three-dimensional graphical display. It allows sectioning of data to view its dependencies on various factors for different perspectives (using pivot tables and the scenario manager).[8] A PivotTable is a tool for data analysis. It does this by simplifying large data sets via PivotTable fields. It has a programming aspect, Visual Basic for Applications, allowing the user to employ a wide variety of numerical methods, for example, for solving differential equations of mathematical physics,[9][10] and then reporting the results back to the spreadsheet. It also has a variety of interactive features allowing user interfaces that can completely hide the spreadsheet from the user, so the spreadsheet presents itself as a so-called application, or decision support system (DSS), via a custom-designed user interface, for example, a stock analyzer,[11] or in general, as a design tool that asks the user questions and provides answers and reports.[12][13] In a more elaborate realization, an Excel application can automatically poll external databases and measuring instruments using an update schedule,[14] analyze the results, make a Word report or PowerPoint slide show, and e-mail these presentations on a regular basis to a list of participants. Excel was not designed to be used as a database.[citation needed]
Microsoft allows for a number of optional command-line switches to control the manner in which Excel starts.[15]
Functions
Excel 2016 has 484 functions.[16] Of these, 360 existed prior to Excel 2010. Microsoft classifies these functions in 14 categories. Of the 484 current functions, 386 may be called from VBA as methods of the object «WorksheetFunction»[17] and 44 have the same names as VBA functions.[18]
With the introduction of LAMBDA, Excel will become Turing complete.[19]
Macro programming
VBA programming
Use of a user-defined function sq(x) in Microsoft Excel. The named variables x & y are identified in the Name Manager. The function sq is introduced using the Visual Basic editor supplied with Excel.
Subroutine in Excel calculates the square of named column variable x read from the spreadsheet, and writes it into the named column variable y.
The Windows version of Excel supports programming through Microsoft’s Visual Basic for Applications (VBA), which is a dialect of Visual Basic. Programming with VBA allows spreadsheet manipulation that is awkward or impossible with standard spreadsheet techniques. Programmers may write code directly using the Visual Basic Editor (VBE), which includes a window for writing code, debugging code, and code module organization environment. The user can implement numerical methods as well as automating tasks such as formatting or data organization in VBA[20] and guide the calculation using any desired intermediate results reported back to the spreadsheet.
VBA was removed from Mac Excel 2008, as the developers did not believe that a timely release would allow porting the VBA engine natively to Mac OS X. VBA was restored in the next version, Mac Excel 2011,[21] although the build lacks support for ActiveX objects, impacting some high level developer tools.[22]
A common and easy way to generate VBA code is by using the Macro Recorder.[23] The Macro Recorder records actions of the user and generates VBA code in the form of a macro. These actions can then be repeated automatically by running the macro. The macros can also be linked to different trigger types like keyboard shortcuts, a command button or a graphic. The actions in the macro can be executed from these trigger types or from the generic toolbar options. The VBA code of the macro can also be edited in the VBE. Certain features such as loop functions and screen prompt by their own properties, and some graphical display items, cannot be recorded but must be entered into the VBA module directly by the programmer. Advanced users can employ user prompts to create an interactive program, or react to events such as sheets being loaded or changed.
Macro Recorded code may not be compatible with Excel versions. Some code that is used in Excel 2010 cannot be used in Excel 2003. Making a Macro that changes the cell colors and making changes to other aspects of cells may not be backward compatible.
VBA code interacts with the spreadsheet through the Excel Object Model,[24] a vocabulary identifying spreadsheet objects, and a set of supplied functions or methods that enable reading and writing to the spreadsheet and interaction with its users (for example, through custom toolbars or command bars and message boxes). User-created VBA subroutines execute these actions and operate like macros generated using the macro recorder, but are more flexible and efficient.
History
From its first version Excel supported end-user programming of macros (automation of repetitive tasks) and user-defined functions (extension of Excel’s built-in function library). In early versions of Excel, these programs were written in a macro language whose statements had formula syntax and resided in the cells of special-purpose macro sheets (stored with file extension .XLM in Windows.) XLM was the default macro language for Excel through Excel 4.0.[25] Beginning with version 5.0 Excel recorded macros in VBA by default but with version 5.0 XLM recording was still allowed as an option. After version 5.0 that option was discontinued. All versions of Excel, including Excel 2021 are capable of running an XLM macro, though Microsoft discourages their use.[26]
Charts
Graph made using Microsoft Excel
Excel supports charts, graphs, or histograms generated from specified groups of cells. It also supports Pivot Charts that allow for a chart to be linked directly to a Pivot table. This allows the chart to be refreshed with the Pivot Table. The generated graphic component can either be embedded within the current sheet or added as a separate object.
These displays are dynamically updated if the content of cells changes. For example, suppose that the important design requirements are displayed visually; then, in response to a user’s change in trial values for parameters, the curves describing the design change shape, and their points of intersection shift, assisting the selection of the best design.
Add-ins
Additional features are available using add-ins. Several are provided with Excel, including:
- Analysis ToolPak: Provides data analysis tools for statistical and engineering analysis (includes analysis of variance and regression analysis)
- Analysis ToolPak VBA: VBA functions for Analysis ToolPak
- Euro Currency Tools: Conversion and formatting for euro currency
- Solver Add-In: Tools for optimization and equation solving
Data storage and communication
Number of rows and columns
Versions of Excel up to 7.0 had a limitation in the size of their data sets of 16K (214 = 16384) rows. Versions 8.0 through 11.0 could handle 64K (216 = 65536) rows and 256 columns (28 as label ‘IV’). Version 12.0 onwards, including the current Version 16.x, can handle over 1M (220 = 1048576) rows, and 16384 (214, labeled as column ‘XFD’) columns.[27]
File formats
| Filename extension |
.xls, (.xlsx, .xlsm, .xlsb — Excel 2007) |
|---|---|
| Internet media type |
application/vnd.ms-excel |
| Uniform Type Identifier (UTI) | com.microsoft.excel.xls |
| Developed by | Microsoft |
| Type of format | Spreadsheet |
Microsoft Excel up until 2007 version used a proprietary binary file format called Excel Binary File Format (.XLS) as its primary format.[28] Excel 2007 uses Office Open XML as its primary file format, an XML-based format that followed after a previous XML-based format called «XML Spreadsheet» («XMLSS»), first introduced in Excel 2002.[29]
Although supporting and encouraging the use of new XML-based formats as replacements, Excel 2007 remained backwards-compatible with the traditional, binary formats. In addition, most versions of Microsoft Excel can read CSV, DBF, SYLK, DIF, and other legacy formats. Support for some older file formats was removed in Excel 2007.[30] The file formats were mainly from DOS-based programs.
Binary
OpenOffice.org has created documentation of the Excel format. Two epochs of the format exist: the 97-2003 OLE format, and the older stream format.[31] Microsoft has made the Excel binary format specification available to freely download.[32]
XML Spreadsheet
The XML Spreadsheet format introduced in Excel 2002[29] is a simple, XML based format missing some more advanced features like storage of VBA macros. Though the intended file extension for this format is .xml, the program also correctly handles XML files with .xls extension. This feature is widely used by third-party applications (e.g. MySQL Query Browser) to offer «export to Excel» capabilities without implementing binary file format. The following example will be correctly opened by Excel if saved either as Book1.xml or Book1.xls:
<?xml version="1.0"?> <Workbook xmlns="urn:schemas-microsoft-com:office:spreadsheet" xmlns:o="urn:schemas-microsoft-com:office:office" xmlns:x="urn:schemas-microsoft-com:office:excel" xmlns:ss="urn:schemas-microsoft-com:office:spreadsheet" xmlns:html="http://www.w3.org/TR/REC-html40"> <Worksheet ss:Name="Sheet1"> <Table ss:ExpandedColumnCount="2" ss:ExpandedRowCount="2" x:FullColumns="1" x:FullRows="1"> <Row> <Cell><Data ss:Type="String">Name</Data></Cell> <Cell><Data ss:Type="String">Example</Data></Cell> </Row> <Row> <Cell><Data ss:Type="String">Value</Data></Cell> <Cell><Data ss:Type="Number">123</Data></Cell> </Row> </Table> </Worksheet> </Workbook>
Current file extensions
Microsoft Excel 2007, along with the other products in the Microsoft Office 2007 suite, introduced new file formats. The first of these (.xlsx) is defined in the Office Open XML (OOXML) specification.
| Format | Extension | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Excel Workbook | .xlsx
|
The default Excel 2007 and later workbook format. In reality, a ZIP compressed archive with a directory structure of XML text documents. Functions as the primary replacement for the former binary .xls format, although it does not support Excel macros for security reasons. Saving as .xlsx offers file size reduction over .xls[33] |
| Excel Macro-enabled Workbook | .xlsm
|
As Excel Workbook, but with macro support. |
| Excel Binary Workbook | .xlsb
|
As Excel Macro-enabled Workbook, but storing information in binary form rather than XML documents for opening and saving documents more quickly and efficiently. Intended especially for very large documents with tens of thousands of rows, and/or several hundreds of columns. This format is very useful for shrinking large Excel files as is often the case when doing data analysis. |
| Excel Macro-enabled Template | .xltm
|
A template document that forms a basis for actual workbooks, with macro support. The replacement for the old .xlt format. |
| Excel Add-in | .xlam
|
Excel add-in to add extra functionality and tools. Inherent macro support because of the file purpose. |
Old file extensions
| Format | Extension | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Spreadsheet | .xls
|
Main spreadsheet format which holds data in worksheets, charts, and macros |
| Add-in (VBA) | .xla
|
Adds custom functionality; written in VBA |
| Toolbar | .xlb
|
The file extension where Microsoft Excel custom toolbar settings are stored. |
| Chart | .xlc
|
A chart created with data from a Microsoft Excel spreadsheet that only saves the chart. To save the chart and spreadsheet save as .XLS. XLC is not supported in Excel 2007 or in any newer versions of Excel. |
| Dialog | .xld
|
Used in older versions of Excel. |
| Archive | .xlk
|
A backup of an Excel Spreadsheet |
| Add-in (DLL) | .xll
|
Adds custom functionality; written in C++/C, Fortran, etc. and compiled in to a special dynamic-link library |
| Macro | .xlm
|
A macro is created by the user or pre-installed with Excel. |
| Template | .xlt
|
A pre-formatted spreadsheet created by the user or by Microsoft Excel. |
| Module | .xlv
|
A module is written in VBA (Visual Basic for Applications) for Microsoft Excel |
| Library | .DLL
|
Code written in VBA may access functions in a DLL, typically this is used to access the Windows API |
| Workspace | .xlw
|
Arrangement of the windows of multiple Workbooks |
Using other Windows applications
Windows applications such as Microsoft Access and Microsoft Word, as well as Excel can communicate with each other and use each other’s capabilities. The most common are Dynamic Data Exchange: although strongly deprecated by Microsoft, this is a common method to send data between applications running on Windows, with official MS publications referring to it as «the protocol from hell».[34] As the name suggests, it allows applications to supply data to others for calculation and display. It is very common in financial markets, being used to connect to important financial data services such as Bloomberg and Reuters.
OLE Object Linking and Embedding allows a Windows application to control another to enable it to format or calculate data. This may take on the form of «embedding» where an application uses another to handle a task that it is more suited to, for example a PowerPoint presentation may be embedded in an Excel spreadsheet or vice versa.[35][36][37][38]
Using external data
Excel users can access external data sources via Microsoft Office features such as (for example) .odc connections built with the Office Data Connection file format. Excel files themselves may be updated using a Microsoft supplied ODBC driver.
Excel can accept data in real-time through several programming interfaces, which allow it to communicate with many data sources such as Bloomberg and Reuters (through addins such as Power Plus Pro).
- DDE: «Dynamic Data Exchange» uses the message passing mechanism in Windows to allow data to flow between Excel and other applications. Although it is easy for users to create such links, programming such links reliably is so difficult that Microsoft, the creators of the system, officially refer to it as «the protocol from hell».[34] In spite of its many issues DDE remains the most common way for data to reach traders in financial markets.
- Network DDE Extended the protocol to allow spreadsheets on different computers to exchange data. Starting with Windows Vista, Microsoft no longer supports the facility.[39]
- Real Time Data: RTD although in many ways technically superior to DDE, has been slow to gain acceptance, since it requires non-trivial programming skills, and when first released was neither adequately documented nor supported by the major data vendors.[40][41]
Alternatively, Microsoft Query provides ODBC-based browsing within Microsoft Excel.[42][43][44]
Export and migration of spreadsheets
Programmers have produced APIs to open Excel spreadsheets in a variety of applications and environments other than Microsoft Excel. These include opening Excel documents on the web using either ActiveX controls, or plugins like the Adobe Flash Player. The Apache POI opensource project provides Java libraries for reading and writing Excel spreadsheet files.
Password protection
Microsoft Excel protection offers several types of passwords:
- Password to open a document[45]
- Password to modify a document[46]
- Password to unprotect the worksheet
- Password to protect workbook
- Password to protect the sharing workbook[47]
All passwords except password to open a document can be removed instantly regardless of the Microsoft Excel version used to create the document. These types of passwords are used primarily for shared work on a document. Such password-protected documents are not encrypted, and a data sources from a set password is saved in a document’s header. Password to protect workbook is an exception – when it is set, a document is encrypted with the standard password «VelvetSweatshop», but since it is known to the public, it actually does not add any extra protection to the document. The only type of password that can prevent a trespasser from gaining access to a document is password to open a document. The cryptographic strength of this kind of protection depends strongly on the Microsoft Excel version that was used to create the document.
In Microsoft Excel 95 and earlier versions, the password to open is converted to a 16-bit key that can be instantly cracked. In Excel 97/2000 the password is converted to a 40-bit key, which can also be cracked very quickly using modern equipment. As regards services that use rainbow tables (e.g. Password-Find), it takes up to several seconds to remove protection. In addition, password-cracking programs can brute-force attack passwords at a rate of hundreds of thousands of passwords a second, which not only lets them decrypt a document but also find the original password.
In Excel 2003/XP the encryption is slightly better – a user can choose any encryption algorithm that is available in the system (see Cryptographic Service Provider). Due to the CSP, an Excel file cannot be decrypted, and thus the password to open cannot be removed, though the brute-force attack speed remains quite high. Nevertheless, the older Excel 97/2000 algorithm is set by the default. Therefore, users who do not change the default settings lack reliable protection of their documents.
The situation changed fundamentally in Excel 2007, where the modern AES algorithm with a key of 128 bits started being used for decryption, and a 50,000-fold use of the hash function SHA1 reduced the speed of brute-force attacks down to hundreds of passwords per second. In Excel 2010, the strength of the protection by the default was increased two times due to the use of a 100,000-fold SHA1 to convert a password to a key.
Other platforms
Excel for mobile
Excel Mobile is a spreadsheet program that can edit XLSX files. It can edit and format text in cells, calculate formulas, search within the spreadsheet, sort rows and columns, freeze panes, filter the columns, add comments, and create charts. It cannot add columns or rows except at the edge of the document, rearrange columns or rows, delete rows or columns, or add spreadsheet tabs.[48][49][50][51][52][53] The 2007 version has the ability to use a full-screen mode to deal with limited screen resolution, as well as split panes to view different parts of a worksheet at one time.[51] Protection settings, zoom settings, autofilter settings, certain chart formatting, hidden sheets, and other features are not supported on Excel Mobile, and will be modified upon opening and saving a workbook.[52] In 2015, Excel Mobile became available for Windows 10 and Windows 10 Mobile on Windows Store.[54][55]
Excel for the web
Excel for the web is a free lightweight version of Microsoft Excel available as part of Office on the web, which also includes web versions of Microsoft Word and Microsoft PowerPoint.
Excel for the web can display most of the features available in the desktop versions of Excel, although it may not be able to insert or edit them. Certain data connections are not accessible on Excel for the web, including with charts that may use these external connections. Excel for the web also cannot display legacy features, such as Excel 4.0 macros or Excel 5.0 dialog sheets. There are also small differences between how some of the Excel functions work.[56]
Microsoft Excel Viewer
Microsoft Excel Viewer was a freeware program for Microsoft Windows for viewing and printing spreadsheet documents created by Excel.[57] Microsoft retired the viewer in April 2018 with the last security update released in February 2019 for Excel Viewer 2007 (SP3).[58][59]
The first version released by Microsoft was Excel 97 Viewer.[60][61] Excel 97 Viewer was supported in Windows CE for Handheld PCs.[62] In October 2004, Microsoft released Excel Viewer 2003.[63] In September 2007, Microsoft released Excel Viewer 2003 Service Pack 3 (SP3).[64] In January 2008, Microsoft released Excel Viewer 2007 (featuring a non-collapsible Ribbon interface).[65] In April 2009, Microsoft released Excel Viewer 2007 Service Pack 2 (SP2).[66] In October 2011, Microsoft released Excel Viewer 2007 Service Pack 3 (SP3).[67]
Microsoft advises to view and print Excel files for free to use the Excel Mobile application for Windows 10 and for Windows 7 and Windows 8 to upload the file to OneDrive and use Excel for the web with a Microsoft account to open them in a browser.[58][68]
Quirks
In addition to issues with spreadsheets in general, other problems specific to Excel include numeric precision, misleading statistics functions, mod function errors, date limitations and more.
Numeric precision
Excel maintains 15 figures in its numbers, but they are not always accurate: the bottom line should be the same as the top line.
Despite the use of 15-figure precision, Excel can display many more figures (up to thirty) upon user request. But the displayed figures are not those actually used in its computations, and so, for example, the difference of two numbers may differ from the difference of their displayed values. Although such departures are usually beyond the 15th decimal, exceptions do occur, especially for very large or very small numbers. Serious errors can occur if decisions are made based upon automated comparisons of numbers (for example, using the Excel If function), as equality of two numbers can be unpredictable.[citation needed]
In the figure, the fraction 1/9000 is displayed in Excel. Although this number has a decimal representation that is an infinite string of ones, Excel displays only the leading 15 figures. In the second line, the number one is added to the fraction, and again Excel displays only 15 figures. In the third line, one is subtracted from the sum using Excel. Because the sum in the second line has only eleven 1’s after the decimal, the difference when 1 is subtracted from this displayed value is three 0’s followed by a string of eleven 1’s. However, the difference reported by Excel in the third line is three 0’s followed by a string of thirteen 1’s and two extra erroneous digits. This is because Excel calculates with about half a digit more than it displays.
Excel works with a modified 1985 version of the IEEE 754 specification.[69] Excel’s implementation involves conversions between binary and decimal representations, leading to accuracy that is on average better than one would expect from simple fifteen digit precision, but that can be worse. See the main article for details.
Besides accuracy in user computations, the question of accuracy in Excel-provided functions may be raised. Particularly in the arena of statistical functions, Excel has been criticized for sacrificing accuracy for speed of calculation.[70][71]
As many calculations in Excel are executed using VBA, an additional issue is the accuracy of VBA, which varies with variable type and user-requested precision.[72]
Statistical functions
The accuracy and convenience of statistical tools in Excel has been criticized,[73][74][75][76][77] as mishandling missing data, as returning incorrect values due to inept handling of round-off and large numbers, as only selectively updating calculations on a spreadsheet when some cell values are changed, and as having a limited set of statistical tools. Microsoft has announced some of these issues are addressed in Excel 2010.[78]
Excel MOD function error
Excel has issues with modulo operations. In the case of excessively large results, Excel will return the error warning #NUM! instead of an answer.[79]
Fictional leap day in the year 1900
Excel includes February 29, 1900, incorrectly treating 1900 as a leap year, even though e.g. 2100 is correctly treated as a non-leap year.[80][81] The bug originated from Lotus 1-2-3 (deliberately implemented to save computer memory), and was also purposely implemented in Excel, for the purpose of bug compatibility.[82] This legacy has later been carried over into Office Open XML file format.[83]
Thus a (not necessarily whole) number greater than or equal to 61 interpreted as a date and time are the (real) number of days after December 30, 1899, 0:00, a non-negative number less than 60 is the number of days after December 31, 1899, 0:00, and numbers with whole part 60 represent the fictional day.
Date range
Excel supports dates with years in the range 1900–9999, except that December 31, 1899, can be entered as 0 and is displayed as 0-jan-1900.
Converting a fraction of a day into hours, minutes and days by treating it as a moment on the day January 1, 1900, does not work for a negative fraction.[84]
Conversion problems
Entering text that happens to be in a form that is interpreted as a date, the text can be unintentionally changed to a standard date format. A similar problem occurs when a text happens to be in the form of a floating-point notation of a number. In these cases the original exact text cannot be recovered from the result. Formatting the cell as TEXT before entering ambiguous text prevents Excel from converting to a date.
This issue has caused a well known problem in the analysis of DNA, for example in bioinformatics. As first reported in 2004,[85] genetic scientists found that Excel automatically and incorrectly converts certain gene names into dates. A follow-up study in 2016 found many peer reviewed scientific journal papers had been affected and that «Of the selected journals, the proportion of published articles with Excel files containing gene lists that are affected by gene name errors is 19.6 %.»[86] Excel parses the copied and pasted data and sometimes changes them depending on what it thinks they are. For example, MARCH1 (Membrane Associated Ring-CH-type finger 1) gets converted to the date March 1 (1-Mar) and SEPT2 (Septin 2) is converted into September 2 (2-Sep) etc.[87] While some secondary news sources[88] reported this as a fault with Excel, the original authors of the 2016 paper placed the blame with the researchers misusing Excel.[86][89]
In August 2020 the HUGO Gene Nomenclature Committee (HGNC) published new guidelines in the journal Nature regarding gene naming in order to avoid issues with «symbols that affect data handling and retrieval.» So far 27 genes have been renamed, including changing MARCH1 to MARCHF1 and SEPT1 to SEPTIN1 in order to avoid accidental conversion of the gene names into dates.[90]
Errors with large strings
The following functions return incorrect results when passed a string longer than 255 characters:[91]
type()incorrectly returns 16, meaning «Error value»IsText(), when called as a method of the VBA objectWorksheetFunction(i.e.,WorksheetFunction.IsText()in VBA), incorrectly returns «false».
Filenames
Microsoft Excel will not open two documents with the same name and instead will display the following error:
- A document with the name ‘%s’ is already open. You cannot open two documents with the same name, even if the documents are in different folders. To open the second document, either close the document that is currently open, or rename one of the documents.[92]
The reason is for calculation ambiguity with linked cells. If there is a cell ='[Book1.xlsx]Sheet1'!$G$33, and there are two books named «Book1» open, there is no way to tell which one the user means.[93]
Versions
Early history
Microsoft originally marketed a spreadsheet program called Multiplan in 1982. Multiplan became very popular on CP/M systems, but on MS-DOS systems it lost popularity to Lotus 1-2-3. Microsoft released the first version of Excel for the Macintosh on September 30, 1985, and the first Windows version was 2.05 (to synchronize with the Macintosh version 2.2) on November 19, 1987.[94][95] Lotus was slow to bring 1-2-3 to Windows and by the early 1990s, Excel had started to outsell 1-2-3 and helped Microsoft achieve its position as a leading PC software developer. This accomplishment solidified Microsoft as a valid competitor and showed its future of developing GUI software. Microsoft maintained its advantage with regular new releases, every two years or so.
Microsoft Windows
Excel 2.0 is the first version of Excel for the Intel platform. Versions prior to 2.0 were only available on the Apple Macintosh.
Excel 2.0 (1987)
The first Windows version was labeled «2» to correspond to the Mac version. It was announced on October 6, 1987, and released on November 19.[96] This included a run-time version of Windows.[97]
BYTE in 1989 listed Excel for Windows as among the «Distinction» winners of the BYTE Awards. The magazine stated that the port of the «extraordinary» Macintosh version «shines», with a user interface as good as or better than the original.
Excel 3.0 (1990)
Included toolbars, drawing capabilities, outlining, add-in support, 3D charts, and many more new features.[97]
Excel 4.0 (1992)
Introduced auto-fill.[98]
Also, an easter egg in Excel 4.0 reveals a hidden animation of a dancing set of numbers 1 through 3, representing Lotus 1-2-3, which is then crushed by an Excel logo.[99]
Excel 5.0 (1993)
With version 5.0, Excel has included Visual Basic for Applications (VBA), a programming language based on Visual Basic which adds the ability to automate tasks in Excel and to provide user-defined functions (UDF) for use in worksheets. VBA includes a fully featured integrated development environment (IDE). Macro recording can produce VBA code replicating user actions, thus allowing simple automation of regular tasks. VBA allows the creation of forms and in‑worksheet controls to communicate with the user. The language supports use (but not creation) of ActiveX (COM) DLL’s; later versions add support for class modules allowing the use of basic object-oriented programming techniques.
The automation functionality provided by VBA made Excel a target for macro viruses. This caused serious problems until antivirus products began to detect these viruses. Microsoft belatedly took steps to prevent the misuse by adding the ability to disable macros completely, to enable macros when opening a workbook or to trust all macros signed using a trusted certificate.
Versions 5.0 to 9.0 of Excel contain various Easter eggs, including a «Hall of Tortured Souls», a Doom-like minigame, although since version 10 Microsoft has taken measures to eliminate such undocumented features from their products.[100]
5.0 was released in a 16-bit x86 version for Windows 3.1 and later in a 32-bit version for NT 3.51 (x86/Alpha/PowerPC)
Excel 95 (v7.0)
Released in 1995 with Microsoft Office for Windows 95, this is the first major version after Excel 5.0, as there is no Excel 6.0 with all of the Office applications standardizing on the same major version number.
Internal rewrite to 32-bits. Almost no external changes, but faster and more stable.
Excel 95 contained a hidden Doom-like mini-game called «The Hall of Tortured Souls», a series of rooms featuring the names and faces of the developers as an easter egg.[101]
Excel 97 (v8.0)
Included in Office 97 (for x86 and Alpha). This was a major upgrade that introduced the paper clip office assistant and featured standard VBA used instead of internal Excel Basic. It introduced the now-removed Natural Language labels.
This version of Excel includes a flight simulator as an Easter Egg.
Excel 2000 (v9.0)
Included in Office 2000. This was a minor upgrade but introduced an upgrade to the clipboard where it can hold multiple objects at once. The Office Assistant, whose frequent unsolicited appearance in Excel 97 had annoyed many users, became less intrusive.
A small 3-D game called «Dev Hunter» (inspired by Spy Hunter) was included as an easter egg.[102][103]
Excel 2002 (v10.0)
Included in Office XP. Very minor enhancements.
Excel 2003 (v11.0)
Included in Office 2003. Minor enhancements.
Excel 2007 (v12.0)
Included in Office 2007. This release was a major upgrade from the previous version. Similar to other updated Office products, Excel in 2007 used the new Ribbon menu system. This was different from what users were used to, and was met with mixed reactions. One study reported fairly good acceptance by users except highly experienced users and users of word processing applications with a classical WIMP interface, but was less convinced in terms of efficiency and organization.[104] However, an online survey reported that a majority of respondents had a negative opinion of the change, with advanced users being «somewhat more negative» than intermediate users, and users reporting a self-estimated reduction in productivity.
Added functionality included Tables,[105] and the SmartArt set of editable business diagrams. Also added was an improved management of named variables through the Name Manager, and much-improved flexibility in formatting graphs, which allow (x, y) coordinate labeling and lines of arbitrary weight. Several improvements to pivot tables were introduced.
Also like other office products, the Office Open XML file formats were introduced, including .xlsm for a workbook with macros and .xlsx for a workbook without macros.[106]
Specifically, many of the size limitations of previous versions were greatly increased. To illustrate, the number of rows was now 1,048,576 (220) and columns was 16,384 (214; the far-right column is XFD). This changes what is a valid A1 reference versus a named range. This version made more extensive use of multiple cores for the calculation of spreadsheets; however, VBA macros are not handled in parallel and XLL add‑ins were only executed in parallel if they were thread-safe and this was indicated at registration.
Excel 2010 (v14.0)
Microsoft Excel 2010 running on Windows 7
Included in Office 2010, this is the next major version after v12.0, as version number 13 was skipped.
Minor enhancements and 64-bit support,[107] including the following:
- Multi-threading recalculation (MTR) for commonly used functions
- Improved pivot tables
- More conditional formatting options
- Additional image editing capabilities
- In-cell charts called sparklines
- Ability to preview before pasting
- Office 2010 backstage feature for document-related tasks
- Ability to customize the Ribbon
- Many new formulas, most highly specialized to improve accuracy[108]
Excel 2013 (v15.0)
Included in Office 2013, along with a lot of new tools included in this release:
- Improved Multi-threading and Memory Contention
- FlashFill[109]
- Power View[110]
- Power Pivot[111]
- Timeline Slicer
- Windows App
- Inquire[112]
- 50 new functions[113]
Excel 2016 (v16.0)
Included in Office 2016, along with a lot of new tools included in this release:
- Power Query integration
- Read-only mode for Excel
- Keyboard access for Pivot Tables and Slicers in Excel
- New Chart Types
- Quick data linking in Visio
- Excel forecasting functions
- Support for multiselection of Slicer items using touch
- Time grouping and Pivot Chart Drill Down
- Excel data cards[114]
Excel 2019, Excel 2021, Office 365 and subsequent (v16.0)
Microsoft no longer releases Office or Excel in discrete versions. Instead, features are introduced automatically over time using Windows Update. The version number remains 16.0. Thereafter only the approximate dates when features appear can now be given.
- Dynamic Arrays. These are essentially Array Formulas but they «Spill» automatically into neighboring cells and does not need the ctrl-shift-enter to create them. Further, dynamic arrays are the default format, with new «@» and «#» operators to provide compatibility with previous versions. This is perhaps the biggest structural change since 2007, and is in response to a similar feature in Google Sheets. Dynamic arrays started appearing in pre-releases about 2018, and as of March 2020 are available in published versions of Office 365 provided a user selected «Office Insiders».
Apple Macintosh
Microsoft Excel for Mac 2011
- 1985 Excel 1.0
- 1988 Excel 1.5
- 1989 Excel 2.2
- 1990 Excel 3.0
- 1992 Excel 4.0
- 1993 Excel 5.0 (part of Office 4.x—Final Motorola 680×0 version[115] and first PowerPC version)
- 1998 Excel 8.0 (part of Office 98)
- 2000 Excel 9.0 (part of Office 2001)
- 2001 Excel 10.0 (part of Office v. X)
- 2004 Excel 11.0 (part of Office 2004)
- 2008 Excel 12.0 (part of Office 2008)
- 2010 Excel 14.0 (part of Office 2011)
- 2015 Excel 15.0 (part of Office 2016—Office 2016 for Mac brings the Mac version much closer to parity with its Windows cousin, harmonizing many of the reporting and high-level developer functions, while bringing the ribbon and styling into line with its PC counterpart.)[116]
OS/2
- 1989 Excel 2.2
- 1990 Excel 2.3
- 1991 Excel 3.0
Summary
| Legend: | Old version, not maintained | Older version, still maintained | Current stable version |
|---|
| Year | Name | Version | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1987 | Excel 2 | 2.0 | Renumbered to 2 to correspond with contemporary Macintosh version. Supported macros (later known as Excel 4 macros). |
| 1990 | Excel 3 | 3.0 | Added 3D graphing capabilities |
| 1992 | Excel 4 | 4.0 | Introduced auto-fill feature |
| 1993 | Excel 5 | 5.0 | Included Visual Basic for Applications (VBA) and various object-oriented options |
| 1995 | Excel 95 | 7.0 | Renumbered for contemporary Word version. Both programs were packaged in Microsoft Office by this time. |
| 1997 | Excel 97 | 8.0 | |
| 2000 | Excel 2000 | 9.0 | Part of Microsoft Office 2000, which was itself part of Windows Millennium (also known as «Windows ME»). |
| 2002 | Excel 2002 | 10.0 | |
| 2003 | Excel 2003 | 11.0 | Released only 1 year later to correspond better with the rest of Microsoft Office (Word, PowerPoint, etc.). |
| 2007 | Excel 2007 | 12.0 | |
| 2010 | Excel 2010 | 14.0 | Due to superstitions surrounding the number 13, Excel 13 was skipped in version counting. |
| 2013 | Excel 2013 | 15.0 | Introduced 50 more mathematical functions (available as pre-packaged commands, rather than typing the formula manually). |
| 2016 | Excel 2016 | 16.0 | Part of Microsoft Office 2016 |
| Year | Name | Version | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1985 | Excel 1 | 1.0 | Initial version of Excel. Supported macros (later known as Excel 4 macros). |
| 1988 | Excel 1.5 | 1.5 | |
| 1989 | Excel 2 | 2.2 | |
| 1990 | Excel 3 | 3.0 | |
| 1992 | Excel 4 | 4.0 | |
| 1993 | Excel 5 | 5.0 | Only available on PowerPC-based Macs. First PowerPC version. |
| 1998 | Excel 98 | 8.0 | Excel 6 and Excel 7 were skipped to correspond with the rest of Microsoft Office at the time. |
| 2000 | Excel 2000 | 9.0 | |
| 2001 | Excel 2001 | 10.0 | |
| 2004 | Excel 2004 | 11.0 | |
| 2008 | Excel 2008 | 12.0 | |
| 2011 | Excel 2011 | 14.0 | As with the Windows version, version 13 was skipped for superstitious reasons. |
| 2016 | Excel 2016 | 16.0 | As with the rest of Microsoft Office, so it is for Excel: Future release dates for the Macintosh version are intended to correspond better to those for the Windows version, from 2016 onward. |
| Year | Name | Version | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1989 | Excel 2.2 | 2.2 | Numbered in between Windows versions at the time |
| 1990 | Excel 2.3 | 2.3 | |
| 1991 | Excel 3 | 3.0 | Last OS/2 version. Discontinued subseries of Microsoft Excel, which is otherwise still an actively developed program. |
Impact
Excel offers many user interface tweaks over the earliest electronic spreadsheets; however, the essence remains the same as in the original spreadsheet software, VisiCalc: the program displays cells organized in rows and columns, and each cell may contain data or a formula, with relative or absolute references to other cells.
Excel 2.0 for Windows, which was modeled after its Mac GUI-based counterpart, indirectly expanded the installed base of the then-nascent Windows environment. Excel 2.0 was released a month before Windows 2.0, and the installed base of Windows was so low at that point in 1987 that Microsoft had to bundle a runtime version of Windows 1.0 with Excel 2.0.[117] Unlike Microsoft Word, there never was a DOS version of Excel.
Excel became the first spreadsheet to allow the user to define the appearance of spreadsheets (fonts, character attributes, and cell appearance). It also introduced intelligent cell re-computation, where only cells dependent on the cell being modified are updated (previous spreadsheet programs recomputed everything all the time or waited for a specific user command). Excel introduced auto-fill, the ability to drag and expand the selection box to automatically copy a cell or row contents to adjacent cells or rows, adjusting the copies intelligently by automatically incrementing cell references or contents. Excel also introduced extensive graphing capabilities.
Security
Because Excel is widely used, it has been attacked by hackers. While Excel is not directly exposed to the Internet, if an attacker can get a victim to open a file in Excel, and there is an appropriate security bug in Excel, then the attacker can gain control of the victim’s computer.[118] UK’s GCHQ has a tool named TORNADO ALLEY with this purpose.[119][120]
Games
Besides the easter eggs, numerous games have been created or recreated in Excel, such as Tetris, 2048, Scrabble, Yahtzee, Angry Birds, Pac-Man, Civilization, Monopoly, Battleship, Blackjack, Space Invaders, and others.[121][122][123][124][125]
In 2020, Excel became an esport with the advent of the Financial Modeling World Cup.[126]
See also
- Comparison of spreadsheet software
- Numbers (spreadsheet)—the iWork equivalent
- Spreadmart
- Financial Modeling World Cup, online esport financial modelling competition using Excel
References
- ^ «Update history for Microsoft Office 2019». Microsoft Docs. Retrieved April 13, 2021.
- ^ a b «C++ in MS Office». cppcon. July 17, 2014. Archived from the original on November 7, 2019. Retrieved June 25, 2019.
- ^ «Microsoft Office Excel 365». Microsoft.com. Retrieved January 25, 2021.
- ^ «Update history for Office for Mac». Microsoft Docs.
- ^ «Microsoft Excel APKs». APKMirror.
- ^ «Microsoft Excel». App Store.
- ^
Harvey, Greg (2006). Excel 2007 For Dummies (1st ed.). Wiley. ISBN 978-0-470-03737-9. - ^
Harvey, Greg (2007). Excel 2007 Workbook for Dummies (2nd ed.). Wiley. p. 296 ff. ISBN 978-0-470-16937-7. - ^
de Levie, Robert (2004). Advanced Excel for scientific data analysis. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-515275-3. - ^
Bourg, David M. (2006). Excel scientific and engineering cookbook. O’Reilly. ISBN 978-0-596-00879-6. - ^
Şeref, Michelle M. H. & Ahuja, Ravindra K. (2008). «§4.2 A portfolio management and optimization spreadsheet DSS». In Burstein, Frad & Holsapple, Clyde W. (eds.). Handbook on Decision Support Systems 1: Basic Themes. Springer. ISBN 978-3-540-48712-8. - ^
Wells, Eric & Harshbarger, Steve (1997). Microsoft Excel 97 Developer’s Handbook. Microsoft Press. ISBN 978-1-57231-359-0. Excellent examples are developed that show just how applications can be designed. - ^
Harnett, Donald L. & Horrell, James F. (1998). Data, statistics, and decision models with Excel. Wiley. ISBN 978-0-471-13398-8. - ^
Some form of data acquisition hardware is required. See, for example, Austerlitz, Howard (2003). Data acquisition techniques using PCs (2nd ed.). Academic Press. p. 281 ff. ISBN 978-0-12-068377-2. - ^
«Description of the startup switches for Excel». Microsoft Help and Support. Microsoft Support. May 7, 2007. Retrieved December 14, 2010.Microsoft Excel accepts a number of optional switches that you can use to control how the program starts. This article lists the switches and provides a description of each switch.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ «Excel functions (alphabetical)». microsoft.com. Microsoft. Retrieved November 4, 2018.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ «WorksheetFunction Object (Excel)». Office VBA Reference. Microsoft. March 30, 2022. Retrieved November 4, 2018.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ «Functions (Visual Basic for Applications)». Office VBA Reference. Microsoft. September 13, 2021. Retrieved November 4, 2018.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ Gordon, Andy (January 25, 2021). «LAMBDA: The ultimate Excel worksheet function». microsoft.com. Microsoft. Retrieved April 23, 2021.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^
For example, by converting to Visual Basic the recipes in Press, William H. Press; Teukolsky, Saul A.; Vetterling, William T. & Flannery, Brian P. (2007). Numerical recipes: the art of scientific computing (3rd ed.). Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-88068-8. Code conversion to Basic from Fortran probably is easier than from C++, so the 2nd edition (ISBN 0521437210) may be easier to use, or the Basic code implementation of the first edition: Sprott, Julien C. (1991). Numerical recipes: routines and examples in BASIC. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-40689-5. - ^ «Excel». Office for Mac. OfficeforMacHelp.com. Archived from the original on June 19, 2012. Retrieved July 8, 2012.
- ^ «Using Excel — PC or Mac? | Excel Lemon». www.excellemon.com. Archived from the original on September 21, 2016. Retrieved July 29, 2015.
- ^ However an increasing proportion of Excel functionality is not captured by the Macro Recorder leading to largely useless macros. Compatibility among multiple versions of Excel is also a downfall of this method. A macro recorder in Excel 2010 may not work in Excel 2003 or older. This is most common when changing colors and formatting of cells.
Walkenbach, John (2007). «Chapter 6: Using the Excel macro recorder». Excel 2007 VBA Programming for Dummies (Revised by Jan Karel Pieterse ed.). Wiley. p. 79 ff. ISBN 978-0-470-04674-6. - ^ Walkenbach, John (February 2, 2007). «Chapter 4: Introducing the Excel object model». cited work. p. 53 ff. ISBN 978-0-470-04674-6.
- ^ «The Spreadsheet Page for Excel Users and Developers». spreadsheetpage.com. J-Walk & Associates, Inc. Retrieved December 19, 2012.
- ^ «Working with Excel 4.0 macros». microsoft.com. Microsoft Office Support. Retrieved December 19, 2012.
- ^ «The «Big Grid» and Increased Limits in Excel 2007″. microsoft.com. May 23, 2014. Retrieved April 10, 2008.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ «How to extract information from Office files by using Office file formats and schemas». microsoft.com. Microsoft. February 26, 2008. Retrieved November 10, 2008.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ a b «XML Spreadsheet Reference». Microsoft Excel 2002 Technical Articles. MSDN. August 2001. Retrieved November 10, 2008.
- ^ «Deprecated features for Excel 2007». Microsoft—David Gainer. August 24, 2006. Retrieved January 2, 2009.
- ^ «OpenOffice.org’s documentation of the Microsoft Excel File Format» (PDF). August 2, 2008.
- ^ «Microsoft Office Excel 97 — 2007 Binary File Format Specification (*.xls 97-2007 format)». Microsoft Corporation. 2007.
- ^ Fairhurst, Danielle Stein (March 17, 2015). Using Excel for Business Analysis: A Guide to Financial Modelling Fundamentals. John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 978-1-119-06245-5.
- ^ a b Newcomer, Joseph M. «Faking DDE with Private Servers». Dr. Dobb’s.
- ^ Schmalz, Michael (2006). «Chapter 5: Using Access VBA to automate Excel». Integrating Excel and Access. O’Reilly Media, Inc. ISBN 978-0-596-00973-1.Schmalz, Michael (2006). «Chapter 5: Using Access VBA to automate Excel». Integrating Excel and Access. O’Reilly Media, Inc. ISBN 978-0-596-00973-1.
- ^ Cornell, Paul (2007). «Chapter 5: Connect to other databases». Excel as Your Database. Apress. p. 117 ff. ISBN 978-1-59059-751-4.
- ^ DeMarco, Jim (2008). «Excel’s data import tools». Pro Excel 2007 VBA. Apress. p. 43 ff. ISBN 978-1-59059-957-0.
- ^
Harts, Doug (2007). «Importing Access data into Excel 2007». Microsoft Office 2007 Business Intelligence: Reporting, Analysis, and Measurement from the Desktop. McGraw-Hill Professional. ISBN 978-0-07-149424-3. - ^ «About Network DDE — Win32 apps». learn.microsoft.com.
- ^ «How to set up and use the RTD function in Excel — Office». learn.microsoft.com.
- ^
DeMarco, Jim (2008). Pro Excel 2007 VBA. Berkeley, CA: Apress. p. 225. ISBN 978-1-59059-957-0.External data is accessed through a connection file, such as an Office Data Connection (ODC) file (.odc)
- ^
Bullen, Stephen; Bovey, Rob & Green, John (2009). Professional Excel Development (2nd ed.). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Addison-Wesley. p. 665. ISBN 978-0-321-50879-9.To create a robust solution, we always have to include some VBA code …
- ^ William, Wehrs (2000). «An Applied DSS Course Using Excel and VBA: IS and/or MS?» (PDF). The Proceedings of ISECON (Information System Educator Conference). p. 4. Archived from the original (PDF) on August 21, 2010. Retrieved February 5, 2010.
Microsoft Query is a data retrieval tool (i.e. ODBC browser) that can be employed within Excel 97. It allows a user to create and save queries on external relational databases for which an ODBC driver is available.
- ^ Use Microsoft Query to retrieve external data Archived March 12, 2010, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ «Password protect documents, workbooks, and presentations — Word — Office.com». Office.microsoft.com. Retrieved April 24, 2013.
- ^ «Password protect documents, workbooks, and presentations — Word — Office.com». Office.microsoft.com. Retrieved April 24, 2013.
- ^ «Password protect worksheet or workbook elements — Excel — Office.com». Office.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on March 26, 2013. Retrieved April 24, 2013.
- ^ Ralph, Nate. «Office for Windows Phone 8: Your handy starter guide». TechHive. Archived from the original on October 15, 2014. Retrieved August 30, 2014.
- ^ Wollman, Dana. «Microsoft Office Mobile for iPhone hands-on». Engadget. Retrieved August 30, 2014.
- ^ Pogue, David. «Microsoft Adds Office for iPhone. Yawn». The New York Times. Retrieved August 30, 2014.
- ^ a b Ogasawara, Todd. «What’s New in Excel Mobile». Microsoft. Archived from the original on February 8, 2008. Retrieved September 13, 2007.
- ^ a b «Unsupported features in Excel Mobile». Microsoft. Archived from the original on October 20, 2007. Retrieved September 21, 2007.
- ^ Use Excel Mobile Archived October 20, 2007, at the Wayback Machine. Microsoft. Retrieved September 21, 2007.
- ^ «Excel Mobile». Windows Store. Microsoft. Retrieved June 26, 2016.
- ^ «PowerPoint Mobile». Windows Store. Microsoft. Retrieved June 26, 2016.
- ^ «Differences between using a workbook in the browser and in Excel — Office Support». support.office.com. Archived from the original on 8 February 2017. Retrieved 7 February 2017.
- ^ «Description of the Excel Viewer». Microsoft. February 17, 2012. Archived from the original on April 6, 2013.
- ^ a b «How to obtain the latest Excel Viewer». Microsoft Docs. May 22, 2020. Retrieved January 3, 2021.
- ^ «Description of the security update for Excel Viewer 2007: February 12, 2019». Microsoft. April 16, 2020. Retrieved January 3, 2021.
- ^ «Microsoft Excel Viewer». Microsoft. 1997. Archived from the original on January 20, 1998.
- ^ «Excel 97/2000 Viewer: Spreadsheet Files». Microsoft. Archived from the original on January 13, 2004.
- ^ «New Features in Windows CE .NET 4.1». Microsoft Docs. June 30, 2006. Retrieved January 3, 2021.
- ^ «Excel Viewer 2003». Microsoft. October 12, 2004. Archived from the original on January 15, 2005.
- ^ «Excel Viewer 2003 Service Pack 3 (SP3)». Microsoft. September 17, 2007. Archived from the original on October 11, 2007.
- ^ «Excel Viewer». Microsoft. January 14, 2008. Archived from the original on September 26, 2010.
- ^ «Excel Viewer 2007 Service Pack 2 (SP2)». Microsoft. April 24, 2009. Archived from the original on April 28, 2012.
- ^ «Excel Viewer 2007 Service Pack 3 (SP3)». Microsoft. October 25, 2011. Archived from the original on December 29, 2011.
- ^ «Supported versions of the Office viewers». Microsoft. April 16, 2020. Retrieved January 3, 2021.
- ^
Microsoft’s overview is found at: «Floating-point arithmetic may give inaccurate results in Excel». Revision 8.2 ; article ID: 78113. Microsoft support. June 30, 2010. Retrieved July 2, 2010. - ^
Altman, Micah; Gill, Jeff; McDonald, Michael (2004). «§2.1.1 Revealing example: Computing the coefficient standard deviation». Numerical issues in statistical computing for the social scientist. Wiley-IEEE. p. 12. ISBN 978-0-471-23633-7. - ^ de Levie, Robert (2004). cited work. pp. 45–46. ISBN 978-0-19-515275-3.
- ^
Walkenbach, John (2010). «Defining data types». Excel 2010 Power Programming with VBA. Wiley. pp. 198 ff and Table 8–1. ISBN 978-0-470-47535-5. - ^ McCullough, Bruce D.; Wilson, Berry (2002). «On the accuracy of statistical procedures in Microsoft Excel 2000 and Excel XP». Computational Statistics & Data Analysis. 40 (4): 713–721. doi:10.1016/S0167-9473(02)00095-6.
- ^ McCullough, Bruce D.; Heiser, David A. (2008). «On the accuracy of statistical procedures in Microsoft Excel 2007». Computational Statistics & Data Analysis. 52 (10): 4570–4578. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.455.5508. doi:10.1016/j.csda.2008.03.004.
- ^ Yalta, A. Talha (2008). «The accuracy of statistical distributions in Microsoft Excel 2007». Computational Statistics & Data Analysis. 52 (10): 4579–4586. doi:10.1016/j.csda.2008.03.005.
- ^ Goldwater, Eva. «Using Excel for Statistical Data Analysis—Caveats». University of Massachusetts School of Public Health. Retrieved November 10, 2008.
- ^
Heiser, David A. (2008). «Microsoft Excel 2000, 2003 and 2007 faults, problems, workarounds and fixes». Archived from the original on April 18, 2010. Retrieved April 8, 2010. - ^
Function improvements in Excel 2010 Archived April 6, 2010, at the Wayback Machine Comments are provided from readers that may illuminate some remaining problems. - ^ «The MOD bug». Byg Software. Archived from the original on January 11, 2016. Retrieved November 10, 2008.
- ^ «Days of the week before March 1, 1900 are incorrect in Excel». Microsoft. Archived from the original on July 14, 2012. Retrieved November 10, 2008.
- ^ «Excel incorrectly assumes that the year 1900 is a leap year». Microsoft. Retrieved May 1, 2019.
- ^ Spolsky, Joel (June 16, 2006). «My First BillG Review». Joel on Software. Retrieved November 10, 2008.
- ^ «The Contradictory Nature of OOXML». ConsortiumInfo.org. January 17, 2007.
- ^ «Negative date and time value are displayed as pound signs (###) in Excel». Microsoft. Retrieved March 26, 2012.
- ^ Zeeberg, Barry R; Riss, Joseph; Kane, David W; Bussey, Kimberly J; Uchio, Edward; Linehan, W Marston; Barrett, J Carl; Weinstein, John N (2004). «Mistaken Identifiers: Gene name errors can be introduced inadvertently when using Excel in bioinformatics». BMC Bioinformatics. 5 (1): 80. doi:10.1186/1471-2105-5-80. PMC 459209. PMID 15214961.
- ^ a b Ziemann, Mark; Eren, Yotam; El-Osta, Assam (2016). «Gene name errors are widespread in the scientific literature». Genome Biology. 17 (1): 177. doi:10.1186/s13059-016-1044-7. PMC 4994289. PMID 27552985.
- ^ Anon (2016). «Microsoft Excel blamed for gene study errors». bbc.co.uk. London: BBC News.
- ^ Cimpanu, Catalin (August 24, 2016). «One in Five Scientific Papers on Genes Contains Errors Because of Excel». Softpedia. SoftNews.
- ^ Ziemann, Mark (2016). «Genome Spot: My personal thoughts on gene name errors». genomespot.blogspot.co.uk. Archived from the original on August 30, 2016.
- ^ Vincent, James (August 6, 2020). «Scientists rename human genes to stop Microsoft Excel from misreading them as dates». The Verge. Retrieved October 9, 2020.
- ^ «Excel: type() and
WorksheetFunction.IsText()fail for long strings». Stack Overflow. November 3, 2018. - ^ Rajah, Gary (August 2, 2004). «Trouble with macros». The Hindu Business Line. Retrieved March 19, 2019.
- ^ Chirilov, Joseph (January 8, 2009). «Microsoft Excel — Why Can’t I Open Two Files With the Same Name?». MSDN Blogs. Microsoft Corporation. Archived from the original on July 29, 2010. Retrieved March 19, 2019.
- ^ Infoworld Media Group, Inc. (July 7, 1986). InfoWorld First Look: Supercalc 4 challenging 1-2-3 with new tactic.
- ^ «The History of Microsoft — 1987». channel9.msdn.com. Archived from the original on September 27, 2010. Retrieved October 7, 2022.
- ^ «The History of Microsoft — 1987». learn.microsoft.com. Retrieved October 7, 2022.
- ^ a b Walkenbach, John (December 4, 2013). «Excel Version History». The Spreadsheet Page. John Walkenbach. Retrieved July 12, 2020.
- ^ Lewallen, Dale (1992). PC/Computing guide to Excel 4.0 for Windows. Ziff Davis. p. 13. ISBN 9781562760489. Retrieved July 27, 2013.
- ^ Lake, Matt (April 6, 2009). «Easter Eggs we have loved: Excel 4». crashreboot.blogspot.com. Retrieved November 5, 2013.
- ^ Osterman, Larry (October 21, 2005). «Why no Easter Eggs?». Larry Osterman’s WebLog. MSDN Blogs. Retrieved July 29, 2006.
- ^ «Excel 95 Hall of Tortured Souls». Retrieved July 7, 2006.
- ^ «Excel Oddities: Easter Eggs». Archived from the original on August 21, 2006. Retrieved August 10, 2006.
- ^ «Car Game In Ms Excel». Totalchoicehosting.com. September 6, 2005. Retrieved January 28, 2014.
- ^ Dostál, M (December 9, 2010). User Acceptance of the Microsoft Ribbon User Interface (PDF). Palacký University of Olomouc. ISBN 978-960-474-245-5. ISSN 1792-6157. Retrieved May 28, 2013.
- ^ [Using Excel Tables to
Manipulate Billing Data https://mooresolutionsinc.com/downloads/Billing_MJ12.pdf] - ^ Dodge, Mark; Stinson, Craig (2007). «Chapter 1: What’s new in Microsoft Office Excel 2007». Microsoft Office Excel 2007 inside out. Microsoft Press. p. 1 ff. ISBN 978-0-7356-2321-7.
- ^ «What’s New in Excel 2010 — Excel». Archived from the original on December 2, 2013. Retrieved September 23, 2010.
- ^ Walkenbach, John (2010). «Some Essential Background». Excel 2010 Power Programming with VBA. Indianapolis, Indiana: Wiley Publishing, Inc. p. 20. ISBN 9780470475355.
- ^ Harris, Steven (October 1, 2013). «Excel 2013 — Flash Fill». Experts-Exchange.com. Experts Exchange. Retrieved November 23, 2013.
- ^ «What’s new in Excel 2013». Office.com. Microsoft. Retrieved January 25, 2014.
- ^ K., Gasper (October 10, 2013). «Does a PowerPivot Pivot Table beat a regular Pivot Table». Experts-Exchange.com. Experts Exchange. Retrieved November 23, 2013.
- ^ K., Gasper (May 20, 2013). «Inquire Add-In for Excel 2013». Experts-Exchange.com. Experts Exchange. Retrieved November 23, 2013.
- ^ «New functions in Excel 2013». Office.com. Microsoft. Retrieved November 23, 2013.
- ^ «What’s new in Office 2016». Office.com. Microsoft. Retrieved August 16, 2015.
- ^ «Microsoft Announces March Availability of Office 98 Macintosh Edition». Microsoft. January 6, 1998. Retrieved December 29, 2017.
- ^ «Office for Mac Is Finally a ‘First-Class Citizen’«. Re/code. July 16, 2015. Retrieved July 29, 2015.
- ^ Perton, Marc (November 20, 2005). «Windows at 20: 20 things you didn’t know about Windows 1.0». switched.com. Archived from the original on April 11, 2013. Retrieved August 1, 2013.
- ^ Keizer, Gregg (February 24, 2009). «Attackers exploit unpatched Excel vulnerability». Computerworld. IDG Communications, Inc. Retrieved March 19, 2019.
- ^ «JTRIG Tools and Techniques». The Intercept. First Look Productions, Inc. July 14, 2014. Archived from the original on July 14, 2014. Retrieved March 19, 2019.
- ^ Cook, John. «JTRIG Tools and Techniques». The Intercept. p. 4. Retrieved March 19, 2019 – via DocumentCloud.
- ^ Phillips, Gavin (December 11, 2015). «8 Legendary Games Recreated in Microsoft Excel». MUO.
- ^ «Excel Games – Fun Things to Do With Spreadsheets». November 10, 2021.
- ^ «Unusual Uses of Excel». techcommunity.microsoft.com. August 5, 2022.
- ^ «Someone made a version of ‘Civilization’ that runs in Microsoft Excel». Engadget.
- ^ Dalgleish, Debra. «Have Fun Playing Games in Excel». Contextures Excel Tips.
- ^ «Microsoft Excel esports is real and it already has an international tournament». ONE Esports. June 9, 2021.
References
- Bullen, Stephen; Bovey, Rob; Green, John (2009). Professional Excel Development: The Definitive Guide to Developing Applications Using Microsoft Excel and VBA (2nd ed.). Boston: Addison Wesley. ISBN 978-0-321-50879-9.
- Dodge, Mark; Stinson, Craig (2007). Microsoft Office Excel 2007 Inside Out. Redmond, Wash.: Microsoft Press. ISBN 978-0-7356-2321-7.
- Billo, E. Joseph (2011). Excel for Chemists: A Comprehensive Guide (3rd ed.). Hoboken, N.J.: John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 978-0-470-38123-6.
- Gordon, Andy (January 25, 2021). «LAMBDA: The ultimate Excel worksheet function». microsoft.com. Microsoft. Retrieved April 23, 2021.
External links
Wikibooks has a book on the topic of: Excel
- Microsoft Excel – official site
Today on Top 10 Excel features you need to know. I am a frequent visitor to StackOverflow to see what is troubling the Excel community (and other developer/analyst communities). It is nothing incredible that many users have issues due to not being aware of some of the most significant features in Excel like PivotTables, Array Formulas, Tables and other. I have seen more than once users reaching out to use VBA macros instead of much easier PivotTables/Charts. Although, I value VBA it should also be the solution of last resort compare to “native” Excel features used more common.
I have decided therefore to list some of the top 10 features regarded often as the most significant and useful to know. So let’s start with the 10 Top Excel Features…
No. 1: PivotTables
You can’t call yourself an advanced Excel user without knowing about PivotTables! There is no other feature in Excel I being used more often and with success. Almost the first thing I always do when analyzing data is pivot the data in multiple manners and analyze the patterns/results. Pivots can process a large amount of data in a short period of time and are optimized in the Excel back-end for performance. This is definitely one of the 10 top Excel features!
PivotTables allow you to transform and analyze data in a structure manner. Just select a range of data (data in columns with headers) and select the ROWS, COLUMNS and VALUES for your Pivot Table! You can also create custom columns (based on formulas), summarize data by groups/rows/columns etc. There is almost no limit in the possibilities.
How to find it in Excel?
Insert->Tables->PivotTables
No. 2: Filtering and sorting data
Filtering and sorting your data is just as useful as using PivotTables. Excel is meant to transform and analyze data and filtering/sorting is one of the key elements. When provided with a table of data you will probably want to sort the data in a descending/ascending manner or filter out rows based on some features (values in certain columns). This is a must-know feature.
How to find it in Excel?
Data->Sort->Filter
No. 3: Excel Tables
If you want your data tables to be neat and structured you need to use Excel Data Tables. What do you get when using Tables in Excel? A consistent structure and formatting of your entire data table, automated copied formulas (across columns), non-repeating column headers and more. It is always good to resort to Excel Data Tables as you will have less work managing your data table and can focus on more interesting work like data transformation/analysis.
How to find it in Excel?
Insert->Tables->Table
No. 4: Conditional formatting
Analyzing/transforming data is important, but it is just as useful to be able to identify variances in a range of values using graphics like colors, bars or icons. Conditional formatting can allow you to notice patterns in data values which might not be obvious when looking at raw numbers.
How to find it in Excel?
Home->Styles->Conditional Formatting
No. 5: Lookup Excel functions
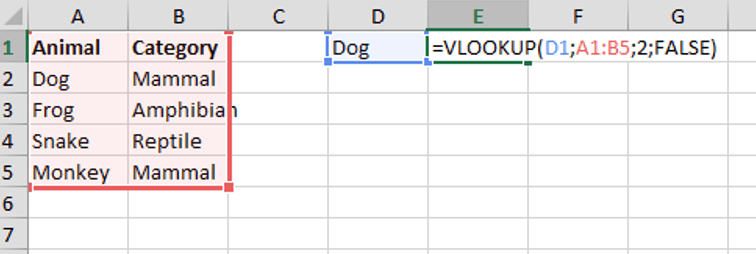
- VLOOKUP – search the first column of a range of cells, and then return a value from any cell on the same row of the range
- HLOOKUP – as above but for columns instead of rows
- INDEX – returns the value of an element in a table or an array, selected by provided index
- MATCH – searches for a specified item in a range of cells, and then returns the relative position of that item in the range
How to use these functions?
The VLOOKUP function will return a corresponding value from another cell of the same row of a value found in the first column of the data table.
The INDEX and MATCH functions are best to be used together (see the links section below). Why? They allow you to basically achieve the same result as the LOOKUP functions HOWEVER these are more flexible. I encourage you to read the links below.
No. 6: Array Formulas
Array Formulas are one of the greatest knowledge gaps in the Excel community in my opinion. I see so often questions which can be easily answered if someone at least made an effort to learn them. Many Excel users fall into the trap of writing a lot of custom VBA just because they are not aware or are too lazy to use a neat Array Formula.
How to use Array Functions?
Go to the links section for a decent tutorial. However, the process itself is quite simple:
- Create a function using an Excel range e.g. A1:A10
- Hit CTRL+SHIFT+ENTER
So easy and yet so powerful! Let’s jump into a simple example:
Excel Array Formula Example
Let’s assume we have a range of value for a certain period of time. We want to get the maximum value for dates after the 1st of March 2015. We can get this in a single Array Formula! See below.
How does it work?
'MAX ( returns all cells from A2:A8 for which B2:B8 are older than 2015-03-01) =MAX(IF(B$2:B$8>DATE(2015;3;1);A$2:A$8))
See the logic? You can also multiply/divide/sum and do other cool thing with Array Formulas. See the tutorial link below.
No. 7: Data Analysis Excel Tools
All tools needed in doing basic data cleansing can be found in the Data Tools section of the Data ribbon. Working on data often? You need to know how and when to use Text to Columns, Data Validation and all the other neat tools.
How to find it in Excel?
Data->Data Tools
No. 8: Naming fields / NameManager
Naming cells/ranges comes in handy when you repeatedly reference certain cells or arrays e.g. USD/EUR currency field, interest rate used in formulas etc. This is a nice and clean way to manage all reference to those fields and allows you to easily relocate these cells or ranges.
How to set a Defined Name to an Excel cell/range?
- Click on the text field in the upper-left with the cell/range reference
- Type in Defined Name for this cell/range – it must not have whitespaces
- Hit ENTER
Now when trying to reference the cell/range in a formula simply type the new Defined Name.
How to find it in Excel?
Formulas->Defined Names
No. 9: VBA macros and recording macros
The reason VBA is placed before last on the 10 Top Excel features list is because, in my opinion, it is so often abused but users who refuse to learn well the remaining Excel features. VBA macros fills the gap of all the missing features/functions in Excel. Macros let’s you program almost anything in Excel, you name it – forms, database connectivity, analytics, web browsing etc. You can’t basically consider yourself an Excel Pro without being able to program macros in VBA. However, it is important to stress that the problem with VBA is that once learned it tends to make analysts lazy – instead of Excel Array Formulas you will see custom macros or hideous UDF-functions. VBA should be used as a tool of last resort!
Typical applications of VBA
- Cleansing/filtering/sorting/copying data
- Custom algorithms (custom analysis of data sets)
- Custom Excel UDF functions (User Defined Functions)
- Excel Forms (making custom user forms to input data or create a custom UI)
How to find it in Excel?
Developer->Code->Visual Basic
Recording macros
The other fantastic thing with Excel is that it enables you to record macros – by recording your actions in Excel and translating them into VBA code. In some cases you need not even understand the code to be able to reuse it e.g. applying custom formatting to selected cells. This is definitely a great feature on it’s own.
How to find it in Excel?
Developer->Code->Record Macro
No. 10: Microsoft Power Add-In’s

PowerPivot basically pumps Excel with more Analytics features by extend the PivotTable with summarization, cross-tabulation, expanded data capacity, advanced calculations, ability to import data from multiple sources, and the ability to publish the workbooks as interactive web applications.
PowerQuery will allow you to easily harness data and access to external data sources such as files, the Web, databases etc. and more easily manipulate and cleanse data. PowerQuery enables you to process enormous data sources/tables counting millions of records (more than an Excel Worksheet can contain).
PowerMap (as quoted on the official MS site) is a three-dimensional (3-D) data visualization tool that lets you look at information in new ways. A power map lets you discover insights you might not see in traditional two-dimensional (2-D) tables and charts.
Both these tools complete one another. If you want to do Business Intelligence in Excel you need to be able to use both these Add-Ins. Microsoft seems to have great plans for them and I would anticipate that both these Add-Ins become a “native” part of Excel in the following versions of Microsoft Excel.
As a business owner, you know that using MS Excel is essential for managing your finances and managing your data. In this article, we will take a look at the main features of MS Excel 2016, so that you can better understand what this powerful spreadsheet can do for you.
What is an Excel Workbook?
The Excel workbook is a document that contains all of the data and information that you need to work on a project. You can save your work in an Excel workbook, so that you can access it later without having to open the file again. You can also share your workbook with other people, so that they can help you with your project.
The Main Features of an Excel Workbook
An Excel workbook is a versatile tool that can be used for a variety of tasks. Here are some of the main features of an Excel workbook:
-You can store data in columns and rows.
-You can create tables and charts to display your data.
-You can format your data using font, color, and borders.
-You can password protect your workbook.
How to Save a Workbook
There are a few main features of Excel that you may want to keep in mind when saving a workbook:
1. You can save a copy of your workbook as a PDF or XLS file.
2. You can password protect your workbook so that only you can access it.
3. You can share your workbook with others by sending them an email or attaching it to an email.
4. You can track changes to your workbook by marking it as read-only and then viewing the changes history.
How to Print a Workbook
If you print your workbook in Microsoft Excel, you can choose to print either the entire workbook or just the sheets you are working on. To print a workbook:
1.Open the workbook you want to print.
2.Click the File tab and then click Print.
3.Select which pages you want to print and then click OK.
4.If you want to include headers and footers on your printout, select them from the Page Setup dialog box that appears and then click OK.
You can also save a copy of your workbook as a PDF file by clicking File > Save As > PDF. In this case, only the pages that have content will be printed, not any headers or footers that you may have selected in the Page Setup dialog box.
How to Open a Workbook in Excel
If you want to open a workbook you already have open in Excel, there are a few different ways you can go about it. The easiest way is to just click on the workbook’s icon on your desktop. If the workbook is open in another application, like Office 2013, you can open it in Excel by clicking the “Open” button on the File tab and selecting “Excel.”
If the workbook isn’t open in any of these ways, you can try one of the following methods:
1. Click on the “File” menu and select “Open.” This will open the file in your default application.
2. Double-click on the file’s name. This will open the file in Excel if it’s not already open.
3. Click on the “Workbooks” tab and select the workbook from the list that appears.
4. Use keyboard shortcuts to open a workbook quickly: F5 (for Microsoft Excel 2013) or Ctrl+O (for Microsoft Excel 2010) will open a workbook in its default location, while Alt+F11 (for Microsoft Excel 2007) or Ctrl+O (for Microsoft Excel 2003
How to Use Functions in an Excel Workbook
If you’re like most people, you use Excel for a variety of tasks—from calculating taxes to planning budgets to tracking progress on projects. But what if you need to do something a little more specific than what Excel can offer? That’s where functions come in handy. In this article, we’ll explain what functions are and how to use them in your Excel workbook.
Functions are special commands that Excel can run automatically whenever you enter particular values into certain cells. For example, you can use the SUM function to calculate the total value of all the cells in a workbook row by row. Or, you could use the VLOOKUP function to lookup a value from a specific cell and return its corresponding value from the first column in the worksheet that contains that cell’s value.
There are dozens of different functions available in Excel, and each one comes with its own set of instructions (or “recipe”) for how it should be used. So don’t be surprised if you’ve never seen or used a function before—just keep reading and gradually start incorporating them into your workflows!
How to Create Tables in an Excel Workbook
In this article, we will be discussing the different features of Microsoft Excel and how to use them to create tables. When working with tables in Excel, it is important to keep in mind that there are a few main features that you should be aware of.
First and foremost, tables in Excel can be used for organizing data. Whether you are working with basic data or more sophisticated information, table formatting can help make your work easier. Additionally, tables in Excel can be used to perform calculations on the data within them. For example, you can use formulas to calculate averages or percentages based on data within a table.
Finally, tables in Excel can be exported as PDF files or CSV (common spreadsheet) files. This allows you to easily share your work with other people and collaborators.
How to Format Cells in an Excel Workbook
If you need to format cells in an Excel workbook, there are a few main features to keep in mind. The easiest way to format a cell is to use the predefined formats that Excel provides. For example, you can set a cell to be a number or a date. You can also use custom formats, which allow you to format cells in a more specific way. For example, you can make a cell bold or underline it.
You can also format text in a cell by using the available formatting options. You can change the font, size, and color of the text. You can also add borders around the text and add highlights. Finally, you can add images to your cells by using the Insert Picture command.
How to Use AutoCorrect in an Excel Workbook
Microsoft Excel offers a number of features that can help you save time and effort when working in the spreadsheet application. One such feature is AutoCorrect, which can automatically correct common typographical errors as you type. This article will explain how AutoCorrect works and what kinds of errors it can correct.
Conclusion
As a business owner, you are likely using Microsoft Excel on a daily basis. Whether you are creating spreadsheets to track expenses or compiling data for presentations, understanding the basics of this software can save you time and help ensure accuracy in your work. In this article, we will take a look at some of the main features of Microsoft Excel so that you can start using it more effectively.
Asked by: Uriah Marvin
Score: 4.4/5
(35 votes)
Microsoft Excel is a spreadsheet developed by Microsoft for Windows, macOS, Android and iOS. It features calculation, graphing tools, pivot tables, and a macro programming language called Visual Basic for Applications.
What is MS Excel explain?
Microsoft Excel is a spreadsheet program included in the Microsoft Office suite of applications. … Spreadsheets present tables of values arranged in rows and columns that can be manipulated mathematically using both basic and complex arithmetic operations and functions.
What is MS Excel Short answer?
Microsoft Excel is a software program produced by Microsoft that allows users to organize, format and calculate data with formulas using a spreadsheet system. This software is part of the Microsoft Office suite and is compatible with other applications in the Office suite.
What are the 3 common uses for Excel?
The three most common general uses for spreadsheet software are to create budgets, produce graphs and charts, and for storing and sorting data. Within business spreadsheet software is used to forecast future performance, calculate tax, completing basic payroll, producing charts and calculating revenues.
How many types of MS Excel?
Excel 2010’s Three Data Types and Their Default Formats — dummies.
38 related questions found
What are the 5 functions in Excel?
To help you get started, here are 5 important Excel functions you should learn today.
- The SUM Function. The sum function is the most used function when it comes to computing data on Excel. …
- The TEXT Function. …
- The VLOOKUP Function. …
- The AVERAGE Function. …
- The CONCATENATE Function.
What is the purpose of Excel?
MS Excel is a spreadsheet programme developed by Microsoft in 1985, with the sole purpose of helping businesses compile all their financial data, yearly credit, and yearly debit sheets. Fast forward to the future after 31 years, it is now the most commonly used program for creating graphs and pivot tables.
What are the main features of Excel?
What are the main features of Microsoft Excel? Ans. The main features of MS Excel include inserting a pivot table, sorting of tabulated data, adding formulas to the sheet, and calculating large data.
What are the tools of Excel?
Excel Add-ins
- Filter Mate. A fast and easy way to work with filtered ranges and Tables in Excel.
- PivotPal. …
- Tab Hound. …
- Paste Buddy. …
- List Search. …
- Quarter Sum Formulas. …
- IFs Filter. …
- Formatting Shortcuts Add-in.
What is the formula for Excel?
In Excel, a formula is an expression that operates on values in a range of cells or a cell. For example, =A1+A2+A3, which finds the sum of the range of values from cell A1 to cell A3.
Why is Excel so popular?
Even after three decades, MS Excel is still the most preferred and used spreadsheet software around the world. Microsoft Excel is commonly used for financially-related activities. The reason for its popularity is that the user can define custom formulas for calculating quarterly, half yearly and annual reports.
Why is learning Excel important?
It can boost your employability and career prospects whilst also being a useful tool to analyse data in everyday life, such as when managing personal finances. Excel is an easily accessible software that is a valuable tool in all aspects of life and should be considered critical for personal development.
What is importance of spreadsheet?
Spreadsheets are an essential business and accounting tool. They can vary in complexity and can be used for various reasons, but their primary purpose is to organize and categorize data into a logical format. Once this data is entered into the spreadsheet, you can use it to help organize and grow your business.
How does excel help students?
Excel reduces the difficulty of plotting data and allows students a means for interpreting the data. … This goes a long way toward helping them understand the relationship between the data and the chart. Excel can easily convert any chart or data set into a web page, making it very easy to share information among groups.
What can I learn in Excel?
5 Tips for Learning Excel
- Practice Simple Math Problems in Excel. When it comes to Excel, it’s easiest to start with basic math. …
- Learn How to Create Tables. …
- Learn How to Create Charts. …
- Take Excel Training Courses. …
- Earn a Microsoft Office Specialist Certification.
What are the main functions of a spreadsheet?
You can use spreadsheets to enter data, calculate equations and create charts and graphs. Spreadsheet software has the capability to create a million rows by 16,000 columns, easily enough space to store large databases of text and data.
What are types of spreadsheet?
Examples of spreadsheet programs
- Google Sheets — (online and free).
- iWork Numbers — Apple Office Suite.
- LibreOffice -> Calc (free).
- Lotus 1-2-3 (discontinued).
- Lotus Symphony — Spreadsheets.
- Microsoft Excel.
- OpenOffice -> Calc (free).
- VisiCalc (discontinued).
Which software is used for spreadsheet?
The 8 Best Spreadsheet Apps
- Microsoft Excel for powerful data crunching and large data sets.
- Google Sheets for spreadsheet collaboration.
- LibreOffice Calc for a free, native spreadsheet app.
- Smartsheet for project management and other non-spreadsheet tasks.
- Quip for integrating spreadsheets into shared documents.
Is Excel worth learning in 2020?
Excel is a great tool to start data analysis and modeling. Increase your earning potential by learning VBA, SQL Python, and Tableau. … Excel is a great tool to start data analysis and modeling. It’s more affordable than other data analytics options and includes most basic analytic functions and a few extras.
How popular is MS Excel?
More Than 30 Million Users Make Microsoft Excel The World’s Most Popular Spreadsheet Program. Excel, making it the most popular spreadsheet of all time. This figure averages more than five new users of Microsoft Excel per minute since the product’s introduction in September 1985.
Who still uses Excel?
Excel is used by an estimated 750 million people worldwide and Satya Nadella has proclaimed it as Microsoft’s most important consumer product . However, mention Excel to techies and it’s often dismissed with a sniff.
What are the top 10 Excel formulas?
Top 10 Most Useful Excel Formulas
- SUM, COUNT, AVERAGE. SUM allows you to sum any number of columns or rows by selecting them or typing them in, for example, =SUM(A1:A8) would sum all values in between A1 and A8 and so on. …
- IF STATEMENTS.
- SUMIF, COUNTIF, AVERAGEIF.
- VLOOKUP. …
- CONCATENATE. …
- MAX & MIN. …
- AND. …
- PROPER.
What is the formula for 25 in Excel?
If you want to calculate a percentage of a number in Excel, simply multiply the percentage value by the number that you want the percentage of. For example, if you want to calculate 25% of 50, multiply 25% by 50. — which gives the result 12.5.
How do you add 15% in Excel?
Even if the column has 100 or 1,000 cells of data, Excel can still handle it in a few steps. Here’s how to do it: Enter the numbers you want to multiply by 15% into a column. In an empty cell, enter the percentage of 15% (or 0.15), and then copy that number by pressing Ctrl-C.
15 Features That Make Excel “Excel”
Hello everybody,
Here we are with another long article again.
As you know, Excel has been an indispensable part of our office life for a long time. We wanted to compile The Features That Make Excel “Excel”.
There are so many topics, so many features… But in this article, we will be talking about the most important features of Excel that you need to know.
Let’s get started.
What are these features?
‣ Shortcuts
‣ Formulas (Functions)
‣ Pivot Table
‣ Conditional Formatting
‣ Data Validation
‣ Sort
‣ Filter
‣ Advanced Filter
‣ Wildcard Characters
‣ Charts
‣ Flash Fill
‣ Find and Replace
‣ Convert Text to Columns
‣ Al Import External Data
‣ VBA (Macro)
► SHORTCUTS
It is disputable that if the shortcuts in Excel are a feature, but it is a very important feature for us. Because shortcuts allows us to access and apply the existing features faster.
Being able to do that is very valuable.
While creating pretty much any program, some keyboard shortcut keys are assigned to some menus and features so that they are accessed in a quicker way. In addition, there are global shortcuts that are frequently used in the computer world.
You can download the 40 Most-Used and Time-Saving Shortcuts in Excel in both Turkish and English below.
Turkish
English
With these shortcuts, we can act faster in Excel and get our job done quicker. And also, they allow us to work more confidently. This way, we sum the table quickly, select the whole table with one action, add filter quickly, and become faster by using the keys assigned to a feature instead of looking for that feature in the menu.
► FUNCTIONS (FORMULAS)
No doubt that one of the biggest reasons why we use Excel is the built-in functions it contains and allows us to use. In a daily use, we usually prepare tables and want to sum the financial numbers, sales stock numbers; produce their statistics and analyze them. Excel offers us many tools for that, and one of them is the Functions.
There are many menus in the Ribbon in Excel, and many features in those menus that are related to the menu’s name and also that are not. But the Formulas menu only has to do with the Formulas. It is a pretty broad subject. Thus, Microsoft has created a menu just for this subject.
There are many formula categories. If we know the functions we need, we start the formula by writing that function’s name directly. But if we don’t know, then we can find the suitable function for our need in the Formulas menu and continue that way.
Many functions in Excel are named wisely based on what they do. For example, if we want to get a year, month or day our of a date, they already have their functions as: YEAR, MONTH, DAY. We can use them. There are many examples of this situation. For example, there are MAX and MIN functions to find out the lowest or highest number in a column. And the MATCH function searches for a specified item in a range of cells, and then returns the relative position of that item in the range.
The working principle of functions is like this: they require some arguments from you and if you give it those arguments, the formula executes the necessary look up and calculation, and returns us a value. Some of these arguments are required/obligatory, and some are optional. Even if you do not enter them, the formula works. But a different result might be returned when the optional arguments are entered. So, it is important to make a good decision about the options.
There are also functions that can change instantly, daily, or with each calculation. For example: NOW(), TODAY(), RANDBETWEEN(). If you write the =TODAY() formula into a cell, it returns you that day’s date. And when you open that file the next day, it returns the date of the next day. Likewise, when you write the =NOW() formula, it will return the date and hour of that moment.
10 Most Popular Functions Stated by Microsoft
|
Function |
Description |
|---|---|
| SUM function | Use this function to add the values in cells. |
| IF function | Use this function to return one value if a condition is true and another value if it’s false. Here’s a video about using the IF function. |
| LOOKUP function | Use this function when you need to look in a single row or column and find a value from the same position in a second row or column. |
| VLOOKUP function | Use this function when you need to find things in a table or a range by row. For example, look up an employee’s last name by her employee number, or find her phone number by looking up her last name (just like a telephone book). Check out this video about using VLOOKUP. |
| MATCH function | Use this function to search for an item in a range of cells, and then return the relative position of that item in the range. For example, if the range A1:A3 contains the values 5, 7, and 38, then the formula =MATCH(7,A1:A3,0) returns the number 2, because 7 is the second item in the range. |
| CHOOSE function | Use this function to select one of up to 254 values based on the index number. For example, if value1 through value7 are the days of the week, CHOOSE returns one of the days when a number between 1 and 7 is used as index_num. |
| DATE function | Use this function to return the sequential serial number that represents a particular date. This function is most useful in situations where the year, month, and day are supplied by formulas or cell references. For example, you might have a worksheet that contains dates in a format that Excel does not recognize, such as YYYYMMDD.
Use the DATEDIF function to calculate the number of days, months, or years between two dates. |
| DAYS function | Use this function to return the number of days between two dates. |
| FIND, FINDB functions | FIND and FINDB locate one text string within a second text string. They return the number of the starting position of the first text string from the first character of the second text string. |
| INDEX function | Use this function to return a value or the reference to a value from within a table or range. |
► PIVOT TABLE
Pivot Table is a strong tool that helps you to calculate, sum and analyze the data in order to see the comparisons, patterns, and trends of your data. You can access it through the Tables group in the Insert menu.
We use this feature when we have a big table and want to create pivot tables based on the fields we want. Even though it is very easy to use, it allows us to execute a very strong and fast data analysis and prepare reports. If you have a table like this, you can get many summary reports from it. If you have a date field in your table, you can create reports by years, quarters, months, weeks and days for all the dates.
You can get many reports from the table below like What is the total amounts and costs based on the Company, import no or product reference; or based on year, quarter, month, or week?
After creating a Pivot Table, the Field List will come to the right. You can select the fields you will use in the summary report or drag and leave them to shape your report.
After creating a Pivot Table, you can edit the design of the report via the Analysis and Design Menus and make its visualization better with a chart by filtering quickly in your report with Slicers, Timeline and Pivot Chart that are Pivot Table tools offered to us.
► CONDITIONAL FORMATTING
Another frequently used feature in Excel is the Conditional Formatting. This feature is usually used to highlight the cells that meet a specific condition. It is in the Styles group in the Home menu.
There are some ready-made conditions that you can use. And when those ready-made conditions are not enough for us, we can create our own rules with formulas and format the cells that meet these rules. Of course, for this you need to know about the formulas first.
We can see the ready-made rules offered to us when we choose Conditional Formatting as below. We can easily format by number, text and date.
If these rules are not enough for us, we can choose the “Use a formula to determine which cells to format” from the New Rule option and write the formula and highlight the cells that meet our conditions.
We can create multiple Conditional Formatting in a field if we want. We can use the Manage Rules option to see or change the conditions of these formattings.
We can use the Clear Rules option to clear rules in a certain field of the page or all the rules in the page.
You can see the examples about Conditional Formatting that have been prepared based on the Data Bars, Color Scales, and Icon Sets rules. You can bring light to your tables and get visual analysis by using formatting rules.
And on top of that, you can highlight without having advanced-knowledge like macros with this built-in feature.
You can see a few examples about the Data Bars, Color Scales, and Icon Sets rules below.
► DATA VALIDATION
We use the Data Validation feature a lot in Excel too.
We can define it like this: It is a feature that enables a certain data to be entered into a cell or cell range and blocks any other data to be entered there. It is in the Data Tools group of the Data menu.
We already have ready-made Data Validation criteria. You can see these criteria in the image below.
Whole Number – to restrict the cell to accept only whole numbers.
Decimal – to restrict the cell to accept only decimal numbers.
List – to pick data from the drop-down list.
Date – to restrict the cell to accept only date.
Time – to restrict the cell to accept only time.
Text Length – to restrict the length of the text.
Custom – for custom formula.
We can create custom criteria with formulas in the List and Custom criteria. If we want, we can create dependent data validation lists as well. For this, you need to create the table appropriately and define the data ranges with the Define Name feature. And then you can relate them to each other.
► SORT
After we write titles in our tables and enter the data one under another or in a prepared list, the data is not always sorted Alphabetically, Numerically or by Date and we feel the need to have our data sorted. Here comes the Sort feature of Excel to our help.
We can access this feature through many ways:
- Through the Editing group on the right of the Home menu
- Through the Sort & Filter group in the Data menu
- Through the Quick Access Toolbar if we add it
- By clicking the Filter arrows activated for filtering
- By coming to Sort in the Right Click menu
The most important mistake made while using the Sort feature is to leave a black column in our table. Sometime we add a column and then hide it instead of deleting and when we sort the table, our table is separated into two and the left and right sides are seen as separate tables. Thus, our table loses its general integrity in any sorting and the data get all mixed up. Such a situation can cause fatal consequences.
If you will sort just one column, it will be enough to choose any cell in that column. You don’t ever have to choose the whole table or a whole column.
And when you want to sort multiple columns, you should use the Custom Sort window.
With the fields in this window, you can sort on Cell Values, Cell Color, Font Color or Conditional Formatting Icon with alphabetical, numeric, date, cell color and Custom Lists order.
► FILTER
We can filter in a field or multiple fields of our table and make only the data we want visible. For this, we use the Filter feature frequently. It is one of the main features of Excel and is usually located next to the Sort feature. So, we can access the Filter feature through the ways we can access the Sort feature.
Shortcut: Ctrl + Shift + L – ( Add Filter if there is none in the table, removes it if there is. )
There is Automatic Filter and Advanced Filter in Excel. We can use the wildcard characters in both of them. In the Filter feature, you can filter more quickly and in a custom way by using the
- Text Filters
- Number Filters
- Date Filters
depending on the data type you want to filter.


Also, if the column was highlighted, you can filter the data with the Filter by Color option. You will see that the cells with the color you choose are filtered.
We have mentioned that you can use the Wildcard Characters when looking up a data.
You can especially use the * character in the Search box and limit your search.
► ADVANCED FILTER
As you know, we can filter by maximum two conditions as and/or in a field with the automatic filter feature. We can use the Advanced Filter feature to filter the data in our table by multiple conditions or to list the results in another field. This feature is right under the Filter with the name of Advanced in the Data menu.
This feature offers us two things:
- To list unique expressions in the stated field or fields on another field
- To filter the data that meet columns and criteria stated in another field on the table or list the results in another place.
You can find the example of the first article below.
Here we say this: List the Unique Records in the F1:F193 cell range starting from the N1 cell. You can see the result in the N column.
You can find the example of the second article below.
Here we say this: If the A1:K193 cell range has the data in the M1:O3 range, list the results starting from the M6 cell.
► WILDCARD CHARACTERS
Just like in many programs, we can use the Wildcard Characters given to us in formulas or some features of Excel. These Wildcard Characters help us to find expressions that are in the beginning or end of a text or within it by writing a certain part of the text.
There are three different Wildcard characters.
- * (Asterisk)
- ? (Question Mark)
- ~ (Tilde)
They are used in looking up letters, and words.
We can use the Wildcard Characters as comparison criteria for the text filters and while searching and changing the content.
* (asterisk) It is used for multiple characters. Covers all the characters in the keyboard.
For example: “İst*” Means the ones that start with İst.
For example: “*ist” Means the ones that end with İst..
For example: “*ist*” Means the ones that has İst in it..
? (Question Mark) It is used for any character.
For example: “Mura?” means that it starts with Mura and is followed by a letter.
For example: “?urat” means that it starts with a letter and is followed by urat.
Helps you to find expressions like Murat, Surat
~ (tilde) is used to find the ones that has a question mark, asterisk or tilde.
You can press ALTGR + Ü and then space to write this character. (In a Turkish keyboard) To create the tilde symbol using a U.S. keyboard hold down the Shift key and press tilde key.
It is used to search/state the Asterisk, Question Mark and Tilde.
For the Asterisk and Question mark, it means that you don’t represent one or more characters, you are just a star or question mark.
We have mentioned that they can be used in formula. Let’s have an example of this if you wish.
It will be enough for us to write “SU*” (“WATER*”) into the criteria part in order to find out the Total Product Sales Amount of the ones that start with SU in the Product (Ürün) column.
We have also mentioned that you can use the Wildcard characters in the Filter feature.
When we write *e? into the Search box of filter, it means that it stars with any characters but the penultimate character is e and ends with any text.
► CHARTS
Charts help you to make your data more visually-pleasing to be more impressive on your target audience. You can prefer charts that are more appealing that presenting with just plain tables. Excel offers us many chart types at this point. It has become easier to create chart especially with Excel 2013 and forward. Now, we don’t think about which chart type we should pick thanks to the suitable chart recommendations for our tables.
We need to simplify our data as much as possible for our chart to be easily comprehended. You can add chart title or axis title to any chart type. The axis type normally can be used in all axes that can be seen in the chart and depth (series) axes in 3-D charts are included. Some chart types (like radar charts) have axes but they can not view axis titles. You can not add axis titles to charts that don’t have an axis (like doughnut or pie charts).
► FLASH FILL
This amazing feature has entered our lives with the Excel 2013 version.
Now, we can see the results that we could only get by writing a few nested formulas before with one click.
You can find this feature in the Data Tools group of the Data menu.
We can say that we are able to get things done that we could only get done with Text Functions or Convert Text to Columns Wizard with one feature.
We have to have this logic while using this feature: first, we state the part we want to get from the main text and how we want to get it in a cell, and then apply it to the other cells with the CTRL + E shortcut.
What Can We Do with This Feature?
- Separate Names and Surnames in a single cell to separate columns.
- Join data in separate columns in a single cell.
- Separate the data you want to get from the data with spaces that is in the beginning, end, or middle of a text.
- Sort out the text and numbers in the cell.
- Convert a text or number to the format you want.
- Change all the letters of the text to capitals.
- Change all the letters of the text to lower case.
- Get the initials of each word.
- Create a date from the day, month and year expressions that are in separate cells.
- Turn the decimal points to comma.
- Separate the decimal part and whole number from a decimal number.
- Convert the phone number in the cell to any format you want.
- Separate the username and domain parts of e-mail and use it in many other text editing actions.
► FIND and REPLACE
As you know, in Excel we can call the Find and Replace window with the CTRL + F and CTRL + H shortcuts while looking for a data in an active cell or in the workbook. We use this feature frequently. And the first thing we should do while using it is to click the Options button. Because, the last search we have made stays in the memory and the choices come as marked if a choice was made out of options before when we call the window and these affect the next search.
Any text written into the Find what box is looked up in the worksheet as contains and if it finds, lists the cells under the window.
Here is a tip: as you can see in the table above, when we make a search, all these are listed and the first record is marked under the window. Since it is marked, we can select all the records with the CTRL+A keys. And you can highlight, delete etc. all the selected cells at once after selecting all.
In addition, we can limit the search with the “Match case” or “Match entire cell contents” options. If you want, you can use the wildcard characters ( * ? ~ ) to search faster and more specifically.
And we can replace the that we looked up with other data in the Replace tab. We can limit the search again by choosing among the options. If you are looking for a format, you can replace it with another format.
We can get extra special work done by using the Wildcard Characters in the Replace window. For example: there are both text and numbers in cells one under another in a column and there is just a space between these two data, just like you can see below. We can say “leave all the characters before the space blank” by using * in the Replace window. This way, all the characters before the space will be erased and only the numbers will be left. For this, write star space (*) into the Find what box and leave the Replace with box empty.
► CONVERT TEXT TO COLUMNS
Sometimes we want to get data from Text or CSV files in Excel, or we receive a ready-made table. In these files the data is usually showed next to each other with commas or semi colons. We can separate these data into different columns with the Convert Text to Columns Wizard and make them look like a decent table.
You can access this feature through the Data Tools group in the Data Menu.
Now, let’s take a look at an example.
We have a table like the one below. We will separate the data in the A columns into the columns next to it from the delimiter points. When we look at our data, our delimiter that we will consider as delimiters are semicolons and points, and we see that they can repeat more than once.
Now let’s convert our data to the table we want using this feature.
- First, we select the range A2: A16 in which we have data.
We choose Convert Text to Columns from the Data menu.
In the first stage of the window, select Delimited and click Next
We select Semicolon and Other from the Delimiters on the left.
Select the Treat consecutive delimiters as one option on the side and click Next
At the last stage, we specify B2 as the Destination and click the Finish button.
As a result, we can separate the complex data on the left from the delimiter points and transform it into a table by separating it to different columns.
And we can get many other similar things done with this feature.
For example:
- We can convert numbers written as 22102019 to the Date format.
- When our thousands and decimal delimiters are written backwards as 1,000.00, we can reverse the delimiters and convert it to 000,00.
- In cases where the negative sign in numbers is at the end of the number, we can put the – (minus) sign in front of the number.
► IMPORT EXTERNAL DATA
It is important to know that Excel is not just a simple app to create tables and make calculations. In our opinion, Excel is the most inclusive and developed application in the world. It shows it is uniqueness with being sector free -anyone who sits in a desk can use this app, so to speak- and its ever-developing nature with each new version.
And the Import External Data feature allows us to connect to many database, data source and online services and import the data to Excel and show that data as Table, Pivot Table, and Pivot Chart and make analysis. It allows you to simply import data from structures like Txt, Csv, Json, XML as well as connecting to very different and broad data sources.
► EXCEL & VBA (MACRO)
Microsoft Office offers the Macro command in some of the Office packages to the users in order to automatize the routine actions.
While preparing Macros, the Visual Basic programming language that works in the background of Excel waits there. When you save anything, this programming language becomes active and translates the macro command you have prepared into the programming language. This way, when you want to run or edit the macro you’ve prepared, Excel offers you this opportunity easily.
Without a doubt, one of Excel’s most powerful features is the VBA , i.e. Macros. By using this language that comes ready in the background when Office is installed, you can codify your daily routines, weekly and monthly reports, and you can list and report your data much faster, even within seconds.
And you can prepare programs for your needs on UserForm and make everyone in your company use these programs.
You can share this article and help many other people get informed as well.
Good bye. 👍🏻
Get Excel training offer right now!