Macro codes can save you a ton of time.
You can automate small as well as heavy tasks with VBA codes.
And do you know?
With the help of macros…
…you can break all the limitations of Excel which you think Excel has.
And today, I have listed some of the useful codes examples to help you become more productive in your day to day work.
You can use these codes even if you haven’t used VBA before that.
But here’s the first thing to know:
What is a Macro Code?
In Excel, macro code is a programming code which is written in VBA (Visual Basic for Applications) language.
The idea behind using a macro code is to automate an action which you perform manually in Excel, otherwise.
For example, you can use a code to print only a particular range of cells just with a single click instead of selecting the range -> File Tab -> Print -> Print Select -> OK Button.
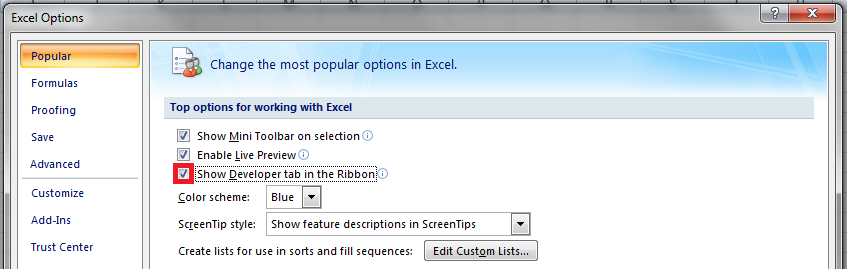
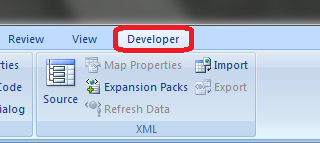
How to use a Macro Code in Excel
Before you use these codes, make sure you have your developer tab on your Excel ribbon to access VB editor. Once you activate developer tab you can use below steps to paste a VBA code into VB editor.
List of Top 100 macro Examples (CODES) for VBA beginners
I have added all the codes into specific categories so that you can find your favorite codes quickly. Just read the title and click on it to get the code.
- This is my Ultimate VBA Library which I update on monthly basis with new codes and Don’t forget to check the VBA Examples Sectionꜜ at the end of this list.
- VBA is one of the Advanced Excel Skills.
- To manage all of these codes make sure to read about Personal Macro Workbook to use these codes in all the workbooks.
- I have tested all of these codes in different versions of Excel (2007, 2010, 2013, 2016, and 2019). If you found any error in any of these codes, make sure to share with me.
Basic Codes
These VBA codes will help you to perform some basic tasks in a flash which you frequently do in your spreadsheets.
1. Add Serial Numbers
Sub AddSerialNumbers()
Dim i As Integer
On Error GoTo Last
i = InputBox("Enter Value", "Enter Serial Numbers")
For i = 1 To i
ActiveCell.Value = i
ActiveCell.Offset(1, 0).Activate
Next i
Last:Exit Sub
End Sub
This macro code will help you to automatically add serial numbers in your Excel sheet which can be helpful for you if you work with large data.
To use this code you need to select the cell from where you want to start the serial numbers and when you run this it shows you a message box where you need to enter the highest number for the serial numbers and click OK. And once you click OK, it simply runs a loop and add a list of serial numbers to the cells downward.
2. Insert Multiple Columns
Sub InsertMultipleColumns()
Dim i As Integer
Dim j As Integer
ActiveCell.EntireColumn.Select
On Error GoTo Last
i = InputBox("Enter number of columns to insert", "Insert Columns")
For j = 1 To i
Selection.Insert Shift:=xlToRight, CopyOrigin:=xlFormatFromRightorAbove
Next j
Last: Exit Sub
End Sub
This code helps you to enter multiple columns in a single click. When you run this code it asks you the number columns you want to add and when you click OK, it adds entered number of columns after the selected cell. If you want to add columns before the selected cell, replace the xlToRight to xlToLeft in the code.
3. Insert Multiple Rows
Sub InsertMultipleRows()
Dim i As Integer
Dim j As Integer
ActiveCell.EntireRow.Select
On Error GoTo Last
i = InputBox("Enter number of columns to insert", "Insert Columns")
For j = 1 To i
Selection.Insert Shift:=xlToDown, CopyOrigin:=xlFormatFromRightorAbove
Next j
Last: Exit Sub
End Sub
With this code, you can enter multiple rows in the worksheet. When you run this code, you can enter the number of rows to insert and make sure to select the cell from where you want to insert the new rows. If you want to add rows before the selected cell, replace the xlToDown to xlToUp in the code.
4. Auto Fit Columns
Sub AutoFitColumns() Cells.Select Cells.EntireColumn.AutoFit End Sub
This code quickly auto fits all the columns in your worksheet. So when you run this code, it will select all the cells in your worksheet and instantly auto-fit all the columns.
5. Auto Fit Rows
Sub AutoFitRows() Cells.Select Cells.EntireRow.AutoFit End Sub
You can use this code to auto-fit all the rows in a worksheet. When you run this code it will select all the cells in your worksheet and instantly auto-fit all the row.
6. Remove Text Wrap
Sub RemoveTextWrap()
Range("A1").WrapText = False
End Sub
This code will help you to remove text wrap from the entire worksheet with a single click. It will first select all the columns and then remove text wrap and auto fit all the rows and columns. There’s also a shortcut that you can use (Alt + H +W) for but if you add this code to Quick Access Toolbar it’s convenient than a keyboard shortcut.
7. Unmerge Cells
Sub UnmergeCells() Selection.UnMerge End Sub
This code simply uses the unmerge options which you have on the HOME tab. The benefit of using this code is you can add it to the QAT and unmerge all the cell in the selection. And if you want to un-merge a specific range you can define that range in the code by replacing the word selection.
8. Open Calculator
Sub OpenCalculator() Application.ActivateMicrosoftApp Index:=0 End Sub
In Windows, there is a specific calculator and by using this macro code you can open that calculator directly from Excel. As I mentioned that it’s for windows and if you run this code in the MAC version of VBA you’ll get an error.
9. Add Header/Footer Date
Sub DateInHeader() With ActiveSheet.PageSetup .LeftHeader = "" .CenterHeader = "&D" .RightHeader = "" .LeftFooter = "" .CenterFooter = "" .RightFooter = "" End With End Sub
This macro adds a date to the header when you run it. It simply uses the tag «&D» for adding the date. You can also change it to the footer or change the side by replacing the «» with the date tag. And if you want to add a specific date instead of the current date you can replace the «&D» tag with that date from the code.
10. Custom Header/Footer
Sub CustomHeader()
Dim myText As String
myText = InputBox("Enter your text here", "Enter Text")
With ActiveSheet.PageSetup
.LeftHeader = ""
.CenterHeader = myText
.RightHeader = ""
.LeftFooter = ""
.CenterFooter = ""
.RightFooter = ""
End With
End Sub
When you run this code, it shows an input box that asks you to enter the text which you want to add as a header, and once you enter it click OK.
If you see this closely you have six different lines of code to choose the place for the header or footer. Let’s say if you want to add left-footer instead of center header simply replace the “myText” to that line of the code by replacing the «» from there.
Formatting Codes
These VBA codes will help you to format cells and ranges using some specific criteria and conditions.
11. Highlight Duplicates from Selection
Sub HighlightDuplicateValues() Dim myRange As Range Dim myCell As Range Set myRange = Selection For Each myCell In myRange If WorksheetFunction.CountIf(myRange, myCell.Value) > 1 Then myCell.Interior.ColorIndex = 36 End If Next myCell End Sub
This macro will check each cell of your selection and highlight the duplicate values. You can also change the color from the code.
12. Highlight the Active Row and Column
Private Sub Worksheet_BeforeDoubleClick(ByVal Target As Range, Cancel As Boolean) Dim strRange As String strRange = Target.Cells.Address & "," & _ Target.Cells.EntireColumn.Address & "," & _ Target.Cells.EntireRow.Address Range(strRange).Select End Sub
I really love to use this macro code whenever I have to analyze a data table. Here are the quick steps to apply this code.
- Open VBE (ALT + F11).
- Go to Project Explorer (Ctrl + R, If hidden).
- Select your workbook & double click on the name of a particular worksheet in which you want to activate the macro.
- Paste the code into it and select the “BeforeDoubleClick” from event drop down menu.
- Close VBE and you are done.
Remember that, by applying this macro you will not able to edit the cell by double click.
13. Highlight Top 10 Values
Sub TopTen() Selection.FormatConditions.AddTop10 Selection.FormatConditions(Selection.FormatConditions.Count).S tFirstPriority With Selection.FormatConditions(1) .TopBottom = xlTop10Top .Rank = 10 .Percent = False End With With Selection.FormatConditions(1).Font .Color = -16752384 .TintAndShade = 0 End With With Selection.FormatConditions(1).Interior .PatternColorIndex = xlAutomatic .Color = 13561798 .TintAndShade = 0 End With Selection.FormatConditions(1).StopIfTrue = False End Sub
Just select a range and run this macro and it will highlight top 10 values with the green color.
14. Highlight Named Ranges
Sub HighlightRanges() Dim RangeName As Name Dim HighlightRange As Range On Error Resume Next For Each RangeName In ActiveWorkbook.Names Set HighlightRange = RangeName.RefersToRange HighlightRange.Interior.ColorIndex = 36 Next RangeName End Sub
If you are not sure about how many named ranges you have in your worksheet then you can use this code to highlight all of them.
15. Highlight Greater than Values
Sub HighlightGreaterThanValues()
Dim i As Integer
i = InputBox("Enter Greater Than Value", "Enter Value")
Selection.FormatConditions.Delete
Selection.FormatConditions.Add Type:=xlCellValue, _
Operator:=xlGreater, Formula1:=i
Selection.FormatConditions(Selection.FormatConditions.Count).S
tFirstPriority
With Selection.FormatConditions(1)
.Font.Color = RGB(0, 0, 0)
.Interior.Color = RGB(31, 218, 154)
End With
End Sub
Once you run this code it will ask you for the value from which you want to highlight all greater values.
16. Highlight Lower Than Values
Sub HighlightLowerThanValues()
Dim i As Integer
i = InputBox("Enter Lower Than Value", "Enter Value")
Selection.FormatConditions.Delete
Selection.FormatConditions.Add _
Type:=xlCellValue, _
Operator:=xlLower, _
Formula1:=i
Selection.FormatConditions(Selection.FormatConditions.Count).S
tFirstPriority
With Selection.FormatConditions(1)
.Font.Color = RGB(0, 0, 0)
.Interior.Color = RGB(217, 83, 79)
End With
End Sub
Once you run this code it will ask you for the value from which you want to highlight all lower values.
17. Highlight Negative Numbers
Sub highlightNegativeNumbers() Dim Rng As Range For Each Rng In Selection If WorksheetFunction.IsNumber(Rng) Then If Rng.Value < 0 Then Rng.Font.Color= -16776961 End If End If Next End Sub
Select a range of cells and run this code. It will check each cell from the range and highlight all cells the where you have a negative number.
18. Highlight Specific Text
Sub highlightValue()
Dim myStr As String
Dim myRg As range
Dim myTxt As String
Dim myCell As range
Dim myChar As String
Dim I As Long
Dim J As Long
On Error Resume Next
If ActiveWindow.RangeSelection.Count > 1 Then
myTxt = ActiveWindow.RangeSelection.AddressLocal
Else
myTxt = ActiveSheet.UsedRange.AddressLocal
End If
LInput: Set myRg = _
Application.InputBox _
("please select the data range:", "Selection Required", myTxt, , , , , 8)
If myRg Is Nothing Then
Exit Sub
If myRg.Areas.Count > 1 Then
MsgBox "not support multiple columns"
GoTo LInput
End If
If myRg.Columns.Count <> 2 Then
MsgBox "the selected range can only contain two columns "
GoTo LInput
End If
For I = 0 To myRg.Rows.Count - 1
myStr = myRg.range("B1").Offset(I, 0).Value
With myRg.range("A1").Offset(I, 0)
.Font.ColorIndex = 1
For J = 1 To Len(.Text)
Mid(.Text, J, Len(myStr)) = myStrThen
.Characters(J, Len(myStr)).Font.ColorIndex = 3
Next
End With
Next I
End Sub
Suppose you have a large data set and you want to check for a particular value. For this, you can use this code. When you run it, you will get an input box to enter the value to search for.
19. Highlight Cells with Comments
Sub highlightCommentCells() Selection.SpecialCells(xlCellTypeComments).Select Selection.Style= "Note" End Sub
To highlight all the cells with comments use this macro.
20. Highlight Alternate Rows in the Selection
Sub highlightAlternateRows() Dim rng As Range For Each rng In Selection.Rows If rng.Row Mod 2 = 1 Then rng.Style = "20% -Accent1" rng.Value = rng ^ (1 / 3) Else End If Next rng End Sub
By highlighting alternate rows you can make your data easily readable, and for this, you can use below VBA code. It will simply highlight every alternate row in selected range.
21. Highlight Cells with Misspelled Words
Sub HighlightMisspelledCells() Dim rng As Range For Each rng In ActiveSheet.UsedRange If Not Application.CheckSpelling(word:=rng.Text) Then rng.Style = "Bad" End If Next rng End Sub
If you find hard to check all the cells for spelling error then this code is for you. It will check each cell from the selection and highlight the cell where is a misspelled word.
22. Highlight Cells With Error in the Entire Worksheet
Sub highlightErrors() Dim rng As Range Dim i As Integer For Each rng In ActiveSheet.UsedRange If WorksheetFunction.IsError(rng) Then i = i + 1 rng.Style = "bad" End If Next rng MsgBox _ "There are total " & i _ & " error(s) in this worksheet." End Sub
To highlight and count all the cells in which you have an error, this code will help you. Just run this code and it will return a message with the number error cells and highlight all the cells.
23. Highlight Cells with a Specific Text in Worksheet
Sub highlightSpecificValues()
Dim rng As range
Dim i As Integer
Dim c As Variant
c = InputBox("Enter Value To Highlight")
For Each rng In ActiveSheet.UsedRange
If rng = c Then
rng.Style = "Note"
i = i + 1
End If
Next rng
MsgBox "There are total " & i & " " & c & " in this worksheet."
End Sub
This code will help you to count the cells which have a specific value which you will mention and after that highlight all those cells.
24. Highlight all the Blank Cells Invisible Space
Sub blankWithSpace() Dim rng As Range For Each rng In ActiveSheet.UsedRange If rng.Value = " " Then rng.Style = "Note" End If Next rng End Sub
Sometimes there are some cells which are blank but they have a single space and due to this, it’s really hard to identify them. This code will check all the cell in the worksheet and highlight all the cells which have a single space.
25. Highlight Max Value In The Range
Sub highlightMaxValue() Dim rng As Range For Each rng In Selection If rng = WorksheetFunction.Max(Selection) Then rng.Style = "Good" End If Next rng End Sub
It will check all the selected cells and highlight the cell with the maximum value.
26. Highlight Min Value In The Range
Sub Highlight_Min_Value() Dim rng As Range For Each rng In Selection If rng = WorksheetFunction.Min(Selection) Then rng.Style = "Good" End If Next rng End Sub
It will check all the selected cells and highlight the cell with the Minimum value.
27. Highlight Unique Values
Sub highlightUniqueValues() Dim rng As Range Set rng = Selection rng.FormatConditions.Delete Dim uv As UniqueValues Set uv = rng.FormatConditions.AddUniqueValues uv.DupeUnique = xlUnique uv.Interior.Color = vbGreen End Sub
This codes will highlight all the cells from the selection which has a unique value.
28. Highlight Difference in Columns
Sub columnDifference()
Range("H7:H8,I7:I8").Select
Selection.ColumnDifferences(ActiveCell).Select
Selection.Style= "Bad"
End Sub
Using this code you can highlight the difference between two columns (corresponding cells).
29. Highlight Difference in Rows
Sub rowDifference()
Range("H7:H8,I7:I8").Select
Selection.RowDifferences(ActiveCell).Select
Selection.Style= "Bad"
End Sub
And by using this code you can highlight difference between two row (corresponding cells).
Printing Codes
These macro codes will help you to automate some printing tasks which can further save you a ton of time.
30. Print Comments
Sub printComments() With ActiveSheet.PageSetup .printComments = xlPrintSheetEnd End With End Sub
Use this macro to activate settings to print cell comments in the end of the page. Let’s say you have 10 pages to print, after using this code you will get all the comments on 11th last page.
31. Print Narrow Margin
Sub printNarrowMargin() With ActiveSheet.PageSetup .LeftMargin = Application .InchesToPoints (0.25) .RightMargin = Application.InchesToPoints(0.25) .TopMargin = Application.InchesToPoints(0.75) .BottomMargin = Application.InchesToPoints(0.75) .HeaderMargin = Application.InchesToPoints(0.3) .FooterMargin = Application.InchesToPoints(0.3) End With ActiveWindow.SelectedSheets.PrintOut _ Copies:=1, _ Collate:=True, _ IgnorePrintAreas:=False End Sub
Use this VBA code to take a print with a narrow margin. When you run this macro it will automatically change margins to narrow.
32. Print Selection
Sub printSelection() Selection.PrintOut Copies:=1, Collate:=True End Sub
This code will help you print selected range. You don’t need to go to printing options and set printing range. Just select a range and run this code.
33. Print Custom Pages
Sub printCustomSelection()
Dim startpage As Integer
Dim endpage As Integer
startpage = _
InputBox("Please Enter Start Page number.", "Enter Value")
If Not WorksheetFunction.IsNumber(startpage) Then
MsgBox _
"Invalid Start Page number. Please try again.", "Error"
Exit Sub
End If
endpage = _
InputBox("Please Enter End Page number.", "Enter Value")
If Not WorksheetFunction.IsNumber(endpage) Then
MsgBox _
"Invalid End Page number. Please try again.", "Error"
Exit Sub
End If
Selection.PrintOut From:=startpage, _
To:=endpage, Copies:=1, Collate:=True
End Sub
Instead of using the setting from print options you can use this code to print custom page range. Let’s say you want to print pages from 5 to 10. You just need to run this VBA code and enter start page and end page.
Worksheet Codes
These macro codes will help you to control and manage worksheets in an easy way and save your a lot of time.
34. Hide all but the Active Worksheet
Sub HideWorksheet() Dim ws As Worksheet For Each ws In ThisWorkbook.Worksheets If ws.Name <> ThisWorkbook.ActiveSheet.Name Then ws.Visible = xlSheetHidden End If Next ws End Sub
Now, let’s say if you want to hide all the worksheets in your workbook other than the active worksheet. This macro code will do this for you.
35. Unhide all Hidden Worksheets
Sub UnhideAllWorksheet() Dim ws As Worksheet For Each ws In ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets ws.Visible = xlSheetVisible Next ws End Sub
And if you want to un-hide all the worksheets which you have hide with previous code, here is the code for that.
36. Delete all but the Active Worksheet
Sub DeleteWorksheets() Dim ws As Worksheet For Each ws In ThisWorkbook.Worksheets If ws.name <> ThisWorkbook.ActiveSheet.name Then Application.DisplayAlerts = False ws.Delete Application.DisplayAlerts = True End If Next ws End Sub
If you want to delete all the worksheets other than the active sheet, this macro is useful for you. When you run this macro it will compare the name of the active worksheet with other worksheets and then delete them.
37. Protect all Worksheets Instantly
Sub ProtectAllWorskeets()
Dim ws As Worksheet
Dim ps As String
ps = InputBox("Enter a Password.", vbOKCancel)
For Each ws In ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets
ws.Protect Password:=ps
Next ws
End Sub
If you want to protect your all worksheets in one go here is a code for you. When you run this macro, you will get an input box to enter a password. Once you enter your password, click OK. And make sure to take care about CAPS.
38. Resize All Charts in a Worksheet
Sub Resize_Charts() Dim i As Integer For i = 1 To ActiveSheet.ChartObjects.Count With ActiveSheet.ChartObjects(i) .Width = 300 .Height = 200 End With Next i End Sub
Make all chart same in size. This macro code will help you to make all the charts of the same size. You can change the height and width of charts by changing it in macro code.
39. Insert Multiple Worksheets
Sub InsertMultipleSheets()
Dim i As Integer
i = _
InputBox("Enter number of sheets to insert.", _
"Enter Multiple Sheets")
Sheets.Add After:=ActiveSheet, Count:=i
End Sub
You can use this code if you want to add multiple worksheets in your workbook in a single shot. When you run this macro code you will get an input box to enter the total number of sheets you want to enter.
40. Protect Worksheet
Sub ProtectWS() ActiveSheet.Protect "mypassword", True, True End Sub
If you want to protect your worksheet you can use this macro code. All you have to do just mention your password in the code.
41. Un-Protect Worksheet
Sub UnprotectWS() ActiveSheet.Unprotect "mypassword" End Sub
If you want to unprotect your worksheet you can use this macro code. All you have to do just mention your password which you have used while protecting your worksheet.
42. Sort Worksheets
Sub SortWorksheets()
Dim i As Integer
Dim j As Integer
Dim iAnswer As VbMsgBoxResult
iAnswer = MsgBox("Sort Sheets in Ascending Order?" & Chr(10) _
& "Clicking No will sort in Descending Order", _
vbYesNoCancel + vbQuestion + vbDefaultButton1, "Sort Worksheets")
For i = 1 To Sheets.Count
For j = 1 To Sheets.Count - 1
If iAnswer = vbYes Then
If UCase$(Sheets(j).Name) > UCase$(Sheets(j + 1).Name) Then
Sheets(j).Move After:=Sheets(j + 1)
End If
ElseIf iAnswer = vbNo Then
If UCase$(Sheets(j).Name) < UCase$(Sheets(j + 1).Name) Then Sheets(j).Move After:=Sheets(j + 1)
End If
End If
Next j
Next i
End Sub
This code will help you to sort worksheets in your workbook according to their name.
43. Protect all the Cells With Formulas
Sub lockCellsWithFormulas() With ActiveSheet .Unprotect .Cells.Locked = False .Cells.SpecialCells(xlCellTypeFormulas).Locked = True .Protect AllowDeletingRows:=True End With End Sub
To protect cell with formula with a single click you can use this code.
44. Delete all Blank Worksheets
Sub deleteBlankWorksheets() Dim Ws As Worksheet On Error Resume Next Application.ScreenUpdating= False Application.DisplayAlerts= False For Each Ws In Application.Worksheets If Application.WorksheetFunction.CountA(Ws.UsedRange) = 0 Then Ws.Delete End If Next Application.ScreenUpdating= True Application.DisplayAlerts= True End Sub
Run this code and it will check all the worksheets in the active workbook and delete if a worksheet is blank.
45. Unhide all Rows and Columns
Sub UnhideRowsColumns() Columns.EntireColumn.Hidden = False Rows.EntireRow.Hidden = False End Sub
Instead of unhiding rows and columns on by one manually you can use this code to do this in a single go.
46. Save Each Worksheet as a Single PDF
Sub SaveWorkshetAsPDF() Dimws As Worksheet For Each ws In Worksheets ws.ExportAsFixedFormat _ xlTypePDF, _ "ENTER-FOLDER-NAME-HERE" & _ ws.Name & ".pdf" Next ws End Sub
This code will simply save all the worksheets in a separate PDF file. You just need to change the folder name from the code.
47. Disable Page Breaks
Sub DisablePageBreaks() Dim wb As Workbook Dim wks As Worksheet Application.ScreenUpdating = False For Each wb In Application.Workbooks For Each Sht In wb.Worksheets Sht.DisplayPageBreaks = False Next Sht Next wb Application.ScreenUpdating = True End Sub
To disable page breaks use this code. It will simply disable page breaks from all the open workbooks.
Workbook Codes
These codes will help you to perform workbook level tasks in an easy way and with minimum efforts.
48. Create a Backup of a Current Workbook
Sub FileBackUp() ThisWorkbook.SaveCopyAs Filename:=ThisWorkbook.Path & _ "" & Format(Date, "mm-dd-yy") & " " & _ ThisWorkbook.name End Sub
This is one of the most useful macros which can help you to save a backup file of your current workbook.
It will save a backup file in the same directory where your current file is saved and it will also add the current date with the name of the file.
49. Close all Workbooks at Once
Sub CloseAllWorkbooks() Dim wbs As Workbook For Each wbs In Workbooks wbs.Close SaveChanges:=True Next wb End Sub
Use this macro code to close all open workbooks. This macro code will first check all the workbooks one by one and close them. If any of the worksheets is not saved, you’ll get a message to save it.
50. Copy Active Worksheet into a New Workbook
Sub CopyWorksheetToNewWorkbook() ThisWorkbook.ActiveSheet.Copy _ Before:=Workbooks.Add.Worksheets(1) End Sub
Let’s say if you want to copy your active worksheet in a new workbook, just run this macro code and it will do the same for you. It’s a super time saver.
51. Active Workbook in an Email
Sub Send_Mail()
Dim OutApp As Object
Dim OutMail As Object
Set OutApp = CreateObject("Outlook.Application")
Set OutMail = OutApp.CreateItem(0)
With OutMail
.to = "Sales@FrontLinePaper.com"
.Subject = "Growth Report"
.Body = "Hello Team, Please find attached Growth Report."
.Attachments.Add ActiveWorkbook.FullName
.display
End With
Set OutMail = Nothing
Set OutApp = Nothing
End Sub
Use this macro code to quickly send your active workbook in an e-mail. You can change the subject, email, and body text in code and if you want to send this mail directly, use «.Send» instead of «.Display».
52. Add Workbook to a Mail Attachment
Sub OpenWorkbookAsAttachment() Application.Dialogs(xlDialogSendMail).Show End Sub
Once you run this macro it will open your default mail client and attached active workbook with it as an attachment.
53. Welcome Message
Sub auto_open() MsgBox _ "Welcome To ExcelChamps & Thanks for downloading this file." End Sub
You can use auto_open to perform a task on opening a file and all you have to do just name your macro «auto_open».
54. Closing Message
Sub auto_close() MsgBox "Bye Bye! Don't forget to check other cool stuff on excelchamps.com" End Sub
You can use close_open to perform a task on opening a file and all you have to do just name your macro «close_open».
55. Count Open Unsaved Workbooks
Sub VisibleWorkbooks() Dim book As Workbook Dim i As Integer For Each book In Workbooks If book.Saved = False Then i = i + 1 End If Next book MsgBox i End Sub
Let’s you have 5-10 open workbooks, you can use this code to get the number of workbooks which are not saved yet.
Pivot Table Codes
These codes will help you to manage and make some changes in pivot tables in a flash.
56. Hide Pivot Table Subtotals
Sub HideSubtotals() Dim pt As PivotTable Dim pf As PivotField On Error Resume Next Set pt = ActiveSheet.PivotTables(ActiveCell.PivotTable.Name) If pt Is Nothing Then MsgBox "You must place your cursor inside of a PivotTable." Exit Sub End If For Each pf In pt.PivotFields pf.Subtotals(1) = True pf.Subtotals(1) = False Next pf End Sub
If you want to hide all the subtotals, just run this code. First of all, make sure to select a cell from your pivot table and then run this macro.
57. Refresh All Pivot Tables
Sub vba_referesh_all_pivots() Dim pt As PivotTable For Each pt In ActiveWorkbook.PivotTables pt.RefreshTable Next pt End Sub
A super quick method to refresh all pivot tables. Just run this code and all of your pivot tables in your workbook will be refresh in a single shot.
58. Create a Pivot Table
Follow this step by step guide to create a pivot table using VBA.
59. Auto Update Pivot Table Range
Sub UpdatePivotTableRange()
Dim Data_Sheet As Worksheet
Dim Pivot_Sheet As Worksheet
Dim StartPoint As Range
Dim DataRange As Range
Dim PivotName As String
Dim NewRange As String
Dim LastCol As Long
Dim lastRow As Long
'Set Pivot Table & Source Worksheet
Set Data_Sheet = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("PivotTableData3")
Set Pivot_Sheet = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Pivot3")
'Enter in Pivot Table Name
PivotName = "PivotTable2"
'Defining Staring Point & Dynamic Range
Data_Sheet.Activate
Set StartPoint = Data_Sheet.Range("A1")
LastCol = StartPoint.End(xlToRight).Column
DownCell = StartPoint.End(xlDown).Row
Set DataRange = Data_Sheet.Range(StartPoint, Cells(DownCell, LastCol))
NewRange = Data_Sheet.Name & "!" & DataRange.Address(ReferenceStyle:=xlR1C1)
'Change Pivot Table Data Source Range Address
Pivot_Sheet.PivotTables(PivotName). _
ChangePivotCache ActiveWorkbook. _
PivotCaches.Create(SourceType:=xlDatabase, SourceData:=NewRange)
'Ensure Pivot Table is Refreshed
Pivot_Sheet.PivotTables(PivotName).RefreshTable
'Complete Message
Pivot_Sheet.Activate
MsgBox "Your Pivot Table is now updated."
End Sub
If you are not using Excel tables then you can use this code to update pivot table range.
60. Disable/Enable Get Pivot Data
Sub activateGetPivotData() Application.GenerateGetPivotData = True End Sub Sub deactivateGetPivotData() Application.GenerateGetPivotData = False End Sub
To disable/enable GetPivotData function you need to use Excel option. But with this code you can do it in a single click.
Charts Codes
Use these VBA codes to manage charts in Excel and save your lot of time.
61. Change Chart Type
Sub ChangeChartType() ActiveChart.ChartType = xlColumnClustered End Sub
This code will help you to convert chart type without using chart options from the tab. All you have to do just specify to which type you want to convert.
Below code will convert selected chart to a clustered column chart. There are different codes for different types, you can find all those types from here.
62. Paste Chart as an Image
Sub ConvertChartToPicture()
ActiveChart.ChartArea.Copy
ActiveSheet.Range("A1").Select
ActiveSheet.Pictures.Paste.Select
End Sub
This code will help you to convert your chart into an image. You just need to select your chart and run this code.
63. Add Chart Title
Sub AddChartTitle()
Dim i As Variant
i = InputBox("Please enter your chart title", "Chart Title")
On Error GoTo Last
ActiveChart.SetElement (msoElementChartTitleAboveChart)
ActiveChart.ChartTitle.Text = i
Last:
Exit Sub
End Sub
First of all, you need to select your chart and the run this code. You will get an input box to enter chart title.
Advanced Codes
Some of the codes which you can use to preform advanced task in your spreadsheets.
64. Save Selected Range as a PDF
Sub HideSubtotals() Dim pt As PivotTable Dim pf As PivotField On Error Resume Next Set pt = ActiveSheet.PivotTables(ActiveCell.PivotTable.name) If pt Is Nothing Then MsgBox "You must place your cursor inside of a PivotTable." Exit Sub End If For Each pf In pt.PivotFields pf.Subtotals(1) = True pf.Subtotals(1) = False Next pf End Sub
If you want to hide all the subtotals, just run this code. First of all, make sure to select a cell from your pivot table and then run this macro.
65. Create a Table of Content
Sub TableofContent()
Dim i As Long
On Error Resume Next
Application.DisplayAlerts = False
Worksheets("Table of Content").Delete
Application.DisplayAlerts = True
On Error GoTo 0
ThisWorkbook.Sheets.Add Before:=ThisWorkbook.Worksheets(1)
ActiveSheet.Name = "Table of Content"
For i = 1 To Sheets.Count
With ActiveSheet
.Hyperlinks.Add _
Anchor:=ActiveSheet.Cells(i, 1), _
Address:="", _
SubAddress:="'" & Sheets(i).Name & "'!A1", _
ScreenTip:=Sheets(i).Name, _
TextToDisplay:=Sheets(i).Name
End With
Next i
End Sub
Let’s say you have more than 100 worksheets in your workbook and it’s hard to navigate now.
Don’t worry this macro code will rescue everything. When you run this code it will create a new worksheet and create a index of worksheets with a hyperlink to them.
66. Convert Range into an Image
Sub PasteAsPicture() Application.CutCopyMode = False Selection.Copy ActiveSheet.Pictures.Paste.Select End Sub
Paste selected range as an image. You just have to select the range and once you run this code it will automatically insert a picture for that range.
67. Insert a Linked Picture
Sub LinkedPicture() Selection.Copy ActiveSheet.Pictures.Paste(Link:=True).Select End Sub
This VBA code will convert your selected range into a linked picture and you can use that image anywhere you want.
68. Use Text to Speech
Sub Speak() Selection.Speak End Sub
Just select a range and run this code. Excel will speak all the text what you have in that range, cell by cell.
69. Activate Data Entry Form
Sub DataForm() ActiveSheet.ShowDataForm End Sub
There is a default data entry form which you can use for data entry.
70. Use Goal Seek
Sub GoalSeekVBA()
Dim Target As Long
On Error GoTo Errorhandler
Target = InputBox("Enter the required value", "Enter Value")
Worksheets("Goal_Seek").Activate
With ActiveSheet.Range("C7")
.GoalSeek_ Goal:=Target, _
ChangingCell:=Range("C2")
End With
Exit Sub
Errorhandler: MsgBox ("Sorry, value is not valid.")
End Sub
Goal Seek can be super helpful for you to solve complex problems. Learn more about goal seek from here before you use this code.
71. VBA Code to Search on Google
Sub SearchWindow32()
Dim chromePath As String
Dim search_string As String
Dim query As String
query = InputBox("Enter here your search here", "Google Search")
search_string = query
search_string = Replace(search_string, " ", "+")
'Uncomment the following line for Windows 64 versions and comment out Windows 32 versions'
'chromePath = "C:Program FilesGoogleChromeApplicationchrome.exe"
'Uncomment the following line for Windows 32 versions and comment out Windows 64 versions
'chromePath = "C:Program Files (x86)GoogleChromeApplicationchrome.exe"
Shell (chromePath & " -url http://google.com/#q=" & search_string)
End Sub
Formula Codes
These codes will help you to calculate or get results which often you do with worksheet functions and formulas.
72. Convert all Formulas into Values
Sub convertToValues()
Dim MyRange As Range
Dim MyCell As Range
Select Case _
MsgBox("You Can't Undo This Action. " _
& "Save Workbook First?", vbYesNoCancel, _
"Alert")
Case Is = vbYes
ThisWorkbook.Save
Case Is = vbCancel
Exit Sub
End Select
Set MyRange = Selection
For Each MyCell In MyRange
If MyCell.HasFormula Then
MyCell.Formula = MyCell.Value
End If
Next MyCell
End Sub
Simply convert formulas into values. When you run this macro it will quickly change the formulas into absolute values.
73. Remove Spaces from Selected Cells
Sub RemoveSpaces()
Dim myRange As Range
Dim myCell As Range
Select Case MsgBox("You Can't Undo This Action. " _
& "Save Workbook First?", _
vbYesNoCancel, "Alert")
Case Is = vbYesThisWorkbook.Save
Case Is = vbCancel
Exit Sub
End Select
Set myRange = Selection
For Each myCell In myRange
If Not IsEmpty(myCell) Then
myCell = Trim(myCell)
End If
Next myCell
End Sub
One of the most useful macros from this list. It will check your selection and then remove all the extra spaces from that.
74. Remove Characters from a String
Public Function removeFirstC(rng As String, cnt As Long) removeFirstC = Right(rng, Len(rng) - cnt) End Function
Simply remove characters from the starting of a text string. All you need is to refer to a cell or insert a text into the function and number of characters to remove from the text string.
It has two arguments «rng» for the text string and «cnt» for the count of characters to remove. For Example: If you want to remove first characters from a cell, you need to enter 1 in cnt.
75. Add Insert Degree Symbol in Excel
Sub degreeSymbol( ) Dim rng As Range For Each rng In Selection rng.Select If ActiveCell <> "" Then If IsNumeric(ActiveCell.Value) Then ActiveCell.Value = ActiveCell.Value & "°" End If End If Next End Sub
Let’s say you have a list of numbers in a column and you want to add degree symbol with all of them.
76. Reverse Text
Public Function rvrse(ByVal cell As Range) As String rvrse = VBA.strReverse(cell.Value) End Function
All you have to do just enter «rvrse» function in a cell and refer to the cell in which you have text which you want to reverse.
77. Activate R1C1 Reference Style
Sub ActivateR1C1() If Application.ReferenceStyle = xlA1 Then Application.ReferenceStyle = xlR1C1 Else Application.ReferenceStyle = xlR1C1 End If End Sub
This macro code will help you to activate R1C1 reference style without using Excel options.
78. Activate A1 Reference Style
Sub ActivateA1() If Application.ReferenceStyle = xlR1C1 Then Application.ReferenceStyle = xlA1 Else Application.ReferenceStyle = xlA1 End If End Sub
This macro code will help you to activate A1 reference style without using Excel options.
79. Insert Time Range
Sub TimeStamp() Dim i As Integer For i = 1 To 24 ActiveCell.FormulaR1C1 = i & ":00" ActiveCell.NumberFormat = "[$-409]h:mm AM/PM;@" ActiveCell.Offset(RowOffset:=1, ColumnOffset:=0).Select Next i End Sub
With this code, you can insert a time range in sequence from 00:00 to 23:00.
80. Convert Date into Day
Sub date2day() Dim tempCell As Range Selection.Value = Selection.Value For Each tempCell In Selection If IsDate(tempCell) = True Then With tempCell .Value = Day(tempCell) .NumberFormat = "0" End With End If Next tempCell End Sub
If you have dates in your worksheet and you want to convert all those dates into days then this code is for you. Simply select the range of cells and run this macro.
81. Convert Date into Year
Sub date2year() Dim tempCell As Range Selection.Value = Selection.Value For Each tempCell In Selection If IsDate(tempCell) = True Then With tempCell .Value = Year(tempCell) .NumberFormat = "0" End With End If Next tempCell End Sub
This code will convert dates into years.
82. Remove Time from Date
Sub removeTime() Dim Rng As Range For Each Rng In Selection If IsDate(Rng) = True Then Rng.Value = VBA.Int(Rng.Value) End If Next Selection.NumberFormat = "dd-mmm-yy" End Sub
If you have time with the date and you want to remove it then you can use this code.
83. Remove Date from Date and Time
Sub removeDate() Dim Rng As Range For Each Rng In Selection If IsDate(Rng) = True Then Rng.Value = Rng.Value - VBA.Fix(Rng.Value) End If NextSelection.NumberFormat = "hh:mm:ss am/pm" End Sub
It will return only time from a date and time value.
84. Convert to Upper Case
Sub convertUpperCase() Dim Rng As Range For Each Rng In Selection If Application.WorksheetFunction.IsText(Rng) Then Rng.Value = UCase(Rng) End If Next End Sub
Select the cells and run this code. It will check each and every cell of selected range and then convert it into upper case text.
85. Convert to Lower Case
Sub convertLowerCase() Dim Rng As Range For Each Rng In Selection If Application.WorksheetFunction.IsText(Rng) Then Rng.Value= LCase(Rng) End If Next End Sub
This code will help you to convert selected text into lower case text. Just select a range of cells where you have text and run this code. If a cell has a number or any value other than text that value will remain same.
86. Convert to Proper Case
Sub convertProperCase() Dim Rng As Range For Each Rng In Selection If WorksheetFunction.IsText(Rng) Then Rng.Value = WorksheetFunction.Proper(Rng.Value) End If Next End Sub
And this code will convert selected text into the proper case where you have the first letter in capital and rest in small.
87. Convert to Sentence Case
Sub convertTextCase() Dim Rng As Range For Each Rng In Selection If WorksheetFunction.IsText(Rng) Then Rng.Value = UCase(Left(Rng, 1)) & LCase(Right(Rng, Len(Rng) - 1)) End If Next Rng End Sub
In text case, you have the first letter of the first word in capital and rest all in words in small for a single sentence and this code will help you convert normal text into sentence case.
88. Remove a Character from Selection
Sub removeChar()
Dim Rng As Range
Dim rc As String
rc = InputBox("Character(s) to Replace", "Enter Value")
For Each Rng In Selection
Selection.Replace What:=rc, Replacement:=""
Next
End Sub
To remove a particular character from a selected cell you can use this code. It will show you an input box to enter the character you want to remove.
89. Word Count from Entire Worksheet
Sub Word_Count_Worksheet() Dim WordCnt As Long Dim rng As Range Dim S As String Dim N As Long For Each rng In ActiveSheet.UsedRange.Cells S = Application.WorksheetFunction.Trim(rng.Text) N = 0 If S <> vbNullString Then N = Len(S) - Len(Replace(S, " ", "")) + 1 End If WordCnt = WordCnt + N Next rng MsgBox "There are total " _ & Format(WordCnt, "#,##0") & _ " words in the active worksheet" End Sub
It can help you to count all the words from a worksheet.
90. Remove the Apostrophe from a Number
Sub removeApostrophes() Selection.Value = Selection.Value End Sub
If you have numeric data where you have an apostrophe before each number, you run this code to remove it.
91. Remove Decimals from Numbers
Sub removeDecimals() Dim lnumber As Double Dim lResult As Long Dim rng As Range For Each rng In Selection rng.Value = Int(rng) rng.NumberFormat = "0" Next rng End Sub
This code will simply help you to remove all the decimals from the numbers from the selected range.
92. Multiply all the Values by a Number
Sub addNumber()
Dim rng As Range
Dim i As Integer
i = InputBox("Enter number to multiple", "Input Required")
For Each rng In Selection
If WorksheetFunction.IsNumber(rng) Then
rng.Value = rng + i
Else
End If
Next rng
End Sub
Let’s you have a list of numbers and you want to multiply all the number with a particular. To use this code: Select that range of cells and run this code. It will first ask you for the number with whom you want to multiple and then instantly multiply all the numbers with it.
93. Add a Number in all the Numbers
Sub addNumber()
Dim rng As Range
Dim i As Integer
i = InputBox("Enter number to multiple", "Input Required")
For Each rng In Selection
If WorksheetFunction.IsNumber(rng) Then
rng.Value = rng + i
Else
End If
Next rng
End Sub
Just like multiplying you can also add a number into a set of numbers.
94. Calculate the Square Root
Sub getSquareRoot() Dim rng As Range Dim i As Integer For Each rng In Selection If WorksheetFunction.IsNumber(rng) Then rng.Value = Sqr(rng) Else End If Next rng End Sub
To calculate square root without applying a formula you can use this code. It will simply check all the selected cells and convert numbers to their square root.
95. Calculate the Cube Root
Sub getCubeRoot() Dim rng As Range Dimi As Integer For Each rng In Selection If WorksheetFunction.IsNumber(rng) Then rng.Value = rng ^ (1 / 3) Else End If Nextrng End Sub
To calculate cube root without applying a formula you can use this code. It will simply check all the selected cells and convert numbers to their cube root.
96. Add A-Z Alphabets in a Range
Sub addsAlphabets1() Dim i As Integer For i = 65 To 90 ActiveCell.Value = Chr(i) ActiveCell.Offset(1, 0).Select Next i End Sub
Sub addsAlphabets2() Dim i As Integer For i = 97 To 122 ActiveCell.Value = Chr(i) ActiveCell.Offset(1, 0).Select Next i End Sub
Just like serial numbers you can also insert alphabets in your worksheet. Beloware the code which you can use.
97. Convert Roman Numbers into Arabic Numbers
Sub convertToNumbers() Dim rng As Range Selection.Value = Selection.Value For Each rng In Selection If Not WorksheetFunction.IsNonText(rng) Then rng.Value = WorksheetFunction.Arabic(rng) End If Next rng End Sub
Sometimes it’s really hard to understand Roman numbers as serial numbers. This code will help you to convert roman numbers into Arabic numbers.
98. Remove Negative Signs
Sub removeNegativeSign() Dim rng As Range Selection.Value = Selection.Value For Each rng In Selection If WorksheetFunction.IsNumber(rng) Then rng.Value = Abs(rng) End If Next rng
This code will simply check all the cell in the selection and convert all the negative numbers into positive. Just select a range and run this code.
99. Replace Blank Cells with Zeros
Sub replaceBlankWithZero() Dim rng As Range Selection.Value = Selection.Value For Each rng In Selection If rng = "" Or rng = " " Then rng.Value = "0" Else End If Next rng End Sub
For data where you have blank cells, you can use the below code to add zeros in all those cells. It makes easier to use those cells in further calculations.
More Codes
100. More VBA Examples and Tutorials
- User Defined Function [UDF] in Excel using VBA
- VBA Interview Questions
- Add a Comment in a VBA Code (Macro)
- Add a Line Break in a VBA Code (Single Line into Several Lines)
- Add a New Line (Carriage Return) in a String in VBA
- Personal Macro Workbook (personal.xlsb)
- Record a Macro in Excel
- VBA Exit Sub Statement
- VBA Immediate Window (Debug.Print)
- VBA Module
- VBA MSGBOX
- VBA Objects
- VBA With Statement
- Count Rows using VBA
- Excel VBA Font (Color, Size, Type, and Bold)
- Excel VBA Hide and Unhide a Column or a Row
- Excel VBA Range – Working with Range and Cells in VBA
- Apply Borders on a Cell using VBA in Excel
- Find Last Row, Column, and Cell using VBA in Excel
- Insert a Row using VBA in Excel
- Merge Cells in Excel using a VBA Code
- Select a Range/Cell using VBA in Excel
- How to SELECT ALL the Cells in a Worksheet using a VBA Code
- use ActiveCell in VBA in Excel
- How to use Special Cells Method in VBA in Excel
- How to use UsedRange Property in VBA in Excel
- VBA AutoFit (Rows, Column, or the Entire Worksheet)
- VBA ClearContents (from a Cell, Range, or Entire Worksheet)
- VBA Copy Range to Another Sheet + Workbook
- VBA Enter Value in a Cell (Set, Get and Change)
- VBA Insert Column (Single and Multiple)
- VBA Named Range
- VBA Range Offset
- VBA Sort Range | (Descending, Multiple Columns, Sort Orientation
- VBA Wrap Text (Cell, Range, and Entire Worksheet)
- How to CLEAR an Entire Sheet using VBA in Excel
- How to Copy and Move a Sheet in Excel using VBA
- How to COUNT Sheets using VBA in Excel
- How to DELETE a SHEET using VBA in Excel
- How to Hide & Unhide a Sheet using VBA in Excel
- How to PROTECT and UNPROTECT a Sheet using VBA in Excel
- RENAME a Sheet using VBA
- Write a VBA Code to Create a New Sheet
- VBA Worksheet Object
- Activate a Sheet using VBA
- Copy an Excel File (Workbook)
- VBA Activate Workbook (Excel File)
- VBA Close Workbook (Excel File)
- VBA Combine Workbooks (Excel Files)
- VBA Create New Workbook (Excel File)
- VBA Delete Workbook (Excel File)
- VBA Open Workbook (Excel File)
- VBA Protect/Unprotect Workbook (Excel File)
- VBA Rename Workbook (Excel File)
- VBA Save Workbook (Excel File)
- VBA ThisWorkbook (Current Excel File)
- VBA Workbook
- Declare Global Variable (Public) in VBA
- Range or a Cell as a Variable in VBA
- Option Explicit Statement in VBA
- Variable in a Message Box
- VBA Constants
- VBA Dim Statement
- VBA Variables (Declare, Data Types, and Scope)
- VBA Add New Value to the Array
- VBA Array
- VBA Array Length (Size)
- VBA Array with Strings
- VBA Clear Array (Erase)
- VBA Dynamic Array
- VBA Loop Through an Array
- VBA Multi-Dimensional Array
- VBA Range to an Array
- VBA Search for a Value in an Array
- VBA Sort Array
- How to Average Values in Excel using VBA
- Get Today’s Date and Current Time using VBA
- Sum Values in Excel using VBA
- Match Function in VBA
- MOD in VBA
- Random Number
- VBA Calculate (Cell, Range, Row, & Workbook)
- VBA Concatenate
- VBA Worksheet Function (Use Excel Functions in a Macro)
- How to Check IF a Sheet Exists using VBA in Excel
- VBA Check IF a Cell is Empty + Multiple Cells
- VBA Check IF a Workbook Exists in a Folder (Excel File)
- VBA Check IF a Workbook is Open (Excel File)
- VBA Exit IF
- VBA IF – IF Then Else Statement
- VBA IF And (Test Multiple Conditions)
- VBA IF Not
- VBA IF OR (Test Multiple Conditions)
- VBA Nested IF
- VBA SELECT CASE Statement (Test Multiple Conditions)
- VBA Automation Error (Error 440)
- VBA Error 400
- VBA ERROR Handling
- VBA Invalid Procedure Call Or Argument Error (Error 5)
- VBA Object Doesn’t Support this Property or Method Error (Error 438)
- VBA Object Required Error (Error 424)
- VBA Out of Memory Error (Error 7)
- VBA Overflow Error (Error 6)
- VBA Runtime Error (Error 1004)
- VBA Subscript Out of Range Runtime Error (Error 9)
- VBA Type Mismatch Error (Error 13)
- Excel VBA Do While Loop and (Do Loop While)
- How to Loop Through All the Sheets using VBA
- Loop Through a Range using VBA
- VBA FOR LOOP
- VBA GoTo Statement
- Input Box in VBA
- VBA Create and Write to a Text File
- VBA ScreenUpdating
- VBA Status Bar
- VBA Wait and Sleep
About the Author
Puneet is using Excel since his college days. He helped thousands of people to understand the power of the spreadsheets and learn Microsoft Excel. You can find him online, tweeting about Excel, on a running track, or sometimes hiking up a mountain.
В этом уроке я покажу Вам самые популярные макросы в VBA Excel, которые вы сможете использовать для оптимизации своей работы. VBA — это язык программирования, который может использоваться для расширения возможностей MS Excel и других приложений MS Office. Это чрезвычайно полезно для пользователей MS Excel, поскольку VBA может использоваться для автоматизации вашей работы и значительно увеличить Вашу эффективность. В этой статье Вы познакомитесь с VBA и я вам покажу некоторые из наиболее полезных, готовых к использованию примеров VBA. Вы сможете использовать эти примеры для создания собственных скриптов, соответствующих Вашим потребностям.
Вам не нужен опыт программирования, чтобы воспользоваться информаций из этой статьи, но вы должны иметь базовые знания Excel. Если вы еще учитесь работать с Excel, я бы рекомендовал Вам прочитать статью 20 формул Excel, которые вам нeобходимо выучить сейчас, чтобы узнать больше о функциональных возможностях Excel.
Я подготовил для вас несколько самых полезных примеров VBA Excel с большой функциональностью, которую вы сможете использовать для оптимизации своей работы. Чтобы их использовать, вам необходимо записать их в файл. Следующий параграф посвящен установке макроса Excel. Пропустите эту часть, если вы уже знакомы с этим.
Table of Contents
Как включить макросы в Excel
В Excel нажмите комбинацию клавиш alt + F11. Это приведет вас к редактору VBA в MS Excel. Затем щелкните правой кнопкой мыши папку Microsoft Excel Objects слева и выберите Insert => Module. Это место, где сохраняются макросы. Чтобы использовать макрос, вам нужно сохранить документ Excel как макрос. Из табуляции File => Save as, выберите Save as macro-enabled Workbok (расширение .xlsm) Теперь пришло время написать свой первый макрос!
1. Копирование данных из одного файла в другой.
Очень полезный макрос, поскольку он показывает, как скопировать ряд данных изнутри vba и как создать и назвать новую книгу. Вы можете изменить этот макрос в соответствии с вашими собственными требованиями:
Sub CopyFiletoAnotherWorkbook() Sheets("Example 1").Range("B4:C15").Copy Workbooks.Add ActiveSheet.Paste Application.DisplayAlerts = False ActiveWorkbook.SaveAs Filename:="C:TempMyNewBook.xlsx" Application.DisplayAlerts = True End Sub
2. Отображение скрытых строк
Иногда большие файлы Excel можно содержать скрытые строки для большей ясности И для лучшего удобства пользователей. Вот один макрос, который отобразит все строки из активной рабочей таблицы:
Sub ShowHiddenRows() Columns.EntireColumn.Hidden = False Rows.EntireRow.Hidden = False End Sub
3. Удаление пустых строк и столбов
Пустые строки в Excel — может быть проблемой для обработки данных. Вот как избавиться от них:
Sub DeleteEmptyRowsAndColumns() Dim MyRange As Range Dim iCounter As Long Set MyRange = ActiveSheet.UsedRange For iCounter = MyRange.Rows.Count To 1 Step -1 If Application.CountA(Rows(iCounter).EntireRow) = 0 Then Rows(iCounter).Delete End If Next iCounter For iCounter = MyRange.Columns.Count To 1 Step -1 If Application.CountA(Columns(iCounter).EntireColumn) = 0 Then Columns(iCounter).Delete End If Next iCounter End Sub
4. Нахождение пустых ячеек
Sub FindEmptyCell() ActiveCell.Offset(1, 0).Select Do While Not IsEmpty(ActiveCell) ActiveCell.Offset(1, 0).Select Loop End Sub
#### 5. Заполнение пустых ячеек
Как упоминалось ранее, пустые ячейки препятствуют обработке данных и созданию сводных таблиц. Вот один примерный код, который заменяет все пустые ячейки на 0. Этот макрос имеет очень большое приложение, потому что Вы можете использовать его для поиска и замены результатов N/A, а также других символов, таких как точки, запятые или повторяющиеся значения:
Sub FindAndReplace() Dim MyRange As Range Dim MyCell As Range Select Case MsgBox("Can't Undo this action. " & _ "Save Workbook First?", vbYesNoCancel) Case Is = vbYes ThisWorkbook.Save Case Is = vbCancel Exit Sub End Select Set MyRange = Selection For Each MyCell In MyRange If Len(MyCell.Value) = 0 Then MyCell = 0 End If Next MyCell End Sub
#### 6. Сортировка данных
Следующий макрос сортирует по возрастанию все числа из столбца активной ячейки. Просто дважды нажмите любую ячейку из столбца, который вы хотите отсортировать.
NB: Здесь нам нужно поставить этот код в Sheet1 (папка Microsoft Excel Objects), а не в Module1 (папка Modules):
Private Sub Worksheet_BeforeDoubleClick (ByVal Target as Range, Cancel As Boolean) Dim LastRow As Long LastRow = Cells (Rows.Count, 1) .End (xlUp) .Row Rows ("6:" & LastRow) .Sort _ Key1: = Cells (6, ActiveCell.Column), _ Order1: = xlAscending End Sub
#### 7. Удаление пустых пространств
Иногда данные в книге содержат дополнительные пробелы (whitespace charachters), которые могут мешать анализу данных и коррумпировать формулы. Вот один макрос, который удалит все пробелы из предварительно выбранного диапазона ячеек:
Sub TrimTheSpaces() Dim MyRange As Range Dim MyCell As Range Select Case MsgBox("Can't Undo this action. " & _ "Save Workbook First?", vbYesNoCancel) Case Is = vbYes ThisWorkbook.Save Case Is = vbCancel Exit Sub End Select Set MyRange = Selection For Each MyCell In MyRange If Not IsEmpty(MyCell) Then MyCell = Trim(MyCell) End If Next MyCell End Sub
#### 8. Выделение дубликатов цветом
Иногда в нескольких столбцах, которые мы хотели бы осветить, есть повторяющиеся значения. Этот макрос делает именно это:
Sub HighlightDuplicates() Dim MyRange As Range Dim MyCell As Range Set MyRange = Selection For Each MyCell In MyRange If WorksheetFunction.CountIf(MyRange, MyCell.Value) > 1 Then MyCell.Interior.ColorIndex = 36 End If Next MyCell End Sub
#### 9. Выделение десяти самых высоких чисел
Этот код будет отображать десять самых высоких чисел из набора ячеек:
Sub TopTen() Selection.FormatConditions.AddTop10 Selection.FormatConditions(Selection.FormatConditions.Count).SetFirstPriority With Selection.FormatConditions(1) .TopBottom = xlTop10Top .Rank = 10 .Percent = False End With With Selection.FormatConditions(1).Font .Color = -16752384 .TintAndShade = 0 End With With Selection.FormatConditions(1).Interior .PatternColorIndex = xlAutomatic .Color = 13561798 .TintAndShade = 0 End With Selection.FormatConditions(1).StopIfTrue = False End Sub
Вы можете легко настроить код, чтобы выделить различное количество чисел.
#### 10. Выделение данных больших чем данные число
Когда вы запустите этот код, появится окно. Вам надо написать число, которое вы хотите сравнить с выбранными ячейками.
Sub HighlightGreaterThanValues() Dim i As Integer i = InputBox("Enter Greater Than Value", "Enter Value") Selection.FormatConditions.Delete Selection.FormatConditions.Add Type:=xlCellValue, Operator:=xlGreater, Formula1:=i Selection.FormatConditions(Selection.FormatConditions.Count).SetFirstPriority With Selection.FormatConditions(1) .Font.Color = RGB(0, 0, 0) .Interior.Color = RGB(31, 218, 154) End With End Sub
Вы тоже можете настроить этот код, чтобы выделить более низкие чисел.
#### 11. Выделение ячеек комментариями
Простой макрос, который выделяет все ячейки, содержащие комментарии:
Sub HighlightCommentCells() Selection.SpecialCells(xlCellTypeComments).Select Selection.Style= "Note" End Sub
#### 12. Выделение ячеек со словами с ошибками
Это очень полезно, когда вы работаете с функциями, которые принимают строки, однако кто-то ввел строку с ошибкой, и ваши формулы не работают. Вот как решить эту проблему:
Sub ColorMispelledCells() For Each cl In ActiveSheet.UsedRange If Not Application.CheckSpelling(Word:=cl.Text) Then _ cl.Interior.ColorIndex = 28 Next cl End Sub
13. Создание сводной таблицы
Вот как создать сводную таблицу в MS Excel (версия 2007). Особенно полезно, когда вы делаете индивидуальный отчет каждый день. Вы можете оптимизировать создание сводной таблицы следующим образом:
Sub PivotTableForExcel2007() Dim SourceRange As Range Set SourceRange = Sheets("Sheet1").Range("A3:N86") ActiveWorkbook.PivotCaches.Create( _ SourceType:=xlDatabase, _ SourceData:=SourceRange, _ Version:=xlPivotTableVersion12).CreatePivotTable _ TableDestination:="", _ TableName:="", _ DefaultVersion:=xlPivotTableVersion12 End Sub
14. Отправка активного файла по электронной почте
Мой любимый код VBA. Он позволяет вам прикреплять и отправлять файл, с которым вы работаете, с предопределенным адресом электронной почты, заголовком сообщения и телом сообщения! Сначала Вам нужно сделать референцию в Excel на Microsoft Outlook (в редакторе Excel VBA, нажмите tools => references и выберите Microsoft Outlook).
Sub SendFIleAsAttachment() Dim OLApp As Outlook.Application Dim OLMail As Object Set OLApp = New Outlook.Application Set OLMail = OLApp.CreateItem(0) OLApp.Session.Logon With OLMail .To = "admin@datapigtechnologies.com; mike@datapigtechnologies.com" .CC = "" .BCC = "" .Subject = "This is the Subject line" .Body = "Hi there" .Attachments.Add ActiveWorkbook.FullName .Display End With Set OLMail = Nothing Set OLApp = Nothing End Sub
15. Вставка всех графиков Excel в презентацию PowerPoint
Очень удобный макрос, который позволяет вам добавлять все ваши графики Excel в презентацию Powerpoint одним щелчком мыши:
Sub SendExcelFiguresToPowerPoint() Dim PP As PowerPoint.Application Dim PPPres As PowerPoint.Presentation Dim PPSlide As PowerPoint.Slide Dim i As Integer Sheets("Slide Data").Select If ActiveSheet.ChartObjects.Count < 1 Then MsgBox "No charts existing the active sheet" Exit Sub End If Set PP = New PowerPoint.Application Set PPPres = PP.Presentations.Add PP.Visible = True For i = 1 To ActiveSheet.ChartObjects.Count ActiveSheet.ChartObjects(i).Chart.CopyPicture _ Size:=xlScreen, Format:=xlPicture Application.Wait (Now + TimeValue("0:00:1")) ppSlideCount = PPPres.Slides.Count Set PPSlide = PPPres.Slides.Add(SlideCount + 1, ppLayoutBlank) PPSlide.Select PPSlide.Shapes.Paste.Select PP.ActiveWindow.Selection.ShapeRange.Align msoAlignCenters, True PP.ActiveWindow.Selection.ShapeRange.Align msoAlignMiddles, True Next i Set PPSlide = Nothing Set PPPres = Nothing Set PP = Nothing End Sub
16. Вставка таблицы Excel в MS Word
Таблицы Excel обычно помещаются внутри текстовых документов. Вот один автоматический способ экспорта таблицы Excel в MS Word:
Sub ExcelTableInWord() Dim MyRange As Excel.Range Dim wd As Word.Application Dim wdDoc As Word.Document Dim WdRange As Word.Range Sheets("Revenue Table").Range("B4:F10").Cop Set wd = New Word.Application Set wdDoc = wd.Documents.Open _ (ThisWorkbook.Path & "" & "PasteTable.docx") wd.Visible = True Set WdRange = wdDoc.Bookmarks("DataTableHere").Rangе On Error Resume Next WdRange.Tables(1).Delete WdRange.Paste WdRange.Tables(1).Columns.SetWidth _ (MyRange.Width / MyRange.Columns.Count), wdAdjustSameWidth wdDoc.Bookmarks.Add "DataTableHere", WdRange Set wd = Nothing Set wdDoc = Nothing Set WdRange = Nothing End Sub
17. Извлечение слов из текста
Мы можем использовать формулы, если хотим извлечь определенное количество символов. Но что, если мы хотим извлечь только одно слово из предложения или диапазон слов в ячейке? Для этого мы можем сами создать функцию Excel с помощью VBA. Это одна из самых удобных функций VBA, поскольку она позволяет создавать собственные формулы, которые отсутствуют в MS Excel. Давайте продолжим и создадим две функции: findword() и findwordrev():
Function FindWord(Source As String, Position As Integer) As String On Error Resume Next FindWord = Split(WorksheetFunction.Trim(Source), " ")(Position - 1) On Error GoTo 0 End Function Function FindWordRev(Source As String, Position As Integer) As String Dim Arr() As String Arr = VBA.Split(WorksheetFunction.Trim(Source), " ") On Error Resume Next FindWordRev = Arr(UBound(Arr) - Position + 1) On Error GoTo 0 End Function
Отлично, мы уже создали две новые функции в Excel! Теперь попробуйте использовать их в Excel. Функция = FindWordRev (A1,1) берет последнее слово из ячейки A1. Функция = FindWord (A1,3) берет третье слово из ячейки A1 и т. Д.
18. Защита данных в MS Excel
Иногда мы хотим защитить данных нашего файла, чтобы только мы могли его изменять. Вот как это сделать с VBA:
Sub ProtectSheets() Dim ws As Worksheet For Each ws In ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets ws.Protect Password:="1234" Next ws End Sub
Поздравления! Поскольку вы все еще читаете это, вы действительно заинтересованы в изучении VBA. Как вы уже сами видели, язык программирования VBA чрезвычайно полезен и может сэкономить нам много времени. Надеюсь, вы нашли эту информацию полезной и использовали ее, чтобы стать мастером MS Excel, VBA и компьютерных наук в целом.
© 2018 Атанас Йонков
Литература:
1. ExcelChamps.com: Top 100 Useful Excel Macro [VBA] Codes Examples.
2. Michael Alexander, John Walkenbach (2012). 101 Ready-To-Use Excel Macros.
3. BG Excel.info: 14 ready-to-use Macros for Excel.
Полезные макросы Excel для автоматизации рутинной работы с примерами применения для разных задач.
Примеры макросов для автоматизации работы
Как автоматизировать фильтр в сводных таблицах с помощью макроса? Исходные коды макросов для фильтрации и скрытия столбцов в сводной таблице.
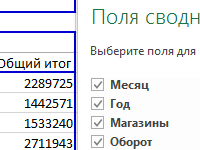
Как автоматически сгенерировать сводную таблицу с помощью макроса? Исходный код VBA для создания и настройки сводных таблиц на основе исходных данных.
Как форматировать ячейки таблицы макросом? Изменение цвета шрифта, заливки и линий границ, выравнивание. Автоматическая настройка ширины столбцов и высоты строк по содержимому с помощью VBA-макроса.
Как одновременно копировать и переименовывать большое количество листов одним кликом мышкой? Исходный код макроса, который умеет одновременно скопировать и переименовать любое количество листов.
Macros code is visual basic for applications (VBA). Macros can be used in excel to automate tasks that are performed regularly and prevent you from manually performing them each and every time. The automation process by the use of macros in excel results in time-saving and produces quality, reliable work. You can create macros in excel by recording the steps of what you want to perform or writing them in person. Writing macros code yourself is advantageous since it gives you a greater scope of control over macros. By using macro, you can perform a wide range of tasks from simple formatting steps to complex export of excel sheets.
How to Run the Macros
1. Go to the Developer tab.
2. Click on Macros.
3. In the dialog box, select the macro you want to run.
4. Click on the Run button.
Below is a list of Macro codes to enable you to get started
Insert multiple columns
This code gives you the option of inserting multiple columns. When it is run, you will feed the number of columns you are interested in, then click ok. The columns will be added after the selected cell.
| Sub InsertMultipleColumns() Dim k As Integer Dim l As Integer ActiveCell.EntireColumn.Select On Error GoTo Last i = InputBox(«Enter number of columns to insert», «Insert Columns») For l = 1 To i Selection.Insert Shift:=xlToRight, CopyOrigin:=xlFormatFromRightorAbove Next l Last: Exit Sub End Sub |
To add the column before the selected cell, replace the code xIToRight with xIToLeft.
Autofit columns
This code will instantly Autofit all the columns in your Worksheet when you Run it.
| Sub AutoFitColumns()
Cells.Select Cells.EntireColumn.AutoFit End Sub |
Remove Text wrap
Removing text wrap code will help remove text wrap in the Worksheet by selecting all columns and removing text wrap.
| Sub RemoveTextWrap() Range(«A1»).WrapText = False End Sub |
Add header
This code has the ability to add a header when run.
| Sub AddCustomHeader() Dim inputText As String inputText = InputBox(«Enter your text here», «Custom Header») ‘Add custom text to the center header With ActiveSheet.PageSetup .LeftHeader = «» .CenterHeader = inputText .RightHeader = «» End With End Sub To put a header or a footer date you can alternatively use this code; Sub DateInHeader() With ActiveSheet.PageSetup .LeftHeader = «» .CenterHeader = «&D» .RightHeader = «» .LeftFooter = «» .CenterFooter = «» .RightFooter = «» End With End Sub |
This macro simply uses the tag «&D» for adding the date. The header can be changed to the footer or side by replacing the » with the «&D.» you can also add a specific date or desired header or footer by replacing the «&D» with your preference.
Highlight the active rows and columns
This code is resourceful when you want to analyze a data table.
| Private Sub Worksheet_BeforeDoubleClick(ByVal Target As Range, Cancel As Boolean) Dim strRange As String strRange = Target.Cells.Address & «,» & _ Target.Cells.EntireColumn.Address & «,» & _ Target.Cells.EntireRow.Address Range(strRange). Select End Sub |
A quick step to apply the code is to open VBE(ALT + F11), then go to project explorer, select your Workbook and double click the particular Worksheet to activate the macro, paste the code into it, and from the event drop menu, select «BeforeDoubleClick,» it’s all done close VBE.
Highlight named ranges
To ascertain how many names you have on your Worksheet, this code can help you highlight all of them.
| Sub HighlightRanges() Dim RangeName As Name Dim HighlightRange As Range On Error Resume Next For Each RangeName In ActiveWorkbook.Names Set HighlightRange = RangeName.RefersToRange HighlightRange.Interior.ColorIndex = 36 Next RangeName End Sub |
Highlight negative numbers
Sometimes your Worksheet may be big, and you may want to only get negative numbers. Macro code has you covered. This code will check every cell from the Range and select those cells with negative numbers.
| Sub highlightNegativeNumbers() Dim Rng As Range For Each Rng In Selection If WorksheetFunction.IsNumber(Rng) Then If Rng.Value < 0 Then Rng.Font.Color= -16776961 End If End If Next End Sub |
Print narrow margin
When this macro code is run, it gives you the liberty to print a narrow margin depending on your set desire.
| Sub printNarrowMargin() With ActiveSheet.PageSetup .LeftMargin = Application .InchesToPoints (0.25) .RightMargin = Application.InchesToPoints(0.25) .TopMargin = Application.InchesToPoints(0.75) .BottomMargin = Application.InchesToPoints(0.75) .HeaderMargin = Application.InchesToPoints(0.3) .FooterMargin = Application.InchesToPoints(0.3) End With ActiveWindow.SelectedSheets.PrintOut _ Copies:=1, _ Collate:=True, _ IgnorePrintAreas:=False End Sub |
Unhide all hidden worksheets
By using this code, it enables you to unhide all hidden Worksheets.
| Sub UnhideAllWorksheets() Dim WS As Worksheet ‘Loop through all Worksheet and set them to visible For Each ws In ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets ws.Visible = xlSheetVisible Next ws End Sub |
Resize all charts in a worksheet
If you have many charts and you want them to be organized to a consistent size, a macro can be of aid just by a single click.
‘the width and height can be adjusted as desired by changing the values below.
| Sub Resize_Charts() Dim counter As Integer For counter = 1 To ActiveSheet.ChartObjects.Count ‘change the height and width to the size required With ActiveSheet.ChartObjects(counter) .Width = 500 .Height = 300 End With Next counter End Sub |
Disable page break
Worksheets have page breaks, and you may at some point not prefer this. You can use this simple code to disable page breaks.
| Sub DisablePageBreaks() Dim wb As Workbook Dim wks As Worksheet Application.ScreenUpdating = False For Each wb In Application.Workbooks For Each Sht In wb.Worksheets Sht.DisplayPageBreaks = False Next Sht Next wb Application.ScreenUpdating = True End Sub |
Close all workbooks at once
Before closing, the macro code will first check all the workbooks one by one and have them closed. For those that are not saved, a message will pop up, alerting you whether to save it or not.
| Sub CloseAllWorkbooks() Dim wbs As Workbook For Each wbs In Workbooks wbs.Close SaveChanges:=True Next wb End Sub |
Refresh all pivot tables.
It is of essence to refresh your pivot tables when you are updating your data. Sometimes, you may forget to do so, but excel macros have made it easy by using this code.
| Sub vba_referesh_all_pivots() Dim pt As PivotTable ‘With just one loop, refresh all pivot tables! For Each pt In ActiveWorkbook.PivotTables pt.RefreshTable Next pt End Sub |
Create a table of content
Anyone who has dealt with excel for a long time can testify that scrolling through a Worksheet that is voluminous is hectic and time-consuming. We can create a table of content using macros to make maneuvering easy for us. Just use this code. It will be fun.
| Sub TableofContent() Dim i As Long On Error Resume Next Application.DisplayAlerts = False Worksheets(«Table of Content»).Delete Application.DisplayAlerts = True On Error GoTo 0 ThisWorkbook.Sheets.Add Before:=ThisWorkbook.Worksheets(1) ActiveSheet.Name = «Table of Content» For i = 1 To Sheets.Count With ActiveSheet .Hyperlinks.Add _ Anchor:=ActiveSheet.Cells(i, 1), _ Address:=»», _ SubAddress:=»‘» & Sheets(i).Name & «‘!A1», _ ScreenTip:=Sheets(i).Name, _ TextToDisplay:=Sheets(i).Name End With Next i End Sub |
Convert Range into an image
| Sub PasteAsPicture() Application.CutCopyMode = False Selection.Copy ActiveSheet.Pictures.Paste.Select End Sub |
Activate the data entry form
| Sub DataForm()
‘Show the default data entry form ActiveSheet.ShowDataForm End Sub |
Convert all formulas into values
When you need to use a lot of volatile heavy functions or send a workbook free from all the sketchy and complex formulas- only the result of the calculations rather than the full excel model, it is essential that you convert all formulas to values. Macros help you by using this simple code.
| Sub convertToValues() Dim MyRange As Range Dim MyCell As Range Select Case _ MsgBox(«You Can’t Undo This Action. » _ & «Save Workbook First?», vbYesNoCancel, _ «Alert») Case Is = vbYes ThisWorkbook.Save Case Is = vbCancel Exit Sub End Select Set MyRange = Selection For Each MyCell In MyRange If MyCell.HasFormula Then MyCell.Formula = MyCell.Value End If Next MyCell End Sub |
Reverse Text
Reverse Text is not included in excel since it is not in use or let’s say rarely used. But those who would want to use it to generate special code, for fun or need to see if a string is a palindrome may use the code below. This code has the ability to display Text backward- it actually converts the Text and puts it in reverse.
| Public Function ReverseText(ByVal cell As Range) As String ‘Reverse text using this function ReverseText = VBA.strReverse(cell.Value) End Function ‘Make sure you have a selection ready Sub ReverseTextInSelection() Dim range As Range Selection.Value= Selection.Value ‘Loop through all the cells For Each Range In Selection ‘Call your function range= ReverseText(range) Next Range End Sub |
Activate A1 reference style
| Sub ActivateA1() If Application.ReferenceStyle = xlR1C1 Then Application.ReferenceStyle = xlA1 Else Application.ReferenceStyle = xlA1 End If End Sub |
Convert a date into years
| Sub date2year() Dim tempCell As Range Selection.Value = Selection.Value For Each tempCell In Selection If IsDate(tempCell) = True Then With tempCell .Value = Year(tempCell) .NumberFormat = «0» End With End If Next tempCell End Sub |
Word count from the entire Worksheet
It is possible that as we work on an excel workbook, we may be interested in getting the word count. Unfortunately, Excel does not have an inbuilt word counter, but luckily we may use Macros code to resolve this problem. In relation to other ways that we may use, Macros have proven to be simple to use. The code below will do the word count for you.
| Sub Word_Count_Worksheet() Dim WordCnt As Long Dim rng As Range Dim S As String Dim N As Long For Each rng In ActiveSheet.UsedRange.Cells S = Application.WorksheetFunction.Trim(rng.Text) N = 0 If S <> vbNullString Then N = Len(S) – Len(Replace(S,»,»)) + 1 End If WordCnt = WordCnt + N Next rng MsgBox «There are total » _ & Format(WordCnt, «#,##0») & _ » words in the active worksheet» End Sub |
Remove decimals from numbers
| Sub removeDecimals() Dim lnumber As Double Dim lResult As Long Dim rng As Range For Each rng In Selection rng.Value = Int(rng) rng.NumberFormat = «0» Next rng End Sub |
Add a number in all the numbers
| Sub addNumber() Dim rng As Range Dim i As Integer i = InputBox(«Enter number to multiple», «Input Required») For Each rng In Selection If WorksheetFunction.IsNumber(rng) Then rng.Value = rng + i Else End If Next rng End Sub |
Alternatively, you may use this as an option.
| Sub InsertNumbers() Dim maxNumber As Integer Dim counter As Integer On Error GoTo Last maxNumber = InputBox(«Enter the Max Value», «Generate 1 to n») ‘Generate all the numbers For counter = 1 To maxNumber ActiveCell.Value = counter ‘Move one cell below ActiveCell.Offset(1, 0).Activate Next counter Last: Exit Sub End Sub |
Replace blank cells with zeros
| Sub replaceBlankWithZero()
Dim rng As Range Selection.Value = Selection.Value For Each rng In Selection If rng = «» Or rng = » » Then rng.Value = «0» Else End If Next rng End Sub |
Close all workbooks at once
This process takes place in two steps; the first is declaring an object variable to represent a workbook project, and the second loop all the open Workbook, finalize by saving and closing them.
| Sub CloseAllWorkbooks() Dim wbs As Workbook ‘Loop through all workbooks and close them For Each wbs In Workbooks wbs.Close SaveChanges:=True Next wb End Sub |
If you don’t want to save, change the SaveChange argument to false.
Save each Worksheet as a separate PDF
This code will help you create PDFs from worksheets.
|
Protect all worksheets instantly
It is possible to protect all your Worksheets. You will need to ask the user for the password then it will be used to protect the worksheets.
|
Sub ProtectAllWorksheets() Dim Worksheet As Worksheet Dim pword As String ‘Get the user’s password pword = InputBox(«Enter a Password to secure your worksheets», «Password») ‘Loop through the worksheets toprotect all of them For Each Worksheet In ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets worksheet.Protect Password:=pword Next Worksheet End Sub |
This code will simply enable you to protect the Worksheet with the user-given password.
Automatically insert the date and time stamp in the adjacent cells
To use this code, right-click the worksheet tab you intend to use and choose the view code from the appearing menu >> use the code below and save it. This will automatically put a new timestamp. Depending on your workbook preference Columns A and B can be changed, and the format of mm/dd/yy hh:mm:ss to what you desire.
| Private Sub Worksheet_Change(ByVal Target As Range) ‘UpdatebyKutools20190919 Dim xRInt As Integer Dim xDStr As String Dim xFStr As String On Error Resume Next xDStr = «A» ‘Data Column xFStr = «B» ‘Timstamp Column If (Not Application.Intersect(Me.Range(xDStr & «:» & xDStr), Target) Is Nothing) Then xRInt = Target.Row Me.Range(xFStr & xRInt) = Format(Now(), «mm/dd/yyyy hh:mm:ss») End End |
Highlight blank cells
It is sometimes difficult to identify cells that are black, especially those containing a single space. This code may ease it up for you by checking them out and highlighting them.
| Sub blankWithSpace() Dim rng As Range For Each rng In ActiveSheet.UsedRange If rng.Value = » » Then rng.Style = «Note» End If Next rng End Sub |
Show a welcome message
|
This code will allow you to have a starting message in excel.
Highlight cells with comments
|
Highlight unique values
Sometimes it may be needful for you to find a list of unique values in excel. This code has simplified it all for you.
|
Print comments
If you are interested in printing only the comments, use this code.
|
Insert multiple worksheets
|
Delete all blank sheets
After finishing your work, there might be a necessity to clean up and remove the unnecessary blank sheets that were not used. This process can be automated using this code.
|
Add a workbook to a normal attachment
If you are done editing your Workbook and are now ready to send it via email, the process is already automated by running this code.
|
Sub AttachWorkbookIntoEmailMessage() Dim OutlookApp As Object Dim OutlookMail As Object Set OutlookApp = CreateObject(«Outlook.Application») Set OutlookMail = OutlookApp.CreateItem(0) ‘Let’s create an email message and display it ‘Remember to change the parameters below With OutlookMail .To = «support@myexcelonline.com» .Subject = «Have a look at this workbook.» .Body = «Hey John, Could you help out on this?» .Attachments.Add ActiveWorkbook.FullName .Display End With Set OutlookMail = Nothing Set OutlookApp = Nothing End Sub |
Auto-update pivot table range
| Sub UpdatePivotTableRange() Dim Data_Sheet As Worksheet Dim Pivot_Sheet As Worksheet Dim StartPoint As Range Dim DataRange As Range Dim PivotName As String Dim NewRange As String Dim LastCol As Long Dim lastRow As Long ‘Set Pivot Table & Source Worksheet Set Data_Sheet = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets(«PivotTableData3») Set Pivot_Sheet = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets(«Pivot3») ‘Enter in Pivot Table Name PivotName = «PivotTable2» ‘Defining Staring Point & Dynamic Range Data_Sheet.Activate Set StartPoint = Data_Sheet.Range(«A1») LastCol = StartPoint.End(xlToRight).Column DownCell = StartPoint.End(xlDown).Row Set DataRange = Data_Sheet.Range(StartPoint, Cells(DownCell, LastCol)) NewRange = Data_Sheet.Name & «!» & DataRange.Address(ReferenceStyle:=xlR1C1) ‘Change Pivot Table Data Source Range Address Pivot_Sheet.PivotTables(PivotName). _ ChangePivotCache ActiveWorkbook. _ PivotCaches.Create(SourceType:=xlDatabase, SourceData:=NewRange) ‘Ensure Pivot Table is Refreshed Pivot_Sheet.PivotTables(PivotName).RefreshTable ‘Complete Message Pivot_Sheet.Activate MsgBox «Your Pivot Table is now updated.» End Sub |
Paste the chart as an image
Depending on preference, sometimes you may need your chart as an image. This code enables you to convert your chart to an image. Use this code.
| Sub ConvertChartToPicture() ActiveChart.ChartArea.Copy ActiveSheet.Range(«A1»).Select ActiveSheet.Pictures.Paste.Select End Sub |
Insert a linked picture
The linked image is a feature in Excel that you can use to create dashboards wherein images can be resized and linked to the actual report. The code can aid in creating your own linked image.
|
Remove characters from a string
You can remove a character from starting of a text string by referring to a cell. You can alternatively insert a text into the function number of characters to remove from a text string. Two arguments are in consideration. «rng» for the text string and «cnt» for character count.
To remove the first character of a cell, enter 1 in cnt.
| Public Function removeFirstC(rng As String, cnt As Long) removeFirstC = Right(rng,Len(rng) – cnt) End |
Remove time and date
This code will help you delete rows based on the date.
| ‘ If Format(Cells(iCntr, 1), «dd-mm-yyyy») = Format(Now(), «dd-mm-yyyy») Then Rows(iCntr).Delete End If |
| Starting program and sub procedure to write VBA code to delete rows based on date. Sub sbDelete_Rows_Based_On_Date() ‘Declaring the variable lRow as long to store the last row number Dim lRow As Long ‘Declaring the variable iCntr as long to use in the For loop Dim iCntr As Long ‘Assigning the last row value to the variable lRow lRow = 20 ‘Using for loop ‘We are checking the each cell value if the cell value equals today’s date. ‘And deleting the row if true For iCntr = lRow To 1 Step -1 |
Convert to upper case
Sub convertUpperCase()
Dim Rng As Range
For Each Rng In Selection
If Application.WorksheetFunction.IsText(Rng) Then
Rng.Value = UCase(Rng)
End If
Next
End Sub
This code will check the Range of selected cells and convert it into uppercase text when run.
Macro code Removing a character from selection in excel
Sub removeChar()
Dim Rng As Range
Dim rc As String
rc = InputBox(«characters», «Enter your Value»)
For Each Rng In Selection
Selection.Replace What:=rc, Replacement:=»»
Next
End Sub
Particular characters may be removed from a selected cell by using this code. An input box will display where you will enter the character you intend to remove.
Add A-Z Alphabets in a range
| Sub addsAlphabets1() Dim i As Integer For i = 65 To 90 ActiveCell.Value = Chr(i) ActiveCell.Offset(1, 0).Select Next i End Sub Sub addsAlphabets2() Dim i As Integer For i = 97 To 122 ActiveCell.Value = Chr(i) ActiveCell.Offset(1, 0).Select Next i End Sub |
Hide pivot table subtotals
Modifying pivot tables is one of the many functionalities entailed in Excel Macros. We can use macros modifying feature that hides pivot table subtotal using this code.
|
‘Select a cell first from your pivot table Sub HidePivotTableSubtotals() Dim pTable As PivotTable Dim pField As PivotField On Error Resume Next ‘Get the pivot table first Set pTable = ActiveSheet.PivotTables(ActiveCell.PivotTable.name) ‘Check if a pivot table is found If pTable Is Nothing Then MsgBox «Please select a cell first from your Pivot Table.» Exit Sub End If ‘For each subtotal, make it hidden For Each pField In pTable.PivotFields pField.Subtotals(1) = True pField.Subtotals(1) = False Next pField End Sub |
Create a pivot table
To create a pivot table, eight steps are important.
1. Variable Declaration- you need first to declare the variables needed in our code to define different things

Dim PSheet As Worksheet (create a sheet for the pivot table)
Dim DSheet As Worksheet (use as datasheet)
Dim PCache As PivotCache (use as name for pivot table cache) Dim PTable As PivotTable(use as name for pivot table)
Dim PRange As Range(define a source of data range)
Dim LastRow As Long
Dim LastCol As Long

3. Define the Range of data
4. The next thing is to create a pivot cache
5. Insert a black pivot table
6. Add rows and columns
7. Put data fields
8. Lastly format pivot table
The code summary of the steps is simplified below and can be used to create a pivot table.
| Sub InsertPivotTable() ‘Macro By ExcelChamps ‘Declare Variables Dim PSheet As Worksheet Dim DSheet As Worksheet Dim PCache As PivotCache Dim PTable As PivotTable Dim PRange As Range Dim LastRow As Long Dim LastCol As Long ‘Insert a New Blank Worksheet On Error Resume Next Application.DisplayAlerts = False Worksheets(«PivotTable»).Delete Sheets.Add Before:=ActiveSheet ActiveSheet.Name = «PivotTable» Application.DisplayAlerts = True Set PSheet = Worksheets(«PivotTable») Set DSheet = Worksheets(«Data») ‘Define Data Range LastRow = DSheet.Cells(Rows.Count, 1).End(xlUp).Row LastCol = DSheet.Cells(1, Columns.Count).End(xlToLeft).Column Set PRange = DSheet.Cells(1, 1).Resize(LastRow, LastCol) ‘Define Pivot Cache Set PCache = ActiveWorkbook.PivotCaches.Create _ (SourceType:=xlDatabase, SourceData:=PRange). _ CreatePivotTable(TableDestination:=PSheet.Cells(2, 2), _ TableName:=»SalesPivotTable») ‘Insert Blank Pivot Table Set PTable = PCache.CreatePivotTable _ (TableDestination:=PSheet.Cells(1, 1), TableName:=»SalesPivotTable») ‘Insert Row Fields With ActiveSheet.PivotTables(«SalesPivotTable»).PivotFields(«Year») .Orientation = xlRowField .Position = 1 End With With ActiveSheet.PivotTables(«SalesPivotTable»).PivotFields(«Month») .Orientation = xlRowField .Position = 2 End With ‘Insert Column Fields With ActiveSheet.PivotTables(«SalesPivotTable»).PivotFields(«Zone») .Orientation = xlColumnField .Position = 1 End With ‘Insert Data Field With ActiveSheet.PivotTables(«SalesPivotTable») .PivotFields («Amount») .Orientation = xlDataField .Function = xlSum .NumberFormat = «#,##0» .Name = «Revenue « End With ‘Format Pivot Table ActiveSheet.PivotTables(«SalesPivotTable»).ShowTableStyleRowStripes = True ActiveSheet.PivotTables(«SalesPivotTable»).TableStyle2 = «PivotStyleMedium9» End Sub |
Change chart type
Changing the property of the chart may be necessary at times when using Excel. This code can be captured in macros and may be helpful to automate the whole process.
|
‘Select your chart first before running this Sub ChangeChartType() ‘This is the clustered column chart, and you can change the type ‘Other chart types are listed at: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/office/vba/api/Excel.XlChartType ActiveChart.ChartType = xlColumnClustered End Sub |
Use Text to speech
If you have an excel edition with Text to speech installed, you can make excel speak using Macros code.
To specify the cell text to be put to speech, use the code below. For example, our code will speak out cell A1 to change to A2 (1, 2) and so on.
| Sub SayThisCell() Cells(1, 1).Speak End Sub Macros can also speak the content of a string by using this code Sub SayThisString() Dim SayThis As String SayThis = «Using excel has given me a nice experience and has made it easy for me in accounting.» Application.Speech.Speak (SayThis) End Sub |
Use goal seek
Goal seek is an amazing feature in excel that takes out the guesswork for you and predicts the value of the input needed to attain a specific goal. Let’s say you expected outcome in mind but no idea of the starting amount that you should invest. Macros can help you execute such kinds of problems just by running this code.
|
‘Make sure the Worksheet is selected to execute the Goal Seek on Sub GoalSeekVBA() Dim TargetGoal As Long ‘Get the target value from the user. TargetGoal = InputBox(«Enter the target value», «Enter Goal») ‘Make sure to change the cell that you want to be changed with the goal ActiveSheet.Range(«E9»).GoalSeek _ Goal:=TargetGoal, _ ChangingCell:=Range(«A9») End Sub |
Create a backup of a current workbook
If you have a very important workbook that you do not want to lose by any chance and need to frequently back it up, Macros has a Code to sort you out.
|
Sub CreateBackup() ‘Create a backup on the specified folder with the date today included ‘Don’t forget to change folder.» ThisWorkbook.SaveCopyAs Filename:=»C:ChangeMe» & Format(Date, «mmddyyyy») & «-» & ThisWorkbook.name End Sub |
I wish this could be done exhaustively, but there is still a lot to learn. Learning is a lifetime work. Using excel is becoming easier and enjoyable and especially with the aid of macros code which automates processes. May this resource not be the end of it. Explore more.
Время на прочтение
7 мин
Количество просмотров 312K
Приветствую всех.
В этом посте я расскажу, что такое VBA и как с ним работать в Microsoft Excel 2007/2010 (для более старых версий изменяется лишь интерфейс — код, скорее всего, будет таким же) для автоматизации различной рутины.

VBA (Visual Basic for Applications) — это упрощенная версия Visual Basic, встроенная в множество продуктов линейки Microsoft Office. Она позволяет писать программы прямо в файле конкретного документа. Вам не требуется устанавливать различные IDE — всё, включая отладчик, уже есть в Excel.
Еще при помощи Visual Studio Tools for Office можно писать макросы на C# и также встраивать их. Спасибо, FireStorm.
Сразу скажу — писать на других языках (C++/Delphi/PHP) также возможно, но требуется научится читать, изменять и писать файлы офиса — встраивать в документы не получится. А интерфейсы Microsoft работают через COM. Чтобы вы поняли весь ужас, вот Hello World с использованием COM.
Поэтому, увы, будем учить Visual Basic.
Чуть-чуть подготовки и постановка задачи
Итак, поехали. Открываем Excel.
Для начала давайте добавим в Ribbon панель «Разработчик». В ней находятся кнопки, текстовые поля и пр. элементы для конструирования форм.
Появилась вкладка.
Теперь давайте подумаем, на каком примере мы будем изучать VBA. Недавно мне потребовалось красиво оформить прайс-лист, выглядевший, как таблица. Идём в гугл, набираем «прайс-лист» и качаем любой, который оформлен примерно так (не сочтите за рекламу, пожалуйста):
То есть требуется, чтобы было как минимум две группы, по которым можно объединить товары (в нашем случае это будут Тип и Производитель — в таком порядке). Для того, чтобы предложенный мною алгоритм работал корректно, отсортируйте товары так, чтобы товары из одной группы стояли подряд (сначала по Типу, потом по Производителю).
Результат, которого хотим добиться, выглядит примерно так:
Разумеется, если смотреть прайс только на компьютере, то можно добавить фильтры и будет гораздо удобнее искать нужный товар. Однако мы хотим научится кодить и задача вполне подходящая, не так ли?
Кодим
Для начала требуется создать кнопку, при нажатии на которую будет вызываться наша програма. Кнопки находятся в панели «Разработчик» и появляются по кнопке «Вставить». Вам нужен компонент формы «Кнопка». Нажали, поставили на любое место в листе. Далее, если не появилось окно назначения макроса, надо нажать правой кнопкой и выбрать пункт «Назначить макрос». Назовём его FormatPrice. Важно, чтобы перед именем макроса ничего не было — иначе он создастся в отдельном модуле, а не в пространстве имен книги. В этому случае вам будет недоступно быстрое обращение к выделенному листу. Нажимаем кнопку «Новый».
И вот мы в среде разработки VB. Также её можно вызвать из контекстного меню командой «Исходный текст»/«View code».
Перед вами окно с заглушкой процедуры. Можете его развернуть. Код должен выглядеть примерно так:
Sub FormatPrice()End Sub
Напишем Hello World:
Sub FormatPrice()
MsgBox "Hello World!"
End Sub
И запустим либо щелкнув по кнопке (предварительно сняв с неё выделение), либо клавишей F5 прямо из редактора.
Тут, пожалуй, следует отвлечься на небольшой ликбез по поводу синтаксиса VB. Кто его знает — может смело пропустить этот раздел до конца. Основное отличие Visual Basic от Pascal/C/Java в том, что команды разделяются не ;, а переносом строки или двоеточием (:), если очень хочется написать несколько команд в одну строку. Чтобы понять основные правила синтаксиса, приведу абстрактный код.
Примеры синтаксиса
' Процедура. Ничего не возвращает
' Перегрузка в VBA отсутствует
Sub foo(a As String, b As String)
' Exit Sub ' Это значит "выйти из процедуры"
MsgBox a + ";" + b
End Sub' Функция. Вовращает Integer
Function LengthSqr(x As Integer, y As Integer) As Integer
' Exit Function
LengthSqr = x * x + y * y
End FunctionSub FormatPrice()
Dim s1 As String, s2 As String
s1 = "str1"
s2 = "str2"
If s1 <> s2 Then
foo "123", "456" ' Скобки при вызове процедур запрещены
End IfDim res As sTRING ' Регистр в VB не важен. Впрочем, редактор Вас поправит
Dim i As Integer
' Цикл всегда состоит из нескольких строк
For i = 1 To 10
res = res + CStr(i) ' Конвертация чего угодно в String
If i = 5 Then Exit For
Next iDim x As Double
x = Val("1.234") ' Парсинг чисел
x = x + 10
MsgBox xOn Error Resume Next ' Обработка ошибок - игнорировать все ошибки
x = 5 / 0
MsgBox xOn Error GoTo Err ' При ошибке перейти к метке Err
x = 5 / 0
MsgBox "OK!"
GoTo ne
Err:
MsgBox
"Err!"
ne:
On Error GoTo 0 ' Отключаем обработку ошибок
' Циклы бывает, какие захотите
Do While True
Exit DoLoop 'While True
Do 'Until False
Exit Do
Loop Until False
' А вот при вызове функций, от которых хотим получить значение, скобки нужны.
' Val также умеет возвращать Integer
Select Case LengthSqr(Len("abc"), Val("4"))
Case 24
MsgBox "0"
Case 25
MsgBox "1"
Case 26
MsgBox "2"
End Select' Двухмерный массив.
' Можно также менять размеры командой ReDim (Preserve) - см. google
Dim arr(1 to 10, 5 to 6) As Integer
arr(1, 6) = 8Dim coll As New Collection
Dim coll2 As Collection
coll.Add "item", "key"
Set coll2 = coll ' Все присваивания объектов должны производится командой Set
MsgBox coll2("key")
Set coll2 = New Collection
MsgBox coll2.Count
End Sub
Грабли-1. При копировании кода из IDE (в английском Excel) есь текст конвертируется в 1252 Latin-1. Поэтому, если хотите сохранить русские комментарии — надо сохранить крокозябры как Latin-1, а потом открыть в 1251.
Грабли-2. Т.к. VB позволяет использовать необъявленные переменные, я всегда в начале кода (перед всеми процедурами) ставлю строчку Option Explicit. Эта директива запрещает интерпретатору заводить переменные самостоятельно.
Грабли-3. Глобальные переменные можно объявлять только до первой функции/процедуры. Локальные — в любом месте процедуры/функции.
Еще немного дополнительных функций, которые могут пригодится: InPos, Mid, Trim, LBound, UBound. Также ответы на все вопросы по поводу работы функций/их параметров можно получить в MSDN.
Надеюсь, что этого Вам хватит, чтобы не пугаться кода и самостоятельно написать какое-нибудь домашнее задание по информатике. По ходу поста я буду ненавязчиво знакомить Вас с новыми конструкциями.
Кодим много и под Excel
В этой части мы уже начнём кодить нечто, что умеет работать с нашими листами в Excel. Для начала создадим отдельный лист с именем result (лист с данными назовём data). Теперь, наверное, нужно этот лист очистить от того, что на нём есть. Также мы «выделим» лист с данными, чтобы каждый раз не писать длинное обращение к массиву с листами.
Sub FormatPrice()
Sheets("result").Cells.Clear
Sheets("data").Activate
End Sub
Работа с диапазонами ячеек
Вся работа в Excel VBA производится с диапазонами ячеек. Они создаются функцией Range и возвращают объект типа Range. У него есть всё необходимое для работы с данными и/или оформлением. Кстати сказать, свойство Cells листа — это тоже Range.
Примеры работы с Range
Sheets("result").Activate
Dim r As Range
Set r = Range("A1")
r.Value = "123"
Set r = Range("A3,A5")
r.Font.Color = vbRed
r.Value = "456"
Set r = Range("A6:A7")
r.Value = "=A1+A3"
Теперь давайте поймем алгоритм работы нашего кода. Итак, у каждой строчки листа data, начиная со второй, есть некоторые данные, которые нас не интересуют (ID, название и цена) и есть две вложенные группы, к которым она принадлежит (тип и производитель). Более того, эти строки отсортированы. Пока мы забудем про пропуски перед началом новой группы — так будет проще. Я предлагаю такой алгоритм:
- Считали группы из очередной строки.
- Пробегаемся по всем группам в порядке приоритета (вначале более крупные)
- Если текущая группа не совпадает, вызываем процедуру AddGroup(i, name), где i — номер группы (от номера текущей до максимума), name — её имя. Несколько вызовов необходимы, чтобы создать не только наш заголовок, но и всё более мелкие.
- После отрисовки всех необходимых заголовков делаем еще одну строку и заполняем её данными.
Для упрощения работы рекомендую определить следующие функции-сокращения:
Function GetCol(Col As Integer) As String
GetCol = Chr(Asc("A") + Col)
End FunctionFunction GetCellS(Sheet As String, Col As Integer, Row As Integer) As Range
Set GetCellS = Sheets(Sheet).Range(GetCol(Col) + CStr(Row))
End FunctionFunction GetCell(Col As Integer, Row As Integer) As Range
Set GetCell = Range(GetCol(Col) + CStr(Row))
End Function
Далее определим глобальную переменную «текущая строчка»: Dim CurRow As Integer. В начале процедуры её следует сделать равной единице. Еще нам потребуется переменная-«текущая строка в data», массив с именами групп текущей предыдущей строк. Потом можно написать цикл «пока первая ячейка в строке непуста».
Глобальные переменные
Option Explicit ' про эту строчку я уже рассказывал
Dim CurRow As Integer
Const GroupsCount As Integer = 2
Const DataCount As Integer = 3
FormatPrice
Sub FormatPrice()
Dim I As Integer ' строка в data
CurRow = 1
Dim Groups(1 To GroupsCount) As String
Dim PrGroups(1 To GroupsCount) As String
Sheets(
"data").Activate
I = 2
Do While True
If GetCell(0, I).Value = "" Then Exit Do
' ...
I = I + 1
Loop
End Sub
Теперь надо заполнить массив Groups:
На месте многоточия
Dim I2 As Integer
For I2 = 1 To GroupsCount
Groups(I2) = GetCell(I2, I)
Next I2
' ...
For I2 = 1 To GroupsCount ' VB не умеет копировать массивы
PrGroups(I2) = Groups(I2)
Next I2
I = I + 1
И создать заголовки:
На месте многоточия в предыдущем куске
For I2 = 1 To GroupsCount
If Groups(I2) <> PrGroups(I2) Then
Dim I3 As Integer
For I3 = I2 To GroupsCount
AddHeader I3, Groups(I3)
Next I3
Exit For
End If
Next I2
Не забудем про процедуру AddHeader:
Перед FormatPrice
Sub AddHeader(Ty As Integer, Name As String)
GetCellS("result", 1, CurRow).Value = Name
CurRow = CurRow + 1
End Sub
Теперь надо перенести всякую информацию в result
For I2 = 0 To DataCount - 1
GetCellS("result", I2, CurRow).Value = GetCell(I2, I)
Next I2
Подогнать столбцы по ширине и выбрать лист result для показа результата
После цикла в конце FormatPrice
Sheets("Result").Activate
Columns.AutoFit
Всё. Можно любоваться первой версией.
Некрасиво, но похоже. Давайте разбираться с форматированием. Сначала изменим процедуру AddHeader:
Sub AddHeader(Ty As Integer, Name As String)
Sheets("result").Range("A" + CStr(CurRow) + ":C" + CStr(CurRow)).Merge
' Чтобы не заводить переменную и не писать каждый раз длинный вызов
' можно воспользоваться блоком With
With GetCellS("result", 0, CurRow)
.Value = Name
.Font.Italic = True
.Font.Name = "Cambria"
Select Case Ty
Case 1 ' Тип
.Font.Bold = True
.Font.Size = 16
Case 2 ' Производитель
.Font.Size = 12
End Select
.HorizontalAlignment = xlCenter
End With
CurRow = CurRow + 1
End Sub
Уже лучше:
Осталось только сделать границы. Тут уже нам требуется работать со всеми объединёнными ячейками, иначе бордюр будет только у одной:
Поэтому чуть-чуть меняем код с добавлением стиля границ:
Sub AddHeader(Ty As Integer, Name As String)
With Sheets("result").Range("A" + CStr(CurRow) + ":C" + CStr(CurRow))
.Merge
.Value = Name
.Font.Italic = True
.Font.Name = "Cambria"
.HorizontalAlignment = xlCenterSelect Case Ty
Case 1 ' Тип
.Font.Bold = True
.Font.Size = 16
.Borders(xlTop).Weight = xlThick
Case 2 ' Производитель
.Font.Size = 12
.Borders(xlTop).Weight = xlMedium
End Select
.Borders(xlBottom).Weight = xlMedium ' По убыванию: xlThick, xlMedium, xlThin, xlHairline
End With
CurRow = CurRow + 1
End Sub
Осталось лишь добится пропусков перед началом новой группы. Это легко:
В начале FormatPrice
Dim I As Integer ' строка в data
CurRow = 0 ' чтобы не было пропуска в самом начале
Dim Groups(1 To GroupsCount) As String
В цикле расстановки заголовков
If Groups(I2) <> PrGroups(I2) Then
CurRow = CurRow + 1
Dim I3 As Integer
В точности то, что и хотели.
Надеюсь, что эта статья помогла вам немного освоится с программированием для Excel на VBA. Домашнее задание — добавить заголовки «ID, Название, Цена» в результат. Подсказка: CurRow = 0 CurRow = 1.
Файл можно скачать тут (min.us) или тут (Dropbox). Не забудьте разрешить исполнение макросов. Если кто-нибудь подскажет человеческих файлохостинг, залью туда.
Спасибо за внимание.
Буду рад конструктивной критике в комментариях.
UPD: Перезалил пример на Dropbox и min.us.
UPD2: На самом деле, при вызове процедуры с одним параметром скобки можно поставить. Либо использовать конструкцию Call Foo(«bar», 1, 2, 3) — тут скобки нужны постоянно.