After you create a table, Microsoft Office Word 2007 offers you many ways to format that table. If you decide to use Table Styles, you can format your table all at once, and even see a preview of what your table will look like formatted in a particular style before you actually apply the style.
You can create a custom look for tables by splitting or merging cells, adding or deleting columns or rows, or adding borders. If you’re working with a long table, you can repeat the table headings on each page on which the table appears. To prevent awkward page breaks that disrupt the flow of your table, you can also specify just how and where the table should break across pages.
What do you want to do?
-
Use Table Styles to format an entire table
-
Add or remove borders
-
Display or hide gridlines
-
Add a cell, row, or column
-
Delete a cell, row, or column
-
Merge or split cells
-
Repeat a table heading on subsequent pages
-
Control where a table is divided
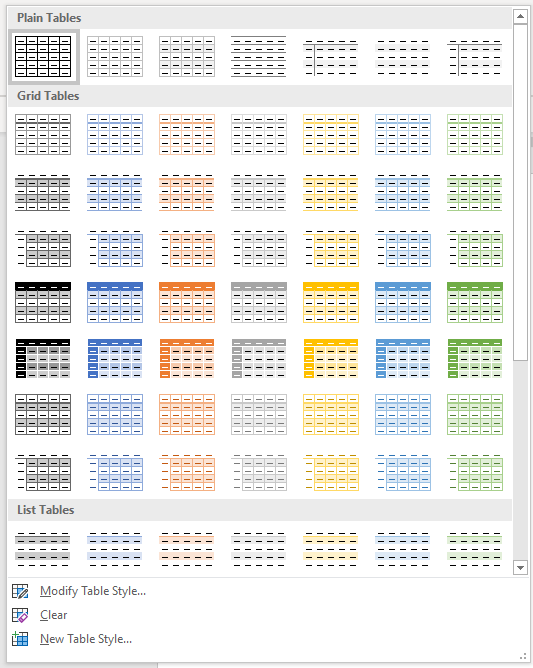
Use Table Styles to format an entire table
After you create a table, you can format the entire table by using Table Styles. By resting your pointer over each of the preformatted table styles, you can preview what the table will look like.
-
Click in the table that you want to format.
-
Under Table Tools, click the Design tab.
-
In the Table Styles group, rest the pointer over each table style until you find a style that you want to use.
Note: To see more styles, click the More arrow
.
-
Click the style to apply it to the table.
-
In the Table Style Options group, select or clear the check box next to each the table element to apply or remove the selected style.
Top of Page
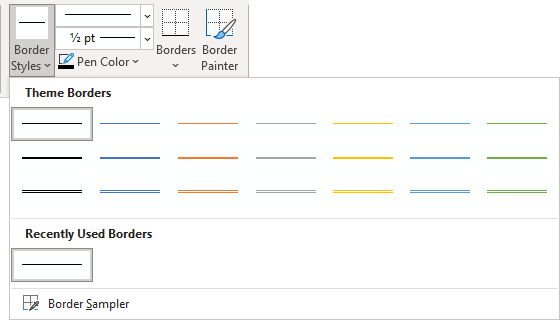
Add or remove borders
You can add or remove borders to format a table the way that you want.
Add table borders
-
Under Table Tools, click the Layout tab.
-
In the Table group, click Select, and then click Select Table.
-
Under Table Tools, click the Design tab.
-
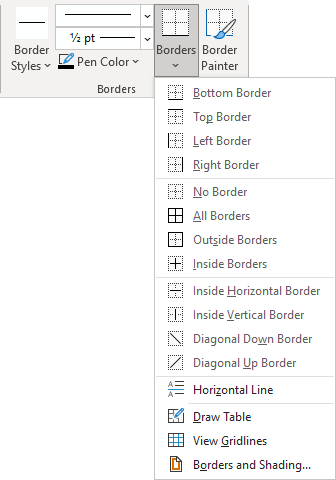
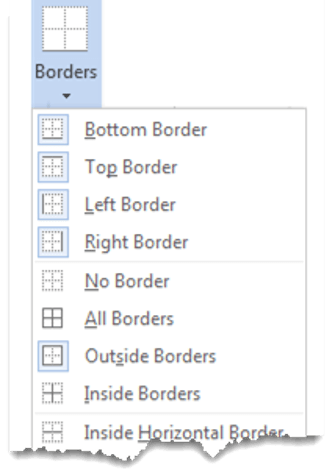
In the Table Styles group, click Borders, and then do one of
the following:-
Click one of the predefined border sets.
-
Click Borders and Shading, click the Borders tab, and then choose the options that you want.
-
Remove table borders from the whole table
-
Under Table Tools, click the Layout tab.
-
In the Table group, click Select, and then click Select Table.
-
Under Table Tools, click the Design tab.
-
In the Table Styles group, click Borders, and then click No Border.
Add table borders to specified cells only
-
On the Home tab, in the Paragraph group, click Show/Hide.
-
Select the cells that you want, including their end-of-cell marks.
-
Under Table Tools, click the Design tab.
-
In the Table Styles group, click Borders, and then click the border that you want to add.
Remove table borders from specified cells only
-
On the Home tab, in the Paragraph group, click Show/Hide.
-
Select the cells that you want, including their end-of-cell marks.
-
Under Table Tools, click the Design tab.
-
In the Table Styles group, click Borders, and then click No Border.
Top of Page
Display or hide gridlines
Gridlines show the cell boundaries of a table on the screen wherever the table doesn’t have borders applied. If you hide the gridlines in a table that has borders, you won’t see the change because the gridlines are behind the borders. To view the gridlines, remove the borders.
Unlike borders, gridlines appear only on the screen; they are never printed. If you turn off gridlines, the table is displayed as it will be printed.
Note: Gridlines are not visible when you view a document in a Web browser or in Print Preview.
Display or hide table gridlines in a document
-
Under Table Tools, on the Layout tab, in the Table group, click View Gridlines.
Top of Page
Add a cell, row, or column
Add a cell
-
Click in a cell that is located just to the right of or above where you
want to insert a cell. -
Under Table Tools, on the Layout tab, click the Rows & Columns Dialog Box Launcher.
-
Click one of the following options:
|
Click this |
To do this |
|
Shift cells right |
Insert a cell and move all other cells in that row to the right. Note: This option may result in a row that has more cells than the other rows. |
|
Shift cells down |
Insert a cell and move remaining existing cells in that column down one row each. A new row will be added at the bottom of the table to contain the last existing cell. |
|
Insert entire row |
Insert a row just above the cell that you clicked in. |
|
Insert entire column |
Insert a column just to the right of the cell that you clicked in. |
Add a row
-
Click in a cell that is located just below or above where you want to add a row.
-
Under Table Tools, click the Layout tab.
-
Do one of the following:
-
To add a row just above the cell that you clicked in, in the Rows and Columns group, click Insert Above.
-
To add a row just below the cell that you clicked in, in the Rows and Columns group, click Insert Below.
-
Add a column
-
Click in a cell that is located just to the right or left of where you want to add a column.
-
Under Table Tools, click the Layout tab.
-
Do one of the following:
-
To add a column just to the left of the cell that you clicked in, in the Rows and Columns group, click Insert Left.
-
To add a column just to the right of the cell that you clicked in, in the Rows and Columns group, click Insert Right.
-
Top of Page
Delete a cell, row, or column
-
Do one of the following:
To select
Do this
A cell
Click the left edge of the cell.
.
A row
Click to the left of the row.
A column
Click the column’s top gridline or top border.
-
Under Table Tools, click the Layout tab.
-
In the Rows & Columns group, click Delete, and then click Delete Cells, Delete Rows, or Delete Columns, as appropriate.
Top of Page
Merge or split cells
Merge cells
You can combine two or more cells in the same row or column into a single cell. For example, you can merge several cells horizontally to create a table heading that spans several columns.
-
Select the cells that you want to merge by clicking the left edge of a cell and then dragging across the other cells that you want.
-
Under Table Tools, on the Layout tab, in the Merge group, click Merge Cells.
Split cells
-
Click in a cell, or select multiple cells that you want to split.
-
Under Table Tools, on the Layout tab, in the Merge group, click Split Cells.
-
Enter the number of columns or rows that you want to split the selected cells into.
Top of Page
Repeat a table heading on subsequent pages
When you work with a very long table, it will be divided wherever a page break occurs. You can make adjustments to the table so that the table headings are repeated on each page.
Repeated table headings are visible only in Print Layout view and when you print the document.
-
Select the heading row or rows. The selection must include the first row of the table.
-
Under Table Tools, on the Layout tab, in the Data group, click Repeat Header Rows.
Note: Word automatically repeats the table headings on each new page that results from an automatic page break. Word does not repeat a heading if you insert a manual page break within a table.
Top of Page
Control where a table is divided
When you work with a very long table, it must be divided wherever a page break occurs. By default, if a page break occurs within a large row, Microsoft Word allows a page break to divide the row between the two pages.
You can make adjustments to the table to make sure that the information appears as you want it to when the table spans multiple pages.
Prevent a
table row from breaking across pages
-
Click in the table.
-
Under Table Tools, click the Layout tab.
-
In the Table group, click Properties, and then click the Row tab.
-
Clear the Allow row to break across pages check box.
Force a table to break across pages at a particular row
-
Click in the row that you want to appear on the next page.
-
Press CTRL+ENTER.
Top of Page
Select the table
- Using the mouse: Move the mouse over the table until you see the table selection icons in the upper-left corner of the table and click it:
Note: You can also click on the table selection icon in the bottom-right corner (resizing handle) for the same effect.
- Using the keyboard: To select table elements, on the Table Layout tab, on the Table group, click the Select button, then select the option you prefer:
- Select Cell
- Select Column
- Select Row
- Select Table
Format the table
After positioning the cursor anywhere in a table or selecting a table element, Word shows two tabs: Table Design and Layout. E.g.:
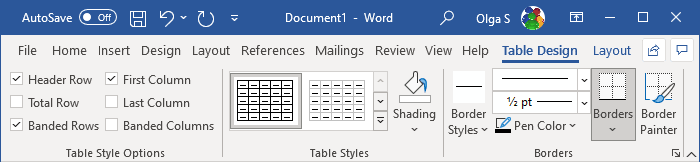
See also Select and format table elements in Word.
Apply a predefined Table style
There are several predefined styles you can use for the table. Styles include a variety of borders, colors, and other attributes that give a table a very professional appearance.
To choose any of the predefined styles, do the following:
1. Select the table.
2. On the Table Design tab, in the Table Styles group, in the Styles Gallery, click the More arrow to see the complete list of styles:
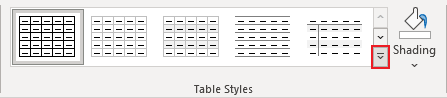
3. Select the table style you want:
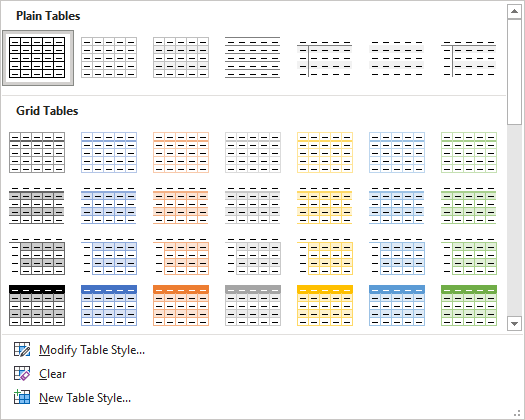
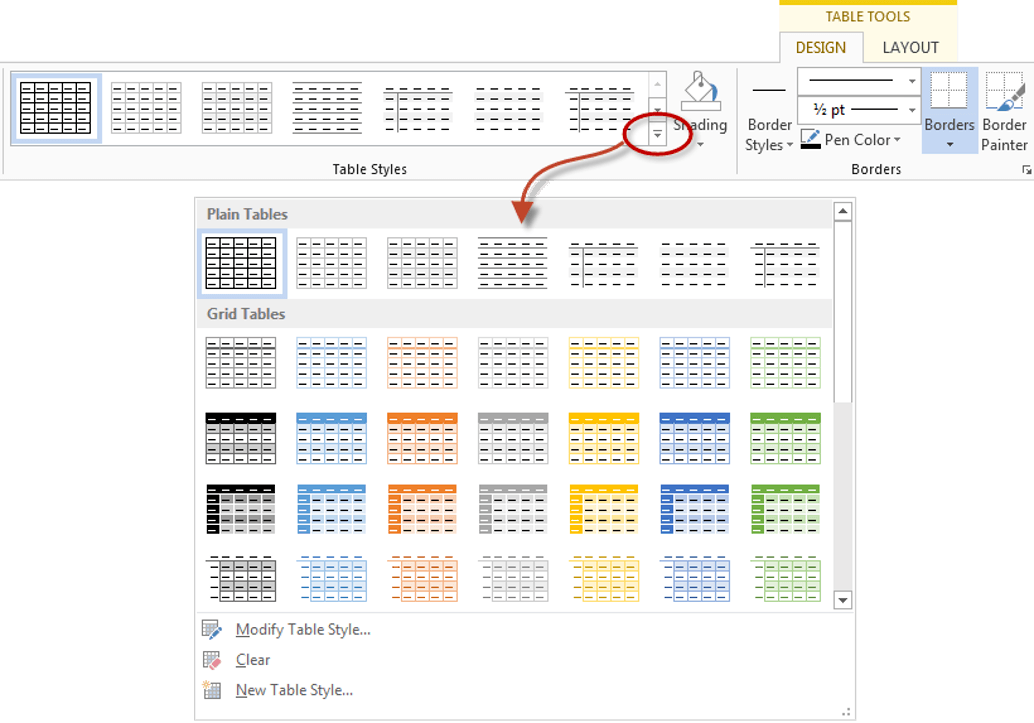
The Table Styles gallery includes three categories of styles:
- Plain Tables have minimal formatting.
- Grid Tables include vertical separators between columns.
- List Tables do not include vertical column separators:

Note: The selected style overrides any previously added style changes for the table.
Modify the table style options
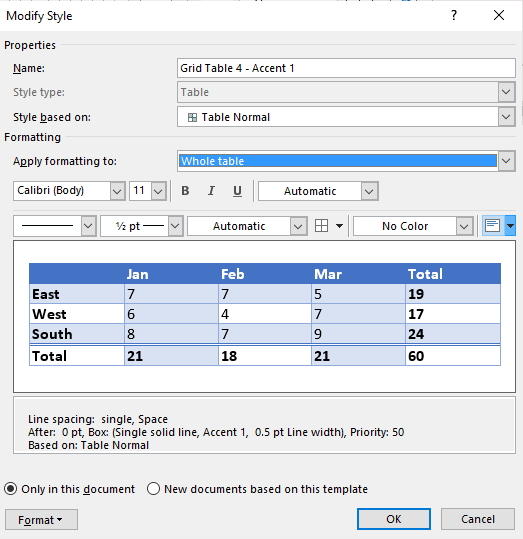
To change the table or selected style, on the Table Design tab, in the Table Style group, click Modify Table Style…:
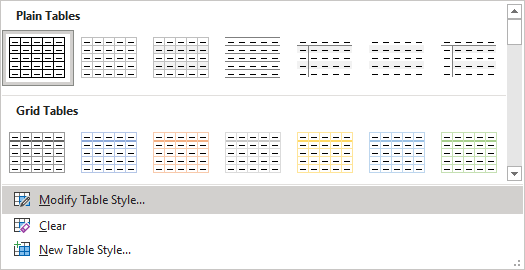
In the Modify Style dialog box, make changes you want:
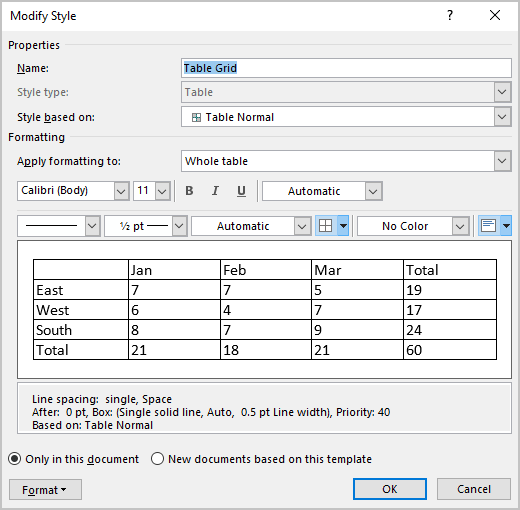
Note: Click the Format button at the bottom of the dialog box to change other options such as Font or Paragraph. See also how to clear formatting.
Customize the table formatting
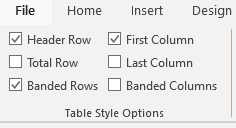
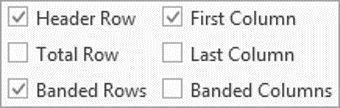
After applying a table style, you can turn various options on or off to change their appearance. On the Table Design tab, in the Table Style Options group, there are six options:
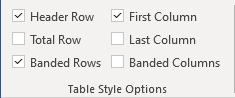
- Header Row is the first row of the table that contains Headers that helps identify the contents of a particular column. Usually, the Header Row is formatted differently and should be repeated at the beginning of each new page for tables that extend beyond one page.
Note: According to most requirements, data tables should have a header row to provide a contextual structure that aids navigation.
- Total Row is the last row of the table. If this option is selected, the last row will be formatted differently from the body rows, designed to summarize the rows above it (see how to insert formulas).
- First Column used special formatting to the column. Usually, the First Column contains the row headings.
- Last Column applies special formatting to the column to summarize the earlier columns (see how to insert formulas).
- Banded Rows and Banded Columns alternate the background color of rows and columns (see how to change the background color for the selected cells below).
Note: Certain Table Style Options may have a different effect depending on the Table Style you’ve chosen. You might need to experiment to get the look you want.
Apply the border styles
To apply and remove cell borders, do the following:
1. Select the cells or entire table to which you want to add a border.
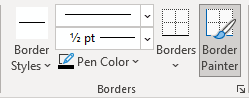
2. On the Table Design tab, in the Borders group, choose the desired Border Styles, Line Style, Line Weight, and Pen Color:
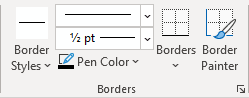
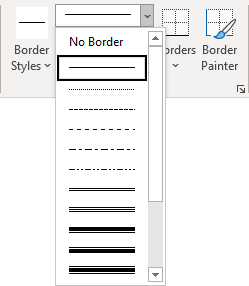
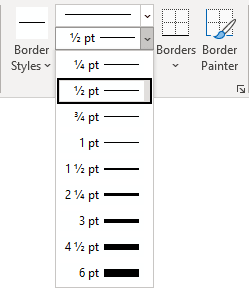
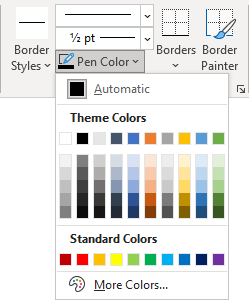
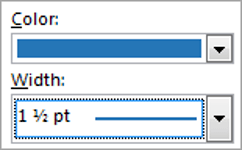
- Select the predefined Line Style, Line Weight, and Line Color from the Border Styles dropdown list:
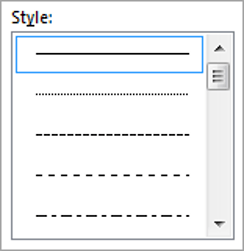
- Select the Line Style:
- Select a border thickness from the Line Weight dropdown list:
- Select the border color from the Pen Color dropdown list:
- Select the borders from the Borders dropdown list:
Note: Select No Borders from the Borders dropdown list to remove borders from the selected cells.
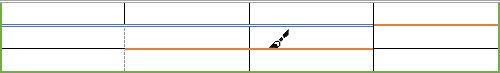
- Draw the border where you want:
- After selecting border style or color, the Border Painter button is automatically checked, or
- If all that you want is selected already, just click the Border Painter button by yourself:
After any of these actions, your cursor changes to the brush. Now, draw the border where you need it:
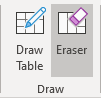
Note: Use the Eraser button in the Draw group on the Table Layout tab to remove the unnecessary border:
Apply background colors and shading
To change the background color for some table elements, select them, then on the Table Design tab, in the Table Styles group, click the Shading button, then select the background color you prefer:
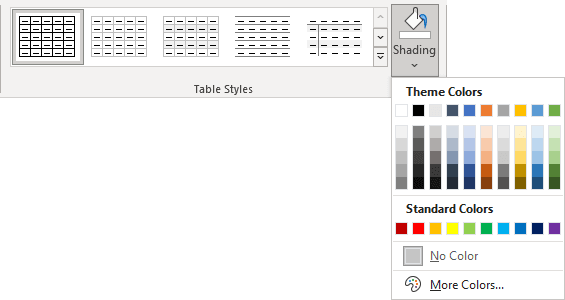
Note: To use a pattern instead of a solid color, on the Table Design tab, in the Borders group, click the dialog box launcher:
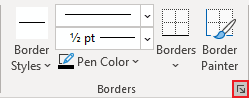
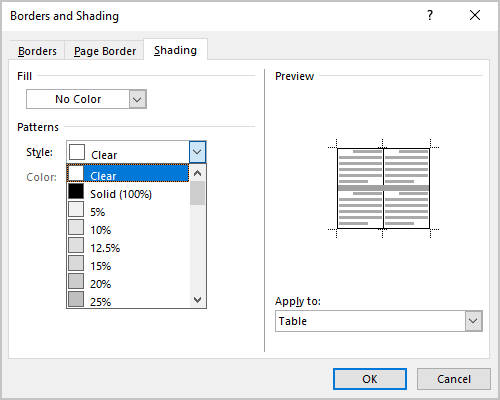
In the Borders and Shading dialog box, on the Shading tab, select a pattern in the Style list:
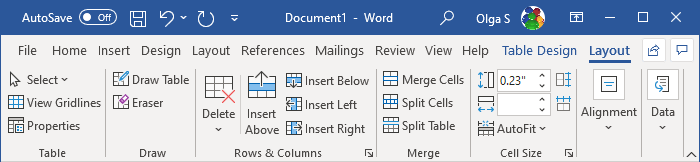
Layout of the table
The Table Layout tab includes commands for changing the entire table format, as well as commands for changing the appearance of individual table components such as cells, columns, rows:
See Select and format table elements in Word for more details.
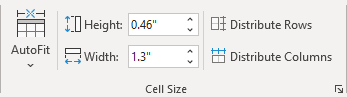
Resize a table
- Using the mouse: To resize a table in a Word document, move the mouse over the table until you see the table resizing icons (handle) in the bottom-right corner of the table and click it:
Drag the table to the size you need, and then release the handle.
- Using the keyboard: Select a table (see also how to resize individual cells, specific rows, or columns); the do one of the following:
- On the Layout tab, in the Cell Size group, change the values in the Height and Width fields:
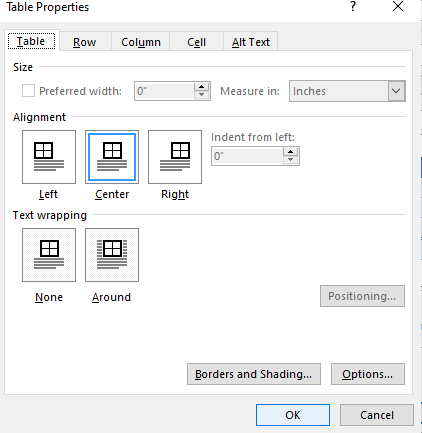
- Open the Table Properties dialog box by doing one of the following:
- On the Table Layout tab, in the Table group, click the Properties button:
- Right-click the table and select Table Properties… in the popup menu:
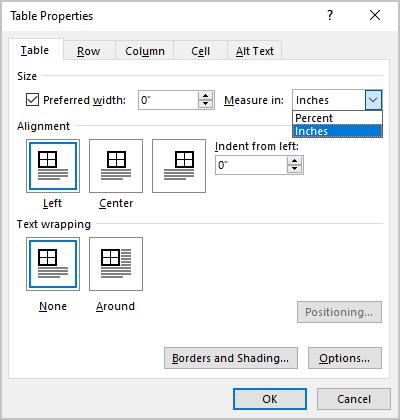
In the Table Properties dialog box, on the Table tab, in the Size section, select the Preferred width check box, then:
- In the Preferred width field, type or select the value you need,
- In the Measure in dropdown list, select one of the items:
- Percent to specify the percentage of the table width,
- Inches to fix the column width:
- On the Table Layout tab, in the Table group, click the Properties button:
- On the Layout tab, in the Cell Size group, change the values in the Height and Width fields:
See how to resize table elements for more details.
Freeze the table
Some Word tables change the width of their columns according to the data. To stop changing the table size when new data is inserted, do the following:
1. Select the table.
2. Open the Table Properties dialog box.
3. In the Table Properties dialog box, on the Table tab, click the Options… button:
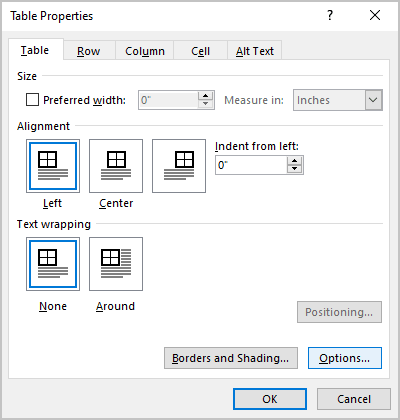
4. In the Table Options dialog box, deselect the Automatically resize to fit contents check box:
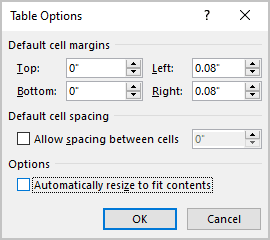
See also how to fix the height of table rows.
Move a table
To move a table to a new page or a new document, select it, then use the Cut and Paste commands. You can also use the Copy command to leave a copy of the table in the original location.
Create, Modify and Apply Table Styles in Word Documents
by Avantix Learning Team | Updated August 21, 2022
Applies to: Microsoft® Word® 2013, 2016, 2019, 2021 or 365 (Windows)
You can apply table styles to your Word tables to format them quickly and consistently. Word is shipped with several built-in table styles or you can create your own. You can edit table styles by modifying borders, shading, character formatting, paragraph formatting and table properties. If your document includes multiple tables, table styles can save a lot of time.
Note: Buttons and Ribbon tabs may display in a different way (with or without text) depending on your version of Word, the size of your screen and your Control Panel settings. For newer versionns of Word, Ribbon tabs may appear with different names. For example, the Table Tools Design tab may appear as Table Design.
Recommended article: How to Keep a Microsoft Word Table Together on One Page
Do you want to learn more about Microsoft Word? Check out our virtual classroom or live classroom Word courses >
Table styles and themes
Every Word document uses a document theme which includes a font theme and color theme. The colors used in table styles are based on the color theme.
You can select document themes, color themes and font themes using the Themes, Colors or Fonts drop-down menus on the Design tab in the Ribbon:
You can also create your own custom color themes so your tables can be formatted using your organization’s colors.
Display gridlines
When you are working with tables, it’s a good idea to turn gridlines on. Borders, which are a format, will print. Gridlines do not print.
To display gridlines:
- Click in a table.
- Click the Table Tools Layout or Table Layout tab.
- Click View Gridlines. Gridlines will stay on for all Word documents.
View Gridlines appears on the Table Tools Layout or Table Layout tab when you click in a table:
Apply a table style
If your Word document contains multiple tables that you want to format in a consistent way, it’s best to use table styles rather than applying manual or direct formatting to each table.
To apply a table style to a table:
- Click in the table.
- Click the Table Tools Design or Table Design tab in the Ribbon.
- Click the More down arrow on the bottom right in the Table Styles gallery. A drop-down menu appears.
- Hover over the various table styles. The table formatting will change as you move over different table styles in the gallery.
- Click the table style you want to apply.
Below is the Table Styles gallery (the current theme is the Office theme):
Note: Table styles do not include row height, column width or custom cell formatting for individual cells. If a user applies manual or direct formatting to a table (such as fills and borders) on the Table Tools Design or Table Design tab, this formatting will override the table style.
Apply Table Style Options
Once you have selected a table style, you can select or check different Table Style Options (which are affected by the formats in the selected table style).
The six Table Style Options that you can apply are: Header Row, Total Row, Banded Rows, First Column, Last Column and Banded Columns. If you have selected a plain table style, you may not notice any changes in the table formatting if you select different Table Style Options.
Table Style Options appear on the Table Tools Design or Table Design tab as follows when you click in a table:
To select Table Style Options:
- Click in the table.
- Click the Table Tools Design or Table Design tab in the Ribbon.
- In Table Style Options, check or uncheck Header Row. If this option is checked, the header row will be formatted differently from the body rows.
- In Table Style Options, check or uncheck Total Row. If this option is checked, the last row will be formatted differently from the body rows.
- In Table Style Options, check or uncheck Banded Rows or Banded Columns for alternate row or column shading.
- In Table Style Options, check First Column or Last Column if you want the first or last column formatted differently from the other columns.
In the following table, Header Row and Banded Rows are checked in Table Style Options:
Modify a table style
You can modify a table style in a Word document and all tables using that table style will change.
To modify a table style:
- Click in the table.
- Click the Table Tools Design or Table Design tab in the Ribbon.
- Click the More down arrow on the bottom right in the Table Styles gallery. A drop-down menu appears.
- Click Modify Table Style. A dialog box appears. You can also right-click a table style and select Modify.
- From the Apply Formatting to drop-down menu, select the element that you want to modify (such as Header row).
- Select the desired formatting such as font, font size, font color, fill and border.
- From the Apply Formatting to drop-down menu, select the next element that you want to modify.
- Select the desired formatting such as font, font size, font color, fill and border.
- Repeat for other elements.
- Select Only in this document or New documents based on this template. If you select Only in this document, the modified style will only be available for the current document. If you select New documents based on this template, then the table style will be modified for future documents based on the current template (usually the Normal template).
- Click OK.
Below is the Modify Style dialog box:
You can also click Format at the bottom of the dialog box and choose other options such as Font or Paragraph.
If you modify a table style and the tables using that style do not change, it’s likely that direct or manual formatting has been applied to the table which then overrides the table style. You may need to clear formatting in the table by selecting the table and clicking Clear Formatting on the Home tab in the Font group.
You can also modify Table Properties in a table style. Table properties include table alignment, row settings and cell margins.
To modify Table Properties in a table style:
- Click in the table.
- Click the Table Tools Design or Table Design tab in the Ribbon.
- Click the More down arrow on the bottom right in the Table Styles gallery. A drop-down menu appears.
- Click Modify Table Style. A dialog box appears. You can also right-click a table style and select Modify.
- Click Format on the bottom left of the dialog box. A drop-down menu appears.
- Click Table Properties. A dialog box appears.
- Click the Table tab and select an Alignment.
- Click the Row tab and select the desired options. For example, turn off Allow row to break across pages.
- Select any other formatting options you want to apply to the entire table.
- Click OK.
- Select Only in this document or New documents based on this template.
- Click OK.
Below is the Table Properties dialog box with the Table tab selected:
Create a new table style
You can also create a new or custom table style.
To create a custom table style:
- Click in the table.
- Click the Table Tools Design or Table Design tab in the Ribbon.
- Click the More down arrow on the bottom right in the Table Styles gallery. A drop-down menu appears.
- Click a table style to apply it as a base style.
- Click the More down arrow on the bottom right in the Table Styles gallery. A drop-down menu appears.
- Click New Table Style. A dialog box appears.
- Enter a name for the new table style in the Name box.
- Select the desired formatting.
- Select Only in this document or New documents based on this template.
- Click OK.
New Table Style appears at the bottom of the Table Styles gallery:
The new table style will appear in the Table Styles gallery under Custom (at the top of the gallery). If you want to delete it, right-click it in the gallery and select Delete Table Style.
Clear a table style
To clear a table style and remove formatting:
- Click in the table.
- Click the Table Tools Design or Table Design tab in the Ribbon.
- Click the More down arrow on the bottom right in the Table Styles gallery. A drop-down menu appears.
- Click Clear.
Clear appears at the bottom of the Table Styles gallery:
Set a default table style
You can also set a default table style for new tables in the current document or all new documents.
To set a default table style:
- Click in the table.
- Click the Table Tools Design or Table Design tab in the Ribbon.
- Click the More down arrow on the bottom right in the Table Styles gallery. A drop-down menu appears.
- Right-click the table style you want to use as the default style and select Set as Default from the drop-down menu. A dialog box appears.
- Select This document only or All documents based on the Normal.dotm template (the default template in Word is the Normal template).
- Click OK.
If you are working with documents with multiple tables, formatting with table styles can ensure that your tables are formatted consistently and save a lot of time.
Subscribe to get more articles like this one
Did you find this article helpful? If you would like to receive new articles, JOIN our email list.
More resources
4 Ways to Create a Table in Word
14 Shortcuts to Quickly Select Text in Microsoft Word
How to Create Headings in Word (Using Heading Styles)
How to Quickly Remove Hard Returns in Word Documents
10 Microsoft Word Tips, Tricks and Shortcuts for Selecting in Tables
Related courses
Microsoft Word: Intermediate / Advanced
Microsoft Excel: Intermediate / Advanced
Microsoft PowerPoint: Intermediate / Advanced
Microsoft Word: Long Documents Master Class
Microsoft Word: Styles, Templates and Tables of Contents
Microsoft Word: Designing Dynamic Word Documents Using Fields
VIEW MORE COURSES >
Our instructor-led courses are delivered in virtual classroom format or at our downtown Toronto location at 18 King Street East, Suite 1400, Toronto, Ontario, Canada (some in-person classroom courses may also be delivered at an alternate downtown Toronto location). Contact us at info@avantixlearning.ca if you’d like to arrange custom instructor-led virtual classroom or onsite training on a date that’s convenient for you.
Copyright 2023 Avantix® Learning
Microsoft, the Microsoft logo, Microsoft Office and related Microsoft applications and logos are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation in Canada, US and other countries. All other trademarks are the property of the registered owners.
Avantix Learning |18 King Street East, Suite 1400, Toronto, Ontario, Canada M5C 1C4 | Contact us at info@avantixlearning.ca
Tables in Word are useful in so many situations. In this post you’ll discover how to create tables, then manipulate and design them in the quickest and easiest way to provide that visual punch.
Clickable Table of Contents
Enhance your Word tables with these advanced features
1. What are tables in Word good for?
Tables are useful for 2 distinct reasons.
- To show an actual table of data, or
- To organise and postion text, images and other elements on the page.
Many years ago, typewriters ruled the world. And a feature of a good typewriter was the tab stop, which was a device that essentially let you control indentation.
Over the years many people have continued to use tabs to indent text, because of its convenience, but they are hard work to set up properly.
Tables provide a much easier way to organise content on a page.
1. Select the Insert tab.
2. Click the Tables icon in the Tables group.
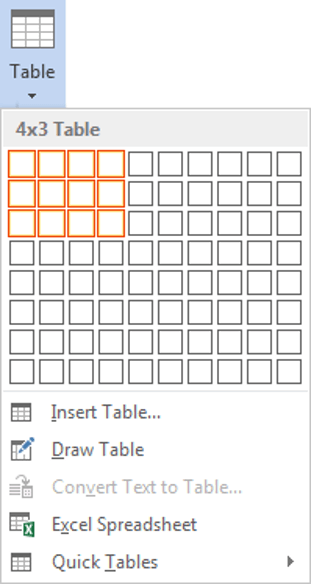
3. Move your mouse pointer into the table grid until the required number of rows and columns are highlighted orange, then left-click.
An empty table is inserted into the document.
Two new tabs, Design and Layout are also added to the ribbon area, under the banner of Table Tools.
3. MOVING AROUND A Word TABLE
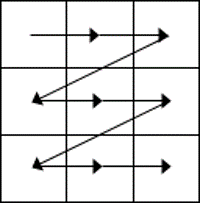
- While the table is empty, you can use the cursor keys to move around the cells. However, when the cells contain information, using the cursor keys will move through the cell content first before moving to the next cell
- You can left-click in any cell to position the cursor.
- Press Tab to move to the next cell. The cursor will move across and then down the table.
- Press Shift + Tab to move to the previous cell.
NB. Using Tab is better than using the cursors as it will move to the next/previous cell regardless of whether there is information in the cells.
NB2. If you press Tab while you are in the last cell, a new row will be added to the bottom of your table
4. SELECTING A CELL, ROW, COLUMN OR THE ENTIRE TABLE
To select a cell:
1. Position the mouse pointer inside the cell on the bottom-left corner of the cell.
The pointer will change shape to a solid black arrow that points up and right.
2. Left-click.
To select a row of a table:
1. Position the mouse pointer in the left margin in line with the row you want to select.
The mouse pointer will change to a white arrow that points up and right.
2. Left-click.
To select a column
1. Position the mouse pointer so that it rests on the top border of the table, above the column you want to select.
The mouse pointer will change to a solid black arrow pointing down.
2. Left-click.
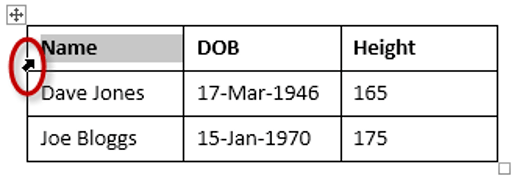
To select the entire table:
1. Position your mouse pointer over the 4-headed arrow icon situated at the top-left of the table.
2. Left-click.
5. INSERTING AN EXTRA ROW OR COLUMN
To insert an extra row:
1. Position the cursor in a cell.
2. Select the Layout tab, under the Table Tools banner.
3. Click Insert Above or Insert Below in the Rows and Columns group
Here is a quick way to insert new rows:
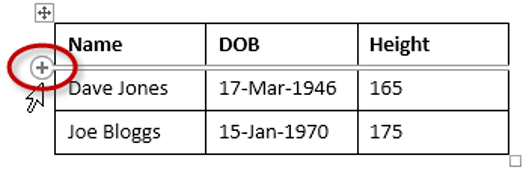
1. Position the cursor to the left of the table, but in close proximity.
2. A plus symbol will appear above or below the mouse pointer indicating where the new row will be added.
3. Nudge the mouse pointer up or down to move the plus sign above or below.
4. Left-click to insert the new row,
To insert an extra column:
1. Position the cursor in a cell.
2. Select the Layout tab, under the Table Tools banner.
3. Click Insert Left or Insert Right in the Rows and Columns group
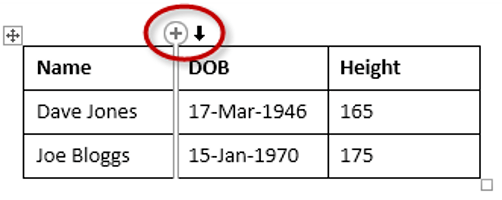
Here is a quick way to insert a new column:
1. Position the cursor above a column, but in close proximity to the table.
2. A plus symbol will appear to the left or right of the mouse pointer indicating where the new column will be added.
3. Nudge the mouse pointer left or right to move the plus sign to the left or the right of the column.
4. Left-click to insert the new column,
6. DELETING A ROW OR COLUMN
To delete the current row or column:
1. Position the cursor in any cell of the row you want to delete.
2. Select the Layout tab, under the Table Tools banner.
3. Click the Delete icon in the Rows and Columns group.
4. Choose Delete Row or Delete Column from the drop-down menu.
7. Quickly fORMATTING tables in Word
Word provides you with a number of pre-set table designs. This means that it formats the headings and the data, applies a variety of borders and colours the cells in a way that makes it look like a professionally produced table. As a beginner this simple technique will give you a good-looking table.
1. Position the cursor in any cell in the table.
2. Select the Design tab under the Table Tools banner.
The Table Styles group lists a number of table designs. To get the full list, click the More button beneath the table styles scroll bar
The default table style is Table Grid in the Plain Tables category which adds simple gridlines but no shading to your table.
Live Preview allows you to hover over a design and see it applied to your table. If you like what you see, click to select the table design.
In the Table Style Options group of the Design tab, tick the components that you have in your table. For example, if your table has column headings, tick Header Row. In doing this, the various parts of your table are formatted accordingly
Header Row
This will emphasise the header row by making the text bold or applying a different cell colour (depending on the table style selected.
Total Row
This will emphasise the bottom table row by making the text bold or applying a different cell colour (depending on the table style selected.
First Column
This will emphasise the first column (for labels etc.) by making the text bold or applying a different cell colour (depending on the table style selected.
Last Column
This will emphasise the last column (for row totals etc.) by making the text bold or applying a different cell colour (depending on the table style selected.
Banded Rows
This will make odd rows one colour and even rows a different colour. This helps readability.
Banded Columns
This will make odd columns one colour and even columns a different colour. This helps readability.
8. SETTING THE BORDERS AND SHADING
The Table Styles Gallery allows you to completely format a table with one click. Whereas you used to need some nous, anybody can now create a professional looking design.
However, you will often still need to apply your own border and shading, and manually change a table design. With a little effort can add a lot of flavour to your page and dramatically enhance the overall appearance of the document.
To set the borders for tables in Word:
1. Select the portion of the table that you wish to set the borders for. This may be the entire table, a row or rows, a column or columns or a selection of cells.
2. Select the Design tab under the Table Tools banner.
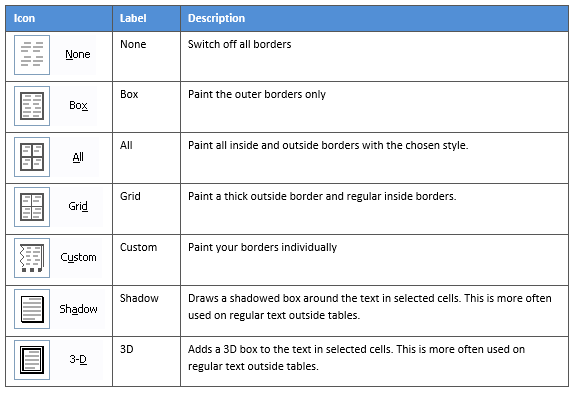
3. Select the Borders icon. A drop-down list appears. This list shows every combination of border that can be turned on or off. The icons with a shaded background are currently switched on. The rest are switched off.
4. Click any icon to switch the border on or off. The border style that is applied is the default style (½ pt solid black line ) or the last style that was used.
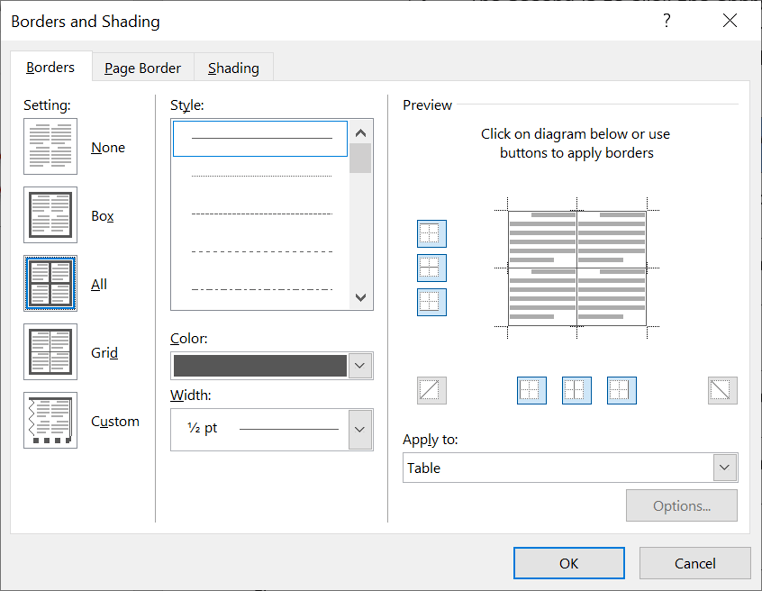
5. To apply customised borders, with different colours, styles and widths, click the Borders & Shading option at the bottom of the list to display the Borders and Shading dialog box.
Your selection will always have an outer border, and if you selected more than one cell, you will have some inside borders as well. The easiest way to use the dialog box is to start on the bottom-middle and work your way up and right.
1. Select the colour and width (thickness) that you would like for your border.
2. Choose a style (e.g. dotted, dashed, double, solid etc.)
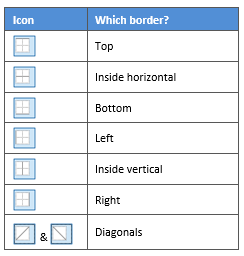
3. Paint your borders. There are two ways to do this.
- The first way is to click directly on a border in the Preview itself.
- The second way is to click the appropriate icon around the edge of the Preview section that represents each border. Depending on which cells you selected in your table, some of these icons may not be available.
On the left-hand side of the dialog box, there are some pre-defined border combinations which you can use to save yourself some time. Depending on your selection of cells, the pre-defined options may differ. Here’s a run-down:
To shade the cells of tables in Word:
1. Select the portion of the table that you wish to shade. This may be the entire table, a row or rows, a column or columns or a selection of cells.
2. Select the Design tab under the Table Tools banner.
3. Click the Shading icon.
The colours that you see displayed match the current them of the document. Themes were discussed earlier in the course.
4. Click a colour in the palette.
While you can pick any colour, it is recommended to stick with the light colour shades, otherwise your tables will appear very loud and ugly, like they’re shouting in your face. Subtle is the order of the day. The exception to this is column headings or other cells that you wish to differentiate. Under these circumstances, you can use a dark colour, but use a light font with it.
If you cannot find the exact colour you need,
- Click the More Colours link underneath the palette. This displays a larger, more accurate colour palette.
- And if that’s not enough, click the Custom tab and you’ll get a really fine selection of colours (you can even enter your own RGB settings if you know them)
9. REPEATING table HEADINGS ON EVERY PAGE WHEN PRINTING
When you have large tables that occupy two or more pages, many people insert manual page breaks, then copy and paste their table header rows at the top of each page.
When rows are added or removed from tables in Word, the table headers end up half way down the page.
There is a simple tool that will eliminate this problem
1. Ensure that the table is a single table, with no manual page breaks in the middle, and one header at the top. The table header may occupy more than one row, it doesn’t affect the way this feature works.
2. Position the cursor somewhere in the top row of the table.
3. Select the Layout tab under the Table Tools banner.
4. Click the Repeat Header Rows icon ion the Data group.
Now, it doesn’t matter how many rows tables in Word contain, if the table ever spills across into another page, the header row (which normally displays the column headings) will always appear at the top of the table.
10. All the key points again
- Tables in Word serve 2 distinct purpose: to display a table of data and to organise and position items on the page
- To create table, select 2 tabs — Design and Layout under the Table Tools banner.
- There are 2 tabs — Design and Layout under the Table Tools banner.
- You can press the TAB key to move direct to the next cell and SHIFT and TAB together to move backwards through a table.
- The four elements of a table are cells, rows, columns and the whole table. Each can be selected.
- Rows can be inserted by selecting the Layout tab under Table Tools, then clicking the Insert Above or Insert Below icons. Alternatively, hover to the left of a row and click the plus symbol that appears above or below the mouse pointer.
- Columns can be inserted by selecting the Layout tab under Table Tools, then clicking the Insert
Left or Insert Right icons. Alternatively, hover above a table column and click the plus symbol that appears to the left or right of the mouse pointer. - Columns and rows and be removed from the table, by positioning the cursor in the row or column to be removed, then clicking the Delete icon on the Layout tab of Table Tools and choosing Delete
Row or Delete Column. - Tables can be formatted using the Table Style gallery or by manually setting the shading and borders manually. Both sets of tools are found on the Design ribbon of the Table Tools.
- When using the Microsoft Table Styles, you can control the behaviour of the formatting by setting the Table Style options – 6 tick boxes that define the structure of your table.
- For long tables that spill across onto subsequent pages, the top row, which normally contains the column headings can be set to repeat automatically. So there is no excuse for cutting and pasting headings midway through your table or taping pages together to make sense of the table!
I hope you found plenty of value in this post. I’d love to hear your biggest takeaway in the comments below together with any questions you may have.
Have a fantastic day.
About the author
Jason Morrell
Jason loves to simplify the hard stuff, cut the fluff and share what actually works. Things that make a difference. Things that slash hours from your daily work tasks. He runs a software training business in Queensland, Australia, lives on the Gold Coast with his wife and 4 kids and often talks about himself in the third person!
SHARE
There are five different types of style (collection of formatting settings) in Microsoft Word. There’s three styles for text plus Tables and List styles.
Paragraph styles
Originally, Word only had paragraph styles. Styles could only be applied to an entire paragraph. Any changes to an individual word or phrase had to be done individually.
Get into the basics of Styles in Word
Character Styles
More recently, we got Character Styles. A character style can apply to any group of letters or words within a paragraph.
For example, a Style called ‘Names’ can ensure that all names in a document are consistently formatted say, in bold or italic, upper case etc.
Character styles were a welcome addition but created a new problem. Users had to make two styles with the same formatting settings, a Paragraph style and a matching Character style.
Linked Styles
Linked (paragraph and character) style is a (relatively) new and special type of style. It can act as either a paragraph style or a character style depending on how you use it.
Here’s the Heading 1 style used as both a paragraph style in heading and as a character style within the paragraph.

Before Linked Styles, users needed to maintain two styles – a paragraph version (eg ‘Heading 3’) and a character style (eg ‘Heading 3 char’).
As we’ve noted before, ‘Linked’ isn’t the best choice of terms for this type of style. Most styles are already ‘linked’ to others through style inheritance. ‘Merged’ or ‘Combined’ might have been clearer to most people – but we’re stuck with ‘Linked’.
All three text styles, Paragraph, Character and Linked are shown on the Modify Style | Style Type.
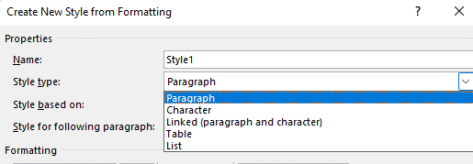
Icons for Paragraph, Character and Linked styles
A quick way to see what type of style is on the Styles list, look at the icon at right.
- ¶ (pilcrow) for Paragraph style
- a for character style
- ¶a for linked style

There are now other Styles – List and Table let you group settings for these Word elements under a single name.
Table Style
All the Table design settings can be grouped into a Table Style. The in-built Table Styles are on the Table | Design tab in the Table Styles gallery.
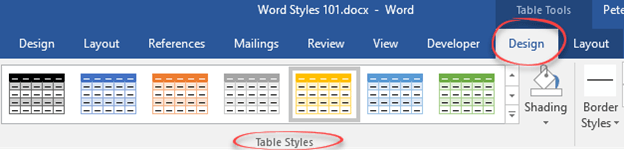
Pull-down the large Table Styles gallery, at the bottom there are style options. Or right-click on a style in the gallery to see more choices.
See 8 ways to improve on Word’s Table Styles
List Style
It’s similar for multi-level lists. There’s a gallery of in-built or custom List styles.

A list style can define the look of each level of a list as well as overall settings.
Check out
What is a Style in Word, Excel or Outlook?
Word: get a list of styles in a document
Word Styles from the beginning
Word: where are all the Style controls?
Word Style inheritance made clear and simple
Styles in Excel
OneNote 2010 Heading styles
Style Separators in Word

 .
.