When we need to collect data from others, they may write different things from their perspective. Still, we need to make all the related stories under one. Also, it is common that while entering the data, they make mistakes because of typo errors. For example, assume in certain cells, if we ask users to enter either “YES” or “NO,” one will enter “Y,” someone will insert “YES” like this, and we may end up getting a different kind of results. So in such cases, creating a list of values as pre-determined values allows the users only to choose from the list instead of users entering their values. Therefore, in this article, we will show you how to create a list of values in Excel.
Table of contents
- Create List in Excel
- #1 – Create a Drop-Down List in Excel
- #2 – Create List of Values from Cells
- #3 – Create List through Named Manager
- Things to Remember
- Recommended Articles
You can download this Create List Excel Template here – Create List Excel Template
#1 – Create a Drop-Down List in Excel
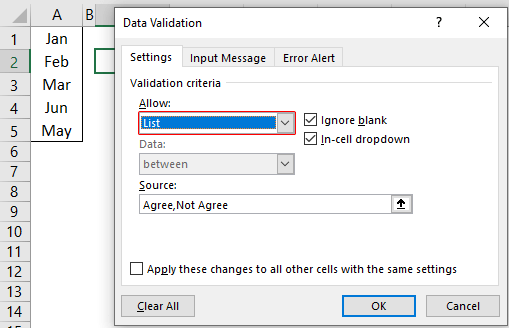
We can create a drop-down list in Excel using the “Data Validation in excelThe data validation in excel helps control the kind of input entered by a user in the worksheet.read more” tool, so as the word itself says, data will be validated even before the user decides to enter. So, all the values that need to be entered are pre-validated by creating a drop-down list in Excel. For example, assume we need to allow the user to choose only “Agree” and “Not Agree,” so we will create a list of values in the drop-down list.
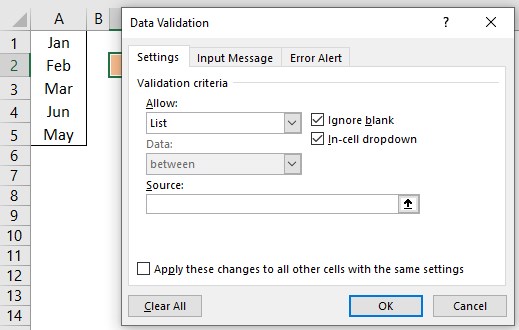
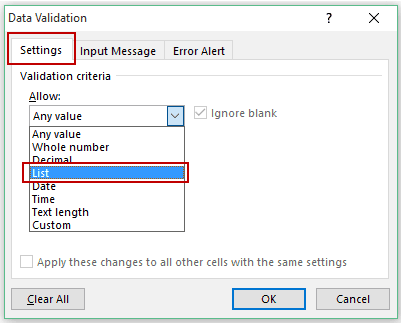
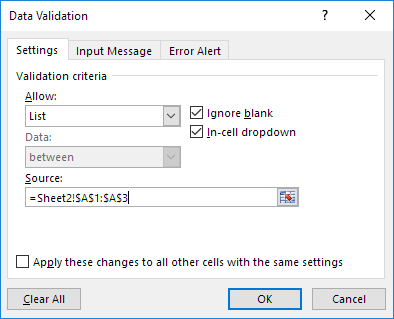
- In the Excel worksheet under the “Data” tab, we have an option called “Data Validation” from this again, choose “Data Validation.”
- As a result, this will open the “Data Validation” tool window.
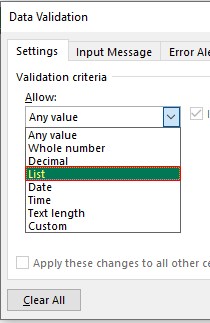
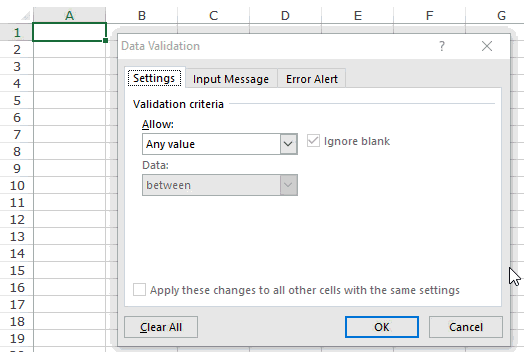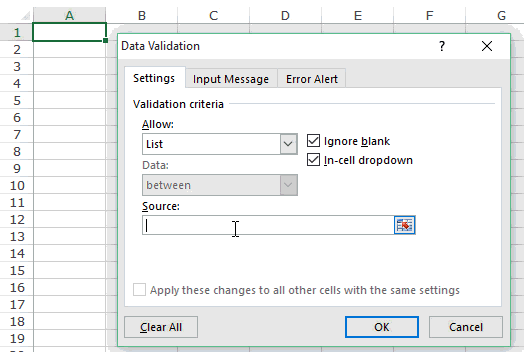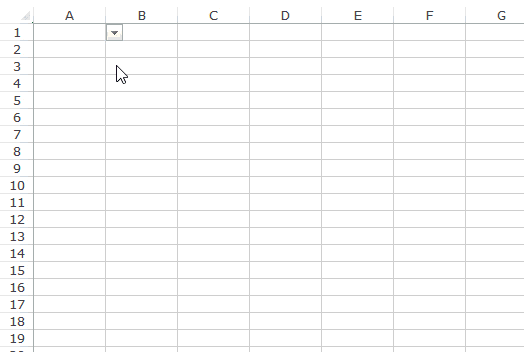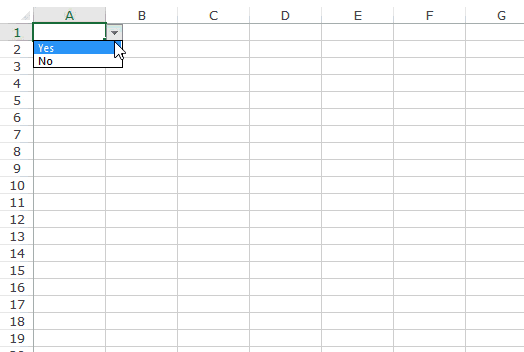
- The “Settings” tab will be shown by default, and now we need to create validation criteria. Since we are creating a list of values, choose “List” as the option from the “Allow” drop-down list.
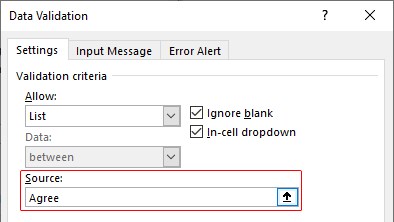
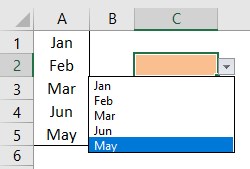
- For this “List,” we can give a list of values to be validated in the following way, i.e., by directly entering the values in the “Source” list.
- Enter the first value as “Agree.”
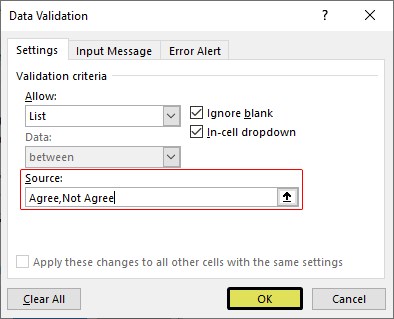
- Once the first value to be validated is entered, we need to enter “comma” (,) as the list separator before entering the next value. So, enter “comma” and enter the following values as “Not Agree.”
- After that, click on “Ok,” and the list of values may appear in the form of the “drop-down” list.
#2 – Create a List of Values from Cells
The above method is to get started, but imagine the scenario of creating a long list of values or your list of values changing now and then. Then, it may get difficult to return and edit the list of values manually. So, by entering values in the cell, we can easily create a list of values in Excel.
Follow the steps to create a list from cell values.
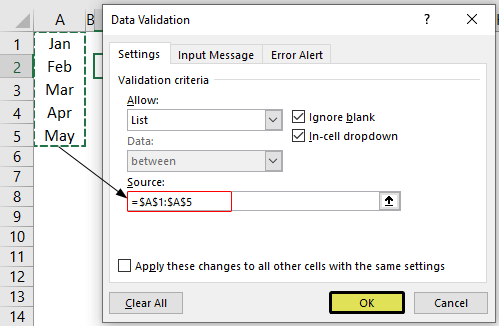
- We must first insert all the values in the cells.
- Then, open “Data Validation” and choose the validation type as “List.”
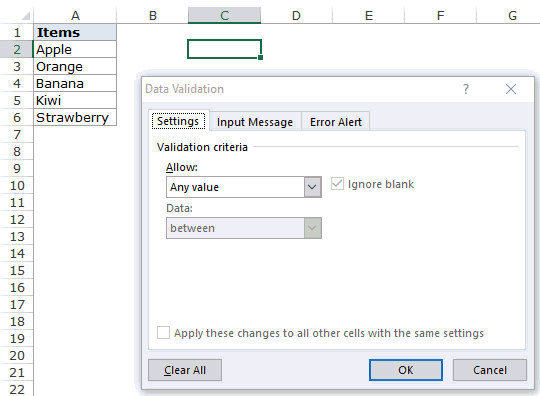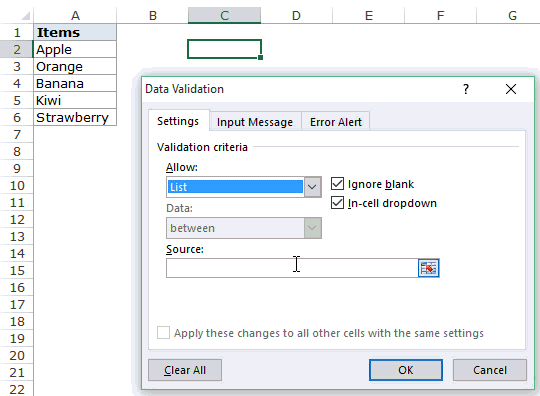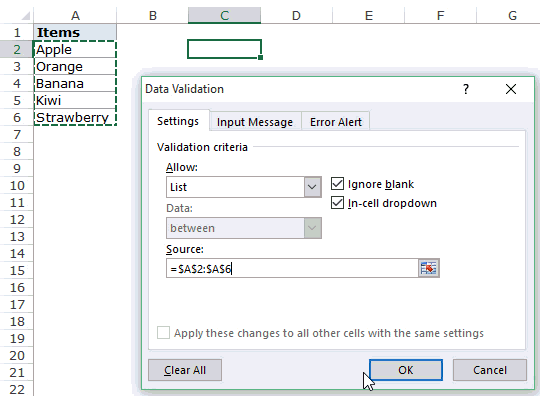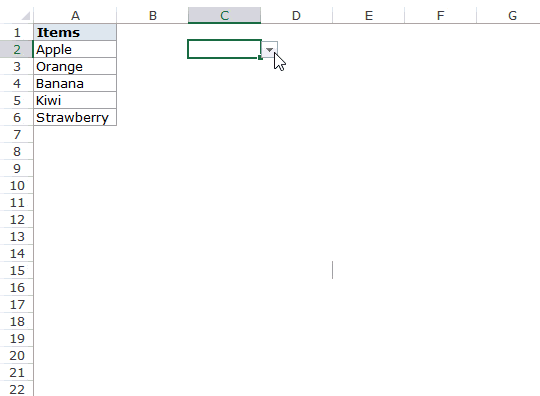
- Next, in the “Source” box, we need to place the cursor and select the list of values from the range of cells A1 to A5.
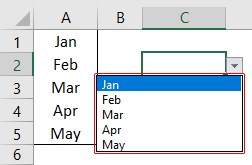
- Click on “OK,” and we will have the list ready in cell C2.
So values to this list are supplied from the range of cells A1 to A5. Any changes in these referenced cells will also impact the drop-down list.
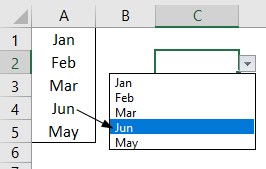
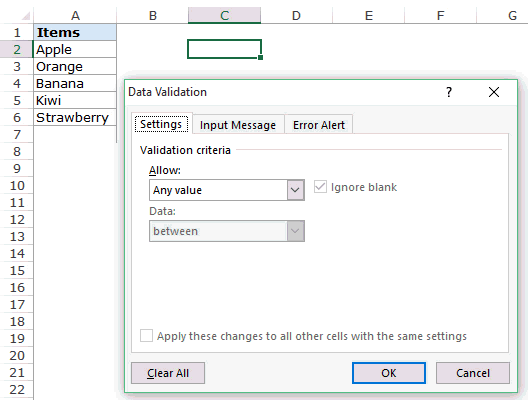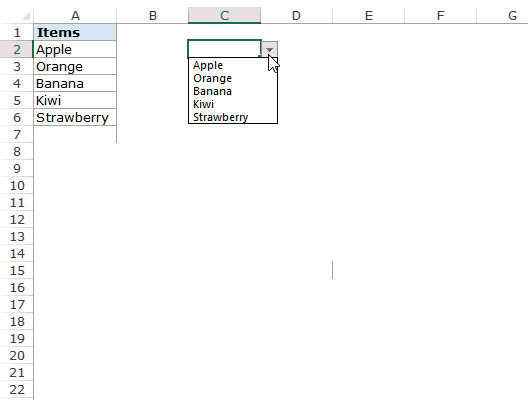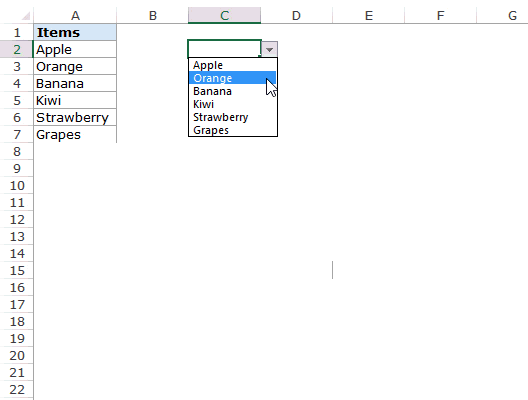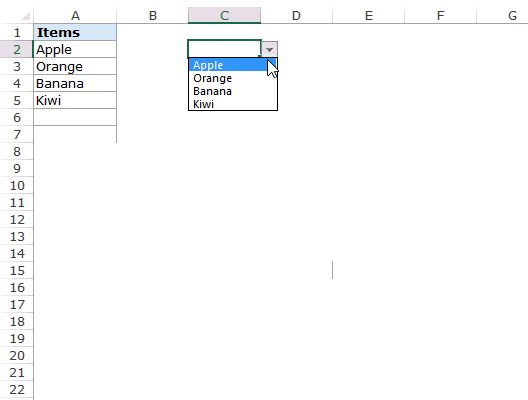
For example, in cell A4, we have a value as “Apr,” but now we will change that to “Jun” and see what happens in the drop-down list.
Now, look at the result of the drop-down list. Instead of “Apr,” we see “Jun” because we had given the list source as cell range, not manual entries.
#3 – Create List through Named Manager
There is another way to create a list of values, i.e., through named ranges in excelName range in Excel is a name given to a range for the future reference. To name a range, first select the range of data and then insert a table to the range, then put a name to the range from the name box on the left-hand side of the window.read more.
- We have values from A1 to A5 in the above example, naming this range “Months.”
- Now, select the cell where we need to create a list and open the drop-down list.
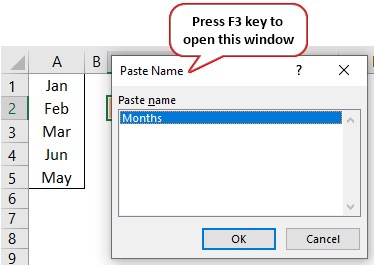
- Now place the cursor in the “Source” box and press the F3 key to an open list of named ranges.
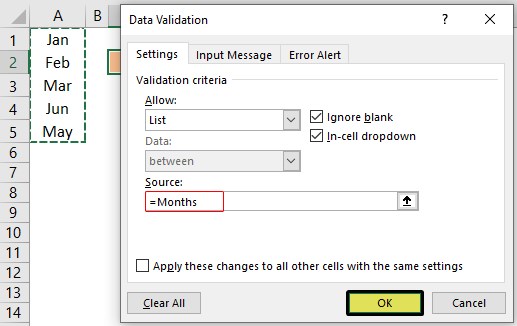
- As we can see above, we have a list of names, choose the name “Months” and click on “OK” to get the name to the “Source” box.
- Click on “OK,” and the drop-down list is ready.
Things to Remember
- The shortcut key to open data validation is “ALT + A + V + V.“
- We must always create a list of values in the cells so that it may impact the drop-down list if any change happens in the referenced cells.
Recommended Articles
This article has been a guide to Excel Create List. Here, we learn how to create a list of values in Excel also, create a simple drop-down method and make a list through name manager along with examples and downloadable Excel templates. You may learn more about Excel from the following articles: –
- Custom List in Excel
- Drop Down List in Excel
- Compare Two Lists in Excel
- How to Randomize List in Excel?
Download Article
Download Article
If you’re wondering how to create a multiple-line list in a single cell in Microsoft Excel, you’ve come to the right place. Whether you want a cell to contain a bulleted list with line breaks, a numbered list, or a drop-down list, inserting a list is easy once you know where to look. This wikiHow will teach you three helpful ways to insert any type of list to one cell in Excel.
-
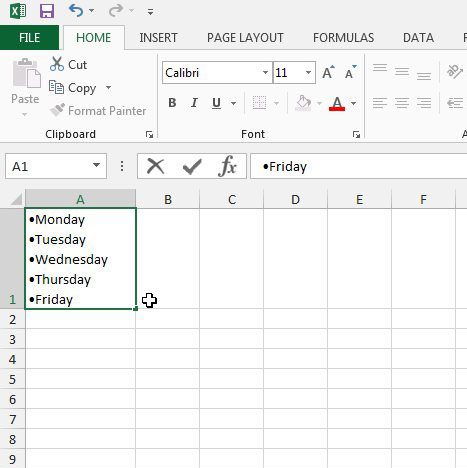
1
Double-click the cell you want to edit. If you want to create a bullet or numerical list in a single cell with each item on its own line, start by double-clicking the cell into which you want to type the list.
-
2
Insert a bullet point (optional). If you want to preface each list item with a bullet rather than a number or other character, you can use a key shortcut to insert the bullet symbol. Here’s how:
- Mac: Press Option + 8.
-
Windows:
- If you have a numeric keypad on the side of your keyboard, hold down the Alt key while pressing 7 on the keypad.[1]
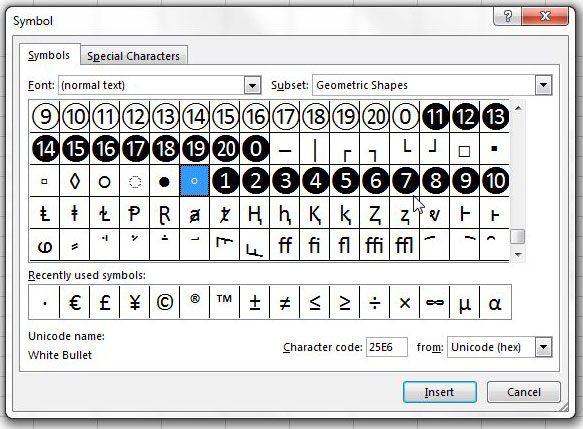
- If not, click the Insert menu, select Symbol, type 2022 into the «Character code» box at the bottom, and then click Insert.
- If 2022 didn’t bring up a bullet point, select the Wingdings font instead, and then enter 159 as the character code. You can then click Insert to add the bullet point.
- If you have a numeric keypad on the side of your keyboard, hold down the Alt key while pressing 7 on the keypad.[1]
Advertisement
-
3
Type your first list item. Don’t press Enter or Return after typing.
- If you want your list to be numbered, preface the first list item with 1. or 1).
-
4
Press Alt+↵ Enter (PC) or Control+⌥ Option+⏎ Return on a Mac. This adds a line break so you can start typing on the next line of the same cell.[2]
-
5
Type the remaining list items. To continue your list, just enter another bullet point on the second line, type the list item, and press Alt + Enter or Control + Option + Return to open a new line. When you’re finished, you can click anywhere else on your sheet to exit the cell.
Advertisement
-
1
Create your list in another app. If you’re trying to paste a bullet list (or other type of list) into a single cell rather than have it spread across multiple cells, there’s a trick to pasting the list. Start by creating your list in an app like Word, TextEdit, or Notepad.
- If you create a bulleted list in Word, the bullets will copy over to your cell when pasted into Excel. Bullets may not copy from other apps.
-
2
Copy the list. To do this, just highlight the list, right-click the highlighted area, and then select Copy.
-
3
Double-click a cell in Excel. Double-clicking the cell before pasting makes it so the list items will all appear in the same cell.
-
4
Right-click the cell. The context menu will expand.
-
5
Click the clipboard icon under «Paste Options.» The icon has a clipboard and a black rectangle. This pastes the list into the cell you double-clicked. Each list item will appear on its own line within the same cell.
Advertisement
-
1
Open the workbook in which you want to create a drop-down list. If you want to be able to click a cell to view and select from a drop-down list, you can create a list with Excel’s data validation tool.[3]
-
2
Create a new worksheet in the workbook. You can do this by clicking the + next to the existing workbook sheets at the bottom of Excel. This worksheet is where you’ll enter the items that you want to appear in your drop-down list.
- After you create the list on a separate sheet and add it to a table, you’ll be able to create a drop-down list containing the list data in any cell you want.
-
3
Type each list item into a single column. Enter every possible list choice into its own separate cell. The items you type will all be available in the drop-down list.
- If you plan to make a lot of drop-down menus and want to use this same sheet to create all of them, add a header to the top of the list. For example, if you’re making a list of cities, you could type City into the first cell. This header won’t actually appear on the drop-down list you create—it’s just for organization on this sheet that contains list data.
-
4
Highlight the entire table and press Ctrl+T. Include the header at the top of the list when highlighting. This opens the Create Table dialog.
-
5
Choose a header option and click OK. If you added a header to the top of your list, check the box next to «My table has headers.» If not, make sure there is no checkmark there before clicking OK.
- Now that your list is in a table, you can make changes to it after creating your drop-down list, and your drop-down list will update automatically.
-
6
Sort the list alphabetically. This will keep your list organized once you add it to your sheet. To do this, just click the arrow next to your header cell and select Sort A to Z.
-
7
Click the cell on the worksheet in which you want to add the list. This can be any cell on any worksheet in the workbook.
-
8
Type a name for the list into the cell. This is the cell where the list will appear, so give it a name that indicates the type of option you should choose from that list. For example, if you made a list of cities, you could type City here.
-
9
Click the Data tab and select Data Validation. Make sure the cell is selected before doing this. If you don’t see Data Validation in the toolbar, click the icon in the «Data Tools» section that has two black rectangles with a green checkmark and a red circle with a line through it. This opens the Data Validation window.
-
10
Click the «Allow» menu and select List. Additional options will expand.
-
11
Click the up-arrow in the «Source» field. This minimizes the Data Validation window so you can select your list data.
-
12
Select the list (without the header) and press ↵ Enter or ⏎ Return. Click back over to the tab that has your list data and drag the mouse cursor over just the list items. Pressing Enter or Return will add the range to the «Source» field.
-
13
Click OK. The selected cell now has a drop-down list. If you need to add or remove items from the list, you can simply make those changes on your new worksheet and they’ll automatically propagate to the list.
Advertisement
Ask a Question
200 characters left
Include your email address to get a message when this question is answered.
Submit
Advertisement
Thanks for submitting a tip for review!
About This Article
Article SummaryX
1. Double-click the cell.
2. Press Alt + 7 or Option + 8 to add a bullet point.
3. Type a list item.
4. Press Alt + Enter (PC) or Control + Option + Return (Mac) to go to the next line.
5. Repeat until your list is finished.
Did this summary help you?
Thanks to all authors for creating a page that has been read 62,222 times.
Is this article up to date?
Create a drop-down list
You can help people work more efficiently in worksheets by using drop-down lists in cells. Drop-downs allow people to pick an item from a list that you create.
-
In a new worksheet, type the entries you want to appear in your drop-down list. Ideally, you’ll have your list items in an
Excel table
. If you don’t, then you can quickly convert your list to a table by selecting any cell in the range, and pressing
Ctrl+T
.Notes:
-
Why should you put your data in a table? When your data is in a table, then as you
add or remove items from the list
, any drop-downs you based on that table will automatically update. You don’t need to do anything else. -
Now is a good time to
Sort data in a range or table
in your drop-down list.
-
-
Select the cell in the worksheet where you want the drop-down list.
-
Go to the
Data
tab on the Ribbon, then
Data Validation
.Note:
If you can’t click
Data Validation
, the worksheet might be protected or shared.
Unlock specific areas of a protected workbook
or stop sharing the worksheet, and then try step 3 again. -
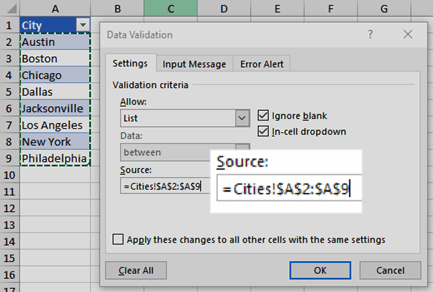
On the
Settings
tab, in the
Allow
box, click
List
. -
Click in the
Source
box, then select your list range. We put ours on a sheet called Cities, in range A2:A9. Note that we left out the header row, because we don’t want that to be a selection option: -
If it’s OK for people to leave the cell empty, check the
Ignore blank
box. -
Check the
In-cell dropdown
box. -
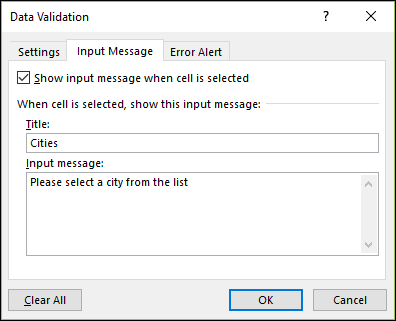
Click the
Input Message
tab.-
If you want a message to pop up when the cell is clicked, check the
Show input message when cell is selected
box, and type a title and message in the boxes (up to 225 characters). If you don’t want a message to show up, clear the check box.
-
-
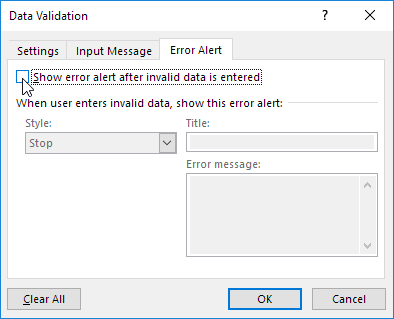
Click the
Error Alert
tab.-
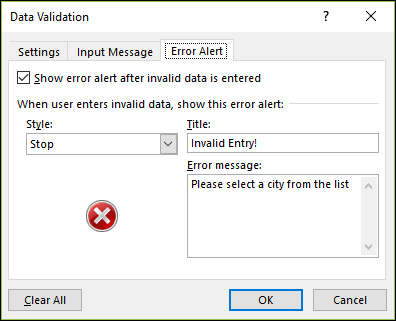
If you want a message to pop up when someone enters something that’s not in your list, check the
Show error alert after invalid data is entered
box, pick an option from the
Style
box, and type a title and message. If you don’t want a message to show up, clear the check box.
-
-
Not sure which option to pick in the
Style
box?-
To show a message that doesn’t stop people from entering data that isn’t in the drop-down list, click
Information
or Warning. Information will show a message with this icon
and Warning will show a message with this icon
. -
To stop people from entering data that isn’t in the drop-down list, click
Stop
.Note:
If you don’t add a title or text, the title defaults to «Microsoft Excel» and the message to: «The value you entered is not valid. A user has restricted values that can be entered into this cell.»
-
You can download an example workbook with multiple data validation examples like the one in this article. You can follow along, or create your own data validation scenarios.
Download Excel data validation examples
.
Data entry is quicker and more accurate when you restrict values in a cell to choices from a drop-down list.
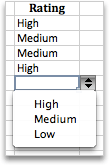
Start by making a list of valid entries on a sheet, and sort or rearrange the entries so that they appear in the order you want. Then you can use the entries as the source for your drop-down list of data. If the list is not large, you can easily refer to it and type the entries directly into the data validation tool.
-
Create a list of valid entries for the drop-down list, typed on a sheet in a single column or row without blank cells.
-
Select the cells that you want to restrict data entry in.
-
On the
Data
tab, under
Tools
, click
Data Validation
or
Validate
.Note:
If the validation command is unavailable, the sheet might be protected or the workbook may be shared. You cannot change data validation settings if your workbook is shared or your sheet is protected. For more information about workbook protection, see
Protect a workbook
. -
Click the
Settings
tab, and then in the
Allow
pop-up menu, click
List
. -
Click in the
Source
box, and then on your sheet, select your list of valid entries.The dialog box minimizes to make the sheet easier to see.
-
Press RETURN or click the
Expand
button to restore the dialog box, and then click
OK
.Tips:
-
You can also type values directly into the
Source
box, separated by a comma. -
To modify the list of valid entries, simply change the values in the source list or edit the range in the
Source
box. -
You can specify your own error message to respond to invalid data inputs. On the
Data
tab, click
Data Validation
or
Validate
, and then click the
Error Alert
tab.
-
See also
Apply data validation to cells
-
In a new worksheet, type the entries you want to appear in your drop-down list. Ideally, you’ll have your list items in an
Excel table
.Notes:
-
Why should you put your data in a table? When your data is in a table, then as you
add or remove items from the list
, any drop-downs you based on that table will automatically update. You don’t need to do anything else. -
Now is a good time to
Sort your data in the order you want it to appear
in your drop-down list.
-
-
Select the cell in the worksheet where you want the drop-down list.
-
Go to the
Data
tab on the Ribbon, then click
Data Validation
. -
On the
Settings
tab, in the
Allow
box, click
List
. -
If you already made a table with the drop-down entries, click in the
Source
box, and then click and drag the cells that contain those entries. However, do not include the header cell. Just include the cells that should appear in the drop-down. You can also just type a list of entries in the
Source
box, separated by a comma like this:
Fruit,Vegetables,Grains,Dairy,Snacks
-
If it’s OK for people to leave the cell empty, check the
Ignore blank
box. -
Check the
In-cell dropdown
box. -
Click the
Input Message
tab.-
If you want a message to pop up when the cell is clicked, check the
Show message
checkbox, and type a title and message in the boxes (up to 225 characters). If you don’t want a message to show up, clear the check box.
-
-
Click the
Error Alert
tab.-
If you want a message to pop up when someone enters something that’s not in your list, check the
Show Alert
checkbox, pick an option in
Type
, and type a title and message. If you don’t want a message to show up, clear the check box.
-
-
Click
OK
.
After you create your drop-down list, make sure it works the way you want. For example, you might want to check to see if
Change the column width and row height
to show all your entries. If you decide you want to change the options in your drop-down list, see
Add or remove items from a drop-down list
. To delete a drop-down list, see
Remove a drop-down list
.
Need more help?
You can always ask an expert in the Excel Tech Community or get support in the Answers community.
See also
Add or remove items from a drop-down list
Video: Create and manage drop-down lists
Overview of Excel tables
Apply data validation to cells
Lock or unlock specific areas of a protected worksheet
Need more help?
Microsoft Excel’s list function allows you to display several different values in a single cell using the form of a drop-down menu. When you activate the menu, you can view all of the values in the list. While the lists can be used as a space-saving convenience, they’re also useful in Excel forms when you want to make data entry easier or limit users to specific entries. You can populate your list with text, numbers or even formulas.
-
Open the worksheet where you want to create the list, and then open a new worksheet by clicking the «+» or the new worksheet icon at the bottom of the window.
-
Enter the values you want displayed in the list. The values should be in a single row or column on the new worksheet. Return to the original worksheet, and select the cell that will contain the list.
-
Select the «Data» tab, and then click «Data Validation» in the Data Tools section of the ribbon. The Data Validation dialog box appears.
-
Click the drop-down button next to «Allow,» and select «List» from the options. Make sure the box next to «In-cell Drop-down» is checked.
-
Click inside the «Source» field, and then switch to the worksheet containing the list values.
-
Select the range of cells containing the values. As you select the cells, the cell addresses automatically populate the «Source» field in the dialog box.
-
Click «OK» in the dialog box to create the list. Excel returns the focus to the original worksheet, and the cell containing the list has a new drop-down button. Click the button to view the list and select one of the values.
Bottom Line: Learn 4 different techniques for creating a list of numbers in Excel. These include both static and dynamic lists that change when items are added or deleted from the list.
Skill Level: Beginner
Watch the Tutorial
Download the Excel File
You can download the worksheet that I use in the video here:
If you have a list of items in Excel and you’d like to insert a column that numbers the items, there are several ways to accomplish this. Let’s look at four of those ways.
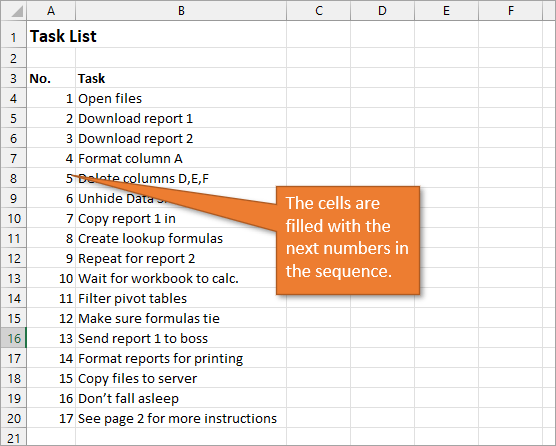
1. Create a Static List Using Auto-Fill
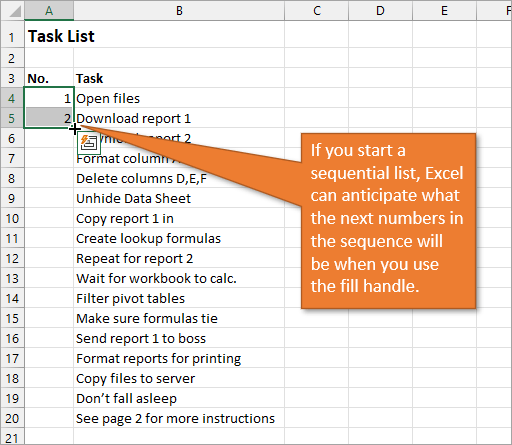
The first way to number a list is really easy. Start by filling in the first two numbers of your list, select those two numbers, and then hover over the bottom right corner of your selection until your cursor turns into a plus symbol. This is the fill handle.
When you double-click on that fill handle (or drag it down to the end of your list), Excel will fill in the blanks with the next numbers in the sequence.
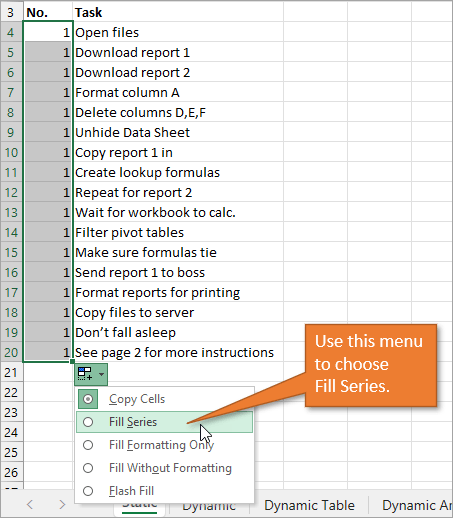
An alternate way to create this same numbered list is to type a 1 in the first cell and then double-click the fill handle. Because Excel doesn’t have a second number to identify a sequence or pattern, it will fill down the columns with 1s. But you will notice that a menu is available at the end of your column, and from that menu, you can select the option to Fill Series. This will change the 1s to a sequential list of numbers.
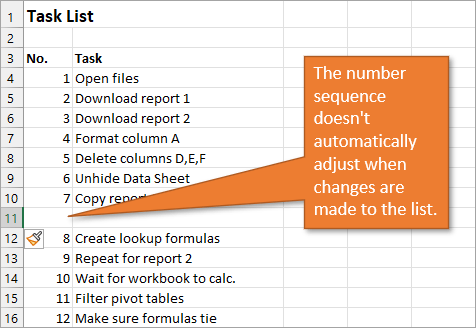
The numbered column we’ve created in both instances is static. This means it doesn’t change when you make additions or deletions to the corresponding list of items. For example, if I insert a new row in order to add another task, there is a break in the numbered column as well, and I would have to repeat the same steps to correct the list.
So, unless we want the numbers to always remain as they are, a better option would be to create a dynamic list.
2. Create a Dynamic List Using a Formula
We can use formulas to create a dynamic list where the numbers update when we add or delete rows from the list.
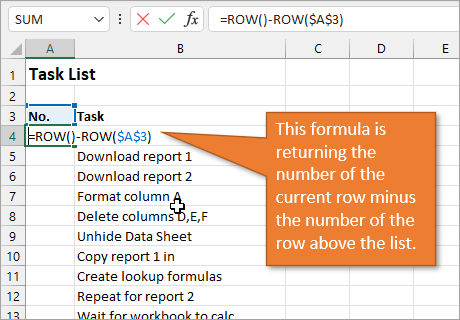
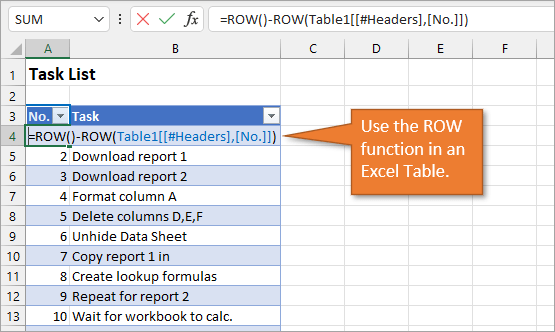
To use a formula for creating a dynamic number list, we can use the ROW function. The ROW function returns the row number of a cell. If we don’t specify a cell for ROW, it just returns the current row number of whatever is selected.
In our example, the first cell in our list doesn’t start on Row 1. It starts on Row 4. But we don’t want our list to start at 4; we want it to start at 1. To subtract the extra 3, our formula will include a minus sign and then the ROW function again, but this time pointed to the cell above our formula (which is in Row 3).
We use the absolute values (dollar signs) in our cell selection because we don’t want that number to change as we copy the formula down the list. In other words, we always want to subtract 3 from the row number to give us our list number.
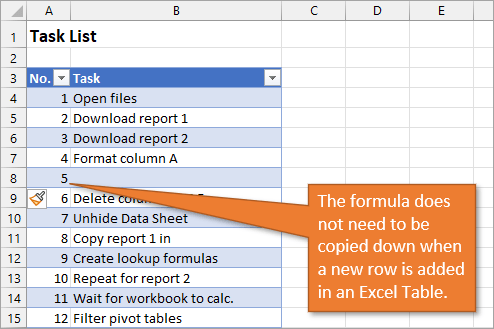
When we copy down the formula, we have a numbered list that will adjust when we add or delete rows. However, when adding a row, we will have to copy the formula into the newly inserted cell.
This additional step of copying the formula into new rows can be avoided if we use Excel Tables.
3. Create a Dynamic List Using a Formula in an Excel Table
If we write the same formula but we use an Excel table, the only difference we will make in the formula is that we reference the column header instead of the absolute cell value.
Because we are using an Excel Table, the formula automatically fills down to the other rows. When we add a row to the table, the formula will automatically populate in the new cell.
4. Create a Dynamic List Using Dynamic Array Formulas
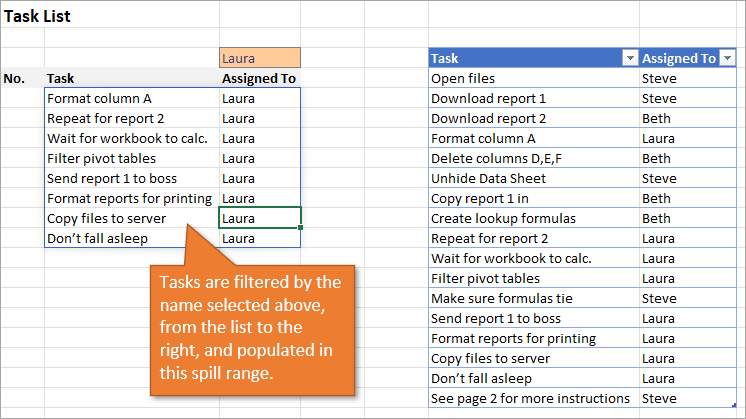
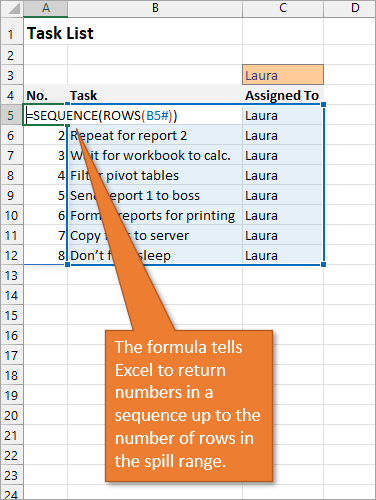
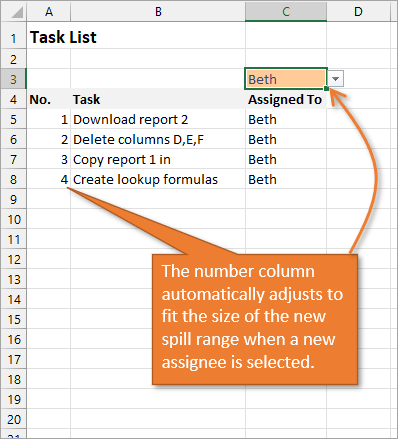
Below, I have a table that is populated using Dynamic Array Formulas. The FILTER formula spills a range of results based on whatever name is selected in the orange cell.
The Dynamic Array formula we will use is SEQUENCE. This will return a sequence for the number of rows we identify in the formula. To tell Excel how many rows there are, we will use the ROW function as the argument for sequence. The argument for ROW is just the spill range. The way to notate the spill range is to simply place a hashtag after the name of the first cell in the range. So our formula looks like this:
=SEQUENCE(ROWS(B5#))
Once we complete our formula and hit Enter, the list will be numbered.
With this formula in place, if the size of the range changes when a new name is selected, the numbered column for the list will automatically adjust as well.
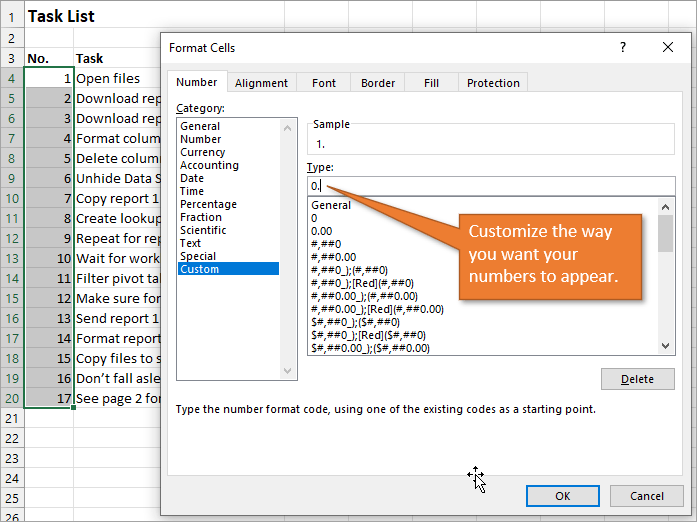
Bonus Tip: Formatting Your Numbered List
If you want to add periods or other punctuation to your numbered list:
- Select the entire list and right-click to choose Format Cells. Or use the keyboard shortcut Ctrl + 1.
- Choose the Custom option on the Number tab.
- Then in the Type field, type in the number 0 with whatever punctuation you would like to surround your number.
Here, I’ve just added a period.
When you hit OK, you will have formatted the entire selection.
Related Posts
Here are a few similar posts that may interest you.
- Excel Tables Tutorial Video – Beginners Guide for Windows & Mac
- New Excel Features: Dynamic Array Formulas & Spill Ranges
- How to Prevent Excel from Freezing or Taking A Long Time when Deleting Rows
Conclusion
I hope these four ways to create ordered lists are helpful for you. If you have questions or feedback, I would love to hear them in the comments. Have a great week!
A drop-down list is an excellent way to give the user an option to select from a pre-defined list.
It can be used while getting a user to fill a form, or while creating interactive Excel dashboards.
Drop-down lists are quite common on websites/apps and are very intuitive for the user.
Watch Video – Creating a Drop Down List in Excel
In this tutorial, you’ll learn how to create a drop down list in Excel (it takes only a few seconds to do this) along with all the awesome stuff you can do with it.
How to Create a Drop Down List in Excel
In this section, you will learn the exacts steps to create an Excel drop-down list:
- Using Data from Cells.
- Entering Data Manually.
- Using the OFFSET formula.
#1 Using Data from Cells
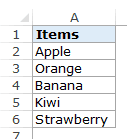
Let’s say you have a list of items as shown below:
Here are the steps to create an Excel Drop Down List:
- Select a cell where you want to create the drop down list.
- Go to Data –> Data Tools –> Data Validation.
- In the Data Validation dialogue box, within the Settings tab, select List as the Validation criteria.
- As soon as you select List, the source field appears.
- As soon as you select List, the source field appears.
- In the source field, enter =$A$2:$A$6, or simply click in the Source field and select the cells using the mouse and click OK. This will insert a drop down list in cell C2.
- Make sure that the In-cell dropdown option is checked (which is checked by default). If this option in unchecked, the cell does not show a drop down, however, you can manually enter the values in the list.
- Make sure that the In-cell dropdown option is checked (which is checked by default). If this option in unchecked, the cell does not show a drop down, however, you can manually enter the values in the list.
Note: If you want to create drop down lists in multiple cells at one go, select all the cells where you want to create it and then follow the above steps. Make sure that the cell references are absolute (such as $A$2) and not relative (such as A2, or A$2, or $A2).
#2 By Entering Data Manually
In the above example, cell references are used in the Source field. You can also add items directly by entering it manually in the source field.
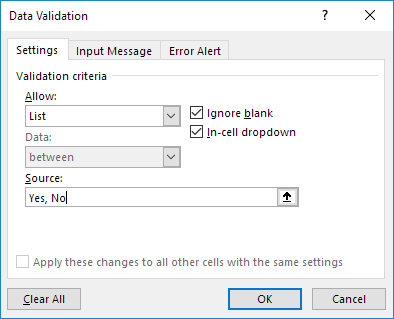
For example, let’s say you want to show two options, Yes and No, in the drop down in a cell. Here is how you can directly enter it in the data validation source field:
This will create a drop-down list in the selected cell. All the items listed in the source field, separated by a comma, are listed in different lines in the drop down menu.
All the items entered in the source field, separated by a comma, are displayed in different lines in the drop down list.
Note: If you want to create drop down lists in multiple cells at one go, select all the cells where you want to create it and then follow the above steps.
#3 Using Excel Formulas
Apart from selecting from cells and entering data manually, you can also use a formula in the source field to create an Excel drop down list.
Any formula that returns a list of values can be used to create a drop-down list in Excel.
For example, suppose you have the data set as shown below:
Here are the steps to create an Excel drop down list using the OFFSET function:
This will create a drop-down list that lists all the fruit names (as shown below).
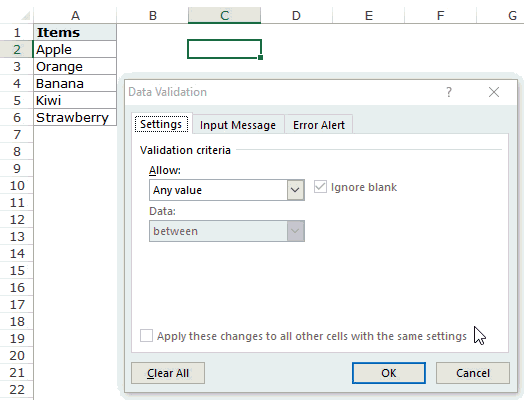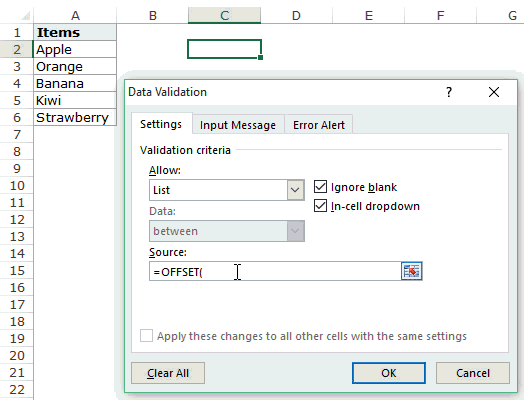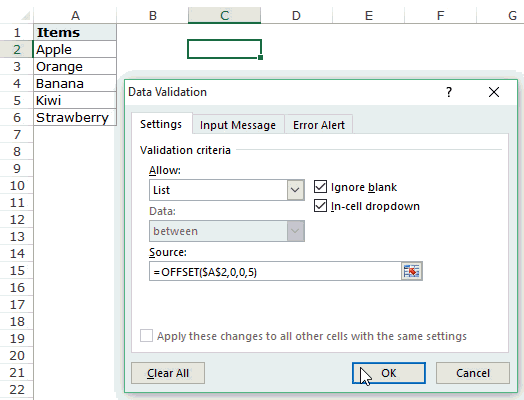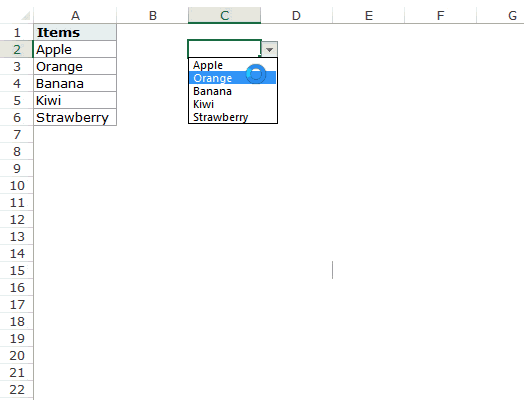
How this formula Works??
In the above case, we used an OFFSET function to create the drop down list. It returns a list of items from the ra
It returns a list of items from the range A2:A6.
Here is the syntax of the OFFSET function: =OFFSET(reference, rows, cols, [height], [width])
It takes five arguments, where we specified the reference as A2 (the starting point of the list). Rows/Cols are specified as 0 as we don’t want to offset the reference cell. Height is specified as 5 as there are five elements in the list.
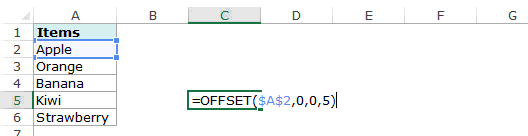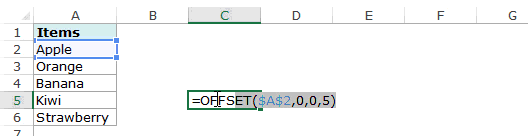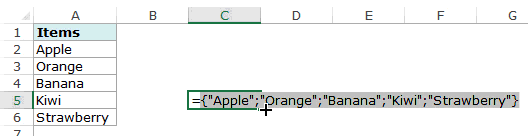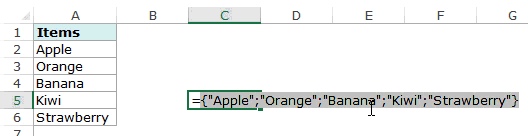
Now, when you use this formula, it returns an array that has the list of the five fruits in A2:A6. Note that if you enter the formula in a cell, select it and press F9, you would see that it returns an array of the fruit names.
Creating a Dynamic Drop Down List in Excel (Using OFFSET)
The above technique of using a formula to create a drop down list can be extended to create a dynamic drop down list as well. If you use the OFFSET function, as shown above, even if you add more items to the list, the drop down would not update automatically. You will have to manually update it each time you change the list.
Here is a way to make it dynamic (and it’s nothing but a minor tweak in the formula):
- Select a cell where you want to create the drop down list (cell C2 in this example).
- Go to Data –> Data Tools –> Data Validation.
- In the Data Validation dialogue box, within the Settings tab, select List as the Validation criteria. As soon as you select List, the source field appears.
- In the source field, enter the following formula: =OFFSET($A$2,0,0,COUNTIF($A$2:$A$100,”<>”))
- Make sure that the In-cell drop down option is checked.
- Click OK.
In this formula, I have replaced the argument 5 with COUNTIF($A$2:$A$100,”<>”).
The COUNTIF function counts the non-blank cells in the range A2:A100. Hence, the OFFSET function adjusts itself to include all the non-blank cells.
Note:
- For this to work, there must NOT be any blank cells in between the cells that are filled.
- If you want to create a drop-down list in multiple cells at one go, select all the cells where you want to create it and then follow the above steps. Make sure that the cell references are absolute (such as $A$2) and not relative (such as A2, or A$2, or $A2).
Copy Pasting Drop-Down Lists in Excel
You can copy paste the cells with data validation to other cells, and it will copy the data validation as well.
For example, if you have a drop-down list in cell C2, and you want to apply it to C3:C6 as well, simply copy the cell C2 and paste it in C3:C6. This will copy the drop-down list and make it available in C3:C6 (along with the drop down, it will also copy the formatting).
If you only want to copy the drop down and not the formatting, here are the steps:
This will only copy the drop down and not the formatting of the copied cell.
Caution while Working with Excel Drop Down List
You need to to be careful when you are working with drop down lists in Excel.
When you copy a cell (that does not contain a drop down list) over a cell that contains a drop down list, the drop down list is lost.
The worst part of this is that Excel will not show any alert or prompt to let the user know that a drop down will be overwritten.
How to Select All Cells that have a Drop Down List in it
Sometimes, it ‘s hard to know which cells contain the drop down list.
Hence, it makes sense to mark these cells by either giving it a distinct border or a background color.
Instead of manually checking all the cells, there is a quick way to select all the cells that have drop-down lists (or any data validation rule) in it.
This would instantly select all the cells that have a data validation rule applied to it (this includes drop down lists as well).
Now you can simply format the cells (give a border or a background color) so that visually visible and you don’t accidentally copy another cell on it.
Here is another technique by Jon Acampora you can use to always keep the drop down arrow icon visible. You can also see some ways to do this in this video by Mr. Excel.
Creating a Dependent / Conditional Excel Drop Down List
Here is a video on how to create a dependent drop-down list in Excel.
If you prefer reading over watching a video, keep reading.
Sometimes, you may have more than one drop-down list and you want the items displayed in the second drop down to be dependent on what the user selected in the first drop-down.
These are called dependent or conditional drop down lists.
Below is an example of a conditional/dependent drop down list:
In the above example, when the items listed in ‘Drop Down 2’ are dependent on the selection made in ‘Drop Down 1’.
Now let’s see how to create this.
Here are the steps to create a dependent / conditional drop down list in Excel:
Now, when you make the selection in Drop Down 1, the options listed in Drop Down List 2 would automatically update.
Download the Example File
How does this work? – The conditional drop down list (in cell E3) refers to =INDIRECT(D3). This means that when you select ‘Fruits’ in cell D3, the drop down list in E3 refers to the named range ‘Fruits’ (through the INDIRECT function) and hence lists all the items in that category.
Important Note While Working with Conditional Drop Down Lists in Excel:
- When you have made the selection, and then you change the parent drop down, the dependent drop down would not change and would, therefore, be a wrong entry. For example, if you select the US as the country and then select Florida as the state, and then go back and change the country to India, the state would remain as Florida. Here is a great tutorial by Debra on clearing dependent (conditional) drop down lists in Excel when the selection is changed.
- If the main category is more than one word (for example, ‘Seasonal Fruits’ instead of ‘Fruits’), then you need to use the formula =INDIRECT(SUBSTITUTE(D3,” “,”_”)), instead of the simple INDIRECT function shown above. The reason for this is that Excel does not allow spaces in named ranges. So when you create a named range using more than one word, Excel automatically inserts an underscore in between words. So ‘Seasonal Fruits’ named range would be ‘Seasonal_Fruits’. Using the SUBSTITUTE function within the INDIRECT function makes sure that spaces are converted into underscores.
You May Also Like the Following Excel Tutorials:
- Extract Data from Drop Down List Selection in Excel.
- Select Multiple Items from a Drop Down List in Excel.
- Creating a Dynamic Excel Filter Search Box.
- Display Main and Subcategory in Drop Down List in Excel.
- How to Insert Checkbox in Excel.
- Using a Radio Button (Option Button) in Excel.
- How to Remove Drop-Down List in Excel?
Microsoft Excel’s default layout of cells in rows and columns is a great place to start when you’re organizing data. But you might be wondering how to add a bulleted or numbered list in Excel cell objects if you need another level of organization.
How to Add Bullets in Excel 2013
- Click inside the cell where you want to add bullets.
- Hold down the Alt key, then press 0, then 1, then 4, then 9.
- Enter the information for the first bullet, then hold down the Alt key on your keyboard and press Enter to move to the next line within that cell.
- Repeat steps 2 and 3 for each additional bullet item that you wish to add in Excel.
Our guide continues below with additional information on adding a bulleted or numbered list in Excel cell, including pictures of these steps.
Adding bullets in Excel is something that might seem like an obvious feature to include in the program but, if you are reading this article, you have probably found that it is not the case.
Microsoft Word and Powerpoint make it very easy to create bulleted or numbered lists, and you can also learn how to put a bullet point on Google Slides. This can happen so easily that you might not even be trying to create a list. But Excel 2013 does not offer a similar automatic list option, nor is there a way on the ribbon for you to enter one manually.
Fortunately, you can add a bullet before a list item using a keyboard shortcut. You can even elect to add multiple bulleted items into a single cell with the help of a line break keyboard shortcut.
Our guide below will show you how.
How to Make a Multi-Item Bullet Lists in a Single Cell in Excel 2013 (guide with Pictures)
The steps in this article are going to show you how to create a bulleted list of two or more items inside a single cell of an Excel worksheet.
Step 1: Open a worksheet in Excel 2013.
Step 2: Click inside the cell where you would like to insert the bulleted list.
You can resize the row or resize the column now if you want, or you can do it later. It’s up to you.
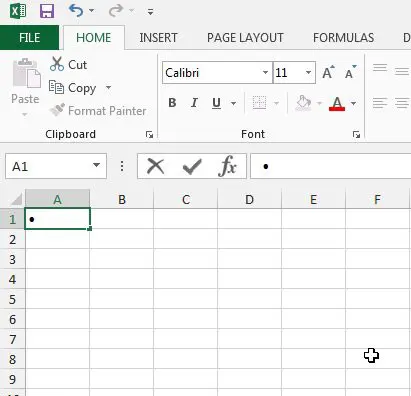
Step 3: Hold down the Alt key on your keyboard, then press 0, then 1, then 4, then 9.
This should insert a bullet into the cell.
Step 4: You can then type the information that you want to include as the first bulleted item.
Once you have reached the end of the first line, hold down the Alt key on the keyboard, then press Enter. You can continue adding bullets by pressing Alt +0149 and adding line breaks by pressing Alt + Enter.
Rather than bullets you could also just type a number followed by a period, then use the Alt + Enter line break option for a numbered list in an Excel cell.
You can use different items as bullets by selecting them from the Symbols menu on the Insert tab as well, clicking a symbol on the menu, then clicking the Insert button to insert it into the cell.
For example, if you wanted to use a numbered list in Excel cell formatting, then you could use these numbers instead of the bullets that we discussed above.
You can force Excel 2013 to automatically resize rows or columns to fit the size of their data by reading this article – https://www.solveyourtech.com/automatically-resize-row-height-excel-2013/ . This can save some frustration if your row or column sizing is acting difficultly.
Additional Sources
Matthew Burleigh has been writing tech tutorials since 2008. His writing has appeared on dozens of different websites and been read over 50 million times.
After receiving his Bachelor’s and Master’s degrees in Computer Science he spent several years working in IT management for small businesses. However, he now works full time writing content online and creating websites.
His main writing topics include iPhones, Microsoft Office, Google Apps, Android, and Photoshop, but he has also written about many other tech topics as well.
Read his full bio here.
Create a Drop-down List | Allow Other Entries | Add/Remove Items | Dynamic Drop-down List | Remove a Drop-down List | Dependent Drop-down Lists | Table Magic
Drop-down lists in Excel are helpful if you want to be sure that users select an item from a list, instead of typing their own values.
Create a Drop-down List
To create a drop-down list in Excel, execute the following steps.
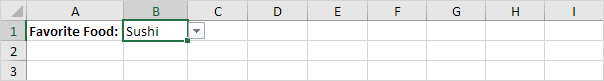
1. On the second sheet, type the items you want to appear in the drop-down list.
Note: if you don’t want users to access the items on Sheet2, you can hide Sheet2. To achieve this, right click on the sheet tab of Sheet2 and click on Hide.
2. On the first sheet, select cell B1.
3. On the Data tab, in the Data Tools group, click Data Validation.
The ‘Data Validation’ dialog box appears.
4. In the Allow box, click List.
5. Click in the Source box and select the range A1:A3 on Sheet2.
6. Click OK.
Result:
Note: to copy/paste a drop-down list, select the cell with the drop-down list and press CTRL + c, select another cell and press CTRL + v.
7. You can also type the items directly into the Source box, instead of using a range reference.
Note: this makes your drop-down list case sensitive. For example, if a user types yes, an error alert will be displayed.
Allow Other Entries
You can also create a drop-down list in Excel that allows other entries.
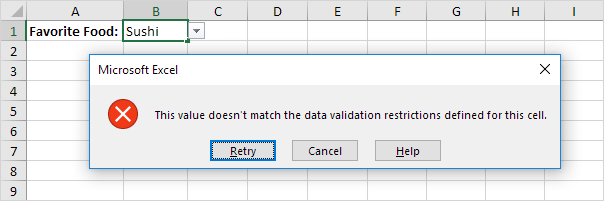
1. First, if you type a value that is not in the list, Excel shows an error alert.
To allow other entries, execute the following steps.
2. On the Data tab, in the Data Tools group, click Data Validation.
The ‘Data Validation’ dialog box appears.
3. On the Error Alert tab, uncheck ‘Show error alert after invalid data is entered’.
4. Click OK.
5. You can now enter a value that is not in the list.
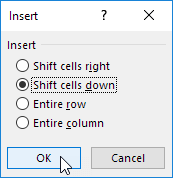
Add/Remove Items
You can add or remove items from a drop-down list in Excel without opening the ‘Data Validation’ dialog box and changing the range reference. This saves time.
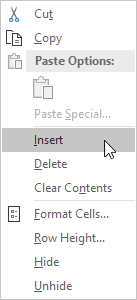
1. To add an item to a drop-down list, go to the items and select an item.
2. Right click, and then click Insert.
3. Select «Shift cells down» and click OK.
Result:
Note: Excel automatically changed the range reference from Sheet2!$A$1:$A$3 to Sheet2!$A$1:$A$4. You can check this by opening the ‘Data Validation’ dialog box.
4. Type a new item.
Result:
5. To remove an item from a drop-down list, at step 2, click Delete, select «Shift cells up» and click OK.
Dynamic Drop-down List
You can also use a formula that updates your drop-down list automatically when you add an item to the end of the list.
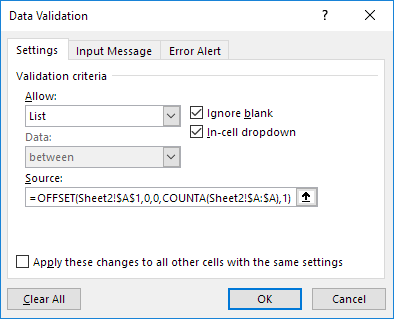
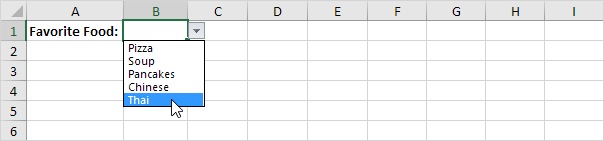
1. On the first sheet, select cell B1.
2. On the Data tab, in the Data Tools group, click Data Validation.
The ‘Data Validation’ dialog box appears.
3. In the Allow box, click List.
4. Click in the Source box and enter the formula: =OFFSET(Sheet2!$A$1,0,0,COUNTA(Sheet2!$A:$A),1)
Explanation: the OFFSET function takes 5 arguments. Reference: Sheet2!$A$1, rows to offset: 0, columns to offset: 0, height: COUNTA(Sheet2!$A:$A) and width: 1. COUNTA(Sheet2!$A:$A) counts the number of values in column A on Sheet2 that are not empty. When you add an item to the list on Sheet2, COUNTA(Sheet2!$A:$A) increases. As a result, the range returned by the OFFSET function expands and the drop-down list will be updated.
5. Click OK.
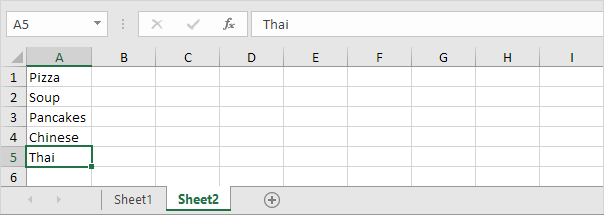
6. On the second sheet, simply add a new item to the end of the list.
Result:
Remove a Drop-down List
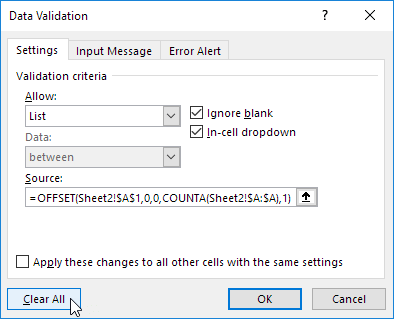
To remove a drop-down list in Excel, execute the following steps.
1. Select the cell with the drop-down list.
2. On the Data tab, in the Data Tools group, click Data Validation.
The ‘Data Validation’ dialog box appears.
3. Click Clear All.
Note: to remove all other drop-down lists with the same settings, check «Apply these changes to all other cells with the same settings» before you click on Clear All.
4. Click OK.
Dependent Drop-down Lists
Want to learn even more about drop-down lists in Excel? Learn how to create dependent drop-down lists.
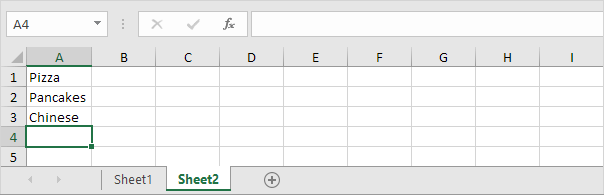
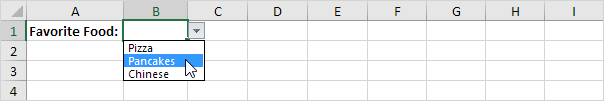
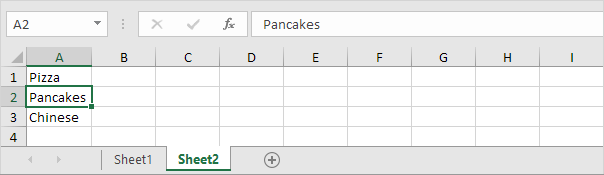
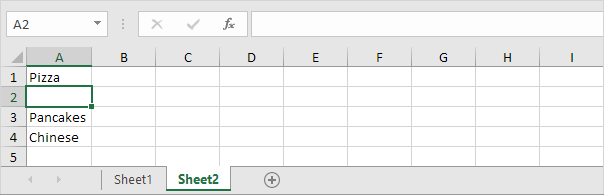
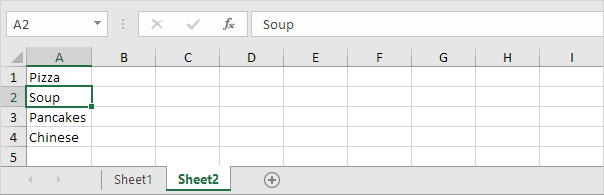
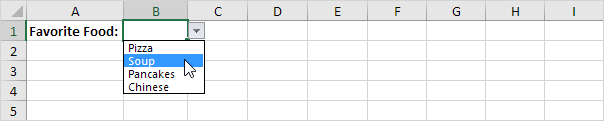
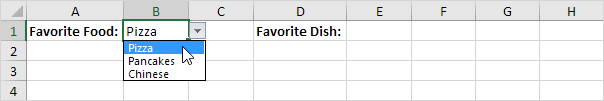
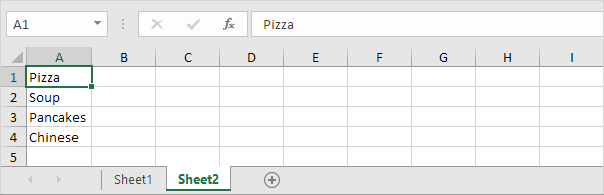
1. For example, if the user selects Pizza from a first drop-down list.
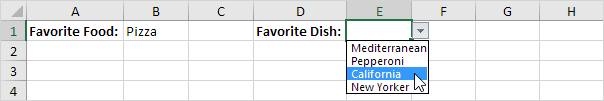
2. A second drop-down list contains the Pizza items.
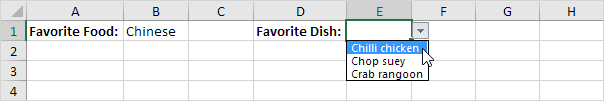
3. But if the user selects Chinese from the first drop-down list, the second drop-down list contains the Chinese dishes.
Table Magic
You can also store your items in an Excel table to create a dynamic drop-down list.
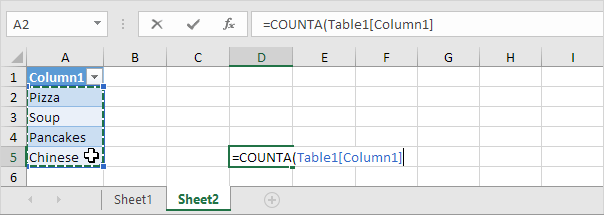
1. On the second sheet, select a list item.
2. On the Insert tab, in the Tables group, click Table.
3. Excel automatically selects the data for you. Click OK.
4. If you select the list, Excel reveals the structured reference.
5. Use this structured reference to create a dynamic drop-down list.
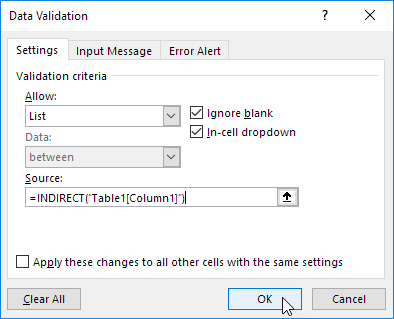
Explanation: the INDIRECT function in Excel converts a text string into a valid reference.
6. On the second sheet, simply add a new item to the end of the list.
Result:
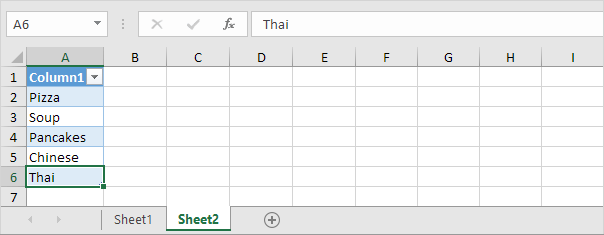
Note: try it yourself. Download the Excel file and create this drop-down list.
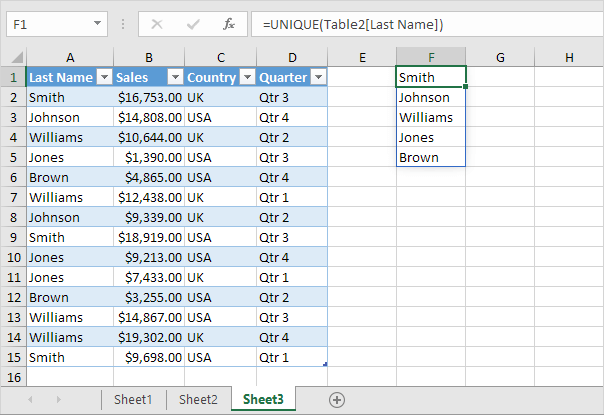
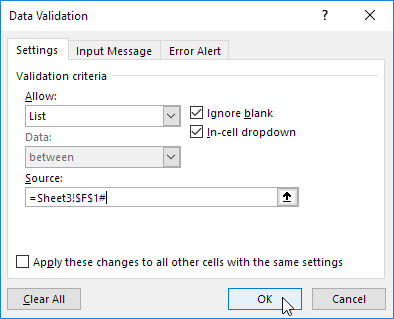
7. When using tables, use the UNIQUE function in Excel 365/2021 to extract unique list items.
Note: this dynamic array function, entered into cell F1, fills multiple cells. Wow! This behavior in Excel 365/2021 is called spilling.
8. Use this spill range to create a magic drop-down list.
Explanation: always use the first cell (F1) and a hash character to refer to a spill range.
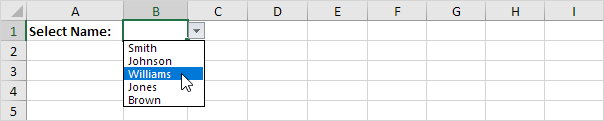
Result:
Note: when you add new records, the UNIQUE function automatically extracts new unique list items and Excel automatically updates the drop-down list.
A Custom List in Excel is very handy to fill a range of cells with your own personal list.
It could be a list of your team members at work, countries, regions, phone numbers, or customers. The main goal of a custom list is to remove repetitive work and manual errors.
It is extremely useful when you need to fill in the same data from time to time. There are two options to create a list in Excel that can be used repeatedly by using the fill handle.
In this tutorial, you will learn how to create a list in Excel:
- Using Pre-existing List
- Create a list in Excel manually
- Import from another worksheet
Let’s look at each of these methods one-by-one!
Watch it on YouTube and give it a thumbs-up!
Download this Excel Workbook and follow along with the tutorial on how to create a list in Excel :
Using Pre-existing List
At first, it might seem like magic how Excel does this!
There are some lists that are already stored in Excel like days of the week and months in a year.
To demonstrate the power of Excel’s Custom Lists, we’ll explore what’s currently in Excel’s memory as a default list:
STEP 1: Type February in the first cell
STEP 2: From that first cell, click the lower right corner and drag it to the next 5 cells to the right
STEP 3: Release and you will see it get auto-populated to July (The succeeding months after February)
Create a list in Excel manually
You can also manually add new values in the Custom List box and re-use them whenever you wish to.
Let us go straight into the Options in Excel to view how it’s being done, and how you can create your own Custom List:
STEP 1: Select the File tab
STEP 2: Click Options
STEP 3: Select the Advanced option
STEP 4: Scroll all the way down and under the General section, click Edit Custom Lists.
Here you can see the built-in default Excel lists of the calendar months and the days.
If you click on a Custom List, you will see under List entries that it is greyed out and you cannot make any changes. This indicated that it is a default Excel Custom List.
STEP 5: You can create & add your own Custom List under the List entries section.
Click on NEW LIST under the Custom Lists area and then manually enter your list, entering one entry per line:
After typing the values, click Add.
In our screenshot below, we added the values of the Greek alphabet (alpha, beta, gamma, and so on)
Click OK once done.
STEP 6: Click OK again
STEP 7: Now let’s go back into our Excel workbook to see our new Custom List in action. Type alpha on a cell.
STEP 8: From that cell, click the lower right corner and drag it to the next 5 cells to the right
STEP 9: Release and you will see it get auto-populated to zeta, which is based on our Custom List created in Step 8
Next up is a demonstration of how to make a list in Excel by importing data from another worksheet.
Import from another worksheet
You can easily import a custom list from another worksheet. Follow the steps below to get this done:
STEP 1: Go to the File Tab.
STEP 2: Select Options from the left panel.
STEP 3: In the Excel Options dialog box, select Advanced.
STEP 4: Under the General section, click on the Edit Custom List button.
STEP 5: In the Custom List dialog box, select the small arrow up button.
STEP 6: Select the range containing the custom list.
STEP 7: Click on Import.
STEP 8: Once the list will appear under list entries and click OK.
STEP 9: Click OK.
Now, your custom list is stored in Excel!
STEP 10: Type the first entry of the list “XS” in cell A8.
STEP 11: From that first cell, click the lower right corner and drag it to the next 6 cells to the right.
The entire list will be displayed in the selected range!
You can even create this list vertically. Simply, type the XS in a cell. Click on the lower right corner and drag the cell downwards.
The list will appear vertically!
Conclusion
In this article, you have learned how to make a list in Excel so that you don’t have to type the same list over and over again. You use the Custom list feature in Excel and store it in Excel and use it whenever necessary.
You can either use the pre-existing list, manually type the list or link it from another worksheet!
Make sure to download our FREE PDF on the 333 Excel keyboard Shortcuts here:
You can learn more about how to use Excel by viewing our FREE Excel webinar training on Formulas, Pivot Tables, Power Query, and Macros & VBA!
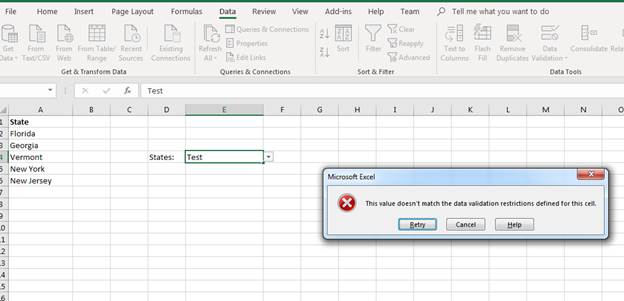
Excel 2019 is used in many organizations to fill out information on customers, orders and products. Some of the data items are repetitive, meaning that you don’t type data into a cell but rather select from a data list. For instance, you might want to select a state from a dropdown list in a column that stores the state for a customer address. You can make it easier to fill out forms in Excel 2019 using data lists, and this article shows you how to create them.
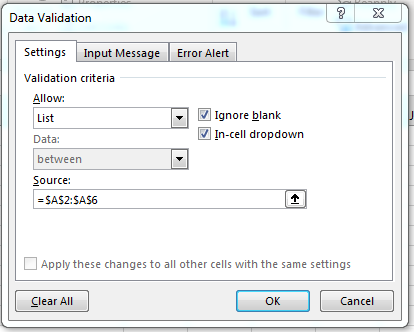
Set Up the List
Before you create a dropdown list in Excel, you need a list of data to use. Since you can make multiple worksheets in one Excel workbook, most people use a separate sheet to populate the data list. You can then configure any specific cell in the Excel form to point to this list of data. You then set the cell as a list, and Excel does the rest for you.
You don’t have to use a separate sheet to populate a data list. You can use the same sheet or even a separate workbook. You can use a separate workbook, but any changes to this workbook could affect the data list. Also, if the workbook is moved to a different directory or storage location, your list will no longer function.
For simplicity, this article’s examples use the same workbook and worksheet, but just know that you can use references to separate worksheets and workbooks for your own data lists.
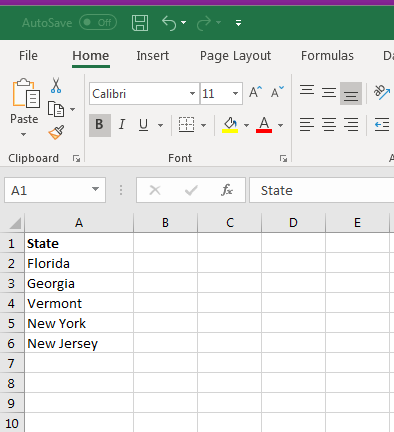
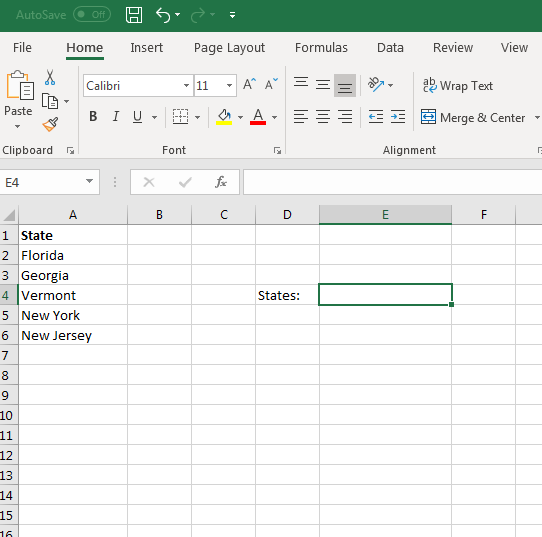
Create a blank worksheet in a currently opened workbook, or you can create a new workbook to store the new data list. In the following scenario, a list of states is used for a data list. We’ll add five states to the first column (A) in a new worksheet.
(List of states set up for a dropdown)
In the image above, five states were added to their own cells. Notice at the top that «State» is used to label the column list. This is beneficial for the dropdown that we’ll make, and it helps label data so that others can understand what the list is used for. The list can be as long as it needs to be, but we’ve only added five states for simplicity.
You now need a place to display the dropdown that will contain these values. For simplicity, we’ll set up a dropdown in the same worksheet. Make sure that you label the dropdown as well so that users know what the dropdown list is for.
(Location of the state dropdown and its label)
In the image above, the cell E4 is selected as the cell that will contain the dropdown list. In D4, the label «States:» is displayed so that users know a list of states will be shown in the dropdown. It also helps users understand that they must select a state when they fill out the form. Labeling cells is an important part of creating effective spreadsheets that store the right data, especially among several users that add data and revise it periodically.
Creating a Dropdown Based on External Data
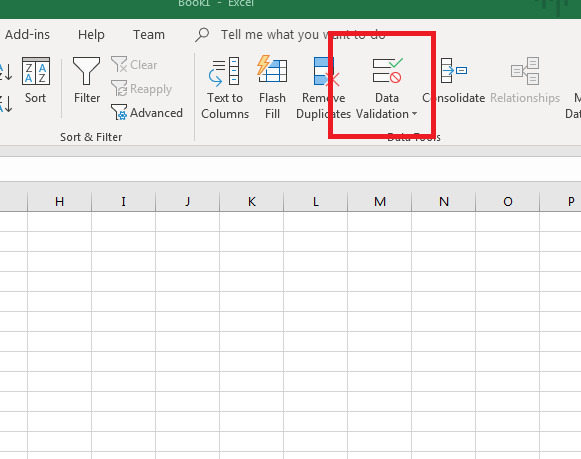
With the cell next to the «States:» label selected, click the «Data» tab. The «Data» tab has several data tools that you can use to work with lists. Click the «Data Validation» button, which is found in the «Data Tools» section of the «Data» tab.
(Location of the «Data Validation» button)
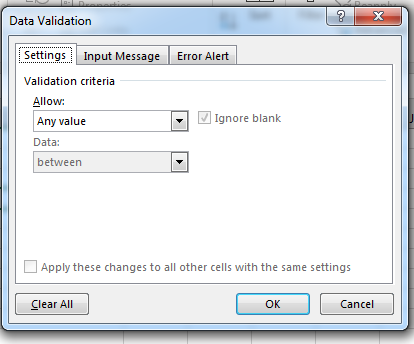
Clicking this button displays another dropdown selection. Click the «Data Validation» option, and a new window opens where you can configure your data list and cell that contains the options for a user to choose from.
(Data validation configuration window)
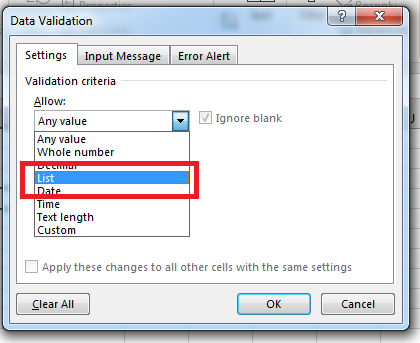
In the window above, you have several options to set a dropdown using a list of data. For a dropdown, you need to choose the «List» option. The «List» option is found in the «Allow» dropdown box.
(Select «List» for the validation criteria)
In the image above, notice that the «Allow» dropdown has the «List» option selected. This option tells Excel 2019 that you want to use a data list. If you hadn’t already created a data list in an external workbook or in a worksheet in the current workbook, you would need to cancel out of this window and create a list. For this reason, it’s better to create a list of data that you want to display in a dropdown before setting up this configuration option.
When you select «List» from the dropdown, a new list of options display in the «Data Validation» window. The «Source» text box is where you can type the range of cells. With a list of only five states, it’s easy to take a look at the cells that contain states and type them into this text box. However, when you have a range of cells that span several rows, you’d have to scroll down the spreadsheet to find the last cell in the list. You could also have empty cells that you miss as you scroll down the list. Instead of typing the cell range manually, you can click the arrow up button adjacent to the «Source:» text box. This opens a view of your spreadsheet where you can use your mouse to select the cells that contain a list of data.
Click the arrow button next to the «Source» text box to trigger the data selection feature. The «Data Validation» window collapses and then only the Source text box displays. Use the mouse to highlight each state. You don’t need to click the states individually. Instead, click the first state and drag your mouse to the last state in the list. The data validation tool will automatically create the range in the text box with the right textual labels that reference cells containing the information to display in the dropdown.
(Data list selected and displayed in Source text box)
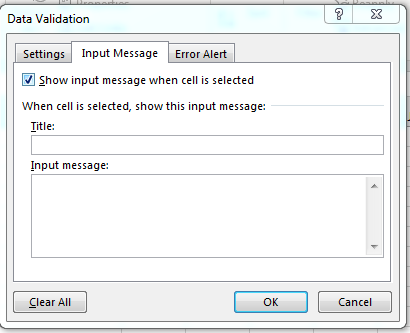
Click the «Input Message» tab to see a list of options to prompt the user with information when the input cell is selected. In some scenarios, having a label such as «State» is not enough to explain what the user should input. You might need additional information to explain what is needed using a prompt. You could set a Note but these notes are used for revisions and not the best option for setting instructional information. With an Input Message, you can prompt the user and display additional information when the cell is selected.
(Input message configuration window)
The input configuration window contains a title and an input message. The «Title» text box is where you set up the main title that the user will see when clicking the cell. The «Input Message» is arguably the more important input text box. This text box describes the purpose of the input selected by the user. It gives additional information to help the user understand the right data selection when filling out the Excel 2019 form.
Fill out these two input fields if you think more information is needed for the user as the form is filled out. Click the «Error Alert» tab to set up an error message or warning for the user should one occur.
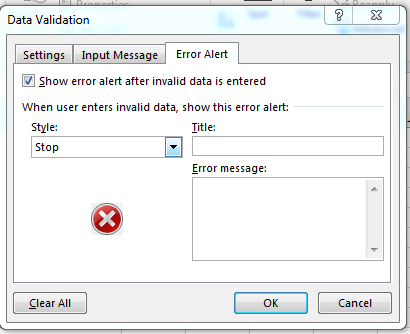
(Error alert option for a data dropdown)
In the configuration window above, the check box labeled «Show error alert after invalid data is entered» tells Excel to stop the user and display the configured error should the user enter invalid input. For instance, we have five states from which the user can select in a dropdown. If the user decides to enter a state that isn’t in the list, then Excel would display an error and prompt the user to re-enter information to valid input. You can remove this selection to skip the option, but you should only skip this option if you do not want to restrict data entry to only what’s available in the dropdown list.
In the «Style» dropdown, you can choose if you want to stop the user (the default), or if you want the message to show as an informational note or a warning. This gives you granular control of invalid data errors, so that you can choose if you want to allow the user to continue filling out the form even if data is incorrectly entered.
The «Title» and «Error message» input boxes are the text displayed to the user. Just like the ‘Input Message» option, the «Error message» text box is the most important because it gives the user detailed information on why the input is invalid.
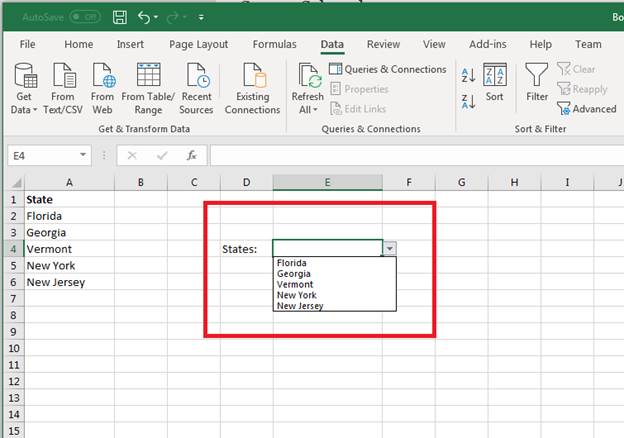
After you make your choices in all three tabs, click the «OK» button, and Excel 2019 sets up the dropdown list in the selected cell.
(Dropdown using a data list)
You can test the new dropdown data list by selecting data. You can also test the error messages by setting the cell to a state that does not match one in the set list.
For instance, first click the arrow in the dropdown and select «Florida.» Notice that no error message is displayed. Next, click the dropdown cell, which is E4 in this example. Type the word «Text» in the input cell. Click away from the input cell by clicking cell F1. Notice that an error message displays indicating that incorrect input was detected.
(Error message displayed from invalid input)
This error and validation control let you stop invalid input so that you can keep a spreadsheet of data that follows a strict rule set. By blocking invalid input, you can ensure that only a specific set of data is added to your input forms.
Dropdown lists are a common part of forms, and Excel makes it easy to create them whether the list contains 2 or 2000 cells. Dropdown lists are valuable when you have a set list of items from which you want users to choose, so they cannot just type any value into a cell. Using data lists makes creating long forms with multiple dropdown lists faster and remember that you aren’t limited to just the current sheet. You can reference any worksheet or workbook that contains your data by just adding the appropriate reference syntax in your data validation options.
Managing Data
Entering and managing lots of data can be a daunting task. It’s easy to get overwhelmed in all of those rows and columns of information. The solution is to use a form. A form is simply a dialog box that lets you display or enter information one record (or row) at a time. It can also make the information more visually appealing and easier to understand.
Most people who are familiar with the MS Office suite associate complex forms with Excel’s sister program Access, but you can use them in Excel as well. In fact, you can even share data between the two programs.
There are two kinds of forms available in MS Excel: data forms and worksheet forms.
-
Data forms are generally used for data entry. They are simple forms that list the contents of a single column. What’s more, they can display up to 32 fields at a time. This is especially helpful when dealing with a data range that reaches across more columns than will fit on a screen. You can insert, alter, delete, and even find records with data forms.
-
Worksheet forms are more sophisticated and specialized. They can be customized to fit the information at hand or to fill a particular need. They can even be complex and appealing enough to be printed or distributed online. Worksheet forms must be created using the Microsoft Visual Basic Editor.
Adding the Form Button to the Quick Access Toolbar
The Form button is not included in the ribbon, but you can add it to the Quick Access Toolbar, which, if you remember, is in the upper left hand corner of the application window.
To add the Form button, click the arrow to the right of the Quick Launch toolbar and select More Commands. This will launch the Excel Options window, which can also be accessed by clicking Options on the File tab.
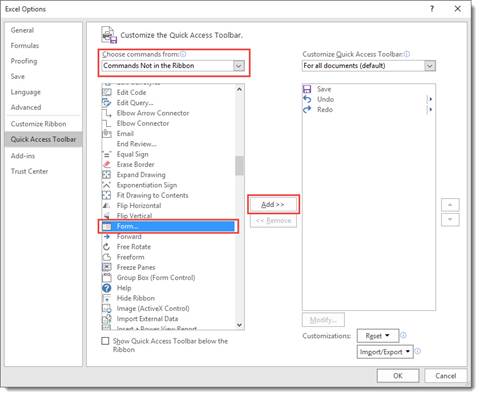
In the «Choose commands from» box, select Commands Not In the Ribbon, then scroll down through the list until you find Forms. Select it and click Add. When you are finished, click OK.
This is what the Form button looks like: 
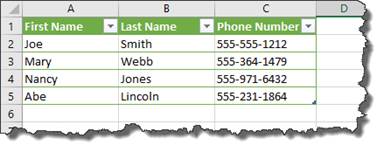
Adding Records Using the Data Form
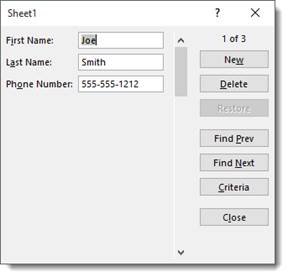
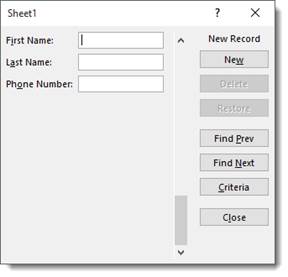
When you click the Form button for the first time, Excel will analyze the row of field names and entries for the first record. It uses that information to create a data form.
Let’s click on the Form button now.
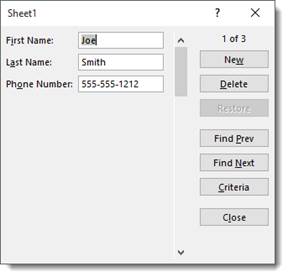
The first record appears in the dialogue box:
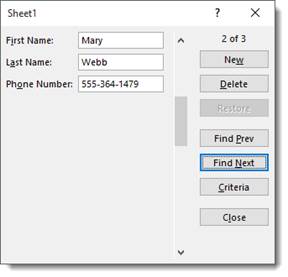
Click Find Next to find the next record.
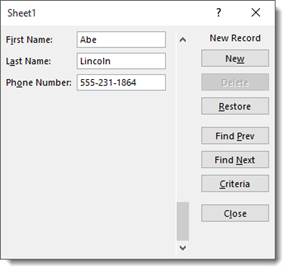
If you want to add a new record using the data form, click New.
As you can see in the snapshots above, the number of the record appears above the New button.
However, when you click the New button, it lets you know that it’s a new record.
Let’s add a new record.
Enter the information, then hit Enter.
The new record appears in your list:
You can hit ESC when you’re done adding records.
Editing Records in the Data Form
In addition to adding records, you can also edit them. You can use the data form to find records that need updated or removed from the list.
To do this, click the Form button on the Quick Access Toolbar.
Find the record that you want to update or remove.
Now click in any of the fields to update the data. You can also delete data in the field.
Hit Enter.
Navigating Through Records in the Data Form
If you have a lot of records, navigating through them can be a challenge. The data form makes it a bit easier.
If you want to move to the next record in the data form, press Enter or the down arrow key.
To move to the previous record, hit the up arrow or press Shift+Enter.
To move to the first record in the data list, press CTRL+ ? (up arrow) or press CTRL+PgUp.
To go to a new data form that comes after the last record, press CTRL+ ? (down arrow) or CTRL+PgDn.
Find Records in the Data Form
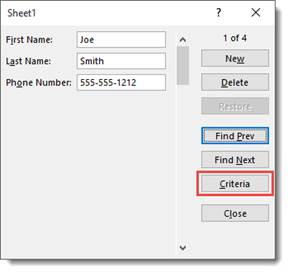
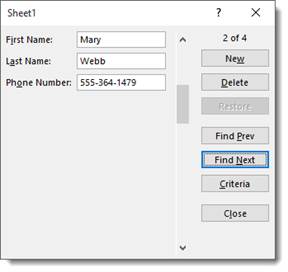
If you want to find a specific record, you can use the Criteria button in the data form. It’s pictured below.
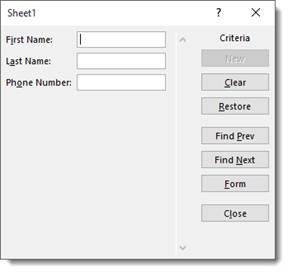
When you click the Criteria button, Excel 2019 clears the field entries in the data form. Instead, the word Criteria is displayed.
Let’s push the Criteria button to show you what we mean.
We now see a blank data form.
Notice that the word Criteria is above the new button, and the new button is inactive since we’re searching for a record.
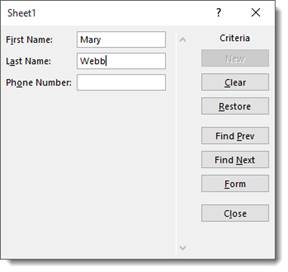
Now, let’s say you’re looking for a woman named Mary Webb, but you have 5000 women named Mary in your list.
Enter the criteria: Mary Webb.
Now click the Find Next button.
As you can see, it brings up the record.
You can also include the following operators in search criteria to help you find the record you need:
-
? for single
-
* for multiple wildcard characters
-
= Equal to
-
> Greater than
-
< Less than
-
>= Greater than or equal to
-
<= Less than or equal to
-
<> Not equal to
Data Validation
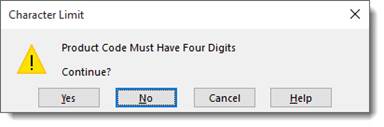
Data Validation lets you choose what information is acceptable to enter into a cell. For instance, you may have a product code that has four digits. You can set up a cell so that anything other than a 4-digit number will display an error message.
To set up data validation, select a cell or cells, then click the Data tab. Go to Data Validation in the Data Tools group.
Choose Data Validation from the dropdown menu.
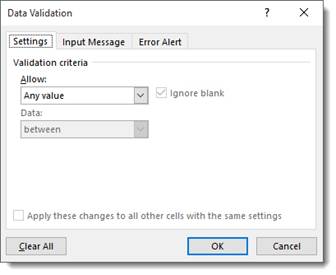
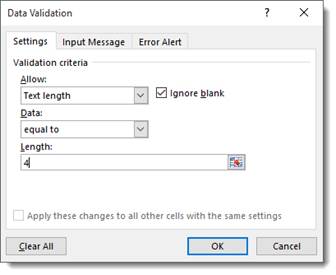
You’ll see this window:
Since we’re going to set up a cell to accept only a 4-digit number, we will select Text length from the drop down menu that says «Allow» over it. From the Data dropdown menu, we are going to select «equal to» and in the length text field we will type «4.» That tells Excel we want an entry with four characters.
From here, we can hit OK and have Excel 2019 provide a generic warning that looks like this:
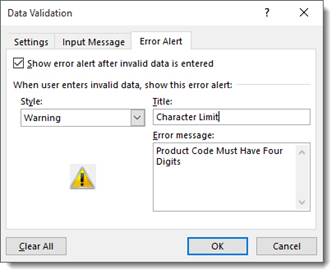
Alternatively, we can create a custom warning by selecting the Error Alert tab. Which looks like this:
Here we have selected the Warning style and entered the text for our error alert.
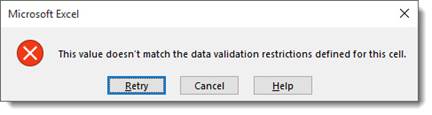
When a user enters a code of less or greater than four digits, the message will look like this:
There are three kinds of error messages available in Excel: information messages, warning messages, and stop messages. Information messages and warning messages do not prevent invalid information to be entered into the cell; they simply inform the user that such an entry has been made. Users can choose to ignore the warning. A stop message, on the other hand, will not allow an invalid entry. It has two buttons, Cancel and Retry. Cancel restores the cell to its original value, and retry returns them to the cell for further editing.
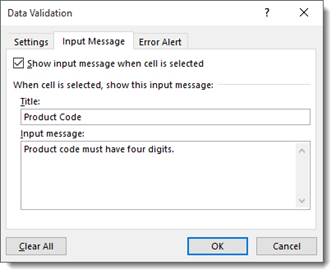
You can also set up a message to remind users what the restrictions or expectations are. Use the Input Message tab to create a custom reminder.
It will display anytime the cell or the range of cells is selected, as in the example below.
Auditing
MS Excel gives you a variety of tools to audit information in a worksheet. Just like data forms, formula auditing can take some of the confusion and frustration out of dealing with lots of different formulas. You can also see which cells have invalid information in them.
To use these tools, go to the Formulas tab, then the Formula Auditing group.
Select Error Checking and choose Error Checking from the dropdown menu.
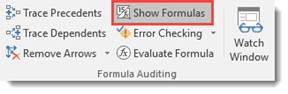
That said, it is not always apparent which cells have formulas in them. Therefore, the first step to evaluate the formulas is to find them. Click the Show Formulas button, as highlighted below.
As you can see in the example below, the whole numbers will be changed to the formulas and the formula cells will be selected.
To make it easier to see the cells when they are no longer selected, you can click the fill 
Let’s take a closer look at the other functions in the Formula Auditing group.
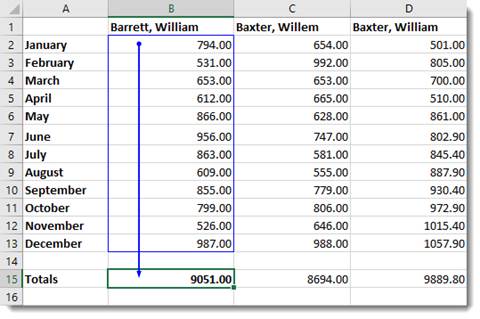
These two buttons allow you to trace (and turn off trace) precedents in a formula. A precedent cell is one that is referred to by a formula in another cell.
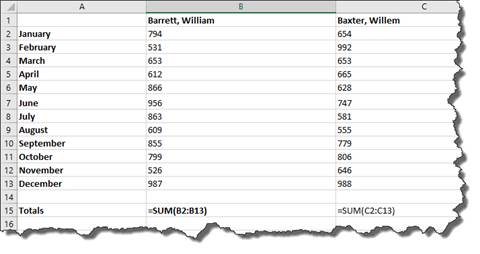
B2 thru B13 are precedents because they are referred to in the formula in cell B15. As you can see, the trace precedents button shows you the relationship between the cells.
The next button removes all arrows. 
The Watch Window (pictured below) is useful when you’re not sure if alterations to the value in a cell will affect a formula. You can easily remind yourself of the formula by adding it to the watch window.
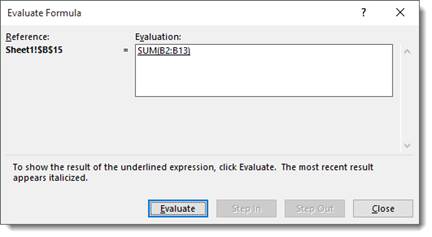
The Evaluate Formula function will perform the calculations of a formula in slow motion so you can see each step. To use it, select a formula, then click the Evaluate Formula button 
Click the Evaluate button to see Excel 2019 perform the calculations in slow motion. Use the Step In and Step Out buttons to navigate through each step in the formula.
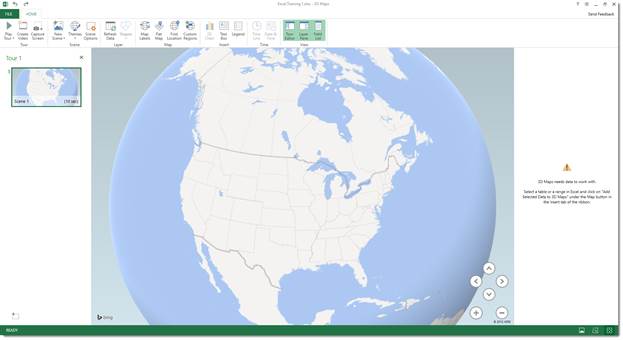
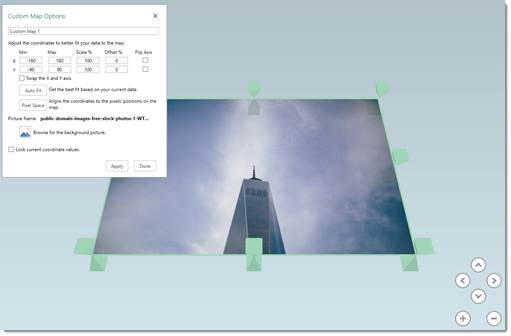
Introduction to Data Plotting Using 3D Maps
Excel lets you explore your data in a worksheet by plotting it on a map. For example, you might want to create a 3D map to show the cities where your customers live. You will need an image of a map in either .jpg, .png, or .bmp format. If the data you wish to plot on a map doesn’t relate to cities, but perhaps instead locations in a warehouse, you’ll want to upload an image that relates to your data. That said, you will also need data that relates to the picture so that your data can be plotted using an XY coordinate system.
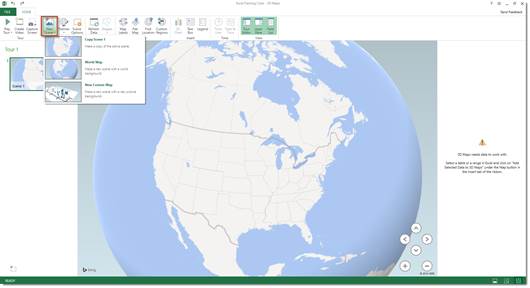
To create the 3D map, go to the Insert tab, then click the 3D Map button.
It may take a moment to load, but you will see the 3D Map screen.
To create a map customized for your data, click New Tour.
Go to Home>New Scene in the 3D Map screen.
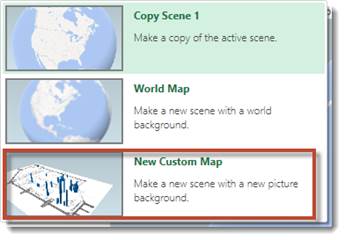
From the dropdown menu, select New Custom Map.
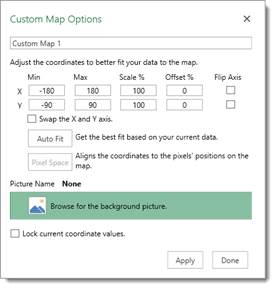
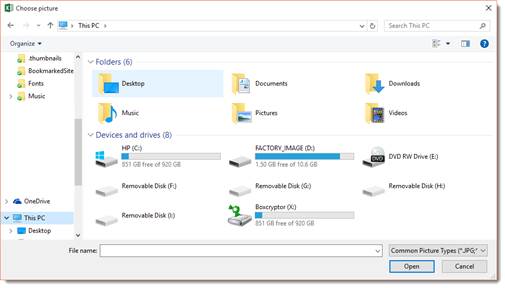
You will then see this dialogue box:
Locate the background picture you want to use.
Click Open.
You can now see your picture open in the 3D Map window. Use the dialogue box to adjust the XY coordinates if needed.
Click Apply, then Done.