-
Task Type: Key Word Transformations
-
Focus: Lexical and grammatical
-
-
Format: Six separate items, each with a lead-in sentence and a gapped second
sentence to be completed in two to five words, one of which is a given
‘key word’
-
-
Number of questions: 6
-
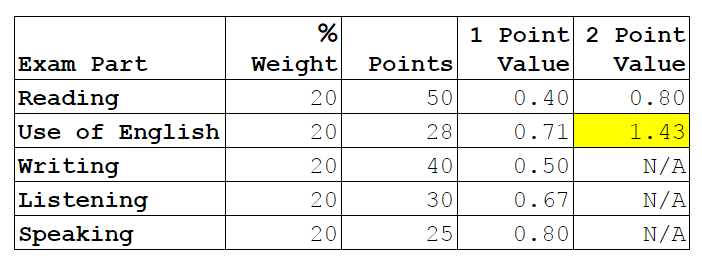
How many marks are there: Up to two marks for each correct answer
What is testing:
- modal verbs and semi-modal verbы
- phrasal verbs
- verb patterns
- direct speach to reported speach
- active voice to passive voice
- linking words/do and make/idioms/conditionals/unreal past
General Advice
- Write between two and five words as your answer
- Contractions like can’t or mustn’t are counted as two words
- Take a guess if necessary! You will not loose marks
- Remember that you cannot change the key word
cambridge english first certificate (fce) test
Key Word Transformations
- FCE : Key Word Transformations 1
- FCE : Key Word Transformations 2
- FCE : Key Word Transformations 3
- FCE : Key Word Transformations 4
- FCE : Key Word Transformations 5
- FCE : Key Word Transformations 6
- FCE : Key Word Transformations 7
- FCE : Key Word Transformations 8
- FCE : Key Word Transformations 9
- FCE : Key Word Transformations 10
- FCE : Key Word Transformations 11
- FCE : Key Word Transformations 12
- FCE : Key Word Transformations 13
- FCE : Key Word Transformations 14
- FCE : Key Word Transformations 15
- FCE : Key Word Transformations 16
- FCE : Key Word Transformations 17
- FCE : Key Word Transformations 18
- FCE : Key Word Transformations 19
- FCE : Key Word Transformations 20
-
There i
s no p
oint in
doing
It is n
ot wort
h doin
g
Its no
use d
oing
Its no
good
doing
Do no
t bothe
r to do
/doing
It happ
ened fo
r the se
cond y
ear ru
nning.
It happ
ened fo
r the se
cond y
ear in
succes
sion.
It happ
ened fo
r the se
cond y
ear in
a row.
He is a
bout to
do it.
He is o
n the ve
rge of
doing
it.
He is o
n the p
oint of
doing
it.
FCE — CAE
-
GRAMMAR & VOCABULARY www.aprendeinglesenleganes.com
HOW TO USE THIS EBOOK. PRESS Ctrl + F to open up the search box
in your PDF reader or editor. Type in the word or expression you
want to find. Note: You will find that the subjects and objects in
the examples have been substituted for: X = 1st Subject or 1st
Object (someone/something)Y = 2nd Subject or Object
(someone/something)Z = 3rd Subject or object.
(someone/something) -
GRAMMAR & VOCABULARY www.aprendeinglesenleganes.com
1- Someone will always remember X / doing X.
Someone will never forget X / doing X.
2- I think doing X is a waste of time. There is no point in
doing X. There isnt any point in doing X.It is not worth doing X. Its no use doing X.
Its no good doing X. Do not bother to do /doing X
3- Its possible that X did Y.
X might have done Y.
4- X continued to do Y. X carried on doing Y.
5- There isnt much chance of X doing Y. X isnt likely to do Y.
There is little prospect of x doing Y.6- X is not going to do Y anymore/ X is going to stop doing Y. X
is going to give up doing Y.7- Im sure X was very Y. X must have been very Y. 8- X really
ought to do Y.It is high time for X to do Y / It is high time (that) X did Y.
It is about time for X to do Y / It is about time (that) X did
Y.9- X wishes he had done Y / X wishes he had not done Y X regrets
not having done Y / X regrets having done Y10- Although / even though it was X. Despite / In spite of it
being X. -
GRAMMAR & VOCABULARY www.aprendeinglesenleganes.com
11- He doesnt like either of them. He likes neither of them. 12-
X should think about Y. X should take Y into consideration. 13- X
does not stop Y from doing A. X is ineffective at stopping Y from
doing A. 14- X wants to learn / start learning Y.X want to start doing Y. X wants to take up Y / doing Y 15- X
became quite Y. X was overcome with/by Y. 16- X went somewhere on
his/her own. X went somewhere by himself/herself. X went somewhere
alone. 17- X saw something and did Y immediately. X saw something
and did Y without hesitation. 18- Its the most X Ive ever seen. I
have never seen such an X / I have never seen a more X. 19- Do you
think you could give me a hand to do Y? Would you mind giving me a
hand to do Y? I would appreciate it if you could give me a hand to
do Y. I would appreciate it if you gave me a hand to do Y. I would
appreciate your giving me a hand to do Y. I would appreciate you
giving me a hand to do Y. 20- X is not as good at A as Y. Y is
better at A than X. 21- X wants to do Y. X is interested in doing
Y. X has an interest in doing Y -
GRAMMAR & VOCABULARY www.aprendeinglesenleganes.com
22- X will only do A if Y does B. X will not do A unless Y does
B. X will do A as long as / so long as Y does B. X will do A
provided (that) Y does B 23- X can do A provided (that) he doesnt
do B. X can do A providing (that) he doesnt do B.X can do A , but only if he doesnt do B X can do A on the
condition (that) he doesnt do B. X can do A as long as he doesnt do
B. 24- X demanded to do Y. X insisted on doing Y. 25- X should
consider A before doing B. X should take into account A before
doing B. 26- X was led to believe Y… X was under the impression
(that) Y… X was given the impression (that) Y 27- Feel free to do
Y. Do not hesitate to do Y. 28- When you decide to do Y. When you
make up your mind to do Y. When you come to the decision to do Y
When you make the decision to do Y 29- X would never have guessed
that …X would never have though that Little did X know that… 30- Do
you mind if I do Y? Do you have any objection to me/my doing Y? 31-
Not as many people do X as when Y. There are a lot fewer people
doing X than when Y. -
GRAMMAR & VOCABULARY www.aprendeinglesenleganes.com
32- X was shocked/ surprised by Y.
X was taken aback by Y. 33- X knows / knew nothing about Y X is
/ was in the dark about Y. 34- X happened for the second year
running. X happened for the second year in succession. X happened
for the second year in a row. 35- X must never do A without doing Y
first. On no account must X do A without doing Y first. X shouldnt
do A without doing Y first. 36- X is not very likely to be given Y.
X has little chance of being given Y. 37- If you dont do X you
shouldnt do Y. Dont do Y unless you do X. 38- He dismantled X to
see what the problem was. He took X apart to see what the problem
was. 39- X is rumored to be (doing) Y. Rumor has it that X is
(doing) Y. Word spread that X is (doing) Y. Word got out/around
that X is (doing) Y 40- X is about to do Y. X is on the verge of
doing Y. X is on the point of doing Y. 41- X does not intend to do
Y. X has no intention of doing Y. X would not dream of doing Y. X
is not planning to do Y. X is not planning on doing Y -
GRAMMAR & VOCABULARY www.aprendeinglesenleganes.com
42- X has a good reputation for Y. X is highly regarded for Y. X
is held in high repute for Y. 43- X was surprised to be given Y.
Being given Y came as a surprise to X. Much to his surprise, X was
given Y. 44- X is improving. X is changing for the better. X is
making an improvement. X is getting better. X is looking up. 45- X
is going to get worse. X is going to change for the worse. X is
going to worsen / deteriorate. 46- X was very disappointed when Y
decided to leave. Ys decision to leave, came as a disappointment to
X. Much to Xs disappointment, Y decided to leave. To Xs great
disappointment, Y decided to leave. 47- Much to Xs
surprise/amazement/annoyance , Y happened.To Xs great surprise/amazement/annoyance , Y happened. Y came as
a surprise/amazement/annoyance to X.48- X is almost certain to get Y. X has every chance of getting
Y. There is no doubt that X will get Y. X is bound to get Y. 49- If
X had had more time he would have done Y. If X had not been short
on/of time he would have done Y. 50- X did not mention Y. X made no
reference to Y. -
GRAMMAR & VOCABULARY www.aprendeinglesenleganes.com
51- X didnt arrive on time. X failed to arrive on time. 52- X
never thought of doing Y. It never occurred to Y to do Y. The
thought of doing Y never crossed Xs mind. 53- Despite all his
efforts X could not do Y. No matter how hard X tried , he could not
do Y. However hard X tried, he could not do Y. 54- X is going to
become Y one day. It is only a matter of time before X becomes Y.
55- X will not tolerate Y. X will not put up with Y. 56- X can do Y
provided (that) Z happens. As long as Z happens X can do Y. 57- X
couldnt do / wasnt able to do Y because Z. Z made it impossible for
X to do Y. 58- X said that he/she would not do Y. X refused to do
Y. 59- There is no way X will do Y. X has no intention of doing Y.
X has no thought of doing Y. X wouldnt dream of doing Y. 60- X
needs to make a decision about Y . X needs to make up his/her mind
about Y. 61- X claims must be submitted before Y. You needs to put
in your x claims before Y. 62- There are various ways of avoiding
Y.Y can be prevented in various ways.
-
GRAMMAR & VOCABULARY www.aprendeinglesenleganes.com
63- X thinks learning Y is a waste of time. X cant see the point
in/of learning Y. X sees no point in learning Y 64- Y should be
turned off at all times during Z. Under no circumstances should Y
be kept turned on during Z. Whatever happens, Y should never be
kept turned on during Z.65- If X doesnt do Y on time , his Z will be rejected. Failure
to do Y on time will result in Z being rejected. 66- X soon
recovered after Y. X made a quick/fast/speedy/rapid recovery after
Y. 67- X has a good reputation in the city. X is highly regarded in
the city. X is highly thought of in the city. X is highly spoken of
in the city. 68- There are no fewer than X. There are as many as X.
69- X ignored what Y said.X took no notice of what Y said. X didnt take any notice of what
Y said. X didnt heed what Y said. X paid no heed to what Y said. X
didnt pay any heed to what Y said.70- X was certain that Y would be OK. X was in no doubt that Y
would be OK. 71- X had completely forgotten Y / that he did Y. X
didnt have any recollection of Y/ of doing Y. X had no recollection
of Y/ of doing Y. 72- If X hadnt done Y, he might have become a
famous Z. If X hadnt done Y , he might have made a name for himself
as a Z -
GRAMMAR & VOCABULARY www.aprendeinglesenleganes.com
73- X said Y was his fault. X took the blame / took
responsibility for Y. 74- Nobody ever told X that Y. At no point
was X told that Y. 75- X didnt know he had to do Y. X didnt know he
was meant to do Y. X didnt know he was supposed to do Y. 76- X
tried really hard , but never got Y. No matter how hard he tried ,
he never got Y. However hard he tried, he never got Y. 77- X said Y
, but Im sure he is wrong. X said Y, but Im sure hes made a
mistake. X said Y, but he must have made a mistake. 78- You should
do Y so that you are sure to succeed. Its worth doing Y just in
case you dont succeed. 79- X likes to look/ looking after Y. X
likes to take/taking care of Y. X enjoys taking care of Y. 80- It
is possible that X didnt do Y. X might not have done Y. 81- X didnt
manage to win Y. X didnt succeed in winning Y. 82- It is difficult
to accept Y.It is difficult to get used to Y It is difficult to come to
terms with Y. 83- X will be punctual today. X will be on time
today. -
GRAMMAR & VOCABULARY www.aprendeinglesenleganes.com
84- X was not used to Y. Y was something X was not accustomed
to. 85- Some people really struggle with X. Some people find X /
doing X very difficult/hard. 86- X found it difficult to think of
the right answer. X found it hard to come up with the right answer.
87- X shows that Y has risen sharply today. According to X there
has been a dramatic rise in Y today. 88- The flight leaves New York
at 2pm. The flight takes off from New York at 2pm. 89- There was a
fault with X and the Y didnt work. The Y whose X was faulty/ had a
fault. 90- Y was too expensive for X to buy. X didnt have enough
money to buy Y. 91- Y is easier than Z. Y is not as hard as Z. 92-
We have not arranged a date for X yet. A date for X has not been
arranged yet. 93- Ill call you later tonight, X promised. X
promised that he would call later that night. 94- X did Y so that
he would be ready for the race. X did Y in order to be ready for
the race. X did Y so as to be ready for the race. 95- X had to
finish Y before he went out. X had to stay in until he had finished
Y. 96- X had not expected Y to be so good. Y was better than X had
expected. -
GRAMMAR & VOCABULARY www.aprendeinglesenleganes.com
97- Do you know the way to the restaurant? X asked Y. X asked Y
if she knew where the restaurant was. 98- X decided to advertise Y
on the internet. X decided to put an ad / advert/ advertisement for
Y on the internet. 99- X did Y a month ago. It has been a month
since X did Y. It is a month since X did Y.100- The meeting was cancel because Y. The meeting was called
off because Y.101- X is interested in learning Y. X would like to learn Y.
102- Did you go to the tournament on Saturday? David asked me.
David wanted to know if I had been to the tournament on
Saturday.103- X never takes any notice of Y. X never pays any attention
to Y. 104- X is really excited about Y / doing Y. X is looking
forward to Y/ doing Y. X cant wait to do Y 105- They are said to be
worried about Y. There is said to be concern among them about Y.
106- I dont think they should abolish Y. They shouldnt do away with
Y.107- X has to reduce the number of Ys he eats. X has to cut down
on the number of Ys he eats. 108- X will let you stay with them. X
will put you up. X will take you in. -
GRAMMAR & VOCABULARY www.aprendeinglesenleganes.com
109- X says he prefers to do something on his own.
X says hed rather not do something with other people.
110- X said he had not done X X denied having done X. X denied
doing X 111- It took X five minutes to do Y.X took five minutes to do Y. X spent five minutes doing Y.
112- X will take place after Y. Y will be followed by X. X will
be held after Y 113- X did Y although he had never done Z. In spite
of X never having done Z he did Y. 114- It is thought that X cannot
do Y.X is thought to be unable to do Y.
115- X needs doing. X needs to get done. 116- There is no point
in doing X. Its no use doing X. Its no good doing X. Its not worth
doing X 117- X cried his eyes out immediately when he was told Y. X
burst into tears as soon as he was told Y. X broke in/into tears as
soon as he was told Y. X broke out in/into tears as soon as he was
told Y. 118- X managed to persuade Y to do Z. X managed to talk Y
into Z / into doing Z. -
GRAMMAR & VOCABULARY www.aprendeinglesenleganes.com
119- X managed to persuade Y no to do Z. X managed to talk Y out
of Z / out of doing Z. 120- X does Y now and again. X does Y
(every) now and then X does Y (every) once in a while X does Y from
time to time 121- Nearly every X there is Y Hardly an X passes
without there being a Y 122- Nobody can foresee how X will react.
It remains to be seen how X will react. 123- X said he objected to
Y. X raised /voiced objections to Y. X had objections to Y. 124- X
owed Y 200. X was 200 in debt to Y. 125- X owed 200 to Y. X was in
debt to Y for 200.126- X was easy for to do Y. X had no difficulty (in) doing Y X
didnt have any difficulty (in) doing Y. X didnt find it hard to do
Y. 127- X arrived at X just in time to do Z. X made (it to) X just
in time to do Z. 128- X made Y go to bed early because she had to
do Z X would have let Y stay up late if she hadnt had to do Z 129-
X escaped in a white Mercedes X made his getaway in a white
Mercedes -
GRAMMAR & VOCABULARY www.aprendeinglesenleganes.com
130- X said it was Ys fault that Z happened. X placed the blame
on Y for Z having happened. X laid/pin/put/place the blame on Y for
Z . Y got the blame for Z happening. Y came in for the blame of
131- X finds it very satisfying doing Y.X gets a lot of satisfaction from doing Y.
132- It doesnt seem to me as if Y is Z. As far as I can tell Y
is not Z. 133- X maintains that he kept his word that he would not
tell anyone Xssecret. X denies breaking his promise to keep Xs secret.
134- X studied history because he/she wanted to become a Y. X
studied history with a view to becoming a Y.X studied history with a eye to becoming a Y.
135- It wasnt necessary for X to do Y but he did it. X neednt
have done Y.136- Perhaps X did Y and Z happened. X may have done Y and Z
happened137- X is certain Y did Z. Y must have done Z 136. X didnt feel
like doing Y that night.X was not in the mood for doing Y that night. X was not in the
mood to do Y that night.137. X was offended by what Y said. X took exception to what Y
said. X took offence at what Y said.138. X thinks it would be better to get on as quickly as
possible. X would prefer us TO MAKE AS MUCH progress as we can. -
GRAMMAR & VOCABULARY www.aprendeinglesenleganes.com
139. X wishes to express his concern over Y.
X feels he must say HOW WORRIED HE IS BY Y.
140. X was astonished by Y as he hadn’t thought he would win a
Z. Not HAVING EXPECTED a Z, X was completely astonished by Y.141. X found it difficult to get used to the fact that he’d lost
his job. X found it hard TO COME TO TERMS WITH the fact that he’d
lost his job.142. X was upset that Y didn’t support him in the argument. X
was upset Y DIDN’T BACK HIM UP in the argument.143. X is sure that Y can solve the problems. X is sure that Y
can COME UP WITH A SOLUTION to the problems.144. They say X is Y. X is reputed/said to be Y
145. Doing Y is my number one priority. It is of the utmost
importance that I do Y.146. X had to try for months before he got Y. Only after trying
for months did X get Y. Only after having tried for months did X
get Y.147. X rarely does Y. Rarely does X do Y.
148. As soon as X did Y somebody’s phone rang. No sooner had X
done Y than somebodys phone rang.149. X has never read such a boring book before. Never before
has X read such a boring book. -
GRAMMAR & VOCABULARY www.aprendeinglesenleganes.com
150. This door must not be left open at any time.
At no time must this door be left open.
151. X only caught Y when his wife came. Only when his wife
came, did X catch Y.152. X is not revealed until the very last page. Not until the
very last page , is X revealed.153. X would never do Y again. Never again would X do Y.
154. X had hardly done Y when the phone rang. Hardly had X done
Y when the phone rang155. X had not enjoyed himself so much since Y. Not since Y, had
X enjoyed himself so much..156. X had never been to such a fantastic Y. Never had John been
to such a fantastic Y.157. X in no way wants to be associated with Y. In no way does X
want to be associated with Y.158. X had scarcely finished Y when Z happened. Scarcely had X
finished Y when Z happened.159. X seldom does Y so early . Seldom does X do Y so early.
160. X rarely appreciates Y . Rarely does X appreciate Y. X
hardly ever appreciates Y.161. X would understand Y only later . Only later would X
understand Y.. -
GRAMMAR & VOCABULARY www.aprendeinglesenleganes.com
162. X had seen such Y nowhere before .
Nowhere before had X seen such Y.
163. X understood little about the situation. Little did X
understand about the situation…164. X always gives the impression that hes very confident. X
always comes across as being very confident.165. X didnt know that x were so expensive X had no idea that x
cost so much.166. Dont get depressed because of X. Dont let X get you
down.167. X is recovering in hospital. X is making a recovery in
hospital. 168. X must take as much advantage as possible of YX must make the most of Y
169. X doesnt mind where we go. It doesnt matter to X where we
go. Its all the same to X where we go.170. There is no more X available in Y. Y has run out of X.
171. X doesnt like Y very much. X is not very keen on Y. 172. X
needed Y yesterday but he couldnt get it. X could have done with Y
yesterday.173. Im sure she will do a good job. She is bound to do a good
job. There is no doubt in my mind that she will do a good job. -
GRAMMAR & VOCABULARY www.aprendeinglesenleganes.com
174. X had an argument with Y and are not talking to each other
anymore. X fell out with Y. 175. X caught a cold.X came down with a cold. X went down with a cold. 176. X was
affected by Y X felt the effects of Y 177. X has been too busy to
do YX has not got round to doing Y yet. 178. X didnt know how to do
Y , so he made a mistake. Not knowing how to do Y , X made a
mistake. 179. I think there are going to be X. In my opinion ,
there are going to be X. In my estimation, there are going to be X.
If you ask me, there are going to be X.180. Having finished X, John went home.
After finishing X , John went home. After he had finished X ,
John went home. 181. I dont believe that Y will do Z. It is my
belief that Y won`t do Z. I have/get the impression that Y do wont
Z. I have/get a feeling that Y wont do Z. I have/get the feeling
that Y wont do Z. There is no reason to believe that Y will do Z.
182. While X was walking down the street , he saw Y. While walking
down the street , X saw Y. When X was walking down the street , he
saw Y. It was while X was walking down the street that he saw
Y. -
GRAMMAR & VOCABULARY www.aprendeinglesenleganes.com
183. X disagreed with Y, so he resigned
xxx Xs resignation resulted from his disagreement with Y Xs
disagreement with Y resulted in his resignation. Xs disagreement
with Y led to his resignation.184. X couldnt understand what had happened.
X couldnt work out what had happened X couldnt put the finger on
what had happened X couldnt piece together what had happened.185. X is becoming quite well known as a Y X is making a name
for himself/herself as a Y186. X made his mark on Y X had an important effect on Y
187. When it comes to X As far as X is concerned
188. You need to have a lot of X to do Y Y calls for a lot of
X189. He didnt do X until Y happened. It was only when Y happened
that he did X190. It seems unbelievable that X is Y when it is so Z X is so Z
that it is hard to believe that it is Y.191. X could do with Y X could use a Y X could benefit from Y Y
would do X good192. Y is impossible for X. Y is out of the question for X.
There is no question for X of Its out of the question for X to do Y
There is no question of doing Y There is no question of X doing
Y -
GRAMMAR & VOCABULARY www.aprendeinglesenleganes.com
193. X watched Y while Z did
X guarded Y while z did X kept an eye on Y while Z did
194. X assumed Y was coming X took for granted Y was coming X
took it as read that Y was coming195. X let Y know what was going on. X put Y in the picture
about what was going on. X brought Y up to speed about/with what
was going on. X filled Y in on what was going on.196. The company struggled to replace X The company struggle to
fill the vacancy/post created/left by X197. X headed to/for the door X made his/her way to the
door.198. X was faced with some difficulties. X came up against some
difficulties. X met with some difficulties.199. X found Y by chance. X came across Y. X bumped into Y.
200. The meeting has been postponed until next week. The meeting
has been put off until next week.201. X found it difficult to understand Y. X struggled to
understand Y. X found it hard to get/come to grips with Y. X found
it difficult to get his head around Y.202- X did not realise how important Y was. X failed to realise
the importance of Y -
GRAMMAR & VOCABULARY www.aprendeinglesenleganes.com
203- X was raised by his parents.
X was brought up by his parents.
204- X is investigating allegations of Y. X is looking into
allegations of Y.205- X is considering ways of cutting costs. X is looking at
ways of cutting costs.206- I will consider it and give you an answer next week. I will
think it over and give you an answer next week.207- X cant ride a bike, so he certainly cant ride a motorcycle.
X cant ride a bike, much less a motorcycle. X cant ride a bike,
even less a motorcycle. X cant ride a bike, still less a
motorcycle. X cant ride a bike, let alone a motorcycle.208- X tends to do Y X is in the habit of doing X X has the
habit of doing X209- When X first met him, he thought he was very polite. When X
first met him, He struck him as (being) very polite. When X first
met him X got/had the impression that he was veryvvv polite.
210- X said he was sorry for doing Y. X said he regretted doing
Y X apologized for doing Y.211- X doesnt care if Y does it or not. It makes no difference
to X whether/if Y does it or not. Its all the same to X whether /if
Y does it or not. It is of no consequence to X whether /if Y does
it or not.212- X impressed Y. X made a good impression on Y.
-
GRAMMAR & VOCABULARY www.aprendeinglesenleganes.com
213- X can alter depending on the weather.
X is subject to alteration depending on the weather. X is
subject to change depending on the weather.214- Hopefully, this will help us to understand what happened.
Hopefully, this will shed/ cast/ throw some light on what
happened.215- X corrected Y on a number of points which Y had
misunderstood. X set/put Y right on a number of points which Y had
misunderstood. X set/put Y straight on a number of points which Y
had misunderstood.216- X concluded that there was nothing else he could do. X came
to the conclusion that there was nothing else he could do. X
reached the conclusion that there was nothing else he could do. X
drew the conclusion that there was nothing else he could do.217- X is so + adjective (e.g. powerful, beautiful, interesting,
etc.) that Such is Xs + noun (e.g. power, beauty, interest, etc.)
that218- In the end X got home on Tuesday. X ended up getting home
on Tuesday. Eventually, X got home on Tuesday. X finally got home
on Tuesday.219- X always does Y when Z happens. X has a tendency to do Y
when Z happens.220- X says that Y was not as good as he expected. X says that Y
didnt live up to his expectations. X says that Y fell short of his
expectations.221- X is a much better mechanic than Y. Y is nowhere near as
good as a mechanic as X.222- Only X prevented Y. Had it not been for X , Y would have
happened.223- One day something will happen. Its only a matter of time
before something happens. -
GRAMMAR & VOCABULARY www.aprendeinglesenleganes.com
224- X treats Y as a brother rather than as a friend
X treats Y not so much as a friend as a brother.
225- X didnt do it because he didnt want Y to happen. X didnt do
it for fear of Y happening.226- Since X is inevitable, we need to learn to do Y. As X is
inevitable, we need to learn to do Y. Given that X is inevitable,
we need to learn to do Y. Because X is inevitable, we need to learn
to do Y.227- X will need to do Y every day if he wants to succeed. Only
by doing Y every day will X succeed.228- X is thought to have caused Y. Y is thought to have been
brought about by X. X is thought to have given rise to Y.229- X has been thinking about Y all day. Y has been on Xs mind
all day.230- X wishes Y would stop criticizing his work. X wishes Y
would stop finding fault with his work.231- Its impossible to say who will win. There is no (way of)
telling who will win.232- More than 100 people came to the meeting. More than 100
people show up at/for the meeting. More than 100 people turn up
at/for the meeting. More than 100 people attended the meeting. Over
a 100 people came to the meeting.233- X wants to do Y as far as I know. To (the best of) my
knowledge, x wants to do Y. From what I understand, X wants to do
Y. My understanding is that X wants to do Y. -
GRAMMAR & VOCABULARY www.aprendeinglesenleganes.com
234- X has very little Y.
X hardly has any Y.
235- Women outnumbered men by two to one at the concert. There
were twice as many women as men at the concert.236- X says that he cant promise that you will succeed. X says
that he cant guarantee that you will succeed.237- X wants to do Y but has not found the time to do it yet. X
wants to do Y but has not got (a)round to doing it yet.238- The traffic jam delayed X for several hours. The traffic
jam held X up for several hours.239- X told Y not to go there because it was snowing. X warned Y
against/ off going there because it was snowing. X warned Y not to
go there because it was snowing.240- The cost of X has come down.
The has been a drop in the cost of X. The has been a fall in the
cost of X.241- X was bitterly disappointed he was not given Y.
To Xs bitter disappointment, he was not given Y.
242- Even if it is hard, we want to do it. Hard though it may
be, we want to do it.243- X started doing Y seriously. X got down to doing Y. 243. X
was forced to do Y. X had no choice but to do Y. 244. X replaced Y
after the meeting.X took the place of Y after the meeting. X substituted for Y
after the meeting. -
GRAMMAR & VOCABULARY www.aprendeinglesenleganes.com
245. X has a feeling of great respect for Ys dedication.
X admires Y for his dedication. X looks up to Y for his
dedication.246. X finds Y really annoying. Y gets on Xs nerves.
247. The building is going to be destroyed. The building is
going to be knocked down. The building is going to be
demolished.248. It is Xs responsibility to do Y. It is Xs decision to do Y.
It is down to X to do Y. It is up to X to do Y.249. X is scheduled to start at 5 p.m. X is to start at 5
p.m.250. I cant remember her name. I cant recall her name. I cant
bring her name to mind. I cant call her name to mind. I cant think
of her name. Her name doesnt come to me.251. X didnt realized what it meant at the beginning. The
meaning didnt sink in with X at the beginning. X didnt understand
what it meant at the beginning.252. Doing Y is not allowed here. Doing Y is not permitted here.
Doing Y is forbidden here.253. X was dismissed for being late. X was fired for being late.
X was got the sack for being late. X was given the sack/ given the
boot for being late. X was removed from his job for being late. -
GRAMMAR & VOCABULARY www.aprendeinglesenleganes.com
254. X doesnt have enough money to buy expensive clothes.
X cant afford to buy expensive clothes. Xs salary doesnt run to
(buying) expensive clothes.255. If X doesnt do Y his reputation will be damaged. X wants to
do Y to live up to his reputation.256. What happened confirmed what X predicted. Xs predictions
were borne out by what happened.257. The only person who didnt come was X. Everybody came apart
from X. Everybody came except for X.258. X didnt accept the job he was offered. X rejected the job
he was offered. X turned down the job he was offered.259. X has a natural ability for computers. X has a natural
talent for computers. X has a flair for computers. X is very
skilful with computers. X has always been very good with
computers.260. X is having his house decorated. X is having improvements
made to his house. X is having his house done up.261. It is not probable that he will be returning to England. It
is improbable that he will be returning to England. It is not
likely that he will be returning to England. It is unlikely that he
will be returning to England. He is unlikely to be returning to
England. He is not likely to be returning to England.262. I regret not telling the truth. I wish I had told the
truth. If only I had told the truth. -
GRAMMAR & VOCABULARY www.aprendeinglesenleganes.com
263. Do you mind if I phone you later? Can I get back to you
later?264. X has done Y for as far as he can remember. X cant remember
when he started doing Y.265. X was so thrilling that Y couldnt stop cheering. Y was so
thrilled by X that he couldnt stop cheering.266. Mike, you broke my computer. Said Nigel. Nigel accused Mike
of breaking his computer.267. X didnt want to go out. X didnt feel like going out. X was
not up for going out. X was not in the mood for going out.268. X was determined to do Y. X insisted on doing Y.
269. X cant drive because of his disability. Xs disability
prevents him (from) driving.270. When X was a kid, he would play football every Friday When
X was a kid, he used to play football every Friday When X was a
kid, he was in the habit of playing football every When X was a
kid, he was accustomed to playing football every271. X was very tired, after working so much that day. X ran
himself into the ground that day. X drove himself into the ground
that day. X worked himself into the ground that day.272. X only managed to see the thief for a second as he ran
away. X saw the thief briefly, as he ran away. X only caught a
glimpse of the thief as he ran away. X only caught sight of the
thief as he ran away.273. X lost his job because of his laziness. X lost his job on
the grounds of his laziness. -
GRAMMAR & VOCABULARY www.aprendeinglesenleganes.com
274. X becomes/gets angry when people shout at him.
X loses him temper when people shout at him. X gets mad when
people shout at him. X flies off the handle when people shout at
him.275. X realised he could never be an actor. X realised he was
not the right type of person to be an actor. X realised he was not
cut out to be an actor.276. X caused Y to be cancelled. Y was cancelled because of X. Y
was cancelled as a result of X.277. X didnt seem to realize the magnitude of the problem. X
didnt seem to understand the magnitude of the problem. X didnt seem
to be aware of the magnitude of the problem. X seemed to be unaware
of the magnitude of the problem. X didnt seem to grasp the
magnitude of the problem.278. X wants to throw Y away. X wants to remove Y. X wants to
get rid of Y.279. X is head of this company. X is in charge of this company.
X is the person leading this company.280. She is by nature not critical. Its not in her nature to be
critical. She is not one to be critical. Its not like her to be
critical. It would be out of character of her to be critical. It is
not in her character to be critical.281. Xs application was turned down because he didnt have Y.
Xs application was turned down on the grounds that he didnt have
Y.282. X didnt do Y because it was raining heavily. But for the
heavy rain, X would have done Y. -
GRAMMAR & VOCABULARY www.aprendeinglesenleganes.com
283. X was highest in November. X was at its highest in
November. X reached a peak in November.284. So much responsibility was putting pressure on X. So much
responsibility was weighing X down. So much responsibility was
weighing down on her.285. X fell slightly yesterday. There was a brief dip in X
yesterday.286. X expects to do Y before he is thirty. X expects to do Y by
the time he is thirty.287. Scientists have made an unexpected discovery. There has
been an unexpected breakthrough.288. X felt very comfortable doing Y. X was very confident and
relaxed doing y. X was at ease doing Y.289. X made Y stop. X put an end to Y.
290. Explaining what you mean to a kid can be difficult. Getting
your point across to a kid can be difficult. Getting your message
across to a kid can be difficult.291. X is living there temporarily. X is living there for the
moment. X is living there for the time being.292. I need to make her understand that I dont want to see her
anymore. I need to get it across to her that I dont want to see her
anymore. I need to get it through to her that I dont want to see
her anymore.293. If was a mistake not to do Y. I should have made it a point
of doing Y. I should have made it my business to do Y. -
GRAMMAR & VOCABULARY www.aprendeinglesenleganes.com
294. X did Y easily. X had no problem in doing Y. X had no
problem doing Y. X had no problems doing Y. X didnt have any
problems doing Y. X had no difficulty in doing Y. X had no
difficulty doing Y.295. The business has been bought by X. The business has been
taken over by X. The business is under new management. The business
is under the management of X.296. How much did you pay for X? How much did X cost you? How
much did X set you back? How much did you spend on X?297. X is too lazy to do Y. It is too much effort for X to do Y.
X cant be bothered to do Y.298. X had to deal with a serious problem. X was faced with a
serious problem. X came up against a serious problem. X met with a
serious problem. X encountered a serious problem.299. X has no connection with (being)Y. X is not the cause of
(being)Y. X is not related to (being)Y. X has nothing to do with
(being) Y. X doesnt equate to/with (being) Y.300. X wanted to save some money for Y. X wanted to set aside
some money for Y. X wanted to set some money aside for Y. X wanted
to put aside some money for Y. X wanted to put some aside money for
Y. -
Also available at www.aprendeinglesenleganes.com
WORD TRANSFORMATION
This book contains a compilation of the expressions that come up
most frequently in the Key Word Transformation task of the
Cambridge Reading and Use of English paper. It will help you to
familiarise yourself with the usual transformations among set
phrases , phrasal verbs, phrasal prepositional verbs, idioms
,etc.http://www.aprendeinglesenleganes.com/word-formation-guide.phphttp://www.aprendeinglesenleganes.com/open-cloze—tips-and-tricks.phphttp://www.aprendeinglesenleganes.com/gapped-text-made-easy.php
Если вы когда-нибудь готовились к олимпиадам и международным экзаменам, вам наверняка встречалось задание Key Word Transformations. Не встречалось? Значит плохо готовились. При хорошей подготовке пройти мимо трансформаций невозможно.
В этой статье мы подробно разберём, что такое перефразирование, из чего оно состоит и как к нему готовиться. Если вам нужна не теория, а практика, перейдите на страницу Key Word Transformations — упражнения.
Где могут встретиться key word transformations?
Key word transformations всегда присутствуют на международных экзаменах FCE, CAE, CPE и периодически попадаются на олимпиадах. Например, на Всероссийской олимпиаде школьников это задание встречалось на школьных этапах в 2012/13 и 2016/17 годах, на муниципальных — в 2013/14 и 2016/17, на региональных — 2015/16 и 2016/17. Олимпиады «Высшая проба» и «Ломоносов» также давали задания на трансформации в финальных турах.
Что такое key word transformations?
Задание на перефразирование выглядит примерно так:
I regret ever telling her about my plans.
WISH
I ____________________ her about my plans.
Как мы видим, в задании есть три элемента:
- предложение;
- слово;
- предложение с пропуском.
Наша задача — дописать предложение с пропуском таким образом, чтобы оно не отличалось от первого по смыслу, и чтобы в нём присутствовало данное нам слово (именно оно называется key word).
Для приведенного примера ответ может быть таким: wish I had not told. Мы использовали в ответе данное нам слово WISH и получили предложение, аналогичное исходному по смыслу: I regret ever telling her about my plans. = I wish I had not told her about my plans.
В задании всегда обозначено, сколько слов нужно дописать. Например, на FCE это, как правило, 2–5 слов, на CPE — 3–8, на региональном этапе ВОШ в 2017 году указывалось точное количество слов в каждом отдельном предложении. Обязательно внимательно читайте задание! Если слов нужно 2–5, а вы напишете 6, то балл снимут, даже если перефразированное предложение будет правильным.
Key word менять нельзя. Например, если написано WISH, нельзя переделывать его на WISHES или WISHED. Если дано NO, нельзя вместо него использовать NOT.
Проверяйте, нет ли в вашем ответе лишних слов. Например, в приведенном примере слово her уже присутствует в предложении с пропуском. Если вы укажете в качестве ответа фразу wish I had not told her вместо wish I had not told, вы потеряете балл.
Какие бывают трансформации?
Все трансформации можно условно разделить на два типа: грамматические и лексические. В задания обычно включают и те, и другие. Однако грамматические трансформации проще лексических, поэтому чем выше уровень экзамена или олимпиады, тем больше встречается лексических трансформаций и тем меньше грамматических.
Сложность лексических трансформаций объясняется их разнообразием. Они не поддаются классификации, и единственный надежный путь их освоить — расширять словарный запас всеми доступными способами, делая особый акцент на устойчивых словосочетаниях и фразовых глаголах.
Примеры лексических трансформаций:
The manager had the respect of everyone in the office.
UP
Everyone in the office _______________________ the manager.
Ответ: looked up to
You must do exactly what your manager tells you.
CARRY
You must _______________________ instructions exactly.
Ответ: carry out the manager’s
He really wanted to impress the interviewers.
DESPERATE
He _______________________ the interviewers a good impression.
Ответ: was desperate to give
I just can’t decide where to go on holiday.
MIND
I just can’t _______________________ where to go on holiday.
Ответ: make up my mind
Грамматические перефразирования менее разнообразны, и можно очертить круг тем, на базе которых они обычно создаются. Например, часто встречаются такие темы:
Passive and Active Voice
Преобразование из активного залога в пассивный и наоборот.
Claire was not allowed to stay out late when she lived at home with her parents.
LET
Claire’s parents _______________________ stay out late when she lived at home.
Ответ: did not let her
Conditionals
В этой категории очень популярны предложения со словами wish и in case.
I wished I’d done more to help.
HAVING
I regretted _______________________ more to help.
Ответ: having not done
Изменение одного времени на другое
Часто проверяется умение использовать грамматику со словами no sooner, first time, last и им подобными.
Sally hasn’t contacted us for over six weeks.
HEARD
We _______________________ over six weeks ago.
Ответ: last heard from her
Modals
Модальные глаголы и модальные эквиваленты часто встречаются в трансформациях.
Can you do the shopping tomorrow?
ABLE
Will _______________________ the shopping tomorrow?
Ответ: you be able to do
Linking words
Излюбленные слова в этой категории — despite, in spite of, although, until.
We played tennis despite the cold weather.
EVEN
We played tennis _______________________ cold.
Ответ: even though the weather was
Reported Speech
Как правило, требуется превратить прямую речь в письменную.
‘I’m sorry I’m late,’ he said.
APOLOGIZED
He _______________________ late.
Ответ: apologized for being
So and Such
It was such a stale cake that nobody wanted to eat it.
SO
The cake _______________________ that nobody wanted to eat it.
Ответ: was so stale
Rather and Prefer
I’d prefer him to be back before 11 o’clock.
RATHER
I _______________________ back before 11 o’clock.
Ответ: ‘d rather he was
Comparisons
She needs less sleep than I do.
MORE
I need _______________________ she does.
Ответ: more sleep than
Разумеется, этими группами дело не ограничивается. Key word transformations могут быть на любую грамматику. Но шанс встретить что-нибудь именно из вышеперечисленных тем очень высок.
Как проверяют transformations?
Часто бывает так, что предложение можно перефразировать разными способами. Например:
Claire’s parents DID NOT LET HER stay out late when she lived at home.
Вариант did not let her не является единственным. Наряду с ним возможны didn’t let her, refused to let her, wouldn’t let her и некоторые другие. В ключах, по которым проверяются работы, все эти варианты указаны, и если ваш ответ совпадает с одним из них, он считается правильным.
Обычно за каждое перефразированное предложение дают два балла, если оно перефразировано абсолютно правильно, и один балл, если оно перефразировано правильно наполовину. В примере выше можно заработать два балла, написав did not let her, и один балл, написав, например, will not let her (will not будет считаться неправильным, а let her — правильным). Конечно, возможность получить 0 баллов, написав неправильно обе части, тоже всегда есть.
Как тренироваться?
Если вы хотите безошибочно делать key word transformations, отрабатывайте и повторяйте грамматику, расширяйте словарный запас и обязательно делайте упражнения в формате transformations, чтобы набить руку и не делать досадных ошибок (дописали лишнее слово, изменили key word и прочее).
Sign up for our free newsletter to get special deals and hear about all our newest books and free book promotions before anyone else. You can get on the list here: http://www.aprendeinglesenleganes.com/lists.php
300 most common key word transformations, common key word transformations, frequent key word transformations, b2 key word transformation, b2 first sentence transformation, b2 first use of English part 4, fce key word transformation, fce sentence transformation, fce use of English part 4, c1 advanced key word transformation, c1 advanced sentence transformation, c1 advanced use of English part 4, cae key word transformation, cae sentence transformation, cae use of English part 4, key word transformation cae, sentence transformation c1 advanced , use of English part 4 advanced, part 4 of the use of English, transformación de la palabra clave
by Adam Skimins 7th March 2022
- Article navigation:
- (FCE) 40 Key Word Transformation: Exercises
- B2 First (FCE) Use of English Part 4: Tips & Strategy
The important thing in key word transformations is that you keep the meaning the same – EXACTLY the same. So it’s important that you read through the first sentence and your second sentence to ensure you have kept the meaning the same. Look at these two sentences:
Tommy said he was ready for his driving test and would take it in July.
Tommy said he was ready for his driving test and could take it in July.
One letter has been changed, from “would” to “could” but it changes the meaning of the sentence totally. Be careful of this!
A good way to practise this part of the FCE exam is to get used to writing and re-writing sentences using different structures and without changing the meaning.
(FCE) 40 Key Word Transformation: Exercises
Complete the sentence so that it has a similar meaning. Do not change the word given. You must use between two and five words, including the word given.
Nobody took any notice of his bad behaviour.
Nobodypaid ATTENTION to (ATTENTION) his bad behaviour.
You should try and take advantage of his help.
You should try and (MOST) help he gives you.
make the most of themake the most of any
You must include the word given (MOST)You must use beetwen 2 and 5 words.
My sister was involved in her school spelling competition.
My sister (PART) spelling competition.
took part in her schoolwas part of her school
You must include the word given (PART)You must use beetwen 2 and 5 words.
Could they grow anything here after the war?
Were (ABLE) here after the war?
they able to grow anything
You must include the word given (ABLE)You must use beetwen 2 and 5 words.
‘Why didn’t you call me?’ asked Joe.
Joe (ASKED) not called him.
asked me why i hadasked why i had
You must include the word given (ASKED)You must use beetwen 2 and 5 words.
Driving that fast was a stupid thing to do.
If (ONLY) driving so fast.
only i hadn’t beenonly i had not been
You must include the word given (ONLY)You must use beetwen 2 and 5 words.
I hadn’t seen my sister for about a year, when I saw her last.
About (GONE) before I saw my sister again, after the last time I saw her.
a year had gone by
You must include the word given (GONE)You must use beetwen 2 and 5 words.
Complete the sentence so that it has a similar meaning. Do not change the word given. You must use between two and five words, including the word given.
Nobody took any notice of his bad behaviour.
Nobodypaid ATTENTION to (ATTENTION) his bad behaviour.
I don’t earn anything like the amount I did before.
I earn (NOWHERE) as I did before.
nowhere near as much
You must include the word given (nowhere)You must use beetwen 2 and 5 words.
The date for the Barcelona Conference is the 23rd of March.
The Barcelona Conference (PLACE) the 23rd of March.
takes placewill take placeis taking place on
You must include the word given (place)You must use beetwen 2 and 5 words.
The house was not very attractive in appearance when we first saw it.
The house was (MUCH) at when we first saw it.
not much to look
You must include the word given (much)You must use beetwen 2 and 5 words.
No-one wants to buy this type of music any more.
There (LONGER) for this type of music.
is no longer any demand
You must include the word given (longer)You must use beetwen 2 and 5 words.
Looking back, I think I was right to study mathematics at university.
Looking back, I (REGRET) mathematics at university.
do not regret studyingdon’t regret studying
You must include the word given (regret)You must use beetwen 2 and 5 words.
Our spending will have to be reduced next year.
We will have (BACK) our spending next year.
to cut back on
You must include the word given (back)You must use beetwen 2 and 5 words.
Complete the sentence so that it has a similar meaning. Do not change the word given. You must use between two and five words, including the word given.
Nobody took any notice of his bad behaviour.
Nobodypaid ATTENTION to (ATTENTION) his bad behaviour.
While we were going home yesterday we got caught in a thunderstorm.
We got caught in a thunderstorm while we were (WAY) yesterday.
on our way home
You must include the word given (way)You must use beetwen 2 and 5 words.
Has Mary altered her decision about moving to the countryside?
Do you know if Mary (MIND) about moving to the countryside?
has changed her mind
You must include the word given (mind)You must use beetwen 2 and 5 words.
I’d like Kevin to stop telling me what to do.
I (WISH) telling me what to do!
wish kevin would stopwish that kevin would stop
You must include the word given (wish)You must use beetwen 2 and 5 words.
‘Are you pleased it’s nearly half-term?’ said the teacher to us.
The teacher wanted (KNOW) pleased it was nearly half-term.
to know if we were
You must include the word given (know)You must use beetwen 2 and 5 words.
We are earning less than we are spending, I’m afraid.
Our (EXPENDITURE) our income, I’m afraid.
expenditure is more thanexpenditure is greater than
You must include the word given (expenditure)You must use beetwen 2 and 5 words.
I don’t think having luxuries in life is necessary.
I don’t (NECESSITY) having luxuries in life.
see the necessity ofsee the necessity insee any necessity ofsee any necessity in
You must include the word given (necessity)You must use beetwen 2 and 5 words.
Complete the sentence so that it has a similar meaning. Do not change the word given. You must use between two and five words, including the word given.
Nobody took any notice of his bad behaviour.
Nobodypaid ATTENTION to (ATTENTION) his bad behaviour.
I am starting to find watching television boring.
I am beginning to get (FED) television.
fed up with watching
You must include the word given (fed)You must use beetwen 2 and 5 words.
Bad weather makes me feel really unhappy in the winter.
Bad weather (DOWN) in the winter.
really gets me down
You must include the word given (down)You must use beetwen 2 and 5 words.
Fog delayed my flight to Moscow this morning.
My flight to Moscow (UP) this morning
was held up by fog
You must include the word given (up)You must use beetwen 2 and 5 words.
Help was urgently needed in the flooded area of the country.
They were (NEED) in the flooded area of the country.
in urgent need of help
You must include the word given (need)You must use beetwen 2 and 5 words.
I went to Italy with the intention of learning Italian.
I went to Italy (THAT) Italian.
so that i could learn
You must include the word given (that)You must use beetwen 2 and 5 words.
Remember to return the videos you have rented.
Don’t (BACK) the videos you have rented.
forget to take backforget to bring back
You must include the word given (back)You must use beetwen 2 and 5 words.
Complete the sentence so that it has a similar meaning. Do not change the word given. You must use between two and five words, including the word given.
Nobody took any notice of his bad behaviour.
Nobodypaid ATTENTION to (ATTENTION) his bad behaviour.
To tell the truth, we need a swimming pool for this school.
To tell the truth, (WHAT) a swimming pool for this school.
what we need is
You must include the word given (what)You must use beetwen 2 and 5 words.
Do you know whose this umbrella is, by any chance?
Do you know (BELONGS), by any chance?
who this umbrella belongs to
You must include the word given (belongs)You must use beetwen 2 and 5 words.
Was it Paul’s idea to go to the cinema?
Was it Paul (CAME) the idea of going to the cinema?
who came up withthat came up with
You must include the word given (came)You must use beetwen 2 and 5 words.
The boats began to move slowly out of the harbour.
The boats slowly (WAY) out of the harbour.
made their way
You must include the word given (way)You must use beetwen 2 and 5 words.
One runner did not succeed in finishing the race.
One runner (ABLE) the race.
wasn’t able to finishwas not able to finish
You must include the word given (able)You must use beetwen 2 and 5 words.
It is not my fault that the glass broke.
You cannot (BLAME) the glass.
blame me for breaking
You must include the word given (blame)You must use beetwen 2 and 5 words.
Would you pass B2 First (FCE)?
Sign up, resolve the tests and see what results you get.
Sign up
B2 First (FCE) Use of English Part 4: Tips & Strategy
B2 First (FCE) Use of English: Part 4 question type here is called key word transformation.
You must complete a new sentence that has a similar meaning. You use a word in capitals given in bold for each sentence, which you must not change.
Strategy
- Read the sentence carefully and think about its exact meaning.
- Check your tenses – if the first sentence is in the past tense, the second should be, too!
- Contractions (e.g. haven’t) count as two words.
- Try to keep the same meaning – If the first sentence says ‘Tom said…’ then don’t write ‘He said…’ in the second sentence. (Write ‘Tom said’.)
- Write between two and five words, including the word given.
Tips
Find things that are the same in both sentences and delete them. That helps you to focus on what you actually need to be transforming.
Because of the scoring system, it’s possible to get 50% in this section without getting any of the questions 100% correct. So it’s worth answering every question! Even incomplete answers can get points
Make absolutely sure that the two sentences mean the same thing. For example, if the sentence to transform has names in it, the answer will have to have them too.
Would you pass B2 First (FCE)?
Sign up, resolve the tests and see what results you get.
Sign up
Key word transformations are probably the most identifiable task type in Cambridge exams. You’ll find them at B2 First, C1 Advanced and C2 Proficiency levels. With each level, the questions get longer and more challenging.
When it comes to CAE key word transformations, you’ll need to know your C1 grammar and vocabulary like the palm of your hand. To help, we’ve created a book of 230 C1 key word transformations. The book follows 25 units based on commonly tested grammar and vocabulary in the exam.
Find some free samples of the transformations from this book:
- Advanced (CAE) Transformations – Inversion
- Advanced (CAE) Transformations – Fixed Expressions
The book is available as a digital key word transformation exercises pdf here on Breakout English or grab a physical paperback copy on Amazon.
GET 230 C1 ADVANCED (CAE) KEY WORD TRANSFORMATIONS:
Why are CAE key word transformations important?
It’s only one activity in the entire exam, but it’s arguably the most important activity because it’s worth so many points. Transformations are marked as part of the Use of English paper. This paper consists of Parts 2, 3 and 4 of the Reading and Use of English section of the exam. Even though Part 1 looks like a Use of English task, it’s counted as part of your reading mark.
- Use of English Part 2 – Open cloze – 8 points (1 point per question)
- Use of English Part 3 – Word formation – 8 points (1 point per question)
- Use of English Part 4 – Key word transformations – 12 points (2 points per question)
With only 28 total points available in Cambridge Advanced Use of English, the key word transformations C1 task is worth 43% of your Use of English mark. Compared to other sections of the exam where there are more tasks with more questions and therefore more points available, key word transformations carry the highest per question weight of any task in the entire exam.
C1 key word transformations can be daunting, even for highly proficient users of English. The issue isn’t always the language as much as the task itself. You have to identify the language that is being transformed and then use the right grammar and vocabulary to complete the 2nd sentence. You also have to be extra careful about not making silly mistakes because one error with a preposition, plural or verb pattern can cost you a point or two.
Here’s our step-by-step process for how to do key word transformations. This post includes a downloadable copy of the process to use in class to help train students.
Grammar and Vocabulary for CAE key word transformations
If you’ve studied a C1 level course or seen a C1 level course book, there are always a similar set of grammatical structures and lexical sets that you are taught and expected to know. To pass the Cambridge C1 Advanced exam, you’ll have to have complete control of basic grammar and good control of complex grammar.
For our 230 C1 key word transformations, we’ve highlighted 17 grammar areas and 6 vocabulary areas which are commonly tested at this level. In the real exam, you’ll never know exactly what you’ll be tested on, but if you have mastered all of these areas, there won’t be much that could take you by surprise.
Grammar
- Past tenses
- Future forms
- Modal verbs
- Comparison
- Verb patterns
- Reported speech
- Passive
- Reporting passive
- Causative
- Real conditionals
- Unreal conditionals
- Wishes and regrets
- Relative clauses
- Participle clauses
- Cleft sentences
- Inversion – Available as a free download!
- Determiners
Vocabulary
- Linking words and expressions
- Fixed expressions – Available as a free download!
- Phrasal verbs
- Dependent prepositions
- Frequently confused words
- Idioms
How to prepare for C1 key word transformations
This is undeniably one of the trickiest parts of the exam, so here are Breakout English’s top tips to prepare for C1 key word transformations.
- Familiarise yourself with the exam format – Knowing the format of the exam will give you a sense of what to expect and help you approach the C1 key word transformations task with confidence.
- Study grammar and vocabulary – Make sure you have a strong grasp of grammar and vocabulary commonly tested in the C1 level exam. This will help you identify the language being transformed and complete the 2nd sentence correctly.
- Practice, practice, practice – Practise as many key word transformation exercises as you can, using official CAE materials or resources such as our book of 230 CAE key word transformations.
- Pay attention to details – C1 key word transformations require a lot of attention to detail, so make sure to read the questions carefully, and double-check your answers for silly mistakes. You don’t want to lose a point because of a missing preposition, misspelling or incorrect plural noun!
- Time management – Key word transformations are worth a large portion of your Use of English mark, so make sure to allocate enough time for this task during the exam. If you time the rest of the exam well, you can dedicate about 15 minutes to the 6 transformations questions.
- Stay calm – Remember that the key word transformations task is just one part of the exam and try to stay calm and focused during the exam.
- Don’t get stuck – It can be easy to obsess over one question, using up valuable time. If you find yourself in this situation, move on to the other questions, or even to another part of the exam. You can come back later and try again.
By following these tips, you’ll be well prepared to tackle the CAE key word transformations task and perform to the best of your ability.
Get 230 Advanced (CAE) Key Word Transformations
We’ve created these CAE transformations with the same format and style that you’ll find in the official exam. The book follows 25 units, including a wide variety of grammar and vocabulary topics for you to improve your English and your exam skills.
Ideal for self-study or photocopiable for teachers in the classroom.
Includes:
- Introduction.
- A step-by-step guide on how to do C1 key word transformations.
- 17 tasks based on C1 level grammar.
- 6 tasks based on C1 level vocabulary.
- Answer key.
With the digital download, you receive a key word transformation exercises pdf with all the same content of the paperback book in a pdf format.
These materials have been designed to represent the same quality and standards as authentic exam materials.
Proceeds from paid materials go towards helping Breakout English continue to offer the majority of our quality materials 100% free and accessible to teachers and learners of English. Thank you for your support!
On the Cambridge FCE Reading and Use of English exam, there are seven parts. Today you will learn about and practice Part 4 – Key Word Transformations. Many students think this part of the exam is challenging, but it just takes strategy and practice!
How to do Reading and Use of English Part 4
To begin, in part 4 each question has a sentence and a key word in BOLD. You must use this key word to complete the gap in a second sentence so its meaning is as close as possible to the first sentence.
You MUST use the key word in your answer. You CAN’T CHANGE the key word. For example, if the key word is “WRITTEN,” you cannot use the word “wrote” in your answer.
Use between 2 and 5 words. ** Contractions count as TWO WORDS! For example, won’t = will not. If you are unsure, always write out the entire word.
Use a pencil for this test. Write your answers in CAPITAL LETTERS only.
There are 6 questions total in this part. You can earn up to 2 points for each question.

What grammar structures and vocabulary does part 4 test?
This part of the FCE exam tests different grammar structures and vocabulary. Here are some of the most common ones that appear on the exam.
If you are taking a course, these structures and vocabulary should be covered by your teacher. If you are studying on your own, make sure you know the rules for each one.
GRAMMAR
Passive
Verb patterns
Conditionals
Reported speech
Future forms
Future time clauses
Causative – have/get
Verb tenses – especially perfect forms
Wish and other hypotheticals
VOCABULARY
Phrasal verbs
Set expressions
Words like height, weight, length, width
Linking words
Word forms
Example Key Word Transformation and Strategy
Look at the example question below:
He tried to keep running although he felt tired.
SPITE
He tried to keep running _____________________________ tired.
Step One: Cross out words that are the same.
He tried to keep running although he felt tired.
SPITE
He tried to keep running _____________________________ tired.
First, I cross out any words that are EXACTLY THE SAME in both sentences.
Step Two: Focus on the remaining words and try to find the grammar or vocabulary rule.
He tried to keep running although he felt tired.
SPITE
He tried to keep running _____________________________ tired.
I need to focus on although he felt. Although is a linking word of contrast. This is the structure that I have identified.
Next, I start to think about other linking words and expressions of contrast while keeping in mind that I need to use the word SPITE.
Step Three: Choose your answer between 2 and 5 words.
He tried to keep running although he felt tired.
SPITE
He tried to keep running _____________________________ tired.
In spite of and despite are both linking words/expressions of contrast. Remembering that I have to use the EXACT KEY WORD, I decide not to use despite.
Now, I remember that after in spite of I need a verb + ing form of the verb. So, I look at my original sentence and identify the verb “felt.”
Change the subject + verb in the original sentence to a verb + ing form to fit the second sentence.
My answer is IN SPITE OF FEELING.
Step Four: Check your answer. Did you use the key word? Do you have the correct word count? Did you write your answer in CAPITAL LETTERS?
He tried to keep running although he felt tired.
SPITE
He tried to keep running IN SPITE OF FEELING tired.
Finally, I need to check my answer.
- Key word SPITE? Yes.
- Correct word count? 4 words, yes.
- Capital letters? Yes.

Common mistakes on FCE Key Word Transformations
- Changing the key word – you MUST use the exact word
- Using too many words – maximum of 5 words
- Spending too much time – if you don’t know the answer, take a guess and continue with the next question
- Pronoun gender and agreement- if the first sentence uses a name, try to use the name in your second sentence. Sometimes you will need to use “her / his / she / he” etc. in your answer – make sure it matches the gender in the first sentence
- Subject-verb agreement – make sure your subject and verb match. For example, “she is singing” not “she are singing”
- Writing sentences that are too different – try to use the same words where you can when possible (words like very, really, etc. that appear in the first sentence). Make sure these are expressed in the second sentence as well.
FCE Key word Transformations Practice
Try these 10 key word transformations. Use the steps from above to help you and check your answers at the end of this post.
1. It’s a pity we don’t have a warmer climate!
ONLY
If _____________________ a warmer climate!
2. Someone is going to redecorate our terrace for us next week.
HAVE
We are going to _________________________________ next week.
3. I will only bring a jacket if it rains.
UNLESS
I will _________________ it rains.
4. They found the ring when they were fixing the garden.
CAME
They ____________________________ when they were fixing the garden.
5. I regret not selling my house sooner.
SOLD
I wish _______________________ my house sooner.
6. Fashion is the same as it was in the 1970s.
CHANGED
Fashion _______________________________________ the 1970s.
7. The teacher didn’t let them leave the class.
ALLOWED
They _________________________________ leave the class.
8. How many pyramids did the Egyptians build?
BY
How many pyramids ________________________ the Egyptians?
9. My colleague probably won’t come to the meeting.
UNLIKELY
My colleague ____________________________ to the meeting.
10. You’ve got to decide what you want to study next year.
TIME
It’s _________________________ what you want to study next year.

Answers
How to score your answers:
You can earn up to two points for each answer.
The two parts of the answer are separated by “ — “
If your answer to the left of the “–” is EXACTLY the same, give yourself one point.
If your answer to the right of the “–” is EXACTLY the same, give yourself another point.
Depending on your mistakes, you may earn 0, 1, or 2 points per answer.
- ONLY — WE HAD
- HAVE OUR TERRACE — REDECORATED
- NOT BRING A JACKET — UNLESS
- CAME ACROSS — THE RING
- I HAD — SOLD
- HAS NOT CHANGED — SINCE
- WERE NOT — ALLOWED TO
- WERE BUILT — BY
- IS LIKELY — TO COME
- (HIGH)* TIME — YOU DECIDED
*Words in ( ) are optional. You can still earn the full point for “time” if you didn’t write “high time.”
For more FCE Practice, try these posts.
- FCE Essay Writing Guide
- B2 Reading and Use of English Part 1
- FCE Speaking Exam Tips
В этой статье мы разберем структуру заданий одной из самых значимых частей кембриджских экзаменов Use of English (использование английского — грамматика и лексика) и поделимся советами по их успешному выполнению.
В блоге уже выходили статьи о том, как сдать Writing (письменную часть), Reading (чтение) и Listening (аудирование) на экзаменах FCE, CAE, CPE — советуем ознакомиться с этими материалами. Теперь перейдем к тому, как подготовиться к части Use of English экзаменов FCE, CAE, СPE.
Типы заданий в части Use of English
Раздел Use of English экзаменов FCE, CAE и CPE объединен с разделом Reading. На выполнение всей части Reading and Use of English вам дадут 1 час 15 минут на экзамене FCE и 1 час 30 минут на CAE и CPE. За это время вам надо выполнить порядка 7-8 заданий. Первые 4 задания относятся к части Use of English, которая проверяет ваш словарный запас и знание грамматики, а остальные — к части Reading.
Давайте посмотрим, из каких заданий состоит Use of English на кембриджских экзаменах:
| Экзамен | Multiple choice cloze | Open cloze | Word formation | Key word transformations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FCE, CAE, CPE | Part 1 8 предложений по 1 баллу |
Part 2 8 предложений по 1 баллу |
Part 3 8 предложений по 1 баллу |
Part 4 4-6 предложений по 2 балла |
Экзамены совпадают по структуре, баллам и количеству заданий, но отличаются по степени сложности. Разберем примеры заданий Кембриджских экзаменов с официального сайта: FCE, CAE и CPE.
Part 1: Multiple-choice cloze (выбрать правильный ответ из нескольких предложенных)
Суть задания: Вам нужно заполнить пропуски в тексте, выбрав одно из предложенных четырех слов. Всего пропущено 8 слов. В этом задании проверяется словарный запас (vocabulary) — знание фразовых глаголов, устойчивых выражений, идиом, оттенков значений и т. п.
Техника выполнения: Чтобы получить общее представление о тексте, прочитайте его, не обращая внимания на пропущенные слова. Далее внимательно читайте каждое предложение и варианты ответа. Исключите варианты, которые явно не подходят, затем из оставшихся выберите тот, который логически дополнит предложение и будет сочетаться с рядом стоящими словами. Рассмотрим пример:
They couldn’t (1)… a decision and agreed to meet again after lunch.
a) arrive
b) achieve
c) reach
d) attain
Хорошо зная устойчивые словосочетания, вы выберите вариант reach.
I like to go to the beach (2)… my wife likes to stay in and watch a TV show.
a) then
b) where
c) when
d) whereas
Однозначно не подходят варианты then (в примере указаны не последовательные действия, а параллельные) и where (нелогично, она в номере смотрит шоу, а не на пляже). Выбирая между when и whereas, следует предпочесть «в то время как», в значении противопоставления, а не просто «когда». Правильный ответ — whereas.
Пример задания multiple choice cloze на экзамене FCE
Пример задания multiple choice cloze на экзамене CAE
Пример задания multiple choice cloze на экзамене CPE
Part 2: Open cloze (вставить слово в предложение без вариантов ответа)
Суть задания: Нужно вновь заполнить пропуски в тексте словами, подходящими по смыслу. Пропущено 8 слов, но в этот раз вам не предлагают никаких вариантов.
Техника выполнения: Прочтите текст, не обращая внимания на пропущенные слова. Затем прочитайте внимательно каждое предложение. Обратите внимание, какие слова стоят до и после пропущенного слова. Они подскажут вам, к какой части речи относится это слово, число или время, в котором оно должно стоять. Например:
I really (1)… like this picture! It’s a masterpiece.
Очевидно, что предложение вполне самодостаточное и без вставки. Вместе с тем вы можете увидеть, что перед вами эмоциональное высказывание. Значит, правильно будет вспомнить про вспомогательный глагол do в функции усиления — I really do like this picture! It’s a masterpiece.
The concert has been cancelled (2)… to the epidemic situation in the city.
В первой части предложения — следствие, а во второй — причина. Мы не можем вставить because, так как после него употребляется предлог of, a не to. Необходимо рассмотреть другие варианты, близкие по значению к «потому что» и «из-за». Отлично подойдут owing и due. Иногда могут подходить сразу два варианта ответа, каждый из них будет правильным, но вам все равно нужно вписать один.
Пример задания open cloze на экзамене FCE
Пример задания open cloze на экзамене CAE
Пример задания open cloze на экзамене CPE
Part 3: Word formation (словообразование)
Суть задания: Вам нужно заполнить пропуски в тексте, образуя однокоренные слова от предложенных. Это задание проверяет насколько грамотно вы используете словарный запас.
Техника выполнения: Следует прочитать текст несколько раз — сначала бегло, а затем вдумчиво, обращая внимание на key words и слова, которые идут до и после него. Это поможет вам правильно определить часть речи производного слова. Большинство слов изменяются с помощью приставок, суффиксов и окончаний, например: courage – discourage, circle – circular, health – unhealthy, employ – unemployed. Переведите предложение, чтобы убедиться в правильности выбранной части речи.
Самые распространенные ошибки при выполнении этого задания:
- Путаница в отрицательных и положительных характеристиках
Don’t be so …, I’ll finish the task in a minute. (patience)
Если не обратить внимание на отрицание (don’t be) и использовать прилагательное patient (производное от patience), то это будет ошибкой. Правильный ответ — impatient.
Чтобы избежать ошибки, внимательно читайте весь текст и следите за логикой предложения.
- Неправильная часть речи
My boyfriend is not very … about the idea of going to New York. (enthusiasm)
Правильный ответ — прилагательное enthusiastic. Если использовать вместо него наречие enthusiastically, это будет ошибкой. Выбор наречия вместо прилагательного и наоборот — распространенная ошибка.
- Ошибки в выборе единственного или множественного числа
Tina’s husband is one of the strongest … in her business. (support)
Правильный ответ — supporters. Единственное число — supporter — будет ошибкой. Сбить может тот факт, что мы говорим об одном человеке, но ведь в предложении есть конструкция one of (один из).
- Орфографические ошибки
Чтобы избежать орфографических ошибок, необходимо регулярно практиковать правописание и не лениться проверять слова в словаре.
Пример задания word formation на экзамене FCE
Пример задания word formation на экзамене CAE
Пример задания word formation на экзамене CPE
Part 4: Key word transformations (перефразирование предложения с использованием ключевого слова)
Суть задания: Вам даны предложение и ключевое слово/словосочетание. Необходимо преобразовать предложение таким образом, чтобы в него вошло данное ключевое слово/словосочетание, учитывая ограничения по количеству слов, указанных в задании. Полученное предложение не должно отличаться по смыслу от исходного.
Техника выполнения: Прочитайте исходное предложение и вспомните все устойчивые выражения и фразы с указанным key word. Затем прочитайте второе предложение с пропуском. При трансформации предложения вы не должны выходить за рамки указанного количества слов в задании (с учетом key word). Конечно, нельзя изменять key word. Например, если дано wish, не стоит использовать wishes или wishing. Если дано not, нельзя вместо него использовать no. Также проверяйте, нет ли в вашем ответе лишних слов. Разберем пример:
I regret ever telling her about my private life. (wish)
I ____________________ her about my private life.
Правильный ответ — I wish I had not told her about my private life.
В приведенном примере местоимение her уже есть в предложении с пропуском. Если напишете wish I had not told her вместо wish I had not told, это будет ошибкой. За каждое верно перефразированное предложение вы получаете два балла, и один балл, если вы допустили небольшую ошибку.
Пример задания key word transformations на экзамене FCE
Пример задания key word transformations на экзамене CAE
Пример задания key word transformations на экзамене CPE
Хотите получить международный сертификат? Записывайтесь на курс подготовки к экзаменам.
Как успешно сдать Use of English — 7 советов
- При подготовке много читайте. Желательно, чтобы тексты были различной тематики. Отдавайте предпочтение газетным и научным статьям. Выбирайте серьезные издания, например, The Washington Post или The Guardian. Читая тексты, выписывайте и учите новую для вас лексику, также изучайте и повторяйте готовые подборки устойчивых выражений и идиом. Например, их можно найти в учебной серии Oxford Word Skills Intermediate и Advanced.
- Относитесь к грамматике как к инструменту, который на экзамене поможет вам точно выразить свои мысли. Разбирайте грамматические правила и отрабатывайте их.
- Выполняйте пробные тесты и тренируйтесь распределять время на каждый тип заданий. Обратите внимание, что необходимо брать тестовые задания, изданные не ранее 2015 года, потому что в этом году произошли изменения в формате кембриджских экзаменов.
- Не зацикливайтесь на одном задании. Если вы сомневаетесь, напишите возможные варианты ответа на полях и продолжайте выполнять тест. К пунктам, в которых вы не уверены, вернитесь позже.
- Проверяйте свои ответы каждый раз, как выполнили задание.
- Пользуйтесь подходящими ресурсами:
- Cambridge English Exam Booster — пособие содержит 48 экзаменационных заданий. В книге рассмотрены типичные ошибки и даны рекомендации для успешной сдачи экзамена.
- Cambridge English First 2, Cambridge English Advanced 2 и Cambridge English Proficiency 2 — каждая книга содержит 4 теста для каждого из экзаменов. Пособия ознакомят вас с содержанием и форматом экзаменов FCE, CAE и CPE.
- Cambridge English Teacher Rory — советы по подготовке к FCE и CAE от преподавателя и носителя языка Рори.
- Floe-Joe — тренировочные упражнения в формате экзаменов FCE, CAE, CPE.
- Рекомендуем найти преподавателя, который сам получил международный сертификат и у которого есть опыт подготовки студентов к экзамену. Такой учитель не только проработает с вами типовые задания, но и расскажет о методике сдачи экзамена исходя из своего опыта. Он поможет вам правильно организовать подготовку, структурировать информацию, поделится психологическими приемами. Если вы в поиске такого учителя, обратитесь в нашу школу, и менеджеры подберут преподавателя, который поможет вам сдать экзамен на высокий балл.
Желаем успехов в сдаче экзаменов!
© 2023 englex.ru, копирование материалов возможно только при указании прямой активной ссылки на первоисточник.