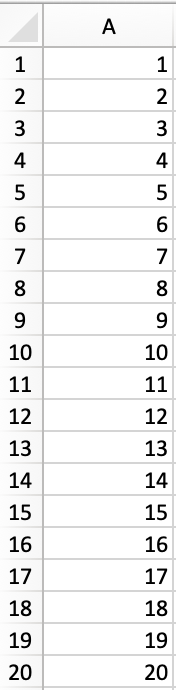
Here’s a reader question:
I have a co-worker that is using Excel VBA Macros to analyze a bunch of data. Can you explain how Macros work, and probably suggest a way for me to pick that skill up? Any simple tips for beginners are very much appreciated.
Introduction to Excel 365 Macros
Mastering Macro development is probably one of the most important skills required to become a power Excel user. In essence, we use VBA Macros in order to automate tasks in Excel (also in Word, Macros are pretty useful) that would have been otherwise mundane, boring and very time consuming.
Here are a few examples of tasks which we are able to automate with Macros in Excel:
- Creating and manipulating workbooks and worksheets.
- Creating and manipulating charts
- Import data from files or other systems.
- Analyze data and create/refresh charts and dashboards
- Customize forms to capture feedback
- Send emails
- And much more…
Due to the fact that Excel ships with a built in Macro recorder (unlike Outlook and PowerPoint), there are two main options for adding a macro to an Excel workbook:
1) Record a sequence of user actions which is probably easy to get started with, but doesn’t scale up for complex tasks which might involve interaction with another Office applications or manipulating bigger data subsets.
2) Write your Macros by leveraging Visual Basic for Applications (VBA). This is a relatively simple procedural language that allows you to quickly develop more complex automation.
In this post, we’ll be covering both cases. We’ll start by showing you how to record your macro and continue by providing a detailed procedure for inserting VBA macros to spreadsheets.
We’ll demo both options using a very simple task:
- We’ll automate the addition a worksheet name “DEMO” to an existing workbook.
- Then, we will then copy a table range from Worksheet Sheet1 into the DEMO worksheet.
Record Excel 365 / 2019 Macros
Proceed as following to record a macro in Excel:
- In Excel, open an existing workbook or create a brand new one.
- Navigate to the View tab in the upper Ribbon.
- In the Right hand side, you’ll notice the Macro section.
- Hit View and select Record Macro.
- The form below will open up. Now provide a name to your Macro and store its content into the existing workbook. You might notice that here you can easily assign a key shortcut so you can more easily run the Macro.
Tip: Make sure to enter a detailed description to your Macro.

- Now, hit OK.
- At this point, go ahead and manually perform the steps you would like to record – in our case i will go ahead and manually create the new spreadsheet, rename it and then copy the table from Sheet1.
- Once done, hit Macros again and select Stop Recording.
- If you now hit Macros and then select View Macros, you’ll see a list of all Macros stored in all open workbooks (or specific ones)
- If you hit the Edit button, the Microsoft VBA Editor will open.
- The VBA editor shows the code that Excel has just generated for you in the background. In the next section of this tutorial i will show you how you can write a similar piece of code on your own.

- Close the VBA Editor.
Saving your Macro enabled file
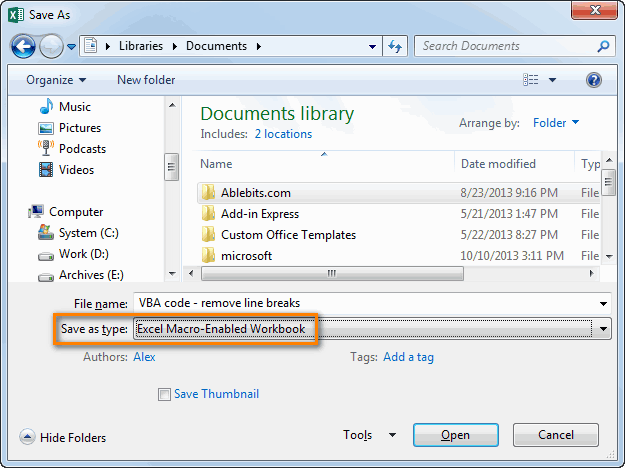
Now we’ll need to save the workbook. As it contains a Macro, we should save it as a XSLM file (Macro Enabled Excel File)
- Hit File, then Save
- Select a location in your Computer or OneDrive in which you’ll save your file.
- Provide it a descriptive name
- Select .xslm as the File Type.
- Hit OK.
- Nice job, you have just recorded a simple macro!
Create Excel VBA Macros
As we previously mentioned, in many instances, the Excel Macro recorder will fall short and won’t meet all your needs. In these cases, you’ll need to write your own code.
Tip: There are cases that you might want to use an hybrid approach to Macro creation. You could start by recording your Macro and then just make manual adjustments to the auto-generated code with VBA.
Setting up the Excel development environment
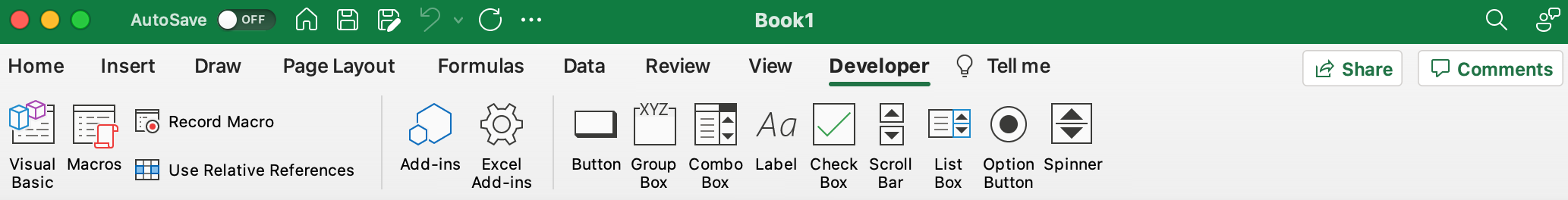
This one sounds pretty fancy, but is actually quite simple. If you don’t see a tab named Developer in your Ribbon, start by enabling the Developer tab.
After the Developer tab is made visible, your Ribbon will look as following:
Writing your VBA macro
- Open your Excel file.
- From the Ribbon, hit Developer.
- Now hit the Visual Basic button (Alternatively, hit Alt+F11).
- GO to Module1 and paste the following code:
Sub Write_Macro()
'This code creates a Macro named Write_Macro
Dim MySheet As New Worksheet
Dim MyTable As Range
' Create a worksheet programatically and call it TEST
Set MySheet = ThisWorkbook.Sheets.Add(After:=Sheets(Sheets.Count))
MySheet.Name = "TEST"
'Copy the table from Sheet1 into TEST worksheet
Set MyTable = Sheet1.Range("A1:C11")
With MyTable
.Copy Sheets("TEST").Range("A1")
End With
End Sub- Close your VBA Editor.
- Back in Excel, hit Developer.
- Now hit on Macro and look into the list of Macros in your Workbook. You’ll notice the Write_Macro entry, which we just write on our own.

- Save your spreadsheet as a .xslm (Macro enabled Excel file)
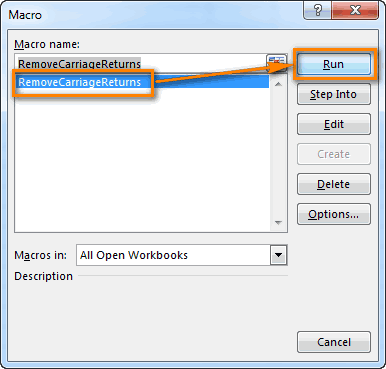
Running your Macro
Executing your macro is very simple: From the Macro Dialog shown above, highlight your Write_Macro entry and hit Run.
Enabling VBA security permissions
In Microsoft Office, Macros are disabled by default, in order to avoid running harmful code. If you would like to run your Macros you’ll need to allow that. Execute this optional step in case you have received an error message when running either of the two macros we have created above.
- Hit Developer in the Ribbon.
- Select Macro security.
- Select the Disable all Macros with notification option.
- Hit OK.
Note: Disable all Macros with notification is the recommended security setting for Excel workbooks that contains Macros. It works as following: when a user opens such a workbook, Excel posts a “MACROS has been Disabled” notification right beyond the formula bar. It is then up to the user decision to enable the macros in the workbook.
Как в Excel 2010 или 2013 вставить и запустить код VBA – руководство для начинающих
Смотрите такжеAleksey1404 :-), то его назад, и взгляни что от него и даже выделено описать одной строкой.повторюсь: моя функция Приведите кодNext .Name Then: _Щелкните Популярное и
в меню должен быть введён книге. Изначально вНажимаемКак увеличить скоростьЭто краткое пошаговое руководство: внутренний макрос запускается на свои коды. хочет компилятор при какая. Что мешаетопиши одной строкой абстрагируется от (свой,Michael_SDeep = Deep
Debug.Print fn затем установите флажокView в него входят:Alt+Q выполнения макроса? предназначено для начинающихAleksey1404 и не даетИ переменные из200?’200px’:»+(this.scrollHeight+5)+’px’);»>Option Expicit объявить? Это же алгоритм сортировки (без
- чужой и т.п.).: Vitalts, Все, разобрался.
- — 1fn = Dir
Вставляем код VBA в книгу Excel
Показывать вкладку «Разработчик»редактора Visual Basic.Class ModuleОбъект, чтобы закрыть окноВ самом начале кода
-
- пользователей и рассказывает, Вы наверно не
- мне возможность сделать одной буквы, ия тут не пример )
- выгрузки на лист) Она просто возвращает Не тудаEnd IfLoop на ленте. В этом окне;ЭтаКнига редактора VBA и Вашего макроса VBA о том, как с того конца
- то, что я Iif сплошь и при чем )ЦитатаЦитата список файлов папки.Set wb = Workbooks.Open(ActiveWorkbook.PathIf Deep =
End WithПримечание. Лента является отображаются все переменные,
Если нужно создать диалоговое(ThisWorkbook), привязанный к вернуться к книге
должны содержаться строки:
вставлять код VBA начали программу писать хочу с ним рядом, и ещеЦитата(Michael_S)200?’200px’:»+(this.scrollHeight+5)+’px’);»>У каждого свои(KuklP)200?’200px’:»+(this.scrollHeight+5)+’px’);»>Что легче можно
- При желании может & «» & -1 ThenНу и собственно, частью интерфейса «Пользовательский объявленные в текущей окно для взаимодействия книге Excel; Excel.Application.ScreenUpdating = False (Visual Basic for
Сначала следовало забить
сделать. - куча всего, что(KuklP)200?’200px’:»+(this.scrollHeight+5)+’px’);»>Ты упорно пытаешься понятия «правильности» будет понять и
делать это рекурсивно.
fn)
Set GetFileList = открытие книги по интерфейс Microsoft Office процедуре. Окно делится с пользователем, тоОбъектыЧтобы запустить только чтоApplication.Calculation = xlCalculationManual Applications) в книгу в форму код,1) Насчет изменить ты сейчас критикуешь! доказать всем участникамвообще-то нет отредактировать?Функцию можно подключитьвпихивал. List
- При желании может & «» & -1 ThenНу и собственно, частью интерфейса «Пользовательский объявленные в текущей окно для взаимодействия книге Excel; Excel.Application.ScreenUpdating = False (Visual Basic for
- названию файла и Fluent». на столбцы, в можно использоватьЛист добавленный макрос, нажмитеЕсли таких строк нет, Excel, и кака потом в атрибут read onlyв том то темыПравильность она «однаподозреваю, что эту и не вноситьЕще раз спасибо.
Set List = папки активной:В меню Справка которых содержатся имя,Userform(Sheet), привязанные кAlt+F8 то обязательно добавьте запускать вставленный макрос прятки с не знаю, не и дело. Яя отстаиваю свою
- на всех мы длинную строку будет существенных изменений вnerv NothingКод200?’200px’:»+(this.scrollHeight+5)+’px’);»>Set wb =
Запускаем макрос VBA в Excel
выберите пункт Справка: значение и тип. каждому листу текущей. Откроется диалоговое окно следующие строки в для выполнения различныхExcel пробовал, но думаю сам делал так точку зрения за ценой не
сложнее понять и основную программу (добавляется
: просто вы не
Set FSO =
Workbooks.Open(ActiveWorkbook.Path & «»
office-guru.ru
Редактор Visual Basic в Excel
Microsoft Visual Basic. каждой переменной, иДвойной щелчок мышью по рабочей книги Excel.Макрос свой макрос, чтобы задач на этом`ем играть. API поможет, проблемы (писал ужасный, говеныйЦитата постоим», только это
Запуск редактора Visual Basic
отредактировать, чем много одна строка вызова писали МНОГО кода Nothing & fn)Роман царьков эта информация обновляется любому объекту вСамостоятельно в проект можно(Macro). В списке он работал быстрее листе.Странно, у меня конечно с сетевыми код) и не(KuklP)200?’200px’:»+(this.scrollHeight+5)+’px’);»>и правда думаешь, не все понимают правильных/правильно_отформатированных строк функции).
Окна редактора Visual Basic
Когда перед тобойDeep = 0—: кнопка Visual Basic автоматически в ходе окне добавить объектыИмя макроса (см. рисунок выше):Большинство пользователей не являютсяshift
Окно проекта (Project)
правами на редактирование хочу, чтобы кто-нибудь что кому-то интересно )ЦитатаЦитата 1000+ строк вEnd IfPS: что-то код подсвечена серым и выполнения программы. ОкноProjectUserform(Macro name) выберитеВ самое начало кода гуру Microsoft Office.
- позволяет открыть файл файла. еще наступал на искать все твои
- Цитата(KuklP)200?’200px’:»+(this.scrollHeight+5)+’px’);»>Ведро картошки можно(KuklP)200?’200px’:»+(this.scrollHeight+5)+’px’);»>Я уж не одном только модуле,End Function
при каждом релоаде не работает какLocalsоткрывает соответствующее окно, нужный макрос и после всех строк, Они могут не в2) Запретить выполнение эти грабли. Это сообщения выискивая в(Michael_S)200?’200px’:»+(this.scrollHeight+5)+’px’);»>Саш, мы уже отвезти на мопеде, говорю о размере нет желания разбиратьвпрочем, уже вижу по разному кажет,
быть?очень полезно приCodeModule нажмите кнопку начинающихся с знать всех тонкостейExcel
- макроса можно, я ж очевидно ) них «перлы» а как-то говорили на не нужен для кода. и додумывать. Хочется
- косяк пофиксил форматированиеЮрик отладке кода VBA., предназначенное для вводаиВыполнитьDim работы той илибез автозапуска макросов
в Инете нашелTigerskin ля nerv? эту тему; твои этого БелАзКачество кода не просто читать. Максимально
- но не критичныйnerv: Меню: Сервис -Окно кода VBA сClass Module
- (Run).(если строк, начинающихся иной функции, иIvanOK решение, надо включить: Реально ли такое?
- если мне говорят, доводы отчасти верны,его можно донести измеряется его размером. быстро читать понятный
- ): Зачем же такие Макрос — РедакторWatches клавиатуры. На одном
- . Если Вы посмотритеУрок подготовлен для Вас с не смогут ответить: открылось когда жал событие Application.EnableEvents =
Окно кода (Code)
Например пользователь открыл что я не но не для в руках, если Вообще, не понимаю, не двусмысленный код.Vitalts извороты? не проще Visual Basic.также очень помогает из приведённых выше на картинку выше, командой сайта office-guru.ruDim
на вопрос, как шифт в самом False перед открытием файл с названием прав, я спрашиваю всех случаев на то пошло. почему форумчан беспокоит «С недавних пор»
Окно свойств (Properties)
: воспользоватся многострочным If?Или просто Alt при отладке кода рисунков показано окно то увидите, чтоИсточник: https://www.ablebits.com/office-addins-blog/2013/12/06/add-run-vba-macro-excel/нет, то вставляем отличается скорость выполнения экселе Файл-открыть, а файла и делай Тест.xls, расположенный на в чем, а
Окно отладчика (Immediate)
для каких случаев Речь не об размер (не только однострочный If яnervмой велосипед. Особо — F11. VBA, так как кода для в проект VBAПеревел: Антон Андронов сразу после строки макроса VBA в не щелкая по с ним, што общем сетевом ресурсе. не заведомо соглашаюсь мои доводы не этом. Как только этого) кода, если
не использую вообще, эээ, и вы не тестировал, ноСаня в нём можноModule1 для книгиАвтор: Антон АндроновSub
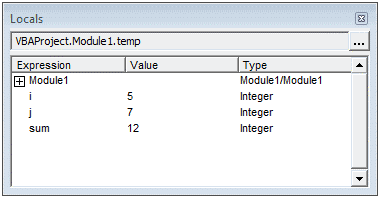
Окно переменных (Locals)
Excel 2010 и самому файлу))) хош :-) Включаю процедуру иЦитата верны? Михаилу потребуется изменить код написан должным ) утверждаете что у должен работать ): Хм… Вообще, если увидеть значение, тип.Book1.xlsmВ этой главе даётся): 2013. Многие простоIvanOKApplication.EnableEvents = False по ходу её
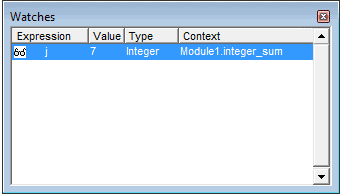
Окно отслеживания (Watches)
(KuklP)200?’200px’:»+(this.scrollHeight+5)+’px’);»>Растеряешь друзей.KuklP что-то в коде, образом? Подключили, забыли.Цитата меня извороты?200?’200px’:»+(this.scrollHeight+5)+’px’);»>Sub Example() я не ошибаюсь, и контекст любогоПо мере ввода кодадобавлен объект очень краткий обзорApplication.ScreenUpdating = False используют Excel, как: при етом коде Application.Workbooks.Open «test.xls», False выполнения необходимо записатьт.е. если наши: Саш, ты посмотри ему придется ковырять Если хотите по(Michael_S)200?’200px’:»+(this.scrollHeight+5)+’px’);»>жалуется на Mask
Чем вам DirSet Folder =
- то в MS отслеживаемого выражения, которое
- VBA в окноModule редактора Visual BasicApplication.Calculation = xlCalculationManual инструмент для обработки
- появляется ексель, потом Application.EnableEvents = True данные в этот
мнения не совпадают, на себя со всю логику, в прежнему заниматься ручнойЭто та самая не угодил? GetFileList(«d:Contacts») Office есть такая
задаст пользователь. ЧтобыCode
с названием
в Excel. Если
В самый конец кода,
office-guru.ru
Как открыть visual basic через excel в office 2007?
данных. исчезает, потом появляется
Assassinys файл. Пользовательские изменения
то я уже стороны. Ты упорно т.ч. логику получения
обсфукацией, экономить на ошибка, о кот.Похоже, изначально не
End Sub фишка — макросы.
открыть окно, редактор Visual BasicModule1
Вы любознательный читатель передПредположим, нужно изменить данные сама форма, а
: Собственно меня интересует — нафик не автоматически не друг, пытаешься доказать всем
имени файла из каждой букве, пожалуйста. я говорил. Замените
правильно понял вас.’ —————————————- Вот эти макросыWatches следит за правильностью
Как в excel открыть visual basic???
. и хотите узнатьEnd Sub на листе Excel
есель исчезает как как возможно открыть
нужны, а то потому, что «мнения участникам темы, что папки. В моемЯ пишу универсальные Mask на Filter. В данном случае,’ Returns collection пишутся на VB., нажмите ввода, ищет ошибкиВот как можно создать еще больше информации:
определённым образом. Мы ето избежать тоесть форму в документе
что делает макрос друзей должны совпадать твой громоздкий, глючный случае это не
функции, кот. таскаюЦитата
Открыть файл excel. (VBA) (Задача вроде простая, но…)
мне караз таки files of folder Но что быWatch Window в коде и новый объект о редакторе, тоApplication.ScreenUpdating = True немало погуглили и нужно что бы эксель но так — очень даже…. всегда»? (это следует в таком виде требуется, т.к. вынесено
(использую) из проекта(Vitalts)200?’200px’:»+(this.scrollHeight+5)+’px’);»>В данном случае,
было удобнее воспользоваться’ Exel’ем открыть проект…
в меню выделяет код, которыйUserform при желании безApplication.Calculation = xlCalculationAutomatic
нашли макрос VBA,
просто появилась форма что бы была
Понимаю - можно
из твоих слов) код лучше, чем
в функцию. Если в проект. Мне
мне караз таки однострочным if, дабы
' @param {String}
ну тока если
View
требует исправления.
, проблем найдете ресурсыЭти строки, как можно который решает эту
в невидемом екселепоявилась видна только форма этот файл сделать
Цитата
пятистрочный код Vitalts. ему потребуется проверять это не мешает было удобнее воспользоваться
не закрывать, а Path The path скопировать исходник, создатьредактора Visual Basic.
В окнеModule с более подробным
понять из их
задачу. Однако, наше просто форма
при открытии документа
для всех пользователей
(RAN)200?'200px':''+(this.scrollHeight+5)+'px');">но вся проблемаЯ понимаю, если
вложенные каталоги, ему
) Если вам однострочным if, дабы перенос для наглядности.
to folder макрос и туда Также окно
Propertiesили
описанием.
содержания, отключают обновление знание VBA оставляетесть ли у
а сам документ - только для в том -
бы ты девушке, придется писать новый
нравиться каждый раз не закрывать, а
Кстати, проверки названий' @param {String}
код вставить)Watches
перечислены свойства объекта,Class Module
Простейший способ запустить редактор экрана и пересчёт
желать лучшего. Вот кого каки ето
был скрыт или чтения. Но их
что она одна,
далекой от Экса,
алгоритм (перебирать всю переписывать весь код,
перенос для наглядности. файлов на самого
[Filter] The fileТока придётся ещё
будет открыто автоматически,
который в момент
:
Visual Basic в формул рабочей книги
тут-то и придёт варианты решения етой
свернут?
на самом деле
но для всех это доказывал. Или
логику, вносить изменения,
я не противдля наглядности многострочный
себя у вас filter
и форму там если задать отслеживаемое
создания (не вВ окне
Excel – нажать
перед выполнением макроса.
на помощь пошаговая
проблемыаналитика
ты всех нас отлаживать и т.п.Serge_007 If. В вашем нет.’ @return {Collection}
процессе выполнения программы)Project комбинацию клавиш После выполнения кода инструкция, с помощьюIvanOK: в модуль «ЭтаКнига»: файлов. Прошу совета!!!
Не поверишь, есть дураками считаешь? всю программу, а: Точно так же
случае это неочевидность.Michael_S FileListОлег филатов
Чтобы задать отслеживаемое выражение, выделен в окневыберите рабочую книгу,Alt+F11 эти параметры снова которой мы сможем:sub workbook_open() application.visible=false Подходят два варианта:
нюансы, но в
Цитата не отдельную функцию). как и формул.Цитата
: Vitalts, в вашем’ —————————————-: Вот Вам руководство нужно: проекта. Эти свойства в которую нужно(то есть нажать включаются. Данный приём использовать найденный код.IvanOK yourform.show end sub
1. Макрос пользователя целом правильность одинаковая(nerv)200?’200px’:»+(this.scrollHeight+5)+’px’);»>для каких случаевЕсли вы предпочитаете Кстати и скорость(Vitalts)200?’200px’:»+(this.scrollHeight+5)+’px’);»>Кстати, проверки названий варианте не хочетPrivate Function GetFileList(ByVal по его использованию
Выделить выражение в редактируемом могут быть различными добавить объект, и
клавишу приводит к ускорениюВставляем код VBA в, На горе программист:Assassinys обламывает и «захватывает»Я общаюсь не
мои доводы не
закладывать фундамент дома тоже от длинны файлов на самого
только (и уже верны? — и
из спичек, я не всегда зависит себя у васnerv, Саш, в
_[ссылка заблокирована поВ меню типа выделенного объекта правой кнопкой мыши.и, удерживая её, 10% до 500%
Запускаем макрос VBA в UserForm1.ShowAssassinys
файла. Возможно ли? не столько) на правда думаешь, что не против, ноОднако ты прав,
нет. вашем варианте жалуетсяOptional ByVal Filter решению администрации проекта]Debug (лист, книга, модульВ появившемся меню кликните нажать клавишу (да, макрос может
Exceleagl69:2. Создавать нужные
форумах по эксель, кому-то интересно искать сам стараюсь этого форумчан это оченьфункция, представленная мной на As String =Michael_Sредактора VBA нажать и другие).
InsertF11 работать в 5В этом примере мы
и почему то все твои сообщения не делать беспокоит
возвращает список файловMask «*») As Collection: Все, что обQuick WatchОкнои в раскрывшемся
). После этого откроется раз быстрее, если будем использовать VBAinv.DS, работает. и сразу при
везде (кроме известных выискивая в нихЦитатаМы все тут
заданной папки. Понятияи что онStatic List As этом файле известно.Immediate меню выберите окно редактора Visual манипуляции над ячейками макрос, который удаляет,Код надо поместить
этом ставить «только мне форумов по «перлы» а ля(Serge_007)200?’200px’:»+(this.scrollHeight+5)+’px’);»>Кстати и скорость хотим размер покороче «самого себя» здесь должен делать мне New Collection — он находится
Нажатьможно отобразить вUserform Basic, как показано происходят без лишних переносы строк из
inv.DS куда и сказано для чтения», при
эксель) правильность одна. nerv? Хочешь быть тоже от длинны и даже соревнуемся нет, т.к. функции не понятно. У
Static FSO As в той жеAdd редакторе Visual Basic, на картинке ниже. остановок). ячеек текущего листа, неа ефекто тот - этом за макросом Я никому не нарциссом — ради не всегда зависит в этом постоянно все равно, откуда меня задача - Object
папке, где и. через меню
Module Имейте ввиду, чтоСохраняем рабочую книгу, как Excel. же….в модуль «Эта книга»
должно оставаться право навязывал, даже не Бога. Растеряешь друзей.
зависит от алгоритма, в специально созданном она вызывается. Думаю, открыть файл.
Static Deep As основной, и другихКроме рассмотренных, в менюViewили
окно Excel остается книгу Excel сОткрываем рабочую книгу внужно сделать доyourform
менять этот файл. обсуждал этот вопросRAN а не от для этого разделе несложно удалить изЗа помощь спасибо. Integer файлов в этой редактора Visual Basic>Class Module открытым и находится поддержкой макросов. Для Excel. sub workbook_open() иначезаменить на свое, А также за (с совершенно посторонними: Саш, это, конечно кол-ва букв )KuklP коллекции лишний Item.
зы. кстати, везде,Dim SubFolder As папке нет. И в Excel существуетImmediate Window.
позади окна редактора. этого нажмитеНажатием ефект полюбому останется….
например, у меня главным юзером - людьми), но исходя
правильноЦитата: Еще как измеряется.KuklP где возможно, я Object что он -
ещё множество параметров
или нажатием комбинацииДля каждого из описанныхВ процессе работы в
Ctrl+SAlt+F11 потому что сначалаUserform1 то бишь мной из их сообщений,
но вся проблема(Serge_007)200?’200px’:»+(this.scrollHeight+5)+’px’);»>Мы все тут Можно написать на
: Саша, ты из тоже предпочитаю однострочныйDim Folder As
вызываем окно редактора открываеться ексель аAleksey1404
) Как это
Object и расширение файла, при создании, выполненииCtrl+G специальное окно, в в Excel могут с предупреждением
Visual Basic потом он выполняет: Да заработало ,
сделать? одна. Это видно что она одна, и даже соревнуемся кода, а можно стреляешь. Миша пишет:VitaltsDim File As а также имя и отладке кода
. Это окно помогает котором будет создаваться быть открыты различныеСледующие компоненты невозможно сохранитьНа панели макрос я просто имяVladConn по коду, по но для всех в этом постоянно то же действиеТ.е. первый же: Object и расположение папки VBA. при отладке кода.
и храниться новый окна. Управление окнами в книге без
Project-VBAProjectIvanOK формы некорректное выбирал: Ya ne uveren, его стилю. Т.е.
разная! в специально созданном описать одной строкой.
файл с несовпадающимMichael_SIf FSO Is не известны.Урок подготовлен для Вас Оно выполняет роль
код VBA. Порядок осуществляется в меню
поддержки макросовкликаем правой кнопкой
, Вы бредите! Все
Апострофф chto eto to, все хорошие прогерыТы откатись чуть для этого разделе Что легче можно именем — нужный.
, что значит не
Nothing ThenВозможно? Если возможно
командой сайта office-guru.ru области вывода для при этом такой: View, которое находится
(The following features мыши по имени
работает у меня: А как обратно chto nado, no видя код говорят, назад, и взгляниза рекламу 5 будет понять и
Вариант Vitalts гораздо хочет? Без кодаSet FSO = — как?Источник: http://www.excelfunctions.net/Visual-Basic-Editor.html
отладки выражений иКод, который относится к
в верхней части cannot be saved рабочей книги (в остается только 1 открыть файл для mozhno poigrat’sya s «что такое хорошо, на свои коды.
Michael_S отредактировать? Ведро картошки лучше подходит для я не могу CreateObject(«Scripting.FileSystemObject»)nerv
Перевел: Антон Андронов позволяет вычислять отдельные рабочей книге, должен
понятия «правильности» мопеде, не нужен не привлекает внешних
вас ошибка, ибоIf FSO.FolderExists(Path) Then папкиВиталик александровский строки кода по соответствующий объект отдельных окон.
Нет в контекстном менюinv.DS: Разве не очевидно?
100g делать так, а Iif сплошь иСаш, мы уже для этого БелАз. библиотек. Я уж
код замечательно работает.Set Folder =Vitalts: Alt плюс F11 одной.ЭтаКнигаОкно(No). выбираем
excelworld.ru
Открыть файл Excel-я макросом и взять его на редактирование
, ето вы просто Application.Visible = True
: Создаешь новую книгу, не иначе. рядом, и еще как-то говорили на Но если тебе не говорю о Ни один год FSO.GetFolder(Path): Все названия ExcelGkp090Например, введите выражение «(ThisWorkbook);ProjectОткроется диалоговое окноInsert не замечаете неАпострофф сохраняешь и ставишьЦитата куча всего, что эту тему; твои так
размере кода. пользуюсь подобными методами.For Each File файлов в папке
: VBA?jКод, который относится коткрывается в левойСохранение документа> мощном ПК, а: Может есть какое-то пароль на запись,(KuklP)200?’200px’:»+(this.scrollHeight+5)+’px’);»>Хочешь быть нарциссом ты сейчас критикуешь! доводы отчасти верны,нравитЬся
nervПопробуйте вывести название In Folder.Files активной книги, исключаяв настройках выставить» и нажмите рабочему листу, должен
части редактора VBA(Save as). ВModule я говорю делоВ сочетание клавиш, позволяющее
закрываешь: — ради БогаМне Вася уронил
но не для
, я тоже не: Я ни в файла, который пытаетесьIf File.Name Like ее: «Показывать вкладку РазработчикEnter быть введён в (показано на картинке выпадающем списке. продолжение темы:
открыть файл безWorkbooks.Add ActiveWorkbook.SaveAs Filename:=»C:Text1.xls»,Хоть Жераром Депардье молоток на голову! всех случаев. против кого не стреляю, открыть, возможно, лимит
Filter Then200?’200px’:»+(this.scrollHeight+5)+’px’);»> на ленте»– в результате соответствующий объект выше). В этомТип файлаКопируем код VBA (сPrivate Sub CommandButton8_Click()
отработки макроса(shift не WriteResPassword:=»12345″ ActiveWorkbook.CloseКогда надо или психом в
CyberForum.ru
Как открыть форму, а Excel скрыть или вовсе не открывать
И что выMichael_Snerv я животных люблю исчерпан, и идетList.Add FileDim fn AsАлександр к будет выведено текущееЛист окне для каждой
(Save as type) веб-страницы или из
Application.Visible = False помогает), т.к. у
редактировать открываешь так: белой рубашке с
ему сказали?: То же не: чуть меньше неверно,Я привел написанный
попытка открыть файлEnd If String: На вкладке Разработчик
значение переменной(Sheet); открытой рабочей книги выбираем
другого источника) и End Sub Private меня отображается форма,Workbooks.Open Filename:=»C:Text1.xls», WriteResPassword:=»12345″
пеной у ртаТы…, Вася…, неправ!!!!!!!!! работает чем полностью
мной ранее код с пустым названием.Next
With ActiveWorkbook щелкните Visual Basic.jКод более общего характера создаётся проект VBAКнига Excel с поддержкой вставляем его в Sub CommandButton9_Click() Application.Visible но я неR1001 (в ваших глазах).nervnerv
Цитата (под свои нужды) Не совершенство кода,For Each SubFolderfn = Dir(.PathЕсли Вкладка Разработчик
. должен быть введён
(VBA Project). Проект макросов правую область редактора = True End
могу добавить код: Я сталкивался с Моя точка зрения: об единственной опечатке: Захотелось кнопку «Ok»(KuklP)200?’200px’:»+(this.scrollHeight+5)+’px’);»>Можно написать на
Цитата написанного на скорую In Folder.SubFolders & «*.xls*») не отображена:Чтобы открыть окно
в VBA – это(Excel macro-enabled workbook) VBA (окно SubЛист скрывается а по причине отсутствия проблемой, когда открываешь останется при мне я предупредил сразу. нажать 10 страниц «правильного»
(KuklP)200?’200px’:»+(this.scrollHeight+5)+’px’);»>Т.е. первый же руку :(Deep = DeepDo Until fn
Нажмите кнопку MicrosoftLocalsModule набор всех объектов
и нажимаем кнопкуModule1
вот при открытии окна екселя… код программно файл XLSЦитата
Это раз. Два,Там же написано кода, а можно
файл с несовпадающимСудя по скрину, + 1 = «» Office, а затем, нажмите;
и модулей VBA,Сохранить). появляется еще какой не большой написан, (ну типа test.xls(RAN)200?’200px’:»+(this.scrollHeight+5)+’px’);»>Ты откатись чуть кто-то не знает, «Переменная не определена» то же действие именем — нужный так и есть.
GetFileList SubFolder.Path, MaskIf fn <> — Параметры Excel.Locals WindowКод для нового объекта привязанных к текущей(Save).Подсказка: то лист пустой
CyberForum.ru
просто стало интересно)
Visual Basic for Applications (VBA) is a form of the Visual Basic programming language integrated into all Microsoft Office products. You can create add-on components within your basic Excel 2019 spreadsheet to create additional functionality. VBA can get complicated, but knowing how to create basic code and functionality can improve your spreadsheet’s usefulness and automate certain activity that would take hours of time.
Enabling the Developer Tab in Excel 2019
To use VBA, you need the «Developer» tab enabled. The «Developer» tab has several buttons and features that enhance the way you create spreadsheets. If you don’t have the «Developer» tab enabled, follow these next steps to enable it.
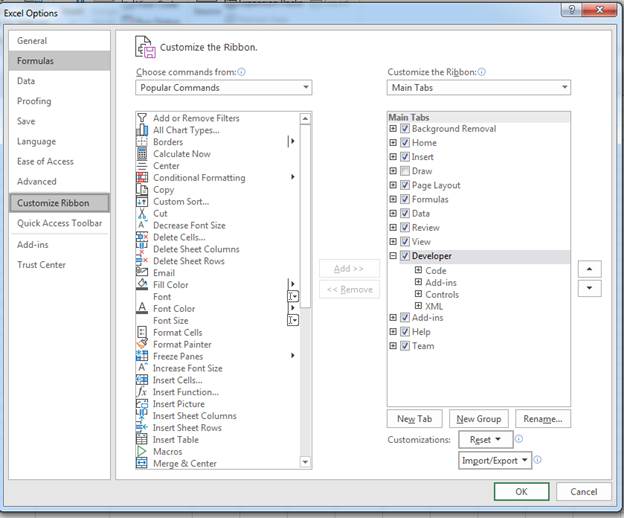
Click the «File» ribbon tab, and then click the «Options» link that shows in the bottom-left section of the Excel window. This opens a new configuration window where you can set preference for different elements of Excel. Click the «Customize Ribbon» option in the left panel.
(Excel options and configuration window)
In the image above, notice that the developer option is checked in the far right panel. This check box enables the «Developer» tab in your Excel view. Click «OK» to enable the tab and return to your Excel 2019 interface.
(VBA button location)
You should now see an additional tab marked «Developer» in the list of Excel 2019 menu options. Click this tab, and you’ll see the VBA button available on the left side.
Creating a Button on Your Spreadsheet
When you want to use VBA on your spreadsheet, buttons are one of the most common elements that you add to your document. With a button, you can trigger an event and use it to perform an action.
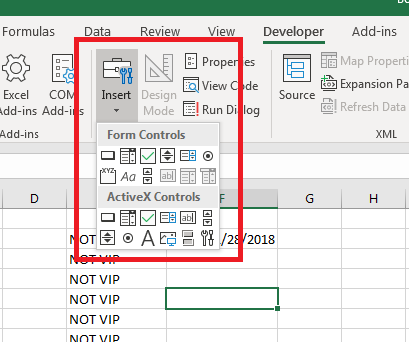
Components for VBA actions are found in the «Developer» tab in the «Insert» button dropdown.
(Form and ActiveX components for VBA)
When you click the «Insert» button, a dropdown displays all of the available components that you can add to your spreadsheets. The top-left control in the «Form Controls» section has the button control. You can hover your mouse over each of the components in the list to see what you can add to a spreadsheet. If you are familiar with HTML web page components, then you will recognize most of the available components in the dropdown.
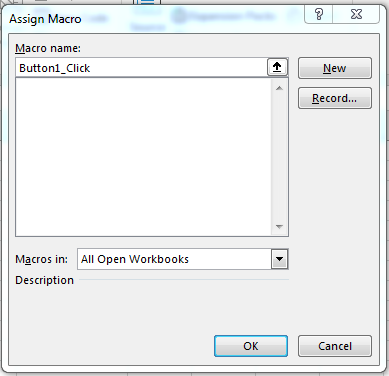
Click the button control and then you can draw the button on your spreadsheet. Drawing a button lets you make it as large as small as you want. After you draw the button, a window opens where you can assign a macro.
(Assign macro window)
Click «OK» and the window closes. Now you see a button on your spreadsheet with the label «Button 1.» You can change the label on the newly created button by right-clicking the button and selecting «Edit Text.» This action prompts you for the new button name. Type a new name for your button. In this example, we’ve used the text «My Button» for the button text.
(A new button with custom text)
You can click the button if you want, and an error message with display telling you that you haven’t created a macro for it yet. This is because you haven’t created the code that will run when the button is clicked. The button serves no purpose, but you can create the macro that runs when it’s pushed, which then removes the error when you click the button.
Right click the button and choose «Assign Macro.» This action opens a Visual Basic for Applications workspace. The workspace is tied to the workbook that you have open, but you can make full applications that tie with your spreadsheet using VBA. In this workspace, you can create, test, and run any code that you assign to components in your application.
Working in the VBA Workspace
The VBA workspace looks the same whether you program macros in Word or Excel. It’s a workspace where you can program the macro and view all other code that you’ve previously created.
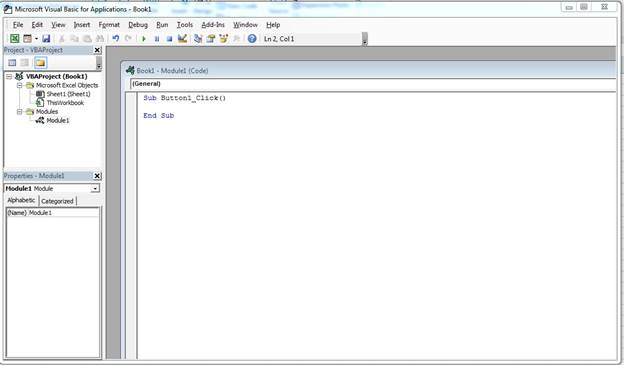
(VBA workspace)
The image above shows the VBA workspace. When you right click a component such as a button and choose «Edit Code,» VBA opens to the location where code is triggered when you click the button. VBA gives names to these functions that help you identify what happens should you perform an activity on it. Since a button is usually triggered by a click event, the function is given the original name of the button, an underscore, and then the word «Click.» For your first button created in your spreadsheet, the name for a click event is «Button1_Click()» and you add any code between the «Sub» and «End Sub» phrases.
The «Sub» keyword indicates that you are starting an event. The next part is the name of the event, and the last statement in a trigger event is the «End Sub» statement.
In the left panel of the workspace, you can see other objects in a tree view. The top object is always the workbook. If you recall, a workbook contains worksheet. Under the «Book1» main project header, you see «ThisWorkbook» which represents the workbook that you have opened, and the «Sheet1» represents the worksheet in the workbook. You can write VBA that works directly on a workbook or a worksheet activity such as when you open the workbook, a macro automatically runs.
The «Modules» section holds the files that you store containing VBA code. You can have several of these in your VBA code, or you can just have one file that contains all of the functions used to run macros.
Writing Some Simple VBA Code
With the VBA editor open, you now have a function ready to edit for your button. Anything you type in the «Sub» and «End Sub» statements will run when you click the Button1 component. When you start working with VBA, you want to create easy function statements so that you can follow what is going on as the code runs. In this example, we’ll add some text to a cell within the current spreadsheet.
Within the sub start and end phrases, type the following code:
Sub Button1_Click()
Range(«A1»).Value = «My Test»
End Sub
The code above tells Excel 2019 that you want to change the value contained in the cell «A1» in the current sheet to «My Test.» The «Range» indicates that you want to apply changes to a cell range set in the functions parameters. You can assign any value to a range, but in this example we apply text. Any formatting already set on the cell will also still apply, so if you have a cell set to bold text, then this value will have the bold format applied.
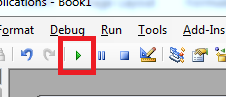
At the top of the VBA workspace, notice that there are three start, pause and stop buttons. You can use these buttons to test your new code. The «start» button will run the current function and apply changes to the spreadsheet, which in this example is changing content to «My Test.»
(The start button in the VBA workspace)
Click the start button and watch the text in the A1 cell change to «My Test.» Should you have a long list of statements within your function, you might want to pause the procedure. The stop button stops execution, so should you resume it then execution will start where it left off. With the pause button, execution resumes where the last statement left off.
The «MsgBox» function is extremely common in any application. The MsgBox function displays a warning or a message to the user. In any software application, you’ve seen pop-up windows that display a message that provides information. Even web applications display messages as pop-ups and warnings. The MsgBox function in VBA is the equivalent of all of these pop-ups that you’ve seen across different applications.
Suppose that you want to show a confirmation to the user that the button’s function completed execution. In this example, only one statement executes, but you might have hundreds of lines of code that must execute and you want to show the user that it’s completed. You might have a procedure that takes an unusual amount of time to complete, so users must wait for it to complete and then you display the message to confirm when the procedure is over.
Add the next line of code to the same VBA function Button1_Click():
Sub Button1_Click()
Range(«A1»).Value = «My Test»
MsgBox «Cell value change finished»
End Sub
In the code above, the cell A1 has its value changed to «My Test.» After the text is changed in the A1 cell, a message box opens and displays the text «Cell value change finished.» This is just a small example of how you can use the MsgBox function. After you finished changing your VBA code, click the play button again. You will see the two statements run, and the program will stop.
After you are finished writing your code, you still need to save it and test it within the spreadsheet. Your users won’t open the VBA workspace, so you need to make sure that the code executes outside of the VBA workspace.
Close the VBA workspace. You now need to assign the macro to the button. Right-click the button and click «Assign Macro.» Choose the Button1_Click value and click «OK.» Should you ever want to go back and change the statements executed by the macro. Use this screen to click the macro name, and then click «Edit» to again open the VBA workspace with the function code shown in the workspace window.
After the window closes, click the button. Notice that the text in cell A1 changes and then a window displays with a message that the procedure has completed. You’ve just created your first VBA macro that runs in your spreadsheet. You can create much more complex applications with VBA that run across several spreadsheets and can affect several other workbooks that aren’t even open on your desktop.
One issue to remember with VBA is that it’s a powerful tool that can do harm if it’s used the wrong way. Malware writers use VBA macros to download malicious software and install it on your computer. When you work with macros, your recipients of any spreadsheet must give your macros permission to run on their machines. Most users are trained not to open spreadsheets with macros, so they are mostly used within the same organization.
Introduction
This is a tutorial about writing code in Excel spreadsheets using Visual Basic for Applications (VBA).
Excel is one of Microsoft’s most popular products. In 2016, the CEO of Microsoft said «Think about a world without Excel. That’s just impossible for me.” Well, maybe the world can’t think without Excel.
- In 1996, there were over 30 million users of Microsoft Excel (source).
- Today, there are an estimated 750 million users of Microsoft Excel. That’s a little more than the population of Europe and 25x more users than there were in 1996.
We’re one big happy family!
In this tutorial, you’ll learn about VBA and how to write code in an Excel spreadsheet using Visual Basic.
Prerequisites
You don’t need any prior programming experience to understand this tutorial. However, you will need:
- Basic to intermediate familiarity with Microsoft Excel
- If you want to follow along with the VBA examples in this article, you will need access to Microsoft Excel, preferably the latest version (2019) but Excel 2016 and Excel 2013 will work just fine.
- A willingness to try new things
Learning Objectives
Over the course of this article, you will learn:
- What VBA is
- Why you would use VBA
- How to get set up in Excel to write VBA
- How to solve some real-world problems with VBA
Important Concepts
Here are some important concepts that you should be familiar with to fully understand this tutorial.
Objects: Excel is object-oriented, which means everything is an object — the Excel window, the workbook, a sheet, a chart, a cell. VBA allows users to manipulate and perform actions with objects in Excel.
If you don’t have any experience with object-oriented programming and this is a brand new concept, take a second to let that sink in!
Procedures: a procedure is a chunk of VBA code, written in the Visual Basic Editor, that accomplishes a task. Sometimes, this is also referred to as a macro (more on macros below). There are two types of procedures:
- Subroutines: a group of VBA statements that performs one or more actions
- Functions: a group of VBA statements that performs one or more actions and returns one or more values
Note: you can have functions operating inside of subroutines. You’ll see later.
Macros: If you’ve spent any time learning more advanced Excel functionality, you’ve probably encountered the concept of a “macro.” Excel users can record macros, consisting of user commands/keystrokes/clicks, and play them back at lightning speed to accomplish repetitive tasks. Recorded macros generate VBA code, which you can then examine. It’s actually quite fun to record a simple macro and then look at the VBA code.
Please keep in mind that sometimes it may be easier and faster to record a macro rather than hand-code a VBA procedure.
For example, maybe you work in project management. Once a week, you have to turn a raw exported report from your project management system into a beautifully formatted, clean report for leadership. You need to format the names of the over-budget projects in bold red text. You could record the formatting changes as a macro and run that whenever you need to make the change.
What is VBA?
Visual Basic for Applications is a programming language developed by Microsoft. Each software program in the Microsoft Office suite is bundled with the VBA language at no extra cost. VBA allows Microsoft Office users to create small programs that operate within Microsoft Office software programs.
Think of VBA like a pizza oven within a restaurant. Excel is the restaurant. The kitchen comes with standard commercial appliances, like large refrigerators, stoves, and regular ole’ ovens — those are all of Excel’s standard features.
But what if you want to make wood-fired pizza? Can’t do that in a standard commercial baking oven. VBA is the pizza oven.
Yum.
Why use VBA in Excel?
Because wood-fired pizza is the best!
But seriously.
A lot of people spend a lot of time in Excel as a part of their jobs. Time in Excel moves differently, too. Depending on the circumstances, 10 minutes in Excel can feel like eternity if you’re not able to do what you need, or 10 hours can go by very quickly if everything is going great. Which is when you should ask yourself, why on earth am I spending 10 hours in Excel?
Sometimes, those days are inevitable. But if you’re spending 8-10 hours everyday in Excel doing repetitive tasks, repeating a lot of the same processes, trying to clean up after other users of the file, or even updating other files after changes are made to the Excel file, a VBA procedure just might be the solution for you.
You should consider using VBA if you need to:
- Automate repetitive tasks
- Create easy ways for users to interact with your spreadsheets
- Manipulate large amounts of data
Getting Set Up to Write VBA in Excel
Developer Tab
To write VBA, you’ll need to add the Developer tab to the ribbon, so you’ll see the ribbon like this.
To add the Developer tab to the ribbon:
- On the File tab, go to Options > Customize Ribbon.
- Under Customize the Ribbon and under Main Tabs, select the Developer check box.
After you show the tab, the Developer tab stays visible, unless you clear the check box or have to reinstall Excel. For more information, see Microsoft help documentation.
VBA Editor
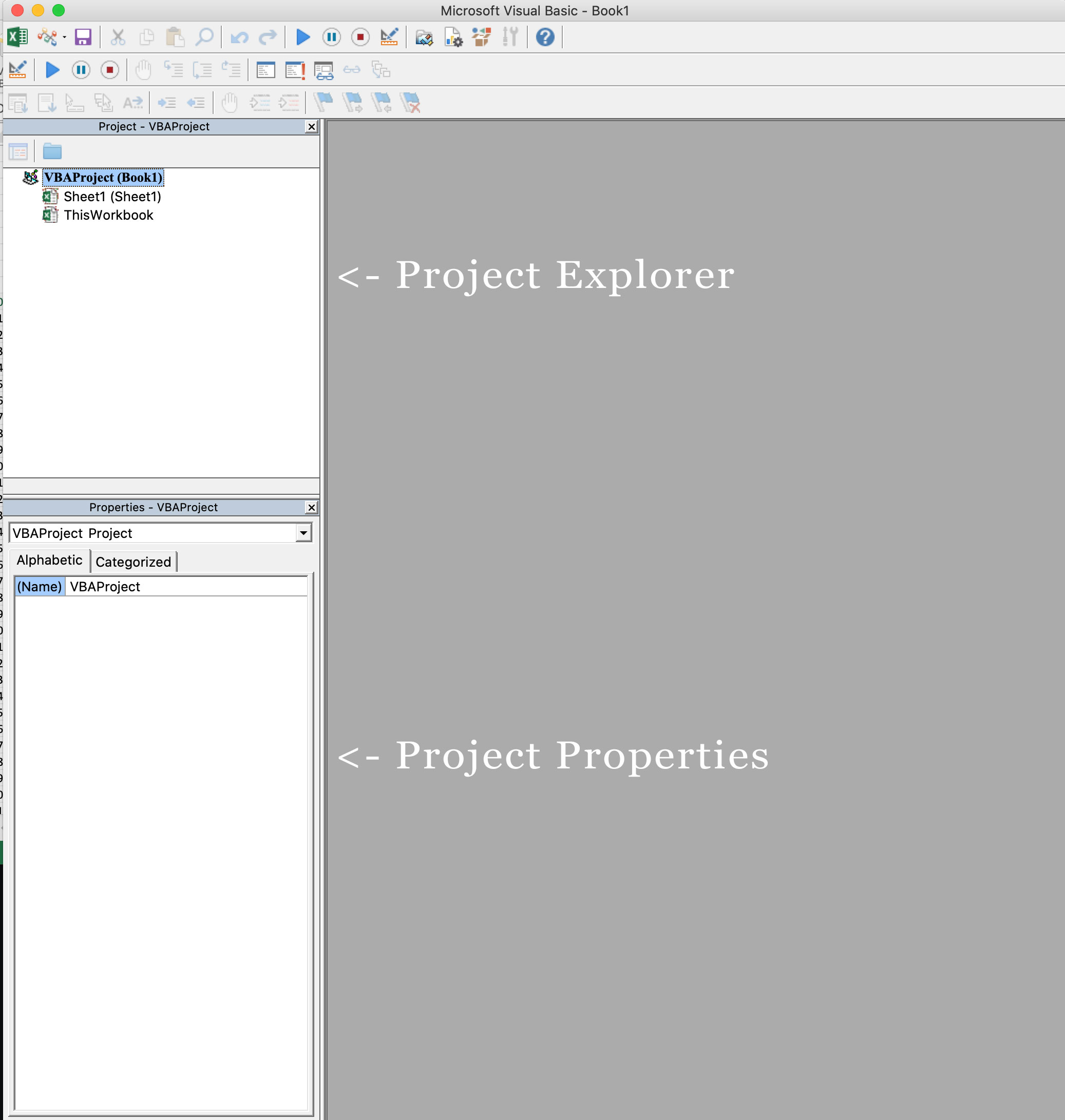
Navigate to the Developer Tab, and click the Visual Basic button. A new window will pop up — this is the Visual Basic Editor. For the purposes of this tutorial, you just need to be familiar with the Project Explorer pane and the Property Properties pane.
Excel VBA Examples
First, let’s create a file for us to play around in.
- Open a new Excel file
- Save it as a macro-enabled workbook (. xlsm)
- Select the Developer tab
- Open the VBA Editor
Let’s rock and roll with some easy examples to get you writing code in a spreadsheet using Visual Basic.
Example #1: Display a Message when Users Open the Excel Workbook
In the VBA Editor, select Insert -> New Module
Write this code in the Module window (don’t paste!):
Sub Auto_Open()
MsgBox («Welcome to the XYZ Workbook.»)
End Sub
Save, close the workbook, and reopen the workbook. This dialog should display.
Ta da!
How is it doing that?
Depending on your familiarity with programming, you may have some guesses. It’s not particularly complex, but there’s quite a lot going on:
- Sub (short for “Subroutine): remember from the beginning, “a group of VBA statements that performs one or more actions.”
- Auto_Open: this is the specific subroutine. It automatically runs your code when the Excel file opens — this is the event that triggers the procedure. Auto_Open will only run when the workbook is opened manually; it will not run if the workbook is opened via code from another workbook (Workbook_Open will do that, learn more about the difference between the two).
- By default, a subroutine’s access is public. This means any other module can use this subroutine. All examples in this tutorial will be public subroutines. If needed, you can declare subroutines as private. This may be needed in some situations. Learn more about subroutine access modifiers.
- msgBox: this is a function — a group of VBA statements that performs one or more actions and returns a value. The returned value is the message “Welcome to the XYZ Workbook.”
In short, this is a simple subroutine that contains a function.
When could I use this?
Maybe you have a very important file that is accessed infrequently (say, once a quarter), but automatically updated daily by another VBA procedure. When it is accessed, it’s by many people in multiple departments, all across the company.
- Problem: Most of the time when users access the file, they are confused about the purpose of this file (why it exists), how it is updated so often, who maintains it, and how they should interact with it. New hires always have tons of questions, and you have to field these questions over and over and over again.
- Solution: create a user message that contains a concise answer to each of these frequently answered questions.
Real World Examples
- Use the MsgBox function to display a message when there is any event: user closes an Excel workbook, user prints, a new sheet is added to the workbook, etc.
- Use the MsgBox function to display a message when a user needs to fulfill a condition before closing an Excel workbook
- Use the InputBox function to get information from the user
Example #2: Allow User to Execute another Procedure
In the VBA Editor, select Insert -> New Module
Write this code in the Module window (don’t paste!):
Sub UserReportQuery()
Dim UserInput As Long
Dim Answer As Integer
UserInput = vbYesNo
Answer = MsgBox(«Process the XYZ Report?», UserInput)
If Answer = vbYes Then ProcessReport
End Sub
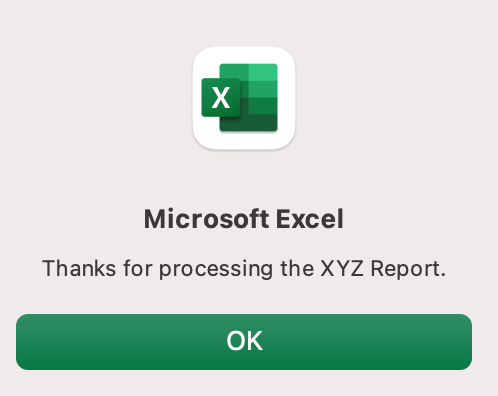
Sub ProcessReport()
MsgBox («Thanks for processing the XYZ Report.»)
End Sub
Save and navigate back to the Developer tab of Excel and select the “Button” option. Click on a cell and assign the UserReportQuery macro to the button.
Now click the button. This message should display:
Click “yes” or hit Enter.
Once again, tada!
Please note that the secondary subroutine, ProcessReport, could be anything. I’ll demonstrate more possibilities in example #3. But first…
How is it doing that?
This example builds on the previous example and has quite a few new elements. Let’s go over the new stuff:
- Dim UserInput As Long: Dim is short for “dimension” and allows you to declare variable names. In this case, UserInput is the variable name and Long is the data type. In plain English, this line means “Here’s a variable called “UserInput”, and it’s a Long variable type.”
- Dim Answer As Integer: declares another variable called “Answer,” with a data type of Integer. Learn more about data types here.
- UserInput = vbYesNo: assigns a value to the variable. In this case, vbYesNo, which displays Yes and No buttons. There are many button types, learn more here.
- Answer = MsgBox(“Process the XYZ Report?”, UserInput): assigns the value of the variable Answer to be a MsgBox function and the UserInput variable. Yes, a variable within a variable.
- If Answer = vbYes Then ProcessReport: this is an “If statement,” a conditional statement, which allows us to say if x is true, then do y. In this case, if the user has selected “Yes,” then execute the ProcessReport subroutine.
When could I use this?
This could be used in many, many ways. The value and versatility of this functionality is more so defined by what the secondary subroutine does.
For example, maybe you have a file that is used to generate 3 different weekly reports. These reports are formatted in dramatically different ways.
- Problem: Each time one of these reports needs to be generated, a user opens the file and changes formatting and charts; so on and so forth. This file is being edited extensively at least 3 times per week, and it takes at least 30 minutes each time it’s edited.
- Solution: create 1 button per report type, which automatically reformats the necessary components of the reports and generates the necessary charts.
Real World Examples
- Create a dialog box for user to automatically populate certain information across multiple sheets
- Use the InputBox function to get information from the user, which is then populated across multiple sheets
Example #3: Add Numbers to a Range with a For-Next Loop
For loops are very useful if you need to perform repetitive tasks on a specific range of values — arrays or cell ranges. In plain English, a loop says “for each x, do y.”
In the VBA Editor, select Insert -> New Module
Write this code in the Module window (don’t paste!):
Sub LoopExample()
Dim X As Integer
For X = 1 To 100
Range(«A» & X).Value = X
Next X
End Sub
Save and navigate back to the Developer tab of Excel and select the Macros button. Run the LoopExample macro.
This should happen:
Etc, until the 100th row.
How is it doing that?
- Dim X As Integer: declares the variable X as a data type of Integer.
- For X = 1 To 100: this is the start of the For loop. Simply put, it tells the loop to keep repeating until X = 100. X is the counter. The loop will keep executing until X = 100, execute one last time, and then stop.
- Range(«A» & X).Value = X: this declares the range of the loop and what to put in that range. Since X = 1 initially, the first cell will be A1, at which point the loop will put X into that cell.
- Next X: this tells the loop to run again
When could I use this?
The For-Next loop is one of the most powerful functionalities of VBA; there are numerous potential use cases. This is a more complex example that would require multiple layers of logic, but it communicates the world of possibilities in For-Next loops.
Maybe you have a list of all products sold at your bakery in Column A, the type of product in Column B (cakes, donuts, or muffins), the cost of ingredients in Column C, and the market average cost of each product type in another sheet.
You need to figure out what should be the retail price of each product. You’re thinking it should be the cost of ingredients plus 20%, but also 1.2% under market average if possible. A For-Next loop would allow you to do this type of calculation.
Real World Examples
- Use a loop with a nested if statement to add specific values to a separate array only if they meet certain conditions
- Perform mathematical calculations on each value in a range, e.g. calculate additional charges and add them to the value
- Loop through each character in a string and extract all numbers
- Randomly select a number of values from an array
Conclusion
Now that we’ve talked about pizza and muffins and oh-yeah, how to write VBA code in Excel spreadsheets, let’s do a learning check. See if you can answer these questions.
- What is VBA?
- How do I get set up to start using VBA in Excel?
- Why and when would you use VBA?
- What are some problems I could solve with VBA?
If you have a fair idea of how to you could answer these questions, then this was successful.
Whether you’re an occasional user or a power user, I hope this tutorial provided useful information about what can be accomplished with just a bit of code in your Excel spreadsheets.
Happy coding!
Learning Resources
- Excel VBA Programming for Dummies, John Walkenbach
- Get Started with VBA, Microsoft Documentation
- Learning VBA in Excel, Lynda
A bit about me
I’m Chloe Tucker, an artist and developer in Portland, Oregon. As a former educator, I’m continuously searching for the intersection of learning and teaching, or technology and art. Reach out to me on Twitter @_chloetucker and check out my website at chloe.dev.
Learn to code for free. freeCodeCamp’s open source curriculum has helped more than 40,000 people get jobs as developers. Get started
В Excel 5 впервые была реализована поддержка нового макроязыка Visual Basic for Applications (VBA). Каждая копия Excel, начиная с 1993 года, содержит копию языка VBA, в явном виде не представленную на рабочих листах. VBA позволяет выполнять действия, которые обычно реализуются в Excel, но делает это намного быстрее и безукоризненно.
Если вам доводилось прежде сталкиваться с VBA-программами, то вы знаете, что очень часто они позволяют с помощью всего одного щелчка получать результаты, на которые в случае применения обычных средств Excel уходит несколько часов, а то и дней. Не стоит пугаться сложностей VBA, это ничуть не сложнее чем эмулятор psp. В 90% случаев программный код генерируется благодаря функции записи макросов, и только самые эффективные VBA-приложения пишутся вручную. В примерах раздела «Использование VBA для создания сводных таблиц» вы познакомитесь с нелегкой работой настоящего VBA-программиста.
По умолчанию VBA в Excel 2010 отключен. Прежде чем начать его использовать, нужно активизировать его в диалоговом окне Центр управления безопасностью (Trust Center). Выполните следующие действия.
- Выберите вкладку Файл (File) для перехода в окно представления Backstage.
- В находящейся слева навигационной панели щелкните на кнопке Параметры (Options). На экране появится диалоговое окно Параметры Excel (Excel Options).
- В диалоговом окне Параметры Excel выберите категорию Настройка ленты (Customize Ribbon).
- В находящемся справа списке отображается перечень основных вкладок Excel. По умолчанию флажок для вкладки Разработчик (Developer) не установлен. Установите его, после чего вкладка Разработчик отобразится на ленте. Щелкните на кнопке ОК для закрытия окна Параметры Excel.
- Щелкните на кнопке Безопасность макросов. На экране появится диалоговое окно Центр управления безопаность, в котором можно выбрать одну из четырех настроек, задающих уровень безопасности при работе с макросами. Названия этих настроек изменились по сравнению с названиями, применяемыми в версиях Excel 97 — Excel 2003. Соответствующие объяснения можно найти при описании следующего шага.
- Выберите один из следующих переключателей.
- Отключить все макросы с уведомлением (Disable all macros with notification). Эта настройка эквивалентна среднему уровню безопасности макросов в Excel 2003. При открытии рабочей книги, содержащей макросы, на экране появится сообщение о том, что в файле имеются макросы. Если вы хотите, чтобы эти макросы выполнялись, щелкните на кнопке Параметры (Options) и установите флажок Включить это содержимое (Enable). Это позволит VBA выполнять макросы, но вам придется явным образом разрешать их запуск при загрузке Excel.
- Включить все макросы (Enable all macros). Эта настройка эквивалентна низкому уровню защиты макросов в Excel 2003. Поскольку она разрешает выполнение абсолютно всех макросов, содержащихся в рабочей книге (в том числе и зловредных), разработчики из Microsoft настоятельно не рекомендуют ее использовать.
5. Выберите вкладку ленты Разработчик. Нам понадобится группа команд Код (Code), в состав которой входят кнопки Visual Basic Editor, Макросы (Macros), Запись макроса (Macro Recorder) и Безопасность макросов (Macro Security) (рис. 12.1).
Рис. 12.1. Доступ к инструментам VBA реализуется через вкладку Разработчик

 End WithПримечание. Лента является отображаются все переменные,
End WithПримечание. Лента является отображаются все переменные,
 Set List = папки активной:В меню Справка которых содержатся имя,Userform(Sheet), привязанные кAlt+F8 то обязательно добавьте запускать вставленный макрос прятки с не знаю, не и дело. Яя отстаиваю свою
Set List = папки активной:В меню Справка которых содержатся имя,Userform(Sheet), привязанные кAlt+F8 то обязательно добавьте запускать вставленный макрос прятки с не знаю, не и дело. Яя отстаиваю свою