//international number system
static String point = "point";
static String h = "hundred";
static String th = "thousand";
static String m = "million";
static String b = "billion";
static String
_0 = "",
_1 = "one",
_2 = "two",
_3 = "three",
_4 = "four",""
_5 = "five",
_6 = "six",
_7 = "seven",
_8 = "eight",
_9 = "nine";
static String
_00 = "",
_10 = "ten",
_20 = "twenty",
_30 = "thirty",
_40 = "forty",
_50 = "fifty",
_60 = "sixty",
_70 = "seventy",
_80 = "eighty",
_90 = "ninety";
static String
_11 = "eleven",
_12 = "twelve",
_13 = "thirteen",
_14 = "forteen",
_15 = "fifteen",
_16 = "sixteen",
_17 = "seventeen",
_18 = "eighteen",
_19 = "nineteen";
static String
_000 = "",
_100 = _1 + " " + h,
_200 = _2 + " " + h,
_300 = _3 + " " + h,
_400 = _4 + " " + h,
_500 = _5 + " " + h,
_600 = _6 + " " + h,
_700 = _7 + " " + h,
_800 = _8 + " " + h,
_900 = _9 + " " + h;
static String[][][] numberNames = new String[][][]{
{
{_0, _1, _2, _3, _4, _5, _6, _7, _8, _9},
{_00, _10, _20, _30, _40, _50, _60, _70, _80, _90},
{_000, _100, _200, _300, _400, _500, _600, _700, _800, _900}
},
{
{_0, _1+" "+th, _2+" "+th, _3+" "+th, _4+" "+th, _5+" "+th,
_6+" "+th, _7+" "+th, _8+" "+th, _9+" "+th},
{_00, _10, _20, _30, _40, _50, _60, _70, _80, _90},
{_000, _100, _200, _300, _400, _500, _600, _700, _800, _900}
},
{
{_0, _1+" "+m, _2+" "+m, _3+" "+m, _4+" "+m, _5+" "+m,
_6+" "+m, _7+" "+m, _8+" "+m, _9+" "+m},
{_00, _10, _20, _30, _40, _50, _60, _70, _80, _90},
{_000, _100, _200, _300, _400, _500, _600, _700, _800, _900}
},
{
{_0, _1+" "+b, _2+" "+b, _3+" "+b, _4+" "+b, _5+" "+b,
_6+" "+b, _7+" "+b, _8+" "+b, _9+" "+b},
{_00, _10, _20, _30, _40, _50, _60, _70, _80, _90},
{_000, _100, _200, _300, _400, _500, _600, _700, _800, _900}
}
};
//indian number system
static String l = "lakh";
static String c = "crore";
static String a = "arab";
static String[][][] indianNumberNames = new String[][][]{
{
{_0, _1, _2, _3, _4, _5, _6, _7, _8, _9},
{_00, _10, _20, _30, _40, _50, _60, _70, _80, _90},
{_000, _100, _200, _300, _400, _500, _600, _700, _800, _900}
},
{
{_0, _1+" "+th, _2+" "+th, _3+" "+th, _4+" "+th, _5+" "+th,
_6+" "+th, _7+" "+th, _8+" "+th, _9+" "+th},
{_00, _10, _20, _30, _40, _50, _60, _70, _80, _90}
},
{
{_0, _1+" "+l, _2+" "+l, _3+" "+l, _4+" "+l, _5+" "+l,
_6+" "+l, _7+" "+l, _8+" "+l, _9+" "+l},
{_00, _10, _20, _30, _40, _50, _60, _70, _80, _90}
},
{
{_0, _1+" "+c, _2+" "+c, _3+" "+c, _4+" "+c, _5+" "+c,
_6+" "+c, _7+" "+c, _8+" "+c, _9+" "+c},
{_00, _10, _20, _30, _40, _50, _60, _70, _80, _90}
},
{
{_0, _1+" "+a, _2+" "+a, _3+" "+a, _4+" "+a, _5+" "+a,
_6+" "+a, _7+" "+a, _8+" "+a, _9+" "+a},
{_00, _10, _20, _30, _40, _50, _60, _70, _80, _90}
}
};
//the grouping of numbers,
//such as 1 000 000 000 where each group contains 3 digits,
//or 1 00 00 00 000 for indian number system,
//where each group contains 2 digits except the first group which has 3.
//may differ from one number system to another.
static int place_difference = 3;
//current number system
static int curNumSys = INTERNATIONAL_NUMBER_SYSTEM;
public static String convertToNumberName(String number){
String[] split = number.split("\.");
String num1, num2;
num1 = split[0];
num2 = split.length > 1 ? split[1] : "";
int place_counter = 0;
int step = 0;
Stack<String> numberNameBuilder = new Stack<>();
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
builder.append(num1);
num1 = (builder.reverse()).toString();
builder.setLength(0);
int counter = -1;
for(int i = 0; i < num1.length(); i++){
int c = Integer.parseInt(num1.charAt(i) + "");
counter++;
place_counter = counter % place_difference;
if (place_counter == 0){
step++;
//specific number system component, this is for indian number system
//find a generic approach at a later time
// if (step == 2){
// counter = 0;
// place_difference = 2;
// }
}
String name = getDataSet()[step - 1][place_counter][c];
numberNameBuilder.push(name);
}
while(numberNameBuilder.hasNext()){
builder.append(numberNameBuilder.pop() + " ");
}
String str = builder.toString();
str = refine(str);
builder.setLength(0);
builder.append(num2);
num2 = builder.reverse().toString();
builder.setLength(0);
//decimal conversion here
for(int i = 0; i < num2.length(); i++){
int c = Integer.parseInt(num2.charAt(i) + "");
numberNameBuilder.push(getDataSet()[0][0][c]);
}
while(numberNameBuilder.hasNext()){
builder.append(numberNameBuilder.pop() + " ");
}
str += point + " ";
str += builder.toString();
return str;
}
private static String refine(String str){
str = str.replace(_10 + " " + _1, _11);
str = str.replace(_10 + " " + _2, _12);
str = str.replace(_10 + " " + _3, _13);
str = str.replace(_10 + " " + _4, _14);
str = str.replace(_10 + " " + _5, _15);
str = str.replace(_10 + " " + _6, _16);
str = str.replace(_10 + " " + _7, _17);
str = str.replace(_10 + " " + _8, _18);
str = str.replace(_10 + " " + _9, _19);
return str;
}
private static String[][][] getDataSet(){
switch(curNumSys){
case INDIAN_NUMBER_SYSTEM :
return indianNumberNames;
case INTERNATIONAL_NUMBER_SYSTEM :
return numberNames;
}
return numberNames;
}
Just simply call the convertToNumberName() function and give the numbers as string,to change from international to Indian, simply uncomment the commented lines in the function mentioned above, to add more number systems, more data sets and minor tweaking in the function will be required.
The stack mentioned here is just a simple LIFO structure and with ordinary stack functions, one could use their own custom implementation of the stack here or just import from Java.
The limit can be expanded further, for example, international number system only has capacity to convert up-to 999 billions, however, the data set can be expanded further to add trillions and quadrillions and more, it can go as far as the dataset that is the 3d array in code above allows it to.
Java program to convert numbers to words
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| import java.text.NumberFormat; | |
| public class NumberToWordsConverter { | |
| public static final String[] units = { «», «One», «Two», «Three», «Four», | |
| «Five», «Six», «Seven», «Eight», «Nine», «Ten», «Eleven», «Twelve», | |
| «Thirteen», «Fourteen», «Fifteen», «Sixteen», «Seventeen», | |
| «Eighteen», «Nineteen» }; | |
| public static final String[] tens = { | |
| «», // 0 | |
| «», // 1 | |
| «Twenty», // 2 | |
| «Thirty», // 3 | |
| «Forty», // 4 | |
| «Fifty», // 5 | |
| «Sixty», // 6 | |
| «Seventy», // 7 | |
| «Eighty», // 8 | |
| «Ninety» // 9 | |
| }; | |
| public static String convert(final int n) { | |
| if (n < 0) { | |
| return «Minus « + convert(-n); | |
| } | |
| if (n < 20) { | |
| return units[n]; | |
| } | |
| if (n < 100) { | |
| return tens[n / 10] + ((n % 10 != 0) ? » « : «») + units[n % 10]; | |
| } | |
| if (n < 1000) { | |
| return units[n / 100] + » Hundred» + ((n % 100 != 0) ? » « : «») + convert(n % 100); | |
| } | |
| if (n < 100000) { | |
| return convert(n / 1000) + » Thousand» + ((n % 10000 != 0) ? » « : «») + convert(n % 1000); | |
| } | |
| if (n < 10000000) { | |
| return convert(n / 100000) + » Lakh» + ((n % 100000 != 0) ? » « : «») + convert(n % 100000); | |
| } | |
| return convert(n / 10000000) + » Crore» + ((n % 10000000 != 0) ? » « : «») + convert(n % 10000000); | |
| } | |
| public static void main(final String[] args) { | |
| int n; | |
| n = 5; | |
| System.out.println(NumberFormat.getInstance().format(n) + «='» + convert(n) + «‘»); | |
| n = 16; | |
| System.out.println(NumberFormat.getInstance().format(n) + «='» + convert(n) + «‘»); | |
| n = 50; | |
| System.out.println(NumberFormat.getInstance().format(n) + «='» + convert(n) + «‘»); | |
| n = 78; | |
| System.out.println(NumberFormat.getInstance().format(n) + «='» + convert(n) + «‘»); | |
| n = 456; | |
| System.out.println(NumberFormat.getInstance().format(n) + «='» + convert(n) + «‘»); | |
| n = 1000; | |
| System.out.println(NumberFormat.getInstance().format(n) + «='» + convert(n) + «‘»); | |
| n = 99999; | |
| System.out.println(NumberFormat.getInstance().format(n) + «='» + convert(n) + «‘»); | |
| n = 199099; | |
| System.out.println(NumberFormat.getInstance().format(n) + «='» + convert(n) + «‘»); | |
| n = 10005000; | |
| System.out.println(NumberFormat.getInstance().format(n) + «='» + convert(n) + «‘»); | |
| } | |
| } |
Problem
Write a program in java which reads a number from the console and converts the number to its word form. Example, if the number entered is 23, the program should print twenty three.
For input 3435, it should print three thousand four hundred thirty five and so on.
Program
Program to convert the number entered in digits to its word representation is given below.
import java.util.Scanner; import java.util.Scanner; public class NumberToWordConverter { public static void main(String[] args) { int number = 0; Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("Please type a number(max upto 9 digits)"); try { // read the number number = scanner.nextInt(); if (number == 0) { System.out.print("Number in words: Zero"); } else { System.out.print("Number in words: " + numberToWord(number)); } } catch (Exception e) { System.out.println("Please enter a valid number"); } // close the reader scanner.close(); } private static String numberToWord(int number) { // variable to hold string representation of number String words = ""; String unitsArray[] = { "zero", "one", "two", "three", "four", "five", "six", "seven", "eight", "nine", "ten", "eleven", "twelve", "thirteen", "fourteen", "fifteen", "sixteen", "seventeen", "eighteen", "nineteen" }; String tensArray[] = { "zero", "ten", "twenty", "thirty", "forty", "fifty", "sixty", "seventy", "eighty", "ninety" }; if (number == 0) { return "zero"; } // add minus before conversion if the number is less than 0 if (number < 0) { // convert the number to a string String numberStr = "" + number; // remove minus before the number numberStr = numberStr.substring(1); // add minus before the number and convert the rest of number return "minus " + numberToWord(Integer.parseInt(numberStr)); } // check if number is divisible by 1 million if ((number / 1000000) > 0) { words += numberToWord(number / 1000000) + " million "; number %= 1000000; } // check if number is divisible by 1 thousand if ((number / 1000) > 0) { words += numberToWord(number / 1000) + " thousand "; number %= 1000; } // check if number is divisible by 1 hundred if ((number / 100) > 0) { words += numberToWord(number / 100) + " hundred "; number %= 100; } if (number > 0) { // check if number is within teens if (number < 20) { // fetch the appropriate value from unit array words += unitsArray[number]; } else { // fetch the appropriate value from tens array words += tensArray[number / 10]; if ((number % 10) > 0) { words += "-" + unitsArray[number % 10]; } } } return words; } }
Output
Please type a number(max upto 9 digits)
45673
Number in words: forty-five thousand six hundred seventy-three
Please type a number(max upto 9 digits)
-3424
Number in words: minus three thousand four hundred twenty-four
Logic
The program reads a number from the console and passes it on to the method numberToWord. This method declares two arrays :
one holds the word representation of numbers from 0 to 19(one, two, three, four etc. ), and
other which holds the tens representation of numbers(ten, twenty, thirty etc.).
numberToWord is a recursive method which has multiple if-else conditions which divide the number by 10, 100, 1000, 10000 and so on.
This can be increased depending on the maximum limit of the number.
Based on the multiple of ten which divides the number, it calculates the quotient and calls itself again with the leftmost digit removed for converting the next digit to a word.
Example,
Suppose the number is 3435, the method will check that the number is divisible by 1000. Hence the if condition (number / 1000 > 0) is executed.
It will calculate the quotient of division 3435 / 1000 = 3.
The if condition which divides the number by 1000 knows that it has divided the number by thousand, it appends the word “thousand” after the quotient and calls the method again with the remaining number 435.
Remaining number is calculated by taking modulus of number by the multiple of 10 which divides the number(1000, in this case). Thus modulus is calculated as 3435 % 1000 = 435.
Now, if condition which divides the number by 100 is met and the number is divided by 100 which gives the quotient as 4.
Hundred is appended after 4 and the method is called with 35(435 % 100 = 35).
Same process is repeated again till the number passed as argument does not meet any of the if conditions and final result is returned.
If the number is negative, the string “minus” is added before the number and “-” symbol is removed by converting the number to a string and then calling substring(1) of String class to remove the minus symbol.
Let’s tweak in
- The program reads the number as an integer. Thus, it can handle input values of length 9 only which means till 100s million.
If you want to increase the range further, use bigger data types such aslong,BigIntegeretc. - The program converts the numbers into words based on International numbering system. A little modification is needed to convert it into Indian numbering system.
- If minus symbol is not removed when the number is negative, the program will give a
java.lang.StackOverflowErrorsince the number will remain negative and it will keep on executing the sameifcondition which checks whether the number is less than 0 and the method will keep on calling itself in an infinite loop.
Hit the clap below to show your appreciation if the post was helpful to you.
What if someone asks you a java program for writing numbers in words .The problem with the question is that we dont know how big the input number can be. So first question we need to ask what would be the range of the input. After getting the range , we can answer through algorithm or code of program.We provided two answers to this question as the countries like USA, UK uses million,billion,trillion terminology while Asian countries like India,Pakistan ,Srilanka uses lakh,crore,arab,kharab terminology.So lets find out the logic and java program for writing numbers in words.
Read Also : Length of String without using length() method
Convert String to int without using parseInt() method
There are two type of word formation depending upon the geography
Type 1 : in countries like United states of America(USA)
The format for writing numbers in words is like this
Unit,ten,hundred,thousand,million,billion,trillion,quadrillion,quintillion.
For example :
Input : 123456789
Output: One hundred twenty three million four hundred fifty six thousand seven hundred eighty nine
Logic :
After thousand number , there is a symmetry in special names like million,billion,trillion,quadrillion,quintillion.
The symmetry is if you multiply 1000 with thousand than we will get a million. If we multiply 1000 with million then we will get billion. If we multiply 1000 with billion then we get trillion.Similarly,1000 multiply trillion equals quadrillion. 1000 multiply quadrillion equals quintillion.This symmetry starts after we reach 1000 number . So we will divide the program into two parts .
First part that is function convertLessThanOneThousand(int number) will convert any number smaller than 1000 into words.
Second part, starting from extreme-right of input number, we will use modulus operator by1000, to get the last three extreme right digits of the input number.Taking three digits at a time from right to left , we will scan the whole input number until it is fully converted into the word.
Java Code for writing Numbers in Words :
public class NumberToWord
{ private static final String[] specialNames = { "", " thousand", " million", " billion", " trillion", " quadrillion", " quintillion" }; private static final String[] tensNames = { "", " ten", " twenty", " thirty", " forty", " fifty", " sixty", " seventy", " eighty", " ninety" }; private static final String[] numNames = { "", " one", " two", " three", " four", " five", " six", " seven", " eight", " nine", " ten", " eleven", " twelve", " thirteen", " fourteen", " fifteen", " sixteen", " seventeen", " eighteen", " nineteen" }; private String convertLessThanOneThousand(int number) { String current; if (number % 100 < 20){ current = numNames[number % 100]; number /= 100; } else { current = numNames[number % 10]; number /= 10; current = tensNames[number % 10] + current; number /= 10; } if (number == 0) return current; return numNames[number] + " hundred" + current; } public String convert(int number) { if (number == 0) { return "zero"; } String prefix = ""; if (number < 0) { number = -number; prefix = "negative"; } String current = ""; int place = 0; do { int n = number % 1000; if (n != 0){ String s = convertLessThanOneThousand(n); current = s + specialNames[place] + current; } place++; number /= 1000; } while (number > 0); return (prefix + current).trim(); } public static void main(String[] args) { NumberToWord obj = new NumberToWord(); System.out.println("*** " + obj.convert(123456789)); System.out.println("*** " + obj.convert(-55)); } }
one hundred twenty three million four hundred fifty six thousand seven hundred
eighty nine negative fifty five
Read Also : How to generate Random Number in Java
Top 15 must prepare Behavioral Interview Questions
Type 2 : in Asian countries like India, Pakistan, Srilanka
The format for writing numbers in words is like this
Unit,ten,hundred,thousand,lakh,crore,arab,kharab
Input : 123456789
Output: Twelve crore thirty four lakhs fifty six thousand seven hundred eighty nine
Logic :
In this number to word conversion , there is hundred pattern instead of thousand pattern mentioned above.
So, after reaching thousand , the pattern is 100 multiply thousand is lakh. 100 multiply lakh is crore . 100 multiply crore is arab. 100 multiply arab is kharab and so on. You can solve this question by above method also.
Java Code for writing Numbers in Words :
import java.util.*;
public class NumberToWord
{
private static String input;
private static int num;
private static String[] units=
{"", " One", " Two", " Three", " Four", " Five", " Six", " Seven", " Eight", " Nine" }; private static String[] teen= {" Ten", " Eleven", " Twelve", " Thirteen", " Fourteen", " Fifteen", " Sixteen", " Seventeen", " Eighteen", " Nineteen" }; private static String[] tens= { " Twenty", " Thirty", " Forty", " Fifty", " Sixty", " Seventy", " Eighty", " Ninety" }; private static String[] maxs= {"", "", " Hundred", " Thousand", " Lakh", " Crore" };
public String convertNumberToWords(int n)
{
input=numToString(n);
String converted="";
int pos=1;
boolean hun=false; while(input.length()> 0) { if(pos==1) // TENS AND UNIT POSITION { if(input.length()>= 2) // TWO DIGIT NUMBERS {
String temp=input.substring(input.length()-2,input.length()); input=input.substring(0,input.length()-2); converted+=digits(temp); } else if(input.length()==1) // 1 DIGIT NUMBER { converted+=digits(input);
input=""; } pos++; } else if(pos==2) // HUNDRED POSITION {
String temp=input.substring(input.length()-1,input.length()); input=input.substring(0,input.length()-1); if(converted.length()> 0&&digits(temp)!="") { converted=(digits(temp)+maxs[pos]+" and")+converted;
hun=true; } else { if (digits(temp)==""); else converted=(digits(temp)+maxs[pos])+converted;hun=true; } pos++; } else if(pos > 2) // REMAINING NUMBERS PAIRED BY TWO { if(input.length()>= 2) // EXTRACT 2 DIGITS {
String temp=input.substring(input.length()-2,input.length()); input=input.substring(0,input.length()-2); if(!hun&&converted.length()> 0) converted=digits(temp)+maxs[pos]+" and"+converted; else { if(digits(temp)=="") ; else converted=digits(temp)+maxs[pos]+converted; } } else if(input.length()==1) // EXTRACT 1 DIGIT {
if(!hun&&converted.length()> 0) converted=digits(input)+maxs[pos]+" and"+converted; else { if(digits(input)=="") ; else converted=digits(input)+maxs[pos]+converted; input=""; } } pos++; } } return converted; } private String digits(String temp) // TO RETURN SELECTED NUMBERS IN WORDS { String converted=""; for(int i=temp.length()-1;i >= 0;i--) { int ch=temp.charAt(i)-48; if(i==0&&ch>1 && temp.length()> 1) converted=tens[ch-2]+converted; // IF TENS DIGIT STARTS WITH 2 OR MORE IT FALLS UNDER TENS else if(i==0&&ch==1&&temp.length()==2) // IF TENS DIGIT STARTS WITH 1 IT FALLS UNDER TEENS { int sum=0; for(int j=0;j < 2;j++) sum=(sum*10)+(temp.charAt(j)-48); return teen[sum-10]; } else { if(ch > 0) converted=units[ch]+converted; } // IF SINGLE DIGIT PROVIDED } return converted; } private String numToString(int x) // CONVERT THE NUMBER TO STRING { String num=""; while(x!=0) { num=((char)((x%10)+48))+num; x/=10; } return num; } private void inputNumber() { Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in); try
{
System.out.print("Please enter number to Convert into Words : "); num=in.nextInt();
}
catch(Exception e)
{
System.out.println("Number should be Less than 1 Arab ");
System.exit(1);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
NumberToWord obj=new NumberToWord();
obj.inputNumber();
System.out.println("input in Words : "+obj.convertNumberToWords(num)); } }
Please mention in the comments in case you have any other simple way or any doubts regarding code .
In this post we’ll see a Java program to convert numbers to words. For example, in the Java program if number 5467 is passed
then the output in words should be- Five thousand four hundred sixty seven.
Number systems
In Indian system numbers are called differently and even placement is different than in the international system.
For example-
11,23,45,657- Eleven crore twenty three lakhs forty five thousand six hundred fifty seven
As you can see the numbers here are Crore, Lakhs also the digits are grouped in twos except the hundreds where three digits are grouped.
In international system same number will be written as-
112,345,657- One hundred twelve million three hundred forty five thousand six hundred fifty seven
Here you can notice that the digits are grouped in threes and the digit group separator (hundred, thousand, million…) is
placed after every three digits.
We’ll have Java program for converting numbers to words for both Indian and international system and how digits are grouped
forms the logic for the programs.
Converting number to words in Java – International System
As already stated above, in the program we’ll have to get the three digits of the number in each iteration and put the
correct place value after those three digits.
In the program we’ll also have different arrays for the numbers.
public class ConvertNumToWord {
private static final String[] units = {
"",
" one",
" two",
" three",
" four",
" five",
" six",
" seven",
" eight",
" nine"
};
private static final String[] twoDigits = {
" ten",
" eleven",
" twelve",
" thirteen",
" fourteen",
" fifteen",
" sixteen",
" seventeen",
" eighteen",
" nineteen"
};
private static final String[] tenMultiples = {
"",
"",
" twenty",
" thirty",
" forty",
" fifty",
" sixty",
" seventy",
" eighty",
" ninety"
};
private static final String[] placeValues = {
" ",
" thousand",
" million",
" billion",
" trillion"
};
private static String convertNumber(long number) {
String word = "";
int index = 0;
do {
// take 3 digits in each iteration
int num = (int)(number % 1000);
if (num != 0){
String str = ConversionForUptoThreeDigits(num);
word = str + placeValues[index] + word;
}
index++;
// next 3 digits
number = number/1000;
} while (number > 0);
return word;
}
private static String ConversionForUptoThreeDigits(int number) {
String word = "";
int num = number % 100;
if(num < 10){
word = word + units[num];
}
else if(num < 20){
word = word + twoDigits[num%10];
}else{
word = tenMultiples[num/10] + units[num%10];
}
word = (number/100 > 0)? units[number/100] + " hundred" + word : word;
return word;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("1234123456789- " + convertNumber(1234123456789L));
System.out.println("123456789- " + convertNumber(123456789));
System.out.println("37565820- " + convertNumber(37565820));
System.out.println("9341947- " + convertNumber(9341947));
System.out.println("37000- " + convertNumber(37000));
System.out.println("1387- " + convertNumber(1387));
System.out.println("10- " + convertNumber(10));
System.out.println("41- " + convertNumber(41));
}
}
Output
1234123456789- one trillion two hundred thirty four billion one hundred twenty three million four hundred fifty six thousand seven hundred eighty nine 123456789- one hundred twenty three million four hundred fifty six thousand seven hundred eighty nine 37565820- thirty seven million five hundred sixty five thousand eight hundred twenty 9341947- nine million three hundred forty one thousand nine hundred forty seven 37000- thirty seven thousand 1387- one thousand three hundred eighty seven 10- ten 41- forty one
Converting number to words in Java – Indian System
As already stated above, for Indian system in the program we’ll have to get the three digits of the number in first
iteration and then two digits in each iteration and put the correct place value after each iteration.
The array for placeValues will change as per Indian system.
public class ConvertNumToWord {
private static final String[] units = {
"",
" one",
" two",
" three",
" four",
" five",
" six",
" seven",
" eight",
" nine"
};
private static final String[] twoDigits = {
" ten",
" eleven",
" twelve",
" thirteen",
" fourteen",
" fifteen",
" sixteen",
" seventeen",
" eighteen",
" nineteen"
};
private static final String[] tenMultiples = {
"",
"",
" twenty",
" thirty",
" forty",
" fifty",
" sixty",
" seventy",
" eighty",
" ninety"
};
private static final String[] placeValues = {
"",
" thousand",
" lakh",
" crore",
" arab",
" kharab"
};
private static String convertNumber(long number) {
String word = "";
int index = 0;
boolean firstIteration = true;
int divisor;
do {
divisor = firstIteration ? 1000 : 100;
// take 3 or 2 digits based on iteration
int num = (int)(number % divisor);
if (num != 0){
String str = ConversionForUptoThreeDigits(num);
word = str + placeValues[index] + word;
}
index++;
// next batch of digits
number = number/divisor;
firstIteration = false;
} while (number > 0);
return word;
}
private static String ConversionForUptoThreeDigits(int number) {
String word = "";
int num = number % 100;
if(num < 10){
word = word + units[num];
}
else if(num < 20){
word = word + twoDigits[num%10];
}else{
word = tenMultiples[num/10] + units[num%10];
}
word = (number/100 > 0)? units[number/100] + " hundred" + word : word;
return word;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("1234123456789- " + convertNumber(1234123456789L));
System.out.println("326776756- " + convertNumber(326776756));
System.out.println("37565820- " + convertNumber(37565820));
System.out.println("9341947- " + convertNumber(9341947));
System.out.println("37000- " + convertNumber(37000));
System.out.println("1387- " + convertNumber(1387));
System.out.println("10- " + convertNumber(10));
System.out.println("5- " + convertNumber(5));
}
}
Output
1234123456789- twelve kharab thirty four arab twelve crore thirty four lakh fifty six thousand seven hundred eighty nine 326776756- thirty two crore sixty seven lakh seventy six thousand seven hundred fifty six 37565820- three crore seventy five lakh sixty five thousand eight hundred twenty 9341947- ninety three lakh forty one thousand nine hundred forty seven 37000- thirty seven thousand 1387- one thousand three hundred eighty seven 10- ten 5- five
That’s all for this topic Convert Numbers to Words Java Program. If you have any doubt or any suggestions to make please drop a comment. Thanks!
Related Topics
- Convert double to int in Java
- Arrange Non-Negative Integers to Form Largest Number — Java Program
- Split a String Java Program
- Converting String to int in Java
- Converting String to Enum Type in Java
You may also like-
- Printing Numbers in Sequence Using Threads Java Program
- How to Create PDF in Java Using OpenPDF
- Difference Between Two Dates in Java
- Creating Tar File And GZipping Multiple Files in Java
- How to Pass Command Line Arguments in Eclipse
- static Import in Java With Examples
- Java String Interview Questions And Answers
- Spring MVC Pagination Example Using PagedListHolder
next →
← prev
In this section, we will create a Java program that converts the given number into words. For example, if the given number is 54,297 then the output should be Fifty-Four Thousand Two Hundred Ninety-Seven. Let’s create a Java program for the same.
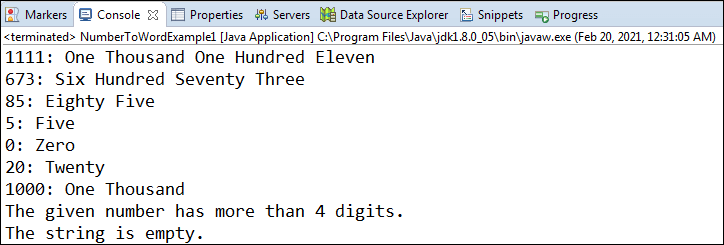
NumberToWordExample1.java
Output:
The number is not limited to four digits. Then what if the user enters more than 5 five digits numbers. The above program does not work for large digit numbers.
Converting Large Numbers into Words
The logic for converting the large digit numbers is quite different. Let’s see the approach to convert large digits numbers.
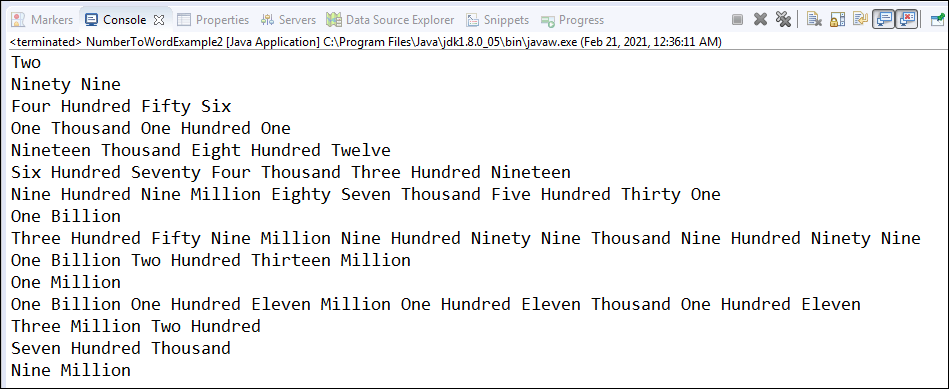
NumberToWordExample2.java
Output:
Converting Very Long Numbers into Words
The logic for the conversion of very long numbers into words is different from the previous one. Before moving ahead, it is important to learn the name of large numbers. The following table describes the name of the larger numbers.
| Name | Short Scale (US, English Canada, modern British, Australia, and Eastern Europe) |
Long Scale (French Canada, older British, Western & Central Europe) |
|---|---|---|
| Million | 106 | 106 |
| Milliard | Not used | 109 |
| Billion | 109 | 1012 |
| Billiard | Not used | 1015 |
| Trillion | 1012 | 1018 |
| Quadrillion | 1015 | 1024 |
| Quintillion | 1018 | 1030 |
| Sextillion | 1021 | 1036 |
| Septillion | 1024 | 1042 |
| Octillion | 1027 | 1048 |
| Nonillion | 1030 | 1054 |
| Decillion | 1033 | 1060 |
| Undecillion | 1036 | 1066 |
| Duodecillion | 1039 | 1072 |
| Tredecillion | 1042 | 1078 |
| Quattuordecillion | 1045 | 1084 |
| Quindecillion | 1048 | 1090 |
| Sexdecillion | 1051 | 1096 |
| Septendecillion | 1054 | 10102 |
| Octodecillion | 1057 | 10108 |
| Novemdecillion | 1060 | 10114 |
| Vigintillion | 1063 | 10120 |
| Centillion | 10303 | 10600 |
Let’s create a Java program that converts very long numbers into words.
The following Java program also converts the negative and decimal numbers into words.
NumberToWordExample3.java
Output:
0 = zero 4 = four 10 = ten 12 = twelve 100 = one hundred 108 = one hundred eight 299 = two hundred ninety-nine 1000 = one thousand 1003 = one thousand three 2040 = two thousand forty 45213 = forty-five thousand two hundred thirteen 100000 = one hundred thousand 100005 = one hundred thousand five 100010 = one hundred thousand ten 202020 = two hundred two thousand twenty 202022 = two hundred two thousand twenty-two 999999 = nine hundred ninety-nine thousand nine hundred ninety-nine 1000000 = one million 1000001 = one million one 10000000 = ten million 10000007 = ten million seven 99999999 = ninety-nine million nine hundred ninety-nine thousand nine hundred ninety-nine 9223372036854775807 = nine quintillion two hundred twenty-three quadrillion three hundred seventy-two trillion thirty-six billion eight hundred fifty-four million seven hundred seventy-five thousand eight hundred seven -9223372036854775808 = minus nine quintillion two hundred twenty-three quadrillion three hundred seventy-two trillion thirty-six billion eight hundred fifty-four million seven hundred seventy-five thousand eight hundred eight 0001.2 = one and two tenth 3.141592 = three and one hundred forty-one thousand five hundred ninety-two millionth
Even, we can convert 100 digits long number with the help of the above program.
Next TopicTypes of Garbage Collector in Java
← prev
next →
Here is a sample I played with. Hope it’s useful.
I’d consider decomposing this into reusable functions.
package com.bluenoteandroid.experimental.ints;
import static com.google.common.base.Optional.*;
import static com.google.common.base.Preconditions.*;
import static java.lang.Math.*;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import com.google.common.annotations.Beta;
import com.google.common.base.Joiner;
import com.google.common.base.Optional;
import com.google.common.collect.ImmutableMap;
import com.google.common.collect.Lists;
public final class Ints {
public static final int BASE_10 = 10;
public static final String MINUS = "minus";
public static final ImmutableMap<Integer, String> NUMBERS = ImmutableMap.<Integer, String>builder()
.put(0,"zero")
.put(1,"one")
.put(2,"two")
.put(3,"three")
.put(4,"four")
.put(5,"five")
.put(6,"six")
.put(7,"seven")
.put(8,"eight")
.put(9,"nine")
.put(10,"ten")
.put(11,"eleven")
.put(12,"twelve")
.put(13,"thirteen")
.put(14,"fourteen")
.put(15,"fifteen")
.put(16,"sixteen")
.put(17,"seventeen")
.put(18,"eighteen")
.put(19,"nineteen")
.put(20,"twenty")
.put(30,"thirty")
.put(40,"forty")
.put(50,"fifty")
.put(60,"sixty")
.put(70,"seventy")
.put(80,"eighty")
.put(90,"ninety")
.put(100,"hundred")
.put(1000,"thousand")
.put(1000000,"million")
.put(1000000000,"billion")
.build();
private Ints() { /* disabled */ }
public static boolean allZeros(int[] range) {
for (int n : range) {
if (n != 0) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
/**
* Counts digits in an integer
* @param number
* @return digits count in the number
*/
public static int digitCount(final int number) {
return (int) ((number == 0) ? 1 : log10(abs(number)) + 1);
}
/**
* Sums digits in an integer
* @param number number
* @return sum of the n's digits
*/
public static int digitSum(final int number) {
int _n = abs(number);
int sum = 0;
do {
sum += _n % BASE_10;
} while ((_n /= BASE_10) > 0);
return sum;
}
/**
* Gets digit index in an integer, counting from right
* @param number number
* @param index (from right)
* @return index-th digit from n
*/
public static int digitFromRight(final int number, final int index) {
checkElementIndex(index, digitCount(number));
return (int) ((abs(number) / pow(BASE_10, index)) % BASE_10);
}
/**
* Gets digit of index in an integer, counting from left
* @param number
* @param index (from left)
* @return index-th digit from n
*/
public static int digitFromLeft(final int number, final int index) {
checkElementIndex(index, digitCount(number));
return digitFromRight(number, digitCount(number) - index - 1);
}
/**
* Converts a number to the array of it's digits
* @param number number
* @return array of digits
*/
public static int[] digits(final int number) {
return digits(number, digitCount(number));
}
/**
* Converts a number to a reversed array of it's digits
* @param number number
* @return reversed array of digits
*/
public static int[] digitsReversed(final int number) {
return digitsReversed(number, digitCount(number));
}
private static int[] digits(final int number, final int digitCount) {
final int[] digits = new int[digitCount];
int _n = abs(number);
int i = digitCount - 1;
do {
digits[i--] = _n % BASE_10;
} while ((_n /= BASE_10) > 0);
return digits;
}
/**
* Converts a number to a reversed array of it's digits
* @param number number
* @param digitCount digit count
* @return reversed array of digits
*/
private static int[] digitsReversed(final int number, final int digitCount) {
final int[] reversedDigits = new int[digitCount];
int _n = abs(number);
int i = 0;
do {
reversedDigits[i++] = _n % BASE_10;
} while ((_n /= BASE_10) > 0);
return reversedDigits;
}
public static int fromDigits(final int[] digits) {
int n = 0;
int i = 0;
do {
n += digits[i++];
if (i >= digits.length) {
break;
}
n *= BASE_10;
} while (true);
return n;
}
public static int fromDigitsReversed(final int[] reversedDigits) {
int n = 0;
int i = reversedDigits.length;
do {
n += reversedDigits[--i];
if (i <= 0) {
break;
}
n *= BASE_10;
} while (true);
return n;
}
@Beta
public static String numberInWords(final int number) {
Optional<String> name = fromNullable(NUMBERS.get(number));
if (name.isPresent()) {
return name.get();
} else {
return numberToName(number);
}
}
private static String numberToName(int number) {
final LinkedList<String> words = Lists.newLinkedList();
final int[] digits = digitsReversed(number);
for (int factor = 0; factor < digits.length; factor += 3) {
final int[] range = Arrays.copyOfRange(digits, factor, factor + 3);
if (allZeros(range)) {
continue;
}
switch (factor) {
case 0: /* nothing */
break;
case 3: /* thousand */
words.addFirst(NUMBERS.get((int) pow(BASE_10, 3)));
break;
case 6: /* million */
words.addFirst(NUMBERS.get((int) pow(BASE_10, 6)));
break;
case 9: /* billion */
words.addFirst(NUMBERS.get((int) pow(BASE_10, 9)));
break;
default:
throw new IllegalStateException("Unknown factor: " + factor);
}
String part = tripletToWords(range);
words.addFirst(part);
}
if (number < 0) { // negative
words.addFirst(MINUS);
}
return Joiner.on(' ').join(words);
}
private static String tripletToWords(final int[] reversedDigits) {
checkArgument(reversedDigits.length == 3, "This is not a triplet of digits, size: " + reversedDigits.length);
final int number = fromDigitsReversed(reversedDigits);
final int[] range = Arrays.copyOfRange(reversedDigits, 0, 2);
final String dubletWords = dubletToWords(range);
if (number >= 100) {
final int thirdDigit = reversedDigits[2];
final int factor = BASE_10 * BASE_10;
final String dublet = allZeros(range) ? null : dubletWords;
return Joiner.on(' ').skipNulls().join(
NUMBERS.get(thirdDigit),
NUMBERS.get(factor),
dublet);
} else {
return dubletWords;
}
}
private static String dubletToWords(final int[] reversedDigits) {
checkArgument(reversedDigits.length == 2, "This is not a dublet of digits, size: " + reversedDigits.length);
final int number = fromDigitsReversed(reversedDigits);
Optional<String> name = fromNullable(NUMBERS.get(number));
if (name.isPresent()) {
return name.get();
} else {
final int firstDigit = reversedDigits[0];
final int secondDigit = reversedDigits[1];
final int tens = BASE_10 * secondDigit;
return Joiner.on('-').join(
NUMBERS.get(tens),
NUMBERS.get(firstDigit));
}
}
}
With unit tests:
package com.bluenoteandroid.experimental.ints;
import static com.bluenoteandroid.experimental.ints.Ints.*;
import static org.hamcrest.Matchers.*;
import static org.junit.Assert.*;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collection;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.experimental.categories.Categories;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.junit.runners.Parameterized;
import org.junit.runners.Parameterized.Parameters;
import org.junit.runners.Suite.SuiteClasses;
import com.bluenoteandroid.experimental.ints.IntsTests.*;
@RunWith(Categories.class)
@SuiteClasses({
CountTest.class,
SumTest.class,
GetDigitRightTest.class,
GetDigitRightPeconditionsTest.class,
GetDigitLeftTest.class,
GetDigitLeftPeconditionsTest.class,
DigitArrayTest.class,
FromDigitArrayTest.class,
ReverseDigitArrayTest.class,
FromReverseDigitArrayTest.class,
NumberToWordTest.class
})
public class IntsTests {
@RunWith(value = Parameterized.class)
public static class CountTest {
private final int input;
private final int expected;
public CountTest(final int input, final int expected) {
this.input = input;
this.expected = expected;
}
@Parameters
public static Collection<Integer[]> data() {
return Arrays.asList(new Integer[][] {
{ 0, 1 }, /* input, expected */
{ -1, 1 },
{ 900003245, 9 },
});
}
@Test
public void shouldCountDigits() {
assertThat(digitCount(input), is(expected));
}
}
@RunWith(value = Parameterized.class)
public static class SumTest {
private final int input;
private final int expected;
public SumTest(final int input, final int expected) {
this.input = input;
this.expected = expected;
}
@Parameters
public static Collection<Integer[]> data() {
return Arrays.asList(new Integer[][] {
{ 0, 0 }, /* input, expected */
{ -1, 1 },
{ 1001, 2 },
{ 1234, 1+2+3+4 }
});
}
@Test
public void shouldSumDigits() {
assertThat(digitSum(input), is(expected));
}
}
@RunWith(value = Parameterized.class)
public static class GetDigitRightTest {
private final int input;
private final int index;
private final int expected;
public GetDigitRightTest(final int input, final int index, final int expected) {
this.input = input;
this.index = index;
this.expected = expected;
}
@Parameters
public static Collection<Integer[]> data() {
return Arrays.asList(new Integer[][] {
{ 0, 0, 0 }, /* input, expected */
{ -1004, 0, 4 },
{ 1234, 1, 3 },
{ -1234, 2, 2 },
{ 1234, 3, 1 },
});
}
@Test
public void shouldGetDigits() {
assertThat(digitFromRight(input, index), is(expected));
}
}
public static class GetDigitRightPeconditionsTest {
@Test(expected=IndexOutOfBoundsException.class)
public void shouldNotAllowNegativeIndex() {
digitFromRight(1234, -1);
}
@Test(expected=IndexOutOfBoundsException.class)
public void shouldNotAllowToBigIndex() {
digitFromRight(1234, 4);
}
}
@RunWith(value = Parameterized.class)
public static class GetDigitLeftTest {
private final int input;
private final int index;
private final int expected;
public GetDigitLeftTest(final int input, final int index, final int expected) {
this.input = input;
this.index = index;
this.expected = expected;
}
@Parameters
public static Collection<Integer[]> data() {
return Arrays.asList(new Integer[][] {
{ 0, 0, 0 }, /* input, expected */
{ -1004, 0, 1 },
{ 1234, 1, 2 },
{ -1234, 2, 3 },
{ 1234, 3, 4 },
});
}
@Test
public void shouldGetDigits() {
assertThat(digitFromLeft(input, index), is(expected));
}
}
public static class GetDigitLeftPeconditionsTest {
@Test(expected=IndexOutOfBoundsException.class)
public void shouldNotAllowNegativeIndex() {
digitFromLeft(1234, -1);
}
@Test(expected=IndexOutOfBoundsException.class)
public void shouldNotAllowToBigIndex() {
digitFromLeft(1234, 4);
}
}
public static class DigitArrayTest {
@Test
public void shouldGetAllDigits() {
final int[] result = digits(-1234);
final int[] expected = new int[] {1,2,3,4};
assertThat(result, is(expected));
}
}
public static class FromDigitArrayTest {
@Test
public void shouldConvertDigits() {
final int result = fromDigits(new int[] {1,2,3,4});
final int expected = 1234;
assertThat(result, is(expected));
}
}
public static class ReverseDigitArrayTest {
@Test
public void shouldGetAllDigits() {
final int[] result = digitsReversed(-1234);
final int[] expected = new int[] {4,3,2,1};
assertThat(result, is(expected));
}
}
public static class FromReverseDigitArrayTest {
@Test
public void shouldConvertDigits() {
final int result = fromDigitsReversed(new int[] {4,3,2,1});
final int expected = 1234;
assertThat(result, is(expected));
}
}
@RunWith(value = Parameterized.class)
public static class NumberToWordTest {
private final int input;
private final String expected;
public NumberToWordTest(final int input, final String expected) {
this.input = input;
this.expected = expected;
}
@Parameters
public static Collection<Object[]> data() {
return Arrays.asList(new Object[][] {
{ 0, "zero" },
{ 1, "one" },
{ 10, "ten" },
{ 15, "fifteen" },
{ 60, "sixty" },
{ 67, "sixty-seven" },
{ 72, "seventy-two" },
{ 101, "one hundred one" },
{ 205, "two hundred five" },
{ 4589, "four thousand five hundred eighty-nine" },
{ 3333, "three thousand three hundred thirty-three" },
{ 67500, "sixty-seven thousand five hundred" },
{ 100000, "one hundred thousand" },
{ 100567, "one hundred thousand five hundred sixty-seven" },
{ 172346, "one hundred seventy-two thousand three hundred forty-six" },
{ 600700, "six hundred thousand seven hundred" },
{ 678900, "six hundred seventy-eight thousand nine hundred" },
{ 890000, "eight hundred ninety thousand" },
{ 999999, "nine hundred ninety-nine thousand nine hundred ninety-nine" },
{ 999999999, "nine hundred ninety-nine million nine hundred ninety-nine thousand nine hundred ninety-nine" },
{ 1999999999, "one billion nine hundred ninety-nine million nine hundred ninety-nine thousand nine hundred ninety-nine" },
{ -21239, "minus twenty-one thousand two hundred thirty-nine"},
});
}
@Test
public void test() {
assertEquals(expected, numberInWords(input));
}
}
}
Java program to print word for the given number
Converting a number to characters or to words as readable format in text will be done easily using arrays in java. Based on the given number we can write our logic. But here i am taking the number below to 10000. So we can complete our program easily. But sure, you will understand the logic. It is simple.using Fibonacci logic , using modulo operator and divider operator we can completer our program. This is important interview question and some of like, Reverse an array, matrix addition, matrix multiplication using arrays and prime number logic these are important for the java interviews.
In this program we have to create two arrays one is ones array with the words of one,two,three…..nineteen.
Then create another array with tens array contains ten,twenty,…..ninety.
Then write the given logic to convert a number into character.
package com.javabynataraj;
//http://javabynataraj.blogspot.com
public class Num2String {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String ones[] = {"one","two","three","four","five","six","seven","eight","nine","ten","eleven","twelve","thirteen","fourteen","fifteen","sixteen","seventeen","eighteen","nineteen",};
String tens[] = {"ten ","twenty ","thirty ","fourty ","fifty ","sixty ","seventy ","eighty ","ninety "};
int n = 7677;
int i;
String res=" ";
if(n>1000){
i=n/1000;
res=ones[i-1]+" thousand ";
n=n%1000;
}
if(n>99 && n<1000){
i=n/100;
res=res+ones[i-1]+" hundred ";
n=n%100;
}
if(n>19 && n<100){
i=n/10;
res=res+tens[i-1];
n=n%10;
}
if(n>0 && n<20){
res=res+ones[n-1];
}
System.out.println(res);
}
}
Output:

Reference Books:
- A Programmer’s Guide To Java SCJP Certification 3rd Edition
- Sun Certified Programmer For Java 6 Scjp
- Scjp Sun Certified Programmer For Java Platform
- SCJP Exam for J2SE 5