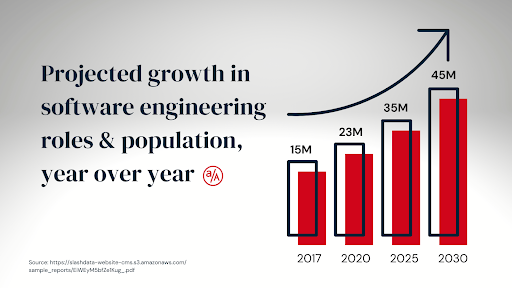
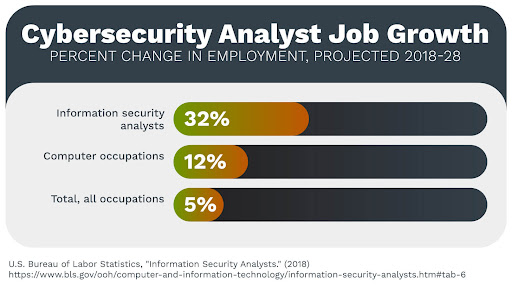
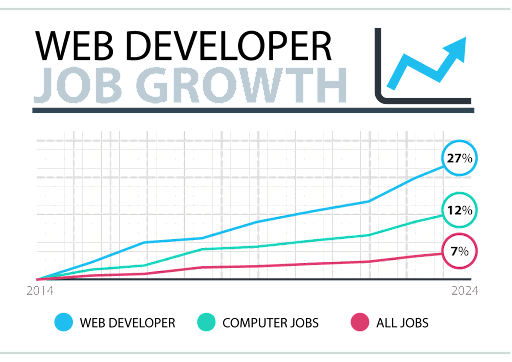
If you love technology and you’re looking for a job with high pay and a robust occupational outlook, you’re in luck. The tech sector is booming, and IT occupations are expected to continue to grow over the next decade. These jobs also pay far more than the median wage for all occupations.
Types of IT Jobs
People with jobs in information technology (IT) use computers, software, networks, servers, and other technology to manage and store data. IT job titles can vary significantly from one company to another.
For instance, one company may recruit a «developer» while another company recruits a «programmer»—but the work may be precisely the same at the two companies, despite the job title variation. Also, many of the skills in this field are transferable, which means candidates may be qualified for many different roles.
Make sure that your resume displays the most sought-after industry skills relevant to your expertise.
IT Job and Education Requirements
Some IT jobs with higher pay require that candidates have a bachelor’s degree, ideally in computer science, software engineering, etc. Some employers care more about the quality of your work than they do about your formal education. As such, many companies evaluate candidates based on their portfolio and experience.
IT Job Outlook
According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), jobs in IT are growing well above average rates of all other occupations, with 11% growth expected from 2019 to 2029.
The BLS predicts that the IT industry will add 531,200 new jobs by 2029. These occupations are high-paying: the median annual salary for IT jobs was $88,240 in May 2019, more than twice the median wage for all jobs.
Information Technology Job Titles
Below is a list of some of the most common job titles from the IT industry, as well as a description of each. For more information about each job title, check out the Bureau of Labor Statistics’ Occupational Outlook Handbook.
Cloud Computing Engineer
Cloud computing engineers define, design, build, and maintain systems and solutions leveraging systems and infrastructure managed by cloud providers such as Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Microsoft Azure.
- Cloud Architect
- Cloud Consultant
- Cloud Product and Project Manager
- Cloud Services Developer
- Cloud Software and Network Engineer
- Cloud System Administrator
- Cloud System Engineer
Computer Network Specialist
Computer network specialists and analysts define, design, build, and maintain a variety of data communication networks and systems. They typically have a bachelor’s degree in computer science or a related field. Some also have a master’s degree in business administration (MBA), with a focus on information systems. Computer network architects can earn notably high salaries: according to the BLS, the median salary for this role is $112,690.
- Computer and Information Research Scientist
- Computer and Information Systems Manager
- Computer Network Architect
- Computer Systems Analyst
- Computer Systems Manager
- IT Analyst
- IT Coordinator
- Network Administrator
- Network Architect
- Network and Computer Systems Administrator
- Network Engineer
- Network Systems Administrator
- Senior Network Architect
- Senior Network Engineer
- Senior Network System Administrator
- Telecommunications Specialist
Computer Support Specialist
Computer support specialists and network administrators help computer users and organizations. Some of these workers support computer networks by testing and evaluating network systems and ensuring that the day-to-day operations work. Others provide customer service by helping people with their computer problems. Some require a bachelor’s degree, while others need an associate degree or post-secondary classes.
- Customer Support Administrator
- Customer Support Specialist
- Desktop Support Manager
- Desktop Support Specialist
- Help Desk Specialist
- Help Desk Technician
- IT Support Manager
- IT Support Specialist
- IT Systems Administrator
- Senior Support Specialist
- Senior System Administrator
- Support Specialist
- Systems Administrator
- Technical Specialist
- Technical Support Engineer
- Technical Support Specialist
Database Administrator
Database administrators help store and organize data or companies and/or customers. They protect the data from unauthorized users. Some work for companies that provide computer design services. Others work for organizations with large database systems, such as educational institutions, financial firms, and more.
These jobs are growing at a faster-than-average rate, with an expected 10% growth in jobs between 2019-2029, according to BLS data. The median pay for this job is $93,750 per year.
- Data Center Support Specialist
- Data Quality Manager
- Database Administrator
- Senior Database Administrator
Information Technology Analyst
IT analysts are responsible for designing and implementing organizational technology for businesses. They create solutions for collecting and analyzing market data, customer input, and client information.
- Application Support Analyst
- Senior System Analyst
- Systems Analyst
- Systems Designer
Information Technology Leadership
Leadership in IT draws from candidates with strong technology backgrounds and superior management skills. They have experience in creating and implementing policies and systems to meet IT objectives, and the ability to budget the time and funds necessary.
- Chief Information Officer (CIO)
- Chief Technology Officer (CTO)
- Director of Technology
- IT Director
- IT Manager
- Management Information Systems Director
- Technical Operations Officer
Information Security Specialist
The increased incidence of security breaches and the associated danger of identity theft has enhanced the importance of protecting data on commercial and governmental sites. Information security analysts help defend an organization’s computer network and computer systems.
They plan and carry out a variety of security measures, such as installing and using software, and simulating cyber-attacks to test systems. Information security jobs are expected to grow much faster than average, according to the BLS, with an increase of 31% between 2019 and 2029. These positions pay a median annual salary of $99,730.
- Information Security Analyst
- Security Specialist
- Senior Security Specialist
Software/Application Developer
Software developers design, run, and test various computer programs and applications. Application Developers create new applications and code solutions. They usually have a bachelor’s degree in computer science or a related field. They also have strong programming skills.
The BLS expects the number of software developer jobs to grow by 22% between 2019 and 2029. The median salary of a software developer is $107,510.
- Application Developer
- Applications Engineer
- Associate Developer
- Computer Programmer
- Developer
- Java Developer
- Junior Software Engineer
- .NET Developer
- Programmer
- Programmer Analyst
- Senior Applications Engineer
- Senior Programmer
- Senior Programmer Analyst
- Senior Software Engineer
- Senior System Architect
- Senior System Designer
- Senior Systems Software Engineer
- Software Architect
- Software Developer
- Software Engineer
- Software Quality Assurance Analyst
- System Architect
- Systems Software Engineer
Web Developer
Web developers design, create, and modify websites. They are responsible for maintaining a user-friendly, stable website that offers the necessary functionality for their client’s needs. Some jobs require a bachelor’s degree, while others need an associate degree, including classes in HTML, JavaScript, or SQL.
These jobs are expected to grow 8% between 2019 and 2029, according to the BLS. The median annual salary for a web developer is $73,760.
- Front End Developer
- Senior Web Administrator
- Senior Web Developer
- Web Administrator
- Web Developer
If you’re interested in a tech career, read on. The industry is growing rapidly, and new opportunities are emerging every day, so it’s important to determine the job you’re interested in early on to improve your chances of finding job success. But which types of IT jobs should you pursue?
Fortunately, there are plenty of exciting jobs to choose from. Whether you’re a software engineer or a project manager, there’s something for everyone. Pursuing a career in tech has several benefits, and a high-paying salary is one of them. It’s not only the most dynamic and developing sector on the globe; it also exhibits rapid expansion.
So, if you’re a young professional contemplating a new career path or finding the best resources for your business, you’ve come to the right place. The following article summarizes the best IT jobs that are in demand in 2023.
By the end of this article, you’ll understand the roles of different IT jobs so you can climb your career ladder or hire the best talent for your business to grow.
9 career-worthy types of jobs in IT
There are several jobs in IT, an industry that continues to need professionals as the world increasingly becomes digital. As technology advances, IT companies are ready to adopt digital transformation in their operations and are trying their hardest to get their hands on the best talent.
This means more transactions, communications, and even recruiting operations will be made easier using online tools. If you’re just starting, there is a wide range of choices you can choose from.
You can have a career in fast-paced startups, innovative tech companies, and small IT departments. Many of these jobs offer opportunities for advancement and competitive pay. It’s important to avoid common mistakes when job seeking. Here are some IT Jobs to help you better understand what’s out there.
1. Data scientist
The request for data science skills has grown remarkably over the years, and the ‘boom’ it has created in the job market isn’t going away anytime soon. In fact, just the average annual salary is between $97,000 and $108,000 – a good start to a rewarding career.
Data-science-related jobs will continue to rule the roost in 2023, increasing the value of data scientists. The significant increase in data collection via individuals and companies multiplies the availability of information via the internet.
Because of this, the presented data can become extensively complex and need better architecture. For example, look at stock data or company statistics. It’s becoming clearer by the day that data processing has enormous value; that is where a data scientist comes in.
1.1 — Primary responsibilities
The primary duties of a data scientist are to collect, analyze, and interpret large chunks of information with the help of data architecture pipelines to ensure meaningful insights. Simply put, companies need data scientists to help them organize data and make insightful decisions.
An experienced data scientist will know how to scout for meaningful information with whatever data he comes across and, in turn, help the company make the right decisions.
1.2 — Key skills of a data scientist include
- Programming
- Deep learning
- Machine learning
- Communication skills
- Identifying opportunities
- Processing large sets of data
2. Software engineer
A career in software engineering is quickly becoming one of the most exciting paths in the IT industry. According to recent trends, the growth in employment opportunities for software developers is expected to remain over 20%.
Digital experts now understand the importance of software engineering and its impact – both good and bad on a company’s bottom line. So what do software engineers do?
2.1 — Primary responsibilities
A software engineer typically applies software engineering principles in designing and creating software. This includes all stages of the software development process, including designing, developing, maintaining, and testing.
For instance, the software used on our computers, phones, and TVs is the result of software engineering. Software that you can purchase, like an automated email virtual assistant or intranet software, is also made by software engineers to help streamline your business operations and improve the efficiency of employees.
On the other hand, experts in software development are also responsible for developing software for analyzing and planning marketing campaigns for different companies.
Let’s take a sample client here. If an admission coaching firm taps them to create an automated training program for different educational exams, they should first study and analyze the project, doing intensive research along the way to create a solution that meets client expectation.
2.2 — Key skills of a software engineer include
- Subject matter experts
- Software development
- Computer programming and coding
- Problem-solving and logical thinking
- Object Oriented Design (OOD) using software equipment
- Understanding complex software programs such as Adobe and Photoshop
3. Data security analyst
In recent times, securing data has become increasingly important. With every sector moving its informational systems online, from financial institutions to the education industry, there has been an ever-increasing demand to protect computer systems and networks from data breaches.
The emerging technology-related security also brings related security risks; thus, the demand for data security professionals remains high and is expected to be the 10th growing occupation over the next decade.
3.1 — Primary responsibilities
Data security analysts are trained professionals with advanced degrees who work in many IT departments. The average salary for a data security analyst is $74,475 per year in the US. These security experts plan and safeguard digital data from unwanted access, corruption, or threat.
To prevent such intrusions, they thoroughly study and analyze methods of cyber attacks and the behaviors of cybercriminals.
3.2 — Key skills of a data security specialist include
- Knowledge of security across various platforms
- Relevant experience in computer forensics skills
- Previous experience working with data in daily operations
- An understanding of in-depth hacking skills including knowledge of Mathematics and substantive expertise
4. Web developer
With faster network speeds and the emergence of smartphones, developers are taking full advantage of these innovative technologies. Fortunately, web development is growing as an industry, and the need for web developers increases each year, with over 19,000 jobs expected by 2029.
4.1 — Job responsibilities
Web developers are primarily responsible for planning and developing software applications using HTML, CSS, and MySQL. They help with effective website development leading to more sales.
While most web developers are responsible for developing software solutions and maintaining a company’s website, the developer’s day-to-day work highly depends on constantly evolving internet innovations.
Most web developers start their career with a single focus, usually as back-end or front-end developers, and ultimately move on to be full-stack developers. As a web developer, you can work for a company, agency, or as a freelancer.
4.2 — Key skills of a web developer include
- Analytical skills
- JavaScript skills
- Back-end basics
- HTML/CSS skills
- Administrative tasks
- Responsive design skills
- Testing and debugging skills
4.3 — Web developer vs. network administrator & web designer
Often used interchangeably, web developer and web/network administrator are completely different terms. A web administrator is responsible for maintaining websites and ensuring they work perfectly.
Their daily operations mainly include setting up an organization’s web hosts using platforms like WooCommerce host, granting access to specific users, and adding email accounts for staff.
On the other hand, a web developer mainly develops software applications for business clients using web forms and other front-end functionalities. It’s also important to consider the role of web designers.
While site developers and designers work together, their functions are completely different. A site designer focuses on designing a website’s layout and visual appearance. Their primary goal is to create something that is not only visually pleasing but also streamlined and easy to use.
This is crucial because the perception of the audience about a brand influences a customer’s purchase intention. Web designers typically utilize easy navigation, sitemaps, and visual graphics on a site’s design.
In creating modern website designs, they included unique typography and hamburger menus that make a customer more comfortable navigating the site. Look at my favorite example, AthSport’s web design. They went for a clean and clutter-free display that makes navigation easy. Web designers for this eCommerce store used their creative skills to design an easy-to-navigate website to create better experiences for visitors.
5. Marketing analyst
The job growth for market analysts in the US will increase by 19% by 2031. In the past, marketing was just one big shot in the dark, as you couldn’t be sure where any given lead came from. Marketing analytics allows you to gather the information needed to find high-fit leads and allows businesses to understand their customers better.
5.1 — Primary responsibilities
Marketing analysts study retail conditions to help companies understand what the customers want, making it one of the best business practices. They gather data on consumer demographics, needs, and buying habits using interviews, questionnaires, and literature reviews.
Hence, marketing insights are at an all-time high as companies scramble to analyze and predict consumer buying trends and stay on top of the competition.
Typically, marketing analysts, especially those specializing in the digital sphere, also master marketing tactics for inbound, outbound, and social media marketing. This includes in-depth knowledge of email marketing, content marketing, Facebook marketing, Instagram marketing, and TikTok marketing.
5.2 — Key skills of a marketing analyst include
- Attribution modeling
- Present results to clients and managers
- Technical skills such as digital media and design
- Customer service know-how in business decisions
- Assess the effectiveness of marketing campaigns and strategies across different business fields
6. User experience designer
The rise of the internet and social media has directed the power and balance of producers toward consumers. Companies are responding to this change by creating positive experiences for customers. An effective user experience (UX) designer is at the top of this list.
It’s no surprise, then, that according to stats, there will be a 3% year-on-year growth (through 2028) in demand for industrial UX designers.
6.1 — Primary responsibilities
User experience is about how a person interacts when communicating with a system. This includes mobile applications, websites, or human-device interaction. While many companies design user experiences, the term is mostly associated with the digital design of websites.
The role of a UX designer is to provide positive experiences and overall satisfaction to keep a user true to the product or brand. You can think of a UX designer as the customer’s advocate, always looking for ways to enhance the customer experience.
Typically, a UX designer will create an understanding of who their customers are. Each website caters to different customer needs, so the method will differ.
For instance, a UX designer for a company selling virtual wish cards will focus more on creating an emotional connection to improve customer experience than a sports company looking to advertise sportswear that will focus more on personal touch.
Additionally, a user experience designer is involved with all the facets of product development regarding purchasing, usability, and functionality. The right UX designer will check all the boxes needed to increase traffic and boost sales.
Essentially, this includes the designer’s role in understanding the importance of UX specifics when targeting a particular audience and product. Most UX designs for websites targeting adult audiences will focus mainly on visual accessibility and responsiveness compared to a children’s website where engagement is the main purpose.
Similarly, different products will elicit different design responses. UX designers for a website selling face masks will have different color schemes or graphics compared to a company selling makeup products.
To sum up, an effective UX designer will blend both user needs and business goals to help brands make consistently successful products.
6.2 — Key skills of a user experience designer include
- Researching
- Decision mapping
- Basic front-end coding
- Effective communication
- Visual design and design software
7. Project management
According to a job type growth study, the request for successful project management (and skilled project managers) will continue to expand as an estimated 22 million project management jobs will be accessible by 2027 and beyond.
This is no coincidence as companies are expecting to deliver more radical products and services, so they understand the need for effective project management tied to executing them. Another reason why project management is essential today is that the need for alignment and visibility has substantially increased.
Today, it’s easier for project managers to get bogged down in the weeds of project work and ultimately lose sight of other organizational priorities. Project management allows the company to see the “big picture” and understand the projects to meet those goals.
7.1 — Primary responsibilities
Typically, project managers play the primary role in planning, executing, monitoring, and closing out projects. In other words, they are in charge of the entire project scope and the success or failure of a project. The role requires a strategic business mindset, conflict resolution, and problem-solving abilities.
7.2 — Key skills of a project manager include
- Leadership
- Risk management
- Scheduling and time management
- Relevant experience in technical expertise
8. Computer programmer
In the digital world that we are in now, the ability to interact with computers is essential. Hence many new jobs will depend on programming because services and products are becoming digitized.
In addition, applications are written using programming languages. Since programming and having basic knowledge of programs is important today, it will be much more critical in the future as our lives are becoming increasingly dependent on them. So what does a computer programmer do?
8.1 — Primary responsibilities
Typically, programmers or application developers are responsible for writing codes to help software applications operate more efficiently. Their duties include developing and managing computing infrastructure and different software systems.
They are also responsible for reviewing current software programs and finding ways to update and enhance them for the user.
8.2 — Key skills of a computer programmer include
- Attention to detail
- Excellent communication
- Comprehension of Algebra topics
- Ability to fix any error in programs
- Ability to work under pressure and meet deadlines
9. Quality assurance tester
Moving to the digital era, the influence of software is far more significant, making protecting software from failing important to many companies. Hence, the need for quality assurance testers has risen significantly, with an expected 308,390 new jobs filled by 2029 and with an average salary of around $60,000.
9.1 — Primary responsibilities
Quality assurance testers are engineers or technicians responsible for uncovering issues within a company’s website, software, products, or any other user experience malfunction.
Thus, a quality assurance tester is critical in delivering high-quality functioning software and web applications to users. This is common for gaming systems, mobile applications, and other forms of technology that need further testing.
A QA tester’s responsibilities include providing continuous support to the development team throughout its software development cycle. For instance, a QA in the gaming industry will likely focus on finding and reproducing game errors.
By tracking and reporting bugs in computer games such as an anagram solver or a word finder, a QA specialist can identify certain issues affecting its performance, such as poor manipulation of understanding words.
In addition, QA testers are in charge of finding flaws, tracing error sources, and problem-solving independently in QA teams. This way, they work closely with developers to improve the workplace’s functionality, effectiveness, and productivity.
9.2 — Key skills of a quality assurance tester
- Dev tools
- Front-end skills
- Programming languages
- Understanding different operating systems and operations
Conclusion
These top 9 jobs will be in high demand in 2023 and beyond. With the digital age we are in now, there is room for several options to choose from in the technology field offering high salaries and great opportunities.
If you’re passionate about learning new concepts and applying them to other problems, you can try out to be a programmer. Likewise, if you want to organize and plan out projects you can be a project manager.
However, with all these jobs in mind, it’s important to choose something that not only interests you but also helps in enhancing your career journey. For greater chances of choosing the right career path in tech, you can research these different roles to see which ones fit you best and then apply accordingly.
Did you find this post helpful? Subscribe for more articles like this one.
Block
Are you looking to get certified in DevOps, SRE and DevSecOps?
LET’S TALK
DevOps
Get Certified!
SRE
Ahead from others!
DevSecOps
Security is Key
Kubernetes
Tomorow’s Platform!
Uncategorised
Rajesh Kumar
November 27, 2020
comments off
Popular Job Roles and Job Titles Software Engineering Domain
- CEO
- CTO
- CIO/Chief Digital Officer/Chief Innovation Officer
- VP of Product Management/Head of Product
- Product Manager
- VP of Marketing
- VP of Engineering/Director of Engineering
- Chief Architect
- Software Architect
- Engineering Project Manager/Engineering Manager
- Technical Lead/Engineering Lead/Team Lead
- Principal Software Engineer
- Senior Software Engineer/Senior Software Developer
- Software Engineer
- Software Developer
- Junior Software Developer
- Intern Software Developer
Jobs and Roles Titles for Software Company Management Team
- CTO
- CIO/Chief Digital Officer/Chief Innovation Officer
- VP of Product Management/Head of Product
- Product Manager
- VP of Marketing
- VP of Engineering
- Director of Engineering
- Chief Architect
- Software Architect
- Engineering Project Manager
- Engineering Manager
- Technical Project Manager
- Project Manager
- Business Account Manager
- Senior Manager IT
- IT Infra Manager
- Procurement manager
- Learning and Development Manager
- Learning and Development co-ordinators
Roles and job titles in recruitment industry
- HR Coordinator
- Payroll Coordinator
- Recruiting Coordinator
- HR Specialist
- HR Generalist
- Recruiter
- Human Resource Information Specialist
- HR Manager
- Recruiting Manager
- HR Business Partner
- HR Director
- Recruiting Director
- VP of HR
- Chief Human Resource Officer
- Career Consultant
- Career Advisor
- Assignment Coordinator
- Placement Coordinator
- Career Development Strategist
- Personnel Agent
- Human Resources Officer
Roles and job titles in Social Media Marketing & Digital Marketing & Search Engine Optimization
- SEO Manager
- SEO Engineer
- Digital Marketing Manager
- Digital Marketing Analyst
- Social Media Marketing Manager
- Social Media Marketing Analyst
- MARKETING TECHNOLOGIST
- SEO CONSULTANT
- WEB ANALYTICS DEVELOPER
- DIGITAL MARKETING MANAGER
- SOCIAL MEDIA MANAGER
- GROWTH HACKER
- CONTENT MANAGER
- CONTENT STRATEGIST
Complete list of Job Roles and Job Titles Software and IT companies
–
- Admin Big Data
- Ansible Operations Engineer
- Artifactory Administrator
- Artificial intelligence / Machine Learning Engineer
- Artificial Intelligence / Machine Learning Leader
- Artificial Intelligence / Machine Learning Sr.Leader
- Artificial intelligence Architect
- Artificial Intelligence Researcher
- Big Data Architect
- Big Data Engineer
- Big Data Specialist
- Build and Release Engineer
- Build Engineer
- Chef Operations Engineer
- Data Analysts
- Data Architect
- DevOps Architect
- DevOps Engineer
- ELK Engineer
- Gerrit Administrator
- Gerrit Administrator
- Jenkins Engineer
- Jira Administrator
- Kubernetes Operations Engineer
- Machine learning Architect
- Machine Learning Engineer
- Operations Engineer
- Principle Engineer in Artificial Intelligence
- Principle Engineer in Big Data
- Principle Engineer in Data Analysis
- Principle Engineer in Machine Learning
- Production Support Engineer
- Puppet Operations Engineer
- Senior Build and Release Engineer
- Senior Build Engineer
- Senior DevOps Engineer
- Senior Site reliability Engineer
- Site Reliability Engineer (Kubernetes – Docker)
- Splunk Engineer
- .NET Developer
- ACCESSIBILITY SPECIALIST
- AGILE PROJECT MANAGER
- Android Developer
- Ansible Automation Engineer
- AppDynamics Engineer
- Application Security Engineer
- Artifactory Engineer
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) / Machine Learning Engineer
- AWS DevOps Engineer
- AWS Solutions Architect
- Azure DevOps Engineer
- Bamboo Engineer
- Bitbucket Engineer
- Blockchain Developer
- BUSINESS SYSTEMS ANALYST
- C# Developer
- Chef InSpec Engineer
- Cloud administrator
- CLOUD ARCHITECT
- Cloud architect
- Cloud automation engineer
- Cloud engineer
- Cloud network engineer
- Cloud Security Engineer
- CNC Programmer
- Coder
- COMPUTER GRAPHICS ANIMATOR
- Computer Hardware Engineer
- Computer Network Architect
- Computer Programmer
- Computer Research Scientist
- Computer Systems Analyst
- Confluence Engineer
- Consul Engineer
- Coverage.py Engineer
- DATA ANALYST
- Data Analyst
- DATA ARCHITECT
- Data Engineer
- DATA MODELER
- DATA SCIENTIST
- Data Scientist
- DATABASE ADMINISTRATOR
- Database Administrator
- Datadog Engineer
- Developer
- DevOps Architect
- DevOps Engineer
- DevOps Engineer
- DEVOPS MANAGER
- DevSecOps Architect
- DevSecOps Engineer
- Director of Engineering
- Docker Engineer
- ELK Engineer
- Embedded Software Engineer
- Entry Level Developer
- Entry Level Network Engineer
- Entry Level Programmer
- Entry Level Software Developer
- Entry Level Software Engineer
- Entry Level Web Developer
- Envoy Engineer
- Falco Engineer
- FluentD Engineer
- Fortify Engineer
- FRAMEWORKS SPECIALIST
- Front End Developer
- Front End Web Developer
- FRONT-END DESIGNER
- FRONT-END DEVELOPER
- Full Stack Developer
- Full Stack JAVA Developer/Programmer/Engineer
- Full Stack Python Developer/Programmer/Engineer
- FULL-STACK DEVELOPER
- Game Developer
- GAME DEVELOPER
- GCP DevOps Engineer
- Gerrit Engineer
- Git Engineer
- Github Engineer
- GitLab Engineer
- GitLab Engineer
- Gradle Engineer
- Grafana Engineer
- Groovy Engineer
- INFORMATION ARCHITECT
- Information Security Analyst
- INTERACTION DESIGNER
- IOS Developer
- Istio Engineer
- IT Manager
- JaCoCO Engineer
- Java Developer
- Java Developer
- JavaScript Developer
- Jenkins Engineer
- JIRA Engineer
- Jr Developer
- Junior Developer
- Junior Front End Developer
- Junior IOS Developer
- Junior Software Developer
- Junior Software Engineer
- Junior Web Developer
- JUnit Engineer
- kubernetes Administrator
- Kubernetes Engineer
- Machine Learning Engineer
- MAVEN Engineer
- Micro services / API Lead Designer
- MOBILE APP DEVELOPER
- Mobile Application Developer
- MOBILE DEVELOPER
- Mulesoft Developer
- Nagios Engineer
- Network and Systems Administrator
- Network Engineer
- New Grad Software Engineer
- New Relic Engineer
- Nexus Engineer
- Nomad Engineer
- Notary Engineer
- Octopus Deploy Engineer
- OpenShift Engineer
- OpenStack Engineer
- Oracle Developer
- Oracle SQL Developer
- Packer Engineer
- PHP Developer
- PHP Developer
- Powershell Engineer
- PRODUCT MANAGER
- Programmer
- Programmer Analyst
- Prometheus Engineer
- Puppet Engineer
- PyTest Engineer
- Python Developer
- PYTHON DEVELOPER
- Python Developer
- QA (QUALITY ASSURANCE) SPECIALIST
- QA Engineer
- React Developer
- Robotics Engineer
- RUBY ON RAILS DEVELOPER
- Salesforce Developer
- Search Engine Optimization
- SECURITY SPECIALIST
- Selenium Engineer
- Senior Ansible Development Engineer
- Senior Cloud Architect
- Senior DevOps Architect
- Senior DevOps Engineer
- Senior DevSecOps Architect
- Senior DevSecOps Engineer
- Senior SRE Architect
- Senior SRE Engineer
- Sharepoint Developer
- Software Developer
- SOFTWARE DEVELOPERS
- Software Engineer
- Software Engineer
- SonarQube Engineer
- Splunk Engineer
- Splunk Enterprise Security Engineer
- SQL Developer
- SRE Architect
- SRE Engineer
- SYSTEMS ADMINISTRATOR
- SYSTEMS ENGINEER
- TeamCity Engineer
- Tech Sales Engineer
- TECHNICAL ACCOUNT MANAGER
- TECHNICAL LEAD
- Terraform Engineer
- TFS Engineer
- Twistkock Engineer
- UDeploy Engineer
- UI DESIGNER
- UI Developer
- Unity Developer
- UX DESIGNER
- Vault Engineer
- Web Designer (UI/UX Designer)
- Web Developer
- Web Developer
- WordPress Developer
- WORDPRESS DEVELOPER
- XL Deploy Engineer
- Zabbix Engineer
- Author
- Recent Posts
Follow me
Rajesh Kumar
Mentor for DevOps — DevSecOps — SRE — Cloud — Container & Micorservices at Cotocus
Join my following certification courses…
— DevOps Certified Professionals (DCP)
— Site Reliability Engineering Certified Professionals (SRECP)
— Master in DevOps Engineering (MDE)
— DevSecOps Certified Professionals (DSOCP)
URL — https://www.devopsschool.com/certification/
My Linkedin — https://www.linkedin.com/in/rajeshkumarin
My Email — contact@DevOpsSchool.com
Follow me
Latest posts by Rajesh Kumar (see all)
- Newrelic Tutorials: How to Integrate Apache2 in ubuntu — April 10, 2023
- Introduction of Oracle RAC — April 7, 2023
- Terraform Tutorials: Templating in Terraform — April 5, 2023
What names should you use for your IT job titles?
It starts with using the same language as candidates. Below is a list of IT job titles ranked by the number of times people (most likely candidates!) Google-searched the title name and the word “jobs”. Our source is the excellent SEO resource ahrefs.
Note: This list of job titles in IT does NOT include titles related to developing software. There are so many developer-related titles that we dedicated a separate article to that called The Top 50 Software Job Titles. These articles on job titles are part of our ongoing series called Job Titles: The Definitive Guide (which includes the hugely popular The 16 Best Sales Job Titles).
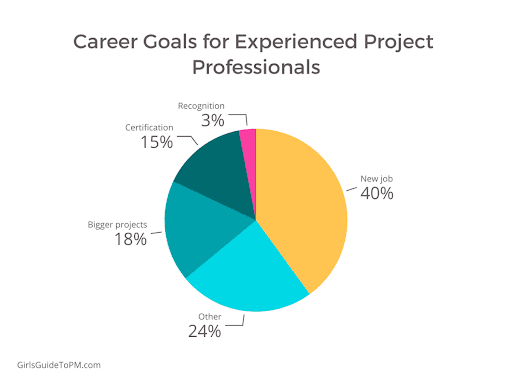
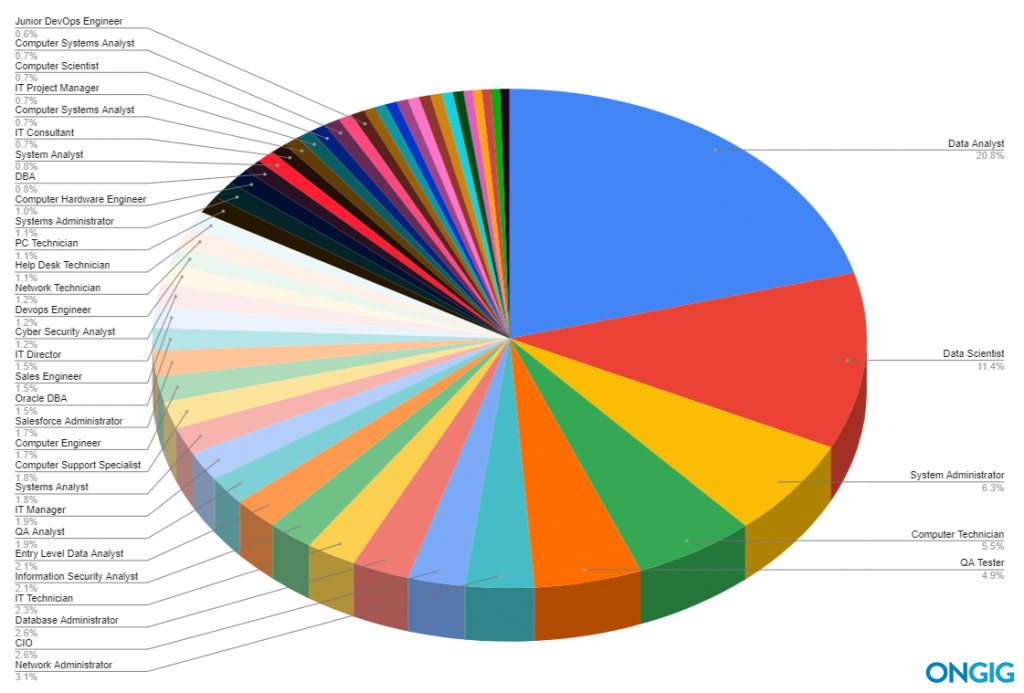
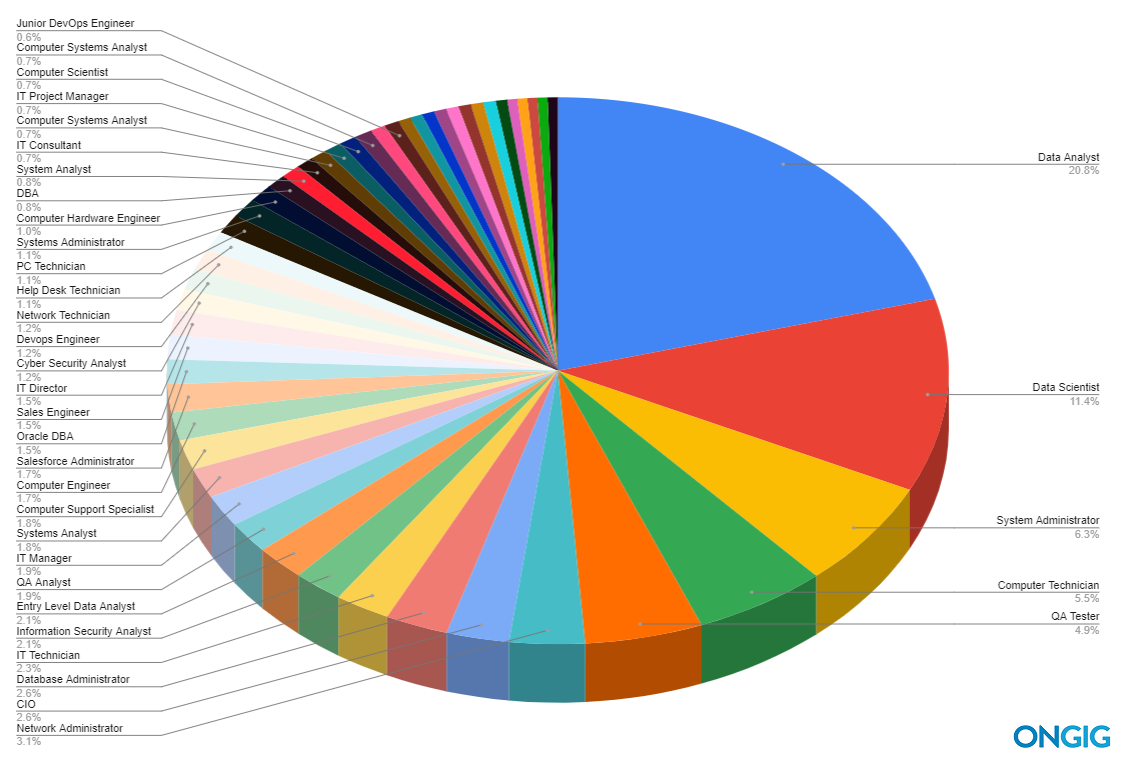
Here’s a pie chart list of the top 35 IT titles searched for by candidates. Enjoy!
Top IT Job Titles with Brief Job Description
Below is a list of the top IT titles with:
- A brief job description
- Alternative titles to use for the IT positions
- Title Search Volume — The # of Google searches that “[job title] jobs” gets per month
Note: Some of the job titles in the pie chart above are excluded below because they are redundant (e.g. a DBA is the same as a Database Administrator so we list just the Database Administrator (the more popular IT title with candidates)).
1. Data Analyst
A data analyst collects, interprets and visualizes data to uncover insights. A data analyst assigns a numerical value to business functions so performance is assessed and compared over time. The data analyst enables an organization to make more informed decisions.
Alternative IT Job Titles: Business Analyst, Business Intelligence Analyst
# of Google Searches = 20,000
2. Data Scientist
A data scientist is an analytical expert who uses technology and social science to find trends and manage data. They’re part mathematician, part computer scientist, and part mathematician. A good Data Scientist often has both the technical skills to solve complex problems and the curiosity to explore what problems need to be solved.
Alternative IT Job Titles: Statistician, Data Architect
# of Google Searches = 11,000
3. System Administrator
A system administrator (aka SysAdmin) is responsible for the upkeep, configuration, and operation of computer systems and servers. This includes installing and managing desktop and laptop computers, servers, networks, IT security systems, and other critical components of an organization’s IT infrastructure. A system administrator is also responsible for determining appropriate IT policies for businesses, supervising technician staff, and also may be in charge of purchasing IT equipment. The system administrator’s performance is usually measured by the uptime and security of the systems they manage.
Alternative IT Job Titles: SysAdmin, Systems Administrator
# of Google Searches = 6,100
4. Computer Technician
A computer technician’s role is to maintain computer systems, troubleshoot problems, make fixes/repairs, and provide technical support. The “computer technician” job title might be used for any range of roles such as A) a PC technician in a retail location; or B) a member of a company’s internal IT/Help Desk Support team or C) technical support person helping customers with their computer issues over the phone.
Alternative IT Job Titles: IT Technician, Computer Support Specialist, Help Desk Technician, PC Technician, Computer Repair Technician, Personal Computer Technician, Desktop Support Technician, IT Support Technician
# of Google Searches = 5,300
5. QA Tester
A QA tester’s job is to test new and existing features in software for defects or other bugs. They typically report such errors and failures to a manager of the software development/engineering team.
Alternative IT Job Titles: Quality Assurance Tester, QA Analyst, Quality Assurance Technician and Software Quality Assurance Engineer,
# of Google Searches = 4,700
6. Network Administrator
A network administrator’s job is to keep networked computer systems working. A network administrator installs, maintains and upgrades software or hardware required to run a computer network. The IT or computer network may extend to the Internet, Intranet, local area network (LAN) and wide area network (WAN).
Alternative IT Job Titles: Network Manager
# of Google Searches = 3,000
7. CIO
A CIO (Chief Information Officer) is the senior IT management job title responsible for all information technology and computer systems. The role of the CIO is to set and lead the technology strategy for an organization. The CIO acts as the bridge or interface between the IT department and the rest of the organization.
Alternative IT Job Titles: Chief Information Officer
# of Google Searches = 2,500
8. Database Administrator
A database administrator (DBA) uses specialized software to store and organize data. Their tasks include maintaining the data dictionary, monitoring performance, and enforcing organizational standards and security. There are 2 types of database administrators: 1) System DBAs oversee database administration, debugging code and upgrading software. Application DBAs manage specific database applications
Alternative IT Job Titles: DBA
# of Google Searches = 2,500
9. IT Technician
An IT Technician installs and maintains computer systems and provides end-user technical support. They are often the main point of contact for technological issues. An IT Technician may also train end-users on software and hardware.
Alternative IT Job Titles: Computer Support Specialist, Help Desk Technician, Desktop Support Technician, IT Support Technician.
# of Google Searches = 2,200
10. Information Security Analyst
An information security analyst designs security countermeasures to defend against cyber threats and cyber-attacks. The main goal of an information security analyst is to protect an organization’s data. They do this by using software, such as firewalls and data encryption, conducting penetration testing (aka pen tests) and monitoring for, and investigating security breaches.
Alternative IT Job Titles: Cyber Security Analyst, Information Security Consultant
# of Google Searches = 2,000
11. QA Analyst
The QA Analyst applies software quality assurance practices to the development of software. Software Quality Assurance covers the testing of software to detect errors or discrepancies between the software’s requirements and actual results. A QA Analyst may also fix the process that caused software errors. A QA Analyst differs from a QA Tester in that a QA Analyst is usually involved in a wider range of the software development cycle.
Alternative IT Job Titles: Quality Analyst, Quality Assurance Analyst
# of Google Searches = 1,800
12. IT Manager
An IT manager is responsible for the coordination of computer and information systems. An IT manager, also known as an information technology manager, coordinates the installation and maintenance of network hardware and software. An IT manager is also tasked with monitoring operational requirements and researches technology strategies and solutions.
Alternative IT Job Titles: Information Technology Manager
# of Google Searches = 1,800
13. Systems Analyst
A Systems Analyst is responsible for maintaining and upgrading existing technological systems in an organization. A Systems Analyst also designs new computer systems and frameworks, provides troubleshooting for technical issues, and creates system guideline manuals for training purposes.
Alternative IT Job Title: Computer Systems Analyst, System Analyst
# of Google Searches = 1,700
14. Computer Support Specialist
A computer support specialist provides technical support for a company’s customers or employees. A computer support specialist tasks include assisting users with issues related to computers, software, and printers. A computer support specialist can provide either in-house or customer support.
Alternative IT Job Titles: Computer User Support Specialist, Technical Support Specialist, IT Specialist, Computer Technician
# of Google Searches =1,700
15. Computer Engineer
A computer engineer is responsible for testing, evaluating and developing the software for computer programs. A computer engineer, also known as a software engineer, is tasked with the development of new computer games and business applications. A computer engineer also designs and develops new operating systems.
Alternative IT Job Titles: Software Engineer
# of Google Searches = 1,600
16. Salesforce Administrator
A salesforce administrator is in charge of overseeing the setup and implementation of the Salesforce suite of products. A salesforce administrator is the point of contact for Salesforce users within a company in need of training or troubleshooting. A salesforce administrator is typically employed by large corporations using the Salesforce suite.
Alternative IT Job Titles: Salesforce System Administrator
# of Google Searches = 1,600
17. Oracle DBA
An Oracle DBA (Database Administrator) is proficient in Oracle database architecture. Their tasks include installation, administration, performance tuning, and troubleshooting. An Oracle DBA also manages the upgrades of Oracle servers and application tools. Oracle database systems can be large, so Oracle DBA’s often share the responsibility of managing databases with other database administrators.
Alternative IT Job Titles: DBA, Oracle Database Administrator
# of Google Searches = 1,400
18. Sales Engineer
A sales engineer uses both technical knowledge and sales skills to sell scientific and technological products or services to businesses. A sales engineer must have extensive knowledge of technical products and how they function. A sales engineer is tasked with delivering a unified vision of the engineering, strategic, and market value of a technical product to the customer and their business.
Alternative IT Job Titles: Technical Sales Engineer
# of Google Searches = 1,400
19. IT Director
An IT Director is responsible for the management, strategy, and execution of IT (information technology) of an organization. Their tasks include directing the effective delivery of networks and data recovery systems. An IT Director oversees technical projects based on organizational goals. The IT Director supervises a department of technical employees while also working closely with external vendors, advisors, and the management team.
Alternative IT Job Titles: Chief Information Officer, Director of Information Technology
# of Google Searches = 1,400
20. Cyber Security Analyst
A cyber security analyst plans and executes security measures to protect a business’s computer systems and networks. A Cyber Security Analyst monitors threats to organizational networks and creates contingency plans for cyber attacks. A Cyber Security Analyst is also tasked with reporting breaches and weak spots, researches IT trends, and installs software and encryption to protect the company’s network.
Alternative IT Job Title: CyberSecurity Analyst, Information Security Analyst
# of Google Searches = 1,200
21. Devops Engineer
A DevOps Engineer works with IT developers to oversee code releases. A DevOps Engineer aims to help better coordination among operations, development, and testing functions by automating and streamlining the integration and deployment processes. Their goal is often to better align IT operations with the rest of the organization.
Alternative IT Job Title: Site Reliability Engineer (SRE)
# of Google Searches = 1,200
22. Network Technician
A Network Technician, also known as a Computer Network Technician, is responsible for building and troubleshooting computer networks. A Network Technician tasks include setup, installation, and repair of hardware, software, equipment, and wiring components. A Network Technician may also perform data backups, disaster recovery operations, and conduct tests for security and quality control.
Alternative IT Job Title: Computer Network Technician
# of Google Searches = 1,200
23.Help Desk Technician
A Help Desk Technician is vital to the IT workforce because they provide technical customer support and troubleshooting services to end-users needing help with their computer hardware or software. A Help Desk Technician also writes training manuals and train computer users on various technical products. A Help Desk Technician does daily performance checks to keep technologies up to date and running smoothly.
Alternative IT Job Title: Customer Support Technician
# of Google Searches = 1,100
24. PC Technician
A PC technician is responsible for identifying, troubleshooting and resolving computer issues. A PC technician is tasked with repairing and maintaining computer hardware, software, and network issues. A PC technician also installs new power systems, upgrades firmware and repairs computer hardware. Their tasks also include troubleshooting and installation of software, computer applications, and virus scanning.
Alternative IT Job Titles: Computer Repair Technician, PC Repair Technician
# of Google Searches = 1,100
25.Computer Hardware Engineer
A Computer Hardware Engineer builds and tests various types of computer models. A Computer Hardware Engineer researches, designs, and develops computer systems and components such as circuit boards processors, networks, routers, and memory devices. Computer Hardware Engineers use complex problem-solving skills to evaluate and improve existing models. They often work in a research laboratory.
Alternative IT Job Title: Hardware Engineer
# of Google Searches = 1,000
If you’re curious about IT position titles at either the entry-level or leadership levels, here are 2 more rankings that might interest you:
Entry Level IT Job Titles
The top 10 entry level IT job titles that candidates search for when they are just starting out are:
- Entry Level Data Analyst (2,000)
- Junior Dev Ops Engineer (600)
- Entry Level Data Scientist (500)
- Entry Level QA Tester (500)
- Entry Level Dev Ops Engineer (400)
- Junior Data Scientist (350)
- Entry Level Network Administrator (350)
- Junior Salesforce Administrator (250)
- Entry Level Computer Engineer (200)
- IT Intern (150)
Tip for Entry Level IT Job Titles: Using qualifiers like “Entry Level” and “Junior” can be effective when you want to attract ONLY entry-level candidates (e.g. if you have a hierarchy of IT job titles such as Entry Level Data Analyst, Data Analyst, Senior Data Analyst, etc.). If, on the other hand, you don’t use a hierarchy, then you’re better off going with the most-searched job title (e.g. “Data Analyst” instead of “Entry Level Data Analyst”)).
Top IT Management Job Titles
And which IT titles are used for leadership positions?
The top 10 IT management job titles searched for are:
- CIO (2,500)
- IT Manager (1,800)
- IT Director (1,400)
- CTO (600)
- Chief Information Officer (350)
- Director of Technology (200)
- Chief Technology Officer (200)
- Chief Information Security Officer (150)
- Director of IT (150)
- Interim CIO (100)
Tip for IT Manager titles: Candidates prefer to search for acronyms like CIO, IT, CTO versus spelling out the longer phrases they stand for.
Funny IT Job Titles
You might be tempted to use a clever or funny IT job title such as the examples below found on the Web.
Don’t! A general rule of thumb with IT titles (and any job titles) is to keep it clean and simple. Those avoid confusion and get you the most search queries
- Digital Overlord
- Señor System Administrator
- Social Media Sith Lord
- Digital Sorcery/Sorceress
- Chief Geek
- Head Unicorn Wrangler
- Lord of All Things Technical
- Director of Spam Reception
- Wiz Kid
- Techno-Bull
- Interwebs Mechanic
- Codeling
- C3PO – Chief Power Plugs & Patches Officer
- Electromagnetic Wrangler Extraordinaire
- Mass Bit Manipulator
- Logic Gate Operator
- Computational Wizard
- King of Signals
- Emporer of Bit-Land
- Professional Technology Manipulator
- Mr Computer
- Dr Fix IT
Special thanks to Beep Translator on Reddit and Blaine L. Pardoe for so many of the funny IT job titles above.
I hope you enjoyed our research on IT department job titles. Please ping me if you feel like I missed something.
Why I wrote this?
My team and I at Ongig are on a mission to transform job descriptions. One way we do this is to have our software optimize your job descriptions to give you insights on the most effective job titles to use. Check out Ongig and please ask for a demo if you’d like to learn more.
January 2, 2020 by in Job Titles
Updated: 10/18/2022 by
Notice
Computer Hope is not hiring for any of these positions. When jobs are made available, they are posted on our hiring page.
The following list was created for users who enjoy computers but are uncertain what field to enter. Each section contains a description of a job, the requirements, and recommendations on how to proceed if you’re interested.
This page does not contain salary information because it varies greatly depending on the company and its location. However, it’s safe to assume that with the increased difficulty and experience requirements comes higher pay. If you are looking for a pay range, refer to your local listings (newspaper) or online salary sites for a general overview.
The qualifications and requirements for these jobs vary, but many of them have entry-level positions. We suggest looking at data entry, freelancer, sales, quality assurance, or technical support jobs as your first computer job or if you’re looking to get your foot in the door.
3D animation or graphic design
Description: A position where you design and create either a graphic or 3D animations for software programs, games, movies, and web pages, often with a team of other designers. The position may also require you to work on existing graphics, animations, and movies, created by other people.
Requirements: An individual applying for this job would need to be talented in design and creating visuals, and for most people, this is not something you could learn in training. Also, you must have a good understanding of the software programs used to create visual designs or 3D animations.
Recommendations: To get into graphic design, learn how to use major graphics programs, such as Adobe Photoshop, Adobe Illustrator, and other programs used to create pictures or edit photos. If you’re applying for any design or animation company, it’s also a good idea to have a portfolio of your work.
- Definition of animation and a list of animation software.
- What program can I use to view, edit, or create images?
Difficulty: (MEDIUM — HIGH) Many of the programs used to create a graphic, edit a photo, or create a 3D render are complex and often require prior experience gained through training or schooling.
Customer service
Description: Helping customers with general questions relating to the company, ordering, status on orders, account information or status, etc.
Requirements: Need good communication skills and a general understanding of the company and its products.
Recommendations: Great starting position for anyone looking to get their foot in the door of a company. Once working for a company, you’ll have a better chance of changing to the position you want.
Difficulty: (LOW) Customer service jobs only require basic computer proficiency and the ability to navigate through the company’s system, but solemnly require the employee to be skilled in more technical areas.
Data analyst
Description: A data analyst is responsible for collecting, cleaning, and interpreting data to help companies solve questions and problems related to that data.
Requirements: Know and be able to use the required programming languages (e.g., Python), spreadsheets, and use databases like SQL.
Recommendations: Learn a programming language like Python and practice using it to scrape and collect data. Practice using spreadsheets to organize and present data, and familiarize yourself with databases.
Difficulty: (HIGH) A good data analyst must be able to understand and use the tools required to collect data, sort and organize that data, and then be able to understand and present that data.
Data entry
Description: A job that commonly requires the employee to take information from a hard copy or another source and enter it into an electronic format. Position may also be taking electronic data and entering it into a database for easy sorting and locating.
Requirements: Requires someone capable of typing 40-50 or more WPM, basic computer proficiency, and familiarity with word processors.
Recommendations: Practice your typing and take online typing tests to determine your overall speed.
- How to test how many words a minute you can type.
Difficulty: (LOW) Most data entry jobs are beginner-level jobs and don’t require much or any prior experience or formal education.
Database
Description: A job that requires creating, testing, and maintaining one or more databases.
Requirements: Requires familiarity with or extensive knowledge of databases at the place of employment. For example, knowledge with Access, FoxPro, MySQL, SQL, and Sybase database systems.
Recommendations: Become familiar with the database used in the business. If the job is for the continued development of a database, you need a good understanding of its corresponding programming language. Often, this knowledge requires experience or formal education.
Difficulty: (MEDIUM — HIGH) Developing or maintaining a database is a difficult and complicated job. As mentioned above, you need to have experience or formal education to be considered by most companies.
Electronics technician or engineer
Description: Assembling, testing, and repairing electronic equipment.
Requirements: A strong understanding of basic and advanced electronics.
Recommendations: Get a formal education in electronics and electro-mechanical, or self-teach yourself by building an electronic system or device.
Difficulty: (HIGH) Having a strong understanding of electronics often takes several years of formal education or on-the-job experience.
Engineer
Description: An engineer designs and implements mechanical and electronic equipment. A broad and difficult field, engineering often requires a college degree or at very least several certifications. Although used broadly on this page, the engineer is usually specified in the job requirement. For example, a software development engineer may be a highly skilled computer programmer.
Requirements: The requirements for this job change, depending on the engineering field that interests you. However, as mentioned above, any engineering job requires a vast knowledge of the subject matter; usually from school, certifications, training, or years of experience.
Recommendations: Get training and education on the subject of interest from books, college, the Internet, and other sources. Often before you can qualify for many engineer positions, you need experience; therefore, it’s a good idea to get an entry-level job in the same field. For example, if you want to be a software engineer, get a job in programming, or create a program. If you want to become a network engineer, get a job that requires you to set up, maintain, or otherwise work with professional networks. You can start learning by setting up your home network.
Difficulty: (HIGH) At the median level, this job and position requires experience or a degree.
Freelancer or virtual assistant
Description: Thanks to the Internet, it’s possible for anyone to become a freelancer and apply for positions around the world.
- How to make money online.
Requirements: Computer and high-speed Internet connection.
Recommendations: There is a wide array of freelance jobs available online, so it is difficult to give any specific recommendation. However, know that working from home can be difficult, there are more distractions, and it’s hard to keep a schedule. Set a strict work schedule and always make sure you work for what you feel your time is worth.
Difficulty: (LOW — HIGH) This all depends on the job you apply for since there are low difficulty freelance jobs such as customer service and high difficulty jobs like freelance programming.
Hardware
Description: A position as a hardware designer, circuit design, embedded systems, firmware, etc. is a job that requires you to design and create a complete hardware package or portions of a hardware device.
Requirements: Jobs that design or create hardware devices require you to have a good understanding of electronics, circuits, firmware, or design. For this position, you need to have several years of prior experience or a degree in the field.
Recommendations: If you are interested in this field, we suggest you get a degree in the field.
Difficulty: (HIGH) Hardware design is a difficult position to learn and understand unless you get training or a degree.
Networking or system administrator
Description: Computer networking jobs involve designing, setting up, and maintaining a network.
Requirements: Although most users today have a home network, setting up, troubleshooting, and maintaining a corporate network is a more complicated task. Networking jobs also require a good understanding of how a network works, and in some cases, how the underlying protocols and structure work.
Recommendations: Numerous network and network-related certifications available today, such as the CCNA, MCSE, etc. Often depending on the level of certification and the job, the certifications are more than enough to qualify you for most network jobs. Some higher networking positions, especially in the development of network hardware or programming side, may also require experience in networking or a degree.
Difficulty: (MEDIUM — HIGH) Depending on the job specifications and the complexity of the network usually determines the difficulty of this job.
Programmer or software developer
Description: A job that requires the development or continued development and maintenance of a software program.
Requirements: A basic to an extensive understanding of a programming language. Because most job positions require the ability to help develop a program, they require several years of experience or a degree.
Tip
With software on the Internet, a developer is often classified as someone who works on the back end.
Recommendations: Learn one or more programming languages. Depending on what programs or scripts you want to create may change the language you want to learn. See the programming language definition for a listing of popular programming languages and programs they create. If you need experience, creating software programs or working on an open-source project is a great way to learn a language and demonstrate your abilities at a job interview.
Difficulty: (HIGH) Learning a programming language can be as difficult as learning a second language and takes experience and practice to become a skilled programmer.
Quality assurance, system analyst, or tester
Description: This job requires that the employee test all the features of a product for any problems or usability issues.
Requirements: Requires you to have a good understanding of computer software, hardware, and the product being tested.
Recommendations: Become familiar with computers, software, hardware, and the products the company makes.
Difficulty: (LOW — MEDIUM) What is being tested and how thorough in depth the troubleshooting process is determines the difficulty of this job. However, for users familiar with the product or similar products, there’s not have much difficulty locating and reporting issues.
Repair and fix
Description: A job that requires you to fix and repair computers and computer equipment. Often this involves removing a component from in the computer and replacing it with a good component.
Requirements: A good understanding of computer hardware, computer disassembly, proper tools, and good troubleshooting skills.
Recommendations: Build a computer or disassemble and re-assemble a computer. Become familiar with computers, software, hardware, and the products the company makes.
Difficulty: (MEDIUM — HIGH) This job requires a good understanding of disassembling a computer, knowing what can be repaired, and how to fix or replace components.
Sales
Description: Selling a product or service to another person or company.
Requirements: Good communication skills and a general understanding of computers and the product that is being sold.
Recommendations: If you are selling computers, computer hardware, or computer software, become familiar with all aspects of the product. Sites like Computer Hope are a great resource to learn about computers. If you are selling a specialized product developed by the company, visit their web page, and become as familiar with the product as possible.
Difficulty: (LOW) Sales for computer software, hardware, electronics, or related products is a good first job and is a good way to learn more about computers.
Technical support (technician or help desk)
Description: Helping an end-user or company employee with their computers, software programs, and hardware devices. A technical support position is a great first step for people interested in working in the computer industry.
Requirements: A basic understanding of computers, computer software, and hardware.
Recommendations: Become as familiar as possible with computers, computer software, and computer hardware. Although almost all technical support centers provide some form of training, most still require you to be familiar with computers.
Help desks for corporations do not usually have any training; these positions require you to have a good understanding of computers and troubleshooting computer problems.
- How to become a computer technician.
- How to learn more about computers.
Difficulty: (LOW — MEDIUM) The difficulty of this job depends on the training you get. However, someone familiar with computers or works with computers often has an easy time with these positions after a few days.
Technical writing
Description: This position often involves creating or editing technical papers or manuals.
Requirements: This position often requires that the individual has a basic understanding of the subject being written about and have good writing skills.
Recommendations: Many of these positions require you to have a degree and often test a user before hiring them. It is also a good idea to be familiar with at least one major word processor and a CMS (content management system) if writing online.
Difficulty: (LOW — MEDIUM) For someone who has good writing skills and familiarity with the subject, this job can be easy.
Security expert
Description: Test and find vulnerabilities in a system, hardware device, or software program.
Requirements: This position is for someone who has a strong familiarity with how software, hardware, and networks work and how to exploit them. Often, you need to have a good understanding of how the overall system works and good programming skills.
Recommendations: Keep up-to-date with all security news, advisories, and other related news. To get a good understanding of vulnerabilities and how to identify them, you’ll need to understand how to program and how software interacts with computers.
- How to create a computer program.
Difficulty: (MEDIUM — HIGH) The difficulty of this job depends on what you are testing or how you are testing for vulnerabilities.
Webmaster or web designer
Description: Create, maintain, or completely design a web page.
Requirements: For basic web designing positions, a good understanding of HTML, the Internet, and web servers is needed. Have a good understanding of the technologies and code used to create a web page and the HTML editor or program used to create the page. More advanced positions may also require familiarity with CGI, CSS, Flash, FTP, JavaScript, jQuery, Linux, Perl, PHP, Python, RSS, SSI, Unix, or XHTML.
Tip
A designer is often classified as someone who works on the front end.
Recommendations: One of the best learning experiences for people who are interested in this job is to create a web page or help maintain another website. Keep in mind, that designing and posting a web page using a WYSIWYG editor without some basic understanding of HTML may not be enough for most jobs.
Difficulty: (MEDIUM — HIGH) The complexity of this job depends on the project. Creating and posting a simple website with no interaction is not that hard. However, creating an interactive site with forms, databases, and overall more interaction with the user and the server can increase the difficulty of the job significantly.