Excel для Microsoft 365 Excel для Microsoft 365 для Mac Excel 2021 Excel 2021 для Mac Excel 2019 Excel 2019 для Mac Excel 2016 Excel 2016 для Mac Excel 2013 Excel 2010 Excel 2007 Excel для Mac 2011 Еще…Меньше
С помощью средств анализа «что если» в Excel вы можете экспериментировать с различными наборами значений в одной или нескольких формулах, чтобы изучить все возможные результаты.
Например, можно выполнить анализ «что если» для формирования двух бюджетов с разными предполагаемыми уровнями дохода. Или можно указать нужный результат формулы, а затем определить, какие наборы значений позволят его получить. В Excel предлагается несколько средств для выполнения разных типов анализа.
Обратите внимание на то, что в этой статье приведен только обзор инструментов. Подробные сведения о каждом из них можно найти по ссылкам ниже.
Анализ «что если» — это процесс изменения значений в ячейках, который позволяет увидеть, как эти изменения влияют на результаты формул на листе.
В Excel предлагаются средства анализа «что если» трех типов: сценарии, таблицы данных и подбор параметров. В сценариях и таблицах данных берутся наборы входных значений и определяются возможные результаты. Таблицы данных работают только с одной или двумя переменными, но могут принимать множество различных значений для них. Сценарий может содержать несколько переменных, но допускает не более 32 значений. Подбор параметров отличается от сценариев и таблиц данных: при его использовании берется результат и определяются возможные входные значения для его получения.
Помимо этих трех средств можно установить надстройки для выполнения анализа «что если», например надстройку Поиск решения. Эта надстройка похожа на подбор параметров, но позволяет использовать больше переменных. Вы также можете создавать прогнозы, используя маркер заполнения и различные команды, встроенные в Excel.
Для более сложных моделей можно использовать надстройку Пакет анализа.
Сценарий
— это набор значений, которые сохраняются в Excel и могут автоматически подставляться в ячейки на листе. Вы можете создавать и сохранять различные группы значений на листе, а затем переключиться на любой из этих новых сценариев, чтобы просмотреть другие результаты.
Предположим, у вас есть два сценария бюджета: для худшего и лучшего случаев. Вы можете с помощью диспетчера сценариев создать оба сценария на одном листе, а затем переключаться между ними. Для каждого сценария вы указываете изменяемые ячейки и значения, которые нужно использовать. При переключении между сценариями результат в ячейках изменяется, отражая различные значения изменяемых ячеек.
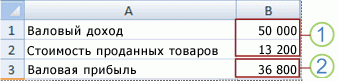
1. Изменяемые ячейки
2. Ячейка результата
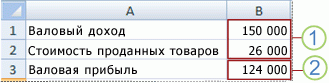
1. Изменяемые ячейки
2. Ячейка результата
Если у нескольких человек есть конкретные данные в отдельных книгах, которые вы хотите использовать в сценариях, вы можете собрать эти книги и объединить их сценарии.
После создания или сбора всех нужных сценариев вы можете создать сводный отчет по сценариям, в который включаются данные из этих сценариев. В отчете по сценариям все данные отображаются в одной таблице на новом листе.
Примечание: В отчетах по сценариям автоматический пересчет не выполняется. Изменения значений в сценарии не будут отражается в уже существующем сводном отчете. Вам потребуется создать новый сводный отчет.
Если вы знаете нужный результат формулы, но не знаете, какое входные значения требуется для получения этого результата, используйте функцию «Поиск окна». Предположим, что вам нужно занять денег. Вы знаете, сколько вам нужно, на какой срок и сколько вы сможете выплачивать каждый месяц. С помощью средства подбора параметров вы можете определить, какая процентная ставка вам подойдет.
Ячейки B1, B2 и B3 — это значения для суммы займа, длины срока и процентной ставки.
Ячейка B4 отображает результат формулы =PMT(B3/12;B2;B1).
Примечание: В средстве поиска окна можно ввести только одно значение переменной. Если вы хотите определить несколько входных значений, например сумму займа и сумму ежемесячного платежа по кредиту, используйте надстройка «Надстройка «Найти решение». Дополнительные сведения о надстройки «Решение» см. в разделе Подготовка прогнозов и расширенных бизнес-моделей ипо ссылкам в разделе См. также.
Если у вас есть формула с одной или двумя переменными либо несколько формул, в которых используется одна общая переменная, вы можете просмотреть все результаты в одной таблице данных. С помощью таблиц данных можно легко и быстро проверить несколько возможностей. Поскольку используются всего одна или две переменные, результат можно без труда прочитать или опубликовать в табличной форме. Если для книги включен автоматический пересчет, данные в таблицах данных сразу же пересчитываются, и вы всегда видите свежие данные.
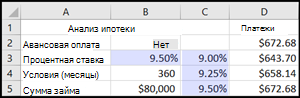
Ячейка B3 содержит входные значения.
Ячейки C3, C4 и C5 являются значениями, Excel заменяются на основе значения, введенного в ячейку B3.
В таблицу данных нельзя помещать больше двух переменных. Для анализа большего количества переменных используйте сценарии. Несмотря на то что переменных не может быть больше двух, можно использовать сколько угодно различных значений переменных. В сценарии можно использовать не более 32 различных значений, зато вы можете создать сколько угодно сценариев.
При подготовке прогнозов вы можете использовать Excel для автоматической генерации будущих значений на базе существующих данных или для автоматического вычисления экстраполированных значений на основе арифметической или геометрической прогрессии.
Вы можете заполнить ряд значений, которые соответствуют простому линейному или экспоненциальному тренду роста, с помощью ручки заполнения или команды Ряд. Для расширения сложных и нелинейных данных можно использовать функции или средство регрессионного анализа надстройки «Надстройка анализа».
В средстве подбора параметров можно использовать только одну переменную, а с помощью надстройки Поиск решения вы можете создать обратную проекцию для большего количества переменных. Надстройка «Поиск решения» помогает найти оптимальное значение для формулы в одной ячейке листа, которая называется целевой.
Над решением работает группа ячеек, связанных с формулой в целевой ячейке. «Решение» изменяет значения изменяемых ячеек, которые вы указываете (регулируемые ячейки), чтобы получить результат, который вы указываете из формулы целевой ячейки. Ограничения можно применять для ограничения значений, которые можно использовать в модели, а ограничения могут ссылаться на другие ячейки, влияющие на формулу целевой ячейки.
Дополнительные сведения
Вы всегда можете задать вопрос специалисту Excel Tech Community или попросить помощи в сообществе Answers community.
См. также
Сценарии
Подбор параметров
Таблицы данных
Использование «Решения» для бюджетов с использованием средств на счете вех
Использование «Решение» для определения оптимального сочетания продуктов
Постановка и решение задачи с помощью надстройки «Поиск решения»
Надстройка «Надстройка анализа»
Полные сведения о формулах в Excel
Рекомендации, позволяющие избежать появления неработающих формул
Обнаружение ошибок в формулах
Сочетания клавиш в Excel
Функции Excel (по алфавиту)
Функции Excel (по категориям)
Нужна дополнительная помощь?
Анализ «Что Если» в Excel позволяет попробовать различные значения (сценарии) для формул.
Следующий пример поможет Вам освоить Анализ «что если» быстро и легко.
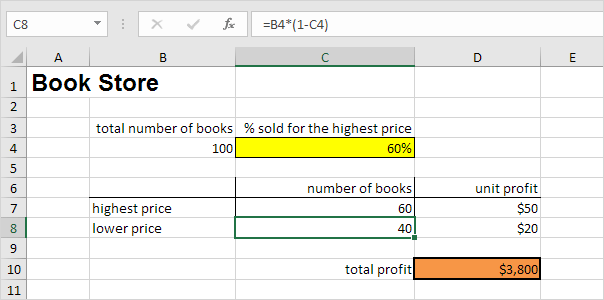
Предположим, у вас есть книжный магазин и есть 100 книг на продажу. Вы продаете определенный % книг по самой высокой цене в $ 50 и определенный % книг по более низкой цене $ 20.
Если вы продаете 60% книг по самой высокой цене, ячейка D10 вычисляет общую прибыль в размере 60 * $ 50 + 40 * $ 20 = $ 3800.
Скачать рассматриваемый пример Вы можете по этой ссылке: Пример анализа «что если» в Excel.
Создание различных сценариев
Что будет, если Вы продадите 70% книг по высокой цене? А что будет, если Вы продадите 80% книг? Или 90%, или 100%? Каждый другой процент продажи книг — это различный сценарий.
Вы можете использовать «Диспетчер сценариев» для создания этих сценариев.
Примечание: Вы можете просто ввести другой процент в ячейку C4, что бы увидеть результат в ячейке C10. Однако, Анализ «что если» позволит Вам сравнить результаты различных сценариев.
Итак, приступим.
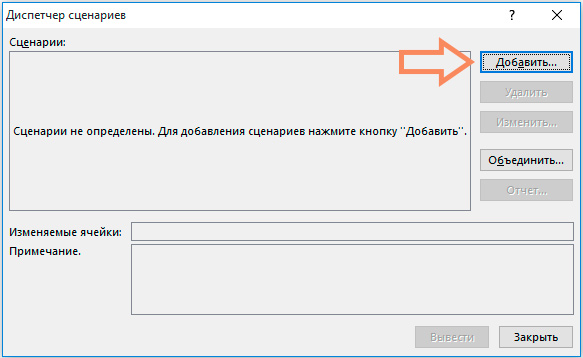
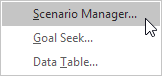
1. На вкладке Данные выберите Анализ «что если» и выберите Диспетчер сценариев из списка.
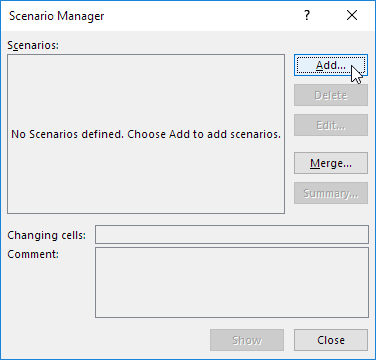
Откроется диалоговое окно Диспетчер сценариев.
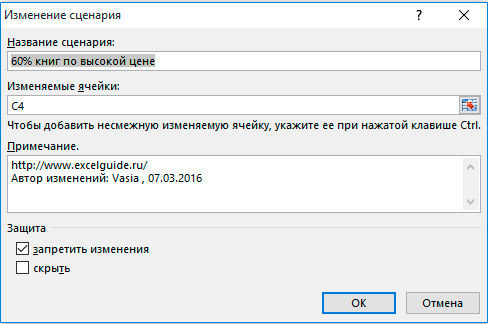
2. Добавьте сценарий, нажав на кнопку Добавить.
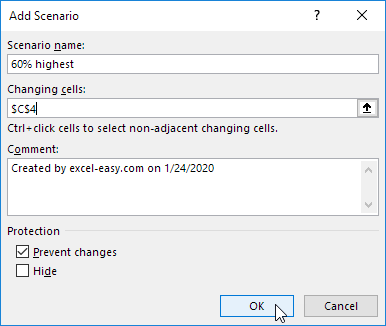
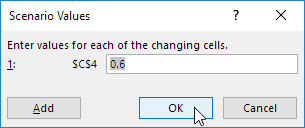
3. Введите имя (60% книг по высокой цене), выберите ячейку C4 (% книг, которые продаются по высокой цене) для изменяемой ячейки и нажмите на кнопку OK.
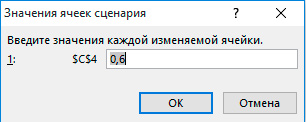
4. Введите соответствующее значение 0,6 и нажмите на кнопку OK еще раз.
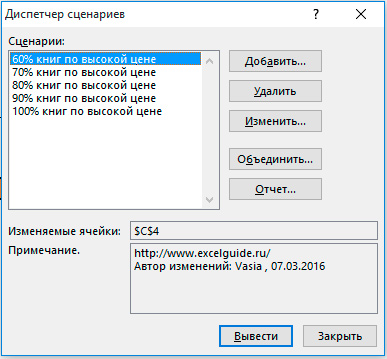
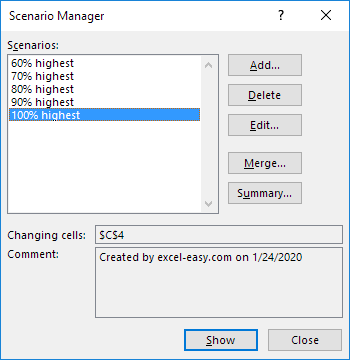
5. Далее, добавьте еще 4 других сценария (70%, 80%, 90% и 100% соответсвенно).
И, наконец, ваш Диспетчер сценариев должен соответствовать картинке ниже:
Примечание: чтобы увидеть результат сценария, выберите сценарий и нажмите на кнопку Вывести. Excel изменит значение ячейки C4 в соответствии со сценарием, что бы Вы смогли увидеть результат на листе.
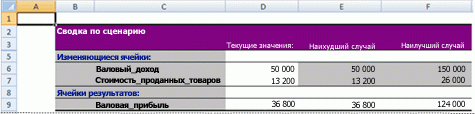
Отчет по сценариям
Для того, чтобы легко сравнить результаты этих сценариев, выполните следующие действия:
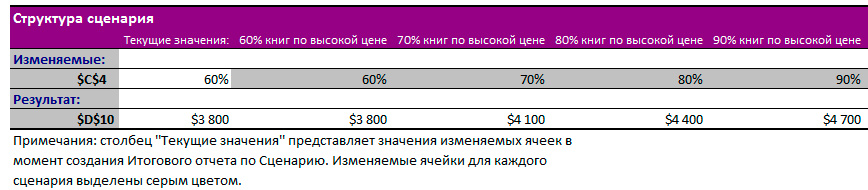
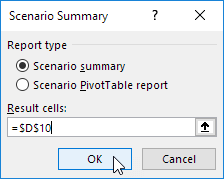
1. Кликните по кнопке «Отчет» в Диспетчере сценариев.
2. Далее, выберите ячейку C10 (итого выручка) в качестве ячейки результата и нажмите ОК.
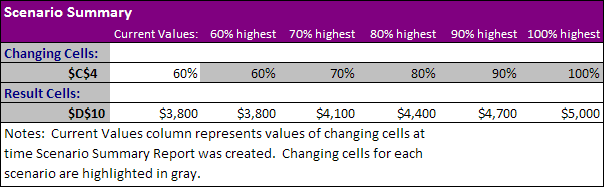
Результат:
Вывод: Если вы продаете 70% книг по высокой цене, то Вы получите общую выручку в размере $ 4100, если Вы продаете 80% книг по высокой цене, то Вы получаете общую прибыль в размере $ 4400 и т.д. Вот как легко можно использовать Анализ «что если» в Excel.
Подписывайтесь на нас в социальных сетях, оставляйте комментарии к статье. Надеюсь пример использования анализа «что если» в Excel Вам понравился.
Excel’s What-If Analysis Scenario Manager helps you compare multiple data sets and decide based on data analysis.
Excel has many powerful tools, including the What-If Analysis, which helps you perform different types of mathematical calculations. It allows you to experiment with different formula parameters to explore the effects of variations in the result.
So, instead of dealing with complex mathematical calculations to get the answers you seek, you can simply use the What-If Analysis in Excel.
When Is What-If Analysis Used?
You should use the What-If Analysis if you would like to see how a change of value in your cells will affect the outcome of the formulas in your worksheet.
Excel provides different tools that will help you perform all sorts of analyses that fit your needs. So it all comes down to what you want.
For example, you can use the What-If Analysis if you want to build two budgets, both of which will require a certain level of revenue. With this tool, you could also determine what sets of values you need in order to produce a certain result.

There are three kinds of What-If Analysis tools that you have in Excel: Goal Seek, Scenarios, and Data Tables.
Goal Seek
When you create a function or a formula in Excel, you put different parts together to get appropriate results. However, Goal Seek works oppositely, as you get to start with the result you want.
Goal Seek is most often used if you want to know the value that you need to get a certain result. For example, if you want to calculate the grade, you would need to get in school in order for you to pass the class.
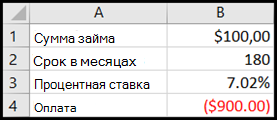
A simple example would look like this. If you would like your final grade to have an average of 70 points, you first need to calculate your overall average, including the empty cell.
You can do that with this function:
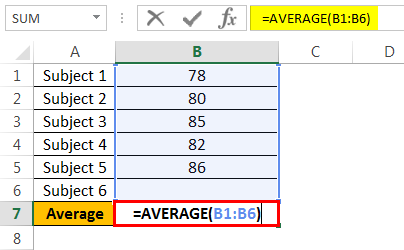
<strong>=AVERAGE(B2:B6)</strong>
Once you know your average, you should go to Data > What-If Analysis > Goal Seek. Then calculate the Goal Seek using the information that you have. In this case, that would be:
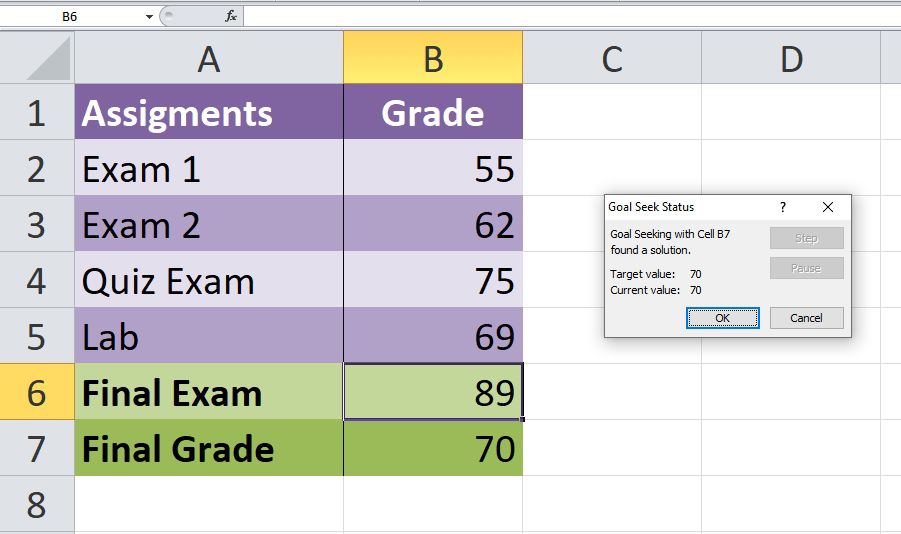
If you want to learn more about it, you can check out our following guide on Goal Seek.
Scenarios
In Excel, Scenarios allow you to substitute values for multiple cells simultaneously (up to 32). You can create many Scenarios and compare them without having to change the values manually.
For example, if you have the worst and the best-case scenarios, you can use the Scenario Manager in Excel to create both of these scenarios.
In both scenarios, you need to specify the cells that change values, and the values that might be used for that scenario. You can find a good example of this on Microsoft’s website.
Data Tables
Unlike Goal Seek or Scenarios, this option allows you to see multiple results simultaneously. You can replace one or two variables in a formula with as many different values as you like and then see the results in a table.
This makes it easy to examine a range of possibilities with just one glance. However, a Data Table cannot accommodate more than 2 variables. If that is what you were hoping for, you should use Scenarios instead.

Visualize Your Data With What-If Analysis in Excel
If you use Excel frequently, you will discover many formulas and functions that make life easier. The What-If Analysis is just one of many examples that can simplify your most complex mathematical calculations.
With the What-If Analysis in Excel, you get to experiment with different answers to the same question, even if your data is incomplete. To get the most out of the What-If Analysis, you should be fairly comfortable with functions and formulas in Excel.
What-If Analysis in Excel is a tool that helps us create different models, scenarios, and Data Tables. This article will look at the ways of using What-If Analysis.
Table of contents
- What is a What-If Analysis in Excel?
- #1 Scenario Manager in What-If Analysis
- #2 Goal Seek in What-If Analysis
- #3 Data Table in What-If Analysis
- Things to Remember
- Recommended Articles
We have three parts of What-If Analysis in Excel. They are as follows:
- Scenario Manager
- Goal Seek in Excel
- Data Table in Excel
You can download this What-If Analysis Excel Template here – What-If Analysis Excel Template
#1 Scenario Manager in What-If Analysis
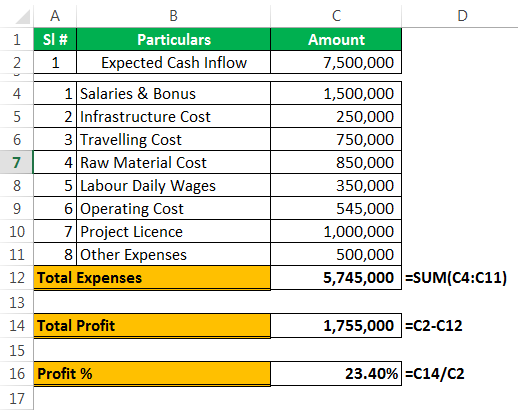
As a business head, it is important to know the different scenarios of your future project. Based on the scenarios, the business head will make decisions. For example, you are going to undertake one of the important projects. You have done your homework and listed all the possible expenditures from your end, and below is the list of all your expenses.
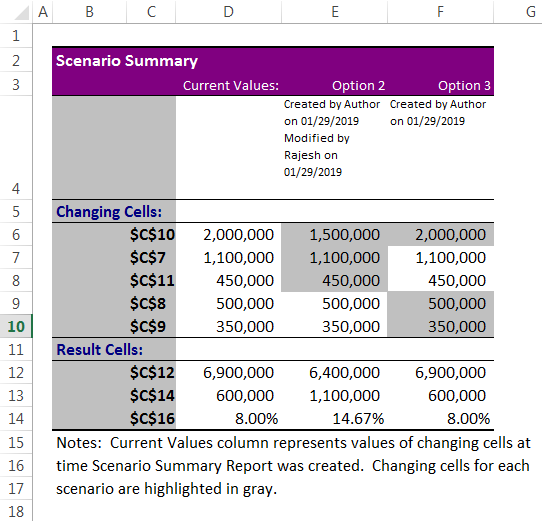
The expected cash flow from this project is $75 million, which is in cell C2. Total expenses comprise all your fixed and variable expenses, the total cost is $57.45 million in cell C12. Total profit is $17.55 million in cell C14, and profit % is 23.40% of your cash inflow.
It is the basic scenario of your project. Now, you need to know the profit scenario if some of your expenses increase or decrease.
Scenario 1
- In a general case scenario, you have estimated the “Project License” cost to be $10 million, but you are sure anticipating it to be $15 million
- Raw material costs to be increased by $2.5 million
- Other expensesOther expenses comprise all the non-operating costs incurred for the supporting business operations. Such payments like rent, insurance and taxes have no direct connection with the mainstream business activities.read more to be decreased by 50 thousand.
Scenario 2
- The “Project Cost” to be at $20 million
- The “Labor Daily Wages” to be at $5 million
- The “Operating Cost” is to be at $3.5 million
Now, you have listed out all the scenarios in the form. Based on these scenarios, you need to create a table about how it will impact your profit and profit %.
To create What-If Analysis scenarios, follow the below steps.
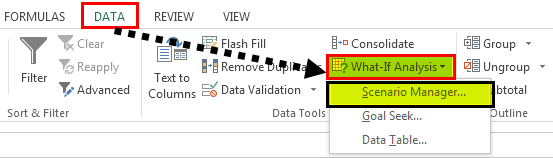
- Go to DATA > What-If Analysis > Scenario Manager.
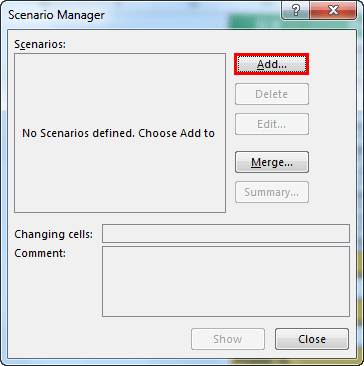
- Once you click “Scenario Manager,” it will show you below the dialog box.
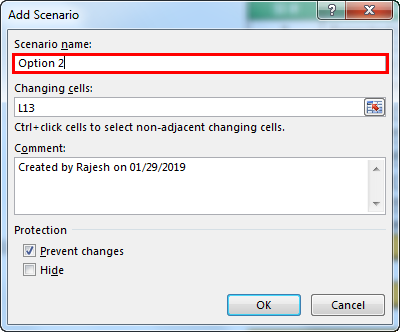
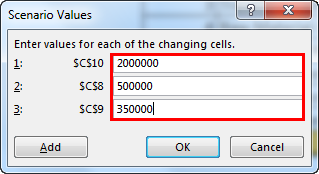
- Click on “Add.” Then, give “Scenario name.”
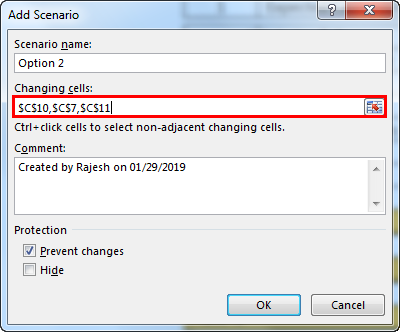
- In changing cells, select the first scenario changes you have listed out. The changes are Project License (cell C10) at $15 million, Raw Material Cost (cell C7) at $11 million, and Other Expenses (cell C11) at $4.5 million. Mention these three cells here.
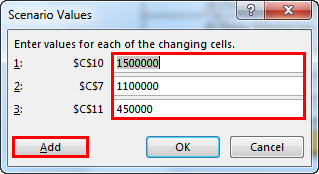
- Click on “OK.” It will ask you to mention the new values as listed in scenario 1.
- Do not click on “OK” but click on “OK Add.” It will save this scenario for you.
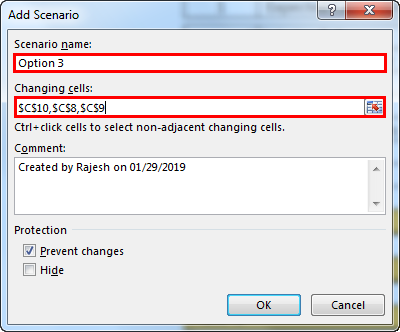
- Now, it will ask you to create one more scenario. As we listed in scenario 2, make the changes. This time we need to change Project Cost (C10), Labour Cost (C8), and Operating Cost (C9).
- Now, add new values here.
- Now click on “OK.” It will show all the scenarios we have created.
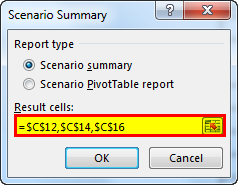
- Click on “Scenario summary.” It will ask you which result cells you want to change. Here, we need to change the Total Expense Cell (C12), Total Profit Cell (C14), and Profit % cell (C16).
- Click on “OK.” It will create a summary report for you in the new worksheet.
Total Excel has created three scenarios even though we have supplied only two scenario changes because Excel will show existing reports as one scenario.
From this table, we can easily see the impact of changes in pour profit %.
#2 Goal Seek in What-If Analysis
Now, we know the Scenario Manager’s advantage. What-if-Analysis Goal Seek can tell you what you must do to achieve the target.
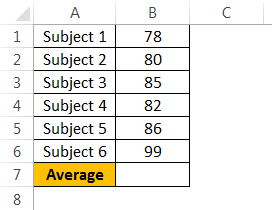
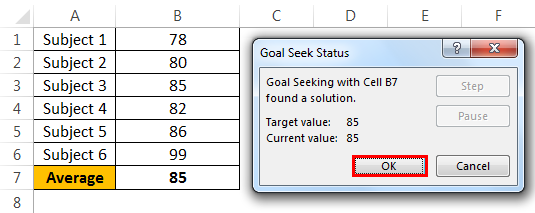
Andrew is a class 10th student. His target is to achieve an average score of 85 in the final exam. He has already completed 5 exams and left with only 1 exam. Therefore, in the completed 5 exams.
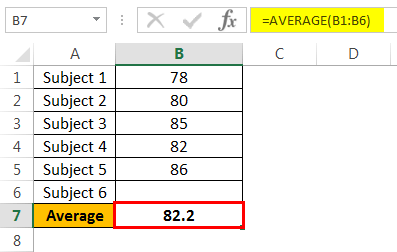
To calculate the current average, apply the average formula in the B7 cell.
The current average is 82.2.
Andrew’s GOAL is 85. His current average is 82.2. He is short by 3.8 with one exam.
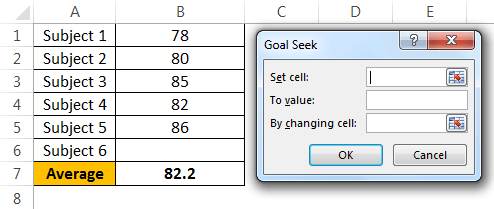
Now, the question is how much he has to score in the final exam to eventually get an overall average of 85. It can be found by the What-If Analysis GOAL SEEK tool.
- Step 1: Go to DATA > What-If Analysis > Goal Seek.
- Step 2: It will show you below the dialog box.
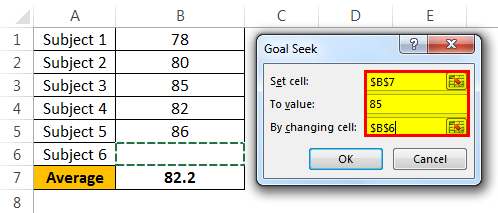
- Step 3: Here, we need to set the cell first. “Set cell” is nothing but which cell we need for the final result, i.e., our overall average cell (B7). Next is “To value.” Again, Andrew’s overall average GOAL is nothing but for what value we need to set the cell (85).
The next and final step is changing which cell you want to see the impact on. So, we need to change cell B6, the cell for the final subject’s score.
- Step 4: Click on “OK.” Excel will take a few seconds to complete the process, but it eventually shows the result like the one below.
Now, we have our results here. To get an overall average of 85, Andrew has to score 99 in the final exam.
#3 Data Table in What-If Analysis
We have already seen two wonderful techniques under What-If Analysis in Excel. First, the Data Table can create different scenario tables based on the variable change. We have two kinds of Data Tables here: one variable Data Table and a “Two-variable data tableA two-variable data table helps analyze how two different variables impact the overall data table. In simple terms, it helps determine what effect does changing the two variables have on the result.read more.” This article will show you One variable data table in ExcelOne variable data table in excel means changing one variable with multiple options and getting the results for multiple scenarios. The data inputs in one variable data table are either in a single column or across a row.read more.
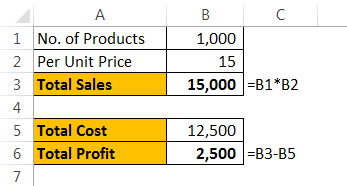
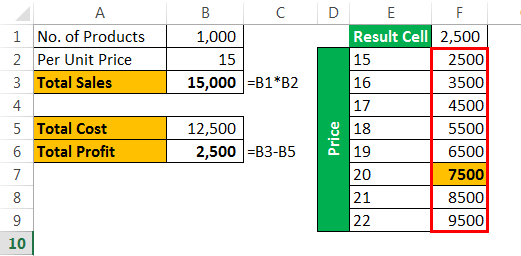
Assume you are selling 1,000 products at ₹15, your total anticipated expense is ₹12,500, and your profit is ₹2,500.
You are not happy with the profit you are getting. Your anticipated profit is ₹7,500. You have decided to increase your per-unit price to increase your profit, but you do not know how much you need to increase.
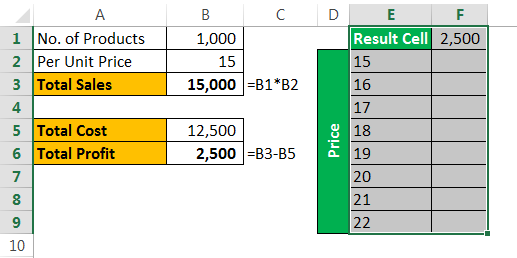
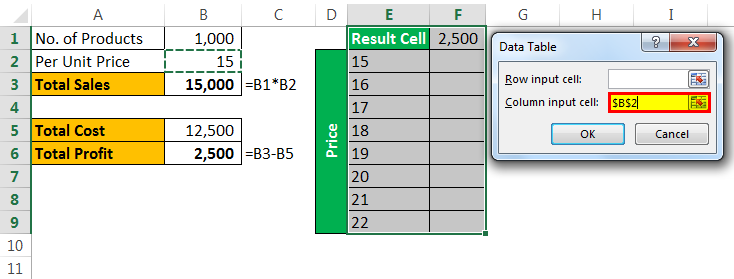
Data tables can help you. Create a table below.
Now, in the cell, F1 links to the “Total Profit” cell, B6.
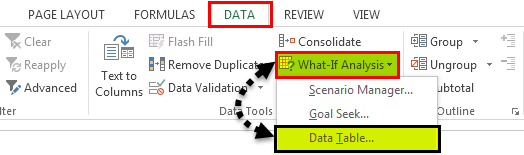
- Step 1: Select the newly created table.
- Step 2: Go to DATA > What-if Analysis > Data Table.
- Step 3: Now, you will see below dialog box.
- Step 4: Since we are showing the result vertically, leave the ”Row input cell.” In the “Column input cell,” select cell B2, which is the original selling price.
- Step 5: Click on “OK” to get the results. It will list out profit numbers in the new table.
So, we have our Data Table ready. To profit from ₹7,500, you need to sell at ₹20 per unit.
Things to Remember
- The What-If Analysis data table can be performed with two variable changes. Refer to our article on What-If Analysis two-variable Data Table.
- What-If Analysis Goal Seek takes a few seconds to perform calculations.
- What-If Analysis Scenario Manager can give a summary with input numbers and current values together.
Recommended Articles
This article is a guide to What-If Analysis in Excel. Here, we discuss three types of What-If Analysis in Excel such as 1) Scenario Manager, 2) Goal Seek, 3) Data Tables along with practical examples, and a downloadable Excel template. You may learn more about Excel from the following articles: –
- Pareto Analysis in ExcelA pareto chart is a graph which is a combination of a bar graph and a line graph, indicates the defect frequency and its cumulative impact. It helps in finding the defects to observe the best possible and overall improvement measure.read more
- Goal Seek in VBA
- Sensitivity Analysis in Excel
Create Different Scenarios | Scenario Summary | Goal Seek
What-If Analysis in Excel allows you to try out different values (scenarios) for formulas. The following example helps you master what-if analysis quickly and easily.
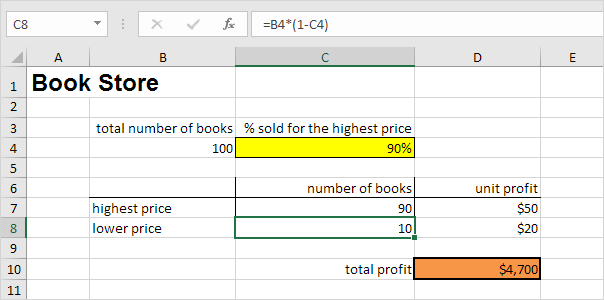
Assume you own a book store and have 100 books in storage. You sell a certain % for the highest price of $50 and a certain % for the lower price of $20.
If you sell 60% for the highest price, cell D10 calculates a total profit of 60 * $50 + 40 * $20 = $3800.
Create Different Scenarios
But what if you sell 70% for the highest price? And what if you sell 80% for the highest price? Or 90%, or even 100%? Each different percentage is a different scenario. You can use the Scenario Manager to create these scenarios.
Note: You can simply type in a different percentage into cell C4 to see the corresponding result of a scenario in cell D10. However, what-if analysis enables you to easily compare the results of different scenarios. Read on.
1. On the Data tab, in the Forecast group, click What-If Analysis.
2. Click Scenario Manager.
The Scenario Manager dialog box appears.
3. Add a scenario by clicking on Add.
4. Type a name (60% highest), select cell C4 (% sold for the highest price) for the Changing cells and click on OK.
5. Enter the corresponding value 0.6 and click on OK again.
6. Next, add 4 other scenarios (70%, 80%, 90% and 100%).
Finally, your Scenario Manager should be consistent with the picture below:
Note: to see the result of a scenario, select the scenario and click on the Show button. Excel will change the value of cell C4 accordingly for you to see the corresponding result on the sheet.
Scenario Summary
To easily compare the results of these scenarios, execute the following steps.
1. Click the Summary button in the Scenario Manager.
2. Next, select cell D10 (total profit) for the result cell and click on OK.
Result:
Conclusion: if you sell 70% for the highest price, you obtain a total profit of $4100, if you sell 80% for the highest price, you obtain a total profit of $4400, etc. That’s how easy what-if analysis in Excel can be.
Goal Seek
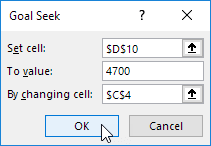
What if you want to know how many books you need to sell for the highest price, to obtain a total profit of exactly $4700? You can use Excel’s Goal Seek feature to find the answer.
1. On the Data tab, in the Forecast group, click What-If Analysis.
2. Click Goal Seek.
The Goal Seek dialog box appears.
3. Select cell D10.
4. Click in the ‘To value’ box and type 4700.
5. Click in the ‘By changing cell’ box and select cell C4.
6. Click OK.
Result. You need to sell 90% of the books for the highest price to obtain a total profit of exactly $4700.
Note: visit our page about Goal Seek for more examples and tips.