Проверка переменных и выражений с помощью встроенных функций VBA Excel: IsArray, IsDate, IsEmpty, IsError, IsMissing, IsNull, IsNumeric, IsObject.
Проверка переменных и выражений
Встроенные функции VBA Excel — IsArray, IsDate, IsEmpty, IsError, IsMissing, IsNull, IsNumeric, IsObject — проверяют значения переменных и выражений на соответствие определенному типу данных или специальному значению.
Синтаксис функций для проверки переменных и выражений:
Expression — выражение, переменная или необязательный аргумент для IsMissing.
Все функции VBA Excel для проверки переменных и выражений являются логическими и возвращают значение типа Boolean — True или False.
Функция IsArray
Описание функции
Функция IsArray возвращает значение типа Boolean, указывающее, является ли переменная массивом:
- True — переменная является массивом;
- False — переменная не является массивом.
Пример с IsArray
|
Sub Primer1() Dim arr1(), arr2(1 To 10), arr3 Debug.Print IsArray(arr1) ‘Результат: True Debug.Print IsArray(arr2) ‘Результат: True Debug.Print IsArray(arr3) ‘Результат: False arr3 = Array(1, 2, 3, 4, 5) Debug.Print IsArray(arr3) ‘Результат: True End Sub |
Как показывает пример, функция IsArray возвращает True и в том случае, если переменная только объявлена как массив, но еще не содержит значений.
Функция IsDate
Описание функции
Функция IsDate возвращает логическое значение, указывающее, содержит ли переменная значение, которое можно интерпретировать как дату:
- True — переменная содержит дату, выражение возвращает дату, переменная объявлена с типом As Date;
- False — в иных случаях.
Пример с IsDate
|
Sub Primer2() Dim d1 As String, d2 As Date Debug.Print IsDate(d1) ‘Результат: False Debug.Print IsDate(d2) ‘Результат: True d1 = «14.01.2023» Debug.Print IsDate(d1) ‘Результат: True Debug.Print IsDate(Now) ‘Результат: True End Sub |
Функция IsEmpty
Описание функции
Функция IsEmpty возвращает значение типа Boolean, указывающее, содержит ли переменная общего типа (As Variant) значение Empty:
- True — переменная содержит значение Empty;
- False — переменной присвоено значение, отличное от Empty.
Пример с IsEmpty
|
Sub Primer3() Dim s As String, v As Variant Debug.Print IsEmpty(s) ‘Результат: False Debug.Print IsEmpty(v) ‘Результат: True v = 125 Debug.Print IsEmpty(v) ‘Результат: False Range(«A1»).Clear Debug.Print IsEmpty(Range(«A1»)) ‘Результат: True Range(«A1») = 123 Debug.Print IsEmpty(Range(«A1»)) ‘Результат: False End Sub |
Как видно из примера, функцию IsEmpty можно использовать для проверки ячеек на содержание значения Empty (пустая ячейка общего формата).
Функция IsError
Описание функции
Функция IsError возвращает логическое значение, указывающее, является ли аргумент функции значением ошибки, определенной пользователем:
- True — аргумент функции является значением ошибки, определенной пользователем;
- False — в иных случаях.
Пользователь может определить одну или несколько ошибок для своей процедуры или функции с рекомендациями действий по ее (их) исправлению. Возвращается номер ошибки с помощью функции CVErr.
Пример с IsError
Допустим, пользователь определил, что ошибка №25 означает несоответствие аргумента функции Vkuba числовому формату:
|
Function Vkuba(x) If IsNumeric(x) Then Vkuba = x ^ 3 Else Vkuba = CVErr(25) End If End Function Sub Primer4() Debug.Print Vkuba(5) ‘Результат: 125 Debug.Print IsError(Vkuba(5)) ‘Результат: False Debug.Print Vkuba(«пять») ‘Результат: Error 25 Debug.Print IsError(Vkuba(«пять»)) ‘Результат: True End Sub |
Функция IsMissing
Описание функции
Функция IsMissing возвращает значение типа Boolean, указывающее, был ли необязательный аргумент типа данных Variant передан процедуре:
- True — если в процедуру не было передано значение для необязательного аргумента;
- False — значение для необязательного аргумента было передано в процедуру.
Пример с IsMissing
|
Function Scepka(x, Optional y) If Not IsMissing(y) Then Scepka = x & y Else Scepka = x & » (а необязательный аргумент не подставлен)» End If End Function Sub Primer5() Debug.Print Scepka(«Тропинка», » в лесу») ‘Результат: Тропинка в лесу Debug.Print Scepka(«Тропинка») ‘Результат: Тропинка (а необязательный аргумент не подставлен) End Sub |
Функция IsNull
Описание функции
Функция IsNull возвращает логическое значение, указывающее, является ли Null значением переменной или выражения:
- True — значением переменной или выражения является Null;
- False — в иных случаях.
Пример с IsNull
Функция IsNull особенно необходима из-за того, что любое условие с выражением, в которое входит ключевое слово Null, возвращает значение False:
|
Sub Primer6() Dim Var Var = Null If Var = Null Then Debug.Print Var ‘Результат: «» If Var <> Null Then Debug.Print Var ‘Результат: «» If IsNull(Var) Then Debug.Print Var ‘Результат: Null End Sub |
Функция IsNumeric
Описание функции
Функция IsNumeric возвращает значение типа Boolean, указывающее, можно ли значение выражения или переменной рассматривать как число:
- True — если аргумент функции может рассматриваться как число;
- False — в иных случаях.
Пример с IsNumeric
|
Sub Primer7() Debug.Print IsNumeric(«3,14») ‘Результат: True Debug.Print IsNumeric(«четыре») ‘Результат: False End Sub |
Функция IsObject
Описание функции
Функция IsObject возвращает логическое значение, указывающее, является ли переменная объектной:
- True — переменная содержит ссылку на объект или значение Nothing;
- False — в иных случаях.
Функция IsObject актуальна для переменных типа Variant, которые могут содержать как ссылки на объекты, так и значения других типов данных.
Пример с IsObject
|
Sub Primer8() Dim myObj As Object, myVar As Variant Debug.Print IsObject(myObj) ‘Результат: True Debug.Print IsObject(myVar) ‘Результат: False Set myVar = ActiveSheet Debug.Print IsObject(myVar) ‘Результат: True End Sub |
VBA IsNumeric
IsNumber an excel function is used for identifying whether the cell content is a number or not. A numeric value can be a whole value or integer. An IsNumeric function can also be performed in VBA as well. In VBA this is available with the name “IsNumeric“. IsNumeric works in the same manner as IsNumber does. It analyzes the cell value and returns the answer whether it is a number or not.
IsNumeric considers only Boolean, which only gives result in the form of TRUE and FALSE.
Syntax of IsNumeric in Excel VBA
VBA IsNumeric has the following syntax in VBA:
How to Use Excel VBA IsNumeric?
We will learn how to use a VBA IsNumeric with few examples in excel.
You can download this VBA IsNumeric Excel Template here – VBA IsNumeric Excel Template
VBA IsNumeric – Example #1
Let’s see an easy example where we will select a cell with any content and in a separate cell, we will see whether cell content is a Number or Not.
Step 1: For this open, a new module in the VBA window under the Insert menu tab as shown below.
Step 2: Write a Subcategory in the name of a performed function or in any other name as shown below.
Code:
Sub VBA_Isnumeric1() End Sub
Step 3: Now we will use the If-Else loop for this complete condition. For this open and close If bracket as shown below.
Code:
Sub VBA_Isnumeric1() If End If End Sub
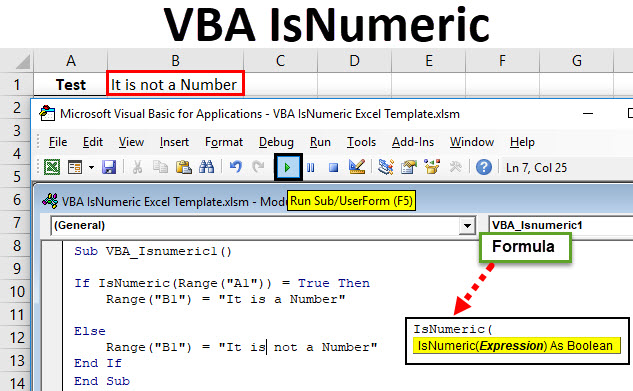
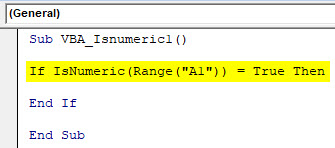
Step 4: Now in If write and select IsNumeric function and select any Range cell from where we will analyze the content. Here we have selected cell A1 as TRUE.
Code:
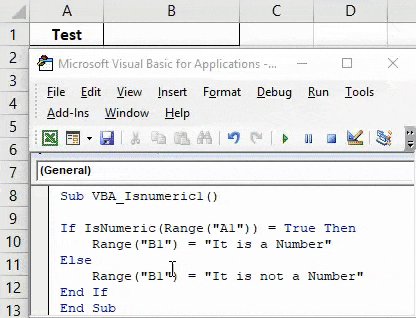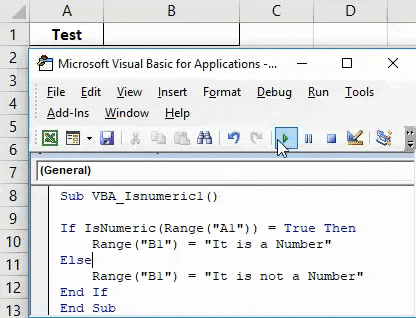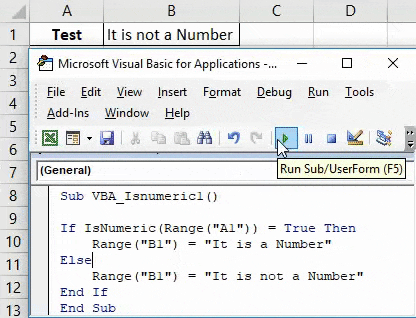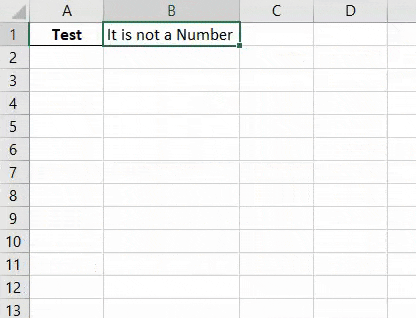
Sub VBA_Isnumeric1() If IsNumeric(Range("A1")) = True Then End If End Sub
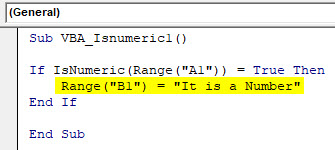
Step 5: If cell value at cell A1 is TRUE it means it is a number then we can choose writing any sentence in cell B1 which will say “It is a Number” or put any text as per your choice.
Code:
Sub VBA_Isnumeric1() If IsNumeric(Range("A1")) = True Then Range("B1") = "It is a Number" End If End Sub
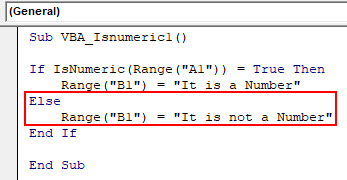
Step 6: Now in Else line of code consider writing what we could see when IF condition doesn’t work. We are selecting cell B1 where we will see the output statement of cell A1 as “It is not a Number” as shown below.
Code:
Sub VBA_Isnumeric1() If IsNumeric(Range("A1")) = True Then Range("B1") = "It is a Number" Else Range("B1") = "It is not a Number" End If End Sub
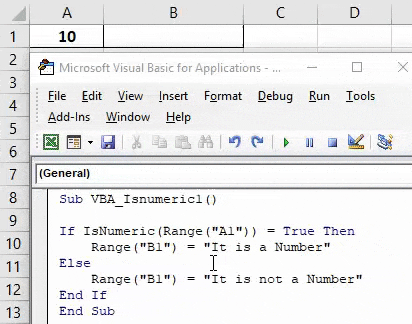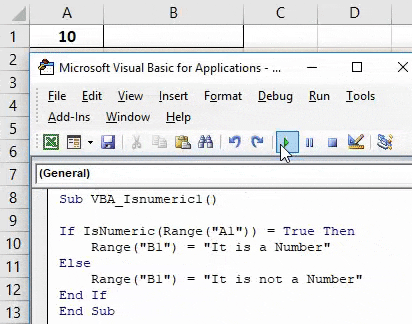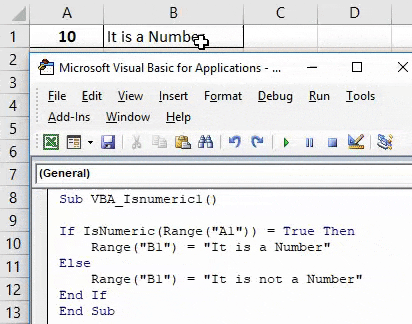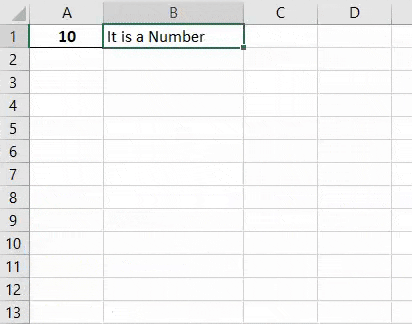
Step 7: Once done then compile and run the complete code. As we can see in the below screenshot for the cell content A1 we got the statement as “It is a Number” in cell B1.
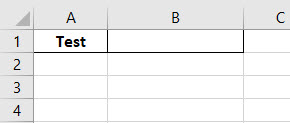
Step 8: Now let’s replace 10 in cell A1 with a text like “Test” and see what we get.
Step 9: Now again run the complete code.
As we can see in the above screenshot, for the cell content A1 we got the statement as “It is not a number” for content “Test” which means cell A1 doesn’t have a number in it.
VBA IsNumeric – Example #2
There is another way to add IsNumeric. By far we all know that Boolean function is used for TRUE/ FALSE on the basis of what we feed and define the condition. Here we will use Boolean to calculate IsNumeric for any content of the cell.
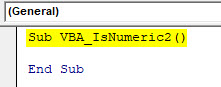
Step 1: Write a Subcategory in the name of a performed function as shown below.
Code:
Sub VBA_IsNumeric2() End Sub
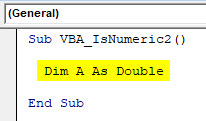
Step 2: Now define a dimension “DIM” as A and assign it to Double. We can assign it as Integer or Long too. But that would only consider whole numbers and long text/numbers. Double is used where we are expecting to get numbers in decimal forms.
Code:
Sub VBA_IsNumeric2() Dim A As Double End Sub
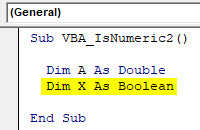
Step 3: Now define one more dimension “DIM” as X. And assign it as Boolean. We can consider any word, name or alphabet for defining dimensions in VBA.
Code:
Sub VBA_IsNumeric2() Dim A As Double Dim X As Boolean End Sub
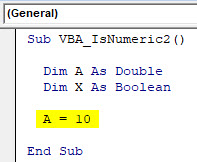
Step 4: Now for Dim A double, first assign the value as 10 which is a whole number.
Code:
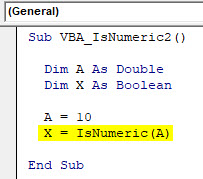
Sub VBA_IsNumeric2() Dim A As Double Dim X As Boolean A = 10 End Sub
Step 5: Now for Boolean X, use IsNumeric function and assign defined Double A into the brackets of IsNumeric. By doing this IsNumeric will fetch the value stored in Dim A and analyze whether that value is a number or not.
Code:
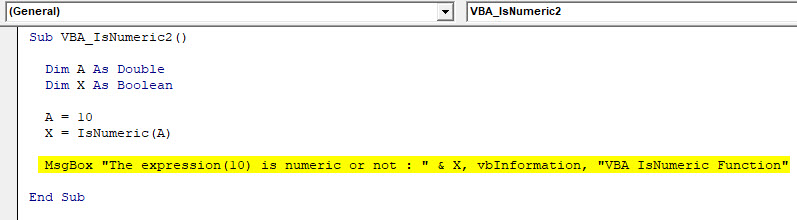
Sub VBA_IsNumeric2() Dim A As Double Dim X As Boolean A = 10 X = IsNumeric(A) End Sub
Step 6: To get the answer of an analysis done by Isnumeric, we will assign it to a message box where we will see the result.
Code:
Sub VBA_IsNumeric2() Dim A As Double Dim X As Boolean A = 10 X = IsNumeric(A) MsgBox "The expression(10) is numeric or not : " & X, vbInformation, "VBA IsNumeric Function" End Sub
Step 7: Once done compile and run the code.
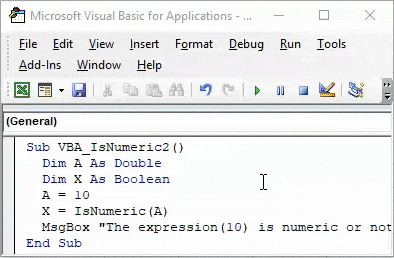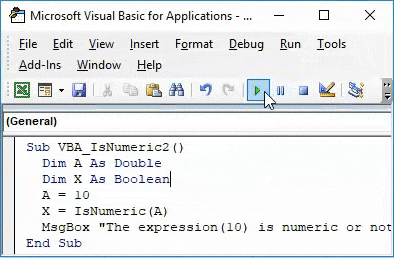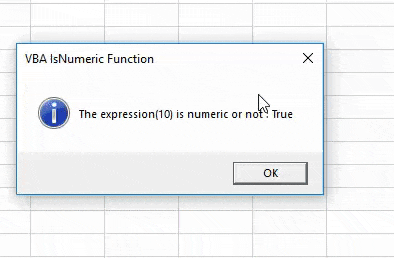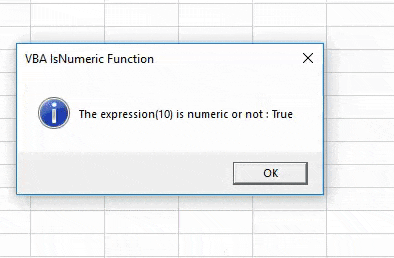
As we can see a pop-up dialog box in the above image, the expression(10) is a TRUE numeric value.
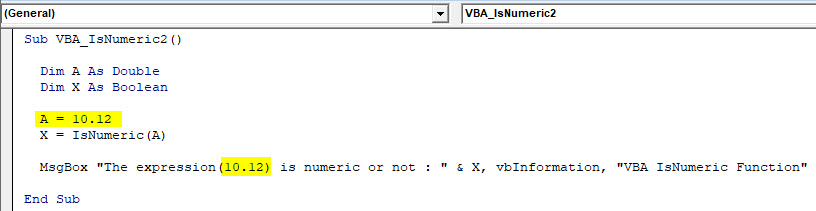
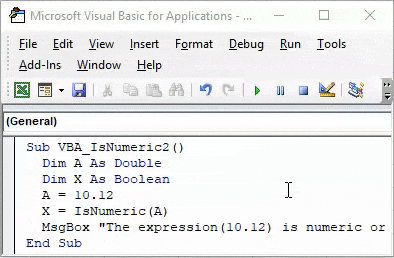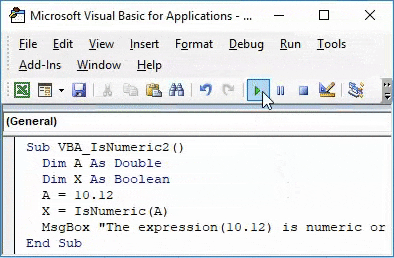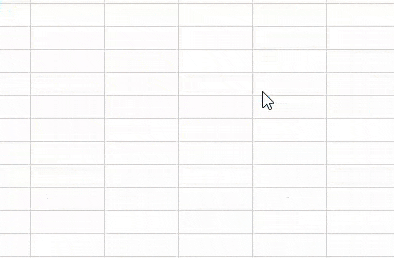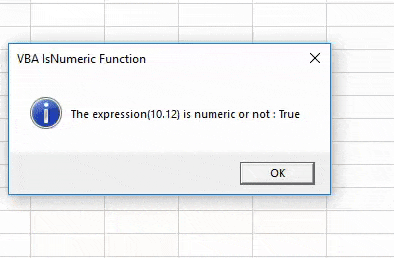
Step 8: Now let’s change the value and put some decimal value in IsNumeric as shown below and see what output we get. Here we have to change the value of A as 10.12 and updated the message box with expression(10.12).
Code:
Sub VBA_IsNumeric2() Dim A As Double Dim X As Boolean A = 10.12 X = IsNumeric(A) MsgBox "The expression(10.12) is numeric or not : " & X, vbInformation, "VBA IsNumeric Function" End Sub
Step 9: Now again compile and run the complete code.
We will again get TRUE for the value 10.12 which is a decimal value.
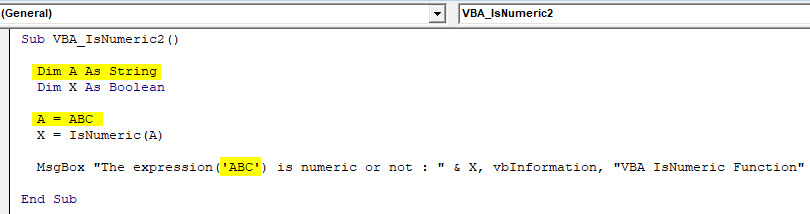
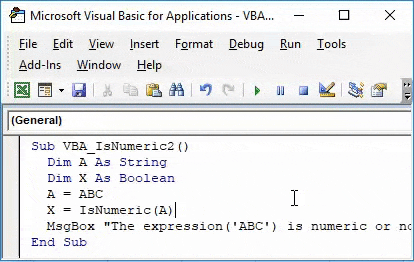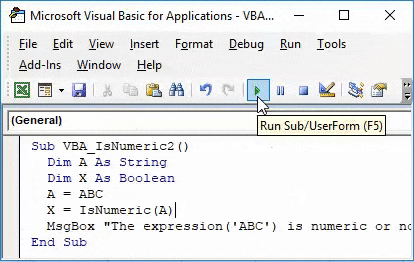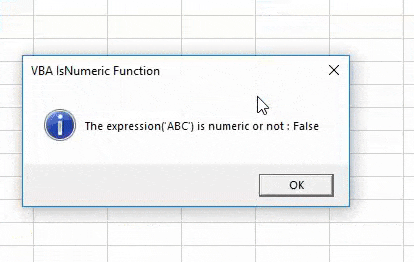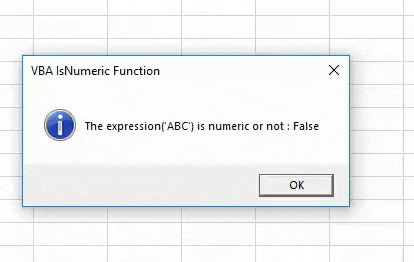
Step 10: Now let’s see if the current defined syntax of IsNumeric still works for other than numbers or not. For this, we need to change the Dim A as String which means we will be entering the Text value here. And change value entered for A. We have considered sample value as “ABC”. Make all necessary changes in related fields where we can place text instead of numbers and keep the rest of the things as it is.
Code:
Sub VBA_IsNumeric2() Dim A As String Dim X As Boolean A = ABC X = IsNumeric(A) MsgBox "The expression('ABC') is numeric or not : " & X, vbInformation, "VBA IsNumeric Function" End Sub
Step 11: After that compile and run the complete code.
Pros of Excel VBA IsNumeric
- It is so easy to apply IsNumeric in VBA. It is as simple as applying Isnumber through insert function.
- IsNumeric and IsNumber give the same result.
Cons of Excel VBA IsNumeric
- Applying example-2 where we need to insert text makes the simple process lengthy.
Things To Remember
- Recording a macro is also a way to perform IsNumeric function in VBA.
- Save the file in Macro-Enabled Excel, This is the best way to avoid losing written code.
- Best way to avoid any error while running the code is to first compile the complete code before we fix it as final.
- Assigning the created code into a button is also a way to perform created macro quickly, this saves time.
- If you are applying IsNumeric by example-2 method then remember to keep text in the single quote (‘Text’) otherwise it will give an error.
- As IsNumeric in VBA is used, in excel it used in the name of IsNumber.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to VBA IsNumeric. Here we discussed how to use Excel VBA IsNumeric along with practical examples and downloadable excel template. You can also go through our other suggested articles –
- VBA Dim
- VBA RGB
- VBA IFError
- VBA Login
In VBA, to test whether an expression is a number, the IsNumeric function can be used.
Description
The IsNumeric function evaluates whether the input expression is a number and returns a Boolean value (TRUE or FALSE). It returns True if the entire expression is a number; otherwise, it returns False.
Syntax
IsNumeric(expression)
The input expression is either a numeric expression or a string expression.
VBA examples of IsNumeric
Example 1 – Using IsNumeric with IF-THEN-ELSE
The following VBA function CheckNumeic uses IsNumeric to test whether input1 is numeric or not with an IF-THEN-ELSE statement.
Function CheckNumeric(ByVal input1) As String
If IsNumeric(input1) = True Then
MyFunction1 = "Input is numeric"
Else
MyFunction1 = "Input is not numeric"
End If
End Function
I would want to draw your attention to line 2. While this line is correct, it is not necessary. Instead, it can be written as:
If IsNumeric(input1) Then
In VBA, whenever you perform a logical test, for the condition of TRUE, you don’t have to type the =TRUE in the statement.
Example2 – Negate the result of IsNumeric
The VBA function below returns the opposite of IsNumeric. The function uses the same IF-THEN-ELSE structure.
Function IsNumericReverse(ByVal input1) As Boolean
If IsNumeric(input1) = True Then
IsNumericReverse = False
Else
IsNumericReverse = True
End If
End Function
However, this entire structure is not necessary. Instead, the function can be simplified as follows. The Not logical operator can be used to reverse (negate) the answer of IsNumeric, which serves the objective of the function in this case.
Function IsNumericReverse(ByVal input1) As Boolean
IsNumericReverse = Not (IsNumeric(input1))
End Function
Example 3 – VBA action if not numeric
The VBA function counts the number of non-numeric cells in the input range. In line 5, note the use of Not with IsNumeric. In the sentence structure here, putting a space after Not is enough, which is equivalent to using a bracket after Not to wrap the condition being tested.
Function countNonNumeric(range1 As Range) As Long
Dim cell As Range
Dim counter As Long
For Each cell In range1.Cells
If Not IsNumeric(cell.Value) Then 'use Not to test for non-numeric
counter = counter + 1
End If
Next
countNonNumeric = counter
End Function
Special Case with Blank
When using IsNumeric, you need to be aware that “blank” (string of zero length) does not mean zero (0) and it is considered to be non-numeric:
IsNumeric("") returns False
Therefore, when you write your macro, if you want to treat blank as numeric, you may have to use conditional statements to handle the case of blank string inputs.
Special Case with Dates
Another special case with IsNumeric is the treatment of date inputs. Most people conceptually think dates are numeric (after all, they can be converted into date-serials in the computer). However the IsNumeric function in VBA considers dates as non-Numeric:
IsNumeric("10/2/2020") returns False
Even if you try to input a date truly in Date format, IsNumeric still returns False:
IsNumeric(DateSerial(2020, 10, 2)) returns False
Therefore, you may also need to use conditional statements to handle the case of dates expressions.
Special Case with Time
Handling of time expressions by the ISNUMERIC is difficult to manage, or I would describe it as unpredictable. Therefore, when you input expressions contain time expressions, you must test your macro thoroughly.
There are three possibilities with time expressions. Let’s experiment with the macro below. In cell A1, we place a time of “3:00:00 AM” first. Then we run the macro which test 3 cases:
- time in form of string (variable x1)
- time in form of time value (variable x2)
- time placed in a cell in an Excel sheet (variable x3)
Sub TimeCases()
Dim y
x1 = IsNumeric("3:00:00 AM")
x2 = IsNumeric(TimeSerial(3, 0, 0))
y = Range("A1").Value
x3 = IsNumeric(y)
MsgBox x1 &amp;amp;amp;amp; Chr(10) &amp;amp;amp;amp; x2 &amp;amp;amp;amp; Chr(10) &amp;amp;amp;amp; x3
End Sub
Run the macro and the answers will be displayed in the Msgbox:
Calling Excel Worksheet Function ISNUMBER() in VBA
As an alternative to IsNumeric in VBA, you may call the Excel worksheet function ISNUMBER() in your macro. There are two ways to do this. See line 2 and line 3 in the VBA function below, which do the same job. (I personally prefer Method 2.)
Function CallIsNumber(input1) As Boolean x = WorksheetFunction.IsNumber(input1) 'Method 1' x = Application.IsNumber(input1) 'Method 2' CallIsNumber = x End Function
VBA ISNUMERIC vs ISNUMBER Worksheet Function
Although you can either use IsNumeric or Excel worksheet function ISNUMBER to check whether an input expression is numeric, you have to be aware of the differences between the two methods in order to program your macros correctly to produce expected result.
| Expression | Date type of expression | ISNUMERIC returns (VBA) | ISNUMBER returns (worksheet function) |
| 123 | Number | TRUE | TRUE |
| “123” | Number in form of string | TRUE | FALSE |
| 12/2/2020 | Date | FALSE | TRUE |
| “12/2/2020” | Date in form of String | FALSE | FALSE |
| DateSerial(2020,10,2) | Date in form of Date Value | FALSE | FALSE |
| 3:00:00 AM | Time placed in a cell | TRUE | TRUE |
| “3:00:00 AM” | Time in form of String | FALSE | FALSE |
| TimeSerial(3, 0,0) | Time in form of Time Value | FALSE | FALSE |
| “” (blank) | String | FALSE | TRUE |
See also:
- Else if in VBA
Return to VBA Code Examples
This tutorial will teach you how to use the IsNumeric and IsNumber functions in VBA to check if values are numbers.
IsNumeric is a built-in VBA function, while IsNumber is an Excel function which can be called from VBA code.
Difference between IsNumber and IsNumeric in VBA
IsNumber checks if a value is stored as a number. Whereas, IsNumeric checks if a value can be converted into a number.
For example, if you pass a blank cell as a parameter, IsNumber will return FALSE, while IsNumeric will return TRUE. Also, if you pass a cell containing number stored as a text, IsNumber will return FALSE and IsNumeric TRUE.
You need to pay attention to these limitations of both functions and decide in which cases is better to use IsNumeric and when IsNumber.
Using IsNumeric in VBA
IsNumeric is the VBA function which checks if a value is numeric and returns a Boolean TRUE or FALSE as a result.
The function can take a variable or a cell value.
Here is an example of taking a cell value:
If IsNumeric(Sheet1.Range("A1").Value) = True Then
MsgBox "The value in A1 is numeric"
Else
MsgBox "The value in A1 is not numeric"
End IfIn this example, we check if the value from the cell A1 is numeric using the IsNumeric. This function returns the appropriate message, depending on the result of the function.
This next example perform the same operation, except with a variable instead of a cell value:
Dim n as Variant
n = Sheet1.Range("A1").Value
If IsNumeric(n) = True Then
MsgBox "The value in A1 is numeric"
Else
MsgBox "The value in A1 is not numeric"
End IfUsing IsNumber in VBA
IsNumber is an Excel Function, which can be used in VBA. It has an almost similar output as IsNumeric. Let’s look at the example of the IsNumber function:
If Application.WorksheetFunction.IsNumber(Sheet1.Range("A1").Value) = True Then
MsgBox "The value in A1 is numeric"
Else
MsgBox "The value in A1 is not numeric"
End IfAs you can see from the code, the difference is in the syntax when calling the function. Since IsNumber is the Excel function, we need to put Application.WorksheetFunction before the function call.
VBA Coding Made Easy
Stop searching for VBA code online. Learn more about AutoMacro — A VBA Code Builder that allows beginners to code procedures from scratch with minimal coding knowledge and with many time-saving features for all users!
Learn More!
В этом учебном материале вы узнаете, как использовать Excel функцию ISNUMERIC с синтаксисом и примерами.
Описание
Microsoft Excel функция ISNUMERIC возвращает true, если выражение является допустимым числом. В противном случае возвращается false.
Функция ISNUMERIC — это встроенная в Excel функция, которая относится к категории информационных функций. Её можно использовать как функцию VBA в Excel.
В качестве функции VBA вы можете использовать эту функцию в коде макроса, который вводится через редактор Microsoft Visual Basic Editor.
Синтаксис
Синтаксис функции ISNUMERIC в Microsoft Excel:
IsNumeric( expression )
Аргументы или параметры
- expression
- Это вариант, который нужно оценивать как число.
Возвращаемое значение
Функция ISNUMERIC возвращает true, если expression является допустимым числом.
Функция ISNUMERIC возвращает false, если expression не является допустимым числом.
Применение
- Excel для Office 365, Excel 2019, Excel 2016, Excel 2013, Excel 2011 для Mac, Excel 2010, Excel 2007, Excel 2003, Excel XP, Excel 2000
Тип функции
- Функция VBA
Пример (как функция VBA)
Функция ISNUMERIC может использоваться только в коде VBA в Microsoft Excel.
Давайте взглянем на некоторые примеры Excel функции ISNUMERIC, чтобы понять, как использовать Excel функцию ISNUMERIC в коде Excel VBA:
|
IsNumeric(786) Результат: true IsNumeric(«Microsoft») Результат: false IsNumeric(«234») Результат: true IsNumeric(«123xyz») Результат: false |
Например:
|
Dim LValue As Boolean LValue = IsNumeric(«Microsoft») |
В этом примере переменная LValue будет содержать значение false.