Communication is the process of exchanging feelings, information, ideas, messages, and opinions with or without words. Effective interaction is one of the essential life skills.
Communication is extremely crucial to produce better perception. Communication occurs when one person interacts with another person or more than one person.
In the process of communicating, two persons are necessary. Verbal Communication and Written Communication are essential for exchanging thoughts and ideas.
Key Takeaways
- Verbal communication involves using spoken language to convey a message, while written communication involves using written language.
- Verbal communication is more immediate and allows for real-time feedback, while written communication can be more precise and permanent.
- Written communication can be shared with a wider audience and is often used for formal or official communication, while verbal communication is often used for informal or interpersonal communication.
Verbal communication refers to using spoken or written words to convey a message from one person to another and involves using language to share thoughts and information. Written communication refers to exchanging information, ideas, or messages through written words, symbols, or signs.
Want to save this article for later? Click the heart in the bottom right corner to save to your own articles box!
Spoken words, sounds, face-to-face talk, speech, seminars, group discussions, phone call conversations, conferences, and interviews are examples of Verbal Communication. In this case, one can convey the message clearly and get immediate feedback.
The mediums of Written Communication are letters, messages, notes, emails, and many other ways. Written Communication is the most reliable process to convey a message.
Comparison Table
| Parameters of Comparison | Verbal Communication | Written Communication |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | The Verbal Communication process is called Oral Communication, where the idea transmits through spoken words. | Written communication is a form of communication where we use a written or printed format to send a message. |
| Type of Communication | Both formal and informal. | Formal. |
| Medium of Communication | Spoken language, sound, words, face-to-face talk, speech, seminar, group discussion, phone call conversation, conference, interview, radio, etc. | Letters, messages, notes, emails, telegram, newspapers, journals, magazines, office memos, reports, contracts, faxes, etc. |
| Literacy | Not required. | Required. |
| Feedback | One can get immediate feedback. | Sometimes feedback takes time. |
| Personal Presence | Required. | Not required. |
| Transmission of Message | Fast | Slow |
| Proof or Record | Sometimes no proof or record of communication is there. | As it is written, proof or record is there. |
| Chance of Misunderstanding | High possibility of misunderstanding. | Low chance of misunderstanding. |
What is Verbal Communication?
In Verbal Communication we generally use spoken words as the medium of communication.
Spoken language, sound, spoken word, face-to-face talk, speech, phone call conversation, group discussion, conference are examples of Verbal Communication.
The Verbal Communication method is a spontaneous and faster process for communicating. Powerful words are more effective than action.
One can notice someone’s body language, voice tone, expressions during the communication process.
In this process, people talk to each other and communicate by exchanging their feelings, likes, dislikes, views, etc.
Sound is the most strong element in Verbal Communication, as most people have vocal cords that produce sounds.
Good Verbal Communication skills are essential for collaborating and communicating with others. It increases the ability of individuals to share feelings and ideas.
To speak concisely and politely with customers or clients, one needs good Verbal Communication skills.
There are four types of Verbal Communication, Intrapersonal Communication, Interpersonal Communication, Small Group Communication, Public Communication.
Intrapersonal Communication is a form of communication that is very private and confidential. Interpersonal Communication takes place between two persons.
Small-Group Communication takes place within few people. Public Communication develops with so many people through television, social media, live telecast, radio, etc.
Verbal Communication is essential in every aspect of a business. Verbal Communication is suitable for both literate and illiterate people to communicate.
What is Written Communication?
Written Communication develops through sending and receiving a message in written format. We can convey messages through letters, emails, messaging, notes, journals, and many other ways.
It is a very reliable way of communication because we can preserve, carefully drafted, and formal. This mode is preferred in the business and official world. Written Communication is easy to keep.
In this mode, we can convey the message plan fully and very carefully. Very little chance of misinterpretation or wrong delivery of the message as it is organized and words are chosen very carefully.
Written Communication is a lengthy process quick feedback is sometimes not possible. This form of communication is not suitable for illiterate people. It is compatible with literate people.
Written Communication skills are necessary at every stage and essential to get a job. Written Communication relies on grammar, word choice, and punctuation.
The disadvantage of Written Communication is that the sender will never know that the receiver has read the message or not.
A well-written communication helps identify problems and arrive at solutions. In Written Communication, some elements are significant as structure, style, and content.
Main Differences Between Verbal and Written Communication
- Verbal Communication is the process of communicating through spoken words or tone of voice, whereas in Written Communication printed text or typed format of the message is used to communicate.
- Verbal or Oral Communication comparatively faster than Written Communication where one can get immediate feedback.
- In Verbal Communication literacy of the person is not essential. On the other hand, in Written Communication the person must be literate.
- Written Communication is reliable and preserves proper records. On the other hand, Verbal or Oral Communication is proofless.
- In Verbal Communication misinterpretation of the message is possible, whereas in Written Communication there are no possibilities of misinterpretation.
- Verbal Communication is faster than Written Communication.
- Verbal Communication is spontaneous. We can’t erase what we uttered once. On the other hand, in Written Communication we can edit and recheck the message before delivery.
References
- https://books.google.com/books?hl=en&lr=&id=m9-1B8xKJo6IC&oi=fnd&pg=PR11&dq=written+communication&ots=bZn38_bX_a&sig=xpAgMIKdybSicGO5UpwXT15Jr
- https://books.google.com/books?hl=en&lr=&id=RcN5AgAAQBAJ&oi=fnd&pg=PP1&dq=verbal+communication&ots=ZxRJ4dAzP0&sig=xekeWqY7JwpjtxVU_idvownoW-8
Emma Smith holds an MA degree in English from Irvine Valley College. She has been a Journalist since 2002, writing articles on the English language, Sports, and Law. Read more about me on her bio page.
Written and verbal communication are ways of communicating to other people, or your audience, but they both have major differences that set them apart. For example, written communication is done quietly and discreetly, while verbal communication is more open and exposed. Another difference is that written communication is conveyed through words we choose to write or type on a keyboard, while verbal communication is the act of speaking words out of our mouths. Both written and verbal communication involve time; however, written communication is carefully thought out and planned and gives you a longer time to respond. Verbal communication is spontaneous and is spoken at a relatively fast pace.
2 different patterns between written and verbal communication
There are two different patterns between these types of communication. Written communication is accomplished in a criss-cross pattern, meaning both parties have their own way of getting their message across and can be easily misunderstood. Verbal communication carries a pattern that is similar to both parties, due to direct eye contact, mirrored gestures, and most of the time, mutual agreement.
So, now that you’ve learned some differences between the two, let’s take a look and learn more about how each type of communication works.
What written communication means is that you’re communicating to others, through the words you choose to write. This type of communication doesn’t require immediate attention, giving you more time to choose your words, carefully. A lot of thought, feelings, ideas, and opinions go into written communication, because it is considered more personal, private, and informative. The form of written communication also involves critical thinking with information arranged in logical order. Examples of this, include helpful resource information, useful reference guides, and important documentation, such as in court cases. Written communication is also considered formal, due to the growing popularity of new technologies. It is a form of communication that has to be read before it can be understood. This way of communication is not seen, but rather felt, to the receiver. It deals with what is not said. Written communication has a way of speaking to our hearts and is considered more sentimental. Written communication also fills our minds with all kinds of thoughts and questions and leaving us with a visual imagination.
Some forms of written communication
- text messaging (the sender tries to figure out what the receiver will say)
- newspaper
- magazines
- cards
- letters
- books
- Bible
- RSVP’s
- Internet
- Braille
So then, what is verbal communication?
Verbal communication is the interaction of words, physically spoken out loud by using our mouth. This type of communication is translated to another person. Verbal communication also involves actions performed, not only because actions speak louder than words, but also because movement can be interpreted into a message or some meaning. You have to be a great listener to engage in verbal conversation, because the exchange of words are spoken at a fairly fast pace. There is a lot of misinterpretation and misconception with verbal communication, so be careful of what you say.
In relation to written communication, verbal communication is the use of words, shared by both parties. Verbal communication also involves speaking correct grammar, so it can be translated in a way that both parties understand. This type of communication looks for feedback, from the receiver, so expect some questions to be asked for clarification, during your conversation. Because verbal communication can cause a lot of confusion and conflict, it should be expressed precisely and concisely, meaning your message should be clear and easy to understand, as well as accurate.
Two key points to remember with verbal communication
- Think before you speak
- Do not interrupt the speaker, until he or she is finished speaking.
Sometimes, verbal communication is a hard matter

Some people have a hard time, verbally, communicating with others because they lack in the need to be concise. But, don’t let that hinder you from engaging in social activity. If you need help in communicating to others, click here to learn the skills you need to communicate, effectively.
Forms of verbal communication
- Self talk
- talking on the phone
- sign language
- body language, such as a handshake (physically sends out a message, by movement)
- engaging and exchanging thoughts, feelings, ideas, and opinions
- speeches
- discussions
- presentations
- prayer
When written communication proceeds to verbal communication

Oftentimes, written communication leads to verbal communication, especially when clarity is needed or questions need to be asked or answered. In the case of this scenario, information is given and received, in greater detail and follow-ups may occur, as well. Remember, it is considered professional and polite for the receiver to acknowledge all information that is contained within written communication, back to the sender, prior to discussing other non-related topics. FYI: Keep important written communication as documentation and only shred when the information is no longer needed.
Now, let’s look at some ways when writing can be like a conversation, but first…….I have a question to ask. Have you ever read something, from someone, and it felt like you were having a conversation with that person? I have, and it gave me, somewhat, of a friendly vibe. It allowed me to feel a connection with that person, and it made reading the information much easier and more enjoyable, for me.
Now, let’s dive into another way of writing…..
10 tips for writing in a conversational tone
- Use contractions. Contractions help shorten our sentences and prevents them from sounding “robotic”. Here’s an example w/out contractions: The lady did not stop at the store so, she will not be able to bake the cake. – OR – The lady didn’t stop at the store, so she won’t be able to bake the cake. Which one was easier to read and which one took the less amount of time to read? I say the second sentence, wouldn’t you? The first sentence sounds too wordy. Writing in a conversational tone should be written, using short sentences, which leads to tip # 2.
- Shorten your sentences w/ sentence fragments (. ; ! ? ,). Shorter sentences make it easier for your listeners to gather information, quickly. Also, when we speak, we don’t worry too much about the length of our sentences or how we complete them. By using sentence fragments, your writing sounds more like a conversation, making your writing more efficient, casual, and effective.
- Use common words. Jargon or complex words should not be used in conversational writing. i.e. The dining room table looks magnificent! – OR – The dining room table looks wonderful. Which sentence was easier to understand? The second one, right? FYI: Most people are common readers, meaning they don’t know the meaning of fancy words.
- Don’t use slang. When you use slang, you are really not explaining yourself, in full. Slang can be interpreted in so many different ways and gets the reader way off the topic being discussed. Also, slang talk has a hard time reaching a wide variety of people. Some people think slang is rude and dirty and that is doesn’t come from educated people. An example of slang is: That man is eating high on the hog!
- Ask questions. By asking hypothetical questions, you make the reader feel more engaged and like you’re speaking directly to him or her. Asking questions gives your reader something to actively, figure out on their own.
- Use examples, smiley faces, and metaphors. Examples and metaphors help make complex sentences easier to understand. This style of writing also helps to strengthen your message. Smiley faces make your writing seem to be more friendly.
- Don’t go overboard. Writing in a conversational tone isn’t appropriate in some situations, such as in court or when giving specific orders. Try matching your conversation with your audience. In other words, you don’t want to use slang when your audience is using formal words. Now, that would be downright embarrassing!
- Write in first and second person. First person pronouns make your writing more personable, and second person pronouns involves your audience and brings them into the message.
- Write like you’re talking to your best friend. This style releases tension and stress and keeps you from being nervous. You are able to write with much relaxation, allowing your story to flow much easier.
- Read it back to yourself, out loud. Pay attention to the places, in your writing, where you have to stop and take a breath. These are places where you should use sentence fragments or shorten your sentences. Also, take note of any section that sounds awkward to you, or feels like a tongue twister to say. These are the places where you need to rephrase the text to make it sound clearer.
The next time you engage in written communication, take notice of what format it is in, such as formal, first or second person or conversational. And the next time you speak verbally to someone, be aware of what your body language is saying to that person, as well.
Thanks for reading : )
Renae
This kind of communication involves any kind of exchange of information in written form. To put it simply, written language communication is communication by means of written symbols that are communicated by or to, or between people or groups. Thus, written communication is the presentation of ideas or essays that make a clear point, supply details supporting that point, and demonstrate unity and coherence of thought.
[toc]
For example, e-mails, texts, letters, reports, SMS, posts on social media platforms, documents, handbooks, posters, flyers, etc. Written communication requires careful consideration. Writing is a result of long practice and patience in learning. The written word is an indelible record of proceedings in a business environment and therefore needs to be carefully planned.
Definition of Written Communication
These are some simple and understandable definitions of written communication:
Written communication involves any type of massage which makes use of the written word. Written communication is the most important and the most effective for any mode of business communication.
Written communication is the expression of language by means of visible signs. Despite the far wider use of oral communication, modern civilization cannot function without the written form. Business organizations need it to run their systems efficiently and effectively. It should be noted that written communication is not merely oral communication written down. It has its own dynamics. Its importance is mainly in organizing and documenting knowledge.
Written communication is a type of verbal communication. The communication which is performed through various written documents is called written communication. It is a word-based communication that takes place in a written form.
Examples of written communications generally used with clients or other businesses include proposals, letters, advertisements emails, the internet, websites, etc. Written communication within an organization includes circular letters, order letters, inquiry letters, collection letters, etc. All these letters serve important and multidimensional business purposes.
Types of Written Communication
Some important types of Written Communication include:
- Emails
- Proposals
- Reports
- Brochures
Emails
Emails are the most common type of written business communication, according to Startupbizhub, an online reference site. Business professionals use emails to communicate with each other, set up meetings, send documents, confirm appointments, and contact job candidates. Despite their relative casualness, your emails should still come across as professional.
Make sure you address your emails to all intended parties. Leaving just one person out can hinder your email’s effectiveness. Also, list the specific topic of your email in the “Subject” area. Avoid writing long paragraphs in emails. Instead, break your text up with bullet points and shorter paragraphs, according to Forbes online magazine.
Proposals
Proposals are documents that outline upcoming projects. For example, business consultants and advertising agencies submit proposals to companies for projects or special assignments. A marketing manager may submit a proposal to the research and development department to conduct product research.
Proposals are often just one or two pages long. Many companies use specific forms for their proposals. Make sure you clearly identify all the project steps and tasks in your proposal. Include the associated costs of each specific task as well. For example, list the printing, mailing, and postage costs if you are writing up a proposal for a direct mail project.
Reports
Reports are another type of written business communication. Companies use reports to inform employees about various aspects of the business. For example, the finance department will write financial reports to summarize a company’s profit and sales.
Similarly, a marketing research manager may write a report which summarizes the results of a customer phone survey. Write your reports in a structured format. Provide a brief introduction to your report. For example, tell department managers how and when you conducted a customer phone survey.
Include the key objectives you intended for the project. Summarize your findings in the body of your report. Add graphs and charts to clarify more complex concepts. Include an executive summary section in your report that highlights key findings or results. Moreover, always include a cover letter with your report to introduce it to managers or executives.
Brochures
Brochures are literature that features your products and services. Companie uses brochures to sell products or assist sales reps with sales calls. Companies produce brochures in many shapes and sizes. Some brochures are letter size while others are folded in half or thirds. Use color and pictures in your brochures that feature your main products or services. Break up each page of your brochure with plenty of blank space, which makes the brochure more readable.
6 Principles of Written Communication
The following are the six principles of written communication:
- Clarity
- Completeness
- Conciseness
- Consideration
- Courtesy
- Correctness

Clarity
Written communication requires clarity of thought and clarity of expression like using simple words, active construction, avoiding ambiguity and Jargon, using simple sentences, etc.
Completeness
The writer needs to check the completeness of the message. He should verify whether all questions are answered in the message or not.
Conciseness
Conciseness is communicating complete information about the idea in a few words. Concise writing also involves being mindful of word choice. Brevity is very important for effective writing. The writer should include only relevant facts and avoid repetitions.
Consideration
This principle advocates that the writer should consider the reader in his writing. It is always better to emphasize positive and pleasant facts. The writings should reflect the integrity of the writer.
Courtesy
According to this principle, courtesy will be observed through promptness in writing and giving replies, avoidance of imitating expressions, sincere apology for an omission, and generous thanks for a favor.
Correctness
According to this principle, the writer should give correct facts in the message. The message should be sent to the reader at the right time and in the correct style.
Written communication is accurate and serves as a permanent record. One can reach a large number of people through this media simultaneously. You can also fix responsibility for the people through this communication. However, written communication is much more time-consuming and more expensive when compared to oral communication.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Written Communication
These are the followings advantages and disadvantages of written communication:
- Advantages of Written Communication
- Disadvantages of Written Communication
Advantages of Written Communication
There are several advantages of written communication some are given below:
- Suitable for Lengthy Message
- Written Proof
- Clear Message
- Less Expensive Method
- Time-Saving
- Presence of Both Parties Not Necessary
- True and Effective
- Communication in Different Places
- Use as a Reference
- Longevity
- Delegation of Authority
- Effective Communication
- Maintaining Image
- Proper Information
- No Opportunity to Misinterpret
- Controlling Tool
- Easy to Verify

Suitable for Lengthy Message
Suitable for Lengthy Message: The lengthy message can clearly communicated with the help of written communication.
Written Proof
Written Proof: Some documents with regard to some special facts have to be kept for future reference. This is possible only through written communication.
Clear Message
Clear Message: A message may be long or short, it can be made understandable in written communication. There is no fear of anything being left out in such a system.
Less Expensive Method
Less Expensive Method: Messages are to be sent to distant places, if there is no urgency involved, it can be sent at a little expense through this method. But if the message is to be sent to a distant place quickly, this method is not useful.
Time-Saving
Time-Saving: Underwritten communication, there is no open conversation with a big human group. Hence, time is not lost in useless talks.
Presence of Both Parties Not Necessary
Presence of both parties not necessary: In this system, it is not necessary that the receiver should be present before the sender.
True and Effective
True and effective: The written communication is true and hence effective. A sender sends the information after careful consideration because of the written proof it carries with it.
Communication in Different Places
Communication in different places: When messages have to be sent to different places, written communication proves to be useful.
Use as a Reference
Use as a reference: If it is needed, written communication can be used as a future reference.
Longevity
Longevity: Written documents can be preserved for a long time easily. That is why; all the important issues of an organization should be back and white.
Delegation of Authority
Delegation of Authority: Written communication can help the authority delegate the power and authority to the subordinate. It is quite impossible to delegate power without a written document.
Effective Communication
Effective communication: Written communication helps to make communication effective. It is more dependable and effective than those other forms of communication.
Maintaining Image
Maintaining image: Written communication helps to maintain the images of both the person and the organization. It also protects the image of the company or organization.
Proper Information
Proper information: It is a proper and complete communication system. There is no opportunity to include any unnecessary information in a written document.
No Opportunity to Misinterpret
No opportunity to misinterpret: there is an opportunity to misinterpret the information or messages of written communication.
Controlling Tool
Controlling tool: Written communication can help to control the organizational activity. The written document may be used as a tool for controlling.
Easy to Verify
The information and messages that are preserved can be verified easily. If there arises any misunderstanding any party can easily verify the information.
Others: Clear understanding, Legal document, Acceptability, Reduction of risk, Creating confidence, Easy circulation, Wide access or coverage, etc.
Disadvantages of Written Communication
Now let’s clarify the disadvantages of written communication which are given below:
- Unfit for Uneducated Persons
- Lack of Secrecy
- Wastage of Time
- No Quick Information About Feedback
- Expensive
- Red-Tapism
- Lack of Flexibility
- Delay in Response
- Delay in Decision Making
- Complex Words
- Lack of Direct Relation
- Other

Unfit for Uneducated Persons
Unfit for Uneducated Persons: Written communication has no significance for uneducated people. They can only be made to understand orally.
Lack of Secrecy
Lack of secrecy: Because of written proof, nothing can remain secret.
Wastage of Time
Wastage of time: Because of the organizational constraints it is essential to send less important facts in writing, it shall be the waste of time, labor, and money.
No Quick Information About Feedback
No quick information about feedback: Some difficulty is felt when the reactions of the receivers are not known immediately. It also becomes difficult to bring an immediate change in the message.
Expensive
Expensive: Written communication is comparatively expensive. For this communication paper, pen, ink, typewriter, computer and a large number of employees are needed.
Red-Tapism
Red-Tapism: Red-Tapism is one of the most disadvantages of written communication. It means to take time for approval of a project.
Lack of Flexibility
Lack of flexibility: Since writing, documents cannot be changed easily at any time. Lack of flexibility is one of the most important limitations of written communication.
Delay in Response
Delay in response: It takes much time to get a response from the message receiver; prompt response is not possible in the case of written communication but is possible in oral communication.
Delay in Decision Making
Delay in decision-making: Written communication takes much time to communicate with all the parties concerned. So the decision maker cannot take decisions quickly.
Complex Words
Complex words: Sometimes the writer uses complex words in writing a message. It becomes difficult to mean out to the reader. So the objectives of the communication may lose.
Lack of Direct Relation
Lack of direct relation: If there is no direct relation between the writer and the reader, writer communication cannot help to establish a direct relation between them.
Other
Other: Prompt feedback is impossible, Slowness, Bureaucratic attitude, Understanding-problem between boss and subordinates, lack of quick clarification and correction, formality problem, lack of personal intimacy, etc.
Ways to Improve Written Communication
When trying to get your point across to others in writing, here are some ways to improve written communication:
- Vocabulary, Spelling, and Grammar
- Proof-Reading and Editing
- Brevity and Simplicity
- Logical Progression of Ideas
- Authenticity
- Confusing Language
- Poor Sentence Structure
- Information Overload

Vocabulary, Spelling, and Grammar
Vocabulary, spelling, and grammar these things do matter. A written document with a lot of spelling mistakes or grammatical errors loses credibility. It can look as if the writer doesn’t care about the quality of his or her work.
Proof-Reading and Editing
Few pieces of written work are born perfectly formed. Usually, you will need to read over a piece of writing a few times, making changes every time, to obtain a good quality finished product. If you can, it’s often a good idea to go away from a piece of writing for a few hours, days, or even weeks, so that you come back to it again with ‘fresh eyes.
Brevity and Simplicity
Try to get your written points across as simply and concisely as possible. As you gain writing experience and confidence, you can experiment with making your sentences and paragraphs more complex, but if in doubt, do keep it simple.
Logical Progression of Ideas
Most pieces of good writing from the shortest email to the longest thesis follow a very simple rule. This is that your written work should have a clear beginning or introduction, middle or main body, and end or conclusion.
Authenticity
Don’t pass other people’s written work or ideas off as your own – learn how to cite and reference other people’s work appropriately. Work on developing a fluid, personal writing style, and on finding your own voice.
Confusing Language
Confusing language means confusing words that can mislead the reader and cause communication breakdown or barriers between the writer and the reader. Some words are ambiguous, bombastic, vague, sexist, trendy, exaggerated, inflated, and archaic.
Again, we must always remember to write to convey meaning in plain English. It is better to use the familiar word for the far-fetched, the concrete word for the abstract, the single word for the circumlocution, and the short word for the long.
Poor Sentence Structure
Poor sentence structure relates to writing fragments instead of complete sentences and writing sentences that lack unity. Try to keep your sentence(s) short and compact to ensure that they are correct, logical, and easy to read. Long, complicated sentences can be difficult to read and understand. Word order is important for meaning.
Information Overload
Information overload means giving too much information, hence, the reader becomes overwhelmed and confused. This may also cause frustration and cast doubts on the writer’s credibility. Therefore, as a writer, you must decide what sort of information is required in order to produce a clear, concise, and relevant written work.
Read More Related Articles
What is Communication? | Mass Communication
Types of Communication | Principles of Communication
Types of Communication
- Types of Communication
- Verbal Communication
- Non-Verbal Communication
- Written Communication
- Visual Communication
- Feedback Communication
- Mass Communication
- Group Communication
Nonverbal Communication | Verbal Communication
Written Communication | Oral Communication
Business Communication | Organizational Communication
Formal Communication | Informal Communication
Interpersonal Communication | Informal Communication
Downward Communication | Upward Communication
Barriers to Communication | Horizontal or Lateral Communication
Self Development | Effective Communication
Difference Between Oral and Written Communication | Theories of Communication
FAQ Section
What is written communication explained?
This kind of communication involves any kind of exchange of information in written form. To put it simply, written language communication is communication by means of written symbols that are communicated by or to, or between people or groups. Thus, written communication is the presentation of ideas or essays that make a clear point, supply details supporting that point, and demonstrate unity and coherence of thought.
Why do you want to improve your written communication?
Because of these reasons: letters, reports, SMS, posts on social media platforms, documents, handbooks, posters, flyers, etc. written communication requires careful consideration. Writing is a result of long practice and patience in learning. The written word is an indelible record of proceedings in a business environment and therefore needs to be carefully planned.
What is written communication simple words?
Written communication involves any form of message which makes use of the written word. Written communication is the most important and the most effective for any type of business communication.
How can you improve written communication in the workplace?
Following are the ways to improve written communication:
1. Vocabulary, Spelling and Grammar
2. Proof-Reading and Editing
3. Brevity and Simplicity
4. Logical Progression of Ideas
5. Authenticity
6. Confusing Language
7. Poor Sentence Structure
8. Information Overload.
What are the principles of written communication?
These are the six principles of written communication:
1. Clarity
2. Completeness
3. Conciseness
4. Consideration
5. Courtesy
6. Correctness.
What are the advantages of written communication?
Advantages of written communication given below:
1. Suitable for Lengthy Message
2. Written Proof
3. Clear Message
4. Less Expensive Method
5. Time-Saving
6. Presence of Both Parties Not Necessary
7. True and Effective
8. Communication in Different Places
9. Use as a Reference
10. Longevity
11. Delegation of Authority
12. Effective Communication
13. Maintaining Image
14. Proper Information
15. No Opportunity to Misinterpret
16. Controlling Tool
17. Easy to Verify.
What are the disadvantages of written communication?
These are the disadvantages of written communication:
1. Unfit for Uneducated Persons
2. Lack of Secrecy
3. Wastage of Time
4. No Quick Information About Feedback
5. Expensive
6. Red-Tapism
7. Lack of Flexibility
8. Delay in Response
9. Delay in Decision Making
10. Complex Words.
When messages or information is exchanged or communicated through words, it is called verbal communication. There are two types of communication in this sub-group; they are:
Written and oral communication: this communication process takes place through face-to-face conversations, group discussions, counselling, interview, radio, television, calls, memos, letters, reports, notes, email, etc. Some definitions of verbal or spoken communication are as follows:
According to Bovee and others: Verbal communication is the expression of information through language which is composed of words and grammar.”
According to Penrose and others, “Verbal communication consists of sharing thoughts thought the meaning of words.”
So, verbal communication is the process of exchange of information or message between two or more persons through written or oral words.
The tone of voice can portray different connotations; whether it is a vocal tone, angry tone, or any other voice tone will make a huge difference in communication.
What is non-verbal communication?
When messages or information is exchanged or communicated without using any spoken or written word, it is referred to as nonverbal communication. Nonverbal communication (NVC) is usually understood as the communication process involving sending and receiving wordless messages.
Non-verbal communication is a powerful arsenal in face-to-face communication encounters, expressed consciously in the presence of others and perceived either consciously or unconsciously. Much of non-verbal communication is an unintentional communicative gesture as people may not even be aware that messages are being relayed. Non-verbal communication takes place through gestures, body posture, eye contact, body position, physical proximity, touching, etc. Below are some important definitions of non-verbal communication:
According to L. C. Bove and others, “Non-verbal communication is communication that takes place through non-verbal cues: through such form of non-verbal communication as gesture, eye contact, facial expression, clothing and space; and through the non-verbal vocal communication known as Para-language.”
According to Lesikar and Pettit, “Nonverbal communication means all communication that occurs without words (body movements, space, time, touch, voice patterns, color, layout, design of surroundings.)”
According to Himstreet and Baty, “Non-verbal communication includes any communication occurring without the use of words.”
Non-verbal communication is the exchange of information or message between two or more persons through gestures, facial expressions, body position, eye contact, proximity, touching, etc. and without using any spoken or written word.
Characteristics of non-verbal communication
Nonverbal communication is any information that is communicated without using words. The important characteristics of non-verbal communicative gestures are as follows:
- No use of words: it is generally a communication without words or language like oral or written communication. It uses nonverbal behavior like gestures, facial expressions, lack of eye contact, body position, physical proximity, body language, touching, etc. for interpersonal communication.
- Culturally determined: some nonverbal communication are learned during childhood, passed on to you by your parents and others with whom you associate. Through this process of growing up in a particular society, you adopt the taints and mannerisms of your social space and cultural group.
- Different meaning: nonverbal symbols and gestural communication can have many meanings. Cross-culture aspects of communication give various meanings to same expression in respect of non-verbal communication.
- Vague and imprecise: nonverbal communication is quite vague and imprecise. Since in this communication, there is no use of words or language which expresses clear meaning to the receiver.
- May conflict with verbal message: nonverbal communication is so deeply rooted, so unconscious, that you can express a verbal message and then directly contradict it with a nonverbal message.
- Largely unconscious: nonverbal communication is unconscious in the sense that it is usually not planned nor rehearsed nor require any learning activities with its attributed level of understanding. It comes almost instantaneously.
- Shows feelings and attitudes: Facial expressions, gestures, body movements, the way you use your eyes – all communicate your feelings and emotions to others. It helps to provide a personal level of understanding as a communication of compassion which could be a barrier to effective communications.
- Informality: nonverbal communication does not follow any rules, formality or structure like other communication skills. Most of cases people unconsciously and habitually engaged in non-verbal communication by moving the various parts of the body; whether during educational communication, communication on success, or communication during teaching.
Major types of Verbal and Non-verbal communication
There are conversational gestures and symbolic gestures that promotes cultural values and effective communication in our daily life. Some of their types known are listed below;
Types of verbal communication
- Intrapersonal communication;
- Interpersonal communication;
- Small group communication; and
- Public communication.
Types of non-verbal communication
- Body movement and postures;
- Facial expressions;
- Gestures;
- Eye contact; and
- Touch.
Both spoken and nonverbal communication are essential in everyday life. However, how we utilize them in conveying effective messages is what counts. You must stay clear of sending information with wrong signals to avoid mixed message or bad body language. Always relay messages with top-notch effectiveness!
There was a time when communication was simple.
You either spoke with someone face to face or trusted that a note tied to a pigeon would eventually make it to the right person. With time, however, communication advanced in a lot of different directions, eventually making it almost effortless to send and receive messages.
Some would think that modern communication is simpler than the old-fashioned methods. It’s fast, easy and convenient. Simple, right? Nope! The opposite is actually true. With countless approaches to sending and receiving information, communicating is now a lot more complex.
If you want to learn more about a specific type of communication, jump ahead:
- Verbal communication
- Nonverbal communication
- Written communication
- Visual communication
And if communication has become more complicated in general, imagine what has happened to business communication. When we take an extra minute to think about a message we are about to send, we start to wonder:
What type of communication should I be using?
How do I know which channel to use?
Is this subject appropriate to discuss using this method?
The proper use of the types of communication is crucial to the way people receive our messages. And while the number of communication channels can continue to grow, the types of communication will stay the same. This makes understanding the types of communication the first step to being the best communicator possible. In business, this workplace soft skill can make or break your success.
There are four types of communication that each include multiple channels.
But before we go on, let’s make one thing clear: there is a difference between types of communication and communication channels.
A communication channel is the actual tool we use to send information. The type of communication is the category that the channel falls under. For example, say you send an instant message. The type of communication is written communication because you wrote the message. The communication channel is the instant messaging software you used to send the message.
Alright, let’s get after it. Here are the types of communication and some channels that they include.
1. Verbal communication
There is power in spoken words. A simple “yes” can open a door to a new opportunity and a harsh “no” can slam it in your face. Either way, the message is sent using verbal communication.
Verbal communication refers to the use of speech to send a message. We banter, gossip and tell jokes with friends, but there are also times we need to get serious about verbal communication. For example, in the workplace.
No matter the field you work in, verbal communication skills are necessary in business. Chefs holler when an order is up, ranch hands yell to corral livestock, and salespeople turn on the language charm to intrigue clients.
Like most types of communication, verbal communication includes a variety of channels to use.
In-person communication is perfect for adding a personal touch to a conversation. You can email a remote coworker as much as you want, but nothing beats that first face-to-face impression to help you understand what kind of person, and worker, they really are. Most importantly, sensitive topics should exclusively be discussed face to face. Using an impersonal type of communication to tell someone important news, good or bad, undermines the seriousness of the situation.
Verbal communication also includes speaking over the phone. While not as personal as meeting in person, phone conversations allow people who are not physically in the same place to have a quick conversation. The topics can resemble a formal meeting or ones that are discussed when you stop by someone’s desk for a quick question or clarification.
And finally, video call is thrown into the mix. A great way to still add the pleasure of seeing someone’s face, but not needing to be in the same place if it is a hassle.
Consider the information you are about to discuss. If it is sensitive, verbal communication is your best bet. It may be difficult at times, but it is the most respectful way to share information.
2. Nonverbal communication
If you have ever interacted with a baby who still can’t speak, you have had to make some guesses about what they are thinking, what they want, and whether or not they are happy through their actions. Successful or not, you are picking up on nonverbal communication cues to understand them.
Nonverbal communication is the way we communicate without using words. And while your posture, hands, and eyes can’t speak, they are saying more than you think.
In business, our nonverbal communication speaks volumes. We are expected to act and appear a certain way in the workplace to be considered professional. People around us pick up on the way we carry ourselves and translate those suggestions into levels of energy, interest, and respect.
The only channel we have for nonverbal communication is our body, but there are multiple carriers within it.
Body language, facial expressions, and eye contact are the loudest of nonverbal communication tactics. Leaning back in a chair with an expressionless face comes across as disinterested and unfocused. On the other more lively hand, sitting up straight and looking curiously into the speaker’s eyes conveys that you are intrigued and understanding the information being presented to you, even if that’s not really the case.
Parts of nonverbal communication that are often forgotten are our appearance and proxemics. The way we dress, keep our hair, and stay generally clean speaks to how much we value the situation we are in, people we are with, and place we are located.
Proxemics refers to the distance between the speaker and the speaker’s audience.. It may seem unimportant, but imagine a situation where the person you were speaking with stood so far away that you had to raise your voice. Or so close that you had to take a step back to avoid their bad breath. Stand close enough so the conversation is still personal, but not too close that the other person feels uncomfortable.
Check yourself. The nonverbal messages you are sending can easily be trumped by what you’re doing, or not doing.
3. Written communication
“Write this down.” A good clue that significant information is coming your way. Thankfully, written communication provides us the tools we need to take note of it all.
Written communication is using the written word to convey information. The best attribute of written communication is that it can send large amounts of information without the risk of someone forgetting because it can be referred back to for reminders.
In business, this is especially important. Take a second to think about the number of messages circulating in a business.
What time is the meeting?
What do I need to include in that report?
What is included in the new benefits package?
It’s a lot. And the more these questions and answers are thrown around, the easier it is to forget important information. This is why businesses rely heavily on written communication. There are plenty of channel options to choose from, and situations that call for each one.
Email has taken over the business world. The convenience, handy features, and access from anywhere with Internet make it hard to beat. Email has wide ranges of formality and message length, giving it endless uses. However, it is easy to get caught up in the convenience of email. Some conversations are hard to have face to face, and it is tempting to avoid that by using email to discuss the touchy subjects. Recognize which topics are email appropriate, but more importantly, ones that aren’t.
Instant messaging is another tool that has contributed to the way people within a business communicate with each other. Typically used for internal communications, instant messaging is perfect for a quick, casual conversation that gets right to the point.
Technology is wonderful, but don’t forget about written messages on paper! Yes, as old fashioned as it may be, there are still plenty of uses for this type of written communication.
When delivering a large amount of important information, it might be best to go with a written communication channel. But be careful. Not all topics are appropriate for written communication.
4. Visual communication
Imagine someone describing a sunset with words only. Not very thrilling, right? However, once an image is added, you begin to grasp the true beauty of it. The words spoken about the sunset can help you imagine it, but visual communication is what helps you understand it.
Visual communication refers to messages that can be seen.
In business, visual communication can be characterized as a helper. Whenever a heavy amount of information is presented, a visual aid can help the message receiver comprehend the message.
Graphs are a common and useful visual aid. A lot of talk and writing around the office can be packed with data about the business. Revenue and growth, debt and decline. Good to know, but hard to listen to. No matter how important it is, listing data can cause information to go in one ear of the audience and right out the other. A graph helps them turn those numbers into something more meaningful.
Other forms of visual communication, like photographs, models and physical objects can come in handy when you are struggling to find the right words to describe something. A photograph can help complete a message that is hard to describe with words. A model gives an example of an ideal final product for someone producing it for the first time. An object can help people better understand how something works, so they can relay that information to others.
Take a look at the information you are delivering. If it is loaded with numbers or phrases that could use some help from a visual aid, be sure to include one. Your audience will appreciate it.
Choose wisely
As we sit in the midst of the Information Age, knowledge has never been more powerful. And as technology continues to muster up new innovations, there have never been more ways to communicate it. When sending a message, consider your audience and the information at hand. Bring both of those together to find the right type of communication and the appropriate channel.
Not so worried about internal communications and want more about the external side? Check out our resource on integrated marketing communications.
Read this article to learn about various forms of communication like Verbal Communication – Written, Oral and Non-Verbal Communication!
1. Verbal Communication – Written, Oral:
The word verbal means ‘connected with words and use of words.’ Any communication using words is verbal communication.
Words are the most precise and powerful sets of symbols. Words denote as well as connote meanings. That is why all serious or formal communication is usually in words. Words, as we are all aware, can be written or spoken.
Thus, verbal communication can further be divided into two types:
(a) Oral Communication:
“A wound inflicted by speech is more painful than a wound inflicted by a sword”. As the term itself suggests, communication through the spoken word is known as oral communication. Of the working time spent in verbal communication, 9 % is in writing, 16 % in reading, 30 % in speaking and 45 % in listening.
In oral communication, words should be chosen very carefully so that what they connote has the precise shade of meaning. The sender of the message or his representative is usually the speaker, while the receiver or his representative, the listener. Listening is also an important aspect of oral communication.
Factors in oral communication:
(i) The speaker
(ii) How he speaks
(iii) What he speaks
(iv) To whom he speaks
(v) Whether he receives a feedback
Pre-requisites of oral communication:
(i) Clear and proper pronunciation of words
(ii) Clarity and exactitude
(iii) Conciseness
(iv) Right tone
(v) Right style and vocabulary
Merits of oral communication:
(i) Saving of time and money:
Oral communication saves money as well as time. No money needs to be spent for producing oral communication since it involves only the spoken word. Oral communication is, therefore, economical.
Secondly, there is hardly any delay from the time when the sender sends the message and the receiver receives it. The words are received and understood as soon as they are spoken. Oral communication, therefore, saves time, too.
(ii) Immediate feedback:
The feedback in most oral communication is immediate. The words are received as soon as they are spoken, and the receiver can also give his reaction immediately. The speaker can gauge the mood and the response of the listener. The immediate feedback is an advantage for the speaker.
(iii) Saves paperwork:
Paperwork is minimal since communication is in the form of spoken words.
(iv) An effective tool for exhortation:
When the communication is oral, you can try to persuade the listener. Doubts can be cleared immediately.
(v) Builds a healthy climate:
A friendly atmosphere is created when you communicate orally since there is less formality. You can also make modifications in the communication immediately on the basis of the feedback and response from the listener.
(vi) Best tool during emergency:
Oral communication is the quickest tool during an emergency. It is the best method of communication when an immediate and fast response is critical.
Demerits of oral communication (limitations):
(i) Greater chances of misunderstanding:
Unless it is recorded, you cannot refer to an oral message again. There are, therefore, greater chances of a message being misunderstood or misinterpreted. In fact, there is also a chance that the message may not be understood at all.
(ii) Bad speaker:
Only an individual who can satisfy all the requisites of effective oral communication can produce good results. More often than not, a bad speaker may send the wrong message. When speaking, one communicates through the articulation, voice modulation and body language, too.
A message may be misunderstood if there is a disharmony among these components. Also, as mentioned earlier, what the words connote and what they denote should be in harmony, else the message may lead to a conflict in understanding.
(iii) Ineffective for lengthy communication:
Oral communication is not useful for lengthy communication. Because of human limitations, there is every likelihood that something important will be missed out.
(iv) Lower retention rate:
Oral communication suffers from the drawback of a low retention rate. A listener may absorb only some part of an oral message since the attention span differs from person to person. People also tend to forget an oral message quickly.
(v) No legal validity:
Oral communication lacks proof of record. There is no permanent record or proof of what has been said. An individual who has given a message may deny it later; similarly, an individual who has been given an oral message or instruction may say he never received it. Hence, oral communication has very little value from the legal point of view.
(vi) Difficult to fix responsibility:
Since a message is transmitted orally, it is difficult to fix responsibility. This may also lead to carelessness in the implementation of a message.
(b) Written communication:
A message constitutes written communication when it is put in “black and white.” It is a formal type of communication. The sender of the message or his representative constitutes the writer.
Written communication is usually considered binding on business organizations and is often used as evidence. Technological advancement has enlarged the gamut of written communication through email and other such facilities.
Factors in written communication:
(i) The writer
(ii) The content
(iii) The language used
(iv) The purpose of the communication
(v) The style adopted – formal or friendly
(vi) The receiver
Pre-requisites of written communication:
(i) How much to put in writing
(ii) What to leave out
(iii) When to stop
(iv) When to convey
(v) By what means to convey
Merits:
(i) Precise and accurate:
Written communication is generally prepared with great care and precision. The very prospect of writing makes a person conscious. You have to be very serious and organised while communicating in the written form, because written communication is open to verification.
(ii) Easily verified:
Since written communication is on paper etc., it can be read and re-read. It also offers itself to verification. There is also, thus, less ‘chance of someone twisting the message to his or her own advantage.
(iii) Permanent record:
Written communication constitutes a permanent record. It also acts like evidence. It proves very useful for future reference as it can be preserved for years. For example, old orders and decisions can serve as the basis for new ones.
(iv) Suitable for lengthy and complicated messages:
Lengthy and complicated messages can be understood better when they are in the written form rather than in the oral. There is less chance of misinterpretation and misunderstanding. Also, the language used is less subject to change.
(v) Responsibility can be easily fixed:
In written communication, responsibilities of sender and receiver can be fixed easily. People have the tendency of shifting responsibilities for mistakes, but this is difficult if the onus is obvious in black and white.
(vi) Has legal validity:
Written communication is acceptable as a legal document. Written communication has been used as evidence since time immemorial.
Demerits:
(i) Slower method of communication:
Written communication can be time-consuming since it may take even two or even three days to reach the receiver (by letters, for instance). By contrast, oral communication is immediate.
(ii) Further delay if clarifications are required:
Written communication hampers quick clarifications. The receiver may write back for clarifications and wait for a reply, making the process tedious. Even if clarifications are not needed, there is still a delay between the time the sender writes a message and the receiver receives it.
(iii) Leads to too much of paperwork:
Since written communication is basically done on paper, one may tend to use it as escape mechanism Paper-free offices remain a dream.
(iv) Always a possibility of ambiguity or lack of comprehensibility:
It is quite possible that the receiver is not able to comprehend the exact meaning of a written message that he has received. The clarity of a written message also depends upon the skill, or the lack of it, in the sender. If the message has not been written properly, it will not be understood, either.
(v) Costly in terms of money and man-hours:
Writing letters is a costly process not only because you need to spend money on postage, but also because several persons are involved in the process of sending out a letter from an organisation. Their time costs organisation money. While oral communication can be short and quick, written communication, because of its very nature, tends to be lengthy.
(vi) No flexibility:
The written word is not subject to instant change after communication. Therefore, conveying an afterthought may prove very lengthy, and, at times, even impossible.
(vii) Literacy essential:
It goes without saying that in written communication, the sender as well as the receiver should be literate. In fact, we may wrongly presume that they are so. In many Asian Countries, where literacy is low, a written message will be meaningless for large masses of illiterate persons.
Literacy also means literacy in the language of the message. The receiver should know the language in which a message has been written. It is no use receiving a message in English if you are not conversant with that language.
Notwithstanding its limitations, it can be safely concluded that written communication remains the spine of an organisation. Almost all formal communication is in the written form.
Visual Aids:
A visual aid is an illustration in tabular, graphic, schematic or pictorial from. Visual aids help communicators to get their message across more effectively to their audience. Visual aids help by making the material more interesting, clarifying and simplifying complex subjects and highlighting important points for better retention by the audience.
A checklist for creating effective visuals is given below:
(i) Visuals should be simple and easy to understand and the design and layout should contribute to the overall understanding of the subject.
(ii) Visuals should depict the data accurately and important points should be emphasized.
(iii) Visuals should be appropriate for the intended audience.
(iv) Care should be taken that the type-face and fonts are clear and readable and the captions short and informative.
2. Non-Verbal Communication:
Scientific analysis has shown that body movements and gestures constitute 55% of effective communication. Hence, non-verbal communication merits great consideration.
Non-verbal communication involves things such as gestures, posture, physical appearance etc. It takes place without written or spoken words.
Non-verbal communication is those messages that are expressed by means other than linguistic. While you can refuse to speak or write, it is impossible to avoid behaving non-verbally.
Non-verbal communication is classified here in two different ways:
I.

II. a. Body language or kinesics – body movement, facial expressions, posture, etc.
b. Vocal characteristics – paralanguage
c. Space – proxemics
d. Surroundings
e. Silence
Kinesics:
The study of bodily movement stoat form a part of non-verbal communication is known as kinesics. It is an integral part our communication. Existence as a receiver is supposed to observe non-verbal communication 55% of the time. Our body consciously as well as unconsciously, conveys messages, moods attitudes etc. in the same way as language uses sets of symbols to convey meaning.
(i) Facial expressions:
The face is said to be the mirror of the mind. Whatever we feel reflected on our face. The face can convey energy, anger, grief, sincerity and a host of other feelings and emotions. A smile means friendliness, while a frown means anger.
A creased forehead shows worry while a raised eyebrow shows surprise hence it is very important to exercise a check and control over our feelings. Although this is a difficult task, you can get positive results with continuous efforts.
(ii) Gestures:
Gestures are small body movements that transmit some message. It can even be the transmission of specific information. Some gestures maybe conscious while others may be involuntary. Some gestures have an almost universal meaning, such as a headshake for a “no” or a handshake as a “hello”.
Then there are other gestures that may have regional meanings. Strictly speaking, gestures are a part of body language because our head and hands tend to communicate by themselves in their own Way.
(iii) Posture:
Posture is the position adopted by the body. It helps in conveying a message. Each movement or position of the body has expressive or defensive functions. Thus, the posture is an important element in non-verbal communication. It reveals a great deal about an individual.
Posture concerns the overall bearing of the body. It includes the angle of inclination and the position of the arms and the legs. A raised head indicates openness, while a tilted head indicates curiosity.
However, one should remember that none of these postures have any specific meanings of their own. They acquire meanings in association with other symbols and in the context of communication.
(iv) Clothes:
A man is often judged by his appearance. His clothes play an important role in enhancing his personality. Shabbily dressed people may cut a sorry figure. It is vital for one to look professional and efficient. Accessories also play a major role in non-verbal communication.
Clothes and accessories relate to physical as well as socio-cultural characteristics. Sometimes, clothes and accessories manage to live up to the expectations of the receiver, while at times they send a message through a violation of these expectations.
(v) Eye contact:
Eyes are the windows to the soul. Eye contact constitutes a very important factor of face-to-face communication. Through eye- contact, the speaker gets signals whether the channel of communication is open.
Discomfiture or nervousness results only in a brief eye contact; on the other hand, a long and fixed gaze shows interest. Depending on our feelings, we have smiling eyes, angry eyes, painful eyes, evasive eyes, and so on.
(vi) Silence:
Silence speaks louder than words. It lays down the relationship between communicators and their attitude towards each other. Silence shows the inability to converse further. A student who has not done his homework will stay mum when the teacher asks him for it.
Indicators of Non-verbal Communication:
Positive:
(i) Smile
(ii) Open posture
(iii) Interested expression
(iv) Moderate eye contact
(v) Accurate pitch and volume of voice
Negative – Submissive:
(i) Floundering voice
(ii) Defensive arms / legs
(iii) Slow speech
(iv) Fretting expressions
(v) Deceitful looks
Negative – Aggressive:
(i) Harsh voice
(ii) Wagging finger
(iii) Fast speech
(iv) Supercilious expressions
(v) Immoderate eye contact
Body language:
Body language stands for the way the body communicates without words, through the movement of its parts. The nodding of our heads, blinking of our eyes, waving of our hands, shrugging of our shoulders, etc., are expressions of our thoughts and feelings.
All these movements are the signals that our body sends out to communicate. That is why this area of study has been called body language. Just as language uses sets of symbols to convey meaning, our body, consciously as well as unconsciously, conveys messages, attitudes, moods, status relationships, etc.
The body language is very important. It has been observed that we may play fast and loose with words, but our body speaks out the truth. Even if we try to hide the truth or anything that we want to suppress, our body, our eyes, our gestures may speak out loud and clear.
Paralanguage:
The world of communication that involves signs, signals, pitch, tone and fluctuations to convey meaning is paralanguage. Para means ‘like’ or ‘akin’. Paralanguage means “like language,” but not actually a language.
Anything that performs the task of communication as a language without being a language in the conventional sense of the word falls within the purview of paralanguage. Paralanguage is used to describe a wide range of vocal characteristics which help to express and reflect the speaker’s attitude. It is non-verbal because it does not consist of words.
Verbal communication is concerned with the content of the message – what is being conveyed? On the other hand, paralanguage is concerned with the manner in which the message is conveyed – how is it being conveyed?
Paralanguage depends on voice, intonation, pitch, pause, volume, stress, gestures, and signals. Through pitch and volume variation, stress on words, etc. one’s voice can convey enthusiasm, confidence, anxiety and the speaker’s mental state and temperament.
Voice:
Voice is the first signal that we receive or use. A good listener can gauge a lot from the voice itself. There are various categories of voices. A voice can be sweet, soft, musical, cultivated, pleasant, nasty, clear or indistinct, among other things. The voice can help reveal a speaker’s background, mental state, education, sex and temperament.
Intonation:
Intonation is the modulation of the voice and the shift in stress. Intonation is a part of effective communication. For example, a message with serious content should not be delivered in a high tone, but in a somber tone.
Pitch:
Pitch is the vocal slant of the voice. It is very important because it reveals the speaker’s frame of mind. An unusually high pitch may reflect agitation. An unchanging pitch maybe boring or monotonous, decreasing the listener’s span of attention.
The pitch may also help us understand the speaker’s social position. A person in a position of authority uses a higher pitch than a subordinate. The flaring of tempers usually results in a change in the pitch.
Pause:
A pause emphasizes a message. A pause is to speech what a comma is to prose. A pause at the wrong place may lead to miscommunication. For example, the difference between ‘fruit trees’ and ‘fruit, trees’ is vast.
Volume variation:
The speaker should adjust the volume of his voice depending on the size of the audience. Larger the audience, the louder the voice should be. Volume variation makes the speech effective. Sometimes changing from loud to soft and from soft to loud have the desired effect.
Mixed signals:
Mixed signals occur when the tone, pitch and facial expressions of the speaker do not match the words that he is speaking. This confuses the listener as to the exact motive of the speaker.
For example, an individual may congratulate another, but his tone may be cold. In this case, the listener will not be sure whether the speaker is really happy or is merely fulfilling a formality. Praise delivered in a sarcastic tone conveys mockery.
Proper word stress:
Communication can be made more effective by putting proper emphasis or stress on the right words.
Overall impression:
A message is understood by the listener not only by the content, but also by the manner in which the speaker conveys it. The speaker’s bearing, attitude, dressing style, physical appearance, age, gender, accent and the quality and tone of the voice also affect the message that gets communicated. For a message to be effective, the overall impression given by the individual should be in consonance with the message that he wants to convey.
Advantages of paralanguage:
(i) No oral communication is complete without paralanguage as it is closely connected to language itself.
(ii) To a large extent, paralanguage indicates the position and situation of the speaker, whether in an organisation or in society.
(iii) It also reflects the speaker’s personality and background to a great extent.
(iv) Paralanguage is indicative of the mental state of the speaker. A discerning listener can derive the right conclusions from the pitch, tone and speed of a message. This can often be very useful.
Limitations of paralanguage:
(i) Paralanguage is ‘semi’ or ‘like’ a language. It is not language by itself. Therefore, not all the advantages associated with actual language can be attributed to paralanguage.
(ii) Paralanguage involves the drawing of conclusions on the basis of a number of peripheral (side) attributes. Such drawing of conclusions need not always be right. In such a case, they may also serve to create undue bias. This, in itself, makes paralanguage misleading or confusing at times.
(iii) Also, as speakers may come from different backgrounds, cultures and situations, the conclusions from paralanguage may be difficult to draw, especially to convey a message in its entirety.
Proxemics or territory or space:
Proxemics is another important type of non-verbal communication. The term, proxemics is derived from the word proximity, which means closeness. Proxemics is used with reference to space or territory. A lot of communication takes place non-verbally through the sheer manner in which we use the space around us.
Scholars have also attributed a lot of non-verbal communication to the colour, design, layout and utilisation of the space around us. This is also proxemics. The space around us can be broadly classified as under:
Intimate space:
Most body movements take place within 18 inches around us. It is our most intimate circle of space. Only very close people or family members can enter this space, be it through a whisper, a pat on the back or a handshake. It means that the less the space between the two persons communicating, the more intimate is the nature of communication.
Personal space:
Personal space extends from 18 inches to four feet where we have normal conversation with friends, colleagues and associates. It is used in informal talks and impromptu discussions in which one may not be averse to taking important decisions.
Social Space:
This can be anywhere between four feet and 12 feet. It reflects a formality of relationship. It also reflects a lack of spontaneous behaviour. An individual’s responses are more collected and well thought-out. Social space reflects reason, planning and control, usually associated with business communication within a formal relationship.
Public Space:
This starts from a distance of 12 feet. One has to raise one’s voice to be heard. There is a lack of personal feelings and an added sense of detachment.
Paralanguage:
(i) Reflects feelings and attitudes of the speaker through a wide range of vocal characteristics.
(ii) Paralanguage gives important clues about the speaker’s educational, national/regional background and mental state.
(iii) It is a systematic study of how an individual verbalizes.
Proxemics:
(i) Feelings and attitudes are reflected by the way people use space around them.
(ii) Proxemics helps us to understand relationships and interaction patterns between people.
(iii) Proxemics is also concerned with the use of space by groups of people.
Surroundings:
How you organize the surroundings also contributes to the communication. The room where you meet your visitors may be dazzling or simple. It may be gaudy or sober. The decor of the place, the furniture, and the artistic pieces that adorn your office, tell about yourself and your taste.
Communication is the process of passing information and understanding the same from one person to another. Thus, communication means to understand information, facts or opinions of someone.
Communication may be in various forms, it may be classified on the following basis:
- On the basis of Organisational Structure
- On the basis of Direction
- On the basis of Mode of Expression
- Formal Communication
- Informal Communication
- Downward Communication
- Upward Communication
- Horizontal Communication
- Diagonal Communication
- Non Verbal Communication
- Verbal Communication
- Oral Communication
- Written Communication
Table of Content
- 1 Types of Communication
- 2 On the basis of Organisational Structure
- 2.1 Formal Communication
- 2.1.1 Advantages of formal communication
- 2.1.2 Disadvantage of formal communication
- 2.2 Informal Communication
- 2.2.1 Advantages of informal communication
- 2.2.2 Disadvantages of informal communication
- 2.1 Formal Communication
- 3 On the basis of Direction
- 3.1 Downward Communication
- 3.1.1 Advantages of downward communication
- 3.1.2 Disadvantages of downward communication
- 3.2 Upward Communication
- 3.2.1 Advantages of upward communication
- 3.2.2 Disadvantages of upward communication
- 3.3 Horizontal Communication
- 3.3.1 Advantages of horizontal communication
- 3.3.2 Disadvantages of horizontal communication
- 3.4 Diagonal Communication
- 3.4.1 Advantages of diagonal communication
- 3.4.2 Disadvantages of diagonal communication
- 3.1 Downward Communication
- 4 On the basis of Mode of Expression
- 4.1 Non Verbal Communication
- 4.1.1 Advantages of non verbal Communication
- 4.1.2 Disadvantages of non verbal Communication
- 4.2 Verbal Communication
- 4.2.1 Oral Communication
- 4.2.2 Written Communication
- 4.1 Non Verbal Communication
- 5 Business Communication Notes
- 6 Reference
- Organisational Structure
- Formal Communication
- Informal Communication
- Direction
- Downward Communication
- Upward Communication
- Horizontal Communication
- Diagonal Communication
- Mode of Expression
- Non-Verbal Communication
- Verbal Communication
- Oral Communication
- Written Communication
On the basis of Organisational Structure
In the organization structure of enterprise communication, there are two types of communication:
- Formal communication
- Informal Communication
Formal Communication
Formal communication is a flow of information through formally established channels in an organization. These type of communication may be oral or written.
- Mostly controlled by managers
- It is hierarchical in nature and associated with the superior and subordinate relationship
- Generally linked with formal status and positions of a person
- It may be upward, downward and horizontal.
Advantages of formal communication
- Follows the principle of unity of command
- The orderly flow of information and systematic
- Helps in fixing responsibilities for better efficiency
- Managers have full control of nature and direction of communication
- Helps in maintaining authority relationship
- The flow of instruction is very specific, clear and definite.
- Helpful in maintaining direct contact with subordinates.
Disadvantage of formal communication
- It is a time-consuming process
- It lacks personal contacts and relationship
- It may be resisted and distorted
- It delays the communication message due to the formal procedure
- It obstructs the free, smooth and accurate circulation of information
Informal Communication
Informal Communication refers to communication on the basis of personal relations. It is a type of communication which is unstructured, unofficial and unplanned.
- It does not follow the formal channels established by the management
- It often flows between friends and intimates and related to personal rather than ‘positional’ matters.
- It cannot be demonstrated on the chart and not regulated by formal rules and procedure.
The informal communication system is built around the social relationship of the members of the organisationHerbert Simon
Informal communication is a result of social interaction and satisfies the natural desire of people to communicate with each other. Informal communication is helpful in countering the effects of work fatigue and monotony and serving as a source of job-related information.
It is also referred to as grapevine communication. Grape wine communication carries unofficial information. It is not a reliable source of communication. Managers should be very careful about such communication.
Advantages of informal communication
- It is a flexible and reliable channel of communication
- It creates mutual co-operation
- It may work as a valuable aid in communicating organizational rules, values and morale
- It is helpful in building teamwork in the organisation
- It provides effective feedback to the manager
- It supplements formal communication
- It creates successful public relations in the organisation
- If implemented efficiently, it will leads to the success
Disadvantages of informal communication
- It creates misunderstanding and uncertainty
- Due to different perceptions of the persons involved in whispering, chain interpretations of information may change
- It is difficult to believe in information as its source cannot be identified
- It sometimes leads to leak secret information
- The information passes through it is inaccurate and distorted
- It is difficult to control it as its flow and direction cannot be checked
On the basis of Direction
On the basis of directions communication may be of four types of communication:
- Downward Communication
- Upward Communication
- Horizontal Communication
- Diagonal Communication
Downward Communication
Communication that takes place from superiors to subordinates in a chain of command is known as downward communication.
Such type of communication may be in the form of orders, instructions, policies, programmes etc. It may be written or verbal.
The following messages are induced in this type of communication:
- Confirmation regarding performance
- Work assignment and directions
- Orders, guidance and responsibilities
- Ideological type of information
- Organisation Procedure and practices.
Advantages of downward communication
- It is helpful in controlling the subordinate
- It explains the plans and policies of the organisation to employees.
- It is a tool to delegate authority
- It is helpful to tie among employees at a different level
- It encourages the effectiveness of upward communication through feedback
- It helps in preparing the people to introduce change
Disadvantages of downward communication
- It tends to promote one-way communication
- It is time-consuming because information passes through various levels
- Sometimes a manager may filter the information or hold back some of the information due to fear that it might be unpalatable
- As communication takes time, sometimes message become ineffective and can lose significance
Upward Communication
When message are transmitted from bottom to top of the organisational hierarchy, it is known as upward communication.
The main function of upward communication is to supply information to top management. It is essentially participative in nature and can flourish only in a democratic organisational environment. It may be in the form of progress report, suggestions, grievances, complaints etc.
Advantages of upward communication
- Management can use feedback effectively in their plan and procedures
- Help subordinate to communicate their views to top management
- It supports innovative ideas and suggestion
- Support in harmony and mutual co-operation among management and subordinate
- The managers are able to evaluate the impact of communication
Disadvantages of upward communication
- Subordinate provides only favourable information to upper management
- It may be discouraged due to lack of proper response of top management
- It takes a lot of time to pass the message to higher level
- Possibility of wilful manipulation of information to attain personal goals.
- There arise a threat that superior may react negatively
Horizontal Communication
When communication takes place between two or more persons who are working at same levels it is known as horizontal communication.
This type of communication takes place mostly during a committee meeting or conferences. The main object of such communication is to establish inter-departmental co-ordination.
Advantages of horizontal communication
- It helps in avoiding duplication of work
- It solves inter-department conflicts
- It facilitates establishing co-ordination between different departments of the organisation
- Communication process is computed smoothly without any barrier.
- It helps in maintaining social and emotional support among the peer group.
Disadvantages of horizontal communication
- There is a lack of motivation to communicate
- Usually, they hide information due to rivalry between them
- It lacks authoritativeness
Diagonal Communication
Diagonal communication is an exchange of information between the persons at a different level across departmental lines.
This type of communication is used to spread information at different levels of an organization to improve understanding and co-ordination so as to achieve organisational objectives.
Thus, where the persons who are neither working in the same department nor has similar level are communicating, it is said to be diagonal communication. It cuts across the levels of organisational structure.
Advantages of diagonal communication
- It increases organisational effectiveness
- It facilitates organisational change
- It creates integrity and harmony in the organisation
- It helps to speed up the action and save time
Disadvantages of diagonal communication
- It violates the principle of unity of command
- It is an unsystematic manner of communicating.
On the basis of Mode of Expression
- Non Verbal Communication
- Verbal Communication
Non Verbal Communication
Communication through expressions, gestures or posture is nonverbal communication. It refers to the flow of information, through facial expressions, tone of voice and other body movements.
In other words, it is a type of communication other than words. It conveys the feeling, emotions, attitude of a person to another. A person can communicate his feeling to others quickly and economically by using a non-verbal form of communications. This does not require the use of words as a person can express his feelings by his body language.
Some important of nonverbal communication are:
- Body Language: Posture, Gesture, Eye Contact, Silence etc.
- Proximity: Space (intimate space, public space), Time, Surroundings etc.
- Para Language: Voice, Volume, Pause, Pitch, Proper stress etc
Advantages of non verbal Communication
- It is reliable source of information
- Message may be conveyed quickly
- It is an economic way of communications
- It creates better-understanding
Disadvantages of non verbal Communication
- Expressions and gestures are seen by anyone so it lacks secrecy.
- It creates misunderstanding due to non-understanding of the gestures
- It requires the physical presence of both parties
- Long and detailed message cannot be conveyed
- The meaning of gesture changes according to time and place, thus it is difficult to understand universally
- There is no written proof in case of any dispute in future.
Verbal Communication
Verbal Communication is an exchange of information by words either written or oral. Verbal communication consists of speaking, listening, writing, reading etc. It is the most preferred mode of communication.
It may be of two types of Verbal Communication:
- Oral Communication
- Written Communication
Oral Communication
When a message is expressed through spoken words, it may be either through face to face conversations or with the help of electronic mode such as telephone, cellular phone, etc.
It may also be in the form of informal conversation, group discussions, meeting etc. It is a more effective means of exchange of information because the receiver not only hears the message but also observes the physical gestures of the speaker.
Advantages of oral communication
- Oral communication is useful in providing good leadership
- It provides an opportunity to participate in all the members in decision making
- It saves time and message reach to the receiver very quickly
- It is an economic source of communications
- It is more effective as body language can be observed along with the hearing of the message
- Reaction can be received easily and quickly
- The message can be conveyed clearly because, in case of any confusion, the clarification can be sought immediately.
Disadvantages of oral communication
- It requires the presence of both parties, i.e. sender and receiver
- The major drawback of this type of communication is lack of proof, thus it has no legal validity
- It is not suitable when the messages are lengthy
- It does not provide sufficient time for thinking before conveying the message
- It involves a high cost if both parties are at distance place
- The message can be distorted.
Written Communication
When opinions are exchanged in written form, rather than by spoken words, it is knows as written communication.
It may be expressed through charts, pictures and diagrams. It includes newspapers, reports, letters, circulars magazines etc. While using written communication, words should be select very carefully because message ones sent can not be altered. it is formal in nature and cannot be overlooked.
Advantages of written communication
- It provides a future reference: it becomes a permanent record and beneficial for formulating new policies.
- It is accurate. Mistakes are not likely to occur as it is open for verification and its authenticity can be checked.
- It does not require the physical presence of both parties.
- It ensures transmission of information in a uniform manner
- It is useful to transmit complex information and it facilitates the assignation of responsibilities
- It usually removes conflicts and misunderstanding
- It facilitates to convey a message to a large number of persons at the same time
- Written communication is acceptable as a legal document.
Disadvantages of written communication
- It is a time and money consuming way of communication
- It lacks secrecy because message passes through various hands, thus, it is said to be a double-edged weapon
- It is not useful in emergency circumstances
- It has no chance to alter the message ones transmitted
- It is not possible to get immediate feedback
- It becomes unimpressive if drafted poorly
- It may be interpreted in the wrong manner
- It requires unnecessary formalities.
Business Communication Notes
(Click on Topic to Read)
- What is Business Communication?
- What is Communication?
- Types of Communication
- 7 C of Communication
- Barriers To Business Communication
- Oral Communication
- Types Of Non Verbal Communication
- Written Communication
- Soft Skills
- Interpersonal vs Intrapersonal communication
- Barriers to Communication
- Organisational Communication
- Horizontal Communication
- Grapevine Communication
- Downward Communication
- Verbal Communication Skills
- Upward Communication
- Flow of Communication
- Emotional Intelligence
- Public Speaking
- Upward vs Downward Communication
- Internal vs External Communication
Reference
- Murphy, Hildebrandt (1991), Effective Business Communication, McGraw Hill, New York.
- Business Communication: “ K.K. Sinha, Golgotia Publishing Company.
- Business Communication: “M.K. Sehgal, Vandana Khetrapal, Excel Books.
- Essentials of Business Communication: Rajendra Pal, J.S Korlahalli, Sultan Chand & Sons.
Go On, Share & Help your Friend
Did we miss something in Business Communication Tutorial or You want something More? Come on! Tell us what you think about our post on Types of Communication | Business Communication in the comments section and Share this post with your friends.

Trying to brush up on your basic communication knowledge? We’ve got you covered — read all about the five types of communication: verbal, nonverbal, written, visual, and listening. Yes, listening is a type of communication too! Communication happens between the sender and receiver, and can occur in groups as well. People often take it for granted, but it is an essential part of being human.
Learn all about the five types of communication below.
Importance of Communication
Variety in Communication: Choose Wisely
We are lucky as humans to have a whole host of communication types available for us at our fingertips. But with great variety comes the responsibility to choose your method wisely!
For example, the best way to apply for a job is a written message (preferably over email) to the hiring manager — not a verbal, spoken message in passing. Similarly, you may not want to break bad news using a written form over text, but rather in verbal/visual form where you can accurately portray your message in a sensitive matter. More on these types below!
Interpersonal Communication
When referencing communication types, people are usually speaking about interpersonal communication, as opposed to intrapersonal communication. The difference is simple. Interpersonal communication is communication that occurs between people or between groups, whereas intrapersonal communication is communication that occurs within one’s own mind.
One common form of interpersonal communication is that which occurs between a small group of people. Group members are usually face-to-face and participate in dialogue with one another, which can either be directed, planned, or spontaneous. Having open interpersonal communication with others helps to break down barriers and increase understanding. It is important for intercultural communication, workplace communication, and for personal relationships as well.
 Photo by Brooke Cagle on Unsplash
Photo by Brooke Cagle on Unsplash
The five types of communication you need to know about are verbal communication, nonverbal communication, written communication, visual communication, and listening.
1. Verbal Communication
Verbal communication encompasses all communication using spoken words, or unspoken words as in the case with sign language. It is important to understand how to effectively communicate your ideas verbally in order to avoid misunderstandings and maximize interest while you speak. Make sure to use the right type of language, speak clearly, know your audience, respond in the best way, and use an appropriate tone when speaking.
 Photo by Anna Vander Stel on Unsplash
Photo by Anna Vander Stel on Unsplash
2. Nonverbal Communication
What is actually being said is only half the battle — the rest lies in what isn’t being said. This means your tone, facial expressions, body language, hand movements, and eye contact. When you make yourself aware of what the rest of you is doing as you speak, you can make corrections and eventually use all the right nonverbal cues to convey your point.
3. Written Communication
Written communication is a form of verbal communication, but it is so different than spoken verbal communication that this form gets its own separate type. Written communication can take the form of anything you write or type such as letters, emails, notes, texts, billboards, even a message written in the sky! With written communication, it is important you know your audience, your purpose, and maintain consistency throughout your written message.
4. Visual Communication
Visual communication is one you may not have heard of, but it is one that complements the other types of communication well. Visual communication is delivering information, messages, and points by way of graphical representations, or visual aids.
Some commonly used examples are slide presentations, diagrams, physical models, drawings, and illustrations. When you use visual communication in addition to verbal, nonverbal, and written communication, you create a very effective way for your message to be heard and understood.
 Photo by Volodymyr Hryshchenko on Unsplash
Photo by Volodymyr Hryshchenko on Unsplash
5. Listening
Listening is a surprisingly important part of communication and in order to be a great communicator, you must master the art of listening. Remember that listening doesn’t just mean hearing, or politely waiting for your turn to speak. When others are speaking, you should practice active listening, which means that you are engaging your mind while the person speaks, intently focusing on what they are saying.
Formal Communication vs Informal Communication
Another way that types of communication can be broken down into is in formal vs informal communication. There are times when one should be used over the other, such as when delivering a speech (formal), or when making brunch plans with a friend (informal).
In formal communication, where conversation partners are part of a group, organization, or society, there are three types of communication:
- Vertical: Information flows freely up and down the organizational structure. For example, your boss’s boss speaks to you, you speak to your boss, and you speak to the employees under you.
- Horizontal: This is where information or communication flows across a structure. For example, you and your coworkers speak together back and forth.
- Diagonal: Finally, there is diagonal formal communication where all levels communicate with one another in any direction.
Online Communication
Communicating over the internet comes with special considerations. When you combine anonymity with a wide reach, messages can get muddled. Just think about how communication works on social media platforms.
With the University of the People, however, we make it a point to deliver the most effective online communication possible — we are 100% online, after all. Through their discussion boards and peer assessments, students communicate thoughts and ideas wherever and whenever they want.
 Photo by Glenn Carstens-Peters on Unsplash
Photo by Glenn Carstens-Peters on Unsplash
Emotional Awareness in Communication
One of the most poorly covered, but very important aspects of communication is emotional awareness. Emotional awareness is the ability to understand others’ feelings as well as your own, and take note of how that may be affecting a current situation. It is imperative that you have high emotional awareness in order to be an effective communicator. Here are some ways to improve your emotional awareness in communication:
- Use Empathy: Empathetic people are able to understand others’ emotions. Once you have that down, you can start to relate to them during your conversation.
- Consider Your Own Emotions: Your own feelings may be getting in the way of either delivering or receiving the message clearly. Check how you are feeling and be aware of how that may influence your communication ability.
- Think of Others’ Emotions: Remember the ways your own mood and emotions affect your ability to communicate and apply that to others. Take time to consider that someone’s mood or previous experience may be affecting their actions.
- Build Trust: You can build trust by having open and honest conversations, as well as matching your nonverbal cues such as tone, facial expressions, and body language to your verbal ones.
- Recognize and Correct Misunderstandings: Misunderstandings are the barrier to great communication. The more quickly to discover and correct them, the more calm everyone will be, and the quicker you’ll get on the right track.
Communicating in Difficult Situations
One of the hardest parts of communication is when you need to deliver some not-so-great information. It’s important to choose the best type of communication in that case, whether it is in person, written, formal or informal — only you know the message and who you need to deliver it to.
When you communicate in difficult situations, it can be overwhelming or emotional for both the sender and receiver of the message. Try to remember emotional awareness in difficult situations and you will do fine!
The Bottom Line
It’s important to know and understand all types of communication so that you can learn to use them effectively and become a great communicator. You are already on your way there after reading this guide — happy communicating!
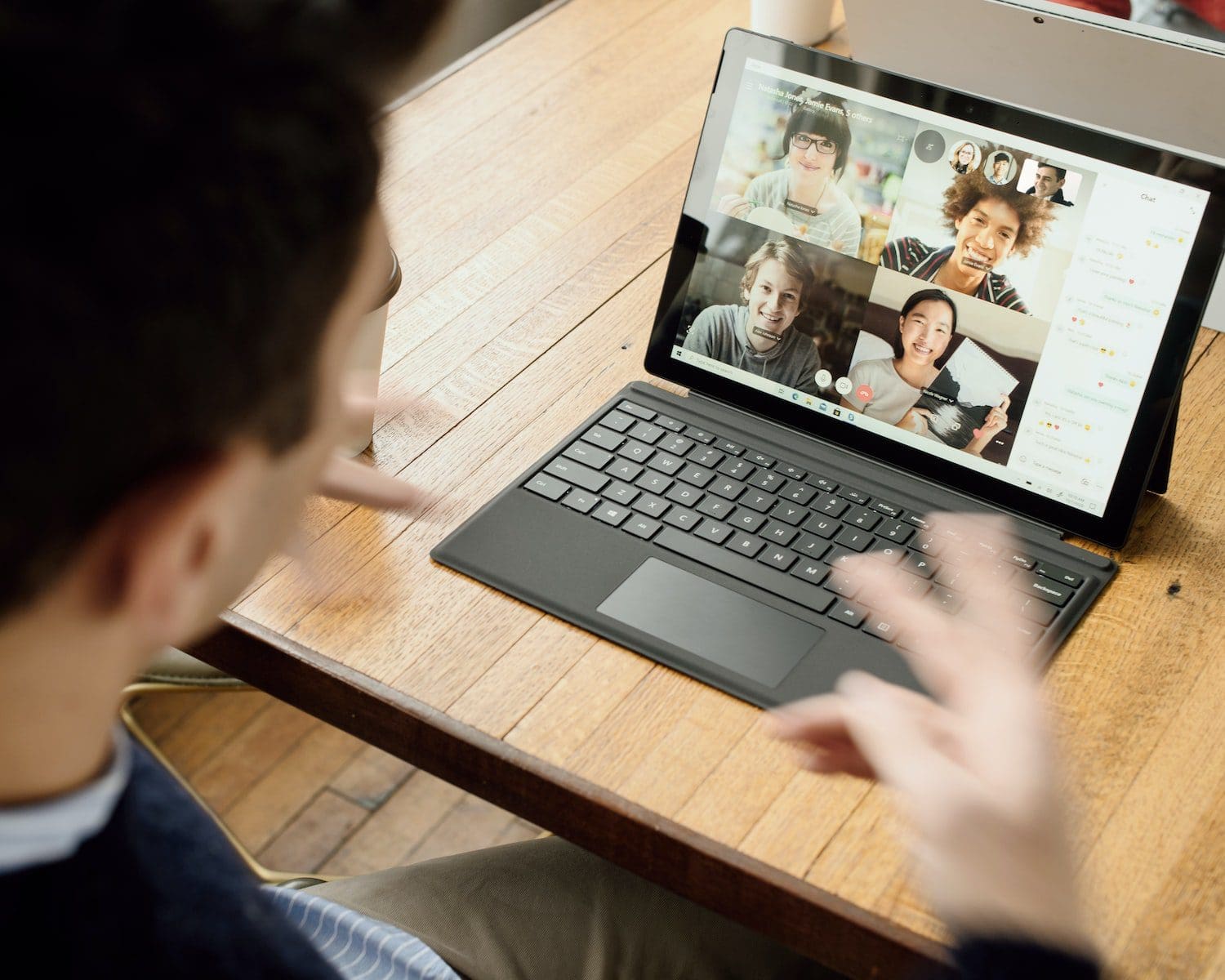
























 Photo by Brooke Cagle on Unsplash
Photo by Brooke Cagle on Unsplash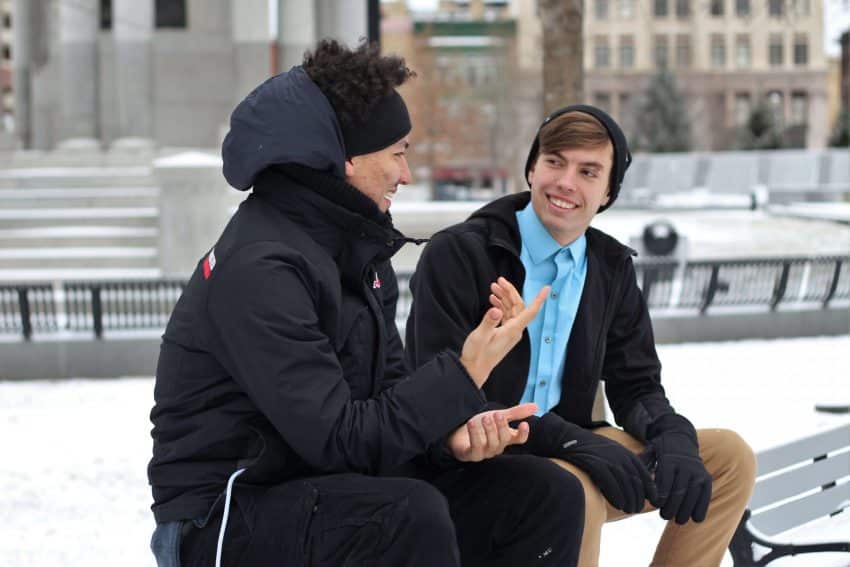 Photo by Anna Vander Stel on Unsplash
Photo by Anna Vander Stel on Unsplash Photo by Volodymyr Hryshchenko on Unsplash
Photo by Volodymyr Hryshchenko on Unsplash Photo by Glenn Carstens-Peters on Unsplash
Photo by Glenn Carstens-Peters on Unsplash