Wiki User
∙ 11y ago
Best Answer
Copy
Yes. Without is a compound word.
Wiki User
∙ 11y ago
This answer is:
Study guides
More answers
Anonymous ∙
Lvl 1
∙ 2y ago
Copy
Yes
This answer is:
Add your answer:
Earn +
20
pts
Q: Is without a compound word
Write your answer…
Submit
Still have questions?
Related questions
People also asked
Every word has its own meaning. You can search for the definition of every term in the dictionary. But do you know that you can put two words together and have a brand new meaning? Of course, not all words can be put together for such a case. However, many ones are already accepted in the English language. These words are called compound words.
What Are Compound Words?
Compound words are formed when two or more words are combined to produce a new one. This newly-constructed word has its own meaning that can either be related to the base words or not.
Types of Compound Words
Open Compound Words
Open compound words remain separate when written but are used together to create a new idea. For example, “peanut” and “butter” are unrelated to each other. But when you combine them and use them as one word, you will have “peanut butter,” which is already a different noun with its own meaning.
Closed Compound Words
Closed compound words are formed by combining two fully independent words together without space in between. An example of a closed-form compound word is “grandfather,” in which “grand” and “father” are put together.
Hyphenated Compound Words
Another possible form of a compound word is the hyphenated one. From the word itself, the independent terms used are separated by a hyphen or dash. A common example is “mother-in-law.”
Compound Nouns
Compound nouns are simply compound words that act as nouns. Nouns are names of people, animals, places, things, or events. However, it does not mean that the two words comprising it should only be nouns. A compound noun can be formed by combining two nouns, an adjective and a noun, a verb and a noun, and many more.
Compound Verbs
A compound verb is also called a complex predicate. It is a multi-word compound that acts as a single verb. It can be constructed by putting together a verb and a preposition or a verb and an adverb (phrasal verbs). Auxiliary verbs that are followed by the main verb can also be considered compounds. Some other combinations that involve a verb and a non-verb word can also be considered compound verbs if they indicate action.
Compound Adjectives
Two or more words that function as one and describe a noun are called compound adjectives. Usually, they are separated by a hyphen.
List of Compound Words
Open Compound Words
- Ice cream
- Ice cream cake
- Ice cube
- Cream cheese
- Hot dog
- Corn dog
- Corned beef
- Apple pie
- Sugar plum
- Web page
- Table cloth
- Fire drill
- Fire drill
- Fire exit
- High school
- Roller coaster
- Living room
- First aid
- Full moon
- Tea cup
- Serving spoon
- Real estate
- Car pool
- Cotton bud
- Cotton ball
- Video game
- Coffee grain
- Coffee mug
- Post office
- Upper deck
- Hand towel
- Sweet tooth
- Common sense
- Dance hall
- Police officer
- Vice president
- Science fiction
- Root word
- Candy cane
- Christmas tree
- Cell membrane
- Jumping jack
- Report card
- Credit card
- Debit card
- Radio wave
- Snack house
- Coffee shop
- Bus stop
- Swimming pool
- Rubber band
- Ice hockey
- Ice skate
- Break up
- Take away
- Take out
- Break away
- Lift up
- Push down
- Pull down
- Ask out
- Ask around
- Make up
- Turn in
- Fill up
- Fill out
- Fill in
Closed Compound Words
- Basketball
- Football
- Baseball
- Worldwide
- Overpass
- Southeast
- Northeast
- Northwest
- Southwest
- Bushfire
- Mailbox
- Snowball
- Skateboard
- Sailboat
- Birthday
- Blackboard
- Everything
- Anything
- Anyone
- Everyone
- Classmate
- Schoolmate
- Playmate
- Grandmother
- Grandfather
- Granddaughter
- Grandson
- Grasshopper
- Sunflower
- Sunrise
- Sunshine
- Moonlight
- Freelance
- Eyeball
- Eyebrow
- Eyelash
- Armpit
- Playground
- Teamwork
- Stoplight
- Flashlight
- Lighthouse
- Fireman
- Rainbow
- Raindrop
- Bedroom
- Popcorn
- Keyboard
- Notepad
- Keyhole
- Keystone
- Pothole
- Bowtie
- Necktie
- Brainwash
- Proofread
- Babysit
- Horseshoe
- Highlight
- Notebook
- Bookstore
- Lipstick
- Makeup
- Toothpaste
- Toothbrush
- Airbrush
- Crosswalk
- Crossroad
- Crossover
- Nightfall
- Riverbank
- Nutcracker
- Candlelight
- Backstroke
- Hamburger
- Cheeseburger
- Sandwich
- Homesick
- Uptown
- Rattlesnake
- Workplace
- Wrongdoing
- Springtime
- Underdog
- Strawberry
- Blueberry
- Watermelon
- Pineapple
- Cupcake
Hyphenated Compound Words
- Mother-in-law
- Father-in-law
- Sister-in-law
- Brother-in-law
- Sergeant-at-arms
- Merry-go-round
- Happy-go-lucky
- Editor-in-chief
- Over-the-counter
- Up-to-date
- State-of-the-art
- Long-term
- High-speed
- Left-handed
- Right-handed
- In-depth
- Full-length
- Part-time
- Long-haired
- Sun-dried
- Breath-taking
- Self-centered
- Well-off
- Well-known
- Gift-wrap
- Follow-up
- Well-being
- Single-minded
- Knee-length
- Short-tempered
- Off-site
- Runner-up
- One-sided
- Tip-off
- Blush-on
- Sugar-free
- Ice-cold
- Far-flung
- High-rise
- Life-size
- King-size
- Warm-blooded
- Cold-blooded
- Get-together
- Next-door
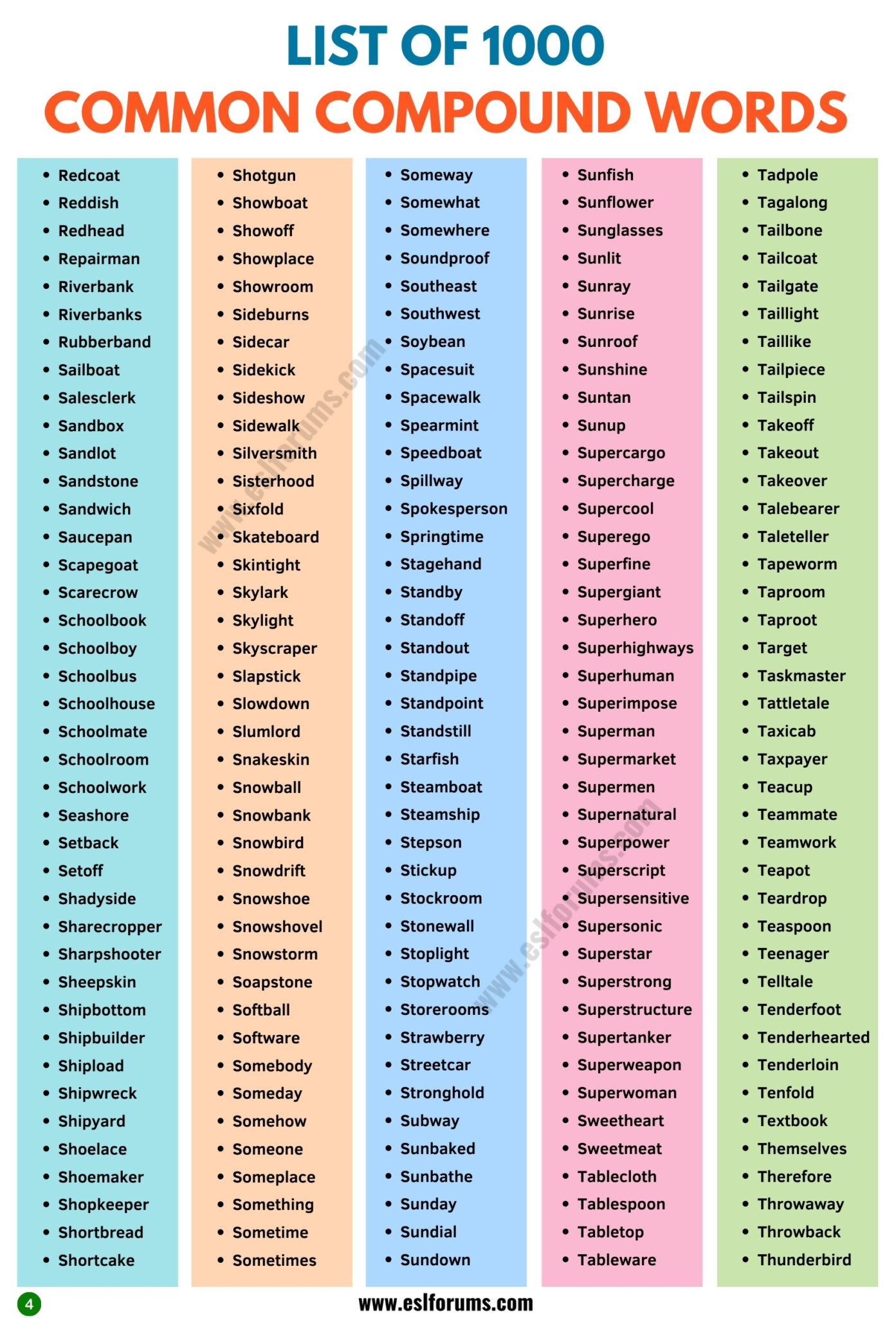
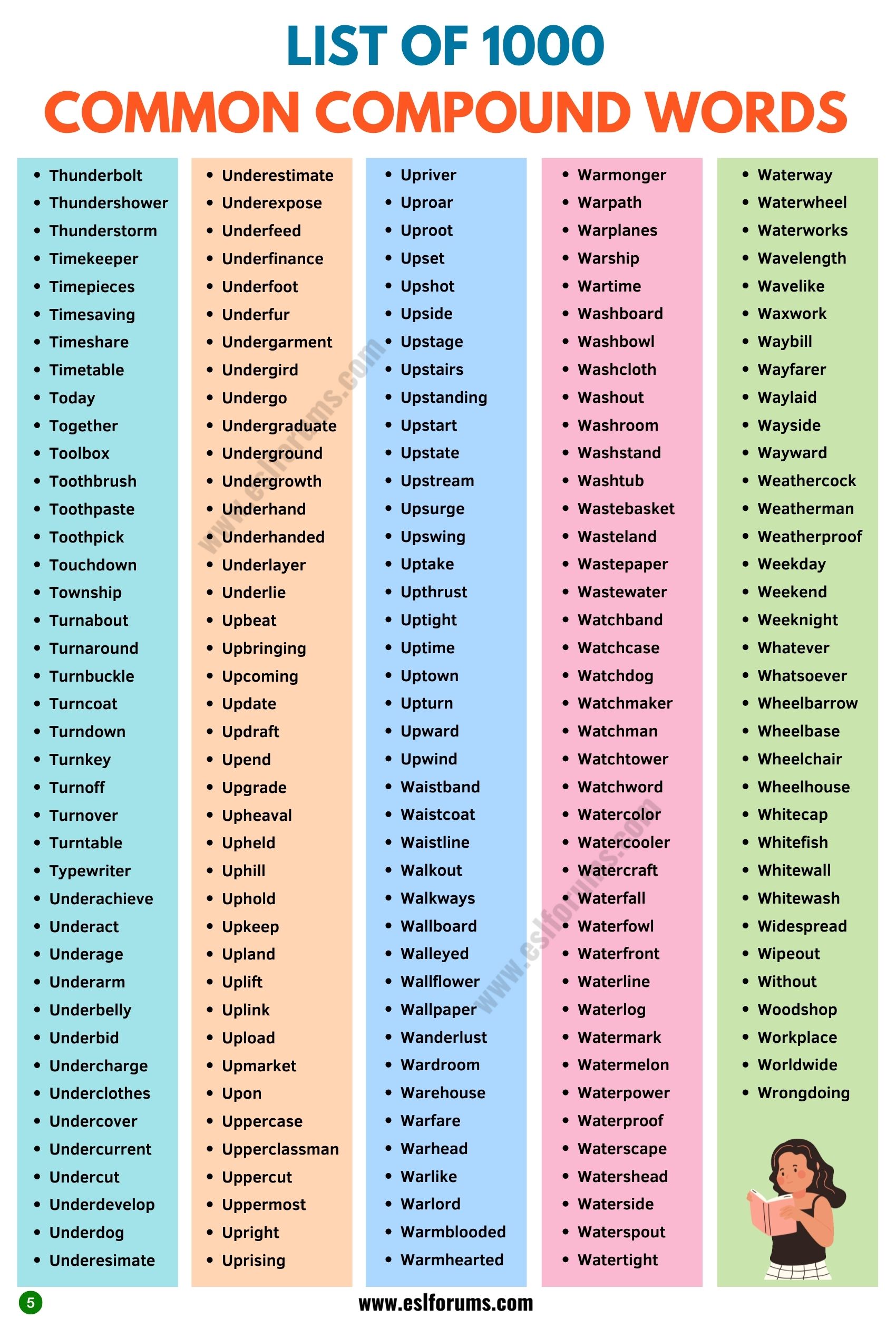
A Huge List of Compound Words
Following is a list of 1000 close compound words in English
- Aboveboard
- Afterbirth
- Afterburner
- Afterglow
- Afterimage
- Afterlife
- Aftermath
- Afternoon
- Airbrush
- Aircraft
- Airfield
- Airlift
- Airline
- Airliner
- Airmail
- Airman
- Airmen
- Airplane
- Airport
- Airship
- Airtime
- Allover
- Allspice
- Alongside
- Also
- Another
- Anybody
- Anyhow
- Anymore
- Anyone
- Anyplace
- Anything
- Anytime
- Anyway
- Anywhere
- Armchair
- Armpit
- Around
- Arrowhead
- Ashtray
- Authorship
- Babysit
- Babysitter
- Backache
- Backbite
- Backbone
- Backbreaker
- Backdrop
- Backfield
- Backfire
- Background
- Backhand
- Backlash
- Backlog
- Backpack
- Backside
- Backslap
- Backslide
- Backspace
- Backspin
- Backstage
- Backstop
- Backstretch
- Backstroke
- Backtrack
- Backward
- Ballpark
- Ballroom
- Bankbook
- Bankroll
- Baseball
- Basketball
- Beachcomb
- Became
- Because
- Become
- Bedbug
- Bedclothes
- Bedrock
- Bedroll
- Bedroom
- Bellbottom
- Bellboy
- Bellhop
- Below
- Birthday
- Blackball
- Blackberries
- Blackbird
- Blackboard
- Blackjack
- Blacklist
- Blackmail
- Blackout
- Blacksmith
- Blacktop
- Bluebell
- Blueberry
- Bluebird
- Bluefish
- Bluegrass
- Blueprint
- Boardwalk
- Bodyguard
- Bodywork
- Boldface
- Bookbinder
- Bookcase
- Bookend
- Bookkeeper
- Booklet
- Bookmark
- Bookmobile
- Bookseller
- Bookshelf
- Bookstore
- Bookworm
- Bootstrap
- Bowtie
- Brainchild
- Brainstorm
- Brainwash
- Bugspray
- Bushfire
- Buttercup
- Butterfat
- Butterfingers
- Butterflies
- Buttermilk
- Butternut
- Butterscotch
- Bypass
- Cabdriver
- Cancan
- Candid
- Candlelight
- Candlestick
- Cannot
- Cardboard
- Cardsharp
- Cardstock
- Carefree
- Caretaker
- Careworn
- Carfare
- Cargo
- Carhop
- Carload
- Carpetbagger
- Carpool
- Carport
- Carrack
- Carryall
- Carsick
- Cartwheel
- Carwash
- Cattail
- Catwalk
- Caveman
- Centercut
- Cheeseburger
- Cheesecake
- Classmate
- Clockwise
- Coffeemaker
- Comeback
- Comedown
- Commonplace
- Commonwealth
- Cornball
- Cornmeal
- Cornstalk
- Cornwall
- Cottonmouth
- Cottontail
- Cottonwood
- Countdown
- Counterattack
- Counterbalance
- Counterclockwise
- Counterintelligence
- Countermeasure
- Counteroffensive
- Counterpane
- Counterpart
- Counterpoint
- Counterpoise
- Courthouse
- Courtroom
- Courtyard
- Crewcut
- Crossbow
- Crossbreed
- Crosscut
- Crossover
- Crossroad
- Crosstown
- Crosswalk
- Crossword
- Cupcake
- Dairymaid
- Daisywheel
- Daybed
- Daybook
- Daybreak
- Daydream
- Daylight
- Daytime
- Deadend
- Deadline
- Dishcloth
- Dishpan
- Dishwasher
- Dishwater
- Diskdrive
- Dogwood
- Doorstop
- Downbeat
- Downunder
- Drawbridge
- Driveway
- Duckbill
- Duckpin
- Earache
- Eardrop
- Eardrum
- Earring
- Earthbound
- Earthquake
- Earthward
- Earthworm
- Egghead
- Eggshell
- Elsewhere
- Everyone
- Everything
- Eyeball
- Eyeballs
- Eyebrow
- Eyecatching
- Eye-catching
- Eyeglasses
- Eyelash
- Eyelid
- Eyesight
- Eyewitness
- Fatherland
- Fatherless
- Firearm
- Fireball
- Fireboat
- Firebomb
- Firebox
- Firebreak
- Firecracker
- Firefighter
- Fireflies
- Firehouse
- Fireman
- Fireproof
- Firewater
- Fireworks
- Fishbowl
- Fisherman
- Fisheye
- Fishhook
- Fishlike
- Fishmonger
- Fishnet
- Fishpond
- Fishtail
- Flashlight
- Football
- Foothill
- Foothold
- Footlights
- Footlocker
- Footnote
- Footpath
- Footprints
- Footrest
- Forbearer
- Forbid
- Forearm
- Forebear
- Forecast
- Forecastle
- Foreclose
- Foreclosure
- Foredoom
- Forefather
- Forefinger
- Forefront
- Forehand
- Forehead
- Foreleg
- Foreman
- Foremost
- Forepaws
- Forerunner
- Foresee
- Foresight
- Forestall
- Forestland
- Forever
- Forget
- Forgive
- Forklift
- Format
- Fortnight
- Freelance
- Friendship
- Fruitcup
- Gearshift
- Glassmaking
- Goodbye
- Goodnight
- Grandaunt
- Grandchild
- Grandchildren
- Granddaughter
- Grandfather
- Grandmaster
- Grandmother
- Grandnephew
- Grandnieces
- Grandparent
- Grandson
- Grandstand
- Granduncle
- Grasshopper
- Graveyard
- Gumball
- Haircut
- Hamburger
- Hammerhead
- Hamstring
- Handball
- Handbook
- Handcuff
- Handgun
- Handmade
- Handout
- Headache
- Headdress
- Headhunter
- Headlight
- Headline
- Headquarters
- Hedgehop
- Heirloom
- Hellcat
- Hellhole
- Helpmate
- Helpmeet
- Hemstitch
- Henceforth
- Henchman
- Henpeck
- Hereabout
- Hereafter
- Hereby
- Herein
- Hereof
- Hereupon
- Herself
- Highball
- Highchair
- Highland
- Highlight
- Highway
- Himself
- Homemade
- Homesick
- Hometown
- Honeybee
- Honeycomb
- Honeydew
- Honeymoon
- Honeysuckle
- Hookup
- Hookworm
- Horseback
- Horsefly
- Horsehair
- Horseplay
- Horsepower
- Horseradish
- Horseshoe
- Houseboat
- Housecoat
- Household
- Housekeeper
- Housetop
- Housewife
- Housework
- However
- Ideal
- Inchworm
- Income
- Indoors
- Inflow
- Infold
- Infuse
- Infusion
- Inhale
- Inkblot
- Inkwell
- Inland
- Inmate
- Inpatient
- Inroad
- Inset
- Inside
- Intake
- Ironwork
- Itself
- Jackpot
- Jackson
- Jailbait
- Jailbird
- Jawbone
- Jawbreaker
- Jaywalk
- Jellybean
- Jellyfish
- Jerkwater
- Jerrybuild
- Jetliner
- Jetport
- Jigsaw
- Jimsonweed
- Jitterbug
- Jobholder
- Johnnycake
- Jumpshot
- Keepsake
- Keyboard
- Keyhole
- Keynote
- Keypad
- Keypunch
- Keystone
- Keystroke
- Keyway
- Keyword
- Landmark
- Landslide
- Landward
- Lapland
- Lapwing
- Larkspur
- Laughingstock
- Lawgiver
- Lawmaker
- Lawsuit
- Layman
- Layoff
- Layout
- Layover
- Leapfrog
- Lifeblood
- Lifeboat
- Lifeguard
- Lifelike
- Lifeline
- Lifelong
- Lifesaver
- Lifetime
- Lifework
- Lighthouse
- Limelight
- Limestone
- Lipstick
- Longhand
- Longhorn
- Longhouse
- Lukewarm
- Mailbox
- Mainland
- Mainline
- Mainspring
- Mainstream
- Makeup
- Matchbox
- Meadowland
- Meantime
- Meanwhile
- Moonbeam
- Moonlight
- Moonlit
- Moonscape
- Moonshine
- Moonstone
- Moonstruck
- Moonwalk
- Moreover
- Mothball
- Motherhood
- Motorcycle
- Nearby
- Necktie
- Nevermore
- Newborn
- Newfound
- Newsboy
- Newsbreak
- Newscast
- Newscaster
- Newsdealer
- Newsletter
- Newsman
- Newsmen
- Newspaper
- Newsperson
- Newsprint
- Newsreel
- Newsroom
- Newsstand
- Newsworthy
- Nightfall
- Nobody
- Noisemaker
- Northeast
- Northwest
- Notebook
- Notepad
- Noteworthy
- Nowhere
- Nursemaid
- Nutcracker
- Oneself
- Onetime
- Overabundance
- Overboard
- Overcoat
- Overflow
- Overland
- Overpass
- Overshoes
- Pacemaker
- Pancake
- Parkway
- Passbook
- Passkey
- Passover
- Passport
- Password
- Pasteboard
- Patchwork
- Pathfinder
- Pathway
- Pawnbroker
- Pawnshop
- Paycheck
- Payload
- Paymaster
- Payoff
- Payroll
- Peppermint
- Pickup
- Pineapple
- Pinhole
- Pinpoint
- Pinstripe
- Pinup
- Pinwheel
- Playback
- Playboy
- Playground
- Playhouse
- Playmate
- Playthings
- Ponytail
- Popcorn
- Postcard
- Pothole
- Proofread
- Racquetball
- Railroad
- Railway
- Rainbow
- Raincheck
- Raincoat
- Raindrop
- Rainfall
- Rainmaker
- Rainstorm
- Rainwater
- Ratline
- Ratsbane
- Rattlesnake
- Rattletrap
- Rawboned
- Rawhide
- Readywitted
- Rearmost
- Rearrange
- Rearward
- Redcap
- Redcoat
- Reddish
- Redhead
- Repairman
- Riverbank
- Riverbanks
- Rubberband
- Sailboat
- Salesclerk
- Sandbox
- Sandlot
- Sandstone
- Sandwich
- Saucepan
- Scapegoat
- Scarecrow
- Schoolbook
- Schoolboy
- Schoolbus
- Schoolhouse
- Schoolmate
- Schoolroom
- Schoolwork
- Seashore
- Setback
- Setoff
- Shadyside
- Sharecropper
- Sharpshooter
- Sheepskin
- Shipbottom
- Shipbuilder
- Shipload
- Shipwreck
- Shipyard
- Shoelace
- Shoemaker
- Shopkeeper
- Shortbread
- Shortcake
- Shotgun
- Showboat
- Showoff
- Showplace
- Showroom
- Sideburns
- Sidecar
- Sidekick
- Sideshow
- Sidewalk
- Silversmith
- Sisterhood
- Sixfold
- Skateboard
- Skintight
- Skylark
- Skylight
- Skyscraper
- Slapstick
- Slowdown
- Slumlord
- Snakeskin
- Snowball
- Snowbank
- Snowbird
- Snowdrift
- Snowshoe
- Snowshovel
- Snowstorm
- Soapstone
- Softball
- Software
- Somebody
- Someday
- Somehow
- Someone
- Someplace
- Something
- Sometime
- Sometimes
- Someway
- Somewhat
- Somewhere
- Soundproof
- Southeast
- Southwest
- Soybean
- Spacesuit
- Spacewalk
- Spearmint
- Speedboat
- Spillway
- Spokesperson
- Springtime
- Stagehand
- Standby
- Standoff
- Standout
- Standpipe
- Standpoint
- Standstill
- Starfish
- Steamboat
- Steamship
- Stepson
- Stickup
- Stockroom
- Stonewall
- Stoplight
- Stopwatch
- Storerooms
- Strawberry
- Streetcar
- Stronghold
- Subway
- Sunbaked
- Sunbathe
- Sunday
- Sundial
- Sundown
- Sunfish
- Sunflower
- Sunglasses
- Sunlit
- Sunray
- Sunrise
- Sunroof
- Sunshine
- Suntan
- Sunup
- Supercargo
- Supercharge
- Supercool
- Superego
- Superfine
- Supergiant
- Superhero
- Superhighways
- Superhuman
- Superimpose
- Superman
- Supermarket
- Supermen
- Supernatural
- Superpower
- Superscript
- Supersensitive
- Supersonic
- Superstar
- Superstrong
- Superstructure
- Supertanker
- Superweapon
- Superwoman
- Sweetheart
- Sweetmeat
- Tablecloth
- Tablespoon
- Tabletop
- Tableware
- Tadpole
- Tagalong
- Tailbone
- Tailcoat
- Tailgate
- Taillight
- Taillike
- Tailpiece
- Tailspin
- Takeoff
- Takeout
- Takeover
- Talebearer
- Taleteller
- Tapeworm
- Taproom
- Taproot
- Target
- Taskmaster
- Tattletale
- Taxicab
- Taxpayer
- Teacup
- Teammate
- Teamwork
- Teapot
- Teardrop
- Teaspoon
- Teenager
- Telltale
- Tenderfoot
- Tenderhearted
- Tenderloin
- Tenfold
- Textbook
- Themselves
- Therefore
- Throwaway
- Throwback
- Thunderbird
- Thunderbolt
- Thundershower
- Thunderstorm
- Timekeeper
- Timepieces
- Timesaving
- Timeshare
- Timetable
- Today
- Together
- Toolbox
- Toothbrush
- Toothpaste
- Toothpick
- Touchdown
- Township
- Turnabout
- Turnaround
- Turnbuckle
- Turncoat
- Turndown
- Turnkey
- Turnoff
- Turnover
- Turntable
- Typewriter
- Underachieve
- Underact
- Underage
- Underarm
- Underbelly
- Underbid
- Undercharge
- Underclothes
- Undercover
- Undercurrent
- Undercut
- Underdevelop
- Underdog
- Underesimate
- Underestimate
- Underexpose
- Underfeed
- Underfinance
- Underfoot
- Underfur
- Undergarment
- Undergird
- Undergo
- Undergraduate
- Underground
- Undergrowth
- Underhand
- Underhanded
- Underlayer
- Underlie
- Upbeat
- Upbringing
- Upcoming
- Update
- Updraft
- Upend
- Upgrade
- Upheaval
- Upheld
- Uphill
- Uphold
- Upkeep
- Upland
- Uplift
- Uplink
- Upload
- Upmarket
- Upon
- Uppercase
- Upperclassman
- Uppercut
- Uppermost
- Upright
- Uprising
- Upriver
- Uproar
- Uproot
- Upset
- Upshot
- Upside
- Upstage
- Upstairs
- Upstanding
- Upstart
- Upstate
- Upstream
- Upsurge
- Upswing
- Uptake
- Upthrust
- Uptight
- Uptime
- Uptown
- Upturn
- Upward
- Upwind
- Waistband
- Waistcoat
- Waistline
- Walkout
- Walkways
- Wallboard
- Walleyed
- Wallflower
- Wallpaper
- Wanderlust
- Wardroom
- Warehouse
- Warfare
- Warhead
- Warlike
- Warlord
- Warmblooded
- Warmhearted
- Warmonger
- Warpath
- Warplanes
- Warship
- Wartime
- Washboard
- Washbowl
- Washcloth
- Washout
- Washroom
- Washstand
- Washtub
- Wastebasket
- Wasteland
- Wastepaper
- Wastewater
- Watchband
- Watchcase
- Watchdog
- Watchmaker
- Watchman
- Watchtower
- Watchword
- Watercolor
- Watercooler
- Watercraft
- Waterfall
- Waterfowl
- Waterfront
- Waterline
- Waterlog
- Watermark
- Watermelon
- Waterpower
- Waterproof
- Waterscape
- Watershead
- Waterside
- Waterspout
- Watertight
- Waterway
- Waterwheel
- Waterworks
- Wavelength
- Wavelike
- Waxwork
- Waybill
- Wayfarer
- Waylaid
- Wayside
- Wayward
- Weathercock
- Weatherman
- Weatherproof
- Weekday
- Weekend
- Weeknight
- Whatever
- Whatsoever
- Wheelbarrow
- Wheelbase
- Wheelchair
- Wheelhouse
- Whitecap
- Whitefish
- Whitewall
- Whitewash
- Widespread
- Wipeout
- Without
- Woodshop
- Workplace
- Worldwide
- Wrongdoing
Compound Words | Images
Scientists are big into molecular compounds, and there is something kind of magical about them. You can start with a couple of atoms of hydrogen, add another atom of oxygen, and bada bing: water. Two distinct elements come together to create something entirely different.
It’s exactly the same with words. Well, maybe not exactly the same, but English is such a flexible, creative language that it’s filled with compound words—and new ones are popping up all the time to suit our ever-changing world. Some useful compound words recently added to Merriam-Webster are clickbait, photobomb, binge-watch, humblebrag, and spit-take.
So what is a compound word? How do you know whether it should be a closed compound, a hyphenated compound, or an open compound? What about compound sentences? We’ll look at all of these in this post.
When two (or occasionally, three) words work together to express a single idea, that’s a compound word. Compound words can be open, closed, or hyphenated, and they can function as nouns, adjectives, or adverbs. English is full of preexisting compound words—or you can make up your own to suit the situation.
No one at the Star Trek convention really appreciated my Klingon-librarian costume.
The lung-collapsing dead-flower stench of my aunt Penelope’s perfume was headache-inducingly strong.
What is an open compound word?
An open compound word is two separate words (without even a hyphen to link them) functioning as a single idea.
When we were in high school, we regularly ate French fries, hot dogs, and ice cream with peanut butter as an afterschool snack.
What is a hyphenated compound word?
A hyphenated compound word is a term composed of two (or more) words connected by a hyphen. Like other compound words, a hyphenated compound can be a noun, adjective, or adverb.
The gun-toting, card-carrying FBI agent hid her angst well.
What is a closed compound word?
A closed compound word is a single word constructed of two or more other words. Most closed compound words were once open or hyphenated, but continued use solidified them—made them a single unit. Today’s open or hyphenated compounds are tomorrow’s closed compounds.
The moonlight coming through my bedroom window is so bright it outshines my flashlight.
Every afternoon, she wrote another story in her notebook; my favorite is the one about the starfish who loved rainbows and strawberries.
How do you know whether a compound word is open, hyphenated, or closed?
There’s really no trick to this! You look it up in a dictionary (like Merriam-Webster). Compound words evolve over time, so what was once black-bird is now blackbird, and what was once a web site is now almost always a website.
Don’t worry if you find dictionaries contradicting each other! Not every dictionary agrees on which compounds are open, hyphenated, or closed. Some offer health care and voice mail, for example, as two words, but others hyphenate or close those same compounds. In such cases, you’re free to use the spelling you prefer, except if you’re supposed to be following a particular style guide.
For example, the Chicago Manual of Style (CMoS) says that when a compound modifier comes before a noun, it’s never wrong to hyphenate it, since it can aid readability.
The seventy-year-old professor despaired for the dull-witted students in her late-afternoon class.
But (Chicago goes on to say) when compound modifiers follow the noun, leave them unhyphenated (even if they’re hyphenated in the dictionary).
The professor, who was almost seventy years old, couldn’t understand why her students were so dull witted by late afternoon.
What is a compound noun?
Compound words can be nouns, adjectives, adverbs—and even verbs (like pole-vault or double-click). In each case, they can be open, hyphenated, or closed. Compound nouns are perhaps the most common type of compound word. Here are some examples of compound nouns (some closed, some open, some hyphenated).
Susan’s grandmother, my mother-in-law, had a skylight above the bookcase in her living room that let in rainwater.
Watch out for the sometimes-unusual plurals of hyphenated compound nouns.
The workmen fixing the two merry-go-rounds in the local park typically catcalled all passersby, but they stopped once our attorneys-at-law sent them a warning.
What is a compound name?
A compound name is essentially a compound proper noun—a multiword term (often an open compound, though not always) that names a single entity.
Like Popeye, Black Panther gets at least some of his powers from eating his greens—in his case, the heart-shaped herb. But I bet Superman liked Cheez-Its better.
What’s important here is that these proper nouns are always preexisting compounds, so if you’re turning an open compound name into part of a compound modifier (see more about compound adjectives and adverbs below), you’ll need to use an en dash rather than a hyphen.
My new World War I–era cloche didn’t really go with anything in my New York–style wardrobe, so naturally I had to go shopping.
What is a compound adjective?
A compound adjective is a single adjective made up of more than one word—and it’s often a compound noun (or even compound name) being used to modify another noun. According to CMoS, it’s never wrong to hyphenate multiword adjectives when they precede a noun, even if they’re familiar open compounds like high school.
High-school students often have more brain-draining homework than college students.
My silly-voiced sister found her calling in advertising.
When a compound name functions as an adjective, there’s no need for a hyphen.
Penny was thrilled to win Dolly Parton tickets.
The Los Angeles weather is typically hot and sunny.
As touched on above, when a compound adjective follows a noun, the hyphen is usually not necessary.
Georgia is a well-read academic.
Georgia is well read.
I found a useful list of low-calorie cocktails.
I found a useful list of cocktails, all of them low calorie.
Remember that compound adjectives made from an adverb ending in –ly plus an adjective are never hyphenated. The -ly is enough of a signal that what follows is meant to be read together with the preceding word.
Sarah’s short-tempered grandfather griped about her recital, calling it a really dull concert.
Sarah’s grandfather, always short tempered, griped about her recital, describing it as really dull.
What is a compound adverb?
A compound adverb looks like a single word but (closely examined) is actually made up of two or more words working together to function as a single adverb. They’re often rather old fashioned, and they can sound stuffy and pompous so are best used sparingly: notwithstanding, nevertheless, heretofore, albeit, and so on.
Phrasal adverbs are very similar to compound adverbs, and they’re rather more useful.
I scattered rose petals here and there.
The newly married couple walked arm in arm.
Joseph goes running every day.
What is a compound sentence?
And here’s the bonus section (because the last thing we want to do is compound anyone’s confusion about compounds)!
Compound sentences are grammatically unrelated to compound words, but that still doesn’t answer the key question: What is a compound sentence? A compound sentence is when two or more independent clauses, each with its own subject and verb plus attendant objects and phrases, are joined with a coordinating conjunction (one of the FANBOYS: for, and, nor but, or, yet, so). Here, the key thing to remember is to always include a comma after the first independent clause and before the conjunction.
I read this blog post about compound words, but they didn’t explain about compound sentences, so I had to keep on searching.
My son’s story about the strawberry-loving starfish was really cute, so I sent it to my sister, and she loved it too.
Word-composition
(compounding)
is the formation of words by morphologically joining two or more
stems.
A
compound
word
is a word consisting of at least two stems which usually occur in the
language as free forms, e.g. university
teaching award committee member.
The
compound inherits
most of its semantic and syntactic information from its head,
i.e. the most important member of a compound word modified by the
other component.
The
structural
pattern
of English compounds
[
X Y]
y
X
= {root, word, phrase},
Y
= {root, word},
y
= grammatical properties inherited from Y
According
to the
type
of the linking element:
compounds
without
a linking element, e.g. toothache,
bedroom, sweet-heart;
compounds
with a
vowel linking element,
e.g. handicraft,
speedometer;
compounds
with a
consonant linking element,
e.g. statesperson,
craftsman;
compounds
with a
preposition linking stem,
e.g. son-in-law,
lady-in-waiting;
compounds
with a
conjunction linking stem,
e.g. bread-and-butter.
According
to the
type
of relationship
between the components
-in
coordinative
(copulative)
compounds neither of the components dominates the other, e.g.
fifty-fifty,
whisky-and-soda, driver-conductor;
-in
subordinative
(determinative)
compounds the components are neither structurally nor semantically
equal in importance but are based on the domination of one component
over the other, e.g. coffeepot,
Oxford-educated, to headhunt,
blue-eyed,
red-haired
etc.
According
to the
type
of relationship
between the components, subordinative compounds are classified into:
-syntactic
compounds
if their components are placed in the order that resembles the order
of words in free phrases made up according to the rules of Modern
English syntax, e.g. a
know-nothing
— to know nothing, a
blackbird
– a black bird;
-asyntactic
compounds
if they do not conform to the grammatical patterns current in
present-day English, e.g. baby-sitting
– to sit with a baby, oil-rich
– to be rich in oil.
According
to the
way of composition:
—compound
proper
is a compound formed after a composition pattern, i.e. by joining
together the stems of words already available in the language, with
or without the help of special linking elements, e.g. seasick,
looking-glass, helicopter-rescued, handicraft;
-derivational
compound is
a compound which is formed by two simultaneous processes of
composition and derivation; in a derivational compound the structural
integrity of two free stems is ensured by a suffix referring to the
combination as a whole, e.g. long-legged,
many-sided, old-timer, left-hander.
According
to the
semantic relations
between the constituents:
non-idiomatic
compounds,
whose meanings can be described as the sum of their constituent
meanings, e.g. a
sleeping-car, an evening-gown, a snowfall;
compounds
one of the components of which has undergone semantic derivation,
i.e. changed its meaning, e.g. a
blackboard,
a
bluebell;
idiomatic
compounds,
the meaning of which cannot be deduced from the meanings of the
constituents, e.g. a
ladybird,
a
tallboy,
horse-marine.
The
bahuvrihi compounds
(Sanskrit ‘much riced’) are idomatic formations in which a
person, animal or thing is metonymically named after some striking
feature (mainly in their appearance) they possess; their
word-building pattern is an
adjectival stem + a noun stem,
e.g.
bigwig,
fathead, highbrow, lowbrow, lazy-bones.
Соседние файлы в предмете [НЕСОРТИРОВАННОЕ]
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
The word compound means one thing that is composed of two or more elements. When you hear the word compound, you might think of a chemical compound, compound interest, or you might just use the word as a synonym for a mixture. Compounding is also a grammatical phenomenon, and there is a lengthy list of compound words in the English language.
Compound Words Definition
Simply put, compound means one thing made of many things. The definition for compound words means just that.
Compound words: two or more words joined to create a new meaning.
Compound words are not two random words thrust together. Compound words will be two words that are frequently found together, such as late-night, nice-looking, or seafood.
Compound words are usually two base words used together. Remember, base words are standalone words that signal a particular meaning, even when stripped of affixes (example: success in successful).
That’s not to say, however, that compound words can’t use derived words. Derived words are words that are built on a root, typically with the addition of an affix (example: teach + er = teacher). Many compound words include derived words (coffee maker, sewing machine, skyscraper).
The process of compounding is different from derivation and inflection — both of which typically involve adding an affix to change a word’s grammatical category. While derivation, inflection, and compounding are all a process for creating new words, compounding uses two base words, rather than a single base word and an affix (e.g., -ing, im—, or -ed).
Compounding in English Examples
Compounds help us understand words as a single unit, which in some cases helps to clarify the meaning of a word or phrase in English.
Let’s look for a vegan-friendly restaurant.

Using a hyphen here shows the reader that the words vegan and friendly should be taken as a single unit. Otherwise, it might be read as, “Let’s look for a vegan friendly restaurant,” with vegan and friendly being two different adjectives to describe a restaurant.
When new things, ideas, or phrases come into the collective consciousness of the public, they need a name or something people can say to refer to them. Compounding words is one of the most (if not the most) common types of word formation in English because it is so easy to do.
These new words can be figurative like chairman (the head of a committee or group, not a chair-shaped man), or simply a combination of the meaning of each of the base words, like lighthouse (a house of light).
Just email me, and I’ll respond to it later.
The word email wasn’t used until the late twentieth century because email, or electronic mail, didn’t exist until then. There was a need to create a word to communicate this new idea of sending a message electronically, and e-mail —which became email, without the hyphen — was a simple option.
Types of Compound Words
There are three types of compound words: open, closed, and hyphenated.
Open Compounds
Open compound words are formed by combining an adjective with the noun it modifies to create a new noun. These compound words are usually the result of two words being so frequently used together that they eventually come to mean one specific thing.
Shopping cart
Potting soil
Real estate
Even though these words are separated with a space, they’re still considered a single unit. You can tell it’s an open compound word, rather than merely a noun modified by an adjective, because the two words are so regularly used together to mean something specific.
For example, real is not used as the modification of the word estate to express it’s real as opposed to a fake estate. Real estate is the business of buying and selling property and buildings on said property.
Closed Compounds
Closed compound words look the most like a “real word” because there is no space between the two roots.
Keyboard
Pothole
Tablecloth
Two words might form a closed compound because they are so frequently used together.

In the 1990s when someone wanted to connect to the internet, they might say they were going to go on-line (cue the sounds of dial-up internet and a male voice saying, “You’ve got mail”). Today in the twenty-first century, the internet is a part of our everyday experience, and so the word has lost its hyphen and is typically shortened to online.
Hyphenated Compounds
The final type of compound words are hyphenated compounds. These are words that — just like closed and open compounds — are frequently used together. The hyphen connects these words, so they function as one unit.
A hyphen (-) is a punctuation mark that shouldn’t be confused with a dash (–). A hyphen connects two words or word parts, whereas dashes indicate a pause or range. Dashes can be short (an “en dash” which is the length of the letter n) or long (an “em dash” which is the length of the letter m).
Long-term
Close-up
Empty-handed
Many hyphenated compounds become closed compounds if they’re used frequently enough.
Hyphenating Compound Words
You might wonder, “How do I know when to hyphenate a compound word?” There are many rules regarding hyphens in general, and here are the ones that are key in hyphenating compound words.
-
Only hyphenate when the compound comes before the noun it will modify. If it comes after, don’t include a hyphen.
The man-eating bear was only a few yards away. vs. The bear was definitely a man eater.
-
When a compound modifier contains an adverb ending in -ly and a participle or adjective, don’t use a hyphen.
A highly contested race.
Unfortunately, there is not always a consensus about whether to hyphenate compound words or create a closed compound word. If you’re ever in doubt about whether to hyphenate a compound word, consult a dictionary or the appropriate style guide for a definitive answer.
Compound Words List
Here is a longer compound words list for reference.
Open Compound Words
-
Sun room
-
Cheer up
-
Summer break
-
Garage sale
-
Dress up
-
Fire pit
-
Jumping jack
-
Science fiction
-
Vice President
-
Swimming pool
Closed Compound Words
-
Dishware
-
Bookstore
-
Seatbelt
-
Birthday
-
Carpool
-
Limelight
-
Comeback
-
Candlelit
-
Football
-
Lawsuit
Hyphenated Compound Words
-
House-of-mirrors
-
Self-contempt
-
Father-in-law
-
Well-read
-
Full-length
-
Free-fall
-
High-rise
-
Life-size
-
Deep-fried
-
Right-handed
Compounding — Key takeaways
- Compound words are two or more words joined to create a new meaning.
- Compound words are usually two base words used together.
- Compounds help us understand words as a single unit, which in some cases helps to clarify the meaning of a word or phrase.
- There are three types of compound words: open, closed, and hyphenated.
- There is not always a consensus about whether to hyphenate compound words or create a closed compound word.
The words pancake, living room, and merry-go-round have something in common.
They are all examples of compound words.
The noun compound means something made up of two or more separate components. Compound can also be an adjective meaning consisting of two or more parts or components.
A compound word is one word, or one unit of meaning, that is created by joining two or more separate words together.
What Are Compound Words?
A compound word is a word made up of usually two but sometimes more words that are joined together. The two (or more) that make the compound word are independent words; they have their own distinct meanings. When those words are joined and form a compound word, that compound word has its own new meaning.
The Three Types of Compound Words
Compound words can take three possible forms: closed, open, or hyphenated. In closed form, there is no space between the joined words. In open form, there is a space between the “joined” words that still act as one unit, and in hyphenated form—you guessed it! There is a hyphen between the joined words.
These general “rules”—which are somewhat fluid and flexible—provide guidance as to what format a compound word takes.
-
Closed compound words are usually nouns: They put on makeup.
-
Open compound words are usually nouns or verbs: I have to make up (verb) that exam at my high school. (noun)
-
Hyphenated compound words are usually adjectives or adverb-adjective combinations: I have to take a make-up (adjective) exam. I will be well-prepared. (adverb + adjective)
The key word in each of those examples is “usually.” Some compound words break the rules. We’ll see how soon.
1. Closed Compound Words
To review: closed compound words are usually made up of two separate words that are put together to form a new word. There is no space between the two words in a closed-form compound word; the compound appears as one single word.
Examples of Closed Compound Words
-
Cup + cake becomes cupcake
-
Basket + ball becomes basketball
-
Key + board becomes keyboard
-
Extra + ordinary becomes extraordinary
-
Birth + day becomes birthday
You can see through these examples that the meaning of the compound word is not just a merger of the independent definitions of the individual words that join together to make that compound.
However, there is a relationship between the individual word meanings and the compounds. Compound words have been integrated into language as speakers have discovered those relationships. It makes perfect sense to call a cake that could fit into a cup a cupcake and to call a ball thrown through a basket (now a hoop) a basketball.
The rules for compound words, listed earlier in the post, include the word usually. That word means the rules are not hard and fast, and there are examples of compound words that break those rules.
For example, compound words that are verbs are usually open form, but here are rule-breaking closed-form compound verbs that remind us to hold those rules loosely:
-
I need to proofread my essay.
-
I think the clerk shortchanged me.
-
I have to babysit my little sister.
2. Open Compound Words
In an open compound word, there is a space between the two independent words, though they are still treated as one unit with a new “compound meaning.”
Examples of Open Compound Words
-
Living room: as a unit, this compound noun refers to a room in a house.
-
High school: as a unit, this compound noun refers to a school that has students in grades 9-12.
-
Post office: as a unit, this compound refers to a building where mail is collected, sorted, and sent.
-
Give up: as a unit, this compound verb means to stop trying.
-
Ask for: as a unit, this compound verb means to request something.
3. Hyphenated Compound Words
Hyphenated compound words have hyphens between each of the independent words that serve as connectors. The hyphens are a visual cue that the words form one unit.
Some compound words are always hyphenated.
-
Merry-go-round
-
Mother-in-law (and brother-, sister-, and father-in-law)
-
Self-esteem
Did you notice that all of those examples are nouns? Remember: the rules are flexible!
Examples of Hyphenated Compound Adjectives:
When compound words are used as adjectives (officially known as compound adjectives), the hyphenation rules change depending on where the compound adjective comes in the sentences.
If the compound adjective comes before the noun it modifies (describes), you should usually add a hyphen:
-
High-speed chase
-
Part-time employee
-
Full-time job
-
Fire-resistant pajamas
-
Good-looking person
-
Well-respected politician
-
Up-to-date records
Of course, there are exceptions. Remember, those “rules” are flexible. Some compound adjectives that precede the nouns they modify never take a hyphen. For example, ice cream and high school:
- High school students
- Ice cream sundae
There’s really no “why” to explain these exceptions; we’ve just adopted these forms and made them part of our language.
Examples of Open-Form Compound Adjectives
If the compound adjective comes after the noun it modifies, the hyphen is usually omitted.
-
Make sure the files are up to date. “Up to date” modifies, but comes after, the noun “files.”
-
The cat is two years old. “Two years old” modifies, but comes after, the noun “cat.”
Though post-noun modifiers don’t technically take hyphens, according to Merriam-Webster, usage trends indicate the hyphens are often included anyway, if the compounds “continue to function as unit modifiers.” So there’s that flexibility again.
What About Adverb Compounds?
It’s easy to find examples of closed, open, and hyphenated adverbs.
As for the closed-form examples, we probably don’t even register them as compound words much of the time.
-
Sometimes
-
Thereafter
-
Somewhere
Open-form adverbs occur when the adverb is the first word in the compound and ends in —ly. You should not hyphenate after an —ly adverb.
-
We made the discovery early on.
-
Her opinion is highly regarded.
-
They entered the dimly lit room.
What to Do If You’re Not Sure Which Form Is Right
While those flexible rules can help you, there may still be times when you feel confused about which compound form to use. Don’t stress too much.
According to Merriam Webster, the rules are more like patterns. You may see differences in different publications depending on editorial choice and style. For example, I looked on Amazon for a teapot. I saw mostly teapots, but also a few tea pots. Out of curiosity I put “tea pot” into a New York Times search bar, and found articles from the 1800s that included “tea-pot” in the title!
While interesting, those stylistic changes and choices shouldn’t be too surprising. Language is fluid and ever-evolving. Compound words themselves are proof of that evolution.
Keep Clarity the Focus
The purpose of hyphens in compound words is to ensure clarity. For example,
-
I bought over-the-counter medication.
-
He passed the medicine over the counter.
In the first example, I know by the hyphen that the medicine «I» bought did not require a prescription. «Over-the-counter» is one unit—one compound—describing a type of medicine.
In the second example, «over the counter» is serving another purpose and, while the words form a phrase to tell me where «he» passed the medicine, hyphens do nothing to make the purpose of the phrase clear and are therefore unnecessary.
Now look at these examples:
- He owned a little-used car.
- He owned a little used car.
In the first example, I know the man owns a car that has not been driven much. The car is described by the compound modifier «little-used.»
In the second example, it seems that the man owns a used car that is also small, or little. In this example, putting a comma after «little» would help to separate the two words, «little» and «used,» and show that they aren’t intended to work as a compound.
ProWritingAid Can Help
Though you’re a compound-word expert now, if you find yourself with lingering doubts, remember that ProWritingAid is here to help. It will let you know if you’ve added an unnecessary hyphen after an -ly adverb, or if you’ve left one out of a pre-noun compound adjective. You don’t have to write alone!
Take your writing to the next level:
20 Editing Tips from Professional Writers
Whether you are writing a novel, essay, article, or email, good writing is an essential part of communicating your ideas.
This guide contains the 20 most important writing tips and techniques from a wide range of professional writers.
First, what are compound words, and what are the 3 types of compound words?
Compound Definition/Compound Words Definition
A compound is a noun, an adjective or a verb made of two or more words, written as one or more words. A compound word can be closed ( for example, seafood), open for example, water ice) or hyphenated (for example, first-class).
- Closed compound words form one single word.
- Open compound words are spelled as two separate words.
- Hyphenated compound words are joined by a hyphen.
English Compound Words Examples/Compound Words List
- Closed compound words: Seafood, outcome, overcome, worksheet, downpour, seabird, sunflower, skincare, proofread, etc.
- Open compound words: Water ice, big hair, high school, dining table, dining room, etc.
- Hyphenated compound words: big-hearted, big-headed, self-actualization, well-known, well-cooked, etc.
Compound words examples
List of compound words
The following compound words lists are not comprehensive.
Compound Words: Compound Adjectives list
A compound adjective (also called compound modifier) is made up of two or more words that work jointly to modify the same noun. When compound adjectives are used before the noun they modify, they are usually hyphenated (joined together by a hyphen).
Compound adjectives whose first part is self are hyphenated as well. The words joined together by a hyphen are also known as hyphenated words.
Here is a hyphenated adjectives list:
- He is a well-off businessman.
- He belongs to a well-off family.
- His father is well off.
- She is a well-known writer.
- Stephen R. Covey is well known.
- Self-absorbed
- Self-aware = self-conscious
- Self-confident
- Self-contained
- Self-critical
- Self-educated
- Self-imposed
Compound adjectives can be created by joining multiple words; they can be in different combinations. Compound adjectives can be made up of adjectives, nouns, participles, quantifiers, and adverbs.
Here are some examples of the various combinations that we can make to come up with compound adjectives:
Compound adjectives lists:
- Adjective + Adjective: Top-right, top-left, blue-green, etc.
- Adjective + Noun: Part-time, full-time, good-time, etc.
- Noun + Adjective: Sugar-free, ice-cold, duty-free, homesick, etc.
As you can notice above we combine different parts of speech to create a new word.
Present and past participles can be joined with adjectives, nouns, and adverbs to make compound adjectives:
- Adjective + participle: Good-looking, hard-working, nice-looking, old-fashioned, open-minded, big-hearted, absent-minded, etc.
- Noun + participle: record-breaking, mouth-watering, human being, man-sized, home-made,
- Adverb + participle: Well-known, well-oiled, well rounded, badly-written, well-written, well-paid, dimly-lit, brightly-lit, early-rising, well-running,
Prepositions can also be employed to form compound adjectives:
- up-to-date laptops.
- a broken-down car.
- a beaten-up old truck.
- built-up areas.
- a cashed-up businesswoman.
- a built-in cupboard.
- a clapped out machine ( old and in bad condition)
Another way to form compound adjectives is to join a quantifier and a noun.
- A five-star hotel.
- A three-floor building.
- A three-storey building.
- A fifteen-year-old teenager.
A compound adjective with a number never takes the ‘s’ of the plural.
- There are 3 five-star hotels in this city.
- 10 three-floor buildings.
Compound Words: Compound adjectives to describe a person or something
Compound adjectives for character ( Compound adjectives personality) are usually used to describe people’s personality or character. The adjectives list below contains a number of compound adjectives tha can describe character. The other compoud adjectives can be used to describe something or someone not someone’s personality.
Compound Adjectives Examples
Hard-working is a compound adjective example
Here is a list of compound adjectives with self along with meaning
- Self-assured
you have confidence in your own abilities.
- Well-behaved
behave in a quiet and polite way.
- Self-centered
interested only in yourself.
- Self-conscious
uncomfortable or nervous because you are worried about what other people think about you or your behavior.
- Self-absorbed
a self-absorbed person is a person who is concerned about or interested in himself/herself.
- Self-addressed:
If an envelpoe is self-addressed, someone has written his/her own address on it.
- Self-adhesive
It can be stuck to something without the use glue, etc.
- Self-acting
Acting of or by itself.
- Self-appointed
A self appointed president is a president who has apointed himself/herself without the greement of his/her people.
- Self-assembly (esp, furniture)
Bought in several parts that you have to put together yourself.
- Self-assertive
A self-assertive man is a man who is very confident and not afraid to express his opinion about something or someone.
- Self-colour
Having one colour all over.
- Self-confessed
Admitting that you have done something, especially something bad.
- Self-contained (= independent)
If you are a self-contained woman, you don’t depend on other people or you do not need them.
- Self-contradictory
Containing two statements or ideas that connot both be true.
- Self-correcting
That can adjust or correct itself by itself.
- Self-critical
A self-critical person criticises himself/herself.
- Self-defeating
If a plan is self-defeating, it contains elements that will cause it to fail.
- Self-drive
A self-drive car is a car that you hire and drive by yourself.
- Self-deniying
Without concern for one’s own advantage; selfless.
- Self-effacing
A self-effacing man is a modest and does not want to attract attention to himeself or his abilities.
- Self-employed
If you are self-employed, you work for yourself and are not employed by a company, a person, etc.
- Self-evident
Obvious and does not need further explanation or proof.
- Self-explanatory
Easy to understand and does not nee any more explanation.
- Self-important
A slef-important person thinks that he/she is more important than others.
Other compound adjectives describing character
- Hard-working:
always doing a lot of work.
- Good-natured
naturally friendly and does not get angry easily.
- Over-confident
too sure about yourself and your abilities.
- Strong-willed
very determined to do what you want to do.
- Weak-willed
not determined enough to succeed in what you want to do.
- Strong-minded
somebody who is strong-minded is not willing to change their opinions and beliefs.
- Broad-minded
happy to accept ideas and ways of life different to your own.
- Open-minded
willing to accept opinions and ideas which are different from yours.
- Narrow-minded
not willing to accept ideas or ways of behaving that are different from your own.
- Bad-tempered
often annoyed, angry, or impatient.
- Short-tempered
if someone is short-tempered, he or she gets angry easily for no good reason.
- Easy-going
calm and relaxed; not easily worried or upset.
- Big-headed
you think you are more intelligent or more important than you really are.
- Thick-skinned
if you are thick-skinned, you are not easily hurt by criticism.
- Cold-hearted
if you are cold-hearted, you don’t feel sorry about other people’s suffering.
- Level headed
Calm and sensible; able to make good decisions even in difficult situations.
- Laid-back: You are not usually worried about other people’s behavior or things that need to be done.
These compound adjectives describing character traits are really interesting. So, which compound adjectives describe your personality?
Do this character adjectives quiz here to test your knowledge of compound adjectives.
Compound Nouns
Definition for compound noun
What is a compound noun? How do you make a compound noun? What are compound nouns?
A compound noun refers to a noun that is composed of two or more words. These compound words work together as a single unit to name a place, a person, or a thing. Compound nouns are usually created by joining two nouns or an adjective and a noun together (adjective+noun) (noun+adjective) (adjective+adjective), etc.
Compound nouns types
There are 3 types of compound nouns, namely open compound nouns. They are written as separate words ( living room, swimming pool, secretary general, etc.), closed compound nouns. They are written as one single word (blackbird, policeman, makeup, etc.), and hyphenated compound words (mother-in-law, father-in-law, check-in, etc.)
Compound Noun Examples
Here is a compound nouns list
20 + examples of compound nouns
There are different combinations of compound nouns, but they are usually combined this way: (noun + noun) (adjective + noun), (noun + adjective), (verb + noun), etc.
- Football (noun + noun)
- Snowman
- Sunflower
- Dragonfly
- Seafood
- Bookcase
- Toothpaste
- Backpack
- Living room
- Bedroom
- Bathroom
- Dining room
- Bathtub
- Website
- Policeman
- Policewoman
- Watercolor
- Bus stop
- Handbag
- Whiteboard ( adjective + noun)
- Blackboard
- Blackbird
- Greenhouse
- Greenpeace
- Software
- Mobile phone
- Full moon
- Full board
- Blackberry
- Check-in ( verb + preposition)
- Checkout
- Makeup
- lookout
- Drawback
- Fall-off
- Falling-out
- Fill-up
- Sunrise (noun + verb)
- Sunset
- Haircut
- Rainfall
Tip: To turn compound nouns into the plural, we usually add ‘s’, ‘es’ or ‘ies’ to the main word of the compound noun.
The main word is usually the second word, but there are exceptions.
A bookcase bookcases
A bedroom bedrooms
A handbag handbags
A website websites
But
A father-in-law fathers-in-law
A secretary general secretaries general
A passerby passers-by
We believe that this post is good for learners of English who want to broaden their knowledge of compound words. It can even be used by teachers to teach compound words.
Compound words video
Noun+noun compound nouns
| Noun | Noun | Compound noun |
| Sea | Food | Seafood |
| Sea | Farer | Seafarer |
| Home | Front | Home front |
| Home | Ground | Home ground |
| Home | Help | Home help |
| Home | Land | Homeland |
| Bus | Stop | Bus stop |
| Snow | Man | Snowman |
| Snow | Ball | Snowball |
Noun+adjective compound nouns
| Noun | Adjective | Compound noun |
| Spoon | Fu | Spoonful |
| Truck | Full | Truckful |
Here, you’ll find very important words that describe appearance.
Other useful links:
- The definite article in English
- Short stories with morals
- Best language learning quotes
Learn English online with Englishdotcom